使用 PyTorch 逐步检测单个对象
一、说明
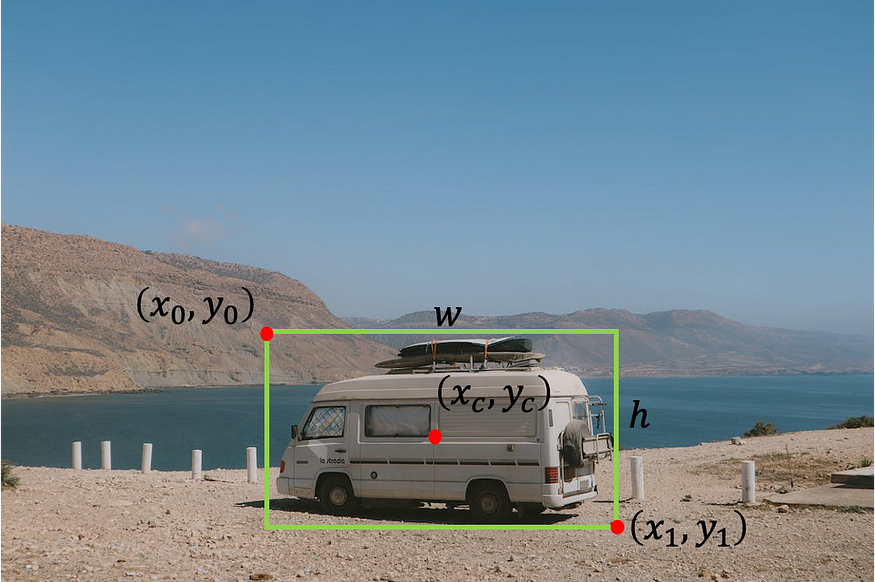
在对象检测任务中,我们希望找到图像中对象的位置。我们可以搜索一种类型的对象(单对象检测,如本教程所示)或多个对象(多对象检测)。通常,我们使用边界框定义对象的位置。有几种方法可以表示边界框:
- 左上角的宽度和高度点 — [x0, y0, w, h],其中 x0 是框的左侧,y0 是框的顶部,w 和 h 分别是框的宽度和高度。
- 左上点和右下点 — [x0 ,y0 ,x1 ,y1],其中 x0 是框的左侧,y0 是框的顶部,x1 是框的右侧,y1 是框的底部。
- 具有宽度和高度的中心点 — [xc, yc, w, h],其中 xc 是框中心的 x 坐标,yc 是框中心的 y 坐标,w 和 h 分别是框的宽度和高度。
照片由Pexels的Indiana Barriopedro拍摄,由作者编辑。
在本教程中,我们将重点介绍在iChallenge-AMD竞赛的医学眼部图像中找到中央凹的中心。
二、获取数据
我们将使用年龄相关性黄斑变性(AMD)患者的眼睛图像。
来自 AMD 数据集的眼睛图像
有两个主要资源可以获取数据。第一个是iChallenge-AMD网站 https://amd.grand-challenge.org/。您首先需要注册参加比赛,然后可以下载数据。第二种方式不需要注册,它是从 https://ai.baidu.com/broad/download 下载。在这里,您需要下载图像的“[训练]图像和AMD标签”和带有标签的Excel文件的“[训练]光盘和中央凹注释”。
下载并提取数据后,您应该有一个文件夹 Training400,其中包含子文件夹 AMD(包含 89 张图像)和非 AMD(包含 311 张图像)以及一个 Excel 文件Fovea_location.xlsx,其中包含每个图像中中央凹的中心位置。
三、探索数据
让我们首先使用 Pandas 加载 Excell 文件
从 pathlib 导入 路径
导入熊猫作为 pdpath_to_parent_dir = 路径('.')
path_to_labels_file = path_to_parent_dir / 'Training400' /'Fovea_location.xlsx'labels_df = pd.read_excel(path_to_labels_file, index_col='ID')print('Head')print(labels_df.head()) # 显示 excell 文件中
的前 5 行 print('\nTail')print(labels_df.tail()) # 显示 excell 文件中的最后 5 行
数据框的打印结果
我们看到该表由四列组成:
- ID — 我们将其用作数据框的索引
- imgName ― 图像的名称。我们注意到,带有 AMD 的图像以 A 开头,而没有 AMD 的图像以 N 开头。
- Fovea_X — 图像中中央凹质心的 x 坐标
- Fovea_Y — 图像中中央凹质心的 y 坐标
我们可以在图像中绘制中央凹的质心,以了解中央凹位置的分布。
%matplotlib inline # 如果使用 Jupyter notebook 或 Colabimport seaborn as snsimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltplt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (10, 6)amd_or_non_amd = ['AMD' if name.startswith('A') else 'Non-AMD' for name inlabels_df.imgName]
sns.scatterplot(x='Fovea_X', y='Fovea_Y', hue=amd_or_non_amd, data=labels_df, alpha=0.7)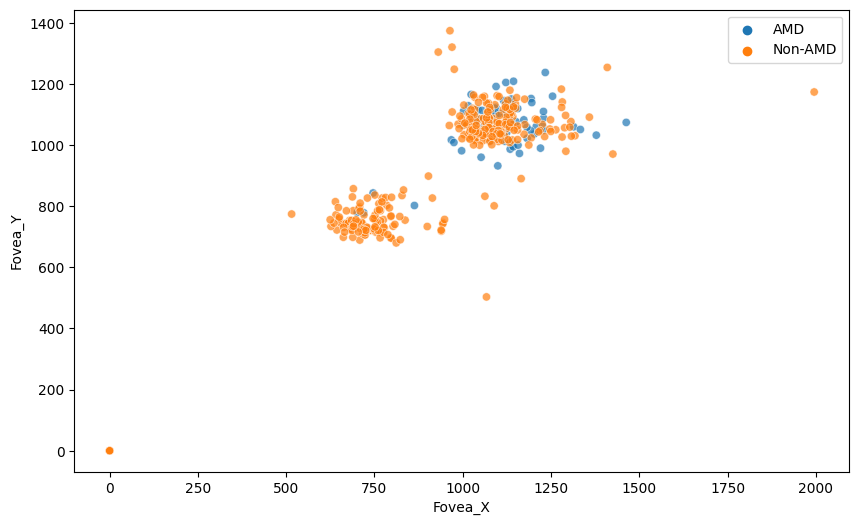
我们可以看到中央凹位置的两个主要组,但更重要的是,对于某些图像,中央凹质心的标签是(0,0)。最好从数据框中移除这些图像。
labels_df = labels_df[(labels_df[['Fovea_X', 'Fovea_Y']] != 0)。all(axis=1)]
amd_or_non_amd = ['AMD' if name.startswith('A') else 'Non-AMD' for name in labels_df.imgName]现在我们想查看图像的随机样本并标记中央凹的中心。为此,让我们定义一个函数来加载带有标签的图像,另一个函数根据标签在中央凹周围绘制一个边界框。
从 PIL import Image, ImageDrawdef 导入 numpy 作为 npload_image_with_label(labels_df, id):image_name = labels_df.loc[id, 'imgName']data_type = 'AMD' 如果 image_name.startswith('A') else 'Non-AMD'image_path = path_to_ parent_dir / 'Training400' / data_type / image_name 图像 =图像。open(image_path) label = (labels_df.loc[id, 'Fovea_X'], labels_df.loc[id, 'Fovea_Y'])返回图像, label def show_image_with_bounding_box(图像, 标签, w_h_bbox=(50, 50), 厚度=2):W, h =w_h_bbox c_x , c_y = labelimage = image.copy() ImageDraw.Draw(image).rectangle(((c_x-w//2, c_y-h//2), (c_x+w//2, c_y+h//2)), outline='green', width=thick) plt.imshow(image)We randomly sample six images and show them.
rng = np.random.default_rng(42) # 创建具有种子的生成器对象 42 n_rows = 2 # 图像子图中的行数 n_cols = 3 # # 图像子图中
的列数 索引 = rng.choice(labels_df.index,
n_rows *
n_cols)对于 ii, 枚举中的 id (索引, 1):
image, label = load_image_with_label(labels_df, id) plt.subplot(n_rows, n_cols, ii) show_image_with_bounding_box(image, label, (250, 250), 20)plt.title(labels_df.loc[id, 'imgName'])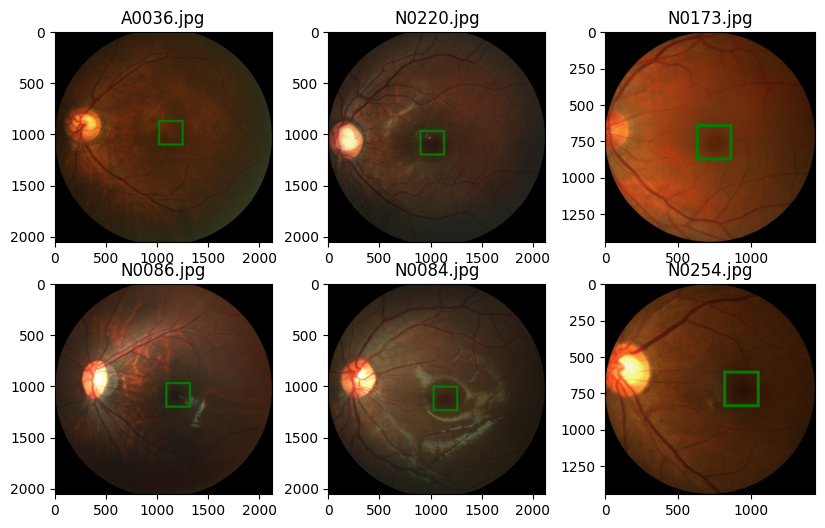
从上图中我们需要注意的第一件事是,对于不同的图像,图像的尺寸是不同的。我们现在想了解图像尺寸的分布。为此,我们在数据集中收集图像的高度和宽度。
heights = []widths = []for image_name, data_type in zip(labels_df['imgName'], amd_or_non_amd):image_path = path_to_parent_dir / 'Training400' / data_type / image_nameh, w = Image。open(image_path).sizeheights.append(h) widths.append(w)sns.histplot(x=heights, hue=amd_or_non_amd)
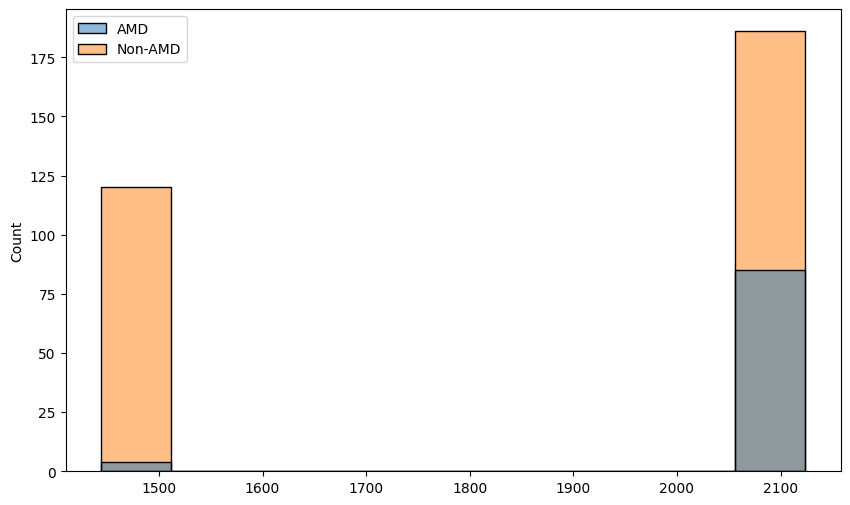
sns.histplot(x=widths, hue=amd_or_non_amd) 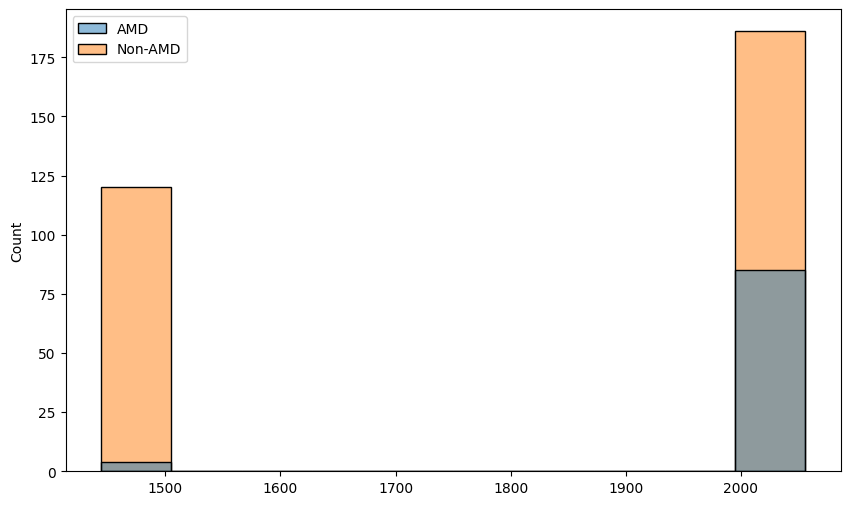
四、数据增强和转换
数据增强是非常重要的一步,它让我们扩展数据集(特别是当我们有一个小数据集时,就像我们的情况一样)并使网络更加健壮。我们还想应用一些转换来使网络的输入保持一致(在我们的例子中,我们需要调整图像的大小,使它们具有恒定的维度)。
除了图像的增强和转换外,我们还需要照顾标签。例如,如果我们垂直翻转图像,中央凹的质心将获得我们需要更新的新坐标。为了更新标签和图像的转换,我们将自己编写一些转换类。
import torch
import torchvision.transforms.functional as tfclass Resize:'''Resize the image and convert the labelto the new shape of the image'''def __init__(self, new_size=(256, 256)):self.new_width = new_size[0]self.new_height = new_size[1]def __call__(self, image_label_sample):image = image_label_sample[0]label = image_label_sample[1]c_x, c_y = labeloriginal_width, original_height = image.sizeimage_new = tf.resize(image, (self.new_width, self.new_height))c_x_new = c_x * self.new_width /original_widthc_y_new = c_y * self.new_height / original_heightreturn image_new, (c_x_new, c_y_new)class RandomHorizontalFlip:'''Horizontal flip the image with probability p.Adjust the label accordingly'''def __init__(self, p=0.5):if not 0 <= p <= 1:raise ValueError(f'Variable p is a probability, should be float between 0 to 1')self.p = p # float between 0 to 1 represents the probability of flippingdef __call__(self, image_label_sample):image = image_label_sample[0]label = image_label_sample[1]w, h = image.sizec_x, c_y = labelif np.random.random() < self.p:image = tf.hflip(image)label = w - c_x, c_yreturn image, labelclass RandomVerticalFlip:'''Vertically flip the image with probability p.Adjust the label accordingly'''def __init__(self, p=0.5):if not 0 <= p <= 1:raise ValueError(f'Variable p is a probability, should be float between 0 to 1')self.p = p # float between 0 to 1 represents the probability of flippingdef __call__(self, image_label_sample):image = image_label_sample[0]label = image_label_sample[1]w, h = image.sizec_x, c_y = labelif np.random.random() < self.p:image = tf.vflip(image)label = c_x, h - c_yreturn image, labelclass RandomTranslation:'''Translate the image by randomaly amount inside a range of values.Translate the label accordingly'''def __init__(self, max_translation=(0.2, 0.2)):if (not 0 <= max_translation[0] <= 1) or (not 0 <= max_translation[1] <= 1):raise ValueError(f'Variable max_translation should be float between 0 to 1')self.max_translation_x = max_translation[0]self.max_translation_y = max_translation[1]def __call__(self, image_label_sample):image = image_label_sample[0]label = image_label_sample[1]w, h = image.sizec_x, c_y = labelx_translate = int(np.random.uniform(-self.max_translation_x, self.max_translation_x) * w)y_translate = int(np.random.uniform(-self.max_translation_y, self.max_translation_y) * h)image = tf.affine(image, translate=(x_translate, y_translate), angle=0, scale=1, shear=0)label = c_x + x_translate, c_y + y_translatereturn image, labelclass ImageAdjustment:'''Change the brightness and contrast of the image and apply Gamma correction.No need to change the label.'''def __init__(self, p=0.5, brightness_factor=0.8, contrast_factor=0.8, gamma_factor=0.4):if not 0 <= p <= 1:raise ValueError(f'Variable p is a probability, should be float between 0 to 1')self.p = pself.brightness_factor = brightness_factorself.contrast_factor = contrast_factorself.gamma_factor = gamma_factordef __call__(self, image_label_sample):image = image_label_sample[0]label = image_label_sample[1]if np.random.random() < self.p:brightness_factor = 1 + np.random.uniform(-self.brightness_factor, self.brightness_factor)image = tf.adjust_brightness(image, brightness_factor)if np.random.random() < self.p:contrast_factor = 1 + np.random.uniform(-self.brightness_factor, self.brightness_factor)image = tf.adjust_contrast(image, contrast_factor)if np.random.random() < self.p:gamma_factor = 1 + np.random.uniform(-self.brightness_factor, self.brightness_factor)image = tf.adjust_gamma(image, gamma_factor)return image, labelclass ToTensor:'''Convert the image to a Pytorch tensor withthe channel as first dimenstion and values between 0 to 1. Also convert the label to tensorwith values between 0 to 1'''def __init__(self, scale_label=True):self.scale_label = scale_labeldef __call__(self, image_label_sample):image = image_label_sample[0]label = image_label_sample[1]w, h = image.sizec_x, c_y = labelimage = tf.to_tensor(image)if self.scale_label:label = c_x/w, c_y/hlabel = torch.tensor(label, dtype=torch.float32)return image, labelclass ToPILImage:'''Convert a tensor image to PIL Image. Also convert the label to a tuple withvalues with the image units'''def __init__(self, unscale_label=True):self.unscale_label = unscale_labeldef __call__(self, image_label_sample):image = image_label_sample[0]label = image_label_sample[1].tolist()image = tf.to_pil_image(image)w, h = image.sizeif self.unscale_label:c_x, c_y = labellabel = c_x*w, c_y*hreturn image, label让我们尝试一下新的转换。我们为每个转换类创建对象,并使用 torchvision 将它们连接起来。然后,我们将完整转换应用于带有标签的图像。Compose
from torchvision.transforms import Compose
image, label = load_image_with_label(labels_df, 1)
transformation = Compose([Resize(), RandomHorizontalFlip(), RandomVerticalFlip(), RandomTranslation(), ImageAdjustment(), ToTensor()])
new_image, new_label = transformation((image, label))
print(f'new_im type {new_image.dtype}, shape = {new_image.shape}')
print(f'{new_label=}')# new_im type torch.float32, shape = torch.Size([3, 256, 256]
# new_label=tensor([0.6231, 0.3447])我们如预期的那样得到了结果。我们还希望将新的张量转换为 PIL 图像,并将标签转换回图像坐标,以便我们可以使用我们的 show 方法显示它。
new_image, new_label = ToPILImage()((new_image, new_label))
show_image_with_bounding_box(new_image, new_label)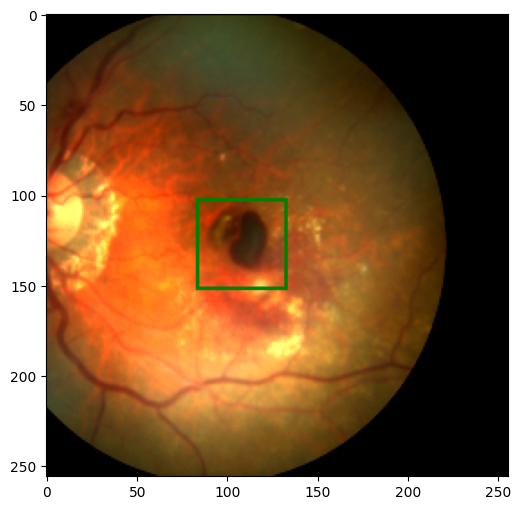
五、制作数据集和数据加载器
要将数据加载到我们的模型中,我们首先需要构建一个自定义数据集类(它是 PyTorch 数据集类的子类)。为此,我们需要实现三种方法:
__init__()- 构造和初始化数据集对象__getitem__()- 处理我们可以通过索引从整个数据集中获取图像和标签的方式__len__()- 返回我们拥有的数据集的长度
import torch
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoaderdevice = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'class AMDDataset(Dataset):def __init__(self, data_path, labels_df, transformation):self.data_path = Path(data_path)self.labels_df = labels_df.reset_index(drop=True)self.transformation = transformationdef __getitem__(self, index):image_name = self.labels_df.loc[index, 'imgName']image_path = self.data_path / ('AMD' if image_name.startswith('A') else 'Non-AMD') / image_nameimage = Image.open(image_path)label = self.labels_df.loc[index, ['Fovea_X','Fovea_Y']].values.astype(float)image, label = self.transformation((image, label))return image.to(device), label.to(device)def __len__(self):return len(self.labels_df)在实际创建数据集对象之前,我们需要将数据拆分为训练集和验证集。我们用于将其拆分为训练数据帧和验证数据帧。scikit-learnlabels_df
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
labels_df_train, labels_df_val = train_test_split(labels_df, test_size=0.2, shuffle=True, random_state=42)train_transformation = Compose([Resize(), RandomHorizontalFlip(), RandomVerticalFlip(), RandomTranslation(), ImageAdjustment(), ToTensor()])
val_transformation = Compose([Resize(), ToTensor()])train_dataset = AMDDataset('Training400', labels_df_train, train_transformation)
val_dataset = AMDDataset('Training400', labels_df_val, val_transformation)我们可以通过显示图像样本来检查我们的数据集对象。
image, label = train_dataset[0]
show_image_with_bounding_box(*(ToPILImage()((image, label))))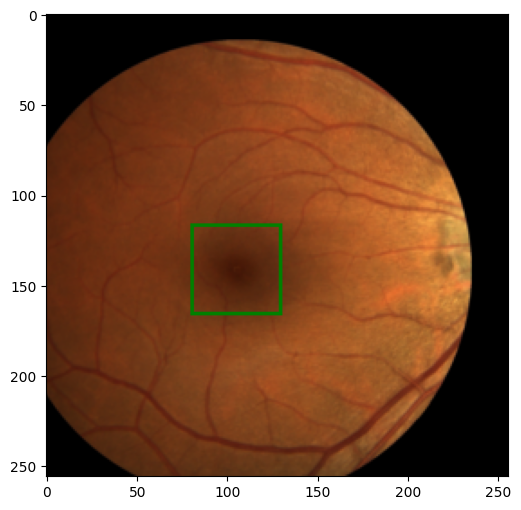
image, label = val_dataset[0]
show_image_with_bounding_box(*(ToPILImage()((image, label))))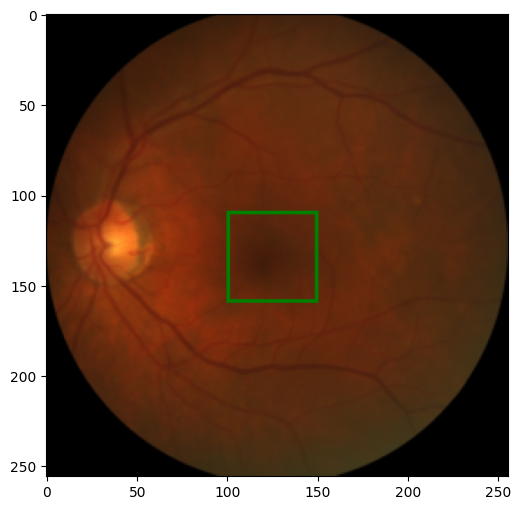
下一步是定义一个数据加载程序,一个用于训练数据集,一个用于验证数据集。
train_dataloader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=8)
val_dataloader = DataLoader(val_dataset, batch_size=16)我们不必在 DataLoader 中进行随机排序,因为当我们将数据拆分为训练数据集和验证数据集时,我们已经对数据进行了随机排序。现在让我们看一个批处理,看看结果是否符合预期。
image_batch, labels_batch = next(iter(train_dataloader))
print(image_batch.shape, image_batch.dtype)
print(labels_batch, labels_batch.dtype)# torch.Size([8, 3, 256, 256]) torch.float32
# tensor([[0.4965, 0.3782],
# [0.6202, 0.6245],
# [0.5637, 0.4887],
# [0.5114, 0.4908],
# [0.3087, 0.4657],
# [0.5330, 0.5309],
# [0.6800, 0.6544],
# [0.5828, 0.4034]], device='cuda:0') torch.float32六、构建模型
我们希望构建一个模型,该模型获取调整大小的 RGB 图像,并为 x 和 y 坐标返回两个值。我们将以类似于使用跳过连接的 ResNet 的方式使用残差块。我们从定义基本的重新块开始
from torch.nn.modules.batchnorm import BatchNorm2d
import torch.nn as nnclass ResBlock(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels):super().__init__()self.base1 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_channels, in_channels, kernel_size=3, padding='same'),nn.BatchNorm2d(in_channels),nn.ReLU(True) )self.base2 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding='same'),nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),nn.ReLU(True))def forward(self, x):x = self.base1(x) + xx = self.base2(x)return x此块有两个步骤。首先,它使用卷积层,然后进行批量归一化和 ReLU。然后我们将原始输入添加到结果中并应用第二步,该步骤再次由卷积层组成,然后是批量归一化和 ReLU,但这次我们更改了过滤器的数量。现在,我们已准备好构建模型。
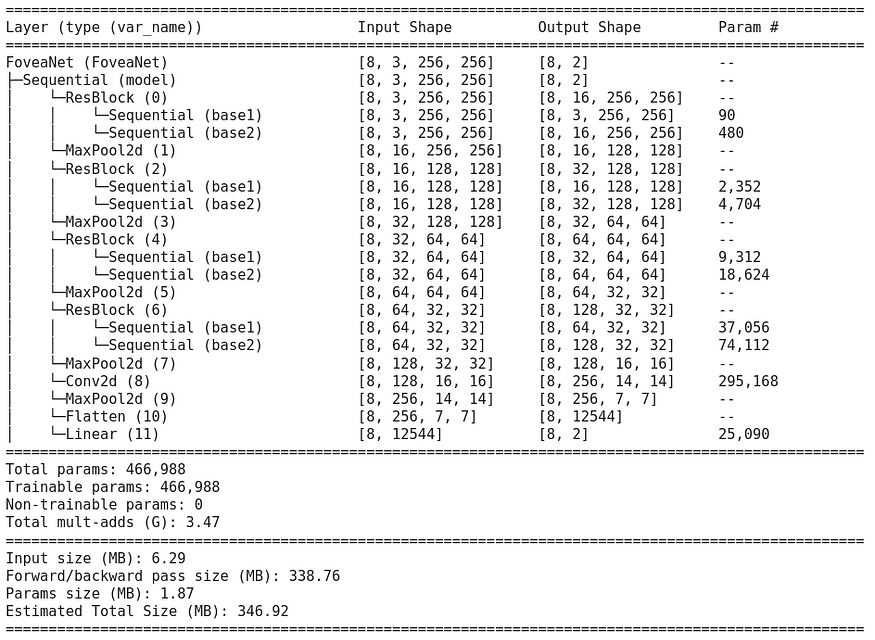
class FoveaNet(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_channels, first_output_channels):super().__init__()self.model = nn.Sequential(ResBlock(in_channels, first_output_channels),nn.MaxPool2d(2),ResBlock(first_output_channels, 2 * first_output_channels),nn.MaxPool2d(2),ResBlock(2 * first_output_channels, 4 * first_output_channels),nn.MaxPool2d(2),ResBlock(4 * first_output_channels, 8 * first_output_channels),nn.MaxPool2d(2),nn.Conv2d(8 * first_output_channels, 16 * first_output_channels, kernel_size=3),nn.MaxPool2d(2),nn.Flatten(),nn.Linear(7 * 7 * 16 * first_output_channels, 2))def forward(self, x):return self.model(x)我们可以使用包更好地查看我们的模型torchinfo
! pip install torchinfo -q # install torchinfofrom torchinfo import summary
net = FoveaNet(3, 16)summary(model=net, input_size=(8, 3, 256, 256), # (batch_size, color_channels, height, width)col_names=["input_size", "output_size", "num_params"],col_width=20,row_settings=["var_names"]
)
七、损失和优化器
我们首先使用平滑 L1 损失定义损失函数。通常,当绝对差值小于 2 时,此损失的行为类似于 L1,否则与 L1 类似。
loss_func = nn.SmoothL1Loss()对于优化器,我们将使用 Adam。
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=1e-4)作为性能指标,我们使用“交集于联合”指标 (IoU)。此指标计算两个边界框的交点与其并集之间的比率。
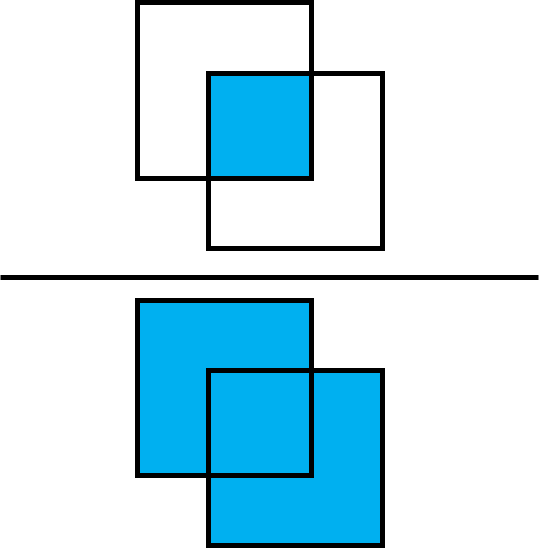
首先,我们需要定义一个函数,该函数获取质心作为输入,并返回形式为 [x0, y0, x1, y1] 的边界框作为输出
def centroid_to_bbox(centroids, w=50/256, h=50/256):x0_y0 = centroids - torch.tensor([w/2, h/2]).to(device)x1_y1 = centroids + torch.tensor([w/2, h/2]).to(device)return torch.cat([x0_y0, x1_y1], dim=1)以及计算一批标签的 IoU 的函数
from torchvision.ops import box_iou
def iou_batch(output_labels, target_labels):output_bbox = centroid_to_bbox(output_labels)target_bbox = centroid_to_bbox(target_labels)return torch.trace(box_iou(output_bbox, target_bbox)).item()接下来,我们为批处理定义一个损失函数
def batch_loss(loss_func, output, target, optimizer=None):loss = loss_func(output, target)with torch.no_grad():iou_metric = iou_batch(output, target)if optimizer is not None:optimizer.zero_grad()loss.backward()optimizer.step()return loss.item(), iou_metric八、训练模型
在此步骤中,我们将训练模型以找到中央凹。我们首先定义一个辅助函数来进行训练步骤,这意味着遍历数据加载器中的所有数据,使用我们之前的函数获取损失(并更新训练案例中的权重),并跟踪损失和 IoU 指标。batch_loss
def train_val_step(dataloader, model, loss_func, optimizer=None):if optimizer is not None:model.train()else:model.eval()running_loss = 0running_iou = 0for image_batch, label_batch in dataloader:output_labels = model(image_batch)loss_value, iou_metric_value = batch_loss(loss_func, output_labels, label_batch, optimizer)running_loss += loss_valuerunning_iou += iou_metric_valuereturn running_loss/len(dataloader.dataset), running_iou/len(dataloader.dataset)现在,我们有了进行培训所需的一切。我们定义了两个字典来跟踪损失和 IoU 指标,以便在每个 epoch 之后进行训练和验证。我们还保存了提供最佳结果的模型权重。
num_epoch = 100
loss_tracking = {'train': [], 'val': []}
iou_tracking = {'train': [], 'val': []}
best_loss = float('inf')model = FoveaNet(3, 16).to(device)
loss_func = nn.SmoothL1Loss(reduction="sum")
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=5e-5)for epoch in range(num_epoch):print(f'Epoch {epoch+1}/{num_epoch}')training_loss, trainig_iou = train_val_step(train_dataloader, model, loss_func, optimizer)loss_tracking['train'].append(training_loss)iou_tracking['train'].append(trainig_iou)with torch.inference_mode():val_loss, val_iou = train_val_step(val_dataloader, model, loss_func, None)loss_tracking['val'].append(val_loss)iou_tracking['val'].append(val_iou)if val_loss < best_loss:print('Saving best model')torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'best_model.pt')best_loss = val_lossprint(f'Training loss: {training_loss:.6}, IoU: {trainig_iou:.2}')print(f'Validation loss: {val_loss:.6}, IoU: {val_iou:.2}')让我们绘制每个纪元的平均损失和平均 IoU 作为纪元的函数。
plt.plot(range(1, num_epoch+1), loss_tracking['train'], label='train')
plt.plot(range(1, num_epoch+1), loss_tracking['val'], label='validation')
plt.xlabel('epoch')
plt.ylabel('loss')
plt.legend()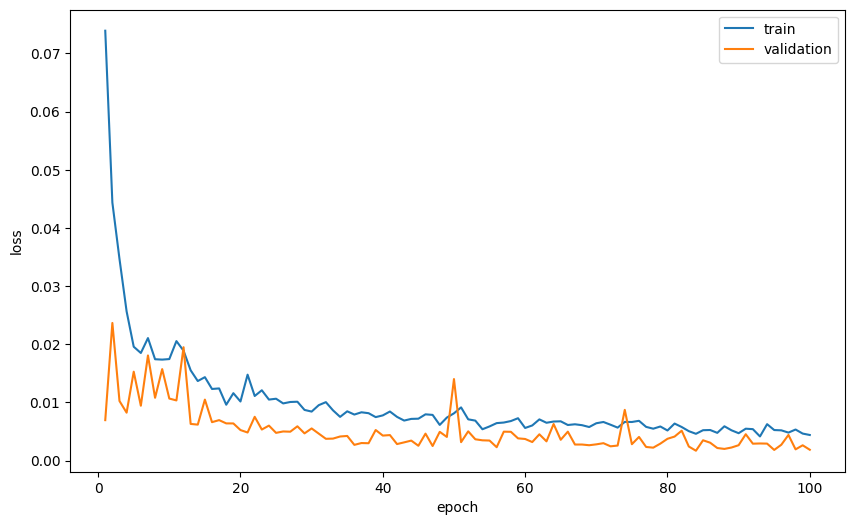
plt.plot(range(1, num_epoch+1), iou_tracking['train'], label='train')
plt.plot(range(1, num_epoch+1), iou_tracking['val'], label='validation')
plt.xlabel('epoch')
plt.ylabel('iou')
plt.legend()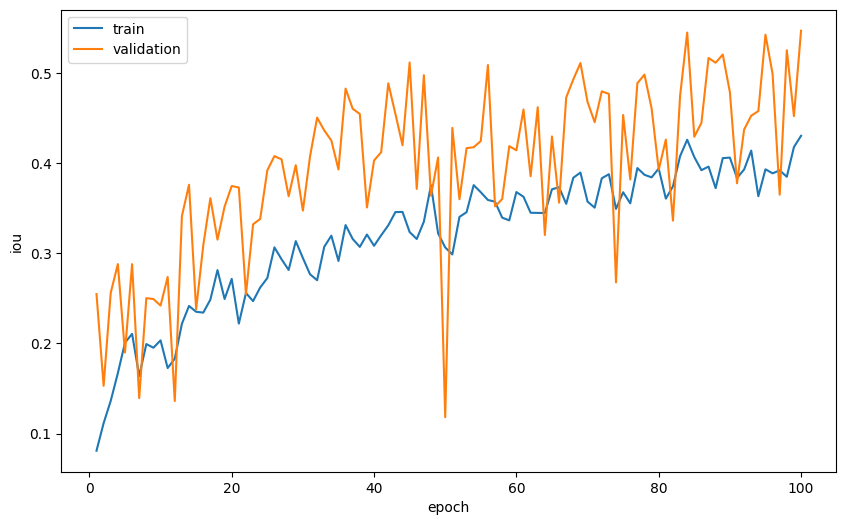
最后,我们想看一些图像,看看模型的预测在多大程度上接近中央凹的真实坐标。为此,我们基于之前的函数定义一个新函数,但这次我们为预测(绿色)和目标(红色)绘制边界框。show_image_with_bounding_box
def show_image_with_2_bounding_box(image, label, target_label, w_h_bbox=(50, 50), thickness=2):w, h = w_h_bboxc_x , c_y = labelc_x_target , c_y_target = target_labelimage = image.copy()ImageDraw.Draw(image).rectangle(((c_x-w//2, c_y-h//2), (c_x+w//2, c_y+h//2)), outline='green', width=thickness)ImageDraw.Draw(image).rectangle(((c_x_target-w//2, c_y_target-h//2), (c_x_target+w//2, c_y_target+h//2)), outline='red', width=thickness)plt.imshow(image)现在我们加载我们得到的最佳模型,并对图像样本进行预测并查看结果
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('best_model.pt'))
model.eval()
rng = np.random.default_rng(0) # create Generator object with seed 0
n_rows = 2 # number of rows in the image subplot
n_cols = 3 # # number of cols in the image subplot
indexes = rng.choice(range(len(val_dataset)), n_rows * n_cols, replace=False)for ii, id in enumerate(indexes, 1):image, label = val_dataset[id]output = model(image.unsqueeze(0))iou = iou_batch(output, label.unsqueeze(0))_, label = ToPILImage()((image, label))image, output = ToPILImage()((image, output.squeeze()))plt.subplot(n_rows, n_cols, ii)show_image_with_2_bounding_box(image, output, label)plt.title(f'{iou:.2f}')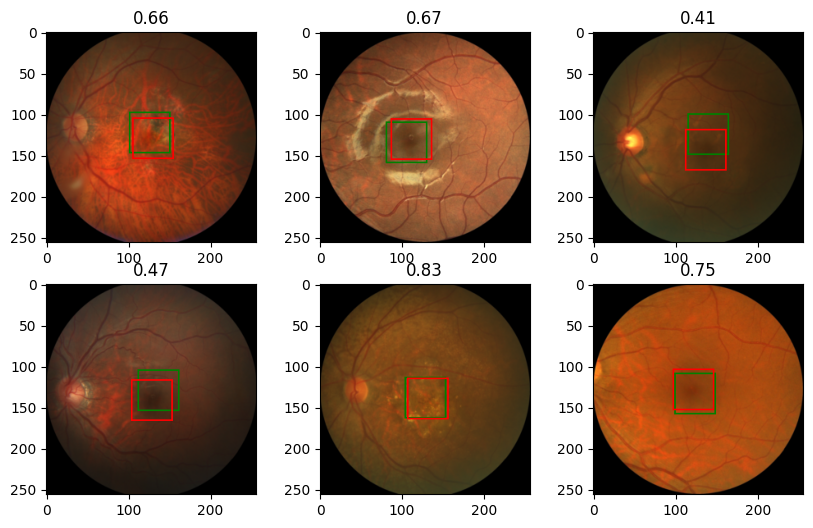
九、结论
在本教程中,我们介绍了为单个对象检测任务构建网络所需的所有主要步骤。我们首先探索数据,清理和排列数据,然后构建数据增强函数以及数据集和DataLoader对象,最后构建和训练模型。我们得到了相对不错的结果,欢迎您尝试通过更改模型的学习参数和架构来提高性能。
相关文章:

使用 PyTorch 逐步检测单个对象
一、说明 在对象检测任务中,我们希望找到图像中对象的位置。我们可以搜索一种类型的对象(单对象检测,如本教程所示)或多个对象(多对象检测)。通常,我们使用边界框定义对象的位置。有几种方法可以…...
Node.js |(二)Node.js API:fs模块 | 尚硅谷2023版Node.js零基础视频教程
学习视频:尚硅谷2023版Node.js零基础视频教程,nodejs新手到高手 文章目录 📚文件写入🐇writeFile 异步写入🐇writeFileSync 同步写入🐇appendFile / appendFileSync 追加写入🐇createWriteStrea…...

Android 13 Hotseat定制化修改——002 hotseat图标数量修改
目录 一.背景 二.实践方案 一.背景 由于需求是需要自定义修改Hotseat,所以此篇文章是记录如何自定义修改hotseat的,应该可以覆盖大部分场景,修改点有修改hotseat布局方向,hotseat图标数量,hotseat图标大小࿰…...
Flask实现接口mock,安装及使用教程(一)
1、什么是接口mock 主要是针对单元测试的应用,它可以很方便的解除单元测试中各种依赖,大大的降低了编写单元测试的难度 2、什么是mock server 正常情况下:测试客户端——测试——> 被测系统 ——依赖——>外部服务依赖 在被测系统和…...

分立式BUCK电路原理与制作持续更新
目录 一、分立式BUCK电路总体原理图 二、BUCK电路与LDO的区别 三、BUCK电路为什么要加电感 四、BUCK电路要加续流二极管 五、BUCK电路导通与断开的回路 六、电源公式的中的几个表示方式 1、输入功率用Pin表示 2、输出功率用Po表示 3、电源的效率公式:电源的…...

2023年大数据与计算国际会议 (WBDC 2023)| EI、Scoups检索
会议简介 Brief Introduction 2023年大数据与计算国际会议(WBDC 2023) 会议时间:2023年11月17 -19日 召开地点:中国西安 大会官网:www.iwbdc.org 2023年大数据与计算国际会议(WBDC 2023)将围绕“…...
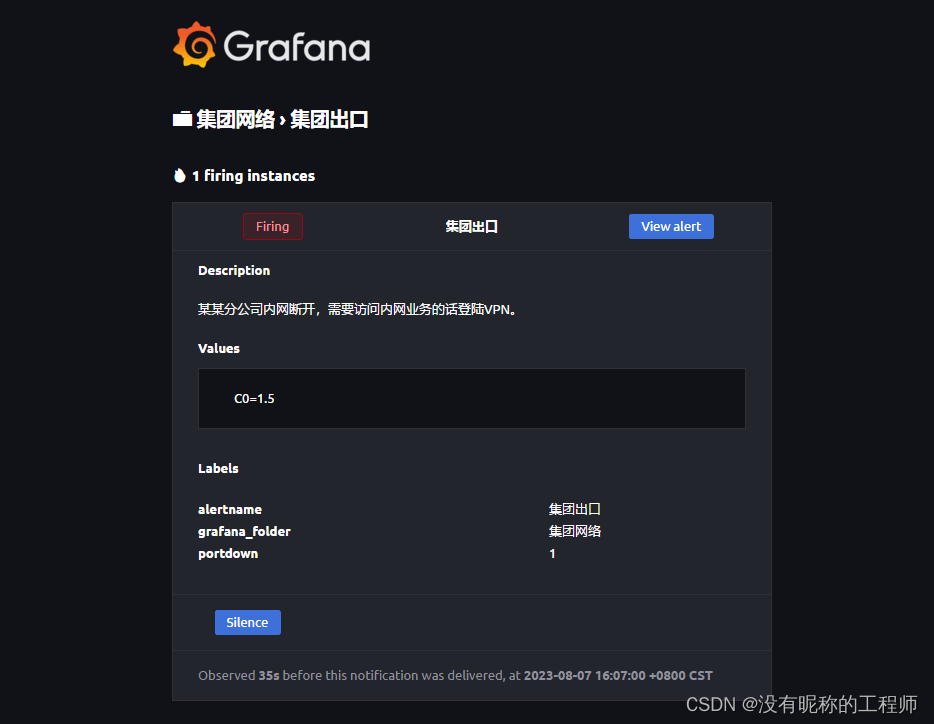
Grafana V10 告警推送 邮件
最近项目建设完成,一个城域网项目,相关zabbix和grafana展示已经完,想了想,不想天天看平台去盯网络监控平台,索性对告警进行分类调整,增加告警的推送,和相关部门的提醒,其他部门看不懂…...

【OpenCV常用函数:视频捕获函数】cv2.VideoCapture
文章目录 1、cv2.VideoCapture() 1、cv2.VideoCapture() 输入视频路径,创建VideoCapture的对象 cv2.VideoCapture(filename) filename: 视频文件的路径视频名扩展名该类的函数有: 1)video.isOpened: 检查视频捕获是否成功 2)vid…...
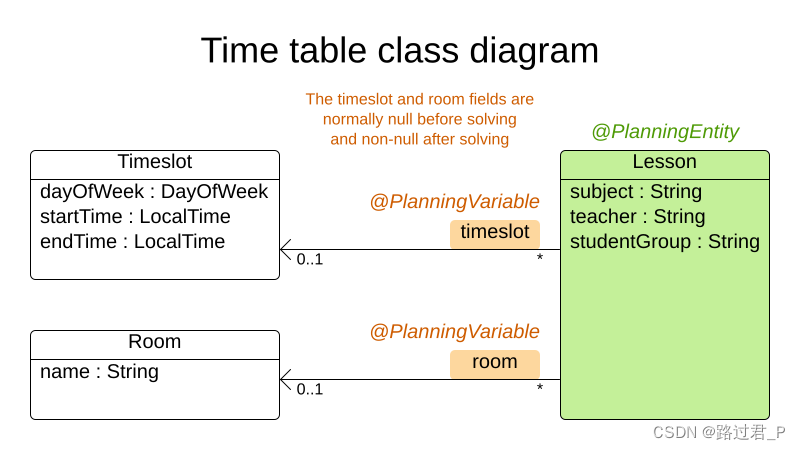
OptaPlanner笔记2
1.5.3 使用maven 修改pom.xml 导入optaplanner-bom以避免为每一个依赖项重复添加版本号 <project>...<dependencyManagement><dependencies><dependency><groupId>org.optaplanner</groupId><artifactId>optaplanner-bom</art…...

c++文件流详细笔记
c++流 IO :向设备输入数据和输出数据 C++的IO流 设备: 文件控制台特定的数据类型(stringstream)c++中,必须通过特定的已经定义好的类, 来处理IO(输入输出) 文件流 文件流: 对文件进行读写操作 头文件: 类库: ifstream 对文件输入(读文件) ofstream 对文件输出(写…...

CNN经典网络模型之GoogleNet论文解读
目录 1. GoogleNet 1.1 Inception模块 1.1.1 1x1卷积 1.2 辅助分类器结构 1.3 GoogleNet网络结构图 1. GoogleNet GoogleNet,也被称为Inception-v1,是由Google团队在2014年提出的一种深度卷积神经网络架构,专门用于图像分类和特征提取任…...

【C++】开源:CGAL计算几何库配置使用
😏★,:.☆( ̄▽ ̄)/$:.★ 😏 这篇文章主要介绍CGAL计算几何库配置使用。 无专精则不能成,无涉猎则不能通。——梁启超 欢迎来到我的博客,一起学习,共同进步。 喜欢的朋友可以关注一下,…...

Redis分布式锁相关
Redis分布式锁实现Redisson 15问 分布式锁:Redisson源码解析-MultiLock、RedLock 看懂Redisson分布式锁源码,其实并不难...

Nginx环境搭建以及Docker环境部署
目录 Nginx环境搭建 1.首先创建Nginx的目录并进入 2.下载Nginx的安装包 可以通过FTP工具上传离线环境包,也可通过wget命令在线获取安装包 没有wget命令的可通过yum命令安装 3.解压Nginx的压缩包 4.下载并安装Nginx所需的依赖库和包 安装方式一 安装方式二 --- 也…...

2023牛客暑期多校训练营7(C/I/M)
目录 C.Beautiful Sequence I.We Love Strings M.Writing Books C.Beautiful Sequence 思路:显然若得到了a[1],则整个序列a我们都知道了。所以我们要求出第k大的a[1],这个可以利用序列a为不递减序列的性质来得出。 首先,由题…...
阿里云服务器手动搭建FTP教程(Windows操作系统)
阿里云百科介绍使用阿里云服务器搭建FTP教程,云服务器为Windows操作系统,当需要远程连接Windows实例进行文件传输时,可以通过搭建FTP站点实现。本文将介绍如何在Windows实例中搭建FTP站点。 目录 准备工作 步骤一:添加IIS以及F…...
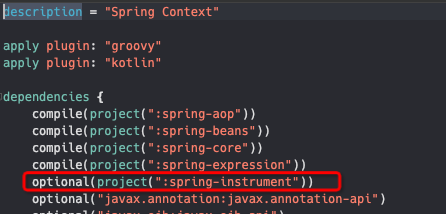
idea+gradle阅读spring5.2.9源码之源码构建报错解决方案
注意 1、先确保gradle版本和spring、jdk版本对应 本文:gradle:5.6.4/spring 5.2.9/jdk1.8(gradle和jdk都要先安装好,gradle还要配置好本地资源文件路径) 2、原来项目乱了的话,先重新导入下载的源码项目 3、进入源码所在根目录&…...
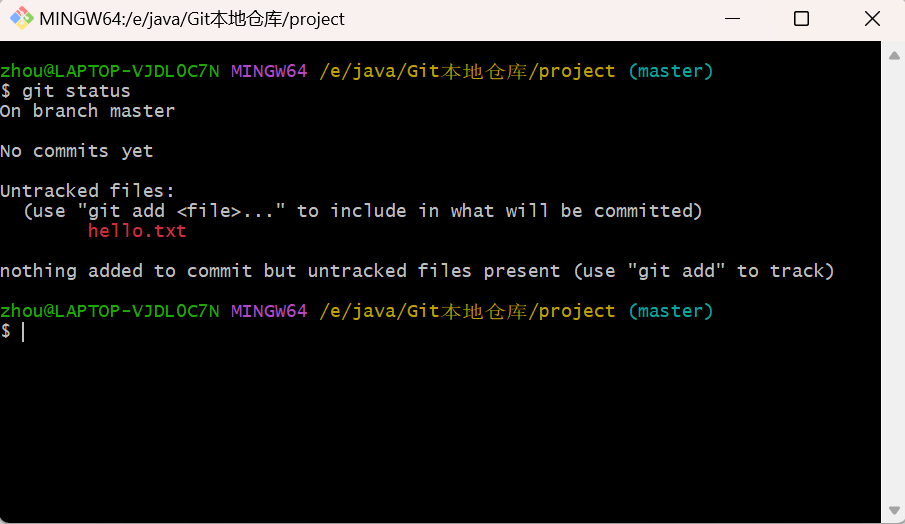
一文详解Git
一. Git 概述 1.1 什么是 Git Git 是一个免费的、开源的分布式版本控制工具, 主要用于管理开发过程中的源代码文件,在软件开发过程中被广泛使用。通过Git仓库来存储和管理这些文件,Git仓库分为二种: 本地仓库:开发人…...
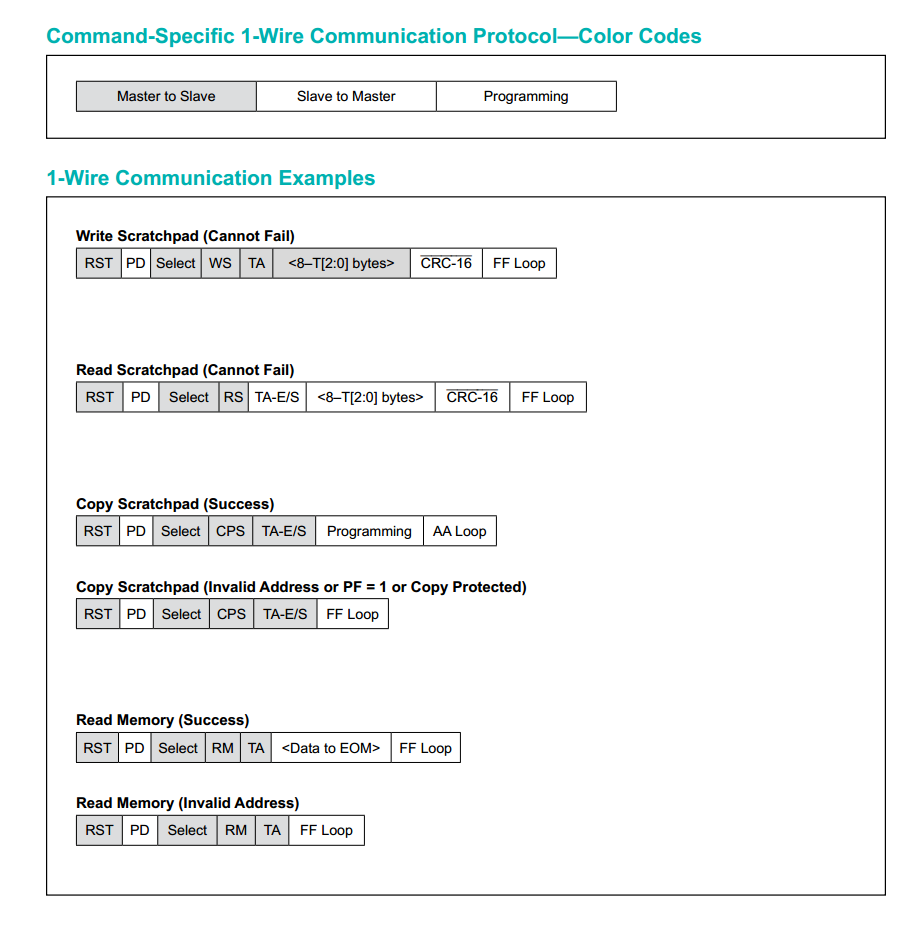
【单片机】DS2431英文手册,中文手册,翻译
DS2431是一款1024位的1-Wire EEPROM芯片,以每个256位的四个内存页面组织。数据被写入8字节的暂存区,经过验证,然后复制到EEPROM存储器中。作为一个特殊功能,四个内存页面可以单独地被写保护,或者被置于EPROM仿真模式&a…...

centos7部署openldap开启memberof并接入jumpserver
文章目录 前言1.yum安装openldap2.配置密码3.导入配置4.定义域5.配置memberof6.配置base dn7.安装phpldapadmin管理8.调整httpd的配置9.调整php的配置10.登陆php管理页面11.同步旧ldapsever用户数据(可省略)12.客户端配置13.对接jumpserver 前言 介绍如何在centos7上部署openl…...
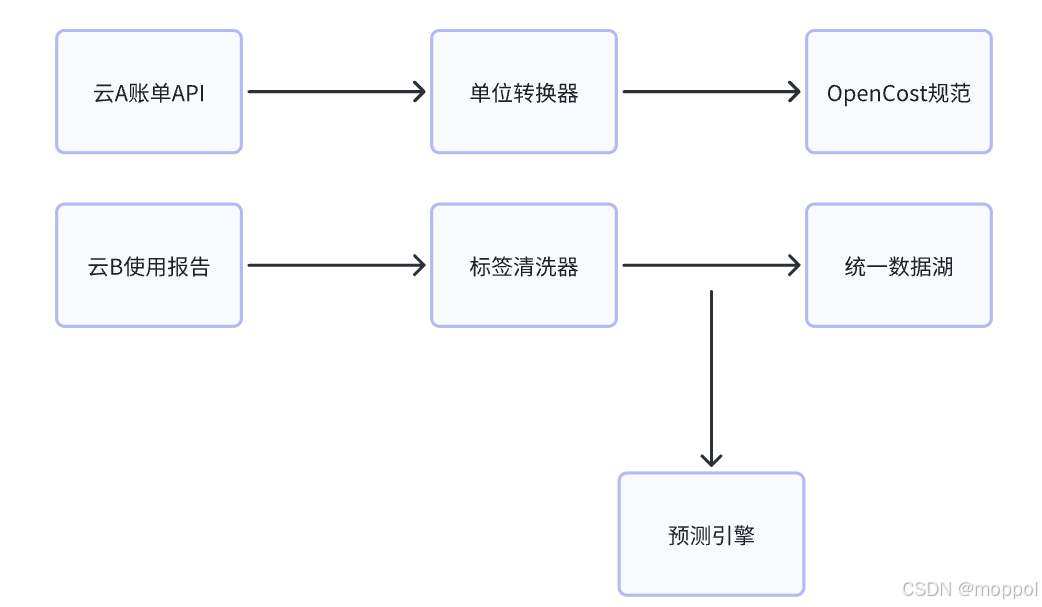
多云管理“拦路虎”:深入解析网络互联、身份同步与成本可视化的技术复杂度
一、引言:多云环境的技术复杂性本质 企业采用多云策略已从技术选型升维至生存刚需。当业务系统分散部署在多个云平台时,基础设施的技术债呈现指数级积累。网络连接、身份认证、成本管理这三大核心挑战相互嵌套:跨云网络构建数据…...

应用升级/灾备测试时使用guarantee 闪回点迅速回退
1.场景 应用要升级,当升级失败时,数据库回退到升级前. 要测试系统,测试完成后,数据库要回退到测试前。 相对于RMAN恢复需要很长时间, 数据库闪回只需要几分钟。 2.技术实现 数据库设置 2个db_recovery参数 创建guarantee闪回点,不需要开启数据库闪回。…...
)
云计算——弹性云计算器(ECS)
弹性云服务器:ECS 概述 云计算重构了ICT系统,云计算平台厂商推出使得厂家能够主要关注应用管理而非平台管理的云平台,包含如下主要概念。 ECS(Elastic Cloud Server):即弹性云服务器,是云计算…...

.Net框架,除了EF还有很多很多......
文章目录 1. 引言2. Dapper2.1 概述与设计原理2.2 核心功能与代码示例基本查询多映射查询存储过程调用 2.3 性能优化原理2.4 适用场景 3. NHibernate3.1 概述与架构设计3.2 映射配置示例Fluent映射XML映射 3.3 查询示例HQL查询Criteria APILINQ提供程序 3.4 高级特性3.5 适用场…...

Objective-C常用命名规范总结
【OC】常用命名规范总结 文章目录 【OC】常用命名规范总结1.类名(Class Name)2.协议名(Protocol Name)3.方法名(Method Name)4.属性名(Property Name)5.局部变量/实例变量(Local / Instance Variables&…...
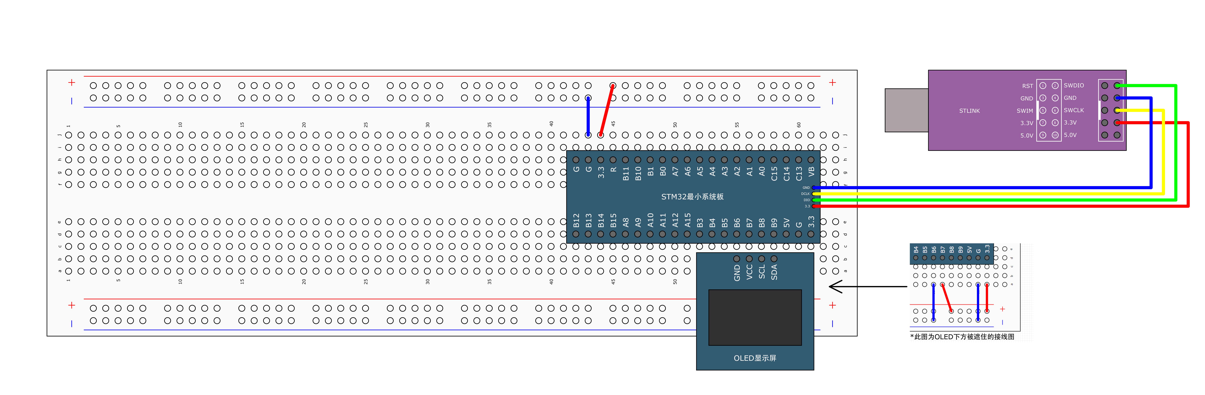
STM32标准库-DMA直接存储器存取
文章目录 一、DMA1.1简介1.2存储器映像1.3DMA框图1.4DMA基本结构1.5DMA请求1.6数据宽度与对齐1.7数据转运DMA1.8ADC扫描模式DMA 二、数据转运DMA2.1接线图2.2代码2.3相关API 一、DMA 1.1简介 DMA(Direct Memory Access)直接存储器存取 DMA可以提供外设…...

OkHttp 中实现断点续传 demo
在 OkHttp 中实现断点续传主要通过以下步骤完成,核心是利用 HTTP 协议的 Range 请求头指定下载范围: 实现原理 Range 请求头:向服务器请求文件的特定字节范围(如 Range: bytes1024-) 本地文件记录:保存已…...

ETLCloud可能遇到的问题有哪些?常见坑位解析
数据集成平台ETLCloud,主要用于支持数据的抽取(Extract)、转换(Transform)和加载(Load)过程。提供了一个简洁直观的界面,以便用户可以在不同的数据源之间轻松地进行数据迁移和转换。…...
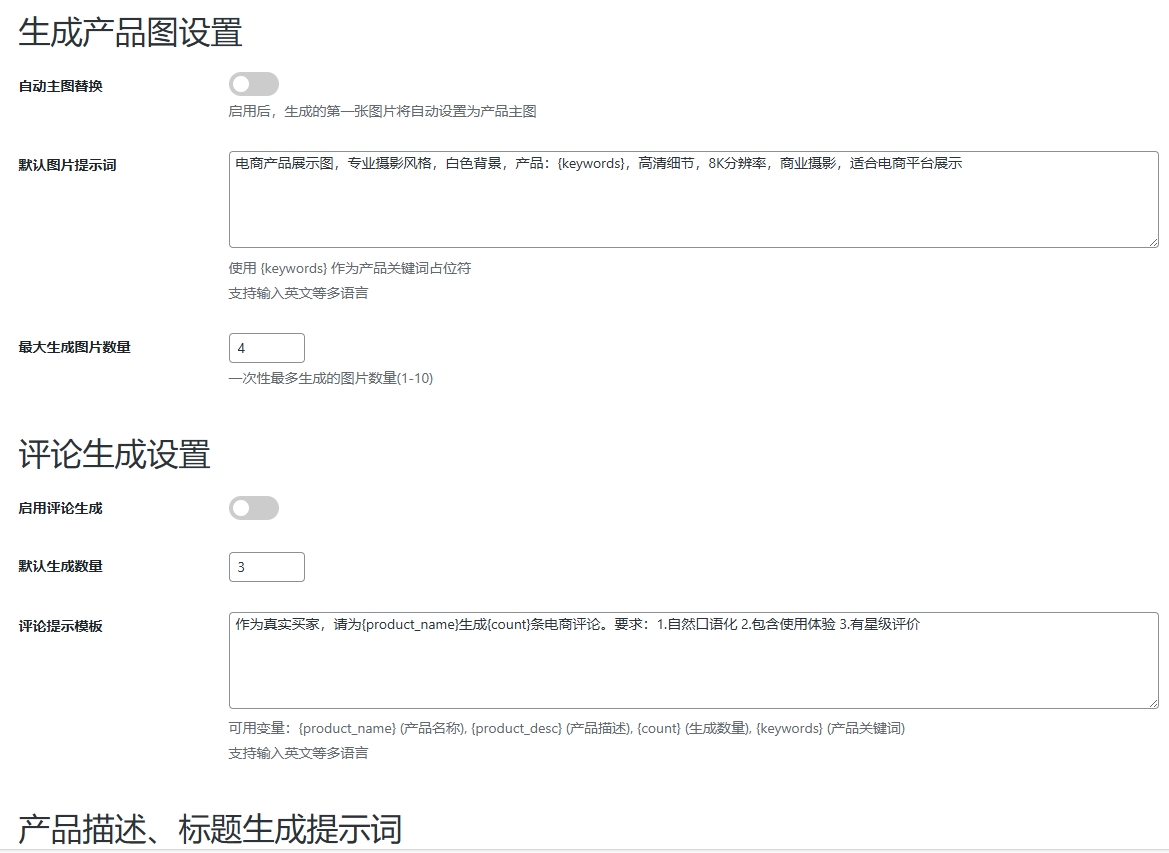
WordPress插件:AI多语言写作与智能配图、免费AI模型、SEO文章生成
厌倦手动写WordPress文章?AI自动生成,效率提升10倍! 支持多语言、自动配图、定时发布,让内容创作更轻松! AI内容生成 → 不想每天写文章?AI一键生成高质量内容!多语言支持 → 跨境电商必备&am…...

leetcodeSQL解题:3564. 季节性销售分析
leetcodeSQL解题:3564. 季节性销售分析 题目: 表:sales ---------------------- | Column Name | Type | ---------------------- | sale_id | int | | product_id | int | | sale_date | date | | quantity | int | | price | decimal | -…...
