@Bean的处理流程,源码分析@Bean背后发生的事
文章目录
写在前面
日常开发中,我们都会使用@Bean定义一个Spring的Bean,那么这简单的一个注解,背后隐藏着多少的秘密?
今天我们就一起把这个秘密拆解开。
关键类ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
该场景只适用于基于注解方式启动的容器。
1、ConfigurationClassPostProcessor的注册
先上一段代码:
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();// 注册 Configuration Class
context.register(LiveBeansViewDemo.class);// 启动 Spring 应用上下文
context.refresh();// 关闭 Spring 应用上下文
context.close();
代码很简单,其中,@Bean的处理关键类ConfigurationClassPostProcessor的处理就隐藏在new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext()这个代码里,我们继续往下看:
// org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext#AnnotationConfigApplicationContext()
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext() {this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
}
上面源码中,会new一个AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader,而Springboot启动web项目也会new这样一个类,它们的处理逻辑基本是相同的。
在AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader构造器中,会进行以下的处理:
public AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {this(registry, getOrCreateEnvironment(registry));
}
public AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Environment environment) {Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");Assert.notNull(environment, "Environment must not be null");this.registry = registry;this.conditionEvaluator = new ConditionEvaluator(registry, environment, null);// 注册AnnotationConfigProcessorsAnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry);
}
在源码最后,会调用工具类注册AnnotationConfigProcessors:
// org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigUtils#registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry)
public static void registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(registry, null);
}public static Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, @Nullable Object source) {DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = unwrapDefaultListableBeanFactory(registry);if (beanFactory != null) {if (!(beanFactory.getDependencyComparator() instanceof AnnotationAwareOrderComparator)) {beanFactory.setDependencyComparator(AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE);}if (!(beanFactory.getAutowireCandidateResolver() instanceof ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver)) {beanFactory.setAutowireCandidateResolver(new ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver());}}Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefs = new LinkedHashSet<>(8);// 注册ConfigurationClassPostProcessor到if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class);def.setSource(source);beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));}if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);def.setSource(source);beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));}// Check for JSR-250 support, and if present add the CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.if (jsr250Present && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);def.setSource(source);beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));}// Check for JPA support, and if present add the PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.if (jpaPresent && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition();try {def.setBeanClass(ClassUtils.forName(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME,AnnotationConfigUtils.class.getClassLoader()));}catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot load optional framework class: " + PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME, ex);}def.setSource(source);beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));}if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(EventListenerMethodProcessor.class);def.setSource(source);beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));}if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME)) {RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(DefaultEventListenerFactory.class);def.setSource(source);beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME));}return beanDefs;
}
上面源码我们可以分析出来,会依次注册ConfigurationClassPostProcessor、AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor、CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor、PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor、EventListenerMethodProcessor、DefaultEventListenerFactory等,很多BeanPostProcessor顾名思义,就能知道大体是干什么的。
我们今天主要是研究ConfigurationClassPostProcessor。
到此为止,ConfigurationClassPostProcessor已经注册到BeanFactory中作为一个BeanDefinition了。
2、ConfigurationClassPostProcessor的处理过程
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,就有了Bean的依赖查找和注入注册的能力,实现postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法可以在 IOC容器启动的BeanFactory 后置处理阶段-invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors阶段,进行调用,更多请移步Spring应用上下文生命周期详解及源码分析,Spring IOC容器启动及关闭过程超详细解释(上)。
我们来分析一下ConfigurationClassPostProcessor的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法:
// org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassPostProcessor#postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {int registryId = System.identityHashCode(registry);if (this.registriesPostProcessed.contains(registryId)) {throw new IllegalStateException("postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry already called on this post-processor against " + registry);}if (this.factoriesPostProcessed.contains(registryId)) {throw new IllegalStateException("postProcessBeanFactory already called on this post-processor against " + registry);}this.registriesPostProcessed.add(registryId);processConfigBeanDefinitions(registry);
}public void processConfigBeanDefinitions(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {List<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates = new ArrayList<>();String[] candidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();for (String beanName : candidateNames) {BeanDefinition beanDef = registry.getBeanDefinition(beanName);if (beanDef.getAttribute(ConfigurationClassUtils.CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("Bean definition has already been processed as a configuration class: " + beanDef);}}else if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(beanDef, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {configCandidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDef, beanName));}}// Return immediately if no @Configuration classes were foundif (configCandidates.isEmpty()) {return;}// Sort by previously determined @Order value, if applicableconfigCandidates.sort((bd1, bd2) -> {int i1 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd1.getBeanDefinition());int i2 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd2.getBeanDefinition());return Integer.compare(i1, i2);});// Detect any custom bean name generation strategy supplied through the enclosing application contextSingletonBeanRegistry sbr = null;if (registry instanceof SingletonBeanRegistry) {sbr = (SingletonBeanRegistry) registry;if (!this.localBeanNameGeneratorSet) {BeanNameGenerator generator = (BeanNameGenerator) sbr.getSingleton(AnnotationConfigUtils.CONFIGURATION_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR);if (generator != null) {this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator = generator;this.importBeanNameGenerator = generator;}}}if (this.environment == null) {this.environment = new StandardEnvironment();}// Parse each @Configuration classConfigurationClassParser parser = new ConfigurationClassParser(this.metadataReaderFactory, this.problemReporter, this.environment,this.resourceLoader, this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator, registry);Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<>(configCandidates);Set<ConfigurationClass> alreadyParsed = new HashSet<>(configCandidates.size());do {// 关键方法!(见(1))parser.parse(candidates);parser.validate();Set<ConfigurationClass> configClasses = new LinkedHashSet<>(parser.getConfigurationClasses());configClasses.removeAll(alreadyParsed);// Read the model and create bean definitions based on its contentif (this.reader == null) {this.reader = new ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader(registry, this.sourceExtractor, this.resourceLoader, this.environment,this.importBeanNameGenerator, parser.getImportRegistry());}// 关键方法!(见(2))this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configClasses);alreadyParsed.addAll(configClasses);candidates.clear();if (registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() > candidateNames.length) {String[] newCandidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();Set<String> oldCandidateNames = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(candidateNames));Set<String> alreadyParsedClasses = new HashSet<>();for (ConfigurationClass configurationClass : alreadyParsed) {alreadyParsedClasses.add(configurationClass.getMetadata().getClassName());}for (String candidateName : newCandidateNames) {if (!oldCandidateNames.contains(candidateName)) {BeanDefinition bd = registry.getBeanDefinition(candidateName);if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bd, this.metadataReaderFactory) &&!alreadyParsedClasses.contains(bd.getBeanClassName())) {candidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(bd, candidateName));}}}candidateNames = newCandidateNames;}}while (!candidates.isEmpty());// Register the ImportRegistry as a bean in order to support ImportAware @Configuration classesif (sbr != null && !sbr.containsSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME)) {sbr.registerSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME, parser.getImportRegistry());}if (this.metadataReaderFactory instanceof CachingMetadataReaderFactory) {// Clear cache in externally provided MetadataReaderFactory; this is a no-op// for a shared cache since it'll be cleared by the ApplicationContext.((CachingMetadataReaderFactory) this.metadataReaderFactory).clearCache();}
}
上面源码中我们可以看出,在注释标注的Parse each @Configuration class的这一部分,是主要用于处理配置类的,关键代码就是使用了ConfigurationClassParser的parse方法,parse方法会调用processConfigurationClass方法,然后调用doProcessConfigurationClass方法,在该方法里,会统一处理@Component、@PropertySources以及@ComponentScans的扫描、@ImportResource。
// org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassParser#parse(java.util.Set<org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinitionHolder>)
public void parse(Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates) {for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : configCandidates) {BeanDefinition bd = holder.getBeanDefinition();try {if (bd instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {parse(((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) bd).getMetadata(), holder.getBeanName());}else if (bd instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition && ((AbstractBeanDefinition) bd).hasBeanClass()) {parse(((AbstractBeanDefinition) bd).getBeanClass(), holder.getBeanName());}else {parse(bd.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());}}catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {throw ex;}catch (Throwable ex) {throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Failed to parse configuration class [" + bd.getBeanClassName() + "]", ex);}}this.deferredImportSelectorHandler.process();
}
(1)parse方法中,@Bean方法的处理
并且还会处理@Bean标注的方法(本文只分析@Bean的处理),在此截取doProcessConfigurationClass对@Bean的处理部分:
// Process individual @Bean methods
Set<MethodMetadata> beanMethods = retrieveBeanMethodMetadata(sourceClass);
for (MethodMetadata methodMetadata : beanMethods) {configClass.addBeanMethod(new BeanMethod(methodMetadata, configClass));
}
其中,retrieveBeanMethodMetadata就是筛选出所有包含@Bean的方法,有个递归的过程:
// org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassParser#retrieveBeanMethodMetadata
private Set<MethodMetadata> retrieveBeanMethodMetadata(SourceClass sourceClass) {AnnotationMetadata original = sourceClass.getMetadata();Set<MethodMetadata> beanMethods = original.getAnnotatedMethods(Bean.class.getName());if (beanMethods.size() > 1 && original instanceof StandardAnnotationMetadata) {// Try reading the class file via ASM for deterministic declaration order...// Unfortunately, the JVM's standard reflection returns methods in arbitrary// order, even between different runs of the same application on the same JVM.try {AnnotationMetadata asm =this.metadataReaderFactory.getMetadataReader(original.getClassName()).getAnnotationMetadata();Set<MethodMetadata> asmMethods = asm.getAnnotatedMethods(Bean.class.getName());if (asmMethods.size() >= beanMethods.size()) {Set<MethodMetadata> selectedMethods = new LinkedHashSet<>(asmMethods.size());for (MethodMetadata asmMethod : asmMethods) {for (MethodMetadata beanMethod : beanMethods) {if (beanMethod.getMethodName().equals(asmMethod.getMethodName())) {selectedMethods.add(beanMethod);break;}}}if (selectedMethods.size() == beanMethods.size()) {// All reflection-detected methods found in ASM method set -> proceedbeanMethods = selectedMethods;}}}catch (IOException ex) {logger.debug("Failed to read class file via ASM for determining @Bean method order", ex);// No worries, let's continue with the reflection metadata we started with...}}return beanMethods;
}处理完retrieveBeanMethodMetadata方法之后,将@Bean的方法信息存入了configClass中。
(2)注册解析@Bean标注的方法
// org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader#loadBeanDefinitions
public void loadBeanDefinitions(Set<ConfigurationClass> configurationModel) {TrackedConditionEvaluator trackedConditionEvaluator = new TrackedConditionEvaluator();for (ConfigurationClass configClass : configurationModel) {loadBeanDefinitionsForConfigurationClass(configClass, trackedConditionEvaluator);}
}private void loadBeanDefinitionsForConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClass configClass, TrackedConditionEvaluator trackedConditionEvaluator) {if (trackedConditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(configClass)) {String beanName = configClass.getBeanName();if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.registry.containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {this.registry.removeBeanDefinition(beanName);}this.importRegistry.removeImportingClass(configClass.getMetadata().getClassName());return;}if (configClass.isImported()) {registerBeanDefinitionForImportedConfigurationClass(configClass);}// 以下是用于处理@Bean标注的方法的逻辑for (BeanMethod beanMethod : configClass.getBeanMethods()) {loadBeanDefinitionsForBeanMethod(beanMethod);}loadBeanDefinitionsFromImportedResources(configClass.getImportedResources());loadBeanDefinitionsFromRegistrars(configClass.getImportBeanDefinitionRegistrars());
}
我们继续看loadBeanDefinitionsForBeanMethod方法,该方法就是对@Bean标注的方法进行最终处理的逻辑:
// org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader#loadBeanDefinitionsForBeanMethod
private void loadBeanDefinitionsForBeanMethod(BeanMethod beanMethod) {ConfigurationClass configClass = beanMethod.getConfigurationClass();MethodMetadata metadata = beanMethod.getMetadata();String methodName = metadata.getMethodName();// Do we need to mark the bean as skipped by its condition?// 判断Conditionif (this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(metadata, ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN)) {configClass.skippedBeanMethods.add(methodName);return;}if (configClass.skippedBeanMethods.contains(methodName)) {return;}// 再次校验是不是有@Bean注解AnnotationAttributes bean = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(metadata, Bean.class);Assert.state(bean != null, "No @Bean annotation attributes");// Consider name and any aliasesList<String> names = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(bean.getStringArray("name")));String beanName = (!names.isEmpty() ? names.remove(0) : methodName);// Register aliases even when overriddenfor (String alias : names) {this.registry.registerAlias(beanName, alias);}// Has this effectively been overridden before (e.g. via XML)?if (isOverriddenByExistingDefinition(beanMethod, beanName)) {if (beanName.equals(beanMethod.getConfigurationClass().getBeanName())) {throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanMethod.getConfigurationClass().getResource().getDescription(),beanName, "Bean name derived from @Bean method '" + beanMethod.getMetadata().getMethodName() +"' clashes with bean name for containing configuration class; please make those names unique!");}return;}ConfigurationClassBeanDefinition beanDef = new ConfigurationClassBeanDefinition(configClass, metadata);beanDef.setResource(configClass.getResource());beanDef.setSource(this.sourceExtractor.extractSource(metadata, configClass.getResource()));// 如果是静态方法,不需要配置类先加载,可以优先加载静态方法if (metadata.isStatic()) {// static @Bean methodif (configClass.getMetadata() instanceof StandardAnnotationMetadata) {beanDef.setBeanClass(((StandardAnnotationMetadata) configClass.getMetadata()).getIntrospectedClass());}else {beanDef.setBeanClassName(configClass.getMetadata().getClassName());}beanDef.setUniqueFactoryMethodName(methodName);}else {// instance @Bean method// 如果是实例方法,会先关联配置类,所以首先要配置类加载之后才能加载实例方法beanDef.setFactoryBeanName(configClass.getBeanName());beanDef.setUniqueFactoryMethodName(methodName);}if (metadata instanceof StandardMethodMetadata) {beanDef.setResolvedFactoryMethod(((StandardMethodMetadata) metadata).getIntrospectedMethod());}beanDef.setAutowireMode(AbstractBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR);beanDef.setAttribute(org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.SKIP_REQUIRED_CHECK_ATTRIBUTE, Boolean.TRUE);AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations(beanDef, metadata);// 处理其他属性Autowire autowire = bean.getEnum("autowire");if (autowire.isAutowire()) {beanDef.setAutowireMode(autowire.value());}boolean autowireCandidate = bean.getBoolean("autowireCandidate");if (!autowireCandidate) {beanDef.setAutowireCandidate(false);}String initMethodName = bean.getString("initMethod");if (StringUtils.hasText(initMethodName)) {beanDef.setInitMethodName(initMethodName);}String destroyMethodName = bean.getString("destroyMethod");beanDef.setDestroyMethodName(destroyMethodName);// Consider scopingScopedProxyMode proxyMode = ScopedProxyMode.NO;AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(metadata, Scope.class);if (attributes != null) {beanDef.setScope(attributes.getString("value"));proxyMode = attributes.getEnum("proxyMode");if (proxyMode == ScopedProxyMode.DEFAULT) {proxyMode = ScopedProxyMode.NO;}}// Replace the original bean definition with the target one, if necessaryBeanDefinition beanDefToRegister = beanDef;if (proxyMode != ScopedProxyMode.NO) {BeanDefinitionHolder proxyDef = ScopedProxyCreator.createScopedProxy(new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDef, beanName), this.registry,proxyMode == ScopedProxyMode.TARGET_CLASS);beanDefToRegister = new ConfigurationClassBeanDefinition((RootBeanDefinition) proxyDef.getBeanDefinition(), configClass, metadata);}if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace(String.format("Registering bean definition for @Bean method %s.%s()",configClass.getMetadata().getClassName(), beanName));}this.registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, beanDefToRegister);
}
相关文章:

@Bean的处理流程,源码分析@Bean背后发生的事
文章目录写在前面关键类ConfigurationClassPostProcessor1、ConfigurationClassPostProcessor的注册2、ConfigurationClassPostProcessor的处理过程(1)parse方法中,Bean方法的处理(2)注册解析Bean标注的方法写在前面 …...
)
论文解读:交大港大上海AI Lab开源论文 | 宇树机器人多姿态起立控制强化学习框架(二)
HoST框架核心实现方法详解 - 论文深度解读(第二部分) 《Learning Humanoid Standing-up Control across Diverse Postures》 系列文章: 论文深度解读 + 算法与代码分析(二) 作者机构: 上海AI Lab, 上海交通大学, 香港大学, 浙江大学, 香港中文大学 论文主题: 人形机器人…...
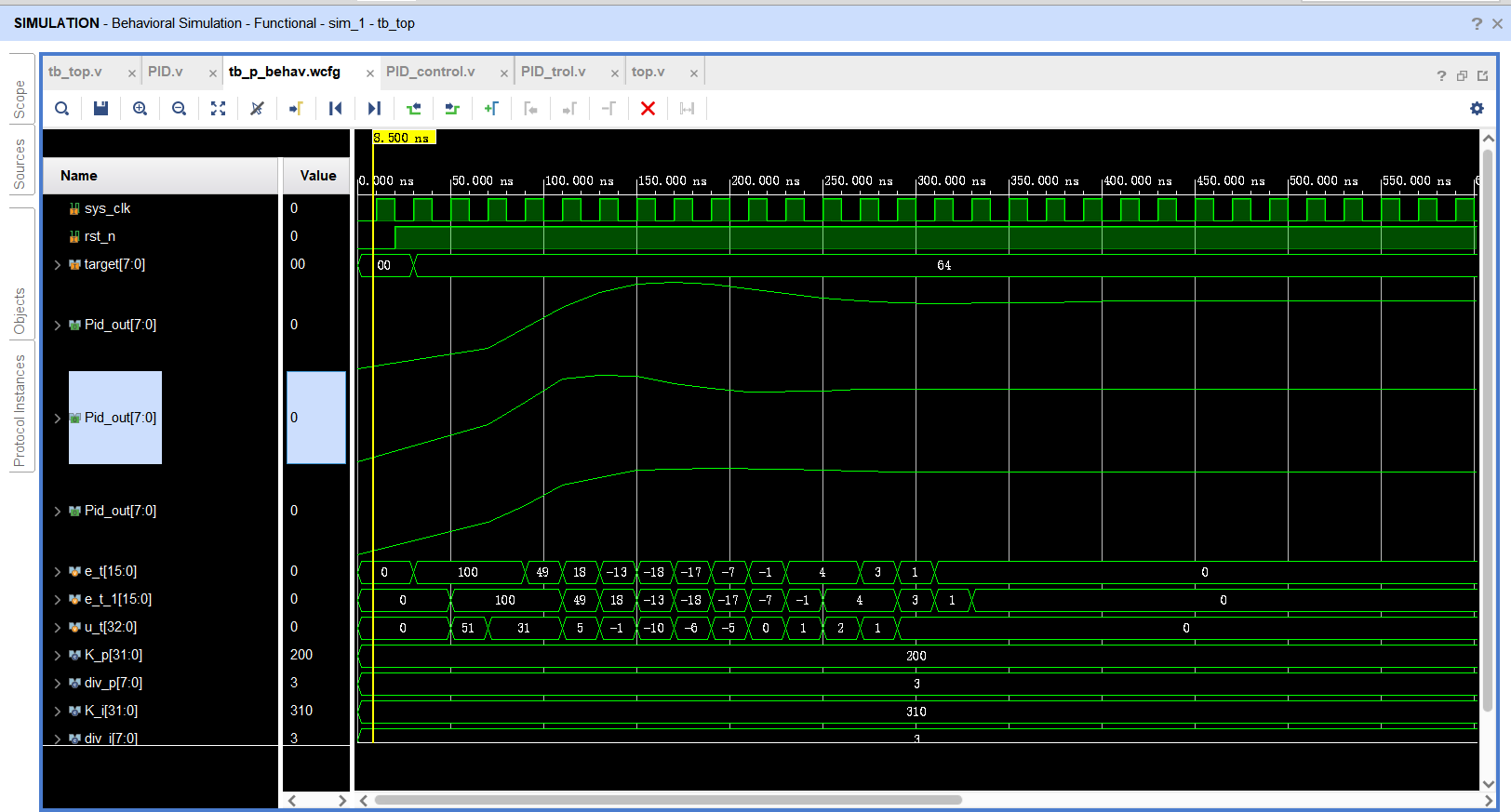
基于FPGA的PID算法学习———实现PID比例控制算法
基于FPGA的PID算法学习 前言一、PID算法分析二、PID仿真分析1. PID代码2.PI代码3.P代码4.顶层5.测试文件6.仿真波形 总结 前言 学习内容:参考网站: PID算法控制 PID即:Proportional(比例)、Integral(积分&…...
visual studio 2022更改主题为深色
visual studio 2022更改主题为深色 点击visual studio 上方的 工具-> 选项 在选项窗口中,选择 环境 -> 常规 ,将其中的颜色主题改成深色 点击确定,更改完成...
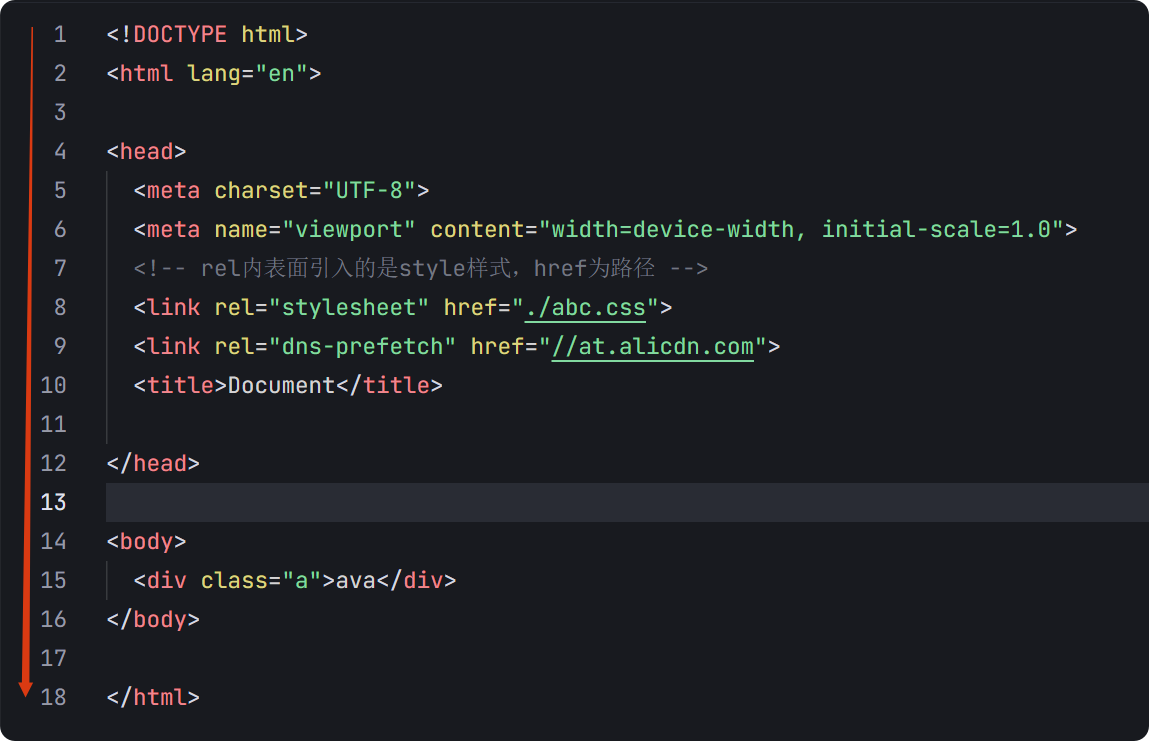
04-初识css
一、css样式引入 1.1.内部样式 <div style"width: 100px;"></div>1.2.外部样式 1.2.1.外部样式1 <style>.aa {width: 100px;} </style> <div class"aa"></div>1.2.2.外部样式2 <!-- rel内表面引入的是style样…...
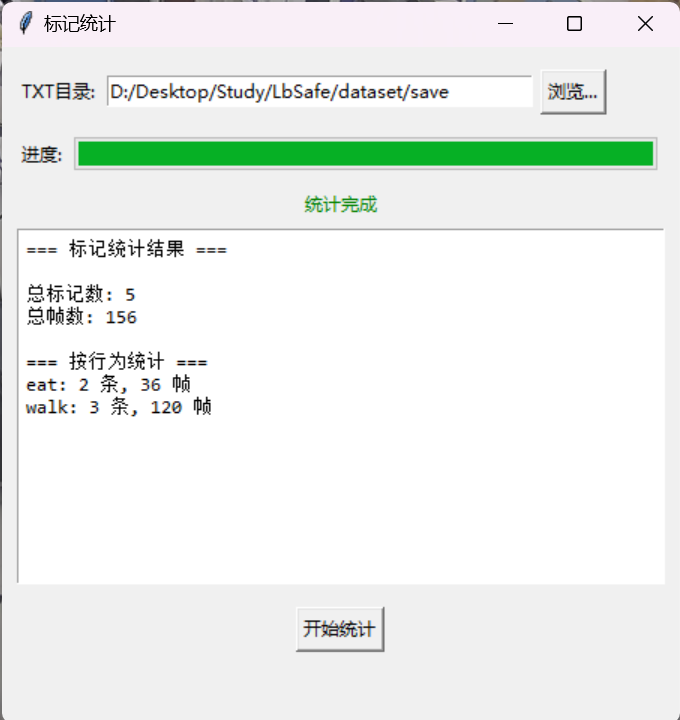
视频行为标注工具BehaviLabel(源码+使用介绍+Windows.Exe版本)
前言: 最近在做行为检测相关的模型,用的是时空图卷积网络(STGCN),但原有kinetic-400数据集数据质量较低,需要进行细粒度的标注,同时粗略搜了下已有开源工具基本都集中于图像分割这块,…...
uniapp 开发ios, xcode 提交app store connect 和 testflight内测
uniapp 中配置 配置manifest 文档:manifest.json 应用配置 | uni-app官网 hbuilderx中本地打包 下载IOS最新SDK 开发环境 | uni小程序SDK hbulderx 版本号:4.66 对应的sdk版本 4.66 两者必须一致 本地打包的资源导入到SDK 导入资源 | uni小程序SDK …...

go 里面的指针
指针 在 Go 中,指针(pointer)是一个变量的内存地址,就像 C 语言那样: a : 10 p : &a // p 是一个指向 a 的指针 fmt.Println(*p) // 输出 10,通过指针解引用• &a 表示获取变量 a 的地址 p 表示…...

React父子组件通信:Props怎么用?如何从父组件向子组件传递数据?
系列回顾: 在上一篇《React核心概念:State是什么?》中,我们学习了如何使用useState让一个组件拥有自己的内部数据(State),并通过一个计数器案例,实现了组件的自我更新。这很棒&#…...

20250607在荣品的PRO-RK3566开发板的Android13系统下实现长按开机之后出现插入适配器不会自动启动的问题的解决
20250607在荣品的PRO-RK3566开发板的Android13系统下实现长按开机之后出现插入适配器不会自动启动的问题的解决 2025/6/7 17:20 缘起: 1、根据RK809的DATASHEET,短按开机【100ms/500ms】/长按关机,长按关机。6s/8s/10s 我在网上找到的DATASHE…...

【AI学习】wirelessGPT多任务无线基础模型摘要
收看了关于WirelessGPT多任务无线基础模型的演讲视频,边做一个记录。 应该说,在无线通信大模型的探索方面,有一个非常有益的尝试。 在沈学明院士带领下开展 https://www.chaspark.com/#/live/1125484184592834560...
