AI大模型的使用-让AI帮你写单元测试
1.体验多步提示语
我们本节就让AI帮我们写一个单元测试,全程用AI给我们答案,首先单元测试前需要有代码,那么我们让AI给我们生成一个代码,要求如下:
用Python写一个函数,进行时间格式化输出,比如:
输入 输出
1 1s
61 1min1s
要求仅需要格式化到小时(?h?min?s),即可假如AI给了我们这样一段代码,比如,输入 1 就返回 1s,输入 61 就返回 1min1s,代码如下:
def format_time(seconds):minutes, seconds = divmod(seconds, 60)hours, minutes = divmod(minutes, 60)if hours > 0:return f"{hours}h{minutes}min{seconds}s"elif minutes > 0:return f"{minutes}min{seconds}s"else:return f"{seconds}s"
print(format_time(1))我们可以用单元测试一下下面代码,单元测试包采取pytest
!pip install pytest
import pytestdef test_format_time():assert format_time(1) == "1s"assert format_time(59) == "59s"assert format_time(60) == "1min0s"assert format_time(61) == "1min1s"assert format_time(3600) == "1h0min0s"assert format_time(3661) == "1h1min1s"ok,没有问题,但是关注点放入这个单元测试,我们发现这个单元测试过于简单,很多边界情况或者容易出现异常的情况都没有测试到,如,没有包含异常情况以及类型不一致或者空情况的测试。
我们想让AI生成完美的单元测试就需要一步一步引导,让它理解代码是干什么的,才能进行单元测试的编写。
下面我们就给出代码让它解释出我们的代码是干嘛的,看解释的是否准确,代码比较简单,
1.定义代码变量code母的是将代码给到openAI让它解释这段代码,
2.定义prompt跟Ai说明需求,这里需求是“让它写单元测试,并用Python 3.10和pytest高级特性写代码出合适的单元测试代码验证有效性,写代码之前,先去了解作者的意图”将需求promot和代码传给 AI即可,
3.最后我们防止直接给出代测试代码(不完美的单元测试),我们需要用stop及时停止,让它只返回代码解释说明,看看它有没有理解。
#! pip install openai
import openai
openai.api_key='sk'
# 使用text-davinci-002模型,是一个通过监督学习微调的生成文本的模型。因为这里我们希望生成目标明确的文本的代码解释,所以选用了这个模型。
# openAI调用
def gpt35(prompt, model="text-davinci-002", temperature=0.4, max_tokens=1000, top_p=1, stop=["\n\n", "\n\t\n", "\n \n"]):response = openai.Completion.create(model=model,prompt = prompt,temperature = temperature,max_tokens = max_tokens,top_p = top_p,stop = stop)message = response["choices"][0]["text"]return message# 代码
code = """
def format_time(seconds):minutes, seconds = divmod(seconds, 60)hours, minutes = divmod(minutes, 60)if hours > 0:return f"{hours}h{minutes}min{seconds}s"elif minutes > 0:return f"{minutes}min{seconds}s"else:return f"{seconds}s"
"""# promot跟AI说明要做什么
def explain_code(function_to_test, unit_test_package="pytest"):prompt = f""""# How to write great unit tests with {unit_test_package}In this advanced tutorial for experts, we'll use Python 3.10 and `{unit_test_package}` to write a suite of unit tests to verify the behavior of the following function.
```python
{function_to_test}Before writing any unit tests, let's review what each element of the function is doing exactly and what the author's intentions may have been.
- First,"""response = gpt35(prompt)return response, prompt
# 在最后一行用 “- First” 开头,引导 GPT 模型,逐步分行描述要测试的代码干了什么。# 封装调用
code_explaination, prompt_to_explain_code = explain_code(code)-
print(code_explaination)结果:
the function `format_time` takes in a single parameter `seconds` which should be a `float` or an `int`.
- The function then uses `divmod` to calculate the number of `minutes` and `seconds` from the total number of `seconds`.
- Next, `divmod` is used again to calculate the number of `hours` and `minutes` from the total number of `minutes`.
- Finally, the function returns a `string` formatted according to the number of `hours`, `minutes`, and `seconds`.接下来根据上面的反馈以及进一步的需求,让它帮忙写出一个简单的但是包含多种情况的单元测试例子,我们提出测试单元的需求,看看它能否给出可靠的全面的测试要求,代码如下,
# 要求如下
# 1.我们要求测试用例,尽量考虑输入的范围广一些。
# 2.我们要求 AI 想一些连代码作者没有想到过的边界条件。
# 3.我们希望 AI 能够利用好 pytest 这个测试包的特性。
# 4.希望测试用例清晰易读,测试的代码要干净。
# 5.我们要求测试代码的输出结果是确定的,要么通过,要么失败,不要有随机性。
def generate_a_test_plan(full_code_explaination, unit_test_package="pytest"):prompt_to_explain_a_plan = f"""A good unit test suite should aim to:
- Test the function's behavior for a wide range of possible inputs
- Test edge cases that the author may not have foreseen
- Take advantage of the features of `{unit_test_package}` to make the tests easy to write and maintain
- Be easy to read and understand, with clean code and descriptive names
- Be deterministic, so that the tests always pass or fail in the same way`{unit_test_package}` has many convenient features that make it easy to write and maintain unit tests. We'll use them to write unit tests for the function above.For this particular function, we'll want our unit tests to handle the following diverse scenarios (and under each scenario, we include a few examples as sub-bullets):
-"""prompt = full_code_explaination + prompt_to_explain_a_planresponse = gpt35(prompt)return response, prompttest_plan, prompt_to_get_test_plan = generate_a_test_plan(prompt_to_explain_code + code_explaination)
print(test_plan)结果:当然每次执行返回不一样,因为大模型的随机性。可以看到它能够考虑到异常情况,以及字符不符合会出现什么问题。
Normal inputs- `format_time(0)` should return `"0s"`- `format_time(1)` should return `"1s"`- `format_time(59)` should return `"59s"`- `format_time(60)` should return `"1min0s"`- `format_time(61)` should return `"1min1s"`- `format_time(3599)` should return `"59min59s"`- `format_time(3600)` should return `"1h0min0s"`- `format_time(3601)` should return `"1h0min1s"`- `format_time(3660)` should return `"1h1min0s"`- `format_time(7199)` should return `"1h59min59s"`- `format_time(7200)` should return `"2h0min0s"`
- Invalid inputs- `format_time(None)` should raise a `TypeError`- `format_time("1")` should raise a `TypeError`- `format_time(-1)` should raise a `ValueError`可以根据它提供的修改为可执行的单元测试:
import pytestdef test_format_time():assert format_time(0) == "0s"assert format_time(1) == "1s"assert format_time(59) == "59s"assert format_time(60) == "1min0s"assert format_time(61) == "1min1s"assert format_time(3600) == "1h0min0s"assert format_time(3661) == "1h1min1s"assert format_time(7200) == "2h0min0s"assert format_time(None) == "TypeError"assert format_time("1") == "TypeError"assert format_time(-1) == "ValueError"没问题继续往下走,要是生成的测试计划数不满意,可以判断用例数是否小于指定的数,如果是那么就继续promot让其再生成按照如下的要求。
not_enough_test_plan = """The function is called with a valid number of seconds- `format_time(1)` should return `"1s"`- `format_time(59)` should return `"59s"`- `format_time(60)` should return `"1min"`
"""approx_min_cases_to_cover = 7
# 上下文用例数是否小于指定数字
elaboration_needed = test_plan.count("\n-") +1 < approx_min_cases_to_cover
# 是的话就提需求,在调用下AI
if elaboration_needed:prompt_to_elaborate_on_the_plan = f"""In addition to the scenarios above, we'll also want to make sure we don't forget to test rare or unexpected edge cases (and under each edge case, we include a few examples as sub-bullets):
-"""more_test_plan, prompt_to_get_test_plan = generate_a_test_plan(prompt_to_explain_code + code_explaination + not_enough_test_plan + prompt_to_elaborate_on_the_plan)print(more_test_plan)结果:
The function is called with a valid number of seconds- `format_time(1)` should return `"1s"`- `format_time(59)` should return `"59s"`- `format_time(60)` should return `"1min"`
- The function is called with an invalid number of seconds- `format_time(-1)` should raise a `ValueError`- `format_time("1")` should raise a `TypeError`
- The function is called with a valid number of minutes- `format_time(60)` should return `"1min"`- `format_time(119)` should return `"1min59s"`
- The function is called with an invalid number of minutes- `format_time(-1)` should raise a `ValueError`- `format_time("1")` should raise a `TypeError`
- The function is called with a valid number of hours- `format_time(3600)` should return `"1h"`- `format_time(7199)` should return `"1h59min"`
- The function is called with an invalid number of hours- `format_time(-1)` should raise a `ValueError`- `format_time("1")` should raise a `TypeError`2.根据测试计划生成测试代码
我们根据上面给的需求以及AI给的答案拼装到新添加的prompt的给到AI,然后让它给我们一个测试单元代码
def generate_test_cases(function_to_test, unit_test_package="pytest"):# 将内容加载到prompt的{starter_comment}中starter_comment = "Below, each test case is represented by a tuple passed to the @pytest.mark.parametrize decorator"# promptprompt_to_generate_the_unit_test = f"""Before going into the individual tests, let's first look at the complete suite of unit tests as a cohesive whole. We've added helpful comments to explain what each line does.```pythonimport {unit_test_package} # used for our unit tests{function_to_test}#{starter_comment}"""# 将所有的需求和ai给的结果拼接到prompt里,目的为了给的结果更准确full_unit_test_prompt = prompt_to_explain_code + code_explaination + test_plan + prompt_to_generate_the_unit_testreturn gpt35(model="text-davinci-003", prompt=full_unit_test_prompt, stop="```"), prompt_to_generate_the_unit_testunit_test_response, prompt_to_generate_the_unit_test = generate_test_cases(code)
print(unit_test_response)结果:可以拿过去直接执行
#The first element of the tuple is the name of the test case, and the second element is a dict
#containing the arguments to be passed to the function.
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_case_name, test_case_args",[("positive_integer", {"seconds": 1}),("positive_integer_60", {"seconds": 60}),("positive_integer_3600", {"seconds": 3600}),("positive_integer_3601", {"seconds": 3601}),("negative_integer", {"seconds": -1}),("negative_integer_60", {"seconds": -60}),("negative_integer_3600", {"seconds": -3600}),("negative_integer_3601", {"seconds": -3601}),("float", {"seconds": 1.5}),("float_60", {"seconds": 60.5}),("float_3600", {"seconds": 3600.5}),("string", {"seconds": "1"}),("string_60", {"seconds": "60"}),("string_3600", {"seconds": "3600"}),("string_3601", {"seconds": "3601"}),("decimal", {"seconds": Decimal("1")}),("decimal_60", {"seconds": Decimal("60")}),("decimal_3600", {"seconds": Decimal("3600")}),("decimal_3601", {"seconds": Decimal("3601")}),],
)
def test_format_time(test_case_name, test_case_args):# Here, we use the test case name to determine the expected output.# This allows us to DRY up our code and avoid repeating ourselves.if "positive_integer" in test_case_name:expected = f"{test_case_args['seconds']}s"elif "positive_integer_60" in test_case_name:expected = "1min"elif "positive_integer_3600" in test_case_name:expected = "1h"elif "positive_integer_3601" in test_case_name:expected = "1h0min1s"elif "negative_integer" in test_case_name:expected = f"-{test_case_args['seconds']}s"elif "negative_integer_60" in test_case_name:expected = "-1min"elif "negative_integer_3600" in test_case_name:expected = "-1h"elif "negative_integer_3601" in test_case_name:expected = "-1h0min1s"elif "float" in test_case_name:expected = f"{test_case_args['seconds']}s"elif "float_60" in test_case_name:expected = "1min0.5s"elif "float_3600" in test_case_name:expected = "1h0.5s"elif "string" in test_case_name:expected = f"{test_case_args['seconds']}s"elif "string_60" in test_case_name:expected = "1min"elif "string_3600" in test_case_name:expected = "1h"elif "string_3601" in test_case_name:expected = "1h0min1s"elif "decimal" in test_case_name:expected = f"{test_case_args['seconds']}s"elif "decimal_60" in test_case_name:expected = "1min"elif "decimal_3600" in test_case_name:expected = "1h"elif "decimal_3601" in test_case_name:expected = "1h0min1s"# Now that we have the expected output, we can call the function and assert that the output is那么如果全程自动化的话,我并不知道是否给的代码是否是有语句错误等行为,所以我们可以借用AST 库进行语法检查。
3.通过AST 库进行语法检查
可以检测下AI生成的代码,用Python 的 AST 库来完成。代码也是很简单,我们找到代码片段,将代码传给ast.parse()进行校验,有问题则抛出异常
# 语义检查
import ast
# 找到代码的索引
code_start_index = prompt_to_generate_the_unit_test.find("```python\n") + len("```python\n")
# 找到prompt_to_generate_the_unit_test里从187到最后的内容,并拼接单元测试代码的内容
code_output = prompt_to_generate_the_unit_test[code_start_index:] + unit_test_response
print("code_output:",code_output)# 进行语义检查
try:ast.parse(code_output)
except SyntaxError as e:print(f"Syntax error in generated code: {e}")本节知识资料感谢徐文浩老师的《AI大模型之美》,让我感受它是真的美!
相关文章:

AI大模型的使用-让AI帮你写单元测试
1.体验多步提示语 我们本节就让AI帮我们写一个单元测试,全程用AI给我们答案,首先单元测试前需要有代码,那么我们让AI给我们生成一个代码,要求如下: 用Python写一个函数,进行时间格式化输出,比…...
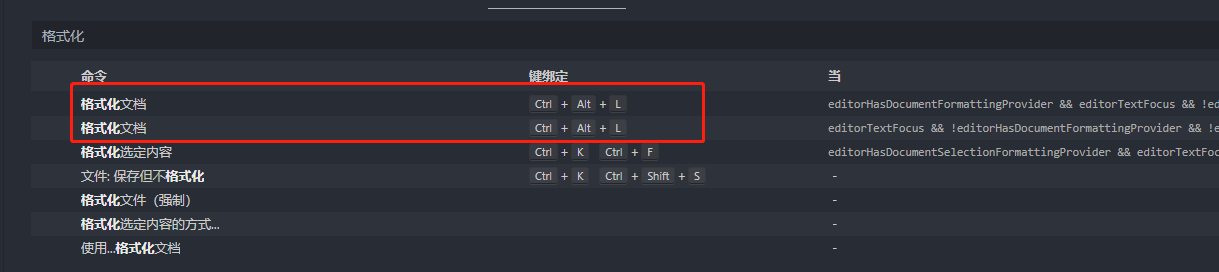
vscode调教配置:快捷修复和格式化代码
配置vscode快捷键,让你像使用idea一样使用vscode,我们最常用的两个功能就是格式化代码和快捷修复,所以这里修改一下快捷修复和格式化代码的快捷键。 在设置中,找到快捷键配置: 然后搜索:快捷修复 在快捷键…...

pear admin 后端启动
pear admin 后端启动 一、项目结构二、启动 一、项目结构 应用结构: Pear Admin Flask ├─applications # 应用 │ ├─rights # │ ├─system # 静态资源文件 │ ├─users # │ └─views # 视图部分 ├─common # 公共模块 ├─models # 数据模…...
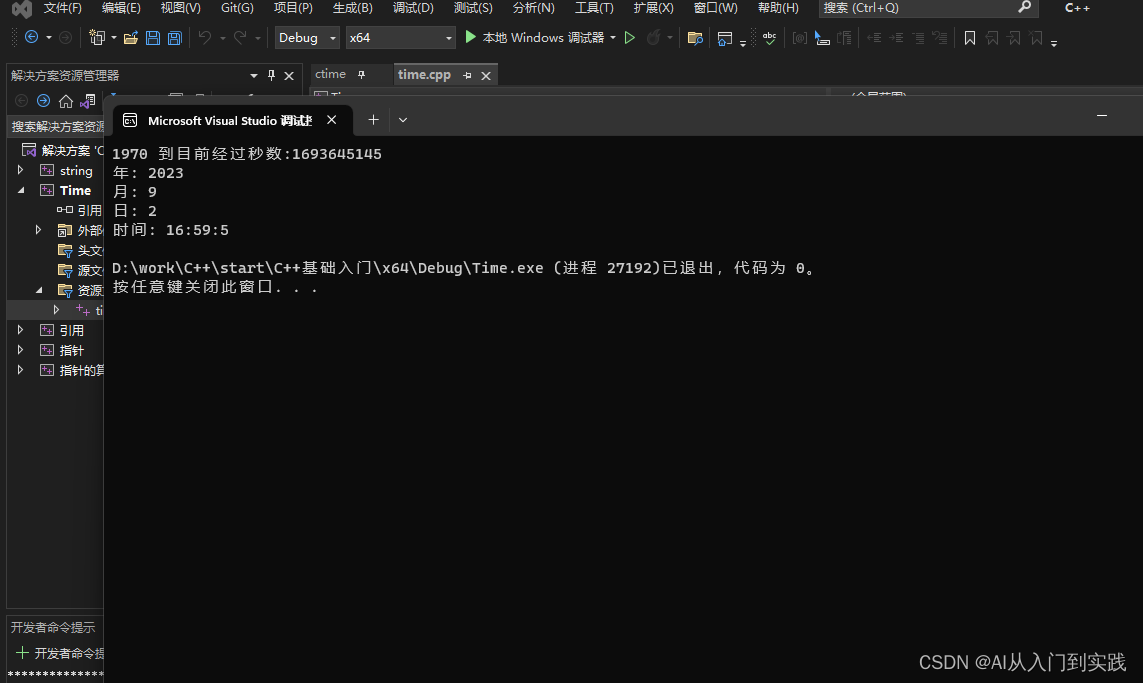
C++:输出系统时间(及报错处理)
#include <iostream> #include <ctime>using namespace std;int main() {// 基于当前系统的当前日期/时间time_t now time(0);cout << "1970 到目前经过秒数:" << now << endl;tm* ltm localtime(&now);// 输出 tm 结构的各个组…...
使用Windbg动态调试排查软件启动不了的问题
目录 1、问题说明 2、初步分析 3、使用Windbg启动程序进行动态调试 4、进一步分析 5、何时使用Windbg静态分析?何时使用Windbg进行动态调试? 6、最后 VC常用功能开发汇总(专栏文章列表,欢迎订阅,持续更新...&…...

Swift 技术 视频播放器滚动条(源码)
一直觉得自己写的不是技术,而是情怀,一个个的教程是自己这一路走来的痕迹。靠专业技能的成功是最具可复制性的,希望我的这条路能让你们少走弯路,希望我能帮你们抹去知识的蒙尘,希望我能帮你们理清知识的脉络࿰…...
PixelSNAIL论文代码学习(2)——门控残差网络的实现
文章目录 引言正文门控残差网络介绍门控残差网络具体实现代码使用pytorch实现 总结 引言 阅读了pixelSNAIL,很简短,就用了几页,介绍了网络结构,介绍了试验效果就没有了,具体论文学习链接 这段时间看他的代码,还是挺痛…...
---使用Pipeline Overridable Constants)
WebGPU学习(9)---使用Pipeline Overridable Constants
使用Pipeline Overridable Constants WebGPU 的着色器语言是 WGSL,但与 GLSL 和 HLSL 不同,不支持 #ifdef 等宏。为了实现各种着色器变体,迄今为止,宏一直是着色器编程中非常重要的功能。那么应该如何处理没有宏的 WGSLÿ…...
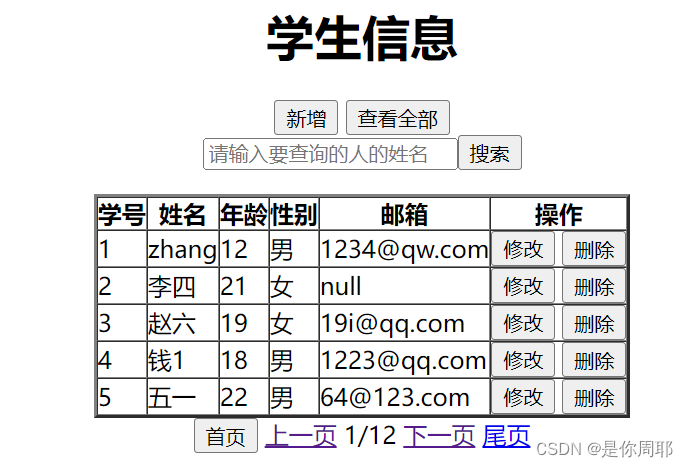
javaweb入门版学生信息管理系统-增删改查+JSP+Jstl+El
dao public class StudentDao {QueryRunner queryRunner QueryRunnerUtils.getQueryRunner();//查询全部学生信息public List<Student> selectStudent(){String sql "select * from tb_student";List<Student> students null;try {students queryRunn…...
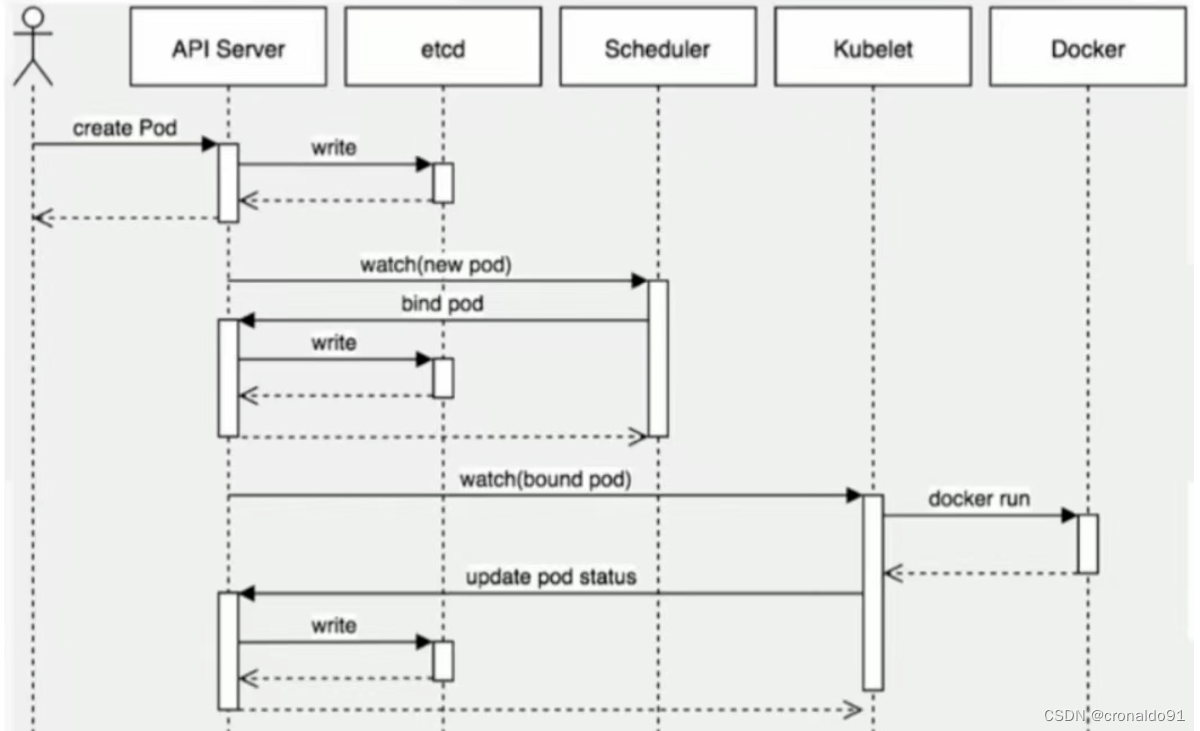
云原生Kubernetes:K8S概述
目录 一、理论 1.云原生 2.K8S 3.k8s集群架构与组件 二、总结 一、理论 1.云原生 (1)概念 云原生是一种基于容器、微服务和自动化运维的软件开发和部署方法。它可以使应用程序更加高效、可靠和可扩展,适用于各种不同的云平台。 如果…...
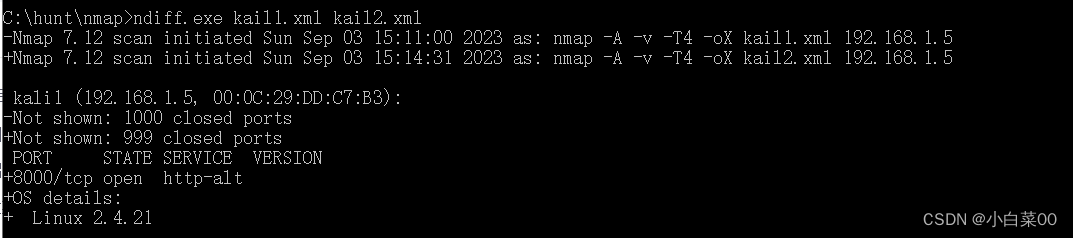
nmap的使用
目录 nmap简介 主要作用 nmap原理 namp使用 options nmap列举远程机器开放端口 普通扫描 扫描范围端口 对几个端口探测 对所有端口进行探测 指定协议探测端口 扫描对应协议的所有端口 端口状态 nmap识别目标机器上服务的指纹 服务指纹 识别目标机器服务信息 …...
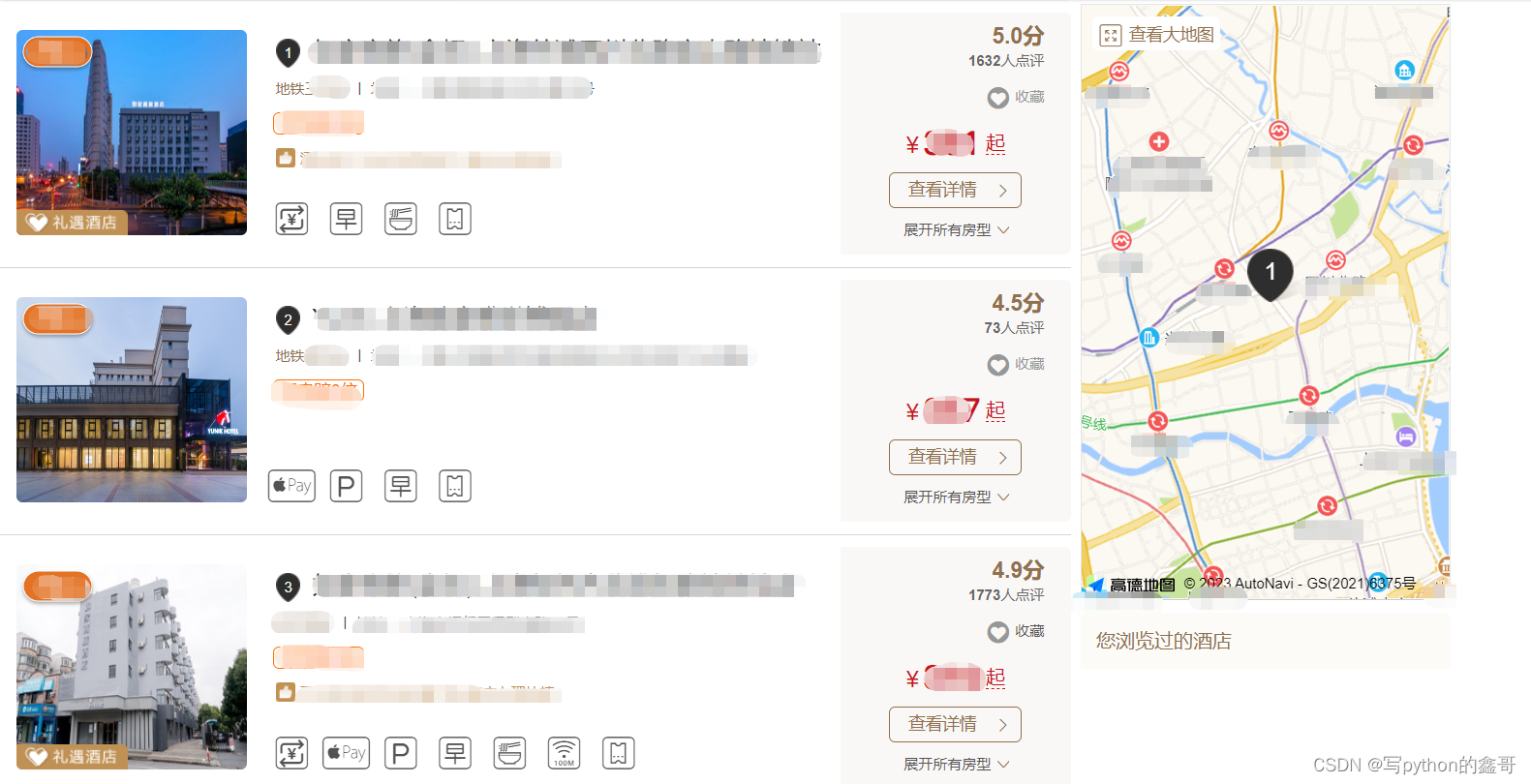
Python爬虫-某网酒店数据
前言 本文是该专栏的第5篇,后面会持续分享python爬虫案例干货,记得关注。 本文以某网的酒店数据为例,实现根据目标城市获取酒店数据。具体思路和方法跟着笔者直接往下看正文详细内容。(附带完整代码) 正文 地址:aHR0cHM6Ly93d3cuYnRoaG90ZWxzLmNvbS9saXN0L3NoYW5naGFp …...

了解atoi和offsetof
提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档 文章目录 目录 文章目录 一、简介 二、深度剖析 1.atoi 2.offsetof 三、应用场景 一、简介二、深度剖析 1.atoi2.offsetof三、应用场景 一、简介 在C语言中,有许多…...
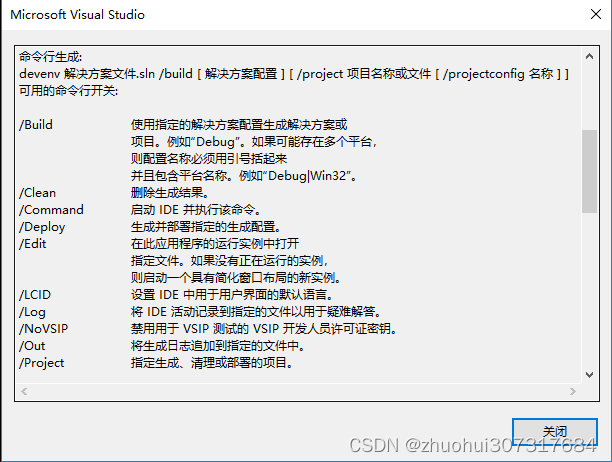
命令行编译VS工程
先输入以下命令,因为命令出错了,就会弹出帮助,如下: "C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio 11.0\Common7\IDE\devenv.exe" /help 反正就是Microsoft Visual Studio 的安装路径。 帮助界面如下:…...

Linux防火墙命令
开启防火墙 systemctl start firewalld关闭防火墙 systemctl stop firewalld # 暂时关闭防火墙 systemctl disable firewalld # 永久关闭防火墙(禁用开机自启) systemctl enable firewalld # 永久开启防火墙(启用开机自启)重启防火墙 systemctl restart firewalld重载规则 …...

大数据平台数据脱敏是什么意思?有哪些方案?
大数据平台包含了海量多样化数据,所以保障大数据平台数据安全非常重要,数据脱敏就是手段之一。今天我们就来简单聊聊大数据平台数据脱敏是什么意思?有哪些方案? 大数据平台数据脱敏是什么意思? 大数据平台数据脱敏简…...

前后端分离不存在会话,sessionid不一致问题
目录 1.使用拦截器解决跨域的示例: 2.使用redis,不使用session 前后端不分离项目我们可以通过session存储数据,但是前后端分离时不存在会话,每次请求sessionid都会改变,当值我们储存的数据不能取出来。 1.使用拦截器…...

Python 3+ 安装及pip配置
Python 3 安装及pip安装升级 1. 安装Python依赖2. 在Linux服务器下载3. 创建python链接4. 配置pip 服务器环境:Linux CentOS 7 内核版本3.10 Python版本:3.10.6 由于CentOS 7默认安装python2.7,使用yum可以查到最新的python3版本为3.6.8&…...

StarRocks入门到熟练
1、部署 1.1、注意事项 需要根据业务需求设计严谨的集群架构,一般来说,需要注意以下几项: 1.1.1、FE数量及高可用 FE的Follower要求为奇数个,且并不建议部署太多,通常我们推荐部署1个或3个Follower。在三个Followe…...

Zabbix Api监控项值推送:zabbix_sender
用法示例: zabbix_sender [-v] -z server [-p port] [-I IP-address] [-t timeout] -s host -k key -o value其中: -z 即 --zabbix-server,Zabbix server的主机名或IP地址。如果主机由proxy监控,则应使用proxy的主机名或IP地址-…...
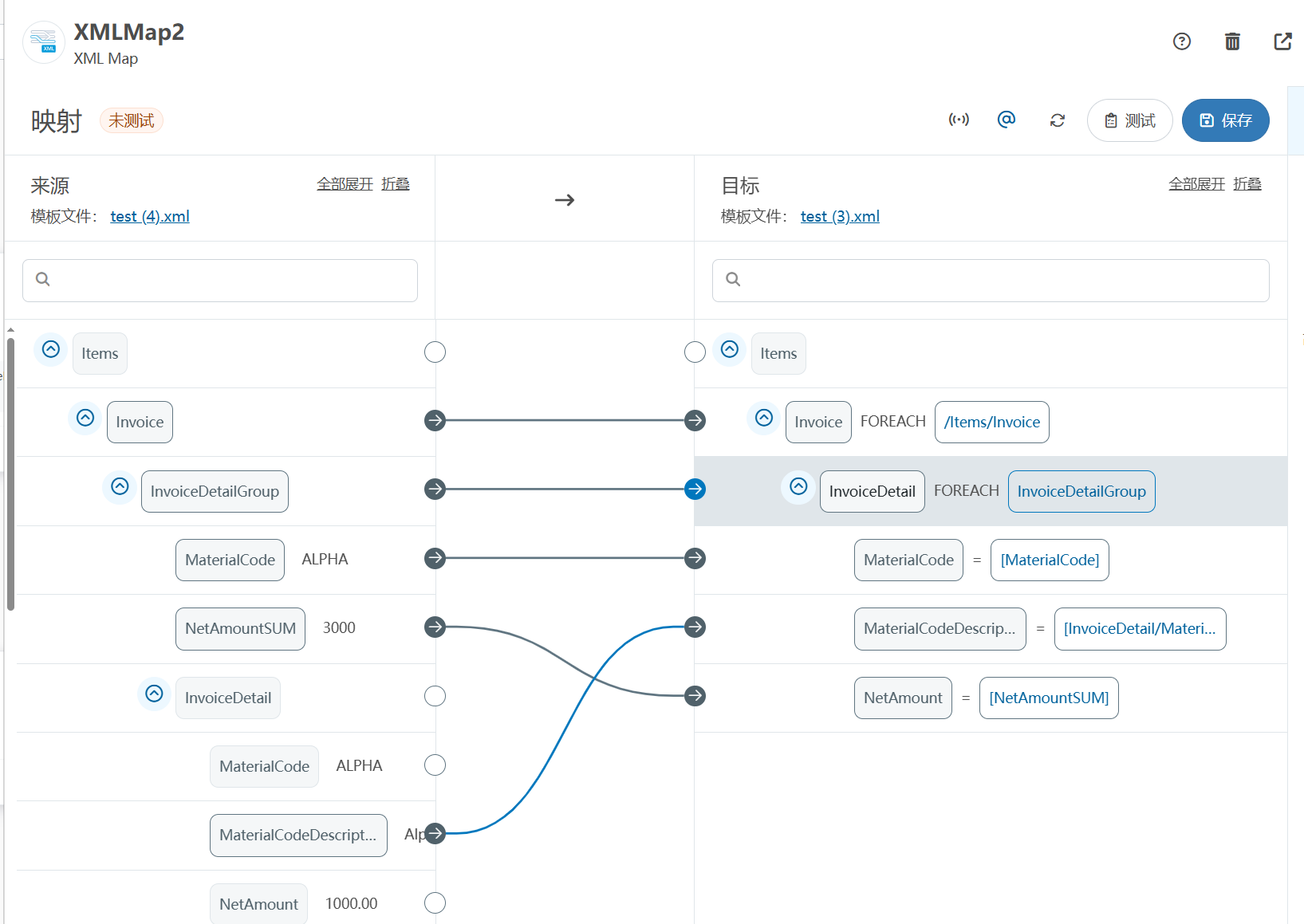
XML Group端口详解
在XML数据映射过程中,经常需要对数据进行分组聚合操作。例如,当处理包含多个物料明细的XML文件时,可能需要将相同物料号的明细归为一组,或对相同物料号的数量进行求和计算。传统实现方式通常需要编写脚本代码,增加了开…...
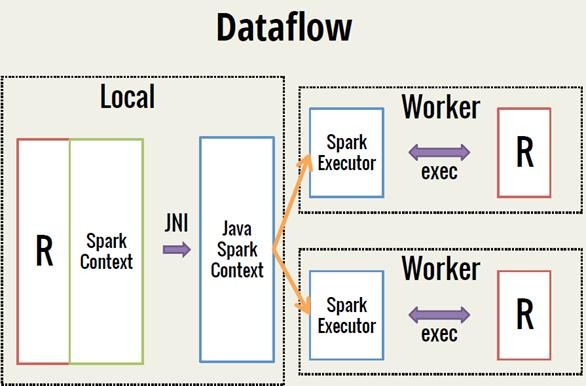
Spark 之 入门讲解详细版(1)
1、简介 1.1 Spark简介 Spark是加州大学伯克利分校AMP实验室(Algorithms, Machines, and People Lab)开发通用内存并行计算框架。Spark在2013年6月进入Apache成为孵化项目,8个月后成为Apache顶级项目,速度之快足见过人之处&…...
【力扣数据库知识手册笔记】索引
索引 索引的优缺点 优点1. 通过创建唯一性索引,可以保证数据库表中每一行数据的唯一性。2. 可以加快数据的检索速度(创建索引的主要原因)。3. 可以加速表和表之间的连接,实现数据的参考完整性。4. 可以在查询过程中,…...
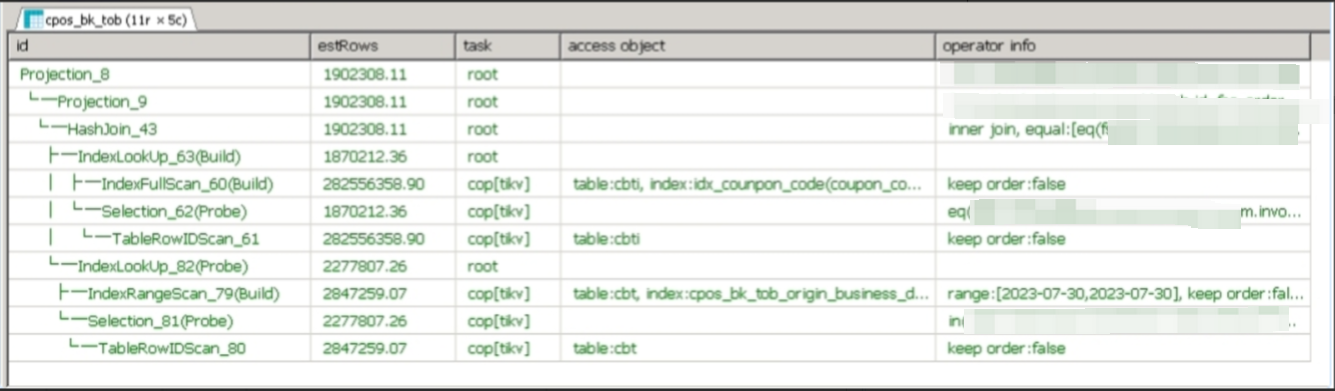
【入坑系列】TiDB 强制索引在不同库下不生效问题
文章目录 背景SQL 优化情况线上SQL运行情况分析怀疑1:执行计划绑定问题?尝试:SHOW WARNINGS 查看警告探索 TiDB 的 USE_INDEX 写法Hint 不生效问题排查解决参考背景 项目中使用 TiDB 数据库,并对 SQL 进行优化了,添加了强制索引。 UAT 环境已经生效,但 PROD 环境强制索…...
k8s业务程序联调工具-KtConnect
概述 原理 工具作用是建立了一个从本地到集群的单向VPN,根据VPN原理,打通两个内网必然需要借助一个公共中继节点,ktconnect工具巧妙的利用k8s原生的portforward能力,简化了建立连接的过程,apiserver间接起到了中继节…...

AI,如何重构理解、匹配与决策?
AI 时代,我们如何理解消费? 作者|王彬 封面|Unplash 人们通过信息理解世界。 曾几何时,PC 与移动互联网重塑了人们的购物路径:信息变得唾手可得,商品决策变得高度依赖内容。 但 AI 时代的来…...

Java求职者面试指南:Spring、Spring Boot、MyBatis框架与计算机基础问题解析
Java求职者面试指南:Spring、Spring Boot、MyBatis框架与计算机基础问题解析 一、第一轮提问(基础概念问题) 1. 请解释Spring框架的核心容器是什么?它在Spring中起到什么作用? Spring框架的核心容器是IoC容器&#…...
【笔记】WSL 中 Rust 安装与测试完整记录
#工作记录 WSL 中 Rust 安装与测试完整记录 1. 运行环境 系统:Ubuntu 24.04 LTS (WSL2)架构:x86_64 (GNU/Linux)Rust 版本:rustc 1.87.0 (2025-05-09)Cargo 版本:cargo 1.87.0 (2025-05-06) 2. 安装 Rust 2.1 使用 Rust 官方安…...
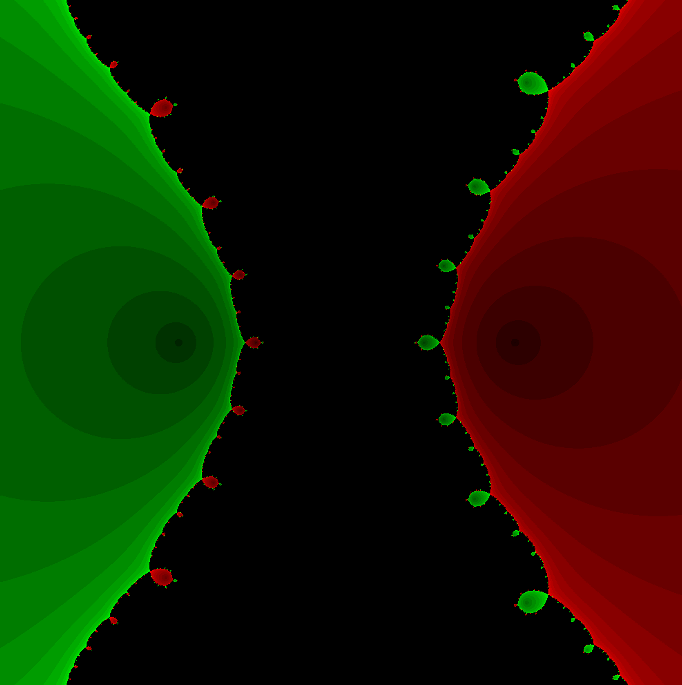
在Mathematica中实现Newton-Raphson迭代的收敛时间算法(一般三次多项式)
考察一般的三次多项式,以r为参数: p[z_, r_] : z^3 (r - 1) z - r; roots[r_] : z /. Solve[p[z, r] 0, z]; 此多项式的根为: 尽管看起来这个多项式是特殊的,其实一般的三次多项式都是可以通过线性变换化为这个形式…...

4. TypeScript 类型推断与类型组合
一、类型推断 (一) 什么是类型推断 TypeScript 的类型推断会根据变量、函数返回值、对象和数组的赋值和使用方式,自动确定它们的类型。 这一特性减少了显式类型注解的需要,在保持类型安全的同时简化了代码。通过分析上下文和初始值,TypeSc…...
