【C++】list模拟实现
个人主页 : zxctscl
如有转载请先通知
文章目录
- 1. 前言
- 2. list源码
- 3. 初始化
- 3.1 构造
- 3.2 拷贝构造
- 3.3 赋值
- 3.4 析构
- 4. 迭代器
- 4.1 后置加加和前置加加
- 4.2 后置减减和前置减减
- 4.3 解引用
- 4.4 `!=`和`==`
- 4.5 begin 和 end
- 4.6 const迭代器
- 4.7 迭代器优化
- 5. Modifiers
- 5.1 insert
- 5.2 push_back
- 5.3 push_front
- 5.4 erase
- 5.5 pop_back
- 5.6 pop_front
- 5.7 重载operator->
- 5.8 swap
- 5.9 clear
- 6. 附代码
1. 前言
在前面一篇博客中分享了list的相关介绍 【C++】list介绍,这次来模拟实现一下list。
2. list源码
成员变量:

无参构造:


插入:
3. 初始化
在库里面定义节点需要全部公有时用到的就是struct:

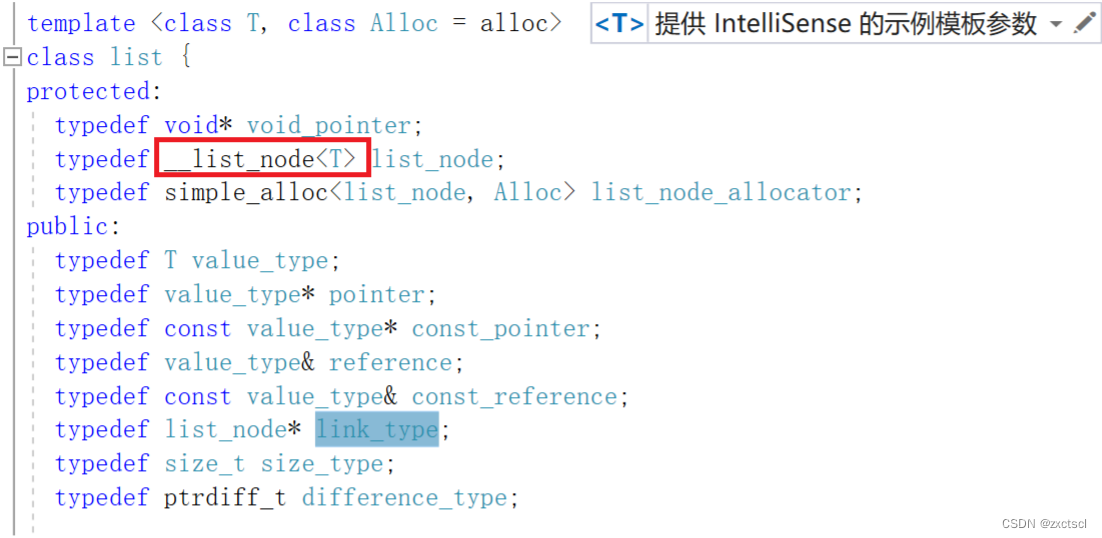
这里我们也用相同方法自己定义出一个节点:
template<class T>struct ListNode{ListNode<T>* _next;ListNode<T>* _prev;T _data;ListNode(const T& x = T()):_next(nullptr),_prev(nullptr),_data(x){}};
然后在写list类时候就要用到上面结构体。
list类里面成员变量就有:
private:Node* _head;3.1 构造
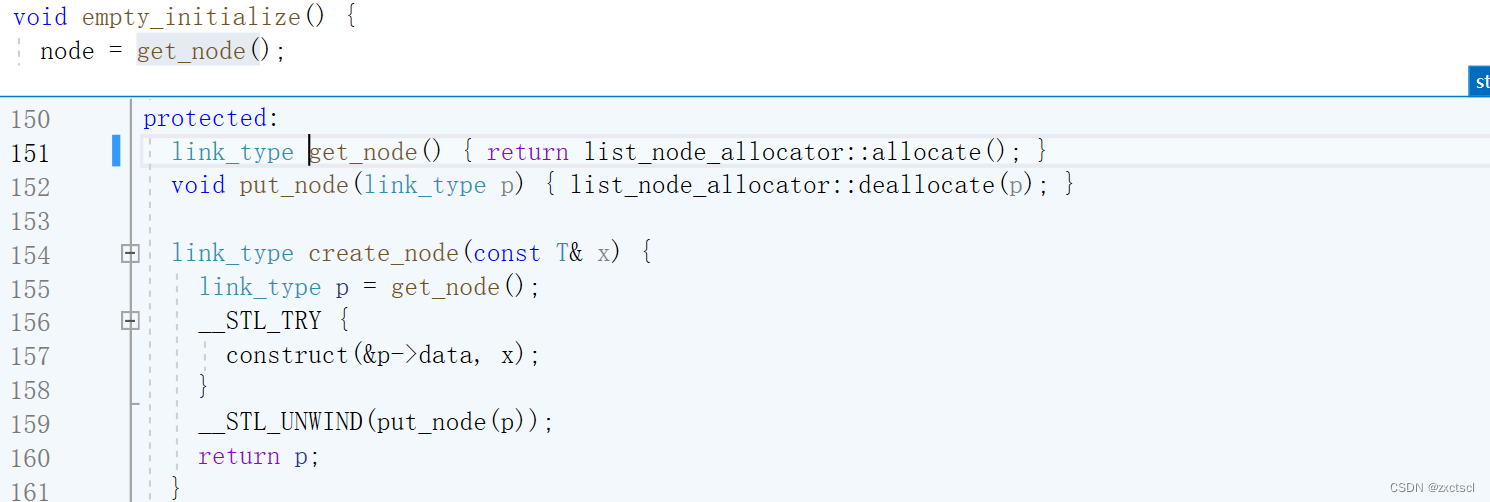
先来一个无参构造,实现的双向带头循环链表,先定义哨兵位节点,让它的next和prev都指向自己:
list(){_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;_size = 0;}
3.2 拷贝构造
链表的拷贝构造,先写一个初始化链表的函数:
void empty_init(){_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;_size = 0;}
就直接在初始化的基础上,遍历拷贝的数据,再把数据全部插入到新链表就可以了:
list(const list<T>& lt){empty_init();for (auto& e : lt){push_back(e);}}
测试一下:
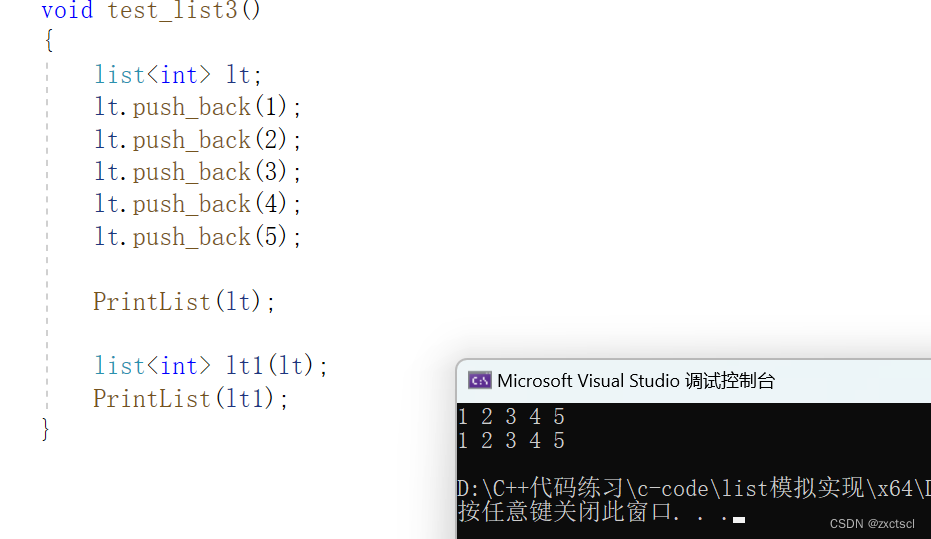
void test_list3(){list<int> lt;lt.push_back(1);lt.push_back(2);lt.push_back(3);lt.push_back(4);lt.push_back(5);PrintList(lt);list<int> lt1(lt);PrintList(lt1);}
3.3 赋值
直接复用swap,出了作用域lt之前的数据会销毁,再返回*this就可以了。
list<T>& operator=(list<T> lt){swap(lt);return *this;}
3.4 析构
析构在clear的基础上,要把哨兵位也删除
~list(){clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}
怎么判断要不要析构?
如果需要析构,一般就需要自己写深拷贝
如果不需要析构,一般就不需要自己写深拷贝,默认浅拷贝就可以
4. 迭代器
这里原生指针不能充当迭代器,list物理空间不连续,这里Node*加加不能到下一个节点,而且解引用Node*是Node也不能找到数据。这时Node*已经不能满足需求了,这里就得封装一个类。内置类型不能满足需求,就自定义类型。
来看看库里面是怎么实现的:

来实现一下:
typedef ListNode<T> Node;typedef ListIterator<T> Self;Node* _node;ListIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}4.1 后置加加和前置加加
实现加加,加加就到下一个位置,需要迭代器去访问
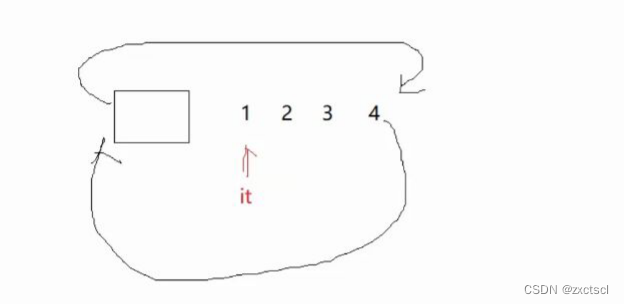
代码实现:
Self& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}
前置加加:返回的是加加之前的node,所以得先记录下数据(拷贝构造一份),再加加,然后返回之前记录下的节点。
Self& operator++(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}
4.2 后置减减和前置减减
后置减减和后置加加类似:
Self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}前置减减和前置加加类似:
Self& operator--(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}
4.3 解引用
这里*it返回的是什么值?
要返回的时节点里面的data
T& operator*(){return _node->_data;}
4.4 !=和==
比较两个迭代器相不相等,比较的是节点的指针
bool operator!=(const Self& it){return _node != it._node;}
重载==:
bool operator==(const Self& it){return _node == it._node;}
4.5 begin 和 end
begin执行第一个节点,也就是head的next
iterator begin(){return iterator(_head->_next);}
这里是用来匿名对象来构造迭代器:

还可以写成:
单参数的构造,支持隐私类型转换
iterator begin(){return _head->_next;}

end指向的是head
iterator end(){return iterator(_head);}
4.6 const迭代器
不能直接在原来的迭代器上面加上const,会导致普通迭代器就不能修改了。
const迭代器,需要是迭代器不能修改,还是迭代器指向的内容?
迭代器指向的内容不能修改!const iterator不是我们需要const迭代器,所以不能在普通迭代器的前面加const。
使用就增加一个重载的const迭代器:
const_iterator begin() const{return _head->_next;}const_iterator end() const{return _head;
那么就得单独搞一个类ListConstIterator,让const迭代器*it不能修改:再把相同的操作符重载一下
template<class T>struct ListConstIterator{typedef ListNode<T> Node;typedef ListConstIterator<T> Self;Node* _node;ListConstIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}// *itconst T& operator*(){return _node->_data;}// it->const T* operator->(){return &_node->_data;}// ++itSelf& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}Self operator++(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}Self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}Self operator--(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const Self& it){return _node != it._node;}bool operator==(const Self& it){return _node == it._node;}};
4.7 迭代器优化
发现普通迭代器和const迭代器里面很多运算符都是一样的,而const迭代器里面就直是不能修改指向的内容,代码显得冗余。就可以用模板来修改这两个类,把他们两个融成一个类。
就是返回值的类型不同,就用模板变,用一个模板参数:template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>:
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>struct ListIterator{typedef ListNode<T> Node;typedef ListIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;Node* _node;ListIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}// *it//T& operator*()Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}// it->//T* operator->()Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}// ++itSelf& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}Self operator++(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}Self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}Self operator--(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const Self& it){return _node != it._node;}bool operator==(const Self& it){return _node == it._node;}};
本质上相当于我们写了一个类模板,编译器实例化生成两个类。
从而在list类里面就修改为:
typedef ListIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef ListIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
5. Modifiers
5.1 insert
insert实现在某一个位置之前插入一个节点
先搞一个节点,然后记录原链表pos位置的指针,然后一前一后改指向
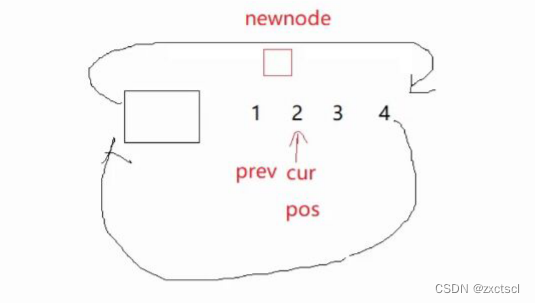
void insert(iterator pos, const T& x){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* newnode = new Node(x);Node* prev = cur->_prev;prev->_next = cur;newnode->_prev = prev;newnode->_next = cur;cur->prev = newnode;}
5.2 push_back
新开一个节点,然后让原链表的tail指向新节点,让新节点的prev指向tail,再把head的prev改为新节点,新节点的next改为head。
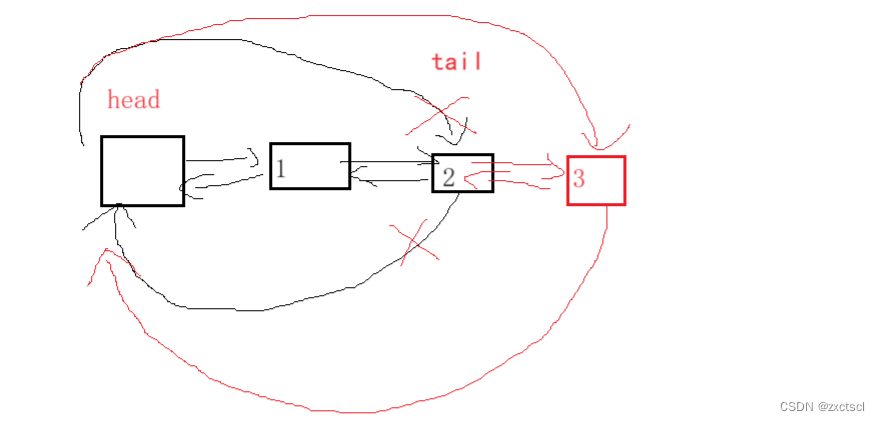
代码实现:
void push_back(const T& x){Node* newnode = new Node(x);Node* tail = _head->_prev;tail->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = tail;newnode->_next = _head;_head->_prev = newnode;}
来测试一下:
void test_list1(){list<int> lt;lt.push_back(1);lt.push_back(2);lt.push_back(3);lt.push_back(4);lt.push_back(5);list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();while (it != lt.end()){cout << *it << " ";it++;}cout << endl;}
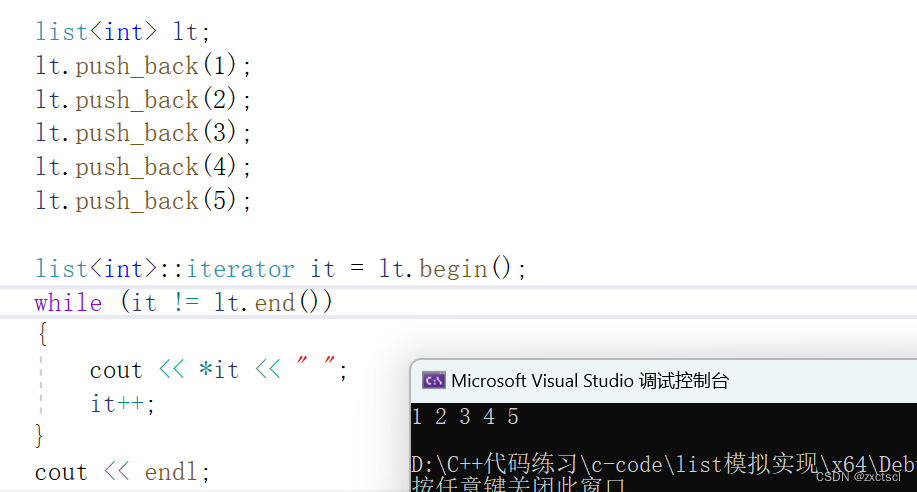

push_back用erase来实现会更简单:在end位置插入一个数
void push_back(const T& x){insert(end(), x);}
5.3 push_front
头插就是在begin插入一个数:
void push_front(const T& x){insert(begin(), x);}
测试一下:
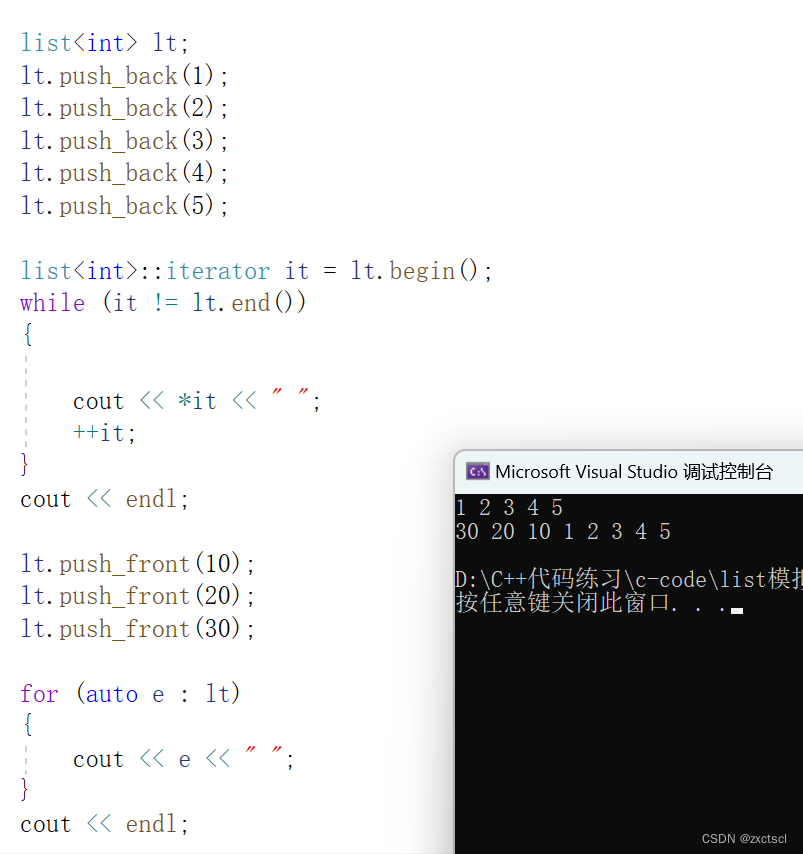
5.4 erase
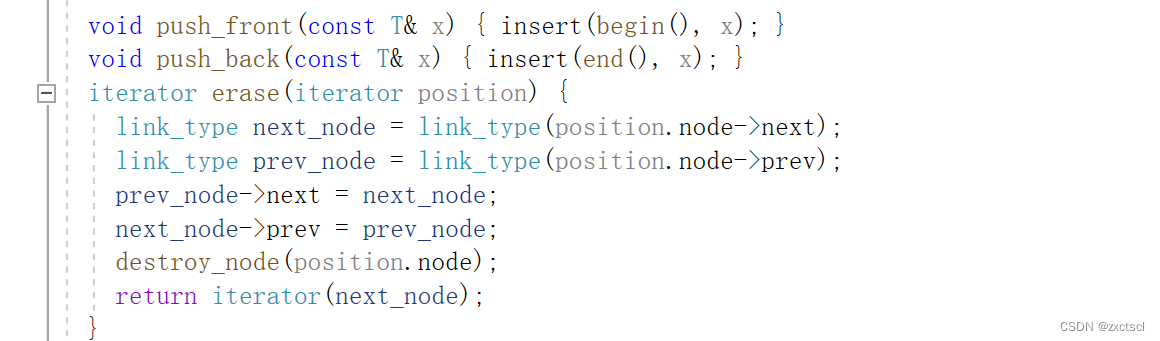
先记录下要删除的节点,和它前一个节点prev 还有它的后一个节点next。然后让prev的_next 指向next;next的_prev 指向 prev。
删除会导致迭代器失效的问题,为了避免,就返回删除节点的下一个位置。
iterator erase(iterator pos){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* next = cur->_next;prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete cur;return iterator(next);}
5.5 pop_back
尾删复用erase,而尾是在end前面的一个位置,所以先减减end再删除
void pop_back(){erase(--end());}
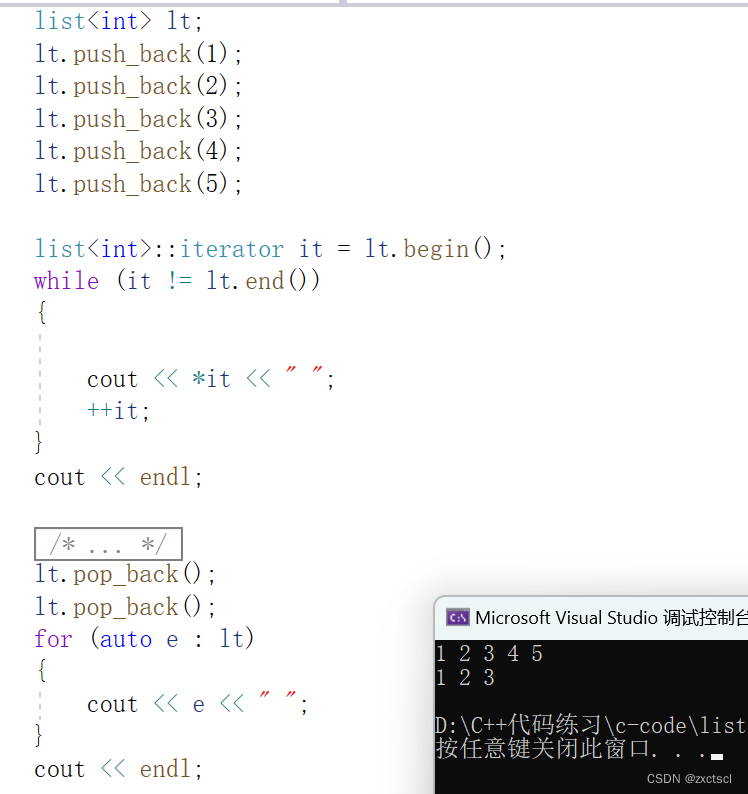
5.6 pop_front
因为begin所在的位置就是头节点,所以直接删除begin就可以:
void pop_front(){erase(begin());}
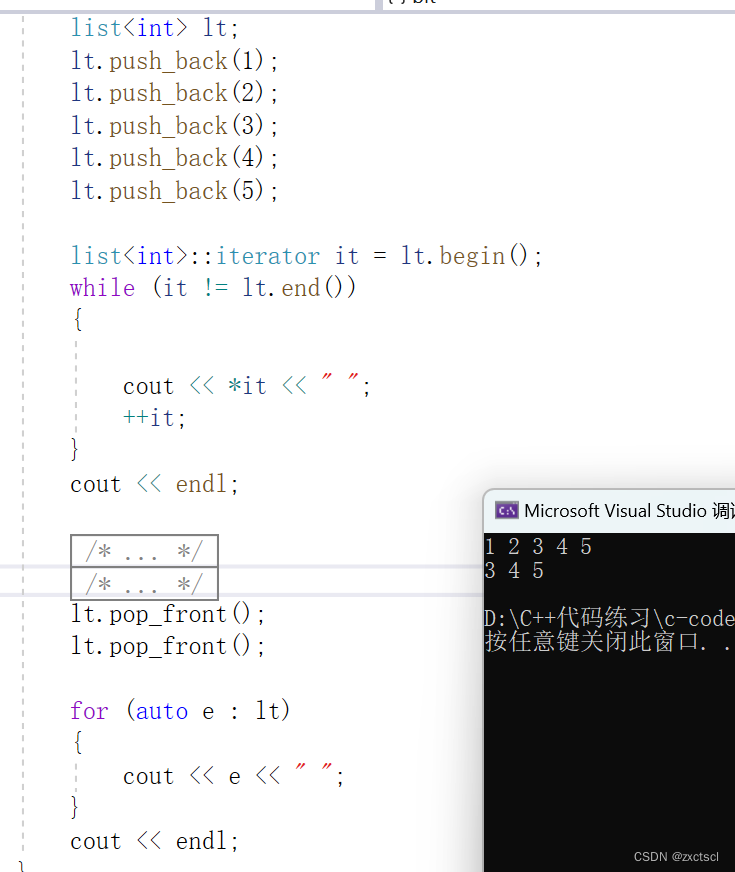
5.7 重载operator->
用户自定义一个类型:
struct A{int _a1;int _a2;A(int a1 = 0, int a2 = 0):_a1(a1), _a2(a2){}};
调用push_back插入数据,可以是匿名对象,也可以多参数进行隐式类型转换:
list<A> lt;A aa1(1, 1);A aa2 = { 1, 1 };lt.push_back(aa1);lt.push_back(aa2);lt.push_back(A(2, 2));lt.push_back({ 3, 3 });lt.push_back({ 4, 4 });
但是要把数据输出到屏幕上,使用*it是不可以的:
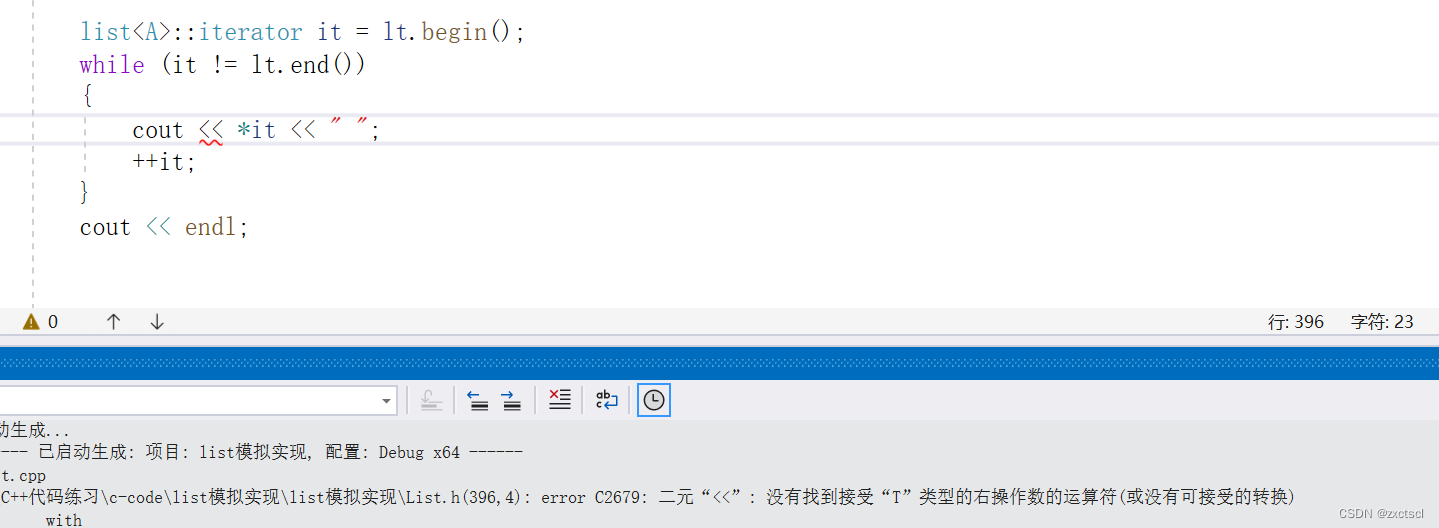
A是一个自定义类型,A不支持流插入,要想指出就得自己写一个重载一个。如果不想写,可以换个方式,这里的数据是公有的可以直接访问。
就直接*it返回的是A,再拿到a1和a2的数据就可以:
list<A>::iterator it = lt.begin();while (it != lt.end()){cout <<(*it)._a1<<":" << (*it)._a2 <<endl;++it;}cout << endl;
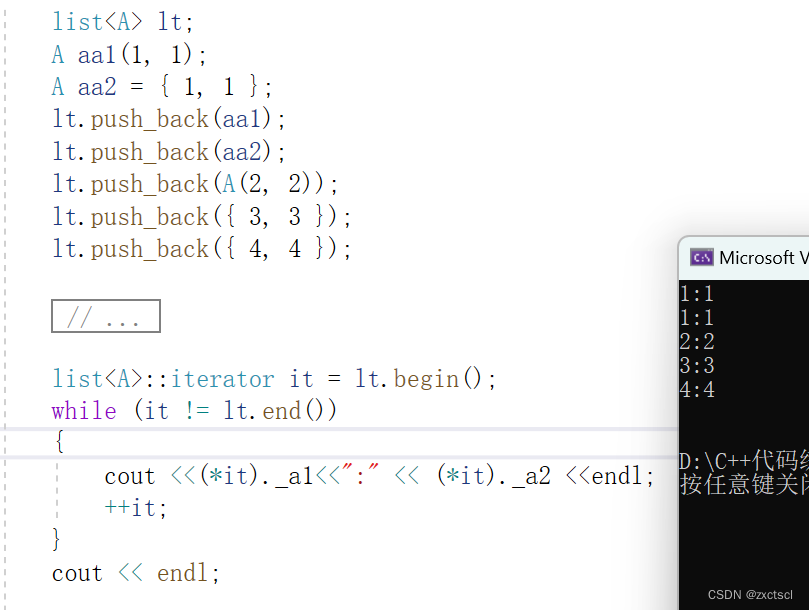

这里A*的一个指针访问数据是先解引用,返回A对象,再来.对象里面的成员变量:
A* ptr = &aa1;(*ptr)._a1;
迭代器就是想要模仿A*的行为,所以迭代器就重载了一个->:it->,它返回的是data的地址。
T* operator->(){return &_node->_data;}
访问它里面的就是这样:
cout << it->_a1 << ":" << it->_a2 << endl;
其实是编译器为了可读性,省略了一个箭头:第一个箭头是运算符重载,就返回data里面的地址也就是A*,第二个箭头就能访问A里面的数据了。
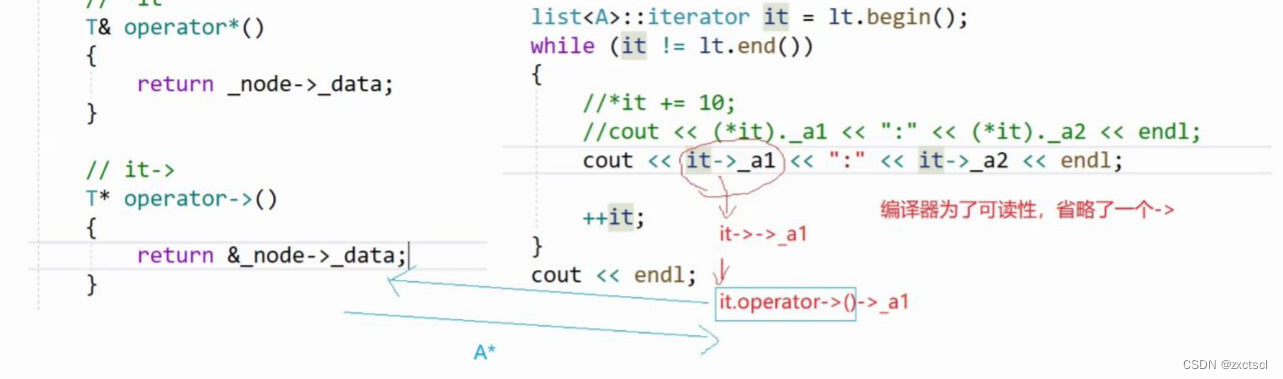
原生指针的行为就是:
cout << it.operator->()->_a1 << ":" << it.operator->()->_a2 << endl;
测试一下都能使用:
void test_list2(){list<A> lt;A aa1(1, 1);A aa2 = { 1, 1 };lt.push_back(aa1);lt.push_back(aa2);lt.push_back(A(2, 2));lt.push_back({ 3, 3 });lt.push_back({ 4, 4 });list<A>::iterator it = lt.begin();while (it != lt.end()){cout << it->_a1 << ":" << it->_a2 << endl;cout << it.operator->()->_a1 << ":" << it.operator->()->_a2 << endl;++it;}cout << endl;}
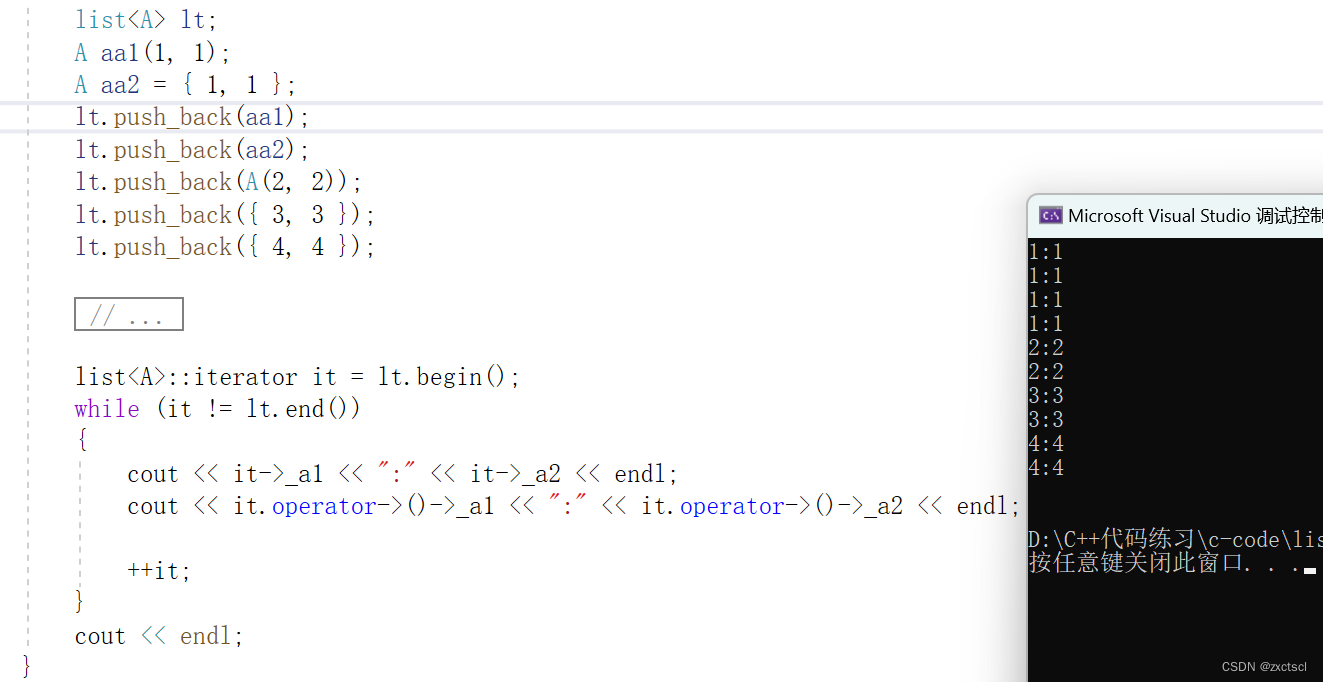
5.8 swap
直接调用库里面的swap来交换:
void swap(list<T>& lt){std::swap(_head, lt._head);std::swap(_size, lt._size);}
5.9 clear
clear清理掉所有数据,直接复用迭代器来把数据全部删除,但是没有清理掉哨兵位head
void clear(){iterator it = begin();while (it != end()){it = erase(it);}}
6. 附代码
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<assert.h>namespace bit
{template<class T>struct ListNode{ListNode<T>* _next;ListNode<T>* _prev;T _data;ListNode(const T& x = T()):_next(nullptr), _prev(nullptr), _data(x){}};// typedef ListIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;// typedef ListIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>struct ListIterator{typedef ListNode<T> Node;typedef ListIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;Node* _node;ListIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}// *it//T& operator*()Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}// it->//T* operator->()Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}// ++itSelf& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}Self operator++(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}Self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}Self operator--(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const Self& it){return _node != it._node;}bool operator==(const Self& it){return _node == it._node;}};//template<class T>//struct ListConstIterator//{// typedef ListNode<T> Node;// typedef ListConstIterator<T> Self;// Node* _node;// ListConstIterator(Node* node)// :_node(node)// {}// // *it// const T& operator*()// {// return _node->_data;// }// // it->// const T* operator->()// {// return &_node->_data;// }// // ++it// Self& operator++()// {// _node = _node->_next;// return *this;// }// Self operator++(int)// {// Self tmp(*this);// _node = _node->_next;// return tmp;// }// Self& operator--()// {// _node = _node->_prev;// return *this;// }// Self operator--(int)// {// Self tmp(*this);// _node = _node->_prev;// return tmp;// }// bool operator!=(const Self& it)// {// return _node != it._node;// }// bool operator==(const Self& it)// {// return _node == it._node;// }//};template<class T>class list{typedef ListNode<T> Node;public://typedef ListIterator<T> iterator;//typedef ListConstIterator<T> const_iterator;typedef ListIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef ListIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;//iterator begin()//{// //return iterator(_head->_next);// iterator it(_head->_next);// return it;//}iterator begin(){return _head->_next;}iterator end(){return _head;}const_iterator begin() const{return _head->_next;}const_iterator end() const{return _head;}void empty_init(){_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;_size = 0;}list(){empty_init();}// lt2(lt1)list(const list<T>& lt){empty_init();for (auto& e : lt){push_back(e);}}void swap(list<T>& lt){std::swap(_head, lt._head);std::swap(_size, lt._size);}// lt1 = lt3list<T>& operator=(list<T> lt){swap(lt);return *this;}void clear(){iterator it = begin();while (it != end()){it = erase(it);}}~list(){clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}/*void push_back(const T& x){Node* newnode = new Node(x);Node* tail = _head->_prev;tail->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = tail;newnode->_next = _head;_head->_prev = newnode;}*/void push_back(const T& x){insert(end(), x);}void push_front(const T& x){insert(begin(), x);}void pop_back(){erase(--end());}void pop_front(){erase(begin());}void insert(iterator pos, const T& val){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* newnode = new Node(val);Node* prev = cur->_prev;// prev newnode cur;prev->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = prev;newnode->_next = cur;cur->_prev = newnode;_size++;}iterator erase(iterator pos){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* next = cur->_next;prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete cur;_size--;return iterator(next);}size_t size() const{return _size;}bool empty(){return _size == 0;}private:Node* _head;size_t _size;};void test_list1(){list<int> lt;lt.push_back(1);lt.push_back(2);lt.push_back(3);lt.push_back(4);lt.push_back(5);list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();while (it != lt.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;/*lt.push_front(10);lt.push_front(20);lt.push_front(30);*//*lt.pop_back();lt.pop_back();for (auto e : lt){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;*/lt.pop_front();lt.pop_front();for (auto e : lt){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;}struct A{int _a1;int _a2;A(int a1 = 0, int a2 = 0):_a1(a1), _a2(a2){}};void test_list2(){list<A> lt;A aa1(1, 1);A aa2 = { 1, 1 };lt.push_back(aa1);lt.push_back(aa2);lt.push_back(A(2, 2));lt.push_back({ 3, 3 });lt.push_back({ 4, 4 });//A* ptr = &aa1;//(*ptr)._a1;//ptr->_a1;//list<A>::iterator it = lt.begin();//while (it != lt.end())//{// cout <<(*it)._a1<<":" << (*it)._a2 <<endl;// ++it;//}//cout << endl;list<A>::iterator it = lt.begin();while (it != lt.end()){cout << it->_a1 << ":" << it->_a2 << endl;cout << it.operator->()->_a1 << ":" << it.operator->()->_a2 << endl;++it;}cout << endl;}void PrintList(const list<int>& clt){list<int>::const_iterator it = clt.begin();while (it != clt.end()){//*it += 10;cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;}void test_list3(){list<int> lt;lt.push_back(1);lt.push_back(2);lt.push_back(3);lt.push_back(4);lt.push_back(5);PrintList(lt);list<int> lt1(lt);PrintList(lt1);}}相关文章:

【C++】list模拟实现
个人主页 : zxctscl 如有转载请先通知 文章目录 1. 前言2. list源码3. 初始化3.1 构造3.2 拷贝构造3.3 赋值3.4 析构 4. 迭代器4.1 后置加加和前置加加4.2 后置减减和前置减减4.3 解引用4.4 !和4.5 begin 和 end4.6 const迭代器4.7 迭代器优化 5. Modifi…...

ETL工具-nifi干货系列 第八讲 处理器PutDatabaseRecord 写数据库(详细)
1、本节通过一个小例子来讲解下处理器PutDatabaseRecord,该处理器的作用是将数据写入数据库。 如下流程通过处理器GenerateFlowFile 生成数据,然后通过处理器JoltTransformJSON转换结构,最后通过处理器PutDatabaseRecord将数据写入数据库。如…...
【MySQL】如何判断一个数据库是否出问题
在实际的应用中,其实大多数是主从结构。而采用主备,一般都需要一定的费用。 对于主备,如果主机故障,那么只需要直接将流量打到备机就可以,但是对于一主多从,还需要将从库连接到主库上。 对于切换的操作&a…...

SQLite数据库的性能问题并不是单纯地由数据量的大小决定的,而是受到多种因素的综合影响。以下是一些可能导致SQLite性能问题的因素
SQLite数据库的性能问题并不是单纯地由数据量的大小决定的,而是受到多种因素的综合影响。以下是一些可能导致SQLite性能问题的因素: 数据量:当SQLite数据库中的数据量增长到一定程度时,查询、插入和更新等操作可能会变得缓慢。这…...
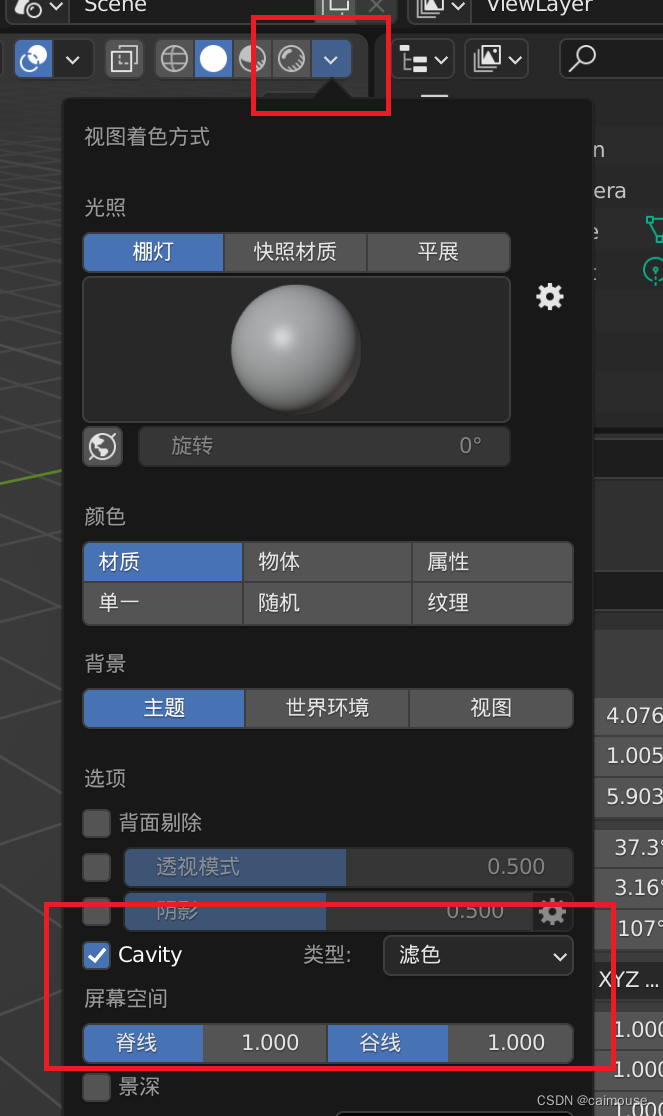
Blender怎么样启动默认移动和Cavity效果
在使用Blender的过程中,有一些特殊的技巧很重要。 比如默认地设置blender打开时,就是移动物体,这样怎么样设置的呢? 需要在界面里打开下面的菜单: 这样就找到默认设置的地方,把下面的移动勾选起来,这样点…...

Android 解决TextView多行滑动与NestedScrollView嵌套滑动冲突的问题
关键计算地方: 1.当前是上滑动还是下滑动(相对于屏幕) ,使用ev.getRawY()获得当前滑动位置在屏幕哪个地方 2. 计算文本客滑动到哪里即可停止, (行高*总文本行数)- (行高 * 最多显示行数) int sum getLineHeight() * getLineCount() - getLineHeight() * getMaxLines(); …...

Laravel 开发Api规范
一,修改时区 配置 config/app.php 文件 // 时区修改,感觉两者皆可,自己根据实际情况定义 timezone > PRC, // 大陆时间二,设置 Accept 头中间件 accept头即为客户端请求头,做成中间件来使用。Accept 决定了响应返…...
蓝色wordpress外贸建站模板
蓝色wordpress外贸建站模板 https://www.mymoban.com/wordpress/7.html...
windos环境,使用docker容器运行项目的,新增外部访问地址配置
对于运行在 Docker 容器中的项目,你需要在容器内部编辑 resolv.conf 文件。以下是一种常见的方法: 进入正在运行的 Docker 容器:docker exec -it [container_id] bash其中 [container_id] 是你正在运行的 Docker 容器的 ID。 在容器内部使…...

设计模式:生活中的组合模式
想象一下,你正在组织一个大型的家庭聚会。在这个聚会中,你需要准备各种菜肴,每个菜肴又包含不同的食材。你的目标是能够以统一的方式处理整个聚会的准备工作,不论是处理单个食材还是一整道菜肴。 在这个场景中,我们可…...

WPF OnStartup
在Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF)框架中,OnStartup 是 System.Windows.Application 类的一个受保护的虚方法,它是应用程序启动过程中的一个重要环节。当一个 WPF 应用程序启动时,其入口点通常是 App.xaml 文件和对应的后台代码文件 A…...

docker-相关
打镜像 1、编写dockfile文件,请自行百度 2、docker build -t 镜像名称:版本号 dockerFile路径 3、docker save -o 镜像压缩包名称.tar 镜像名称:镜像版本号 部署镜像 1、将镜像tar包放到部署机器上 2、加载镜像:docker load -i 镜像tar包路径 3、dock…...

二十、Rust AOP 切面增强
用过 java spring 的同学,应该会对 AspectJ 的 前置、后置、环绕 增强 念念不忘,巧了 rust 也有类似能力,稍显不同的是,为了向 “零成本抽象” 靠齐,Rust 的 “增强” 是在编译期 完成的。 编译期生成,则离…...
)
掌握Go语言:Go语言精细错误,清晰、高效的错误处理实践(32)
错误处理是任何编程语言中都至关重要的一部分,Go 语言提供了一套简单而强大的错误处理机制,使得处理错误变得高效而清晰。 Go 错误类型 在 Go 中,错误是一个普通的接口类型,即 error 接口,其定义如下: t…...

Spring与Web环境的集成
1. ApplicationContext应用上下文获取方式 应用上下文对象是通过new ClasspathXmlApplicationContext(spring配置文件) 方式获取的,但是每次从容器中获得Bean时都要编写new ClasspathXmlApplicationContext(spring配置文件) ,这样的弊端是配置文件加载多…...
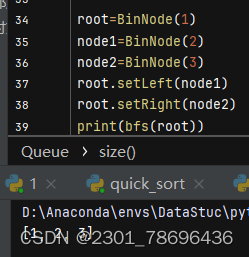
二叉树的遍历——bfs广度优先搜索
1、BinNode类的创建 (1)代码总览 ##(2)测试示例 2、二叉树的遍历 (1)图示 (2)代码总览 (3)测试示例...
飞鸟写作可靠吗 #职场发展#经验分享#经验分享
飞鸟写作是一个非常便捷的论文写作工具,不仅可以帮助用户高效地完成论文写作,还可以提供查重降重的功能,帮助用户确保论文的原创性。那么,飞鸟写作到底可靠吗?答案是肯定的。 首先,飞鸟写作提供的查重降重功…...
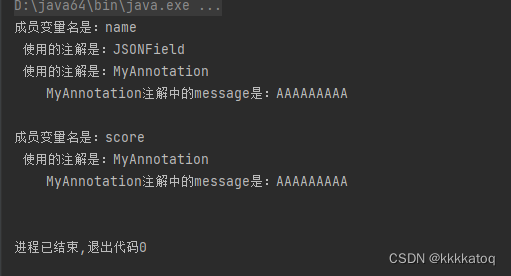
Java 实现自定义注解
一、interface 关键字 我们想定义一个自己的注解 需要使用 interface 关键字来定义。 如定义一个叫 MyAnnotation 的注解: public interface MyAnnotation { } 二、元注解 光加上 interface 关键字 还不够,我们还需要了解5大元注解 RetentionTargetDo…...

代码随想录Day48
Day 48 动态规划part09 今日任务 198.打家劫舍213.打家劫舍II337.打家劫舍III 代码实现 基础打家劫舍 class Solution {public static int rob(int[] nums) {if (nums null || nums.length 0) return 0;if (nums.length 1) return nums[0];int[] dp new int[nums.leng…...
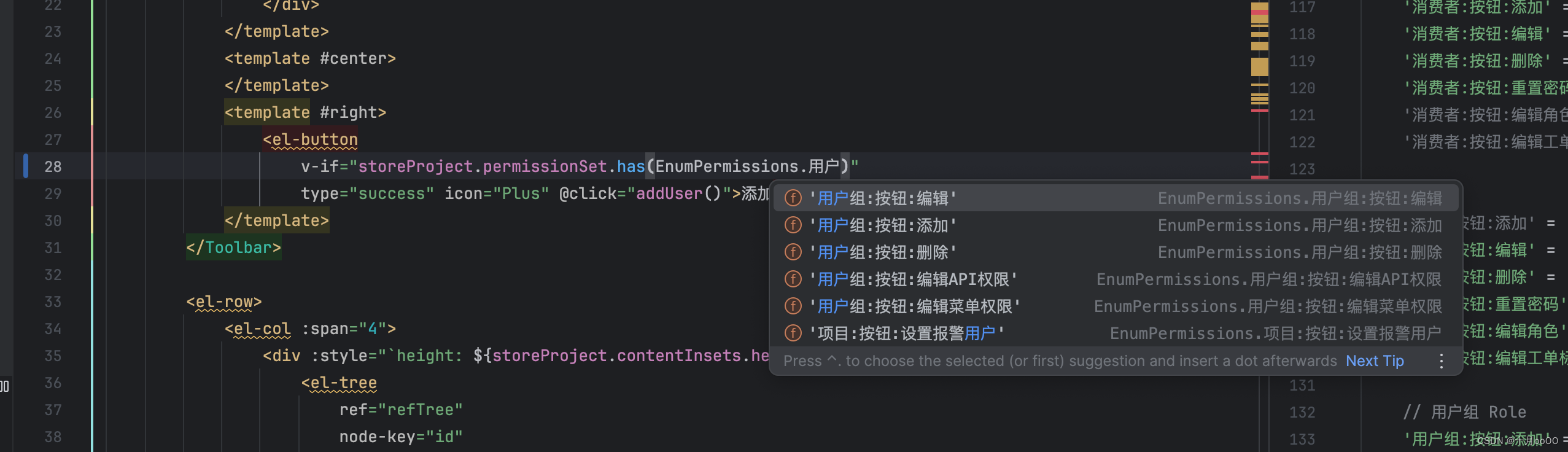
Web 后台项目,权限如何定义、设置、使用:菜单权限、按钮权限 ts element-ui-Plus
Web 后台项目,权限如何定义、设置、使用:菜单权限、按钮权限 ts element-ui-Plus 做一个后台管理项目,里面需要用到权限管理。这里说一下权限定义的大概,代码不多,主要讲原理和如何实现它。 一、权限管理的原理 权限…...

调用支付宝接口响应40004 SYSTEM_ERROR问题排查
在对接支付宝API的时候,遇到了一些问题,记录一下排查过程。 Body:{"datadigital_fincloud_generalsaas_face_certify_initialize_response":{"msg":"Business Failed","code":"40004","sub_msg…...
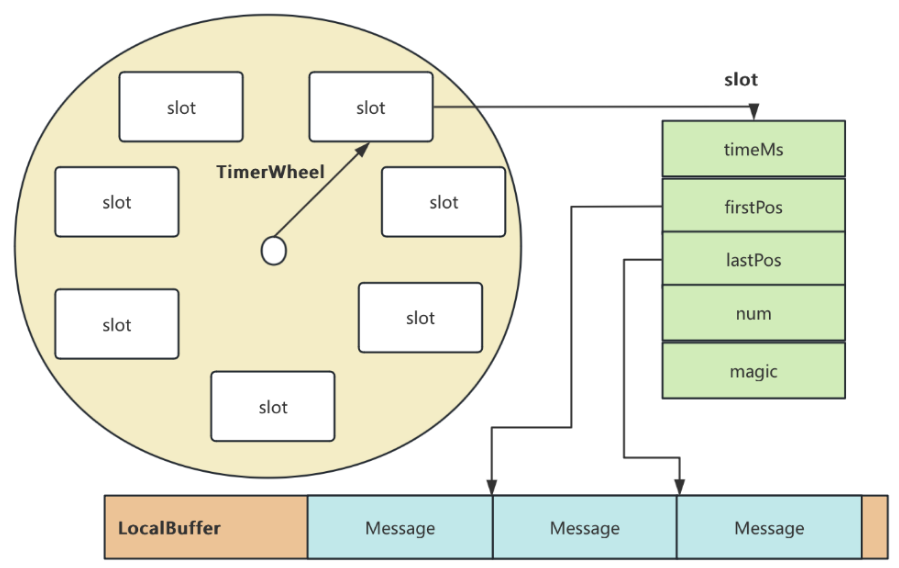
RocketMQ延迟消息机制
两种延迟消息 RocketMQ中提供了两种延迟消息机制 指定固定的延迟级别 通过在Message中设定一个MessageDelayLevel参数,对应18个预设的延迟级别指定时间点的延迟级别 通过在Message中设定一个DeliverTimeMS指定一个Long类型表示的具体时间点。到了时间点后…...

前端倒计时误差!
提示:记录工作中遇到的需求及解决办法 文章目录 前言一、误差从何而来?二、五大解决方案1. 动态校准法(基础版)2. Web Worker 计时3. 服务器时间同步4. Performance API 高精度计时5. 页面可见性API优化三、生产环境最佳实践四、终极解决方案架构前言 前几天听说公司某个项…...

FastAPI 教程:从入门到实践
FastAPI 是一个现代、快速(高性能)的 Web 框架,用于构建 API,支持 Python 3.6。它基于标准 Python 类型提示,易于学习且功能强大。以下是一个完整的 FastAPI 入门教程,涵盖从环境搭建到创建并运行一个简单的…...
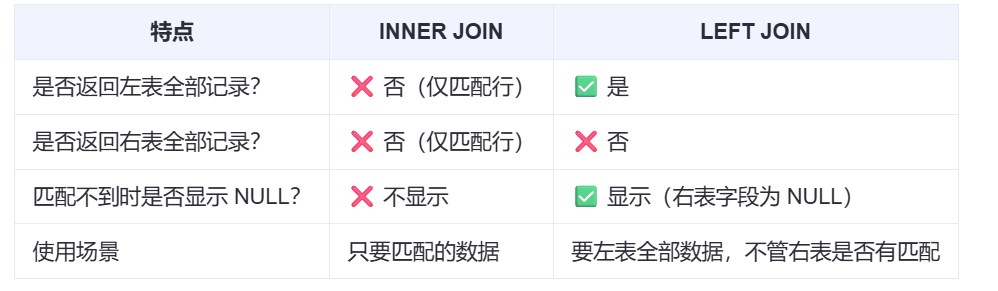
【SQL学习笔记1】增删改查+多表连接全解析(内附SQL免费在线练习工具)
可以使用Sqliteviz这个网站免费编写sql语句,它能够让用户直接在浏览器内练习SQL的语法,不需要安装任何软件。 链接如下: sqliteviz 注意: 在转写SQL语法时,关键字之间有一个特定的顺序,这个顺序会影响到…...

linux 下常用变更-8
1、删除普通用户 查询用户初始UID和GIDls -l /home/ ###家目录中查看UID cat /etc/group ###此文件查看GID删除用户1.编辑文件 /etc/passwd 找到对应的行,YW343:x:0:0::/home/YW343:/bin/bash 2.将标红的位置修改为用户对应初始UID和GID: YW3…...
微服务商城-商品微服务
数据表 CREATE TABLE product (id bigint(20) UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 商品id,cateid smallint(6) UNSIGNED NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT 类别Id,name varchar(100) NOT NULL DEFAULT COMMENT 商品名称,subtitle varchar(200) NOT NULL DEFAULT COMMENT 商…...

Linux C语言网络编程详细入门教程:如何一步步实现TCP服务端与客户端通信
文章目录 Linux C语言网络编程详细入门教程:如何一步步实现TCP服务端与客户端通信前言一、网络通信基础概念二、服务端与客户端的完整流程图解三、每一步的详细讲解和代码示例1. 创建Socket(服务端和客户端都要)2. 绑定本地地址和端口&#x…...

回溯算法学习
一、电话号码的字母组合 import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List;import javax.management.loading.PrivateClassLoader;public class letterCombinations {private static final String[] KEYPAD {"", //0"", //1"abc", //2"…...

解决:Android studio 编译后报错\app\src\main\cpp\CMakeLists.txt‘ to exist
现象: android studio报错: [CXX1409] D:\GitLab\xxxxx\app.cxx\Debug\3f3w4y1i\arm64-v8a\android_gradle_build.json : expected buildFiles file ‘D:\GitLab\xxxxx\app\src\main\cpp\CMakeLists.txt’ to exist 解决: 不要动CMakeLists.…...
