EventBus 开源库学习(二)
整体流程阅读
EventBus在使用的时候基本分为以下几步:
1、注册订阅者
EventBus.getDefault().register(this);
2、订阅者解注册,否者会导致内存泄漏
EventBus.getDefault().unregister(this);
3、在订阅者中编写注解为Subscribe的事件处理函数
@Subscribe(threadMode = ThreadMode.MAIN, sticky = true, priority = 1)
public void onMsgEventReceived(MsgEvent event) {Toast.makeText(this, event.getMsg(), Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
4、事件发送
EventBus.getDefault().post("msg1 - coming!!!");
我们先按使用的流程大体看下源码逻辑,源码版本3.3.1:
注册源码逻辑
public static EventBus getDefault() {EventBus instance = defaultInstance;if (instance == null) {synchronized (EventBus.class) {instance = EventBus.defaultInstance;if (instance == null) {instance = EventBus.defaultInstance = new EventBus();}}}return instance;}
EventBus 使用了双重校验锁的单例设计模式,保证用到的对象是唯一的,首次使用对象为空的时候通过下面构造创建一个。
public EventBus() {this(DEFAULT_BUILDER);}
DEFAULT_BUILDER是一个final常量,在加载的时候就进行初始化,赋一个EventBusBuilder对象如下面代码所示。
private static final EventBusBuilder DEFAULT_BUILDER = new EventBusBuilder();
EventBusBuilder是EventBus的建造类,里面参数在加载的时候进行了初始化。
public class EventBusBuilder {private final static ExecutorService DEFAULT_EXECUTOR_SERVICE = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();boolean logSubscriberExceptions = true;boolean logNoSubscriberMessages = true;boolean sendSubscriberExceptionEvent = true;boolean sendNoSubscriberEvent = true;boolean throwSubscriberException;boolean eventInheritance = true;boolean ignoreGeneratedIndex;boolean strictMethodVerification;ExecutorService executorService = DEFAULT_EXECUTOR_SERVICE;List<Class<?>> skipMethodVerificationForClasses;List<SubscriberInfoIndex> subscriberInfoIndexes;Logger logger;MainThreadSupport mainThreadSupport;...
}
如果有需要的话,我们也可以通过配置EventBusBuilder来更改EventBus的属性,在EventBus中有一个静态方法直接返回一直新的EventBusBuilder对象,设置完参数后调用build()来以新的配置来新建一个EventBus对象。
#EventBuspublic static EventBusBuilder builder() {return new EventBusBuilder();}#EventBusBuilder/** Builds an EventBus based on the current configuration. */public EventBus build() {return new EventBus(this);}
然后通过下面的调用来设置:
EventBus.builder().eventInheritance(false).logSubscriberExceptions(false).build().register(this);
拿到EventBus对象以后,我们可以调用其register方法进行订阅者注册了。
public void register(Object subscriber) {Class<?> subscriberClass = subscriber.getClass();List<SubscriberMethod> subscriberMethods = subscriberMethodFinder.findSubscriberMethods(subscriberClass);synchronized (this) {for (SubscriberMethod subscriberMethod : subscriberMethods) {subscribe(subscriber, subscriberMethod);}}}
首先获取订阅者类subscriber,然后通过findSubscriberMethods方法获取该类中以@Subscribe注解的函数,由于一个类中可能监听多个事件,因此获取的方法可能是多个,所有的方法赋值到一个List列表中,然后遍历这个列表进行注册。
private void subscribe(Object subscriber, SubscriberMethod subscriberMethod) {Class<?> eventType = subscriberMethod.eventType;Subscription newSubscription = new Subscription(subscriber, subscriberMethod);CopyOnWriteArrayList<Subscription> subscriptions = subscriptionsByEventType.get(eventType);if (subscriptions == null) {subscriptions = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();subscriptionsByEventType.put(eventType, subscriptions);} else {if (subscriptions.contains(newSubscription)) {throw new EventBusException("Subscriber " + subscriber.getClass() + " already registered to event "+ eventType);}}int size = subscriptions.size();for (int i = 0; i <= size; i++) {if (i == size || subscriberMethod.priority > subscriptions.get(i).subscriberMethod.priority) {subscriptions.add(i, newSubscription);break;}}List<Class<?>> subscribedEvents = typesBySubscriber.get(subscriber);if (subscribedEvents == null) {subscribedEvents = new ArrayList<>();typesBySubscriber.put(subscriber, subscribedEvents);}subscribedEvents.add(eventType);....}
上面就是注册最主要的代码,步骤解析如下:
-
根据注解方法获取监听事件的类型
eventType,并对订阅者subscriber和订阅函数subscriberMethod建立一个订阅关系对象newSubscription; -
根据
eventType在subscriptionsByEventType(HashMap)中获取所有该事件类型的订阅关系列表subscriptions; -
如果订阅关系列表
subscriptions为空就新建一个,然后以key为eventType,value为newSubscription添加进去; -
如果订阅关系列表
subscriptions不为空,判断是否存在newSubscription,如果存在,说明之前已经注册过,抛出异常; -
如果订阅关系列表
subscriptions不为空,列表页没有订阅关系newSubscription,我们遍历添加进去,这里通过订阅函数的priority来决定存放在列表中的位置,从这里也能看出priority越大,存放位置越靠前,和上一篇中分析的:值越大,优先级越高,越优先接收到事件。我们可以猜出是通过遍历这个表来进行事件发送的,在表里的位置越靠前,越先收到事件。 -
然后通过订阅者
subscriber在另一个HashMap- typesBySubscriber中获取该订阅者订阅的所有事件,因为一个订阅者可以订阅多个不同的事件,因此获取的是个List列表subscribedEvents; -
首先判断
subscribedEvents列表是不是空的,如果是空说明以前没有订阅过任何事件,新建一个List,然后以key为subscriber,value为subscribedEvents添加到typesBySubscriber; -
然后在新建的
subscribedEvents中添加我们订阅的事件eventType。
这里出现了两个HashMap:
subscriptionsByEventType与typesBySubscriber,通过上面的解析可以知道:
subscriptionsByEventType:一个事件可能有多个订阅者,key是事件,value是所有订阅该事件的所有的订阅者;
typesBySubscriber:一个订阅者可能订阅多个事件,key是订阅者,value是订阅者订阅的所有事件;
看命名就知道By后面的是key值,前面的是value值,一个好的命名就是这样吧。
解注册源码逻辑
在使用EventBus时,注册完后我习惯接着去写解注册的代码,怕后面会忘,因此按照写代码习惯在讲下解注册的源码实现。
/** Unregisters the given subscriber from all event classes. */public synchronized void unregister(Object subscriber) {List<Class<?>> subscribedTypes = typesBySubscriber.get(subscriber);if (subscribedTypes != null) {for (Class<?> eventType : subscribedTypes) {unsubscribeByEventType(subscriber, eventType);}typesBySubscriber.remove(subscriber);} else {logger.log(Level.WARNING, "Subscriber to unregister was not registered before: " + subscriber.getClass());}}
如果是我们自己写这部分代码,根据前面注册的过程,我们肯定是要把添加到两个HashMap中的值移除掉。好了,看上面源码,首先在typesBySubscriber中获取该订阅者订阅的事件列表subscribedTypes;
如果为空说明该订阅者没有订阅任何事件,无任何操作;如果不为空,遍历所有事件调用unsubscribeByEventType方法进行解注册,然后在typesBySubscriber中移除这个订阅者subscriber。
/** Only updates subscriptionsByEventType, not typesBySubscriber! Caller must update typesBySubscriber. */private void unsubscribeByEventType(Object subscriber, Class<?> eventType) {List<Subscription> subscriptions = subscriptionsByEventType.get(eventType);if (subscriptions != null) {int size = subscriptions.size();for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {Subscription subscription = subscriptions.get(i);if (subscription.subscriber == subscriber) {subscription.active = false;subscriptions.remove(i);i--;size--;}}}}
在上一个方法中,已经把typesBySubscriber这个订阅者移除了,那么unsubscribeByEventType函数就是遍历事件所有的订阅者,然后把解注册的订阅者在subscriptionsByEventType中给移除掉。上面的逻辑就是干这个事情。不过一边遍历一边移除是有风险的,这个大家要注意,index需要也跟着进行减少。
总结下:注册和解注册就是往两个HashMap添加和移除数据的过程。
事件发送post源码逻辑
/** Posts the given event to the event bus. */public void post(Object event) {PostingThreadState postingState = currentPostingThreadState.get();List<Object> eventQueue = postingState.eventQueue;eventQueue.add(event);····}
上面是部分post代码,第一行先解释这个变量currentPostingThreadState及内部类PostingThreadState。
private final ThreadLocal<PostingThreadState> currentPostingThreadState = new ThreadLocal<PostingThreadState>() {@Overrideprotected PostingThreadState initialValue() {return new PostingThreadState();}};/** For ThreadLocal, much faster to set (and get multiple values). */final static class PostingThreadState {final List<Object> eventQueue = new ArrayList<>();boolean isPosting;boolean isMainThread;Subscription subscription;Object event;boolean canceled;}
currentPostingThreadState是一个ThreadLocal,相当于是线程的私有财产,里面维护的变量只属于当前线程,线程间不会共享。维护的变量是一个自定义类PostingThreadState,用来保存发送线程的发送状态信息:当前线程是否为主线程,是否在发送事件,发送的事件列表、接收事件的订阅者等。
/** Posts the given event to the event bus. */public void post(Object event) {PostingThreadState postingState = currentPostingThreadState.get();List<Object> eventQueue = postingState.eventQueue;eventQueue.add(event);if (!postingState.isPosting) {postingState.isMainThread = isMainThread();postingState.isPosting = true;if (postingState.canceled) {throw new EventBusException("Internal error. Abort state was not reset");}try {while (!eventQueue.isEmpty()) {postSingleEvent(eventQueue.remove(0), postingState);}} finally {postingState.isPosting = false;postingState.isMainThread = false;}}}
现在继续看post逻辑。首先,获取到当前线程的发送状态postingState,然后拿到事件列表,并把需要post的事件加入到列表中。判断是否启动了事件发送流程,如果已经启动了,不在做处理,加入列表中的事件会轮到处理。如果没有启动就启动处理流程,并将isPosting赋值为true。循环从事件列表中获取事件,通过postSingleEvent进行处理。
private void postSingleEvent(Object event, PostingThreadState postingState) throws Error {Class<?> eventClass = event.getClass();boolean subscriptionFound = false;if (eventInheritance) {List<Class<?>> eventTypes = lookupAllEventTypes(eventClass);int countTypes = eventTypes.size();for (int h = 0; h < countTypes; h++) {Class<?> clazz = eventTypes.get(h);subscriptionFound |= postSingleEventForEventType(event, postingState, clazz);}} else {subscriptionFound = postSingleEventForEventType(event, postingState, eventClass);}if (!subscriptionFound) {if (logNoSubscriberMessages) {logger.log(Level.FINE, "No subscribers registered for event " + eventClass);}if (sendNoSubscriberEvent && eventClass != NoSubscriberEvent.class &&eventClass != SubscriberExceptionEvent.class) {post(new NoSubscriberEvent(this, event));}}}
在postSingleEvent中,有一个变量的判断eventInheritance,这个变量表示是否查找发送事件的父类或接口的订阅者,默认是true。例如,发送事件MsgEvent这个对象,MsgEvent继承至Event这个抽象类,发送后,不光所有订阅MsgEvent的订阅者可以收到事件,所有订阅Event的这个事件的订阅者也会收到事件。前面有分析这个字段的值是可以重新配置的,代码如下。
EventBus.builder().eventInheritance(false) //发送的时候不考虑事件父类.logSubscriberExceptions(false).build().register(this);
eventInheritance为true,通过lookupAllEventTypes,向上找到所有父类事件类,然后遍历找到所有事件的订阅者,并发送事件,如果为false,直接将当前事件发送给订阅者。
postSingleEvent函数主要是找到需要post的所有相关事件,然后进一步调用postSingleEventForEventType发送给订阅者,因此函数后面的逻辑是判断postSingleEventForEventType的返回值subscriptionFound,即判断当前事件有没有订阅者进行处理,如果没有处理的,会发送一个NoSubscriberEvent。例如:如果我在上一节的例子中post一个新的对象student,但是没有订阅者和接收函数,如果监听了NoSubscriberEvent,会收到一个NoSubscriberEvent的事件,告知调用者你post的对象没有订阅者。
@Subscribe()
public void onMsgEventReceived(NoSubscriberEvent event) {Log.i(TAG, "NoSubscriberEvent : " + event);
}Student student = new Student(1,"jane");
EventBus.getDefault().post(student);
private boolean postSingleEventForEventType(Object event, PostingThreadState postingState, Class<?> eventClass) {CopyOnWriteArrayList<Subscription> subscriptions;synchronized (this) {subscriptions = subscriptionsByEventType.get(eventClass);}if (subscriptions != null && !subscriptions.isEmpty()) {for (Subscription subscription : subscriptions) {postingState.event = event;postingState.subscription = subscription;boolean aborted;try {postToSubscription(subscription, event, postingState.isMainThread);aborted = postingState.canceled;} finally {postingState.event = null;postingState.subscription = null;postingState.canceled = false;}if (aborted) {break;}}return true;}return false;}
从前面分析可知,最后都走到了postSingleEventForEventType这个函数里面,首先在subscriptionsByEventType中找到所有订阅该事件的订阅者subscriptions,subscriptions为空或者个数是0则返回false。有订阅者的话,遍历订阅者,然后通过postToSubscription进行发送,并返回true。
private void postToSubscription(Subscription subscription, Object event, boolean isMainThread) {switch (subscription.subscriberMethod.threadMode) {case POSTING:invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);break;case MAIN:if (isMainThread) {invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);} else {mainThreadPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);}break;case MAIN_ORDERED:if (mainThreadPoster != null) {mainThreadPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);} else {// temporary: technically not correct as poster not decoupled from subscriberinvokeSubscriber(subscription, event);}break;case BACKGROUND:if (isMainThread) {backgroundPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);} else {invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);}break;case ASYNC:asyncPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);break;default:throw new IllegalStateException("Unknown thread mode: " + subscription.subscriberMethod.threadMode);}}
这段代码比较简单就是根据订阅者中注解@Subscribe中threadMode值来分别进行处理,上一节也讲过,POSTING表示在哪个线程发送就在哪个线程接收处理,因此直接调用invokeSubscriber通过反射来调用订阅者中的接收事件的方法。
void invokeSubscriber(Subscription subscription, Object event) {try {subscription.subscriberMethod.method.invoke(subscription.subscriber, event);} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {handleSubscriberException(subscription, event, e.getCause());} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected exception", e);}}
如果threadMode是MAIN,而当前线程是子线程,通过 mainThreadPoster.enqueue(subscription, event)将事件加入主线程队列。
mainThreadSupport = builder.getMainThreadSupport();
mainThreadPoster = mainThreadSupport != null ? mainThreadSupport.createPoster(this) : null;public interface MainThreadSupport {boolean isMainThread();Poster createPoster(EventBus eventBus);
}public class DefaultAndroidMainThreadSupport implements MainThreadSupport {public boolean isMainThread() {return Looper.getMainLooper() == Looper.myLooper();}@Overridepublic Poster createPoster(EventBus eventBus) {return new HandlerPoster(eventBus, Looper.getMainLooper(), 10);}
}
mainThreadPoster是由mainThreadSupport 创建的,mainThreadSupport是MainThreadSupport实例,而MainThreadSupport是一个接口,实现类为DefaultAndroidMainThreadSupport,因此,最终是调用到的DefaultAndroidMainThreadSupport中的createPoster,新建了一个HandlerPoster。
public class HandlerPoster extends Handler implements Poster {private final PendingPostQueue queue;private final int maxMillisInsideHandleMessage;private final EventBus eventBus;private boolean handlerActive;public HandlerPoster(EventBus eventBus, Looper looper, int maxMillisInsideHandleMessage) {super(looper);this.eventBus = eventBus;this.maxMillisInsideHandleMessage = maxMillisInsideHandleMessage;queue = new PendingPostQueue();}public void enqueue(Subscription subscription, Object event) {PendingPost pendingPost = PendingPost.obtainPendingPost(subscription, event);synchronized (this) {queue.enqueue(pendingPost);if (!handlerActive) {handlerActive = true;if (!sendMessage(obtainMessage())) {throw new EventBusException("Could not send handler message");}}}}@Overridepublic void handleMessage(Message msg) {...}
}
从上面的源码可以看到,HandlerPoster就是一个Handler,当执行mainThreadPoster.enqueue(subscription, event)时,会将订阅者和事件封装成一个PendingPost,然后加入到PendingPostQueue这个队列中,如果handlerActive为true表示当前Handler正常处理事件,将入队列的事件等着被处理即可。如果为false则启动处理,调用sendMessage发送消息。
public class HandlerPoster extends Handler implements Poster {private final PendingPostQueue queue;private final int maxMillisInsideHandleMessage;private final EventBus eventBus;private boolean handlerActive;public HandlerPoster(EventBus eventBus, Looper looper, int maxMillisInsideHandleMessage) {super(looper);...}public void enqueue(Subscription subscription, Object event) {...}@Overridepublic void handleMessage(Message msg) {boolean rescheduled = false;try {long started = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();while (true) {PendingPost pendingPost = queue.poll();if (pendingPost == null) {synchronized (this) {// Check again, this time in synchronizedpendingPost = queue.poll();if (pendingPost == null) {handlerActive = false;return;}}}eventBus.invokeSubscriber(pendingPost);long timeInMethod = SystemClock.uptimeMillis() - started;if (timeInMethod >= maxMillisInsideHandleMessage) {if (!sendMessage(obtainMessage())) {throw new EventBusException("Could not send handler message");}rescheduled = true;return;}}} finally {handlerActive = rescheduled;}}
}
在handleMessage()方法将中将PendingPost对象循环出队列,交给invokeSubscriber()方法进一步处理。这样就把线程通过Handler切回了主线程。
backgroundPoster.enqueue()和asyncPoster.enqueue也类似,内部都是先将事件入队列,然后再出队列,但是会通过线程池去进一步处理事件。
粘性事件发送postSticky源码逻辑
public void postSticky(Object event) {synchronized (stickyEvents) {stickyEvents.put(event.getClass(), event);}// Should be posted after it is putted, in case the subscriber wants to remove immediatelypost(event);}
从上面代码可以看到,先把事件放在了stickyEvents列中中,然后调用了post,也就是上面我们解析过的流程。让我们再来回顾下注册的代码:
// Must be called in synchronized blockprivate void subscribe(Object subscriber, SubscriberMethod subscriberMethod) {Class<?> eventType = subscriberMethod.eventType;Subscription newSubscription = new Subscription(subscriber, subscriberMethod);CopyOnWriteArrayList<Subscription> subscriptions = subscriptionsByEventType.get(eventType);...subscribedEvents.add(eventType);if (subscriberMethod.sticky) {if (eventInheritance) {// Existing sticky events of all subclasses of eventType have to be considered.// Note: Iterating over all events may be inefficient with lots of sticky events,// thus data structure should be changed to allow a more efficient lookup// (e.g. an additional map storing sub classes of super classes: Class -> List<Class>).Set<Map.Entry<Class<?>, Object>> entries = stickyEvents.entrySet();for (Map.Entry<Class<?>, Object> entry : entries) {Class<?> candidateEventType = entry.getKey();if (eventType.isAssignableFrom(candidateEventType)) {Object stickyEvent = entry.getValue();checkPostStickyEventToSubscription(newSubscription, stickyEvent);}}} else {Object stickyEvent = stickyEvents.get(eventType);checkPostStickyEventToSubscription(newSubscription, stickyEvent);}}}
注册源码分析的时候,就分析到subscriberMethod.sticky这个句上面,现在让我们看看下面的逻辑,同样先判断eventInheritance的值,然后将之前放在stickyEvents中的事件拿出来,执行checkPostStickyEventToSubscription。
private void checkPostStickyEventToSubscription(Subscription newSubscription, Object stickyEvent) {if (stickyEvent != null) {// If the subscriber is trying to abort the event, it will fail (event is not tracked in posting state)// --> Strange corner case, which we don't take care of here.postToSubscription(newSubscription, stickyEvent, isMainThread());}}
checkPostStickyEventToSubscription中的代码比较水,又调用了postToSubscription,这个方法上面贴出来了,这里方面看再贴一遍,熟悉的味道:
private void postToSubscription(Subscription subscription, Object event, boolean isMainThread) {switch (subscription.subscriberMethod.threadMode) {case POSTING:invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);break;case MAIN:if (isMainThread) {invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);} else {mainThreadPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);}break;case MAIN_ORDERED:if (mainThreadPoster != null) {mainThreadPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);} else {// temporary: technically not correct as poster not decoupled from subscriberinvokeSubscriber(subscription, event);}break;case BACKGROUND:if (isMainThread) {backgroundPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);} else {invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);}break;case ASYNC:asyncPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);break;default:throw new IllegalStateException("Unknown thread mode: " + subscription.subscriberMethod.threadMode);}}
所以,在注册的时候,如果你订阅者的接收方法加了sticky注解,那么在注册的时候就会看下订阅的事件之前有没有通过postSticky发送过,如果有就会立马收到这个事件。
以上是我们平时使用过程的源码解析,码字不易,喜欢就点赞收藏啊。
参考文章:
EventBus 原理解析
相关文章:
)
EventBus 开源库学习(二)
整体流程阅读 EventBus在使用的时候基本分为以下几步: 1、注册订阅者 EventBus.getDefault().register(this);2、订阅者解注册,否者会导致内存泄漏 EventBus.getDefault().unregister(this);3、在订阅者中编写注解为Subscribe的事件处理函数 Subscri…...

4_Apollo4BlueLite电源管理
1.Cortex-M4 Power Modes Apollo4BlueLite支持以下4种功耗模式: ▪ High Performance Active (not a differentiated power mode for the Cortex-M4) ▪ Active ▪ Sleep ▪ Deep Sleep (1)High Performance Mode 高性能模式不是arm定…...

Pytorch入门学习——快速搭建神经网络、优化器、梯度计算
我的代码可以在我的Github找到 GIthub地址 https://github.com/QinghongShao-sqh/Pytorch_Study 因为最近有同学问我如何Nerf入门,这里就简单给出一些我的建议: (1)基本的pytorch,机器学习,深度学习知识&a…...

举例说明typescript的Exclude、Omit、Pick
一、提前知识说明:联合类型 typescript的联合类型是一种用于表示一个值可以是多种类型中的一种的类型。我们使用竖线(|)来分隔每个类型,所以number | string | boolean是一个可以是number,string或boolean的值的类型。…...

记录一次Linux环境下遇到“段错误核心已转储”然后利用core文件解决问题的过程
参考Linux 下Coredump分析与配置 在做项目的时候,很容易遇到“段错误(核心已转储)”的问题。如果是语法错误还可以很快排查出来问题,但是碰到coredump就没办法直接找到问题,可以通过设置core文件来查找问题࿰…...

WPF中自定义Loading图
纯前端方式,通过动画实现Loading样式,如图所示 <Grid Width"35" Height"35" HorizontalAlignment"Center" VerticalAlignment"Center" Name"Loading"><Grid.Resources><DrawingBrus…...
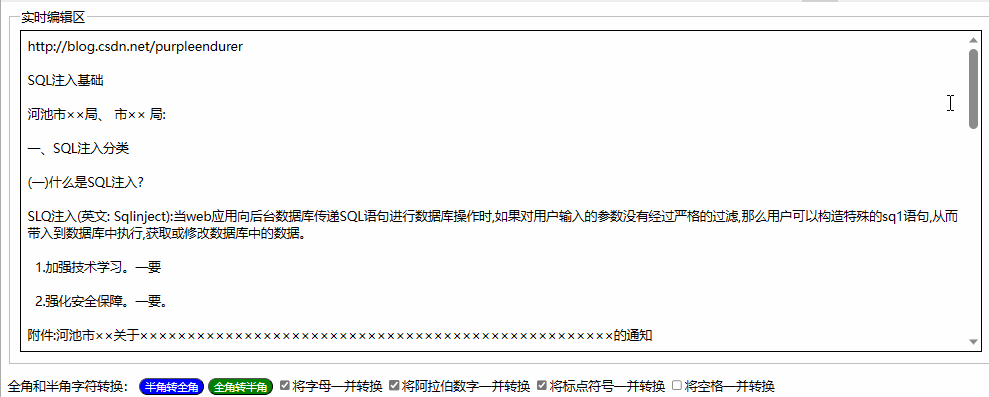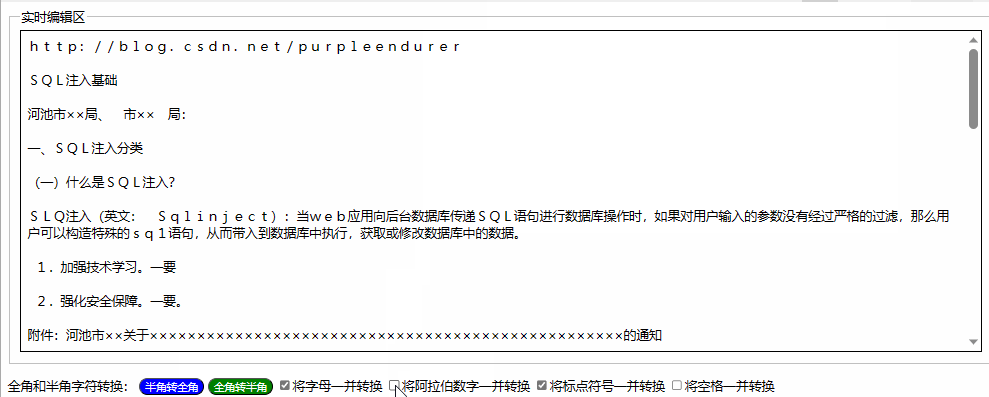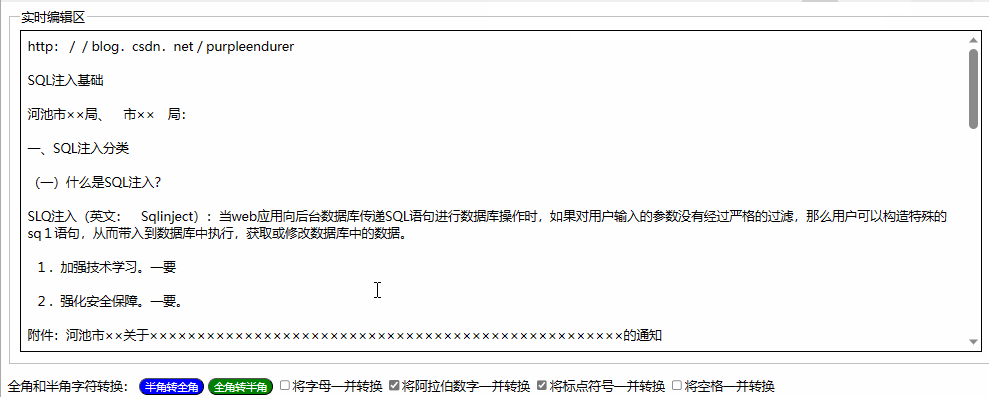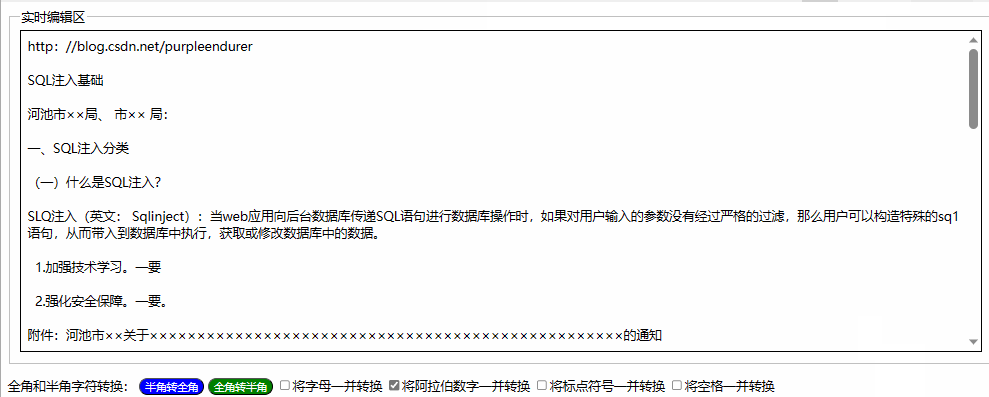
用html+javascript打造公文一键排版系统14:为半角和全角字符相互转换功能增加英文字母、阿拉伯数字、标点符号、空格选项
一、实际工作中需要对转换选项细化内容 在昨天我们实现了最简单的半角字符和全角字符相互转换功能,就是将英文字母、阿拉伯数字、标点符号、空格全部进行转换。 在实际工作中,我们有时只想英文字母、阿拉伯数字、标点符号、空格之中的一两类进行转换&a…...

叮咚买菜财报分析:叮咚买菜第二季度财报将低于市场预期
来源:猛兽财经 作者:猛兽财经 卖方分析师对叮咚买菜第二季度财报的预测 尽管叮咚买菜(DDL)尚未明确披露第二季度财报的具体日期,但根据其以往的业绩公告,猛兽财经认为叮咚买菜很有可能会在8月的第二周发布…...
设计模式行为型——中介者模式
目录 什么是中介者模式 中介者模式的实现 中介者模式角色 中介者模式类图 中介者模式代码实现 中介者模式的特点 优点 缺点 使用场景 注意事项 实际应用 什么是中介者模式 中介者模式(Mediator Pattern)属于行为型模式,是用来降低…...

Vue——formcreate表单设计器自定义组件实现(二)
前面我写过一个自定义电子签名的formcreate表单设计器组件,那时初识formcreate各种使用也颇为生疏,不过总算套出了一个组件不是。此次时隔半年又有机会接触formcreate,重新熟悉和领悟了一番各个方法和使用指南。趁热打铁将此次心得再次分享。…...
 和 人脸识别(Face recognition) 的区别)
人脸验证(Face verification) 和 人脸识别(Face recognition) 的区别
人脸验证(Face verification) 和 人脸识别(Face recognition) 的区别 Face verification 和 Face recognition 都是人脸识别的技术,但是它们的应用和目的不同。 Face verification(人脸验证)是指通过比对两张人脸图像,判断它们是…...

前端如何打开钉钉(如何唤起注册表中路径与软件路径不关联的软件)
在前端唤起本地应用时,我查询了资料,在注册表中找到腾讯视频会议的注册表情况,如下: 在前端代码中加入 window.location.href"wemeet:"; 就可以直接唤起腾讯视频会议,但是我无法唤起钉钉 之所以会这样&…...

数据可视化入门指南
数据可视化是一种将抽象的数值和数据转换为易于理解的图像的方法。它可以帮助人们更好地理解数据的含义,并且可以揭示数据中可能被忽视的模式和趋势。本文将为你提供一个简单的数据可视化入门指南。 为什么数据可视化重要? 在我们的生活中,数…...

React 18 响应事件
参考文章 响应事件 使用 React 可以在 JSX 中添加 事件处理函数。其中事件处理函数为自定义函数,它将在响应交互(如点击、悬停、表单输入框获得焦点等)时触发。 添加事件处理函数 如需添加一个事件处理函数,需要先定义一个函数…...
面试总结-c++
1该吹牛逼吹牛逼。在自己能说出个所以然的情况下,该吹就吹,不吹没工作,吹了有希望。 比如 c组长,确有其事,但是挺唬人。说自己在北京定居也是侧面吹牛逼,证明自己的能力。还有媳妇在研究所。 2.对自己做过…...
 - 解惑 spring 嵌套事务.2)
Spring(九) - 解惑 spring 嵌套事务.2
1. 事务传播特性 在所有使用 spring 的应用中, 声明式事务管理可能是使用率最高的功能了, 但是, 从我观察到的情况看,绝大多数人并不能深刻理解事务声明中不同事务传播属性配置的的含义, 让我们来看一下 TransactionDefinition 接口中的定义 Java代码 /** * Support a cu…...

Android Studio API 33 获取当前连接的WIFI名称
常规流程失败流程 常规流程 以下内容在 API 33 成功实现,低版本API还请自行尝试(仅推荐 API 29 - 33 用户食用) 先(至少)添加以下权限到你的 AndroidManifest.xml 文件 <uses-permission android:name"andr…...
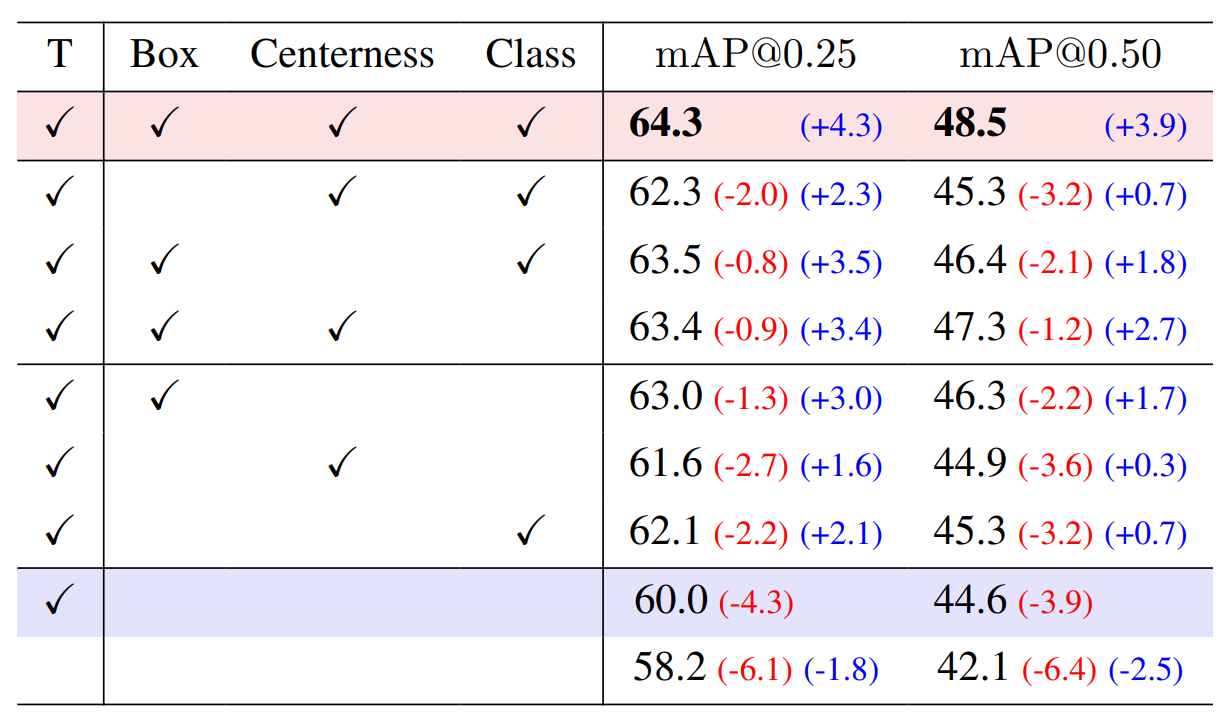
ICCV 2023 | 半监督三维目标检测新SOTA:密集匹配和量化补偿
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2304.13031 开源代码仓库地址:https://github.com/AIR-DISCOVER/DQS3D 方法效果对比图:有效在半监督情况下处理临近小物体 01. 简介 本文旨在解决三维室内场景中高昂的标注成本问题,特别关注半监…...
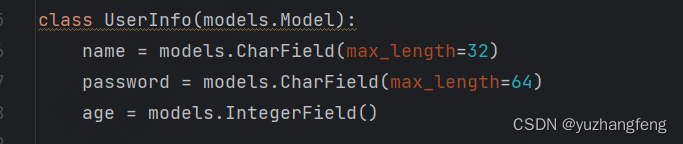
python+django+mysql项目实践三(用户管理)
python项目实践 环境说明: Pycharm 开发环境 Django 前端 MySQL 数据库 Navicat 数据库管理 用户列表展示 urls view models html <!DOCTYPE html> <html...

Java多线程 | 操作线程的方法详解
文章目录 一、线程的启动1.1 start()方法 二、线程的休眠与中断2.1 Thread.sleep()方法2.2 interrupt()方法 三、线程的等待与唤醒3.1 wait()方法3.2 Object类的notify()和notifyAll()方法3.3 await()和signal()方法3.4 使用join()方法等待线程执行完成 四、线程的状态控制与管…...

iOS 26 携众系统重磅更新,但“苹果智能”仍与国行无缘
美国西海岸的夏天,再次被苹果点燃。一年一度的全球开发者大会 WWDC25 如期而至,这不仅是开发者的盛宴,更是全球数亿苹果用户翘首以盼的科技春晚。今年,苹果依旧为我们带来了全家桶式的系统更新,包括 iOS 26、iPadOS 26…...
YSYX学习记录(八)
C语言,练习0: 先创建一个文件夹,我用的是物理机: 安装build-essential 练习1: 我注释掉了 #include <stdio.h> 出现下面错误 在你的文本编辑器中打开ex1文件,随机修改或删除一部分,之后…...
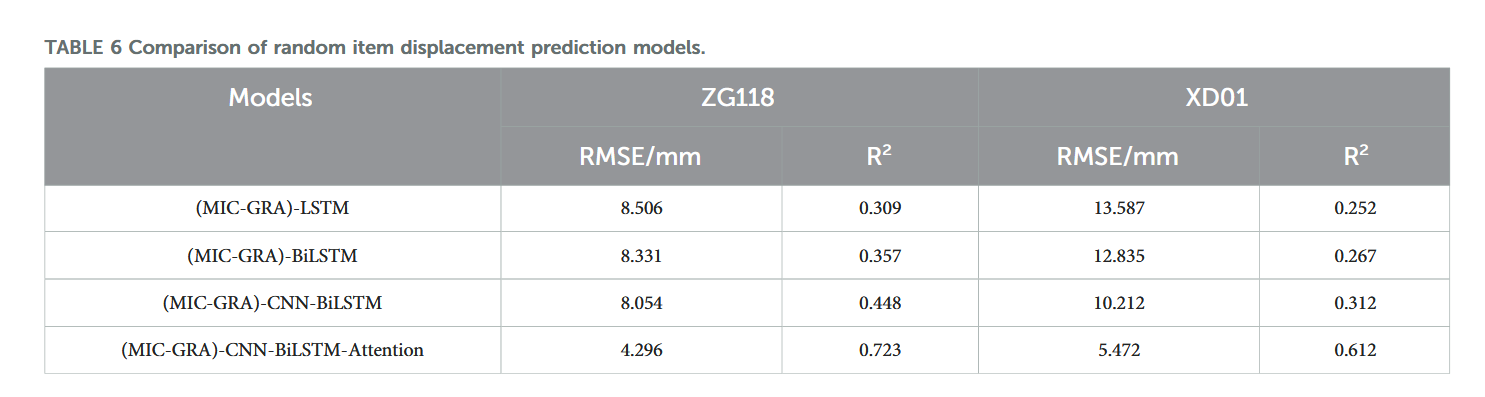
【论文阅读28】-CNN-BiLSTM-Attention-(2024)
本文把滑坡位移序列拆开、筛优质因子,再用 CNN-BiLSTM-Attention 来动态预测每个子序列,最后重构出总位移,预测效果超越传统模型。 文章目录 1 引言2 方法2.1 位移时间序列加性模型2.2 变分模态分解 (VMD) 具体步骤2.3.1 样本熵(S…...

Device Mapper 机制
Device Mapper 机制详解 Device Mapper(简称 DM)是 Linux 内核中的一套通用块设备映射框架,为 LVM、加密磁盘、RAID 等提供底层支持。本文将详细介绍 Device Mapper 的原理、实现、内核配置、常用工具、操作测试流程,并配以详细的…...
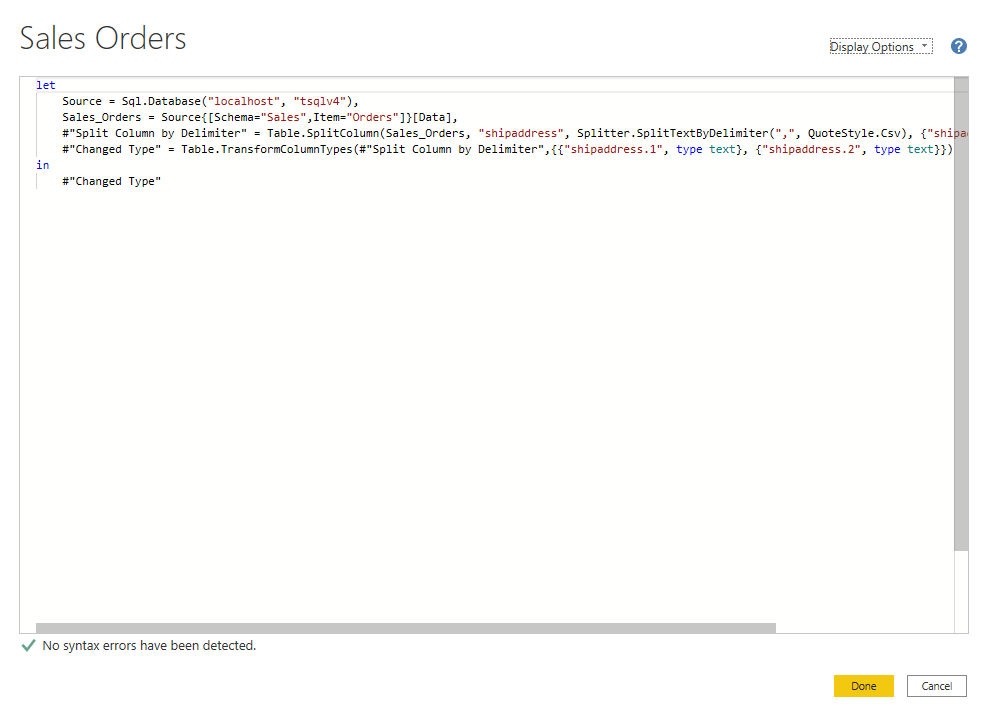
微软PowerBI考试 PL300-在 Power BI 中清理、转换和加载数据
微软PowerBI考试 PL300-在 Power BI 中清理、转换和加载数据 Power Query 具有大量专门帮助您清理和准备数据以供分析的功能。 您将了解如何简化复杂模型、更改数据类型、重命名对象和透视数据。 您还将了解如何分析列,以便知晓哪些列包含有价值的数据,…...

在QWebEngineView上实现鼠标、触摸等事件捕获的解决方案
这个问题我看其他博主也写了,要么要会员、要么写的乱七八糟。这里我整理一下,把问题说清楚并且给出代码,拿去用就行,照着葫芦画瓢。 问题 在继承QWebEngineView后,重写mousePressEvent或event函数无法捕获鼠标按下事…...
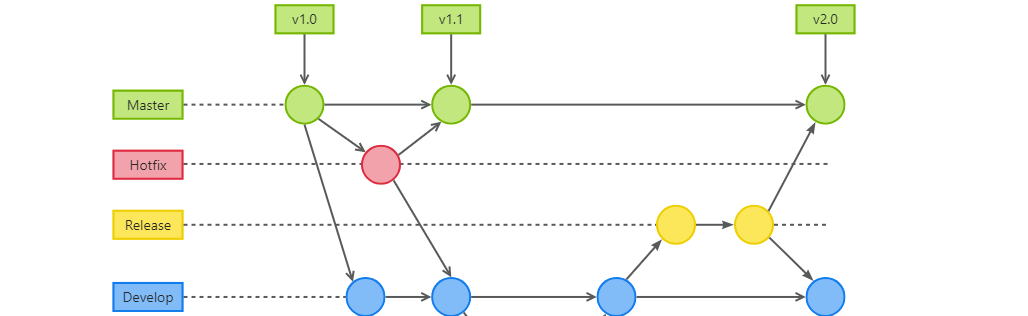
GitFlow 工作模式(详解)
今天再学项目的过程中遇到使用gitflow模式管理代码,因此进行学习并且发布关于gitflow的一些思考 Git与GitFlow模式 我们在写代码的时候通常会进行网上保存,无论是github还是gittee,都是一种基于git去保存代码的形式,这样保存代码…...

elementUI点击浏览table所选行数据查看文档
项目场景: table按照要求特定的数据变成按钮可以点击 解决方案: <el-table-columnprop"mlname"label"名称"align"center"width"180"><template slot-scope"scope"><el-buttonv-if&qu…...

vue3 daterange正则踩坑
<el-form-item label"空置时间" prop"vacantTime"> <el-date-picker v-model"form.vacantTime" type"daterange" start-placeholder"开始日期" end-placeholder"结束日期" clearable :editable"fal…...

Axure 下拉框联动
实现选省、选完省之后选对应省份下的市区...
