LLVM学习笔记(62)
4.4.3.3.2. 指令处理的设置
4.4.3.3.2.1. 目标机器相关设置
除了基类以外,X86TargetLowering构造函数本身也是一个庞然大物,我们必须要分段来看。V7.0做了不小的改动,改进了代码的结构,修改了一些指令的设置。
100 X86TargetLowering::X86TargetLowering(const X86TargetMachine &TM,
101 const X86Subtarget &STI)
102 : TargetLowering(TM), Subtarget(&STI) {
103 bool UseX87 = !Subtarget.useSoftFloat() && Subtarget.hasX87();
104 X86ScalarSSEf64 = Subtarget->hasSSE2();
105 X86ScalarSSEf32 = Subtarget->hasSSE1();
106 MVT PtrVT = MVT::getIntegerVT(TM.getPointerSizeInBits(0));
107
108 // Set up the TargetLowering object.
109
110 // X86 is weird. It always uses i8 for shift amounts and setcc results.
111 setBooleanContents(ZeroOrOneBooleanContent);
112 // X86-SSE is even stranger. It uses -1 or 0 for vector masks.
113 setBooleanVectorContents(ZeroOrNegativeOneBooleanContent);
114
115 // For 64-bit, since we have so many registers, use the ILP scheduler.
116 // For 32-bit, use the register pressure specific scheduling.
117 // For Atom, always use ILP scheduling.
118 if (Subtarget->isAtom())
119 setSchedulingPreference(Sched::ILP);
120 else if (Subtarget->is64Bit())
121 setSchedulingPreference(Sched::ILP);
122 else
123 setSchedulingPreference(Sched::RegPressure);
124 const X86RegisterInfo *RegInfo = Subtarget->getRegisterInfo();
125 setStackPointerRegisterToSaveRestore(RegInfo->getStackRegister());
126
127 // Bypass expensive divides on Atom when compiling with O2.
128 if (TM.getOptLevel() >= CodeGenOpt::Default) {
129 if (Subtarget->hasSlowDivide32())
130 addBypassSlowDiv(32, 8);
131 if (Subtarget->hasSlowDivide64() && Subtarget->is64Bit())
132 addBypassSlowDiv(64, 32);
133 }
134
135 if (Subtarget->isTargetKnownWindowsMSVC() ||
136 Subtarget.isTargetWindowsItanium()) {
137 // Setup Windows compiler runtime calls.
138 setLibcallName(RTLIB::SDIV_I64, "_alldiv");
139 setLibcallName(RTLIB::UDIV_I64, "_aulldiv");
140 setLibcallName(RTLIB::SREM_I64, "_allrem");
141 setLibcallName(RTLIB::UREM_I64, "_aullrem");
142 setLibcallName(RTLIB::MUL_I64, "_allmul");
143 setLibcallCallingConv(RTLIB::SDIV_I64, CallingConv::X86_StdCall);
144 setLibcallCallingConv(RTLIB::UDIV_I64, CallingConv::X86_StdCall);
145 setLibcallCallingConv(RTLIB::SREM_I64, CallingConv::X86_StdCall);
146 setLibcallCallingConv(RTLIB::UREM_I64, CallingConv::X86_StdCall);
147 setLibcallCallingConv(RTLIB::MUL_I64, CallingConv::X86_StdCall);
148 }
149
150 if (Subtarget->isTargetDarwin()) {
151 // Darwin should use _setjmp/_longjmp instead of setjmp/longjmp.
152 setUseUnderscoreSetJmp(false);
153 setUseUnderscoreLongJmp(false);
154 } else if (Subtarget->isTargetWindowsGNU()) {
155 // MS runtime is weird: it exports _setjmp, but longjmp!
156 setUseUnderscoreSetJmp(true);
157 setUseUnderscoreLongJmp(false);
158 } else {
159 setUseUnderscoreSetJmp(true);
160 setUseUnderscoreLongJmp(true);
161 }
162
163 // Set up the register classes.
164 addRegisterClass(MVT::i8, &X86::GR8RegClass);
165 addRegisterClass(MVT::i16, &X86::GR16RegClass);
166 addRegisterClass(MVT::i32, &X86::GR32RegClass);
167 if (Subtarget->is64Bit())
168 addRegisterClass(MVT::i64, &X86::GR64RegClass);
111行将布尔值的表示方式更改为ZeroOrOneBooleanContent(原是UndefinedBooleanContent)。118~123行根据CPU类型更改调度模式。125行的getStackRegister()返回X86RegisterInfo的StackPtr成员(它在X86RegisterInfo构造函数里根据目标机器设置)。
基类TargetLoweringBase类型为DenseMap<unsigned int, unsigned int>的BypassSlowDivWidths的容器用于通知代码生成器绕过慢的除法或取余指令。例如,BypassSlowDivWidths[32,8]格式代码生成器在操作数为小于256的正整数时,使用8位div/rem指令绕过32位div/rem指令。上面130行为类似Atom的处理器设置这个容器项。
164行以下的GRXRegClass都是由TableGen根据.td文件描述生成在X86GenRegisterInfo.inc文件里的对象定义。为了关联这些对象与它们的类型,定义了容器AvailableRegClasses(类型std::vector< std::pair<MVT, const TargetRegisterClass*>>)与容器const TargetRegisterClass *RegClassForVT[MVT:: LAST_VALUETYPE],并通过addRegisterClass()实现关联。
4.4.3.3.2.2. 标量操作数类型的处理设置
下面根据目标X86芯片支持的指令集为各种操作设置处理活动。这是一些比较繁琐的工作。要针对每种IR操作与每种操作数类型来设置。下面Expand的含义是建议将操作数分为较小的两部分。
X86TargetLowering::X86TargetLowering(续)
170 for (MVT VT : MVT::integer_valuetypes())
171 setLoadExtAction(ISD::SEXTLOAD, VT, MVT::i1, Promote);
172
173 // We don't accept any truncstore of integer registers.
174 setTruncStoreAction(MVT::i64, MVT::i32, Expand);
175 setTruncStoreAction(MVT::i64, MVT::i16, Expand);
176 setTruncStoreAction(MVT::i64, MVT::i8 , Expand);
177 setTruncStoreAction(MVT::i32, MVT::i16, Expand);
178 setTruncStoreAction(MVT::i32, MVT::i8 , Expand);
179 setTruncStoreAction(MVT::i16, MVT::i8, Expand);
180
181 setTruncStoreAction(MVT::f64, MVT::f32, Expand);
182
183 // SETOEQ and SETUNE require checking two conditions.
184 setCondCodeAction(ISD::SETOEQ, MVT::f32, Expand);
185 setCondCodeAction(ISD::SETOEQ, MVT::f64, Expand);
186 setCondCodeAction(ISD::SETOEQ, MVT::f80, Expand);
187 setCondCodeAction(ISD::SETUNE, MVT::f32, Expand);
188 setCondCodeAction(ISD::SETUNE, MVT::f64, Expand);
189 setCondCodeAction(ISD::SETUNE, MVT::f80, Expand);
190
191 // Integer absolute.
192 if (Subtarget.hasCMov()) {
193 setOperationAction(ISD::ABS , MVT::i16 , Custom);
194 setOperationAction(ISD::ABS, MVT::i32 , Custom);
195 if (Subtarget.is64Bit())
196 setOperationAction(ISD::ABS, MVT::i64 , Custom);
197 }
198
199 // Promote all UINT_TO_FP to larger SINT_TO_FP's, as X86 doesn't have this
200 // operation.
201 setOperationAction(ISD::UINT_TO_FP , MVT::i1 , Promote);
202 setOperationAction(ISD::UINT_TO_FP , MVT::i8 , Promote);
203 setOperationAction(ISD::UINT_TO_FP , MVT::i16 , Promote);
204
205 if (Subtarget.is64Bit()) {
206 if (!Subtarget.useSoftFloat() && Subtarget.hasAVX512())
207 // f32/f64 are legal, f80 is custom.
208 setOperationAction(ISD::UINT_TO_FP , MVT::i32 , Custom);
209 else
210 setOperationAction(ISD::UINT_TO_FP , MVT::i32 , Promote);
211 setOperationAction(ISD::UINT_TO_FP , MVT::i64 , Custom);
212 } else if (!Subtarget.useSoftFloat()) {
213 // We have an algorithm for SSE2->double, and we turn this into a
214 // 64-bit FILD followed by conditional FADD for other targets.
215 setOperationAction(ISD::UINT_TO_FP , MVT::i64 , Custom);
216 // We have an algorithm for SSE2, and we turn this into a 64-bit
217 // FILD or VCVTUSI2SS/SD for other targets.
218 setOperationAction(ISD::UINT_TO_FP , MVT::i32 , Custom);
219 } else {
220 setOperationAction(ISD::UINT_TO_FP , MVT::i32 , Expand);
221 }
222
223 // Promote i1/i8 SINT_TO_FP to larger SINT_TO_FP's, as X86 doesn't have
224 // this operation.
225 setOperationAction(ISD::SINT_TO_FP , MVT::i1 , Promote);
226 setOperationAction(ISD::SINT_TO_FP , MVT::i8 , Promote);
227
228 if (!Subtarget->useSoftFloat()) {
229 // SSE has no i16 to fp conversion, only i32
230 if (X86ScalarSSEf32) {
231 setOperationAction(ISD::SINT_TO_FP , MVT::i16 , Promote);
232 // f32 and f64 cases are Legal, f80 case is not
233 setOperationAction(ISD::SINT_TO_FP , MVT::i32 , Custom);
234 } else {
235 setOperationAction(ISD::SINT_TO_FP , MVT::i16 , Custom);
236 setOperationAction(ISD::SINT_TO_FP , MVT::i32 , Custom);
237 }
238 } else {
239 setOperationAction(ISD::SINT_TO_FP , MVT::i16 , Promote);
240 setOperationAction(ISD::SINT_TO_FP , MVT::i32 , Promote Expand);
241 }
242
243 // Promote i1/i8 FP_TO_SINT to larger FP_TO_SINTS's, as X86 doesn't have
244 // this operation.
245 setOperationAction(ISD::FP_TO_SINT , MVT::i1 , Promote);
246 setOperationAction(ISD::FP_TO_SINT , MVT::i8 , Promote);
247
248 if (!Subtarget.useSoftFloat()) {
249 // In 32-bit mode these are custom lowered. In 64-bit mode F32 and F64
250 // are Legal, f80 is custom lowered.
251 setOperationAction(ISD::FP_TO_SINT , MVT::i64 , Custom);
252 setOperationAction(ISD::SINT_TO_FP , MVT::i64 , Custom);
253
254 if (X86ScalarSSEf32) {
255 setOperationAction(ISD::FP_TO_SINT , MVT::i16 , Promote);
256 // f32 and f64 cases are Legal, f80 case is not
257 setOperationAction(ISD::FP_TO_SINT , MVT::i32 , Custom);
258 } else {
259 setOperationAction(ISD::FP_TO_SINT , MVT::i16 , Custom);
260 setOperationAction(ISD::FP_TO_SINT , MVT::i32 , Custom);
261 }
262 } else {
263 setOperationAction(ISD::FP_TO_SINT , MVT::i16 , Promote);
264 setOperationAction(ISD::FP_TO_SINT , MVT::i32 , Expand);
265 setOperationAction(ISD::FP_TO_SINT , MVT::i64 , Expand);
266 }
267
268 // Handle FP_TO_UINT by promoting the destination to a larger signed
269 // conversion.
270 setOperationAction(ISD::FP_TO_UINT , MVT::i1 , Promote);
271 setOperationAction(ISD::FP_TO_UINT , MVT::i8 , Promote);
272 setOperationAction(ISD::FP_TO_UINT , MVT::i16 , Promote);
273
274 if (Subtarget.is64Bit()) {
275 if (!Subtarget.useSoftFloat() && Subtarget.hasAVX512()) {
276 // FP_TO_UINT-i32/i64 is legal for f32/f64, but custom for f80.
277 setOperationAction(ISD::FP_TO_UINT , MVT::i32 , Custom);
278 setOperationAction(ISD::FP_TO_UINT , MVT::i64 , Custom);
279 } else {
280 setOperationAction(ISD::FP_TO_UINT , MVT::i32 , Promote);
281 setOperationAction(ISD::FP_TO_UINT , MVT::i64 , Expand);
282 }
283 } else if (!Subtarget.useSoftFloat()) {
284 // Since AVX is a superset of SSE3, only check for SSE here.
285 if (Subtarget.hasSSE1() && !Subtarget.hasSSE3())
286 // Expand FP_TO_UINT into a select.
287 // FIXME: We would like to use a Custom expander here eventually to do
288 // the optimal thing for SSE vs. the default expansion in the legalizer.
289 setOperationAction(ISD::FP_TO_UINT , MVT::i32 , Expand);
290 else
291 // With AVX512 we can use vcvts[ds]2usi for f32/f64->i32, f80 is custom.
292 // With SSE3 we can use fisttpll to convert to a signed i64; without
293 // SSE, we're stuck with a fistpll.
294 setOperationAction(ISD::FP_TO_UINT , MVT::i32 , Custom);
295
296 setOperationAction(ISD::FP_TO_UINT , MVT::i64 , Custom);
297 }
298
299 // TODO: when we have SSE, these could be more efficient, by using movd/movq.
300 if (!X86ScalarSSEf64) {
301 setOperationAction(ISD::BITCAST , MVT::f32 , Expand);
302 setOperationAction(ISD::BITCAST , MVT::i32 , Expand);
303 if (Subtarget->is64Bit()) {
304 setOperationAction(ISD::BITCAST , MVT::f64 , Expand);
305 // Without SSE, i64->f64 goes through memory.
306 setOperationAction(ISD::BITCAST , MVT::i64 , Expand);
307 }
308 } else if (!Subtarget.is64Bit())
309 setOperationAction(ISD::BITCAST , MVT::i64 , Custom);
310
311 // Scalar integer divide and remainder are lowered to use operations that
312 // produce two results, to match the available instructions. This exposes
313 // the two-result form to trivial CSE, which is able to combine x/y and x%y
314 // into a single instruction.
315 //
316 // Scalar integer multiply-high is also lowered to use two-result
317 // operations, to match the available instructions. However, plain multiply
318 // (low) operations are left as Legal, as there are single-result
319 // instructions for this in x86. Using the two-result multiply instructions
320 // when both high and low results are needed must be arranged by dagcombine.
321 for (auto VT : { MVT::i8, MVT::i16, MVT::i32, MVT::i64 }) {
322 setOperationAction(ISD::MULHS, VT, Expand);
323 setOperationAction(ISD::MULHU, VT, Expand);
324 setOperationAction(ISD::SDIV, VT, Expand);
325 setOperationAction(ISD::UDIV, VT, Expand);
326 setOperationAction(ISD::SREM, VT, Expand);
327 setOperationAction(ISD::UREM, VT, Expand);
328 }
329
330 setOperationAction(ISD::BR_JT , MVT::Other, Expand);
331 setOperationAction(ISD::BRCOND , MVT::Other, Custom);
332 for (auto VT : { MVT::f32, MVT::f64, MVT::f80, MVT::f128,
333 MVT::i8, MVT::i16, MVT::i32, MVT::i64 }) {
334 setOperationAction(ISD::BR_CC, VT, Expand);
335 setOperationAction(ISD::SELECT_CC, VT, Expand);
336 }
337 if (Subtarget->is64Bit())
338 setOperationAction(ISD::SIGN_EXTEND_INREG, MVT::i32, Legal);
339 setOperationAction(ISD::SIGN_EXTEND_INREG, MVT::i16 , Legal);
340 setOperationAction(ISD::SIGN_EXTEND_INREG, MVT::i8 , Legal);
341 setOperationAction(ISD::SIGN_EXTEND_INREG, MVT::i1 , Expand);
342 setOperationAction(ISD::FP_ROUND_INREG , MVT::f32 , Expand);
343
344 setOperationAction(ISD::FREM , MVT::f32 , Expand);
345 setOperationAction(ISD::FREM , MVT::f64 , Expand);
346 setOperationAction(ISD::FREM , MVT::f80 , Expand);
347 setOperationAction(ISD::FLT_ROUNDS_ , MVT::i32 , Custom);
348
349 // Promote the i8 variants and force them on up to i32 which has a shorter
350 // encoding.
351 setOperationPromotedToType(ISD::CTTZ , MVT::i8 , MVT::i32);
352 setOperationPromotedToType(ISD::CTTZ_ZERO_UNDEF, MVT::i8 , MVT::i32);
353 if (Subtarget->hasBMI()) {
354 setOperationAction(ISD::CTTZ , MVT::i16 , Custom);
355 setOperationAction(ISD::CTTZ , MVT::i32 , Custom);
356 setOperationAction(ISD::CTTZ_ZERO_UNDEF, MVT::i16 , Legal);
357 setOperationAction(ISD::CTTZ_ZERO_UNDEF, MVT::i32 , Legal);
358 if (Subtarget->is64Bit()) {
359 setOperationAction(ISD::CTTZ , MVT::i64 , Custom);
360 setOperationAction(ISD::CTTZ_ZERO_UNDEF, MVT::i64, Expand);
361 }
362 }
363
364 if (Subtarget->hasLZCNT()) {
365 // When promoting the i8 variants, force them to i32 for a shorter
366 // encoding.
367 setOperationPromotedToType(ISD::CTLZ , MVT::i8 , MVT::i32);
368 setOperationPromotedToType(ISD::CTLZ_ZERO_UNDEF, MVT::i8 , MVT::i32);
369 } else {
370 setOperationAction(ISD::CTLZ , MVT::i8 , Custom);
371 setOperationAction(ISD::CTLZ , MVT::i16 , Custom);
372 setOperationAction(ISD::CTLZ , MVT::i32 , Custom);
373 setOperationAction(ISD::CTLZ_ZERO_UNDEF, MVT::i8 , Custom);
374 setOperationAction(ISD::CTLZ_ZERO_UNDEF, MVT::i16 , Custom);
375 setOperationAction(ISD::CTLZ_ZERO_UNDEF, MVT::i32 , Custom);
376 if (Subtarget->is64Bit()) {
377 setOperationAction(ISD::CTLZ , MVT::i64 , Custom);
378 setOperationAction(ISD::CTLZ_ZERO_UNDEF, MVT::i64, Custom);
379 }
380 }
381
382 // Special handling for half-precision floating point conversions.
383 // If we don't have F16C support, then lower half float conversions
384 // into library calls.
385 if (Subtarget->useSoftFloat() || !Subtarget->hasF16C()) {
386 setOperationAction(ISD::FP16_TO_FP, MVT::f32, Expand);
387 setOperationAction(ISD::FP_TO_FP16, MVT::f32, Expand);
388 }
389
390 // There's never any support for operations beyond MVT::f32.
391 setOperationAction(ISD::FP16_TO_FP, MVT::f64, Expand);
392 setOperationAction(ISD::FP16_TO_FP, MVT::f80, Expand);
393 setOperationAction(ISD::FP_TO_FP16, MVT::f64, Expand);
394 setOperationAction(ISD::FP_TO_FP16, MVT::f80, Expand);
395
396 setLoadExtAction(ISD::EXTLOAD, MVT::f32, MVT::f16, Expand);
397 setLoadExtAction(ISD::EXTLOAD, MVT::f64, MVT::f16, Expand);
398 setLoadExtAction(ISD::EXTLOAD, MVT::f80, MVT::f16, Expand);
399 setTruncStoreAction(MVT::f32, MVT::f16, Expand);
400 setTruncStoreAction(MVT::f64, MVT::f16, Expand);
401 setTruncStoreAction(MVT::f80, MVT::f16, Expand);
402
403 if (Subtarget->hasPOPCNT()) {
404 setOperationPromotedToType(ISD::CTPOP, MVT::i8, MVT::i32);
405 } else {
406 setOperationAction(ISD::CTPOP , MVT::i8 , Expand);
407 setOperationAction(ISD::CTPOP , MVT::i16 , Expand);
408 setOperationAction(ISD::CTPOP , MVT::i32 , Expand);
409 if (Subtarget->is64Bit())
410 setOperationAction(ISD::CTPOP , MVT::i64 , Expand);
411 }
412
413 setOperationAction(ISD::READCYCLECOUNTER , MVT::i64 , Custom);
414
415 if (!Subtarget->hasMOVBE())
416 setOperationAction(ISD::BSWAP , MVT::i16 , Expand);
417
418 // These should be promoted to a larger select which is supported.
419 setOperationAction(ISD::SELECT , MVT::i1 , Promote);
420 // X86 wants to expand cmov itself.
421 for (auto VT : { MVT::f32, MVT::f64, MVT::f80, MVT::f128 }) {
422 setOperationAction(ISD::SELECT, VT, Custom);
423 setOperationAction(ISD::SETCC, VT, Custom);
424 }
425 for (auto VT : { MVT::i8, MVT::i16, MVT::i32, MVT::i64 }) {
426 if (VT == MVT::i64 && !Subtarget.is64Bit())
427 continue;
428 setOperationAction(ISD::SELECT, VT, Custom);
429 setOperationAction(ISD::SETCC, VT, Custom);
430 }
431
432 // Custom action for SELECT MMX and expand action for SELECT_CC MMX
433 setOperationAction(ISD::SELECT, MVT::x86mmx, Custom);
434 setOperationAction(ISD::SELECT_CC, MVT::x86mmx, Expand);
435
436 setOperationAction(ISD::EH_RETURN , MVT::Other, Custom);
437 // NOTE: EH_SJLJ_SETJMP/_LONGJMP are not recommended, since
438 // LLVM/Clang supports zero-cost DWARF and SEH exception handling.
439 setOperationAction(ISD::EH_SJLJ_SETJMP, MVT::i32, Custom);
440 setOperationAction(ISD::EH_SJLJ_LONGJMP, MVT::Other, Custom);
441 setOperationAction(ISD::EH_SJLJ_SETUP_DISPATCH, MVT::Other, Custom);
442 if (TM.Options.ExceptionModel == ExceptionHandling::SjLj)
443 setLibcallName(RTLIB::UNWIND_RESUME, "_Unwind_SjLj_Resume");
444
445 // Darwin ABI issue.
446 for (auto VT : { MVT::i32, MVT::i64 }) {
447 if (VT == MVT::i64 && !Subtarget.is64Bit())
448 continue;
449 setOperationAction(ISD::ConstantPool , VT, Custom);
450 setOperationAction(ISD::JumpTable , VT, Custom);
451 setOperationAction(ISD::GlobalAddress , VT, Custom);
452 setOperationAction(ISD::GlobalTLSAddress, VT, Custom);
453 setOperationAction(ISD::ExternalSymbol , VT, Custom);
454 setOperationAction(ISD::BlockAddress , VT, Custom);
455 }
456
457 // 64-bit shl, sar, srl (iff 32-bit x86)
458 for (auto VT : { MVT::i32, MVT::i64 }) {
459 if (VT == MVT::i64 && !Subtarget.is64Bit())
460 continue;
461 setOperationAction(ISD::SHL_PARTS, VT, Custom);
462 setOperationAction(ISD::SRA_PARTS, VT, Custom);
463 setOperationAction(ISD::SRL_PARTS, VT, Custom);
464 }
465
466 if (Subtarget.hasSSEPrefetch() || Subtarget.has3DNow())
467 setOperationAction(ISD::PREFETCH , MVT::Other, Legal);
468
469 setOperationAction(ISD::ATOMIC_FENCE , MVT::Other, Custom);
470
471 // Expand certain atomics
472 for (auto VT : { MVT::i8, MVT::i16, MVT::i32, MVT::i64 }) {
473 setOperationAction(ISD::ATOMIC_CMP_SWAP_WITH_SUCCESS, VT, Custom);
474 setOperationAction(ISD::ATOMIC_LOAD_SUB, VT, Custom);
475 setOperationAction(ISD::ATOMIC_LOAD_ADD, VT, Custom);
476 setOperationAction(ISD::ATOMIC_LOAD_OR, VT, Custom);
477 setOperationAction(ISD::ATOMIC_LOAD_XOR, VT, Custom);
478 setOperationAction(ISD::ATOMIC_LOAD_AND, VT, Custom);
479 setOperationAction(ISD::ATOMIC_STORE, VT, Custom);
480 }
481
482 if (Subtarget->hasCmpxchg16b()) {
483 setOperationAction(ISD::ATOMIC_CMP_SWAP_WITH_SUCCESS, MVT::i128, Custom);
484 }
485
486 // FIXME - use subtarget debug flags
487 if (!Subtarget->isTargetDarwin() && !Subtarget->isTargetELF() &&
488 !Subtarget->isTargetCygMing() && !Subtarget->isTargetWin64() &&
489 TM.Options.ExceptionModel != ExceptionHandling::SjLj) {
490 setOperationAction(ISD::EH_LABEL, MVT::Other, Expand);
491 }
492
493 setOperationAction(ISD::FRAME_TO_ARGS_OFFSET, MVT::i32, Custom);
494 setOperationAction(ISD::FRAME_TO_ARGS_OFFSET, MVT::i64, Custom);
495
496 setOperationAction(ISD::INIT_TRAMPOLINE, MVT::Other, Custom);
497 setOperationAction(ISD::ADJUST_TRAMPOLINE, MVT::Other, Custom);
498
499 setOperationAction(ISD::TRAP, MVT::Other, Legal);
500 setOperationAction(ISD::DEBUGTRAP, MVT::Other, Legal);
501
502 // VASTART needs to be custom lowered to use the VarArgsFrameIndex
503 setOperationAction(ISD::VASTART , MVT::Other, Custom);
504 setOperationAction(ISD::VAEND , MVT::Other, Expand);
505 bool Is64Bit = Subtarget.is64Bit();
506 setOperationAction(ISD::VAARG, MVT::Other, Is64Bit ? Custom : Expand);
507 setOperationAction(ISD::VACOPY, MVT::Other, Is64Bit ? Custom : Expand);
508
509 setOperationAction(ISD::STACKSAVE, MVT::Other, Expand);
510 setOperationAction(ISD::STACKRESTORE, MVT::Other, Expand);
511
512 setOperationAction(ISD::DYNAMIC_STACKALLOC, getPointerTy(*TD) PtrVT, Custom);
513
514 // GC_TRANSITION_START and GC_TRANSITION_END need custom lowering.
515 setOperationAction(ISD::GC_TRANSITION_START, MVT::Other, Custom);
516 setOperationAction(ISD::GC_TRANSITION_END, MVT::Other, Custom);
X86TargetLowering构造函数非常冗长,但不算太复杂。上面所调用的AddPromotedToType()是将指定的操作,指定的操作数类型,与提升类型关联。维持这个关联关系的容器是PromoteToType(类型std::map<std::pair<unsigned, MVT::SimpleValueType>, MVT::SimpleValueType>,其中std::pair记录操作与操作数原始类型)。
V7.0进行了一些代码结构上的改良,例如将setOperationAction()与AddPromotedToType()组合为setOperationPromotedToType(),并修改了一些指令与指定类型操作数的处理。
518行的useSoftFloat()如果返回true,表示目标机器使用软件方法实现浮点操作。不过X86处理器族都使用硬件实现浮点操作。那么下面开始处理浮点操作。
X86TargetLowering::X86TargetLowering(续)
518 if (!Subtarget->useSoftFloat() && X86ScalarSSEf64) {
519 // f32 and f64 use SSE.
520 // Set up the FP register classes.
521 addRegisterClass(MVT::f32, Subtarget.hasAVX512() ? &X86::FR32XRegClass
522 : &X86::FR32RegClass);
523 addRegisterClass(MVT::f64, Subtarget.hasAVX512() ? &X86::FR64XRegClass
524 : &X86::FR64RegClass);
525
526 for (auto VT : { MVT::f32, MVT::f64 }) {
527 // Use ANDPD to simulate FABS.
528 setOperationAction(ISD::FABS, VT, Custom);
529
530 // Use XORP to simulate FNEG.
531 setOperationAction(ISD::FNEG, VT, Custom);
532
533 // Use ANDPD and ORPD to simulate FCOPYSIGN.
534 setOperationAction(ISD::FCOPYSIGN, VT, Custom);
535
536 // We don't support sin/cos/fmod
537 setOperationAction(ISD::FSIN , VT, Expand);
538 setOperationAction(ISD::FCOS , VT, Expand);
539 setOperationAction(ISD::FSINCOS, VT, Expand);
540 }
541
542 // Lower this to MOVMSK plus an AND.
543 setOperationAction(ISD::FGETSIGN, MVT::i64, Custom);
544 setOperationAction(ISD::FGETSIGN, MVT::i32, Custom);
545
546 // Expand FP immediates into loads from the stack, except for the special
547 // cases we handle.
548 addLegalFPImmediate(APFloat(+0.0)); // xorpd
549 addLegalFPImmediate(APFloat(+0.0f)); // xorps
550 } else if (UseX87 && X86ScalarSSEf32) {
551 // Use SSE for f32, x87 for f64.
552 // Set up the FP register classes.
553 addRegisterClass(MVT::f32, &X86::FR32RegClass);
554 addRegisterClass(MVT::f64, &X86::RFP64RegClass);
555
556 // Use ANDPS to simulate FABS.
557 setOperationAction(ISD::FABS , MVT::f32, Custom);
558
559 // Use XORP to simulate FNEG.
560 setOperationAction(ISD::FNEG , MVT::f32, Custom);
561
562 setOperationAction(ISD::UNDEF, MVT::f64, Expand);
563
564 // Use ANDPS and ORPS to simulate FCOPYSIGN.
565 setOperationAction(ISD::FCOPYSIGN, MVT::f64, Expand);
566 setOperationAction(ISD::FCOPYSIGN, MVT::f32, Custom);
567
568 // We don't support sin/cos/fmod
569 setOperationAction(ISD::FSIN , MVT::f32, Expand);
570 setOperationAction(ISD::FCOS , MVT::f32, Expand);
571 setOperationAction(ISD::FSINCOS, MVT::f32, Expand);
572
573 // Special cases we handle for FP constants.
574 addLegalFPImmediate(APFloat(+0.0f)); // xorps
575 addLegalFPImmediate(APFloat(+0.0)); // FLD0
576 addLegalFPImmediate(APFloat(+1.0)); // FLD1
577 addLegalFPImmediate(APFloat(-0.0)); // FLD0/FCHS
578 addLegalFPImmediate(APFloat(-1.0)); // FLD1/FCHS
579
580 // Always expand sin/cos functions even though x87 has an instruction.
581 setOperationAction(ISD::FSIN , MVT::f64, Expand);
582 setOperationAction(ISD::FCOS , MVT::f64, Expand);
583 setOperationAction(ISD::FSINCOS, MVT::f64, Expand);
584 } else if (UseX87) {
585 // f32 and f64 in x87.
586 // Set up the FP register classes.
587 addRegisterClass(MVT::f64, &X86::RFP64RegClass);
588 addRegisterClass(MVT::f32, &X86::RFP32RegClass);
589
590 for (auto VT : { MVT::f32, MVT::f64 }) {
591 setOperationAction(ISD::UNDEF, VT, Expand);
592 setOperationAction(ISD::FCOPYSIGN, VT, Expand);
593
594 // Always expand sin/cos functions even though x87 has an instruction.
595 setOperationAction(ISD::FSIN , VT, Expand);
596 setOperationAction(ISD::FCOS , VT, Expand);
597 setOperationAction(ISD::FSINCOS, VT, Expand);
598 }
599 addLegalFPImmediate(APFloat(+0.0)); // FLD0
600 addLegalFPImmediate(APFloat(+1.0)); // FLD1
601 addLegalFPImmediate(APFloat(-0.0)); // FLD0/FCHS
602 addLegalFPImmediate(APFloat(-1.0)); // FLD1/FCHS
603 addLegalFPImmediate(APFloat(+0.0f)); // FLD0
604 addLegalFPImmediate(APFloat(+1.0f)); // FLD1
605 addLegalFPImmediate(APFloat(-0.0f)); // FLD0/FCHS
606 addLegalFPImmediate(APFloat(-1.0f)); // FLD1/FCHS
607 }
608
609 // We don't support FMA.
610 setOperationAction(ISD::FMA, MVT::f64, Expand);
611 setOperationAction(ISD::FMA, MVT::f32, Expand);
612
613 // Long double always uses X87.
614 if (UseX87) {
615 if (Subtarget.is64Bit() && Subtarget.hasMMX()) {
616 addRegisterClass(MVT::f128, &X86::VR128RegClass);
617 ValueTypeActions.setTypeAction(MVT::f128, TypeSoftenFloat);
618 setOperationAction(ISD::FABS , MVT::f128, Custom);
619 setOperationAction(ISD::FNEG , MVT::f128, Custom);
620 setOperationAction(ISD::FCOPYSIGN, MVT::f128, Custom);
621 }
622
623 addRegisterClass(MVT::f80, &X86::RFP80RegClass);
624 setOperationAction(ISD::UNDEF, MVT::f80, Expand);
625 setOperationAction(ISD::FCOPYSIGN, MVT::f80, Expand);
626 {
627 APFloat TmpFlt = APFloat::getZero(APFloat::x87DoubleExtended);
628 addLegalFPImmediate(TmpFlt); // FLD0
629 TmpFlt.changeSign();
630 addLegalFPImmediate(TmpFlt); // FLD0/FCHS
631
632 bool ignored;
633 APFloat TmpFlt2(+1.0);
634 TmpFlt2.convert(APFloat::x87DoubleExtended, APFloat::rmNearestTiesToEven,
635 &ignored);
636 addLegalFPImmediate(TmpFlt2); // FLD1
637 TmpFlt2.changeSign();
638 addLegalFPImmediate(TmpFlt2); // FLD1/FCHS
639 }
640
641 // Always expand sin/cos functions even though x87 has an instruction.
642 setOperationAction(ISD::FSIN , MVT::f80, Expand);
643 setOperationAction(ISD::FCOS , MVT::f80, Expand);
644 setOperationAction(ISD::FSINCOS, MVT::f80, Expand);
645
646 setOperationAction(ISD::FFLOOR, MVT::f80, Expand);
647 setOperationAction(ISD::FCEIL, MVT::f80, Expand);
648 setOperationAction(ISD::FTRUNC, MVT::f80, Expand);
649 setOperationAction(ISD::FRINT, MVT::f80, Expand);
650 setOperationAction(ISD::FNEARBYINT, MVT::f80, Expand);
651 setOperationAction(ISD::FMA, MVT::f80, Expand);
652 }
653
654 // Always use a library call for pow.
655 setOperationAction(ISD::FPOW , MVT::f32 , Expand);
656 setOperationAction(ISD::FPOW , MVT::f64 , Expand);
657 setOperationAction(ISD::FPOW , MVT::f80 , Expand);
658
659 setOperationAction(ISD::FLOG, MVT::f80, Expand);
660 setOperationAction(ISD::FLOG2, MVT::f80, Expand);
661 setOperationAction(ISD::FLOG10, MVT::f80, Expand);
662 setOperationAction(ISD::FEXP, MVT::f80, Expand);
663 setOperationAction(ISD::FEXP2, MVT::f80, Expand);
664 setOperationAction(ISD::FMINNUM, MVT::f80, Expand);
665 setOperationAction(ISD::FMAXNUM, MVT::f80, Expand);
上面的addLegalFPImmediate()向容器LegalFPImmediates(类型std::vector<APFloat>)记录指令选择能合法用于浮点指令的浮点立即数。
相关文章:
)
LLVM学习笔记(62)
4.4.3.3.2. 指令处理的设置 4.4.3.3.2.1. 目标机器相关设置 除了基类以外,X86TargetLowering构造函数本身也是一个庞然大物,我们必须要分段来看。V7.0做了不小的改动,改进了代码的结构,修改了一些指令的设置。 100 X86Targ…...
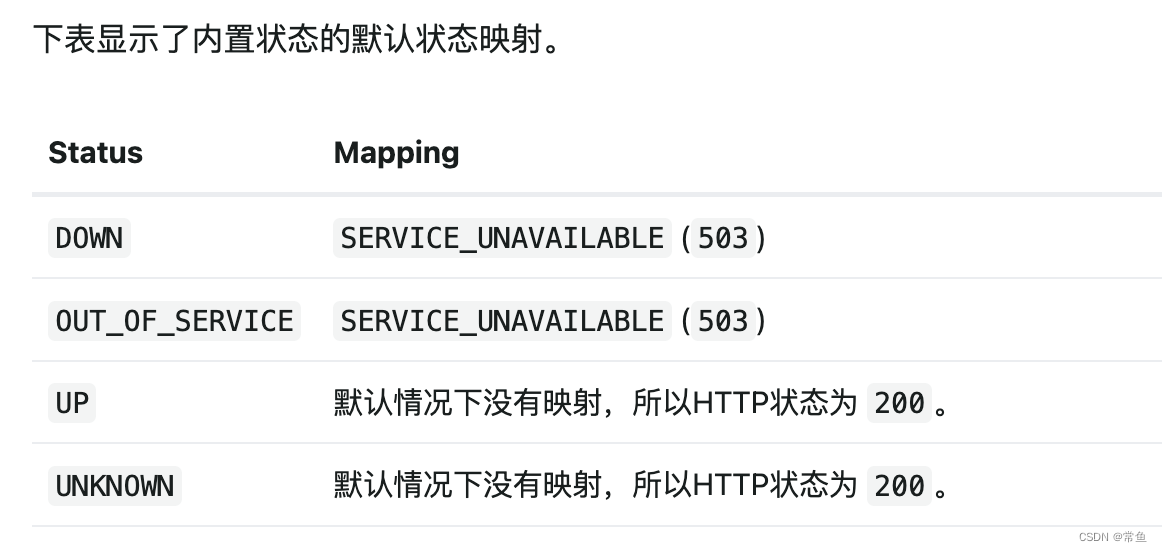
解决Spring Boot应用在Kubernetes上健康检查接口返回OUT_OF_SERVICE的问题
现象 在将Spring Boot应用部署到Kubernetes上时,健康检查接口/healthcheck返回的状态为{"status":"OUT_OF_SERVICE","groups":["liveness","readiness"]},而期望的是返回正常的健康状态。值得注意的…...

Java对象逃逸
关于作者:CSDN内容合伙人、技术专家, 从零开始做日活千万级APP。 专注于分享各领域原创系列文章 ,擅长java后端、移动开发、商业变现、人工智能等,希望大家多多支持。 未经允许不得转载 目录 一、导读二、概览三、相关知识3.1 逃逸…...

Greenplum的数据库年龄检查处理
概述 Greenplum是基于Postgresql数据库的分布式数据库,而PG数据库在事务及多版本并发控制的实现方式上很特别,采用的是递增事务id的方法,事务id大的事务,认为比较新,反之事务id小,认为比较旧。 事务id的上…...
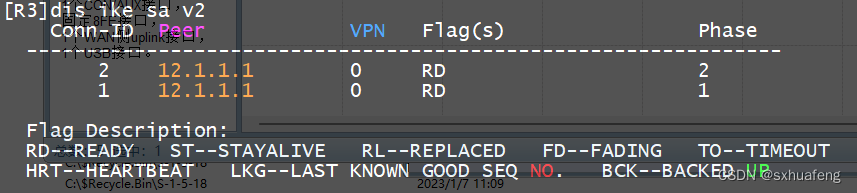
[HCIE] IPSec-VPN (IKE自动模式)
概念: IKE:因特网密钥交换 实验目标:pc1与pc2互通 步骤1:R1与R3配置默认路由 R1: ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 12.1.1.2 R2: ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 23.1.1.2 步骤2:配ACL…...

Qt/QML编程学习之心得:一个Qt工程的学习笔记(九)
这里是关于如何使用Qt Widget开发,而Qt Quick/QML的开发是另一种方式。 1、.pro文件 加CONFIG += c++11,才可以使用Lamda表达式(一般用于connect的内嵌槽函数) 2、QWidget 这是Qt新增加的一个类,基类,窗口类,QMainWindow和QDialog都继承与它。 3、Main函数 QApplicati…...

c++ 课程笔记
105课: cpp文件分为 .h .cpp .cpp 文件 110课:124课 深拷贝 浅拷贝 自建拷贝构造解决浅拷贝释放new后堆区析构函数的问题 (浅拷贝 拷贝内存地址, 释放堆区时 导致源数据 释放时,该地址无数据?而报错) 浅拷贝: 拷贝了对方的值和 堆区内存地址(删除 影响原数据堆区) 深拷贝…...
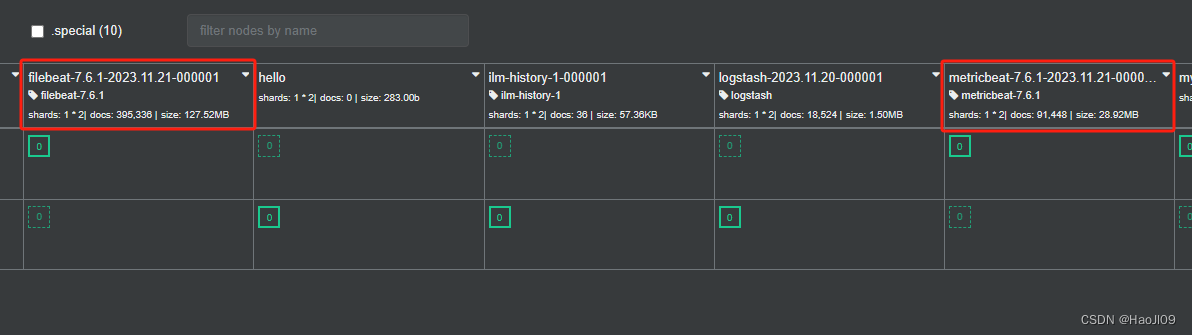
ELK企业级日志分析平台——ES集群监控
启用xpack认证 官网:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.6/configuring-tls.html#node-certificates 在elk1上生成证书 [rootelk1 ~]# cd /usr/share/elasticsearch/[rootelk1 elasticsearch]# bin/elasticsearch-certutil ca[rootelk1 ela…...
Twincat使用:EtherCAT通信扫描硬件设备链接PLC变量
EtherCAT通信采用主从架构,其中一个主站设备负责整个EtherCAT网络的管理和控制,而从站设备则负责在数据环网上传递数据。 主站设备可以是计算机、工控机、PLC等, 而从站设备可以是传感器、执行器、驱动器等。 EL3102:MDP5001_300_CF8D1684;…...
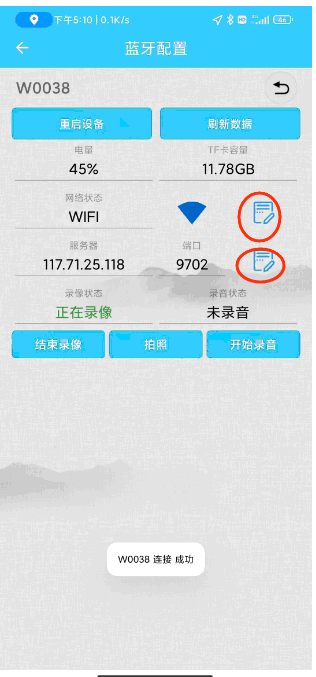
手机APP-MCP走蓝牙无线遥控智能安全帽~执法记录仪~拍照录像,并可做基础的配置,例如修改服务器IP以及配置WiFi等
手机APP-MCP走蓝牙无线遥控智能安全帽~执法记录仪~拍照录像,并可做基础的配置,例如修改服务器IP以及配置WiFi等 手机APP-MCP走蓝牙无线遥控智能安全帽~执法记录仪~拍照录像,并可做基础的配置,例如修改服务器IP以及配置WiFi等, AIoT万物智联,智能安全帽…...
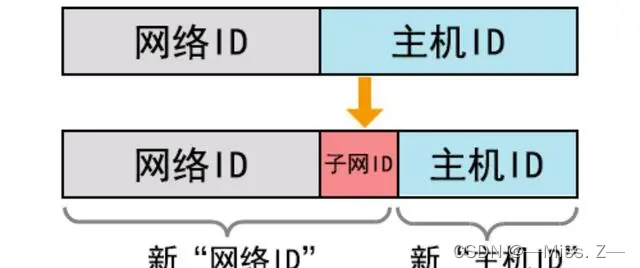
网络互联与IP地址
目录 网络互联概述网络的定义与分类网络的定义网络的分类 OSI模型和DoD模型网络拓扑结构总线型拓扑结构星型拓扑结构环型拓扑结构 传输介质同轴电缆双绞线光纤 介质访问控制方式CSMA/CD令牌 网络设备网卡集线器交换机路由器总结 IP地址A、B、C类IP地址特殊地址形式 子网与子网掩…...
Android设计模式--模板方法模式
一,定义 定义一个操作中的算法的框架,而将一些步骤延迟到子类中,使得子类可以不改变一个算法的结构即可重定义该算法的某些特定步骤。 在面向对象的开发过程中,通常会遇到这样一个问题,我们知道一个算法所需的关键步…...

大语言模型——BERT和GPT的那些事儿
前言 自然语言处理是人工智能的一个分支。在自然语言处理领域,有两个相当著名的大语言模型——BERT和GPT。两个模型是同一年提出的,那一年BERT以不可抵挡之势,让整个人工智能届为之震动。据说当年BERT的影响力是GPT的十倍以上。而现在&#…...

Docker 命令详解
1. 容器生命周期管理 命令说明文档run创建一个新的容器并运行一个命令Docker run 命令start/stop/restart启动、停止、重启容器Docker start/stop/restart 命令kill杀掉一个运行中的容器Docker kill 命令rm删除一个或多个容器Docker rm 命令pause/unpause暂停 恢复容器中所有的…...
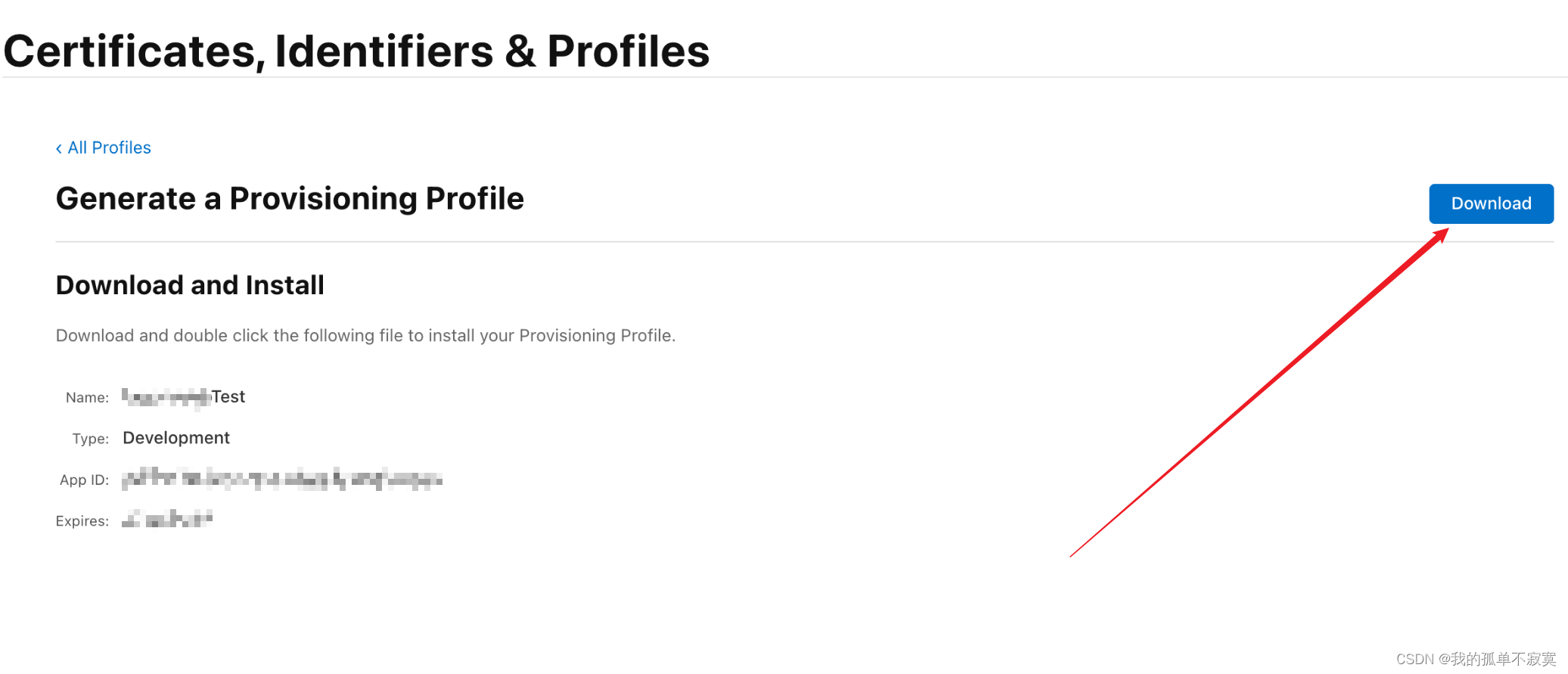
ios打包,证书获取
HBuilderX 打包ios界面: Bundle ID(AppID): 又称应用ID,是每一个ios应用的唯一标识,就像一个人的身份证号码; 每开发一个新应用,首先都需要先去创建一个Bundle ID Bundle ID 格式: 一般为&…...
linux(nginx安装配置,tomcat服务命令操作)
首先进系统文件夹 /usr/lib/systemd/systemLs | grep mysql 查看带有命名有MySQL的文件夹修改tomcat.service文件复制jdk目录替换成我们的路径替换成我们的路径进入这个目录,把修改好的文件拖到我们的工具里面重新刷新系统 systemctl daemon-reload查看tomcat状态…...
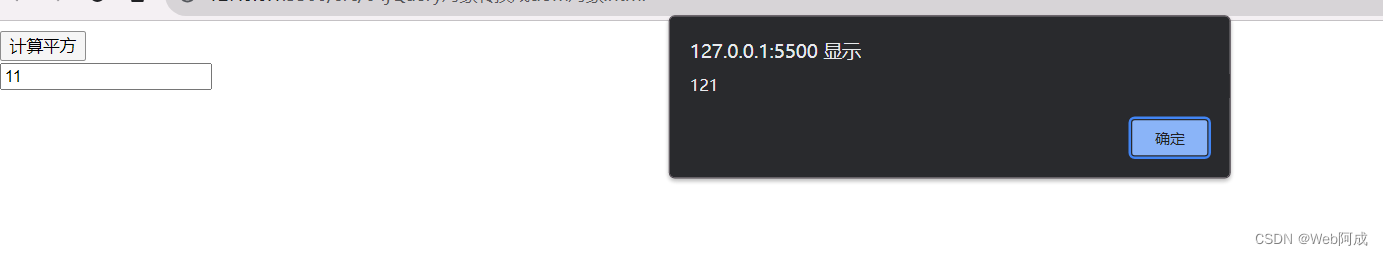
jQuery_03 dom对象和jQuery对象的互相转换
dom对象和jQuery对象 dom对象 jQuery对象 在一个文件中同时存在两种对象 dom对象: 通过js中的document对象获取的对象 或者创建的对象 jQuery对象: 通过jQuery中的函数获取的对象。 为什么使用dom或jQuery对象呢? 目的是 要使用dom对象的函数或者属性 以及呢 要…...

Mysql 中如何导入数据?
文章目录 前言使用 LOAD DATA 导入数据使用 mysqlimport 导入数据mysqlimport的常用选项介绍后言 前言 hello world欢迎来到前端的新世界 😜当前文章系列专栏:Mysql 🐱👓博主在前端领域还有很多知识和技术需要掌握,正…...
深入了解前馈网络、CNN、RNN 和 Hugging Face 的 Transformer 技术!
一、说明 本篇在此对自然语言模型做一个简短总结,从CNN\RNN\变形金刚,和抱脸的变形金刚库说起。 二、基本前馈神经网络: 让我们分解一个基本的前馈神经网络,也称为多层感知器(MLP)。此代码示例将࿱…...

Flink Table API 读写MySQL
Flink Table API 读写 MySQL import org.apache.flink.connector.jdbc.table.JdbcConnectorOptions; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment; import org.apache.flink.table.api.DataTypes; import org.apache.flink.table.api.Envi…...
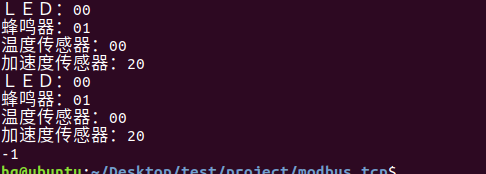
网络编程(Modbus进阶)
思维导图 Modbus RTU(先学一点理论) 概念 Modbus RTU 是工业自动化领域 最广泛应用的串行通信协议,由 Modicon 公司(现施耐德电气)于 1979 年推出。它以 高效率、强健性、易实现的特点成为工业控制系统的通信标准。 包…...

反向工程与模型迁移:打造未来商品详情API的可持续创新体系
在电商行业蓬勃发展的当下,商品详情API作为连接电商平台与开发者、商家及用户的关键纽带,其重要性日益凸显。传统商品详情API主要聚焦于商品基本信息(如名称、价格、库存等)的获取与展示,已难以满足市场对个性化、智能…...

Swift 协议扩展精进之路:解决 CoreData 托管实体子类的类型不匹配问题(下)
概述 在 Swift 开发语言中,各位秃头小码农们可以充分利用语法本身所带来的便利去劈荆斩棘。我们还可以恣意利用泛型、协议关联类型和协议扩展来进一步简化和优化我们复杂的代码需求。 不过,在涉及到多个子类派生于基类进行多态模拟的场景下,…...
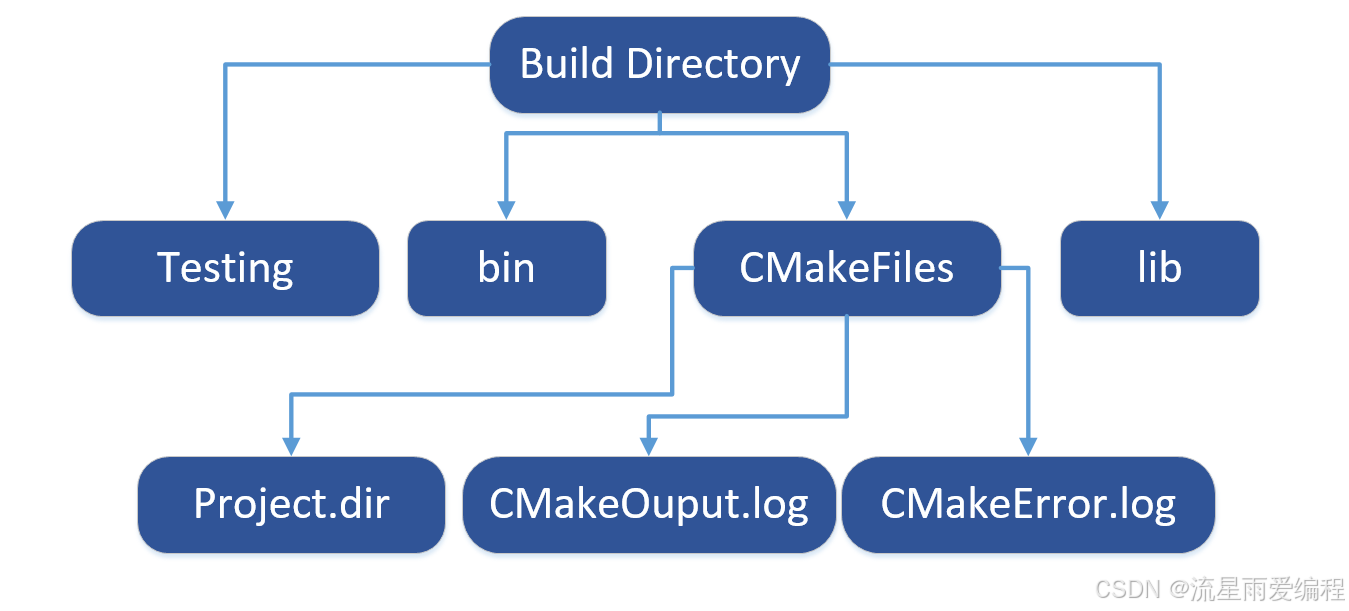
CMake基础:构建流程详解
目录 1.CMake构建过程的基本流程 2.CMake构建的具体步骤 2.1.创建构建目录 2.2.使用 CMake 生成构建文件 2.3.编译和构建 2.4.清理构建文件 2.5.重新配置和构建 3.跨平台构建示例 4.工具链与交叉编译 5.CMake构建后的项目结构解析 5.1.CMake构建后的目录结构 5.2.构…...

C# 类和继承(抽象类)
抽象类 抽象类是指设计为被继承的类。抽象类只能被用作其他类的基类。 不能创建抽象类的实例。抽象类使用abstract修饰符声明。 抽象类可以包含抽象成员或普通的非抽象成员。抽象类的成员可以是抽象成员和普通带 实现的成员的任意组合。抽象类自己可以派生自另一个抽象类。例…...
)
WEB3全栈开发——面试专业技能点P2智能合约开发(Solidity)
一、Solidity合约开发 下面是 Solidity 合约开发 的概念、代码示例及讲解,适合用作学习或写简历项目背景说明。 🧠 一、概念简介:Solidity 合约开发 Solidity 是一种专门为 以太坊(Ethereum)平台编写智能合约的高级编…...
Docker 本地安装 mysql 数据库
Docker: Accelerated Container Application Development 下载对应操作系统版本的 docker ;并安装。 基础操作不再赘述。 打开 macOS 终端,开始 docker 安装mysql之旅 第一步 docker search mysql 》〉docker search mysql NAME DE…...

uniapp 字符包含的相关方法
在uniapp中,如果你想检查一个字符串是否包含另一个子字符串,你可以使用JavaScript中的includes()方法或者indexOf()方法。这两种方法都可以达到目的,但它们在处理方式和返回值上有所不同。 使用includes()方法 includes()方法用于判断一个字…...

C语言中提供的第三方库之哈希表实现
一. 简介 前面一篇文章简单学习了C语言中第三方库(uthash库)提供对哈希表的操作,文章如下: C语言中提供的第三方库uthash常用接口-CSDN博客 本文简单学习一下第三方库 uthash库对哈希表的操作。 二. uthash库哈希表操作示例 u…...
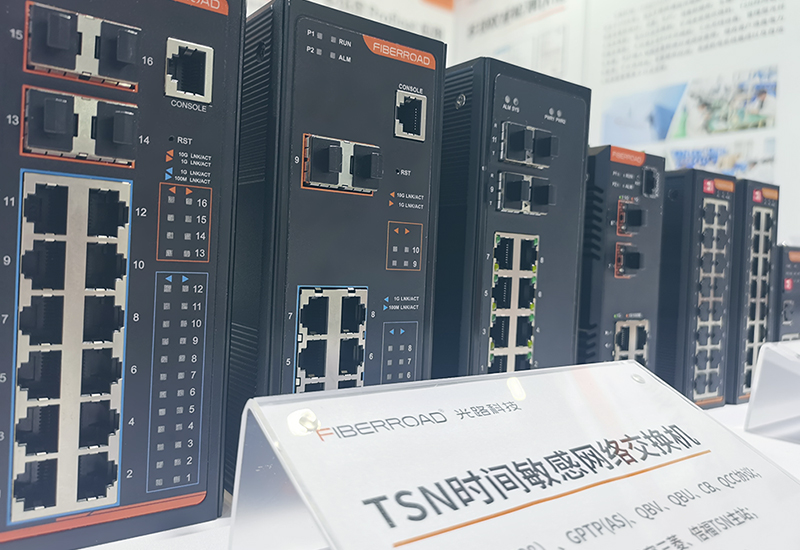

TSN交换机正在重构工业网络,PROFINET和EtherCAT会被取代吗?
在工业自动化持续演进的今天,通信网络的角色正变得愈发关键。 2025年6月6日,为期三天的华南国际工业博览会在深圳国际会展中心(宝安)圆满落幕。作为国内工业通信领域的技术型企业,光路科技(Fiberroad&…...
