Linux进程与线程的内核实现
进程描述符task_struct
- 进程描述符(struct task_struct)
- pid与tgid
- 进程id编号分配规则
- 内存管理mm_struct
- 进程与文件,文件系统
进程,线程创建的本质
- clone函数原型
- 线程创建的实现
- 进程创建的实现
总结
进程描述符task_struct
进程描述符(struct task_struct)
task_struct称为进程描述符结构,该结构定义在<include/linux/sched.h>文件中。进程描述符中包含一个具体进程的所有信息
进程描述符中包含的数据能完整地描述一个正在执行的程序:它打开的文件,进程的地址空间,挂起的信号,进程的状态等
struct task_struct {volatile long state; /* -1 unrunnable, 0 runnable, >0 stopped */void *stack;atomic_t usage;unsigned int flags; /* per process flags, defined below */unsigned int ptrace;#ifdef CONFIG_SMPstruct llist_node wake_entry;int on_cpu;
#endifint on_rq;int prio, static_prio, normal_prio;unsigned int rt_priority;const struct sched_class *sched_class;struct sched_entity se;struct sched_rt_entity rt;
#ifdef CONFIG_CGROUP_SCHEDstruct task_group *sched_task_group;
#endif#ifdef CONFIG_PREEMPT_NOTIFIERS/* list of struct preempt_notifier: */struct hlist_head preempt_notifiers;
#endif/** fpu_counter contains the number of consecutive context switches* that the FPU is used. If this is over a threshold, the lazy fpu* saving becomes unlazy to save the trap. This is an unsigned char* so that after 256 times the counter wraps and the behavior turns* lazy again; this to deal with bursty apps that only use FPU for* a short time*/unsigned char fpu_counter;
#ifdef CONFIG_BLK_DEV_IO_TRACEunsigned int btrace_seq;
#endifunsigned int policy;cpumask_t cpus_allowed;#ifdef CONFIG_PREEMPT_RCUint rcu_read_lock_nesting;char rcu_read_unlock_special;struct list_head rcu_node_entry;
#endif /* #ifdef CONFIG_PREEMPT_RCU */
#ifdef CONFIG_TREE_PREEMPT_RCUstruct rcu_node *rcu_blocked_node;
#endif /* #ifdef CONFIG_TREE_PREEMPT_RCU */
#ifdef CONFIG_RCU_BOOSTstruct rt_mutex *rcu_boost_mutex;
#endif /* #ifdef CONFIG_RCU_BOOST */#if defined(CONFIG_SCHEDSTATS) || defined(CONFIG_TASK_DELAY_ACCT)struct sched_info sched_info;
#endifstruct list_head tasks;
#ifdef CONFIG_SMPstruct plist_node pushable_tasks;
#endifstruct mm_struct *mm, *active_mm;
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT_BRKunsigned brk_randomized:1;
#endif
#if defined(SPLIT_RSS_COUNTING)struct task_rss_stat rss_stat;
#endif
/* task state */int exit_state;int exit_code, exit_signal;int pdeath_signal; /* The signal sent when the parent dies */unsigned int jobctl; /* JOBCTL_*, siglock protected *//* ??? */unsigned int personality;unsigned did_exec:1;unsigned in_execve:1; /* Tell the LSMs that the process is doing an* execve */unsigned in_iowait:1;/* Revert to default priority/policy when forking */unsigned sched_reset_on_fork:1;unsigned sched_contributes_to_load:1;#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_HARDIRQS/* IRQ handler threads */unsigned irq_thread:1;
#endifpid_t pid;pid_t tgid;#ifdef CONFIG_CC_STACKPROTECTOR/* Canary value for the -fstack-protector gcc feature */unsigned long stack_canary;
#endif/* * pointers to (original) parent process, youngest child, younger sibling,* older sibling, respectively. (p->father can be replaced with * p->real_parent->pid)*/struct task_struct __rcu *real_parent; /* real parent process */struct task_struct __rcu *parent; /* recipient of SIGCHLD, wait4() reports *//** children/sibling forms the list of my natural children*/struct list_head children; /* list of my children */struct list_head sibling; /* linkage in my parent's children list */struct task_struct *group_leader; /* threadgroup leader *//** ptraced is the list of tasks this task is using ptrace on.* This includes both natural children and PTRACE_ATTACH targets.* p->ptrace_entry is p's link on the p->parent->ptraced list.*/struct list_head ptraced;struct list_head ptrace_entry;/* PID/PID hash table linkage. */struct pid_link pids[PIDTYPE_MAX];struct list_head thread_group;struct completion *vfork_done; /* for vfork() */int __user *set_child_tid; /* CLONE_CHILD_SETTID */int __user *clear_child_tid; /* CLONE_CHILD_CLEARTID */cputime_t utime, stime, utimescaled, stimescaled;cputime_t gtime;
#ifndef CONFIG_VIRT_CPU_ACCOUNTINGcputime_t prev_utime, prev_stime;
#endifunsigned long nvcsw, nivcsw; /* context switch counts */struct timespec start_time; /* monotonic time */struct timespec real_start_time; /* boot based time */
/* mm fault and swap info: this can arguably be seen as either mm-specific or thread-specific */unsigned long min_flt, maj_flt;struct task_cputime cputime_expires;struct list_head cpu_timers[3];/* process credentials */const struct cred __rcu *real_cred; /* objective and real subjective task* credentials (COW) */const struct cred __rcu *cred; /* effective (overridable) subjective task* credentials (COW) */struct cred *replacement_session_keyring; /* for KEYCTL_SESSION_TO_PARENT */char comm[TASK_COMM_LEN]; /* executable name excluding path- access with [gs]et_task_comm (which lockit with task_lock())- initialized normally by setup_new_exec */
/* file system info */int link_count, total_link_count;
#ifdef CONFIG_SYSVIPC
/* ipc stuff */struct sysv_sem sysvsem;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_DETECT_HUNG_TASK
/* hung task detection */unsigned long last_switch_count;
#endif
/* CPU-specific state of this task */struct thread_struct thread;
/* filesystem information */struct fs_struct *fs;
/* open file information */struct files_struct *files;
/* namespaces */struct nsproxy *nsproxy;
/* signal handlers */struct signal_struct *signal;struct sighand_struct *sighand;sigset_t blocked, real_blocked;sigset_t saved_sigmask; /* restored if set_restore_sigmask() was used */struct sigpending pending;unsigned long sas_ss_sp;size_t sas_ss_size;int (*notifier)(void *priv);void *notifier_data;sigset_t *notifier_mask;struct audit_context *audit_context;
#ifdef CONFIG_AUDITSYSCALLuid_t loginuid;unsigned int sessionid;
#endifseccomp_t seccomp;/* Thread group tracking */u32 parent_exec_id;u32 self_exec_id;
/* Protection of (de-)allocation: mm, files, fs, tty, keyrings, mems_allowed,* mempolicy */spinlock_t alloc_lock;/* Protection of the PI data structures: */raw_spinlock_t pi_lock;#ifdef CONFIG_RT_MUTEXES/* PI waiters blocked on a rt_mutex held by this task */struct plist_head pi_waiters;/* Deadlock detection and priority inheritance handling */struct rt_mutex_waiter *pi_blocked_on;
#endif#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_MUTEXES/* mutex deadlock detection */struct mutex_waiter *blocked_on;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_TRACE_IRQFLAGSunsigned int irq_events;unsigned long hardirq_enable_ip;unsigned long hardirq_disable_ip;unsigned int hardirq_enable_event;unsigned int hardirq_disable_event;int hardirqs_enabled;int hardirq_context;unsigned long softirq_disable_ip;unsigned long softirq_enable_ip;unsigned int softirq_disable_event;unsigned int softirq_enable_event;int softirqs_enabled;int softirq_context;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_LOCKDEP
# define MAX_LOCK_DEPTH 48ULu64 curr_chain_key;int lockdep_depth;unsigned int lockdep_recursion;struct held_lock held_locks[MAX_LOCK_DEPTH];gfp_t lockdep_reclaim_gfp;
#endif/* journalling filesystem info */void *journal_info;/* stacked block device info */struct bio_list *bio_list;#ifdef CONFIG_BLOCK
/* stack plugging */struct blk_plug *plug;
#endif/* VM state */struct reclaim_state *reclaim_state;struct backing_dev_info *backing_dev_info;struct io_context *io_context;unsigned long ptrace_message;siginfo_t *last_siginfo; /* For ptrace use. */struct task_io_accounting ioac;
#if defined(CONFIG_TASK_XACCT)u64 acct_rss_mem1; /* accumulated rss usage */u64 acct_vm_mem1; /* accumulated virtual memory usage */cputime_t acct_timexpd; /* stime + utime since last update */
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_CPUSETSnodemask_t mems_allowed; /* Protected by alloc_lock */seqcount_t mems_allowed_seq; /* Seqence no to catch updates */int cpuset_mem_spread_rotor;int cpuset_slab_spread_rotor;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_CGROUPS/* Control Group info protected by css_set_lock */struct css_set __rcu *cgroups;/* cg_list protected by css_set_lock and tsk->alloc_lock */struct list_head cg_list;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_FUTEXstruct robust_list_head __user *robust_list;
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPATstruct compat_robust_list_head __user *compat_robust_list;
#endifstruct list_head pi_state_list;struct futex_pi_state *pi_state_cache;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PERF_EVENTSstruct perf_event_context *perf_event_ctxp[perf_nr_task_contexts];struct mutex perf_event_mutex;struct list_head perf_event_list;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_NUMAstruct mempolicy *mempolicy; /* Protected by alloc_lock */short il_next;short pref_node_fork;
#endifstruct rcu_head rcu;/** cache last used pipe for splice*/struct pipe_inode_info *splice_pipe;
#ifdef CONFIG_TASK_DELAY_ACCTstruct task_delay_info *delays;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_FAULT_INJECTIONint make_it_fail;
#endif/** when (nr_dirtied >= nr_dirtied_pause), it's time to call* balance_dirty_pages() for some dirty throttling pause*/int nr_dirtied;int nr_dirtied_pause;unsigned long dirty_paused_when; /* start of a write-and-pause period */#ifdef CONFIG_LATENCYTOPint latency_record_count;struct latency_record latency_record[LT_SAVECOUNT];
#endif/** time slack values; these are used to round up poll() and* select() etc timeout values. These are in nanoseconds.*/unsigned long timer_slack_ns;unsigned long default_timer_slack_ns;struct list_head *scm_work_list;
#ifdef CONFIG_FUNCTION_GRAPH_TRACER/* Index of current stored address in ret_stack */int curr_ret_stack;/* Stack of return addresses for return function tracing */struct ftrace_ret_stack *ret_stack;/* time stamp for last schedule */unsigned long long ftrace_timestamp;/** Number of functions that haven't been traced* because of depth overrun.*/atomic_t trace_overrun;/* Pause for the tracing */atomic_t tracing_graph_pause;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_TRACING/* state flags for use by tracers */unsigned long trace;/* bitmask and counter of trace recursion */unsigned long trace_recursion;
#endif /* CONFIG_TRACING */
#ifdef CONFIG_CGROUP_MEM_RES_CTLR /* memcg uses this to do batch job */struct memcg_batch_info {int do_batch; /* incremented when batch uncharge started */struct mem_cgroup *memcg; /* target memcg of uncharge */unsigned long nr_pages; /* uncharged usage */unsigned long memsw_nr_pages; /* uncharged mem+swap usage */} memcg_batch;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_HAVE_HW_BREAKPOINTatomic_t ptrace_bp_refcnt;
#endif
};pid与tgid

tgid全名thread group ID,一个内部有多线程的进程,进程中每个线程的id都不一样,但是对外表现出同一个进程整体
struct task_struct{pid_t pid;//进程的唯一标识pid_t tgid;// 线程组的领头线程的pid成员的值
};
进程id编号分配规则
Linux 内核限制进程号需小于等于 32767。新进程创建时,内核会按顺序将下一个可用的进程号分配给其使用。每当进程号达到 32767 的限制时,内核将重置进程号计数器,以便从小整数开始分配。
一旦进程号达到 32767,会将进程号计数器重置为 300,而不是 1。之所以如此,是因为低数值的进程号为系统进程和守护进程所长期占用,在此范围内搜索尚未使用的进程号只会是浪费时间。
内存管理mm_struct
struct task_struct{struct mm_struct* mm;
}
每个进程都有自己独立的虚拟地址空间,使用mm_struct结构体来管理内存,这里的mm指针指向了mm_struct结构体,包含了内存资源的页表,内存映射等
struct mm_struct{struct vm_area_struct* mmap;struct re_root mm_rb;//...pgd_t* pgd; }
进程与文件,文件系统
task_struct与文件相关的字段最常用的下面这两个
struct task_struct{//文件系统的信息的指针,包含了进程运行的目录信息struct fs_struct* fs;//打开的文件描述符资源表struct files_struct* files;
}
进程,线程创建的本质
fork()和pthread_create()函数最后都会进入clone()系统调用
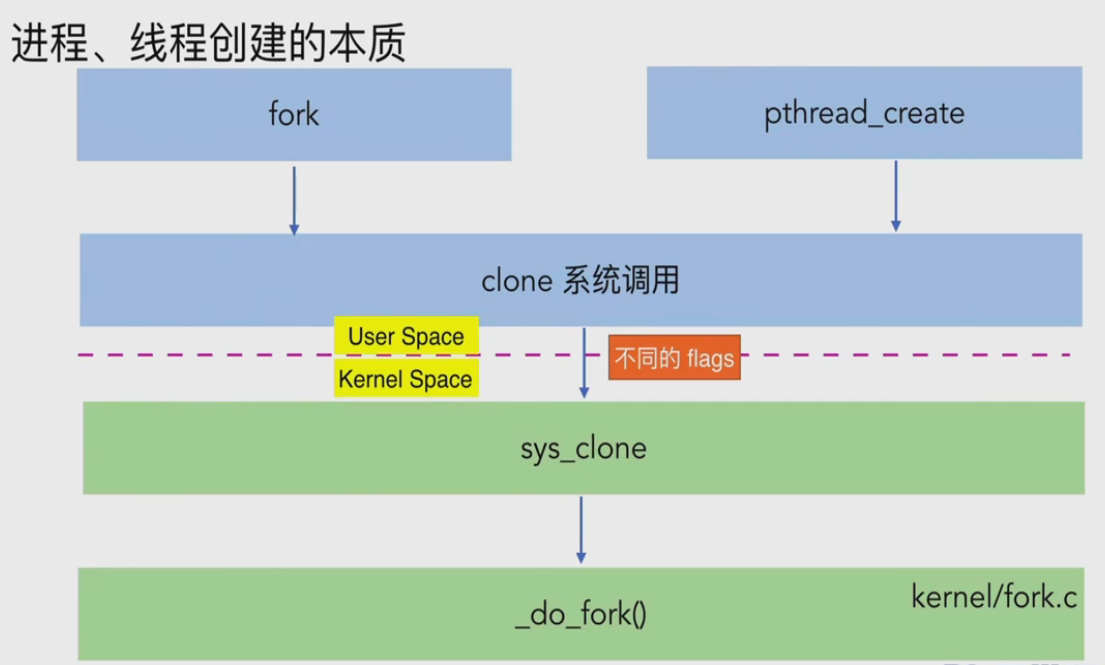
clone函数原型
- fn:表示clone生成的子进程的起始调用函数,参数由第四个参数arg指定
- stack:表示生成的子进程的栈空间
- flags:关键参数,用于区分生成的子进程与父进程如何共享资源(内存,打开文件描述符等)
- 剩下的参数与线程实现有关
int clone(int (*fn)(void *), void *stack, int flags, void *arg, .../* pid_t *parent_tid, void *tls, pid_t *child_tid */ );
线程创建的实现pthread_create()
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>void* run(void* arg){}int main()
{pthread_t t1;pthread_create(&t1, 0, &run, 0);pthread_join(t1, 0);return 0;
}
此时clone系统调用的flags=CLONE_VM | CLONE_FS | CLONE_FILES | CLONE_SIGHAND | CLONE_THREAD | …
| 标志 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| CLONE_VM | 共享虚拟内存 |
| CLONE_FS | 共享文件与系统相关的属性 |
| CLONE_FILES | 共享打开的文件描述符 |
| CLONE_SIGHAND | 共享对信号的处置 |
| CLONE_THREAD | 置于父进程所属的线程组中 |
进程创建的实现fork()
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>int main()
{pid_t pid;pid = fork();if(pid == 0){//此处是子进程的代码分支}else if(pid > 0){//此处是父进程的代码分支}return 0;
}
此时clone系统调用的flags=CLONE_SIGCHLD | …
本质:不共享资源,使用cow,任何一个修改都会造成分裂
| 标志 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| CLONE_SIGCHLD | 接收子进程退出的信号 |
总结
- fork()和pthread_create()创建进程或者线程都会调用clone()系统调用
- pthread_create()调用clone()时传入的flags参数会设置共享虚拟内存,共享文件与系统相关的属性,共享打开的文件描述符,共享对信号的处置,置于父进程所属的线程组中
- fork()调用clone()时传入的flags参数只会设置接收子进程退出的信号
- 在内核态中没有进程和线程的概念,内核不会区分进程和线程的操作
相关文章:

Linux进程与线程的内核实现
进程描述符task_struct 进程描述符(struct task_struct)pid与tgid进程id编号分配规则内存管理mm_struct进程与文件,文件系统 进程,线程创建的本质 clone函数原型线程创建的实现进程创建的实现 总结 进程描述符task_struct 进程描述符(st…...
Flink转换算子(Transformation))
Flink学习之旅:(四)Flink转换算子(Transformation)
1.基本转换算子 基本转换算子说明映射(map)将数据流中的数据进行转换,形成新的数据流过滤(filter)将数据流中的数据根据条件过滤扁平映射(flatMap)将数据流中的整体(如:集…...
CesiumJS 中绘制大多边形
本文翻译自Cesium官方,有改动。 本文中提及到的“大多边形”就如下图所示。 在Cesium的早期版本和一些引擎中,我们绘制这种跨度比较大的多边形,经常会看到一些奇怪的冲突问题,如下图所示。 要渲染任何几何体,我们必…...

FreeRTOS移植以及任务
FreeRTOS移植 1.在sys.h中需要把SYSTEM_SUPPORT_OS 改为 1,支持我们使用 FreeRTOS //0,不支持 os //1,支持 os #define SYSTEM_SUPPORT_OS 1 //定义系统文件夹是否支持 OS2.出现报错 …\SYSTEM\usart\usart.c(6): error: #5: cannot open source input file “incl…...
)
笙默考试管理系统-MyExamTest----codemirror(41)
笙默考试管理系统-MyExamTest----codemirror(40) 目录 一、 笙默考试管理系统-MyExamTest 二、 笙默考试管理系统-MyExamTest 三、 笙默考试管理系统-MyExamTest 四、 笙默考试管理系统-MyExamTest 五、 笙默考试管理系统-MyExamTest 笙默考试…...

C#数据结构--数组和ArrayList
目录 本章目录: 2.1 数组基本概念 2.1.1 数组的声明和初始化 2.1.2 数组元素的设置和存取访问 2.1.4 多维数组 2.1.5 参数数组 2.2ArrayList 类 2.2.1ArrayList 类的成员 2.2.2 应用 ArrayList 类 数组和ArrayList之间的区别以及使用的场景 数组…...

Stable Diffusion WebUI扩展adetailer安装及功能介绍
ADetailer是Stable Diffusion WebUI的一个扩展,类似于检测细节器。 目录 安装地址 如何安装 1. Windows系统 (1)手动安装 (2)一体机...

Linux安装MINIO
MINIO简介MINIO目录 mkdir -p /opt/minio/data && cd /opt/minio MINIO下载 wget https://dl.minio.org.cn/server/minio/release/linux-amd64/minio MINIO授权 chmod x minio MINIO端口 firewall-cmd --zonepublic --add-port7171/tcp --permanent && firewal…...

Java架构师分布式搜索架构
目录 1 导学1.1 初识Elasticsearch1.1.1 Elasticsearch的作用1.1.2 ELK技术栈1.1.3 Elasticsearch和lucene1.1.4.为什么不是其他搜索技术?1.1.5.总结2 Elasticsearch快速建立知识体系3 Elasticsearch和MySQL实体建立联系3.1.mapping映射属性3.2 数据分组聚合3.2.1.聚合的种类3…...
简单宿舍管理系统(springboot+vue)
简单宿舍管理系统(springbootvue) 1.创建项目1.前端2.数据库3.后端 2.登陆1.前端1.准备工作2.登陆组件3.配置 2.后端1.链接数据库2.创建用户实体类3.数据操作持久层1.配置2.内容3.测试 4.中间业务层1.异常2.业务实现3.测试 5.响应前端控制层 3.前后对接4…...

Socks5代理、IP代理的关键作用
Socks5代理与SK5代理:网络安全的卫士 Socks5代理作为一项先进的代理协议,其多协议支持、身份验证功能以及UDP支持使其成为网络安全的重要支持者。 IP代理:隐私保护与无限访问的利器 IP代理技术通过隐藏真实IP地址,保护用户隐私…...

前端 CSS 经典:box-shadow
1. 基础属性 /* box-shadow: h-shadow v-shadow blur spread color inset; */ box-shadow: 10px 10px 2px 2px red inset; h-shadow: 必填,水平阴影的位置,允许负值 v-shadow: 必填,垂直阴影的位置,允许负值 blur: 可选ÿ…...

使用数组方法打印出 1 - 10000 之间的所有对称数。例如:121、1331等
(我从别的人那复制的,原文章请点击此处) 源代码: function getNum (start, end) {var arr [];for(var i start; i < end; i) {if (i.toString() i.toString().split().reverse().join() && i.toString().length &…...
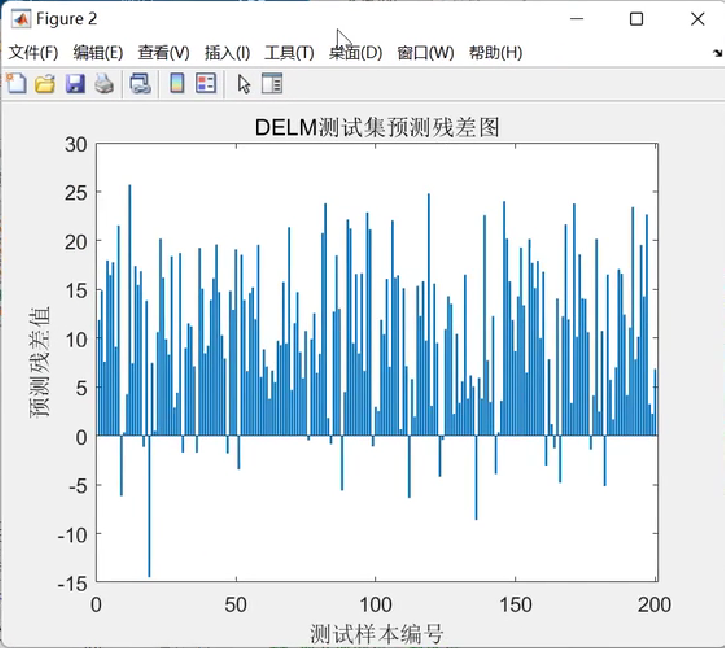
DELM深度极限学习机回归预测研究(Matlab代码实现)
💥💥💞💞欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️💥💥 🏆博主优势:🌞🌞🌞博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。 ⛳️座右铭&a…...

Spark大数据分析与实战笔记(第一章 Scala语言基础-5)
文章目录 每日一句正能量章节概要1.5 Scala的模式匹配与样例类1.5.1 模式匹配字符匹配匹配字符串守卫匹配类型匹配数组、元组、集合 1.5.2 样例类 课外补充偏函数 每日一句正能量 “成功的秘诀,在于对目标的执着追求。”——爱迪生 无论是在工作、学习、还是生活中&…...

shell学习脚本04(小滴课堂)
他就可以直接读出来了。不需要在sh后面加参数。 可以用-s隐藏内容: 可以用-t进行指定几秒后显示。 -n限制内容长度。 输入到长度为5自动打印。 我们把-s放到-p后面的话: 这样会出错。 如果最后加5m会一直闪烁。 大家可以按照需求自行使用。...
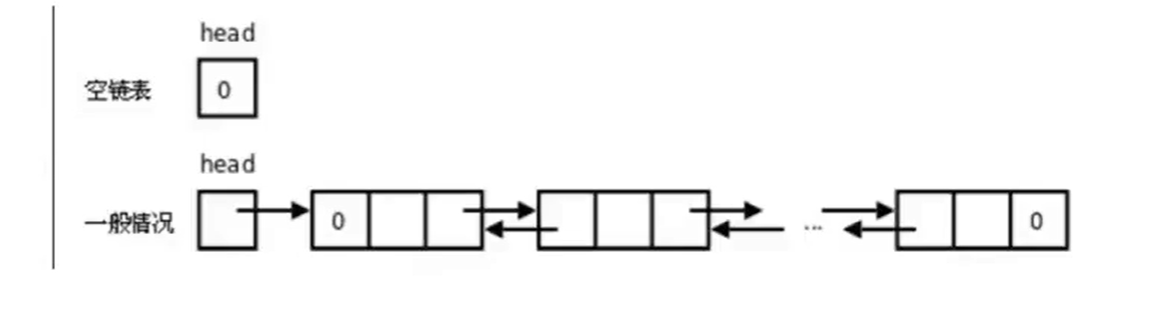
Python数据结构(链表)
Python数据结构(链表) 单向链表 单向链表也叫单链表,是链表中最简单的一种形式,它的每个节点包含两个域,一个信息域(元素域)和一个链接域。这个链接指向链表中的下一个节点,而最后一个节点的链接域则指向…...
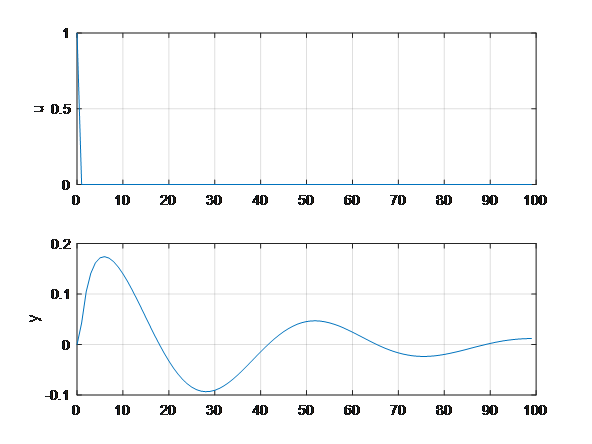
连续/离散的控制系统阶跃测试(包括MATLAB里的step()函数)
阶跃测试 只要是连续时间系统,无论是传递函数还是连续状态空间形式的模型,直接可以用**step()**做阶跃测试;但是对于离散系统而言,不能用step()函数,可以自行编写代码,如下。 1、离散系统:x(k…...
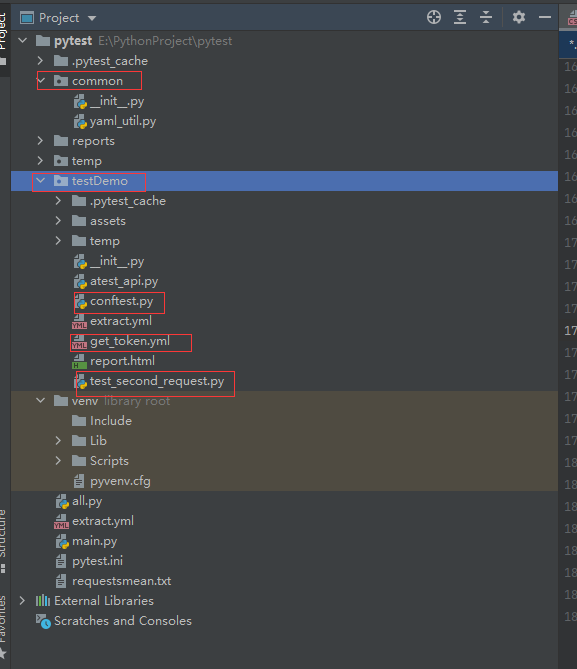
【六:pytest框架介绍】
常见的请求对象requests.get()requests.post()requests.delete()requests.put()requests.request()常见的响应对象reprequests.request()//返回字符串格式数据print(req.text)//返回字节格式数据print(req.content)//返回字典格式数据print(req.json)#状态码print(req.status_c…...
提升医院安全的关键利器——医院安全(不良)事件报告系统源码
医院是人们寻求医疗服务和康复的场所,安全是医院运营的基石。然而,医疗过程中不可避免地会出现不良事件,如药物错误、手术事故等。为了及时发现、评估和解决这些问题,医院安全(不良)事件报告系统应运而生。…...
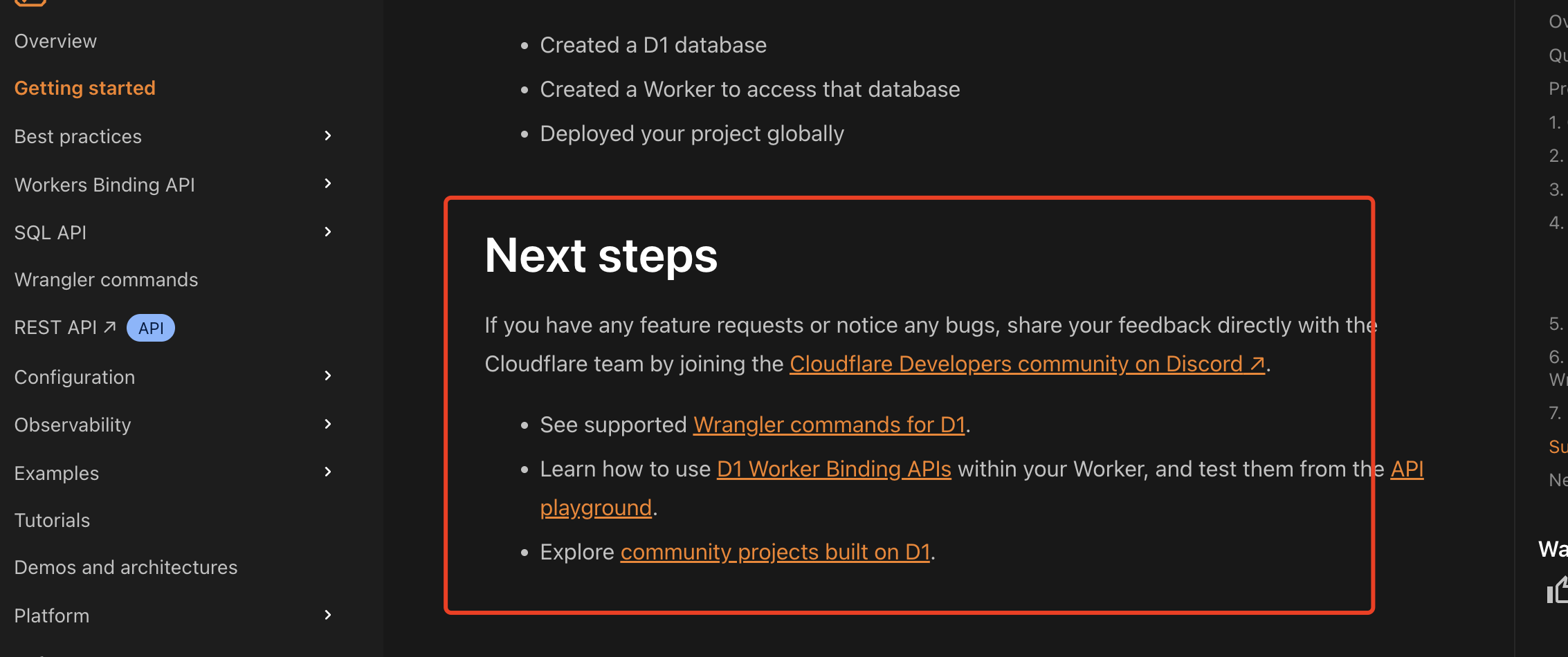
通过Wrangler CLI在worker中创建数据库和表
官方使用文档:Getting started Cloudflare D1 docs 创建数据库 在命令行中执行完成之后,会在本地和远程创建数据库: npx wranglerlatest d1 create prod-d1-tutorial 在cf中就可以看到数据库: 现在,您的Cloudfla…...
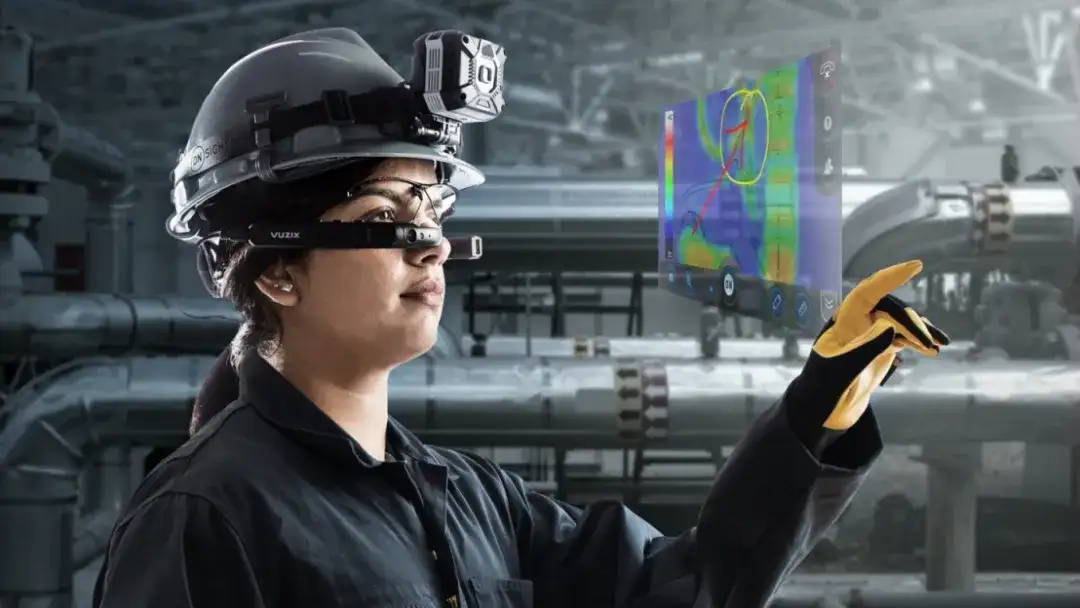

安宝特方案丨XRSOP人员作业标准化管理平台:AR智慧点检验收套件
在选煤厂、化工厂、钢铁厂等过程生产型企业,其生产设备的运行效率和非计划停机对工业制造效益有较大影响。 随着企业自动化和智能化建设的推进,需提前预防假检、错检、漏检,推动智慧生产运维系统数据的流动和现场赋能应用。同时,…...

深入理解JavaScript设计模式之单例模式
目录 什么是单例模式为什么需要单例模式常见应用场景包括 单例模式实现透明单例模式实现不透明单例模式用代理实现单例模式javaScript中的单例模式使用命名空间使用闭包封装私有变量 惰性单例通用的惰性单例 结语 什么是单例模式 单例模式(Singleton Pattern&#…...

React Native在HarmonyOS 5.0阅读类应用开发中的实践
一、技术选型背景 随着HarmonyOS 5.0对Web兼容层的增强,React Native作为跨平台框架可通过重新编译ArkTS组件实现85%以上的代码复用率。阅读类应用具有UI复杂度低、数据流清晰的特点。 二、核心实现方案 1. 环境配置 (1)使用React Native…...
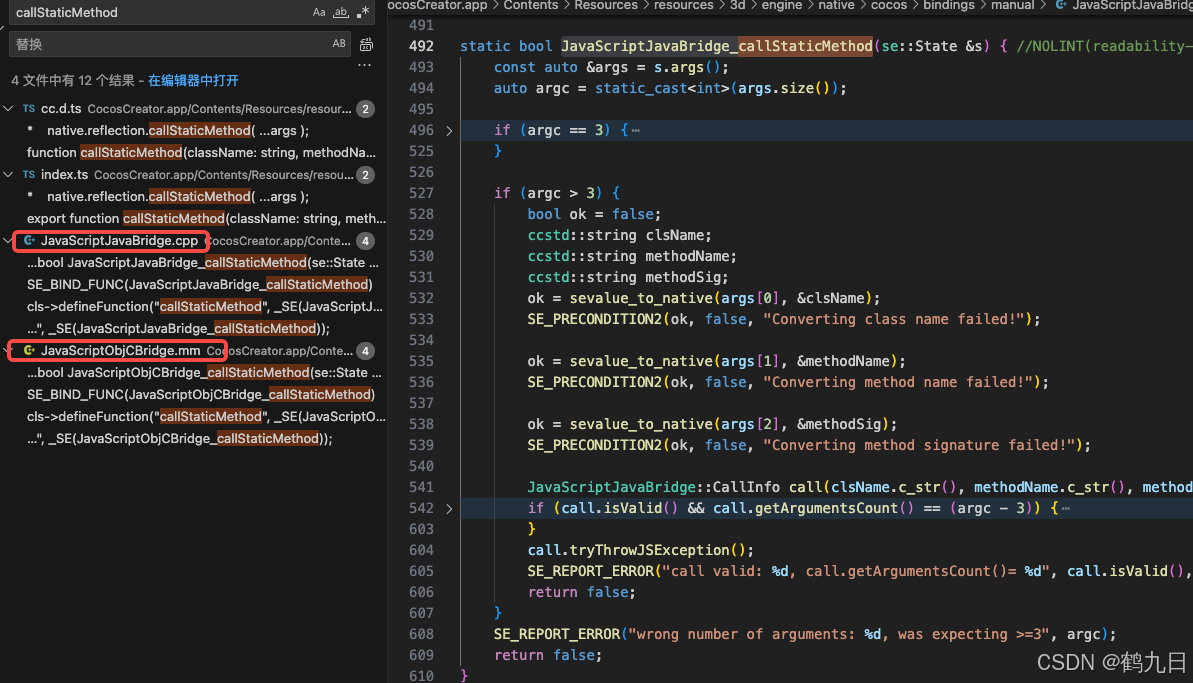
CocosCreator 之 JavaScript/TypeScript和Java的相互交互
引擎版本: 3.8.1 语言: JavaScript/TypeScript、C、Java 环境:Window 参考:Java原生反射机制 您好,我是鹤九日! 回顾 在上篇文章中:CocosCreator Android项目接入UnityAds 广告SDK。 我们简单讲…...
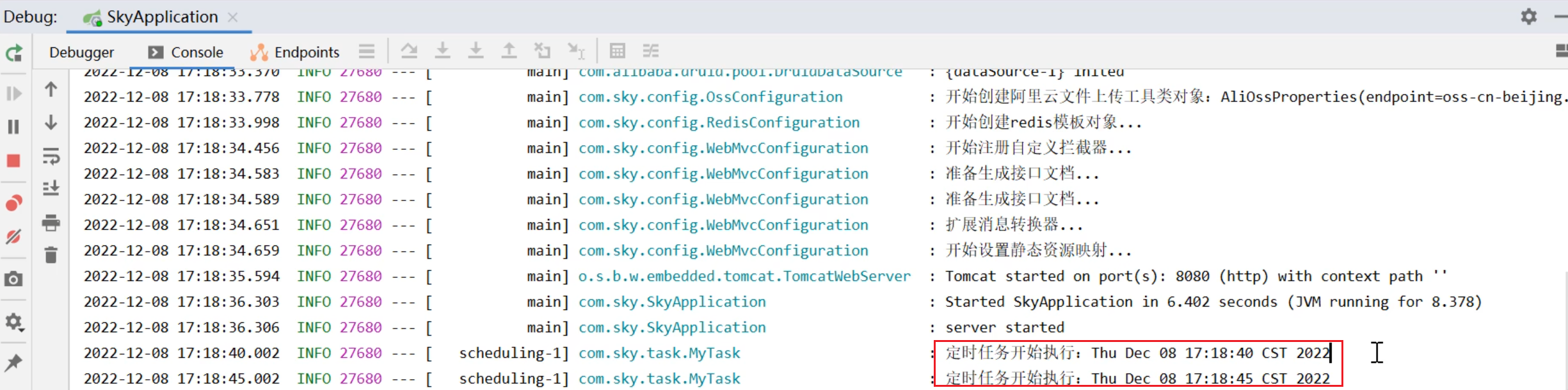
SpringTask-03.入门案例
一.入门案例 启动类: package com.sky;import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCach…...

全面解析各类VPN技术:GRE、IPsec、L2TP、SSL与MPLS VPN对比
目录 引言 VPN技术概述 GRE VPN 3.1 GRE封装结构 3.2 GRE的应用场景 GRE over IPsec 4.1 GRE over IPsec封装结构 4.2 为什么使用GRE over IPsec? IPsec VPN 5.1 IPsec传输模式(Transport Mode) 5.2 IPsec隧道模式(Tunne…...
selenium学习实战【Python爬虫】
selenium学习实战【Python爬虫】 文章目录 selenium学习实战【Python爬虫】一、声明二、学习目标三、安装依赖3.1 安装selenium库3.2 安装浏览器驱动3.2.1 查看Edge版本3.2.2 驱动安装 四、代码讲解4.1 配置浏览器4.2 加载更多4.3 寻找内容4.4 完整代码 五、报告文件爬取5.1 提…...

tree 树组件大数据卡顿问题优化
问题背景 项目中有用到树组件用来做文件目录,但是由于这个树组件的节点越来越多,导致页面在滚动这个树组件的时候浏览器就很容易卡死。这种问题基本上都是因为dom节点太多,导致的浏览器卡顿,这里很明显就需要用到虚拟列表的技术&…...

Hive 存储格式深度解析:从 TextFile 到 ORC,如何选对数据存储方案?
在大数据处理领域,Hive 作为 Hadoop 生态中重要的数据仓库工具,其存储格式的选择直接影响数据存储成本、查询效率和计算资源消耗。面对 TextFile、SequenceFile、Parquet、RCFile、ORC 等多种存储格式,很多开发者常常陷入选择困境。本文将从底…...
