VINS-MONO拓展1----手写后端求解器,LM3种阻尼因子策略,DogLeg,构建Hessian矩阵
文章目录
- 0. 目标及思路
- 1. 非线性优化求解器
- 2. 基于VINS-MONO的Marginalization框架构建Hessian矩阵
- 2.1 estimator.cpp移植
- 2.2 solve.cpp/preMakeHessian()
- 2.3 solve.cpp/makeHessian()
- 3. solve.cpp/solveLinearSystem()求解正规方程
- 4. 更新状态
- 5. 迭代求解
- 6. EVO评估结果
- 7. 待填的坑
- 8. Reference
- 9. Appendix
- 9.1 estimator.cpp
- 9.2 solve.cpp
- 9.3 solve.h
- 9.4 系统整体待优化参数维度debug
- 9.5 LM的 λ \lambda λ初始化中的 τ \tau τ取值是否合适?
- 9.6 Schur消元求解之后更新先验的residual
- 9.7 计算 χ = e T W e \chi=e^TWe χ=eTWe时需要考虑loss_function
- 9.8 先验的参数实际上就是V0,P0~P10,Tbc,td,而不是一个单独的特殊量
- 9.9 Hessian可视化
- 9.10 load pose_graph
0. 目标及思路
完成VIO课程大作业T1

VINS-MONO使用Ceres的求解器,在factor中实现了Jacobian block的构建,为了探究非线性优化求解过程,我们不使用Ceres,手动完成求解,整体思路如下:
- 非线性优化求解器
- Hessian矩阵构建
- 求解正规方程
- 更新状态
- 迭代求解
- EVO评估结果
以下章节将分别对各个部分进行详细介绍,并在最后给出完整代码。
1. 非线性优化求解器
主要包括LM和DogLeg(DL),本文以LM为主进行讲解,在LM实现的基础上,DL方法按照论文实现即可较容易完成求解。
关于LM的介绍可以参考之前课程Ch3的博客,论文可以参考[1],此处不再赘述。
这里强调一下在实现过程中遇到的最难解的问题:关于 b b b的符号问题。
在一次迭代求解中,我们的目标是求解正规方程
H Δ x = − b \begin{align} H\Delta x=-b \end{align} HΔx=−b
然后更新
x = x + Δ x \begin{align} x=x+\Delta x \end{align} x=x+Δx
关于(1)中右边的 − b -b −b,不同地方对于符号的定义不统一,导致理解有偏差, b = J T e b=J^Te b=JTe是在marginalization_factor.cpp的MarginalizationInfo::marginalize()最后从Hessian中反解出来的,但是在正规方程中右边是 − b -b −b,所以我们后面再求解(1)之前,构造b之后需要取一下负,否则解出来的 Δ x \Delta x Δx要么非常大,要么非常小(1e-30量级的,更新不动 x x x),因为之前在这里卡了很久,所以在这里先强调一下,在第2部分中会结合代码讲解具体在哪里操作。
linearized_jacobians = S_sqrt.asDiagonal() * saes2.eigenvectors().transpose();
linearized_residuals = S_inv_sqrt.asDiagonal() * saes2.eigenvectors().transpose() * b;
记录一下之前阅读Ceres LM源码debug的记录。
在ceres源码中可以找到答案:在LevenbergMarquardtStrategy::ComputeStep()函数中有注释是这样的:
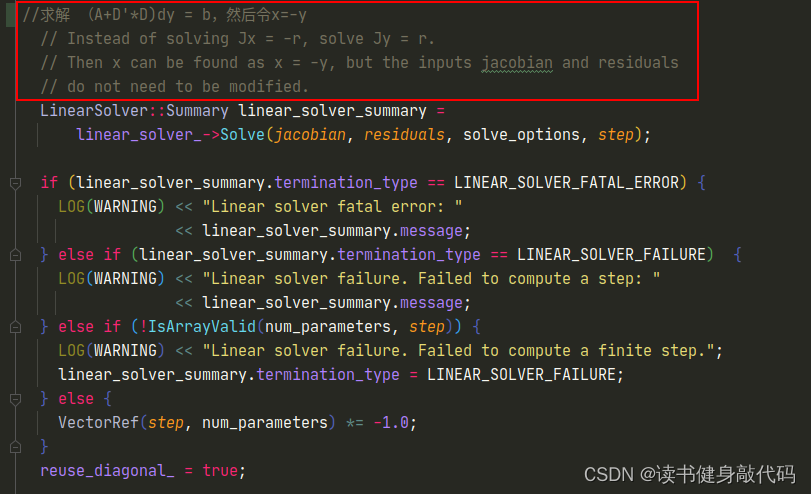
ceres里面只要求传入Jacobian和residual,内部求解的方程 ( A + D ′ D ) d y = b (A+D'D)dy=b (A+D′D)dy=b,而不是LM正规方程的形式 ( A + λ I ) d x = b (A+\lambda I)dx=b (A+λI)dx=b(ceres中的 D D D是根据Jacobian构建的一个与 λ \lambda λ有关的系数阵,叠加到 A A A上,这里不做详细介绍,有兴趣的可以看看ceres的源码),而我们自己构建的 b b b是 J T e J^Te JTe
所以之前求解的一直是 − Δ x -\Delta x −Δx,按照 Δ x \Delta x Δx更新给 x x x,属于是错误的方向,那么 χ 2 \chi^2 χ2不下降也是正常的,进一步地, ρ \rho ρ也就很那下降,因为 x x x更新方向不对。至此,找到了最根本的问题,解决办法是在makeHessian()最后将b取负,那么就是手动求解的正确的正规方程了。
Hessian_ = A;b_ = -b;
接下来就是LM的一系列调参:
- LM初始化时的 τ \tau τ,设为 1 e − 15 1e-15 1e−15
- 优化退出条件
delta_x_.squaredNorm() <= 1e-10 || false_cnt > 6 - 优化PCG(预处理共轭梯度法 preconditioned conjugate gradient method)求解速度
- 迭代次数设为
Hessian_.rows()+1 - 迭代停止阈值设为
double threshold = 1e-5 * r0.norm() - 优化PCG:对角线预处理和不完备的Cholesky预处理(还未做,参考博客)
- 迭代次数设为
2. 基于VINS-MONO的Marginalization框架构建Hessian矩阵
2.1 estimator.cpp移植
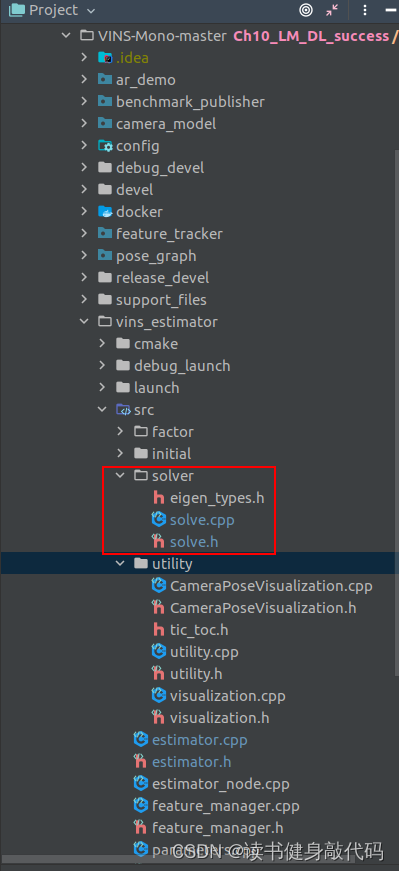
手动构建Hessian的步骤其实在marg时已经有过,所以我们直接借鉴marg部分的代码,将其移植成整个系统的Hessian构建,并加上我们的LM和DL,整个代码结构如下,添加了solver文件夹
marg部分第5篇博客讲过,marg掉的变量实际上就是WINDOW[0]帧相关的待优化变量,包括 P 0 , V 0 P_0,V_0 P0,V0和strat from [0]的landmark的观测,marg的大致流程如下:
- 以factor方式将各个参数块添加到
problem中,包括MarginalizationFactor,IMUFactor,ProjectionTdFactor(ProjectionFactor), - 构建
residual_block_info来待优化参数,同时marg的变量。指定方式是通过drop_set - 调用
addResidualBlockInfo函数将每一个ResidualBlockInfo添加到problem中 - 调用
preMarginalize()函数计算各个factor的Jacobian和residual - 调用
marginalize()函数对待优化变量排序,marg放前面,remain放后面,多线程构建Hessian矩阵,运用Schur compliment执行marg,得到marg后留下的先验,从先验A中反解出该线性化点处的linearized_jacobians和linearized_residuals。 - addr_shift地址映射。
我们需要构建整个系统的Hessian,与VINS-MONO的marg不同的是,我们可以选择marg,也可以选择不marg,重点是需要明白,我们这里求取Hessian的目的与VINS-MONO的marg不同:
- VINS-MONO的marg目的是为了求取marg之后留下的先验,并不需要求解式(1),所以Schur compliment,反解出
linearized_jacobians和linearized_residuals之后,marg的任务就完成了,至于这个线性化点值为多少并不关心(当然也可以(1)求解,(2)更新求出这个线性化点)。 - 而我们现在的目的是为了求解出本次迭代优化之后的线性化点,也就是我们的待优化变量,所以式(1)(2)是我们需要在marg的基础上进一步往下走的。
理清了二者的区别,我们的目标就具体很多了:基于VINS-MONO的margHessian构建框架,我们可以顺利地构建出整个系统的Hessian矩阵,和b,也就完成了式(1)的构建,然后求解式(1)得 Δ x \Delta x Δx,带入式(2)即可完成本次迭代。
接下来的核心任务:
- 完成VINS-MONO的marg框架移植,构建出Hessian矩阵
- 求解式(1)
下面详细讲解marg的移植:(以下内容可根据Appendix中的相关代码来理解)
- 新建
solve.cpp,solve.h,照搬marginalization_factor.cpp/h的所有内容,并封上自己的namespace:solve, - 为了便于对比调试,在
estimator.cpp中加上宏隔离CERES_SOLVE,用于区分使用Ceres求解和我们自己的手动求解。 - 需要注意,我们虽然是照搬marg部分,但是我们修改的是后端求解不分,所以是在求解部分而不是marg部分添加我们的代码,如,ceres部分添加prior residualbolck是
MarginalizationFactor *marginalization_factor = new MarginalizationFactor(last_marginalization_info);
problem.AddResidualBlock(marginalization_factor, NULL,last_marginalization_parameter_blocks);
我们则是
solve::ResidualBlockInfo *residual_block_info = new solve::ResidualBlockInfo(marginalization_factor, NULL, last_marginalization_parameter_blocks, vector<int>{});
solver.addResidualBlockInfo(residual_block_info);
其他factor如法炮制。
需要指出,我们在求解式(1)时有好几种实现方法,其中一种是使用Schur消元,利用Hessian的稀疏性加快式(1)的求解速度,这就意味着我们需要指定需要作为 x m m x_{mm} xmm的部分,通过drop_set来指定。由于landmark的Jacobian较为稀疏,所以我们这里指定了WINDOW内的landmark为 x m m x_{mm} xmm,如下所示:
solve::ResidualBlockInfo *residual_block_info = new solve::ResidualBlockInfo(f, loss_function, vector<double*>{para_Pose[imu_i], para_Pose[imu_j], para_Ex_Pose[0], para_Feature[feature_index]}, vector<int>{3});
solver.addResidualBlockInfo(residual_block_info);
- 为了表意更强,我们将
preMarginalize()和marginalize()改名为preMakeHessian()和makeHessian(),功能大体不变,分别是求J,e和构造H,b。
estimator.cpp总体讲解完毕,下面讲解Hessian的构建。
2.2 solve.cpp/preMakeHessian()
solve::ResidualBlockInfo组织了各个factor的信息,其中最重要的是Evaluate()函数,在Solver::preMakeHessian()会调用,主要通过多态求解各个factor的J,e,每次更新完x之后就需要调用preMakeHessian(),并重新makeHessian()。- 除此之外,由于LM和DLza求解过程中,如果 ρ < 0 \rho<0 ρ<0,会涉及到参数的回滚,但是频繁地加减会造成精度下降,所以对之前的参数备份进行备份,在
preMakeHessian()中还开了新的数据parameter_block_data_backup(实际上parameter_block_data也是够用的,只是backup表意更强)。
2.3 solve.cpp/makeHessian()
- 整体部分和marg中一样,只是我们这里仅仅只构建Hessian,至于原来marg后面的Schur compliment,我们放到求解中去做。这里需要注意,我们最终构建出来了
Hessian_和b_,这里的b_即 J T e J^Te JTe,跟(1)中差了个负号,所以最后需要取个负,在前面已经强调过了:
Hessian_ = A;b_ = -b;
LM到这里就可以结束了,但是DOGLEG由于在迭代时需要Jacobian和residual,所以我们需要在这里反解出J,e(反解出J,e在我的机器上大约需要24ms左右,耗时较长,对于DL方法的迭代影响较大。这里应该有办法构建出J和e,但是在VINS-MONO的marg的框架下,我目前没想到太好的办法)
//DOGLEG需反解出J和eif(method_==solve::Solver::kDOGLEG) {TicToc t_solve_J;TicToc t_SelfAdjoint;Eigen::SelfAdjointEigenSolver<Eigen::MatrixXd> saes2(A);//这一句24.3msROS_DEBUG("\nt_SelfAdjoint cost: %f ms", t_SelfAdjoint.toc());Eigen::VectorXd S = Eigen::VectorXd((saes2.eigenvalues().array() > eps).select(saes2.eigenvalues().array(), 0));Eigen::VectorXd S_sqrt = S.cwiseSqrt();//开根号linearized_jacobians = S_sqrt.asDiagonal() * saes2.eigenvectors().transpose();Eigen::VectorXd S_inv = Eigen::VectorXd((saes2.eigenvalues().array() > eps).select(saes2.eigenvalues().array().inverse(), 0));Eigen::VectorXd S_inv_sqrt = S_inv.cwiseSqrt();linearized_residuals = S_inv_sqrt.asDiagonal() * saes2.eigenvectors().real().transpose() * b;ROS_DEBUG("\nt_solve_J cost: %f ms", t_solve_J.toc());//25ms}
3. solve.cpp/solveLinearSystem()求解正规方程
构建完Hessian和b之后,就需要对式(1)进行求解,此部分主要函数:solveLinearSystem()。
3种求解思路:
- 直接
Hessian.inverse() - 使用PCG(预处理共轭梯度法 preconditioned conjugate gradient method)求解式(1)
- Schur消元+PCG求解(采用)
第1种就不讲了,直接调函数即可。
第2种,使用PCG()迭代求解,这里给出PCG的实现,PCG拓展可以看这里
Eigen::MatrixXd Solver::pcgSolver(const MatXX &A, const VecX &b, int maxIter = -1) {assert(A.rows() == A.cols() && "PCG solver ERROR: A is not a square matrix");int rows = b.rows();int n = maxIter < 0 ? rows : maxIter;VecX x(VecX::Zero(rows));MatXX M_inv = A.diagonal().asDiagonal().inverse();//取对角线阵的逆矩阵VecX r0(b); // initial r = b - A*0 = bVecX z0 = M_inv * r0;VecX p(z0);VecX w = A * p;double r0z0 = r0.dot(z0);double alpha = r0z0 / p.dot(w);VecX r1 = r0 - alpha * w;int i = 0;double threshold = 1e-5 * r0.norm(); //比例调大可以提高阈值,放宽停止条件while (r1.norm() > threshold && i < n) {i++;VecX z1 = M_inv * r1;double r1z1 = r1.dot(z1);double belta = r1z1 / r0z0;z0 = z1;r0z0 = r1z1;r0 = r1;p = belta * p + z1;w = A * p;alpha = r1z1 / p.dot(w);x += alpha * p;r1 -= alpha * w;}ROS_DEBUG("\nPCG iter times: %d, n: %d, r1.norm(): %f, threshold: %f", i, n, r1.norm(), threshold);return x;
}
第3种,结合之前ResidualBlockInfo时指定的drop_set,在求解时使用Schur消元求出舒尔补,然后使用PCG求出delta_x_rr,最后求出delta_x_mm,组合即得整体delta_x_,完成式(1)的求解(经试验,方法3的速度最快)。
注意,这里采用Schur compliment的方法要和VINS-MONO的marginalize()中的Schur compliment目的区分开,VINS-MONO那里是为了求出prior information matrix,SelfAdjointEigenSolver部分是为了反解出J,e,而这里是为了在Schur compliment实现消元的基础上进一步求解出整个delta_x_,整体求解代码如下:
/*Solve Hx = b, we can use PCG iterative method or use sparse Cholesky*/
//TODO:使用PCG迭代而非SVD分解求解
void Solver::solveLinearSystem() {
//method1:直接求逆求解
// delta_x_ = Hessian_.inverse() * b_;
// delta_x_ = H.ldlt().solve(b_);//method2:Schur消元求解,marg掉drop_set中的parameter
#ifdef USE_SCHUR//step1:Schur消元求//求解Hx=b,之前marg时不用求出△x,只需要H,所以不用对方程组求解,但现在优化时需要求解出整个△xTicToc t_Schur_PCG;Eigen::MatrixXd Amm_solver = 0.5 * (Hessian_.block(0, 0, m, m) + Hessian_.block(0, 0, m, m).transpose());Eigen::VectorXd bmm_solver = b_.segment(0, m);Eigen::MatrixXd Amr_solver = Hessian_.block(0, m, m, n);Eigen::MatrixXd Arm_solver = Hessian_.block(m, 0, n, m);Eigen::MatrixXd Arr_solver = Hessian_.block(m, m, n, n);Eigen::VectorXd brr_solver = b_.segment(m, n);//求Amm_solver^(-1)TicToc t_Amm_inv;Eigen::MatrixXd Amm_inv_solver = Amm_solver.inverse();//SelfAdjointEigenSolver和直接求逆速度差不多ROS_DEBUG("\nt_Amm_inv cost: %f ms", t_Amm_inv.toc());Eigen::MatrixXd tmpA_solver = Arm_solver * Amm_inv_solver;//step1: Schur补Eigen::MatrixXd Arr_schur = Arr_solver - tmpA_solver * Amr_solver;Eigen::VectorXd brr_schur = brr_solver - tmpA_solver * bmm_solver;ROS_DEBUG("here1");// step2: solve Arr_schur * delta_x_rr = brr_schur
// method1:直接求逆
// Eigen::MatrixXd Arr_schur_inv = Arr_schur.inverse();
// Eigen::VectorXd delta_x_rr = Arr_schur_inv * brr_schur;// method2:使用PCG求解TicToc t_PCG_xrr;Eigen::VectorXd delta_x_rr = pcgSolver(Arr_schur, brr_schur, Arr_schur.rows()+1); //0.3msROS_DEBUG("\n t_PCG_xrr cost %f ms", t_PCG_xrr.toc());Eigen::VectorXd delta_x_mm = Amm_inv_solver * (bmm_solver - Amr_solver * delta_x_rr);delta_x_.tail(n) = delta_x_rr;delta_x_.head(m) = delta_x_mm;memcpy(delta_x_array_, delta_x_.data(), sizeof(double) * (int)delta_x_.size());//转为数组ROS_DEBUG("\nin solveLinearSystem solve equation cost %f ms", t_Schur_PCG.toc());
#elseTicToc t_solve_equation;
// delta_x_ = Hessian_.ldlt().solve(b_);int pcg_iter_num = Hessian_.rows()+1; // PCG迭代次数,原来给的是rows()*2delta_x_ = pcgSolver(Hessian_, b_, pcg_iter_num); //0.3msROS_DEBUG("\nin solveLinearSystem solve equation cost %f ms, pcg_iter_num: %d", t_solve_equation.toc(), pcg_iter_num);//15msmemcpy(delta_x_array_, delta_x_.data(), sizeof(double) * (int)delta_x_.size());//转为数组,供状态更新使用ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nhere3 solve complete, delta_x_.size()=" << delta_x_.size() << ", delta_x_.norm()= "<< delta_x_.norm()<< ", delta_x_.squaredNorm()=" << delta_x_.squaredNorm() );ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\ndelta_x_:" << delta_x_.transpose());
#endif
}
4. 更新状态
完成式(1)的求解之后,需要带入式(2)更新状态,这里难点有2:
- 按照VINS-MONO marg的数据管理方法来更新参数,是pose部分由于有四元数,需要特殊处理。
- LM和DL涉及到状态的回滚和备份。
相关函数:
bool Solver::updateStates(double weight);//weight是LM strategy2时的权重,默认传-1.0,不加权
bool Solver::backupStates();//备份状态,便于后面回滚
bool Solver::rollbackStates();//回滚状态变量
bool Solver::updatePose(const double *x, const double *delta, double *x_plus_delta);
主要是一些地址的操作,仔细一些就好,看代码很好理解,这里讲两点:
- 在
rollbackStates()中将状态变量备份到parameter_block_data_backup中,便于后面回滚。 - 注意
memcpy()第3个参数len最好结合数据类型(这里是double)给定,sizeof()地址或者直接给int数值都是不对的。
具体代码:
bool Solver::updatePose(const double *x, const double *delta, double *x_plus_delta)
{Eigen::Map<const Eigen::Vector3d> _p(x);Eigen::Map<const Eigen::Quaterniond> _q(x + 3);Eigen::Map<const Eigen::Vector3d> dp(delta);//数组转四元数Eigen::Quaterniond dq = Utility::deltaQ(Eigen::Map<const Eigen::Vector3d>(delta + 3));Eigen::Map<Eigen::Vector3d> p(x_plus_delta);Eigen::Map<Eigen::Quaterniond> q(x_plus_delta + 3);//Jacobian和residual都是按照6维来处理的,但是更新rotation时需要按照四元数来更新p = _p + dp;q = (_q * dq).normalized();//四元数乘法并归一化return true;
}//只更新状态量p,q,v,ba,bg,λ,注意prior不是状态量,虽然在待优化变量中,但是其residual是跟状态量有关,Jacobian在一轮优化中不变,
//这里更新状态的目的是因为计算chi时会用到residual,而residual和状态量有关,而先验的residual更新:f' = f + J*δxp,其中δxp=x-x0,也跟状态量x有关,
//但是因为在先验factor在Evaluate时会计算residual,所以不用手动更新,只需要更新最核心的x即可。其他的factor相同。
bool Solver::updateStates(double weight) {int array_size = 1000 + (WINDOW_SIZE + 1) * (SIZE_POSE + SIZE_SPEEDBIAS) + SIZE_POSE + 1 + 100;double used_delta_x[array_size];if(weight != -1.0)std::transform(delta_x_array_, delta_x_array_ + array_size, used_delta_x, [weight](double x) { return x * weight; });//对delta_x加权elsememcpy(used_delta_x, delta_x_array_, sizeof(double) * array_size);//使用idx来找对应的paramdouble cur_x_array[1000 + (WINDOW_SIZE + 1) * (SIZE_POSE + SIZE_SPEEDBIAS) + SIZE_POSE + 1 + 100];for (auto it : parameter_block_idx){const long addr = it.first;const int idx = it.second;const int tmp_param_block_size = parameter_block_size[addr];
/* ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nidx: " << idx << ", tmp_param_block_size: " << tmp_param_block_size);*///保存一份待优化变量,和delta_x进行数量级对比memcpy( &cur_x_array[idx], reinterpret_cast<double *>(addr), sizeof(double) *(int)SIZE_POSE);if(tmp_param_block_size == SIZE_POSE) {updatePose(reinterpret_cast<double *>(addr), &delta_x_array_[idx], reinterpret_cast<double *>(addr));//TODO:这个backup应该可以用parameter_block_data替代/* ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\npose after update: " << tmp_pose.transpose());*/} else {Eigen::Map<const Eigen::VectorXd> x{parameter_block_data_backup[addr], tmp_param_block_size};Eigen::Map<const Eigen::VectorXd> delta_x{&delta_x_array_[idx], tmp_param_block_size};Eigen::Map<Eigen::VectorXd> x_plus_delta{reinterpret_cast<double *>(addr), tmp_param_block_size};/*ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nother parameters before update: " << x_plus_delta.transpose() << "\ndelta_x: " << delta_x.transpose());*/x_plus_delta = x + delta_x;/*ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nother parameters after update: " << x_plus_delta.transpose());*/}}// 初始化Eigen向量Eigen::Map<Eigen::VectorXd> cur_x(cur_x_array, m+n);ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\ncur_x: " << cur_x.transpose());preMakeHessian();//计算更新后的Jacobian和residualreturn true;
}//备份状态量
bool Solver::backupStates() {for (auto it : parameter_block_idx){const long addr = it.first;const int tmp_param_block_size = parameter_block_size[addr];memcpy(parameter_block_data_backup[addr], reinterpret_cast<double *>(addr), sizeof(double) * (int)tmp_param_block_size);}return true;
}//回滚状态量
bool Solver::rollbackStates() {for (auto it : parameter_block_idx){const long addr = it.first;const int tmp_param_block_size = parameter_block_size[addr];memcpy(reinterpret_cast<double *>(addr), parameter_block_data_backup[addr], sizeof(double) * (int)tmp_param_block_size);}preMakeHessian();//计算更新后的Jacobian和residualreturn true;
}
5. 迭代求解
此部分就不赘述,由于前面使用updateStates()已经对状态进行了更新,所以真正的状态更新就更新之后是不回滚,且备份当前状态,简言之,在updateStates(weight)之后调用backupStates()即实现真正的状态更新,循环更新,直至达到迭代停止条件( Δ x \Delta x Δx过小或者cost下降了很多或者其他)。
6. EVO评估结果
完成所有iteration轮的迭代之后就完成了本次后端求解部分,按照optimization()的整理流程,接下来就是marginalization,addr_shift,这些我们就不讲了。
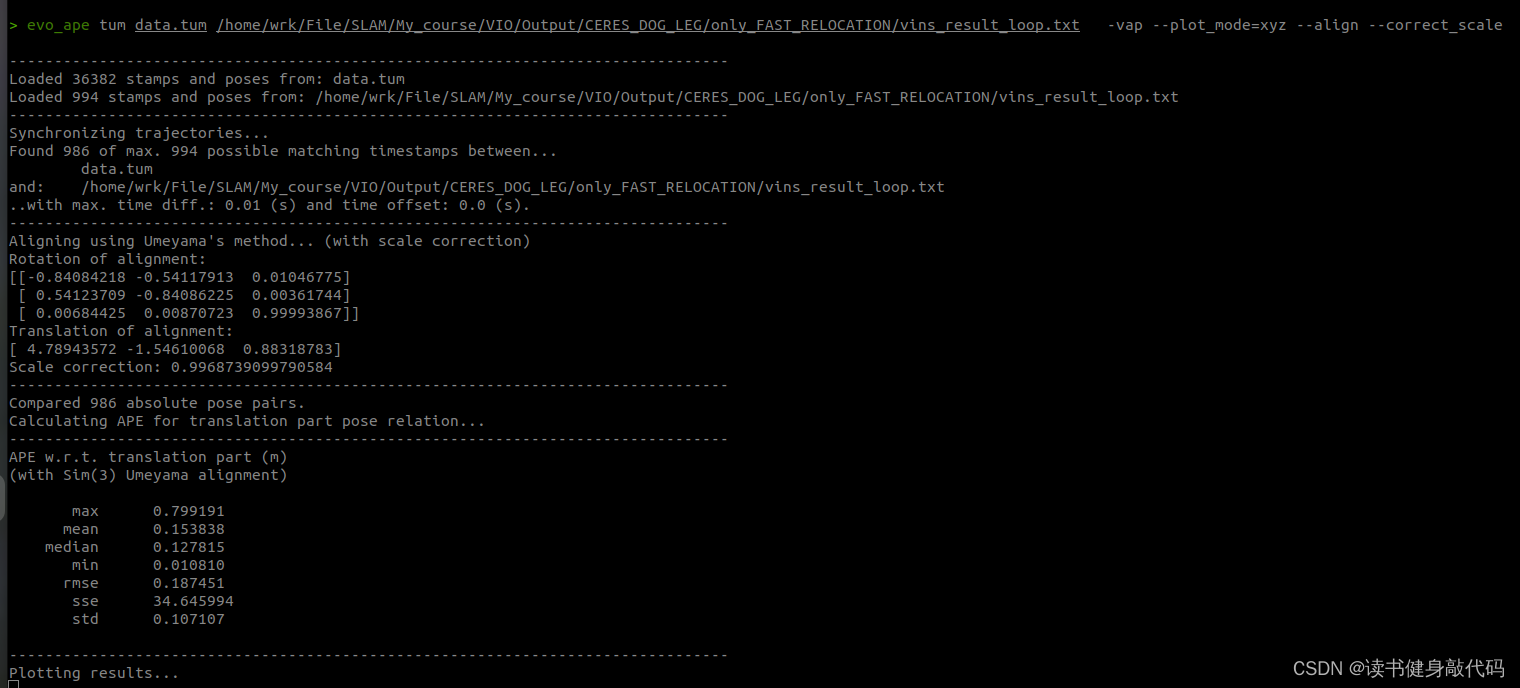
在estimator线程求解完成,参数更新之后,会发送topic给pose_graph线程,在所有数据跑完之后,pose_graph线程会存下待估计参数的值,存为.csv文件,我们使用evo工具、此文件、ground truth文件来对我们的系统进行评估,在评估之前我们需要调整VINS-MONO的输出格式,使其适配EVO,参考以下博客:
参考博客1
参考博客2
虽然更改了VINS的输出格式,但是pose_graph保存的实际上是描述子和特征点,这方面没改,所以仍然可以load pose_graph
- VINS输出数据类型转换:
t n s , t x , t y , t z , R w , R x , R y , R z t_{ns},t_x,t_y, t_z,R_w,R_x,R_y,R_z tns,tx,ty,tz,Rw,Rx,Ry,Rz要转换为 t s , t x , t y , t z , R x , R y , R z , R w t_{s},t_x,t_y, t_z,R_x,R_y,R_z,R_w ts,tx,ty,tz,Rx,Ry,Rz,Rw
时间戳由 n s ns ns转为 s s s,旋转四元数由 w , x , y , z w,x,y,z w,x,y,z顺序转为 x , y , z , w x,y,z,w x,y,z,w顺序。 - ground truth需要使用以下命令转为tum格式(evo只支持tum格式的绘制)
evo_traj euroc data.csv --save_as_tum
evo评估命令:
evo_ape tum /你的GroundTruth路径/data.tum /你的手写VINS输出路径/vins_result_loop.txt -vap --plot_mode=xyz --align --correct_scale
最终evo的评估如下图所示:
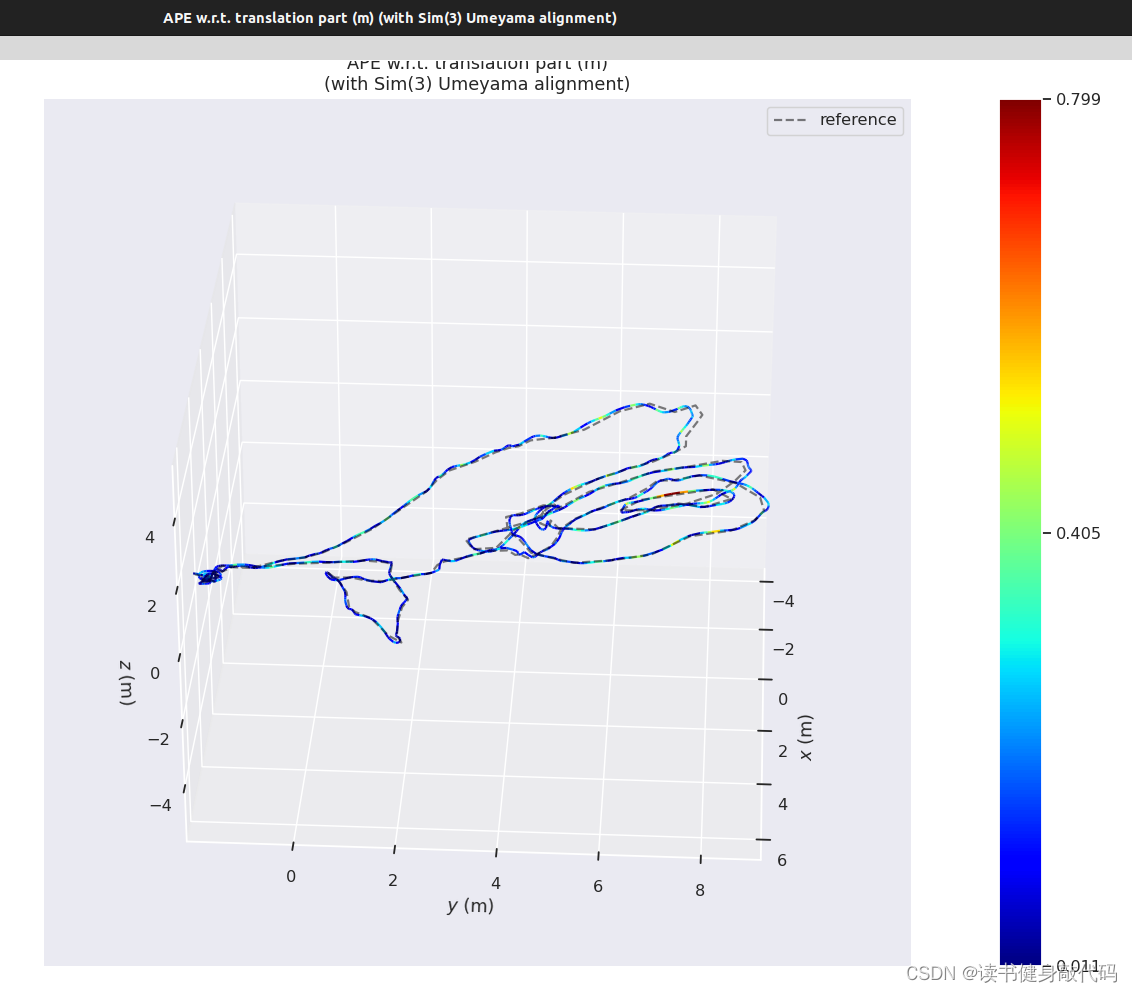
本文实验使用的是MH_01数据集,evo时都有-a,对比结果如下(LM另外两种strategy还没仔细调参,所先挖个坑):
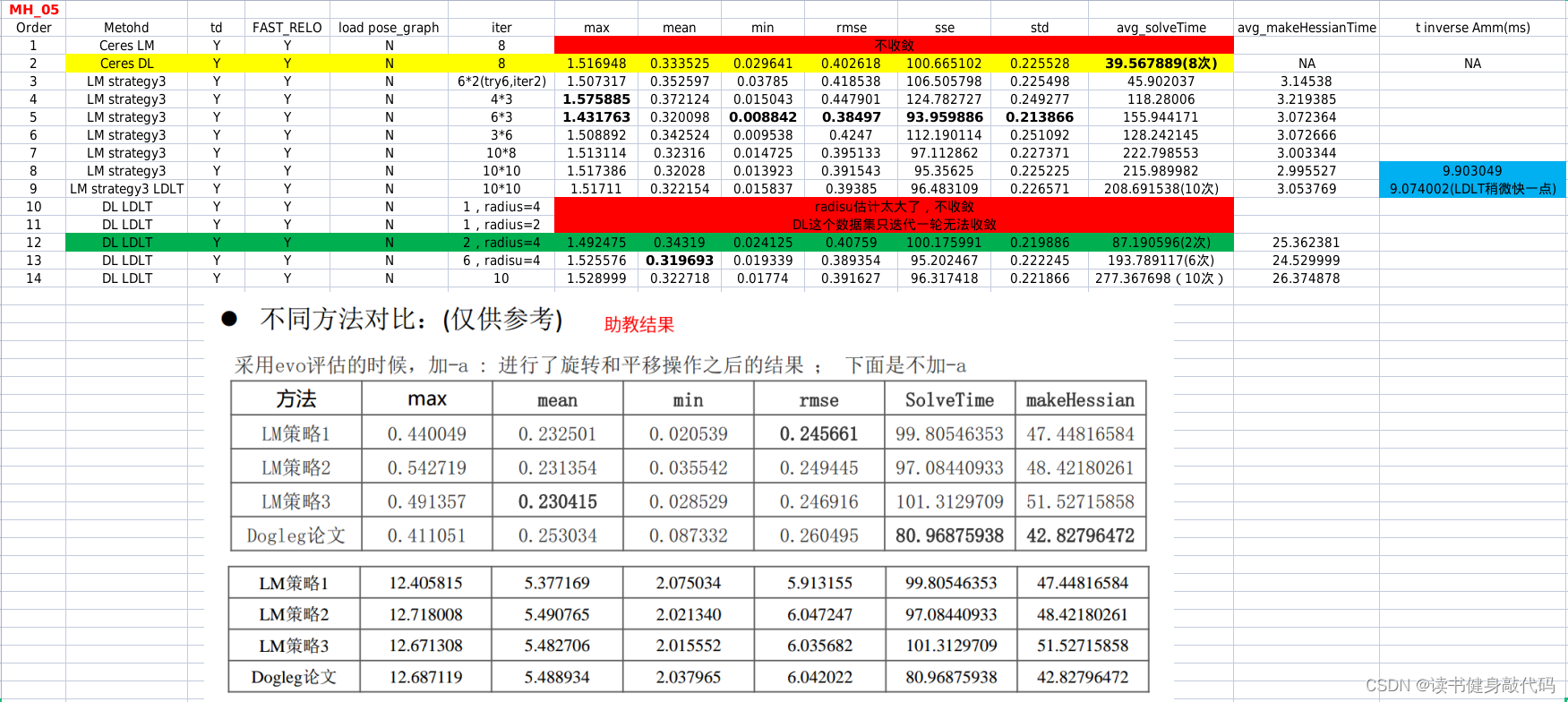
MH_05,助教的RMSE精度比我高很多,但是我用Ceres的LM和DL都跑不出来这么高的精度,LM甚至不收敛(也可能是我没调好)。
简单对比:
- Ceres DL综合精度和计算实时性,性能最优。就使用Ceres的体验来看,DL无论是在速度还是精度方面应该都优于LM。
- 基于我上面的实现的LM和DL,通过调参都能收敛,,综合考虑精度和计算实时性,LM的组3较好,DL的组12较好(DL主要是makeHessian中的反解太耗时,不然可以优化更多轮数,这也是需要解决的问题。)
至于DOGLEG算法的实现,可以完全按照[1]的3.3节来实现,在LM的基础上实现DL很容易,这里就不过多赘述。
至此T1整体工作已完成,部分细节后面再细化。
7. 待填的坑
- LM strategy1,2调参没调完。
- DL反解时间过长,没有想到好/的构建Jacobian的方法。
- PCG的改进
- EVO多个结果比较如何进行?
8. Reference
[1] Madsen, K., Nielsen, H. B., & Tingleff, O. (2004). Methods for Non-Linear Least Squares Problems (2nd ed.).
[2] Lourakis, M.I., & Argyros, A.A. (2005). Is Levenberg-Marquardt the most efficient optimization algorithm for implementing bundle adjustment? Tenth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV’05) Volume 1, 2, 1526-1531 Vol. 2.
9. Appendix
整体代码:
9.1 estimator.cpp
#include "estimator.h"
#include "solver/solve.h"//#define CERES_SOLVE
uint8_t strategy = 3;//先定义为全局变量,后面再优化Estimator::Estimator(): f_manager{Rs}
{ROS_INFO("init begins");clearState();
}//视觉测量残差的协方差矩阵
void Estimator::setParameter()
{for (int i = 0; i < NUM_OF_CAM; i++){tic[i] = TIC[i];ric[i] = RIC[i];}f_manager.setRic(ric);//这里假设标定相机内参时的重投影误差△u=1.5 pixel,(Sigma)^(-1)=(1.5/f * I(2x2))^(-1) = (f/1.5 * I(2x2))ProjectionFactor::sqrt_info = FOCAL_LENGTH / 1.5 * Matrix2d::Identity();ProjectionTdFactor::sqrt_info = FOCAL_LENGTH / 1.5 * Matrix2d::Identity();td = TD;
}void Estimator::clearState()
{for (int i = 0; i < WINDOW_SIZE + 1; i++){Rs[i].setIdentity();Ps[i].setZero();Vs[i].setZero();Bas[i].setZero();Bgs[i].setZero();dt_buf[i].clear();linear_acceleration_buf[i].clear();angular_velocity_buf[i].clear();if (pre_integrations[i] != nullptr)delete pre_integrations[i];pre_integrations[i] = nullptr;}for (int i = 0; i < NUM_OF_CAM; i++){tic[i] = Vector3d::Zero();ric[i] = Matrix3d::Identity();}for (auto &it : all_image_frame){if (it.second.pre_integration != nullptr){delete it.second.pre_integration;it.second.pre_integration = nullptr;}}solver_flag = INITIAL;first_imu = false,sum_of_back = 0;sum_of_front = 0;frame_count = 0;solver_flag = INITIAL;initial_timestamp = 0;all_image_frame.clear();td = TD;if (tmp_pre_integration != nullptr)delete tmp_pre_integration;if (last_marginalization_info != nullptr)delete last_marginalization_info;tmp_pre_integration = nullptr;last_marginalization_info = nullptr;last_marginalization_parameter_blocks.clear();f_manager.clearState();failure_occur = 0;relocalization_info = 0;drift_correct_r = Matrix3d::Identity();drift_correct_t = Vector3d::Zero();
}//IMU预积分:IntegrationBase类,IMU预积分具体细节
void Estimator::processIMU(double dt, const Vector3d &linear_acceleration, const Vector3d &angular_velocity)
{if (!first_imu){first_imu = true;acc_0 = linear_acceleration;//保存本次measurement中的第一帧IMU数据(有啥用?)gyr_0 = angular_velocity;}if (!pre_integrations[frame_count])//如果frame_count的积分为空则new一个预积分对象{pre_integrations[frame_count] = new IntegrationBase{acc_0, gyr_0, Bas[frame_count], Bgs[frame_count]};}if (frame_count != 0)//第0帧[0]没有预积分,第[0]与第[1]帧之间才有预积分{pre_integrations[frame_count]->push_back(dt, linear_acceleration, angular_velocity);//调用IntegrationBase中定义的成员函数push_back,保存变量并propagate预积分//if(solver_flag != NON_LINEAR)tmp_pre_integration->push_back(dt, linear_acceleration, angular_velocity);dt_buf[frame_count].push_back(dt);//保存这两帧IMU之间的时间间隔,用于预积分linear_acceleration_buf[frame_count].push_back(linear_acceleration);angular_velocity_buf[frame_count].push_back(angular_velocity);//IMU预积分(为什么这里要重新再算一遍?push_back里面不是重新算过了吗?为什么不直接把delta_p等结果拿出直接用?)// 用IMU数据进行积分,当积完一个measurement中所有IMU数据后,就得到了对应图像帧在世界坐标系中的Ps、Vs、Rs(这里为什么是相对于世界坐标系呢?为什么不把关于world系的抽出来呢?)// 下面这一部分的积分,在没有成功完成初始化时似乎是没有意义的,因为在没有成功初始化时,对IMU数据来说是没有世界坐标系的// 当成功完成了初始化后,下面这一部分积分才有用,它可以通过IMU积分得到滑动窗口中最新帧在世界坐标系中的P V Rint j = frame_count;//到后面frame_count一直为window_size即10Vector3d un_acc_0 = Rs[j] * (acc_0 - Bas[j]) - g;//为什么要有重力g?Vector3d un_gyr = 0.5 * (gyr_0 + angular_velocity) - Bgs[j];Rs[j] *= Utility::deltaQ(un_gyr * dt).toRotationMatrix();Vector3d un_acc_1 = Rs[j] * (linear_acceleration - Bas[j]) - g;Vector3d un_acc = 0.5 * (un_acc_0 + un_acc_1);//mid-point中值法计算a,w在k~k+1时刻内的测量值Ps[j] += dt * Vs[j] + 0.5 * dt * dt * un_acc;Vs[j] += dt * un_acc;}acc_0 = linear_acceleration;//更新本次预积分的初始值gyr_0 = angular_velocity;
}//实现了视觉与IMU的初始化以及非线性优化的紧耦合
void Estimator::processImage(const map<int, vector<pair<int, Eigen::Matrix<double, 7, 1>>>> &image, const std_msgs::Header &header)
{ROS_DEBUG("new image coming ------------------------------------------");ROS_DEBUG("Adding feature points %lu", image.size());// 把当前帧图像(frame_count)的特征点添加到f_manager.feature容器中// 计算第2最新帧与第3最新帧之间的平均视差(当前帧是第1最新帧),判断第2最新帧是否为KF// 在未完成初始化时,如果窗口没有塞满,那么是否添加关键帧的判定结果不起作用,滑动窗口要塞满// 只有在滑动窗口塞满后,或者初始化完成之后,才需要滑动窗口,此时才需要做关键帧判别,根据第2最新关键帧是否为关键帧选择相应的边缘化策略if (f_manager.addFeatureCheckParallax(frame_count, image, td))marginalization_flag = MARGIN_OLD;//如果第2新帧是KF则marg掉最老的一帧elsemarginalization_flag = MARGIN_SECOND_NEW;//如果第二新帧不是KF则直接丢掉最新帧的视觉measurement,并对IMU积分propogateROS_DEBUG("this frame is--------------------%s", marginalization_flag ? "reject" : "accept");ROS_DEBUG("%s", marginalization_flag ? "Non-keyframe" : "Keyframe");ROS_DEBUG("Solving %d", frame_count);ROS_DEBUG("number of feature: %d", f_manager.getFeatureCount());Headers[frame_count] = header;ImageFrame imageframe(image, header.stamp.toSec());imageframe.pre_integration = tmp_pre_integration;all_image_frame.insert(make_pair(header.stamp.toSec(), imageframe));//用于下一个measurement进行积分tmp_pre_integration = new IntegrationBase{acc_0, gyr_0, Bas[frame_count], Bgs[frame_count]};//不知道关于外参的任何info,需要标定if(ESTIMATE_EXTRINSIC == 2){ROS_INFO("calibrating extrinsic param, rotation movement is needed");if (frame_count != 0){// 找相邻两帧(bk, bk+1)之间的tracking上的点,构建一个pair,所有pair是一个vector,即corres(pondents),first=前一帧的去畸变的归一化平面上的点,second=后一帧的// 要求it.start_frame <= frame_count_l && it.endFrame() >= frame_count_rvector<pair<Vector3d, Vector3d>> corres = f_manager.getCorresponding(frame_count - 1, frame_count);Matrix3d calib_ric;//旋转约束+SVD分解求取Ric旋转外参//delta_q即qbk_bk+1,是从k时刻积分到k+1,所以是qbk_bk+1(从左往右读)if (initial_ex_rotation.CalibrationExRotation(corres, pre_integrations[frame_count]->delta_q, calib_ric)){ROS_WARN("initial extrinsic rotation calib success");ROS_WARN_STREAM("initial extrinsic rotation: " << endl << calib_ric);ric[0] = calib_ric;RIC[0] = calib_ric;ESTIMATE_EXTRINSIC = 1;}}}if (solver_flag == INITIAL)// 需要初始化{if (frame_count == WINDOW_SIZE)// 滑动窗口中塞满了才进行初始化(初始化并不影响KF的筛选,KF筛选仍然使用:视差>=10和tracked_num<20来判断,满足其一则是KF{bool result = false;if( ESTIMATE_EXTRINSIC != 2 && (header.stamp.toSec() - initial_timestamp) > 0.1) //确保有足够的frame参与初始化,有外参,且当前帧时间戳大于初始化时间戳+0.1秒{result = initialStructure();//执行视觉惯性联合初始化initial_timestamp = header.stamp.toSec();}//初始化成功则进行一次非线性优化,不成功则进行滑窗操作if(result){solver_flag = NON_LINEAR;//求解solveOdometry();//重新三角化,并后端求解slideWindow();ROS_DEBUG("Ps[0] addr: %ld", reinterpret_cast<long>(&Ps[0]));f_manager.removeFailures();ROS_INFO("Initialization finish!");last_R = Rs[WINDOW_SIZE];last_P = Ps[WINDOW_SIZE];last_R0 = Rs[0];last_P0 = Ps[0];}elseslideWindow();}elseframe_count++;//只在这里自增,自增到WINDOW_SIZE(10)之后就不再自增了,后面都是WINDOW_SIZE(10),即后面的优化都是需要进行marg的}else//flag==NON_LINEAR,初始化完成,需要求解后端{TicToc t_solve;solveOdometry();ROS_DEBUG("solver costs: %fms", t_solve.toc());// 以下5种情况会判定为fail:// 1,2:ba或bg过大// 3,4,5:本次WINDOW内和上次WINDOW内的最后一帧pose(Tw_b[k])之间的relative pose的t或z或角度变化过大// fail之后会clear state并重启系统(重新初始化)if (failureDetection()){ROS_WARN("failure detection!");failure_occur = 1;clearState();//所有buff,预积分等都clear,erase,deletesetParameter();//清零外参,time offsetROS_WARN("system reboot!");return;}TicToc t_margin;slideWindow();//根据marg flag marg掉old或者2nd,管理优化变量,数据,深度等ROS_DEBUG("Ps[0] addr: %ld", reinterpret_cast<long>(&Ps[0]));f_manager.removeFailures();//去掉未三角化出正深度的landmarkROS_DEBUG("marginalization costs: %fms", t_margin.toc());// prepare output of VINS(本次优化且划窗之后,保存WINDOW内的所有KF的translation)key_poses.clear();//slideWindow后最后两个Ps相同,所以用11个数据无所谓for (int i = 0; i <= WINDOW_SIZE; i++)key_poses.push_back(Ps[i]);last_R = Rs[WINDOW_SIZE];//保留这一WINDOW内的最新一帧的信息,供下次failureDetection()使用last_P = Ps[WINDOW_SIZE];last_R0 = Rs[0];last_P0 = Ps[0];}
}//执行视觉惯性联合初始化,包含两部分:1. visual SfM,2.visual和IMU的align(估计gyro bias,scale,重力细化RefineGravity)
bool Estimator::initialStructure()
{TicToc t_sfm;//check imu observibility{map<double, ImageFrame>::iterator frame_it;Vector3d sum_g;//遍历window内所有的ImageFramefor (frame_it = all_image_frame.begin(), frame_it++; frame_it != all_image_frame.end(); frame_it++){double dt = frame_it->second.pre_integration->sum_dt;//该帧总时间Vector3d tmp_g = frame_it->second.pre_integration->delta_v / dt;//速度/时间=加速度sum_g += tmp_g;}Vector3d aver_g;aver_g = sum_g * 1.0 / ((int)all_image_frame.size() - 1);//线加速度均值,因为第一帧没有,所以-1double var = 0;for (frame_it = all_image_frame.begin(), frame_it++; frame_it != all_image_frame.end(); frame_it++){double dt = frame_it->second.pre_integration->sum_dt;Vector3d tmp_g = frame_it->second.pre_integration->delta_v / dt;var += (tmp_g - aver_g).transpose() * (tmp_g - aver_g);//cout << "frame g " << tmp_g.transpose() << endl;}var = sqrt(var / ((int)all_image_frame.size() - 1));//求线加速度的标准差//ROS_WARN("IMU variation %f!", var);if(var < 0.25)//如果加速度方差小于0.25,则证明加速度波动较小,证明IMU激励不够(TODO:这个0.25跟标定qcb旋转外参SVD的特征值的那个0.25有关系吗?){ROS_INFO("IMU excitation not enouth!");//return false;}}// global sfmQuaterniond Q[frame_count + 1];//存放window内所有帧相对____的pose T___iVector3d T[frame_count + 1];//把window内所有id对应的所有feature都存到一个vector<SFMFeature>中map<int, Vector3d> sfm_tracked_points;vector<SFMFeature> sfm_f;for (auto &it_per_id : f_manager.feature)//feature是list,元素是装了window内的所有该id的feature的vector,即一个feature_id对应一个vector{int imu_j = it_per_id.start_frame - 1;SFMFeature tmp_feature;tmp_feature.state = false;//未被三角化tmp_feature.id = it_per_id.feature_id;for (auto &it_per_frame : it_per_id.feature_per_frame)//window内该id对应的所有的Matrix<double, 7, 1>{imu_j++;Vector3d pts_j = it_per_frame.point;tmp_feature.observation.push_back(make_pair(imu_j, Eigen::Vector2d{pts_j.x(), pts_j.y()}));//observation: 所有观测到该特征点的图像帧ID和图像坐标}sfm_f.push_back(tmp_feature);} Matrix3d relative_R;Vector3d relative_T;int l;//选择window内第一个满足“tracking数量>20,平均视差>30”的帧(l)与最新帧之间的relative pose,是从最新帧到第l帧Tl_cur,就是下面的Tw_curif (!relativePose(relative_R, relative_T, l)){ROS_INFO("Not enough features or parallax; Move device around");return false;}l_ = l;//将l赋给成员,便于外面查看l的帧数//求解SfM问题:对窗口中每个图像帧求解sfm问题,得到所有图像帧相对于参考帧l的旋转四元数Q、平移向量T和特征点坐标sfm_tracked_points。GlobalSFM sfm;if(!sfm.construct(frame_count + 1, Q, T, l,relative_R, relative_T,sfm_f, sfm_tracked_points)){ROS_DEBUG("global SFM failed!");//如果初始化不成功,就marg掉最老的帧(在all_image_frame中把最老的帧也删掉,但是在MARGIN_SECOND_NEW时就不会删掉all_image_frame中的帧)marginalization_flag = MARGIN_OLD;return false;}//solve pnp for all frame(直接用cv的库函数,没有再使用ceres构建problem)// 由于并不是第一次视觉初始化就能成功,此时图像帧数目有可能会超过滑动窗口的大小// 所以再视觉初始化的最后,要求出滑动窗口外的帧的位姿// 最后把世界坐标系从帧l的相机坐标系,转到帧l的IMU坐标系// 4.对于非滑动窗口的所有帧,提供一个初始的R,T,然后solve pnp求解posemap<double, ImageFrame>::iterator frame_it;map<int, Vector3d>::iterator it;frame_it = all_image_frame.begin( );//时间戳map映射ImgFrame,ImageFrame是里面有的所有id->features的map,features是pair<camera_id, Mat<7,1>>for (int i = 0; frame_it != all_image_frame.end( ); frame_it++){// provide initial guesscv::Mat r, rvec, t, D, tmp_r;if((frame_it->first) == Headers[i].stamp.toSec()) // all_image_frame与滑动窗口中对应的帧,SfM阶段已经计算过,无需再次计算{frame_it->second.is_key_frame = true;// 滑动窗口中所有帧都是关键帧frame_it->second.R = Q[i].toRotationMatrix() * RIC[0].transpose();// 根据各帧相机坐标系的姿态和外参,得到用各帧IMU坐标系的姿态(对应VINS Mono论文(2018年的期刊版论文)中的公式(6))。frame_it->second.T = T[i];i++;continue;}if((frame_it->first) > Headers[i].stamp.toSec()){i++;}// 为滑动窗口外的帧提供一个初始位姿Matrix3d R_inital = (Q[i].inverse()).toRotationMatrix();//qwc^(-1)=qcwVector3d P_inital = - R_inital * T[i];cv::eigen2cv(R_inital, tmp_r);cv::Rodrigues(tmp_r, rvec);cv::eigen2cv(P_inital, t);frame_it->second.is_key_frame = false;// 初始化时位于滑动窗口外的帧是非关键帧vector<cv::Point3f> pts_3_vector;// 用于pnp解算的3D点vector<cv::Point2f> pts_2_vector;// 用于pnp解算的2D点for (auto &id_pts : frame_it->second.points) // 对于该帧中的特征点{int feature_id = id_pts.first;// 特征点idfor (auto &i_p : id_pts.second)// 由于可能有多个相机,所以需要遍历。i_p对应着一个相机所拍图像帧的特征点信息{it = sfm_tracked_points.find(feature_id);if(it != sfm_tracked_points.end())//如果找到了已经Triangulation的,说明在sfm_tracked_points中找到了相应的3D点{// 记录该已被Triangulated的id特征点的3D位置Vector3d world_pts = it->second;cv::Point3f pts_3(world_pts(0), world_pts(1), world_pts(2));pts_3_vector.push_back(pts_3);// 记录该id的特征点在该帧图像中的2D位置Vector2d img_pts = i_p.second.head<2>();cv::Point2f pts_2(img_pts(0), img_pts(1));pts_2_vector.push_back(pts_2);}}}cv::Mat K = (cv::Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1); if(pts_3_vector.size() < 6){cout << "pts_3_vector size " << pts_3_vector.size() << endl;ROS_DEBUG("Not enough points for solve pnp !");return false;}if (! cv::solvePnP(pts_3_vector, pts_2_vector, K, D, rvec, t, 1)) // pnp求解失败{ROS_DEBUG("solve pnp fail!");return false;}cv::Rodrigues(rvec, r);MatrixXd R_pnp,tmp_R_pnp;cv::cv2eigen(r, tmp_R_pnp);R_pnp = tmp_R_pnp.transpose();//qwc = qcw^(-1)MatrixXd T_pnp;cv::cv2eigen(t, T_pnp);T_pnp = R_pnp * (-T_pnp);frame_it->second.R = R_pnp * RIC[0].transpose(); // Tc0_ck * Tbc^(-1) = Tc0_bk转到c0系下看bkframe_it->second.T = T_pnp;}ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nhere l_: " << l_ << "\nKF[0] Rs[0]:\n" << all_image_frame[Headers[0].stamp.toSec()].R);if (visualInitialAlign())//视觉惯性对齐:bg,gc0,s,v的估计return true;else{ROS_INFO("misalign visual structure with IMU");return false;}}bool Estimator::visualInitialAlign()
{TicToc t_g;VectorXd x;//待优化变量[vk,vk+1,w,s],维度是(all_image_frame.size() * 3 + 2 + 1)//估计陀螺仪的偏置,速度、重力和尺度初始化,重力细化bool result = VisualIMUAlignment(all_image_frame, Bgs, g, x);if(!result){ROS_DEBUG("solve g failed!");return false;}//原文:we can get the rotation qw c0 between the world frame and the//camera frame c0 by rotating the gravity to the z-axis. We then//rotate all variables from the reference frame (·)c0 to the world//frame (·)w.// change state(以下仅对WINDOW内的frame进行操作)for (int i = 0; i <= frame_count; i++){Matrix3d Ri = all_image_frame[Headers[i].stamp.toSec()].R;//IMU相对于world(即c0,此时还是l帧)的pose:Tc0_b[k]Vector3d Pi = all_image_frame[Headers[i].stamp.toSec()].T;//Rc0_b[k]Ps[i] = Pi;Rs[i] = Ri;all_image_frame[Headers[i].stamp.toSec()].is_key_frame = true;}ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nhere l_: " << l_<< "\nKF Rs[0]:\n" << Rs[0]);//1.梳理一下:此时all_image_frame[Headers[i].stamp.toSec()].R,T都是Tc0_bk//所以Ps,Rs也都是Tc0_bk//将三角化出的深度均设为-1,重新三角化VectorXd dep = f_manager.getDepthVector();//获取WINDOW内所有成功Triangulated出深度的landmark,求其逆深度for (int i = 0; i < dep.size(); i++)dep[i] = -1;f_manager.clearDepth(dep);//重新赋深度(都是-1)//triangulat on cam pose , no tic//平移tic未标定,设为0Vector3d TIC_TMP[NUM_OF_CAM];for(int i = 0; i < NUM_OF_CAM; i++)TIC_TMP[i].setZero();ric[0] = RIC[0];f_manager.setRic(ric);f_manager.triangulate(Ps, &(TIC_TMP[0]), &(RIC[0]));//Ps是tc0_bk(里面要转为tc_ck使用)double s = (x.tail<1>())(0);//取优化出的scale//gyro bias bg改变了,需要重新IMU预积分for (int i = 0; i <= WINDOW_SIZE; i++){//对每两帧camera之间的IMU数据重新进行积分(每次积分的观测初值(acc_0,gyro_0)仍然使用之前保存的linearized_acc, linearized_gyro)pre_integrations[i]->repropagate(Vector3d::Zero(), Bgs[i]);}ROS_INFO_STREAM("TIC[0]:\n" << TIC[0].transpose());//2.这里将Ps转换为(c0)tb0_bkfor (int i = frame_count; i >= 0; i--) {//论文式(6),看起来Rs应该是Rc0_bk(这个时候c0应该还没变为world,所以应该是在恢复米制单位)Ps[i] = s * Ps[i] - Rs[i] * TIC[0] - (s * Ps[0] - Rs[0] * TIC[0]);//这里输入的Ps还是tc0_bk,输出的Ps是(c0)tb0_bk,是在c0系下看的这个translation//TIC[0]为0代表第一项 s * Ps[i] - Rs[i] * TIC[0]=s*Ps[i],即s*tc0_b[k]=s*tc0_c[k](因为此时Ps=tc0_b[k])ROS_INFO_STREAM("TIC[0]:" << TIC[0].transpose()<< "\ns * Ps[i] - Rs[i] * TIC[0]: " << (s * Ps[i] - Rs[i] * TIC[0]).transpose()<< "\ns * Ps[i]: " << (s * Ps[i]).transpose()<< "\nl_: " << l_<< "\nPs[0]: " << Ps[0].transpose()//看他是否为0,如果不是0则证明我把c0和c[0]弄混了<< "\ns * Ps[0]: " << (s * Ps[0]).transpose());}//速度,深度处理int kv = -1;map<double, ImageFrame>::iterator frame_i;for (frame_i = all_image_frame.begin(); frame_i != all_image_frame.end(); frame_i++){if(frame_i->second.is_key_frame){kv++;Vs[kv] = frame_i->second.R * x.segment<3>(kv * 3);//更新bk系下的速度:Rc0_bk * (bk)vk = (c0)vk}}for (auto &it_per_id : f_manager.feature){it_per_id.used_num = it_per_id.feature_per_frame.size();if (!(it_per_id.used_num >= 2 && it_per_id.start_frame < WINDOW_SIZE - 2))continue;it_per_id.estimated_depth *= s;//恢复真实世界下尺度的深度}//g是world系下的重力向量,Rs[0]是Rc0_b[0]ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nRs[0] is Rc0_b0:\n" << Rs[0]<<"\nRbc^T:\n" << RIC[0].transpose());Matrix3d R0 = Utility::g2R(g);//求出gc0->gw(0,0,1)的pitch和roll方向的旋转R0ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nhere1 R0.yaw = \n" << Utility::R2ypr(R0).x());Eigen::Vector3d here1_Rs0_ypr = Utility::R2ypr(Rs[0]);double here1_Rs0_yaw = here1_Rs0_ypr.x();//Rs[0].yawdouble yaw = Utility::R2ypr(R0 * Rs[0]).x();//和transformed_yaw相等,说明不是运算精度的问题,可能就是旋转之后yaw会受到影响R0 = Utility::ypr2R(Eigen::Vector3d{-yaw, 0, 0}) * R0;ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nhere2 yaw = :\n" << yaw <<"\nRs[0].yaw = :\n" << here1_Rs0_yaw <<"\neventually, R0.yaw = \n" << Utility::R2ypr(R0).x());g = R0 * g;//将估计的重力g旋转到world系:yaw * Rwc0*g^(c0)=g^w,//Matrix3d rot_diff = R0 * Rs[0].transpose();Matrix3d rot_diff = R0;//rotdiff最后使得在world系下,b[0]真的yaw为0°//(PRV)w_b[k] = Rw_b[0] * (PRV)c0_b[k]for (int i = 0; i <= frame_count; i++){Ps[i] = rot_diff * Ps[i];Rs[i] = rot_diff * Rs[i];//(w)vb0_bkVs[i] = rot_diff * Vs[i];//(w)vb0_bkROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\ni=" << i <<" Rs[i].yaw = \n" << Utility::R2ypr(Rs[i]).x());}ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("g0 " << g.transpose());ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("my R0 " << Utility::R2ypr(Rs[0]).transpose()); return true;
}//选择window内第一个满足tracking数量>20,平均视差>30的帧(l)与最新帧之间的relative pose,是从最新帧到第l帧
bool Estimator::relativePose(Matrix3d &relative_R, Vector3d &relative_T, int &l)
{// find previous frame which contians enough correspondance and parallex with newest frame//对应论文V.A节for (int i = 0; i < WINDOW_SIZE; i++){vector<pair<Vector3d, Vector3d>> corres;// 找第i帧和buffer内最后一帧,(i, WINDOW_SIZE),之间的tracking上的点,构建一个pair,// 所有pair是一个vector,即corres(pondents),first=前一帧的去畸变的归一化平面上的点,second=后一帧的corres = f_manager.getCorresponding(i, WINDOW_SIZE);if (corres.size() > 20)//要求两帧的共视点大于20对{double sum_parallax = 0;double average_parallax;for (int j = 0; j < int(corres.size()); j++){Vector2d pts_0(corres[j].first(0), corres[j].first(1));Vector2d pts_1(corres[j].second(0), corres[j].second(1));double parallax = (pts_0 - pts_1).norm();//计算共视点的视差(欧氏距离)sum_parallax = sum_parallax + parallax;}average_parallax = 1.0 * sum_parallax / int(corres.size());//平均视差//用内参将归一化平面上的点转化到像素平面fx*X/Z + cx,cx相减抵消,z=1,所以直接就是fx*X//求的Rt是当前帧([WINDOW_SIZE]帧)到第l帧的坐标系变换Rl_[WINDOW_SIZE]if(average_parallax * 460 > 30 && m_estimator.solveRelativeRT(corres, relative_R, relative_T)){l = i;
// l = l+2;
// ROS_DEBUG("change l to l+2 = %d", l);ROS_DEBUG("average_parallax %f choose l %d and newest frame to triangulate the whole structure", average_parallax * 460, l);return true;}}}return false;
}void Estimator::solveOdometry()
{//需要在WINDOW满之后才进行求解,没满之前,初始化阶段pose由sfm等求解if (frame_count < WINDOW_SIZE)return;//if (solver_flag == NON_LINEAR){TicToc t_tri;//在optimize和marg,在新的start_frame上重新三角化landmarkf_manager.triangulate(Ps, tic, ric);ROS_DEBUG("triangulation costs %f", t_tri.toc());optimization();}
}//vector转换成double数组,因为ceres使用数值数组
//Ps、Rs转变成para_Pose,Vs、Bas、Bgs转变成para_SpeedBias
void Estimator::vector2double()
{for (int i = 0; i <= WINDOW_SIZE; i++){para_Pose[i][0] = Ps[i].x();para_Pose[i][1] = Ps[i].y();para_Pose[i][2] = Ps[i].z();Quaterniond q{Rs[i]};para_Pose[i][3] = q.x();para_Pose[i][4] = q.y();para_Pose[i][5] = q.z();para_Pose[i][6] = q.w();para_SpeedBias[i][0] = Vs[i].x();para_SpeedBias[i][1] = Vs[i].y();para_SpeedBias[i][2] = Vs[i].z();para_SpeedBias[i][3] = Bas[i].x();para_SpeedBias[i][4] = Bas[i].y();para_SpeedBias[i][5] = Bas[i].z();para_SpeedBias[i][6] = Bgs[i].x();para_SpeedBias[i][7] = Bgs[i].y();para_SpeedBias[i][8] = Bgs[i].z();}for (int i = 0; i < NUM_OF_CAM; i++){para_Ex_Pose[i][0] = tic[i].x();para_Ex_Pose[i][1] = tic[i].y();para_Ex_Pose[i][2] = tic[i].z();Quaterniond q{ric[i]};para_Ex_Pose[i][3] = q.x();para_Ex_Pose[i][4] = q.y();para_Ex_Pose[i][5] = q.z();para_Ex_Pose[i][6] = q.w();}VectorXd dep = f_manager.getDepthVector();for (int i = 0; i < f_manager.getFeatureCount(); i++)para_Feature[i][0] = dep(i);if (ESTIMATE_TD)para_Td[0][0] = td;
}// 优化一次之后,求出优化前后的第一帧的T,用于后面作用到所有的轨迹上去
// 数据转换,vector2double的相反过程
// 同时这里为防止优化结果往零空间变化,会根据优化前后第一帧的位姿差进行修正。
void Estimator::double2vector()
{//窗口第一帧优化前的位姿Vector3d origin_R0 = Utility::R2ypr(Rs[0]);//R[0]Vector3d origin_P0 = Ps[0];if (failure_occur){origin_R0 = Utility::R2ypr(last_R0);origin_P0 = last_P0;failure_occur = 0;}//窗口第一帧优化后的位姿 q(wxyz)Vector3d origin_R00 = Utility::R2ypr(Quaterniond(para_Pose[0][6],para_Pose[0][3],para_Pose[0][4],para_Pose[0][5]).toRotationMatrix());//(R_before_after).yaw(转到被减,变换到before)//TODO:确定到底是哪个 若是R_after_before.x()则下面使用rot_diff做的矫正就不对了,para_Pose肯定是after的double y_diff = origin_R0.x() - origin_R00.x();//TODO:了解欧拉角奇异点Matrix3d rot_diff = Utility::ypr2R(Vector3d(y_diff, 0, 0));if (abs(abs(origin_R0.y()) - 90) < 1.0 || abs(abs(origin_R00.y()) - 90) < 1.0){ROS_DEBUG("euler singular point!");rot_diff = Rs[0] * Quaterniond(para_Pose[0][6],para_Pose[0][3],para_Pose[0][4],para_Pose[0][5]).toRotationMatrix().transpose();}// 根据位姿差做修正,即保证第一帧优化前后位姿不变(似乎只是yaw不变,那tilt呢?)for (int i = 0; i <= WINDOW_SIZE; i++){Rs[i] = rot_diff * Quaterniond(para_Pose[i][6], para_Pose[i][3], para_Pose[i][4], para_Pose[i][5]).normalized().toRotationMatrix();Ps[i] = rot_diff * Vector3d(para_Pose[i][0] - para_Pose[0][0],para_Pose[i][1] - para_Pose[0][1],para_Pose[i][2] - para_Pose[0][2]) + origin_P0;Vs[i] = rot_diff * Vector3d(para_SpeedBias[i][0],para_SpeedBias[i][1],para_SpeedBias[i][2]);Bas[i] = Vector3d(para_SpeedBias[i][3],para_SpeedBias[i][4],para_SpeedBias[i][5]);Bgs[i] = Vector3d(para_SpeedBias[i][6],para_SpeedBias[i][7],para_SpeedBias[i][8]);}//外参for (int i = 0; i < NUM_OF_CAM; i++){tic[i] = Vector3d(para_Ex_Pose[i][0],para_Ex_Pose[i][1],para_Ex_Pose[i][2]);ric[i] = Quaterniond(para_Ex_Pose[i][6],para_Ex_Pose[i][3],para_Ex_Pose[i][4],para_Ex_Pose[i][5]).toRotationMatrix();}//转为逆深度,并置flagVectorXd dep = f_manager.getDepthVector();for (int i = 0; i < f_manager.getFeatureCount(); i++)dep(i) = para_Feature[i][0];f_manager.setDepth(dep);//time offsetif (ESTIMATE_TD)td = para_Td[0][0];// relative info between two loop frameif(relocalization_info){//按照WINDOW内第一帧的yaw角变化对j帧进行矫正Matrix3d relo_r;//j帧矫正之后的TVector3d relo_t;relo_r = rot_diff * Quaterniond(relo_Pose[6], relo_Pose[3], relo_Pose[4], relo_Pose[5]).normalized().toRotationMatrix();relo_t = rot_diff * Vector3d(relo_Pose[0] - para_Pose[0][0],relo_Pose[1] - para_Pose[0][1],relo_Pose[2] - para_Pose[0][2]) + origin_P0;//保证第[0]帧不变之后,+origin_P0转为世界系下的t//由于pitch和roll是可观的,所以我们在BA中一直都在优化pitch和roll,但由于yaw不可观,//所以即使漂了,可能还是满足我们BA的最优解,所以需要手动进行矫正//prev_relo_r=Tw1_bi, relo_Pose=Tw2_bi,这两个pose间的yaw和t的漂移Rw1_w2,tw1_w2double drift_correct_yaw;//yaw drift, Rw1_bi.yaw() - Rw2_bi.yaw=Rw1_w2.yaw()drift_correct_yaw = Utility::R2ypr(prev_relo_r).x() - Utility::R2ypr(relo_r).x();drift_correct_r = Utility::ypr2R(Vector3d(drift_correct_yaw, 0, 0));//tw1_w2drift_correct_t = prev_relo_t - drift_correct_r * relo_t;//Tw2_bi^(-1) * Tw2_bj = Tbi_bjrelo_relative_t = relo_r.transpose() * (Ps[relo_frame_local_index] - relo_t);relo_relative_q = relo_r.transpose() * Rs[relo_frame_local_index];//Rw2_bj.yaw() - Rw2_bi.yaw() = Rbi_bj.yaw()relo_relative_yaw = Utility::normalizeAngle(Utility::R2ypr(Rs[relo_frame_local_index]).x() - Utility::R2ypr(relo_r).x());/* //验证Tw1w2是否正确。 结果不一样,不知道为啥。//1.计算Rw1_w2 = Rw1_bi * Rw2_bi^(-1)Matrix3d Rw1_w2 = prev_relo_r * relo_r;//2. 计算Tw1_w2中的Rw1_w2 = Tw1_bi.R * Tbi_bj.R * Rw2_bj^(-1)Matrix3d Rw1_w2_prime = prev_relo_r * relo_relative_q.toRotationMatrix() * Rs[relo_frame_local_index].transpose();ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\ncheck Rw1_w2:\n" << Rw1_w2 << "\nRw1_w2_prime:\n" << Rw1_w2_prime);*///cout << "vins relo " << endl;//cout << "vins relative_t " << relo_relative_t.transpose() << endl;//cout << "vins relative_yaw " <<relo_relative_yaw << endl;relocalization_info = 0;}
}bool Estimator::failureDetection()
{//最后一帧tracking上的点的数量是否足够多if (f_manager.last_track_num < 2){ROS_INFO(" little feature %d", f_manager.last_track_num);//return true;}//ba和bg都不应过大if (Bas[WINDOW_SIZE].norm() > 2.5){ROS_INFO(" big IMU acc bias estimation %f", Bas[WINDOW_SIZE].norm());return true;}if (Bgs[WINDOW_SIZE].norm() > 1.0){ROS_INFO(" big IMU gyr bias estimation %f", Bgs[WINDOW_SIZE].norm());return true;}/*if (tic(0) > 1){ROS_INFO(" big extri param estimation %d", tic(0) > 1);return true;}*///在world系下的pose的t和z变化如果过大则认为failVector3d tmp_P = Ps[WINDOW_SIZE];if ((tmp_P - last_P).norm() > 5){ROS_INFO(" big translation");return true;}if (abs(tmp_P.z() - last_P.z()) > 1){ROS_INFO(" big z translation");return true;}//relative pose过大则fail//求误差的角度大小,对四元数表示的旋转,delta q有//delta q = [1, 1/2 delta theta]//delta theta = [delta q]_xyz * 2,弧度制,视情况转为degreeMatrix3d tmp_R = Rs[WINDOW_SIZE];Matrix3d delta_R = tmp_R.transpose() * last_R;Quaterniond delta_Q(delta_R);double delta_angle;delta_angle = acos(delta_Q.w()) * 2.0 / 3.14 * 180.0;//转为degreeif (delta_angle > 50){ROS_INFO(" big delta_angle ");//return true;}return false;
}//获得当前优化参数,按照自定义solver中的排列方式排列
static void get_cur_parameter(solve::Solver& solver, double* cur_x_array) {for (auto it : solver.parameter_block_idx) {const long addr = it.first;const int idx = it.second;const int tmp_param_block_size = solver.parameter_block_size[addr];ROS_ASSERT_MSG(tmp_param_block_size > 0, "tmp_param_block_size = %d", tmp_param_block_size);memcpy( &cur_x_array[idx], reinterpret_cast<double *>(addr), sizeof(double) *(int)tmp_param_block_size);}
}static bool updatePose(const double *x, const double *delta, double *x_plus_delta)
{Eigen::Map<const Eigen::Vector3d> _p(x);Eigen::Map<const Eigen::Quaterniond> _q(x + 3);Eigen::Map<const Eigen::Vector3d> dp(delta);Eigen::Quaterniond dq = Utility::deltaQ(Eigen::Map<const Eigen::Vector3d>(delta + 3));Eigen::Map<Eigen::Vector3d> p(x_plus_delta);Eigen::Map<Eigen::Quaterniond> q(x_plus_delta + 3);p = -_p + dp ;q = (_q.inverse() * dq).normalized();//四元数乘法并归一化return true;
}//计算ceres优化iteration轮之后的delta_x, solver要传引用,否则会调用析构函数
static void cal_delta_x(solve::Solver& solver, double* x_before, double* x_after, double* delta_x) {for (auto it : solver.parameter_block_idx) {const long addr = it.first;const int idx = it.second;const int tmp_param_block_size = solver.parameter_block_size[addr];double tmp_delta_pose_array[SIZE_POSE];ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nidx: " << idx << ", tmp_param_block_size: " << tmp_param_block_size);
// ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\ndelta_x size: " << delta_x.size());if (tmp_param_block_size == SIZE_POSE) {updatePose(&x_after[idx], &x_before[idx], &delta_x[idx]);} else {Eigen::Map<const Eigen::VectorXd> x_map(&x_before[idx], tmp_param_block_size);Eigen::Map<const Eigen::VectorXd> x_plus_delta_map(&x_after[idx], tmp_param_block_size);Eigen::Map<Eigen::VectorXd> delta_x_map(&delta_x[idx], tmp_param_block_size);delta_x_map = x_plus_delta_map - x_map;
// ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\ndelta_x_map: " << delta_x_map.transpose());}}
}//后端非线性优化
//大作业T1.a思路 这里要添加自己的makehessian的代码AddResidualBlockSolver()//类似于marg一样管理所有的factor,只不过,这里的m是WINDOW内所有的landmark,n是所有的P,V,Tbc,td,relopose
//管理方式也是地址->idx,地址->size一样,在添加的时候指定landmark的drop_set为valid,剩下的为非valid
//在最后求解出整个delta x,在solve中用LM评估迭代效果并继续迭代
void Estimator::optimization()
{ceres::LossFunction *loss_function;//loss_function = new ceres::HuberLoss(1.0);//Huber损失函数loss_function = new ceres::CauchyLoss(1.0);//柯西损失函数ceres::Problem problem;//自己写的solversolve::Solver solver(strategy);solver.method_ = solve::Solver::kDOGLEG;solver.iterations_ = NUM_ITERATIONS;solver.makeHessian_time_sum_ = &(makeHessian_time_sum_);solver.makeHessian_times_ = &makeHessian_times_;if(solver.method_==solve::Solver::kDOGLEG) {solver.epsilon_1_ = 1e-10;solver.epsilon_2_ = 1e-6;//h_dl和radius_减小的倍数阈值solver.epsilon_3_ = 1e-10;}#ifdef CERES_SOLVE//添加ceres参数块//因为ceres用的是double数组,所以在下面用vector2double做类型装换//Ps、Rs转变成para_Pose,Vs、Bas、Bgs转变成para_SpeedBiasfor (int i = 0; i < WINDOW_SIZE + 1; i++){ceres::LocalParameterization *local_parameterization = new PoseLocalParameterization();problem.AddParameterBlock(para_Pose[i], SIZE_POSE, local_parameterization);//ceres里叫参数块,g2o里是顶点和边problem.AddParameterBlock(para_SpeedBias[i], SIZE_SPEEDBIAS);}//ESTIMATE_EXTRINSIC!=0则camera到IMU的外参也添加到估计for (int i = 0; i < NUM_OF_CAM; i++){ceres::LocalParameterization *local_parameterization = new PoseLocalParameterization();problem.AddParameterBlock(para_Ex_Pose[i], SIZE_POSE, local_parameterization);if (!ESTIMATE_EXTRINSIC){ROS_DEBUG("fix extinsic param");problem.SetParameterBlockConstant(para_Ex_Pose[i]);}elseROS_DEBUG("estimate extinsic param");}//相机和IMU硬件不同步时估计两者的时间偏差if (ESTIMATE_TD){problem.AddParameterBlock(para_Td[0], 1);//problem.SetParameterBlockConstant(para_Td[0]);}#else//自己写的solver如何固定住外参呢?不加入ResidualBlockInfo即可
#endifTicToc t_whole, t_prepare;vector2double();//用于check维度std::unordered_map<long, uint8_t> param_addr_check;//所有param维度std::unordered_map<long, uint8_t> landmark_addr_check;//landmark维度//1.添加边缘化残差(先验部分)size_t size_1=0;if (last_marginalization_info){// construct new marginlization_factorMarginalizationFactor *marginalization_factor = new MarginalizationFactor(last_marginalization_info);//里面设置了上次先验的什么size,现在还不懂#ifdef CERES_SOLVEproblem.AddResidualBlock(marginalization_factor, NULL,last_marginalization_parameter_blocks);// /*用于check维度是否正确*/for(int i=0; i<last_marginalization_parameter_blocks.size(); ++i) {size_t tmp_size = last_marginalization_info->parameter_block_size[reinterpret_cast<long>(last_marginalization_parameter_blocks[i])];tmp_size = tmp_size==7 ? 6: tmp_size;//这个double*的地址代表的待优化变量的local_size,把每个地址都记录在map中,分配给待优化变量的地址都是连续的for(int j=0; j<tmp_size; ++j) {param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(last_marginalization_parameter_blocks[i]) + (double)j * (long) sizeof(long)] = 1;}}//打印prior的Jacobian维度ROS_DEBUG("\nlinearized_jacobians (rows, cols) = (%lu, %lu)",last_marginalization_info->linearized_jacobians.rows(), last_marginalization_info->linearized_jacobians.cols());size_1 = param_addr_check.size();//76ROS_DEBUG("\nprior size1=%lu, param_addr_check.size() = %lu, landmark size: %lu, except landmark size = %lu",size_1, param_addr_check.size(), landmark_addr_check.size(), param_addr_check.size()-landmark_addr_check.size());//landmark_addr_check中多加了个td#else//dropset用于指定求解时需要Schur消元的变量,即landmarksolve::ResidualBlockInfo *residual_block_info = new solve::ResidualBlockInfo(marginalization_factor, NULL,last_marginalization_parameter_blocks,vector<int>{});solver.addResidualBlockInfo(residual_block_info);
#endif}//2.添加IMU残差for (int i = 0; i < WINDOW_SIZE; i++){int j = i + 1;//两帧KF之间IMU积分时间过长的不进行优化(可能lost?)if (pre_integrations[j]->sum_dt > 10.0)continue;IMUFactor* imu_factor = new IMUFactor(pre_integrations[j]);//这里的factor就是残差residual,ceres里面叫factor#ifdef CERES_SOLVEproblem.AddResidualBlock(imu_factor, NULL, para_Pose[i], para_SpeedBias[i], para_Pose[j], para_SpeedBias[j]);//check维度long addr = reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[i]);if(param_addr_check.find(addr) == param_addr_check.end()) {ROS_DEBUG("\nIMU add para_Pose[%d]", i);for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {param_addr_check[addr + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;}}addr = reinterpret_cast<long>(para_SpeedBias[i]);if(param_addr_check.find(addr) == param_addr_check.end()) {ROS_DEBUG("\nIMU add para_SpeedBias[%d]", i);for(int k=0; k<SIZE_SPEEDBIAS; ++k) {param_addr_check[addr + (long) k * (long) sizeof(long)] = 1;}}addr = reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[j]);if(param_addr_check.find(addr) == param_addr_check.end()) {ROS_DEBUG("\n IMU add para_Pose[%d]", j);for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {param_addr_check[addr + (long) k * (long) sizeof(long)] = 1;}}addr = reinterpret_cast<long>(para_SpeedBias[j]);if(param_addr_check.find(addr) == param_addr_check.end()) {ROS_DEBUG("\n IMU add para_SpeedBias[%d]", j);for (int k = 0; k < SIZE_SPEEDBIAS; ++k) {param_addr_check[addr + (long) k * (long) sizeof(long)] = 1;}}
#elsesolve::ResidualBlockInfo *residual_block_info =new solve::ResidualBlockInfo(imu_factor, NULL,vector<double *>{para_Pose[i], para_SpeedBias[i], para_Pose[j], para_SpeedBias[j]},vector<int>{});solver.addResidualBlockInfo(residual_block_info);
#endif}
#ifdef CERES_SOLVEsize_t size_2 = param_addr_check.size() - size_1;//96ROS_DEBUG("\nIMU size2=%lu, param_addr_check.size() = %lu, landmark size: %lu, except landmark size = %lu",size_2, param_addr_check.size(), landmark_addr_check.size(), param_addr_check.size()-landmark_addr_check.size());//landmark_addr_check中多加了个td
#endif//3.添加视觉残差int f_m_cnt = 0;int feature_index = -1;for (auto &it_per_id : f_manager.feature){it_per_id.used_num = it_per_id.feature_per_frame.size();//!(至少两次tracking,且最新帧1st的tracking不能算(因为1st可能被marg掉),start_frame最大是[7])if (!(it_per_id.used_num >= 2 && it_per_id.start_frame < WINDOW_SIZE - 2))continue;++feature_index;int imu_i = it_per_id.start_frame, imu_j = imu_i - 1;Vector3d pts_i = it_per_id.feature_per_frame[0].point;//这个id的feature的第一帧和后面所有的帧分别构建residual blockfor (auto &it_per_frame : it_per_id.feature_per_frame){imu_j++;if (imu_i == imu_j){continue;}Vector3d pts_j = it_per_frame.point;//是否要time offsetif (ESTIMATE_TD){//对于一个feature,都跟[it_per_id.start_frame]帧进行优化ProjectionTdFactor *f_td = new ProjectionTdFactor(pts_i, pts_j, it_per_id.feature_per_frame[0].velocity, it_per_frame.velocity,it_per_id.feature_per_frame[0].cur_td, it_per_frame.cur_td,it_per_id.feature_per_frame[0].uv.y(), it_per_frame.uv.y());
#ifdef CERES_SOLVEproblem.AddResidualBlock(f_td, loss_function, para_Pose[imu_i], para_Pose[imu_j], para_Ex_Pose[0], para_Feature[feature_index], para_Td[0]);//check维度for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[imu_i]) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;}for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[imu_j]) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;}for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Ex_Pose[0]) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;}param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Feature[feature_index])] = 1;landmark_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Feature[feature_index])] = 1;param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Td[0])] = 1;/*double **para = new double *[5];para[0] = para_Pose[imu_i];para[1] = para_Pose[imu_j];para[2] = para_Ex_Pose[0];para[3] = para_Feature[feature_index];para[4] = para_Td[0];f_td->check(para);*/
#elsesolve::ResidualBlockInfo *residual_block_info = new solve::ResidualBlockInfo(f_td, loss_function,vector<double*>{para_Pose[imu_i], para_Pose[imu_j], para_Ex_Pose[0], para_Feature[feature_index], para_Td[0]},vector<int>{3});solver.addResidualBlockInfo(residual_block_info);
#endif}else{ProjectionFactor *f = new ProjectionFactor(pts_i, pts_j);
#ifdef CERES_SOLVEproblem.AddResidualBlock(f, loss_function, para_Pose[imu_i], para_Pose[imu_j], para_Ex_Pose[0], para_Feature[feature_index]);//check维度for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[imu_i]) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;}for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[imu_j]) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;}for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Ex_Pose[0]) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;}param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Feature[feature_index])] = 1;landmark_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Feature[feature_index])] = 1;
#elsesolve::ResidualBlockInfo *residual_block_info = new solve::ResidualBlockInfo(f, loss_function,vector<double*>{para_Pose[imu_i], para_Pose[imu_j], para_Ex_Pose[0], para_Feature[feature_index]},vector<int>{3});solver.addResidualBlockInfo(residual_block_info);
#endif}f_m_cnt++;}}#ifdef CERES_SOLVEsize_t size_3 = param_addr_check.size() - size_1 - size_2;//应该和landmark_addr_check.size一样ROS_DEBUG("\nvisual size3=%lu, param_addr_check.size() = %lu, landmark size: %lu, except landmark size = %lu",size_3, param_addr_check.size(), landmark_addr_check.size(), param_addr_check.size()-landmark_addr_check.size());//landmark_addr_check中多加了个td
#endifROS_DEBUG("visual measurement count: %d", f_m_cnt);//总的视觉观测个数,观测可能是在不同帧对同一个landmark进行观测,所以可能查过1000,注意与landmark个数进行区分ROS_DEBUG("prepare for ceres: %f", t_prepare.toc());//4.添加闭环检测残差,计算滑动窗口中与每一个闭环关键帧的相对位姿,这个相对位置是为后面的图优化(pose graph)准备 或者是 快速重定位(崔华坤PDF7.2节)//这里注意relo_pose是Tw2_bi = Tw2_w1 * Tw1_biif(relocalization_info){ROS_DEBUG("\nhas relocation blocks");//printf("set relocalization factor! \n");
#ifdef CERES_SOLVEceres::LocalParameterization *local_parameterization = new PoseLocalParameterization();problem.AddParameterBlock(relo_Pose, SIZE_POSE, local_parameterization);
#endifint retrive_feature_index = 0;int feature_index = -1;for (auto &it_per_id : f_manager.feature){ROS_DEBUG("\nfeature_id: %d", it_per_id.feature_id);it_per_id.used_num = it_per_id.feature_per_frame.size();if (!(it_per_id.used_num >= 2 && it_per_id.start_frame < WINDOW_SIZE - 2))continue;++feature_index;int start = it_per_id.start_frame;ROS_DEBUG("\nmatch_points size: %lu, retrive_feature_index: %d", match_points.size(), retrive_feature_index);if(start <= relo_frame_local_index)//必须之前看到过{//1.先在i中match的点中找到可能是现在这个feature的id的indexwhile((int)match_points[retrive_feature_index].z() < it_per_id.feature_id && retrive_feature_index <= match_points.size()-2)//.z()存的是i,j两帧match上的feature的id{retrive_feature_index++;}ROS_DEBUG("\nrelo here1, retrive_feature_index: %d", retrive_feature_index);//2.如果是,则WINDOW内的it_per_id.feature_id这个id的landmark就是被loop上的landmark,取归一化坐标,if((int)match_points[retrive_feature_index].z() == it_per_id.feature_id){//pts_j是i帧的归一化平面上的点,这里理解relo_Pose及其重要,relo_Pose实际上是Tw2_bi,视觉重投影是从WINDOW内的start帧的camera(在w2系下),投影到i帧(在w1系下),耦合了Tw1_w2Vector3d pts_j = Vector3d(match_points[retrive_feature_index].x(), match_points[retrive_feature_index].y(), 1.0);Vector3d pts_i = it_per_id.feature_per_frame[0].point;//start中的点ProjectionFactor *f = new ProjectionFactor(pts_i, pts_j);//relo_Pose是Tw2_bi
#ifdef CERES_SOLVEproblem.AddResidualBlock(f, loss_function, para_Pose[start], relo_Pose, para_Ex_Pose[0], para_Feature[feature_index]);//check维度for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[start]) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;}for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(relo_Pose) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;}for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Ex_Pose[0]) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;}param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Feature[feature_index])] = 1;landmark_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Feature[feature_index])] = 1;
#elseROS_DEBUG("\nrelo here2");solve::ResidualBlockInfo *residual_block_info = new solve::ResidualBlockInfo(f, loss_function,vector<double*>{para_Pose[start], relo_Pose, para_Ex_Pose[0], para_Feature[feature_index]},vector<int>{});solver.addResidualBlockInfo(residual_block_info);
#endifretrive_feature_index++;ROS_DEBUG("\nrelo here3");}}}ROS_DEBUG("\nrelo here4");}
#ifdef CERES_SOLVEsize_t size_4 = param_addr_check.size() - size_1 - size_2 - size_3;//没有loop时应该为0ROS_DEBUG("\nrelocation size_4=%lu, param_addr_check.size() = %lu, landmark size: %lu, except landmark size = %lu",size_4, param_addr_check.size(), landmark_addr_check.size(), param_addr_check.size()-landmark_addr_check.size());//landmark_addr_check中多加了个tdceres::Solver::Options options;options.linear_solver_type = ceres::DENSE_SCHUR;//options.num_threads = 2;
// options.trust_region_strategy_type = ceres::DOGLEG;//狗腿算法,与LM较为接近options.trust_region_strategy_type = ceres::LEVENBERG_MARQUARDT;//LMoptions.max_num_iterations = NUM_ITERATIONS;//options.use_explicit_schur_complement = true;//options.minimizer_progress_to_stdout = true;//options.use_nonmonotonic_steps = true;if (marginalization_flag == MARGIN_OLD)options.max_solver_time_in_seconds = SOLVER_TIME * 4.0 / 5.0;elseoptions.max_solver_time_in_seconds = SOLVER_TIME;TicToc t_solver;ceres::Solver::Summary summary;/* //获得idx和datasolver.preMakeHessian();solver.makeHessian();ROS_DEBUG("delta1");int cur_x_size = 1000 + (WINDOW_SIZE + 1) * (SIZE_POSE + SIZE_SPEEDBIAS) + SIZE_POSE + 1 + 100;double cur_x_array[cur_x_size], cur_x_array_before[cur_x_size];get_cur_parameter(solver, cur_x_array);memcpy(cur_x_array_before, cur_x_array, sizeof(double) * cur_x_size);Eigen::Map<Eigen::VectorXd> cur_x(cur_x_array, solver.m + solver.n);//cur_x_array变了,cur_x才会变const Eigen::VectorXd cur_x_before = cur_x;*/ROS_DEBUG("delta2");ceres::Solve(options, &problem, &summary);ROS_DEBUG("delta3");/* get_cur_parameter(solver, cur_x_array);double delta_x_ceres[cur_x_size];Eigen::Map<Eigen::VectorXd> delta_x_ceres_map(delta_x_ceres, solver.m + solver.n);cal_delta_x(solver, cur_x_array_before, cur_x_array, delta_x_ceres);ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\ncur_x before: " << cur_x_before.transpose() <<"\ncur_x after: " << cur_x.transpose() <<"\ndelta_x_ceres: "<< delta_x_ceres_map.transpose() <<"\ndelta_x_ceres.norm(): " << delta_x_ceres_map.norm() <<", delta_x_ceres.squaredNorm(): " << delta_x_ceres_map.squaredNorm());*///cout << summary.BriefReport() << endl;ROS_DEBUG("\nIterations : %d", static_cast<int>(summary.iterations.size()));#else //手写求解器求解ROS_DEBUG("\ndelta0");solver.preMakeHessian();solver.makeHessian();ROS_DEBUG("\ndelta1");int cur_x_size = 1000 + (WINDOW_SIZE + 1) * (SIZE_POSE + SIZE_SPEEDBIAS) + SIZE_POSE + 1 + 100;double cur_x_array[cur_x_size], cur_x_array_before[cur_x_size];get_cur_parameter(solver, cur_x_array);memcpy(cur_x_array_before, cur_x_array, sizeof(double) * cur_x_size);Eigen::Map<Eigen::VectorXd> cur_x(cur_x_array, solver.m + solver.n);//cur_x_array变了,cur_x才会变const Eigen::VectorXd cur_x_before = cur_x;ROS_DEBUG("\ndelta2");TicToc t_solver;solver.solve();double vins_finish_time = t_solver.toc();solver_time_sum_ += vins_finish_time;++solve_times_;ROS_DEBUG("\nmy solver costs: %f ms, iter nums: %d, avg_solve_time: %f ms, solver_time_sum_: %f, solve_times_: %f",vins_finish_time, NUM_ITERATIONS, solver_time_sum_/solve_times_, solver_time_sum_, solve_times_);get_cur_parameter(solver, cur_x_array);double delta_x[cur_x_size];Eigen::Map<Eigen::VectorXd> delta_x_map(delta_x, solver.m + solver.n);ROS_DEBUG("\ndelta3");cal_delta_x(solver, cur_x_array_before, cur_x_array, delta_x);TicToc t_print;ROS_DEBUG_STREAM(
// "\ncur_x before: " << cur_x_before.transpose() <<
// "\ncur_x after: " << cur_x.transpose() <<"\ndelta_x: "<< delta_x_map.transpose() <<"\ndelta_x.norm(): " << delta_x_map.norm() <<", delta_x.squaredNorm(): " << delta_x_map.squaredNorm());ROS_DEBUG("\nprint costs: %f ms", t_print.toc());
#endif// 防止优化结果在零空间变化,通过固定第一帧的位姿(如何固定,free,gauge,fix?)double2vector();//边缘化处理//如果次新帧是关键帧,将边缘化最老帧,及其看到的路标点和IMU数据,将其转化为先验:TicToc t_whole_marginalization;//如marg掉xi_2,则需要处理跟xi_2相关的先验信息,IMU信息,视觉信息//1. marg 最老帧[0]if (marginalization_flag == MARGIN_OLD){//new_marg_info,编译器生成默认构造函数MarginalizationInfo *marginalization_info = new MarginalizationInfo();vector2double();//1) 把上一次先验项中的残差项(尺寸为 n) 传递给当前先验项,并从中取出需要丢弃的状态量;// (这一步不是多此一举?第2步中的parameter_block不会保证marg掉para_Pose[0]和para_SpeedBias[0]吗?)//并不是,因为里面要求Jacobian,所以必须按照标准的格式传入才能求出正确的Jacobianif (last_marginalization_info)//如果不是第一帧(因为第一帧没有marg掉之后生成的先验matrix){//如果上次的先验中有本次需要marg的变量,则添加到drop_set中vector<int> drop_set;//本次被marg的参数的idxfor (int i = 0; i < static_cast<int>(last_marginalization_parameter_blocks.size()); i++){if (last_marginalization_parameter_blocks[i] == para_Pose[0] ||last_marginalization_parameter_blocks[i] == para_SpeedBias[0])drop_set.push_back(i);}// construct new marginlization_factor// 用上次marg的info初始化这次的marg_factor,再加到这次的info中,info管理marg的操作,// ceres只管调用marg_factor,不直接管info(当然factor需要info来初始化,所以是marg_factor管info,而不是ceres)MarginalizationFactor *marginalization_factor = new MarginalizationFactor(last_marginalization_info);ResidualBlockInfo *residual_block_info = new ResidualBlockInfo(marginalization_factor, NULL,last_marginalization_parameter_blocks,drop_set);
// ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nadd MARGIN_OLD last_marginalization_info\n " <<
// "\ncost_function->num_residuals(): " << marginalization_factor->num_residuals() <<
// "\ncost_function->parameter_block_sizes().size: " << marginalization_factor->parameter_block_sizes().size());marginalization_info->addResidualBlockInfo(residual_block_info);}//2) 将滑窗内第 0 帧和第 1 帧间的 IMU 预积分因子( pre_integrations[1])放到marginalization_info 中// (不理解为什么para_Pose[1], para_SpeedBias[1]也要marg){if (pre_integrations[1]->sum_dt < 10.0)//两帧间时间间隔少于10s,过长时间间隔的不进行marg{IMUFactor* imu_factor = new IMUFactor(pre_integrations[1]);//drop_set表示只marg掉[0][1],即P0,V0(虽然只drop[0][1],但是evaluate需要所有的变量来计算Jacobian,所以还是全部传进去)ResidualBlockInfo *residual_block_info = new ResidualBlockInfo(imu_factor, NULL,vector<double *>{para_Pose[0], para_SpeedBias[0], para_Pose[1], para_SpeedBias[1]},vector<int>{0, 1});marginalization_info->addResidualBlockInfo(residual_block_info);
// ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nadd imu_factor\n " <<
// "\ncost_function->num_residuals(): " << imu_factor->num_residuals() <<
// "\ncost_function->parameter_block_sizes().size: " << imu_factor->parameter_block_sizes().size());}}//3) 挑 选 出 第 一 次 观 测 帧 为 第 0 帧 的 路 标 点 , 将 对 应 的 多 组 视 觉 观 测 放 到marginalization_info 中,{int feature_index = -1;for (auto &it_per_id : f_manager.feature){it_per_id.used_num = it_per_id.feature_per_frame.size();if (!(it_per_id.used_num >= 2 && it_per_id.start_frame < WINDOW_SIZE - 2))continue;++feature_index;int imu_i = it_per_id.start_frame, imu_j = imu_i - 1;if (imu_i != 0)//只选择从[0]开始tracking的点continue;Vector3d pts_i = it_per_id.feature_per_frame[0].point;//old中的2d坐标for (auto &it_per_frame : it_per_id.feature_per_frame){imu_j++;if (imu_i == imu_j)continue;Vector3d pts_j = it_per_frame.point;if (ESTIMATE_TD){ProjectionTdFactor *f_td = new ProjectionTdFactor(pts_i, pts_j, it_per_id.feature_per_frame[0].velocity, it_per_frame.velocity,it_per_id.feature_per_frame[0].cur_td, it_per_frame.cur_td,it_per_id.feature_per_frame[0].uv.y(), it_per_frame.uv.y());ResidualBlockInfo *residual_block_info = new ResidualBlockInfo(f_td, loss_function,vector<double *>{para_Pose[imu_i], para_Pose[imu_j], para_Ex_Pose[0], para_Feature[feature_index], para_Td[0]},vector<int>{0, 3});//只drop掉[0](P0)和[3](tracking始于old的landmark)marginalization_info->addResidualBlockInfo(residual_block_info);}else{ProjectionFactor *f = new ProjectionFactor(pts_i, pts_j);ResidualBlockInfo *residual_block_info = new ResidualBlockInfo(f, loss_function,vector<double *>{para_Pose[imu_i], para_Pose[imu_j], para_Ex_Pose[0], para_Feature[feature_index]},vector<int>{0, 3});marginalization_info->addResidualBlockInfo(residual_block_info);
// ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nadd ProjectionFactor\n " <<
// "\ncost_function->num_residuals(): " << f->num_residuals() <<
// "\ncost_function->parameter_block_sizes().size: " << f->parameter_block_sizes().size());}}}}//得到 上次的先验、IMU测量、视觉观测(都是factor)对应的参数块(parameter_blocks)、雅可比矩阵(jacobians)、残差值(residuals),//与[0]有关的待优化变量存放于parameter_block_data中TicToc t_pre_margin;marginalization_info->preMarginalize();ROS_DEBUG("\npre marginalization %f ms", t_pre_margin.toc());//多线程计算在X0处的整个先验项的参数块,雅可比矩阵和残差值//5、多线程构造先验项舒尔补AX=b的结构,在X0处线性化计算Jacobian和残差TicToc t_margin;marginalization_info->marginalize();ROS_DEBUG("\nmarginalization %f ms", t_margin.toc());//用marg之后的待优化参数去生成新的last_marg_info和last_marg_parameter_blocks供下一次使用//6.调整参数块在下一次窗口中对应的位置(往前移一格),注意这里是指针,后面slideWindow中会赋新值,这里只是提前占座std::unordered_map<long, double *> addr_shift;for (int i = 1; i <= WINDOW_SIZE; i++){//让指针指向addr_shift[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[i])] = para_Pose[i - 1];addr_shift[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_SpeedBias[i])] = para_SpeedBias[i - 1];double* tmp_para_ptr = para_Pose[i-1];double* tmp_ptr = addr_shift[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[i])];
// for(int j=0; j<7; ++j) {
// ROS_DEBUG("\npara_Pose[%d] data: %f", i, *tmp_para_ptr);
// ++tmp_para_ptr;
// ROS_DEBUG("\naddr_shift[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[%d])] data: %f", i, *tmp_ptr);
// ++tmp_ptr;
// }}for (int i = 0; i < NUM_OF_CAM; i++)addr_shift[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Ex_Pose[i])] = para_Ex_Pose[i];if (ESTIMATE_TD){addr_shift[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Td[0])] = para_Td[0];}vector<double *> parameter_blocks = marginalization_info->getParameterBlocks(addr_shift);if (last_marginalization_info)delete last_marginalization_info;last_marginalization_info = marginalization_info;//保存此次marg infolast_marginalization_parameter_blocks = parameter_blocks;}//2. marg最新帧1st:仅marg掉视觉poseelse{if (last_marginalization_info &&std::count(std::begin(last_marginalization_parameter_blocks), std::end(last_marginalization_parameter_blocks), para_Pose[WINDOW_SIZE - 1])){MarginalizationInfo *marginalization_info = new MarginalizationInfo();vector2double();if (last_marginalization_info){//只drop掉2nd的视觉pose(IMU部分是在slideWindow内继承和delete的)vector<int> drop_set;for (int i = 0; i < static_cast<int>(last_marginalization_parameter_blocks.size()); i++){ROS_ASSERT(last_marginalization_parameter_blocks[i] != para_SpeedBias[WINDOW_SIZE - 1]);if (last_marginalization_parameter_blocks[i] == para_Pose[WINDOW_SIZE - 1])drop_set.push_back(i);}// construct new marginlization_factorMarginalizationFactor *marginalization_factor = new MarginalizationFactor(last_marginalization_info);ResidualBlockInfo *residual_block_info = new ResidualBlockInfo(marginalization_factor, NULL,last_marginalization_parameter_blocks,drop_set);
// ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nin MARGIN_SECOND_NEW add last_marginalization_info\n " <<
// "\ncost_function->num_residuals(): " << marginalization_factor->num_residuals() <<
// "\ncost_function->parameter_block_sizes().size: " << marginalization_factor->parameter_block_sizes().size());marginalization_info->addResidualBlockInfo(residual_block_info);}TicToc t_pre_margin;ROS_DEBUG("begin marginalization");marginalization_info->preMarginalize();ROS_DEBUG("end pre marginalization, %f ms", t_pre_margin.toc());TicToc t_margin;ROS_DEBUG("begin marginalization");marginalization_info->marginalize();ROS_DEBUG("end marginalization, %f ms", t_margin.toc());std::unordered_map<long, double *> addr_shift;for (int i = 0; i <= WINDOW_SIZE; i++){if (i == WINDOW_SIZE - 1)continue;else if (i == WINDOW_SIZE){//看不懂啥意思,后面不是还要操作slideWindow吗,这里搞地址干什么?addr_shift[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[i])] = para_Pose[i - 1];addr_shift[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_SpeedBias[i])] = para_SpeedBias[i - 1];}else{addr_shift[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[i])] = para_Pose[i];addr_shift[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_SpeedBias[i])] = para_SpeedBias[i];}}for (int i = 0; i < NUM_OF_CAM; i++)addr_shift[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Ex_Pose[i])] = para_Ex_Pose[i];if (ESTIMATE_TD){addr_shift[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Td[0])] = para_Td[0];}vector<double *> parameter_blocks = marginalization_info->getParameterBlocks(addr_shift);if (last_marginalization_info)delete last_marginalization_info;last_marginalization_info = marginalization_info;last_marginalization_parameter_blocks = parameter_blocks;}}ROS_DEBUG("whole marginalization costs: %f ms", t_whole_marginalization.toc());ROS_DEBUG("whole time for ceres: %f ms", t_whole.toc());
}//滑窗之后,WINDOW的最后两个Ps,Vs,Rs,Bas,Bgs相同,无论是old还是new,
//因为后面预积分要用最新的预积分初值,所以为了保证窗口内有11个观测,使最后两个相同
void Estimator::slideWindow()
{TicToc t_margin;//把最老的帧冒泡移到最右边,然后delete掉,在new一个新的对象出来if (marginalization_flag == MARGIN_OLD){double t_0 = Headers[0].stamp.toSec();back_R0 = Rs[0];//back_P0 = Ps[0];if (frame_count == WINDOW_SIZE){for (int i = 0; i < WINDOW_SIZE; i++)//循环完成也就冒泡完成到最右侧{Rs[i].swap(Rs[i + 1]);//世界系下old冒泡std::swap(pre_integrations[i], pre_integrations[i + 1]);//每一帧的预积分old冒泡dt_buf[i].swap(dt_buf[i + 1]);//各种buf也冒泡linear_acceleration_buf[i].swap(linear_acceleration_buf[i + 1]);angular_velocity_buf[i].swap(angular_velocity_buf[i + 1]);Headers[i] = Headers[i + 1];//最后一个是 Headers[WINDOW_SIZE-1] = Headers[WINDOW_SIZE]Ps[i].swap(Ps[i + 1]);Vs[i].swap(Vs[i + 1]);Bas[i].swap(Bas[i + 1]);Bgs[i].swap(Bgs[i + 1]);}//这一步是为了 new IntegrationBase时传入最新的预积分的初值acc_0, gyr_0,ba,bg,所以必须要强制等于最新的Headers[WINDOW_SIZE] = Headers[WINDOW_SIZE - 1];Ps[WINDOW_SIZE] = Ps[WINDOW_SIZE - 1];Vs[WINDOW_SIZE] = Vs[WINDOW_SIZE - 1];Rs[WINDOW_SIZE] = Rs[WINDOW_SIZE - 1];Bas[WINDOW_SIZE] = Bas[WINDOW_SIZE - 1];Bgs[WINDOW_SIZE] = Bgs[WINDOW_SIZE - 1];//冒泡到最右边之后把对应的都delete&new或者clear掉delete pre_integrations[WINDOW_SIZE];//delete掉,并new新的预积分对象出来pre_integrations[WINDOW_SIZE] = new IntegrationBase{acc_0, gyr_0, Bas[WINDOW_SIZE], Bgs[WINDOW_SIZE]};dt_buf[WINDOW_SIZE].clear();linear_acceleration_buf[WINDOW_SIZE].clear();angular_velocity_buf[WINDOW_SIZE].clear();
// ROS_DEBUG("marg_flag: %d, before marg, all_image_frame.size(): %lu, WINDOW_SIZE: %d",
// marginalization_flag, all_image_frame.size(), WINDOW_SIZE);if (true || solver_flag == INITIAL){map<double, ImageFrame>::iterator it_0;it_0 = all_image_frame.find(t_0);//t_0是最老帧的时间戳,marg_old时删掉了帧,但是marg2nd的时候没有动,但是在process时候加进来了,说明all_image_frame应该是在增长的delete it_0->second.pre_integration;it_0->second.pre_integration = nullptr;for (map<double, ImageFrame>::iterator it = all_image_frame.begin(); it != it_0; ++it){if (it->second.pre_integration)delete it->second.pre_integration;it->second.pre_integration = NULL;}all_image_frame.erase(all_image_frame.begin(), it_0);//erase掉从开始到被marg掉的old之间所有的帧[begin(), it_0)all_image_frame.erase(t_0);//erase掉old帧}slideWindowOld();//管理feature(landmark)
// ROS_DEBUG("marg_flag: %d, after marg, all_image_frame.size(): %lu, WINDOW_SIZE: %d",
// marginalization_flag, all_image_frame.size(), WINDOW_SIZE);}}//如果2nd不是KF则直接扔掉1st的visual测量,并在2nd基础上对1st的IMU进行预积分,window前面的都不动else{if (frame_count == WINDOW_SIZE){
// ROS_DEBUG("marg_flag: %d, before marg, all_image_frame.size(): %lu, WINDOW_SIZE: %d",
// marginalization_flag, all_image_frame.size(), WINDOW_SIZE);for (unsigned int i = 0; i < dt_buf[frame_count].size(); i++)//对最新帧的img对应的imu数据进行循环{double tmp_dt = dt_buf[frame_count][i];Vector3d tmp_linear_acceleration = linear_acceleration_buf[frame_count][i];Vector3d tmp_angular_velocity = angular_velocity_buf[frame_count][i];pre_integrations[frame_count - 1]->push_back(tmp_dt, tmp_linear_acceleration, tmp_angular_velocity);//2nd对1st进行IMU预积分//imu数据保存,相当于一个较长的KF,eg:// |-|-|-|-|-----|// ↑// 这段img为1st时,2nd不是KF,扔掉了这个2nd的img,但buf了IMU数据,所以这段imu数据较长dt_buf[frame_count - 1].push_back(tmp_dt);linear_acceleration_buf[frame_count - 1].push_back(tmp_linear_acceleration);angular_velocity_buf[frame_count - 1].push_back(tmp_angular_velocity);}//相对世界系的预积分需要继承过来Headers[frame_count - 1] = Headers[frame_count];Ps[frame_count - 1] = Ps[frame_count];Vs[frame_count - 1] = Vs[frame_count];Rs[frame_count - 1] = Rs[frame_count];Bas[frame_count - 1] = Bas[frame_count];Bgs[frame_count - 1] = Bgs[frame_count];delete pre_integrations[WINDOW_SIZE];pre_integrations[WINDOW_SIZE] = new IntegrationBase{acc_0, gyr_0, Bas[WINDOW_SIZE], Bgs[WINDOW_SIZE]};dt_buf[WINDOW_SIZE].clear();linear_acceleration_buf[WINDOW_SIZE].clear();angular_velocity_buf[WINDOW_SIZE].clear();slideWindowNew();
// ROS_DEBUG("marg_flag: %d, after marg, all_image_frame.size(): %lu, WINDOW_SIZE: %d",
// marginalization_flag, all_image_frame.size(), WINDOW_SIZE);}}
}// real marginalization is removed in solve_ceres()
void Estimator::slideWindowNew()
{sum_of_front++;f_manager.removeFront(frame_count);
}
// real marginalization is removed in solve_ceres()
void Estimator::slideWindowOld()
{sum_of_back++;bool shift_depth = solver_flag == NON_LINEAR ? true : false;if (shift_depth){Matrix3d R0, R1;Vector3d P0, P1;//Twb * Tbc = Twc//0:被marg掉的T_marg,1:新的第[0]帧的T_newR0 = back_R0 * ric[0];R1 = Rs[0] * ric[0];P0 = back_P0 + back_R0 * tic[0];P1 = Ps[0] + Rs[0] * tic[0];f_manager.removeBackShiftDepth(R0, P0, R1, P1);//为什么要转移深度?landmark不是删除了吗?}elsef_manager.removeBack();
}void Estimator::setReloFrame(double _frame_stamp, int _frame_index, vector<Vector3d> &_match_points, Vector3d _relo_t, Matrix3d _relo_r)
{relo_frame_stamp = _frame_stamp;//与old frame loop上的WINDOW内的帧(j帧)的时间戳relo_frame_index = _frame_index;//j帧的帧号match_points.clear();match_points = _match_points;//i帧中与j帧中match上的点在i帧中的归一化(x,y,id)//Tw1_bi=Tw1_b_oldprev_relo_t = _relo_t;//i帧poseprev_relo_r = _relo_r;for(int i = 0; i < WINDOW_SIZE; i++){if(relo_frame_stamp == Headers[i].stamp.toSec()){relo_frame_local_index = i;//j帧在WINDOW中的下标relocalization_info = 1;for (int j = 0; j < SIZE_POSE; j++)//注意,这不是赋地址,而是new了一个新的优化变量的内存,relo_Pose虽然赋初值时为Tw2_bj,但是实际上作用是Tw2_birelo_Pose[j] = para_Pose[i][j];}}
}9.2 solve.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>#include "solve.h"
#include "../parameters.h"#define USE_SCHURnamespace solve{/*solver_info相关函数*///计算每个残差,对应的Jacobian,并更新 parameter_block_data
void ResidualBlockInfo::Evaluate()
{//每个factor的残差块总维度 和 残差块具体size//residual总维度,先验=last n=76,IMU=15,Visual=2residuals.resize(cost_function->num_residuals());//有td时,先验factor为13(9*1+6*10+6+1),IMU factor为4(7,9,7,9),每个feature factor size=5(7,7,7,1)//无td时 12 4 4std::vector<int> block_sizes = cost_function->parameter_block_sizes();/* ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\ncost_function->num_residuals(): " << cost_function->num_residuals() <<"\ncost_function->parameter_block_sizes().size: " << cost_function->parameter_block_sizes().size());
for(int i=0; i<cost_function->parameter_block_sizes().size(); ++i) {ROS_DEBUG("\nparameter_block_sizes()[%d]: %d", i, cost_function->parameter_block_sizes()[i]);
}*/raw_jacobians = new double *[block_sizes.size()];//二重指针,指针数组jacobians.resize(block_sizes.size());for (int i = 0; i < static_cast<int>(block_sizes.size()); i++){jacobians[i].resize(cost_function->num_residuals(), block_sizes[i]);raw_jacobians[i] = jacobians[i].data();//二重指针,是为了配合ceres的形参 double** jacobians,看不懂,给data还能够操作地址??//dim += block_sizes[i] == 7 ? 6 : block_sizes[i];}//虚函数,调用的是基类自己实现的Evaluate,即分别是MarginalizationFactor、IMUFactor 和 ProjectionTdFactor(或ProjectionFactor)的Evaluate()函数cost_function->Evaluate(parameter_blocks.data(), residuals.data(), raw_jacobians);//std::vector<int> tmp_idx(block_sizes.size());//Eigen::MatrixXd tmp(dim, dim);//for (int i = 0; i < static_cast<int>(parameter_blocks.size()); i++)//{// int size_i = localSize(block_sizes[i]);// Eigen::MatrixXd jacobian_i = jacobians[i].leftCols(size_i);// for (int j = 0, sub_idx = 0; j < static_cast<int>(parameter_blocks.size()); sub_idx += block_sizes[j] == 7 ? 6 : block_sizes[j], j++)// {// int size_j = localSize(block_sizes[j]);// Eigen::MatrixXd jacobian_j = jacobians[j].leftCols(size_j);// tmp_idx[j] = sub_idx;// tmp.block(tmp_idx[i], tmp_idx[j], size_i, size_j) = jacobian_i.transpose() * jacobian_j;// }//}//Eigen::SelfAdjointEigenSolver<Eigen::MatrixXd> saes(tmp);//std::cout << saes.eigenvalues() << std::endl;//ROS_ASSERT(saes.eigenvalues().minCoeff() >= -1e-6);//这里使用的是CauchyLoss(应该是计算一个scale对residuals进行加权,先不细看,TODO:了解CauchyLoss等loss函数的意义)if (loss_function){double residual_scaling_, alpha_sq_norm_;double sq_norm, rho[3];sq_norm = residuals.squaredNorm();//loss_function 为 robust kernel function,in:sq_norm, out:rho out[0] = rho(sq_norm),out[1] = rho'(sq_norm), out[2] = rho''(sq_norm),loss_function->Evaluate(sq_norm, rho);//求取鲁棒核函数关于||f(x)||^2的一二阶导数//printf("sq_norm: %f, rho[0]: %f, rho[1]: %f, rho[2]: %f\n", sq_norm, rho[0], rho[1], rho[2]);double sqrt_rho1_ = sqrt(rho[1]);if ((sq_norm == 0.0) || (rho[2] <= 0.0)){residual_scaling_ = sqrt_rho1_;alpha_sq_norm_ = 0.0;}else{const double D = 1.0 + 2.0 * sq_norm * rho[2] / rho[1];const double alpha = 1.0 - sqrt(D);//求根公式求方程的根residual_scaling_ = sqrt_rho1_ / (1 - alpha);alpha_sq_norm_ = alpha / sq_norm;}for (int i = 0; i < static_cast<int>(parameter_blocks.size()); i++){jacobians[i] = sqrt_rho1_ * (jacobians[i] - alpha_sq_norm_ * residuals * (residuals.transpose() * jacobians[i]));}residuals *= residual_scaling_;}
}Solver::~Solver()
{ROS_DEBUG("destractor here1");//new出来的是在堆上的内存,需要手动delete释放;malloc的内存使用free来释放if(mem_allocated_) {for (auto it = parameter_block_data.begin(); it != parameter_block_data.end(); ++it)delete[] it->second;ROS_DEBUG("destractor here2");for (auto it = parameter_block_data_backup.begin(); it != parameter_block_data_backup.end(); ++it)delete[] it->second;}ROS_DEBUG("destractor here3");//这个不能在这delete放,因为ceres要用
// for (int i = 0; i < (int)factors.size(); i++)
// {
//
// delete[] factors[i]->raw_jacobians;
// ROS_DEBUG("destractor here31");
// delete[] factors[i]->cost_function;
// ROS_DEBUG("destractor here32");
// delete[] factors[i];
// ROS_DEBUG("destractor here33");
// }ROS_DEBUG("destractor here4");
}void Solver::addResidualBlockInfo(ResidualBlockInfo *residual_block_info)
{factors.emplace_back(residual_block_info);std::vector<double *> ¶meter_blocks = residual_block_info->parameter_blocks;//每个factor的待优化变量的地址std::vector<int> parameter_block_sizes = residual_block_info->cost_function->parameter_block_sizes();//待优化变量的维度//parameter_blocks.size//有td时,先验factor为13(9*1+6*10+6+1),IMU factor为4(7,9,7,9),每个feature factor size=5(7,7,7,1)//无td时 12 4 4for (int i = 0; i < static_cast<int>(residual_block_info->parameter_blocks.size()); i++){double *addr = parameter_blocks[i];int size = parameter_block_sizes[i];//待优化变量的维度//map没有key时会新建key-value对parameter_block_size[reinterpret_cast<long>(addr)] = size;//global size <优化变量内存地址,localSize>
// ROS_DEBUG("in addResidualBlockInfo size: %d", size);}//需要 marg 掉的变量for (int i = 0; i < static_cast<int>(residual_block_info->drop_set.size()); i++){double *addr = parameter_blocks[residual_block_info->drop_set[i]];//获得待marg变量的地址//要marg的变量先占个key的座,marg之前将m放在一起,n放在一起parameter_block_idx[reinterpret_cast<long>(addr)] = 0;//local size <待边缘化的优化变量内存地址,在parameter_block_size中的id>,}
}void Solver::preMakeHessian()
{
// ROS_INFO_STREAM("\nfactors.size(): " << factors.size());int i=0;ROS_DEBUG("factors size=%lu, landmark size=%lu", factors.size(), factors.size()-2); //始于[0]帧的landmarkfor (auto it : factors){
// ROS_INFO_STREAM("\nin preMarginalize i: "<< ++i); //很大,能到900多,说明[0]观测到了很多landmarkit->Evaluate();//计算每个factor的residual和Jacobian//如果完成过就只计算Jacobian和residual(里面已经耦合了sqrt_info,所以直接H=J^T*J,不用J^T*W*J),不用再new内存,重复调用只是为了计算新的Jacobian和residualif(mem_allocated_) {continue;}std::vector<int> block_sizes = it->cost_function->parameter_block_sizes(); //residual总维度,先验=last n=76,IMU=15,Visual=2
/* 测试地址转换之后还能否转换回来long tmp_addr = reinterpret_cast<long>(it->parameter_blocks[0]);double* tmp_pt = reinterpret_cast<double *>(tmp_addr);ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nraw double* = " << it->parameter_blocks[0] << ", cast to long= " << tmp_addr << ", back to double* = " << tmp_pt);*/for (int i = 0; i < static_cast<int>(block_sizes.size()); i++){long addr = reinterpret_cast<long>(it->parameter_blocks[i]);//parameter_blocks是vector<double *>,存放的是数据的地址int size = block_sizes[i];//如果优化变量中没有这个数据就new一片内存放置if (parameter_block_data.find(addr) == parameter_block_data.end()){double *data = new double[size];//dst,srcmemcpy(data, it->parameter_blocks[i], sizeof(double) * size);parameter_block_data[addr] = data;//数据备份double *data_backup = new double[size];memcpy(data_backup, it->parameter_blocks[i], sizeof(double) * size);parameter_block_data_backup[addr] = data_backup;}}}mem_allocated_ = true;
}int Solver::localSize(int size) const
{return size == 7 ? 6 : size;
}int Solver::globalSize(int size) const
{return size == 6 ? 7 : size;
}//线程函数
static void* ThreadsConstructA(void* threadsstruct)
{ThreadsStruct* p = ((ThreadsStruct*)threadsstruct);//遍历该线程分配的所有factors,这factor可能是任何一个factorfor (auto it : p->sub_factors){//遍历该factor中的所有参数块,比如IMU factor传入的是vector<double *>{para_Pose[0], para_SpeedBias[0], para_Pose[1], para_SpeedBias[1]}for (int i = 0; i < static_cast<int>(it->parameter_blocks.size()); i++){int idx_i = p->parameter_block_idx[reinterpret_cast<long>(it->parameter_blocks[i])];int size_i = p->parameter_block_size[reinterpret_cast<long>(it->parameter_blocks[i])];if (size_i == 7) //对于pose来说,是7维的,最后一维为0,这里取左边6size_i = 6;//只提取local size部分,对于pose来说,是7维的,最后一维为0,这里取左边6维;对于其他待优化变量,size_i不变,取全部jacobianEigen::MatrixXd jacobian_i = it->jacobians[i].leftCols(size_i);for (int j = i; j < static_cast<int>(it->parameter_blocks.size()); j++){int idx_j = p->parameter_block_idx[reinterpret_cast<long>(it->parameter_blocks[j])];int size_j = p->parameter_block_size[reinterpret_cast<long>(it->parameter_blocks[j])];if (size_j == 7)size_j = 6;Eigen::MatrixXd jacobian_j = it->jacobians[j].leftCols(size_j);//主对角线if (i == j)p->A.block(idx_i, idx_j, size_i, size_j) += jacobian_i.transpose() * jacobian_j;//非主对角线else{p->A.block(idx_i, idx_j, size_i, size_j) += jacobian_i.transpose() * jacobian_j;p->A.block(idx_j, idx_i, size_j, size_i) = p->A.block(idx_i, idx_j, size_i, size_j).transpose();}}p->b.segment(idx_i, size_i) += jacobian_i.transpose() * it->residuals;}}return threadsstruct;
}bool Solver::updatePose(const double *x, const double *delta, double *x_plus_delta)
{Eigen::Map<const Eigen::Vector3d> _p(x);Eigen::Map<const Eigen::Quaterniond> _q(x + 3);Eigen::Map<const Eigen::Vector3d> dp(delta);//数组转四元数Eigen::Quaterniond dq = Utility::deltaQ(Eigen::Map<const Eigen::Vector3d>(delta + 3));Eigen::Map<Eigen::Vector3d> p(x_plus_delta);Eigen::Map<Eigen::Quaterniond> q(x_plus_delta + 3);//Jacobian和residual都是按照6维来处理的,但是更新rotation时需要按照四元数来更新p = _p + dp;q = (_q * dq).normalized();//四元数乘法并归一化return true;
}void Solver::makeHessian()
{int pos = 0;//Hessian矩阵整体维度//it.first是要被marg掉的变量的地址,将其size累加起来就得到了所有被marg的变量的总localSize=m//marg的放一起,共m维,remain放一起,共n维for (auto &it : parameter_block_idx){it.second = pos;//也算是排序1pos += localSize(parameter_block_size[it.first]);//PQ7为改为6维}m = pos;//要被marg的变量的总维度int tmp_n = 0;//与[0]相关总维度for (const auto &it : parameter_block_size){if (parameter_block_idx.find(it.first) == parameter_block_idx.end())//将不在drop_set中的剩下的维度加起来,这一步实际上算的就是n{parameter_block_idx[it.first] = pos;//排序2tmp_n += localSize(it.second);pos += localSize(it.second);}}n = pos - m;//remain变量的总维度,这样写建立了n和m间的关系,表意更强ROS_DEBUG("\nn: %d, tmp_n: %d", n, tmp_n);ROS_DEBUG("\nSolver, pos: %d, m: %d, n: %d, size: %d", pos, m, n, (int)parameter_block_idx.size());TicToc t_summing;Eigen::MatrixXd A(pos, pos);//总系数矩阵Eigen::VectorXd b(pos);//总误差项A.setZero();b.setZero();Hessian_.resize(pos,pos);b_.resize(pos);delta_x_.resize(pos);//构建信息矩阵可以多线程构建
/* //single thread
for (auto it : factors)
{//J^T*Jfor (int i = 0; i < static_cast<int>(it->parameter_blocks.size()); i++){int idx_i = parameter_block_idx[reinterpret_cast<long>(it->parameter_blocks[i])];//要被marg的second=0int size_i = localSize(parameter_block_size[reinterpret_cast<long>(it->parameter_blocks[i])]);Eigen::MatrixXd jacobian_i = it->jacobians[i].leftCols(size_i);//remain变量的初始jacobianfor (int j = i; j < static_cast<int>(it->parameter_blocks.size()); j++){int idx_j = parameter_block_idx[reinterpret_cast<long>(it->parameter_blocks[j])];int size_j = localSize(parameter_block_size[reinterpret_cast<long>(it->parameter_blocks[j])]);Eigen::MatrixXd jacobian_j = it->jacobians[j].leftCols(size_j);//marg变量的初始jacobian//主对角线,注意这里是+=,可能之前别的变量在这个地方已经有过值了,所以要+=if (i == j)A.block(idx_i, idx_j, size_i, size_j) += jacobian_i.transpose() * jacobian_j;//非主对角线else{A.block(idx_i, idx_j, size_i, size_j) += jacobian_i.transpose() * jacobian_j;A.block(idx_j, idx_i, size_j, size_i) = A.block(idx_i, idx_j, size_i, size_j).transpose();}}b.segment(idx_i, size_i) += jacobian_i.transpose() * it->residuals;//J^T*e}
}
ROS_INFO("summing up costs %f ms", t_summing.toc());*///multi threadTicToc t_thread_summing;pthread_t tids[NUM_THREADS];//4个线程构建//携带每个线程的输入输出信息ThreadsStruct threadsstruct[NUM_THREADS];//将先验约束因子平均分配到4个线程中int i = 0;for (auto it : factors){threadsstruct[i].sub_factors.push_back(it);i++;i = i % NUM_THREADS;}//将每个线程构建的A和b加起来for (int i = 0; i < NUM_THREADS; i++){TicToc zero_matrix;threadsstruct[i].A = Eigen::MatrixXd::Zero(pos,pos);threadsstruct[i].b = Eigen::VectorXd::Zero(pos);threadsstruct[i].parameter_block_size = parameter_block_size;//marg里的block_size,4个线程共享threadsstruct[i].parameter_block_idx = parameter_block_idx;int ret = pthread_create( &tids[i], NULL, ThreadsConstructA ,(void*)&(threadsstruct[i]));//参数4是arg,void*类型,取其地址并强制类型转换if (ret != 0){ROS_WARN("pthread_create error");ROS_BREAK();}}//将每个线程构建的A和b加起来for( int i = NUM_THREADS - 1; i >= 0; i--){pthread_join( tids[i], NULL );//阻塞等待线程完成,这里的A和b的+=操作在主线程中是阻塞的,+=的顺序是pthread_join的顺序A += threadsstruct[i].A;b += threadsstruct[i].b;}//ROS_DEBUG("thread summing up costs %f ms", t_thread_summing.toc());//ROS_INFO("A diff %f , b diff %f ", (A - tmp_A).sum(), (b - tmp_b).sum());Hessian_ = A;b_ = -b;//DOGLEG需反解出J和eif(method_==solve::Solver::kDOGLEG) {TicToc t_solve_J;TicToc t_SelfAdjoint;Eigen::SelfAdjointEigenSolver<Eigen::MatrixXd> saes2(A);//这一句24.3msROS_DEBUG("\nt_SelfAdjoint cost: %f ms", t_SelfAdjoint.toc());Eigen::VectorXd S = Eigen::VectorXd((saes2.eigenvalues().array() > eps).select(saes2.eigenvalues().array(), 0));Eigen::VectorXd S_sqrt = S.cwiseSqrt();//开根号linearized_jacobians = S_sqrt.asDiagonal() * saes2.eigenvectors().transpose();Eigen::VectorXd S_inv = Eigen::VectorXd((saes2.eigenvalues().array() > eps).select(saes2.eigenvalues().array().inverse(), 0));Eigen::VectorXd S_inv_sqrt = S_inv.cwiseSqrt();linearized_residuals = S_inv_sqrt.asDiagonal() * saes2.eigenvectors().real().transpose() * b;ROS_DEBUG("\nt_solve_J cost: %f ms", t_solve_J.toc());//25ms}
}std::vector<double *> Solver::getParameterBlocks(std::unordered_map<long, double *> &addr_shift)
{std::vector<double *> keep_block_addr;//remain的优化变量的地址keep_block_size.clear();keep_block_idx.clear();keep_block_data.clear();for (const auto &it : parameter_block_idx){if (it.second >= m)//如果是remain部分{keep_block_size.push_back(parameter_block_size[it.first]);keep_block_idx.push_back(parameter_block_idx[it.first]);keep_block_data.push_back(parameter_block_data[it.first]);keep_block_addr.push_back(addr_shift[it.first]);//待优化变量的首地址需要不变,但是首地址对应的变量是P0,需要在slideWindow中被冒泡到后面delete掉}}ROS_DEBUG("keep_block_addr[0] long addr: %ld, [1] long addr: %ld",reinterpret_cast<long>(keep_block_addr[0]), reinterpret_cast<long>(keep_block_addr[1]));sum_block_size = std::accumulate(std::begin(keep_block_size), std::end(keep_block_size), 0);return keep_block_addr;
}//只更新状态量p,q,v,ba,bg,λ,注意prior不是状态量,虽然在待优化变量中,但是其residual是跟状态量有关,Jacobian在一轮优化中不变,
//这里更新状态的目的是因为计算chi时会用到residual,而residual和状态量有关,而先验的residual更新:f' = f + J*δxp,其中δxp=x-x0,也跟状态量x有关,
//但是因为在先验factor在Evaluate时会计算residual,所以不用手动更新,只需要更新最核心的x即可。其他的factor相同。
//weight是LM strategy2时的权重,默认传-1.0,不加权
bool Solver::updateStates(double weight) {int array_size = 1000 + (WINDOW_SIZE + 1) * (SIZE_POSE + SIZE_SPEEDBIAS) + SIZE_POSE + 1 + 100;double used_delta_x[array_size];if(weight != -1.0)std::transform(delta_x_array_, delta_x_array_ + array_size, used_delta_x, [weight](double x) { return x * weight; });//对delta_x加权elsememcpy(used_delta_x, delta_x_array_, sizeof(double) * array_size);//使用idx来找对应的paramdouble cur_x_array[1000 + (WINDOW_SIZE + 1) * (SIZE_POSE + SIZE_SPEEDBIAS) + SIZE_POSE + 1 + 100];for (auto it : parameter_block_idx){const long addr = it.first;const int idx = it.second;const int tmp_param_block_size = parameter_block_size[addr];
/* ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nidx: " << idx << ", tmp_param_block_size: " << tmp_param_block_size);*///保存一份待优化变量,和delta_x进行数量级对比memcpy( &cur_x_array[idx], reinterpret_cast<double *>(addr), sizeof(double) *(int)SIZE_POSE);if(tmp_param_block_size == SIZE_POSE) {
/* Eigen::Map<Eigen::VectorXd> delta_pose {&delta_x_array_[idx], tmp_param_block_size};Eigen::Map<Eigen::VectorXd> tmp_pose {reinterpret_cast<double *>(addr), tmp_param_block_size};for(int i=0;i<tmp_param_block_size;++i){tmp_pose[i] = *(reinterpret_cast<double *>(addr + sizeof(double)*i));delta_pose[i] = delta_x_array_[idx+i];}ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\npose before update: " << tmp_pose.transpose() << "\ndelta_pose: " << delta_pose.transpose());*/updatePose(reinterpret_cast<double *>(addr), &delta_x_array_[idx], reinterpret_cast<double *>(addr));//TODO:这个backup应该可以用parameter_block_data替代/* ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\npose after update: " << tmp_pose.transpose());*/} else {Eigen::Map<const Eigen::VectorXd> x{parameter_block_data_backup[addr], tmp_param_block_size};Eigen::Map<const Eigen::VectorXd> delta_x{&delta_x_array_[idx], tmp_param_block_size};Eigen::Map<Eigen::VectorXd> x_plus_delta{reinterpret_cast<double *>(addr), tmp_param_block_size};/*ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nother parameters before update: " << x_plus_delta.transpose() << "\ndelta_x: " << delta_x.transpose());*/x_plus_delta = x + delta_x;/*ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nother parameters after update: " << x_plus_delta.transpose());*/}}// 初始化Eigen向量Eigen::Map<Eigen::VectorXd> cur_x(cur_x_array, m+n);ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\ncur_x: " << cur_x.transpose());preMakeHessian();//计算更新后的Jacobian和residualreturn true;
}//备份状态量
bool Solver::backupStates() {for (auto it : parameter_block_idx){const long addr = it.first;const int tmp_param_block_size = parameter_block_size[addr];memcpy(parameter_block_data_backup[addr], reinterpret_cast<double *>(addr), sizeof(double) * (int)tmp_param_block_size);}return true;
}//回滚状态量
bool Solver::rollbackStates() {for (auto it : parameter_block_idx){const long addr = it.first;const int tmp_param_block_size = parameter_block_size[addr];memcpy(reinterpret_cast<double *>(addr), parameter_block_data_backup[addr], sizeof(double) * (int)tmp_param_block_size);}preMakeHessian();//计算更新后的Jacobian和residualreturn true;
}bool Solver::get_cur_parameter(double* cur_x_array) {for (auto it : parameter_block_idx) {const long addr = it.first;const int idx = it.second;const int tmp_param_block_size = parameter_block_size[addr];ROS_ASSERT_MSG(tmp_param_block_size > 0, "tmp_param_block_size = %d", tmp_param_block_size);memcpy( &cur_x_array[idx], reinterpret_cast<double *>(addr), sizeof(double) *(int)tmp_param_block_size);}return true;
}//在ResidualBlockInfo::Evaluate()中调用的多态Evaluate()函数后已经考虑了loss_function对Jacobian和residual的加权
//分别计算先验和其他factor的chi
double Solver::computeChi() const{//先验的residual维度size_t prior_dim = SIZE_SPEEDBIAS + (SIZE_POSE-1) * WINDOW_SIZE + (SIZE_POSE-1);if(ESTIMATE_TD){prior_dim+=1;}double tmpChi = 0;for (auto it : factors){//TODO:先验的也改成正常更新,按照参数也是PQV来理解先验的话,就应该是正常更新,而不是使用norm(),后面看看对不对double this_Chi = it->residuals.transpose() * it->residuals;tmpChi += this_Chi;// if(it->residuals.size()==prior_dim) {
// double this_Chi = it->residuals.norm();
// tmpChi += this_Chi;
///* ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nprior factor, this_Chi= " << this_Chi
// << ", residuals size: " << it->residuals.size()
// << ", residuals: " << it->residuals.transpose());*/
// } else {
// double this_Chi = it->residuals.transpose() * it->residuals;
// tmpChi += this_Chi;
///* ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nother factor, this_Chi= " << this_Chi
// << ", residuals size: " << it->residuals.size()
// << ", residuals: " << it->residuals.transpose());*/
// }}ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nhere tmpChi= " << tmpChi);return tmpChi;
}/// LM
void Solver::computeLambdaInitLM() {if(strategy_ == 1) {currentChi_ = computeChi();double maxDiagonal = 0;ulong size = Hessian_.cols();assert(Hessian_.rows() == Hessian_.cols() && "Hessian is not square");for (ulong i = 0; i < size; ++i) {maxDiagonal = std::max(fabs(Hessian_(i, i)), maxDiagonal);//取H矩阵的最大值,然后*涛}double tau = 1e1;//[1e-8,1] tau越小,△x越大currentLambda_ = tau * maxDiagonal;} else if(strategy_ == 2) {// set a large value, so that first updates are small steps in the steepest-descent directioncurrentChi_ = computeChi();currentLambda_ = 1e16;
// currentLambda_ = 1e-3;} else if(strategy_ == 3) {ni_ = 2.;currentLambda_ = -1.;currentChi_ = computeChi();stopThresholdLM_ = 1e-6 * currentChi_; // 迭代条件为 误差下降 1e-6 倍double maxDiagonal = 0;ulong size = Hessian_.cols();assert(Hessian_.rows() == Hessian_.cols() && "Hessian is not square");for (ulong i = 0; i < size; ++i) {maxDiagonal = std::max(fabs(Hessian_(i, i)), maxDiagonal);//取H矩阵的最大值,然后*涛}
// double tau = 1e-5;double tau = 1e-15;//[1e-8,1] tau越小,△x越大//currentLambda_ = tau * maxDiagonal;ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nin computeLambdaInitLM currentChi_= " << currentChi_<< ", init currentLambda_=" << currentLambda_<< ", maxDiagonal=" << maxDiagonal);}
}void Solver::addLambdatoHessianLM() {ulong size = Hessian_.cols();assert(Hessian_.rows() == Hessian_.cols() && "Hessian is not square");for (ulong i = 0; i < size; ++i) {if(strategy_==1) {Hessian_(i, i) += currentLambda_ * Hessian_(i, i); //理解: H(k+1) = H(k) + λ H(k) = (1+λ) H(k) 策略1} else if(strategy_==2 || strategy_==3) {Hessian_(i, i) += currentLambda_;}}
}void Solver::removeLambdaHessianLM() {ulong size = Hessian_.cols();assert(Hessian_.rows() == Hessian_.cols() && "Hessian is not square");// TODO:: 这里不应该减去一个,数值的反复加减容易造成数值精度出问题?而应该保存叠加lambda前的值,在这里直接赋值for (ulong i = 0; i < size; ++i) {if(strategy_==1) {Hessian_(i, i) /= 1.0 + currentLambda_;//H回退: H(k) = 1/(1+λ) * H(k+1),策略1} else if(strategy_==2 || strategy_==3) {Hessian_(i, i) -= currentLambda_;}}
}//Nielsen的方法,分母直接为L,判断\rho的符号
bool Solver::isGoodStepInLM() {bool ret = false;assert(Hessian_.rows() == Hessian_.cols() && "Hessian is not square");if(strategy_==1) {double tempChi = computeChi();ulong size = Hessian_.cols();MatXX diag_hessian(MatXX::Zero(size, size));for(ulong i = 0; i < size; ++i) {diag_hessian(i, i) = Hessian_(i, i);}double scale = delta_x_.transpose() * (currentLambda_ * diag_hessian * delta_x_ + b_);//scale就是rho的分母double rho = (currentChi_ - tempChi) / scale;//计算rho// update currentLambda_double epsilon = 0.75;double L_down = 9.0;double L_up = 11.0;if(rho > epsilon && isfinite(tempChi)) {currentLambda_ = std::max(currentLambda_ / L_down, 1e-7);currentChi_ = tempChi;ret = true;ROS_DEBUG("choose L_down");} else {currentLambda_ = std::min(currentLambda_ * L_up, 1e7);ret = false;ROS_DEBUG("choose L_up");}ROS_DEBUG("\nstrategy1: currentLambda_: %e,rho: %f, currentChi_: %e, tempChi: %e, scale: %e",currentLambda_, rho, currentChi_, tempChi, scale);ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nret = " << ret <<", rho>0 = " << (rho>0) <<", rho: " << rho <<", delta_x_.squaredNorm(): " << delta_x_.squaredNorm() <<", delta_x_: " << delta_x_.transpose()<< "\nb_.norm(): " << b_.norm() );
// ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nb_: " << b_.transpose());} else if(strategy_==2) {// 统计所有的残差double tempChi_p_h = 0.0, tempChi_p_alpha_h = 0.0;tempChi_p_h = computeChi();double alpha_up = b_.transpose() * delta_x_;double alpha_down = (tempChi_p_h - currentChi_) / 2. + 2. * alpha_up;double alpha_tmp = alpha_up / alpha_down;double scale = 0;scale = fabs((alpha_tmp * delta_x_).transpose() * (currentLambda_ * (alpha_tmp * delta_x_) + b_));scale += 1e-3; // make sure it's non-zero :)//回滚刚才更新的x=x+△x,使用α重新更新x=x + α*△x,并重新计算残差和chirollbackStates();updateStates(alpha_tmp);preMakeHessian();//更新状态之后就要更新reidualtempChi_p_alpha_h = computeChi();double rho = (currentChi_ - tempChi_p_alpha_h) / scale;if (rho > 0 && isfinite(tempChi_p_alpha_h)) { // last step was good, 误差在下降currentLambda_ = std::max(currentLambda_ / (1 + alpha_tmp), 1e-7);lm_alpha_ = alpha_tmp;currentChi_ = tempChi_p_alpha_h;ret = true;} else {currentLambda_ = currentLambda_ + fabs(tempChi_p_alpha_h - currentChi_) / (2 * alpha_tmp);ret = false;}ROS_DEBUG("\nstrategy2: currentLambda_: %e,alpha_tmp: %e, rho: %f, currentChi_: %e, tempChi_p_h: %e, tempChi_p_alpha_h: %e, scale: %e",currentLambda_, alpha_tmp, rho, currentChi_, tempChi_p_h, tempChi_p_alpha_h, scale);ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nret = " << ret <<", rho>0 = " << (rho>0) <<", rho: " << rho <<", delta_x_.squaredNorm(): " << delta_x_.squaredNorm() << ", delta_x_: " << delta_x_.transpose()<< "\nb_.norm(): " << b_.norm() << ", b_: " << b_.transpose());} else if(strategy_==3) {double scale = 0;scale = fabs(delta_x_.transpose() * (currentLambda_ * delta_x_ + b_));scale += 1e-3; // make sure it's non-zero :)// 统计更新后的所有的chi()double tempChi = computeChi();double rho = (currentChi_ - tempChi) / scale;if (rho > 0 && isfinite(tempChi)) // last step was good, 误差在下降{double alpha = 1. - pow((2 * rho - 1), 3);//更新策略跟课件里面一样//TODO:这个ceres里面没有限制上限为2/3alpha = std::min(alpha, 2. / 3.);double scaleFactor = (std::max)(1. / 3., alpha);currentLambda_ *= scaleFactor;//课程里面应该是μ,需要绘制曲线ni_ = 2; //vcurrentChi_ = tempChi;ret = true;} else {//如果\rho<0则增大阻尼μ,减小步长currentLambda_ *= ni_;ni_ *= 2;//2这个值越大,λ增长越快ret = false;}ROS_DEBUG("\nstrategy3: currentLambda_: %e, ni_: %e, rho: %f, currentChi_: %e, tempChi: %e, scale: %e",currentLambda_, ni_, rho, currentChi_, tempChi, scale);ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nret = " << ret <<", rho>0 = " << (rho>0) <<", rho: " << rho << ", delta_x_.squaredNorm(): " << delta_x_.squaredNorm() << ", delta_x_: " << delta_x_.transpose()<< "\nb_.norm(): " << b_.norm() << ", b_: " << b_.transpose());
/* FILE *fp_lambda = fopen(file_name_.data(), "a");fprintf(fp_lambda, "%d, %f\n", try_iter_, currentLambda_);fflush(fp_lambda);fclose(fp_lambda);*/}ROS_DEBUG("\n%d record lambda finish\n", try_iter_);return ret;
}/*
* @brief conjugate gradient with perconditioning
*
* the jacobi PCG method 共轭梯度法
* 知乎有一篇帖子是针对PCG进行改进的,能减少迭代次数:对角线预处理和不完备的Cholesky预处理* https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/521753443
*/
Eigen::MatrixXd Solver::pcgSolver(const MatXX &A, const VecX &b, int maxIter = -1) {assert(A.rows() == A.cols() && "PCG solver ERROR: A is not a square matrix");int rows = b.rows();int n = maxIter < 0 ? rows : maxIter;VecX x(VecX::Zero(rows));MatXX M_inv = A.diagonal().asDiagonal().inverse();//取对角线阵的逆矩阵VecX r0(b); // initial r = b - A*0 = bVecX z0 = M_inv * r0;VecX p(z0);VecX w = A * p;double r0z0 = r0.dot(z0);double alpha = r0z0 / p.dot(w);VecX r1 = r0 - alpha * w;int i = 0;double threshold = 1e-5 * r0.norm(); //比例调大可以提高阈值,放宽停止条件while (r1.norm() > threshold && i < n) {i++;VecX z1 = M_inv * r1;double r1z1 = r1.dot(z1);double belta = r1z1 / r0z0;z0 = z1;r0z0 = r1z1;r0 = r1;p = belta * p + z1;w = A * p;alpha = r1z1 / p.dot(w);x += alpha * p;r1 -= alpha * w;}ROS_DEBUG("\nPCG iter times: %d, n: %d, r1.norm(): %f, threshold: %f", i, n, r1.norm(), threshold);return x;
}/*Solve Hx = b, we can use PCG iterative method or use sparse Cholesky*/
//TODO:使用PCG迭代而非SVD分解求解
void Solver::solveLinearSystem() {
//method1:直接求逆求解
// delta_x_ = Hessian_.inverse() * b_;
// delta_x_ = H.ldlt().solve(b_);//method2:Schur消元求解,marg掉drop_set中的parameter
#ifdef USE_SCHUR//step1:Schur消元求//求解Hx=b,之前marg时不用求出△x,只需要H,所以不用对方程组求解,但现在优化时需要求解出整个△xTicToc t_Schur_PCG;Eigen::MatrixXd Amm_solver = 0.5 * (Hessian_.block(0, 0, m, m) + Hessian_.block(0, 0, m, m).transpose());Eigen::VectorXd bmm_solver = b_.segment(0, m);Eigen::MatrixXd Amr_solver = Hessian_.block(0, m, m, n);Eigen::MatrixXd Arm_solver = Hessian_.block(m, 0, n, m);Eigen::MatrixXd Arr_solver = Hessian_.block(m, m, n, n);Eigen::VectorXd brr_solver = b_.segment(m, n);//求Amm_solver^(-1)TicToc t_Amm_inv;Eigen::MatrixXd Amm_inv_solver = Amm_solver.inverse();//SelfAdjointEigenSolver和直接求逆速度差不多ROS_DEBUG("\nt_Amm_inv cost: %f ms", t_Amm_inv.toc());Eigen::MatrixXd tmpA_solver = Arm_solver * Amm_inv_solver;//step1: Schur补Eigen::MatrixXd Arr_schur = Arr_solver - tmpA_solver * Amr_solver;Eigen::VectorXd brr_schur = brr_solver - tmpA_solver * bmm_solver;ROS_DEBUG("here1");// step2: solve Arr_schur * delta_x_rr = brr_schur
// method1:直接求逆
// Eigen::MatrixXd Arr_schur_inv = Arr_schur.inverse();
// Eigen::VectorXd delta_x_rr = Arr_schur_inv * brr_schur;// method2:使用PCG求解TicToc t_PCG_xrr;Eigen::VectorXd delta_x_rr = pcgSolver(Arr_schur, brr_schur, Arr_schur.rows()+1); //0.3msROS_DEBUG("\n t_PCG_xrr cost %f ms", t_PCG_xrr.toc());Eigen::VectorXd delta_x_mm = Amm_inv_solver * (bmm_solver - Amr_solver * delta_x_rr);delta_x_.tail(n) = delta_x_rr;delta_x_.head(m) = delta_x_mm;memcpy(delta_x_array_, delta_x_.data(), sizeof(double) * (int)delta_x_.size());//转为数组ROS_DEBUG("\nin solveLinearSystem solve equation cost %f ms", t_Schur_PCG.toc());
#elseTicToc t_solve_equation;
// delta_x_ = Hessian_.ldlt().solve(b_);int pcg_iter_num = Hessian_.rows()+1; // PCG迭代次数,原来给的是rows()*2delta_x_ = pcgSolver(Hessian_, b_, pcg_iter_num); //0.3msROS_DEBUG("\nin solveLinearSystem solve equation cost %f ms, pcg_iter_num: %d", t_solve_equation.toc(), pcg_iter_num);//15msmemcpy(delta_x_array_, delta_x_.data(), sizeof(double) * (int)delta_x_.size());//转为数组,供状态更新使用ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nhere3 solve complete, delta_x_.size()=" << delta_x_.size() << ", delta_x_.norm()= "<< delta_x_.norm()<< ", delta_x_.squaredNorm()=" << delta_x_.squaredNorm() );ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\ndelta_x_:" << delta_x_.transpose());
#endif
}double Solver::dlComputeDenom(const Eigen::VectorXd& h_dl, const Eigen::VectorXd& h_gn,const double dl_alpha, const double dl_beta) const {if(h_dl == h_gn)return currentChi_;else if(h_dl == b_ / b_.norm() * radius_)return ( radius_ * (2.0 * (dl_alpha * b_).norm() - radius_) ) / (2 * dl_alpha); //由于取norm(),所以b_符号不变elsereturn 0.5 * dl_alpha * pow(1 - dl_beta, 2) * b_.squaredNorm() + dl_beta * (2 - dl_beta) * currentChi_;
}//求解器相关函数
bool Solver::solve() {if(method_==kLM) {// ROS_DEBUG("\nlinearized_jacobians (rows, cols) = (%lu, %lu)", linearized_jacobians.rows(), linearized_jacobians.cols());TicToc t_LM_init;// LM 初始化computeLambdaInitLM();ROS_DEBUG("\nsolver computeLambdaInitLM %f ms", t_LM_init.toc());// LM 算法迭代求解bool stop = false;int iter = 0;//尝试的lambda次数try_iter_ = 0;if(strategy_==1) {false_theshold_ = 10;} else if(strategy_==2) {false_theshold_ = 10;} else if (strategy_==3) {false_theshold_ = 6;}ROS_DEBUG("\nstrategy: %d, false_theshold_: %d", strategy_, false_theshold_);//保存LM阻尼阻尼系数lambda
/* file_name_ = "./lambda.csv";
FILE *tmp_fp = fopen(file_name_.data(), "a");
fprintf(tmp_fp, "iter, lambda\n");
fflush(tmp_fp);
fclose(tmp_fp);*/TicToc t_LM_iter;while (!stop && (iter < iterations_)) {ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\niter: " << iter << " , chi= " << currentChi_ << " , Lambda= " << currentLambda_ << "\n");bool oneStepSuccess = false;int false_cnt = 0;while (!oneStepSuccess) // 不断尝试 Lambda, 直到成功迭代一步{++try_iter_;// setLambdaTicToc t_addLambdatoHessianLM;addLambdatoHessianLM();//0.01msROS_DEBUG("\naddLambdatoHessianLM cost %f ms", t_addLambdatoHessianLM.toc());// 第四步,解线性方程 H X = BTicToc t_solveLinearSystem;solveLinearSystem();//8msROS_DEBUG("\nsolveLinearSystem cost %f ms", t_solveLinearSystem.toc());TicToc t_removeLambdaHessianLM;removeLambdaHessianLM();//0.005msROS_DEBUG("\nremoveLambdaHessianLM cost %f ms", t_removeLambdaHessianLM.toc());// 优化退出条件1: delta_x_ 很小则退出 原来是1e-6if (delta_x_.squaredNorm() <= 1e-10 || false_cnt > false_theshold_) {stop = true;ROS_DEBUG("\ndelta_x too small: %e, or false_cnt=%d > 10 break", delta_x_.squaredNorm(), false_cnt);//都是在这出去的break;} else {ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\ndelta_x_ squaredNorm matched: " << delta_x_.squaredNorm() << ", delta_x_ size: " <<delta_x_.size()<< ", delta_x: " << delta_x_.transpose() );}TicToc t_updateStates;updateStates(-1.0);//0.08ms 1.更新状态 2.preMakeHessian()计算新的residualROS_DEBUG("\nupdateStates cost %f ms", t_updateStates.toc());// 判断当前步是否可行以及 LM 的 lambda 怎么更新oneStepSuccess = isGoodStepInLM();//误差是否下降// 后续处理if (oneStepSuccess) {TicToc t_backupStates;backupStates();//若求解成功则备份当前更新的状态量 0.03msROS_DEBUG("\nbackupStates cost %f ms", t_backupStates.toc());// 在新线性化点 构建 hessianTicToc t_makeHessian;makeHessian();double makeHessian_finish_time = t_makeHessian.toc();*makeHessian_time_sum_ += makeHessian_finish_time;++(*makeHessian_times_);ROS_DEBUG("\nmakeHessian cost: %f ms, avg_makeHessian_time: %f ms, makeHessian_time_sum_: %f, makeHessian_times_: %f",makeHessian_finish_time, (*makeHessian_time_sum_)/(*makeHessian_times_), *makeHessian_time_sum_, *makeHessian_times_);// TODO:: 这个判断条件可以丢掉,条件 b_max <= 1e-12 很难达到,这里的阈值条件不应该用绝对值,而是相对值
// double b_max = 0.0;
// for (int i = 0; i < b_.size(); ++i) {
// b_max = max(fabs(b_(i)), b_max);
// }
// // 优化退出条件2: 如果残差 b_max 已经很小了,那就退出
// stop = (b_max <= 1e-12);false_cnt = 0;} else {false_cnt++;TicToc t_rollbackStates;rollbackStates(); // 误差没下降,回滚 0.05msROS_DEBUG("\nrollbackStates cost %f ms", t_rollbackStates.toc());}ROS_DEBUG("\nfalse_cnt: %d", false_cnt);}iter++;// 优化退出条件3: currentChi_ 跟第一次的chi2相比,下降了 1e6 倍则退出if (sqrt(currentChi_) <= stopThresholdLM_) {ROS_DEBUG("\ncurrentChi_ decrease matched break condition");stop = true;}}ROS_DEBUG("\nLM iterate %f ms", t_LM_iter.toc());
/* std::cout << "problem solve cost: " << t_solve.toc() << " ms" << std::endl;
std::cout << " makeHessian cost: " << t_hessian_cost_ << " ms" << std::endl;*/} else if(method_==kDOGLEG) {ROS_DEBUG("\nDL iter num: %d", iterations_);//1.初始化 radius,g=b=J^Teradius_ = 1;epsilon_1_ = 1e-10;//向量无穷范数:cwiseAbs:"coordinate-wise"(逐元素)取绝对值,colwise().sum()计算每行的绝对值之和,maxCoeff()得最大值bool use_last_hessian = true;bool stop = (linearized_residuals.lpNorm<Eigen::Infinity>() < epsilon_3_) ||(b_.lpNorm<Eigen::Infinity>() <= epsilon_1_);int iter = 0;double rho, tempChi;double rho_numerator, rho_denominator;bool stop_cond_1;currentChi_ = computeChi();//2.循环 stop=||e||无穷范数<=阈值3 或 ||g||无穷范数<=阈值1while (!stop && (iter < iterations_)) {ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\niter: " << iter << " , chi= " << currentChi_ << " , radius_= " << radius_ << "\n");
// if(!use_last_hessian)
// makeHessian();double dl_alpha = b_.squaredNorm() / (linearized_jacobians * b_).squaredNorm();//都是取二范数平方,就不区分b的符号了//3.计算h_sdEigen::VectorXd h_sd = dl_alpha * b_;//4.计算g_gnsolveLinearSystem();//比较耗时Eigen::VectorXd h_gn = delta_x_;//5.计算h_dlEigen::VectorXd h_dl;Eigen::VectorXd a = dl_alpha * h_sd;Eigen::VectorXd b = h_gn;double c = a.transpose() * (b - a);double dl_beta;if(c<=0) {double tmp_1 = (b-a).squaredNorm();dl_beta = (-c + sqrt(pow(c,2) + tmp_1 * (pow(radius_, 2) - a.squaredNorm()))) / tmp_1;} else {double tmp_1 = pow(radius_, 2) - a.squaredNorm();dl_beta = tmp_1 / (c + sqrt(pow(c, 2) + (b-a).squaredNorm() * tmp_1));}if(b.norm() <= radius_)h_dl = h_gn;else if(a.norm() >= radius_)h_dl = h_sd / h_sd.norm() * radius_;else {h_dl = a + dl_beta * (h_gn - a);}//判断是否需要继续迭代get_cur_parameter(cur_x_array_);Eigen::Map<const Eigen::VectorXd> x{cur_x_array_, x_size_};double tmp_1 = h_dl.norm();double tmp_2 = epsilon_2_*(x.norm() + epsilon_2_);stop_cond_1 = tmp_1 <= tmp_2;ROS_DEBUG("\ntmp_1: %f, tmp_2: %f, stop_cond_1: %d", tmp_1, tmp_2, stop_cond_1);if(stop_cond_1) {//设为1e-12stop = true;} else {//更新updateStates(-1.0);tempChi = computeChi();rho = 0.0;rho_numerator = currentChi_ - tempChi;rho_denominator = dlComputeDenom(h_dl, h_gn, dl_alpha, dl_beta);rho = rho_numerator / rho_denominator;if(rho > 0) {//执行更新,即保存备份backupStates();preMakeHessian();TicToc t_makeHessian;makeHessian();double makeHessian_finish_time = t_makeHessian.toc();*makeHessian_time_sum_ += makeHessian_finish_time;++(*makeHessian_times_);ROS_DEBUG("\nmakeHessian cost: %f ms, avg_makeHessian_time: %f ms, makeHessian_time_sum_: %f, makeHessian_times_: %f",makeHessian_finish_time, (*makeHessian_time_sum_)/(*makeHessian_times_), *makeHessian_time_sum_, *makeHessian_times_);use_last_hessian = false;} else {rollbackStates();use_last_hessian = true;}get_cur_parameter(cur_x_array_);if(rho > 0.75) {radius_ = std::max(radius_, 3*h_dl.norm());} else {radius_ = 0.5 * radius_;stop = radius_ < epsilon_2_*(x.norm() + epsilon_2_);}}ROS_DEBUG("\nDL: radius_: %e, rho: %f, rho>0 = %d, currentChi_: %e, tempChi: %e, rho_numerator: %e, rho_denominator: %e",radius_, rho, rho>0, currentChi_, tempChi, rho_numerator, rho_denominator);ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\ndelta_x_.squaredNorm(): " << delta_x_.squaredNorm() << ", delta_x_: " << delta_x_.transpose()<< "\nb_.norm(): " << b_.norm() << ", b_: " << b_.transpose());++iter;}ROS_DEBUG("\n finish DL iter, stop: %d or iter: %d >= %d", stop, iter, iterations_);//6.根据h_dl.norm()判断是否迭代// 若迭代则更新x(涉及状态更新,residual计算),计算rho,根据rho来更新x和raidus}return true;
}
}
9.3 solve.h
#ifndef CATKIN_WS_SOLVE_H
#define CATKIN_WS_SOLVE_H#include <ros/ros.h>
#include <ros/console.h>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <ceres/ceres.h>
#include <unordered_map>#include "eigen_types.h"
#include "../utility/tic_toc.h"
#include "../parameters.h"namespace solve {/*定义factor管理类* */
const int NUM_THREADS = 4;struct ResidualBlockInfo
{ResidualBlockInfo(ceres::CostFunction *_cost_function, ceres::LossFunction *_loss_function, std::vector<double *> _parameter_blocks, std::vector<int> _drop_set): cost_function(_cost_function), loss_function(_loss_function), parameter_blocks(_parameter_blocks), drop_set(_drop_set) {}void Evaluate();ceres::CostFunction *cost_function;ceres::LossFunction *loss_function;std::vector<double *> parameter_blocks;//优化变量数据的地址,sizes每个优化变量块的变量大小,以IMU残差为例,为[7,9,7,9]std::vector<int> drop_set;//待边缘化的优化变量iddouble **raw_jacobians;//二重指针,是为了配合ceres的形参 double** jacobiansstd::vector<Eigen::Matrix<double, Eigen::Dynamic, Eigen::Dynamic, Eigen::RowMajor>> jacobians;//这个数据结构看不懂,Eigen::VectorXd residuals;//残差 IMU:15X1 视觉:2X1int localSize(int size){return size == 7 ? 6 : size;}
};struct ThreadsStruct
{std::vector<ResidualBlockInfo *> sub_factors;Eigen::MatrixXd A;Eigen::VectorXd b;std::unordered_map<long, int> parameter_block_size; //global sizestd::unordered_map<long, int> parameter_block_idx; //local size
};class Solver
{
public:Solver(uint8_t strategy): method_(kLM), iterations_(1), strategy_(strategy), lm_alpha_(1), mem_allocated_(false){};~Solver();int localSize(int size) const;int globalSize(int size) const;void addResidualBlockInfo(ResidualBlockInfo *residual_block_info);//加残差块相关信息(优化变量、待marg的变量)void preMakeHessian();//计算每个残差对应的Jacobian,并更新parameter_block_datavoid makeHessian();//pos为所有变量维度,m为需要marg掉的变量,n为需要保留的变量std::vector<double *> getParameterBlocks(std::unordered_map<long, double *> &addr_shift);std::vector<ResidualBlockInfo *> factors;//所有观测项int m, n;//m为要边缘化的变量个数(也就是parameter_block_idx的总localSize,以double为单位,VBias为9,PQ为6,),n为要保留下来的变量个数//parameter_block_size 和 parameter_block_data分别对应block的大小和实际数据std::unordered_map<long, int> parameter_block_size; //global size <优化变量内存地址,localSize>int sum_block_size;std::unordered_map<long, int> parameter_block_idx; //local size 排序前是<待边缘化的优化变量内存地址,在parameter_block_size中的id>,排序后是<marg, id>m维 <remain, id>n维std::unordered_map<long, double *> parameter_block_data;//<优化变量内存地址,数据>std::unordered_map<long, double *> parameter_block_data_backup;//<优化变量内存地址,数据>std::vector<int> keep_block_size; //global sizestd::vector<int> keep_block_idx; //local sizestd::vector<double *> keep_block_data;//之前看到的帖子说这是在marg过程中反解出的线性化点的参数值x0Eigen::MatrixXd linearized_jacobians;//线性化点处的JacobianEigen::VectorXd linearized_residuals;//线性化点处的residualconst double eps = 1e-8;bool solve();void solveLinearSystem();/// 解线性方程bool updateStates(double weight) ;/// 更新状态变量bool backupStates();//回滚状态变量bool rollbackStates(); // 有时候 update 后残差会变大,需要退回去,重来double computeChi() const;void computeLambdaInitLM();/// 计算LM算法的初始Lambdavoid addLambdatoHessianLM();/// Hessian 对角线加上或者减去 Lambdavoid removeLambdaHessianLM();bool isGoodStepInLM();/// LM 算法中用于判断 Lambda 在上次迭代中是否可以,以及Lambda怎么缩放Eigen::MatrixXd pcgSolver(const MatXX &A, const VecX &b, int maxIter);/// PCG 迭代线性求解器enum SolveMethod{kLM = 0,kDOGLEG = 1};SolveMethod method_;int iterations_;//迭代轮数double currentChi_;//LM参数double currentLambda_;//LM中的阻尼因子,DOGLEG中的radiusdouble stopThresholdLM_; // LM 迭代退出阈值条件std::string file_name_;int try_iter_;int false_theshold_;//每轮迭代允许的最大失败次数double ni_; //strategy3控制 Lambda 缩放大小double lm_alpha_; //strategy2更新使用的alpha//求解结果
// VecX delta_x_rr_;
// VecX delta_x_mm_;//DL参数double radius_;double epsilon_1_, epsilon_2_, epsilon_3_;
// double dl_alpha_;/// 整个信息矩阵Eigen::MatrixXd Hessian_;Eigen::VectorXd b_;Eigen::VectorXd delta_x_;//多留100的余量,这个是成员变量,在程序中是局部变量,放在栈区,不需要手动释放内存,因为它会在其作用域结束时自动被销毁const int x_size_ = 1000 + (WINDOW_SIZE + 1) * (SIZE_POSE + SIZE_SPEEDBIAS) + SIZE_POSE + 1 + 100;double cur_x_array_[1000 + (WINDOW_SIZE + 1) * (SIZE_POSE + SIZE_SPEEDBIAS) + SIZE_POSE + 1 + 100];double delta_x_array_[1000 + (WINDOW_SIZE + 1) * (SIZE_POSE + SIZE_SPEEDBIAS) + SIZE_POSE + 1 + 100];//是否已调用preMakeHessian分配过内存bool mem_allocated_;uint8_t strategy_;double *makeHessian_time_sum_;//这个需要手撸才能统计时间,ceres无法统计double *makeHessian_times_;private:bool get_cur_parameter(double* cur_x_array);double dlComputeDenom(const Eigen::VectorXd& h_dl, const Eigen::VectorXd& h_gn,const double dl_alpha, const double dl_beta) const;};
}
#endif //CATKIN_WS_SOLVE_H
后面这些是在debug时的一些记录,可以略过不看。
9.4 系统整体待优化参数维度debug
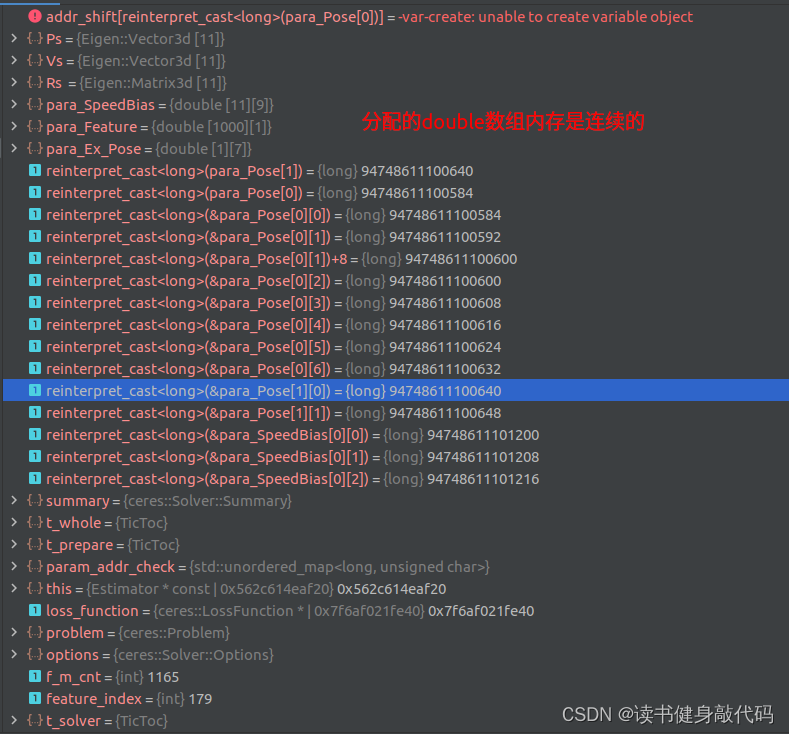
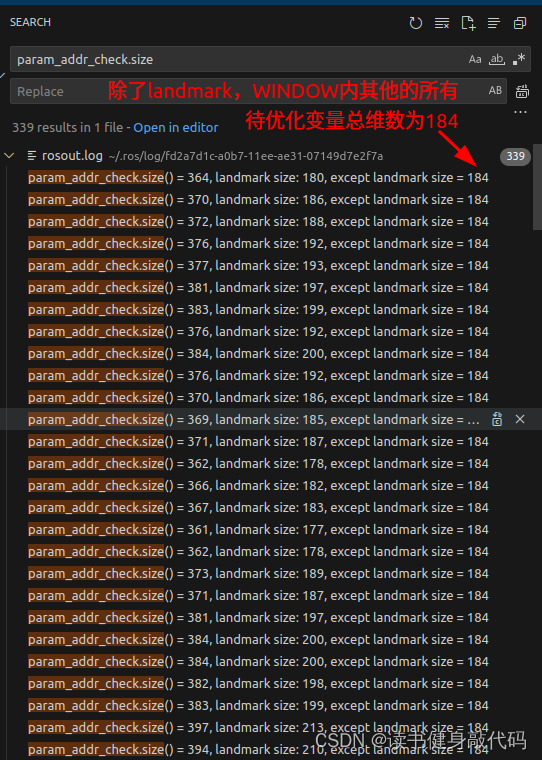
WINDOW内所有待优化变量维度统计,估计 t d t_d td,无快速重定位时共 172 + L 172+L 172+L,其中 L L L为WINDOW内的landmark数量
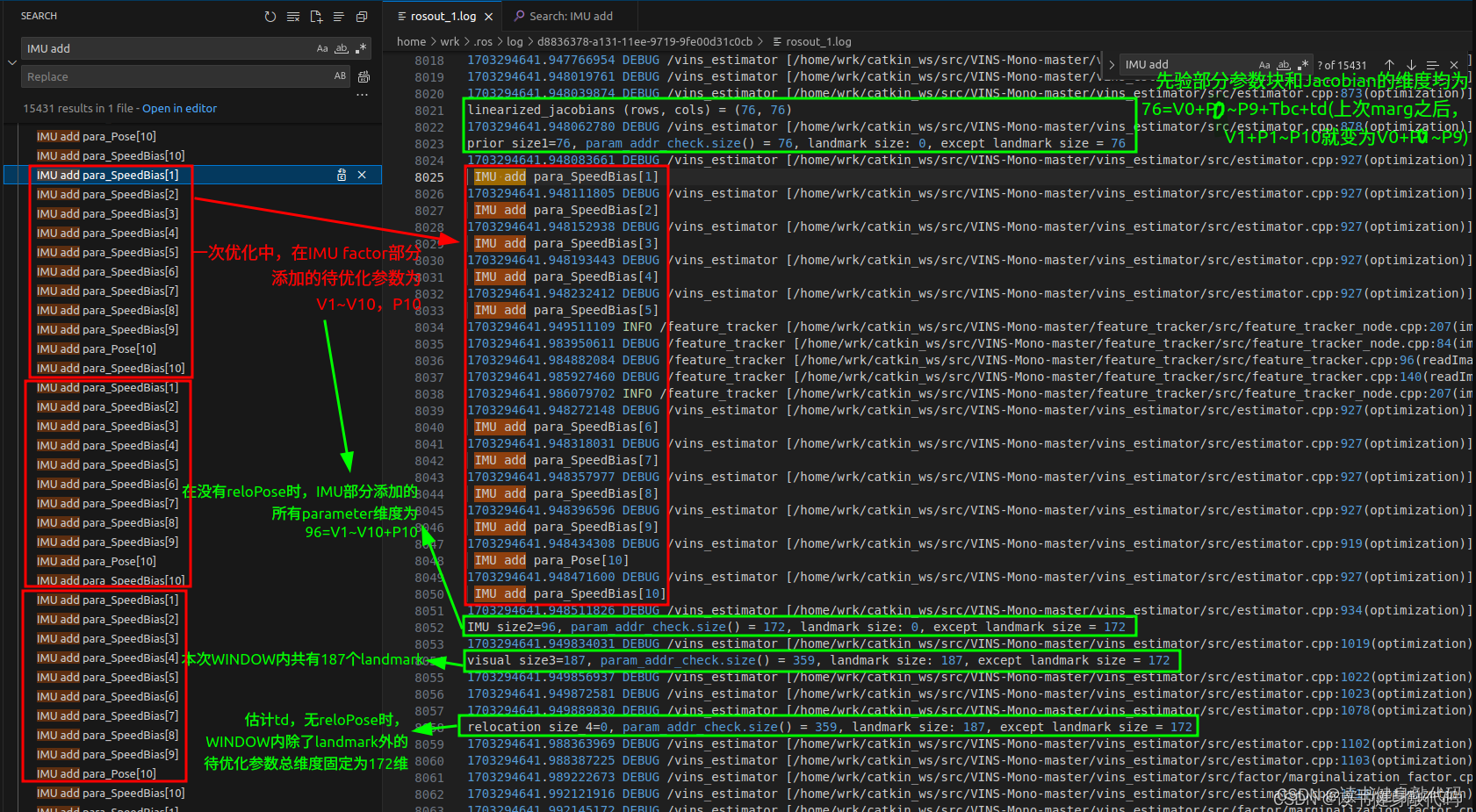
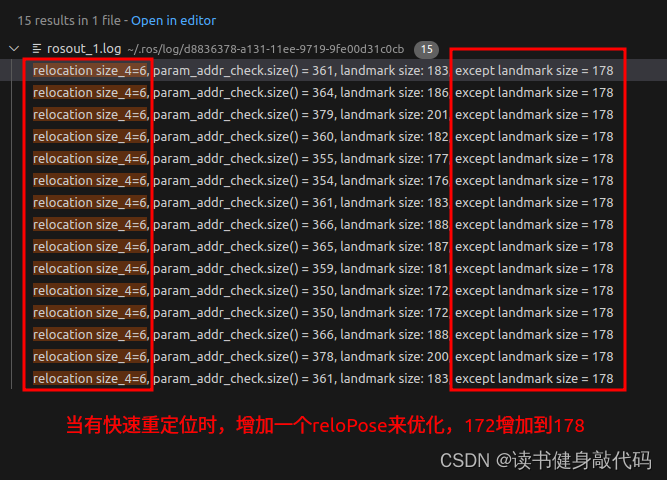
debug代码,定义两个unordered_map容器param_addr_check,landmark_addr_check,注意SIZE_POSE要-1去除冗余来统计:
//用于check维度std::unordered_map<long, uint8_t> param_addr_check;//所有param维度std::unordered_map<long, uint8_t> landmark_addr_check;//landmark维度//1.添加边缘化残差(先验部分)size_t size_1=0;if (last_marginalization_info){// construct new marginlization_factorMarginalizationFactor *marginalization_factor = new MarginalizationFactor(last_marginalization_info);//里面设置了上次先验的什么size,现在还不懂problem.AddResidualBlock(marginalization_factor, NULL,last_marginalization_parameter_blocks);// /*用于check维度是否正确*/
// parameter_block_size[reinterpret_cast<long>(addr)] = size;for(int i=0; i<last_marginalization_parameter_blocks.size(); ++i) {if(last_marginalization_info->parameter_block_size[reinterpret_cast<long>(last_marginalization_parameter_blocks[i])]==1) {ROS_DEBUG("here have 1 dimend");
// landmark_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(last_marginalization_parameter_blocks[i])] = 1;}size_t tmp_size = last_marginalization_info->parameter_block_size[reinterpret_cast<long>(last_marginalization_parameter_blocks[i])];tmp_size = tmp_size==7 ? 6: tmp_size;//这个double*的地址代表的待优化变量的local_size,把每个地址都记录在map中,分配给待优化变量的地址都是连续的for(int j=0; j<tmp_size; ++j) {param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(last_marginalization_parameter_blocks[i]) + (double)j * (long) sizeof(long)] = 1;}}//打印prior的Jacobian维度ROS_DEBUG("\nlinearized_jacobians (rows, cols) = (%lu, %lu)",last_marginalization_info->linearized_jacobians.rows(), last_marginalization_info->linearized_jacobians.cols());size_1 = param_addr_check.size();//应该是76 实际87ROS_DEBUG("\nprior size1=%lu, param_addr_check.size() = %lu, landmark size: %lu, except landmark size = %lu",size_1, param_addr_check.size(), landmark_addr_check.size(), param_addr_check.size()-landmark_addr_check.size());//landmark_addr_check中多加了个td//2.添加IMU残差for (int i = 0; i < WINDOW_SIZE; i++){int j = i + 1;//两帧KF之间IMU积分时间过长的不进行优化(可能lost?)if (pre_integrations[j]->sum_dt > 10.0)continue;IMUFactor* imu_factor = new IMUFactor(pre_integrations[j]);//这里的factor就是残差residual,ceres里面叫factorproblem.AddResidualBlock(imu_factor, NULL, para_Pose[i], para_SpeedBias[i], para_Pose[j], para_SpeedBias[j]);//check维度long addr = reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[i]);if(param_addr_check.find(addr) == param_addr_check.end()) {ROS_DEBUG("\nIMU add para_Pose[%d]", i);for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {param_addr_check[addr + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;}}addr = reinterpret_cast<long>(para_SpeedBias[i]);if(param_addr_check.find(addr) == param_addr_check.end()) {ROS_DEBUG("\nIMU add para_SpeedBias[%d]", i);for(int k=0; k<SIZE_SPEEDBIAS; ++k) {param_addr_check[addr + (long) k * (long) sizeof(long)] = 1;}}addr = reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[j]);if(param_addr_check.find(addr) == param_addr_check.end()) {ROS_DEBUG("\n IMU add para_Pose[%d]", j);for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {param_addr_check[addr + (long) k * (long) sizeof(long)] = 1;}}addr = reinterpret_cast<long>(para_SpeedBias[j]);if(param_addr_check.find(addr) == param_addr_check.end()) {ROS_DEBUG("\n IMU add para_SpeedBias[%d]", j);for (int k = 0; k < SIZE_SPEEDBIAS; ++k) {param_addr_check[addr + (long) k * (long) sizeof(long)] = 1;}}}size_t size_2 = param_addr_check.size() - size_1;//应该是81 V2~V10 实际97为啥???ROS_DEBUG("\nIMU size2=%lu, param_addr_check.size() = %lu, landmark size: %lu, except landmark size = %lu",size_2, param_addr_check.size(), landmark_addr_check.size(), param_addr_check.size()-landmark_addr_check.size());//landmark_addr_check中多加了个td//3.添加视觉残差int f_m_cnt = 0;int feature_index = -1;for (auto &it_per_id : f_manager.feature){it_per_id.used_num = it_per_id.feature_per_frame.size();//!(至少两次tracking,且最新帧1st的tracking不能算(因为1st可能被marg掉),start_frame最大是[7])if (!(it_per_id.used_num >= 2 && it_per_id.start_frame < WINDOW_SIZE - 2))continue;++feature_index;int imu_i = it_per_id.start_frame, imu_j = imu_i - 1;Vector3d pts_i = it_per_id.feature_per_frame[0].point;//这个id的feature的第一帧和后面所有的帧分别构建residual blockfor (auto &it_per_frame : it_per_id.feature_per_frame){imu_j++;if (imu_i == imu_j){continue;}Vector3d pts_j = it_per_frame.point;//是否要time offsetif (ESTIMATE_TD){//对于一个feature,都跟[it_per_id.start_frame]帧进行优化ProjectionTdFactor *f_td = new ProjectionTdFactor(pts_i, pts_j, it_per_id.feature_per_frame[0].velocity, it_per_frame.velocity,it_per_id.feature_per_frame[0].cur_td, it_per_frame.cur_td,it_per_id.feature_per_frame[0].uv.y(), it_per_frame.uv.y());problem.AddResidualBlock(f_td, loss_function, para_Pose[imu_i], para_Pose[imu_j], para_Ex_Pose[0], para_Feature[feature_index], para_Td[0]);//check维度for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[imu_i]) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;}for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[imu_j]) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;}for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Ex_Pose[0]) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;}param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Feature[feature_index])] = 1;landmark_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Feature[feature_index])] = 1;param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Td[0])] = 1;/*double **para = new double *[5];para[0] = para_Pose[imu_i];para[1] = para_Pose[imu_j];para[2] = para_Ex_Pose[0];para[3] = para_Feature[feature_index];para[4] = para_Td[0];f_td->check(para);*/}else{ProjectionFactor *f = new ProjectionFactor(pts_i, pts_j);problem.AddResidualBlock(f, loss_function, para_Pose[imu_i], para_Pose[imu_j], para_Ex_Pose[0], para_Feature[feature_index]);//check维度for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[imu_i]) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;}for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[imu_j]) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;}for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Ex_Pose[0]) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;}param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Feature[feature_index])] = 1;landmark_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Feature[feature_index])] = 1;}f_m_cnt++;}}size_t size_3 = param_addr_check.size() - size_1 - size_2;//应该和landmark_addr_check.size一样ROS_DEBUG("\nvisual size3=%lu, param_addr_check.size() = %lu, landmark size: %lu, except landmark size = %lu",size_3, param_addr_check.size(), landmark_addr_check.size(), param_addr_check.size()-landmark_addr_check.size());//landmark_addr_check中多加了个tdROS_DEBUG("visual measurement count: %d", f_m_cnt);//总的视觉观测个数,观测可能是在不同帧对同一个landmark进行观测,所以可能查过1000,注意与landmark个数进行区分ROS_DEBUG("prepare for ceres: %f", t_prepare.toc());//4.添加闭环检测残差,计算滑动窗口中与每一个闭环关键帧的相对位姿,这个相对位置是为后面的图优化(pose graph)准备 或者是 快速重定位(崔华坤PDF7.2节)//这里注意relo_pose是Tw2_bi = Tw2_w1 * Tw1_biif(relocalization_info){//printf("set relocalization factor! \n");ceres::LocalParameterization *local_parameterization = new PoseLocalParameterization();problem.AddParameterBlock(relo_Pose, SIZE_POSE, local_parameterization);int retrive_feature_index = 0;int feature_index = -1;for (auto &it_per_id : f_manager.feature){it_per_id.used_num = it_per_id.feature_per_frame.size();if (!(it_per_id.used_num >= 2 && it_per_id.start_frame < WINDOW_SIZE - 2))continue;++feature_index;int start = it_per_id.start_frame;if(start <= relo_frame_local_index)//必须之前看到过{//1.先在i中match的点中找到可能是现在这个feature的id的indexwhile((int)match_points[retrive_feature_index].z() < it_per_id.feature_id)//.z()存的是i,j两帧match上的feature的id{retrive_feature_index++;}//2.如果是,则WINDOW内的it_per_id.feature_id这个id的landmark就是被loop上的landmark,取归一化坐标,if((int)match_points[retrive_feature_index].z() == it_per_id.feature_id){//pts_j是i帧的归一化平面上的点,这里理解relo_Pose及其重要,relo_Pose实际上是Tw2_bi,视觉重投影是从WINDOW内的start帧的camera(在w2系下),投影到i帧(在w1系下),耦合了Tw1_w2Vector3d pts_j = Vector3d(match_points[retrive_feature_index].x(), match_points[retrive_feature_index].y(), 1.0);Vector3d pts_i = it_per_id.feature_per_frame[0].point;//start中的点ProjectionFactor *f = new ProjectionFactor(pts_i, pts_j);//relo_Pose是Tw2_biproblem.AddResidualBlock(f, loss_function, para_Pose[start], relo_Pose, para_Ex_Pose[0], para_Feature[feature_index]);retrive_feature_index++;//check维度for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[start]) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;}for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(relo_Pose) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;}for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Ex_Pose[0]) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;}param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Feature[feature_index])] = 1;landmark_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Feature[feature_index])] = 1;ROS_DEBUG("\nhas relocation blocks\n");} }}}size_t size_4 = param_addr_check.size() - size_1 - size_2 - size_3;//没有loop时应该为0ROS_DEBUG("\nrelocation size_4=%lu, param_addr_check.size() = %lu, landmark size: %lu, except landmark size = %lu",size_4, param_addr_check.size(), landmark_addr_check.size(), param_addr_check.size()-landmark_addr_check.size());//landmark_addr_check中多加了个td9.5 LM的 λ \lambda λ初始化中的 τ \tau τ取值是否合适?

上面给的 τ \tau τ在 [ 1 e − 8 , 1 ] [1e-8,1] [1e−8,1] 这个范围内不是绝对的,要根据实际的情况来设定:
- 太大可能导致 λ \lambda λ过大,步长过小,求出的 Δ x \Delta x Δx过小,更新不动 x x x;
- 太小可能导致 λ \lambda λ过大,步长过大, ρ \rho ρ一直 < 0 <0 <0,无法找到正确的迭代方向, x x x一直无法更新。
比如VINS-MONO中,如果使用strategy3,则 τ \tau τ大概为 1 e − 15 1e^{-15} 1e−15数量级左右。
9.6 Schur消元求解之后更新先验的residual
χ \chi χ实际上就是 e T W e e^TWe eTWe
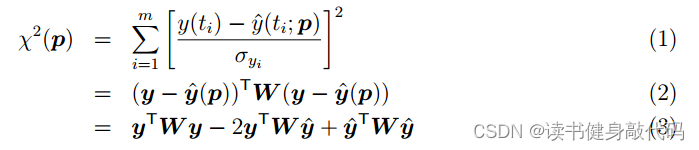
线性化点再挖一个坑:
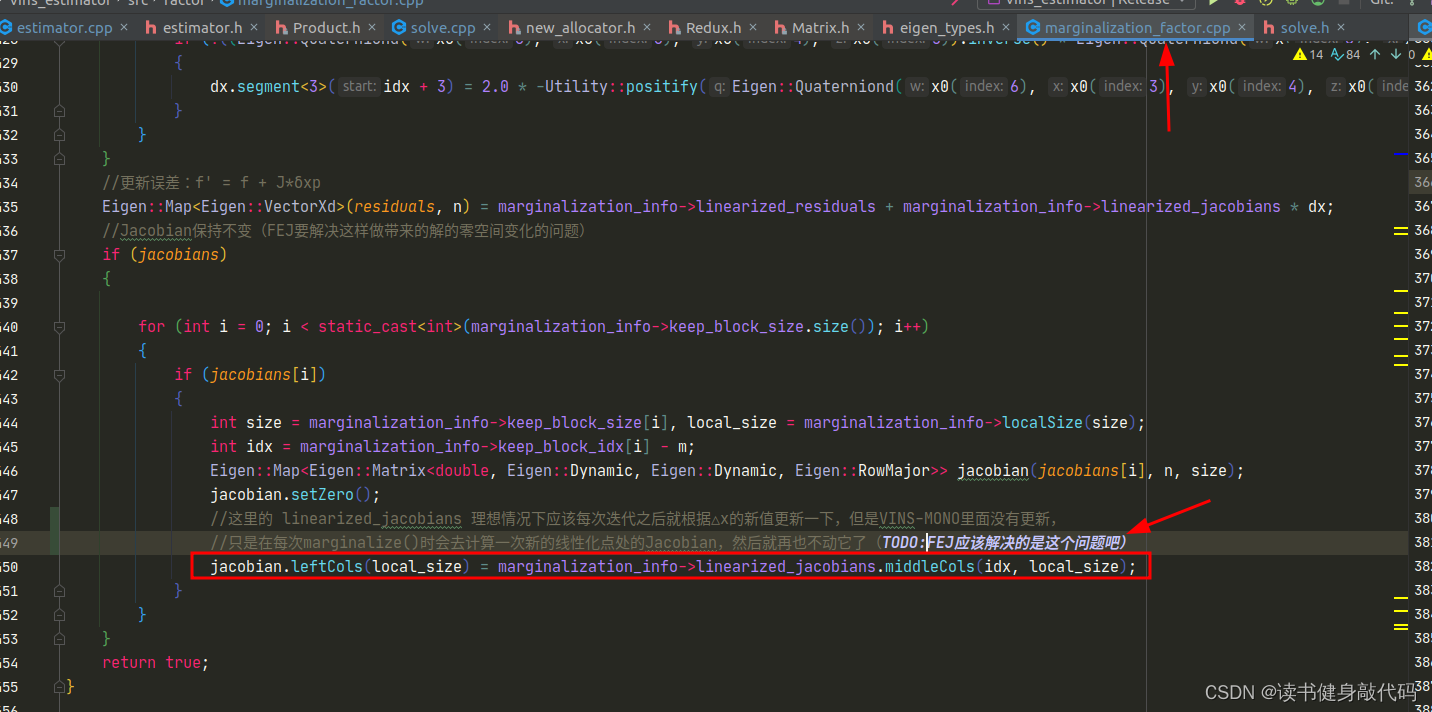
恍然大悟的evaluate()函数得Jacobian
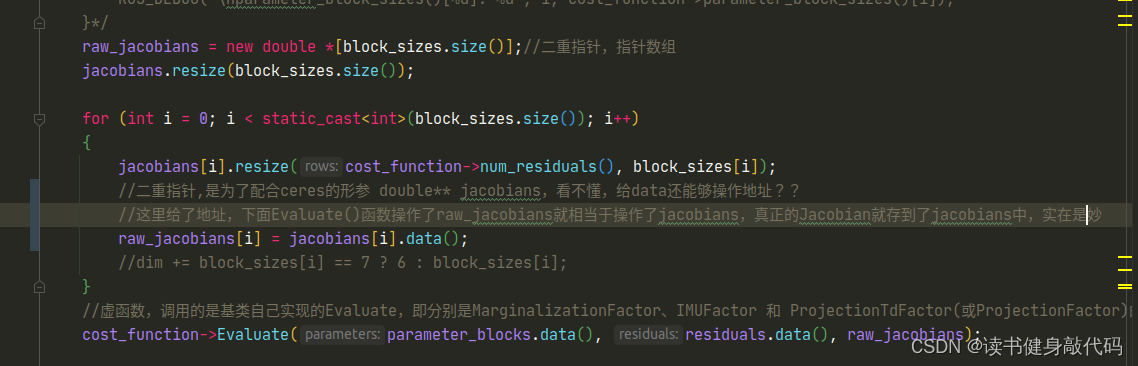
在preMarginalize()中调用的,因为marg不用ceres,不会在内部维护jacobian,所以需要手动调用计算Jacobian,多态调用evaluate(),根据上面,二重指针从raw_jacobians传给jacobians,所以在ThreadsConstructA中可以拿到Jacobian,实在是妙。
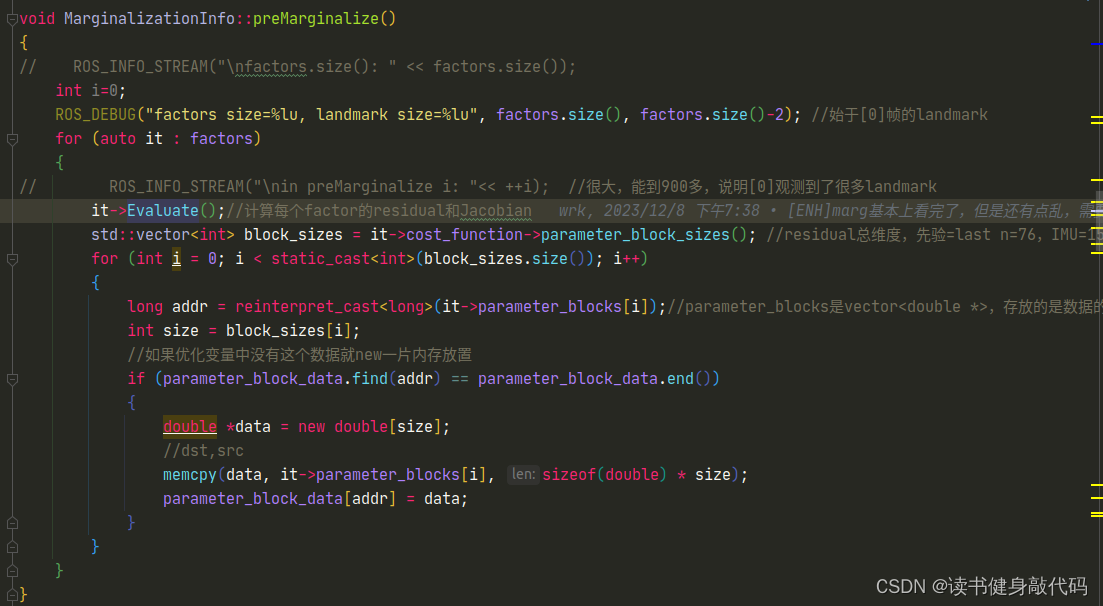
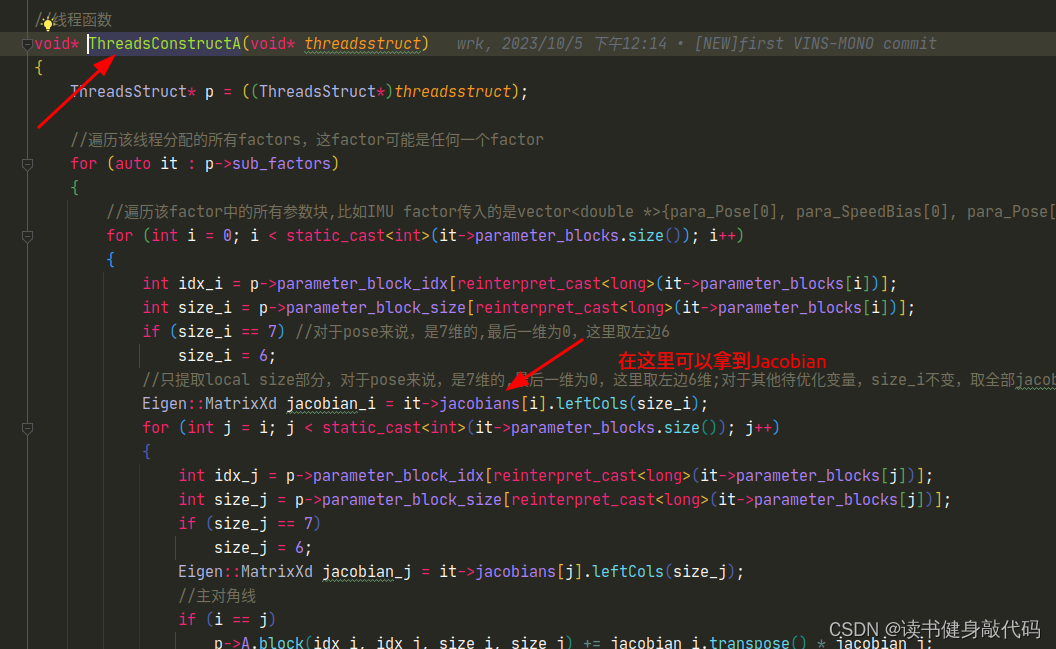
根据以上理解,在LM中每次更新完 x = x + Δ x x=x+\Delta x x=x+Δx后,就需要重新计算一下Jacobian和residual,下次evaluate时就会用到新的residual,
对于prior的residual,和VINS-MONO保持一样,不动Jacobian的值。
9.7 计算 χ = e T W e \chi=e^TWe χ=eTWe时需要考虑loss_function
在ResidualBlockInfo::Evaluate()中调用的多态Evaluate()函数后已经考虑了loss_function对Jacobian和residual的加权
9.8 先验的参数实际上就是V0,P0~P10,Tbc,td,而不是一个单独的特殊量
9.9 Hessian可视化
之前Debug b的时候曾经反解出J并打印出来过,可以看到 J T J J^TJ JTJ还是非常稀疏的:
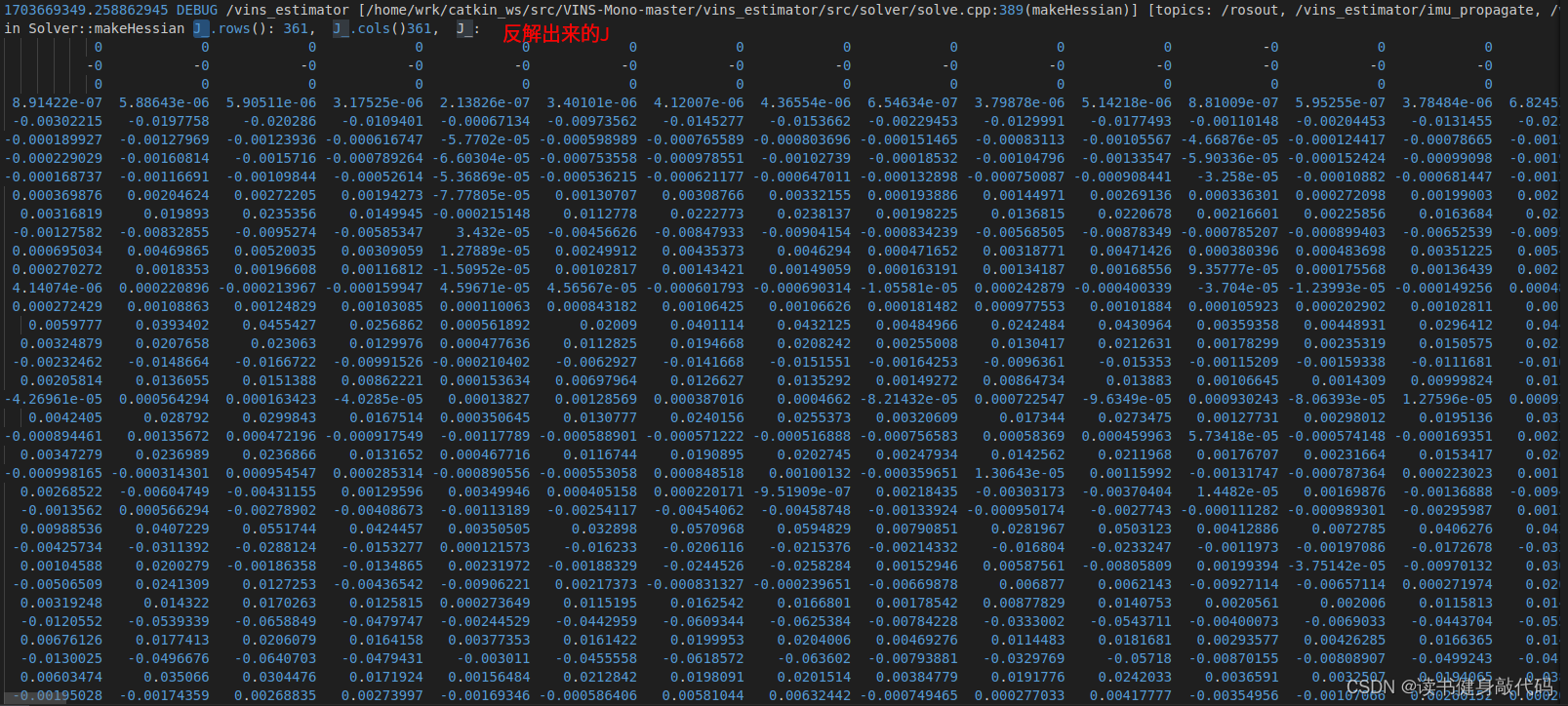

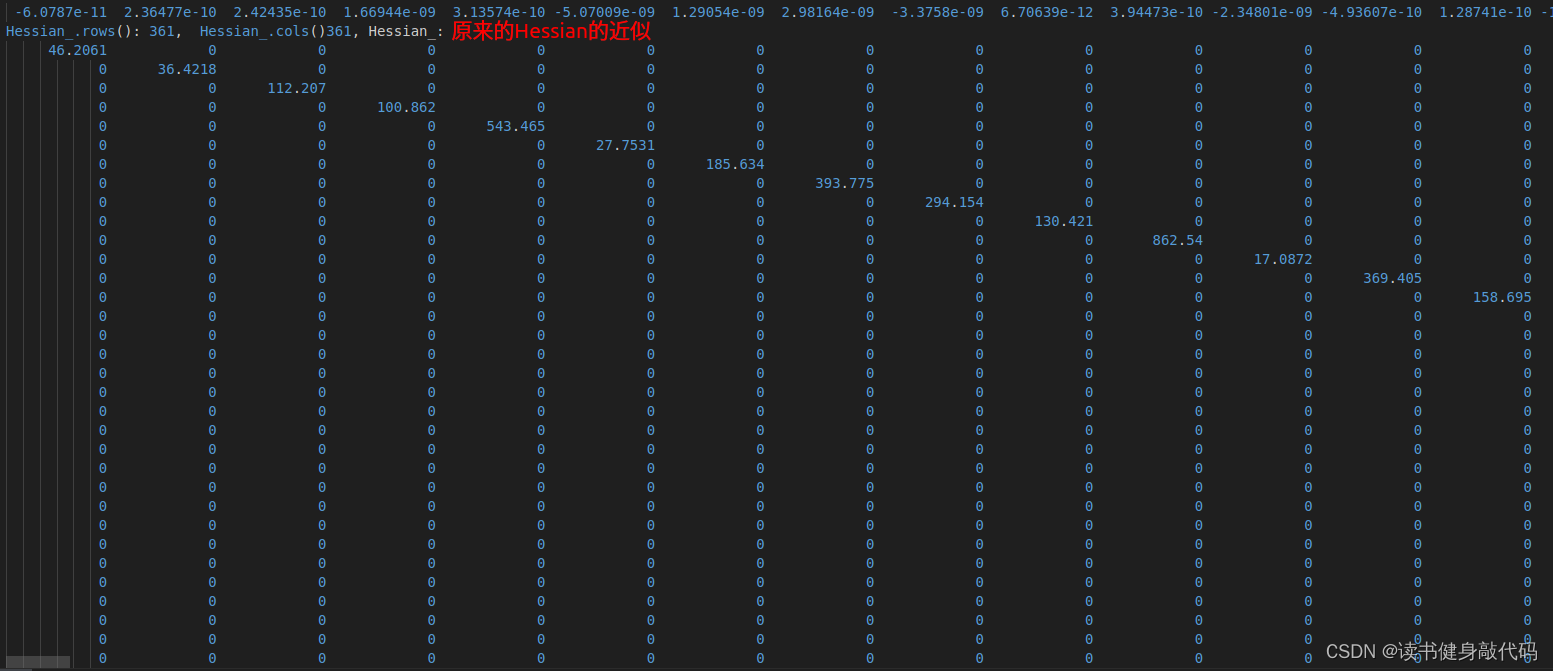
反解之后再算 J T ∗ J J^T*J JT∗J,有些为0的已经不为0了,但是数值很小,大概是1e-10数量级,但主对角线可以看出还是正确的,所以反解总体上没问题。实际上J的rows()应该是观测的总维度(包括11个P,11个V,1个Tbc,1个td,L个landmark所有观测,注意不是L,观测道一次就有二维的reidual,参考《14讲》P247理解),但是从Hessian中只能反解出相同维度的 J J J,此处为 316 = 172 + L 316=172+L 316=172+L,所以不知道观测的总维度为多少。
9.10 load pose_graph
load pose_graph test:
load pose_graph之后发现就很容易产生loop了,因为有了之前的特征和描述子,在rviz中可以看到产生了非常多的loop边,且从一开始就有loop,如果是在同一个地方不同的数据集,这样对于重定位就比较友好。
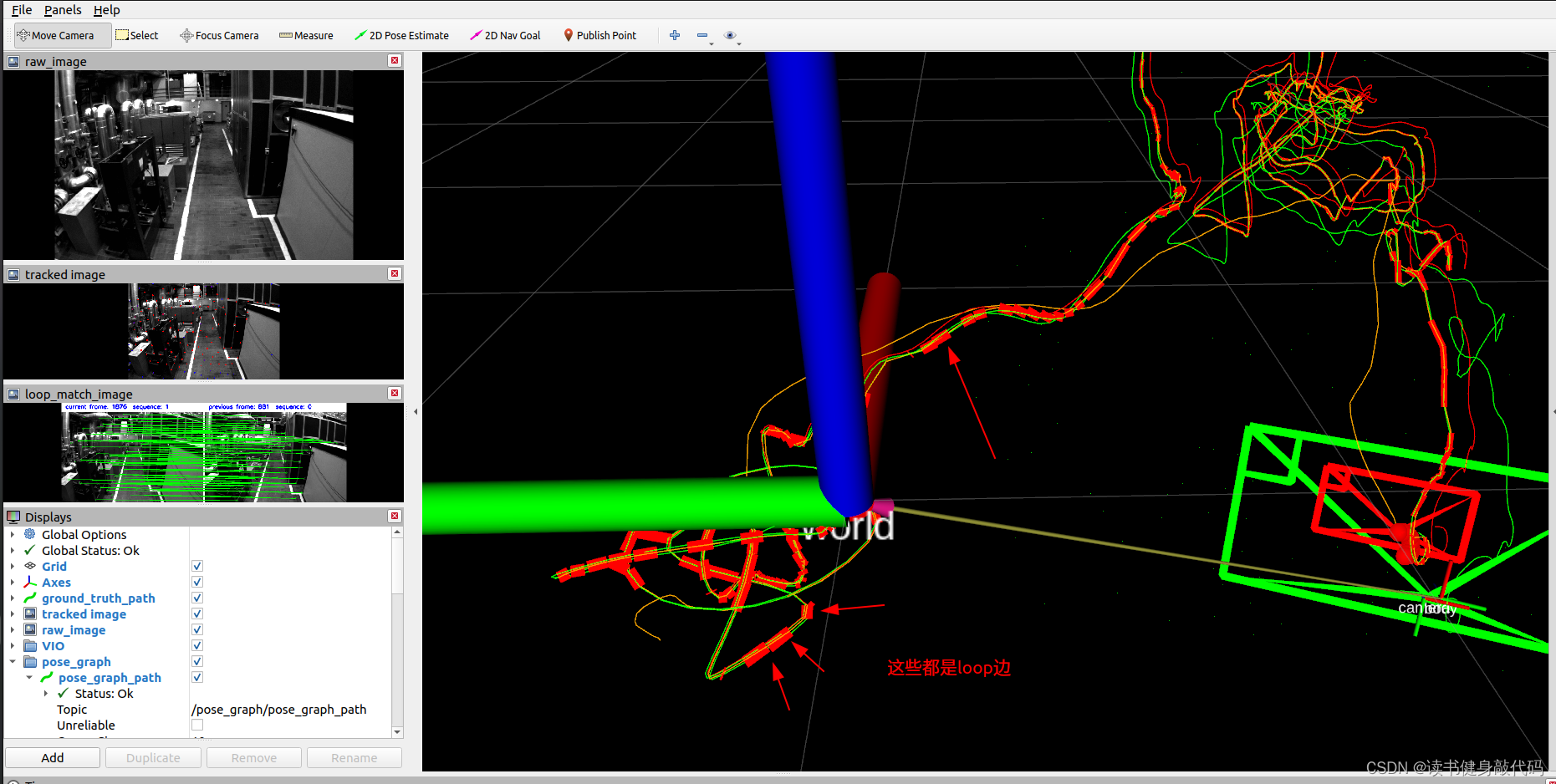
相关文章:

VINS-MONO拓展1----手写后端求解器,LM3种阻尼因子策略,DogLeg,构建Hessian矩阵
文章目录 0. 目标及思路1. 非线性优化求解器2. 基于VINS-MONO的Marginalization框架构建Hessian矩阵2.1 estimator.cpp移植2.2 solve.cpp/preMakeHessian()2.3 solve.cpp/makeHessian() 3. solve.cpp/solveLinearSystem()求解正规方程4. 更新状态5. 迭代求解6. EVO评估结果7. 待…...

RxJS 操作符-学习笔记
提前准备: pipe 方法: 用于组合多个操作符,可以将一系列操作符作为参数传递给 pipe 方法,这些操作符将 依次 对数据流进行处理。这里的依次很关键,也代表着pipe()中组合的这么几个操作符的执行顺序就是从开始一直到结束的,其中的…...

【Linux】linux配置静态IP、动态IP方法汇总
1、systemd-networkd 1.1 说明 systemd-networkd是systemd 的一部分 ,负责 systemd 生态中的网络配置部分(systemd-networkd.service, systemd-resolved.service)。使用 systemd-networkd,你可以为网络设备配置基础的 DHCP/静态IP网络等,还可以配置虚拟网络功能,例如网桥…...

Hive自定义函数支持国密SM4解密
当前项目背景需要使用到国密SM4对加密后的数据进行解密,Hive是不支持的,尝试了华为DWS数仓,华为只支持在DWS中的SM4加密解密,不支持外部加密数据DWS解密 新建Maven工程 只需要将引用的第三方依赖打到jar包中,hadoop和…...
CentOS 8 8.5.2111 网络在线安装系统 —— 筑梦之路
之前写过一篇关于centos 8 官方停止更新维护后解决yum源问题的文章: CentOS 8 停止维护后换可用yum源——筑梦之路_http://ftp.iij.ad.jp/pub/linux/centos-vault/8.5.21-CSDN博客 由于centos 8 dvd的镜像比较大,有时候我们根本不需要去下载一个10G以上…...

安全与认证Week3
目录 Key Management 密钥管理 密钥交换、证书 密钥的类别 密钥管理方面 密钥分发问题 密钥分发方案 混合密钥分发 公钥分发 公钥证书 X.509 理解X.509 X.509证书包含 X.509使用过程 X.509身份验证服务 X.509版本3 取消 由X.509引申关于CA 用户认证、身份管理…...

跟我学c++中级篇——再谈C++20中的协程
一、协程 在前面分析过协程是什么,也对c20中的协程的应用进行了举例说明。所以这次重点分析一下c20中的整体构成及应用的方式。等明白了协程是如何动作的,各种情况下如下何处理相关的事件,那么在以后写协程时就不会死搬硬套了。 二、整体说…...
【计算机毕业设计】SSM企业工资管理系统
项目介绍 本项目包含管理员与普通员工两种角色, 管理员角色包含以下功能: 管理员登录,员工管理,部门管理,岗位管理,职称管理,工龄奖金管理,工资项管理,考勤管理,工资查询,统计图表等功能。 员工角色包含以下功能: 员工登录,个人信息管理…...

x-cmd pkg | doggo - 现代化的 DNS 客户端
目录 简介首次用户快速实验指南功能特点类似工具与竞品进一步探索 简介 doggo 是一个由 Karan Sharma 于 2020 年使用 Go 语言开发的 DNS 客户端。它类似于 dig 命令,但旨在以现代化、简洁和可读的格式输出 DNS 查询结果。 首次用户快速实验指南 使用 x doggo 即可…...
c++-智能指针
1、概念 堆内存的对象需要手动使用delete销毁,如果忘记使用delete销毁就会造成内存泄漏。 所以C在ISO 98标注中引入了智能指针的概念,并在C11 中趋于完善。 使用智能指针可以让堆内存对象具有栈内存对象的特性。原理时给需要自动回收的堆内存对象套上一层…...
烟花燃放如何管控?智能分析网关V4烟火检测保障烟火安全
一、方案背景 随着元旦佳节的热潮退去,春节也即将来临,在众多传统的中国节日里,烟花与烧纸祭祀都是必不可少的,一方面表达了人们对节日的庆祝的期许,另一方面也是一种对故者思念的寄托。烟花爆竹的燃放不仅存在着巨大的…...

Vue实现版本号输入、删除时光标自动移动到上、下一个输入框前端demo
前言 首先声明,我平时的工作主要是后端JAVA开发,该demo为前端练习,记录一下劳动成果,希望对大家有所帮助,如果有写的不妥的地方,欢迎大家指正,一起学习、共同进步。 背景 手机验证码、银行卡…...

【胖虎的逆向之路】Android自制Https证书实现双向认证
Android自制Https证书实现双向认证 1.基本概念1.1 HTTP1.2 HTTPS1.3 加密方式1.3.1 对称加密1.3.2 非对称加密 1.4 SSL 功能1.4.1 客户对服务器的身份认证1.4.2 服务器对客户的身份认证1.4.3 建立服务器与客户之间安全的数据通道 1.5 CA 证书 2.证书生成2.1 生成根证书…...

解析千兆多模光模块SFP-GE-SX
千兆多模光模块是一种基于光纤通信的光电转换模块,具有千兆(Gigabit)级别的传输速率。本文将对千兆多模光模块的定义、传输距离、参数、及其应用领域等进行详细介绍。 一、千兆多模光模块SFP-GE-SX是什么? 千兆多模光模块SFP-GE-S…...
Go语言基础简单了解
文章目录 前言关于Go学习流程 基础语法注释变量常量数据类型运算符fmt库 流程控制if、switch、selectfor、break、continue遍历String 函数值传递和引用传递deferinit匿名、回调、闭包函数 数组和切片Map结构体自定义数据类型接口协程和channel线程锁异常处理泛型文件读取文件写…...

kafka重平衡经验总结
文章目录 概要背景解决方法技术细节小结 概要 关于kafka重平衡问题在实践工作的应用 背景 重平衡包括以下几种场景: 消费者组内成员发生变更,这个变更包括了增加和减少消费者。注意这里的减少有很大的可能是被动的,就是某个消费者崩溃退出了主题的分…...

Py之jupyter_client:jupyter_client的简介、安装、使用方法之详细攻略
Py之jupyter_client:jupyter_client的简介、安装、使用方法之详细攻略 目录 jupyter_client的简介 jupyter_client的安装 jupyter_client的使用方法 1、基础用法 (1)、获取内核信息 (2)、执行代码块 (3)、远程执行代码 jupyter_client的简介 jupyter_client 包含 Jupyter 协…...
61.网游逆向分析与插件开发-游戏增加自动化助手接口-游戏红字公告功能的逆向分析
内容来源于:易道云信息技术研究院VIP课 上一节内容:游戏公告功能的逆向分析与测试-CSDN博客 码云地址(master分支):https://gitee.com/dye_your_fingers/sro_-ex.git 码云版本号:63e04cc40f649d10ba2f4f…...
--apoc)
neo4j查询语言Cypher详解(五)--apoc
APOC (Awesome Procedures on Cypher)是一个Neo4j库,它提供了对其他过程和函数的访问,扩展了Cypher查询语言的使用。 apoc MATCH (n:Movie) CALL apoc.create.addLabels( n, [ n.genre ] ) YIELD node REMOVE node.genre RETURN node;附录 参考 apoc…...

odoo17 | 视图操作按钮
前言 到目前为止,我们主要通过声明字段和视图来构建我们的模块。在上一章中,我们刚刚通过计算字段和onchanges引入了业务逻辑。在任何真实的业务场景中,我们都会希望将一些业务逻辑链接到操作按钮。在我们的房地产示例中,我们希望…...

零门槛NAS搭建:WinNAS如何让普通电脑秒变私有云?
一、核心优势:专为Windows用户设计的极简NAS WinNAS由深圳耘想存储科技开发,是一款收费低廉但功能全面的Windows NAS工具,主打“无学习成本部署” 。与其他NAS软件相比,其优势在于: 无需硬件改造:将任意W…...

高频面试之3Zookeeper
高频面试之3Zookeeper 文章目录 高频面试之3Zookeeper3.1 常用命令3.2 选举机制3.3 Zookeeper符合法则中哪两个?3.4 Zookeeper脑裂3.5 Zookeeper用来干嘛了 3.1 常用命令 ls、get、create、delete、deleteall3.2 选举机制 半数机制(过半机制࿰…...

React Native在HarmonyOS 5.0阅读类应用开发中的实践
一、技术选型背景 随着HarmonyOS 5.0对Web兼容层的增强,React Native作为跨平台框架可通过重新编译ArkTS组件实现85%以上的代码复用率。阅读类应用具有UI复杂度低、数据流清晰的特点。 二、核心实现方案 1. 环境配置 (1)使用React Native…...
华为云Flexus+DeepSeek征文|DeepSeek-V3/R1 商用服务开通全流程与本地部署搭建
华为云FlexusDeepSeek征文|DeepSeek-V3/R1 商用服务开通全流程与本地部署搭建 前言 如今大模型其性能出色,华为云 ModelArts Studio_MaaS大模型即服务平台华为云内置了大模型,能助力我们轻松驾驭 DeepSeek-V3/R1,本文中将分享如何…...

docker 部署发现spring.profiles.active 问题
报错: org.springframework.boot.context.config.InvalidConfigDataPropertyException: Property spring.profiles.active imported from location class path resource [application-test.yml] is invalid in a profile specific resource [origin: class path re…...

Mysql8 忘记密码重置,以及问题解决
1.使用免密登录 找到配置MySQL文件,我的文件路径是/etc/mysql/my.cnf,有的人的是/etc/mysql/mysql.cnf 在里最后加入 skip-grant-tables重启MySQL服务 service mysql restartShutting down MySQL… SUCCESS! Starting MySQL… SUCCESS! 重启成功 2.登…...

Appium下载安装配置保姆教程(图文详解)
目录 一、Appium软件介绍 1.特点 2.工作原理 3.应用场景 二、环境准备 安装 Node.js 安装 Appium 安装 JDK 安装 Android SDK 安装Python及依赖包 三、安装教程 1.Node.js安装 1.1.下载Node 1.2.安装程序 1.3.配置npm仓储和缓存 1.4. 配置环境 1.5.测试Node.j…...
)
2025.6.9总结(利与弊)
凡事都有两面性。在大厂上班也不例外。今天找开发定位问题,从一个接口人不断溯源到另一个 接口人。有时候,不知道是谁的责任填。将工作内容分的很细,每个人负责其中的一小块。我清楚的意识到,自己就是个可以随时替换的螺丝钉&…...

GeoServer发布PostgreSQL图层后WFS查询无主键字段
在使用 GeoServer(版本 2.22.2) 发布 PostgreSQL(PostGIS)中的表为地图服务时,常常会遇到一个小问题: WFS 查询中,主键字段(如 id)莫名其妙地消失了! 即使你在…...

CSS 工具对比:UnoCSS vs Tailwind CSS,谁是你的菜?
在现代前端开发中,Utility-First (功能优先) CSS 框架已经成为主流。其中,Tailwind CSS 无疑是市场的领导者和标杆。然而,一个名为 UnoCSS 的新星正以其惊人的性能和极致的灵活性迅速崛起。 这篇文章将深入探讨这两款工具的核心理念、技术差…...
