Fragment.OnPause的事情
我们知道Fragment的生命周期依附于相应Activity的生命周期,如果activity A调用了onPause,则A里面的fragment也会相应收到onPause回调,这里以support27.1.1版本的源码来说明Fragment生命周期onPause的事情。
当activity执行onPause时,进入如下的代码:
/*** Dispatch onPause() to fragments.*/@Overrideprotected void onPause() {super.onPause();mResumed = false;if (mHandler.hasMessages(MSG_RESUME_PENDING)) {mHandler.removeMessages(MSG_RESUME_PENDING);onResumeFragments();}mFragments.dispatchPause();//关注这里}mFragments.dispatchPause()这里进入到Fragment的生命周期分发流程中,mFragments其实是一个FragmentController对象,dispatchPause相应代码如下:
/*** Moves all Fragments managed by the controller's FragmentManager* into the pause state.* <p>Call when Fragments should be paused.** @see Fragment#onPause()*/public void dispatchPause() {mHost.mFragmentManager.dispatchPause();}这里也是简单的调用转发,进入到FragmentManager里面的dispatchPause方法,如下:
public void dispatchCreate() {mStateSaved = false;mStopped = false;dispatchStateChange(Fragment.CREATED);}public void dispatchActivityCreated() {mStateSaved = false;mStopped = false;dispatchStateChange(Fragment.ACTIVITY_CREATED);}public void dispatchStart() {mStateSaved = false;mStopped = false;dispatchStateChange(Fragment.STARTED);}public void dispatchResume() {mStateSaved = false;mStopped = false;dispatchStateChange(Fragment.RESUMED);}public void dispatchPause() {dispatchStateChange(Fragment.STARTED);}public void dispatchStop() {mStopped = true;dispatchStateChange(Fragment.STOPPED);}public void dispatchReallyStop() {dispatchStateChange(Fragment.ACTIVITY_CREATED);}public void dispatchDestroyView() {dispatchStateChange(Fragment.CREATED);}public void dispatchDestroy() {mDestroyed = true;execPendingActions();dispatchStateChange(Fragment.INITIALIZING);mHost = null;mContainer = null;mParent = null;}private void dispatchStateChange(int nextState) {try {mExecutingActions = true;moveToState(nextState, false);} finally {mExecutingActions = false;}execPendingActions();}这里有一堆的生命周期事件分发入口,说明Activity的相应生命周期事件都会分发到这里对应的方法;当前的onPause会进入dispatchPause方法,然后调用dispatchStateChange方法,注意调用参数为Fragment.STARTED(值为4),这里看看Fragment的几个状态定义如下:
static final int INITIALIZING = 0; // Not yet created.static final int CREATED = 1; // Created.static final int ACTIVITY_CREATED = 2; // The activity has finished its creation.static final int STOPPED = 3; // Fully created, not started.static final int STARTED = 4; // Created and started, not resumed.static final int RESUMED = 5; // Created started and resumed.int mState = INITIALIZING;接着进入moveToState方法,重点来了,即将进入Fragment的状态转换了,传递给moveToState的参数nextState为Fragment.STARTED(值为4),always为false,相应代码如下:
/*** Changes the state of the fragment manager to {@code newState}. If the fragment manager* changes state or {@code always} is {@code true}, any fragments within it have their* states updated as well.** @param newState The new state for the fragment manager* @param always If {@code true}, all fragments update their state, even* if {@code newState} matches the current fragment manager's state.*/void moveToState(int newState, boolean always) {if (mHost == null && newState != Fragment.INITIALIZING) {throw new IllegalStateException("No activity");}if (!always && newState == mCurState) {return;}mCurState = newState;//1关注这里if (mActive != null) {// Must add them in the proper order. mActive fragments may be out of orderfinal int numAdded = mAdded.size();for (int i = 0; i < numAdded; i++) {Fragment f = mAdded.get(i);moveFragmentToExpectedState(f);//2关注这里}// Now iterate through all active fragments. These will include those that are removed// and detached.final int numActive = mActive.size();for (int i = 0; i < numActive; i++) {Fragment f = mActive.valueAt(i);if (f != null && (f.mRemoving || f.mDetached) && !f.mIsNewlyAdded) {moveFragmentToExpectedState(f);}}startPendingDeferredFragments();if (mNeedMenuInvalidate && mHost != null && mCurState == Fragment.RESUMED) {mHost.onSupportInvalidateOptionsMenu();mNeedMenuInvalidate = false;}}}
moveToState中关注两点,首先是将状态newState保存到mCurState(为STARTED,4)中,其次遍历集合mAdded并调用moveFragmentToExpectedState改变相应fragment的生命周期状态。
mAdded:保存当前activity中已经添加的fragment实例。
moveFragmentToExpectedState代码如下:
/*** Moves a fragment to its expected final state or the fragment manager's state, depending* on whether the fragment manager's state is raised properly.** @param f The fragment to change.*/void moveFragmentToExpectedState(Fragment f) {if (f == null) {return;}int nextState = mCurState;if (f.mRemoving) {if (f.isInBackStack()) {nextState = Math.min(nextState, Fragment.CREATED);} else {nextState = Math.min(nextState, Fragment.INITIALIZING);}}//状态转换moveToState(f, nextState, f.getNextTransition(), f.getNextTransitionStyle(), false);if (f.mView != null) {// Move the view if it is out of orderFragment underFragment = findFragmentUnder(f);if (underFragment != null) {final View underView = underFragment.mView;// make sure this fragment is in the right order.final ViewGroup container = f.mContainer;int underIndex = container.indexOfChild(underView);int viewIndex = container.indexOfChild(f.mView);if (viewIndex < underIndex) {container.removeViewAt(viewIndex);container.addView(f.mView, underIndex);}}if (f.mIsNewlyAdded && f.mContainer != null) {// Make it visible and run the animationsif (f.mPostponedAlpha > 0f) {f.mView.setAlpha(f.mPostponedAlpha);}f.mPostponedAlpha = 0f;f.mIsNewlyAdded = false;// run animations:AnimationOrAnimator anim = loadAnimation(f, f.getNextTransition(), true,f.getNextTransitionStyle());if (anim != null) {setHWLayerAnimListenerIfAlpha(f.mView, anim);if (anim.animation != null) {f.mView.startAnimation(anim.animation);} else {anim.animator.setTarget(f.mView);anim.animator.start();}}}}if (f.mHiddenChanged) {completeShowHideFragment(f);}}
该方法主要调用moveToState执行Fragment状态转换,这里将执行真正的生命周期方法,代码如下:
@SuppressWarnings("ReferenceEquality")void moveToState(Fragment f, int newState, int transit, int transitionStyle,boolean keepActive) {// Fragments that are not currently added will sit in the onCreate() state.if ((!f.mAdded || f.mDetached) && newState > Fragment.CREATED) {newState = Fragment.CREATED;}if (f.mRemoving && newState > f.mState) {if (f.mState == Fragment.INITIALIZING && f.isInBackStack()) {// Allow the fragment to be created so that it can be saved later.newState = Fragment.CREATED;} else {// While removing a fragment, we can't change it to a higher state.newState = f.mState;}}// Defer start if requested; don't allow it to move to STARTED or higher// if it's not already started.if (f.mDeferStart && f.mState < Fragment.STARTED && newState > Fragment.STOPPED) {newState = Fragment.STOPPED;}if (f.mState <= newState) {// For fragments that are created from a layout, when restoring from// state we don't want to allow them to be created until they are// being reloaded from the layout.//该分支表示生命周期转换 create -> start -> resume} else if (f.mState > newState) {//该分支表示生命周期转换 pause -> stop -> destoryView -> destory -> detachswitch (f.mState) {case Fragment.RESUMED:if (newState < Fragment.RESUMED) {if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "movefrom RESUMED: " + f);f.performPause();dispatchOnFragmentPaused(f, false);}// fall throughcase Fragment.STARTED:if (newState < Fragment.STARTED) {if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "movefrom STARTED: " + f);f.performStop();dispatchOnFragmentStopped(f, false);}// fall throughcase Fragment.STOPPED:if (newState < Fragment.STOPPED) {if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "movefrom STOPPED: " + f);f.performReallyStop();}// fall throughcase Fragment.ACTIVITY_CREATED:if (newState < Fragment.ACTIVITY_CREATED) {if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "movefrom ACTIVITY_CREATED: " + f);if (f.mView != null) {// Need to save the current view state if not// done already.if (mHost.onShouldSaveFragmentState(f) && f.mSavedViewState == null) {saveFragmentViewState(f);}}f.performDestroyView();dispatchOnFragmentViewDestroyed(f, false);if (f.mView != null && f.mContainer != null) {// Stop any current animations:f.mContainer.endViewTransition(f.mView);f.mView.clearAnimation();AnimationOrAnimator anim = null;if (mCurState > Fragment.INITIALIZING && !mDestroyed&& f.mView.getVisibility() == View.VISIBLE&& f.mPostponedAlpha >= 0) {anim = loadAnimation(f, transit, false,transitionStyle);}f.mPostponedAlpha = 0;if (anim != null) {animateRemoveFragment(f, anim, newState);}f.mContainer.removeView(f.mView);}f.mContainer = null;f.mView = null;f.mInnerView = null;f.mInLayout = false;}// fall throughcase Fragment.CREATED:if (newState < Fragment.CREATED) {if (mDestroyed) {// The fragment's containing activity is// being destroyed, but this fragment is// currently animating away. Stop the// animation right now -- it is not needed,// and we can't wait any more on destroying// the fragment.if (f.getAnimatingAway() != null) {View v = f.getAnimatingAway();f.setAnimatingAway(null);v.clearAnimation();} else if (f.getAnimator() != null) {Animator animator = f.getAnimator();f.setAnimator(null);animator.cancel();}}if (f.getAnimatingAway() != null || f.getAnimator() != null) {// We are waiting for the fragment's view to finish// animating away. Just make a note of the state// the fragment now should move to once the animation// is done.f.setStateAfterAnimating(newState);newState = Fragment.CREATED;} else {if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "movefrom CREATED: " + f);if (!f.mRetaining) {f.performDestroy();dispatchOnFragmentDestroyed(f, false);} else {f.mState = Fragment.INITIALIZING;}f.performDetach();dispatchOnFragmentDetached(f, false);if (!keepActive) {if (!f.mRetaining) {makeInactive(f);} else {f.mHost = null;f.mParentFragment = null;f.mFragmentManager = null;}}}}}}if (f.mState != newState) {Log.w(TAG, "moveToState: Fragment state for " + f + " not updated inline; "+ "expected state " + newState + " found " + f.mState);f.mState = newState;}}
moveToState包含两大分支逻辑,分别是创建与销毁,由于我们这里分析的是onPause,所以创建的分支省略了,这里newState值为Fragment.STARTED,f.mSate为Fragment.RESUMED,因此进入到Fragment.RESUMED对应的销毁分支,即执行如下代码:
case Fragment.RESUMED:if (newState < Fragment.RESUMED) {if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "movefrom RESUMED: " + f);f.performPause();dispatchOnFragmentPaused(f, false);}由于newState为Fragment.STARTED,其值为4小于Fragment.RESUMED(5),因此调用f.performPause,代码如下:
void performPause() {mLifecycleRegistry.handleLifecycleEvent(Lifecycle.Event.ON_PAUSE);if (mChildFragmentManager != null) {mChildFragmentManager.dispatchPause();}mState = STARTED;mCalled = false;onPause();if (!mCalled) {throw new SuperNotCalledException("Fragment " + this+ " did not call through to super.onPause()");}}这里首先处理了生命周期变化handleLifecycleEvent,然后如果当前fragment还有子fragment的话,子fragment的生命周期会通过mChildFragmentManager.dispatchPause()来分发,这里还将当前fragment的mState变量赋值为STARTED(4),最后调用生命周期方法onPause,到这里算是走完了onPause的生命周期流程,为了逻辑的完整性,我们继续分析。
上一步继续调用dispatchOnFragmentPaused方法,代码如下:
void dispatchOnFragmentPaused(Fragment f, boolean onlyRecursive) {if (mParent != null) {FragmentManager parentManager = mParent.getFragmentManager();if (parentManager instanceof FragmentManagerImpl) {((FragmentManagerImpl) parentManager).dispatchOnFragmentPaused(f, true);}}for (Pair<FragmentLifecycleCallbacks, Boolean> p : mLifecycleCallbacks) {if (!onlyRecursive || p.second) {p.first.onFragmentPaused(this, f);}}}首先判断有没有父fragment,有的话同样进行生命周期分发,其次遍历mLifecycleCallbacks并进行生命周期分发,这里的mLifecycleCallbacks其实是我们通过activity的FragmentManager调用registerFragmentLifecycleCallbacks方法注册的生命周期回调函数。
不难看出,onPause对应的Fragment.RESUMED分支,其实只是处理生命周期相关的回调而已。
onPause分支总结:
1 处理mLifecycleRegistry中的回调。
2 通过mChildFragmentManager.dispatchPause()分发其子fragment的生命周期回调。
3 调用onPause执行自己的生命周期方法(同时mState = STARTED)。
4 如果有父framnet,则分发父frament的生命周期回调。
5 执行保存在mLifecycleCallbacks中的生命周期回调(比如LeakCanary的内存泄漏判断就是此时触发的)。
onPause执行完成,注意到moveToState中的分支都不带break,因此会继续执行到下一分支,代码如下:
case Fragment.RESUMED:if (newState < Fragment.RESUMED) {if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "movefrom RESUMED: " + f);f.performPause();dispatchOnFragmentPaused(f, false);}// fall throughcase Fragment.STARTED://执行到这里if (newState < Fragment.STARTED) {if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "movefrom STARTED: " + f);f.performStop();dispatchOnFragmentStopped(f, false);}// fall throughcase Fragment.STOPPED:if (newState < Fragment.STOPPED) {if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "movefrom STOPPED: " + f);f.performReallyStop();}穿透到Fragment.STARTED这里,但是注意这里的代码执行时有条件的,此时newState=Fragment.STARTED,条件不满足因此不会继续执行分支的代码,之后的分支也不满足条件,因此最后跳出整个大的switch块。
自此Fragment的onPause生命周期切换完成。
执行完onPause之后,Fragment的生命周期状态mState为Fragment.STARTED。
相关文章:

Fragment.OnPause的事情
我们知道Fragment的生命周期依附于相应Activity的生命周期,如果activity A调用了onPause,则A里面的fragment也会相应收到onPause回调,这里以support27.1.1版本的源码来说明Fragment生命周期onPause的事情。 当activity执行onPause时ÿ…...
【C++基础】5. 变量作用域
文章目录 【 1. 局部变量 】【 2. 全局变量 】【 3. 局部变量和全局变量的初始化 】 作用域是程序的一个区域,一般来说有三个地方可以定义变量: 在函数或一个代码块内部声明的变量,称为局部变量。 在函数参数的定义中声明的变量,称…...
Python列表排序
介绍一个关于列表排序的sort方法,看下面的案例: """ 列表的sort方法来对列表进行自定义排序 """# 准备列表 my_list [["a", 33], ["b", 55], ["c", 11]]# 排序,基于带名函数 …...
(云HIS)云医院管理系统源码 SaaS模式 B/S架构 基于云计算技术
通过提供“一个中心多个医院”平台,为集团连锁化的医院和区域医疗提供最前沿的医疗信息化云解决方案。 一、概述 云HIS系统源码是一款满足基层医院各类业务需要的健康云产品。该系统能帮助基层医院完成日常各类业务,提供病患预约挂号支持、收费管理、病…...

sql:SQL优化知识点记录(十一)
(1)用Show Profile进行sql分析 新的一个优化的方式show Profile 运行一些查询sql: 查看一下我们执行过的sql 显示sql查询声明周期完整的过程: 当执行过程出现了下面这4个中的时,就会有问题导致效率慢 8这个sql创建…...

leetcode-链表类题目
文章目录 链表(Linked List) 链表(Linked List) 定义:链表(Linked List)是一种线性表数据结构,他用一组任意的存储单元来存储数据,同时存储当前数据元素的直接后继元素所…...

数据结构——哈希
哈希表 是一种使用哈希函数组织数据的数据结构,它支持快速插入和搜索。 哈希表(又称散列表)的原理为:借助 哈希函数,将键映射到存储桶地址。更确切地说, 1.首先开辟一定长度的,具有连续物理地址…...

效果好的it监控系统特点
一个好的IT监控系统应该具备以下特点: 全面性:IT监控系统应该能够监视和管理IT系统的所有方面,包括网络、服务器、应用程序和数据库等。这样可以确保系统的各个方面都得到充分的监视和管理。 可靠性:IT监控系统需要保持高可…...

leetcode1288. 删除被覆盖区间(java)
删除被覆盖区间 题目描述贪心法代码演示 题目描述 难度 - 中等 leetcode1288. 删除被覆盖区间 给你一个区间列表,请你删除列表中被其他区间所覆盖的区间。 只有当 c < a 且 b < d 时,我们才认为区间 [a,b) 被区间 [c,d) 覆盖。 在完成所有删除操作…...

Python 虚拟环境相关命令
一 激活 在 cd venv/scripts 进入虚拟环境 执行命令 activate 1、创建虚拟环境 $ python -m venv 2、激活虚拟环境 $ source <venv>/bin/activate 3、关闭虚拟环境 $ deactivate...

使用U盘同步WSL2中的git项目
1、将U盘挂载到WSL2中 假设U盘在windows资源管理器中被识别为F盘,需要在WSL2中创建一个目录挂载U盘 sudo mkdir /mnt/f sudo mount -t drvfs F: /mnt/f后续所有的操作都完成后,拔掉U盘前,可以使用下面的命令从WSL2中安全的移除U盘 umount …...
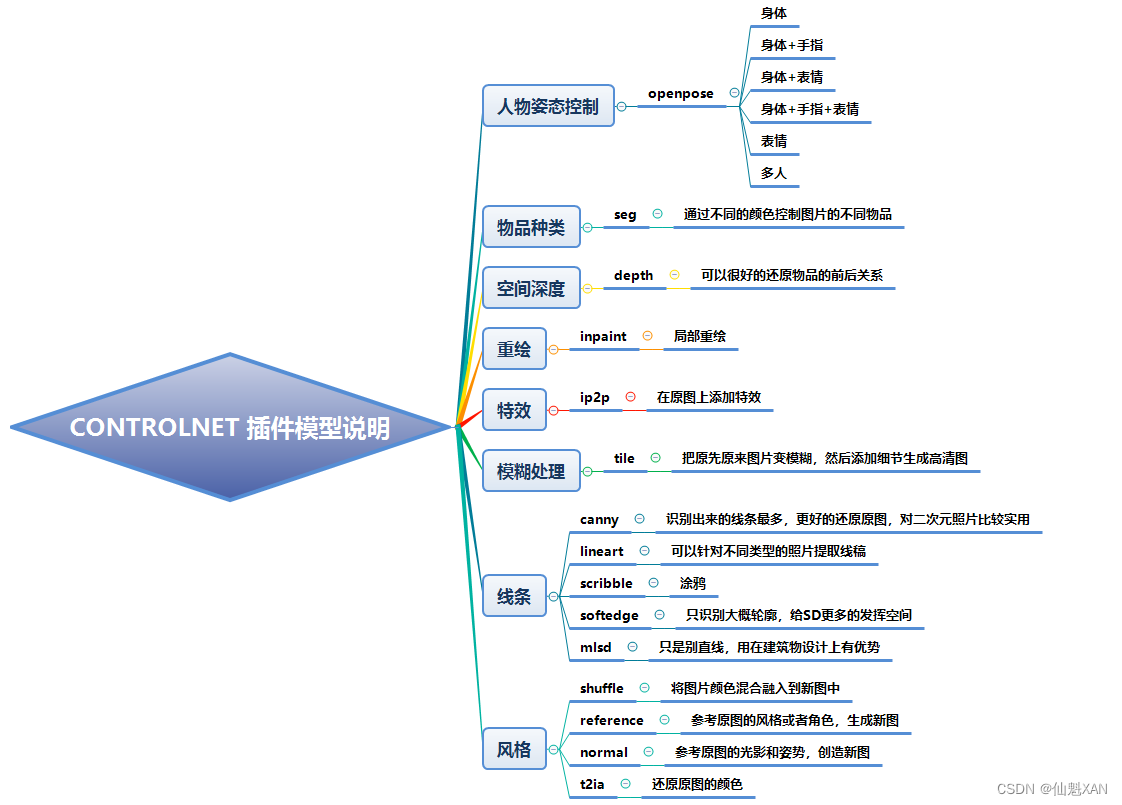
Stable Diffuse AI 绘画 之 ControlNet 插件及其对应模型的下载安装
Stable Diffuse AI 绘画 之 ControlNet 插件及其对应模型的下载安装 目录 Stable Diffuse AI 绘画 之 ControlNet 插件及其对应模型的下载安装 一、简单介绍 二、ControlNet 插件下载安装 三、ControlNet 插件模型下载安装 四、ControlNet 插件其他的下载安装方式 五、Co…...
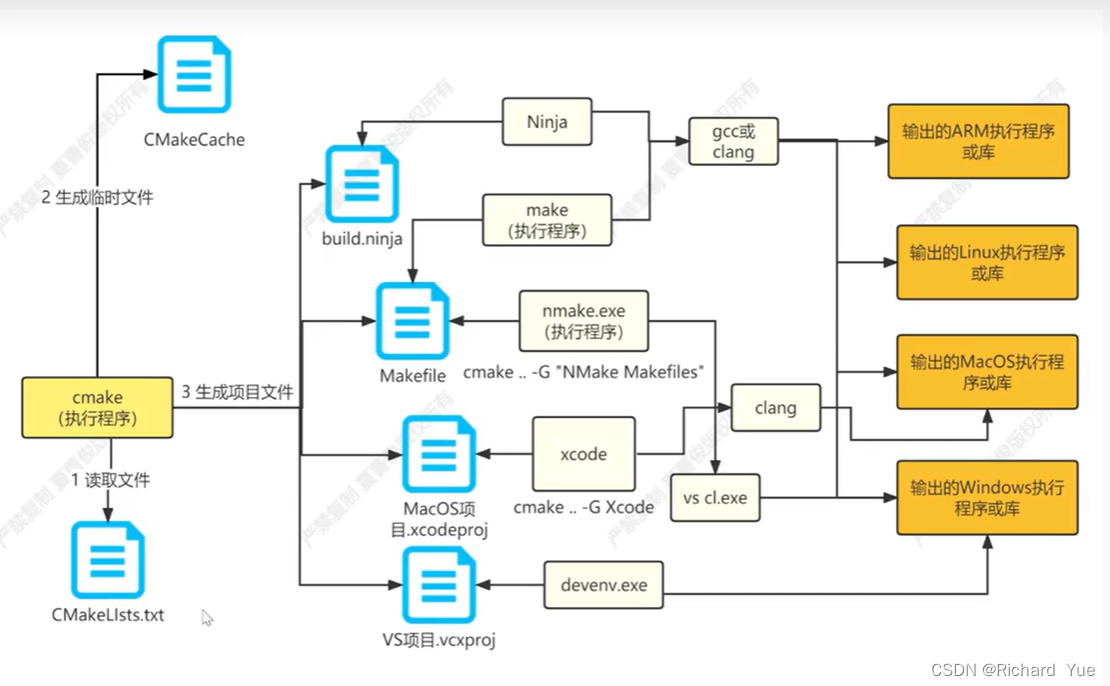
CMAK学习
VS中的cmake_cmake vs_今天也要debug的博客-CSDN博客 利用vs2017 CMake开发跨平台C项目实战_cmake vs2017_神气爱哥的博客-CSDN博客 【【入门】在VS中使用CMake管理若干程序】https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1iz4y117rZ?vd_source0aeb782d0b9c2e6b0e0cdea3e2121eba...

Python 推导式
Python 推导式 Python 推导式是一种独特的数据处理方式,可以从一个数据序列构建另一个新的数据序列的结构体。 Python 支持各种数据结构的推导式: 列表(list)推导式字典(dict)推导式集合(set)推导式元组(tuple)推导式 列表推导式 列表推导式格式为&…...

es6的新特性有哪些
ES6(ECMAScript 2015)是JavaScript的一个重要版本,引入了许多新的语法和功能。以下是ES6的一些主要特性: 块级作用域(Block Scope):引入了let和const关键字,可以在块级作用域中声明变…...

logstash 消费kafka数据,转发到tcp端口
1, logstash 配置文件 [roothost1: ] cat /opt/logstash/kafka-to-tcp.yml input { kafka {bootstrap_servers > "192.168.0.11:9092" #这里可以是kafka集群,如"192.168.149.101:9092,192.168.149.102:9092"consumer_threads &…...

航天智信:严控航天系统研发安全,助力建设“航天强国”
航天智信作为中国航天科工三院在信息装备领域“做大做强”的重要布局,主要从事系统运用与联合体系研究,复杂信息系统的顶层设计、总体论证及研制生产,提供体系级、系统级信息系统整体解决方案,以及信息安全系统的设计研发与集成验…...
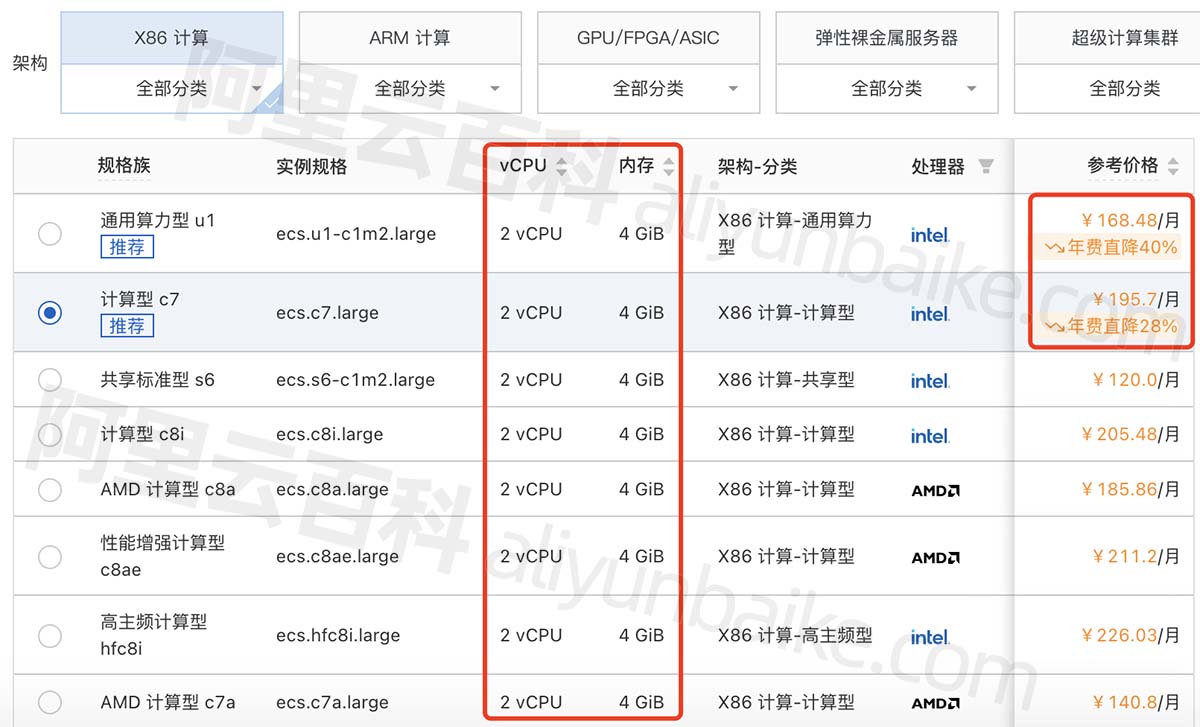
阿里云2核4G服务器5M带宽五年租用价格表
阿里云2核4G服务器5M带宽可以选择轻量应用服务器或云服务器ECS,轻量2核4G4M带宽服务器297元一年,2核4G云服务器ECS可以选择计算型c7、c6或通用算力型u1实例等,买5年可以享受3折优惠,阿腾云分享阿里云服务器2核4G5M带宽五年费用表&…...

基于Laravel通用型内容建站企业官网系统源码 可免费商用
是一个基于 Laravel 企业内容建站系统。模块市场拥有丰富的功能应用,支持后台一键快速安装,让开发者能快的实现业务功能开发。 系统完全开源,免费且不限制商业使用 2023年08月23日增加了以下12个特性: [新功能] 手机端Banner支持…...

风力发电常见问题
目录 叶片失速 风力发电机失速状态是指风力发电机的叶片在高风速下无法继续提供升力,导致叶片停止旋转或减速旋转,从而降低了风力发电机的效率和发电能力。判断风力发电机是否处于失速状态通常可以通过以下方法: 监测风速:最简单…...

KubeSphere 容器平台高可用:环境搭建与可视化操作指南
Linux_k8s篇 欢迎来到Linux的世界,看笔记好好学多敲多打,每个人都是大神! 题目:KubeSphere 容器平台高可用:环境搭建与可视化操作指南 版本号: 1.0,0 作者: 老王要学习 日期: 2025.06.05 适用环境: Ubuntu22 文档说…...

Vue记事本应用实现教程
文章目录 1. 项目介绍2. 开发环境准备3. 设计应用界面4. 创建Vue实例和数据模型5. 实现记事本功能5.1 添加新记事项5.2 删除记事项5.3 清空所有记事 6. 添加样式7. 功能扩展:显示创建时间8. 功能扩展:记事项搜索9. 完整代码10. Vue知识点解析10.1 数据绑…...
家政维修平台实战20:权限设计
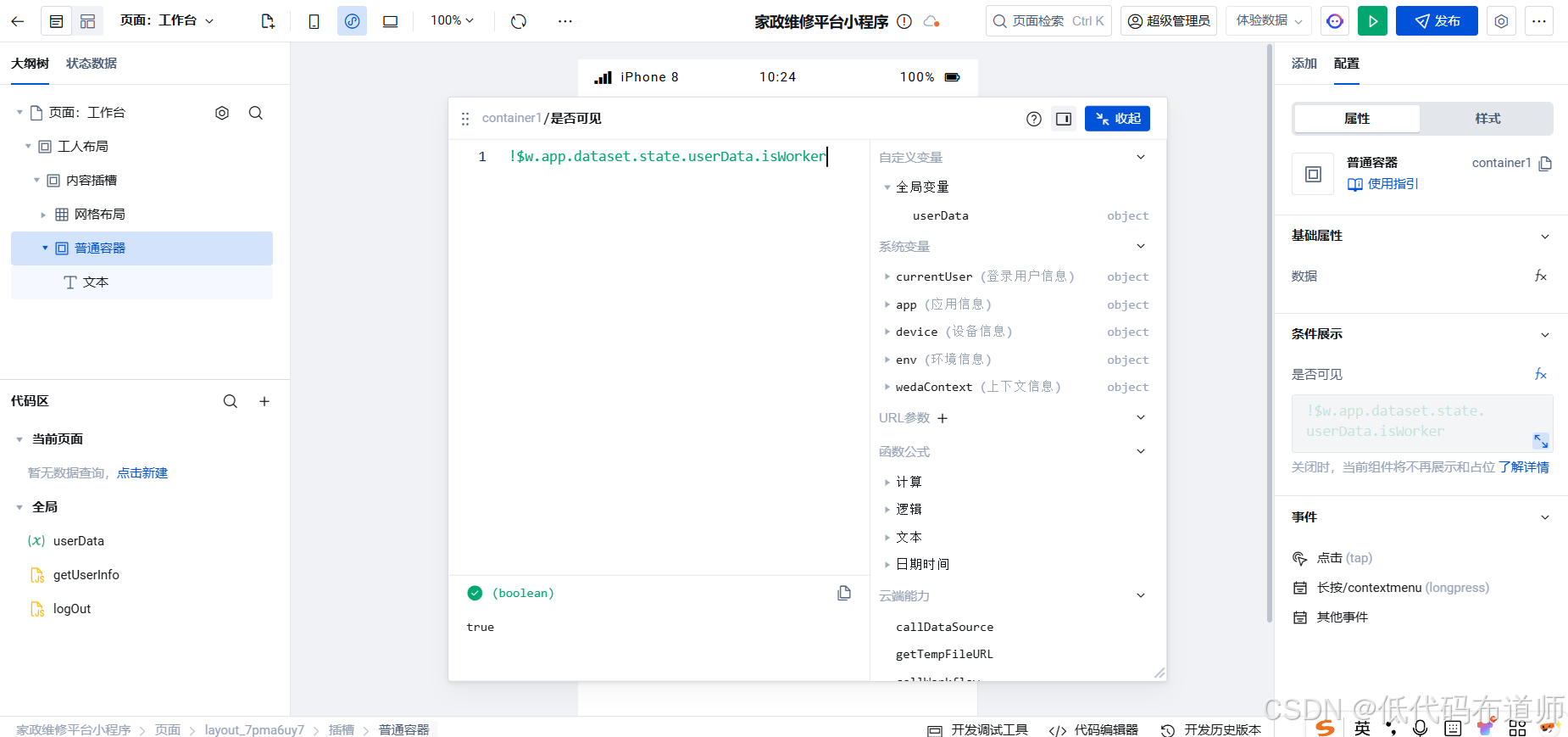
目录 1 获取工人信息2 搭建工人入口3 权限判断总结 目前我们已经搭建好了基础的用户体系,主要是分成几个表,用户表我们是记录用户的基础信息,包括手机、昵称、头像。而工人和员工各有各的表。那么就有一个问题,不同的角色…...
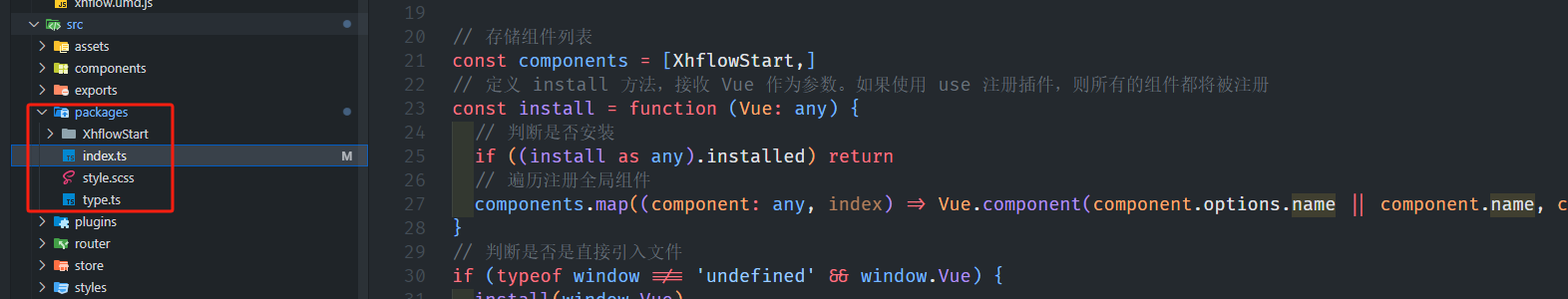
基于当前项目通过npm包形式暴露公共组件
1.package.sjon文件配置 其中xh-flowable就是暴露出去的npm包名 2.创建tpyes文件夹,并新增内容 3.创建package文件夹...

Qt Http Server模块功能及架构
Qt Http Server 是 Qt 6.0 中引入的一个新模块,它提供了一个轻量级的 HTTP 服务器实现,主要用于构建基于 HTTP 的应用程序和服务。 功能介绍: 主要功能 HTTP服务器功能: 支持 HTTP/1.1 协议 简单的请求/响应处理模型 支持 GET…...

UR 协作机器人「三剑客」:精密轻量担当(UR7e)、全能协作主力(UR12e)、重型任务专家(UR15)
UR协作机器人正以其卓越性能在现代制造业自动化中扮演重要角色。UR7e、UR12e和UR15通过创新技术和精准设计满足了不同行业的多样化需求。其中,UR15以其速度、精度及人工智能准备能力成为自动化领域的重要突破。UR7e和UR12e则在负载规格和市场定位上不断优化…...
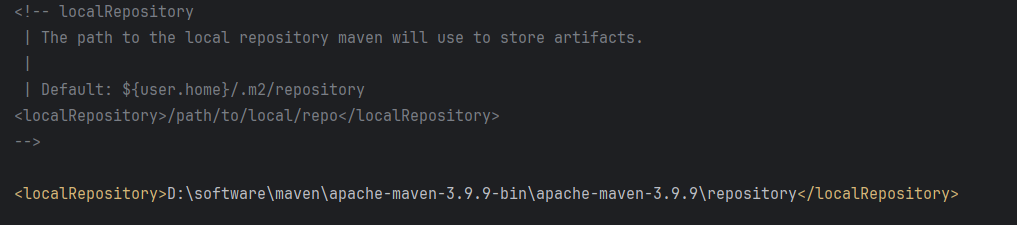
Maven 概述、安装、配置、仓库、私服详解
目录 1、Maven 概述 1.1 Maven 的定义 1.2 Maven 解决的问题 1.3 Maven 的核心特性与优势 2、Maven 安装 2.1 下载 Maven 2.2 安装配置 Maven 2.3 测试安装 2.4 修改 Maven 本地仓库的默认路径 3、Maven 配置 3.1 配置本地仓库 3.2 配置 JDK 3.3 IDEA 配置本地 Ma…...

rnn判断string中第一次出现a的下标
# coding:utf8 import torch import torch.nn as nn import numpy as np import random import json""" 基于pytorch的网络编写 实现一个RNN网络完成多分类任务 判断字符 a 第一次出现在字符串中的位置 """class TorchModel(nn.Module):def __in…...

基于Java Swing的电子通讯录设计与实现:附系统托盘功能代码详解
JAVASQL电子通讯录带系统托盘 一、系统概述 本电子通讯录系统采用Java Swing开发桌面应用,结合SQLite数据库实现联系人管理功能,并集成系统托盘功能提升用户体验。系统支持联系人的增删改查、分组管理、搜索过滤等功能,同时可以最小化到系统…...

数学建模-滑翔伞伞翼面积的设计,运动状态计算和优化 !
我们考虑滑翔伞的伞翼面积设计问题以及运动状态描述。滑翔伞的性能主要取决于伞翼面积、气动特性以及飞行员的重量。我们的目标是建立数学模型来描述滑翔伞的运动状态,并优化伞翼面积的设计。 一、问题分析 滑翔伞在飞行过程中受到重力、升力和阻力的作用。升力和阻力与伞翼面…...
