Day27
Day27
反射案例
案例一:万能数组扩容
注意:copyOf、toString
public class Test01 {/*** 知识点:反射案例 之 万能数组扩容* * 注意:copyOf、toString*/public static void main(String[] args) {String[] ss = {"aaa","bbb","ccc"};String[] copyOf = MyArrays.copyOf(ss, 5);System.out.println(MyArrays.toString(copyOf));} }MyArrays内:
public static <T> T[] copyOf(T[] arr,int newLength){int copyLen = Array.getLength(arr);if(copyLen > newLength){copyLen = newLength;}//arr -- String[].classClass<? extends Object[]> clazz = arr.getClass();//elementType -- String.classClass<?> componentType = clazz.getComponentType();@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")T[] ts = (T[]) Array.newInstance(componentType, newLength);for (int i = 0; i < copyLen; i++) {Object element = Array.get(arr, i);Array.set(ts, i, element);}return ts;} public static String toString(Object[] arr){String str = "[";for (Object element : arr) {if(str.length() != 1){str += ",";}str += element;}str += "]";return str;} }注意:1.copyOf方法使用了泛型 T[],而泛型只适用于引用数据类型,所以此时的copyOf方法是无法传入基本数据类型的数组的,要解决这个问题,应该在下面进行基本数据类型的方法重载。
2.方法重载应该选择挨个地对基本数据类型进行重写,而不是用object类型,原因在于Java 泛型的擦除机制。这个机制是指在编译时,泛型类型信息会被擦除,这意味着在生成的字节码中,泛型类型的信息将被替换为原始类型(或者对象类型)。所以会报错,报错信息为这个方法和上面那个泛型的方法完全一样,因为T泛型进行擦除后就是Object类。
案例二:业务与逻辑分离的思想
需求:让用户选择不同获取数据的方式
public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);showMenu();int num = scan.nextInt();DataSourse dataSourse = getBean(num);dataSourse.getDataSourse();scan.close();}public static DataSourse getBean(int num){DataSourse[] beans = DataCenter.getBean();return beans[num-1];}public static void showMenu(){String[] menus = DataCenter.getMenus();System.out.println("请选择以下获取数据的方式:");for (String string : menus) {System.out.println(string);}}public abstract class DataSourse {public abstract void getDataSourse(); }public class LocalDataSourse extends DataSourse{@Overridepublic void getDataSourse() {System.out.println("获取本地数据");BufferedReader br = null;try {br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("hhy.txt"));char[] cs = new char[1024];int len;while((len = br.read(cs)) != -1){System.out.println(new String(cs, 0, len));}} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {if(br != null){try {br.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}} }//获取网络数据的类 public class NetworkDataSource extends DataSourse{@Overridepublic void getDataSourse() {System.out.println("获取网络数据");try {URL url = new URL("https://suggest.taobao.com/sug?code=gbk&q=始祖鸟&callback=cb");//获取链接对象HttpURLConnection connection = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();//设置参数connection.setConnectTimeout(5000);//设置连接超时时间connection.setReadTimeout(5000);//设置读取超时时间connection.setDoInput(true);//设置允许使用输入流connection.setDoOutput(true);//设置允许使用输出流//获取响应状态码int responseCode = connection.getResponseCode();if(responseCode == HttpURLConnection.HTTP_OK){//获取响应中的数据BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(connection.getInputStream(),"UTF-8"));char[] cs = new char[1024];int len;while((len = br.read(cs)) != -1){System.out.println(new String(cs, 0, len));}br.close();}else if(responseCode == HttpURLConnection.HTTP_NOT_FOUND){System.out.println("响应错误,页面未找到");}} catch (MalformedURLException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}public class OtherDataSourse extends DataSourse{@Overridepublic void getDataSourse() {System.out.println("获取其他资源");}}//从配置文件中读取配置信息,并将这些配置信息用于初始化两个静态列表 public class DataCenter {private static ArrayList<String> menuList;private static ArrayList<DataSourse> beanList;static{menuList = new ArrayList<>();Properties p = new Properties();try {p.load(DataSourse.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("MenuConfig.properties"));} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}String menu = p.getProperty("menu");String[] split = menu.split(",");for (String string : split) {menuList.add(string);}}public static String[] getMenus(){String[] menus = new String[menuList.size()];menuList.toArray(menus);return menus;}static{beanList = new ArrayList<>();Properties p = new Properties();try {p.load(DataSourse.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("BeanConfig.properties"));} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}String path = p.getProperty("path");String[] split = path.split(",");for (String string : split) {try {Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(string);DataSourse dataSourse = (DataSourse) clazz.newInstance();beanList.add(dataSourse);} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (InstantiationException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}public static DataSourse[] getBean(){DataSourse[] beans = new DataSourse[beanList.size()];beanList.toArray(beans);return beans;}}
案例三:获取注解信息
public class Test01 {/*** 知识点:反射案例 之 获取注解信息*/public static void main(String[] args) {Student stu = new Student("侯小康", '男', 23, "2402", "001");String insertSql = ReflexUtil.getInsertSql(stu);System.out.println(insertSql);//insert into s_student(s_name,s_sex,s_age,s_class_id,s_id) values('侯小康','男',23,'2402','001');} }@Target(ElementType.FIELD) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface FieldInfo {String name();String type();int length(); }@Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface TableInfo {String value(); }@TableInfo("s_student") public class Student {@FieldInfo(name="s_name",type="varchar",length=255)private String name;@FieldInfo(name="s_sex",type="varchar",length=255)private char sex;@FieldInfo(name="s_age",type="int",length=255)private int age;@FieldInfo(name="s_class_id",type="varchar",length=255)private String classId;@FieldInfo(name="s_id",type="varchar",length=255)private String id;public Student() {}public Student(String name, char sex, int age, String classId, String id) {this.name = name;this.sex = sex;this.age = age;this.classId = classId;this.id = id;}public String getName() {return name;}public char getSex() {return sex;}public int getAge() {return age;}public String getClassId() {return classId;}public String getId() {return id;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public void setSex(char sex) {this.sex = sex;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}public void setClassId(String classId) {this.classId = classId;}public void setId(String id) {this.id = id;} }ReflexUtil工具类中:
public static String getInsertSql(Object obj){Class<? extends Object> clazz = obj.getClass();//获取表名 -- 获取类上的注解信息TableInfo tableInfo = clazz.getAnnotation(TableInfo.class);String tableName = tableInfo.value();//获取字段名和字段数据 -- 获取属性上的注解信息Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();StringBuffer fieldNameSB = new StringBuffer();StringBuffer valueSB = new StringBuffer();for (Field field : fields) {field.setAccessible(true);//获取属性上的注解信息(字段名和字段类型)FieldInfo fieldInfo = field.getAnnotation(FieldInfo.class);String name = fieldInfo.name();String type = fieldInfo.type();Object value = null;try {value = field.get(obj);} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {e.printStackTrace();}if(fieldNameSB.length() != 0){fieldNameSB.append(",");}fieldNameSB.append(name);if(valueSB.length() != 0){valueSB.append(",");}if(type.equals("varchar")){valueSB.append("'");}valueSB.append(value);if(type.equals("varchar")){valueSB.append("'");}}String insertSql = "insert into " + tableName + "(" + fieldNameSB.toString() + ") values(" + valueSB.toString() + ");";return insertSql;}
JDK1.8新特性简介
- 速度更快 - 优化底层源码,比如HashMap、ConcurrentHashMap
- 代码更少 - 添加新的语法Lambda表达式
- 强大的Stream API
- 便于并行
- 最大化减少空指针异常 - Optional
Lambda表达式
简介
Lambda是一个匿名函数(方法), 允许把函数作为一个方法的参数 。利用Lambda表达式可以写出更简洁、更灵活的代码。作为一种更紧凑的代码风格,使Java的语言表达能力得到了提升。一般都是优化匿名内部类
基础语法
无参数、无返回值的抽象方法
public class Test1 {@Testpublic void test01() {
// I1 i1 = new I1() {
// @Override
// public void method() {
// System.out.println("传统使用匿名内部类的方式");
// }
// };
// i1.method();I1 i1 = ()-> System.out.println("采用Lambda表达式的方式");i1.method();}
}
interface I1{public void method();//无参数、无返回值的抽象方法
}
一个参数、无返回值的抽象方法
public class Test1 {@Testpublic void test01() {I1 i1 = (x)-> System.out.println("采用Lambda表达式的方式 " + x);i1.method(1000);}
}
interface I1{public void method(int num1);//一个参数、无返回值的抽象方法
}
多个参数、无返回值的抽象方法
public class Test1 {@Testpublic void test01() {I1 i1 = (x,y,z)-> System.out.println("采用Lambda表达式的方式 " + x + y + z);i1.method(1000,2000,3000);}
}
interface I1{//多个参数、无返回值的抽象方法public void method(int num1,int num2,int num3);
}
多个参数、有返回值的抽象方法
public class Test1 {@Testpublic void test01() {I1 i1 = (x,y,z)-> x+y+z;int result = i1.method(1000,2000,3000);System.out.println(result);}
}
interface I1{//多个参数、有返回值的抽象方法public int method(int num1,int num2,int num3);
}
注意点
- 重写方法的形参只有一个时,可以不加小括号
- Lambda表达式当中不允许声明一个与局部变量同名的参数或者局部变量
- Lambda表达式中访问外层的局部变量,外层的局部变量自动变成隐式常量,默认添加final
- 重写方法的形参同时加类型或同时不加类型
public class Test1 {@Testpublic void test01() {int x;int num = 10;I1 i1 = x -> System.out.println(x + (num++));i1.method(1000);I2 i2 = (int x,int y) -> {int result = x+y;return result;};int result = i2.method(10, 20);System.out.println(result);}
}
interface I1{public void method(int num1);
}
interface I2{public int method(int num1,int num2);
}
练习
- 调用Collections.sort()方法,通过定制排序比较两个Student对象(先按年龄比较,年龄相同按照薪资比较),使用Lambda表达式作为参数传递
public class Test1 {@Testpublic void test01() {List<Student> stuList = Arrays.asList(new Student("张三", 28, 4800,Course.JAVA),new Student("李四", 36, 7200,Course.JAVA),new Student("王五", 19, 9600,Course.HTML),new Student("赵六", 42, 6100,Course.HTML),new Student("孙七", 23, 9600,Course.PYTHON),new Student("吴八", 31, 3000,Course.PYTHON));Collections.sort(stuList, (a,b)-> {if(a.getAge() == b.getAge()){return Double.compare(a.getSalary(),b.getSalary());}return a.getAge()-b.getAge();});for (Student stu : stuList) {System.out.println(stu);}}
}
enum Course{//课程枚举JAVA,HTML,PYTHON;
}
class Student{//学生类private String name;private int age;private double salary;private Course course;...
}
- 创建I1接口,创建抽象方法:public String getValue(String str),在测试类中编写方法使用接口作为参数,将一个字符串转为大写,并作为方法的返回值
public class Test1 {@Testpublic void test01() {String strHandler = strHandler("abc", x-> x.toUpperCase());System.out.println(strHandler);}public static String strHandler(String str,I1 i1){return i1.getValue(str);}
}
interface I1{public String getValue(String str);
}
- 创建I1<T,R>接口,泛型T为参数,R为返回值,创建抽象方法:public R add(T t1,T t2),在测试类中编写方法使用接口作为参数,计算两个long类型的和
public class Test1 {@Testpublic void test01() {Long addLong = addLong(100L, 200L, (x,y)-> x+y);System.out.println(addLong);}public static Long addLong(Long l1,Long l2,I1<Long,Long> i1){return i1.add(l1, l2);}
}
interface I1<T,R>{public R add(T t1,T t2);
}
函数式接口
简介
函数式接口是指仅仅只包含一个抽象方法的接口,jdk1.8提供了一个@FunctionalInterface注解来定义函数式接口,如果我们定义的接口不符合函数式的规范便会报错。配合Lambda表达式一起使用
四大核心函数式接口
| 函数式接口 | 参数类型 | 返回类型 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Consumer 消费型接口 | T | void | void accept(T t); |
| Supplier 供给型接口 | void | T | T get(); |
| Function<T, R> 函数型接口 | T | R | R apply(T t); |
| Predicate 断言型接口 | T | boolean | booelan test(T t); |
| BiConsumer<T, U> | T,U | void | 对类型为T,U参数应用操作。包含方法为void accept(T t,U u); |
| BiFunction<T, U, R> | T,U | R | 对类型为T,U参数应用操作,并返回R类型的结果。包含方法为R apply(T t,U u); |
| UnaryOperator extends Function<T, T> | T | T | 对类型为T的对象进行一元运算,并返回T类型的结果。包含方法为T apply(T t); |
| BinaryOperator extends BiFunction<T,T,T> | T,T | T | 对类型为T的对象进行二元运算,并返回T类型的结果。包含方法为T apply(T t1,T t2); |
| ToIntFunction ToLongFunction ToDoubleFunction | T | int long double | 分别计算int、long、double值的函数 |
| IntFunction LongFunction DoubleFunction | int long double | R | 参数为int、long、double类型的函数 |
应用场景
当我们编写一个接口,这个接口只有一个抽象方法时,就可以使用函数式接口去替代
public static void main(String[] args) {String method = method("abc", (str)->str.toUpperCase());System.out.println(method);}public static String method(String str,Function<String, String> fun){return fun.apply(str);}
方法、构造方法和数组引用
方法、构造方法和数组引用就是Lamdba的另一种表现形式
方法引用
若Lamdba表达式中的内容由方法已经实现了,可以使用方法引用这个技能
当你需要使用方法引用时,目标引用放在分隔符::前,方法的名称放在后面
对象::实例方法
Lambda表达式中调用方法的参数类型和返回值必须和函数式接口中的抽象方法一致
public class Test1 {@Testpublic void test01() {
// I1 i1 = (x)->System.out.println(x);
// i1.method("abcd");//println里的参数列表和返回值类型必须和method方法一致才行PrintStream ps = System.out;I1 i1 = ps::println;//对象::实例方法 i1.method("abcd"); }
}
interface I1{public void method(String str);
}
类名::静态方法
Lambda表达式中调用方法的参数类型和返回值必须和函数式接口中的抽象方法一致
public class Test1 {@Testpublic void test01() {
// Comparator<Integer> com = (x,y)-> Integer.compare(x, y);
// int compare = com.compare(10, 20);
// System.out.println(compare);//类名::静态方法Comparator<Integer> com = Integer::compare;int compare = com.compare(10, 20);System.out.println(compare);}}
类名::实例方法
Lambda表达式参数列表中第一个参数必须是实例方法的调用者
Lambda表达式参数列表中第二个参数必须是实例方法的参数
public class Test1 {@Testpublic void test01() {
// I1<String> i1 = (x,y) -> x.equals(y);
// boolean method = i1.method("abc", "abc");
// System.out.println(method);//类名::实例方法//注意:Lambda表达式参数列表中第一个参数是equals方法的调用者,// Lambda表达式参数列表中第二个参数是equals方法的参数I1<String> i1 = String::equals;boolean method = i1.method("abc", "abc");System.out.println(method);}
}
interface I1<T>{public boolean method(T t1,T t2);
}
构造方法引用
类名::new
需要调用的构造方法的参数列表必须和函数式接口中抽象方法的参数列表一致
public class Test04 {/*** 知识点:构造方法的引用*/public static void main(String[] args) {//调用Student类的无参构造去创建对象I3 i3 = Student::new;Student stu1 = i3.method();System.out.println(stu1);//调用Student类的有参构造去创建对象I4 i4 = Student::new;Student stu2 = i4.method("小康", 23, 12000, Course.JAVA);System.out.println(stu2);}
}interface I3{public Student method();
}interface I4{public Student method(String name, int age, double salary, Course course);
}
数组引用
语法格式:type[]::new
public class Test1 {@Testpublic void test01() { //创建数组I1<String[]> i1 = String[]::new;System.out.println(Arrays.toString(i1.method(10)));}
}
interface I1<T>{public T method(int capacity);
}
Stream
Stream(流)是数据渠道,用于操作数据源(集合、数组等),生成元素序列。换言之,集合是存储数据的容器,流使用操作这些数据的
Stream可以对集合进行非常复杂的查找、过滤、映射数据等操作,类似于SQL执行数据库查询。Stream提供了一种高效且易于使用的处理数据的方式
注意:
- Stream不会存储数据
- Stream不会改变源数据,通过一系列操作数据源会返回一个持有结果的新Stream
- Stream操作是延迟执行的,意味着流会等到需要结果的时候才执行
执行步骤
- 创建Stream:通过数据源(集合、数组等)获取一个Stream
- 中间操作:中间操作链,对源数据的数据进行处理
- 终止操作:执行中间操作,并产生结果
创建Stream
public class Test01 {/*** 知识点:获取Stream流对象*/@Testpublic void test01(){//方式一:通过集合获取流对象List<Student> stuList = Arrays.asList(new Student("张三", 28, 4800,Course.JAVA),new Student("李四", 36, 7200,Course.JAVA),new Student("王五", 19, 9600,Course.HTML),new Student("赵六", 42, 6100,Course.HTML),new Student("孙七", 23, 9600,Course.PYTHON),new Student("吴八", 31, 3000,Course.PYTHON),new Student("李四", 36, 7200,Course.JAVA));// Stream<Student> stream = stuList.stream(); // stream.forEach(new Consumer<Student>() { // @Override // public void accept(Student t) { // System.out.println(t); // } // });stuList.stream().forEach(System.out::println);}@Testpublic void test02(){//方式二:通过数组获取Stream流对象String[] names = {"aaa","bbb","ccc","ddd","eee"}; // Stream<String> stream = Arrays.stream(names); // stream.forEach(System.out::println);Arrays.stream(names).forEach(System.out::println);}@Testpublic void test03(){//方式三:通过Stream的静态方法of()获取流对象Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("aaa","bbb","ccc","ddd","eee");stream.forEach(System.out::println);}@Testpublic void test04(){//方式四:创建无限流、迭代流Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.iterate(10, (x)->x+100);Stream<Integer> newStram = stream.limit(5);newStram.forEach(System.out::println);}@Testpublic void test05(){//方式四:创建无限流Stream<Double> stream = Stream.generate(Math::random);Stream<Double> newStram = stream.limit(5);newStram.forEach(System.out::println);}}
中间操作 - 筛选与切片
public class Test02 {/*** 知识点:中间操作 - 筛选与切片*/List<Student> stuList = Arrays.asList(new Student("张三", 28, 4800,Course.JAVA),new Student("李四", 36, 7200,Course.JAVA),new Student("王五", 19, 9600,Course.HTML),new Student("赵六", 42, 6100,Course.HTML),new Student("孙七", 23, 9600,Course.PYTHON),new Student("吴八", 31, 3000,Course.PYTHON),new Student("李四", 36, 7200,Course.JAVA));@Testpublic void test01(){//需求1:过滤掉工资小于5000的学生对象stuList.stream().filter((stu)->{double salary = stu.getSalary();if(salary>5000){return true;}return false;}).forEach(System.out::println);}@Testpublic void test02(){//需求2:过滤掉工资小于5000的学生对象,并显示3条 // stuList.stream().filter((stu)->{ // double salary = stu.getSalary(); // if(salary>5000){ // return true; // } // return false; // }).limit(3).forEach(System.out::println);stuList.stream().filter((stu)->{return stu.getSalary()>5000;}).limit(3).forEach(System.out::println);}@Testpublic void test03(){//需求3:过滤掉工资小于5000的学生对象,并跳过第1个学生对象 // stuList.stream().filter((stu)->{ // double salary = stu.getSalary(); // if(salary>5000){ // return true; // } // return false; // }).skip(1).forEach(System.out::println);stuList.stream().filter((stu)->{return stu.getSalary()<5000;}).skip(1).forEach(System.out::println);}@Testpublic void test04(){//需求4:过滤掉工资小于5000的学生对象,并筛选掉重复元素 // stuList.stream().filter((stu)->{ // double salary = stu.getSalary(); // if(salary>5000){ // return true; // } // return false; // }).distinct().forEach(System.out::println);stuList.stream().filter((stu)->stu.getSalary()<5000).distinct().forEach(System.out::println);}}
中间操作 - 映射
public class Test03 {/*** 知识点:中间操作 - 映射*/List<Student> stuList = Arrays.asList(new Student("张三", 28, 4800,Course.JAVA),new Student("李四", 36, 7200,Course.JAVA),new Student("王五", 19, 9600,Course.HTML),new Student("赵六", 42, 6100,Course.HTML),new Student("孙七", 23, 9600,Course.PYTHON),new Student("吴八", 31, 3000,Course.PYTHON),new Student("李四", 36, 7200,Course.JAVA));@Testpublic void test01(){//获取所有学生的姓名//Stream 类的 map 函数用于将流中的每个元素转换为另一种形式 // stuList.stream().map(new Function<Student, String>() { // @Override // public String apply(Student stu) { // return stu.getName(); // } // }).forEach(new Consumer<String>() { // @Override // public void accept(String name) { // System.out.println(name); // } // });// stuList.stream().map((stu)->stu.getName()).forEach(System.out::println);stuList.stream().map(Student::getName).forEach(System.out::println);}}
中间操作 - 排序
public class Test04 {/*** 知识点:中间操作 - 排序*/List<Student> stuList = Arrays.asList(new Student("张三", 28, 4800,Course.JAVA),new Student("李四", 36, 7200,Course.JAVA),new Student("王五", 19, 9600,Course.HTML),new Student("赵六", 42, 6100,Course.HTML),new Student("孙七", 23, 9600,Course.PYTHON),new Student("吴八", 31, 3000,Course.PYTHON),new Student("李四", 36, 7200,Course.JAVA));@Testpublic void test01(){//使用元素原有排序规则(Comparable<T>)//需求:按照年龄排序stuList.stream().sorted().forEach(System.out::println);}@Testpublic void test02(){//使用自定义排序规则(Comparator<T>)//需求:按照工资排序stuList.stream().sorted((stu1,stu2)->{return Double.compare(stu1.getSalary(), stu2.getSalary());}).forEach(System.out::println);}}
终止操作 - 匹配与查找
public class Test1 {List<Student> stuList = Arrays.asList(new Student("张三", 28, 4800,Course.JAVA),new Student("李四", 36, 7200,Course.JAVA),new Student("王五", 19, 9600,Course.HTML),new Student("赵六", 42, 6100,Course.HTML),new Student("孙七", 23, 9600,Course.PYTHON),new Student("吴八", 31, 3000,Course.PYTHON),new Student("吴八", 31, 3000,Course.PYTHON));@Testpublic void test01() { //需求1:检查流中所有元素是否匹配 工资>5000boolean allMatch = stuList.stream().allMatch((stu) -> stu.getSalary()>5000);System.out.println(allMatch);//false//需求2:检查流中所有元素至少匹配一个 工资>5000boolean anyMatch = stuList.stream().anyMatch((stu) -> stu.getSalary()>5000);System.out.println(anyMatch);//true//需求3:检查流中所有元素是否没有匹配 工资>5000boolean noneMatch = stuList.stream().noneMatch((stu) -> stu.getSalary()>5000);System.out.println(noneMatch);//需求4:返回工资最高的学生信息Optional<Student> findFirst = stuList.stream().sorted((stu1,stu2)->Double.compare(stu1.getSalary(),stu2.getSalary())).findFirst();Student stu = findFirst.get();//这种写法防止NullPointerException出现//Student stu = findFirst.orElse(new Student());System.out.println(stu);//需求5:返回随机学生信息(但效果不好)Optional<Student> findAny = stuList.stream().findAny();Student stu = findAny.get();System.out.println(stu);//需求6:获取学生个数long count = stuList.stream().count();System.out.println(count);//需求7:获取最高工资的学生信息Optional<Student> max = stuList.stream().max((stu1,stu2)->Double.compare(stu1.getSalary(),stu2.getSalary()));System.out.println(max.get());//需求8:获取最低工资的学生信息Optional<Student> min = stuList.stream().min((stu1,stu2)->Double.compare(stu1.getSalary(),stu2.getSalary()));System.out.println(min.get());} } enum Course{//课程枚举JAVA,HTML,PYTHON; } class Student implements Comparable<Student>{//学生类private String name;private int age;private double salary;private Course course;... }
终止操作 - 归约
public class Test1 {List<Integer> numList = Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10);List<Student> stuList = Arrays.asList(new Student("张三", 28, 4800,Course.JAVA),new Student("李四", 36, 7200,Course.JAVA),new Student("王五", 19, 9600,Course.HTML),new Student("赵六", 42, 6100,Course.HTML),new Student("孙七", 23, 9600,Course.PYTHON),new Student("吴八", 31, 3000,Course.PYTHON),new Student("李四", 36, 7200,Course.JAVA));@Testpublic void test01() { //需求:获取numList集合中元素的总和Integer reduce = numList.stream().reduce(0, (x,y)->x+y);System.out.println(reduce);}@Testpublic void test02() { //需求:获取stuList集合中所有学生工资总和Optional<Double> reduce = stuList.stream().map(Student::getSalary).reduce(Double::sum);Double sumSalary = reduce.get();System.out.println(sumSalary);} } enum Course{//课程枚举JAVA,HTML,PYTHON; } class Student implements Comparable<Student>{//学生类private String name;private int age;private double salary;private Course course;
终止操作 - 收集
public class Test1 {List<Student> stuList = Arrays.asList(new Student("张三", 28, 4800,Course.JAVA),new Student("李四", 36, 7200,Course.JAVA),new Student("王五", 19, 9600,Course.HTML),new Student("赵六", 42, 6100,Course.HTML),new Student("孙七", 23, 9600,Course.PYTHON),new Student("吴八", 31, 3000,Course.PYTHON),new Student("李四", 36, 7200,Course.JAVA));@Testpublic void test01() {//把数据收集到集合中//需求1:把当前学生姓名提取出来,并把数据放入List集合中List<String> list = stuList.stream().map(Student::getName).collect(Collectors.toList());list.forEach(System.out::println);//需求2:把当前学生姓名提取出来,并把数据放入Set集合中Set<String> set = stuList.stream().map(Student::getName).collect(Collectors.toSet());set.forEach(System.out::println);//需求3:把当前学生姓名提取出来,并把数据放入指定集合中HashSet<String> hashSet = stuList.stream().map(Student::getName).collect(Collectors.toCollection(HashSet::new));hashSet.forEach(System.out::println);} @Testpublic void test02() {//收集流中的各种数据//需求1:收集/获取学生个数Long count = stuList.stream().map(Student::getName).collect(Collectors.counting());System.out.println(count);//需求2:收集/获取学生平均工资Double avg = stuList.stream().collect(Collectors.averagingDouble(Student::getSalary));System.out.println(avg);//需求3:收集/获取学生总工资Double sum = stuList.stream().collect(Collectors.summingDouble(Student::getSalary));System.out.println(sum);//需求4:收集/获取学生工资最大值Optional<Double> max = stuList.stream().map(Student::getSalary).collect(Collectors.maxBy(Double::compareTo));System.out.println(max.get());//需求5:收集/获取学生工资最小值Optional<Double> min = stuList.stream().map(Student::getSalary).collect(Collectors.minBy(Double::compareTo));System.out.println(min.get());//需求6:收集/获取工资最多的学生信息Optional<Student> maxStu = stuList.stream().collect(Collectors.maxBy((stu1,stu2)-> (int)(stu1.getSalary()-stu2.getSalary())));System.out.println(maxStu.get());//需求7:收集/获取工资最少的学生信息Optional<Student> minStu = stuList.stream().collect(Collectors.minBy((stu1,stu2)-> (int)(stu1.getSalary()-stu2.getSalary())));System.out.println(minStu.get());} @Testpublic void test03() {//分组//需求:按照学科分组Map<Course, List<Student>> map = stuList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getCourse));System.out.println(map);}@Testpublic void test04() {//多级分组//需求:按照学科分组,在按照年龄分组Map<Course, Map<String, List<Student>>> map = stuList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getCourse,Collectors.groupingBy((stu)->{if(((Student)stu).getAge() < 28){return "青年";}else if(((Student)stu).getAge() < 40){return "中年";}else{return "老年";}})));System.out.println(map);}@Testpublic void test05() {//分区//需求:按照工资5000为标准分区Map<Boolean, List<Student>> map = stuList.stream().collect(Collectors.partitioningBy((stu) -> stu.getSalary()>5000));System.out.println(map);}@Testpublic void test06() {//获取元素中字段的各种信息//需求:获取学生工资信息,再获取总值、平均值、最大值、最小值DoubleSummaryStatistics collect = stuList.stream().collect(Collectors.summarizingDouble(Student::getSalary));System.out.println(collect.getSum());System.out.println(collect.getAverage()); System.out.println(collect.getMax());System.out.println(collect.getMin());}@Testpublic void test07() {//拼接信息//需求:拼接学生姓名String str1 = stuList.stream().map(Student::getName).collect(Collectors.joining());System.out.println(str1);String str2 = stuList.stream().map(Student::getName).collect(Collectors.joining(","));System.out.println(str2);String str3 = stuList.stream().map(Student::getName).collect(Collectors.joining(",","--","--"));System.out.println(str3);} } enum Course{//课程枚举JAVA,HTML,PYTHON; } class Student implements Comparable<Student>{//学生类private String name;private int age;private double salary;private Course course;... }…
相关文章:

Day27
Day27 反射案例 案例一:万能数组扩容 注意:copyOf、toString public class Test01 {/*** 知识点:反射案例 之 万能数组扩容* * 注意:copyOf、toString*/public static void main(String[] args) {String[] ss {"aaa"…...

uni-app App端实现文字语音播报(Ba-TTS)
前言 最近在遇到消息提示语音播放出来,查了一圈文档发现并没有自带api 后面想起支付宝收钱播报,不受限与系统环境和版本环境(后面查阅他是音频实现的) 如果是由安卓端需要语音播放功能-直接使用Ba-TTs救急(需要付费2…...

在WHM中如何调整max_upload_size 参数大小
今日我们在搭建新网站时需要调整一下PHP参数max_upload_size 的大小,我们公司使用的Hostease的美国独立服务器产品默认5个IP地址,也购买了cPanel面板,因此联系Hostease的技术支持,寻求帮助了解到如何在WHM中调整PHP参数࿰…...

docker system prune命令详解
docker system prune 是 Docker 中的一个命令,用于清理 Docker 系统中的未使用资源,以帮助回收磁盘空间。这个命令执行一系列操作来删除不再需要的项目,具体包括: 删除所有已停止的容器。删除所有未被任何容器引用的网络…...
使用jdk自带jhat工具排查OOM问题
使用jdk自带jhat工具排查OOM问题 OOM java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space排查步骤 编写一个测试类 public class TestJVM {Testpublic void test1() throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {List<A> list new ArrayList<>();for (i…...

独孤思维:付费就是割韭菜,千万别上当
01 很多人觉得付费是坑,是割韭菜。 其实大多数情况,你所付费的,是购买了别人的经验。 让你能够少走很多弯路,让你能够节约大量时间和精力,购买别人的成功路径。 打一个粗俗的比方。 很多人都说,买的资料&am…...
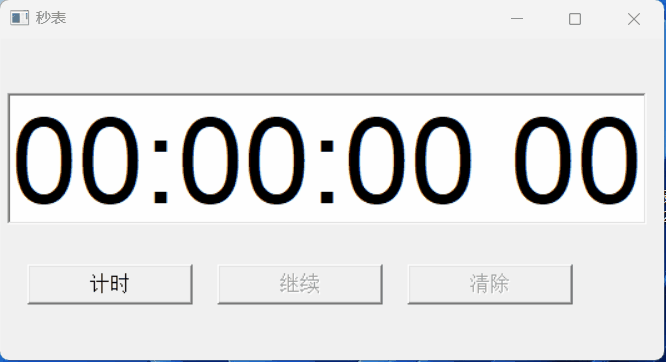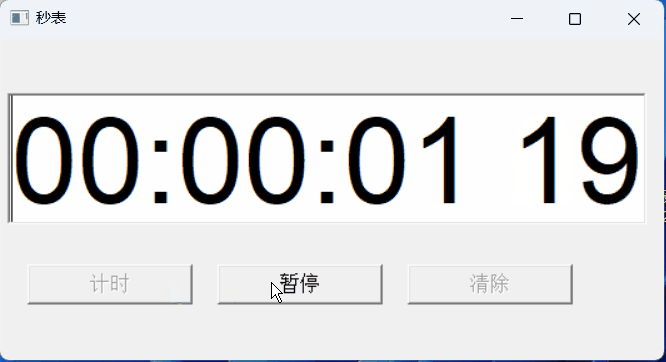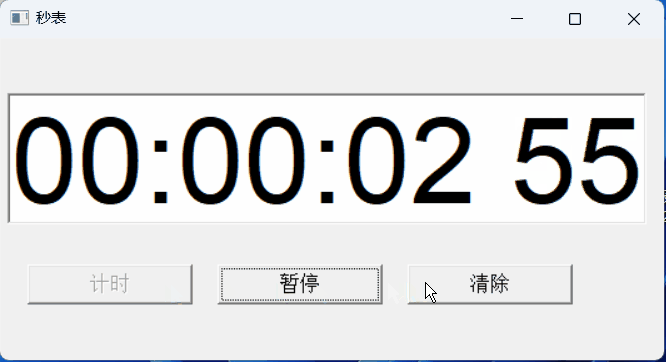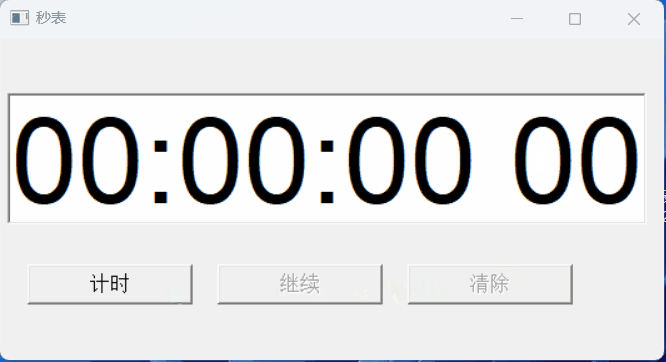
【PB案例学习笔记】-12秒表实现
写在前面 这是PB案例学习笔记系列文章的第11篇,该系列文章适合具有一定PB基础的读者。 通过一个个由浅入深的编程实战案例学习,提高编程技巧,以保证小伙伴们能应付公司的各种开发需求。 文章中设计到的源码,小凡都上传到了gite…...

Linux驱动开发笔记(二) 基于字符设备驱动的GPIO操作
文章目录 前言一、设备驱动的作用与本质1. 驱动的作用2. 有无操作系统的区别 二、内存管理单元MMU三、相关函数1. ioremap( )2. iounmap( )3. class_create( )4. class_destroy( ) 四、GPIO的基本知识1. GPIO的寄存器进行读写操作流程2. 引脚复用2. 定义GPIO寄存器物理地址 五、…...

【ESP32之旅】ESP32 PlatformIO 固件单独烧录
背景 有时候使用PIO编写的代码需要发给客户去验证,相比较于发送源码直接发送bin文件,更加的安全而且高效。不用担心源码的泄漏,也不用帮客户配置PIO环境。 操作方法 1.编译 首先进行代码编译,如编译成功会在 .pio\build\airm2…...
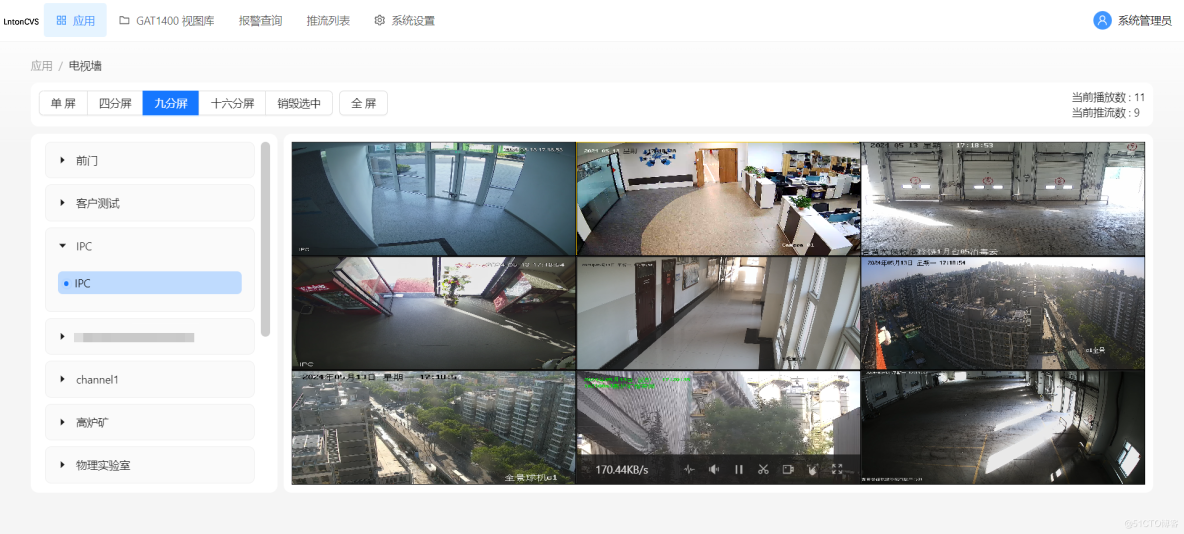
视频监控业务平台LntonCVS运用国标协议对接视频汇聚管理综合平台应用方案
为了实现“以信息化推动应急管理能力现代化”的目标,应急管理部提出了加速现代信息技术与应急管理业务深度融合的计划。这一计划是国家加强和改进应急管理工作的关键举措,也是满足日益严峻的应急管理形势和人民群众不断增长的公共安全需求的紧迫需求。 为…...
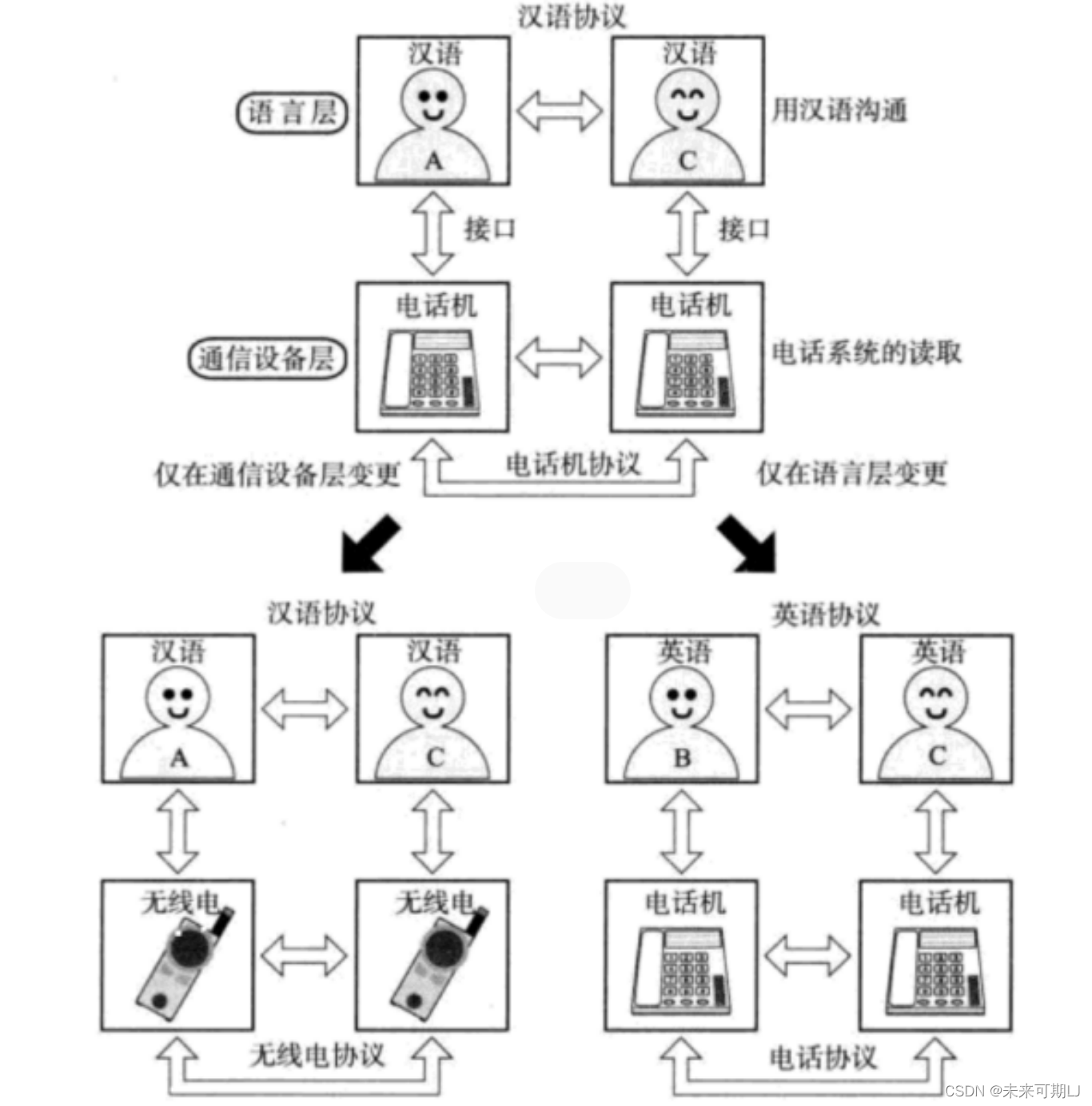
【Linux 网络编程】协议的分层知识!
文章目录 1. 计算机网络背景2. 认识 "协议"3. 协议分层 1. 计算机网络背景 网络互联: 多台计算机连接在一起, 完成数据共享; 🍎局域网(LAN----Local Area Network): 计算机数量更多了, 通过交换机和路由器连接。 🍎 广…...
Firefox国际版
Firefox国际版官方网址: Download the Firefox Browser in English (US) and more than 90 other languagesEveryone deserves access to the internet — your language should never be a barrier. That’s why — with the help of dedicated volunteers around…...

封装和解构是 Python 中常用的技术
目录 前言 一、封装(Packing): 二、解构(Unpacking): 2.1 解构元组或列表: 2.2 解构字典: 2.3 使用*进行解构: 2.4 解构函数返回值 总结 前言 提示:这…...

理解OAuth:服务间的授权机制
理解OAuth:服务间的授权机制 好的,让我来教你一下关于这个奇怪的东西。 在不同的项目中,认证有很多不同的方式。但在我们深入探讨它的使用方式之前,让我们先来看看它最初的用途。 首先,我们可以从名称中得到一些线索。“auth”这个词与什么有关呢?问题是,这里的“aut…...

JRT性能演示
演示视频 君生我未生,我生君已老,这里是java信创频道JRT,真信创-不糊弄。 基础架构决定上层建筑,和给有些品种的植物种植一样,品种不对,施肥浇水再多,也是不可能长成参天大树的。JRT吸收了各方…...

React 使用JSX或者TSX渲染页面
02 Rendering with JSX Your first JSX content In this section, we’ll implement the obligatory " Hello, World " JSX application. At this point, we’re just dipping our toes in the water; more in-depth examples will follow. We’ll also discuss wh…...
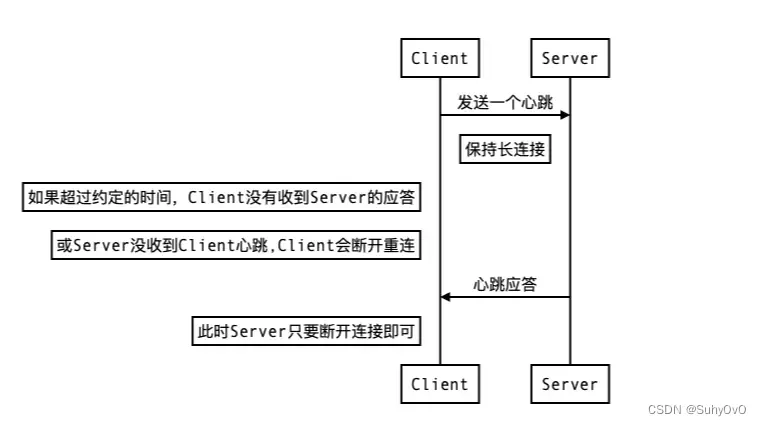
【Linux】Socket中的心跳机制(心跳包)
Socket中的心跳机制(心跳包) 1. 什么是心跳机制?(心跳包) 在客户端和服务端长时间没有相互发送数据的情况下,我们需要一种机制来判断连接是否依然存在。直接发送任何数据包可以实现这一点,但为了效率和简洁,通常发送一个空包&am…...

Java怎样动态给对象添加属性并赋值【代码实现】
本篇文章主要介绍Java如何给已有实体类动态的添加字段并返回新的实体对象且不影响原来的实体对象结构。 参考代码如下: 引入依赖包 <dependency><groupId>cglib</groupId><artifactId>cglib</artifactId><version>2.2.2</…...
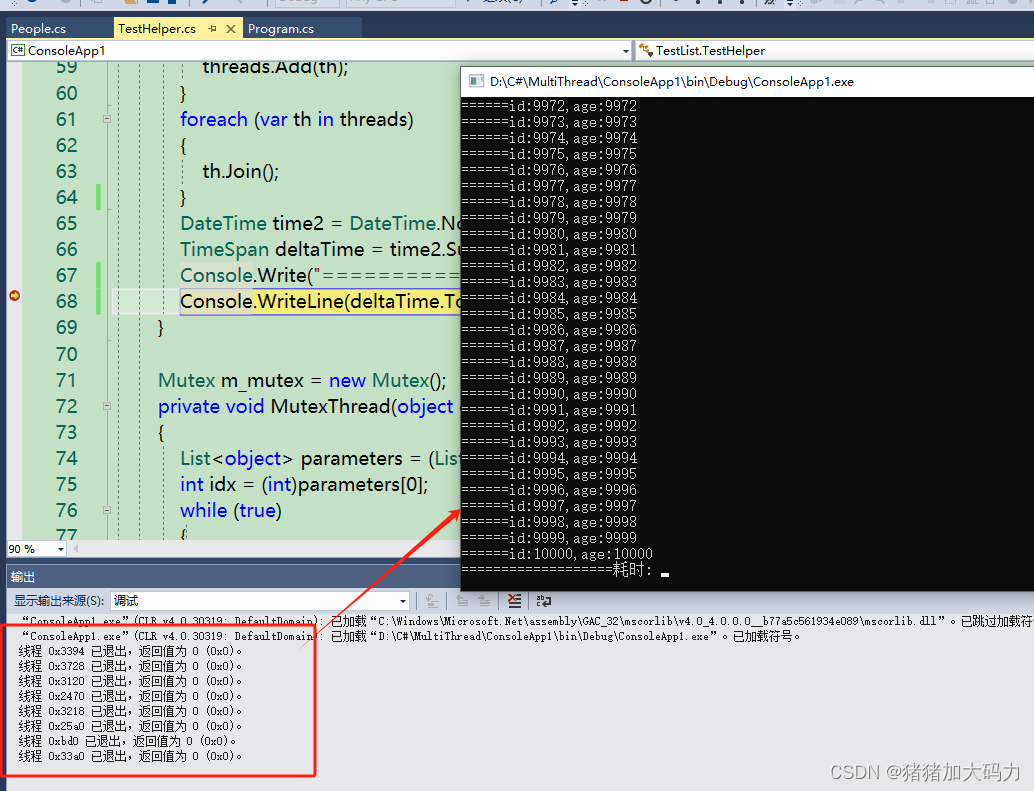
C#多线程同步lock、Mutex
C#使用多线程可以通过System.Threading命名空间下的Thread类来实现 lock和Mutex用于实现线程同步的机制: 上代码: class People{public People(int idd){id idd;}public int id;public int age;}class TestHelper{public TestHelper() { }List<Peo…...
模型实战(21)之 C++ - tensorRT部署yolov8-det 目标检测
C++ - tensorRT部署yolov8-det 目标检测 python环境下如何直接调用推理模型转换并导出:pt -> onnx ->.engineC++ tensorrt 部署检测模型不写废话了,直接上具体实现过程+all代码 1.Python环境下推理 直接命令行推理,巨简单yolo detect predict model=yolov8n.pt source…...
IDEA运行Tomcat出现乱码问题解决汇总
最近正值期末周,有很多同学在写期末Java web作业时,运行tomcat出现乱码问题,经过多次解决与研究,我做了如下整理: 原因: IDEA本身编码与tomcat的编码与Windows编码不同导致,Windows 系统控制台…...
MMaDA: Multimodal Large Diffusion Language Models
CODE : https://github.com/Gen-Verse/MMaDA Abstract 我们介绍了一种新型的多模态扩散基础模型MMaDA,它被设计用于在文本推理、多模态理解和文本到图像生成等不同领域实现卓越的性能。该方法的特点是三个关键创新:(i) MMaDA采用统一的扩散架构…...

基于数字孪生的水厂可视化平台建设:架构与实践
分享大纲: 1、数字孪生水厂可视化平台建设背景 2、数字孪生水厂可视化平台建设架构 3、数字孪生水厂可视化平台建设成效 近几年,数字孪生水厂的建设开展的如火如荼。作为提升水厂管理效率、优化资源的调度手段,基于数字孪生的水厂可视化平台的…...

Neo4j 集群管理:原理、技术与最佳实践深度解析
Neo4j 的集群技术是其企业级高可用性、可扩展性和容错能力的核心。通过深入分析官方文档,本文将系统阐述其集群管理的核心原理、关键技术、实用技巧和行业最佳实践。 Neo4j 的 Causal Clustering 架构提供了一个强大而灵活的基石,用于构建高可用、可扩展且一致的图数据库服务…...
Psychopy音频的使用
Psychopy音频的使用 本文主要解决以下问题: 指定音频引擎与设备;播放音频文件 本文所使用的环境: Python3.10 numpy2.2.6 psychopy2025.1.1 psychtoolbox3.0.19.14 一、音频配置 Psychopy文档链接为Sound - for audio playback — Psy…...

Robots.txt 文件
什么是robots.txt? robots.txt 是一个位于网站根目录下的文本文件(如:https://example.com/robots.txt),它用于指导网络爬虫(如搜索引擎的蜘蛛程序)如何抓取该网站的内容。这个文件遵循 Robots…...
企业如何增强终端安全?
在数字化转型加速的今天,企业的业务运行越来越依赖于终端设备。从员工的笔记本电脑、智能手机,到工厂里的物联网设备、智能传感器,这些终端构成了企业与外部世界连接的 “神经末梢”。然而,随着远程办公的常态化和设备接入的爆炸式…...

【Java学习笔记】BigInteger 和 BigDecimal 类
BigInteger 和 BigDecimal 类 二者共有的常见方法 方法功能add加subtract减multiply乘divide除 注意点:传参类型必须是类对象 一、BigInteger 1. 作用:适合保存比较大的整型数 2. 使用说明 创建BigInteger对象 传入字符串 3. 代码示例 import j…...
基于 TAPD 进行项目管理
起因 自己写了个小工具,仓库用的Github。之前在用markdown进行需求管理,现在随着功能的增加,感觉有点难以管理了,所以用TAPD这个工具进行需求、Bug管理。 操作流程 注册 TAPD,需要提供一个企业名新建一个项目&#…...
)
C#学习第29天:表达式树(Expression Trees)
目录 什么是表达式树? 核心概念 1.表达式树的构建 2. 表达式树与Lambda表达式 3.解析和访问表达式树 4.动态条件查询 表达式树的优势 1.动态构建查询 2.LINQ 提供程序支持: 3.性能优化 4.元数据处理 5.代码转换和重写 适用场景 代码复杂性…...
