《C++ Primer Plus》第17章:输入、输出和文件(7)
编程练习
-
编写一个程序计算输入流中第一个$之前的字符数目,并将$留在输入流中。
#include<iostream>int main() {int ct = 0;while(std::cin.peek()!='$'){ct++;std::cin.get();}std::cout << "num: " << ct << std::endl;return 0; }答:
#include<iostream>int main() {int ct = 0;while(std::cin.peek()!='$'){ct++;std::cin.get();}std::cout << "num: " << ct << std::endl;return 0; } -
编写一个程序,将键盘输入(直到模拟的文件尾)复制到通过命令行指定的文件中。
#include <cstdlib> #include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <string>int main(int argc, char *argv[]){if(argc<2){std::cout << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " <filename>" << std::endl;exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}std::fstream fs;for(int file = 1; file < argc; file++){fs.open(argv[file], std::ios_base::out);if(!fs.is_open()){std::cerr << "error happens when open " << argv[file] << ".\n";exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}std::cout << "Please enter your input: \n";std::string input;getline(std::cin, input);while(input.size()>0){fs << input << std::endl;getline(std::cin, input);}fs.clear();fs.close();fs.open(argv[file], std::ios_base::in); if(!fs.is_open()){std::cerr << "error happens when open " << argv[file] << ".\n";exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}std::cout << "The content of the " << argv[file] << ":\n";char ch;while(fs.get(ch)){std::cout << ch;}if(!fs.eof()){std::cerr << "error happens when read " << argv[file] << ".\n";exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}return 0;} }答:
#include <cstdlib> #include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <string>int main(int argc, char *argv[]){if(argc<2){std::cout << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " <filename>" << std::endl;exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}std::fstream fs;for(int file = 1; file < argc; file++){fs.open(argv[file], std::ios_base::out);if(!fs.is_open()){std::cerr << "error happens when open " << argv[file] << ".\n";exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}std::cout << "Please enter your input: \n";std::string input;getline(std::cin, input);while(input.size()>0){fs << input << std::endl;getline(std::cin, input);}fs.clear();fs.close();fs.open(argv[file], std::ios_base::in); if(!fs.is_open()){std::cerr << "error happens when open " << argv[file] << ".\n";exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}std::cout << "The content of the " << argv[file] << ":\n";char ch;while(fs.get(ch)){std::cout << ch;}if(!fs.eof()){std::cerr << "error happens when read " << argv[file] << ".\n";exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}return 0;} } -
编写一个程序,将一个文件复制到另一个文件中。让程序通过命令行获取文件名。如果文件无法打开,程序将指出这一点。
//#include <cstdlib> #include<fstream> #include<iostream> #include<string>int main(int argc, char* argv[]){if(argc!=3){std::cout << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " <target filename> <sourse filename>.\n";exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}std::ofstream ofs;ofs.open(argv[1], std::ios_base::out);if(!ofs.is_open()){std::cerr << "Error happen when open " << argv[1] << ".\n";exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}std::ifstream ifs;ifs.open(argv[2], std::ios_base::in);if(!ifs.is_open()){std::cerr << "Error happen when open " << argv[2] << ".\n";exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}std::string line;getline(ifs,line);while(line.size()>0){ofs << line << std::endl;getline(ifs,line);}if(!ifs.eof()){std::cerr << "Error happens when read " << argv[1] << ".\n";}return 0; }答:
//#include <cstdlib> #include<fstream> #include<iostream> #include<string>int main(int argc, char* argv[]){if(argc!=3){std::cout << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " <target filename> <sourse filename>.\n";exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}std::ofstream ofs;ofs.open(argv[1], std::ios_base::out);if(!ofs.is_open()){std::cerr << "Error happen when open " << argv[1] << ".\n";exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}std::ifstream ifs;ifs.open(argv[2], std::ios_base::in);if(!ifs.is_open()){std::cerr << "Error happen when open " << argv[2] << ".\n";exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}std::string line;getline(ifs,line);while(line.size()>0){ofs << line << std::endl;getline(ifs,line);}if(!ifs.eof()){std::cerr << "Error happens when read " << argv[1] << ".\n";}return 0; } -
编写一个程序,它打开两个文本文件进行输入,打开一个文本文件进行输出。该程序将两个输入文件中对应的行并接起来,并用空格分隔,然后将结果写入到输出文件中。如果一个文件比另一个短,则将较长文件中余下的几行值复制到输出文件中。例如,假设第一个输入文件的内容如下:
eggs kites donuts balloons hammers stones而第二个输入文件的内容如下:
zero lassitude finance drama则得到的文件的内容将如下:
eggs kites donuts zero lassitude balloons hammers finance drama stones答:
#include <cstdlib> #include<iostream> #include<fstream> #include<string>using namespace std;int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {if(argc!=4){cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " <source file1> <source file2> <target file>.\n";exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}ifstream ifs1(argv[1], ios_base::in);ifstream ifs2(argv[2], ios_base::in);ofstream ofs(argv[3], ios_base::out);if(!ifs1.is_open()) {cerr << "Error when open " << argv[1] << ".\n";}if(!ifs2.is_open()) {cerr << "Error when open " << argv[2] << ".\n";}string line1, line2;getline(ifs1, line1);getline(ifs2,line2);while(line1.size() >0 && line2.size() >0 ){ofs << line1 << ' ' << line2 << endl;getline(ifs1, line1);getline(ifs2,line2);}if(!ifs1.eof()){while(line1.size()>0){ofs << line1 << endl;getline(ifs1, line1);}}if(!ifs2.eof()){while(line2.size()>0){ofs << line2 << endl;getline(ifs2, line2);}}return 0; } -
Mat 和 Pat 想邀请他们的朋友来参加派对,就像第16章中的编程练习8那样,但现在他们希望程序使用文件。他们请您编写一个完成下述任务的程序。
- 从文本文件 mat.dat 中读取 Mat 朋友的清单,其中每行为一个朋友。姓名将被存储在容器,然后按顺序显示出来。
- 从文本文件 pat.dat 中读取 Pat 朋友的姓名清单,其中每行为一个朋友。姓名将被存储在容器,然后按顺序显示出来。
- 合并两个清单,删除重复的条目,并将结果保存在文件 matnpat.dat 中,其中每行为一个朋友。
答:
#include <cstdlib> #include<iostream> #include<fstream> #include<string> #include<vector> #include<set>int main() {using namespace std;ifstream matin("mat.dat", ios_base::in);ifstream patin("pat.dat", ios_base::in);if(!(matin && patin)){cerr << "Failed to open input files.\n";exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}ofstream matnpatout("matnpat.dat", ios_base::out);if(!matnpatout.is_open()){cerr << "Failed to open output files.\n";exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}vector<string> mat;vector<string> pat;string name;while(!matin.eof()) { getline(matin, name);mat.push_back(name);}cout << "Success" << endl;while(!patin.eof()) {getline(patin, name);pat.push_back(name);}cout << "Mat's friends:\n";for(auto& name : mat){cout << name << endl;}cout << "Pat's friends:\n";for(auto& name : pat) {cout << name << endl;}set<string> matnpat;matnpat.insert(mat.begin(), mat.end());matnpat.insert(pat.begin(), pat.end());for(auto& name : matnpat) {matnpatout << name << endl;}return 0; } -
编写一个程序,它使用标准 C++ I/O、文件 I/O 以及 14 章的编程练习5中定义的 employee、manager、fink 和 highfink 类型的数据。该程序应包含程序17.7中的代码行,即允许用户将新数据添加到文件中。该程序首次被运行时,将要求用户输入数据,然后显示所有数据,并将这些信息保存到一个文件中。当该程序再次被运行时,将首先读取并显示文件中的数据,然后让用户添加数据,并显示所有的数据。差别之一是,应通过一个指向 employee 类型的指针来处理数据。这样,指针可以指向 employee 对象,也可以指向从 employee 派生出来的其他三种对象中的任何一种。使数组较小有助于检查程序,例如,您可能将数组限定为最多包含 10 个元素:
const int MAX = 10; // no more than 10 objects ... employee * pc [MAX];为通过键盘输入,程序应使用一个菜单,让用户选择要创建的对象类型。菜单将使用一个 switch,以便使用 new 来创建指定类型的对象,并将它的地址赋给 pc 数组中的一个指针。然后该对象可以使用虚函数 setall() 来提示用户输入相应的数据:
pc[i] -> setall(); // invokes function corresponding to type of object为将数据保存到文件中,应设计一个虚函数 writeall():
for (i = 0; i < index; i++) {pc[i] -> writeall(fout); // fout ofstream connected to output file }注意:对于这个练习,应使用文本 I/O,而不是二进制 I/O(遗憾的是,虚对象包含指向虚函数指针表的指针,而 write() 将把这种信息复制到文件中。使用 read() 读取文件的内容,以填充对象时,函数指针将为乱码,这将扰乱虚函数的行为)。可使用换行符将字段分隔开,这样在输入时将很容易识别各个字段。也可以使用二进制 I/O,但不能将对象作为一个整体写入,而应该提供分别对每个类成员应用 write() 和 read() 的类方法。这样,程序将只把所需的数据保存到文件中。
比较难处理的部分是使用文件恢复数据。问题在于:程序如何才能直到接下来要恢复的项目是 employee 对象、manager 对象、fink 对象还是 highfink 对象?一种方法是,在对象的数据写入文件时,在数据前面加上一个指示对象类型的数据。这样,在文件输入时,程序便可以读取该整数,并使用 switch 语句创建一个适当的对象来接收数据:
enum classkind{Employee, Manager, Fink, Highfink}; // in class header ... int classtype; while((fin>>classtype).get(ch) ) { // newline separates int from dataswitch(classtype) {case Employee : pc[i] = new employee;: break;然后便可以使用指针调用虚函数 getall() 来读取信息:
pc[i++] -> getall();答:
emp.h#ifndef EMP_H_ #define EMP_H_#include<iostream> #include<fstream> #include<string>enum classkind {Employee, Manager, Fink, Highfink}; // in class headerclass ab_emp {; private:std::string fname;std::string lname;std::string job; public:ab_emp();ab_emp(const std::string & fn, const std::string & ln,const std::string & j);virtual void ShowAll() const;virtual void SetAll();virtual std::ofstream & WriteAll(std::ofstream & of) const;friend std::ostream & operator<<(std::ostream & os, const ab_emp & e);virtual ~ab_emp() = 0; };class employee : virtual public ab_emp { public:employee();employee(const std::string & fn, const std::string & ln,const std::string & j);virtual void ShowAll() const;virtual void SetAll();std::ofstream & WriteAll(std::ofstream & of) const; };class manager : virtual public ab_emp { private:int inchargeof; protected:int InChargeOf() const {return inchargeof;}int & InChargeOf() {return inchargeof;} public:manager();manager(const std::string & fn, const std::string & ln,const std::string & j, int ico = 0);manager(const ab_emp & e, int ico);manager(const manager & m);virtual void ShowAll() const;virtual void SetAll();std::ofstream & WriteAll(std::ofstream & of) const; };class fink : virtual public ab_emp { private:std::string reportsto; protected:std::string ReportsTo() const { return reportsto;}std::string & ReportsTo() {return reportsto;} public:fink();fink(const std::string & fn, const std::string ln,const std::string & j, const std::string repo);fink(const ab_emp & e, const std::string repo);fink(const fink & f);virtual void ShowAll() const;virtual void SetAll();std::ofstream & WriteAll(std::ofstream & of) const; };class highfink : public manager, public fink { public:highfink();highfink(const std::string & fn, const std::string & ln,const std::string & j, const std::string & rpo,int ico);highfink(const ab_emp & e, const std::string & rpo, int ico);highfink(const fink & f, int ico);highfink(const manager & m, const std::string & rpo);highfink(const highfink & h);virtual void ShowAll() const;virtual void SetAll();std::ofstream & WriteAll(std::ofstream & fout) const; };#endifemp.cpp
#include"17-6_emp.h" #include <fstream> #include <ostream> #include <string>// ab_emp methods ab_emp::ab_emp() {fname = "none";lname = "none";job = "none"; }ab_emp::ab_emp(const std::string & fn, const std::string & ln,const std::string & j) : fname(fn), lname(ln), job(j) { }ab_emp::~ab_emp() {}void ab_emp::ShowAll() const {std::cout << "firstname: " << fname << std::endl;std::cout << "lastname: " << lname << std::endl;std::cout << "job: " << job << std::endl; }void ab_emp::SetAll() {std::cout << "Enter firstname: ";std::getline(std::cin, fname);std::cout << "Enter lastname: ";std::getline(std::cin, lname);std::cout << "Enter job: ";std::getline(std::cin, job); }std::ofstream & ab_emp::WriteAll (std::ofstream &of) const{of << fname << " " << lname << " " << job;return of; }std::ostream & operator<<(std::ostream & os, const ab_emp & e){os << e.fname << " " << e.lname << " " << e.job;return os; }// employee methods employee::employee(){}employee::employee(const std::string & fn, const std::string & ln,const std::string & j): ab_emp(fn, ln, j) {}void employee::ShowAll() const {ab_emp::ShowAll(); }void employee::SetAll() {ab_emp::SetAll(); }std::ofstream & employee::WriteAll(std::ofstream &of) const {of << Employee << " ";ab_emp::WriteAll(of);return of; }// manager methods manager::manager() {inchargeof = 0; }manager::manager(const std::string & fn, const std::string & ln,const std::string & job, int ico): ab_emp(fn, ln, job), inchargeof(ico) { }manager::manager(const ab_emp & e, int ico) : ab_emp(e), inchargeof(ico) {}manager::manager(const manager & m) : ab_emp(m), inchargeof(m.inchargeof){}void manager::ShowAll() const {ab_emp::ShowAll();std::cout << "InchargeOf: " << inchargeof << std::endl; }void manager::SetAll() {ab_emp::SetAll();std::cout << "Enter inchargeof: ";std::cin >> inchargeof;std::cin.get(); }std::ofstream & manager::WriteAll(std::ofstream &of) const {of << Manager << " ";ab_emp::WriteAll(of) << " " << inchargeof;return of; }// fink methods fink::fink() {reportsto = "none"; }fink::fink(const std::string & fn, const std::string ln,const std::string & job, const std::string repo) : ab_emp(fn,ln,job), reportsto(repo) {}fink::fink(const ab_emp & e, const std::string repo): ab_emp(e), reportsto(repo) {}fink::fink(const fink & f): ab_emp(f) ,reportsto(f.reportsto) { }void fink::ShowAll() const {ab_emp::ShowAll();std::cout << "Reportsto: " << reportsto << std::endl; }void fink::SetAll() {ab_emp::SetAll();std::cout << "Enter reportsto: ";std::getline(std::cin, reportsto); }std::ofstream & fink::WriteAll(std::ofstream & fout) const {fout << Fink << " ";ab_emp::WriteAll(fout)<< " " << reportsto;return fout; }// highfink methods highfink::highfink(){}highfink::highfink(const std::string & fn, const std::string & ln,const std::string & j, const std::string & repo, int ico): ab_emp(fn,ln,j), manager(fn,ln,j,ico), fink(fn,ln,j, repo) {}highfink::highfink(const ab_emp & e, const std::string & repo, int ico): ab_emp(e), manager(e,ico), fink(e,repo) {}highfink::highfink(const fink & f, int ico): ab_emp(f), fink(f), manager((const ab_emp &)f, ico) {}highfink::highfink(const manager & m, const std::string & repo): ab_emp(m), manager(m), fink((const ab_emp &)m, repo) {}highfink::highfink(const highfink & h): ab_emp(h), manager(h), fink(h) {}void highfink::ShowAll() const {ab_emp::ShowAll();std::cout << "ReportsTo: " << fink::ReportsTo() << std::endl;std::cout << "Inchargeof: "<< manager::InChargeOf() << std::endl; }void highfink::SetAll() {ab_emp::SetAll();std::cout << "Enter reportsto: ";std::getline(std::cin, fink::ReportsTo());std::cout << "Enter inchargeof: ";std::cin>>manager::InChargeOf();std::cin.get(); }std::ofstream & highfink::WriteAll(std::ofstream &fout) const {fout << Highfink << " ";ab_emp::WriteAll(fout) << " " << fink::ReportsTo() << " " << manager::InChargeOf();return fout; }main.cpp
#include"17-6_emp.h" #include <fstream>using namespace std;inline void showline(int n); void show_menu(); inline void eatline();const int MAX = 10;int main() {ab_emp* pc[MAX];int ct; // number counterstring fname, lname, job, reportsto;int inchargeof;// read from fileifstream fin("out.txt", ios_base::in);if(fin.is_open()){int kind;while(fin>>kind){switch (kind) {case Employee:fin >> fname;fin >> lname;fin >> job;pc[ct] = new employee(fname, lname, job);break;case Manager:fin >> fname;fin >> lname;fin >> job;fin >> inchargeof;pc[ct] = new manager(fname, lname, job, inchargeof);break;case Fink:fin >> fname;fin >> lname;fin >> job;fin >> reportsto;pc[ct] = new fink(fname, lname, job, reportsto);break;case Highfink:fin >> fname;fin >> lname;fin >> job;fin >> reportsto;fin >> inchargeof;pc[ct] = new highfink(fname, lname, job, reportsto, inchargeof);break;}ct++;}cout << "content in out.txt: " << endl;for(int i=0; i<ct; i++){pc[i]->ShowAll();}fin.close();}// add elementschar choice;show_menu();while(cin>>choice && choice!='q' && ct<MAX){eatline();switch (choice) {case 'e':pc[ct] = new employee;pc[ct]->SetAll();break;case 'm':pc[ct] = new manager;pc[ct]->SetAll();break;case 'f':pc[ct] = new fink;pc[ct]->SetAll();break;case 'h':pc[ct] = new highfink;pc[ct]->SetAll();break;}ct++;show_menu();}for(int i=0 ; i<ct; i++){pc[i]->ShowAll();}// write to fileofstream fout("out.txt", ios_base::out);for(int i=0; i<ct; i++){pc[i]->WriteAll(fout);fout << endl;}fout.close();cout << "all contents written to out.txt\n";for(int i=0; i<ct;i++){delete pc[i];}return 0;}void show_menu(){ios_base::fmtflags old_fmt = cout.setf(ios_base::left, ios_base::adjustfield);showline(35);cout.width(20);cout << "e. employee";cout << "m. manager" << endl;cout.width(20);cout << "f. fink";cout << "h. highfink" << endl;cout << "q. quit" << endl;showline(35);cout << "Select a type: " << endl;cout.setf(old_fmt); }inline void showline(int n){cout.fill('-');cout.width(n);cout << "-" << endl;cout.fill(' '); }inline void eatline() {while(cin.get() != '\n') continue; } -
下面是某个程序的部分代码。该程序将键盘输入读取到一个由 string 对象组成的 vector 中,将字符串内容(而不是 string 对象)存储到一个文件中,然后该文件的内容复制到另一个由 string 对象组成的 vector 中。
int main() {using namespace std;vector<string> vostr;string temp;// acquire stringscout << "Enter strings (empty line to quit) : \n";while (getline(cin, temp) && temp[0] != '\0' ) {vostr.push_back(temp);}cout << "Here is your intput.\n ";for_each(vostr.begin(), vostr.end(), ShowStr);// store in a fileofstream fout("strings.dat", ios_base::out | ios_base::binary);for_each(vostr.begin(), vostr.end(), Store(fout));fout.close;// recover file contentsvector<string> vistr;ifstream fin("strings.dat", ios_base::in | ios_base::binary);if (!fin.is_open() ) {cerr << "Could not open file for input.\n";exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}GetStrs(fin, vistr);cout << "\nHere are the strings read from the file:\n";for_each(vistr.begin(), vistr.end(), ShowStr);return 0; }该程序以二进制格式打开文件,并想使用 read() 和 write() 来完成 I/O。余下的工作如下所述。
- 编写函数 void ShowStr(const string &),它显示一个 string 对象,并在显示完后换行。
- 编写函数符 Store,它将字符串信息写入到文件中。Store 的构造函数应接受一个指定 ifstream 对象的参数,而重载的 operator()(const string &) 应指出要写入到文件中的字符串。一种可行的计划是,首先将字符串的长度写入到文件中,然后将字符串的内容写入到文件中。例如,如果 len 存储了字符串的长度,可以这样做:
成员函数 data() 返回一个指针,该指针指向一个其中存储了字符串中字符的数组。它类似于成员函数 c_str(),只是后者在数组末尾加上了一个空字符。os.write((char *) &len, sizeof(std::size_t)); // store length os.write(s.data(), len); - 编写函数 GetStrs(),它根据文件恢复信息。该函数可以使用 read() 来获得字符串的长度,然后使用一个循环从文件中读取相应数量的字符,并将它们附加到一个原来为空的临时 string 末尾。由于 string 的数据是私有的,因此必须使用 string 类的方法来将数据存储到 string 对象中,而不能直接存储。
答:
#include <cstddef> #include <cstdlib> #include <ios> #include<iostream> #include<fstream> #include <ostream> #include<vector> #include<string> #include<algorithm>using namespace std;class Store { private:ostream &os; public:Store(ostream &o):os(o){}void operator()(const string & s){size_t len = s.length();os.write((const char *)&len, sizeof(std::size_t));os.write(s.data(),len);} };inline void ShowStr(const std::string& s) {cout << s << endl; }void GetStrs(std::ifstream & fin, std::vector<std::string> & vistr);int main(){using namespace std;vector<string> vostr;string temp;// acquire stringscout << "Enter strings (empty line to quit):\n";while(getline(cin, temp)&&temp.size()>0){vostr.push_back(temp);}for_each(vostr.begin(), vostr.end(), ShowStr);// store in a fileofstream fout("string.dat", ios_base::out|ios_base::binary);for_each(vostr.begin(), vostr.end(), Store(fout));fout.close();cin.get();// recover file contentsvector<string> vistr;ifstream fin("string.dat", ios_base::in|ios_base::binary);if (!fin.is_open()){cerr << "Could not open file for input.\n";exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}GetStrs(fin, vistr);cout << "\nHere are the strings read from the file:\n";for_each(vistr.begin(), vistr.end(),ShowStr);return 0;}void GetStrs(std::ifstream & fin, std::vector<std::string> & vistr){size_t len; // string lengthwhile(fin.read( (char*)&len, sizeof(size_t) ) ){string str;char ch;for(int i=0; i< len; i++){fin.read(&ch,sizeof(char));str.push_back(ch);}vistr.push_back(str);} }
相关文章:
)
《C++ Primer Plus》第17章:输入、输出和文件(7)
编程练习 编写一个程序计算输入流中第一个$之前的字符数目,并将$留在输入流中。 #include<iostream>int main() {int ct 0;while(std::cin.peek()!$){ct;std::cin.get();}std::cout << "num: " << ct << std::endl;return 0; }答…...
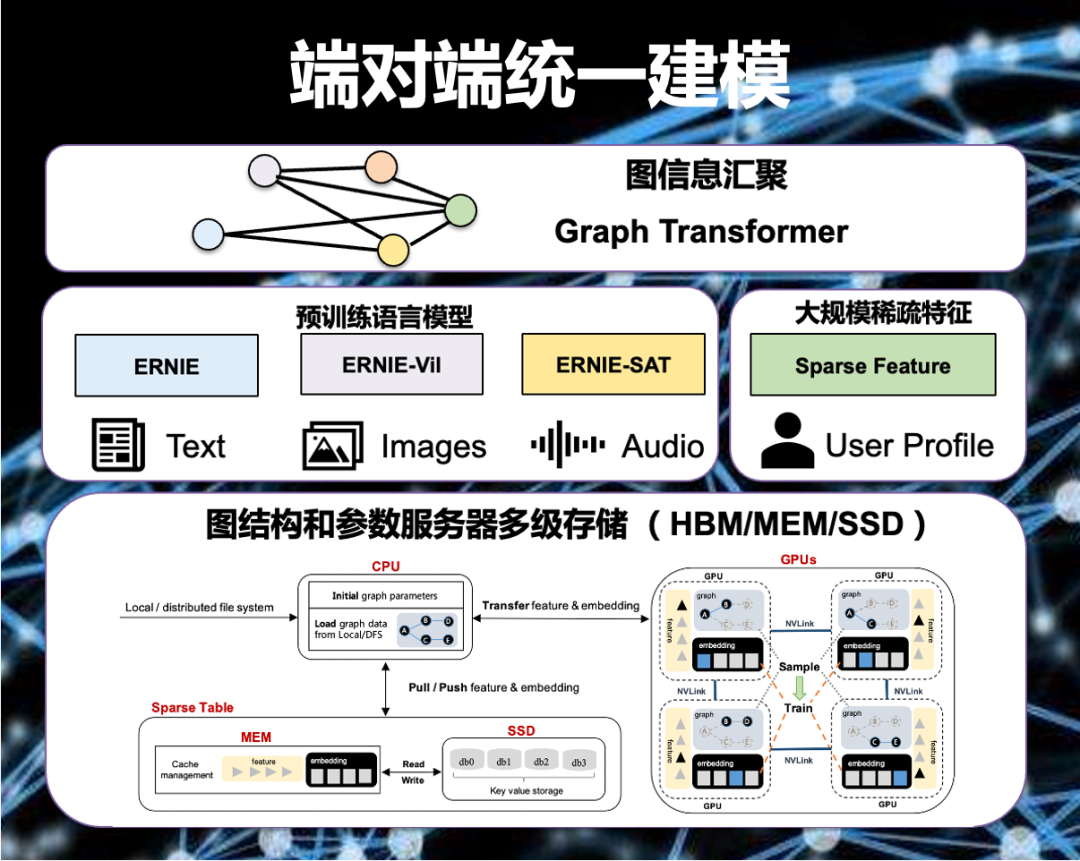
PGLBox 超大规模 GPU 端对端图学习训练框架正式发布
作者 | PGLBox项目组 导读 PGLBox是百度研发的基于GPU的大规模图模型训练框架,支持数百亿节点和边的图模型全GPU训练,已在百度广泛部署。相比业界主流的分布式 CPU 解决方案,PGLBox 具有超高性能、超大规模、算法丰富、灵活易用、落地广泛等优…...

sql-labs-Less1
靶场搭建好了,访问题目路径 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs-master/Less-1/ 我最开始在做sql-labs靶场的时候很迷茫,不知道最后到底要得到些什么,而现在我很清楚,sql注入可以获取数据库中的信息,而获取信息就是我们的目标…...

又一个国内类ChatGPT模型?【秘塔科技上线自研LLM大模型「对话写作猫」】
又一个国内类ChatGPT模型?【秘塔科技上线自研LLM大模型「对话写作猫」】 说个题外话,今天一大早就收到了Biying的邮件。前段时间不是申请了New Biying的内测吗?下午可以尝试一下玩一会儿。如果体验感还不错或者还有很多bug,那我到…...
卷麻了,00后测试用例写的比我还好,简直无地自容......
经常看到无论是刚入职场的新人,还是工作了一段时间的老人,都会对编写测试用例感到困扰?例如: 如何编写测试用例? 作为一个测试新人,刚开始接触测试,对于怎么写测试用例很是头疼,无法…...

动态网页的核心——JSP
文章目录1,JSP 概述2,JSP 小案例2.1 搭建环境2.2 导入 JSP 依赖2.3 创建 jsp 页面2.4 编写代码2.5 测试3,JSP 原理4,JSP 总结4.1 JSP的 缺点4.2技术的发展历程4.3JSP的必要性最后说一句1,JSP 概述 JSP(全称…...
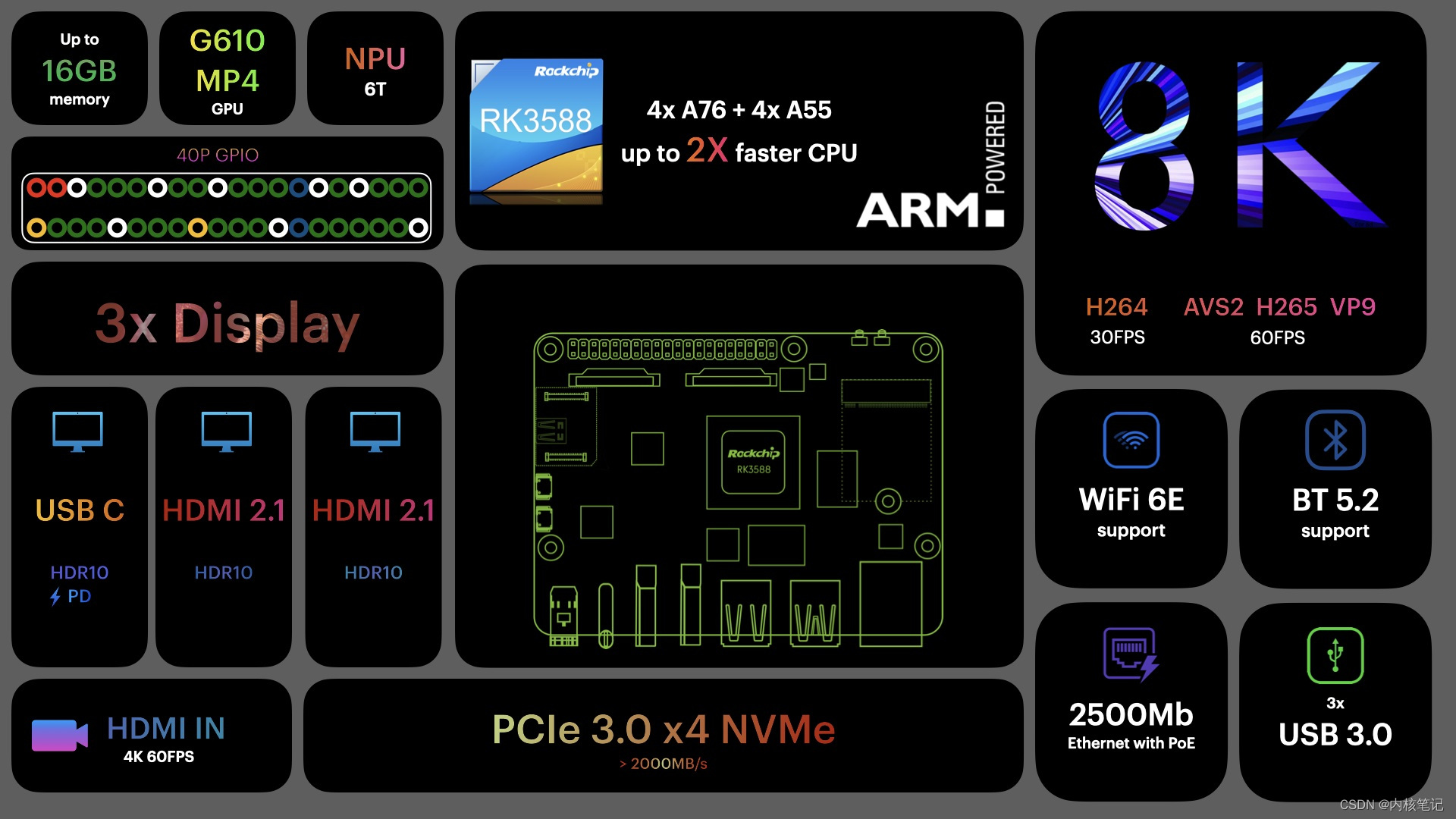
RK3588平台开发系列讲解(系统篇)init.d介绍
平台内核版本安卓版本RK3588Linux 5.10Android 12文章目录 一、Linux启动简介二、sysvinit配置三、inid.d介绍沉淀、分享、成长,让自己和他人都能有所收获!😄 📢本篇介绍init.d相关知识。 一、Linux启动简介 Linux用户空间启动时,第一个会启动init进程,用来引导启动其…...
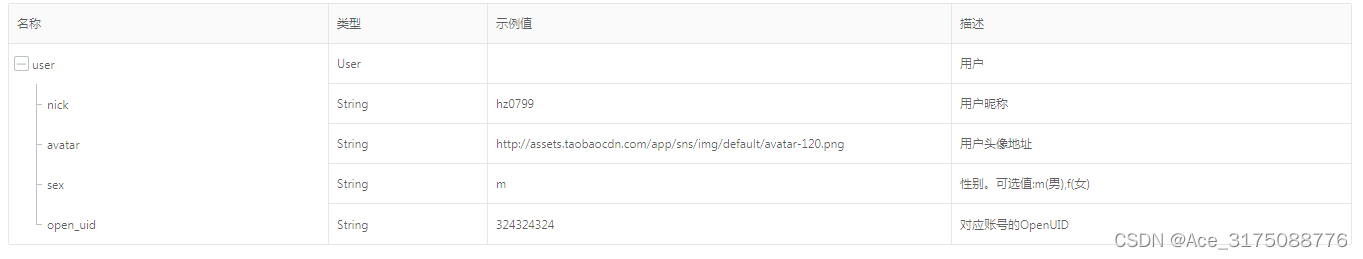
taobao.user.buyer.get( 查询买家信息API )
¥开放平台基础API必须用户授权 查询买家信息API,只能买家类应用调用。 公共参数 请求地址: HTTP地址 http://gw.api.taobao.com/router/rest 公共请求参数: 公共响应参数: 请求参数 响应参数 点击获取key和secret 请求示例 TaobaoClient client new…...
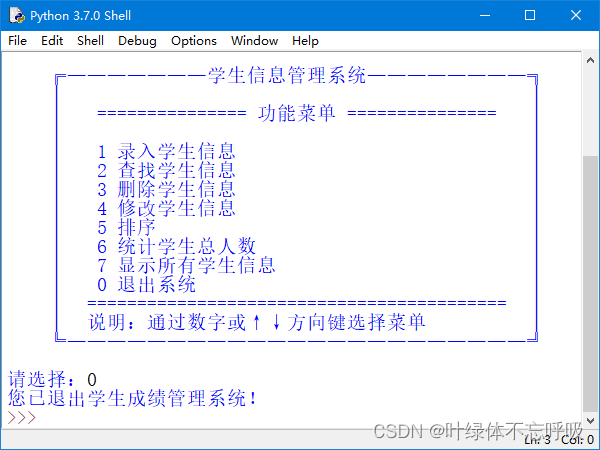
python学生信息管理系统
wx供重浩:创享日记 对话框发送:python学生信息 免费获取完整源码源文件配置教程说明等 在IDLE中运行《学生信息管理系统》即可进入如图1所示的系统主界面。在该界面中可以选择要使用功能对应的菜单进行不同的操作。在选择功能菜单时,有两种方…...

【微信小程序】-- WXML 模板语法 - 条件渲染 -- wx:if hidden (十一)
💌 所属专栏:【微信小程序开发教程】 😀 作 者:我是夜阑的狗🐶 🚀 个人简介:一个正在努力学技术的CV工程师,专注基础和实战分享 ,欢迎咨询! &…...

2023上半年软考,广州/东莞/深圳/江苏报班是明智的选择
软考是全国计算机技术与软件专业技术资格(水平)考试(简称软考)项目,是由国家人力资源和社会保障部、工业和信息化部共同组织的国家级考试,既属于国家职业资格考试,又是职称资格考试。 系统集成…...
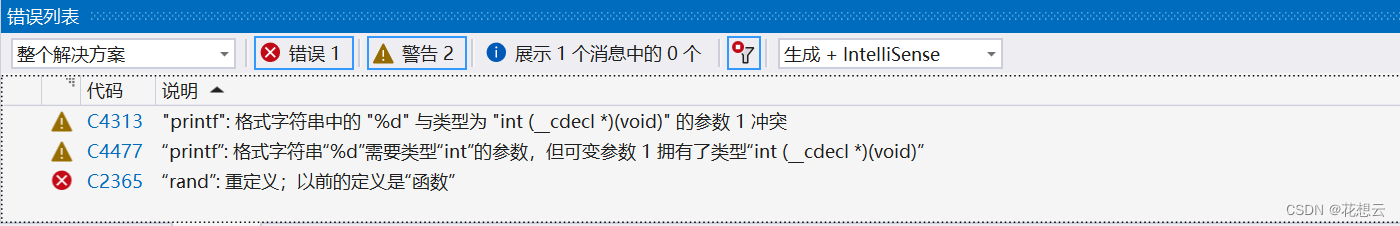
C++修炼之练气期一层——命名空间
目录 1.引例 2.命名空间的定义 3.命名空间的使用 4.命名空间使用注意事项 1.引例 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h>int rand 10;int main() {printf("%d\n", rand);return 0; } 当我们用C语言写下这样的代码,看着并没有什么语法…...
matplotlib综合学习
1.arange函数arange函数需要三个参数,分别为起始点、终止点、采样间隔。采样间隔默认值为1看例子: import numpy as np #import matplotlib.pyplot as plt xnp.arange(-5,5,1) print(x)2.绘制sin(x)曲线import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as …...

IIS .Net Core 413错误和Request body too large解决办法
错误描述图片比较大时,在前端上传就报413错误。根本到不了后端。在网上看到这个文章比较有用。https://blog.csdn.net/wstever/article/details/1288707421、修改网站Web.config配置文件加入下面这段配置<?xmlversion"1.0" encoding"utf-8"…...
—官方原版)
Spring Boot数据访问—(springboot 多数据源)—官方原版
Spring Boot 包含许多用于处理数据源的启动器,本文回答与执行此操作相关的问题。一、配置自定义数据源要配置自己的DataSource,请在配置中定义该类型的Bean。Spring Boot在任何需要的地方重用DataSource,包括数据库初始化。如果需要外部化某些…...

高燃!GitHub上标星75k+超牛的Java面试突击版
前言不论是校招还是社招都避免不了各种面试。笔试,如何去准备这些东西就显得格外重要。不论是笔试还是面试都是有章可循的,我这个有章可循‘说的意思只是说应对技术面试是可以提前准备。运筹帷幄之后,决胜千里之外!不打毫无准备的仗,我觉得大…...
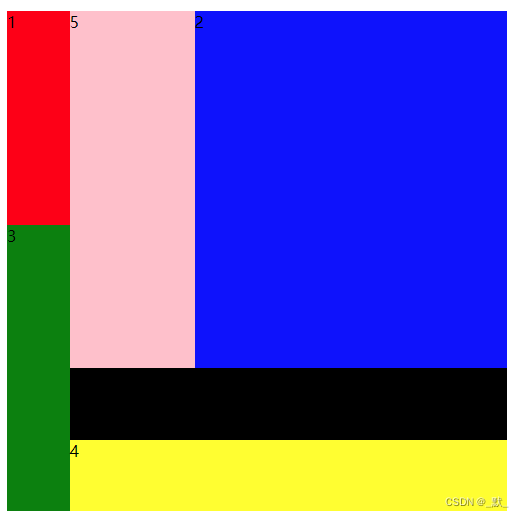
grid宫格布局新手快捷上手-f
前言 grid 网上有很多,但都是大而全的,感觉新人上手很吃力,本文仅以最快捷的方式进行介绍,如何使用grid宫格布局 本文是新人上手,若想了解更多grid布局,请阅读其他文章 使用 声明布局 display: grid;声…...

面试必刷101 Java题解 -- part 3
part1 – https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41080854/article/details/129204480 part2 – https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41080854/article/details/129224785 面试必刷101 Java题解 -- part 3动规五部曲71、斐波那契数列72、跳台阶73、最小花费爬楼梯74、最长公共子序列(二)75、最长公共…...
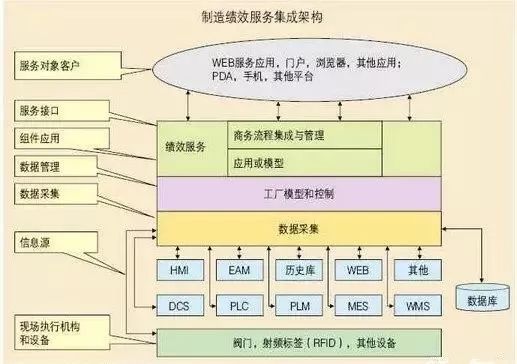
干货满满!MES的简介和运用
导读 谈及MES必须先谈生产,生产体系模型如图所示,涉及人、财、物、信息等资源,产、供、销等环节,以及供应商、客户、合作伙伴等。 其中,生产管理是通过对生产系统的战略计划、组织、指挥、实施、协调、控制等活动&…...
【ElasticSearch系列-01】初识以及安装elasticSearch
elasticSearch入门和安装一,elasticSearch入门1,什么是elasticSearch2,elasticSearch的底层优点2.1,全文检索2.2,倒排索引2.2.1,正排索引2.2.2,倒排索引2.2.3,倒排索引解决的问题2.2…...

KubeSphere 容器平台高可用:环境搭建与可视化操作指南
Linux_k8s篇 欢迎来到Linux的世界,看笔记好好学多敲多打,每个人都是大神! 题目:KubeSphere 容器平台高可用:环境搭建与可视化操作指南 版本号: 1.0,0 作者: 老王要学习 日期: 2025.06.05 适用环境: Ubuntu22 文档说…...
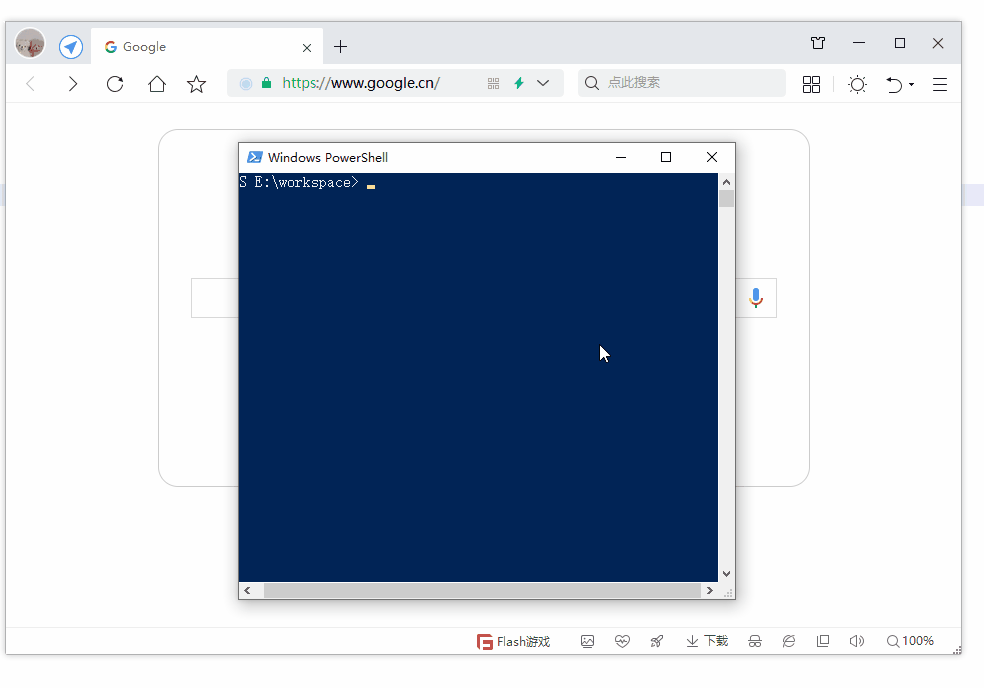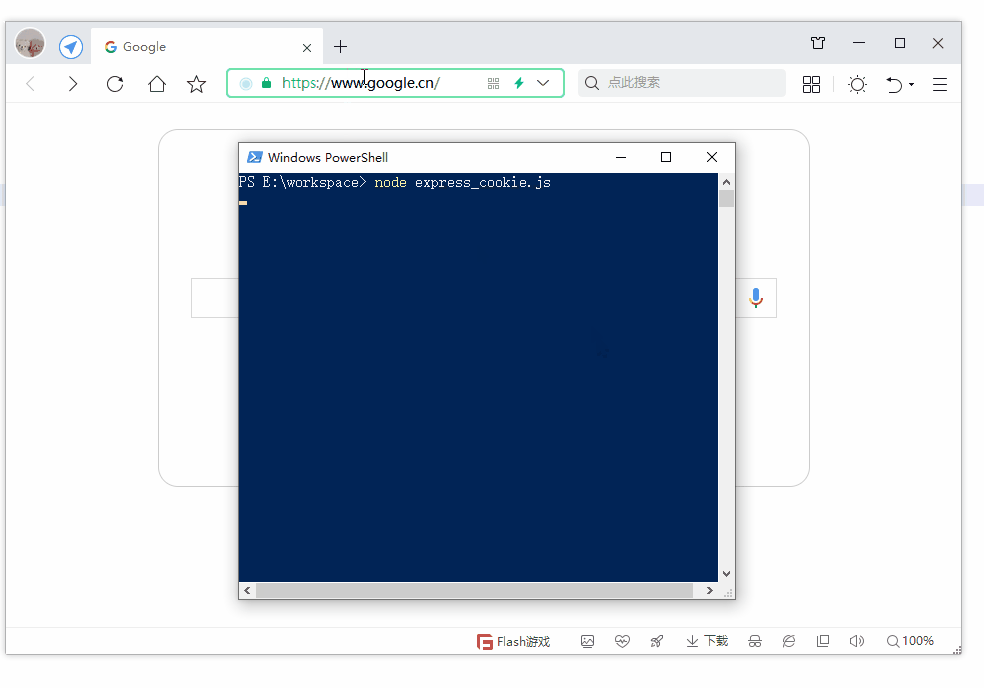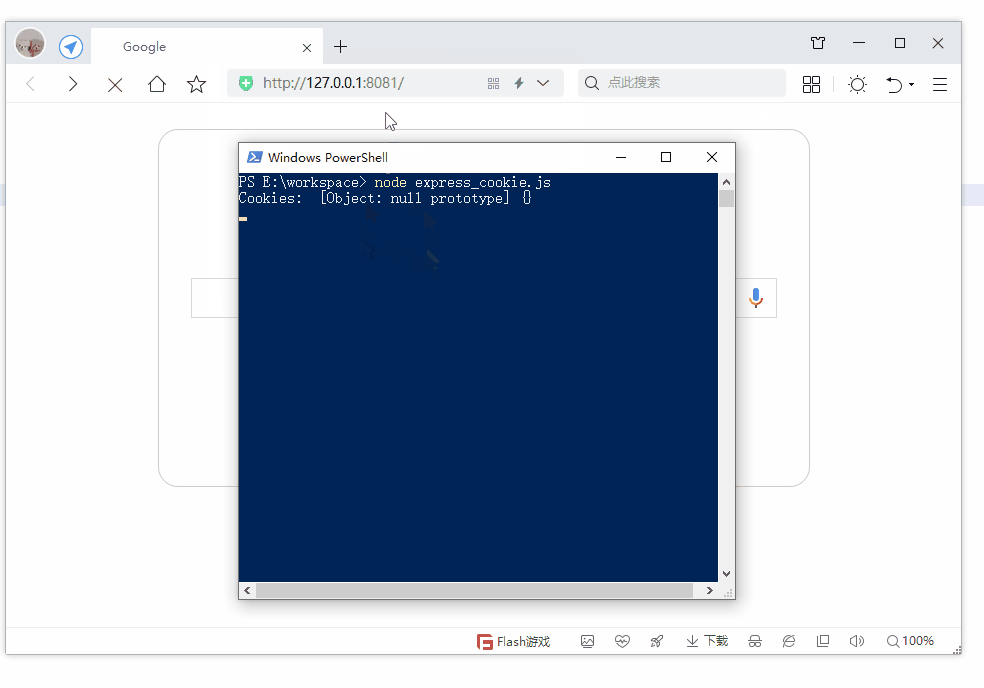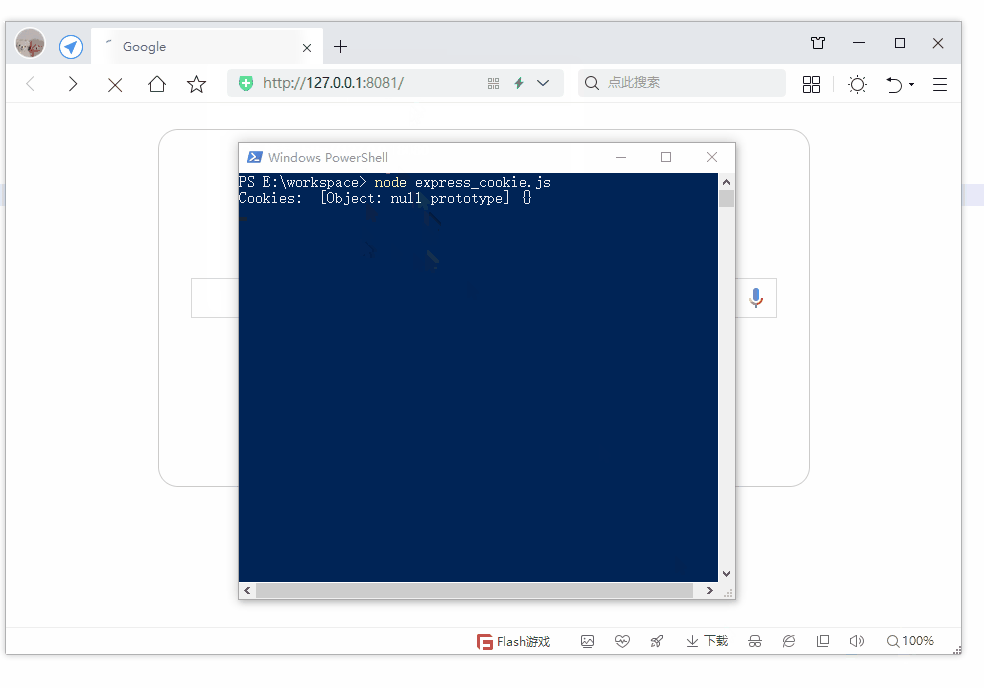
第19节 Node.js Express 框架
Express 是一个为Node.js设计的web开发框架,它基于nodejs平台。 Express 简介 Express是一个简洁而灵活的node.js Web应用框架, 提供了一系列强大特性帮助你创建各种Web应用,和丰富的HTTP工具。 使用Express可以快速地搭建一个完整功能的网站。 Expre…...

【磁盘】每天掌握一个Linux命令 - iostat
目录 【磁盘】每天掌握一个Linux命令 - iostat工具概述安装方式核心功能基础用法进阶操作实战案例面试题场景生产场景 注意事项 【磁盘】每天掌握一个Linux命令 - iostat 工具概述 iostat(I/O Statistics)是Linux系统下用于监视系统输入输出设备和CPU使…...
)
【服务器压力测试】本地PC电脑作为服务器运行时出现卡顿和资源紧张(Windows/Linux)
要让本地PC电脑作为服务器运行时出现卡顿和资源紧张的情况,可以通过以下几种方式模拟或触发: 1. 增加CPU负载 运行大量计算密集型任务,例如: 使用多线程循环执行复杂计算(如数学运算、加密解密等)。运行图…...

中医有效性探讨
文章目录 西医是如何发展到以生物化学为药理基础的现代医学?传统医学奠基期(远古 - 17 世纪)近代医学转型期(17 世纪 - 19 世纪末)现代医学成熟期(20世纪至今) 中医的源远流长和一脉相承远古至…...
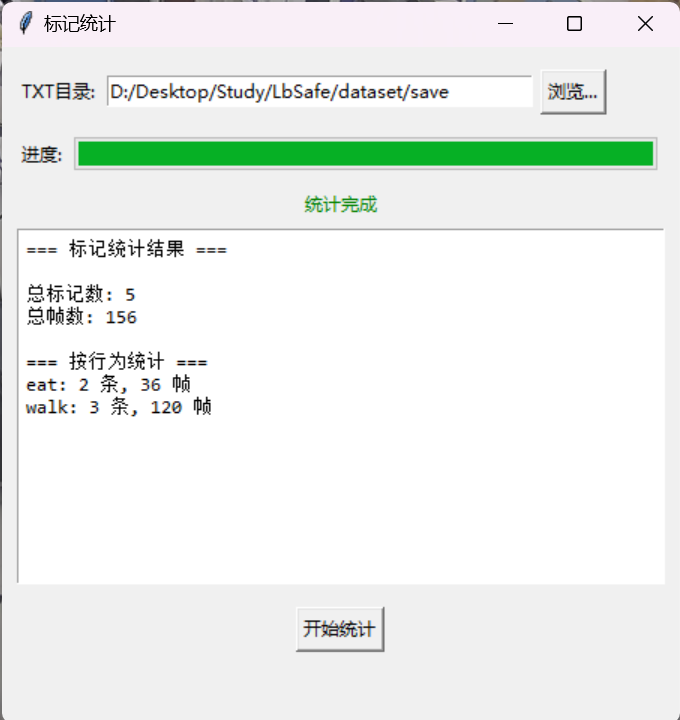
视频行为标注工具BehaviLabel(源码+使用介绍+Windows.Exe版本)
前言: 最近在做行为检测相关的模型,用的是时空图卷积网络(STGCN),但原有kinetic-400数据集数据质量较低,需要进行细粒度的标注,同时粗略搜了下已有开源工具基本都集中于图像分割这块,…...
安装docker)
Linux离线(zip方式)安装docker
目录 基础信息操作系统信息docker信息 安装实例安装步骤示例 遇到的问题问题1:修改默认工作路径启动失败问题2 找不到对应组 基础信息 操作系统信息 OS版本:CentOS 7 64位 内核版本:3.10.0 相关命令: uname -rcat /etc/os-rele…...
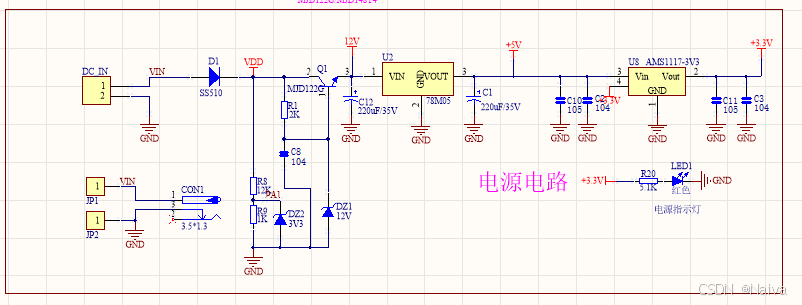
【电力电子】基于STM32F103C8T6单片机双极性SPWM逆变(硬件篇)
本项目是基于 STM32F103C8T6 微控制器的 SPWM(正弦脉宽调制)电源模块,能够生成可调频率和幅值的正弦波交流电源输出。该项目适用于逆变器、UPS电源、变频器等应用场景。 供电电源 输入电压采集 上图为本设计的电源电路,图中 D1 为二极管, 其目的是防止正负极电源反接, …...
集成 Mybatis-Plus 和 Mybatis-Plus-Join)
纯 Java 项目(非 SpringBoot)集成 Mybatis-Plus 和 Mybatis-Plus-Join
纯 Java 项目(非 SpringBoot)集成 Mybatis-Plus 和 Mybatis-Plus-Join 1、依赖1.1、依赖版本1.2、pom.xml 2、代码2.1、SqlSession 构造器2.2、MybatisPlus代码生成器2.3、获取 config.yml 配置2.3.1、config.yml2.3.2、项目配置类 2.4、ftl 模板2.4.1、…...

LOOI机器人的技术实现解析:从手势识别到边缘检测
LOOI机器人作为一款创新的AI硬件产品,通过将智能手机转变为具有情感交互能力的桌面机器人,展示了前沿AI技术与传统硬件设计的完美结合。作为AI与玩具领域的专家,我将全面解析LOOI的技术实现架构,特别是其手势识别、物体识别和环境…...
