gdb调试std::list和std::vector等容器的方法
GDB中print方法并不能直接打印STL容器中保存的变量,其实只要http://www.yolinux.com/TUTORIALS/src/dbinit_stl_views-1.03.txt这个文件保存为~/.gdbinit 就可以使用它提供的方法方便调试容器
指定启动文件:~/.gdbinit,下面的方法任选其一。
1、调用GDB时,指定启动文件。
# gdb -command=~/.gdbinit a.out
2、运行GDB后,指定启动文件。
2.1、“source /.gdbinit”,临时导入/.gdbinit文件。
2.2、添加“add-auto-load-safe-path /.gdbinit”到/.gdbinit文件中,使该文件可以被加载;
2.3、添加“set auto-load safe-path ./”到./.gdbinit文件中,相当于禁用了安全路径的保护;
http://www.yolinux.com/TUTORIALS/src/dbinit_stl_views-1.03.txt内容如下:
cat ~/.gdbinit
#
# STL GDB evaluators/views/utilities - 1.03
#
# The new GDB commands:
# are entirely non instrumental
# do not depend on any "inline"(s) - e.g. size(), [], etc
# are extremely tolerant to debugger settings
#
# This file should be "included" in .gdbinit as following:
# source stl-views.gdb or just paste it into your .gdbinit file
#
# The following STL containers are currently supported:
#
# std::vector<T> -- via pvector command
# std::list<T> -- via plist or plist_member command
# std::map<T,T> -- via pmap or pmap_member command
# std::multimap<T,T> -- via pmap or pmap_member command
# std::set<T> -- via pset command
# std::multiset<T> -- via pset command
# std::deque<T> -- via pdequeue command
# std::stack<T> -- via pstack command
# std::queue<T> -- via pqueue command
# std::priority_queue<T> -- via ppqueue command
# std::bitset<n> -- via pbitset command
# std::string -- via pstring command
# std::widestring -- via pwstring command
#
# The end of this file contains (optional) C++ beautifiers
# Make sure your debugger supports $argc
#
# Simple GDB Macros writen by Dan Marinescu (H-PhD) - License GPL
# Inspired by intial work of Tom Malnar,
# Tony Novac (PhD) / Cornell / Stanford,
# Gilad Mishne (PhD) and Many Many Others.
# Contact: dan_c_marinescu@yahoo.com (Subject: STL)
#
# Modified to work with g++ 4.3 by Anders Elton
# Also added _member functions, that instead of printing the entire class in map, prints a member.#
# std::vector<>
#define pvectorif $argc == 0help pvectorelseset $size = $arg0._M_impl._M_finish - $arg0._M_impl._M_startset $capacity = $arg0._M_impl._M_end_of_storage - $arg0._M_impl._M_startset $size_max = $size - 1endif $argc == 1set $i = 0while $i < $sizeprintf "elem[%u]: ", $ip *($arg0._M_impl._M_start + $i)set $i++endendif $argc == 2set $idx = $arg1if $idx < 0 || $idx > $size_maxprintf "idx1, idx2 are not in acceptable range: [0..%u].\n", $size_maxelseprintf "elem[%u]: ", $idxp *($arg0._M_impl._M_start + $idx)endendif $argc == 3set $start_idx = $arg1set $stop_idx = $arg2if $start_idx > $stop_idxset $tmp_idx = $start_idxset $start_idx = $stop_idxset $stop_idx = $tmp_idxendif $start_idx < 0 || $stop_idx < 0 || $start_idx > $size_max || $stop_idx > $size_maxprintf "idx1, idx2 are not in acceptable range: [0..%u].\n", $size_maxelseset $i = $start_idxwhile $i <= $stop_idxprintf "elem[%u]: ", $ip *($arg0._M_impl._M_start + $i)set $i++endendendif $argc > 0printf "Vector size = %u\n", $sizeprintf "Vector capacity = %u\n", $capacityprintf "Element "whatis $arg0._M_impl._M_startend
enddocument pvectorPrints std::vector<T> information.Syntax: pvector <vector> <idx1> <idx2>Note: idx, idx1 and idx2 must be in acceptable range [0..<vector>.size()-1].Examples:pvector v - Prints vector content, size, capacity and T typedefpvector v 0 - Prints element[idx] from vectorpvector v 1 2 - Prints elements in range [idx1..idx2] from vector
end #
# std::list<>
#define plistif $argc == 0help plistelseset $head = &$arg0._M_impl._M_nodeset $current = $arg0._M_impl._M_node._M_nextset $size = 0while $current != $headif $argc == 2printf "elem[%u]: ", $sizep *($arg1*)($current + 1)endif $argc == 3if $size == $arg2printf "elem[%u]: ", $sizep *($arg1*)($current + 1)endendset $current = $current._M_nextset $size++endprintf "List size = %u \n", $sizeif $argc == 1printf "List "whatis $arg0printf "Use plist <variable_name> <element_type> to see the elements in the list.\n"endend
enddocument plistPrints std::list<T> information.Syntax: plist <list> <T> <idx>: Prints list size, if T defined all elements or just element at idxExamples:plist l - prints list size and definitionplist l int - prints all elements and list sizeplist l int 2 - prints the third element in the list (if exists) and list size
enddefine plist_memberif $argc == 0help plist_memberelseset $head = &$arg0._M_impl._M_nodeset $current = $arg0._M_impl._M_node._M_nextset $size = 0while $current != $headif $argc == 3printf "elem[%u]: ", $sizep (*($arg1*)($current + 1)).$arg2endif $argc == 4if $size == $arg3printf "elem[%u]: ", $sizep (*($arg1*)($current + 1)).$arg2endendset $current = $current._M_nextset $size++endprintf "List size = %u \n", $sizeif $argc == 1printf "List "whatis $arg0printf "Use plist_member <variable_name> <element_type> <member> to see the elements in the list.\n"endend
enddocument plist_memberPrints std::list<T> information.Syntax: plist <list> <T> <idx>: Prints list size, if T defined all elements or just element at idxExamples:plist_member l int member - prints all elements and list sizeplist_member l int member 2 - prints the third element in the list (if exists) and list size
end#
# std::map and std::multimap
#define pmapif $argc == 0help pmapelseset $tree = $arg0set $i = 0set $node = $tree._M_t._M_impl._M_header._M_leftset $end = $tree._M_t._M_impl._M_headerset $tree_size = $tree._M_t._M_impl._M_node_countif $argc == 1printf "Map "whatis $treeprintf "Use pmap <variable_name> <left_element_type> <right_element_type> to see the elements in the map.\n"endif $argc == 3while $i < $tree_sizeset $value = (void *)($node + 1)printf "elem[%u].left: ", $ip *($arg1*)$valueset $value = $value + sizeof($arg1)printf "elem[%u].right: ", $ip *($arg2*)$valueif $node._M_right != 0set $node = $node._M_rightwhile $node._M_left != 0set $node = $node._M_leftendelseset $tmp_node = $node._M_parentwhile $node == $tmp_node._M_rightset $node = $tmp_nodeset $tmp_node = $tmp_node._M_parentendif $node._M_right != $tmp_nodeset $node = $tmp_nodeendendset $i++endendif $argc == 4set $idx = $arg3set $ElementsFound = 0while $i < $tree_sizeset $value = (void *)($node + 1)if *($arg1*)$value == $idxprintf "elem[%u].left: ", $ip *($arg1*)$valueset $value = $value + sizeof($arg1)printf "elem[%u].right: ", $ip *($arg2*)$valueset $ElementsFound++endif $node._M_right != 0set $node = $node._M_rightwhile $node._M_left != 0set $node = $node._M_leftendelseset $tmp_node = $node._M_parentwhile $node == $tmp_node._M_rightset $node = $tmp_nodeset $tmp_node = $tmp_node._M_parentendif $node._M_right != $tmp_nodeset $node = $tmp_nodeendendset $i++endprintf "Number of elements found = %u\n", $ElementsFoundendif $argc == 5set $idx1 = $arg3set $idx2 = $arg4set $ElementsFound = 0while $i < $tree_sizeset $value = (void *)($node + 1)set $valueLeft = *($arg1*)$valueset $valueRight = *($arg2*)($value + sizeof($arg1))if $valueLeft == $idx1 && $valueRight == $idx2printf "elem[%u].left: ", $ip $valueLeftprintf "elem[%u].right: ", $ip $valueRightset $ElementsFound++endif $node._M_right != 0set $node = $node._M_rightwhile $node._M_left != 0set $node = $node._M_leftendelseset $tmp_node = $node._M_parentwhile $node == $tmp_node._M_rightset $node = $tmp_nodeset $tmp_node = $tmp_node._M_parentendif $node._M_right != $tmp_nodeset $node = $tmp_nodeendendset $i++endprintf "Number of elements found = %u\n", $ElementsFoundendprintf "Map size = %u\n", $tree_sizeend
enddocument pmapPrints std::map<TLeft and TRight> or std::multimap<TLeft and TRight> information. Works for std::multimap as well.Syntax: pmap <map> <TtypeLeft> <TypeRight> <valLeft> <valRight>: Prints map size, if T defined all elements or just element(s) with val(s)Examples:pmap m - prints map size and definitionpmap m int int - prints all elements and map sizepmap m int int 20 - prints the element(s) with left-value = 20 (if any) and map sizepmap m int int 20 200 - prints the element(s) with left-value = 20 and right-value = 200 (if any) and map size
enddefine pmap_memberif $argc == 0help pmap_memberelseset $tree = $arg0set $i = 0set $node = $tree._M_t._M_impl._M_header._M_leftset $end = $tree._M_t._M_impl._M_headerset $tree_size = $tree._M_t._M_impl._M_node_countif $argc == 1printf "Map "whatis $treeprintf "Use pmap <variable_name> <left_element_type> <right_element_type> to see the elements in the map.\n"endif $argc == 5while $i < $tree_sizeset $value = (void *)($node + 1)printf "elem[%u].left: ", $ip (*($arg1*)$value).$arg2set $value = $value + sizeof($arg1)printf "elem[%u].right: ", $ip (*($arg3*)$value).$arg4if $node._M_right != 0set $node = $node._M_rightwhile $node._M_left != 0set $node = $node._M_leftendelseset $tmp_node = $node._M_parentwhile $node == $tmp_node._M_rightset $node = $tmp_nodeset $tmp_node = $tmp_node._M_parentendif $node._M_right != $tmp_nodeset $node = $tmp_nodeendendset $i++endendif $argc == 6set $idx = $arg5set $ElementsFound = 0while $i < $tree_sizeset $value = (void *)($node + 1)if *($arg1*)$value == $idxprintf "elem[%u].left: ", $ip (*($arg1*)$value).$arg2set $value = $value + sizeof($arg1)printf "elem[%u].right: ", $ip (*($arg3*)$value).$arg4set $ElementsFound++endif $node._M_right != 0set $node = $node._M_rightwhile $node._M_left != 0set $node = $node._M_leftendelseset $tmp_node = $node._M_parentwhile $node == $tmp_node._M_rightset $node = $tmp_nodeset $tmp_node = $tmp_node._M_parentendif $node._M_right != $tmp_nodeset $node = $tmp_nodeendendset $i++endprintf "Number of elements found = %u\n", $ElementsFoundendprintf "Map size = %u\n", $tree_sizeend
enddocument pmap_memberPrints std::map<TLeft and TRight> or std::multimap<TLeft and TRight> information. Works for std::multimap as well.Syntax: pmap <map> <TtypeLeft> <TypeRight> <valLeft> <valRight>: Prints map size, if T defined all elements or just element(s) with val(s)Examples:pmap_member m class1 member1 class2 member2 - prints class1.member1 : class2.member2pmap_member m class1 member1 class2 member2 lvalue - prints class1.member1 : class2.member2 where class1 == lvalue
end#
# std::set and std::multiset
#define psetif $argc == 0help psetelseset $tree = $arg0set $i = 0set $node = $tree._M_t._M_impl._M_header._M_leftset $end = $tree._M_t._M_impl._M_headerset $tree_size = $tree._M_t._M_impl._M_node_countif $argc == 1printf "Set "whatis $treeprintf "Use pset <variable_name> <element_type> to see the elements in the set.\n"endif $argc == 2while $i < $tree_sizeset $value = (void *)($node + 1)printf "elem[%u]: ", $ip *($arg1*)$valueif $node._M_right != 0set $node = $node._M_rightwhile $node._M_left != 0set $node = $node._M_leftendelseset $tmp_node = $node._M_parentwhile $node == $tmp_node._M_rightset $node = $tmp_nodeset $tmp_node = $tmp_node._M_parentendif $node._M_right != $tmp_nodeset $node = $tmp_nodeendendset $i++endendif $argc == 3set $idx = $arg2set $ElementsFound = 0while $i < $tree_sizeset $value = (void *)($node + 1)if *($arg1*)$value == $idxprintf "elem[%u]: ", $ip *($arg1*)$valueset $ElementsFound++endif $node._M_right != 0set $node = $node._M_rightwhile $node._M_left != 0set $node = $node._M_leftendelseset $tmp_node = $node._M_parentwhile $node == $tmp_node._M_rightset $node = $tmp_nodeset $tmp_node = $tmp_node._M_parentendif $node._M_right != $tmp_nodeset $node = $tmp_nodeendendset $i++endprintf "Number of elements found = %u\n", $ElementsFoundendprintf "Set size = %u\n", $tree_sizeend
enddocument psetPrints std::set<T> or std::multiset<T> information. Works for std::multiset as well.Syntax: pset <set> <T> <val>: Prints set size, if T defined all elements or just element(s) having valExamples:pset s - prints set size and definitionpset s int - prints all elements and the size of spset s int 20 - prints the element(s) with value = 20 (if any) and the size of s
end#
# std::dequeue
#define pdequeueif $argc == 0help pdequeueelseset $size = 0set $start_cur = $arg0._M_impl._M_start._M_curset $start_last = $arg0._M_impl._M_start._M_lastset $start_stop = $start_lastwhile $start_cur != $start_stopp *$start_curset $start_cur++set $size++endset $finish_first = $arg0._M_impl._M_finish._M_firstset $finish_cur = $arg0._M_impl._M_finish._M_curset $finish_last = $arg0._M_impl._M_finish._M_lastif $finish_cur < $finish_lastset $finish_stop = $finish_curelseset $finish_stop = $finish_lastendwhile $finish_first != $finish_stopp *$finish_firstset $finish_first++set $size++endprintf "Dequeue size = %u\n", $sizeend
enddocument pdequeuePrints std::dequeue<T> information.Syntax: pdequeue <dequeue>: Prints dequeue size, if T defined all elementsDeque elements are listed "left to right" (left-most stands for front and right-most stands for back)Example:pdequeue d - prints all elements and size of d
end#
# std::stack
#define pstackif $argc == 0help pstackelseset $start_cur = $arg0.c._M_impl._M_start._M_curset $finish_cur = $arg0.c._M_impl._M_finish._M_curset $size = $finish_cur - $start_curset $i = $size - 1while $i >= 0p *($start_cur + $i)set $i--endprintf "Stack size = %u\n", $sizeend
enddocument pstackPrints std::stack<T> information.Syntax: pstack <stack>: Prints all elements and size of the stackStack elements are listed "top to buttom" (top-most element is the first to come on pop)Example:pstack s - prints all elements and the size of s
end#
# std::queue
#define pqueueif $argc == 0help pqueueelseset $start_cur = $arg0.c._M_impl._M_start._M_curset $finish_cur = $arg0.c._M_impl._M_finish._M_curset $size = $finish_cur - $start_curset $i = 0while $i < $sizep *($start_cur + $i)set $i++endprintf "Queue size = %u\n", $sizeend
enddocument pqueuePrints std::queue<T> information.Syntax: pqueue <queue>: Prints all elements and the size of the queueQueue elements are listed "top to bottom" (top-most element is the first to come on pop)Example:pqueue q - prints all elements and the size of q
end#
# std::priority_queue
#define ppqueueif $argc == 0help ppqueueelseset $size = $arg0.c._M_impl._M_finish - $arg0.c._M_impl._M_startset $capacity = $arg0.c._M_impl._M_end_of_storage - $arg0.c._M_impl._M_startset $i = $size - 1while $i >= 0p *($arg0.c._M_impl._M_start + $i)set $i--endprintf "Priority queue size = %u\n", $sizeprintf "Priority queue capacity = %u\n", $capacityend
enddocument ppqueuePrints std::priority_queue<T> information.Syntax: ppqueue <priority_queue>: Prints all elements, size and capacity of the priority_queuePriority_queue elements are listed "top to buttom" (top-most element is the first to come on pop)Example:ppqueue pq - prints all elements, size and capacity of pq
end#
# std::bitset
#define pbitsetif $argc == 0help pbitsetelsep /t $arg0._M_wend
enddocument pbitsetPrints std::bitset<n> information.Syntax: pbitset <bitset>: Prints all bits in bitsetExample:pbitset b - prints all bits in b
end#
# std::string
#define pstringif $argc == 0help pstringelseprintf "String \t\t\t= \"%s\"\n", $arg0._M_data()printf "String size/length \t= %u\n", $arg0._M_rep()._M_lengthprintf "String capacity \t= %u\n", $arg0._M_rep()._M_capacityprintf "String ref-count \t= %d\n", $arg0._M_rep()._M_refcountend
enddocument pstringPrints std::string information.Syntax: pstring <string>Example:pstring s - Prints content, size/length, capacity and ref-count of string s
end #
# std::wstring
#define pwstringif $argc == 0help pwstringelsecall printf("WString \t\t= \"%ls\"\n", $arg0._M_data())printf "WString size/length \t= %u\n", $arg0._M_rep()._M_lengthprintf "WString capacity \t= %u\n", $arg0._M_rep()._M_capacityprintf "WString ref-count \t= %d\n", $arg0._M_rep()._M_refcountend
enddocument pwstringPrints std::wstring information.Syntax: pwstring <wstring>Example:pwstring s - Prints content, size/length, capacity and ref-count of wstring s
end #
# C++ related beautifiers (optional)
#set print pretty on
set print object on
set print static-members on
set print vtbl on
set print demangle on
set demangle-style gnu-v3
set print sevenbit-strings off
相关文章:

gdb调试std::list和std::vector等容器的方法
GDB中print方法并不能直接打印STL容器中保存的变量,其实只要http://www.yolinux.com/TUTORIALS/src/dbinit_stl_views-1.03.txt这个文件保存为~/.gdbinit 就可以使用它提供的方法方便调试容器 指定启动文件:~/.gdbinit,下面的方法任选其一。…...

python stomp 转发activemq topic消息
import pysimplestomp 连接到ActiveMQ的Topic: # 连接ActiveMQ服务器 server "tcp://localhost:61613" topic "/topic/your_topic"# 连接到ActiveMQ的Topic destination f"destination://{topic}" connection pysimplestomp.con…...
Spring Boot使用AOP
一、为什么需要面向切面编程? 面向对象编程(OOP)的好处是显而易见的,缺点也同样明显。当需要为多个不具有继承关系的对象添加一个公共的方法的时候,例如日志记录、性能监控等,如果采用面向对象编程的方法&…...

C语言通过IXMLHttpRequest以get或post方式发送http请求获取服务器文本或xml数据
做过网页设计的人应该都知道ajax。 Ajax即Asynchronous Javascript And XML(异步的JavaScript和XML)。使用Ajax的最大优点,就是能在不更新整个页面的前提下维护数据。这使得Web应用程序更为迅捷地回应用户动作,并避免了在网络上发…...
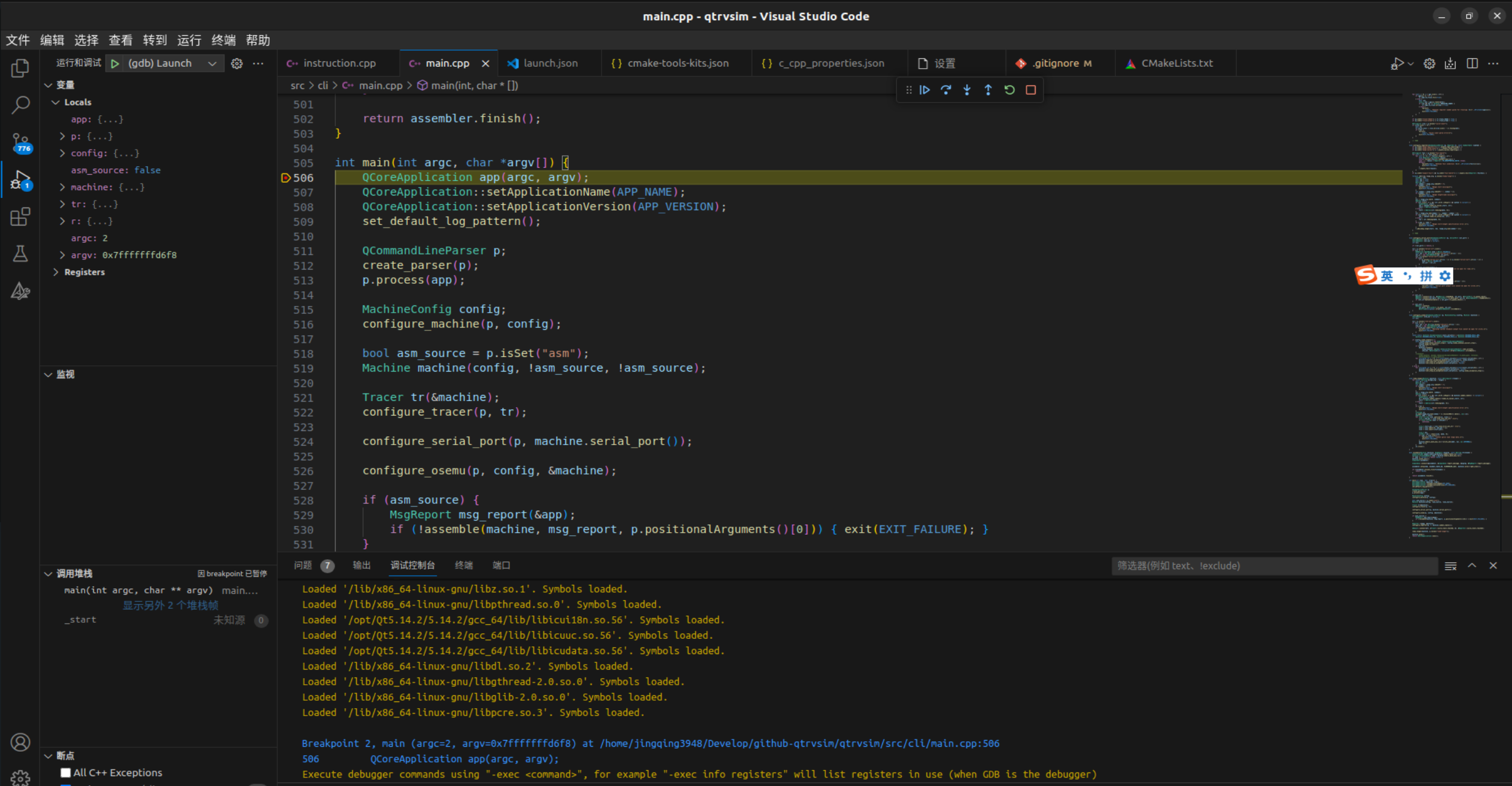
QtRVSim(二)一个 RISC-V 程序的解码流程
继上一篇文章简单代码分析后,本文主要调研如何实现对指令的解析运行。 调试配置 使用 gdb 工具跟踪调试运行。 c_cpp_properties.json 项目配置: {"name": "QtRvSim","includePath": ["${workspaceFolder}/**&quo…...

x-cmd pkg | httpx - 为 Python 设计的下一代 HTTP 客户端库
目录 简介首次用户功能特点进一步探索 简介 HTTPX 是一个为 Python 设计的下一代 HTTP 客户端库,由 Tom Christie 创建。它提供了同步和异步的 API,并支持 HTTP/1.1 和 HTTP/2 协议。与 Requests 库类似,但增加了对异步请求的支持和 HTTP/2 …...
|62. 不同路径)
代码随想录算法训练营第四十二天(动态规划篇)|62. 不同路径
62. 不同路径 题目链接:62. 不同路径 - 力扣(LeetCode) 思路 dp[i][j]: 从0到位置[i, j]共有dp[i][j]条路径。 dp[i][j] dp[i-1][j] dp[i][j-1] 到位置[i,j],可以从它的上面或者左边来,所以路径和为这两个方向的路…...
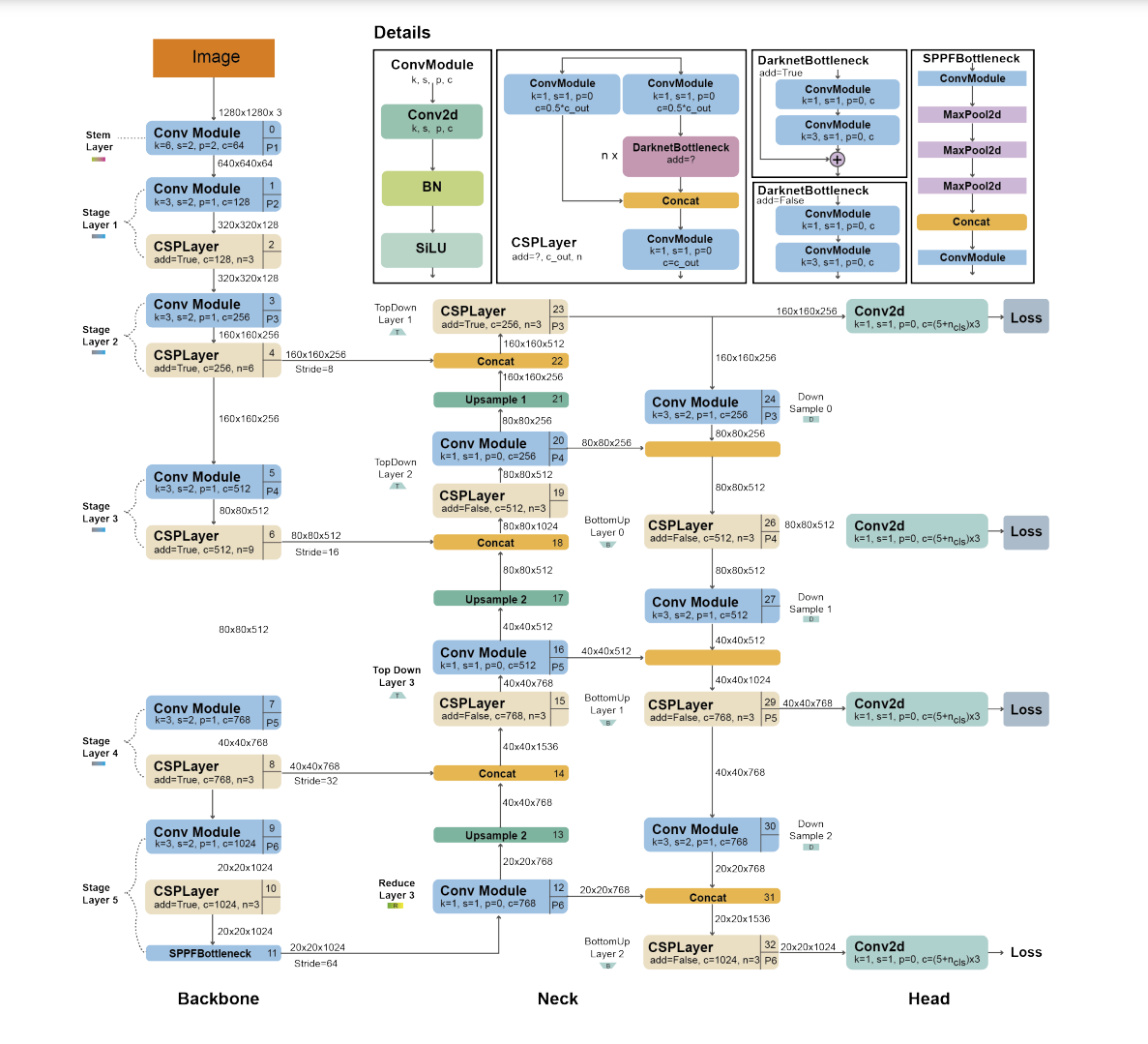
YOLO 全面回顾:从最初的YOLOv1到最新的YOLOv8、YOLO-NAS,以及整合了 Transformers 的 YOLO
YOLO 全面回顾 综述评估指标YOLO v1YOLO v2YOLO v3YOLO v4YOLOv5 与 Scaled-YOLOv4 YOLORYOLOXYOLOv6YOLOv7DAMO-YOLOYOLOv8PP-YOLO, PP-YOLOv2, and PP-YOLOEYOLO-NASYOLO with Transformers 综述 论文:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2304.00501.pdf 代码:gi…...
Android双指缩放ScaleGestureDetector检测放大因子大图移动到双指中心点ImageView区域中心,Kotlin(2)
Android双指缩放ScaleGestureDetector检测放大因子大图移动到双指中心点ImageView区域中心,Kotlin(2) 在 Android ScaleGestureDetector检测双指缩放Bitmap基于Matrix动画移动到双指捏合中心点ImageView区域中心,Kotlin-CSDN博客 …...

同为科技(TOWE)自动控制循环定时插座
随着科技的发展,智能化家居已成为我们生活的重要组成部分。作为国内领先的智能家居品牌,同为科技(TOWE)推出的自动控制循环定时插座,无疑将科技与生活完美地结合在一起。 1.外观设计 同为科技(TOWE&#x…...
游戏设计模式
单列模式 概念 单例模式是一种创建型设计模式,可以保证一个类只有一个实例,并提供一个访问该实例的全局节点。 优点 可以派生:在单例类的实例构造函数中可以设置以允许子类派生。受控访问:因为单例类封装他的唯一实例…...

CUBEMX与FreeRTOS在Arm Compiler 6下的配置方法
在嵌入式开发中,STM32是一种广泛使用的微控制器。为了提高开发效率,我们通常会利用ST公司提供的STM32CubeMX工具来配置硬件,并结合FreeRTOS这一实时操作系统来进行多任务处理。本文将深入探讨如何在这一框架下,使用Arm Compiler 6…...
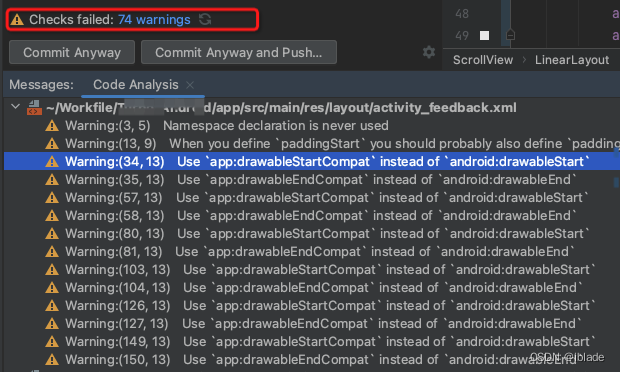
Android Studio 提示Use app:drawableStartCompat instead of android:drawableStart
每次提交代码时,AS这个老妈子总爱唠叨一堆warning,这些Warning都在讲什么? 1.Use app:drawableStartCompat instead of android:drawableStart 在Android开发中,android:drawableStart和app:drawableStartCompat是两个用于设置…...
C# wpf 实现任意控件(包括窗口)更多调整大小功能
WPF拖动改变大小系列 第一节 Grid内控件拖动调整大小 第二节 Canvas内控件拖动调整大小 第三节 窗口拖动调整大小 第四节 附加属性实现拖动调整大小 第五章 拓展更多调整大小功能(本章) 文章目录 WPF拖动改变大小系列前言一、添加的功能1、任意控件Drag…...

Vue+OpenLayers7入门到实战:快速搭建Vue+OpenLayers7地图脚手架项目。从零开始构建Vue项目并整合OpenLayers7.5.2
返回《Vue+OpenLayers7》专栏目录:Vue+OpenLayers7 前言 本章针对Vue初学者,对Vue不熟悉,甚至还不会Vue的入门学生读者。 本章会详细讲解从NodeJS环境到npm环境的各个步骤,再到使用vue-cli脚手架快速生成项目,以及添加OpenLayers7地图库依赖,编写简单的xyz高德地图显示…...

mysql-线上常用运维sql
1.表备份 INSERT INTO table1 SELECT * FROM table2; 2.用一个表中的字段更新另一张表中的字段 UPDATE table2 JOIN table1 ON table2.id table1.id SET table2.column2 table1.column1; 3.在MySQL中,查询一个表的列字段值是否包含另一个表的字段,…...
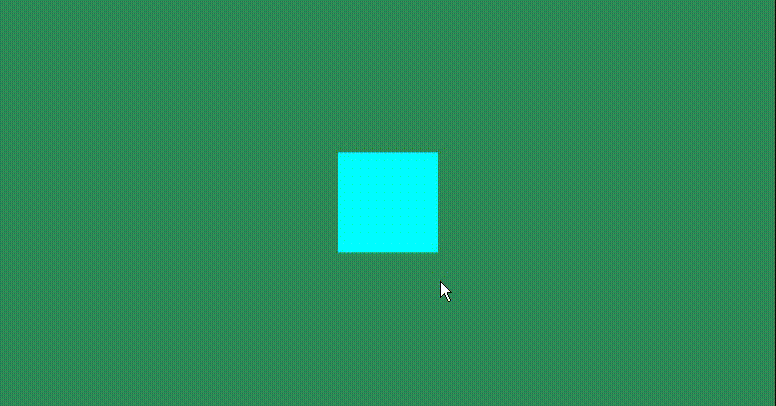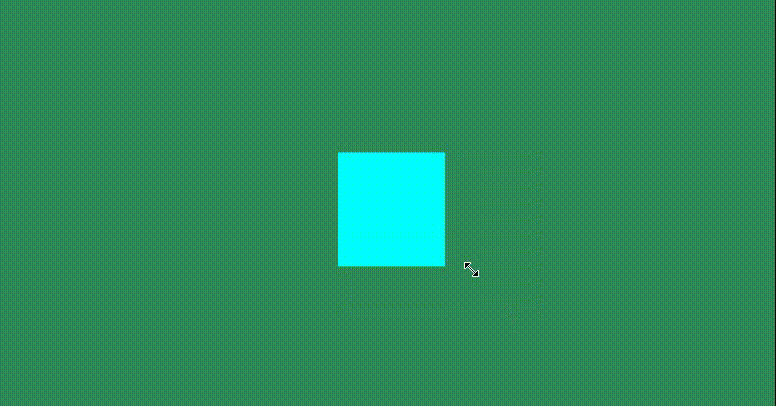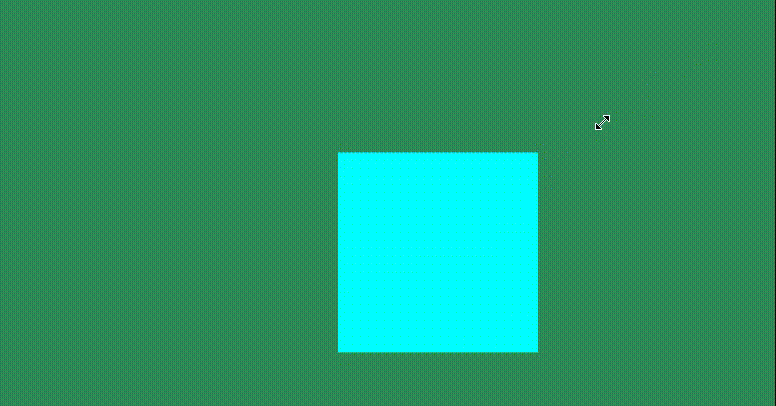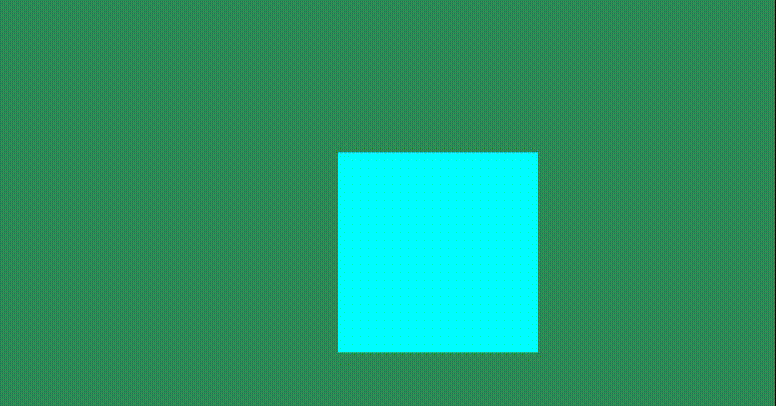
Linux之进程间通信(system V 共享内存)
目录 一、共享内存 1、基本原理 2、共享内存的创建 3、共享内存的释放 4、共享内存的关联 5、共享内存的去关联 6、查看IPC资源 二、完整通信代码 三、共享内存的特点 四、信号量 1、相关概念 2、信号量概念 进程间通信的本质就是让不同的进程看到同一个资源。而前…...

数据库 sql select *from account where name=‘张三‘ 执行过程
select *from account where name张三分析上面语句的执行过程 用到了索引 由于是根据 1.name字段进行查询,所以先根据name张三’到name字段的二级索引中进行匹配查 找。但是在二级索引中只能查找到 Arm 对应的主键值 10。 2.由于查询返回的数据是*,…...
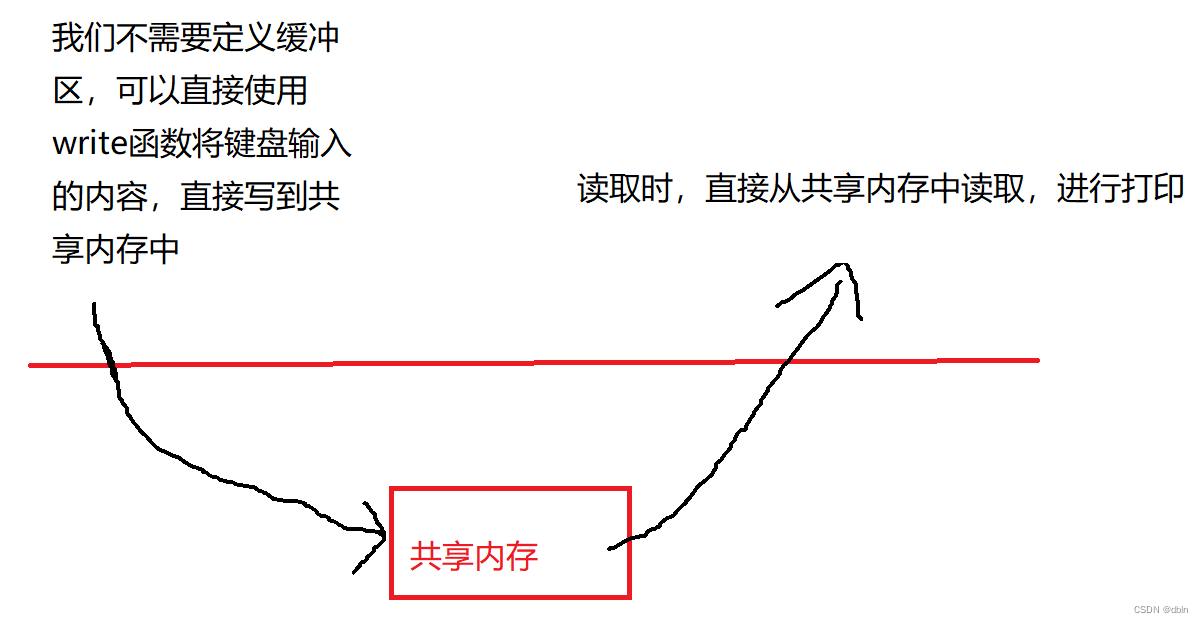
力扣日记1.27-【回溯算法篇】131. 分割回文串
力扣日记:【回溯算法篇】131. 分割回文串 日期:2023.1.27 参考:代码随想录、力扣 131. 分割回文串 题目描述 难度:中等 给你一个字符串 s,请你将 s 分割成一些子串,使每个子串都是 回文串 。返回 s 所有可…...

如何用web界面打开华为防火墙
目录 1.创建一个虚拟网卡 2.cloud操作 3.防火墙上操作 4. 登录 1.创建一个虚拟网卡 2.cloud操作 3.防火墙上操作 4. 登录...
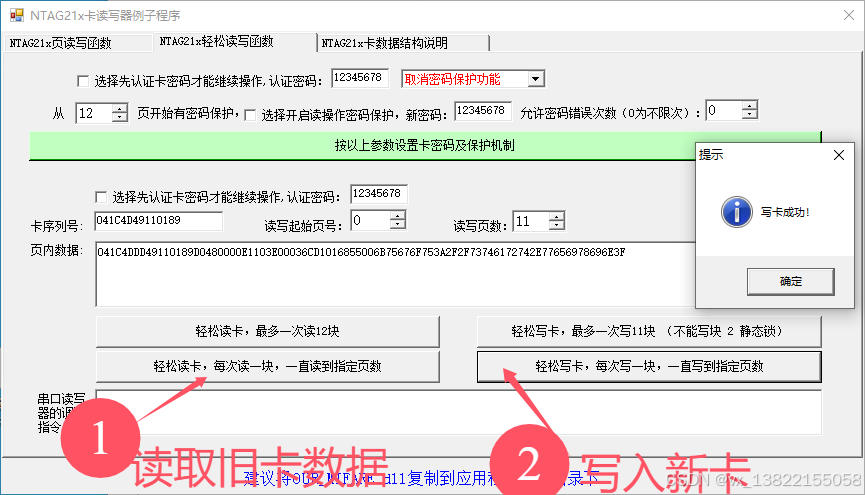
VB.net复制Ntag213卡写入UID
本示例使用的发卡器:https://item.taobao.com/item.htm?ftt&id615391857885 一、读取旧Ntag卡的UID和数据 Private Sub Button15_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button15.Click轻松读卡技术支持:网站:Dim i, j As IntegerDim cardidhex, …...
)
【位运算】消失的两个数字(hard)
消失的两个数字(hard) 题⽬描述:解法(位运算):Java 算法代码:更简便代码 题⽬链接:⾯试题 17.19. 消失的两个数字 题⽬描述: 给定⼀个数组,包含从 1 到 N 所有…...
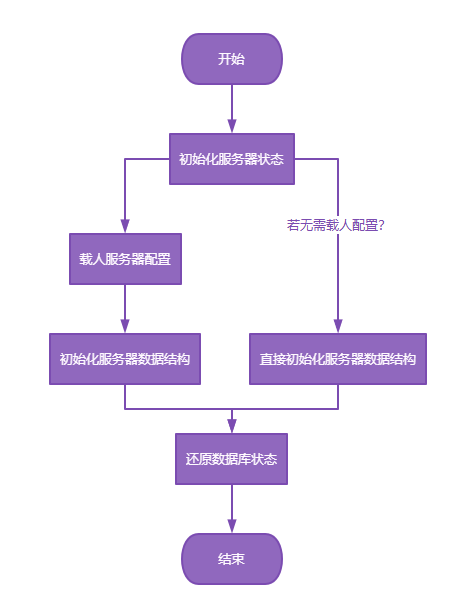
【Redis技术进阶之路】「原理分析系列开篇」分析客户端和服务端网络诵信交互实现(服务端执行命令请求的过程 - 初始化服务器)
服务端执行命令请求的过程 【专栏简介】【技术大纲】【专栏目标】【目标人群】1. Redis爱好者与社区成员2. 后端开发和系统架构师3. 计算机专业的本科生及研究生 初始化服务器1. 初始化服务器状态结构初始化RedisServer变量 2. 加载相关系统配置和用户配置参数定制化配置参数案…...

Java - Mysql数据类型对应
Mysql数据类型java数据类型备注整型INT/INTEGERint / java.lang.Integer–BIGINTlong/java.lang.Long–––浮点型FLOATfloat/java.lang.FloatDOUBLEdouble/java.lang.Double–DECIMAL/NUMERICjava.math.BigDecimal字符串型CHARjava.lang.String固定长度字符串VARCHARjava.lang…...

Java 加密常用的各种算法及其选择
在数字化时代,数据安全至关重要,Java 作为广泛应用的编程语言,提供了丰富的加密算法来保障数据的保密性、完整性和真实性。了解这些常用加密算法及其适用场景,有助于开发者在不同的业务需求中做出正确的选择。 一、对称加密算法…...

【AI学习】三、AI算法中的向量
在人工智能(AI)算法中,向量(Vector)是一种将现实世界中的数据(如图像、文本、音频等)转化为计算机可处理的数值型特征表示的工具。它是连接人类认知(如语义、视觉特征)与…...
华为云Flexus+DeepSeek征文|DeepSeek-V3/R1 商用服务开通全流程与本地部署搭建
华为云FlexusDeepSeek征文|DeepSeek-V3/R1 商用服务开通全流程与本地部署搭建 前言 如今大模型其性能出色,华为云 ModelArts Studio_MaaS大模型即服务平台华为云内置了大模型,能助力我们轻松驾驭 DeepSeek-V3/R1,本文中将分享如何…...

Mac下Android Studio扫描根目录卡死问题记录
环境信息 操作系统: macOS 15.5 (Apple M2芯片)Android Studio版本: Meerkat Feature Drop | 2024.3.2 Patch 1 (Build #AI-243.26053.27.2432.13536105, 2025年5月22日构建) 问题现象 在项目开发过程中,提示一个依赖外部头文件的cpp源文件需要同步,点…...

今日学习:Spring线程池|并发修改异常|链路丢失|登录续期|VIP过期策略|数值类缓存
文章目录 优雅版线程池ThreadPoolTaskExecutor和ThreadPoolTaskExecutor的装饰器并发修改异常并发修改异常简介实现机制设计原因及意义 使用线程池造成的链路丢失问题线程池导致的链路丢失问题发生原因 常见解决方法更好的解决方法设计精妙之处 登录续期登录续期常见实现方式特…...

动态 Web 开发技术入门篇
一、HTTP 协议核心 1.1 HTTP 基础 协议全称 :HyperText Transfer Protocol(超文本传输协议) 默认端口 :HTTP 使用 80 端口,HTTPS 使用 443 端口。 请求方法 : GET :用于获取资源,…...
