AtCoder Beginner Contest 347 (ABCDEF题)视频讲解
A - Divisible
Problem Statement
You are given positive integers N N N and K K K, and a sequence of length N N N, A = ( A 1 , A 2 , … , A N ) A=(A_1,A_2,\ldots,A_N) A=(A1,A2,…,AN).
Extract all elements of A A A that are multiples of K K K, divide them by K K K, and print the quotients.
Constraints
1 ≤ N , K ≤ 100 1\leq N,K\leq 100 1≤N,K≤100
KaTeX parse error: Expected 'EOF', got '&' at position 11: 1\leq A_1 &̲lt; A_2 < \l…
A A A has at least one multiple of K K K.
All given numbers are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N N N K K K
A 1 A_1 A1 A 2 A_2 A2 … \ldots … A N A_N AN
Output
Divide all elements of A A A that are multiples of K K K and print the quotients in ascending order with spaces in between.
Sample Input 1
5 2
2 5 6 7 10
Sample Output 1
1 3 5
The multiples of 2 2 2 among the elements in A A A are 2 2 2, 6 6 6, and 10 10 10. Divide them by 2 2 2 to get 1 1 1, 3 3 3, and 5 5 5, and print them in ascending order with spaces in between.
Sample Input 2
3 1
3 4 7
Sample Output 2
3 4 7
Sample Input 3
5 10
50 51 54 60 65
Sample Output 3
5 6
Solution
具体见文末视频。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define int long longusing namespace std;typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;signed main() {cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);ios::sync_with_stdio(0);int n, k;cin >> n >> k;std::vector<int> a(n);for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {cin >> a[i];if (a[i] % k == 0)cout << a[i] / k << " ";}return 0;
}
B - Substring
Problem Statement
You are given a string S S S consisting of lowercase English letters. How many different non-empty substrings does S S S have?
A substring is a contiguous subsequence. For example, xxx is a substring of yxxxy but not of xxyxx.
Constraints
S S S is a string of length between 1 1 1 and 100 100 100, inclusive, consisting of lowercase English letters.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
S S S
Output
Print the answer.
Sample Input 1
yay
Sample Output 1
5
S S S has the following five different non-empty substrings:
a
y
ay
ya
yay
Sample Input 2
aababc
Sample Output 2
17
Sample Input 3
abracadabra
Sample Output 3
54
Solution
具体见文末视频。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define int long longusing namespace std;typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;signed main() {cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);ios::sync_with_stdio(0);string s;cin >> s;int n = s.size();set<string> res;for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++)for (int j = 1; j <= n - i; j ++)res.insert(s.substr(i, j));cout << res.size() << endl;return 0;
}
C - Ideal Holidays
Problem Statement
In the Kingdom of AtCoder, a week consists of A + B A+B A+B days, with the first through A A A-th days being holidays and the ( A + 1 ) (A+1) (A+1)-th through ( A + B ) (A+B) (A+B)-th being weekdays.
Takahashi has N N N plans, and the i i i-th plan is scheduled D i D_i Di days later.
He has forgotten what day of the week it is today. Determine if it is possible for all of his N N N plans to be scheduled on holidays.
Constraints
1 ≤ N ≤ 2 × 1 0 5 1\leq N\leq 2\times 10^5 1≤N≤2×105
1 ≤ A , B ≤ 1 0 9 1\leq A,B\leq 10^9 1≤A,B≤109
KaTeX parse error: Expected 'EOF', got '&' at position 10: 1\leq D_1&̲lt;D_2<\ldot…
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N N N A A A B B B
D 1 D_1 D1 D 2 D_2 D2 … \ldots … D N D_N DN
Output
Print Yes in a single line if it is possible for all of Takahashi’s N N N plans to be scheduled on holidays, and No otherwise.
Sample Input 1
3 2 5
1 2 9
Sample Output 1
Yes
In this input, a week consists of seven days, with the first through second days being holidays and the third through seventh days being weekdays.
Let us assume today is the seventh day of the week. In this case, one day later would be the first day of the week, two days later would be the second day of the week, and nine days later would also be the second day of the week, making all plans scheduled on holidays. Therefore, it is possible for all of Takahashi’s N N N plans to be scheduled on holidays.
Sample Input 2
2 5 10
10 15
Sample Output 2
No
Sample Input 3
4 347 347
347 700 705 710
Sample Output 3
Yes
Solution
具体见文末视频。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define int long longusing namespace std;typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;const int N = 2e5 + 10;int n, a, b;
int d[N];signed main() {cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin >> n >> a >> b;int l1 = -1e18, r1 = 1e18, l2 = -1e18, r2 = 1e18;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {cin >> d[i];d[i] %= (a + b);int tl = (0 - d[i] + a + b) % (a + b), tr = (a - 1 - d[i] + a + b) % (a + b);if (tl > tr) {l1 = max(0ll, l1), r1 = min(r1, tr);l2 = max(l2, tl), r2 = min(a + b - 1, r2);} elsel1 = max(l1, tl), r1 = min(r1, tr), l2 = max(l2, tl), r2 = min(r2, tr);}if (l1 <= r1 || l2 <= r2) cout << "Yes" << endl;else cout << "No" << endl;return 0;
}
D - Popcount and XOR
Problem Statement
You are given non-negative integers a a a, b b b, and C C C.
Determine if there is a pair of non-negative integers ( X , Y ) (X, Y) (X,Y) that satisfies all of the following five conditions. If such a pair exists, print one.
KaTeX parse error: Expected 'EOF', got '&' at position 10: 0 \leq X &̲lt; 2^{60}
KaTeX parse error: Expected 'EOF', got '&' at position 10: 0 \leq Y &̲lt; 2^{60}
popcount ( X ) = a \operatorname{popcount}(X) = a popcount(X)=a
popcount ( Y ) = b \operatorname{popcount}(Y) = b popcount(Y)=b
X ⊕ Y = C X \oplus Y = C X⊕Y=C
Here, ⊕ \oplus ⊕ denotes the bitwise XOR.
If multiple pairs ( X , Y ) (X, Y) (X,Y) satisfy the conditions, you may print any of them.
1101, so $\operatorname{popcount}(13)=3$. What is bitwise XOR? For non-negative integers $x, y$, the bitwise exclusive OR $x \oplus y$ is defined as follows. The $2^k$'s place $\ (k\geq0)$ in the binary representation of $x \oplus y$ is $1$ if exactly one of the $2^k$'s places $\ (k\geq0)$ in the binary representations of $x$ and $y$ is $1$, and $0$ otherwise. For example, $9$ and $3$ in binary are
1001 and
0011, respectively, so $9 \oplus 3 = 10$ (in binary,
1010). #### Constraints
0 ≤ a ≤ 60 0 \leq a \leq 60 0≤a≤60
0 ≤ b ≤ 60 0 \leq b \leq 60 0≤b≤60
KaTeX parse error: Expected 'EOF', got '&' at position 10: 0 \leq C &̲lt; 2^{60}
All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
a a a b b b C C C
Output
If there is a pair of non-negative integers that satisfies the conditions, choose one such pair ( X , Y ) (X, Y) (X,Y) and print X X X and Y Y Y in this order, with a space in between.
If no such pair exists, print -1.
Sample Input 1
3 4 7
Sample Output 1
28 27
The pair ( X , Y ) = ( 28 , 27 ) (X, Y) = (28, 27) (X,Y)=(28,27) satisfies the conditions.
Here, X X X and Y Y Y in binary are 11100 and 11011, respectively.
X X X in binary is 11100, so popcount ( X ) = 3 \operatorname{popcount}(X) = 3 popcount(X)=3.
Y Y Y in binary is 11011, so popcount ( Y ) = 4 \operatorname{popcount}(Y) = 4 popcount(Y)=4.
X ⊕ Y X \oplus Y X⊕Y in binary is 00111, so X ⊕ Y = 7 X \oplus Y = 7 X⊕Y=7.
If multiple pairs of non-negative integers satisfy the conditions, you may print any of them, so printing 42 45, for example, would also be accepted.
Sample Input 2
34 56 998244353
Sample Output 2
-1
No pair of non-negative integers satisfies the conditions.
Sample Input 3
39 47 530423800524412070
Sample Output 3
540431255696862041 10008854347644927
Note that the values to be printed may not fit in 32 32 32-bit integers.
Solution
具体见文末视频。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define int long longusing namespace std;typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;signed main() {cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);ios::sync_with_stdio(0);int a, b, c;cin >> a >> b >> c;int r1 = 0, r2 = 0;for (int i = 0; i < 61; i ++)if (c >> i & 1) {if (a > b) r1 += (1ll << i), a --;else r2 += (1ll << i), b --;}if (a != b || a < 0 || b < 0) {cout << -1 << endl;return 0;}for (int i = 0; i < 61; i ++)if (!(c >> i & 1) && a && b)r1 += (1ll << i), r2 += (1ll << i), a --, b --;if (a || b) {cout << -1 << endl;return 0;}cout << r1 << " " << r2 << endl;return 0;
}
E - Set Add Query
Problem Statement
There is an integer sequence A = ( A 1 , A 2 , … , A N ) A=(A_1,A_2,\ldots,A_N) A=(A1,A2,…,AN) of length N N N, where all elements are initially set to 0 0 0. Also, there is a set S S S, which is initially empty.
Perform the following Q Q Q queries in order. Find the value of each element in the sequence A A A after processing all Q Q Q queries. The i i i-th query is in the following format:
An integer x i x_i xi is given. If the integer x i x_i xi is contained in S S S, remove x i x_i xi from S S S. Otherwise, insert x i x_i xi to S S S. Then, for each j = 1 , 2 , … , N j=1,2,\ldots,N j=1,2,…,N, add ∣ S ∣ |S| ∣S∣ to A j A_j Aj if j ∈ S j\in S j∈S.
Here, ∣ S ∣ |S| ∣S∣ denotes the number of elements in the set S S S. For example, if S = { 3 , 4 , 7 } S=\lbrace 3,4,7\rbrace S={3,4,7}, then ∣ S ∣ = 3 |S|=3 ∣S∣=3.
Constraints
1 ≤ N , Q ≤ 2 × 1 0 5 1\leq N,Q\leq 2\times10^5 1≤N,Q≤2×105
1 ≤ x i ≤ N 1\leq x_i\leq N 1≤xi≤N
All given numbers are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N N N Q Q Q
x 1 x_1 x1 x 2 x_2 x2 … \ldots … x Q x_Q xQ
Output
Print the sequence A A A after processing all queries in the following format:
A 1 A_1 A1 A 2 A_2 A2 … \ldots … A N A_N AN
Sample Input 1
3 4
1 3 3 2
Sample Output 1
6 2 2
In the first query, 1 1 1 is inserted to S S S, making S = { 1 } S=\lbrace 1\rbrace S={1}. Then, ∣ S ∣ = 1 |S|=1 ∣S∣=1 is added to A 1 A_1 A1. The sequence becomes A = ( 1 , 0 , 0 ) A=(1,0,0) A=(1,0,0).
In the second query, 3 3 3 is inserted to S S S, making S = { 1 , 3 } S=\lbrace 1,3\rbrace S={1,3}. Then, ∣ S ∣ = 2 |S|=2 ∣S∣=2 is added to A 1 A_1 A1 and A 3 A_3 A3. The sequence becomes A = ( 3 , 0 , 2 ) A=(3,0,2) A=(3,0,2).
In the third query, 3 3 3 is removed from S S S, making S = { 1 } S=\lbrace 1\rbrace S={1}. Then, ∣ S ∣ = 1 |S|=1 ∣S∣=1 is added to A 1 A_1 A1. The sequence becomes A = ( 4 , 0 , 2 ) A=(4,0,2) A=(4,0,2).
In the fourth query, 2 2 2 is inserted to S S S, making S = { 1 , 2 } S=\lbrace 1,2\rbrace S={1,2}. Then, ∣ S ∣ = 2 |S|=2 ∣S∣=2 is added to A 1 A_1 A1 and A 2 A_2 A2. The sequence becomes A = ( 6 , 2 , 2 ) A=(6,2,2) A=(6,2,2).
Eventually, the sequence becomes A = ( 6 , 2 , 2 ) A=(6,2,2) A=(6,2,2).
Sample Input 2
4 6
1 2 3 2 4 2
Sample Output 2
15 9 12 7
Solution
具体见文末视频。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define int long longusing namespace std;typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;const int N = 2e5 + 10;int n, q;
int a[N], s[N], res[N], id[N];
int cnt[N], lst[N];signed main() {cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin >> n >> q;int idx = 0;for (int i = 1; i <= q; i ++) {cin >> a[i];if (!id[a[i]]) id[a[i]] = ++ idx;}set<int> S;int r = 0;for (int i = 1; i <= q; i ++) {cnt[a[i]] ++;if (S.count(a[i])) S.erase(a[i]);else S.insert(a[i]);s[i] = s[i - 1] + S.size();r = max(id[a[i]], r);if (S.size()) res[1] += S.size(), res[r + 1] -= S.size();}for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)res[i] += res[i - 1], lst[i] = q;for (int i = q; i >= 1; i --) {if (cnt[a[i]] % 2 == 0) {res[id[a[i]]] -= (s[lst[a[i]]] - s[i - 1]);} else {lst[a[i]] = i - 1;}cnt[a[i]] --;}for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)cout << res[id[i]] << " ";return 0;
}
F - Non-overlapping Squares
Problem Statement
There is an N × N N\times N N×N grid, and the cell at the i i i-th row from the top and the j j j-th column from the left ( 1 ≤ i , j ≤ N ) (1\leq i,j\leq N) (1≤i,j≤N) contains the integer A i , j A _ {i,j} Ai,j.
You are given an integer M M M. When choosing three non-overlapping M × M M\times M M×M grids, find the maximum possible sum of the integers written in the chosen grids.
2 ≤ N ≤ 1000 2\leq N\leq 1000 2≤N≤1000
1 ≤ M ≤ N / 2 1\leq M\leq N/2 1≤M≤N/2
0 ≤ A i , j ≤ 1 0 9 0\leq A _ {i,j}\leq10 ^ 9 0≤Ai,j≤109
All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N N N M M M
A 1 , 1 A _ {1,1} A1,1 A 1 , 2 A _ {1,2} A1,2 … \ldots … A 1 , N A _ {1,N} A1,N
A 2 , 1 A _ {2,1} A2,1 A 2 , 2 A _ {2,2} A2,2 … \ldots … A 2 , N A _ {2,N} A2,N
⋮ \vdots ⋮ ⋮ \ \vdots ⋮ ⋱ \ddots ⋱ ⋮ \vdots ⋮
A N , 1 A _ {N,1} AN,1 A N , 2 A _ {N,2} AN,2 … \ldots … A N , N A _ {N,N} AN,N
Output
Print the answer.
Sample Input 1
7 3
3 1 4 1 5 9 2
6 5 3 5 8 9 7
9 3 2 3 8 4 6
2 6 4 3 3 8 3
2 7 9 5 0 2 8
8 4 1 9 7 1 6
9 3 9 9 3 7 5
Sample Output 1
154
From the given grid, if we choose three 3 × 3 3\times3 3×3 grids as shown in the figure below (this corresponds to setting ( i 1 , j 1 , i 2 , j 2 , i 3 , j 3 ) = ( 1 , 5 , 2 , 1 , 5 , 2 ) (i _ 1,j _ 1,i _ 2,j _ 2,i _ 3,j _ 3)=(1,5,2,1,5,2) (i1,j1,i2,j2,i3,j3)=(1,5,2,1,5,2)), the sum of the numbers written in the chosen grids will be 154 154 154.
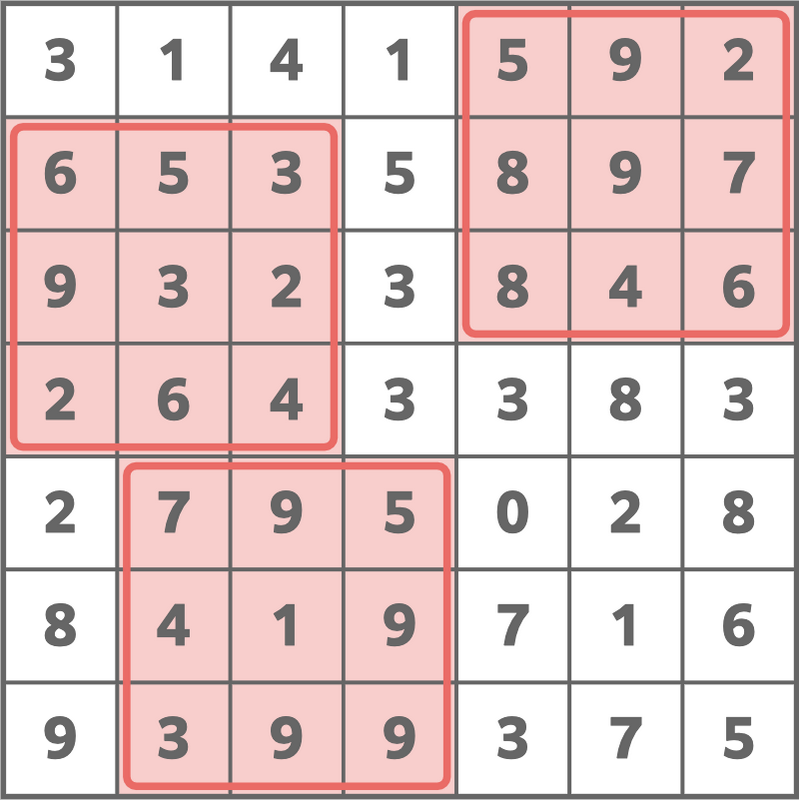
There is no way to make the sum 155 155 155 or greater while satisfying the conditions in the problem statement, so print 154 154 154.
Sample Input 2
7 1
3 1 4 1 5 9 2
6 5 3 5 8 9 7
9 3 2 3 8 4 6
2 6 4 3 3 8 3
2 7 9 5 0 2 8
8 4 1 9 7 1 6
9 3 9 9 3 7 5
Sample Output 2
27
The following choice is optimal.
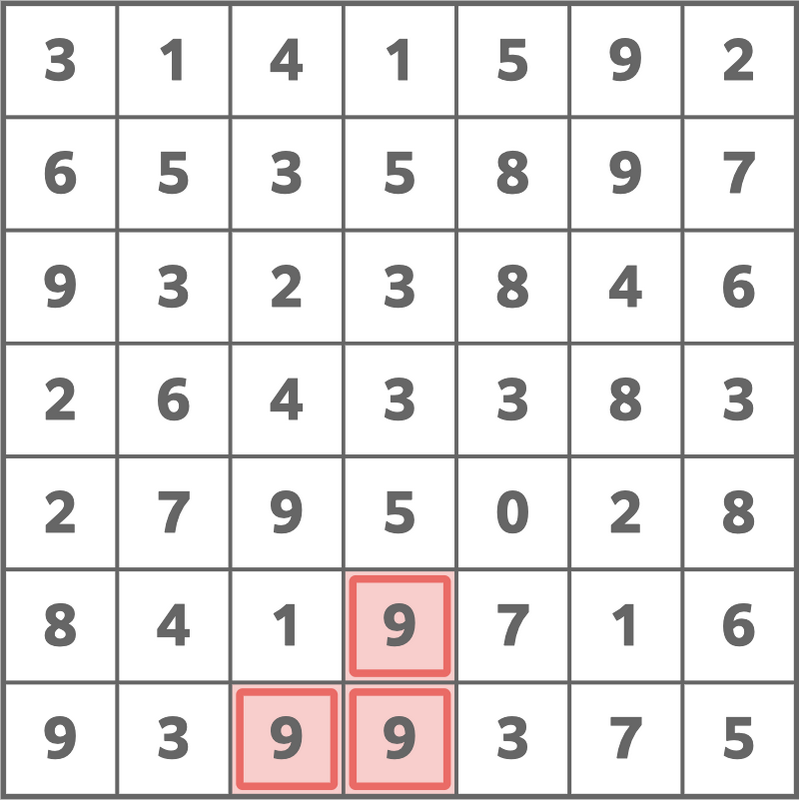
Sample Input 3
16 4
74 16 58 32 97 52 43 51 40 58 13 24 65 11 63 29
98 75 40 77 15 50 83 85 35 46 38 37 56 38 63 55
95 42 10 70 53 40 25 10 70 32 33 19 52 79 74 58
33 91 53 11 65 63 78 77 81 46 81 63 11 82 55 62
39 95 92 69 77 89 14 84 53 78 71 81 66 39 96 29
74 26 60 55 89 35 32 64 17 26 74 92 84 33 59 82
23 69 10 95 94 14 58 58 97 95 62 58 72 55 71 43
93 77 27 87 74 72 91 37 53 80 51 71 37 35 97 46
81 88 26 79 78 30 53 68 83 28 59 28 74 55 20 86
93 13 25 19 53 53 17 24 69 14 67 81 10 19 69 90
88 83 62 92 22 31 27 34 67 48 42 32 68 14 96 87
44 69 25 48 68 42 53 82 44 42 96 31 13 56 68 83
63 87 24 75 16 70 63 99 95 10 63 26 56 12 77 49
94 83 69 95 48 41 40 97 45 61 26 38 83 91 44 31
43 69 54 64 20 60 17 15 62 25 58 50 59 63 88 70
72 95 21 28 41 14 77 22 64 78 33 55 67 51 78 40
Sample Output 3
3295
The following choice is optimal.
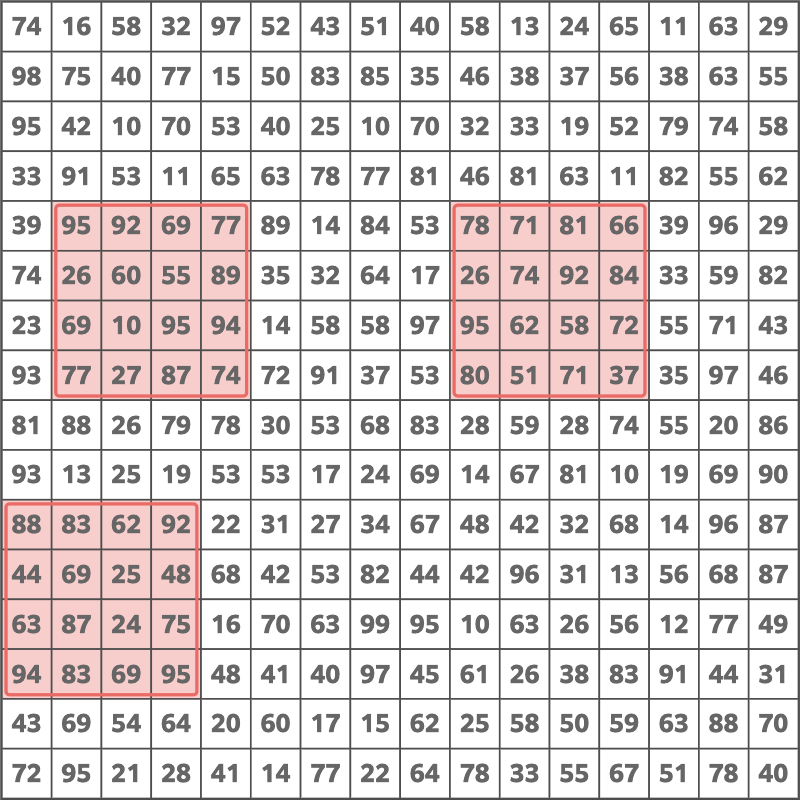
Solution
后期补一下这题目的视频
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define int long longusing namespace std;typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;const int N = 1e3 + 10;int n, m;
int a[N][N], s[N][N], ln[N], cl[N];
int lu[N][N], ld[N][N], ru[N][N], rd[N][N];signed main() {cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin >> n >> m;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++)cin >> a[i][j], a[i][j] += a[i][j - 1] + a[i - 1][j] - a[i - 1][j - 1];for (int i = 1; i <= n - m + 1; i ++)for (int j = 1; j <= n - m + 1; j ++) {s[i][j] = a[i + m - 1][j + m - 1] - a[i - 1][j + m - 1] - a[i + m - 1][j - 1] + a[i - 1][j - 1];ln[i] = max(ln[i], s[i][j]), cl[j] = max(cl[j], s[i][j]);}for (int i = m; i <= n; i ++)for (int j = m; j <= n; j ++)lu[i][j] = max(max(lu[i - 1][j], lu[i][j - 1]), s[i - m + 1][j - m + 1]);for (int i = n - m + 1; i >= 1; i --)for (int j = m; j <= n; j ++)ld[i][j] = max(max(ld[i + 1][j], ld[i][j - 1]), s[i][j - m + 1]);for (int i = m; i <= n; i ++)for (int j = n - m + 1; j >= 1; j --)ru[i][j] = max(max(ru[i - 1][j], ru[i][j + 1]), s[i - m + 1][j]);for (int i = n - m + 1; i >= 1; i --)for (int j = n - m + 1; j >= 1; j --)rd[i][j] = max(max(rd[i + 1][j], rd[i][j + 1]), s[i][j]);int res = 0;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++) {res = max(res, lu[i][j] + ru[i][j + 1] + ld[i + 1][n]);res = max(res, lu[i][j] + ld[i + 1][j] + rd[1][j + 1]);res = max(res, ld[i][j] + rd[i][j + 1] + ru[i - 1][1]);res = max(res, ru[i][j] + rd[i + 1][j] + ld[1][j - 1]);}for (int i = m; i <= n; i ++) {int mx1 = 0, mx2 = 0;for (int j = i + m; j <= n; j ++) {mx1 = max(mx1, ln[j - m + 1]), mx2 = max(mx2, cl[j - m + 1]);res = max(res, ru[i][1] + mx1 + rd[j + 1][1]);res = max(res, ld[1][i] + mx2 + rd[1][j + 1]);}}cout << res << endl;return 0;
}
视频题解
Atcoder Beginner Contest 347(A ~ E 讲解)
欢迎大家关注我的B站空间:https://space.bilibili.com/630340560
最后祝大家早日
相关文章:

AtCoder Beginner Contest 347 (ABCDEF题)视频讲解
A - Divisible Problem Statement You are given positive integers N N N and K K K, and a sequence of length N N N, A ( A 1 , A 2 , … , A N ) A(A_1,A_2,\ldots,A_N) A(A1,A2,…,AN). Extract all elements of A A A that are multiples of K K K, divi…...
【vue2+antvx6】报错Cannot read properties of undefined (reading ‘toUpperCase‘)
我的代码是这样的 <el-collapseref"collapse"v-model"active"accordionclass"collapseStart"change"collapsechange"><el-collapse-item:name"String(index 1)"v-for"(i, index) in List":key"in…...

主流的开发语言、环境及其特点
主流的开发语言及其特点: 1. Python:以其简洁的语法和强大的库支持而闻名,适用于数据科学、人工智能和网络开发等领域。 2. Java:跨平台的编程语言,广泛应用于企业级应用、Android 开发和大型系统开发。 3. C…...

Android知识 - 代码混淆ProGuard规则介绍
ProGuard 的规则及示例 规则概述 ProGuard 是一个代码优化工具,它通过移除未使用的代码、重命名类、字段和方法等方式来减小应用的大小。在 ProGuard 的配置文件中,我们可以定义一系列的规则来控制优化和混淆的过程。 规则语法 ProGuard 的规则通常包…...

【Linux的进程篇章 - 冯诺依曼的体系结构】
Linux学习笔记---005 Linux冯诺依曼体系结构理解1、冯诺依曼体系结构1.1、冯诺依曼体系结构1.2、硬件层面1.3、数据层面1.4、那么冯诺依曼体系能干什么呢? 2、操作系统(Operastor System)2.1、概念2.2、操作系统层的核心功能 3、进程的初步理解 Linux冯诺依曼体系结…...
)
flask-(数据连接池的使用,定制命令,信号的使用,表关系的建立和查询)
文章目录 连接池实例flask定制命令flask 缓存的使用flask信号的使用sqlalchemy原生操作sqlalchemy操作表flask orm操作表一对多的增加和跨表查询 (一对一只需要关联字段加上 ,uniqueTrue)多对多关系的增加和查询多对多基本的增删改查 连接池 import pymy…...
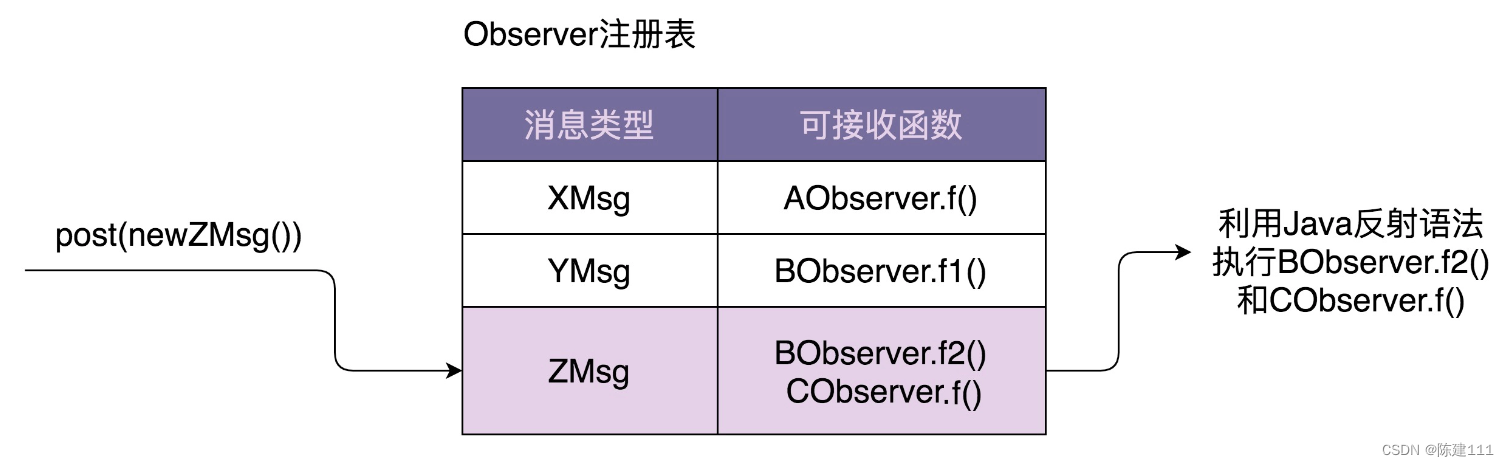
设计模式学习笔记 - 设计模式与范式 -行为型:2.观察者模式(下):实现一个异步非阻塞的EventBus框架
概述 《1.观察者模式(上)》我们学习了观察者模式的原理、实现、应用场景,重点节介绍了不同应用场景下,几种不同的实现方式,包括:同步阻塞、异步非阻塞、进程内、进程间的实现方式。 同步阻塞最经典的实现…...
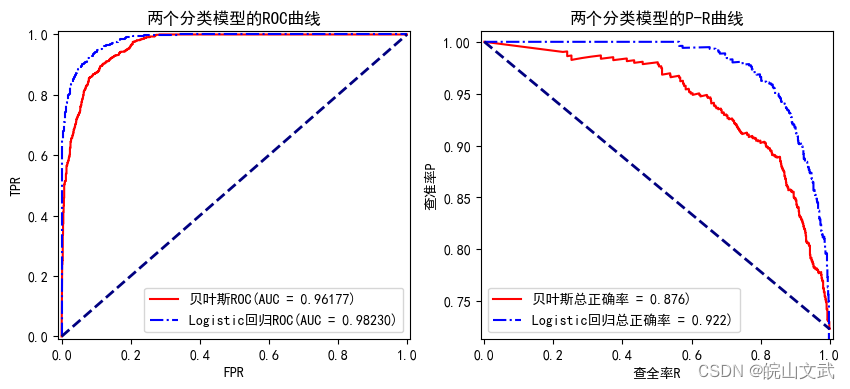
数据挖掘|贝叶斯分类器及其Python实现
分类分析|贝叶斯分类器及其Python实现 0. 分类分析概述1. Logistics回归模型2. 贝叶斯分类器2.1 贝叶斯定理2.2 朴素贝叶斯分类器2.2.1 高斯朴素贝叶斯分类器2.2.2 多项式朴素贝叶斯分类器 2.3 朴素贝叶斯分类的主要优点2.4 朴素贝叶斯分类的主要缺点 3. 贝叶斯分类器在生产中的…...
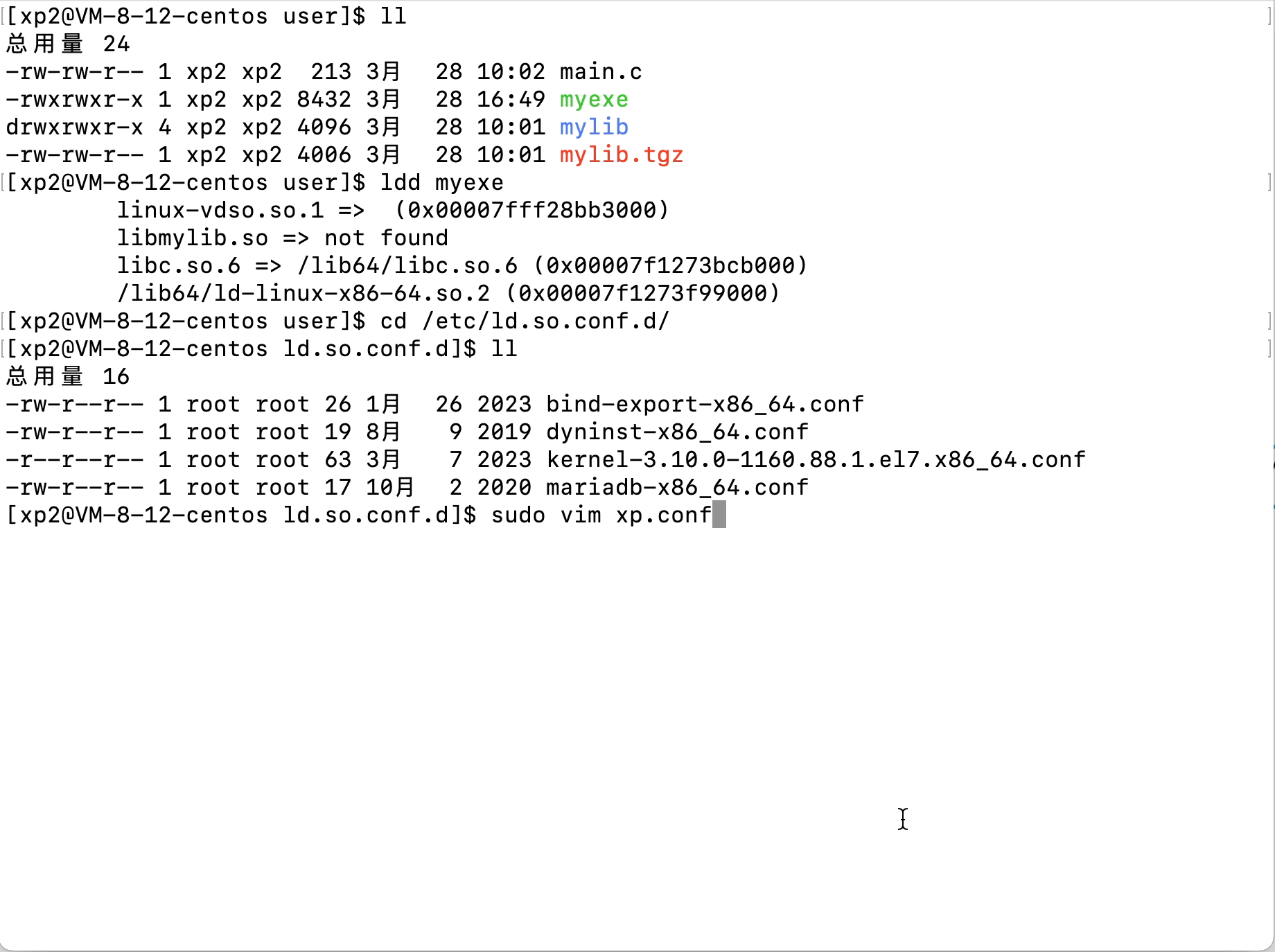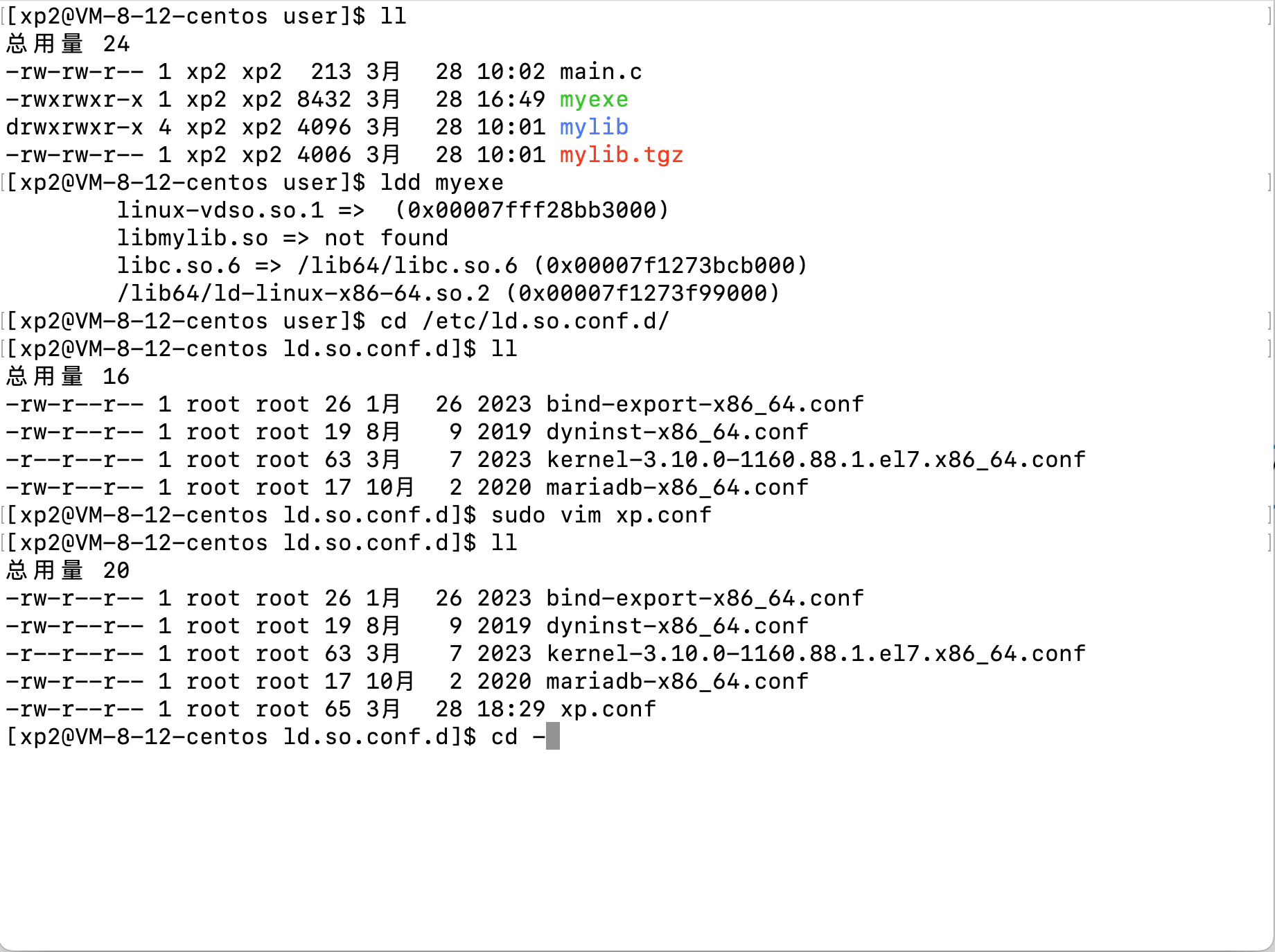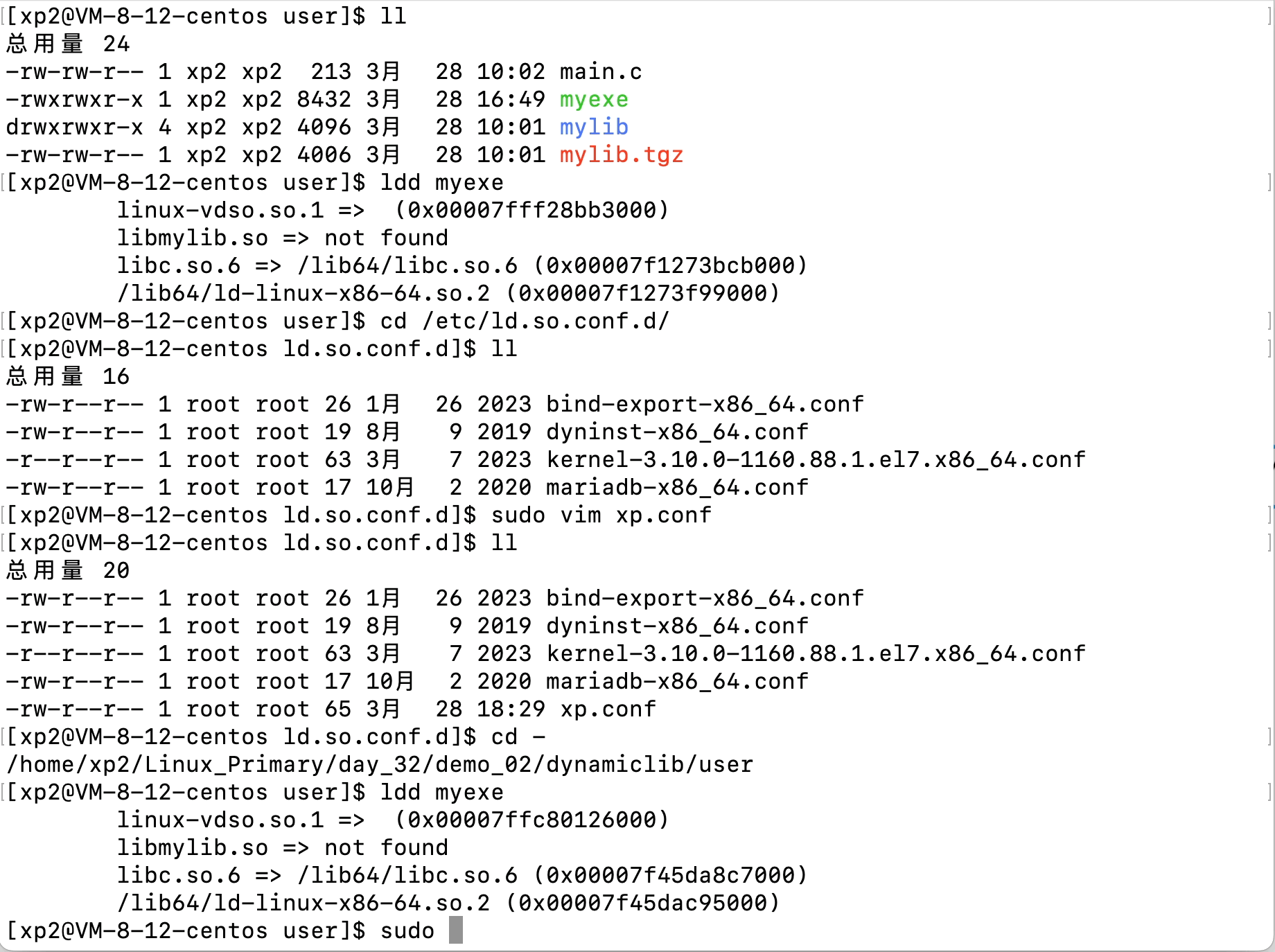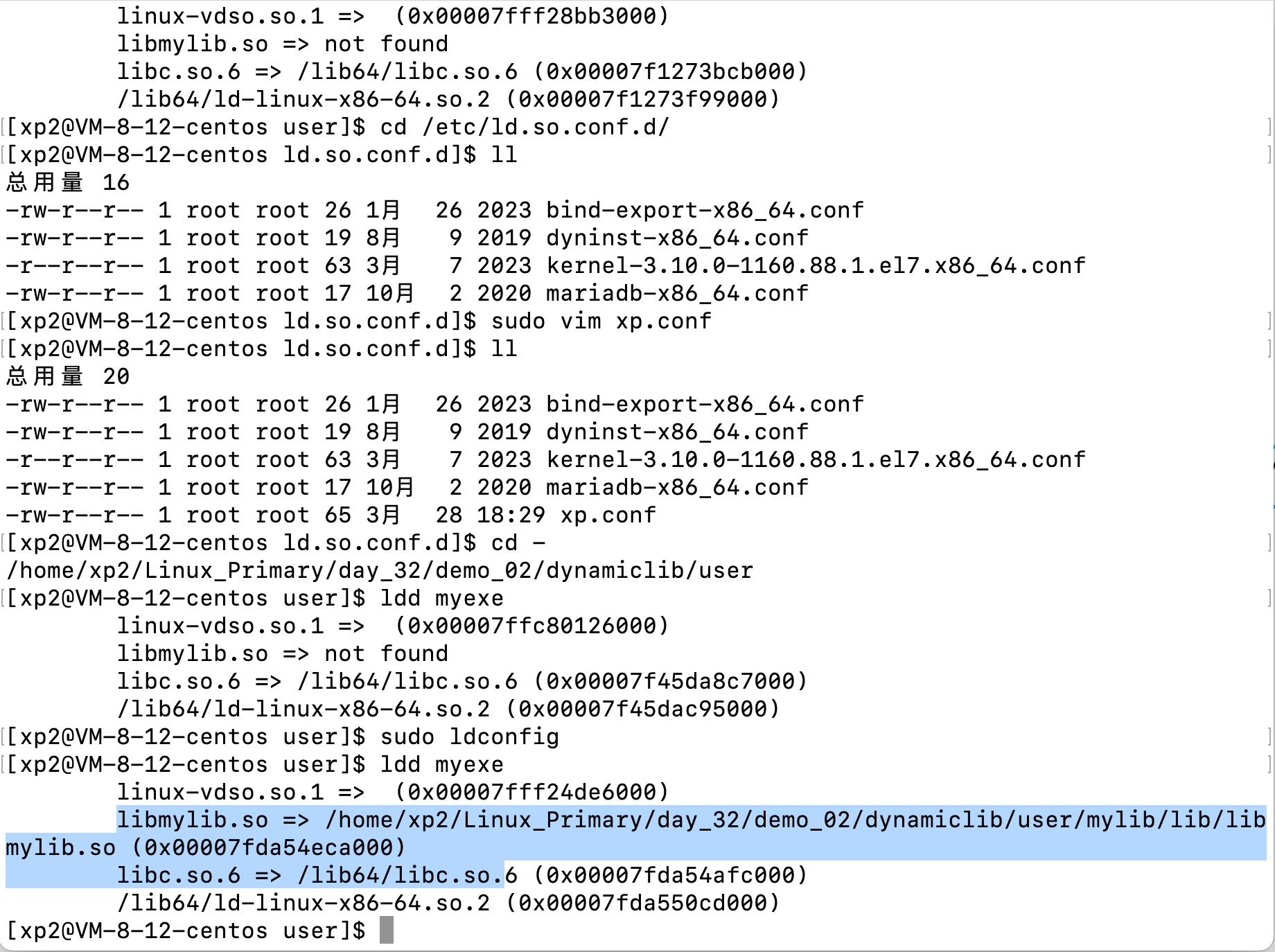
Linux文件(系统)IO(含动静态库的链接操作)
文章目录 Linux文件(系统)IO(含动静态库的链接操作)1、C语言文件IO操作2、三个数据流stdin、stdout、stderr3、系统文件IO3.1、相关系统调用接口的使用3.2、文件描述符fd3.3、文件描述符的分配规则3.3、重定向3.4、自制shell加入重…...
CI/CD实战-jenkins结合ansible 7
配置主机环境 在jenkins上断开并删除docker1节点 重新给master添加构建任务 将server3,server4作为测试主机,停掉其上后面的docker 在server2(jenkins)主机上安装ansible 设置jenkins用户到目标主机的免密 给测试主机创建用户并…...
内网渗透-(黄金票据和白银票据)详解(一)
目录 一、Kerberos协议 二、下面我们来具体分析Kerberos认证流程的每个步骤: 1、KRB_AS-REQ请求包分析 PA-ENC-TIMESTAMP PA_PAC_REQUEST 2、 KRB_AS_REP回复包分析: TGT认购权证 Logon Session Key ticket 3、然后继续来讲相关的TGS的认证过程…...
学习transformer模型-Dropout的简明介绍
Dropout的定义和目的: Dropout 是一种神经网络正则化技术,它在训练时以指定的概率丢弃一个单元(以及连接)p。 这个想法是为了防止神经网络变得过于依赖特定连接的共同适应,因为这可能是过度拟合的症状。直观上&#…...
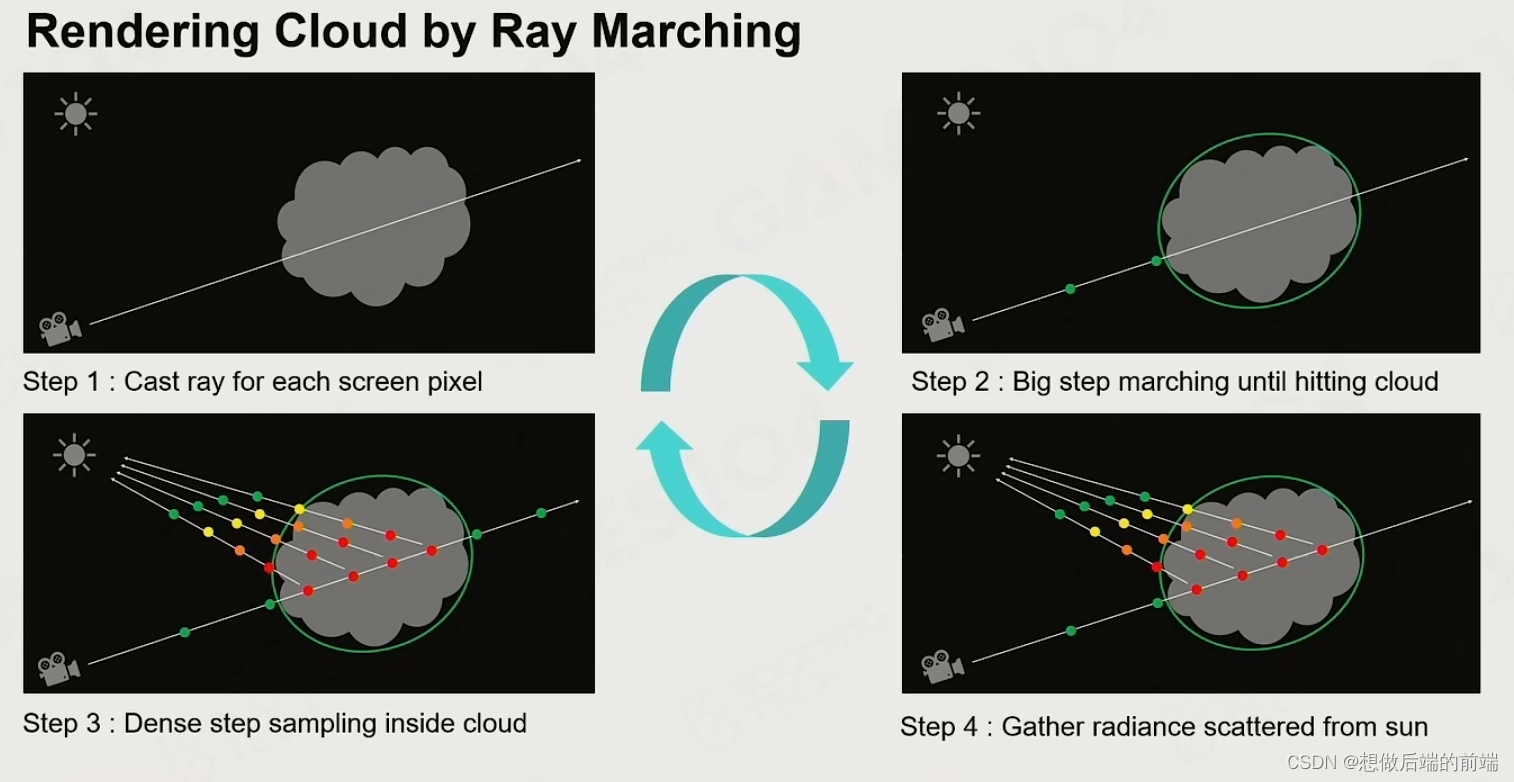
游戏引擎中的大气和云的渲染
一、大气 首先和光线追踪类似,大气渲染也有类似的渲染公式,在实际处理中也有类似 Blinn-Phong的拟合模型。关键参数是当前点到天顶的角度和到太阳的角度 二、大气散射理论 光和介质的接触: Absorption 吸收Out-scattering 散射Emission …...

华为鲲鹏云认证考试内容有哪些?华为鲲鹏云认证考试报名条件
华为鲲鹏云认证考试是华为公司为了验证IT专业人士在鲲鹏计算及云计算领域的专业能力而设立的一项认证考试。以下是关于华为鲲鹏云认证考试的一些详细信息: 考试内容:华为鲲鹏云认证考试的内容主要包括理论考核和实践考核两大部分。理论考核涉及云计算、…...
v3-admin-vite 改造自动路由,view页面自解释Meta
需求 v3-admin-vite是一款不错的后端管理模板,主要是pany一直都在维护,最近将后台管理也进行了升级,顺便完成一直没时间解决的小痛痒: 在不使用后端动态管理的情况下。我不希望单独维护一份路由定义,我希望页面是自解…...

FIFO存储器选型参数,结构原理,工艺与注意问题总结
🏡《总目录》 目录 1,概述2.1,写入操作2.2,读取操作2.3,指针移动与循环2.4,状态检测3,结构特点3.1,双口RAM结构3.2,无外部读写地址线3.3,内部读写指针自动递增3.4,固定深度的缓冲区4,工艺流程4.1,硅晶圆准备...

jvm高级面试题-2024
说下对JVM内存模型的理解 JVM内存模型主要是指Java虚拟机在运行时所使用的内存结构。它主要包括堆、栈、方法区和程序计数器等部分。 堆是JVM中最大的一块内存区域,用于存储对象实例。一般通过new关键字创建的对象都存放在堆中,堆的大小可以通过启动参数…...

DeepL Pro3.1 下载地址及安装教程
DeepL Pro是DeepL公司推出的专业翻译服务。DeepL是一家专注于机器翻译和自然语言处理技术的公司,其翻译引擎被认为在质量和准确性方面表现优秀.DeepL Pro提供了一系列高级功能和服务,以满足专业用户的翻译需求。其中包括: 高质量翻译…...

第十一届 “MathorCup“- B题:基于机器学习的团簇能量预测及结构全局寻优方法
目录 摘 要 第 1 章 问题重述 1.1 问题背景 1.2 问题描述 第 2 章 思路分析...
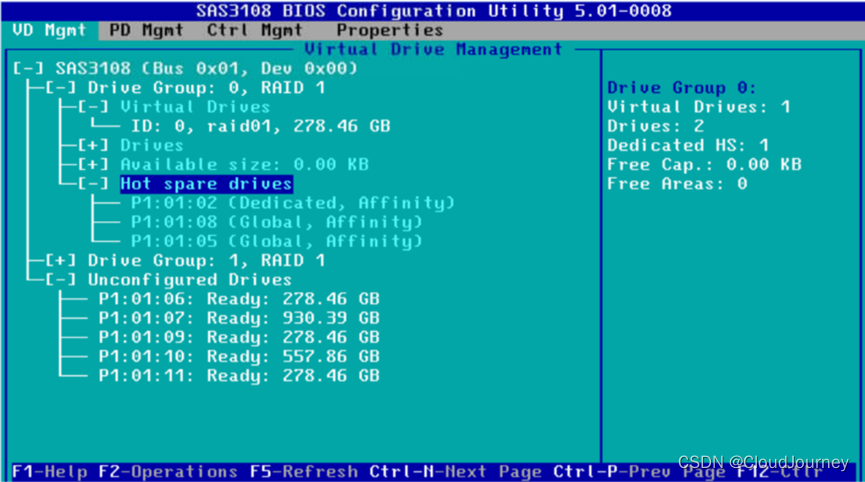
云计算探索-如何在服务器上配置RAID(附模拟器)
一,引言 RAID(Redundant Array of Independent Disks)是一种将多个物理硬盘组合成一个逻辑单元的技术,旨在提升数据存取速度、增大存储容量以及提高数据可靠性。在服务器环境中配置RAID尤其重要,它不仅能够应对高并发访…...
` 方法)
深入浅出:JavaScript 中的 `window.crypto.getRandomValues()` 方法
深入浅出:JavaScript 中的 window.crypto.getRandomValues() 方法 在现代 Web 开发中,随机数的生成看似简单,却隐藏着许多玄机。无论是生成密码、加密密钥,还是创建安全令牌,随机数的质量直接关系到系统的安全性。Jav…...
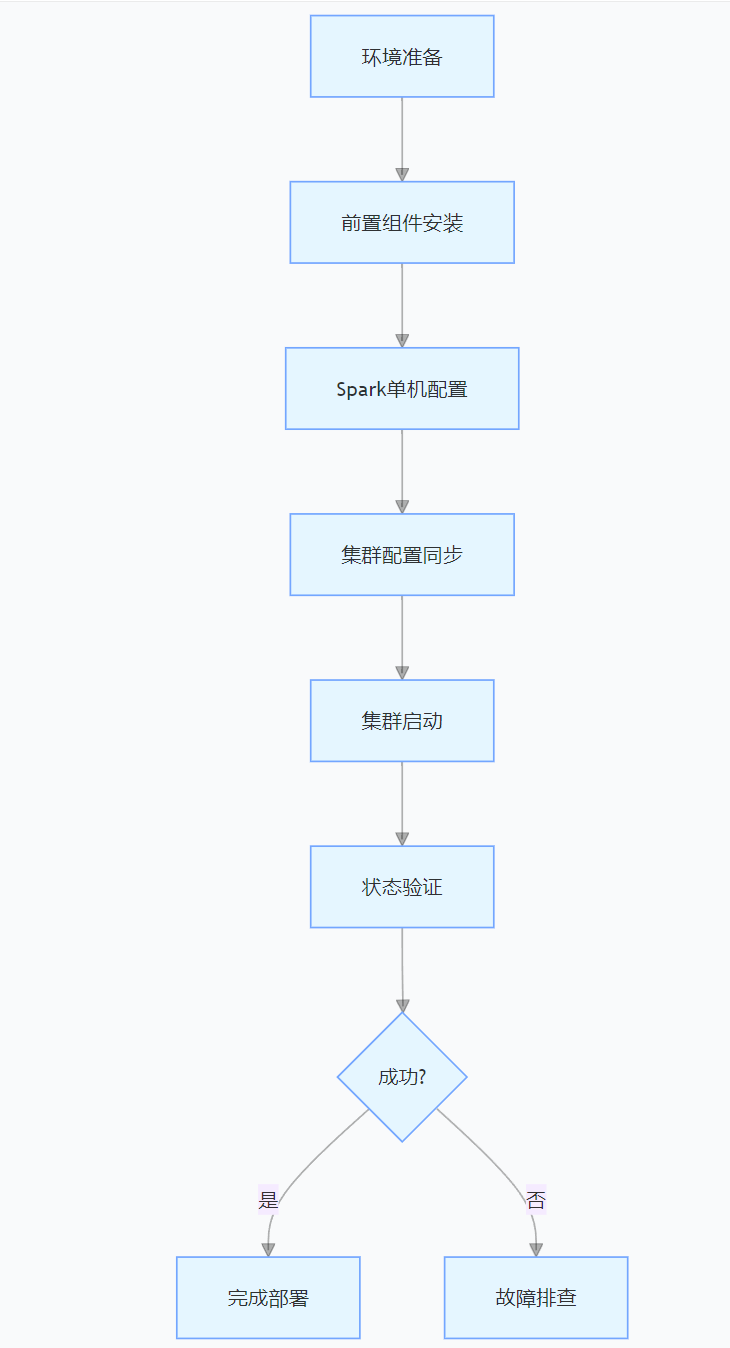
CentOS下的分布式内存计算Spark环境部署
一、Spark 核心架构与应用场景 1.1 分布式计算引擎的核心优势 Spark 是基于内存的分布式计算框架,相比 MapReduce 具有以下核心优势: 内存计算:数据可常驻内存,迭代计算性能提升 10-100 倍(文档段落:3-79…...

JVM垃圾回收机制全解析
Java虚拟机(JVM)中的垃圾收集器(Garbage Collector,简称GC)是用于自动管理内存的机制。它负责识别和清除不再被程序使用的对象,从而释放内存空间,避免内存泄漏和内存溢出等问题。垃圾收集器在Ja…...
Mac软件卸载指南,简单易懂!
刚和Adobe分手,它却总在Library里给你写"回忆录"?卸载的Final Cut Pro像电子幽灵般阴魂不散?总是会有残留文件,别慌!这份Mac软件卸载指南,将用最硬核的方式教你"数字分手术"࿰…...

Java 加密常用的各种算法及其选择
在数字化时代,数据安全至关重要,Java 作为广泛应用的编程语言,提供了丰富的加密算法来保障数据的保密性、完整性和真实性。了解这些常用加密算法及其适用场景,有助于开发者在不同的业务需求中做出正确的选择。 一、对称加密算法…...

解决本地部署 SmolVLM2 大语言模型运行 flash-attn 报错
出现的问题 安装 flash-attn 会一直卡在 build 那一步或者运行报错 解决办法 是因为你安装的 flash-attn 版本没有对应上,所以报错,到 https://github.com/Dao-AILab/flash-attention/releases 下载对应版本,cu、torch、cp 的版本一定要对…...

【C++从零实现Json-Rpc框架】第六弹 —— 服务端模块划分
一、项目背景回顾 前五弹完成了Json-Rpc协议解析、请求处理、客户端调用等基础模块搭建。 本弹重点聚焦于服务端的模块划分与架构设计,提升代码结构的可维护性与扩展性。 二、服务端模块设计目标 高内聚低耦合:各模块职责清晰,便于独立开发…...
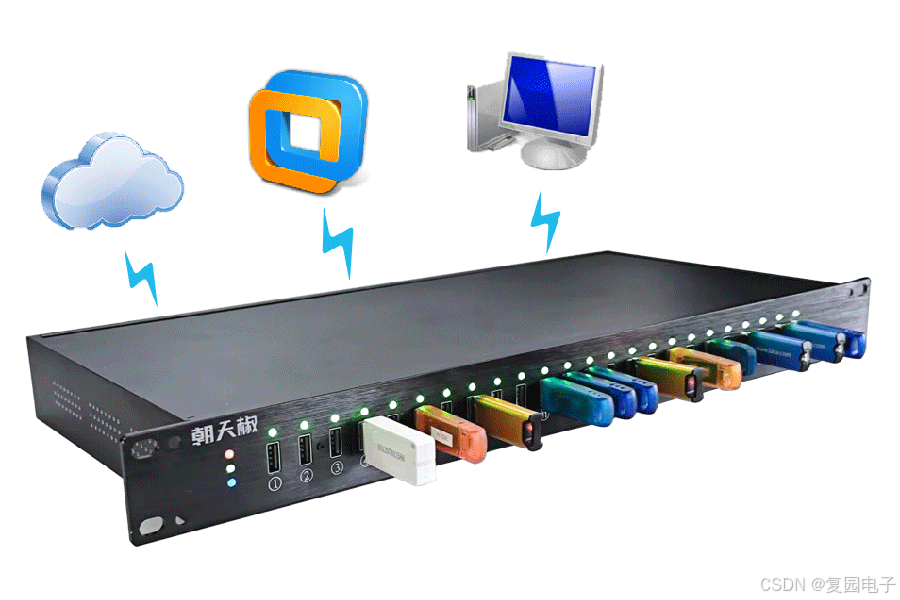
USB Over IP专用硬件的5个特点
USB over IP技术通过将USB协议数据封装在标准TCP/IP网络数据包中,从根本上改变了USB连接。这允许客户端通过局域网或广域网远程访问和控制物理连接到服务器的USB设备(如专用硬件设备),从而消除了直接物理连接的需要。USB over IP的…...
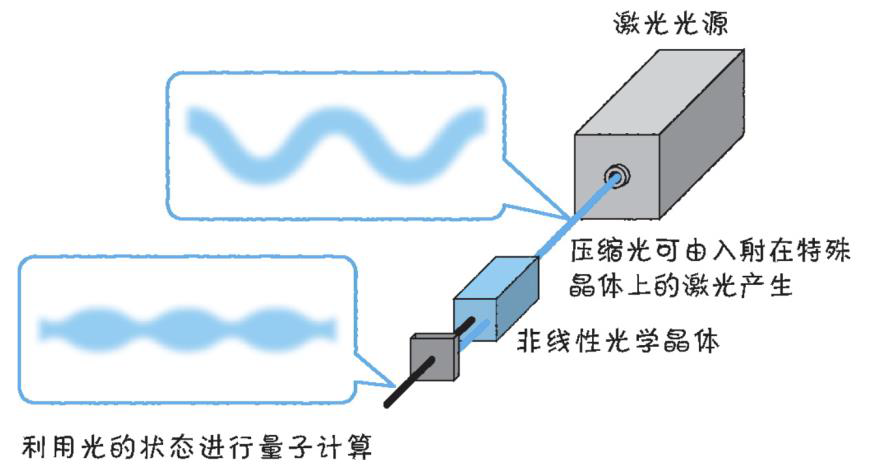
以光量子为例,详解量子获取方式
光量子技术获取量子比特可在室温下进行。该方式有望通过与名为硅光子学(silicon photonics)的光波导(optical waveguide)芯片制造技术和光纤等光通信技术相结合来实现量子计算机。量子力学中,光既是波又是粒子。光子本…...
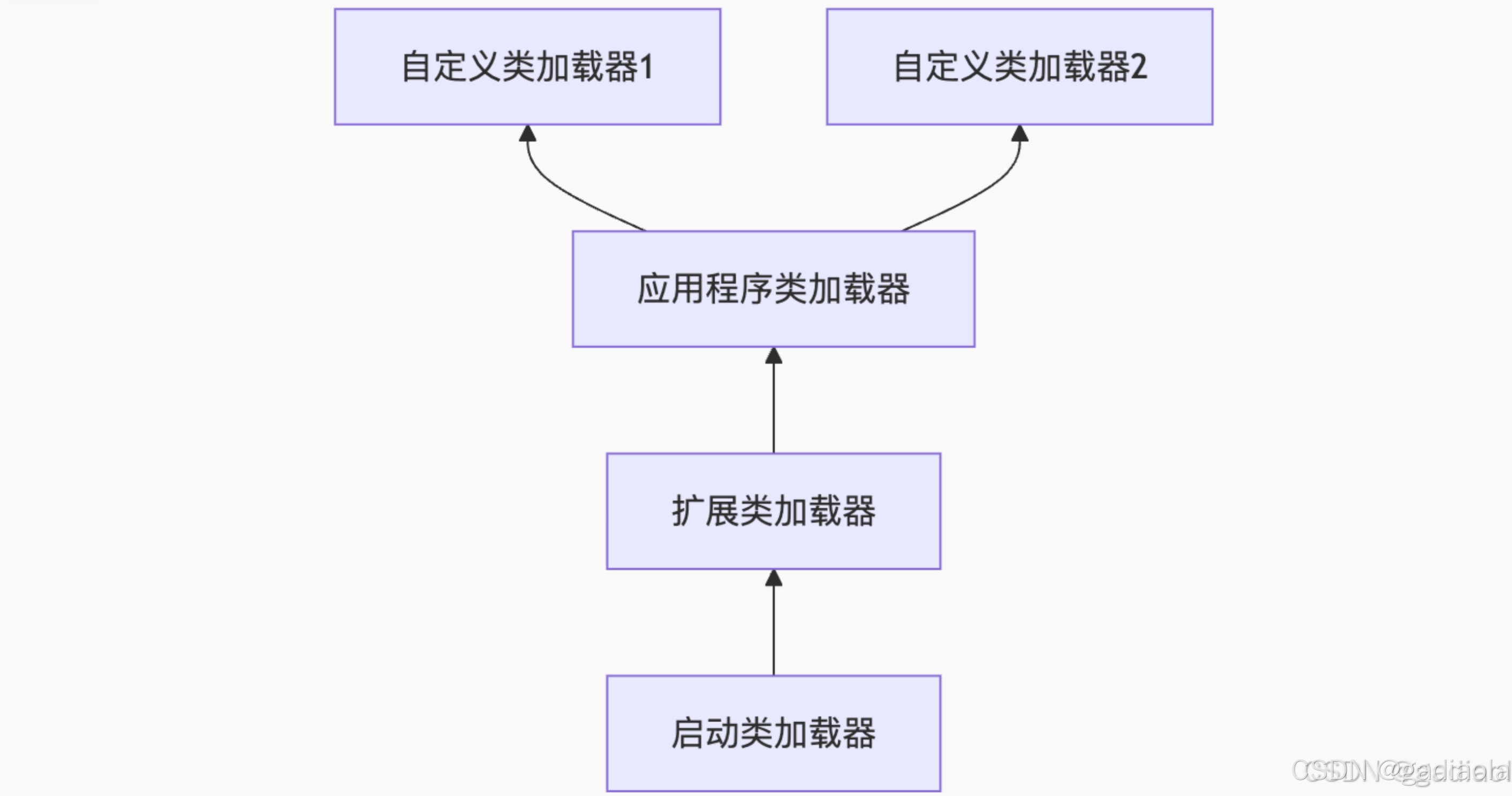
【JVM面试篇】高频八股汇总——类加载和类加载器
目录 1. 讲一下类加载过程? 2. Java创建对象的过程? 3. 对象的生命周期? 4. 类加载器有哪些? 5. 双亲委派模型的作用(好处)? 6. 讲一下类的加载和双亲委派原则? 7. 双亲委派模…...
