数据结构笔记--链表经典高频题
目录
前言
1--反转单向链表
2--反转单向链表-II
3--反转双向链表
4--打印两个有序链表的公共部分
5--回文链表
6--链表调整
7--复制含有随机指针结点的链表
8--两个单链表相交问题
前言
面经:
针对链表的题目,对于笔试可以不太在乎空间复杂度,以时间复杂度为主(能过就行,对于任何题型都一样,笔试能过就行);对于面试,时间复杂度依然处在第一位,但要力求空间复杂度最低的算法(突出亮点);
链表题的重要技巧包括:使用额外的数据结构记录(例如哈希表等),使用快慢指针的思想;
1--反转单向链表

笔试解法:
借助栈先进后出,可以遍历把结点存到栈中,然后不断出栈,这样结点的顺序就反转了;
时间复杂度为O(n),空间复杂度为O(n);
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>struct ListNode {int val;ListNode *next;ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};class Solution {
public:ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {if(head == NULL) return head;std::stack<ListNode*> st;while(head != NULL){st.push(head);head = head->next;}ListNode *new_head = new ListNode(0);ListNode *tmp = new_head;while(!st.empty()){tmp->next = st.top();st.pop();tmp = tmp->next;}tmp->next = NULL;return new_head->next;}
};int main(int argc, char *argv[]){ListNode *Node1 = new ListNode(1);ListNode *Node2 = new ListNode(2);ListNode *Node3 = new ListNode(3);ListNode *Node4 = new ListNode(4);ListNode *Node5 = new ListNode(5);Node1->next = Node2;Node2->next = Node3;Node3->next = Node4;Node4->next = Node5;Solution S1;ListNode *res = S1.reverseList(Node1);while(res != NULL){std::cout << res->val << " ";res = res->next;}return 0;
}面试解法:
不借助栈或递归,通过迭代将空间复杂度优化为O(1);
利用一个额外的前驱结点 pre 来存储当前结点 cur 的前一个结点,不断更新 pre 和 cur即可;
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>struct ListNode {int val;ListNode *next;ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};class Solution {
public:ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {if(head == NULL) return head;ListNode *pre = NULL;ListNode *cur = head;while(cur != NULL){ListNode* next = cur->next;cur->next = pre;pre = cur;cur = next;}return pre;}
};int main(int argc, char *argv[]){ListNode *Node1 = new ListNode(1);ListNode *Node2 = new ListNode(2);ListNode *Node3 = new ListNode(3);ListNode *Node4 = new ListNode(4);ListNode *Node5 = new ListNode(5);Node1->next = Node2;Node2->next = Node3;Node3->next = Node4;Node4->next = Node5;Solution S1;ListNode *res = S1.reverseList(Node1);while(res != NULL){std::cout << res->val << " ";res = res->next;}return 0;
}2--反转单向链表-II
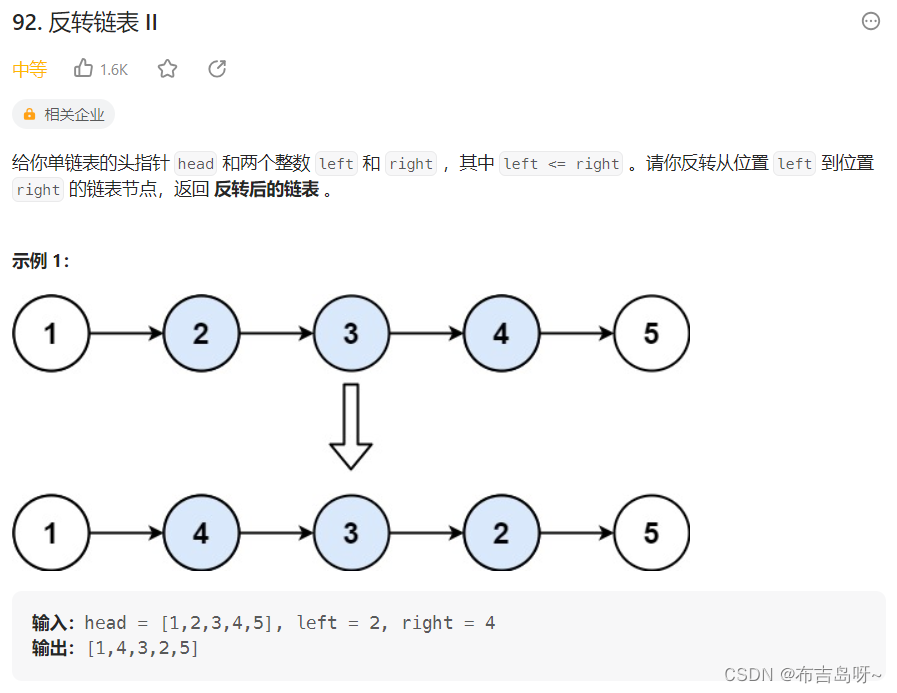
主要思路:
使用三个指针,指针 pre 指向反转区域外的第一个节点,即上图中的 1;指针 cur 指向当前指针,指针 next 指向 cur 的下一个指针;
遍历链表,每次将 next 指针头插,具体过程可以参考官方题解;
#include <iostream>struct ListNode {int val;ListNode *next;ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};class Solution {
public:ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int left, int right) {ListNode *dummyNode = new ListNode(-1);dummyNode->next = head;ListNode *pre = dummyNode;ListNode *cur;ListNode *next;// 经过循环之后,pre指向反转区域前的第一个节点for(int i = 0; i < left - 1; i++){pre = pre->next;}cur = pre->next; // cur指向反转区域的第一个节点for(int i = 0; i < right - left; i++){next = cur->next;cur->next = next->next; // cur指向next的下一个节点,因为next节点要头插到pre节点后面next->next = pre->next; // next节点头插,指向原来的第一个节点pre->next = next; // next节点头插到pre节点后面}return dummyNode->next;}
};int main(){ListNode *Node1 = new ListNode(1);ListNode *Node2 = new ListNode(2);ListNode *Node3 = new ListNode(3);ListNode *Node4 = new ListNode(4);ListNode *Node5 = new ListNode(5);Node1->next = Node2;Node2->next = Node3;Node3->next = Node4;Node4->next = Node5;Solution S1;int left = 2, right = 4;ListNode *res = S1.reverseBetween(Node1, left, right);while(res != NULL){std::cout << res->val << " ";res = res->next;}return 0;
}3--反转双向链表
主要思路:
与反转单向链表类似,使用 pre,cur 和 next 指向前一个节点,当前节点和后一个节点,不断遍历更新三个指针所指向的节点即可,并修改对应的前驱指针和后驱指针;
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>struct ListNode {int val;ListNode *pre;ListNode *next;ListNode() : val(0), pre(nullptr), next(nullptr) {}ListNode(int x) : val(x), pre(nullptr), next(nullptr) {}ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), pre(nullptr), next(next) {}
};class Solution {
public:ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {if(head == NULL) return head;ListNode *pre = NULL;ListNode *cur = head;while(cur != NULL){ListNode* next = cur->next;cur->next = pre;cur->pre = next;pre = cur;cur = next;}return pre;}
};int main(int argc, char *argv[]){ListNode *Node1 = new ListNode(1);ListNode *Node2 = new ListNode(2);ListNode *Node3 = new ListNode(3);ListNode *Node4 = new ListNode(4);ListNode *Node5 = new ListNode(5);Node1->next = Node2;Node2->next = Node3;Node3->next = Node4;Node4->next = Node5;Node2->pre = Node1;Node3->pre = Node2;Node4->pre = Node3;Node5->pre = Node4;Solution S1;ListNode *res = S1.reverseList(Node1);while(res != NULL){std::cout << res->val << " ";if(res->pre != NULL) std::cout << res->pre->val;std::cout << std::endl;res = res->next;}return 0;
}4--打印两个有序链表的公共部分
给定两个有序链表的头指针 head1 和 head2,打印两个链表的公共部分;要求时间复杂度为O(n),额外空间复杂度要求为 O(1);
主要思路:
类似于归并排序,由于两个链表时有序的,因此可以使用两个指针 i 和 j 分别指向两个链表;
对于小的链表节点,指针后移;
当比较到两个指针相等时,打印节点的值,两个指针 i 和 j 同时后移;
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>struct ListNode {int val;ListNode *next;ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};class Solution {
public:std::vector<ListNode*> printlist(ListNode* head1, ListNode* head2) {std::vector<ListNode*> res;if(head1 == NULL || head2 == NULL) return res;ListNode *i = head1;ListNode *j = head2;while(i != NULL && j != NULL){// 小的后移if(i->val < j->val) i = i->next;else if(i->val > j->val) j = j->next;else{ // 相等同时后移res.push_back(i);i = i->next;j = j->next;} }return res;}
};int main(int argc, char *argv[]){ListNode *Node1 = new ListNode(1);ListNode *Node2 = new ListNode(2);ListNode *Node3 = new ListNode(5);ListNode *Node4 = new ListNode(0);ListNode *Node5 = new ListNode(2);ListNode *Node6 = new ListNode(3);ListNode *Node7 = new ListNode(5);Node1->next = Node2;Node2->next = Node3;Node4->next = Node5;Node5->next = Node6;Node6->next = Node7;Solution S1;std::vector<ListNode *> res = S1.printlist(Node1, Node4);for(ListNode * node : res) std::cout << node->val << " ";return 0;
}5--回文链表

主要思路:
面试做法可以参考反转单向链表,将链表反转,与原链表的结点进行比较即可,当反转链表与原链表的结点不相等,表明不是回文链表;
空间复杂度 O(n),时间复杂度 O(n);
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>struct ListNode {int val;ListNode *next;ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};class Solution {
public:bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {if(head == NULL) return true;std::stack<ListNode*> st;ListNode *tmp = head;while(tmp != NULL){st.push(tmp);tmp = tmp->next;}while(!st.empty()){if(head->val != st.top()->val) return false;head = head->next;st.pop();}return true;}
};int main(int argc, char *argv[]){ListNode *Node1 = new ListNode(1);ListNode *Node2 = new ListNode(2);ListNode *Node3 = new ListNode(2);ListNode *Node4 = new ListNode(1);Node1->next = Node2;Node2->next = Node3;Node3->next = Node4;Solution S1;bool res = S1.isPalindrome(Node1);if(res) std::cout << "true" << std::endl;else std::cout << "false" << std::endl;return 0;
}主要思路:
笔试解法:上述解法的空间复杂度是 O(n),使用快慢指针将空间复杂度优化为 O(1);
主要原理是将链表由 1→2→1→2→1 构建为 1→2→1←2←1 的形式,从两端遍历进行比较;
#include <iostream>struct ListNode {int val;ListNode *next;ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};class Solution {
public:bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {if(head == NULL) return true;ListNode *i = head;ListNode *j = head;while(j->next != NULL && j->next->next != NULL){i = i -> next;j = j -> next -> next;}j = i->next; // right part first nodei->next = NULL;ListNode *tmp = NULL;while(j != NULL){tmp = j->next;j->next = i;i = j;j = tmp;}j = i; // 最后一个结点i = head;while(i != NULL && j != NULL){if(i->val != j ->val) return false;i = i->next;j = j->next;}return true;}
};int main(int argc, char *argv[]){ListNode *Node1 = new ListNode(1);ListNode *Node2 = new ListNode(2);ListNode *Node3 = new ListNode(2);ListNode *Node4 = new ListNode(1);Node1->next = Node2;Node2->next = Node3;Node3->next = Node4;Solution S1;bool res = S1.isPalindrome(Node1);if(res) std::cout << "true" << std::endl;else std::cout << "false" << std::endl;return 0;
}6--链表调整
将单向链表按某值划分成左边小、中间相等、右边大的形式;
题目:给定一个单链表的头结点head,结点的值类型是整型,再给定一个整数pivot,实现一个调整链表的的函数,将链表调整为左部分都是值小于pivot的结点,中间部分都是值等于pivot的结点,右部分都是值大于pivot的结点;
要求:调整后所有小于、等于或大于pivot的结点之间的相对顺序和调整前一样,时间复杂度为O(n),空间复杂度为O(1);
#include <iostream>struct ListNode {int val;ListNode *next;ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};class Solution {
public:ListNode* change(ListNode* head, int pivot) {if(head == NULL) return head;ListNode* SH = NULL; // small headListNode* ST = NULL; // small tailListNode* EH = NULL; // equal headListNode* ET = NULL; // equal tailListNode* LH = NULL; // large headListNode* LT = NULL; // large tailListNode* tmp;while(head != NULL){tmp = head->next; // 下一个结点head->next = NULL;// 抽每一个结点出来进行比较if(head->val < pivot){if(SH == NULL && ST == NULL){SH = head;ST = head;}else{ST->next = head;ST = ST->next;}}else if(head->val == pivot){if(EH == NULL && ET == NULL){EH = head;ET = head;}else{ET->next = head;ET = ET->next;}}else{if(LH == NULL && LT == NULL){LH = head;LT = head;}else{LT->next = head;LT = LT->next;}}head = tmp; // 比较下一个结点}// 首尾相连if(ST != NULL){// 有小于区域ST->next = EH;ET = ET == NULL ? ST : ET; // 没有等于区域,ET变成ST} if(ET != NULL) ET->next = LH;return SH != NULL ? SH : (EH != NULL ? EH : LH);}
};int main(int argc, char *argv[]){ListNode *Node1 = new ListNode(4);ListNode *Node2 = new ListNode(6);ListNode *Node3 = new ListNode(3);ListNode *Node4 = new ListNode(5);ListNode *Node5 = new ListNode(8);ListNode *Node6 = new ListNode(5);ListNode *Node7 = new ListNode(2);Node1->next = Node2;Node2->next = Node3;Node3->next = Node4;Node4->next = Node5;Node5->next = Node6;Node6->next = Node7;Solution S1;int pivot = 5;ListNode* res = S1.change(Node1, pivot);while(res != NULL){std::cout << res->val << " ";res = res->next;}return 0;
}7--复制含有随机指针结点的链表
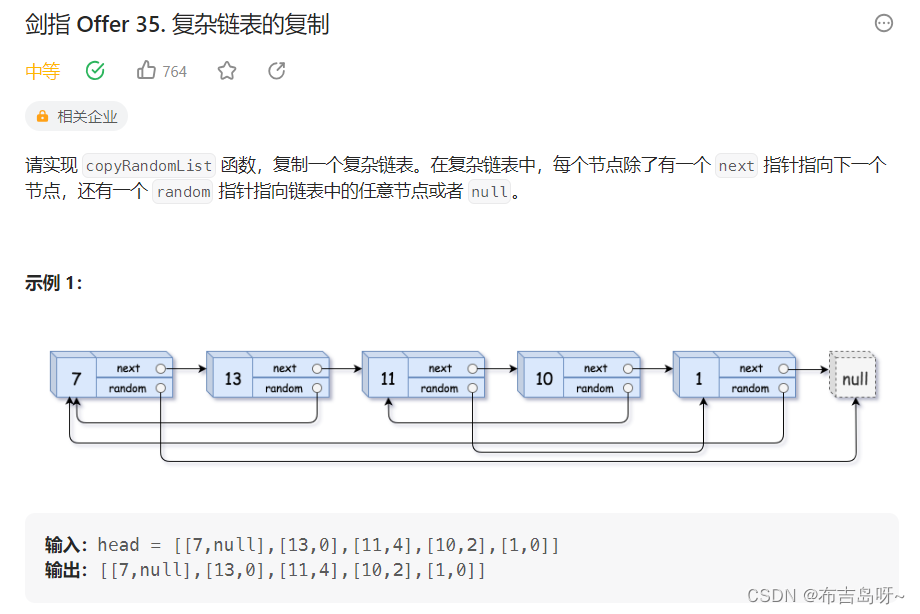
主要思路:
笔试解法,利用哈希表存储结点,即 key 表示原来的结点,value 表示复制的结点;
存储完毕后,遍历结点设置复制结点的 next 指针和 value 指针即可;
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>class Node {
public:int val;Node* next;Node* random;Node(int _val) {val = _val;next = NULL;random = NULL;}
};class Solution {
public:Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {std::unordered_map<Node*, Node*> hash;Node *tmp = head;while(tmp != NULL){hash[tmp] = new Node(tmp->val);tmp = tmp->next;}tmp = head;while(tmp != NULL){hash[tmp]->next = hash[tmp->next];hash[tmp]->random = hash[tmp->random];tmp = tmp->next;}return hash[head];}
};int main(int argc, char *argv[]){Node* Node1 = new Node(7);Node* Node2 = new Node(13);Node* Node3 = new Node(11);Node* Node4 = new Node(10);Node* Node5 = new Node(1);Node1->next = Node2;Node2->next = Node3;Node3->next = Node4;Node4->next = Node5;Node1->random = NULL;Node2->random = Node1;Node3->random = Node5;Node4->random = Node3;Node4->random = Node1;Solution S1;Node* res = S1.copyRandomList(Node1);while(res != NULL){std::cout << res->val << " ";res = res->next;}return 0;
}主要思路:
面试解法,将空间复杂度优化为 O(1);
将原链表Ori_Node1 → Ori_Node2 → Ori_Node3 构造成 Ori_Node1 → New_Node1 → Ori_Node2 → New_Node2 → Ori_Node3 → New_Node3;
接着一对一对地去遍历链表,构建 random 指针;
最后将新旧链表分离,构建 next 指针即可;
#include <iostream>class Node {
public:int val;Node* next;Node* random;Node(int _val) {val = _val;next = NULL;random = NULL;}
};class Solution {
public:Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {if (head == NULL) return NULL;Node* tmp = head;Node* next = NULL;while(tmp != NULL){next = tmp->next; // 原链表下一个结点tmp->next = new Node(tmp->val); // 创建新结点tmp->next->next = next; // 新结点指向原链表地下一个结点tmp = next; // 更新tmp}tmp = head; // 遍历构建random指针while(tmp != NULL){next= tmp->next->next; // 一对一对遍历tmp->next->random = tmp->random != NULL ? tmp->random->next : NULL;tmp = next;}// 分离链表并构建next指针tmp = head;Node *res = head->next;Node *copy;while(tmp != NULL){copy = tmp->next;next = tmp->next->next; // 一对一对分离tmp->next= next;copy->next = next != NULL ? next->next : NULL;tmp = next;}return res;}
};int main(int argc, char *argv[]){Node* Node1 = new Node(7);Node* Node2 = new Node(13);Node* Node3 = new Node(11);Node* Node4 = new Node(10);Node* Node5 = new Node(1);Node1->next = Node2;Node2->next = Node3;Node3->next = Node4;Node4->next = Node5;Node1->random = NULL;Node2->random = Node1;Node3->random = Node5;Node4->random = Node3;Node4->random = Node1;Solution S1;Node* res = S1.copyRandomList(Node1);while(res != NULL){std::cout << res->val << " ";res = res->next;}return 0;
}8--两个单链表相交问题
相关文章:

数据结构笔记--链表经典高频题
目录 前言 1--反转单向链表 2--反转单向链表-II 3--反转双向链表 4--打印两个有序链表的公共部分 5--回文链表 6--链表调整 7--复制含有随机指针结点的链表 8--两个单链表相交问题 前言 面经: 针对链表的题目,对于笔试可以不太在乎空间复杂度&a…...

Android Ble蓝牙App(三)特性和属性
Ble蓝牙App(三)特性使用 前言正文一、获取属性列表二、属性适配器三、获取特性名称四、特性适配器五、加载特性六、显示特性和属性七、源码 前言 在上一篇中我们完成了连接和发现服务两个动作,那么再发现服务之后要做什么呢?发现服…...
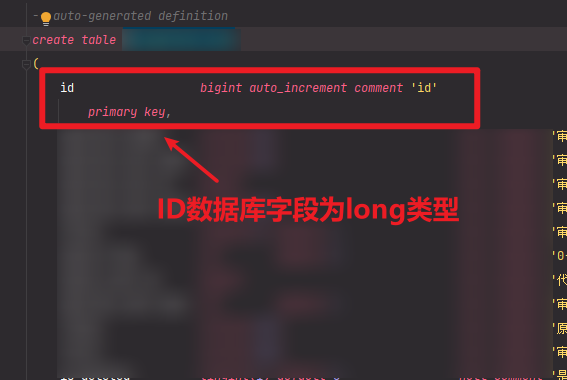
日常BUG——使用Long类型作id,后端返回给前段后精度丢失问题
😜作 者:是江迪呀✒️本文关键词:日常BUG、BUG、问题分析☀️每日 一言 :存在错误说明你在进步! 一、问题描述 数据库long类型Id: 前端返回的Id实体类: Data ApiModel("xxx") public class …...
【C++初阶】string类的常见基本使用
👦个人主页:Weraphael ✍🏻作者简介:目前学习C和算法 ✈️专栏:C航路 🐋 希望大家多多支持,咱一起进步!😁 如果文章对你有帮助的话 欢迎 评论💬 点赞…...
【ArcGIS Pro二次开发】(60):按图层导出布局
在使用布局导图时,会遇到如下问题: 为了切换图层和导图方便,一般情况下,会把相关图层做成图层组。 在导图的时候,如果想要按照图层组进行分开导图,如上图,想导出【现状图、规划图、管控边界】3…...

docker-desktop数据目录迁移
1.退出docker-desktop后执行 wsl --list -v 如下 NAME STATE VERSION * docker-desktop Stopped 2docker-desktop-data Stopped 22.执行以下命令进行数据导出:(需要等待命令执行完成)…...

03.利用Redis实现缓存功能---解决缓存穿透版
学习目标: 提示:学习如何利用Redis实现添加缓存功能解决缓存穿透版 学习产出: 缓存穿透讲解图: 解决方案: 采用缓存空对象采用布隆过滤器 解决方案流程图: 1. 准备pom环境 <dependency><gro…...

全景图!最近20年,自然语言处理领域的发展
夕小瑶科技说 原创 作者 | 小戏、Python 最近这几年,大家一起共同经历了 NLP(写一下全称,Natural Language Processing) 这一领域井喷式的发展,从 Word2Vec 到大量使用 RNN、LSTM,从 seq2seq 再到 Attenti…...

Mybatis参数传递
Map传参, #{}里的key要一一对应不能乱写,如果不存在则会填充NULL,不会报错 Map<String, Object> map new HashMap<>(); // 让key的可读性增强 map.put("carNum", "103"); map.put("brand", "奔驰E300L&…...
手动实现 Spring 底层机制 实现任务阶段一编写自己 Spring 容器-准备篇【2】
😀前言 手动实现 Spring 底层机制的第2篇 实现了任务阶段一编写自己 Spring 容器-准备篇【2】 🏠个人主页:尘觉主页 🧑个人简介:大家好,我是尘觉,希望我的文章可以帮助到大家,您的…...
部署模型并与 TVM 集成
本篇文章译自英文文档 Deploy Models and Integrate TVM tvm 0.14.dev0 documentation 更多 TVM 中文文档可访问 →Apache TVM 是一个端到端的深度学习编译框架,适用于 CPU、GPU 和各种机器学习加速芯片。 | Apache TVM 中文站 本节介绍如何将 TVM 部署到各种平台&…...

Android Navigation 导航切换fragment用法
对于Android Navigation组件的导航到Fragment,您可以按照以下步骤操作: 首先,在您的项目的build.gradle文件中添加Navigation依赖: dependencies {def nav_version "2.3.4"implementation "androidx.navigation…...
Anaconda Prompt使用pip安装PyQt5-tools后无法打开Spyder或闪退
艹!MLGBZD! 真TMD折腾人! 出现原因: 首次安装完Anaconda3-2023.07-1-Windows-x86_64.exe后首次打开Spyder,此时是没有问题的,然后打开Anaconda Prompt,查看有哪些包,pip list 这时候开始首次安…...
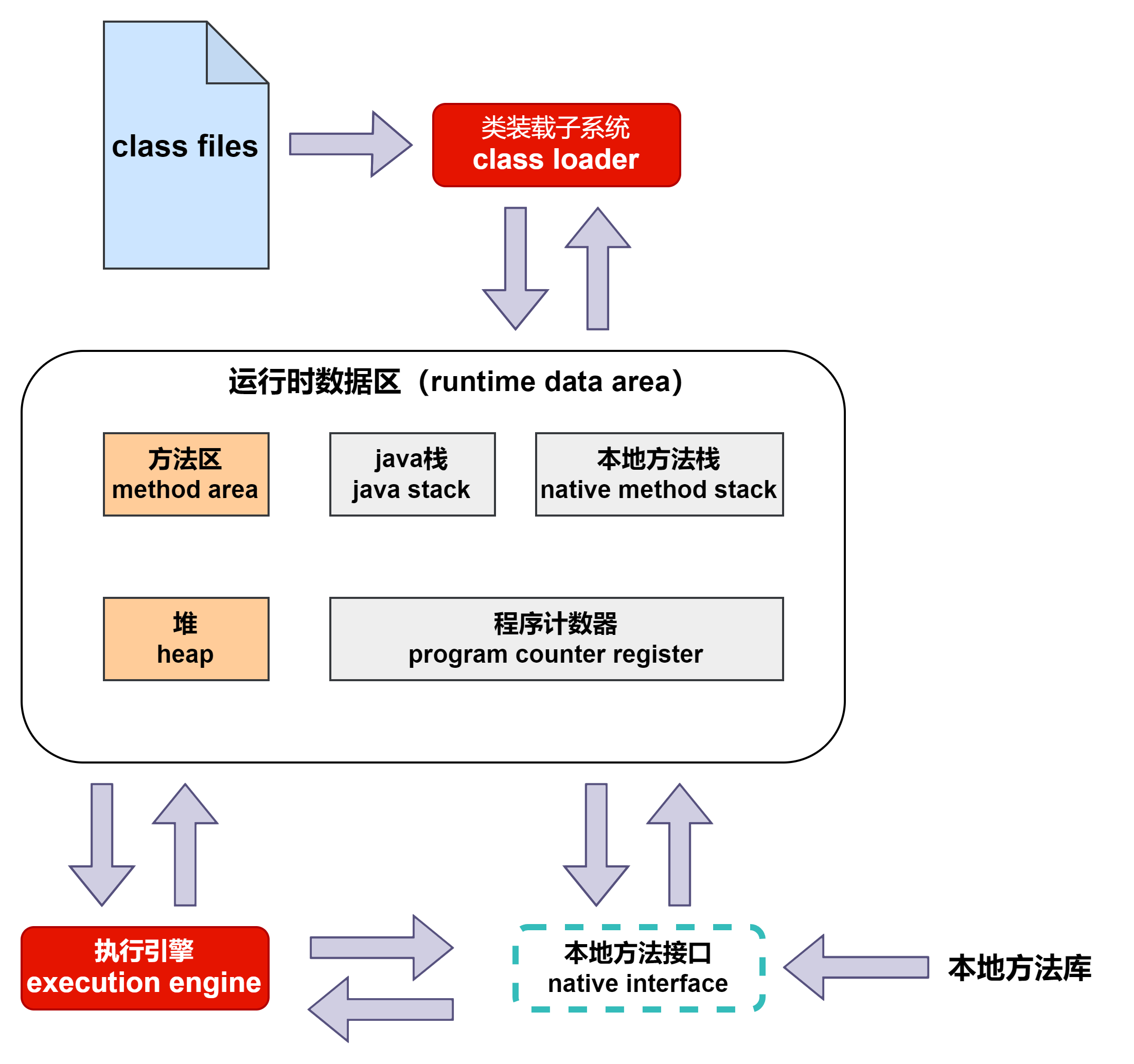
【jvm】jvm整体结构(hotspot)
目录 一、说明二、java代码的执行流程三、jvm的架构模型3.1 基于栈式架构的特点3.2 基于寄存器架构的特点 一、说明 1.hotspot vm是目前市场上高性能虚拟机的代表作之一 2.hotspot采用解释器与即时编译器并存的架构 3.java虚拟机是用来解释运行字节码文件的,入口是字…...

通达信波段选股公式,使用钱德动量摆动指标(CMO)
钱德动量摆动指标(CMO)是由图莎尔钱德发明的,取值范围在-100到100之间,是捕捉价格动量的技术指标。该指标计算近期涨幅之和与近期跌幅之和的差值,然后将计算结果除以同期所有价格波动的总和。本文的波段选股公式使用均线识别趋势,…...
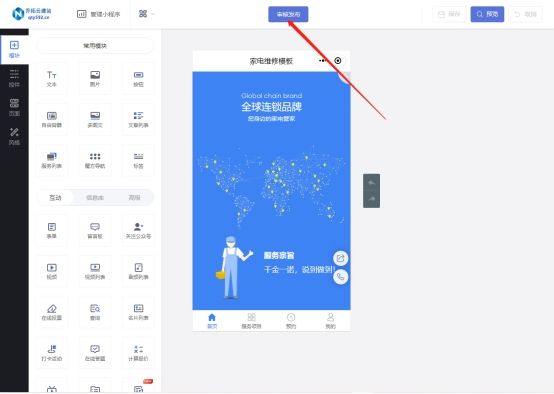
家电维修小程序开发指南:从零搭建到上线
随着科技的发展和人们生活水平的提高,家电已经成为人们生活中不可或缺的一部分。然而,随之而来的是家电维修门店业务的繁忙和效率的考验。为了提高家电维修门店的效率和服务质量,建立一个便捷高效的小程序已成为必要的选择。 本文将介绍一个简…...
玩赚音视频开发高阶技术——FFmpeg
随着移动互联网的普及,人们对音视频内容的需求也不断增加。无论是社交媒体平台、电商平台还是在线教育,都离不开音视频的应用。这就为音视频开发人员提供了广阔的就业机会。根据这些年来网站上的音视频开发招聘需求来看,音视频开发人员的需求…...

python 变量赋值 修改之后 原值改变
python 是一种动态语言,因此变量的类型和值 在运行时均可改变。当我们将一个变量赋值给另一个变量时,实际上是将变量的引用地址传递给新的变量,这意 味着新旧变量将指向同一个位置。因此,在更改其中一个变量的值时,另一…...
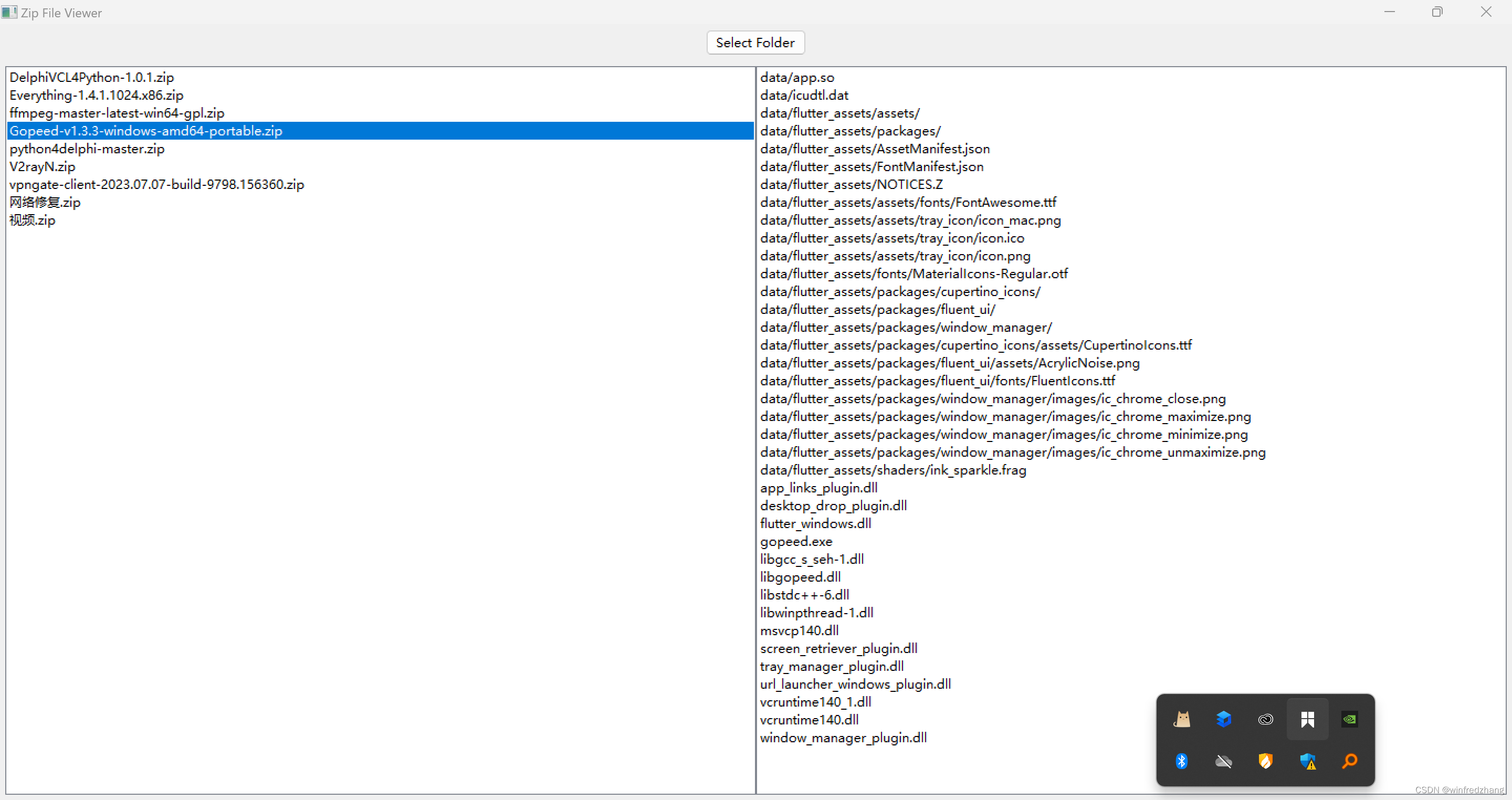
拂袖一挥,zipfile秒列zip包内容
使用wxpython列出文件夹中的zip文件及内容 最近在做一个文件管理的小工具,需要列出选择的文件夹下的所有zip压缩文件,并在点击某个zip文件时能够显示其中的内容。为此我使用了wxpython来实现这个功能。 1. 导入需要的模块 首先导入程序需要的模块: import wx import os imp…...

InnoDB文件物理结构解析2 - FIL_PAGE_INDEX
1. 关于索引组织表 InnoDB使用的是索引组织表(IOT)的方式存储表记录,索引组织表以主键构建一个B-tree的数据结构来存储行记录,行记录存储在树的叶节点内。这与Oracle数据库是不同的,Oracle数据库默认创建的表是堆组织表(HOT),HOT…...
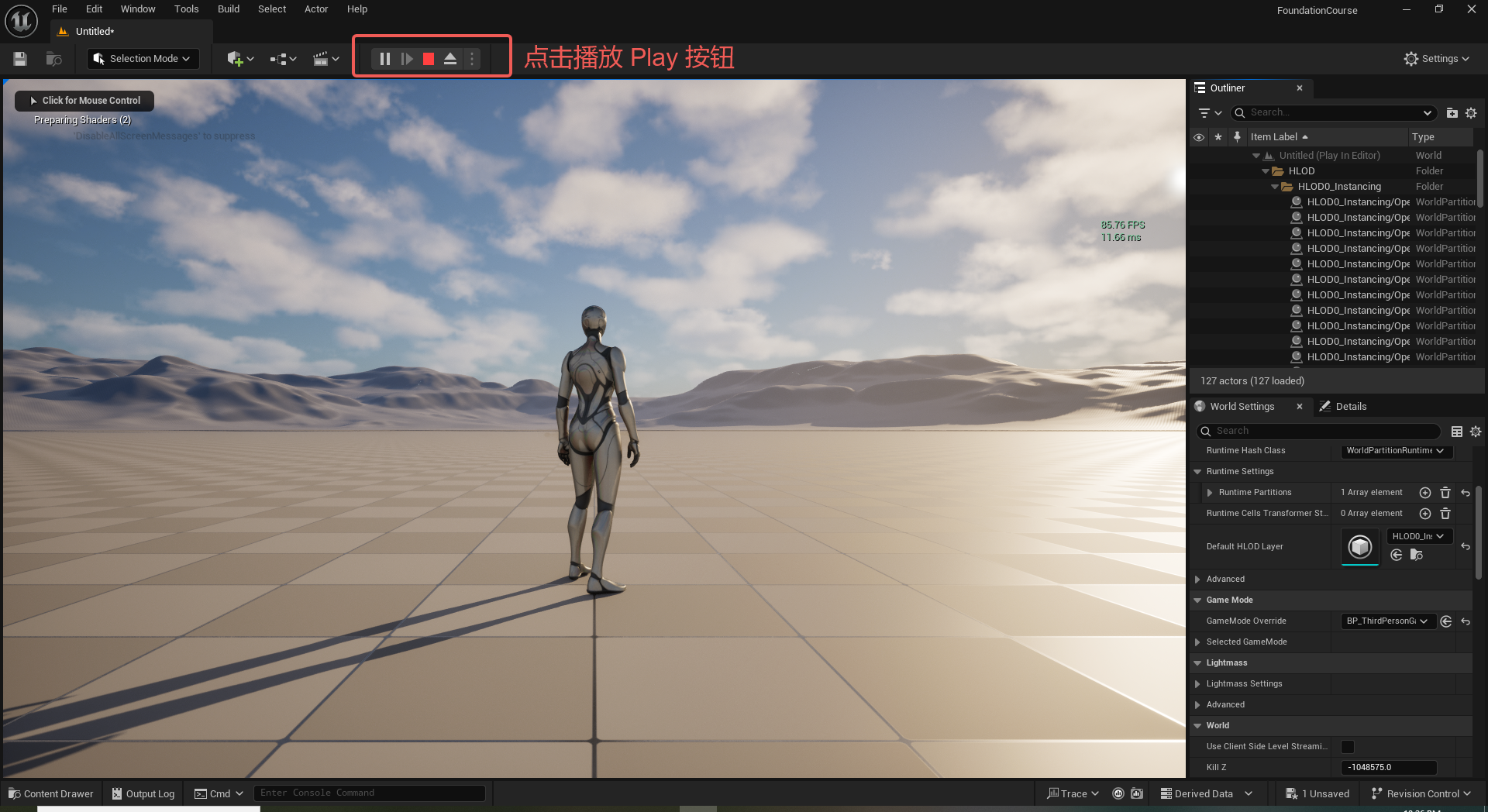
UE5 学习系列(二)用户操作界面及介绍
这篇博客是 UE5 学习系列博客的第二篇,在第一篇的基础上展开这篇内容。博客参考的 B 站视频资料和第一篇的链接如下: 【Note】:如果你已经完成安装等操作,可以只执行第一篇博客中 2. 新建一个空白游戏项目 章节操作,重…...
结构体的进阶应用)
基于算法竞赛的c++编程(28)结构体的进阶应用
结构体的嵌套与复杂数据组织 在C中,结构体可以嵌套使用,形成更复杂的数据结构。例如,可以通过嵌套结构体描述多层级数据关系: struct Address {string city;string street;int zipCode; };struct Employee {string name;int id;…...

手游刚开服就被攻击怎么办?如何防御DDoS?
开服初期是手游最脆弱的阶段,极易成为DDoS攻击的目标。一旦遭遇攻击,可能导致服务器瘫痪、玩家流失,甚至造成巨大经济损失。本文为开发者提供一套简洁有效的应急与防御方案,帮助快速应对并构建长期防护体系。 一、遭遇攻击的紧急应…...
linux之kylin系统nginx的安装
一、nginx的作用 1.可做高性能的web服务器 直接处理静态资源(HTML/CSS/图片等),响应速度远超传统服务器类似apache支持高并发连接 2.反向代理服务器 隐藏后端服务器IP地址,提高安全性 3.负载均衡服务器 支持多种策略分发流量…...

SkyWalking 10.2.0 SWCK 配置过程
SkyWalking 10.2.0 & SWCK 配置过程 skywalking oap-server & ui 使用Docker安装在K8S集群以外,K8S集群中的微服务使用initContainer按命名空间将skywalking-java-agent注入到业务容器中。 SWCK有整套的解决方案,全安装在K8S群集中。 具体可参…...
)
React Native 导航系统实战(React Navigation)
导航系统实战(React Navigation) React Navigation 是 React Native 应用中最常用的导航库之一,它提供了多种导航模式,如堆栈导航(Stack Navigator)、标签导航(Tab Navigator)和抽屉…...

将对透视变换后的图像使用Otsu进行阈值化,来分离黑色和白色像素。这句话中的Otsu是什么意思?
Otsu 是一种自动阈值化方法,用于将图像分割为前景和背景。它通过最小化图像的类内方差或等价地最大化类间方差来选择最佳阈值。这种方法特别适用于图像的二值化处理,能够自动确定一个阈值,将图像中的像素分为黑色和白色两类。 Otsu 方法的原…...

spring:实例工厂方法获取bean
spring处理使用静态工厂方法获取bean实例,也可以通过实例工厂方法获取bean实例。 实例工厂方法步骤如下: 定义实例工厂类(Java代码),定义实例工厂(xml),定义调用实例工厂ÿ…...
前端开发面试题总结-JavaScript篇(一)
文章目录 JavaScript高频问答一、作用域与闭包1.什么是闭包(Closure)?闭包有什么应用场景和潜在问题?2.解释 JavaScript 的作用域链(Scope Chain) 二、原型与继承3.原型链是什么?如何实现继承&a…...
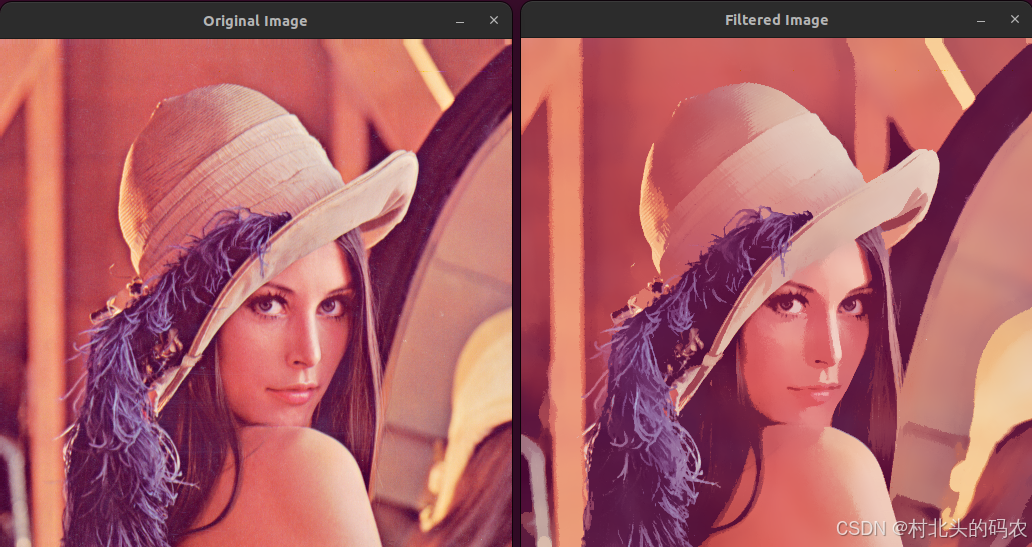
OPenCV CUDA模块图像处理-----对图像执行 均值漂移滤波(Mean Shift Filtering)函数meanShiftFiltering()
操作系统:ubuntu22.04 OpenCV版本:OpenCV4.9 IDE:Visual Studio Code 编程语言:C11 算法描述 在 GPU 上对图像执行 均值漂移滤波(Mean Shift Filtering),用于图像分割或平滑处理。 该函数将输入图像中的…...
