Rust vs Go:常用语法对比(五)

题图来自 Rust vs Go 2023[1]
81. Round floating point number to integer
Declare integer y and initialize it with the rounded value of floating point number x . Ties (when the fractional part of x is exactly .5) must be rounded up (to positive infinity).
按规则取整
package main
import (
"fmt"
"math"
)
func round(x float64) int {
y := int(math.Floor(x + 0.5))
return y
}
func main() {
for _, x := range []float64{-1.1, -0.9, -0.5, -0.1, 0., 0.1, 0.5, 0.9, 1.1} {
fmt.Printf("%5.1f %5d\n", x, round(x))
}
}
-1.1 -1
-0.9 -1
-0.5 0
-0.1 0
0.0 0
0.1 0
0.5 1
0.9 1
1.1 1
fn main() {
let x : f64 = 2.71828;
let y = x.round() as i64;
println!("{} {}", x, y);
}
2.71828 3
82. Count substring occurrences
统计子字符串出现次数
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strings"
)
func main() {
s := "Romaromamam"
t := "mam"
x := strings.Count(s, t)
fmt.Println(x)
}
1
fn main() {
let s = "lorem ipsum lorem ipsum lorem ipsum lorem ipsum";
let t = "ipsum";
let c = s.matches(t).count();
println!("{} occurrences", c);
}
Disjoint matches: overlapping occurrences are not counted.
4 occurrences
83. Regex with character repetition
Declare regular expression r matching strings "http", "htttp", "httttp", etc.
正则表达式匹配重复字符
package main
import (
"fmt"
"regexp"
)
func main() {
r := regexp.MustCompile("htt+p")
for _, s := range []string{
"hp",
"htp",
"http",
"htttp",
"httttp",
"htttttp",
"htttttp",
"word htttp in a sentence",
} {
fmt.Println(s, "=>", r.MatchString(s))
}
}
hp => false
htp => false
http => true
htttp => true
httttp => true
htttttp => true
htttttp => true
word htttp in a sentence => true
extern crate regex;
use regex::Regex;
fn main() {
let r = Regex::new(r"htt+p").unwrap();
assert!(r.is_match("http"));
assert!(r.is_match("htttp"));
assert!(r.is_match("httttp"));
}
84. Count bits set in integer binary representation
Count number c of 1s in the integer i in base 2.E.g. i=6 → c=2
计算十进制整型的二进制表示中 1的个数
package main
import "fmt"
func PopCountUInt64(i uint64) (c int) {
// bit population count, see
// http://graphics.stanford.edu/~seander/bithacks.html#CountBitsSetParallel
i -= (i >> 1) & 0x5555555555555555
i = (i>>2)&0x3333333333333333 + i&0x3333333333333333
i += i >> 4
i &= 0x0f0f0f0f0f0f0f0f
i *= 0x0101010101010101
return int(i >> 56)
}
func PopCountUInt32(i uint32) (n int) {
// bit population count, see
// http://graphics.stanford.edu/~seander/bithacks.html#CountBitsSetParallel
i -= (i >> 1) & 0x55555555
i = (i>>2)&0x33333333 + i&0x33333333
i += i >> 4
i &= 0x0f0f0f0f
i *= 0x01010101
return int(i >> 24)
}
func main() {
for i := uint64(0); i < 16; i++ {
c := PopCountUInt64(i)
fmt.Printf("%4d %04[1]b %d\n", i, c)
}
for i := uint32(0); i < 16; i++ {
c := PopCountUInt32(i)
fmt.Printf("%4d %04[1]b %d\n", i, c)
}
}
0 0000 0
1 0001 1
2 0010 1
3 0011 2
4 0100 1
5 0101 2
6 0110 2
7 0111 3
8 1000 1
9 1001 2
10 1010 2
11 1011 3
12 1100 2
13 1101 3
14 1110 3
15 1111 4
0 0000 0
1 0001 1
2 0010 1
3 0011 2
4 0100 1
5 0101 2
6 0110 2
7 0111 3
8 1000 1
9 1001 2
10 1010 2
11 1011 3
12 1100 2
13 1101 3
14 1110 3
15 1111 4
This was useful only before go 1.9. See math/bits.OnesCount instead
or
package main
import (
"fmt"
"math/bits"
)
func main() {
for i := uint(0); i < 16; i++ {
c := bits.OnesCount(i)
fmt.Printf("%4d %04[1]b %d\n", i, c)
}
}
0 0000 0
1 0001 1
2 0010 1
3 0011 2
4 0100 1
5 0101 2
6 0110 2
7 0111 3
8 1000 1
9 1001 2
10 1010 2
11 1011 3
12 1100 2
13 1101 3
14 1110 3
15 1111 4
fn main() {
println!("{}", 6usize.count_ones())
}
2
85. Check if integer addition will overflow
检查两个整型相加是否溢出
package main
import (
"fmt"
"math"
)
func willAddOverflow(a, b int64) bool {
return a > math.MaxInt64-b
}
func main() {
fmt.Println(willAddOverflow(11111111111111111, 2))
}
false
fn adding_will_overflow(x: usize, y: usize) -> bool {
x.checked_add(y).is_none()
}
fn main() {
{
let (x, y) = (2345678, 9012345);
let overflow = adding_will_overflow(x, y);
println!(
"{} + {} {}",
x,
y,
if overflow {
"overflows"
} else {
"doesn't overflow"
}
);
}
{
let (x, y) = (2345678901, 9012345678);
let overflow = adding_will_overflow(x, y);
println!(
"{} + {} {}",
x,
y,
if overflow {
"overflows"
} else {
"doesn't overflow"
}
);
}
{
let (x, y) = (2345678901234, 9012345678901);
let overflow = adding_will_overflow(x, y);
println!(
"{} + {} {}",
x,
y,
if overflow {
"overflows"
} else {
"doesn't overflow"
}
);
}
{
let (x, y) = (23456789012345678, 90123456789012345);
let overflow = adding_will_overflow(x, y);
println!(
"{} + {} {}",
x,
y,
if overflow {
"overflows"
} else {
"doesn't overflow"
}
);
}
{
let (x, y) = (12345678901234567890, 9012345678901234567);
let overflow = adding_will_overflow(x, y);
println!(
"{} + {} {}",
x,
y,
if overflow {
"overflows"
} else {
"doesn't overflow"
}
);
}
}
2345678 + 9012345 doesn't overflow
2345678901 + 9012345678 doesn't overflow
2345678901234 + 9012345678901 doesn't overflow
23456789012345678 + 90123456789012345 doesn't overflow
12345678901234567890 + 9012345678901234567 overflows
86. Check if integer multiplication will overflow
检查整型相乘是否溢出
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
func multiplyWillOverflow(x, y uint64) bool {
if x <= 1 || y <= 1 {
return false
}
d := x * y
return d/y != x
}
func main() {
{
var x, y uint64 = 2345, 6789
if multiplyWillOverflow(x, y) {
fmt.Println(x, "*", y, "overflows")
} else {
fmt.Println(x, "*", y, "doesn't overflow")
}
}
{
var x, y uint64 = 2345678, 9012345
if multiplyWillOverflow(x, y) {
fmt.Println(x, "*", y, "overflows")
} else {
fmt.Println(x, "*", y, "doesn't overflow")
}
}
{
var x, y uint64 = 2345678901, 9012345678
if multiplyWillOverflow(x, y) {
fmt.Println(x, "*", y, "overflows")
} else {
fmt.Println(x, "*", y, "doesn't overflow")
}
}
}
2345 * 6789 doesn't overflow
2345678 * 9012345 doesn't overflow
2345678901 * 9012345678 overflows
fn main() {
{
let (x, y) = (2345, 6789);
let overflow = multiply_will_overflow(x, y);
println!(
"{} * {} {}",
x,
y,
if overflow {
"overflows"
} else {
"doesn't overflow"
}
);
}
{
let (x, y) = (2345678, 9012345);
let overflow = multiply_will_overflow(x, y);
println!(
"{} * {} {}",
x,
y,
if overflow {
"overflows"
} else {
"doesn't overflow"
}
);
}
{
let (x, y) = (2345678901, 9012345678);
let overflow = multiply_will_overflow(x, y);
println!(
"{} * {} {}",
x,
y,
if overflow {
"overflows"
} else {
"doesn't overflow"
}
);
}
}
fn multiply_will_overflow(x: i64, y: i64) -> bool {
x.checked_mul(y).is_none()
}
2345 * 6789 doesn't overflow
2345678 * 9012345 doesn't overflow
2345678901 * 9012345678 overflows
87. Stop program
Exit immediately.
If some extra cleanup work is executed by the program runtime (not by the OS itself), describe it.
停止程序,立即退出。
package main
import "os"
func main() {
os.Exit(1)
print(2222)
}
fn main() {
std::process::exit(1);
println!("42");
}
88. Allocate 1M bytes
分配1M内存
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
buf := make([]byte, 1000000)
for i, b := range buf {
if b != 0 {
fmt.Println("Found unexpected value", b, "at position", i)
}
}
fmt.Println("Buffer was correctly initialized with zero values.")
}
Buffer was correctly initialized with zero values.
fn main() {
let buf: Vec<u8> = Vec::with_capacity(1024 * 1024);
println!("{:?}", buf.capacity());
}
1048576
89. Handle invalid argument
处理无效参数
package main
import "fmt"
// NewSquareMatrix creates a N-by-N matrix
func NewSquareMatrix(N int) ([][]float64, error) {
if N < 0 {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Invalid size %d: order cannot be negative", N)
}
matrix := make([][]float64, N)
for i := range matrix {
matrix[i] = make([]float64, N)
}
return matrix, nil
}
func main() {
N1 := 3
matrix1, err1 := NewSquareMatrix(N1)
if err1 == nil {
fmt.Println(matrix1)
} else {
fmt.Println(err1)
}
N2 := -2
matrix2, err2 := NewSquareMatrix(N2)
if err2 == nil {
fmt.Println(matrix2)
} else {
fmt.Println(err2)
}
}
[[0 0 0] [0 0 0] [0 0 0]]
Invalid size -2: order cannot be negative
#[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
enum CustomError { InvalidAnswer }
fn do_stuff(x: i32) -> Result<i32, CustomError> {
if x != 42 {
%2
90. Read-only outside
外部只读
type Foo struct {
x int
}
func (f *Foo) X() int {
return f.x
}
x is private, because it is not capitalized.
(*Foo).X is a public getter (a read accessor).
struct Foo {
x: usize
}
impl Foo {
pub fn new(x: usize) -> Self {
Foo { x }
}
pub fn x<'a>(&'a self) -> &'a usize {
&self.x
}
}
91. Load JSON file into struct
json转结构体
package main
import "fmt"
import "io/ioutil"
import "encoding/json"
func readJSONFile() error {
var x Person
buffer, err := ioutil.ReadFile(filename)
if err != nil {
return err
}
err = json.Unmarshal(buffer, &x)
if err != nil {
return err
}
fmt.Println(x)
return nil
}
func main() {
err := readJSONFile()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
type Person struct {
FirstName string
Age int
}
const filename = "/tmp/data.json"
func init() {
err := ioutil.WriteFile(filename, []byte(`
{
"FirstName":"Napoléon",
"Age": 51
}`), 0644)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
{Napoléon 51}
or
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"os"
)
func readJSONFile() error {
var x Person
r, err := os.Open(filename)
if err != nil {
return err
}
decoder := json.NewDecoder(r)
err = decoder.Decode(&x)
if err != nil {
return err
}
fmt.Println(x)
return nil
}
func main() {
err := readJSONFile()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
type Person struct {
FirstName string
Age int
}
const filename = "/tmp/data.json"
func init() {
err := ioutil.WriteFile(filename, []byte(`
{
"FirstName":"Napoléon",
"Age": 51
}`), 0644)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
{Napoléon 51}
#[macro_use] extern crate serde_derive;
extern crate serde_json;
use std::fs::File;
let x = ::serde_json::from_reader(File::open("data.json")?)?;
92. Save object into JSON file
将json对象写入文件
package main
import "fmt"
import "io/ioutil"
import "encoding/json"
func writeJSONFile() error {
x := Person{
FirstName: "Napoléon",
Age: 51,
}
buffer, err := json.MarshalIndent(x, "", " ")
if err != nil {
return err
}
return ioutil.WriteFile(filename, buffer, 0644)
}
func main() {
err := writeJSONFile()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
fmt.Println("Done.")
}
type Person struct {
FirstName string
Age int
}
const filename = "/tmp/data.json"
json.MarshalIndent is more human-readable than json.Marshal.
Done.
extern crate serde_json;
#[macro_use] extern crate serde_derive;
use std::fs::File;
::serde_json::to_writer(&File::create("data.json")?, &x)?
93. Pass a runnable procedure as parameter
Implement procedure control which receives one parameter f, and runs f.
以函数作为参数
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
control(greet)
}
func control(f func()) {
fmt.Println("Before f")
f()
fmt.Println("After f")
}
func greet() {
fmt.Println("Hello, developers")
}
Go supports first class functions, higher-order functions, user-defined function types, function literals, and closures.
Before f
Hello, developers
After f
fn control(f: impl Fn()) {
f();
}
fn hello() {
println!("Hello,");
}
fn main() {
control(hello);
control(|| { println!("Is there anybody in there?"); });
}
Hello,
Is there anybody in there?
94. Print type of variable
打印变量的类型
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
"reflect"
)
func main() {
var x interface{}
x = "Hello"
fmt.Println(reflect.TypeOf(x))
x = 4
fmt.Println(reflect.TypeOf(x))
x = os.NewFile(0777, "foobar.txt")
fmt.Println(reflect.TypeOf(x))
}
string
int
*os.File
or
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
)
func main() {
var x interface{}
x = "Hello"
fmt.Printf("%T", x)
fmt.Println()
x = 4
fmt.Printf("%T", x)
fmt.Println()
x = os.NewFile(0777, "foobar.txt")
fmt.Printf("%T", x)
fmt.Println()
}
string
int
*os.File
#![feature(core_intrinsics)]
fn type_of<T>(_: &T) -> String {
format!("{}", std::intrinsics::type_name::<T>())
}
fn main() {
let x: i32 = 1;
println!("{}", type_of(&x));
}
i32
95. Get file size
获取文件的大小
package main
import (
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"os"
)
func main() {
err := printSize("file.txt")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
func printSize(path string) error {
info, err := os.Stat(path)
if err != nil {
return err
}
x := info.Size()
fmt.Println(x)
return nil
}
func init() {
// The file will only contains the characters "Hello", no newlines.
buffer := []byte("Hello")
err := ioutil.WriteFile("file.txt", buffer, 0644)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
5
use std::fs;
fn filesize(path: &str) -> Result<u64, std::io::Error> {
let x = fs::metadata(path)?.len();
Ok(x)
}
fn main() {
let path = "/etc/hosts";
let x = filesize(path);
println!("{}: {:?} bytes", path, x.unwrap());
}
/etc/hosts: 150 bytes
or
use std::path::Path;
fn filesize(path: &std::path::Path) -> Result<u64, std::io::Error> {
let x = path.metadata()?.len();
Ok(x)
}
fn main() {
let path = Path::new("/etc/hosts");
let x = filesize(path);
println!("{:?}: {:?} bytes", path, x.unwrap());
}
"/etc/hosts": 150 bytes
96. Check string prefix
Set boolean b to true if string s starts with prefix prefix, false otherwise.
检查两个字符串前缀是否一致
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strings"
)
func check(s, prefix string) {
b := strings.HasPrefix(s, prefix)
if b {
fmt.Println(s, "starts with", prefix)
} else {
fmt.Println(s, "doesn't start with", prefix)
}
}
func main() {
check("bar", "foo")
check("foobar", "foo")
}
bar doesn't start with foo
foobar starts with foo
fn main() {
let s = "bananas";
let prefix = "bana";
let b = s.starts_with(prefix);
println!("{:?}", b);
}
true
97. Check string suffix
Set boolean b to true if string s ends with string suffix, false otherwise.
检查字符串后缀
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strings"
)
func check(s, suffix string) {
b := strings.HasSuffix(s, suffix)
if b {
fmt.Println(s, "ends with", suffix)
} else {
fmt.Println(s, "doesn't end with", suffix)
}
}
func main() {
check("foo", "bar")
check("foobar", "bar")
}
foo doesn't end with bar
foobar ends with bar
fn main() {
let s = "bananas";
let suffix = "nas";
let b = s.ends_with(suffix);
println!("{:?}", b);
}
true
98. Epoch seconds to date object
Convert a timestamp ts (number of seconds in epoch-time) to a date with time d. E.g. 0 -> 1970-01-01 00:00:00
时间戳转日期
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
func main() {
ts := int64(1451606400)
d := time.Unix(ts, 0)
fmt.Println(d)
}
2016-01-01 00:00:00 +0000 UTC
extern crate chrono;
use chrono::prelude::*;
fn main() {
let ts = 1451606400;
let d = NaiveDateTime::from_timestamp(ts, 0);
println!("{}", d);
}
2016-01-01 00:00:00
99. Format date YYYY-MM-DD
Assign to string x the value of fields (year, month, day) of date d, in format YYYY-MM-DD.
时间格式转换
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
func main() {
d := time.Now()
x := d.Format("2006-01-02")
fmt.Println(x)
// The output may be "2009-11-10" because the Playground's clock is fixed in the past.
}
2009-11-10
extern crate chrono;
use chrono::prelude::*;
fn main() {
println!("{}", Utc::today().format("%Y-%m-%d"))
}
2021-07-17
100. Sort by a comparator
Sort elements of array-like collection items, using a comparator c.
根据某个字段排序
package main
import "fmt"
import "sort"
type Item struct {
label string
p int
lang string
}
// c returns true if x is "inferior to" y (in a custom way)
func c(x, y Item) bool {
return x.p < y.p
}
type ItemCSorter []Item
func (s ItemCSorter) Len() int { return len(s) }
func (s ItemCSorter) Less(i, j int) bool { return c(s[i], s[j]) }
func (s ItemCSorter) Swap(i, j int) { s[i], s[j] = s[j], s[i] }
func sortItems(items []Item) {
sorter := ItemCSorter(items)
sort.Sort(sorter)
}
func main() {
items := []Item{
{"twelve", 12, "english"},
{"six", 6, "english"},
{"eleven", 11, "english"},
{"zero", 0, "english"},
{"two", 2, "english"},
}
fmt.Println("Unsorted: ", items)
sortItems(items)
fmt.Println("Sorted: ", items)
}
c has type func(Item, Item) bool.
Unsorted: [{twelve 12 english} {six 6 english} {eleven 11 english} {zero 0 english} {two 2 english}]
Sorted: [{zero 0 english} {two 2 english} {six 6 english} {eleven 11 english} {twelve 12 english}]
or
package main
import "fmt"
import "sort"
type Item struct {
label string
p int
lang string
}
type ItemsSorter struct {
items []Item
c func(x, y Item) bool
}
func (s ItemsSorter) Len() int { return len(s.items) }
func (s ItemsSorter) Less(i, j int) bool { return s.c(s.items[i], s.items[j]) }
func (s ItemsSorter) Swap(i, j int) { s.items[i], s.items[j] = s.items[j], s.items[i] }
func sortItems(items []Item, c func(x, y Item) bool) {
sorter := ItemsSorter{
items,
c,
}
sort.Sort(sorter)
}
func main() {
items := []Item{
{"twelve", 12, "english"},
{"six", 6, "english"},
{"eleven", 11, "english"},
{"zero", 0, "english"},
{"two", 2, "english"},
}
fmt.Println("Unsorted: ", items)
c := func(x, y Item) bool {
return x.p < y.p
}
sortItems(items, c)
fmt.Println("Sorted: ", items)
}
ItemsSorter contains c, which can be any comparator decided at runtime.
Unsorted: [{twelve 12 english} {six 6 english} {eleven 11 english} {zero 0 english} {two 2 english}]
Sorted: [{zero 0 english} {two 2 english} {six 6 english} {eleven 11 english} {twelve 12 english}]
or
package main
import "fmt"
import "sort"
type Item struct {
label string
p int
lang string
}
// c returns true if x is "inferior to" y (in a custom way)
func c(x, y Item) bool {
return x.p < y.p
}
func main() {
items := []Item{
{"twelve", 12, "english"},
{"six", 6, "english"},
{"eleven", 11, "english"},
{"zero", 0, "english"},
{"two", 2, "english"},
}
fmt.Println("Unsorted: ", items)
sort.Slice(items, func(i, j int) bool {
return c(items[i], items[j])
})
fmt.Println("Sorted: ", items)
}
Since Go 1.8, a single func parameter is sufficient to sort a slice.
Unsorted: [{twelve 12 english} {six 6 english} {eleven 11 english} {zero 0 english} {two 2 english}]
Sorted: [{zero 0 english} {two 2 english} {six 6 english} {eleven 11 english} {twelve 12 english}]
fn main() {
let mut items = [1, 7, 5, 2, 3];
items.sort_by(i32::cmp);
println!("{:?}", items);
}
[1, 2, 3, 5, 7]
参考资料
Rust vs Go 2023: https://arkiana.com/rust-vs-go/
本文由 mdnice 多平台发布
相关文章:

Rust vs Go:常用语法对比(五)
题图来自 Rust vs Go 2023[1] 81. Round floating point number to integer Declare integer y and initialize it with the rounded value of floating point number x . Ties (when the fractional part of x is exactly .5) must be rounded up (to positive infinity). 按规…...

Flutter 扩展函数项目实用之封装SizedBox
Flutter里扩展函数可以用简化代码写法,关键字为extension,伪代码写法如下: extension 扩展类名 on 扩展类型 { //扩展方法 } 在Flutter页面里实现控件间距会常用到SizedBox,可使用扩展函数封装来达到简化代码的目的࿰…...

EMC学习笔记(二十)EMC常用元件简单介绍(二)
EMC常用元件简单介绍(二) 1.瞬态抑制二极管(TVS)2.气体放电管3.半导体放电管 电磁兼容性元件是解决电磁干扰发射和电磁敏感度问题的关键,正确选择和使用这些元件是做好电磁兼容性设计的前提。由于每一种电子元件都有它各自的特性,…...
基本排序算法
目录 一,插入排序 二,希尔排序 三,选择排序 四,冒泡排序 五,快排 5.1 Hoare法 5.2 挖坑法 5.3 指针法 5.4 非递归写法 六,归并排序 6.1 递归 6.2 非递归 一,插入排序 基本思想&…...
python调用百度ai将图片/pdf识别为表格excel
python调用百度ai将图片识别为表格excel 表格文字识别(异步接口)图片转excel 表格文字识别V2图片/pdf转excel通用 表格文字识别(异步接口) 图片转excel 百度ai官方文档:https://ai.baidu.com/ai-doc/OCR/Ik3h7y238 使用的是表格文字识别(异步接口),同步…...

Ansible最佳实践之Playbook管理滚动更新
写在前面 理解不足小伙伴帮忙指正 傍晚时分,你坐在屋檐下,看着天慢慢地黑下去,心里寂寞而凄凉,感到自己的生命被剥夺了。当时我是个年轻人,但我害怕这样生活下去,衰老下去。在我看来,这是比死亡…...

基于Citespace、vosviewer、R语言的文献计量学可视化分析及SCI论文高效写作方法教程
详情点击链接:基于Citespace、vosviewer、R语言的文献计量学可视化分析技术及全流程文献可视化SCI论文高效写作方法 前言 文献计量学是指用数学和统计学的方法,定量地分析一切知识载体的交叉科学。它是集数学、统计学、文献学为一体,注重量…...

【MATLAB】GM(1,1) 灰色预测模型及算法
一、灰色预测模型概念 灰色预测是一种对含有不确定因素的系统进行预测的方法。 灰色预测通过鉴别系统因素之间发展趋势的相异程度,即进行关联分析,并对原始数据进行生成处理来寻找系统变动的规律,生成有较强规律性的数据序列,然后…...

Go重写Redis中间件 - Go实现Redis协议解析器
Go实现Redis协议解析器 Redis网络协议详解 在解决完通信后,下一步就是搞清楚 Redis 的协议-RESP协议,其实就是一套类似JSON、Protocol Buffers的序列化协议,也就是我们的客户端和服务端通信的协议 RESP定义了5种格式 简单字符串(Simple String) : 服务器用来返回简单的结…...

海外抖音Tiktok强势来袭,有些人半年赚别人十倍工资
TikTok作为一款流行的短视频社交应用程序,确实在全球范围内取得了很大的成功。许多人通过在TikTok上分享有趣、创意或有吸引力的视频内容,获得了广泛的关注和认可。一些用户甚至能够通过TikTok赚取高额的收入,远远超过传统职业所能获得的工资…...

devDept Eyeshot 2024 预告-Update-Crack
即将发布的版本 开发商在一个动态的环境中运作,事情可能会发生变化。本页提供的信息旨在概述 devDept 软件产品的总体方向。它仅供参考,不应作为做出任何决定性的依据。devDept Eyeshot 2024软件产品描述的任何特性或功能的开发、发布和时间安排仍由 dev…...
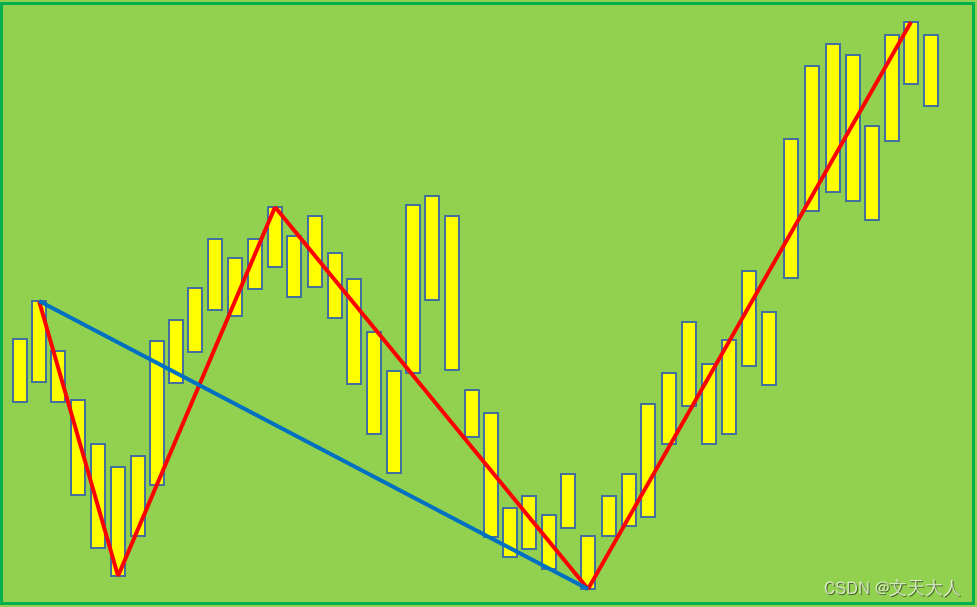
教雅川学缠论05-线段
线段需要满足下面4个条件: 1.是由3条笔,或者3条以上组成,同笔一样,线段也是有方向的 2.如果线段起始于向上笔,则终止与向上笔(一定不会终止与向下笔) 3.如果线段起始于向下笔,则终止…...
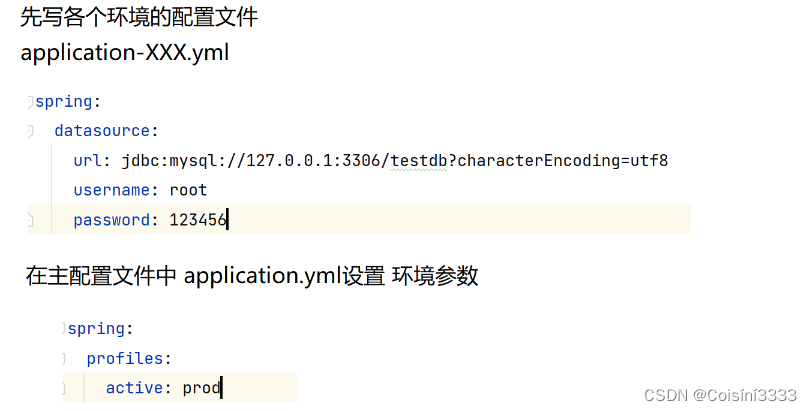
SpringBoot 配置⽂件
1.配置文件作用 整个项⽬中所有重要的数据都是在配置⽂件中配置的,⽐如: 数据库的连接信息(包含⽤户名和密码的设置);项⽬的启动端⼝;第三⽅系统的调⽤秘钥等信息;⽤于发现和定位问题的普通⽇…...
基于Python的电影票房爬取与可视化系统的设计与实现
博主介绍:✌全网粉丝30W,csdn特邀作者、博客专家、CSDN新星计划导师、java领域优质创作者,博客之星、掘金/华为云/阿里云/InfoQ等平台优质作者、专注于Java技术领域和毕业项目实战✌ 🍅文末获取源码联系🍅 👇🏻 精彩专…...
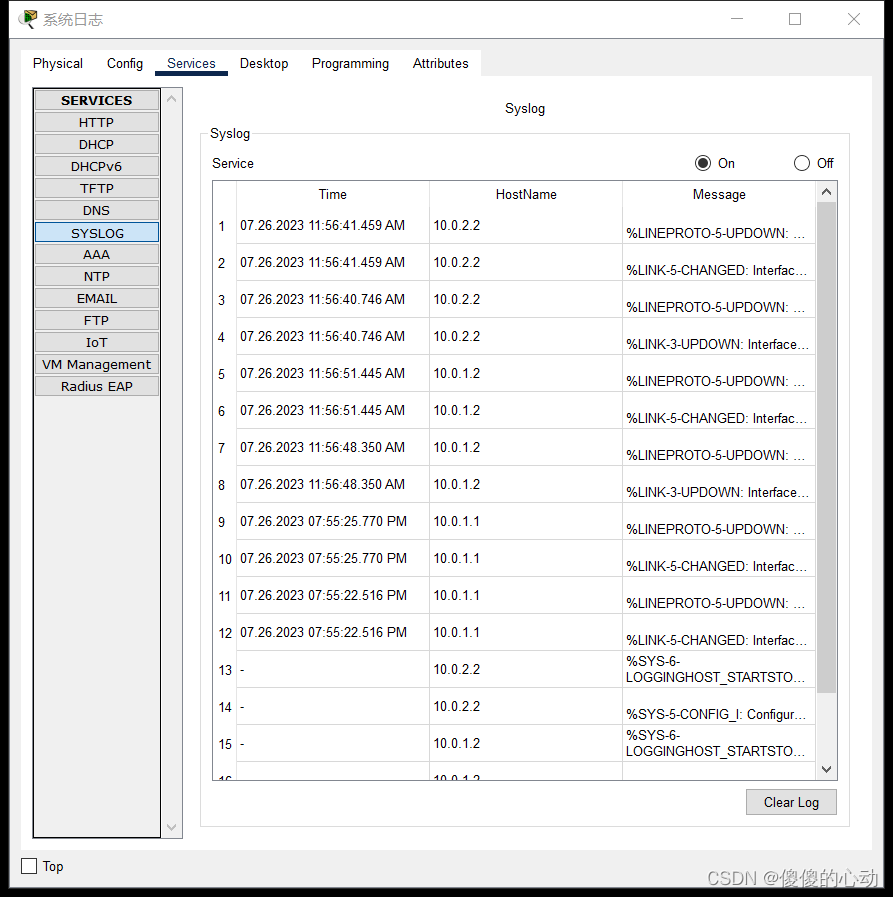
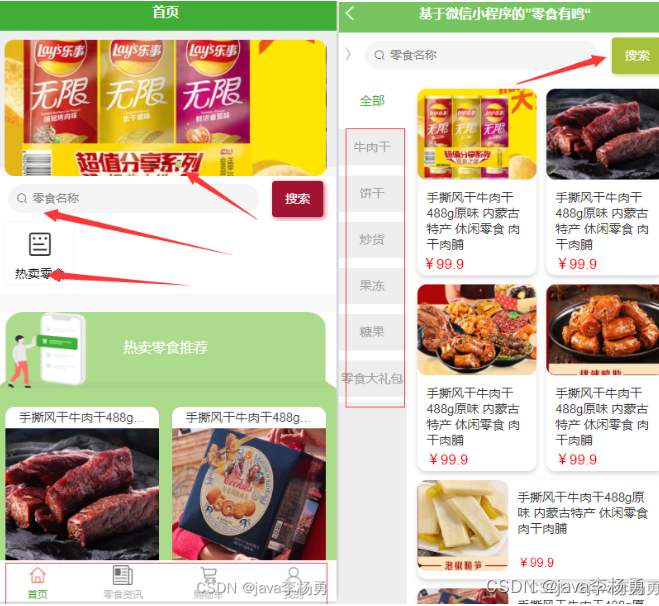
Packet Tracer – 配置系统日志和 NTP
Packet Tracer – 配置系统日志和 NTP 目标 第 1 部分:配置系统日志服务 第 2 部分:生成日志记录事件 第 3 部分:手动设置交换机时钟 第 4 部分:配置 NTP 服务 第 5 部分:验证带时间戳的日志 拓扑图 场景 在本…...

TypeScript 联合类型,类型推断,类型断言
联合类型 取值可以为多种类型中的一个 function func(str: number | string):void{}类型断言 当变量需要调用某属性的时候,有不确定当前的类型是什么,可以使用类型断言; 类型断言的两种方式: 1,<类型> 变量名…...

到底叫 集合还是数组还是list还是列表?
1 总体上可以将数据结构分为数组和集合两种,而列表是一个泛指 数组:在Java中,数组是一种基本数据类型,可以用来存储同一类型的多个元素,数组的长度是固定的。例如:int[] arr new int[10];List:…...
LBERT论文详解
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.07148 代码地址:https://github.com/liuwei1206/LEBERT 模型创新 LEBRT采用句子中的词语对(论文中称为Char-Word Pair)的特征作为输入作者设计Lexicon adapter,在BERT的中间某一…...

C++终止cin输入while循环时多读取^Z或^D的问题
原代码: istream& operator>>(istream& is, map<string, int>&mm) {string ss"";int ii0;is >> ss>>ii;mm[ss]ii;return is; }int main() {map<string,int>msi;while(cin>>msi);return 0; } 问题&…...

c#[WebMethod]方法接收前端传入的JsonArray的方法
一、第一种方法:可以这样接收前端传入的jsonArray字符串到一个类的数组中,然后遍历该数组取值 这种方法需要创建PointConfig类 class PointConfig{public string ptcrossing { get; set; }public string ptcrossingId { get; set; }public string camId …...
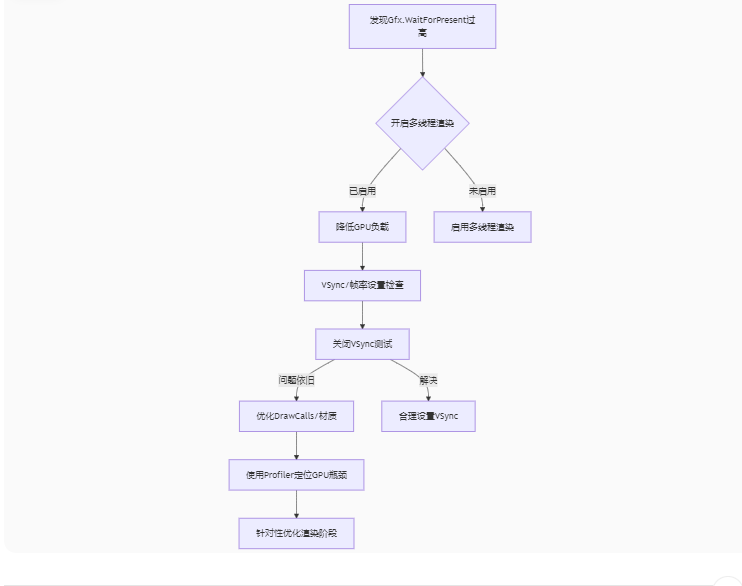
Unity3D中Gfx.WaitForPresent优化方案
前言 在Unity中,Gfx.WaitForPresent占用CPU过高通常表示主线程在等待GPU完成渲染(即CPU被阻塞),这表明存在GPU瓶颈或垂直同步/帧率设置问题。以下是系统的优化方案: 对惹,这里有一个游戏开发交流小组&…...

uni-app学习笔记二十二---使用vite.config.js全局导入常用依赖
在前面的练习中,每个页面需要使用ref,onShow等生命周期钩子函数时都需要像下面这样导入 import {onMounted, ref} from "vue" 如果不想每个页面都导入,需要使用node.js命令npm安装unplugin-auto-import npm install unplugin-au…...

Objective-C常用命名规范总结
【OC】常用命名规范总结 文章目录 【OC】常用命名规范总结1.类名(Class Name)2.协议名(Protocol Name)3.方法名(Method Name)4.属性名(Property Name)5.局部变量/实例变量(Local / Instance Variables&…...

2024年赣州旅游投资集团社会招聘笔试真
2024年赣州旅游投资集团社会招聘笔试真 题 ( 满 分 1 0 0 分 时 间 1 2 0 分 钟 ) 一、单选题(每题只有一个正确答案,答错、不答或多答均不得分) 1.纪要的特点不包括()。 A.概括重点 B.指导传达 C. 客观纪实 D.有言必录 【答案】: D 2.1864年,()预言了电磁波的存在,并指出…...

抖音增长新引擎:品融电商,一站式全案代运营领跑者
抖音增长新引擎:品融电商,一站式全案代运营领跑者 在抖音这个日活超7亿的流量汪洋中,品牌如何破浪前行?自建团队成本高、效果难控;碎片化运营又难成合力——这正是许多企业面临的增长困局。品融电商以「抖音全案代运营…...

镜像里切换为普通用户
如果你登录远程虚拟机默认就是 root 用户,但你不希望用 root 权限运行 ns-3(这是对的,ns3 工具会拒绝 root),你可以按以下方法创建一个 非 root 用户账号 并切换到它运行 ns-3。 一次性解决方案:创建非 roo…...

Mac下Android Studio扫描根目录卡死问题记录
环境信息 操作系统: macOS 15.5 (Apple M2芯片)Android Studio版本: Meerkat Feature Drop | 2024.3.2 Patch 1 (Build #AI-243.26053.27.2432.13536105, 2025年5月22日构建) 问题现象 在项目开发过程中,提示一个依赖外部头文件的cpp源文件需要同步,点…...
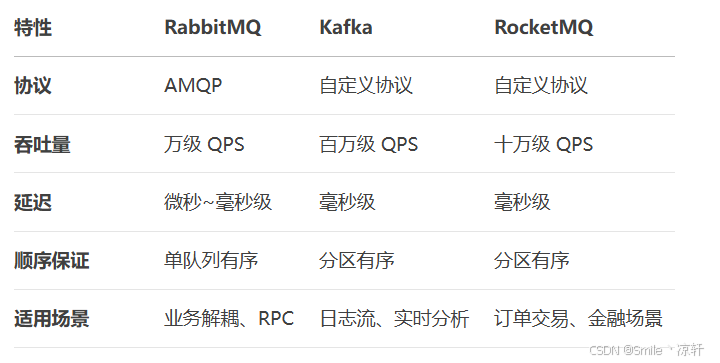
技术栈RabbitMq的介绍和使用
目录 1. 什么是消息队列?2. 消息队列的优点3. RabbitMQ 消息队列概述4. RabbitMQ 安装5. Exchange 四种类型5.1 direct 精准匹配5.2 fanout 广播5.3 topic 正则匹配 6. RabbitMQ 队列模式6.1 简单队列模式6.2 工作队列模式6.3 发布/订阅模式6.4 路由模式6.5 主题模式…...
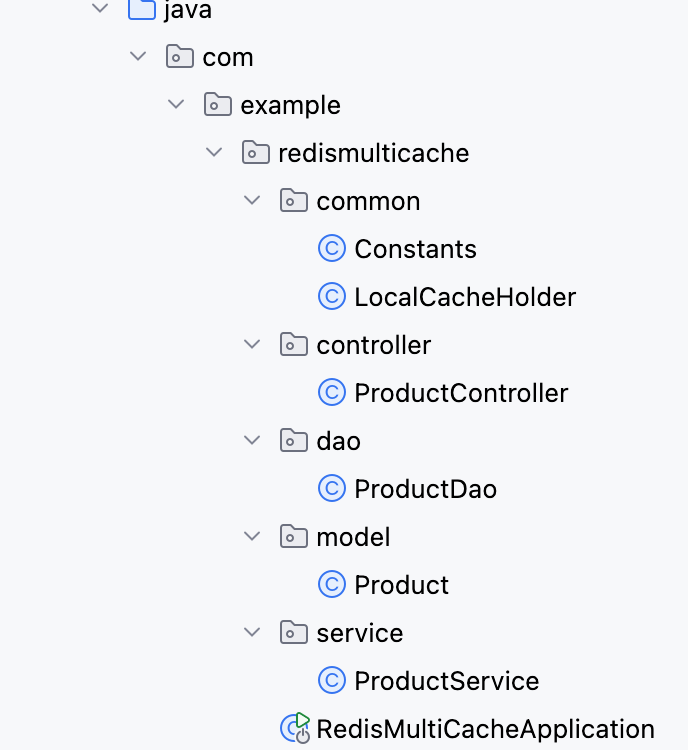
【Redis】笔记|第8节|大厂高并发缓存架构实战与优化
缓存架构 代码结构 代码详情 功能点: 多级缓存,先查本地缓存,再查Redis,最后才查数据库热点数据重建逻辑使用分布式锁,二次查询更新缓存采用读写锁提升性能采用Redis的发布订阅机制通知所有实例更新本地缓存适用读多…...

Linux安全加固:从攻防视角构建系统免疫
Linux安全加固:从攻防视角构建系统免疫 构建坚不可摧的数字堡垒 引言:攻防对抗的新纪元 在日益复杂的网络威胁环境中,Linux系统安全已从被动防御转向主动免疫。2023年全球网络安全报告显示,高级持续性威胁(APT)攻击同比增长65%,平均入侵停留时间缩短至48小时。本章将从…...
