基于Pytorch框架的LSTM算法(二)——多维度单步预测
1.项目说明
**选用Close和Low两个特征,使用窗口time_steps窗口的2个特征,然后预测Close这一个特征数据未来一天的数据
当batch_first=True,则LSTM的inputs=(batch_size,time_steps,input_size)
batch_size = len(data)-time_steps
time_steps = 滑动窗口,本项目中值为lookback
input_size = 2【因为选取了Close和Low两个特征】**
2.数据集
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38633279/article/details/134245512?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501中的数据集
3.数据预处理
3.1 读取数据
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import seaborn as sns
import math, time
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_errorfilepath = './data/rlData.csv'
data = pd.read_csv(filepath)
data = data.sort_values('Date')
data.head()
data.shapesns.set_style("darkgrid")
plt.figure(figsize = (15,9))
plt.plot(data[['Close']])
plt.xticks(range(0,data.shape[0],20), data['Date'].loc[::20], rotation=45)
plt.title("****** Stock Price",fontsize=18, fontweight='bold')
plt.xlabel('Date',fontsize=18)
plt.ylabel('Close Price (USD)',fontsize=18)
plt.show()
3.2 选取Close和Low两个特征
price = data[['Close', 'Low']]
3.3 数据归一化
scaler = MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(-1, 1))
price['Close'] = scaler.fit_transform(price['Close'].values.reshape(-1,1))
price['Low'] = scaler.fit_transform(price['Low'].values.reshape(-1,1))
3.4 数据集的制造[batch_size,time_steps,input_size]
本次选取2个维度特征作为输出,因此,input_size =2
x_train.shape = [batch_size,time_steps,input_size]
y_train.shape = [batch_size,1]
1. 输入选取的是Close和Low列作为多维度的输入,所以选择的是data数据中的第一列和第二列作为x_train【因此input_size=2】
2. 输出是选取的Close列作为预测,所以选取data数据的第一列作为y_train【即Close列作为y_train】。
#2.数据集的制作
def split_data(stock, lookback):data_raw = stock.to_numpy() data = [] for index in range(len(data_raw) - lookback): data.append(data_raw[index: index + lookback])data = np.array(data);test_set_size = int(np.round(0.2 * data.shape[0]))train_set_size = data.shape[0] - (test_set_size)x_train = data[:train_set_size,:-1,:] #x_train.shape = (198, 4, 2)y_train = data[:train_set_size,-1,0:1] #y_train.shape = (198, 1)x_test = data[train_set_size:,:-1,:] #x_test.shape = (49, 4, 2)y_test = data[train_set_size:,-1,0:1] #y_test.shape = (49, 1)return [torch.Tensor(x_train), torch.Tensor(y_train), torch.Tensor(x_test),torch.Tensor(y_test)]lookback = 5
x_train, y_train, x_test, y_test = split_data(price, lookback)
print('x_train.shape = ',x_train.shape)
print('y_train.shape = ',y_train.shape)
print('x_test.shape = ',x_test.shape)
print('y_test.shape = ',y_test.shape)
4.LSTM算法
这里的LSTM算法和单维单步预测中的LSTM预测算法一模一样。只不过我们在制作数据集的时候,对于LSTM模型中输入不一样了。
class LSTM(nn.Module):def __init__(self, input_dim, hidden_dim, num_layers, output_dim):super(LSTM, self).__init__()self.hidden_dim = hidden_dimself.num_layers = num_layersself.lstm = nn.LSTM(input_dim, hidden_dim, num_layers, batch_first=True)self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, output_dim)def forward(self, x):h0 = torch.zeros(self.num_layers, x.size(0), self.hidden_dim).requires_grad_()c0 = torch.zeros(self.num_layers, x.size(0), self.hidden_dim).requires_grad_()out, (hn, cn) = self.lstm(x, (h0.detach(), c0.detach()))out = self.fc(out[:, -1, :])
5.预训练
input_dim = 2
hidden_dim = 32
num_layers = 2
output_dim = 1
num_epochs = 100model = LSTM(input_dim=input_dim, hidden_dim=hidden_dim, output_dim=output_dim, num_layers=num_layers)
criterion = torch.nn.MSELoss()
optimiser = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)hist = np.zeros(num_epochs)
lstm = []for t in range(num_epochs):y_train_pred = model(x_train)loss = criterion(y_train_pred, y_train)hist[t] = loss.item()# print("Epoch ", t, "MSE: ", loss.item())optimiser.zero_grad()loss.backward()optimiser.step()
6.绘制预测值和真实值拟合图形,以及loss图形
predict = pd.DataFrame(scaler.inverse_transform(y_train_pred.detach().numpy()))
original = pd.DataFrame(scaler.inverse_transform(y_train.detach().numpy()))sns.set_style("darkgrid") fig = plt.figure()
fig.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.2, wspace=0.2)plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
ax = sns.lineplot(x = original.index, y = original[0], label="Data", color='royalblue')
ax = sns.lineplot(x = predict.index, y = predict[0], label="Training Prediction (LSTM)", color='tomato')
ax.set_title('Stock price', size = 14, fontweight='bold')
ax.set_xlabel("Days", size = 14)
ax.set_ylabel("Cost (USD)", size = 14)
ax.set_xticklabels('', size=10)plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
ax = sns.lineplot(data=hist, color='royalblue')
ax.set_xlabel("Epoch", size = 14)
ax.set_ylabel("Loss", size = 14)
ax.set_title("Training Loss", size = 14, fontweight='bold')
fig.set_figheight(6)
fig.set_figwidth(16)# make predictions
y_test_pred = model(x_test)# invert predictions
y_train_pred = scaler.inverse_transform(y_train_pred.detach().numpy())
y_train = scaler.inverse_transform(y_train.detach().numpy())
y_test_pred = scaler.inverse_transform(y_test_pred.detach().numpy())
y_test = scaler.inverse_transform(y_test.detach().numpy())# calculate root mean squared error
trainScore = math.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_train[:,0], y_train_pred[:,0]))
print('Train Score: %.2f RMSE' % (trainScore))
testScore = math.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_test[:,0], y_test_pred[:,0]))
print('Test Score: %.2f RMSE' % (testScore))
lstm.append(trainScore)
lstm.append(testScore)
lstm.append(training_time)完整代码
问题描述:
选用Close和Low两个特征,使用窗口time_steps窗口的2个特征,然后预测Close这一个特征数据未来一天的数据
当batch_first=True,则LSTM的inputs=(batch_size,time_steps,input_size)
batch_size = len(data)-time_steps
time_steps = 滑动窗口,本项目中值为lookback
input_size = 2【因为选取了Close和Low两个特征】
#%%
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import seaborn as sns
import math, time
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_errorfilepath = './data/rlData.csv'
data = pd.read_csv(filepath)
data = data.sort_values('Date')
data.head()
data.shapesns.set_style("darkgrid")
plt.figure(figsize = (15,9))
plt.plot(data[['Close']])
plt.xticks(range(0,data.shape[0],20), data['Date'].loc[::20], rotation=45)
plt.title("****** Stock Price",fontsize=18, fontweight='bold')
plt.xlabel('Date',fontsize=18)
plt.ylabel('Close Price (USD)',fontsize=18)
plt.show()#1.选取特征工程2个
price = data[['Close', 'Low']]scaler = MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(-1, 1))
price['Close'] = scaler.fit_transform(price['Close'].values.reshape(-1,1))
price['Low'] = scaler.fit_transform(price['Low'].values.reshape(-1,1))#2.数据集的制作
def split_data(stock, lookback):data_raw = stock.to_numpy() data = [] for index in range(len(data_raw) - lookback): data.append(data_raw[index: index + lookback])data = np.array(data);test_set_size = int(np.round(0.2 * data.shape[0]))train_set_size = data.shape[0] - (test_set_size)x_train = data[:train_set_size,:-1,:] #x_train.shape = (198, 4, 2)y_train = data[:train_set_size,-1,0:1] #y_train.shape = (198, 1)x_test = data[train_set_size:,:-1,:] #x_test.shape = (49, 4, 2)y_test = data[train_set_size:,-1,0:1] #y_test.shape = (49, 1)return [torch.Tensor(x_train), torch.Tensor(y_train), torch.Tensor(x_test),torch.Tensor(y_test)]lookback = 5
x_train, y_train, x_test, y_test = split_data(price, lookback)
print('x_train.shape = ',x_train.shape)
print('y_train.shape = ',y_train.shape)
print('x_test.shape = ',x_test.shape)
print('y_test.shape = ',y_test.shape)class LSTM(nn.Module):def __init__(self, input_dim, hidden_dim, num_layers, output_dim):super(LSTM, self).__init__()self.hidden_dim = hidden_dimself.num_layers = num_layersself.lstm = nn.LSTM(input_dim, hidden_dim, num_layers, batch_first=True)self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, output_dim)def forward(self, x):h0 = torch.zeros(self.num_layers, x.size(0), self.hidden_dim).requires_grad_()c0 = torch.zeros(self.num_layers, x.size(0), self.hidden_dim).requires_grad_()out, (hn, cn) = self.lstm(x, (h0.detach(), c0.detach()))out = self.fc(out[:, -1, :]) return outinput_dim = 2
hidden_dim = 32
num_layers = 2
output_dim = 1
num_epochs = 100model = LSTM(input_dim=input_dim, hidden_dim=hidden_dim, output_dim=output_dim, num_layers=num_layers)
criterion = torch.nn.MSELoss()
optimiser = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)hist = np.zeros(num_epochs)
lstm = []for t in range(num_epochs):y_train_pred = model(x_train)loss = criterion(y_train_pred, y_train)hist[t] = loss.item()# print("Epoch ", t, "MSE: ", loss.item())optimiser.zero_grad()loss.backward()optimiser.step()predict = pd.DataFrame(scaler.inverse_transform(y_train_pred.detach().numpy()))
original = pd.DataFrame(scaler.inverse_transform(y_train.detach().numpy()))sns.set_style("darkgrid") fig = plt.figure()
fig.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.2, wspace=0.2)plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
ax = sns.lineplot(x = original.index, y = original[0], label="Data", color='royalblue')
ax = sns.lineplot(x = predict.index, y = predict[0], label="Training Prediction (LSTM)", color='tomato')
ax.set_title('Stock price', size = 14, fontweight='bold')
ax.set_xlabel("Days", size = 14)
ax.set_ylabel("Cost (USD)", size = 14)
ax.set_xticklabels('', size=10)plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
ax = sns.lineplot(data=hist, color='royalblue')
ax.set_xlabel("Epoch", size = 14)
ax.set_ylabel("Loss", size = 14)
ax.set_title("Training Loss", size = 14, fontweight='bold')
fig.set_figheight(6)
fig.set_figwidth(16)# make predictions
y_test_pred = model(x_test)# invert predictions
y_train_pred = scaler.inverse_transform(y_train_pred.detach().numpy())
y_train = scaler.inverse_transform(y_train.detach().numpy())
y_test_pred = scaler.inverse_transform(y_test_pred.detach().numpy())
y_test = scaler.inverse_transform(y_test.detach().numpy())# calculate root mean squared error
trainScore = math.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_train[:,0], y_train_pred[:,0]))
print('Train Score: %.2f RMSE' % (trainScore))
testScore = math.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_test[:,0], y_test_pred[:,0]))
print('Test Score: %.2f RMSE' % (testScore))
lstm.append(trainScore)
lstm.append(testScore)
lstm.append(training_time)参考:https://gitee.com/qiangchen_sh/stock-prediction/blob/master/%E4%BB%A3%E7%A0%81/LSTM%E4%BB%8E%E7%90%86%E8%AE%BA%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80%E5%88%B0%E4%BB%A3%E7%A0%81%E5%AE%9E%E6%88%98%204%20%E5%A4%9A%E7%BB%B4%E7%89%B9%E5%BE%81%E8%82%A1%E7%A5%A8%E4%BB%B7%E6%A0%BC%E9%A2%84%E6%B5%8B_Pytorch.ipynb
相关文章:
——多维度单步预测)
基于Pytorch框架的LSTM算法(二)——多维度单步预测
1.项目说明 **选用Close和Low两个特征,使用窗口time_steps窗口的2个特征,然后预测Close这一个特征数据未来一天的数据 当batch_firstTrue,则LSTM的inputs(batch_size,time_steps,input_size) batch_size len(data)-time_steps time_steps 滑动窗口&…...

cnn感受野计算方法
No. Layers Kernel Size Stride 1 Conv1 33 1 2 Pool1 22 2 3 Conv2 33 1 4 Pool2 22 2 5 Conv3 33 1 6 Conv4 33 1 7 Pool3 2*2 2 感受野初始值 l 0 1 l_0 1l 0 1,每层的感受野计算过程如下: l 0 1 l_0 1l 0 1 l 1 1 ( 3 − 1 ) 3 l_1 1…...

百分点科技受邀参加“第五届治理现代化论坛”
11月4日,由北京大学政府管理学院主办的“面向新时代的人才培养——第五届治理现代化论坛”举行,北京大学校党委常委、副校长、教务长王博,政府管理学院院长燕继荣参加开幕式并致辞,百分点科技董事长兼CEO苏萌受邀出席论坛…...

基于Springboot的智慧食堂设计与实现(有报告)。Javaee项目,springboot项目。
演示视频: 基于Springboot的智慧食堂设计与实现(有报告)。Javaee项目,springboot项目。 前些天发现了一个巨牛的人工智能学习网站,通俗易懂,风趣幽默,忍不住分享一下给大家。点击跳转到网站。 项…...
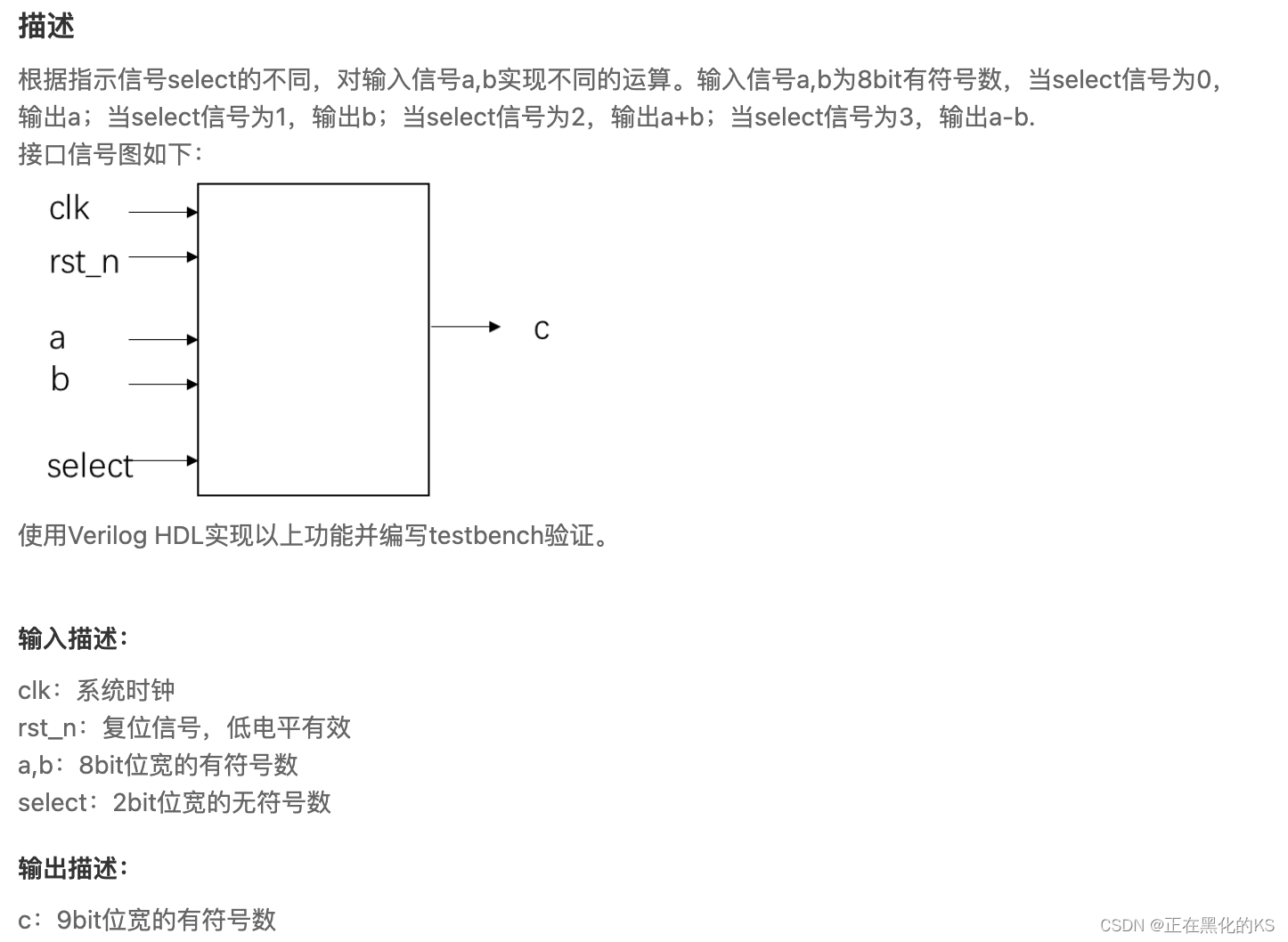
「Verilog学习笔记」多功能数据处理器
专栏前言 本专栏的内容主要是记录本人学习Verilog过程中的一些知识点,刷题网站用的是牛客网 分析 注意题目要求输入信号为有符号数,另外输出信号可能是输入信号的和,所以需要拓展一位,防止溢出。 timescale 1ns/1ns module data_…...

OpenHarmony 4.0 Release 编译异常处理
一、环境配置 编译环境:Ubuntu 20.04 OpenHarmony 软件版本:4.0 Release 设备平台:rk3568 二、下拉代码 参考官网步骤: OpenHarmony 4.0 Release 源码获取 repo init -u https://gitee.com/openharmony/manifest -b OpenHarmo…...

软件测试|MySQL LIKE:深入了解模糊查询
简介 在数据库查询中,模糊查询是一种强大的技术,可以用来搜索与指定模式匹配的数据。MySQL数据库提供了一个灵活而强大的LIKE操作符,使得模糊查询变得简单和高效。本文将详细介绍MySQL中的LIKE操作符以及它的用法,并通过示例演示…...

linux防火墙设置
#查看firewall的状态 firewall-cmd --state (systemctl status firewalld.service) #安装 yum install firewalld #启动, systemctl start firewalld (systemctl start firewalld.service) #设置开机启动 systemctl enable firewalld #关闭 systemctl stop firewalld #取消…...

http 403
一、什么是HTTP ERROR 403 403 Forbidden 是HTTP协议中的一个状态码(Status Code)。可以简单的理解为没有权限访问此站,服务器受到请求但拒绝提供服务。 二、HTTP 403 状态码解释大全 403.1 -执行访问禁止。 403.2 -读访问禁止。 403.3 -写访问禁止。 403.4要…...
RAW图像处理软件Capture One 23 Enterprise mac中文版功能特点
Capture One 23 Enterprise mac是一款专业的图像处理软件,旨在为企业用户提供高效、快速和灵活的工作流程。 Capture One 23 Enterprise mac软件的特点和功能 强大的图像编辑工具:Capture One 23 Enterprise提供了一系列强大的图像编辑工具,…...

Linux 进程终止和等待
目录 一:进程常见的退出方法 1. main 函数返回值 2.调用 exit 3.调用 _exit 二:异常问题 三:进程等待 1.概念 2.进程等待的必要性 3.进程等待的方法 <1>:wait --- 系统调用 <2>:waitpid 进程…...
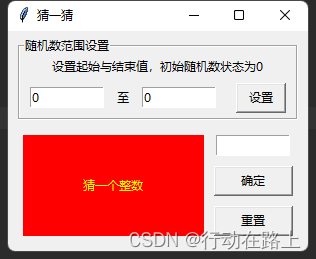
python用tkinter随机数猜数字大小
python用tkinter随机数猜数字大小 没事做,看到好多人用scratch做的猜大小的示例,也用python的tkinter搞一个猜大小的代码玩玩。 猜数字代码 from tkinter import * from random import randint# 定义确定按钮的点击事件 def hit(x,y):global s_Labprint(…...

程序员们保住自己饭碗
在现代社会中,程序员扮演着至关重要的角色。他们不仅仅是编写代码的人,更是保障数字世界安全稳定的守护者。随着科技的迅猛发展,程序员保住自己饭碗的护城河变得愈发重要。本文将探讨程序员如何通过不断学习、技术创新和软实力的发展…...
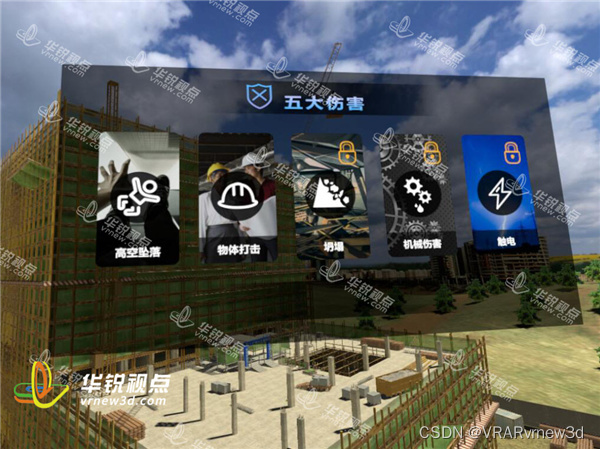
顶板事故防治vr实景交互体验提高操作人员安全防护技能水平
建筑业在我国各行业中属危险性较大且事故多发的行业,在建筑业“八大伤害”(高处坠落、坍塌、物体打击、触电、起重伤害、机械伤害、火灾爆炸及其他伤害)事故中,高处坠落事故的发生率最高、危险性极大。工地现场培训vr坠落体验利用虚拟现实技术还原各种情…...
为什么推荐从Linux开始了解IT技术
IT是什么,是干什么的呢? 说起物联网,云计算,大数据,或许大家听过。但是,你知道,像云计算的底层基座是什么呢?就是我们现在说的Linux操作系统。而云计算就是跑在Linux操作系统上的一个…...
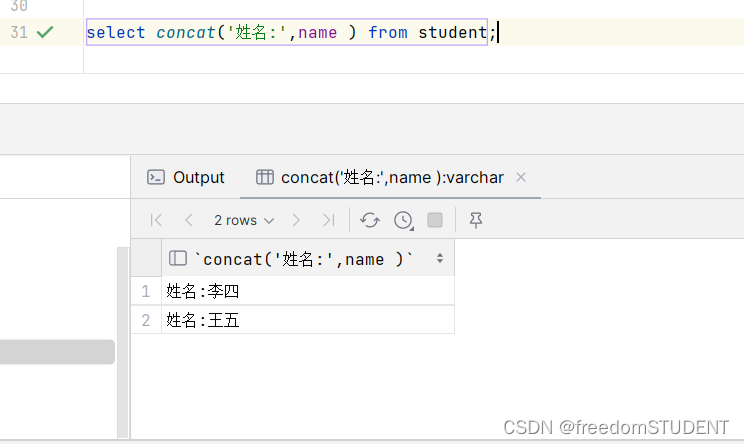
【Mysql】增删改查(基础版)
我使用的工具是Data Grip (SQLyog Naivact 都行) 使用Data Grip创建student表,具体步骤如下(熟悉Data Grip或者使用SQLyog,Naivact可以跳过) https://blog.csdn.net/m0_67930426/article/details/13429…...
文件夹找不到了怎么恢复?4个正确恢复方法分享!
“我在电脑上保存了很多的文件和文件夹,今天在查找文件时,发现我有一整个文件夹都消失了,不知道怎么才能找到呢。有朋友可以帮帮忙吗?” 电脑中文件夹突然找不到了可能会引发焦虑,尤其是如果这些文件夹包含重要的数据。…...
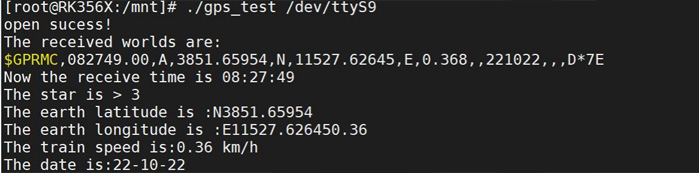
迅为RK3568开发板GPS模块测试实验步骤
1 首先按照上个实验-串口实验,在设备树中打开串口 9 的节点。 2 然后将 GPS 模块连接好之后,用 U 盘将 GPS 测试程序 gps_test 拷贝到开发板的/mnt 目录下。本小节的测试程序存放路径为“iTOP-3568 开发板\02_ 【iTOP-RK3568 开发板】开发资…...
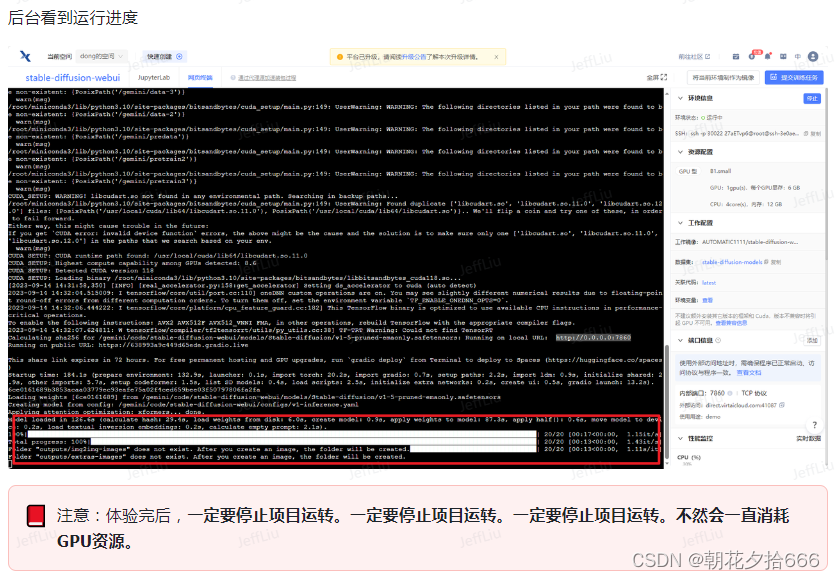
用趋动云GPU部署自己的Stable Diffusion
注:本文内容来自于对DataWhale的开源学习项目——免费GPU线上跑AI项目实践的学习,参见:Docs,引用了多处DataWhale给出的教程。 1.创建项目 1)进入趋动云用户工作台,在当前空间处选择注册时系统自动生成的…...

nfs配置
1.NFS介绍 NFS就是Network File System的缩写,它最大的功能就是可以通过网络,让不同的机器、不同的操 作系统可以共享彼此的文件。 NFS服务器可以让PC将网络中的NFS服务器共享的目录挂载到本地端的文 件系统中,而在本地端的系统中来看&#…...

调用支付宝接口响应40004 SYSTEM_ERROR问题排查
在对接支付宝API的时候,遇到了一些问题,记录一下排查过程。 Body:{"datadigital_fincloud_generalsaas_face_certify_initialize_response":{"msg":"Business Failed","code":"40004","sub_msg…...

Spring Boot+Neo4j知识图谱实战:3步搭建智能关系网络!
一、引言 在数据驱动的背景下,知识图谱凭借其高效的信息组织能力,正逐步成为各行业应用的关键技术。本文聚焦 Spring Boot与Neo4j图数据库的技术结合,探讨知识图谱开发的实现细节,帮助读者掌握该技术栈在实际项目中的落地方法。 …...

Axios请求超时重发机制
Axios 超时重新请求实现方案 在 Axios 中实现超时重新请求可以通过以下几种方式: 1. 使用拦截器实现自动重试 import axios from axios;// 创建axios实例 const instance axios.create();// 设置超时时间 instance.defaults.timeout 5000;// 最大重试次数 cons…...

在QWebEngineView上实现鼠标、触摸等事件捕获的解决方案
这个问题我看其他博主也写了,要么要会员、要么写的乱七八糟。这里我整理一下,把问题说清楚并且给出代码,拿去用就行,照着葫芦画瓢。 问题 在继承QWebEngineView后,重写mousePressEvent或event函数无法捕获鼠标按下事…...
springboot整合VUE之在线教育管理系统简介
可以学习到的技能 学会常用技术栈的使用 独立开发项目 学会前端的开发流程 学会后端的开发流程 学会数据库的设计 学会前后端接口调用方式 学会多模块之间的关联 学会数据的处理 适用人群 在校学生,小白用户,想学习知识的 有点基础,想要通过项…...

Java毕业设计:WML信息查询与后端信息发布系统开发
JAVAWML信息查询与后端信息发布系统实现 一、系统概述 本系统基于Java和WML(无线标记语言)技术开发,实现了移动设备上的信息查询与后端信息发布功能。系统采用B/S架构,服务器端使用Java Servlet处理请求,数据库采用MySQL存储信息࿰…...

CRMEB 中 PHP 短信扩展开发:涵盖一号通、阿里云、腾讯云、创蓝
目前已有一号通短信、阿里云短信、腾讯云短信扩展 扩展入口文件 文件目录 crmeb\services\sms\Sms.php 默认驱动类型为:一号通 namespace crmeb\services\sms;use crmeb\basic\BaseManager; use crmeb\services\AccessTokenServeService; use crmeb\services\sms\…...

HTML前端开发:JavaScript 获取元素方法详解
作为前端开发者,高效获取 DOM 元素是必备技能。以下是 JS 中核心的获取元素方法,分为两大系列: 一、getElementBy... 系列 传统方法,直接通过 DOM 接口访问,返回动态集合(元素变化会实时更新)。…...
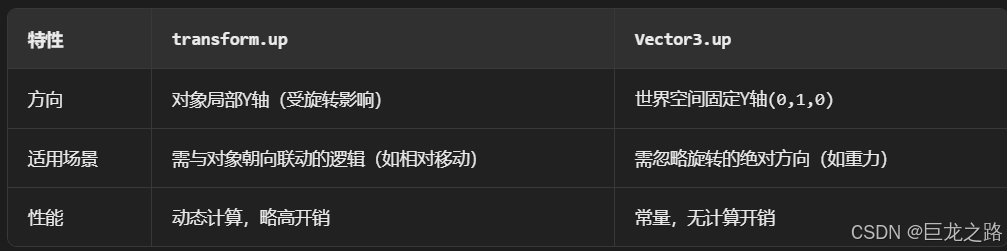
Unity中的transform.up
2025年6月8日,周日下午 在Unity中,transform.up是Transform组件的一个属性,表示游戏对象在世界空间中的“上”方向(Y轴正方向),且会随对象旋转动态变化。以下是关键点解析: 基本定义 transfor…...
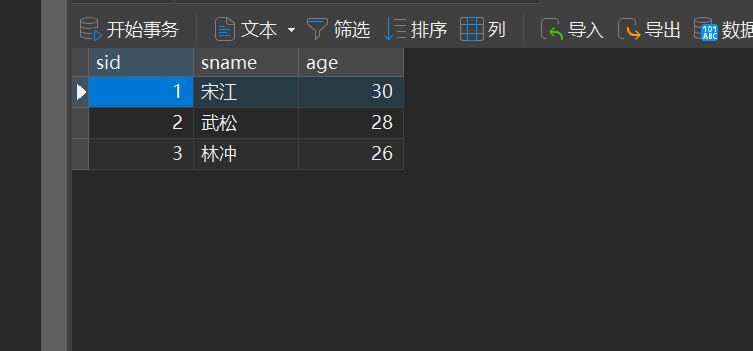
MySQL的pymysql操作
本章是MySQL的最后一章,MySQL到此完结,下一站Hadoop!!! 这章很简单,完整代码在最后,详细讲解之前python课程里面也有,感兴趣的可以往前找一下 一、查询操作 我们需要打开pycharm …...
