学习使用YOLO的predict函数使用
YOLO的 result.py
#2025.1.3
"""
https://docs.ultralytics.com/zh/modes/predict/#inference-arguments
对yolo 目标检测、实例分割、关键点检测结果进行说明https://docs.ultralytics.com/reference/engine/results/#ultralytics.engine.results.Masks.xy
对检测结果(mask) 进行说明https://docs.ultralytics.com/zh/datasets/segment/#what-is-the-auto-annotation-feature-in-ultralytics-yolo
对实例分割数据集的概述,提供将coco标签格式转换为txt标签格式 , 解释yolo实例分割数据集txt特点, 以及yolo自带的分割标注工具,可以对图片自动标注 (使用yolov11x.pt, sam_b.pt,
个人可以先使用yolov11x 对之前标注的 识别框蘑菇数据集进行训练,用来代替 yolov11x.pt 或者两个都可以试一试()!!!!https://docs.ultralytics.com/zh/guides/instance-segmentation-and-tracking/#how-can-i-implement-object-tracking-using-ultralytics-yolo11
YOLOv11实际应用,如 裁剪图像、距离计算、实例分割、停车场管理
"""# C:\Users\Lenovo\miniconda3\envs\yolov8\Lib\site-packages\ultralytics\engine\results.py
"""
本文件主要是对上述yolo的 results.py文件进行学习, 利用yolo检测结果的输出信息
先把其文件代码复制到这里 (以免不小心对源文件进行误改动"""# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
"""
Ultralytics Results, Boxes and Masks classes for handling inference results.Usage: See https://docs.ultralytics.com/modes/predict/
"""from copy import deepcopy
from functools import lru_cache
from pathlib import Pathimport numpy as np
import torchfrom ultralytics.data.augment import LetterBox
from ultralytics.utils import LOGGER, SimpleClass, ops
from ultralytics.utils.checks import check_requirements
from ultralytics.utils.plotting import Annotator, colors, save_one_box
from ultralytics.utils.torch_utils import smart_inference_modeclass BaseTensor(SimpleClass):"""Base tensor class with additional methods for easy manipulation and device handling.Attributes:data (torch.Tensor | np.ndarray): Prediction data such as bounding boxes, masks, or keypoints.orig_shape (Tuple[int, int]): Original shape of the image, typically in the format (height, width).Methods:cpu: Return a copy of the tensor stored in CPU memory.numpy: Returns a copy of the tensor as a numpy array.cuda: Moves the tensor to GPU memory, returning a new instance if necessary.to: Return a copy of the tensor with the specified device and dtype.Examples:>>> import torch>>> data = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])>>> orig_shape = (720, 1280)>>> base_tensor = BaseTensor(data, orig_shape)>>> cpu_tensor = base_tensor.cpu()>>> numpy_array = base_tensor.numpy()>>> gpu_tensor = base_tensor.cuda()"""def __init__(self, data, orig_shape) -> None:"""Initialize BaseTensor with prediction data and the original shape of the image.Args:data (torch.Tensor | np.ndarray): Prediction data such as bounding boxes, masks, or keypoints.orig_shape (Tuple[int, int]): Original shape of the image in (height, width) format.Examples:>>> import torch>>> data = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])>>> orig_shape = (720, 1280)>>> base_tensor = BaseTensor(data, orig_shape)"""assert isinstance(data, (torch.Tensor, np.ndarray)), "data must be torch.Tensor or np.ndarray"self.data = dataself.orig_shape = orig_shape@propertydef shape(self):"""Returns the shape of the underlying data tensor.Returns:(Tuple[int, ...]): The shape of the data tensor.Examples:>>> data = torch.rand(100, 4)>>> base_tensor = BaseTensor(data, orig_shape=(720, 1280))>>> print(base_tensor.shape)(100, 4)"""return self.data.shapedef cpu(self):"""Returns a copy of the tensor stored in CPU memory.Returns:(BaseTensor): A new BaseTensor object with the data tensor moved to CPU memory.Examples:>>> data = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]).cuda()>>> base_tensor = BaseTensor(data, orig_shape=(720, 1280))>>> cpu_tensor = base_tensor.cpu()>>> isinstance(cpu_tensor, BaseTensor)True>>> cpu_tensor.data.devicedevice(type='cpu')"""return self if isinstance(self.data, np.ndarray) else self.__class__(self.data.cpu(), self.orig_shape)def numpy(self):"""Returns a copy of the tensor as a numpy array.Returns:(np.ndarray): A numpy array containing the same data as the original tensor.Examples:>>> data = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])>>> orig_shape = (720, 1280)>>> base_tensor = BaseTensor(data, orig_shape)>>> numpy_array = base_tensor.numpy()>>> print(type(numpy_array))<class 'numpy.ndarray'>"""return self if isinstance(self.data, np.ndarray) else self.__class__(self.data.numpy(), self.orig_shape)def cuda(self):"""Moves the tensor to GPU memory.Returns:(BaseTensor): A new BaseTensor instance with the data moved to GPU memory if it's not already anumpy array, otherwise returns self.Examples:>>> import torch>>> from ultralytics.engine.results import BaseTensor>>> data = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])>>> base_tensor = BaseTensor(data, orig_shape=(720, 1280))>>> gpu_tensor = base_tensor.cuda()>>> print(gpu_tensor.data.device)cuda:0"""return self.__class__(torch.as_tensor(self.data).cuda(), self.orig_shape)def to(self, *args, **kwargs):"""Return a copy of the tensor with the specified device and dtype.Args:*args (Any): Variable length argument list to be passed to torch.Tensor.to().**kwargs (Any): Arbitrary keyword arguments to be passed to torch.Tensor.to().Returns:(BaseTensor): A new BaseTensor instance with the data moved to the specified device and/or dtype.Examples:>>> base_tensor = BaseTensor(torch.randn(3, 4), orig_shape=(480, 640))>>> cuda_tensor = base_tensor.to("cuda")>>> float16_tensor = base_tensor.to(dtype=torch.float16)"""return self.__class__(torch.as_tensor(self.data).to(*args, **kwargs), self.orig_shape)def __len__(self): # override len(results)"""Returns the length of the underlying data tensor.Returns:(int): The number of elements in the first dimension of the data tensor.Examples:>>> data = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])>>> base_tensor = BaseTensor(data, orig_shape=(720, 1280))>>> len(base_tensor)2"""return len(self.data)def __getitem__(self, idx):"""Returns a new BaseTensor instance containing the specified indexed elements of the data tensor.Args:idx (int | List[int] | torch.Tensor): Index or indices to select from the data tensor.Returns:(BaseTensor): A new BaseTensor instance containing the indexed data.Examples:>>> data = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])>>> base_tensor = BaseTensor(data, orig_shape=(720, 1280))>>> result = base_tensor[0] # Select the first row>>> print(result.data)tensor([1, 2, 3])"""return self.__class__(self.data[idx], self.orig_shape)class Results(SimpleClass):"""A class for storing and manipulating inference results.This class encapsulates the functionality for handling detection, segmentation, pose estimation,and classification results from YOLO models.Attributes:orig_img (numpy.ndarray): Original image as a numpy array.orig_shape (Tuple[int, int]): Original image shape in (height, width) format.boxes (Boxes | None): Object containing detection bounding boxes.masks (Masks | None): Object containing detection masks.probs (Probs | None): Object containing class probabilities for classification tasks.keypoints (Keypoints | None): Object containing detected keypoints for each object.obb (OBB | None): Object containing oriented bounding boxes.speed (Dict[str, float | None]): Dictionary of preprocess, inference, and postprocess speeds.names (Dict[int, str]): Dictionary mapping class IDs to class names.path (str): Path to the image file._keys (Tuple[str, ...]): Tuple of attribute names for internal use.Methods:update: Updates object attributes with new detection results.cpu: Returns a copy of the Results object with all tensors on CPU memory.numpy: Returns a copy of the Results object with all tensors as numpy arrays.cuda: Returns a copy of the Results object with all tensors on GPU memory.to: Returns a copy of the Results object with tensors on a specified device and dtype.new: Returns a new Results object with the same image, path, and names.plot: Plots detection results on an input image, returning an annotated image.show: Shows annotated results on screen.save: Saves annotated results to file.verbose: Returns a log string for each task, detailing detections and classifications.save_txt: Saves detection results to a text file.save_crop: Saves cropped detection images.tojson: Converts detection results to JSON format.Examples:>>> results = model("path/to/image.jpg")>>> for result in results:... print(result.boxes) # Print detection boxes... result.show() # Display the annotated image... result.save(filename="result.jpg") # Save annotated image"""def __init__(self, orig_img, path, names, boxes=None, masks=None, probs=None, keypoints=None, obb=None, speed=None) -> None:"""Initialize the Results class for storing and manipulating inference results.Args:orig_img (numpy.ndarray): The original image as a numpy array.path (str): The path to the image file.names (Dict): A dictionary of class names.boxes (torch.Tensor | None): A 2D tensor of bounding box coordinates for each detection.masks (torch.Tensor | None): A 3D tensor of detection masks, where each mask is a binary image.probs (torch.Tensor | None): A 1D tensor of probabilities of each class for classification task.keypoints (torch.Tensor | None): A 2D tensor of keypoint coordinates for each detection.obb (torch.Tensor | None): A 2D tensor of oriented bounding box coordinates for each detection.speed (Dict | None): A dictionary containing preprocess, inference, and postprocess speeds (ms/image).Examples:>>> results = model("path/to/image.jpg")>>> result = results[0] # Get the first result>>> boxes = result.boxes # Get the boxes for the first result>>> masks = result.masks # Get the masks for the first resultNotes:For the default pose model, keypoint indices for human body pose estimation are:0: Nose, 1: Left Eye, 2: Right Eye, 3: Left Ear, 4: Right Ear5: Left Shoulder, 6: Right Shoulder, 7: Left Elbow, 8: Right Elbow9: Left Wrist, 10: Right Wrist, 11: Left Hip, 12: Right Hip13: Left Knee, 14: Right Knee, 15: Left Ankle, 16: Right Ankle"""self.orig_img = orig_imgself.orig_shape = orig_img.shape[:2]self.boxes = Boxes(boxes, self.orig_shape) if boxes is not None else None # native size boxesself.masks = Masks(masks, self.orig_shape) if masks is not None else None # native size or imgsz masksself.probs = Probs(probs) if probs is not None else Noneself.keypoints = Keypoints(keypoints, self.orig_shape) if keypoints is not None else Noneself.obb = OBB(obb, self.orig_shape) if obb is not None else Noneself.speed = speed if speed is not None else {"preprocess": None, "inference": None, "postprocess": None}self.names = namesself.path = pathself.save_dir = Noneself._keys = "boxes", "masks", "probs", "keypoints", "obb"def __getitem__(self, idx):"""Return a Results object for a specific index of inference results.Args:idx (int | slice): Index or slice to retrieve from the Results object.Returns:(Results): A new Results object containing the specified subset of inference results.Examples:>>> results = model("path/to/image.jpg") # Perform inference>>> single_result = results[0] # Get the first result>>> subset_results = results[1:4] # Get a slice of results"""return self._apply("__getitem__", idx)def __len__(self):"""Return the number of detections in the Results object.Returns:(int): The number of detections, determined by the length of the first non-empty attribute(boxes, masks, probs, keypoints, or obb).Examples:>>> results = Results(orig_img, path, names, boxes=torch.rand(5, 4))>>> len(results)5"""for k in self._keys:v = getattr(self, k)if v is not None:return len(v)def update(self, boxes=None, masks=None, probs=None, obb=None):"""Updates the Results object with new detection data.This method allows updating the boxes, masks, probabilities, and oriented bounding boxes (OBB) of theResults object. It ensures that boxes are clipped to the original image shape.Args:boxes (torch.Tensor | None): A tensor of shape (N, 6) containing bounding box coordinates andconfidence scores. The format is (x1, y1, x2, y2, conf, class).masks (torch.Tensor | None): A tensor of shape (N, H, W) containing segmentation masks.probs (torch.Tensor | None): A tensor of shape (num_classes,) containing class probabilities.obb (torch.Tensor | None): A tensor of shape (N, 5) containing oriented bounding box coordinates.Examples:>>> results = model("image.jpg")>>> new_boxes = torch.tensor([[100, 100, 200, 200, 0.9, 0]])>>> results[0].update(boxes=new_boxes)"""if boxes is not None:self.boxes = Boxes(ops.clip_boxes(boxes, self.orig_shape), self.orig_shape)if masks is not None:self.masks = Masks(masks, self.orig_shape)if probs is not None:self.probs = probsif obb is not None:self.obb = OBB(obb, self.orig_shape)def _apply(self, fn, *args, **kwargs):"""Applies a function to all non-empty attributes and returns a new Results object with modified attributes.This method is internally called by methods like .to(), .cuda(), .cpu(), etc.Args:fn (str): The name of the function to apply.*args (Any): Variable length argument list to pass to the function.**kwargs (Any): Arbitrary keyword arguments to pass to the function.Returns:(Results): A new Results object with attributes modified by the applied function.Examples:>>> results = model("path/to/image.jpg")>>> for result in results:... result_cuda = result.cuda()... result_cpu = result.cpu()"""r = self.new()for k in self._keys:v = getattr(self, k)if v is not None:setattr(r, k, getattr(v, fn)(*args, **kwargs))return rdef cpu(self):"""Returns a copy of the Results object with all its tensors moved to CPU memory.This method creates a new Results object with all tensor attributes (boxes, masks, probs, keypoints, obb)transferred to CPU memory. It's useful for moving data from GPU to CPU for further processing or saving.Returns:(Results): A new Results object with all tensor attributes on CPU memory.Examples:>>> results = model("path/to/image.jpg") # Perform inference>>> cpu_result = results[0].cpu() # Move the first result to CPU>>> print(cpu_result.boxes.device) # Output: cpu"""return self._apply("cpu")def numpy(self):"""Converts all tensors in the Results object to numpy arrays.Returns:(Results): A new Results object with all tensors converted to numpy arrays.Examples:>>> results = model("path/to/image.jpg")>>> numpy_result = results[0].numpy()>>> type(numpy_result.boxes.data)<class 'numpy.ndarray'>Notes:This method creates a new Results object, leaving the original unchanged. It's useful forinteroperability with numpy-based libraries or when CPU-based operations are required."""return self._apply("numpy")def cuda(self):"""Moves all tensors in the Results object to GPU memory.Returns:(Results): A new Results object with all tensors moved to CUDA device.Examples:>>> results = model("path/to/image.jpg")>>> cuda_results = results[0].cuda() # Move first result to GPU>>> for result in results:... result_cuda = result.cuda() # Move each result to GPU"""return self._apply("cuda")def to(self, *args, **kwargs):"""Moves all tensors in the Results object to the specified device and dtype.Args:*args (Any): Variable length argument list to be passed to torch.Tensor.to().**kwargs (Any): Arbitrary keyword arguments to be passed to torch.Tensor.to().Returns:(Results): A new Results object with all tensors moved to the specified device and dtype.Examples:>>> results = model("path/to/image.jpg")>>> result_cuda = results[0].to("cuda") # Move first result to GPU>>> result_cpu = results[0].to("cpu") # Move first result to CPU>>> result_half = results[0].to(dtype=torch.float16) # Convert first result to half precision"""return self._apply("to", *args, **kwargs)def new(self):"""Creates a new Results object with the same image, path, names, and speed attributes.Returns:(Results): A new Results object with copied attributes from the original instance.Examples:>>> results = model("path/to/image.jpg")>>> new_result = results[0].new()"""return Results(orig_img=self.orig_img, path=self.path, names=self.names, speed=self.speed)def plot(self,conf=True,line_width=None,font_size=None,font="Arial.ttf",pil=False,img=None,im_gpu=None,kpt_radius=5,kpt_line=True,labels=True,boxes=True,masks=True,probs=True,show=False,save=False,filename=None,color_mode="class",):"""Plots detection results on an input RGB image.Args:conf (bool): Whether to plot detection confidence scores.line_width (float | None): Line width of bounding boxes. If None, scaled to image size.font_size (float | None): Font size for text. If None, scaled to image size.font (str): Font to use for text.pil (bool): Whether to return the image as a PIL Image.img (np.ndarray | None): Image to plot on. If None, uses original image.im_gpu (torch.Tensor | None): Normalized image on GPU for faster mask plotting.kpt_radius (int): Radius of drawn keypoints.kpt_line (bool): Whether to draw lines connecting keypoints.labels (bool): Whether to plot labels of bounding boxes.boxes (bool): Whether to plot bounding boxes.masks (bool): Whether to plot masks.probs (bool): Whether to plot classification probabilities.show (bool): Whether to display the annotated image.save (bool): Whether to save the annotated image.filename (str | None): Filename to save image if save is True.color_mode (bool): Specify the color mode, e.g., 'instance' or 'class'. Default to 'class'.Returns:(np.ndarray): Annotated image as a numpy array.Examples:>>> results = model("image.jpg")>>> for result in results:... im = result.plot()... im.show()"""assert color_mode in {"instance", "class"}, f"Expected color_mode='instance' or 'class', not {color_mode}."if img is None and isinstance(self.orig_img, torch.Tensor):img = (self.orig_img[0].detach().permute(1, 2, 0).contiguous() * 255).to(torch.uint8).cpu().numpy()names = self.namesis_obb = self.obb is not Nonepred_boxes, show_boxes = self.obb if is_obb else self.boxes, boxespred_masks, show_masks = self.masks, maskspred_probs, show_probs = self.probs, probsannotator = Annotator(deepcopy(self.orig_img if img is None else img),line_width,font_size,font,pil or (pred_probs is not None and show_probs), # Classify tasks default to pil=Trueexample=names,)# Plot Segment resultsif pred_masks and show_masks:if im_gpu is None:img = LetterBox(pred_masks.shape[1:])(image=annotator.result())im_gpu = (torch.as_tensor(img, dtype=torch.float16, device=pred_masks.data.device).permute(2, 0, 1).flip(0).contiguous()/ 255)idx = (pred_boxes.idif pred_boxes.id is not None and color_mode == "instance"else pred_boxes.clsif pred_boxes and color_mode == "class"else reversed(range(len(pred_masks))))annotator.masks(pred_masks.data, colors=[colors(x, True) for x in idx], im_gpu=im_gpu)# Plot Detect resultsif pred_boxes is not None and show_boxes:for i, d in enumerate(reversed(pred_boxes)):c, conf, id = int(d.cls), float(d.conf) if conf else None, None if d.id is None else int(d.id.item())name = ("" if id is None else f"id:{id} ") + names[c]label = (f"{name} {conf:.2f}" if conf else name) if labels else Nonebox = d.xyxyxyxy.reshape(-1, 4, 2).squeeze() if is_obb else d.xyxy.squeeze()annotator.box_label(box,label,color=colors(cif color_mode == "class"else idif id is not Noneelse iif color_mode == "instance"else None,True,),rotated=is_obb,)# Plot Classify resultsif pred_probs is not None and show_probs:text = ",\n".join(f"{names[j] if names else j} {pred_probs.data[j]:.2f}" for j in pred_probs.top5)x = round(self.orig_shape[0] * 0.03)annotator.text([x, x], text, txt_color=(255, 255, 255)) # TODO: allow setting colors# Plot Pose resultsif self.keypoints is not None:for i, k in enumerate(reversed(self.keypoints.data)):annotator.kpts(k,self.orig_shape,radius=kpt_radius,kpt_line=kpt_line,kpt_color=colors(i, True) if color_mode == "instance" else None,)# Show resultsif show:annotator.show(self.path)# Save resultsif save:annotator.save(filename)return annotator.result()def show(self, *args, **kwargs):"""Display the image with annotated inference results.This method plots the detection results on the original image and displays it. It's a convenient way tovisualize the model's predictions directly.Args:*args (Any): Variable length argument list to be passed to the `plot()` method.**kwargs (Any): Arbitrary keyword arguments to be passed to the `plot()` method.Examples:>>> results = model("path/to/image.jpg")>>> results[0].show() # Display the first result>>> for result in results:... result.show() # Display all results"""self.plot(show=True, *args, **kwargs)def save(self, filename=None, *args, **kwargs):"""Saves annotated inference results image to file.This method plots the detection results on the original image and saves the annotated image to a file. Itutilizes the `plot` method to generate the annotated image and then saves it to the specified filename.Args:filename (str | Path | None): The filename to save the annotated image. If None, a default filenameis generated based on the original image path.*args (Any): Variable length argument list to be passed to the `plot` method.**kwargs (Any): Arbitrary keyword arguments to be passed to the `plot` method.Examples:>>> results = model("path/to/image.jpg")>>> for result in results:... result.save("annotated_image.jpg")>>> # Or with custom plot arguments>>> for result in results:... result.save("annotated_image.jpg", conf=False, line_width=2)"""if not filename:filename = f"results_{Path(self.path).name}"self.plot(save=True, filename=filename, *args, **kwargs)return filenamedef verbose(self):"""Returns a log string for each task in the results, detailing detection and classification outcomes.This method generates a human-readable string summarizing the detection and classification results. It includesthe number of detections for each class and the top probabilities for classification tasks.Returns:(str): A formatted string containing a summary of the results. For detection tasks, it includes thenumber of detections per class. For classification tasks, it includes the top 5 class probabilities.Examples:>>> results = model("path/to/image.jpg")>>> for result in results:... print(result.verbose())2 persons, 1 car, 3 traffic lights,dog 0.92, cat 0.78, horse 0.64,Notes:- If there are no detections, the method returns "(no detections), " for detection tasks.- For classification tasks, it returns the top 5 class probabilities and their corresponding class names.- The returned string is comma-separated and ends with a comma and a space."""log_string = ""probs = self.probsboxes = self.boxesif len(self) == 0:return log_string if probs is not None else f"{log_string}(no detections), "if probs is not None:log_string += f"{', '.join(f'{self.names[j]} {probs.data[j]:.2f}' for j in probs.top5)}, "if boxes:for c in boxes.cls.unique():n = (boxes.cls == c).sum() # detections per classlog_string += f"{n} {self.names[int(c)]}{'s' * (n > 1)}, "return log_stringdef save_txt(self, txt_file, save_conf=False):"""Save detection results to a text file.Args:txt_file (str | Path): Path to the output text file.save_conf (bool): Whether to include confidence scores in the output.Returns:(str): Path to the saved text file.Examples:>>> from ultralytics import YOLO>>> model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")>>> results = model("path/to/image.jpg")>>> for result in results:... result.save_txt("output.txt")Notes:- The file will contain one line per detection or classification with the following structure:- For detections: `class confidence x_center y_center width height`- For classifications: `confidence class_name`- For masks and keypoints, the specific formats will vary accordingly.- The function will create the output directory if it does not exist.- If save_conf is False, the confidence scores will be excluded from the output.- Existing contents of the file will not be overwritten; new results will be appended."""is_obb = self.obb is not Noneboxes = self.obb if is_obb else self.boxesmasks = self.masksprobs = self.probskpts = self.keypointstexts = []if probs is not None:# Classify[texts.append(f"{probs.data[j]:.2f} {self.names[j]}") for j in probs.top5]elif boxes:# Detect/segment/posefor j, d in enumerate(boxes):c, conf, id = int(d.cls), float(d.conf), None if d.id is None else int(d.id.item())line = (c, *(d.xyxyxyxyn.view(-1) if is_obb else d.xywhn.view(-1)))if masks:seg = masks[j].xyn[0].copy().reshape(-1) # reversed mask.xyn, (n,2) to (n*2)line = (c, *seg)if kpts is not None:kpt = torch.cat((kpts[j].xyn, kpts[j].conf[..., None]), 2) if kpts[j].has_visible else kpts[j].xynline += (*kpt.reshape(-1).tolist(),)line += (conf,) * save_conf + (() if id is None else (id,))texts.append(("%g " * len(line)).rstrip() % line)if texts:Path(txt_file).parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True) # make directorywith open(txt_file, "a") as f:f.writelines(text + "\n" for text in texts)def save_crop(self, save_dir, file_name=Path("im.jpg")):"""Saves cropped detection images to specified directory.This method saves cropped images of detected objects to a specified directory. Each crop is saved in asubdirectory named after the object's class, with the filename based on the input file_name.Args:save_dir (str | Path): Directory path where cropped images will be saved.file_name (str | Path): Base filename for the saved cropped images. Default is Path("im.jpg").Notes:- This method does not support Classify or Oriented Bounding Box (OBB) tasks.- Crops are saved as 'save_dir/class_name/file_name.jpg'.- The method will create necessary subdirectories if they don't exist.- Original image is copied before cropping to avoid modifying the original.Examples:>>> results = model("path/to/image.jpg")>>> for result in results:... result.save_crop(save_dir="path/to/crops", file_name="detection")"""if self.probs is not None:LOGGER.warning("WARNING ⚠️ Classify task do not support `save_crop`.")returnif self.obb is not None:LOGGER.warning("WARNING ⚠️ OBB task do not support `save_crop`.")returnfor d in self.boxes:save_one_box(d.xyxy,self.orig_img.copy(),file=Path(save_dir) / self.names[int(d.cls)] / f"{Path(file_name)}.jpg",BGR=True,)def summary(self, normalize=False, decimals=5):"""Converts inference results to a summarized dictionary with optional normalization for box coordinates.This method creates a list of detection dictionaries, each containing information about a singledetection or classification result. For classification tasks, it returns the top class and itsconfidence. For detection tasks, it includes class information, bounding box coordinates, andoptionally mask segments and keypoints.Args:normalize (bool): Whether to normalize bounding box coordinates by image dimensions. Defaults to False.decimals (int): Number of decimal places to round the output values to. Defaults to 5.Returns:(List[Dict]): A list of dictionaries, each containing summarized information for a singledetection or classification result. The structure of each dictionary varies based on thetask type (classification or detection) and available information (boxes, masks, keypoints).Examples:>>> results = model("image.jpg")>>> summary = results[0].summary()>>> print(summary)"""# Create list of detection dictionariesresults = []if self.probs is not None:class_id = self.probs.top1results.append({"name": self.names[class_id],"class": class_id,"confidence": round(self.probs.top1conf.item(), decimals),})return resultsis_obb = self.obb is not Nonedata = self.obb if is_obb else self.boxesh, w = self.orig_shape if normalize else (1, 1)for i, row in enumerate(data): # xyxy, track_id if tracking, conf, class_idclass_id, conf = int(row.cls), round(row.conf.item(), decimals)box = (row.xyxyxyxy if is_obb else row.xyxy).squeeze().reshape(-1, 2).tolist()xy = {}for j, b in enumerate(box):xy[f"x{j + 1}"] = round(b[0] / w, decimals)xy[f"y{j + 1}"] = round(b[1] / h, decimals)result = {"name": self.names[class_id], "class": class_id, "confidence": conf, "box": xy}if data.is_track:result["track_id"] = int(row.id.item()) # track IDif self.masks:result["segments"] = {"x": (self.masks.xy[i][:, 0] / w).round(decimals).tolist(),"y": (self.masks.xy[i][:, 1] / h).round(decimals).tolist(),}if self.keypoints is not None:x, y, visible = self.keypoints[i].data[0].cpu().unbind(dim=1) # torch Tensorresult["keypoints"] = {"x": (x / w).numpy().round(decimals).tolist(), # decimals named argument required"y": (y / h).numpy().round(decimals).tolist(),"visible": visible.numpy().round(decimals).tolist(),}results.append(result)return resultsdef to_df(self, normalize=False, decimals=5):"""Converts detection results to a Pandas Dataframe.This method converts the detection results into Pandas Dataframe format. It includes informationabout detected objects such as bounding boxes, class names, confidence scores, and optionallysegmentation masks and keypoints.Args:normalize (bool): Whether to normalize the bounding box coordinates by the image dimensions.If True, coordinates will be returned as float values between 0 and 1. Defaults to False.decimals (int): Number of decimal places to round the output values to. Defaults to 5.Returns:(DataFrame): A Pandas Dataframe containing all the information in results in an organized way.Examples:>>> results = model("path/to/image.jpg")>>> df_result = results[0].to_df()>>> print(df_result)"""import pandas as pdreturn pd.DataFrame(self.summary(normalize=normalize, decimals=decimals))def to_csv(self, normalize=False, decimals=5, *args, **kwargs):"""Converts detection results to a CSV format.This method serializes the detection results into a CSV format. It includes informationabout detected objects such as bounding boxes, class names, confidence scores, and optionallysegmentation masks and keypoints.Args:normalize (bool): Whether to normalize the bounding box coordinates by the image dimensions.If True, coordinates will be returned as float values between 0 and 1. Defaults to False.decimals (int): Number of decimal places to round the output values to. Defaults to 5.*args (Any): Variable length argument list to be passed to pandas.DataFrame.to_csv().**kwargs (Any): Arbitrary keyword arguments to be passed to pandas.DataFrame.to_csv().Returns:(str): CSV containing all the information in results in an organized way.Examples:>>> results = model("path/to/image.jpg")>>> csv_result = results[0].to_csv()>>> print(csv_result)"""return self.to_df(normalize=normalize, decimals=decimals).to_csv(*args, **kwargs)def to_xml(self, normalize=False, decimals=5, *args, **kwargs):"""Converts detection results to XML format.This method serializes the detection results into an XML format. It includes informationabout detected objects such as bounding boxes, class names, confidence scores, and optionallysegmentation masks and keypoints.Args:normalize (bool): Whether to normalize the bounding box coordinates by the image dimensions.If True, coordinates will be returned as float values between 0 and 1. Defaults to False.decimals (int): Number of decimal places to round the output values to. Defaults to 5.*args (Any): Variable length argument list to be passed to pandas.DataFrame.to_xml().**kwargs (Any): Arbitrary keyword arguments to be passed to pandas.DataFrame.to_xml().Returns:(str): An XML string containing all the information in results in an organized way.Examples:>>> results = model("path/to/image.jpg")>>> xml_result = results[0].to_xml()>>> print(xml_result)"""check_requirements("lxml")df = self.to_df(normalize=normalize, decimals=decimals)return '<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>\n<root></root>' if df.empty else df.to_xml(*args, **kwargs)def tojson(self, normalize=False, decimals=5):"""Deprecated version of to_json()."""LOGGER.warning("WARNING ⚠️ 'result.tojson()' is deprecated, replace with 'result.to_json()'.")return self.to_json(normalize, decimals)def to_json(self, normalize=False, decimals=5):"""Converts detection results to JSON format.This method serializes the detection results into a JSON-compatible format. It includes informationabout detected objects such as bounding boxes, class names, confidence scores, and optionallysegmentation masks and keypoints.Args:normalize (bool): Whether to normalize the bounding box coordinates by the image dimensions.If True, coordinates will be returned as float values between 0 and 1. Defaults to False.decimals (int): Number of decimal places to round the output values to. Defaults to 5.Returns:(str): A JSON string containing the serialized detection results.Examples:>>> results = model("path/to/image.jpg")>>> json_result = results[0].to_json()>>> print(json_result)Notes:- For classification tasks, the JSON will contain class probabilities instead of bounding boxes.- For object detection tasks, the JSON will include bounding box coordinates, class names, andconfidence scores.- If available, segmentation masks and keypoints will also be included in the JSON output.- The method uses the `summary` method internally to generate the data structure beforeconverting it to JSON."""import jsonreturn json.dumps(self.summary(normalize=normalize, decimals=decimals), indent=2)class Boxes(BaseTensor):"""A class for managing and manipulating detection boxes.This class provides functionality for handling detection boxes, including their coordinates, confidence scores,class labels, and optional tracking IDs. It supports various box formats and offers methods for easy manipulationand conversion between different coordinate systems.Attributes:data (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): The raw tensor containing detection boxes and associated data.orig_shape (Tuple[int, int]): The original image dimensions (height, width).is_track (bool): Indicates whether tracking IDs are included in the box data.xyxy (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): Boxes in [x1, y1, x2, y2] format.conf (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): Confidence scores for each box.cls (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): Class labels for each box.id (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): Tracking IDs for each box (if available).xywh (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): Boxes in [x, y, width, height] format.xyxyn (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): Normalized [x1, y1, x2, y2] boxes relative to orig_shape.xywhn (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): Normalized [x, y, width, height] boxes relative to orig_shape.Methods:cpu(): Returns a copy of the object with all tensors on CPU memory.numpy(): Returns a copy of the object with all tensors as numpy arrays.cuda(): Returns a copy of the object with all tensors on GPU memory.to(*args, **kwargs): Returns a copy of the object with tensors on specified device and dtype.Examples:>>> import torch>>> boxes_data = torch.tensor([[100, 50, 150, 100, 0.9, 0], [200, 150, 300, 250, 0.8, 1]])>>> orig_shape = (480, 640) # height, width>>> boxes = Boxes(boxes_data, orig_shape)>>> print(boxes.xyxy)>>> print(boxes.conf)>>> print(boxes.cls)>>> print(boxes.xywhn)"""def __init__(self, boxes, orig_shape) -> None:"""Initialize the Boxes class with detection box data and the original image shape.This class manages detection boxes, providing easy access and manipulation of box coordinates,confidence scores, class identifiers, and optional tracking IDs. It supports multiple formatsfor box coordinates, including both absolute and normalized forms.Args:boxes (torch.Tensor | np.ndarray): A tensor or numpy array with detection boxes of shape(num_boxes, 6) or (num_boxes, 7). Columns should contain[x1, y1, x2, y2, confidence, class, (optional) track_id].orig_shape (Tuple[int, int]): The original image shape as (height, width). Used for normalization.Attributes:data (torch.Tensor): The raw tensor containing detection boxes and their associated data.orig_shape (Tuple[int, int]): The original image size, used for normalization.is_track (bool): Indicates whether tracking IDs are included in the box data.Examples:>>> import torch>>> boxes = torch.tensor([[100, 50, 150, 100, 0.9, 0]])>>> orig_shape = (480, 640)>>> detection_boxes = Boxes(boxes, orig_shape)>>> print(detection_boxes.xyxy)tensor([[100., 50., 150., 100.]])"""if boxes.ndim == 1:boxes = boxes[None, :]n = boxes.shape[-1]assert n in {6, 7}, f"expected 6 or 7 values but got {n}" # xyxy, track_id, conf, clssuper().__init__(boxes, orig_shape)self.is_track = n == 7self.orig_shape = orig_shape@propertydef xyxy(self):"""Returns bounding boxes in [x1, y1, x2, y2] format.Returns:(torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): A tensor or numpy array of shape (n, 4) containing bounding boxcoordinates in [x1, y1, x2, y2] format, where n is the number of boxes.Examples:>>> results = model("image.jpg")>>> boxes = results[0].boxes>>> xyxy = boxes.xyxy>>> print(xyxy)"""return self.data[:, :4]@propertydef conf(self):"""Returns the confidence scores for each detection box.Returns:(torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): A 1D tensor or array containing confidence scores for each detection,with shape (N,) where N is the number of detections.Examples:>>> boxes = Boxes(torch.tensor([[10, 20, 30, 40, 0.9, 0]]), orig_shape=(100, 100))>>> conf_scores = boxes.conf>>> print(conf_scores)tensor([0.9000])"""return self.data[:, -2]@propertydef cls(self):"""Returns the class ID tensor representing category predictions for each bounding box.Returns:(torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): A tensor or numpy array containing the class IDs for each detection box.The shape is (N,), where N is the number of boxes.Examples:>>> results = model("image.jpg")>>> boxes = results[0].boxes>>> class_ids = boxes.cls>>> print(class_ids) # tensor([0., 2., 1.])"""return self.data[:, -1]@propertydef id(self):"""Returns the tracking IDs for each detection box if available.Returns:(torch.Tensor | None): A tensor containing tracking IDs for each box if tracking is enabled,otherwise None. Shape is (N,) where N is the number of boxes.Examples:>>> results = model.track("path/to/video.mp4")>>> for result in results:... boxes = result.boxes... if boxes.is_track:... track_ids = boxes.id... print(f"Tracking IDs: {track_ids}")... else:... print("Tracking is not enabled for these boxes.")Notes:- This property is only available when tracking is enabled (i.e., when `is_track` is True).- The tracking IDs are typically used to associate detections across multiple frames in video analysis."""return self.data[:, -3] if self.is_track else None@property@lru_cache(maxsize=2) # maxsize 1 should sufficedef xywh(self):"""Convert bounding boxes from [x1, y1, x2, y2] format to [x, y, width, height] format.Returns:(torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): Boxes in [x_center, y_center, width, height] format, where x_center, y_center are the coordinates ofthe center point of the bounding box, width, height are the dimensions of the bounding box and theshape of the returned tensor is (N, 4), where N is the number of boxes.Examples:>>> boxes = Boxes(torch.tensor([[100, 50, 150, 100], [200, 150, 300, 250]]), orig_shape=(480, 640))>>> xywh = boxes.xywh>>> print(xywh)tensor([[100.0000, 50.0000, 50.0000, 50.0000],[200.0000, 150.0000, 100.0000, 100.0000]])"""return ops.xyxy2xywh(self.xyxy)@property@lru_cache(maxsize=2)def xyxyn(self):"""Returns normalized bounding box coordinates relative to the original image size.This property calculates and returns the bounding box coordinates in [x1, y1, x2, y2] format,normalized to the range [0, 1] based on the original image dimensions.Returns:(torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): Normalized bounding box coordinates with shape (N, 4), where N isthe number of boxes. Each row contains [x1, y1, x2, y2] values normalized to [0, 1].Examples:>>> boxes = Boxes(torch.tensor([[100, 50, 300, 400, 0.9, 0]]), orig_shape=(480, 640))>>> normalized = boxes.xyxyn>>> print(normalized)tensor([[0.1562, 0.1042, 0.4688, 0.8333]])"""xyxy = self.xyxy.clone() if isinstance(self.xyxy, torch.Tensor) else np.copy(self.xyxy)xyxy[..., [0, 2]] /= self.orig_shape[1]xyxy[..., [1, 3]] /= self.orig_shape[0]return xyxy@property@lru_cache(maxsize=2)def xywhn(self):"""Returns normalized bounding boxes in [x, y, width, height] format.This property calculates and returns the normalized bounding box coordinates in the format[x_center, y_center, width, height], where all values are relative to the original image dimensions.Returns:(torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): Normalized bounding boxes with shape (N, 4), where N is thenumber of boxes. Each row contains [x_center, y_center, width, height] values normalizedto [0, 1] based on the original image dimensions.Examples:>>> boxes = Boxes(torch.tensor([[100, 50, 150, 100, 0.9, 0]]), orig_shape=(480, 640))>>> normalized = boxes.xywhn>>> print(normalized)tensor([[0.1953, 0.1562, 0.0781, 0.1042]])"""xywh = ops.xyxy2xywh(self.xyxy)xywh[..., [0, 2]] /= self.orig_shape[1]xywh[..., [1, 3]] /= self.orig_shape[0]return xywhclass Masks(BaseTensor):"""A class for storing and manipulating detection masks.This class extends BaseTensor and provides functionality for handling segmentation masks,including methods for converting between pixel and normalized coordinates.Attributes:data (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): The raw tensor or array containing mask data.orig_shape (tuple): Original image shape in (height, width) format.xy (List[numpy.ndarray]): A list of segments in pixel coordinates.xyn (List[numpy.ndarray]): A list of normalized segments.Methods:cpu(): Returns a copy of the Masks object with the mask tensor on CPU memory.numpy(): Returns a copy of the Masks object with the mask tensor as a numpy array.cuda(): Returns a copy of the Masks object with the mask tensor on GPU memory.to(*args, **kwargs): Returns a copy of the Masks object with the mask tensor on specified device and dtype.Examples:>>> masks_data = torch.rand(1, 160, 160)>>> orig_shape = (720, 1280)>>> masks = Masks(masks_data, orig_shape)>>> pixel_coords = masks.xy>>> normalized_coords = masks.xyn"""def __init__(self, masks, orig_shape) -> None:"""Initialize the Masks class with detection mask data and the original image shape.Args:masks (torch.Tensor | np.ndarray): Detection masks with shape (num_masks, height, width).orig_shape (tuple): The original image shape as (height, width). Used for normalization.Examples:>>> import torch>>> from ultralytics.engine.results import Masks>>> masks = torch.rand(10, 160, 160) # 10 masks of 160x160 resolution>>> orig_shape = (720, 1280) # Original image shape>>> mask_obj = Masks(masks, orig_shape)"""if masks.ndim == 2:masks = masks[None, :]super().__init__(masks, orig_shape)@property@lru_cache(maxsize=1)def xyn(self):"""Returns normalized xy-coordinates of the segmentation masks.This property calculates and caches the normalized xy-coordinates of the segmentation masks. The coordinatesare normalized relative to the original image shape.Returns:(List[numpy.ndarray]): A list of numpy arrays, where each array contains the normalized xy-coordinatesof a single segmentation mask. Each array has shape (N, 2), where N is the number of points in themask contour.Examples:>>> results = model("image.jpg")>>> masks = results[0].masks>>> normalized_coords = masks.xyn>>> print(normalized_coords[0]) # Normalized coordinates of the first mask"""return [ops.scale_coords(self.data.shape[1:], x, self.orig_shape, normalize=True)for x in ops.masks2segments(self.data)]@property@lru_cache(maxsize=1)def xy(self):"""Returns the [x, y] pixel coordinates for each segment in the mask tensor.This property calculates and returns a list of pixel coordinates for each segmentation mask in theMasks object. The coordinates are scaled to match the original image dimensions.Returns:(List[numpy.ndarray]): A list of numpy arrays, where each array contains the [x, y] pixelcoordinates for a single segmentation mask. Each array has shape (N, 2), where N is thenumber of points in the segment.Examples:>>> results = model("image.jpg")>>> masks = results[0].masks>>> xy_coords = masks.xy>>> print(len(xy_coords)) # Number of masks>>> print(xy_coords[0].shape) # Shape of first mask's coordinates"""return [ops.scale_coords(self.data.shape[1:], x, self.orig_shape, normalize=False)for x in ops.masks2segments(self.data)]class Keypoints(BaseTensor):"""A class for storing and manipulating detection keypoints.This class encapsulates functionality for handling keypoint data, including coordinate manipulation,normalization, and confidence values.Attributes:data (torch.Tensor): The raw tensor containing keypoint data.orig_shape (Tuple[int, int]): The original image dimensions (height, width).has_visible (bool): Indicates whether visibility information is available for keypoints.xy (torch.Tensor): Keypoint coordinates in [x, y] format.xyn (torch.Tensor): Normalized keypoint coordinates in [x, y] format, relative to orig_shape.conf (torch.Tensor): Confidence values for each keypoint, if available.Methods:cpu(): Returns a copy of the keypoints tensor on CPU memory.numpy(): Returns a copy of the keypoints tensor as a numpy array.cuda(): Returns a copy of the keypoints tensor on GPU memory.to(*args, **kwargs): Returns a copy of the keypoints tensor with specified device and dtype.Examples:>>> import torch>>> from ultralytics.engine.results import Keypoints>>> keypoints_data = torch.rand(1, 17, 3) # 1 detection, 17 keypoints, (x, y, conf)>>> orig_shape = (480, 640) # Original image shape (height, width)>>> keypoints = Keypoints(keypoints_data, orig_shape)>>> print(keypoints.xy.shape) # Access xy coordinates>>> print(keypoints.conf) # Access confidence values>>> keypoints_cpu = keypoints.cpu() # Move keypoints to CPU"""@smart_inference_mode() # avoid keypoints < conf in-place errordef __init__(self, keypoints, orig_shape) -> None:"""Initializes the Keypoints object with detection keypoints and original image dimensions.This method processes the input keypoints tensor, handling both 2D and 3D formats. For 3D tensors(x, y, confidence), it masks out low-confidence keypoints by setting their coordinates to zero.Args:keypoints (torch.Tensor): A tensor containing keypoint data. Shape can be either:- (num_objects, num_keypoints, 2) for x, y coordinates only- (num_objects, num_keypoints, 3) for x, y coordinates and confidence scoresorig_shape (Tuple[int, int]): The original image dimensions (height, width).Examples:>>> kpts = torch.rand(1, 17, 3) # 1 object, 17 keypoints (COCO format), x,y,conf>>> orig_shape = (720, 1280) # Original image height, width>>> keypoints = Keypoints(kpts, orig_shape)"""if keypoints.ndim == 2:keypoints = keypoints[None, :]if keypoints.shape[2] == 3: # x, y, confmask = keypoints[..., 2] < 0.5 # points with conf < 0.5 (not visible)keypoints[..., :2][mask] = 0super().__init__(keypoints, orig_shape)self.has_visible = self.data.shape[-1] == 3@property@lru_cache(maxsize=1)def xy(self):"""Returns x, y coordinates of keypoints.Returns:(torch.Tensor): A tensor containing the x, y coordinates of keypoints with shape (N, K, 2), where N isthe number of detections and K is the number of keypoints per detection.Examples:>>> results = model("image.jpg")>>> keypoints = results[0].keypoints>>> xy = keypoints.xy>>> print(xy.shape) # (N, K, 2)>>> print(xy[0]) # x, y coordinates of keypoints for first detectionNotes:- The returned coordinates are in pixel units relative to the original image dimensions.- If keypoints were initialized with confidence values, only keypoints with confidence >= 0.5 are returned.- This property uses LRU caching to improve performance on repeated access."""return self.data[..., :2]@property@lru_cache(maxsize=1)def xyn(self):"""Returns normalized coordinates (x, y) of keypoints relative to the original image size.Returns:(torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): A tensor or array of shape (N, K, 2) containing normalized keypointcoordinates, where N is the number of instances, K is the number of keypoints, and the lastdimension contains [x, y] values in the range [0, 1].Examples:>>> keypoints = Keypoints(torch.rand(1, 17, 2), orig_shape=(480, 640))>>> normalized_kpts = keypoints.xyn>>> print(normalized_kpts.shape)torch.Size([1, 17, 2])"""xy = self.xy.clone() if isinstance(self.xy, torch.Tensor) else np.copy(self.xy)xy[..., 0] /= self.orig_shape[1]xy[..., 1] /= self.orig_shape[0]return xy@property@lru_cache(maxsize=1)def conf(self):"""Returns confidence values for each keypoint.Returns:(torch.Tensor | None): A tensor containing confidence scores for each keypoint if available,otherwise None. Shape is (num_detections, num_keypoints) for batched data or (num_keypoints,)for single detection.Examples:>>> keypoints = Keypoints(torch.rand(1, 17, 3), orig_shape=(640, 640)) # 1 detection, 17 keypoints>>> conf = keypoints.conf>>> print(conf.shape) # torch.Size([1, 17])"""return self.data[..., 2] if self.has_visible else Noneclass Probs(BaseTensor):"""A class for storing and manipulating classification probabilities.This class extends BaseTensor and provides methods for accessing and manipulatingclassification probabilities, including top-1 and top-5 predictions.Attributes:data (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): The raw tensor or array containing classification probabilities.orig_shape (tuple | None): The original image shape as (height, width). Not used in this class.top1 (int): Index of the class with the highest probability.top5 (List[int]): Indices of the top 5 classes by probability.top1conf (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): Confidence score of the top 1 class.top5conf (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): Confidence scores of the top 5 classes.Methods:cpu(): Returns a copy of the probabilities tensor on CPU memory.numpy(): Returns a copy of the probabilities tensor as a numpy array.cuda(): Returns a copy of the probabilities tensor on GPU memory.to(*args, **kwargs): Returns a copy of the probabilities tensor with specified device and dtype.Examples:>>> probs = torch.tensor([0.1, 0.3, 0.6])>>> p = Probs(probs)>>> print(p.top1)2>>> print(p.top5)[2, 1, 0]>>> print(p.top1conf)tensor(0.6000)>>> print(p.top5conf)tensor([0.6000, 0.3000, 0.1000])"""def __init__(self, probs, orig_shape=None) -> None:"""Initialize the Probs class with classification probabilities.This class stores and manages classification probabilities, providing easy access to top predictions and theirconfidences.Args:probs (torch.Tensor | np.ndarray): A 1D tensor or array of classification probabilities.orig_shape (tuple | None): The original image shape as (height, width). Not used in this class but kept forconsistency with other result classes.Attributes:data (torch.Tensor | np.ndarray): The raw tensor or array containing classification probabilities.top1 (int): Index of the top 1 class.top5 (List[int]): Indices of the top 5 classes.top1conf (torch.Tensor | np.ndarray): Confidence of the top 1 class.top5conf (torch.Tensor | np.ndarray): Confidences of the top 5 classes.Examples:>>> import torch>>> probs = torch.tensor([0.1, 0.3, 0.2, 0.4])>>> p = Probs(probs)>>> print(p.top1)3>>> print(p.top1conf)tensor(0.4000)>>> print(p.top5)[3, 1, 2, 0]"""super().__init__(probs, orig_shape)@property@lru_cache(maxsize=1)def top1(self):"""Returns the index of the class with the highest probability.Returns:(int): Index of the class with the highest probability.Examples:>>> probs = Probs(torch.tensor([0.1, 0.3, 0.6]))>>> probs.top12"""return int(self.data.argmax())@property@lru_cache(maxsize=1)def top5(self):"""Returns the indices of the top 5 class probabilities.Returns:(List[int]): A list containing the indices of the top 5 class probabilities, sorted in descending order.Examples:>>> probs = Probs(torch.tensor([0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5]))>>> print(probs.top5)[4, 3, 2, 1, 0]"""return (-self.data).argsort(0)[:5].tolist() # this way works with both torch and numpy.@property@lru_cache(maxsize=1)def top1conf(self):"""Returns the confidence score of the highest probability class.This property retrieves the confidence score (probability) of the class with the highest predicted probabilityfrom the classification results.Returns:(torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): A tensor containing the confidence score of the top 1 class.Examples:>>> results = model("image.jpg") # classify an image>>> probs = results[0].probs # get classification probabilities>>> top1_confidence = probs.top1conf # get confidence of top 1 class>>> print(f"Top 1 class confidence: {top1_confidence.item():.4f}")"""return self.data[self.top1]@property@lru_cache(maxsize=1)def top5conf(self):"""Returns confidence scores for the top 5 classification predictions.This property retrieves the confidence scores corresponding to the top 5 class probabilitiespredicted by the model. It provides a quick way to access the most likely class predictionsalong with their associated confidence levels.Returns:(torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): A tensor or array containing the confidence scores for thetop 5 predicted classes, sorted in descending order of probability.Examples:>>> results = model("image.jpg")>>> probs = results[0].probs>>> top5_conf = probs.top5conf>>> print(top5_conf) # Prints confidence scores for top 5 classes"""return self.data[self.top5]class OBB(BaseTensor):"""A class for storing and manipulating Oriented Bounding Boxes (OBB).This class provides functionality to handle oriented bounding boxes, including conversion betweendifferent formats, normalization, and access to various properties of the boxes.Attributes:data (torch.Tensor): The raw OBB tensor containing box coordinates and associated data.orig_shape (tuple): Original image size as (height, width).is_track (bool): Indicates whether tracking IDs are included in the box data.xywhr (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): Boxes in [x_center, y_center, width, height, rotation] format.conf (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): Confidence scores for each box.cls (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): Class labels for each box.id (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): Tracking IDs for each box, if available.xyxyxyxy (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): Boxes in 8-point [x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4] format.xyxyxyxyn (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): Normalized 8-point coordinates relative to orig_shape.xyxy (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): Axis-aligned bounding boxes in [x1, y1, x2, y2] format.Methods:cpu(): Returns a copy of the OBB object with all tensors on CPU memory.numpy(): Returns a copy of the OBB object with all tensors as numpy arrays.cuda(): Returns a copy of the OBB object with all tensors on GPU memory.to(*args, **kwargs): Returns a copy of the OBB object with tensors on specified device and dtype.Examples:>>> boxes = torch.tensor([[100, 50, 150, 100, 30, 0.9, 0]]) # xywhr, conf, cls>>> obb = OBB(boxes, orig_shape=(480, 640))>>> print(obb.xyxyxyxy)>>> print(obb.conf)>>> print(obb.cls)"""def __init__(self, boxes, orig_shape) -> None:"""Initialize an OBB (Oriented Bounding Box) instance with oriented bounding box data and original image shape.This class stores and manipulates Oriented Bounding Boxes (OBB) for object detection tasks. It providesvarious properties and methods to access and transform the OBB data.Args:boxes (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): A tensor or numpy array containing the detection boxes,with shape (num_boxes, 7) or (num_boxes, 8). The last two columns contain confidence and class values.If present, the third last column contains track IDs, and the fifth column contains rotation.orig_shape (Tuple[int, int]): Original image size, in the format (height, width).Attributes:data (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): The raw OBB tensor.orig_shape (Tuple[int, int]): The original image shape.is_track (bool): Whether the boxes include tracking IDs.Raises:AssertionError: If the number of values per box is not 7 or 8.Examples:>>> import torch>>> boxes = torch.rand(3, 7) # 3 boxes with 7 values each>>> orig_shape = (640, 480)>>> obb = OBB(boxes, orig_shape)>>> print(obb.xywhr) # Access the boxes in xywhr format"""if boxes.ndim == 1:boxes = boxes[None, :]n = boxes.shape[-1]assert n in {7, 8}, f"expected 7 or 8 values but got {n}" # xywh, rotation, track_id, conf, clssuper().__init__(boxes, orig_shape)self.is_track = n == 8self.orig_shape = orig_shape@propertydef xywhr(self):"""Returns boxes in [x_center, y_center, width, height, rotation] format.Returns:(torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): A tensor or numpy array containing the oriented bounding boxes with format[x_center, y_center, width, height, rotation]. The shape is (N, 5) where N is the number of boxes.Examples:>>> results = model("image.jpg")>>> obb = results[0].obb>>> xywhr = obb.xywhr>>> print(xywhr.shape)torch.Size([3, 5])"""return self.data[:, :5]@propertydef conf(self):"""Returns the confidence scores for Oriented Bounding Boxes (OBBs).This property retrieves the confidence values associated with each OBB detection. The confidence scorerepresents the model's certainty in the detection.Returns:(torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): A tensor or numpy array of shape (N,) containing confidence scoresfor N detections, where each score is in the range [0, 1].Examples:>>> results = model("image.jpg")>>> obb_result = results[0].obb>>> confidence_scores = obb_result.conf>>> print(confidence_scores)"""return self.data[:, -2]@propertydef cls(self):"""Returns the class values of the oriented bounding boxes.Returns:(torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): A tensor or numpy array containing the class values for each orientedbounding box. The shape is (N,), where N is the number of boxes.Examples:>>> results = model("image.jpg")>>> result = results[0]>>> obb = result.obb>>> class_values = obb.cls>>> print(class_values)"""return self.data[:, -1]@propertydef id(self):"""Returns the tracking IDs of the oriented bounding boxes (if available).Returns:(torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray | None): A tensor or numpy array containing the tracking IDs for eachoriented bounding box. Returns None if tracking IDs are not available.Examples:>>> results = model("image.jpg", tracker=True) # Run inference with tracking>>> for result in results:... if result.obb is not None:... track_ids = result.obb.id... if track_ids is not None:... print(f"Tracking IDs: {track_ids}")"""return self.data[:, -3] if self.is_track else None@property@lru_cache(maxsize=2)def xyxyxyxy(self):"""Converts OBB format to 8-point (xyxyxyxy) coordinate format for rotated bounding boxes.Returns:(torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): Rotated bounding boxes in xyxyxyxy format with shape (N, 4, 2), where N isthe number of boxes. Each box is represented by 4 points (x, y), starting from the top-left corner andmoving clockwise.Examples:>>> obb = OBB(torch.tensor([[100, 100, 50, 30, 0.5, 0.9, 0]]), orig_shape=(640, 640))>>> xyxyxyxy = obb.xyxyxyxy>>> print(xyxyxyxy.shape)torch.Size([1, 4, 2])"""return ops.xywhr2xyxyxyxy(self.xywhr)@property@lru_cache(maxsize=2)def xyxyxyxyn(self):"""Converts rotated bounding boxes to normalized xyxyxyxy format.Returns:(torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): Normalized rotated bounding boxes in xyxyxyxy format with shape (N, 4, 2),where N is the number of boxes. Each box is represented by 4 points (x, y), normalized relative tothe original image dimensions.Examples:>>> obb = OBB(torch.rand(10, 7), orig_shape=(640, 480)) # 10 random OBBs>>> normalized_boxes = obb.xyxyxyxyn>>> print(normalized_boxes.shape)torch.Size([10, 4, 2])"""xyxyxyxyn = self.xyxyxyxy.clone() if isinstance(self.xyxyxyxy, torch.Tensor) else np.copy(self.xyxyxyxy)xyxyxyxyn[..., 0] /= self.orig_shape[1]xyxyxyxyn[..., 1] /= self.orig_shape[0]return xyxyxyxyn@property@lru_cache(maxsize=2)def xyxy(self):"""Converts oriented bounding boxes (OBB) to axis-aligned bounding boxes in xyxy format.This property calculates the minimal enclosing rectangle for each oriented bounding box and returns it inxyxy format (x1, y1, x2, y2). This is useful for operations that require axis-aligned bounding boxes, suchas IoU calculation with non-rotated boxes.Returns:(torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): Axis-aligned bounding boxes in xyxy format with shape (N, 4), where Nis the number of boxes. Each row contains [x1, y1, x2, y2] coordinates.Examples:>>> import torch>>> from ultralytics import YOLO>>> model = YOLO("yolov8n-obb.pt")>>> results = model("path/to/image.jpg")>>> for result in results:... obb = result.obb... if obb is not None:... xyxy_boxes = obb.xyxy... print(xyxy_boxes.shape) # (N, 4)Notes:- This method approximates the OBB by its minimal enclosing rectangle.- The returned format is compatible with standard object detection metrics and visualization tools.- The property uses caching to improve performance for repeated access."""x = self.xyxyxyxy[..., 0]y = self.xyxyxyxy[..., 1]return (torch.stack([x.amin(1), y.amin(1), x.amax(1), y.amax(1)], -1)if isinstance(x, torch.Tensor)else np.stack([x.min(1), y.min(1), x.max(1), y.max(1)], -1))使用predict函数保存模型预测的txt信息
from ultralytics import YOLO
import cv2
from PIL import Imagemodel_path = r'E:\pycharm\pythonProject_instance_segmentation\ultralytics-8.3.57_me_use\instance_segment_demo\weights\best.pt'
# image_path = r'E:\pycharm\pythonProject_instance_segmentation\ultralytics-8.3.57_me_use\instance_segment_demo\images_labels_depth\iamges\train\380_1680297422-6515028_rgb_png_jpg.rf.420df37b6dfdb75bb77c0b2149c52e8f.jpg'# image_path = r'E:\pycharm\pythonProject_instance_segmentation\datasets\me\color_images\1128.jpg'
# image_path = r"E:\pycharm\pythonProject_instance_segmentation\yolo_results_study\images\colors\57.jpg"
image_path = r"E:\pycharm\pyProject_d435i\my_demo\demo_photo\images\colors\133.jpg"img = cv2.imread(image_path)# 加载 YOLO 模型
model = YOLO(model_path)# 执行推理
results = model.predict(img )
print('len(results)=',len(results)) #len(results)= 1
# print('results',results) #输出内容与 results[0] 相同
print('len(results[0])=',len(results[0])) #len(results[0])= 9 对应九个掩膜
# print('results[0]',results[0])
"""ultralytics.engine.results.Results object with attributes:boxes: ultralytics.engine.results.Boxes object
keypoints: None
masks: ultralytics.engine.results.Masks object
names: {0: 'mushroom'}
obb: None
orig_img: array([[[ 82, 105, 113],[ 78, 100, 106],[ 89, 104, 107],...,[175, 171, 147],[180, 176, 152],[177, 173, 149]],[[ 82, 105, 113],[ 85, 104, 111],[ 89, 104, 107],...,[178, 174, 150],[180, 176, 152],[176, 172, 148]],[[ 81, 102, 110],[ 86, 105, 112],[ 90, 105, 108],...,[183, 177, 154],[183, 177, 154],[181, 175, 152]],...,[[ 46, 51, 52],[ 47, 52, 53],[ 45, 51, 50],...,[ 98, 95, 80],[ 94, 91, 76],[ 96, 93, 78]],[[ 46, 50, 51],[ 47, 51, 52],[ 46, 51, 50],...,[103, 100, 86],[ 96, 93, 79],[ 96, 93, 79]],[[ 46, 50, 51],[ 48, 52, 53],[ 47, 52, 51],...,[105, 102, 88],[ 99, 96, 82],[ 98, 95, 81]]], dtype=uint8)
orig_shape: (720, 1280)
path: 'image0.jpg'
probs: None
save_dir: None
speed: {'preprocess': 4.985570907592773, 'inference': 38.98024559020996, 'postprocess': 6.981372833251953}"""print('len(results[0][0])=',len(results[0][0])) #len(results[0][0])= 1
# print('results[0][0]',results[0][0]) #输出内容与 results[0] 相同# results[0][0].save_txt("me_133_demo03.txt") #只保存了第一个 掩膜的 txt信息
# results[0][0].show() #显示预测结果的图片png 并保存在Temp文件夹, 并且只显示 第一个掩膜对应的预测结果, 其余8个实例还是与原图一样#可行,保存每个预测信息(9个掩膜)
# for result in results:
# result.save_txt("me_133.txt")# for result in results[0]: #results[1]报错,IndexError: list index out of range
# result.save_txt("me_133_demo02.txt") #保存了每个掩膜的txt信息# results[0].save_txt("me_133_demo.txt") #保存了所有实例的txt 掩膜信息#下述代码可以保存 txt,内容包括9个掩膜信息, 将txt文件保存在 E:\pycharm\pythonProject_instance_segmentation\yolo_results_study_demo02\runs\detect\exp7\labels
model.predict(source=image_path,imgsz=640, #加快推理时间project=r'E:\pycharm\pythonProject_instance_segmentation\yolo_results_study_demo02\runs\detect', #保存预测结果的项目目录name='exp', #保存预测结果的子目录# save=True, #保存预测结果的图片# show=True, #显示预测结果,但是没有一直显示# conf=0.2,# iou=0.7,# agnostic_nms=True,# visualize=True, # visualize model features maps# line_width=2, # line width of the bounding boxesshow_conf=False, # do not show prediction confidenceshow_labels=False, # do not show prediction labelssave_txt=True, # save results as .txt file# save_crop=True, # save cropped images with results)# results.save_txt("me_133_demo.txt") #报错 AttributeError: 'list' object has no attribute 'save_txt'保存的txt文件
0 0.490625 0.0611111 0.490625 0.0694444 0.475 0.0972222 0.475 0.1 0.473437 0.102778 0.473437 0.105556 0.470313 0.111111 0.465625 0.111111 0.465625 0.183333 0.470313 0.183333 0.473437 0.188889 0.473437 0.191667 0.476562 0.197222 0.476562 0.2 0.48125 0.208333 0.482812 0.208333 0.485938 0.213889 0.4875 0.213889 0.489062 0.216667 0.490625 0.216667 0.492188 0.219444 0.496875 0.219444 0.498437 0.222222 0.509375 0.222222 0.510938 0.225 0.523438 0.225 0.525 0.222222 0.53125 0.222222 0.532812 0.219444 0.5375 0.219444 0.542188 0.211111 0.54375 0.211111 0.554688 0.191667 0.554688 0.188889 0.55625 0.186111 0.55625 0.183333 0.559375 0.177778 0.564062 0.177778 0.564062 0.113889 0.559375 0.113889 0.55625 0.108333 0.55625 0.102778 0.5375 0.0694444 0.5375 0.0611111
0 0.278125 0.716667 0.278125 0.725 0.275 0.730556 0.273438 0.730556 0.271875 0.733333 0.270312 0.733333 0.264062 0.744444 0.2625 0.744444 0.254687 0.758333 0.254687 0.761111 0.248437 0.772222 0.248437 0.775 0.245312 0.780556 0.240625 0.780556 0.240625 0.872222 0.246875 0.872222 0.248437 0.875 0.248437 0.877778 0.25625 0.891667 0.25625 0.894444 0.257812 0.897222 0.259375 0.897222 0.264062 0.905556 0.265625 0.905556 0.267188 0.908333 0.270312 0.908333 0.271875 0.911111 0.273438 0.911111 0.276563 0.916667 0.276563 0.925 0.314063 0.925 0.314063 0.916667 0.317187 0.911111 0.31875 0.911111 0.320312 0.908333 0.323438 0.908333 0.325 0.905556 0.326562 0.905556 0.329688 0.9 0.33125 0.9 0.340625 0.883333 0.342187 0.883333 0.342187 0.880556 0.346875 0.872222 0.346875 0.866667 0.348437 0.863889 0.348437 0.861111 0.35 0.858333 0.35 0.855556 0.353125 0.85 0.353125 0.844444 0.354688 0.841667 0.354688 0.833333 0.35625 0.830556 0.35625 0.819444 0.357812 0.816667 0.357812 0.808333 0.359375 0.805556 0.364062 0.805556 0.364062 0.797222 0.359375 0.797222 0.357812 0.794444 0.357812 0.788889 0.35625 0.786111 0.35625 0.777778 0.354688 0.775 0.354688 0.769444 0.353125 0.766667 0.353125 0.763889 0.348437 0.755556 0.348437 0.752778 0.339063 0.736111 0.3375 0.736111 0.334375 0.730556 0.332812 0.730556 0.329688 0.725 0.329688 0.716667
0 0.334375 0.127778 0.334375 0.136111 0.33125 0.141667 0.328125 0.141667 0.326562 0.144444 0.325 0.144444 0.315625 0.161111 0.309375 0.161111 0.309375 0.266667 0.315625 0.266667 0.317187 0.269444 0.317187 0.272222 0.31875 0.275 0.31875 0.277778 0.325 0.288889 0.326562 0.288889 0.33125 0.297222 0.332812 0.297222 0.334375 0.3 0.335938 0.3 0.339063 0.305556 0.339063 0.313889 0.365625 0.313889 0.365625 0.305556 0.367188 0.302778 0.36875 0.302778 0.370313 0.3 0.375 0.3 0.376563 0.297222 0.38125 0.297222 0.382812 0.294444 0.384375 0.294444 0.389062 0.286111 0.390625 0.286111 0.396875 0.275 0.398438 0.275 0.398438 0.272222 0.403125 0.263889 0.403125 0.261111 0.404687 0.258333 0.404687 0.255556 0.40625 0.252778 0.40625 0.25 0.409375 0.244444 0.414062 0.244444 0.414062 0.186111 0.409375 0.186111 0.40625 0.180556 0.40625 0.177778 0.404687 0.175 0.404687 0.172222 0.389062 0.144444 0.385938 0.144444 0.384375 0.141667 0.382812 0.141667 0.38125 0.138889 0.379687 0.138889 0.378125 0.136111 0.378125 0.127778
0 0.489062 0.705556 0.489062 0.716667 0.485938 0.722222 0.484375 0.722222 0.475 0.738889 0.475 0.741667 0.473437 0.744444 0.473437 0.747222 0.470313 0.752778 0.465625 0.752778 0.465625 0.822222 0.470313 0.822222 0.473437 0.827778 0.473437 0.833333 0.475 0.836111 0.475 0.844444 0.476562 0.847222 0.476562 0.85 0.479688 0.855556 0.479688 0.858333 0.48125 0.861111 0.48125 0.863889 0.482812 0.866667 0.484375 0.866667 0.485938 0.869444 0.485938 0.872222 0.489062 0.877778 0.490625 0.877778 0.496875 0.888889 0.498437 0.888889 0.501562 0.894444 0.503125 0.894444 0.504687 0.897222 0.510938 0.897222 0.5125 0.9 0.515625 0.9 0.517187 0.902778 0.51875 0.902778 0.520312 0.905556 0.520312 0.913889 0.534375 0.913889 0.534375 0.905556 0.535937 0.902778 0.5375 0.902778 0.539062 0.9 0.542188 0.9 0.54375 0.897222 0.548437 0.897222 0.55 0.894444 0.553125 0.894444 0.55625 0.888889 0.557813 0.888889 0.570312 0.866667 0.570312 0.863889 0.573438 0.858333 0.573438 0.852778 0.575 0.85 0.575 0.841667 0.578125 0.836111 0.582812 0.836111 0.582812 0.791667 0.578125 0.791667 0.575 0.786111 0.575 0.783333 0.573438 0.780556 0.573438 0.775 0.571875 0.772222 0.571875 0.769444 0.570312 0.766667 0.570312 0.763889 0.567187 0.758333 0.567187 0.752778 0.564062 0.747222 0.564062 0.744444 0.551562 0.722222 0.55 0.722222 0.548437 0.719444 0.546875 0.719444 0.545313 0.716667 0.545313 0.705556
0 0.68125 0.372222 0.68125 0.380556 0.670313 0.4 0.665625 0.4 0.665625 0.511111 0.671875 0.511111 0.675 0.516667 0.675 0.519444 0.676562 0.519444 0.682813 0.530556 0.684375 0.530556 0.689062 0.538889 0.690625 0.538889 0.692187 0.541667 0.7 0.541667 0.701563 0.544444 0.710938 0.544444 0.7125 0.547222 0.714063 0.547222 0.715625 0.55 0.715625 0.558333 0.73125 0.558333 0.73125 0.55 0.732813 0.547222 0.734375 0.547222 0.735937 0.544444 0.739062 0.544444 0.740625 0.541667 0.74375 0.541667 0.75 0.530556 0.751562 0.530556 0.759375 0.516667 0.759375 0.513889 0.760938 0.511111 0.760938 0.508333 0.7625 0.505556 0.7625 0.502778 0.765625 0.497222 0.765625 0.491667 0.767187 0.488889 0.767187 0.486111 0.76875 0.483333 0.76875 0.466667 0.770312 0.463889 0.770312 0.455556 0.76875 0.452778 0.76875 0.438889 0.767187 0.436111 0.767187 0.430556 0.764063 0.425 0.764063 0.422222 0.760938 0.416667 0.760938 0.413889 0.754687 0.402778 0.754687 0.4 0.74375 0.380556 0.74375 0.372222
0 0.510938 0.383333 0.510938 0.394444 0.509375 0.397222 0.507812 0.397222 0.49375 0.422222 0.49375 0.425 0.492188 0.427778 0.492188 0.430556 0.489062 0.436111 0.484375 0.436111 0.484375 0.525 0.489062 0.525 0.492188 0.530556 0.492188 0.538889 0.49375 0.541667 0.49375 0.547222 0.498437 0.555556 0.498437 0.558333 0.501562 0.563889 0.503125 0.563889 0.509375 0.575 0.5125 0.575 0.514063 0.577778 0.515625 0.577778 0.51875 0.583333 0.520312 0.583333 0.521875 0.586111 0.525 0.586111 0.526563 0.588889 0.529688 0.588889 0.532812 0.594444 0.532812 0.602778 0.560938 0.602778 0.560938 0.594444 0.5625 0.591667 0.564062 0.591667 0.565625 0.588889 0.567187 0.588889 0.56875 0.586111 0.570312 0.586111 0.579687 0.569444 0.579687 0.566667 0.582812 0.561111 0.582812 0.558333 0.585938 0.552778 0.585938 0.547222 0.5875 0.544444 0.5875 0.541667 0.590625 0.536111 0.590625 0.533333 0.592188 0.530556 0.592188 0.525 0.59375 0.522222 0.59375 0.519444 0.596875 0.513889 0.601562 0.513889 0.601562 0.447222 0.596875 0.447222 0.59375 0.441667 0.59375 0.436111 0.592188 0.433333 0.592188 0.430556 0.585938 0.419444 0.585938 0.416667 0.578125 0.402778 0.576563 0.402778 0.575 0.4 0.573438 0.4 0.56875 0.391667 0.56875 0.383333
0 0.664062 0.0611111 0.664062 0.0722222 0.6625 0.075 0.660937 0.075 0.657812 0.0805556 0.65625 0.0805556 0.65625 0.0833333 0.65 0.0944444 0.65 0.0972222 0.648438 0.1 0.648438 0.102778 0.645312 0.108333 0.640625 0.108333 0.640625 0.205556 0.645312 0.205556 0.657812 0.227778 0.659375 0.227778 0.665625 0.238889 0.667188 0.238889 0.66875 0.241667 0.673437 0.241667 0.675 0.244444 0.679688 0.244444 0.68125 0.247222 0.682813 0.247222 0.684375 0.25 0.684375 0.258333 0.689062 0.258333 0.689062 0.25 0.690625 0.247222 0.692187 0.247222 0.69375 0.244444 0.696875 0.244444 0.698438 0.241667 0.701563 0.241667 0.703125 0.238889 0.704687 0.238889 0.707812 0.233333 0.709375 0.233333 0.71875 0.216667 0.71875 0.213889 0.720312 0.211111 0.721875 0.211111 0.721875 0.208333 0.723437 0.205556 0.723437 0.202778 0.728125 0.194444 0.728125 0.191667 0.729688 0.188889 0.729688 0.177778 0.73125 0.175 0.73125 0.130556 0.729688 0.127778 0.729688 0.119444 0.728125 0.116667 0.728125 0.113889 0.726562 0.111111 0.726562 0.108333 0.725 0.105556 0.725 0.102778 0.721875 0.0972222 0.721875 0.0944444 0.717188 0.0861111 0.717188 0.0833333 0.714063 0.0777778 0.7125 0.0777778 0.709375 0.0722222 0.709375 0.0611111
0 0.29375 0.361111 0.29375 0.369444 0.290625 0.375 0.289062 0.375 0.282813 0.386111 0.28125 0.386111 0.278125 0.391667 0.278125 0.394444 0.276563 0.397222 0.275 0.397222 0.275 0.4 0.270312 0.408333 0.265625 0.408333 0.265625 0.513889 0.271875 0.513889 0.275 0.519444 0.275 0.522222 0.282813 0.536111 0.282813 0.538889 0.284375 0.538889 0.290625 0.55 0.292188 0.55 0.29375 0.552778 0.296875 0.552778 0.298438 0.555556 0.301562 0.555556 0.303125 0.558333 0.304688 0.558333 0.30625 0.561111 0.30625 0.569444 0.340625 0.569444 0.340625 0.561111 0.34375 0.555556 0.346875 0.555556 0.348437 0.552778 0.35 0.552778 0.353125 0.547222 0.354688 0.547222 0.357812 0.541667 0.359375 0.541667 0.371875 0.519444 0.371875 0.516667 0.375 0.511111 0.375 0.508333 0.378125 0.502778 0.378125 0.5 0.379687 0.497222 0.379687 0.486111 0.38125 0.483333 0.38125 0.452778 0.379687 0.45 0.379687 0.441667 0.378125 0.438889 0.378125 0.433333 0.375 0.427778 0.375 0.425 0.373437 0.422222 0.373437 0.419444 0.371875 0.416667 0.371875 0.413889 0.367188 0.405556 0.367188 0.402778 0.359375 0.388889 0.357812 0.388889 0.353125 0.380556 0.351562 0.380556 0.35 0.377778 0.348437 0.377778 0.346875 0.375 0.345313 0.375 0.342187 0.369444 0.342187 0.361111
0 0.775 0.627778 0.775 0.636111 0.771875 0.641667 0.770312 0.641667 0.76875 0.644444 0.767187 0.644444 0.760938 0.655556 0.759375 0.655556 0.748438 0.675 0.748438 0.677778 0.746875 0.680556 0.740625 0.680556 0.740625 0.766667 0.745313 0.766667 0.748438 0.772222 0.748438 0.775 0.75 0.777778 0.75 0.783333 0.7625 0.805556 0.764063 0.805556 0.765625 0.808333 0.767187 0.808333 0.76875 0.811111 0.770312 0.811111 0.773438 0.816667 0.775 0.816667 0.776563 0.819444 0.779688 0.819444 0.78125 0.822222 0.785937 0.822222 0.789062 0.827778 0.789062 0.836111 0.809375 0.836111 0.809375 0.827778 0.8125 0.822222 0.815625 0.822222 0.817187 0.819444 0.821875 0.819444 0.823438 0.816667 0.826563 0.816667 0.828125 0.813889 0.829687 0.813889 0.839063 0.797222 0.840625 0.797222 0.84375 0.791667 0.84375 0.788889 0.848437 0.780556 0.848437 0.777778 0.853125 0.769444 0.853125 0.766667 0.854688 0.763889 0.854688 0.755556 0.85625 0.752778 0.85625 0.744444 0.857813 0.741667 0.857813 0.738889 0.859375 0.736111 0.864062 0.736111 0.864062 0.713889 0.859375 0.713889 0.85625 0.708333 0.85625 0.7 0.854688 0.697222 0.854688 0.691667 0.853125 0.688889 0.853125 0.683333 0.85 0.677778 0.85 0.675 0.848437 0.672222 0.848437 0.669444 0.84375 0.661111 0.84375 0.658333 0.835938 0.644444 0.834375 0.644444 0.832812 0.641667 0.83125 0.641667 0.828125 0.636111 0.828125 0.627778
参考资料:
1.yolov8预测函数prdict返回结果分析_yolov8 model.predict-CSDN博客
相关文章:

学习使用YOLO的predict函数使用
YOLO的 result.py #2025.1.3 """ https://docs.ultralytics.com/zh/modes/predict/#inference-arguments 对yolo 目标检测、实例分割、关键点检测结果进行说明https://docs.ultralytics.com/reference/engine/results/#ultralytics.engine.results.Masks.xy 对…...
)
零基础在实践中学习网络安全-皮卡丘靶场(第十四期-XXE模块)
本期内容涉及到很多前面的内容,因此复习后可以更好的了解本期内容 介绍 XXE -"xml external entity injection"即"xml外部实体注入漏洞"。 概括一下就是"攻击者通过向服务器注入指定的xml实体内容,从而让服务器按照指定的配置进行执行,导…...

深入浅出Spring Security
一、Spring Security基本组件 Spring Security的设计理念是提供一种可插拔的、高度可定制的安全服务。其核心功能依赖于以下几个关键组件: Authentication (认证): 概念: 确认用户身份的过程,即验证“你是谁”。核心类: Authentication 接口,…...

基于51单片机的红外防盗及万年历仿真
目录 具体实现功能 设计介绍 资料内容 全部内容 资料获取 具体实现功能 具体功能: (1)实时显示年、月、日、时、分、秒、星期信息; (2)红外传感器(仿真中用按键模拟)检测是否有…...

Doris 数据库深度解析:架构、原理与实战应用
一、Doris 的架构与原理 1. 架构组成 Doris 是一个分布式 MPP(大规模并行处理)数据库,它的架构主要由以下几部分组成: FE(Frontend):负责管理元数据、解析 SQL 查询、优化查询计划࿰…...

【飞腾AI加固服务器】全国产化飞腾+昇腾310+PCIe Switch的AI大模型服务器解决方案
以下是全国产化飞腾AI加固服务器采用飞腾昇腾PCIe Switch解决方案: 🖥️ 一、硬件架构亮点 国产算力双擎 飞腾处理器:搭载飞腾FT2000/64核服务器级CPU(主频1.8-2.2GHz),支持高并发任务与复杂计算&a…...

【术语扫盲】评估指标Precision、Recall、F1-score、Support是什么含义?
一、背景 Precision、Recall、F1-score、Support 是分类问题中最常用的评估指标,它们是机器学习、深度学习、数据挖掘中非常基础也非常重要的术语。 二、 详细解释 指标含义公式Precision(精准率)预测为某类的样本中,有多少是真…...

应用层协议:HTTPS
目录 HTTPS:超文本传输安全协议 1、概念 2、通信过程及关键技术 2.1 通信过程 1> TLS握手协商(建立安全通道) 2> 加密数据传输 2.2 关键技术 1> 对称加密算法 2> 非对称加密 3> 对称加密和非对称加密组合 4> 数…...

【ArcGIS技巧】—村庄规划规划用地规划状态字段生成工具
"国土空间规划后续也是走向数据治理,数据建库已经是涉及到城市规划、建筑、市政、农业、地理信息、测绘等等方方面面。不得不说以后数据库建设跟维护,是很多专业的必修课。小编就湖南省的村庄规划建库过程中规划用地用海中规划状态字段写了个小工具…...

React从基础入门到高级实战:React 实战项目 - 项目三:实时聊天应用
React 实战项目:实时聊天应用 欢迎来到本 React 开发教程专栏 的第 28 篇!在前 27 篇文章中,我们从 React 的基础概念逐步深入到高级技巧,涵盖了组件设计、状态管理、路由配置、性能优化和架构模式等核心知识。这一次,…...

Go语言中的if else控制语句
if else是Go语言中最基础也最常用的条件控制语句,用于根据条件执行不同的代码块。下面我将详细介绍Go语言中if else的各种用法和特性。 1. 基本语法 1.1. 最简单的if语句 if 条件表达式 {// 条件为true时执行的代码 } 示例: if x > 10 {fmt.Prin…...

【PCIe总线】-- inbound、outbound配置
PCI、PCIe相关知识整理汇总 【PCIe总线】 -- PCI、PCIe相关实现 由之前的PCIe基础知识可知,pcie的组成有:RC(根节点)、siwtch(pcie桥)、EP(设备)。 RC和EP,以及EP和EP能…...
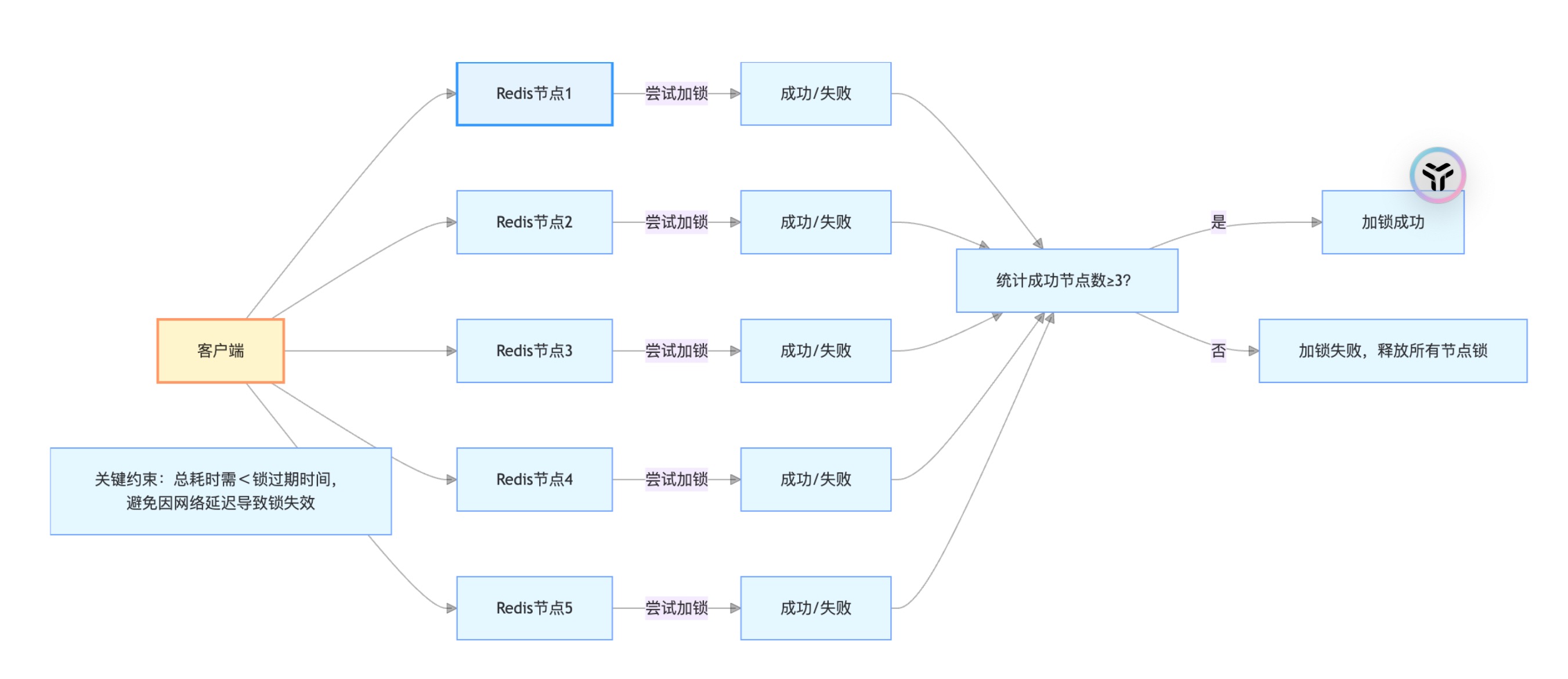
分布式锁实战:Redisson vs. Redis 原生指令的性能对比
分布式锁实战:Redisson vs. Redis 原生指令的性能对比 引言 在DIY主题模板系统中,用户可自定义聊天室的背景、图标、动画等元素。当多个运营人员或用户同时修改同一模板时,若没有锁机制,可能出现“甲修改了背景色,乙…...

MyBatis中foreach集合用法详解
在 MyBatis 中,<foreach> 标签用于遍历集合(Collection、List、Array、Map),常用于构建动态 SQL 语句(如 IN 查询、批量插入等)。以下是详细用法和示例: 核心属性 属性描述collection必填…...

react+taro 开发第五个小程序,解决拼音的学习
1.找一个文件夹 cmd 2.taro init 3.vscode 找开该文件夹cd help-letters 如:我的是(base) PS D:\react\help-letters> pnpm install 4.先编译一下吧。看下开发者工具什么反应。 pnpm dev:weapp 5.开始规则。我用cursor就是不成功。是不是要在这边差不多了&…...

高防IP可以防护什么攻击类型?企业网络安全的第一道防线
“高防IP”成为企业构建网络安全防护体系的重要一环。尤其是对于金融、电商、游戏、政务等业务高度依赖网络稳定性的行业而言,确保系统724小时正常运行已经成为基本要求。高防IP到底可以防护哪些攻击类型?它又是如何帮助企业抵御风险、保障服务稳定运行的…...
)
Wireshark使用教程(含安装包和安装教程)
Wireshark使用入门教程 0.资源下载以及软件安装1.Wireshark中无法显示网卡列表2.Wireshark抓取H264过程 0.资源下载以及软件安装 参考blog: 抓包神器wireshark安装保姆级教程 压缩包下载:Wireshark安装包 1.Wireshark中无法显示网卡列表 Wireshark中无法显示网…...

Asp.Net Core基于StackExchange Redis 缓存
NuGet安装 StackExchange.Redis Microsoft.Extensions.Options 0. appsettings.json初始化配置 {"Logging": {"LogLevel": {"Default": "Information","Microsoft.AspNetCore": "Warning"}},"AllowedHos…...

【Linux】SSH:免密登录
配置 SSH 的免密登录(基于公钥认证)可实现无需输入密码即可登录远程主机,常用于自动化脚本、服务器集群、DevOps 等场景。 生成本地 SSH 密钥对(若尚未存在) 在本地客户端执行: ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 409…...

kafka(windows)
目录 介绍 下载 配置 测试 介绍 Kafka是一个分布式流媒体平台,类似于消息队列或企业信息传递系统。 下载 Kafka对于Zookeeper是强依赖,所以安装Kafka之前必须先安装zookeeper 官网:Apache Kafka 下载此安装包并解压 配置 新建log…...

深度学习习题3
1.训练神经网络过程中,损失函数在一些时期(Epoch)不再减小, 原因可能是: 1.学习率太低 2.正则参数太大 3.卡在了局部最小值 A1 and 2 B. 2 and 3 C. 1 and 3 D. 都是 2.对于分类任务,我们不是将神经网络中的随机权重…...

勒让德多项式
勒让德多项式 (Legendre) 当区间为 [ − 1 , 1 ] [-1,1] [−1,1],权函数 ρ ( x ) 1 ρ(x)1 ρ(x)1时,由 1 , x , . . . , x n , . . . {1,x,...,x^n,...} 1,x,...,xn,...正交化得到的多项式称为勒让德多项式,并用 P 0 ( x ) , P 1 ( x ) ,…...

atc abc409E
原题链接:E - Pair Annihilation 题目背景: n 个点 n - 1 条边的有权无向图,每个点都有一个值,两个连通的点的值可以互相抵消,既将u 的 -1 传给 v 时可以抵消掉 v 的 1 并花费边权值;求最小花费。 考察算…...

Mysql批处理写入数据库
在学习mybatisPlus时,看到一个原本没用过的参数: rewriteBatchedStatementstrue 将上述代码装入jdbc的url中即可使数据库启用批处理写入。 需要注意的是,这个参数仅适用于MySQL JDBC 驱动的私有扩展参数。 作用原理是: 原本的…...

基于安卓的文件管理器程序开发研究源码数据库文档
摘 要 伴随着现代科技的发展潮流,移动互联网技术快速发展,各种基于通信技术的移动终端设备做的也越来越好了,现代智能手机大量的进入到了我们的生活中。电子产品的各种软硬技术技术的发展,操作系统的不断更新换代,谷歌…...

EMC VNXe 存储系统日志收集方法
写在前面 有朋友找来看看VNXe的故障,这种问题总是要收集日志,顺便这里也分享给大家。 注意,VNXe和VNX 属于完全不同的产品,不要看名字很类似,操作系统已经完全重构了,如果说是否有联系,大概就…...

嵌入式链表操作原理详解
嵌入式链表操作原理详解 链表是嵌入式软件开发中最基础的数据结构之一,其设计采用嵌入式链表节点的思想,实现了高度通用的链表管理机制。以下是核心原理和操作的全面解析: 一、基础数据结构 struct list_head {struct list_head *next, *pr…...

从“人找政策”到“政策找人”:智能退税ERP数字化重构外贸生态
离境退税新政核心内容与外贸企业影响 (一)政策核心变化解析 退税商店网络扩容 新政明确鼓励在大型商圈、旅游景区、交通枢纽等境外旅客聚集地增设退税商店,并放宽备案条件至纳税信用M级企业。以上海为例,静安区计划新增1000家退…...

一.设计模式的基本概念
一.核心概念 对软件设计中重复出现问题的成熟解决方案,提供代码可重用性、可维护性和扩展性保障。核心原则包括: 1.1. 单一职责原则 定义:一个类只承担一个职责,避免因职责过多导致的代码耦合。 1.2. 开闭原则 定义…...

以人类演示视频为提示,学习可泛化的机器人策略
25年5月来自清华大学、上海姚期智研究院和星动纪元(RoboEra)公司的论文“Learning Generalizable Robot Policy with Human Demonstration Video as a Prompt”。 最近的机器人学习方法通常依赖于从通过遥操作收集的大量机器人数据集中进行模仿学习…...
