YOLOv9有效改进|使用动态蛇形卷积Dynamic Snake Convolution

专栏介绍:YOLOv9改进系列 | 包含深度学习最新创新,主力高效涨点!!!
一、改进点介绍
使用ICCV2023中的动态蛇形卷积替换YOLOv9网络中的Conv模块。
二、Dynamic Snake Convolution模块详解
2.1 模块简介
应用场景: 适合 具有细长微弱的局部结构特征与复杂多变的全局形态特征的场景。
三、 Dynamic Snake Convolution模块使用教程
3.1 Dynamic Snake Convolution模块的代码
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from conv import Conv__all__ = ['DySnakeConv']class DySnakeConv(nn.Module):def __init__(self, inc, ouc, k=3) -> None:super().__init__()c_ = ouc // 3 // 16 * 16self.conv_0 = Conv(inc, ouc - 2 *c_, k)self.conv_x = DSConv(inc, c_, 0, k)self.conv_y = DSConv(inc, c_, 1, k)def forward(self, x):return torch.cat([self.conv_0(x), self.conv_x(x), self.conv_y(x)], dim=1)class DSConv(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_ch, out_ch, morph, kernel_size=3, if_offset=True, extend_scope=1):"""The Dynamic Snake Convolution:param in_ch: input channel:param out_ch: output channel:param kernel_size: the size of kernel:param extend_scope: the range to expand (default 1 for this method):param morph: the morphology of the convolution kernel is mainly divided into two typesalong the x-axis (0) and the y-axis (1) (see the paper for details):param if_offset: whether deformation is required, if it is False, it is the standard convolution kernel"""super(DSConv, self).__init__()# use the <offset_conv> to learn the deformable offsetself.offset_conv = nn.Conv2d(in_ch, 2 * kernel_size, 3, padding=1)self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(2 * kernel_size)self.kernel_size = kernel_size# two types of the DSConv (along x-axis and y-axis)self.dsc_conv_x = nn.Conv2d(in_ch,out_ch,kernel_size=(kernel_size, 1),stride=(kernel_size, 1),padding=0,)self.dsc_conv_y = nn.Conv2d(in_ch,out_ch,kernel_size=(1, kernel_size),stride=(1, kernel_size),padding=0,)self.gn = nn.GroupNorm(out_ch // 4, out_ch)self.act = Conv.default_actself.extend_scope = extend_scopeself.morph = morphself.if_offset = if_offsetdef forward(self, f):offset = self.offset_conv(f)offset = self.bn(offset)# We need a range of deformation between -1 and 1 to mimic the snake's swingoffset = torch.tanh(offset)input_shape = f.shapedsc = DSC(input_shape, self.kernel_size, self.extend_scope, self.morph)deformed_feature = dsc.deform_conv(f, offset, self.if_offset)if self.morph == 0:x = self.dsc_conv_x(deformed_feature.type(f.dtype))x = self.gn(x)x = self.act(x)return xelse:x = self.dsc_conv_y(deformed_feature.type(f.dtype))x = self.gn(x)x = self.act(x)return x# Core code, for ease of understanding, we mark the dimensions of input and output next to the code
class DSC(object):def __init__(self, input_shape, kernel_size, extend_scope, morph):self.num_points = kernel_sizeself.width = input_shape[2]self.height = input_shape[3]self.morph = morphself.extend_scope = extend_scope # offset (-1 ~ 1) * extend_scope# define feature map shape"""B: Batch size C: Channel W: Width H: Height"""self.num_batch = input_shape[0]self.num_channels = input_shape[1]"""input: offset [B,2*K,W,H] K: Kernel size (2*K: 2D image, deformation contains <x_offset> and <y_offset>)output_x: [B,1,W,K*H] coordinate mapoutput_y: [B,1,K*W,H] coordinate map"""def _coordinate_map_3D(self, offset, if_offset):device = offset.device# offsety_offset, x_offset = torch.split(offset, self.num_points, dim=1)y_center = torch.arange(0, self.width).repeat([self.height])y_center = y_center.reshape(self.height, self.width)y_center = y_center.permute(1, 0)y_center = y_center.reshape([-1, self.width, self.height])y_center = y_center.repeat([self.num_points, 1, 1]).float()y_center = y_center.unsqueeze(0)x_center = torch.arange(0, self.height).repeat([self.width])x_center = x_center.reshape(self.width, self.height)x_center = x_center.permute(0, 1)x_center = x_center.reshape([-1, self.width, self.height])x_center = x_center.repeat([self.num_points, 1, 1]).float()x_center = x_center.unsqueeze(0)if self.morph == 0:"""Initialize the kernel and flatten the kernely: only need 0x: -num_points//2 ~ num_points//2 (Determined by the kernel size)!!! The related PPT will be submitted later, and the PPT will contain the whole changes of each step"""y = torch.linspace(0, 0, 1)x = torch.linspace(-int(self.num_points // 2),int(self.num_points // 2),int(self.num_points),)y, x = torch.meshgrid(y, x, indexing = 'ij')y_spread = y.reshape(-1, 1)x_spread = x.reshape(-1, 1)y_grid = y_spread.repeat([1, self.width * self.height])y_grid = y_grid.reshape([self.num_points, self.width, self.height])y_grid = y_grid.unsqueeze(0) # [B*K*K, W,H]x_grid = x_spread.repeat([1, self.width * self.height])x_grid = x_grid.reshape([self.num_points, self.width, self.height])x_grid = x_grid.unsqueeze(0) # [B*K*K, W,H]y_new = y_center + y_gridx_new = x_center + x_gridy_new = y_new.repeat(self.num_batch, 1, 1, 1).to(device)x_new = x_new.repeat(self.num_batch, 1, 1, 1).to(device)y_offset_new = y_offset.detach().clone()if if_offset:y_offset = y_offset.permute(1, 0, 2, 3)y_offset_new = y_offset_new.permute(1, 0, 2, 3)center = int(self.num_points // 2)# The center position remains unchanged and the rest of the positions begin to swing# This part is quite simple. The main idea is that "offset is an iterative process"y_offset_new[center] = 0for index in range(1, center):y_offset_new[center + index] = (y_offset_new[center + index - 1] + y_offset[center + index])y_offset_new[center - index] = (y_offset_new[center - index + 1] + y_offset[center - index])y_offset_new = y_offset_new.permute(1, 0, 2, 3).to(device)y_new = y_new.add(y_offset_new.mul(self.extend_scope))y_new = y_new.reshape([self.num_batch, self.num_points, 1, self.width, self.height])y_new = y_new.permute(0, 3, 1, 4, 2)y_new = y_new.reshape([self.num_batch, self.num_points * self.width, 1 * self.height])x_new = x_new.reshape([self.num_batch, self.num_points, 1, self.width, self.height])x_new = x_new.permute(0, 3, 1, 4, 2)x_new = x_new.reshape([self.num_batch, self.num_points * self.width, 1 * self.height])return y_new, x_newelse:"""Initialize the kernel and flatten the kernely: -num_points//2 ~ num_points//2 (Determined by the kernel size)x: only need 0"""y = torch.linspace(-int(self.num_points // 2),int(self.num_points // 2),int(self.num_points),)x = torch.linspace(0, 0, 1)y, x = torch.meshgrid(y, x, indexing = 'ij')y_spread = y.reshape(-1, 1)x_spread = x.reshape(-1, 1)y_grid = y_spread.repeat([1, self.width * self.height])y_grid = y_grid.reshape([self.num_points, self.width, self.height])y_grid = y_grid.unsqueeze(0)x_grid = x_spread.repeat([1, self.width * self.height])x_grid = x_grid.reshape([self.num_points, self.width, self.height])x_grid = x_grid.unsqueeze(0)y_new = y_center + y_gridx_new = x_center + x_gridy_new = y_new.repeat(self.num_batch, 1, 1, 1)x_new = x_new.repeat(self.num_batch, 1, 1, 1)y_new = y_new.to(device)x_new = x_new.to(device)x_offset_new = x_offset.detach().clone()if if_offset:x_offset = x_offset.permute(1, 0, 2, 3)x_offset_new = x_offset_new.permute(1, 0, 2, 3)center = int(self.num_points // 2)x_offset_new[center] = 0for index in range(1, center):x_offset_new[center + index] = (x_offset_new[center + index - 1] + x_offset[center + index])x_offset_new[center - index] = (x_offset_new[center - index + 1] + x_offset[center - index])x_offset_new = x_offset_new.permute(1, 0, 2, 3).to(device)x_new = x_new.add(x_offset_new.mul(self.extend_scope))y_new = y_new.reshape([self.num_batch, 1, self.num_points, self.width, self.height])y_new = y_new.permute(0, 3, 1, 4, 2)y_new = y_new.reshape([self.num_batch, 1 * self.width, self.num_points * self.height])x_new = x_new.reshape([self.num_batch, 1, self.num_points, self.width, self.height])x_new = x_new.permute(0, 3, 1, 4, 2)x_new = x_new.reshape([self.num_batch, 1 * self.width, self.num_points * self.height])return y_new, x_new"""input: input feature map [N,C,D,W,H];coordinate map [N,K*D,K*W,K*H] output: [N,1,K*D,K*W,K*H] deformed feature map"""def _bilinear_interpolate_3D(self, input_feature, y, x):device = input_feature.devicey = y.reshape([-1]).float()x = x.reshape([-1]).float()zero = torch.zeros([]).int()max_y = self.width - 1max_x = self.height - 1# find 8 grid locationsy0 = torch.floor(y).int()y1 = y0 + 1x0 = torch.floor(x).int()x1 = x0 + 1# clip out coordinates exceeding feature map volumey0 = torch.clamp(y0, zero, max_y)y1 = torch.clamp(y1, zero, max_y)x0 = torch.clamp(x0, zero, max_x)x1 = torch.clamp(x1, zero, max_x)input_feature_flat = input_feature.flatten()input_feature_flat = input_feature_flat.reshape(self.num_batch, self.num_channels, self.width, self.height)input_feature_flat = input_feature_flat.permute(0, 2, 3, 1)input_feature_flat = input_feature_flat.reshape(-1, self.num_channels)dimension = self.height * self.widthbase = torch.arange(self.num_batch) * dimensionbase = base.reshape([-1, 1]).float()repeat = torch.ones([self.num_points * self.width * self.height]).unsqueeze(0)repeat = repeat.float()base = torch.matmul(base, repeat)base = base.reshape([-1])base = base.to(device)base_y0 = base + y0 * self.heightbase_y1 = base + y1 * self.height# top rectangle of the neighbourhood volumeindex_a0 = base_y0 - base + x0index_c0 = base_y0 - base + x1# bottom rectangle of the neighbourhood volumeindex_a1 = base_y1 - base + x0index_c1 = base_y1 - base + x1# get 8 grid valuesvalue_a0 = input_feature_flat[index_a0.type(torch.int64)].to(device)value_c0 = input_feature_flat[index_c0.type(torch.int64)].to(device)value_a1 = input_feature_flat[index_a1.type(torch.int64)].to(device)value_c1 = input_feature_flat[index_c1.type(torch.int64)].to(device)# find 8 grid locationsy0 = torch.floor(y).int()y1 = y0 + 1x0 = torch.floor(x).int()x1 = x0 + 1# clip out coordinates exceeding feature map volumey0 = torch.clamp(y0, zero, max_y + 1)y1 = torch.clamp(y1, zero, max_y + 1)x0 = torch.clamp(x0, zero, max_x + 1)x1 = torch.clamp(x1, zero, max_x + 1)x0_float = x0.float()x1_float = x1.float()y0_float = y0.float()y1_float = y1.float()vol_a0 = ((y1_float - y) * (x1_float - x)).unsqueeze(-1).to(device)vol_c0 = ((y1_float - y) * (x - x0_float)).unsqueeze(-1).to(device)vol_a1 = ((y - y0_float) * (x1_float - x)).unsqueeze(-1).to(device)vol_c1 = ((y - y0_float) * (x - x0_float)).unsqueeze(-1).to(device)outputs = (value_a0 * vol_a0 + value_c0 * vol_c0 + value_a1 * vol_a1 +value_c1 * vol_c1)if self.morph == 0:outputs = outputs.reshape([self.num_batch,self.num_points * self.width,1 * self.height,self.num_channels,])outputs = outputs.permute(0, 3, 1, 2)else:outputs = outputs.reshape([self.num_batch,1 * self.width,self.num_points * self.height,self.num_channels,])outputs = outputs.permute(0, 3, 1, 2)return outputsdef deform_conv(self, input, offset, if_offset):y, x = self._coordinate_map_3D(offset, if_offset)deformed_feature = self._bilinear_interpolate_3D(input, y, x)return deformed_featureif __name__ == "__main__":model = DySnakeConv(32, 32)print(model(torch.zeros(2, 32, 640, 320)).shape)
3.2 在YOlO v9中的添加教程
阅读YOLOv9添加模块教程或使用下文操作
1. 将YOLOv9工程中models下common.py文件中的最下行增加模块的代码。

2. 将YOLOv9工程中models下yolo.py文件中的第681行(可能因版本变化而变化)增加以下代码。

RepNCSPELAN4, SPPELAN, DySnakeConv}:
3.3 运行配置文件
# YOLOv9
# Powered bu https://blog.csdn.net/StopAndGoyyy
# parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
depth_multiple: 1 # model depth multiple
width_multiple: 1 # layer channel multiple
#activation: nn.LeakyReLU(0.1)
#activation: nn.ReLU()# anchors
anchors: 3# YOLOv9 backbone
backbone:[[-1, 1, Silence, []], # conv down[-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]], # 1-P1/2# conv down[-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]], # 2-P2/4# elan-1 block[-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [256, 128, 64, 1]], # 3# avg-conv down[-1, 1, ADown, [256]], # 4-P3/8# elan-2 block[-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [512, 256, 128, 1]], # 5# avg-conv down[-1, 1, ADown, [512]], # 6-P4/16# elan-2 block[-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [512, 512, 256, 1]], # 7# avg-conv down[-1, 1, ADown, [512]], # 8-P5/32# elan-2 block[-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [512, 512, 256, 1]], # 9]# YOLOv9 head
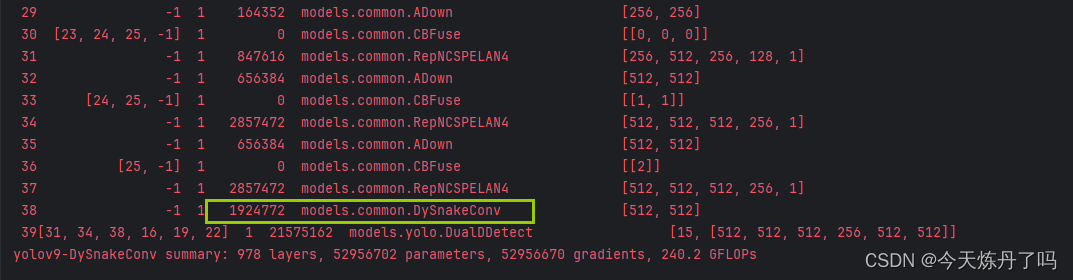
head:[# elan-spp block[-1, 1, SPPELAN, [512, 256]], # 10# up-concat merge[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],[[-1, 7], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P4# elan-2 block[-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [512, 512, 256, 1]], # 13# up-concat merge[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],[[-1, 5], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P3# elan-2 block[-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [256, 256, 128, 1]], # 16 (P3/8-small)# avg-conv-down merge[-1, 1, ADown, [256]],[[-1, 13], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P4# elan-2 block[-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [512, 512, 256, 1]], # 19 (P4/16-medium)# avg-conv-down merge[-1, 1, ADown, [512]],[[-1, 10], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P5# elan-2 block[-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [512, 512, 256, 1]], # 22 (P5/32-large)# multi-level reversible auxiliary branch# routing[5, 1, CBLinear, [[256]]], # 23[7, 1, CBLinear, [[256, 512]]], # 24[9, 1, CBLinear, [[256, 512, 512]]], # 25# conv down[0, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]], # 26-P1/2# conv down[-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]], # 27-P2/4# elan-1 block[-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [256, 128, 64, 1]], # 28# avg-conv down fuse[-1, 1, ADown, [256]], # 29-P3/8[[23, 24, 25, -1], 1, CBFuse, [[0, 0, 0]]], # 30 # elan-2 block[-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [512, 256, 128, 1]], # 31# avg-conv down fuse[-1, 1, ADown, [512]], # 32-P4/16[[24, 25, -1], 1, CBFuse, [[1, 1]]], # 33 # elan-2 block[-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [512, 512, 256, 1]], # 34# avg-conv down fuse[-1, 1, ADown, [512]], # 35-P5/32[[25, -1], 1, CBFuse, [[2]]], # 36# elan-2 block[-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [512, 512, 256, 1]], # 37[-1, 1, DySnakeConv, [512]], # 38# detection head# detect[[31, 34, 38, 16, 19, 22], 1, DualDDetect, [nc]], # DualDDetect(A3, A4, A5, P3, P4, P5)]
3.4 训练过程
欢迎关注!
相关文章:

YOLOv9有效改进|使用动态蛇形卷积Dynamic Snake Convolution
专栏介绍:YOLOv9改进系列 | 包含深度学习最新创新,主力高效涨点!!! 一、改进点介绍 使用ICCV2023中的动态蛇形卷积替换YOLOv9网络中的Conv模块。 二、Dynamic Snake Convolution模块详解 2.1 模块简介 应用场景&#x…...

设计模式学习笔记 - 设计原则 - 1.单一职责原则
前言 前面我们提到过 SOLID 原则,实际上 SOLID 由 5 个设计原则组成,分别是:单一职责原则、开闭原则、里氏替换原则、接口隔离原则和依赖反转原则。它们分别对应 SLOID 中的 S、O、L、I、D 这 5 个英文字母。 今天来学习下 SOLID 原则中的第…...
飞天使-学以致用-devops知识点4-SpringBoot项目CICD实现(实验失败,了解大概流程)
文章目录 代码准备创建jenkins 任务测试推送使用项目里面的jenkinsfile 进行升级操作 文字版本流程项目构建 代码准备 推送代码到gitlab 代码去叩叮狼教育找 k8s 创建jenkins 任务 创建一个k8s-cicd-demo 流水线任务 将jenkins 里面构建时候的地址还有token, 给到…...
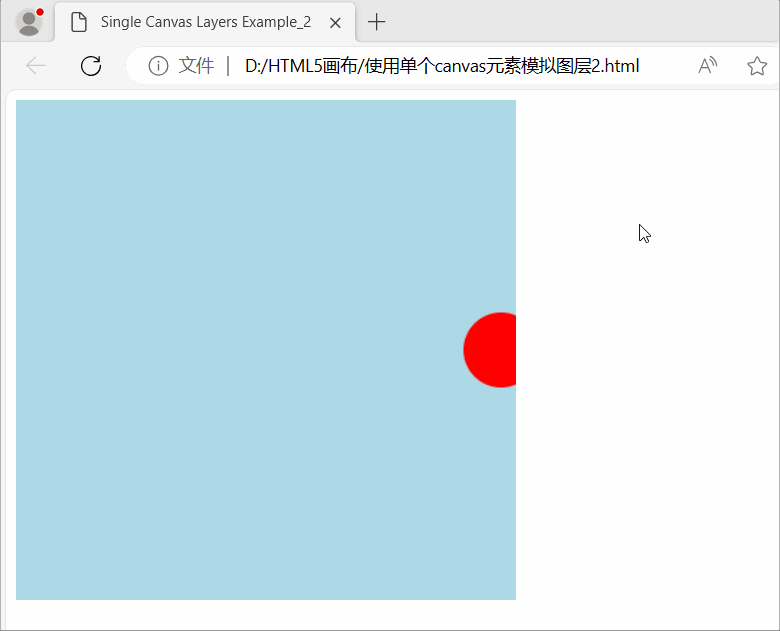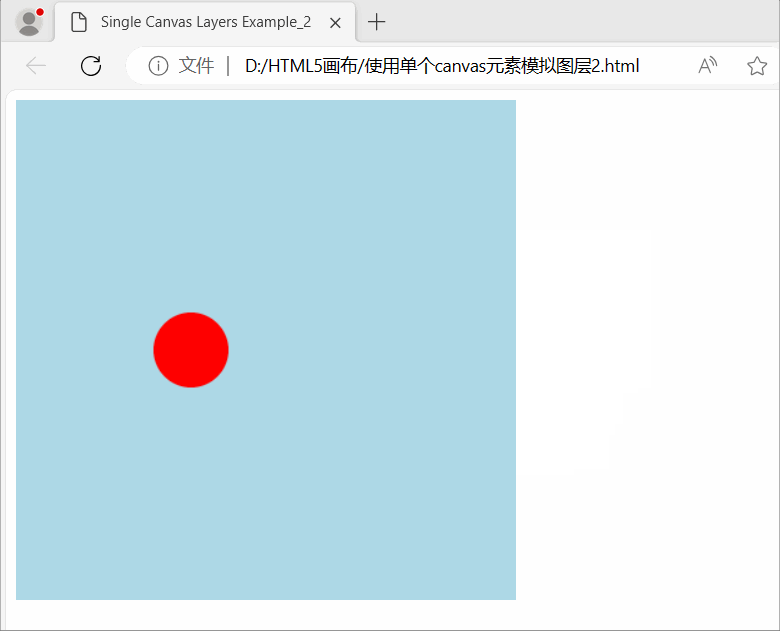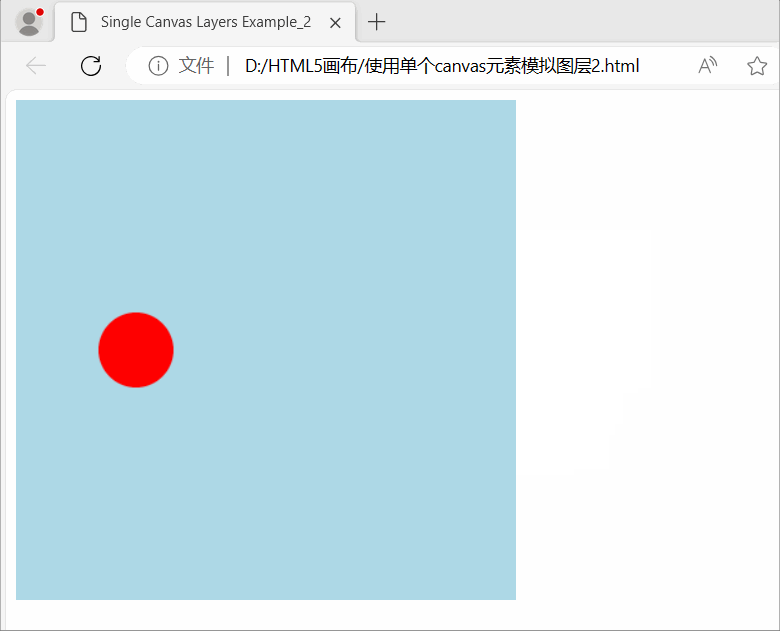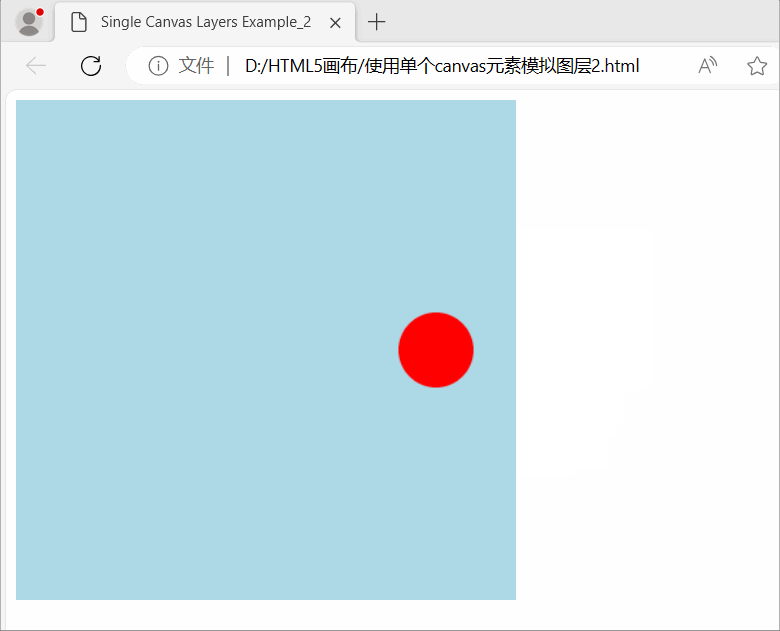
使用HTML5画布(Canvas)模拟图层(Layers)效果
使用HTML5画布(Canvas)模拟图层(Layers)效果 在图形处理和计算机图形学中,图层(Layers)是指将图像分成不同的可独立编辑、组合和控制的部分的技术或概念。每个图层都可以包含不同的图形元素、效…...

违背祖训,微软骚操作强制用户更新至 Win 11 23H2
话说,大伙儿有让 Windows 操作系统一直保持最新版习惯吗? 根据以往惯例,Windows 系统更新是个比较玄学的存在,谁也不能保证随手更新后会不会出现什么奇葩 Bug。 因此对于不少同学来说,Windows 更新到一个稳定版本后&a…...
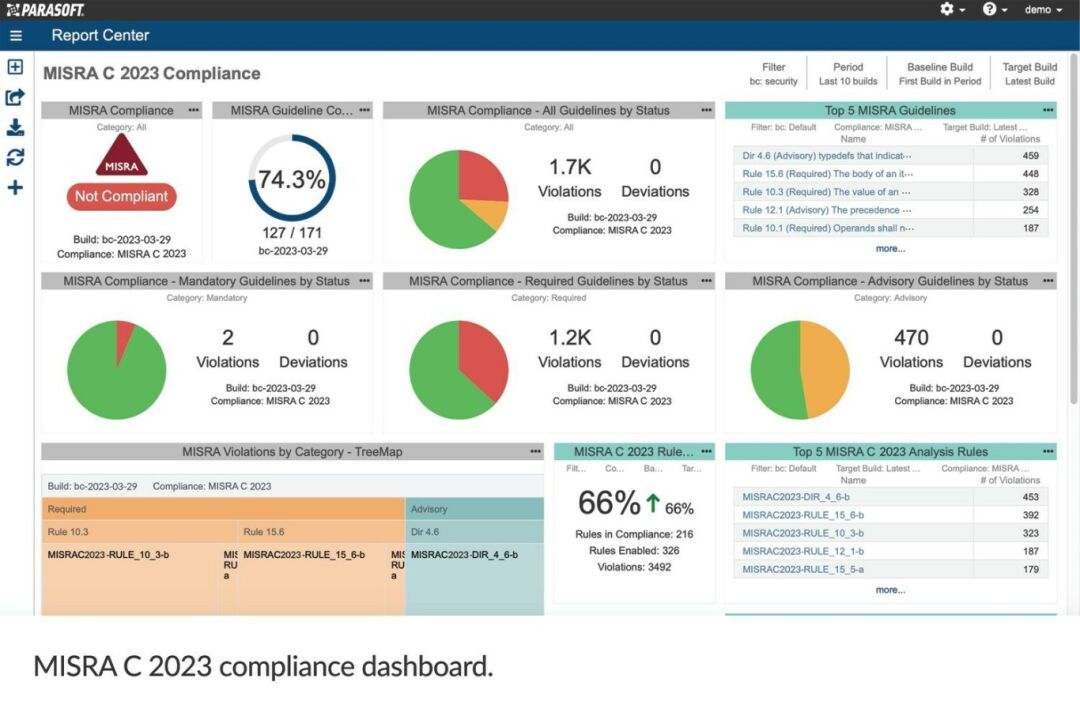
MISRA C++ 2023指南:您需要了解的一切
MISRA C 2023可以帮助使用现代C语言的组织开发安全关键型软件。使用新的MISRA标准,开发人员可以通过确保和记录其软件应用程序的MISRA合规性,满足IEC 6108或ISO 26262等功能安全标准给出的静态分析要求。 什么是MISRA C2023? 以便使用C17进行安全可靠…...
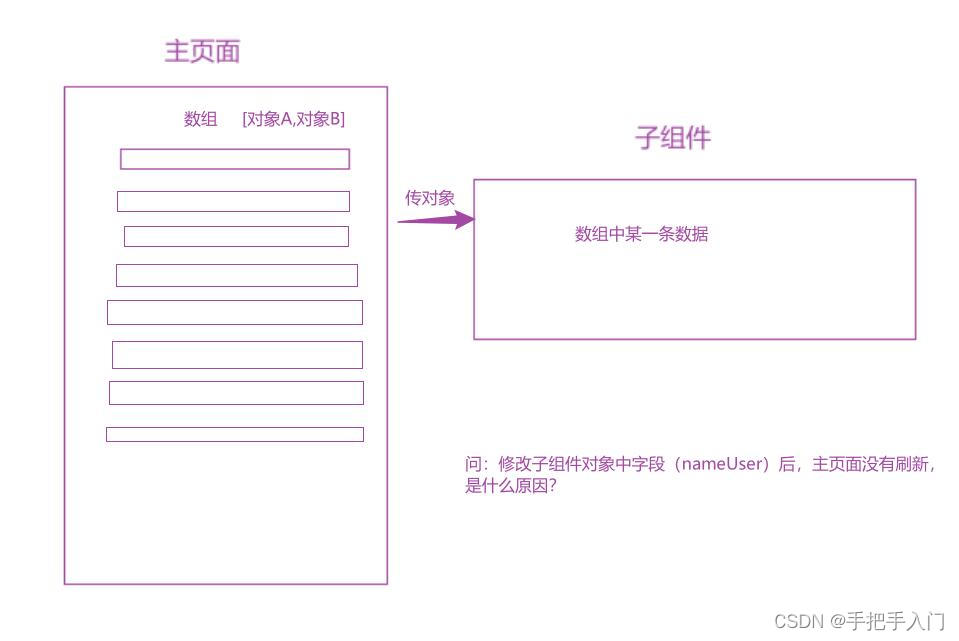
Vue:【亲测可用】父组件数组包对象,传给子组件对象,子组件修改属性(字段)后,父组件没有更新
场景:vue中父组件数组包对象,传给子组件对象,子组件修改属性(字段)后,父组件没有更新 代码: # 父组件 <div v-for"(object, name, index) in arr" :key"index"><…...

hbase学习十:客户端实现与Meta表解析
1、客户端实现 hbase社区的客户端一般是java客户端。 HBase也支持Shell交互式客户端。Shell客户端实质是用JRuby(用Java编写的Ruby解释器,方便Ruby脚本跑在JVM虚拟机上)脚本调用官方HBase客户端来实现的。因此,各种客户端的核心实现都在社区Java版本客户端上。 客户端访…...
《OpenScene: 3D Scene Understanding with Open Vocabularies》阅读笔记1
传统的3D场景理解方法依赖于带标签的3D数据集,用于训练一个模型以进行单一任务的监督学习。我们提出了OpenScene,一种替代方法,其中模型在CLIP特征空间中预测与文本和图像像素共同嵌入的3D场景点的密集特征。这种零样本方法实现了与任务无关的训练和开放词汇查询。例如,为了…...

数据结构 - Trie树(字符串统计、最大异或对)
文章目录 前言Part 1:Trie字符串统计1.题目描述输入格式输出格式数据范围输入样例输出样例 2.算法 Part 2:最大异或对1.题目描述输入格式输出格式数据范围输入样例输出样例 2.算法 前言 本篇博客将介绍Trie树的常见应用,包括:Trie…...
2. vue 工程创建
1. 基于 vite创建 官方文档: https://v3.cn.vuejs.org/guide/installation.html#vite vite官网: https://vitejs.cn 使用vite创建的优势: 开发环境中,无需打包操作,可快速的冷启动。轻量快速的热重载(HMR)。真正的按需编译,不再…...

2024绿色能源、城市规划与环境国际会议(ICGESCE 2024)
2024绿色能源、城市规划与环境国际会议(ICGESCE 2024) 一、【会议简介】 随着全球气候变化和环境问题日益严重,绿色能源和可持续发展已成为全球关注的焦点。本次会议旨在汇聚全球在绿色能源、城市规划与环境领域的专家、学者和实践者,共同探讨和分享关于…...
0门槛电子画册制作
电子画册制作,门槛低至零,也可以制作出如此精美的电子画册吗?别担心,这个问题早已解决,今天就教你如何0门槛制作电子画册。 选择合适的企业宣传册制作软件,如FLBOOK在线制作电子杂志平台等。这个工具提供…...
C语言----冒泡排序进阶
冒泡排序大家应该到写过吧。但大家可能知道到的冒泡排序有两种方法。而我呢,最近学习到了另外一种方法,现在知道三种方法了。所以想与大家分享一下。但是缺点是第三种是第二种的自实现版。第一种就是我们平常写的普通冒泡排序。第二种就是qsort。第三种就…...
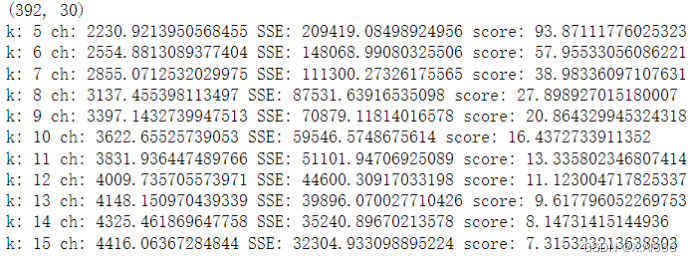
【机器学习】实验5,AAAI 会议论文聚类分析
本次实验以AAAI 2014会议论文数据为基础,要求实现或调用无监督聚类算法,了解聚类方法。 任务介绍 每年国际上召开的大大小小学术会议不计其数,发表了非常多的论文。在计算机领域的一些大型学术会议上,一次就可以发表涉及各个方向…...
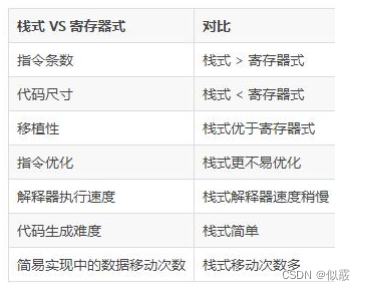
安卓虚拟机ART和Dalvik
目录 一、JVM和Dalvik1.1 基于栈的虚拟机字节码指令执行过程 1.2 基于寄存器的虚拟机 二、ART与Dalvikdex2aotAndroid N的运作方式 三、总结 一、JVM和Dalvik Android应用程序运行在Dalvik/ART虚拟机,并且每一个应用程序对应有一个单独的Dalvik虚拟机实例。 Dalvik…...
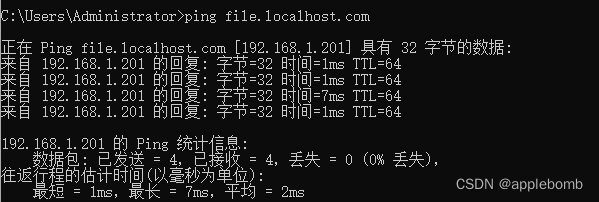
OPENWRT本地局域网模拟域名多IP
本地配置MINIO服务时,会遇到域名多IP的需求。当某一个节点失效时,可以通过域名访问平滑过渡到其它的节点继续服务。 【MINIO搭建过程略】 搭建完毕后,有4个节点,对应的docker搭建命令: docker run --nethost --rest…...
今日学习总结2024.3.2
最近的学习状态比较好,感觉非常享受知识进入脑子的过程,有点上头。 实验室一个星期唯一一天的假期周六,也就是今天,也完全不想放假出去玩啊,在实验室泡了一天。 很后悔之前胆小,没有提前投简历找实习&…...

Java虚拟机(JVM)从入门到实战【上】
Java虚拟机(JVM)从入门到实战【上】,涵盖类加载,双亲委派机制,垃圾回收器及算法等知识点,全系列6万字。 一、基础篇 P1 Java虚拟机导学课程 P2 初识JVM 什么是JVM Java Virtual Machine 是Java虚拟机。…...
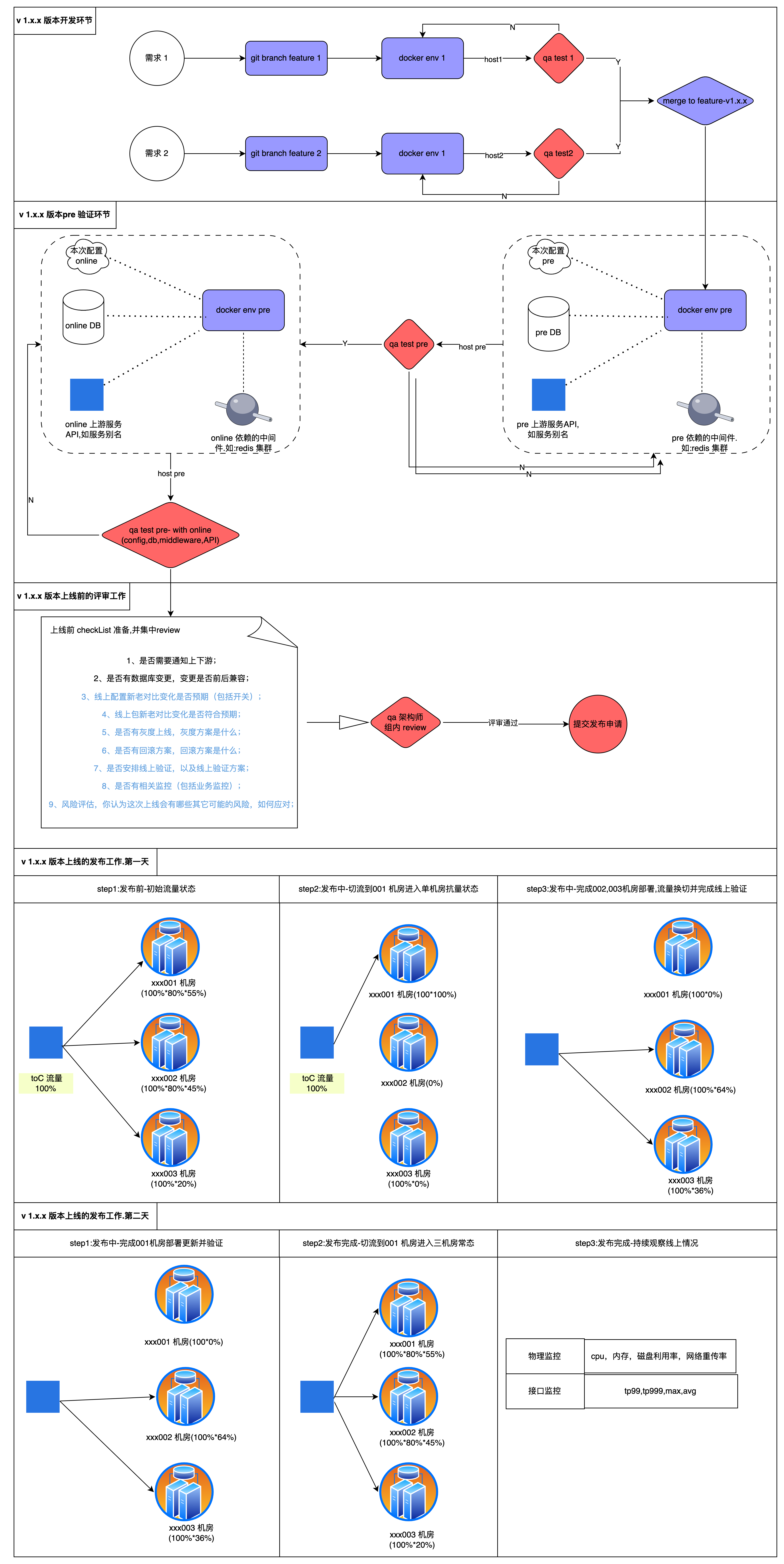
SaaS 电商设计 (九) 动态化且易扩展的实现购物车底部弹层(附:一套普适的线上功能切量的发布方案)
目录 一.背景1.1 业务背景1.2 技术负债 二.技术目标三.方案设计3.1 解决移动端频繁发版3.1.1 场景分析3.1.2 技术方案 3.2 减少后端坏味道代码&无法灵活扩展问题3.2.1 通过抽象接口完成各自单独楼层渲染逻辑3.2.2 通过配置能力做到部分字段可配 四.升级上线(普适于高并发大…...

超短脉冲激光自聚焦效应
前言与目录 强激光引起自聚焦效应机理 超短脉冲激光在脆性材料内部加工时引起的自聚焦效应,这是一种非线性光学现象,主要涉及光学克尔效应和材料的非线性光学特性。 自聚焦效应可以产生局部的强光场,对材料产生非线性响应,可能…...
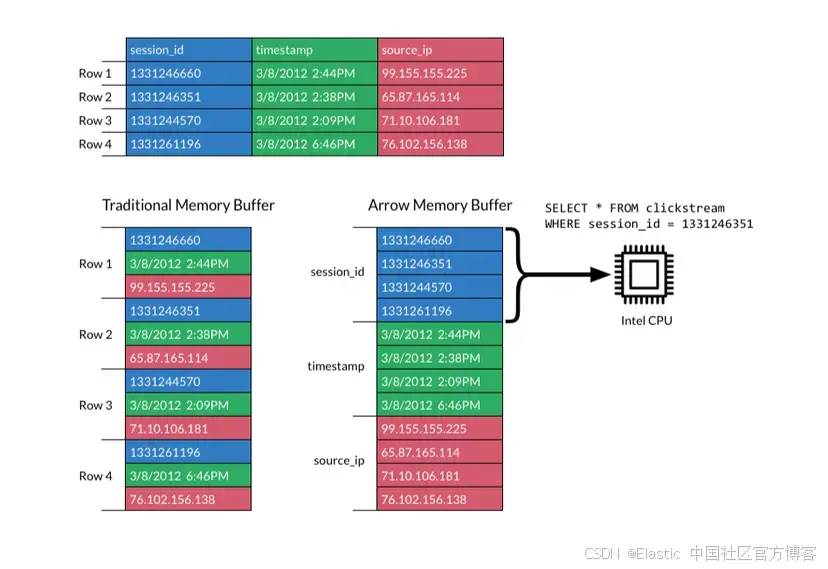
JavaScript 中的 ES|QL:利用 Apache Arrow 工具
作者:来自 Elastic Jeffrey Rengifo 学习如何将 ES|QL 与 JavaScript 的 Apache Arrow 客户端工具一起使用。 想获得 Elastic 认证吗?了解下一期 Elasticsearch Engineer 培训的时间吧! Elasticsearch 拥有众多新功能,助你为自己…...

多场景 OkHttpClient 管理器 - Android 网络通信解决方案
下面是一个完整的 Android 实现,展示如何创建和管理多个 OkHttpClient 实例,分别用于长连接、普通 HTTP 请求和文件下载场景。 <?xml version"1.0" encoding"utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android"http://schemas…...

鸿蒙中用HarmonyOS SDK应用服务 HarmonyOS5开发一个医院挂号小程序
一、开发准备 环境搭建: 安装DevEco Studio 3.0或更高版本配置HarmonyOS SDK申请开发者账号 项目创建: File > New > Create Project > Application (选择"Empty Ability") 二、核心功能实现 1. 医院科室展示 /…...
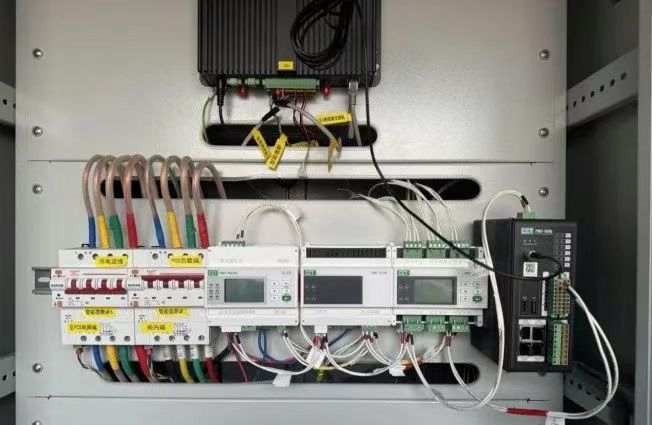
IT供电系统绝缘监测及故障定位解决方案
随着新能源的快速发展,光伏电站、储能系统及充电设备已广泛应用于现代能源网络。在光伏领域,IT供电系统凭借其持续供电性好、安全性高等优势成为光伏首选,但在长期运行中,例如老化、潮湿、隐裂、机械损伤等问题会影响光伏板绝缘层…...
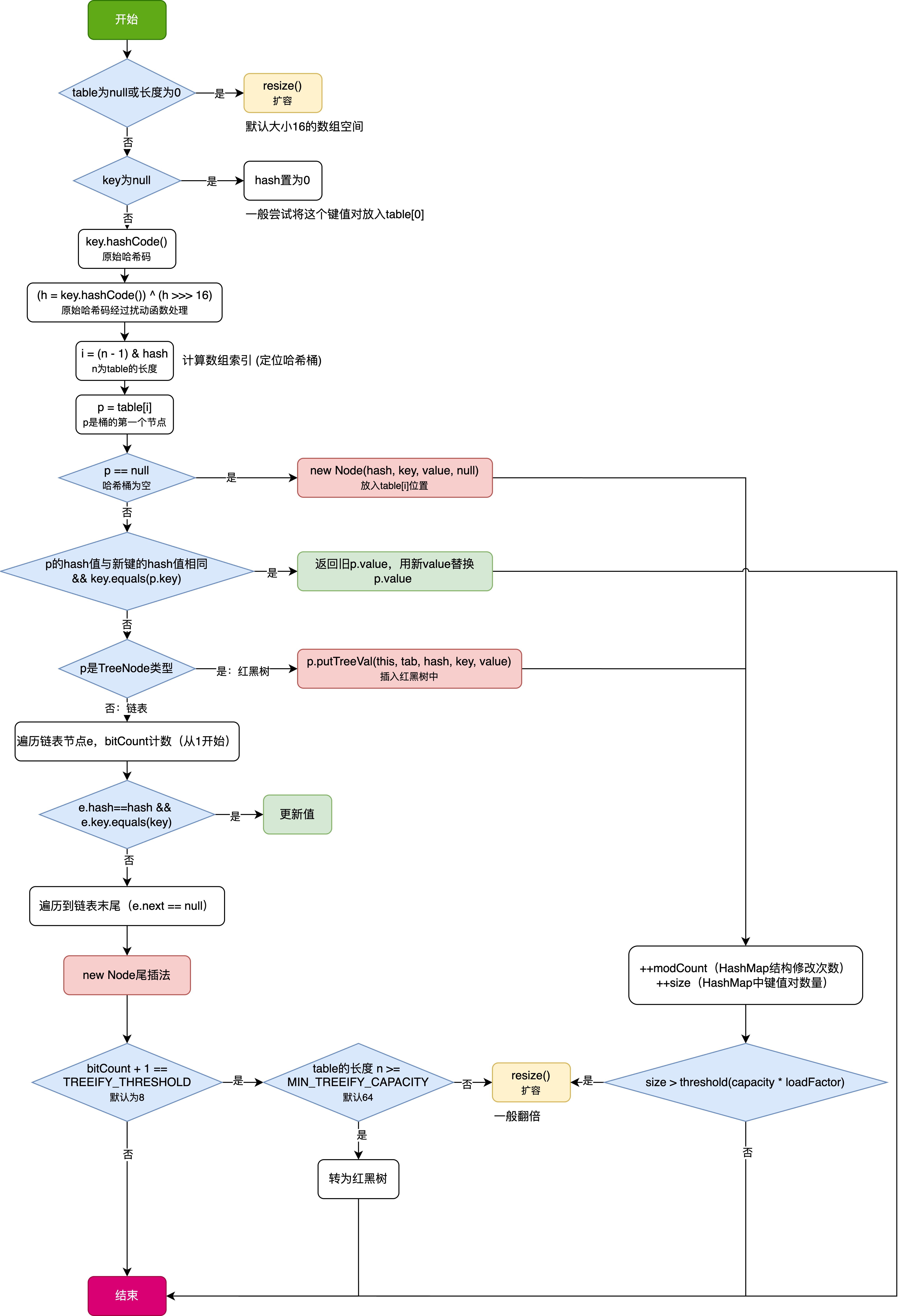
HashMap中的put方法执行流程(流程图)
1 put操作整体流程 HashMap 的 put 操作是其最核心的功能之一。在 JDK 1.8 及以后版本中,其主要逻辑封装在 putVal 这个内部方法中。整个过程大致如下: 初始判断与哈希计算: 首先,putVal 方法会检查当前的 table(也就…...
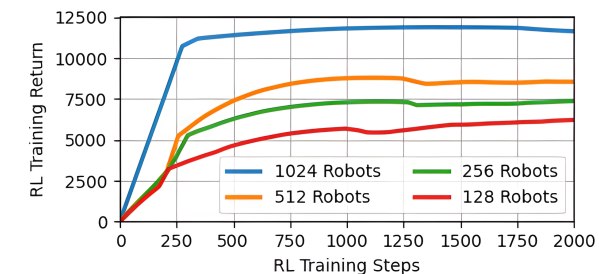
【VLNs篇】07:NavRL—在动态环境中学习安全飞行
项目内容论文标题NavRL: 在动态环境中学习安全飞行 (NavRL: Learning Safe Flight in Dynamic Environments)核心问题解决无人机在包含静态和动态障碍物的复杂环境中进行安全、高效自主导航的挑战,克服传统方法和现有强化学习方法的局限性。核心算法基于近端策略优化…...

SQL慢可能是触发了ring buffer
简介 最近在进行 postgresql 性能排查的时候,发现 PG 在某一个时间并行执行的 SQL 变得特别慢。最后通过监控监观察到并行发起得时间 buffers_alloc 就急速上升,且低水位伴随在整个慢 SQL,一直是 buferIO 的等待事件,此时也没有其他会话的争抢。SQL 虽然不是高效 SQL ,但…...

十九、【用户管理与权限 - 篇一】后端基础:用户列表与角色模型的初步构建
【用户管理与权限 - 篇一】后端基础:用户列表与角色模型的初步构建 前言准备工作第一部分:回顾 Django 内置的 `User` 模型第二部分:设计并创建 `Role` 和 `UserProfile` 模型第三部分:创建 Serializers第四部分:创建 ViewSets第五部分:注册 API 路由第六部分:后端初步测…...
【Veristand】Veristand环境安装教程-Linux RT / Windows
首先声明,此教程是针对Simulink编译模型并导入Veristand中编写的,同时需要注意的是老用户编译可能用的是Veristand Model Framework,那个是历史版本,且NI不会再维护,新版本编译支持为VeriStand Model Generation Suppo…...
