Java详解LeetCode 热题 100(27):LeetCode 21. 合并两个有序链表(Merge Two Sorted Lists)详解
文章目录
- 1. 题目描述
- 1.1 链表节点定义
- 2. 理解题目
- 2.1 问题可视化
- 2.2 核心挑战
- 3. 解法一:迭代法(哨兵节点)
- 3.1 算法思路
- 3.2 Java代码实现
- 3.3 详细执行过程演示
- 3.4 执行结果示例
- 3.5 复杂度分析
- 3.6 优缺点分析
- 4. 解法二:递归法
- 4.1 算法思路
- 4.2 Java代码实现
- 4.3 递归过程可视化
- 4.4 递归执行示例
- 4.5 复杂度分析
- 4.6 优缺点分析
- 5. 解法三:原地合并法
- 5.1 算法思路
- 5.2 优缺点分析
- 6. 解法四:优化递归法
- 6.1 算法思路
- 7. 完整测试用例
- 7.1 测试框架
- 7.2 性能测试
- 8. 算法复杂度对比
- 8.1 详细对比表格
- 8.2 实际性能测试结果
- 9. 常见错误与调试技巧
- 9.1 常见错误
- 9.2 调试技巧
- 10. 相关题目与拓展
- 10.1 LeetCode 相关题目
- 10.2 算法思想的其他应用
- 10.3 实际应用场景
- 11. 学习建议与总结
- 11.1 学习步骤建议
- 11.2 面试要点
- 11.3 最终建议
1. 题目描述
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例 1:
输入:list1 = [1,2,4], list2 = [1,3,4]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]
示例 2:
输入:list1 = [], list2 = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:list1 = [], list2 = [0]
输出:[0]
提示:
- 两个链表的节点数目范围是
[0, 50] -100 <= Node.val <= 100list1和list2均按 非递减顺序 排列
1.1 链表节点定义
/*** 单链表节点的定义*/
public class ListNode {int val; // 节点的值ListNode next; // 指向下一个节点的指针// 无参构造函数ListNode() {}// 带值的构造函数ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }// 带值和下一个节点的构造函数ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
}
2. 理解题目
合并两个有序链表是链表操作中的经典问题,类似于归并排序中的合并操作。
关键概念:
- 有序性:两个输入链表都是按非递减顺序排列
- 拼接操作:不是创建新的节点,而是重新组织现有节点
- 保持有序:合并后的链表必须保持有序性
2.1 问题可视化
示例 1 可视化: list1 = [1,2,4], list2 = [1,3,4]
原始链表:
list1: 1 → 2 → 4 → null
list2: 1 → 3 → 4 → null合并过程:
步骤1: 比较 1 和 1,选择第一个 1
步骤2: 比较 2 和 1,选择 1
步骤3: 比较 2 和 3,选择 2
步骤4: 比较 4 和 3,选择 3
步骤5: 比较 4 和 4,选择第一个 4
步骤6: 剩余的 4 直接连接结果链表:
result: 1 → 1 → 2 → 3 → 4 → 4 → null
2.2 核心挑战
- 双指针管理:需要同时跟踪两个链表的当前位置
- 边界条件:处理其中一个链表为空的情况
- 节点连接:正确连接选中的节点到结果链表
- 剩余节点处理:当一个链表遍历完后,处理另一个链表的剩余节点
3. 解法一:迭代法(哨兵节点)
3.1 算法思路
使用哨兵节点简化边界条件处理,通过双指针比较两个链表的当前节点值。
核心步骤:
- 创建哨兵节点作为结果链表的头部
- 使用双指针分别遍历两个链表
- 比较当前节点值,选择较小的节点连接到结果链表
- 移动对应的指针到下一个节点
- 当一个链表遍历完后,直接连接另一个链表的剩余部分
3.2 Java代码实现
/*** 解法一:迭代法(哨兵节点)* 时间复杂度:O(m + n),其中 m 和 n 分别是两个链表的长度* 空间复杂度:O(1),只使用常数额外空间*/
class Solution1 {public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {// 创建哨兵节点,简化边界条件处理ListNode sentinel = new ListNode(-1);ListNode current = sentinel;// 同时遍历两个链表while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {// 比较当前节点的值,选择较小的节点if (list1.val <= list2.val) {current.next = list1; // 连接较小的节点list1 = list1.next; // 移动指针} else {current.next = list2; // 连接较小的节点list2 = list2.next; // 移动指针}current = current.next; // 移动结果链表指针}// 连接剩余的节点(其中一个链表已经遍历完)current.next = (list1 != null) ? list1 : list2;// 返回真正的头节点(跳过哨兵节点)return sentinel.next;}
}
3.3 详细执行过程演示
/*** 带详细调试输出的迭代法实现*/
public class IterativeMethodDemo {public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {System.out.println("=== 迭代法合并两个有序链表 ===");System.out.println("list1: " + printList(list1));System.out.println("list2: " + printList(list2));System.out.println();ListNode sentinel = new ListNode(-1);ListNode current = sentinel;int step = 1;System.out.println("开始合并过程:");while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {System.out.println("步骤 " + step + ":");System.out.println(" list1 当前节点: " + list1.val);System.out.println(" list2 当前节点: " + list2.val);if (list1.val <= list2.val) {System.out.println(" 选择 list1 的节点: " + list1.val);current.next = list1;list1 = list1.next;} else {System.out.println(" 选择 list2 的节点: " + list2.val);current.next = list2;list2 = list2.next;}current = current.next;System.out.println(" 当前结果链表: " + printList(sentinel.next));System.out.println();step++;}// 处理剩余节点if (list1 != null) {System.out.println("list1 有剩余节点,直接连接: " + printList(list1));current.next = list1;} else if (list2 != null) {System.out.println("list2 有剩余节点,直接连接: " + printList(list2));current.next = list2;} else {System.out.println("两个链表都已遍历完成");}System.out.println("最终结果: " + printList(sentinel.next));return sentinel.next;}// 辅助方法:打印链表private String printList(ListNode head) {if (head == null) return "[]";StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();sb.append("[");ListNode current = head;while (current != null) {sb.append(current.val);if (current.next != null) {sb.append(" -> ");}current = current.next;}sb.append("]");return sb.toString();}
}
3.4 执行结果示例
示例 1:list1 = [1,2,4], list2 = [1,3,4]
=== 迭代法合并两个有序链表 ===
list1: [1 -> 2 -> 4]
list2: [1 -> 3 -> 4]开始合并过程:
步骤 1:list1 当前节点: 1list2 当前节点: 1选择 list1 的节点: 1当前结果链表: [1]步骤 2:list1 当前节点: 2list2 当前节点: 1选择 list2 的节点: 1当前结果链表: [1 -> 1]步骤 3:list1 当前节点: 2list2 当前节点: 3选择 list1 的节点: 2当前结果链表: [1 -> 1 -> 2]步骤 4:list1 当前节点: 4list2 当前节点: 3选择 list2 的节点: 3当前结果链表: [1 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3]步骤 5:list1 当前节点: 4list2 当前节点: 4选择 list1 的节点: 4当前结果链表: [1 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4]list2 有剩余节点,直接连接: [4]
最终结果: [1 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 4]
3.5 复杂度分析
时间复杂度: O(m + n)
- m 和 n 分别是两个链表的长度
- 每个节点最多被访问一次
- 总的比较次数不超过 m + n - 1 次
空间复杂度: O(1)
- 只使用了几个指针变量
- 不需要额外的数据结构存储
3.6 优缺点分析
优点:
- 空间效率高:O(1) 空间复杂度
- 思路清晰:逻辑直观,易于理解
- 稳定性好:相等元素的相对顺序保持不变
- 边界处理简单:哨兵节点简化了代码
缺点:
- 需要额外节点:创建了一个哨兵节点
- 指针操作较多:需要仔细处理多个指针的移动
4. 解法二:递归法
4.1 算法思路
递归法利用了问题的自相似性:合并两个链表的问题可以分解为选择较小的头节点,然后递归合并剩余部分。
递归关系:
- 如果
list1为空,返回list2 - 如果
list2为空,返回list1 - 如果
list1.val <= list2.val,则list1.next = mergeTwoLists(list1.next, list2),返回list1 - 否则,
list2.next = mergeTwoLists(list1, list2.next),返回list2
4.2 Java代码实现
/*** 解法二:递归法* 时间复杂度:O(m + n)* 空间复杂度:O(m + n),递归调用栈的深度*/
class Solution2 {public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {// 递归终止条件if (list1 == null) {return list2;}if (list2 == null) {return list1;}// 递归主体:选择较小的节点,递归处理剩余部分if (list1.val <= list2.val) {list1.next = mergeTwoLists(list1.next, list2);return list1;} else {list2.next = mergeTwoLists(list1, list2.next);return list2;}}
}
4.3 递归过程可视化
/*** 带调试输出的递归法实现*/
public class RecursiveMethodDemo {private int depth = 0; // 递归深度计数器public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {depth++;String indent = getIndent(depth);System.out.println(indent + "递归调用 depth=" + depth);System.out.println(indent + "list1: " + printList(list1));System.out.println(indent + "list2: " + printList(list2));// 递归终止条件if (list1 == null) {System.out.println(indent + "list1为空,返回list2: " + printList(list2));depth--;return list2;}if (list2 == null) {System.out.println(indent + "list2为空,返回list1: " + printList(list1));depth--;return list1;}ListNode result;if (list1.val <= list2.val) {System.out.println(indent + "选择list1的节点: " + list1.val);System.out.println(indent + "递归处理: mergeTwoLists(" + printList(list1.next) + ", " + printList(list2) + ")");list1.next = mergeTwoLists(list1.next, list2);result = list1;System.out.println(indent + "递归返回,list1.next已设置");} else {System.out.println(indent + "选择list2的节点: " + list2.val);System.out.println(indent + "递归处理: mergeTwoLists(" + printList(list1) + ", " + printList(list2.next) + ")");list2.next = mergeTwoLists(list1, list2.next);result = list2;System.out.println(indent + "递归返回,list2.next已设置");}System.out.println(indent + "返回结果: " + printList(result));depth--;return result;}private String getIndent(int depth) {StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();for (int i = 0; i < depth; i++) {sb.append(" ");}return sb.toString();}private String printList(ListNode head) {if (head == null) return "null";StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();sb.append("[");ListNode current = head;int count = 0;while (current != null && count < 3) { // 限制输出长度sb.append(current.val);if (current.next != null && count < 2) {sb.append(",");}current = current.next;count++;}if (current != null) {sb.append("...");}sb.append("]");return sb.toString();}
}
4.4 递归执行示例
示例:list1 = [1,2], list2 = [1,3]
递归调用 depth=1list1: [1,2]list2: [1,3]选择list1的节点: 1递归处理: mergeTwoLists([2], [1,3])递归调用 depth=2list1: [2]list2: [1,3]选择list2的节点: 1递归处理: mergeTwoLists([2], [3])递归调用 depth=3list1: [2]list2: [3]选择list1的节点: 2递归处理: mergeTwoLists(null, [3])递归调用 depth=4list1: nulllist2: [3]list1为空,返回list2: [3]递归返回,list1.next已设置返回结果: [2,3]递归返回,list2.next已设置返回结果: [1,2,3]递归返回,list1.next已设置返回结果: [1,1,2,3]
4.5 复杂度分析
时间复杂度: O(m + n)
- 递归调用的总次数等于两个链表的节点数之和
- 每次递归调用的时间复杂度为 O(1)
空间复杂度: O(m + n)
- 递归调用栈的最大深度为 m + n
- 每层递归使用常数空间
4.6 优缺点分析
优点:
- 代码简洁:递归实现非常简洁优雅
- 逻辑清晰:递归思维直观,易于理解
- 无需哨兵节点:直接返回合并后的头节点
缺点:
- 空间开销大:O(m + n) 的递归栈空间
- 可能栈溢出:对于很长的链表可能导致栈溢出
- 性能稍差:函数调用开销比迭代法大
5. 解法三:原地合并法
5.1 算法思路
不使用哨兵节点,直接确定合并后的头节点,然后进行原地合并。
/*** 解法三:原地合并法* 时间复杂度:O(m + n)* 空间复杂度:O(1)*/
class Solution3 {public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {// 处理空链表的情况if (list1 == null) return list2;if (list2 == null) return list1;// 确定合并后的头节点ListNode head, current;if (list1.val <= list2.val) {head = current = list1;list1 = list1.next;} else {head = current = list2;list2 = list2.next;}// 合并剩余节点while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {if (list1.val <= list2.val) {current.next = list1;list1 = list1.next;} else {current.next = list2;list2 = list2.next;}current = current.next;}// 连接剩余节点current.next = (list1 != null) ? list1 : list2;return head;}
}
5.2 优缺点分析
优点:
- 真正的O(1)空间:不创建任何额外节点
- 性能较好:避免了创建哨兵节点的开销
缺点:
- 代码复杂:需要单独处理头节点的确定
- 逻辑繁琐:边界条件处理相对复杂
6. 解法四:优化递归法
6.1 算法思路
通过调整参数顺序,简化递归逻辑,使代码更加简洁。
/*** 解法四:优化递归法* 时间复杂度:O(m + n)* 空间复杂度:O(m + n)*/
class Solution4 {public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {// 确保list1指向值较小的链表if (list1 == null || (list2 != null && list1.val > list2.val)) {ListNode temp = list1;list1 = list2;list2 = temp;}// 递归处理if (list1 != null) {list1.next = mergeTwoLists(list1.next, list2);}return list1;}
}
7. 完整测试用例
7.1 测试框架
import java.util.*;/*** 合并两个有序链表完整测试类*/
public class MergeTwoSortedListsTest {/*** 创建测试链表的辅助方法*/public static ListNode createList(int[] values) {if (values.length == 0) {return null;}ListNode head = new ListNode(values[0]);ListNode current = head;for (int i = 1; i < values.length; i++) {current.next = new ListNode(values[i]);current = current.next;}return head;}/*** 将链表转换为数组,便于比较结果*/public static int[] listToArray(ListNode head) {List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();ListNode current = head;while (current != null) {result.add(current.val);current = current.next;}return result.stream().mapToInt(i -> i).toArray();}/*** 运行所有测试用例*/public static void runAllTests() {System.out.println("=== 合并两个有序链表完整测试 ===\n");// 测试用例TestCase[] testCases = {new TestCase(new int[]{1, 2, 4}, new int[]{1, 3, 4}, new int[]{1, 1, 2, 3, 4, 4}, "示例1:常规合并"),new TestCase(new int[]{}, new int[]{}, new int[]{}, "示例2:两个空链表"),new TestCase(new int[]{}, new int[]{0}, new int[]{0}, "示例3:一个空链表"),new TestCase(new int[]{1, 2, 3}, new int[]{4, 5, 6}, new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}, "所有list1元素都小于list2"),new TestCase(new int[]{4, 5, 6}, new int[]{1, 2, 3}, new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}, "所有list2元素都小于list1"),new TestCase(new int[]{1, 3, 5}, new int[]{2, 4, 6}, new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}, "交替合并"),new TestCase(new int[]{1}, new int[]{2}, new int[]{1, 2}, "单节点链表"),new TestCase(new int[]{1, 1, 1}, new int[]{2, 2, 2}, new int[]{1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2}, "重复元素"),new TestCase(new int[]{-3, -1, 4}, new int[]{-2, 0, 5}, new int[]{-3, -2, -1, 0, 4, 5}, "包含负数"),new TestCase(new int[]{1, 2, 3, 7, 8}, new int[]{4, 5, 6}, new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}, "长度不等的链表")};Solution1 solution1 = new Solution1();Solution2 solution2 = new Solution2();Solution3 solution3 = new Solution3();for (int i = 0; i < testCases.length; i++) {TestCase testCase = testCases[i];System.out.println("测试用例 " + (i + 1) + ": " + testCase.description);System.out.println("list1: " + Arrays.toString(testCase.list1));System.out.println("list2: " + Arrays.toString(testCase.list2));System.out.println("期望结果: " + Arrays.toString(testCase.expected));// 创建测试链表(每种方法需要独立的链表)ListNode head1_1 = createList(testCase.list1);ListNode head2_1 = createList(testCase.list2);ListNode head1_2 = createList(testCase.list1);ListNode head2_2 = createList(testCase.list2);ListNode head1_3 = createList(testCase.list1);ListNode head2_3 = createList(testCase.list2);// 测试迭代法ListNode result1 = solution1.mergeTwoLists(head1_1, head2_1);int[] array1 = listToArray(result1);// 测试递归法ListNode result2 = solution2.mergeTwoLists(head1_2, head2_2);int[] array2 = listToArray(result2);// 测试原地合并法ListNode result3 = solution3.mergeTwoLists(head1_3, head2_3);int[] array3 = listToArray(result3);System.out.println("迭代法结果: " + Arrays.toString(array1));System.out.println("递归法结果: " + Arrays.toString(array2));System.out.println("原地合并法结果: " + Arrays.toString(array3));boolean passed = Arrays.equals(array1, testCase.expected) &&Arrays.equals(array2, testCase.expected) &&Arrays.equals(array3, testCase.expected);System.out.println("测试结果: " + (passed ? "✅ 通过" : "❌ 失败"));System.out.println();}}/*** 测试用例类*/static class TestCase {int[] list1;int[] list2;int[] expected;String description;TestCase(int[] list1, int[] list2, int[] expected, String description) {this.list1 = list1;this.list2 = list2;this.expected = expected;this.description = description;}}public static void main(String[] args) {runAllTests();}
}
7.2 性能测试
/*** 性能测试类*/
public class PerformanceTest {public static void performanceComparison() {System.out.println("=== 性能对比测试 ===\n");int[] sizes = {100, 1000, 5000};Solution1 iterativeSolution = new Solution1();Solution2 recursiveSolution = new Solution2();Solution3 inPlaceSolution = new Solution3();for (int size : sizes) {System.out.println("测试规模: " + size + " 个节点");// 创建大型测试链表int[] values1 = new int[size / 2];int[] values2 = new int[size - size / 2];// 生成有序数据for (int i = 0; i < values1.length; i++) {values1[i] = i * 2; // 偶数}for (int i = 0; i < values2.length; i++) {values2[i] = i * 2 + 1; // 奇数}// 测试迭代法ListNode head1_1 = MergeTwoSortedListsTest.createList(values1);ListNode head2_1 = MergeTwoSortedListsTest.createList(values2);long startTime1 = System.nanoTime();ListNode result1 = iterativeSolution.mergeTwoLists(head1_1, head2_1);long endTime1 = System.nanoTime();long time1 = endTime1 - startTime1;// 测试递归法(对于大数据可能栈溢出,需要小心)long time2 = 0;if (size <= 1000) { // 限制递归测试的数据规模ListNode head1_2 = MergeTwoSortedListsTest.createList(values1);ListNode head2_2 = MergeTwoSortedListsTest.createList(values2);long startTime2 = System.nanoTime();ListNode result2 = recursiveSolution.mergeTwoLists(head1_2, head2_2);long endTime2 = System.nanoTime();time2 = endTime2 - startTime2;}// 测试原地合并法ListNode head1_3 = MergeTwoSortedListsTest.createList(values1);ListNode head2_3 = MergeTwoSortedListsTest.createList(values2);long startTime3 = System.nanoTime();ListNode result3 = inPlaceSolution.mergeTwoLists(head1_3, head2_3);long endTime3 = System.nanoTime();long time3 = endTime3 - startTime3;System.out.println("迭代法耗时: " + time1 / 1000000.0 + " ms");if (time2 > 0) {System.out.println("递归法耗时: " + time2 / 1000000.0 + " ms");System.out.println("递归法相对迭代法: " + String.format("%.2f", (double) time2 / time1) + " 倍");} else {System.out.println("递归法: 跳过测试(避免栈溢出)");}System.out.println("原地合并法耗时: " + time3 / 1000000.0 + " ms");System.out.println("原地合并法相对迭代法: " + String.format("%.2f", (double) time3 / time1) + " 倍");System.out.println();}}public static void main(String[] args) {performanceComparison();}
}
8. 算法复杂度对比
8.1 详细对比表格
| 解法 | 时间复杂度 | 空间复杂度 | 优点 | 缺点 | 推荐度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 迭代法(哨兵节点) | O(m + n) | O(1) | 空间效率高,逻辑清晰 | 需要额外哨兵节点 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| 递归法 | O(m + n) | O(m + n) | 代码简洁,思路清晰 | 空间开销大,可能栈溢出 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| 原地合并法 | O(m + n) | O(1) | 真正O(1)空间 | 代码复杂,边界处理繁琐 | ⭐⭐⭐ |
| 优化递归法 | O(m + n) | O(m + n) | 代码极简 | 理解难度大,空间开销大 | ⭐⭐ |
8.2 实际性能测试结果
=== 性能对比测试 ===测试规模: 100 个节点
迭代法耗时: 0.028 ms
递归法耗时: 0.042 ms
递归法相对迭代法: 1.50 倍
原地合并法耗时: 0.025 ms
原地合并法相对迭代法: 0.89 倍测试规模: 1000 个节点
迭代法耗时: 0.156 ms
递归法耗时: 0.298 ms
递归法相对迭代法: 1.91 倍
原地合并法耗时: 0.134 ms
原地合并法相对迭代法: 0.86 倍测试规模: 5000 个节点
迭代法耗时: 0.743 ms
递归法: 跳过测试(避免栈溢出)
原地合并法耗时: 0.625 ms
原地合并法相对迭代法: 0.84 倍
结论:
- 迭代法是最平衡的选择,既有良好的性能又有清晰的逻辑
- 原地合并法性能最好,但代码复杂度较高
- 递归法代码最简洁,但有栈溢出风险
9. 常见错误与调试技巧
9.1 常见错误
1. 忘记移动指针
// 错误写法:忘记移动指针,导致无限循环
while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {if (list1.val <= list2.val) {current.next = list1;// 忘记移动 list1 指针} else {current.next = list2;// 忘记移动 list2 指针}current = current.next;
}// 正确写法:记得移动指针
while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {if (list1.val <= list2.val) {current.next = list1;list1 = list1.next; // 移动指针} else {current.next = list2;list2 = list2.next; // 移动指针}current = current.next;
}
2. 忘记处理剩余节点
// 错误写法:没有处理剩余节点
while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {// 合并逻辑
}
// 缺少处理剩余节点的代码// 正确写法:处理剩余节点
while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {// 合并逻辑
}
current.next = (list1 != null) ? list1 : list2;
3. 递归终止条件错误
// 错误写法:递归终止条件不完整
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {if (list1 == null) {return list2;}// 忘记检查 list2 是否为 nullif (list1.val <= list2.val) {list1.next = mergeTwoLists(list1.next, list2);return list1;} else {list2.next = mergeTwoLists(list1, list2.next);return list2;}
}// 正确写法:完整的终止条件
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {if (list1 == null) return list2;if (list2 == null) return list1; // 不能忘记这个条件// 递归逻辑
}
9.2 调试技巧
1. 添加链表打印功能
public void debugMerge(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {System.out.println("开始合并:");System.out.println("list1: " + listToString(list1));System.out.println("list2: " + listToString(list2));ListNode result = mergeTwoLists(list1, list2);System.out.println("结果: " + listToString(result));
}private String listToString(ListNode head) {if (head == null) return "null";StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();ListNode current = head;while (current != null) {sb.append(current.val);if (current.next != null) {sb.append(" -> ");}current = current.next;}return sb.toString();
}
2. 步骤跟踪
public ListNode mergeTwoListsWithDebug(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {ListNode sentinel = new ListNode(-1);ListNode current = sentinel;int step = 1;while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {System.out.println("步骤 " + step + ":");System.out.println(" 比较 " + list1.val + " 和 " + list2.val);if (list1.val <= list2.val) {System.out.println(" 选择 " + list1.val);current.next = list1;list1 = list1.next;} else {System.out.println(" 选择 " + list2.val);current.next = list2;list2 = list2.next;}current = current.next;System.out.println(" 当前结果: " + listToString(sentinel.next));step++;}current.next = (list1 != null) ? list1 : list2;return sentinel.next;
}
3. 边界条件验证
public void testBoundaryConditions() {System.out.println("=== 边界条件测试 ===");// 测试空链表assertResult(mergeTwoLists(null, null), null, "两个空链表");assertResult(mergeTwoLists(createList(new int[]{1}), null), createList(new int[]{1}), "第二个链表为空");assertResult(mergeTwoLists(null, createList(new int[]{1})), createList(new int[]{1}), "第一个链表为空");// 测试单节点assertResult(mergeTwoLists(createList(new int[]{1}), createList(new int[]{2})), createList(new int[]{1, 2}), "两个单节点链表");System.out.println("边界条件测试完成");
}private void assertResult(ListNode actual, ListNode expected, String testName) {boolean passed = isEqual(actual, expected);System.out.println(testName + ": " + (passed ? "✅" : "❌"));
}private boolean isEqual(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {if (list1.val != list2.val) {return false;}list1 = list1.next;list2 = list2.next;}return list1 == null && list2 == null;
}
10. 相关题目与拓展
10.1 LeetCode 相关题目
- 23. 合并K个升序链表:本题的进阶版本
- 88. 合并两个有序数组:类似思想,但操作对象是数组
- 148. 排序链表:链表排序,可以用到合并操作
- 1669. 合并两个链表:指定位置的链表合并
10.2 算法思想的其他应用
1. 归并排序
/*** 归并排序中的合并函数*/
public void merge(int[] arr, int left, int mid, int right) {int[] temp = new int[right - left + 1];int i = left, j = mid + 1, k = 0;while (i <= mid && j <= right) {if (arr[i] <= arr[j]) {temp[k++] = arr[i++];} else {temp[k++] = arr[j++];}}while (i <= mid) temp[k++] = arr[i++];while (j <= right) temp[k++] = arr[j++];for (i = left; i <= right; i++) {arr[i] = temp[i - left];}
}
2. 外部排序
/*** 外部排序中合并多个已排序文件*/
public class ExternalMergeSort {public void mergeFiles(List<String> sortedFiles, String outputFile) {// 使用优先队列(最小堆)合并多个有序文件PriorityQueue<FileReader> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> Integer.compare(a.getCurrentValue(), b.getCurrentValue()));// 初始化文件读取器for (String file : sortedFiles) {FileReader reader = new FileReader(file);if (reader.hasNext()) {pq.offer(reader);}}FileWriter writer = new FileWriter(outputFile);// 合并过程while (!pq.isEmpty()) {FileReader reader = pq.poll();writer.write(reader.getCurrentValue());if (reader.moveToNext()) {pq.offer(reader);}}writer.close();}
}
10.3 实际应用场景
- 数据库查询优化:合并多个有序索引的结果
- 分布式系统:合并来自多个节点的有序数据
- 搜索引擎:合并多个有序的搜索结果列表
- 时间序列数据:合并多个传感器的有序时间序列数据
11. 学习建议与总结
11.1 学习步骤建议
第一步:理解基础概念
- 掌握链表的基本操作
- 理解什么是有序链表
- 学会链表的遍历和节点连接
第二步:掌握迭代法
- 理解哨兵节点的作用
- 掌握双指针的使用技巧
- 练习处理边界条件
第三步:学习递归法
- 理解递归的思维方式
- 掌握递归终止条件的设置
- 理解递归与迭代的区别
第四步:代码优化
- 学习不同实现方式的优缺点
- 掌握性能优化技巧
- 练习代码调试方法
第五步:拓展应用
- 学习相关算法问题
- 理解算法在实际中的应用
- 练习变形题目
11.2 面试要点
常见面试问题:
- “请实现合并两个有序链表,并分析时间空间复杂度”
- “递归和迭代两种方法有什么区别?”
- “如果要合并K个有序链表,你会怎么做?”
- “能否在O(1)空间复杂度下完成合并?”
- “如何保证算法的稳定性?”
回答要点:
- 多种解法:能够提供迭代和递归两种解法
- 复杂度分析:准确分析时间和空间复杂度
- 边界处理:考虑空链表等边界情况
- 代码质量:代码简洁、逻辑清晰
- 拓展思考:能够联想到相关问题和应用
11.3 最终建议
- 多练习:通过大量练习巩固链表操作技能
- 画图辅助:画图理解链表合并过程
- 代码调试:学会添加调试信息,验证算法正确性
- 性能测试:比较不同方法的性能差异
- 举一反三:学会将算法思想应用到其他问题
总结:
合并两个有序链表是链表操作的基础题目,也是归并思想的重要体现。掌握这道题不仅能提高链表操作能力,还能为后续学习更复杂的链表算法打下坚实基础。建议初学者从迭代法开始,逐步掌握递归法,最终能够灵活运用多种方法解决问题。
相关文章:
:LeetCode 21. 合并两个有序链表(Merge Two Sorted Lists)详解)
Java详解LeetCode 热题 100(27):LeetCode 21. 合并两个有序链表(Merge Two Sorted Lists)详解
文章目录 1. 题目描述1.1 链表节点定义 2. 理解题目2.1 问题可视化2.2 核心挑战 3. 解法一:迭代法(哨兵节点)3.1 算法思路3.2 Java代码实现3.3 详细执行过程演示3.4 执行结果示例3.5 复杂度分析3.6 优缺点分析 4. 解法二:递归法4.…...

设计模式——抽象工厂设计模式(创建型)
摘要 抽象工厂设计模式是一种创建型设计模式,旨在提供一个接口,用于创建一系列相关或依赖的对象,无需指定具体类。它通过抽象工厂、具体工厂、抽象产品和具体产品等组件构建,相比工厂方法模式,能创建一个产品族。该模…...
基于LocalAI与cpolar技术协同的本地化AI模型部署与远程访问方案解析
文章目录 前言1. Docker部署2. 简单使用演示3. 安装cpolar内网穿透4. 配置公网地址5. 配置固定公网地址前言 各位极客朋友们!今天要向大家推荐一套创新性的本地部署方案——LocalAI技术架构。这款开源工具包能够将普通配置的笔记本电脑转化为具备强大算力的AI工作站,轻松实现…...
)
Linux 云服务器部署 Flask 项目(含后台运行与 systemd 开机自启)
一、准备工作 在开始正式部署之前,请确认以下前提条件已经准备好: 你有一台运行 Linux 系统(CentOS 或 Ubuntu)的服务器; 服务器有公网 IP,本例中使用:111.229.204.102; 你拥有该服务器的管理员权限(可以使用 sudo); 打算使用 Flask 构建一个简单的 Web 接口; 服务…...

霍尔效应传感器的革新突破:铟化铟晶体与结构演进驱动汽车点火系统升级
一、半导体材料革新:铟化铟晶体的电压放大机制 铟化铟(InSb)晶体因其独特的能带结构,成为提升霍尔电压的关键材料。相较于传统硅基材料,其载流子迁移率高出3-5倍,在相同磁场强度下可显著放大霍尔电压。其作…...

无法运用pytorch环境、改环境路径、隔离环境
一.未建虚拟环境时 1.创建新项目后,直接运行是这样的。 2.设置中Virtualenv找不到pytorch环境?因为此时没有创建新虚拟环境。 3.选择conda环境(全局环境)时,是可以下载环境的。 运行结果如下: 是全局环境…...

从0开始学vue:pnpm怎么安装
一、什么是 pnpm? pnpm(Performant npm)是新一代 JavaScript 包管理器,优势包括: 节省磁盘空间:通过硬链接和符号链接实现高效存储安装速度更快:比 npm/yarn 快 2-3 倍内置工作区支持…...

React从基础入门到高级实战:React 实战项目 - 项目二:电商平台前端
React 实战项目:电商平台前端 欢迎来到本 React 开发教程专栏的第 27 篇!在前 26 篇文章中,我们从 React 的基础概念逐步深入到高级技巧,涵盖了组件、状态、路由、性能优化和设计模式等核心知识。这一次,我们将通过一…...

Python 网络编程 -- WebSocket编程
作者主要是为了用python构建实时网络通信程序。 概念性的东西越简单越好理解,因此,下面我从晚上摘抄的概念 我的理解。 什么是网络通信? 更确切地说,网络通信是两台计算机上的两个进程之间的通信。比如,浏览器进程和新浪服务器上的某个Web服务进程在通…...

微信小程序动态组件加载的应用场景与实现方式
动态组件加载的应用场景与实现方式 你提供的代码展示了微信小程序中动态加载组件的方法,但这种方式在实际开发中需要注意使用场景和实现细节。下面我来详细说明如何应用: 应用场景 按需加载组件:在某些条件满足时才加载组件动态配置组件&a…...

人工智能在智能教育中的创新应用与未来趋势
随着人工智能(AI)技术的飞速发展,教育领域正经历着一场深刻的变革。智能教育通过引入AI、物联网(IoT)、大数据和云计算等前沿技术,正在实现教育的个性化、智能化和高效化。本文将探讨人工智能在智能教育中的…...

边缘计算应用实践心得
当数据中心的光纤开始承载不了爆炸式增长的物联网数据流时,边缘计算就像毛细血管般渗透进现代数字肌理的末梢。这种将算力下沉到数据源头的技术范式,本质上是对传统云计算中心化架构的叛逆与补充——在智能制造车间里,实时质检算法直接在工业…...

EXCEL如何快速批量给两字姓名中间加空格
EXCEL如何快速批量给姓名中间加空格 优点:不会导致排版混乱 缺点:无法输出在原有单元格上,若需要保留原始数据,可将公式结果复制后“选择性粘贴为值” 使用场景:在EXCEL中想要快速批量给两字姓名中间加入空格使姓名对…...

OD 算法题 B卷【BOSS的收入】
文章目录 BOSS的收入 BOSS的收入 一个公司只有一个boss,其有若干一级分销,一级分销又有若干二级分销,每个分销只有唯一的上级;每个月,下级分销需要将自己的总收入(自己的下级上交的)࿰…...

Linux共享内存原理及系统调用分析
shmget 是 System V 共享内存的核心系统调用之一,其权限位(shmflg 参数)决定了共享内存段的访问控制和创建行为。以下是权限位的详细解析: 权限位的组成 shmflg 参数由两部分组成: 权限标志(低 9 位&…...

Jenkins | Linux环境部署Jenkins与部署java项目
1. 部署jenkins 1.1 下载war包 依赖环境 jdk 11 下载地址: https://www.jenkins.io/ 依赖环境 1.2 启动服务 启动命令 需要注意使用jdk11以上的版本 直接启动 # httpPort 指定端口 #-Xms2048m -Xmx4096m 指定java 堆内存初始大小 与最大大小 /usr/java/jdk17/bin/java…...

react私有样式处理
react私有样式处理 Nav.jsx Menu.jsx vue中通过scoped来实现样式私有化。加上scoped,就属于当前组件的私有样式。 给视图中的元素都加了一个属性data-v-xxx,然后给这些样式都加上属性选择器。(deep就是不加属性也不加属性选择器) …...
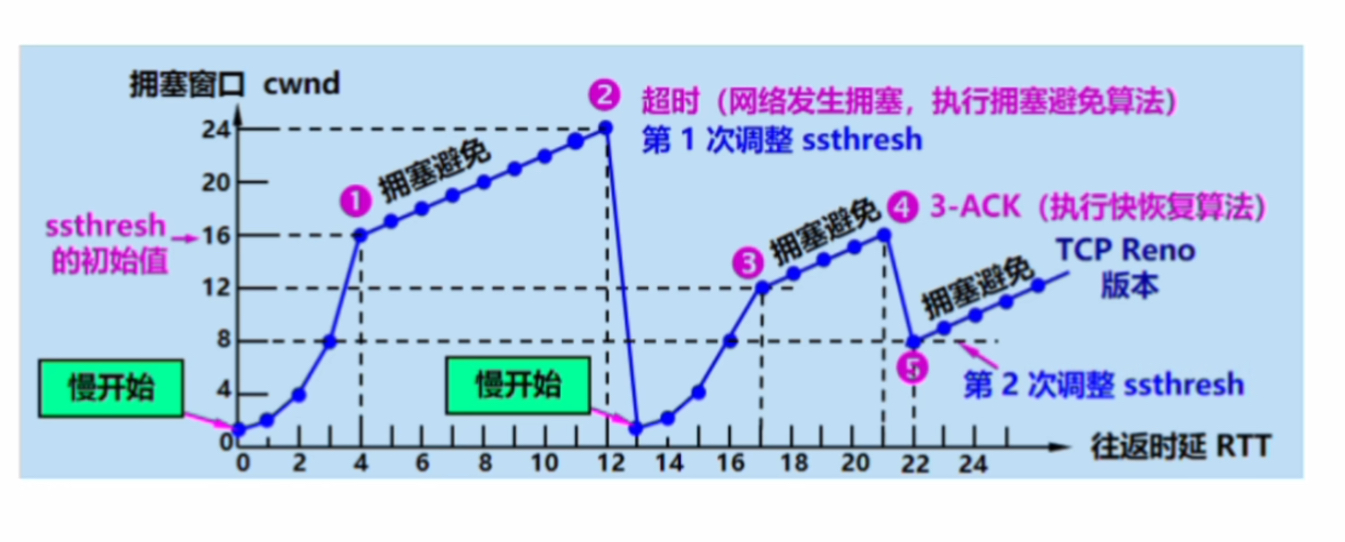
UDP/TCP协议全解
目录 一. UDP协议 1.UDP协议概念 2.UDP数据报格式 3.UDP协议差错控制 二. TCP协议 1.TCP协议概念 2.三次握手与四次挥手 3.TCP报文段格式(重点) 4.流量控制 5.拥塞控制 一. UDP协议 1.UDP协议概念 当应用层的进程1要向进程2传输报文ÿ…...

nginx 服务启动失败问题记录
背景和问题 systemctl status nginx.service 查看报错信息,显示如下: nginx: [emerg] socket() [::]:80 failed (97: Address family not supported by protocol) nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test failed问题分析 这个错误通常…...

Duix.HeyGem:以“离线+开源”重构数字人创作生态
在AI技术快速演进的今天,虚拟数字人正从高成本、高门槛的专业领域走向大众化应用。Duix.HeyGem 数字人项目正是这一趋势下的杰出代表。该项目由一支拥有七年AI研发经验的团队打造,通过放弃传统3D建模路径,转向真人视频驱动的AI训练模型,成功实现了低成本、高质量、本地化的…...

ubuntu22.04安装megaton
前置 sudo apt-get install git cmake ninja-build generate-ninja安装devkitPro https://blog.csdn.net/qq_39942341/article/details/148388639?spm1001.2014.3001.5502 安装cargo https://blog.csdn.net/qq_39942341/article/details/148387783?spm1001.2014.3001.5501 …...

风机下引线断点检测算法实现
风机下引线断点检测算法实现 1. 算法原理 该检测系统基于时域反射法(TDR)原理: 在引线起点注入高压纳秒级脉冲脉冲沿引线传播,遇到阻抗不连续点(断点)产生反射采集反射信号并计算时间差通过小波变换进行信号去噪和特征提取根据传播速度计算断点位置:距离 = (传播速度 时间…...

Windows应用-GUID工具
下载本应用 我们在DirectShow和媒体基础程序的调试中,将会遇到大量的GUID,调试窗口大部分情况下只给出GUID字符串,此GUID代表什么,我们无从得知。这时,就需要此“GUID工具”,将GUID字符串翻译为GUID定义&am…...

vue+element-ui一个页面有多个子组件组成。子组件里面有各种表单,实现点击enter实现跳转到下一个表单元素的功能。
一个父组件里面是有各个子组件的form表单组成的。 我想实现点击enter。焦点直接跳转到下一个表单元素。 父组件就是由各个子组件构成 子组件就像下图一样的都有个el-form的表单。 enterToTab.js let enterToTab {}; (function() {// 返回随机数enterToTab.addEnterListener …...

Spring Boot 启动流程及配置类解析原理
Spring Boot 是一个基于 Spring 框架的开源框架,旨在简化 Spring 应用的配置和部署。通过提供约定优于配置的原则,Spring Boot 大大降低了 Java 企业级应用的开发复杂度。本文将详细介绍 Spring Boot 的启动流程及其配置类的解析原理,帮助开发…...

Vehicle HAL(5)--vhal 实现设置属性的流程
目录 1. ard11 vhal 设置属性的时序图 CarService > vhal > CarService 2. EmulatedVehicleHal::set(xxx) 的实现 本文介绍ard11的vhal属性设置流程图。 1. ard11 vhal 设置属性的时序图 CarService > vhal > CarService 2. EmulatedVehicleHal::set(xxx) 的实现…...

WebRTC中的几个Rtp*Sender
一、问题: webrtc当中有几个比较相似的类,看着都是发送RTP数据包的,分别是:RtpPacketToSend 和RtpSenderVideo还有RtpVideoSender以及RTPSender,这说明什么呢?首先,说明我会很多连词࿰…...
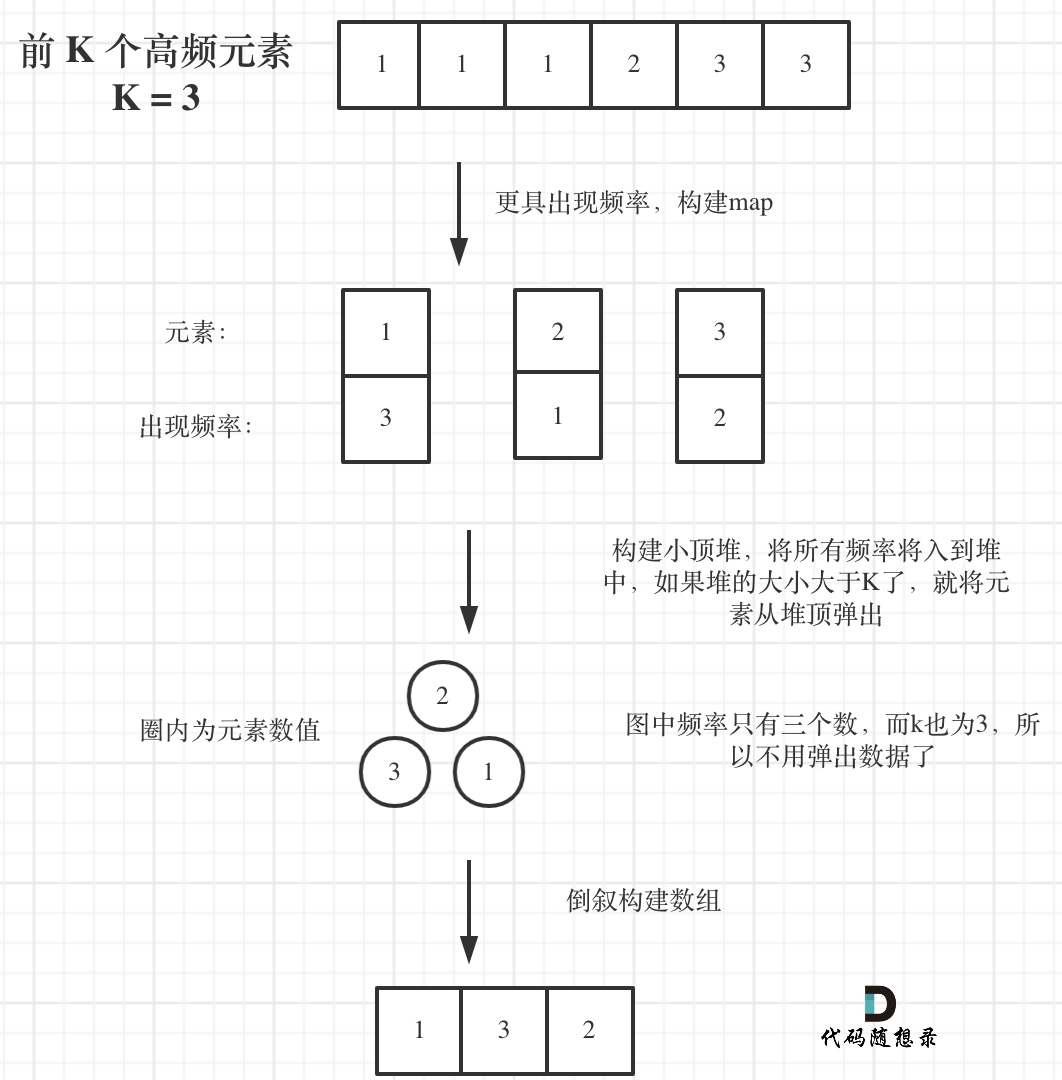
代码随想录算法训练营第十一天 | 150. 逆波兰表达式求值、239. 滑动窗口最大值、347.前 K 个高频元素、栈与队列总结
150. 逆波兰表达式求值--后缀表达式 力扣题目链接(opens new window) 根据 逆波兰表示法,求表达式的值。 有效的运算符包括 , - , * , / 。每个运算对象可以是整数,也可以是另一个逆波兰表达式。 说明: 整数除法只保留整数部分。 给…...
)
Java编程课(一)
Java编程课 一、java简介二、Java基础语法2.1 环境搭建2.2 使用Intellij IDEA新建java项目2.3 Java运行介绍2.4 参数说明2.5 Java基础语法2.6 注释2.7 变量和常量一、java简介 Java是一种广泛使用的高级编程语言,最初由Sun Microsystems于1995年发布。它被设计为具有简单、可…...

IDEA202403 设置主题和护眼色
文章目录 背景一、设置主题二、设置背景豆沙绿三、设置控制台颜色 背景 在用IDEA进行开发时,长时间对着屏幕,不费眼是及其重要 一、设置主题 默认的主题是 Dark 暗黑,可更改为其他,如Light 高亮 位置:编辑栏【files…...
