list 的实现
目录
list
结点类
结点类的构造函数
list的尾插尾删
list的头插头删
迭代器
++运算符重载
--运算符重载
==和!= 运算符重载
* 和 -> 运算符重载
list 的insert
list的erase
list
list实际上是一个带头双向循环链表,要实现list,则首先需要实现一个结点类,而一个结点需要存储的信息为:数据、前驱指针、后继指针
而对于该结点类的成员函数来说,我们只需实现一个构造函数即可,因为该结点类只需要根据数据来构造一个结点即可,而结点的释放则由list的析构函数来完成,
结点类
结点类的基本结构:
template<class T>struct ListNode{ListNode<T>* _next;ListNode<T>* _prev;T _date;ListNode(const T& pos = T()){_next = nullptr;_prev = nullptr;_date = pos;}};这里用struct 的原因是因为ListNode 的 每个成员变量都会被频繁调用。
用struct则不需要封装了。
结点类的构造函数
构造函数直接根据所给数据构造一个结点即可,构造出来的结点的数据域存储的就是所给数据,而前驱指针和后继指针均初始化为空指针即可
ListNode(const T& pos = T()){_next = nullptr;_prev = nullptr;_date = pos;}list的尾插尾删
template<class T>class list{public:typedef ListNode<T> node; list():_head(new node){_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;}void push_back(const T& x){node* head = _head;node* tail = _head->_prev;node* p = new node(x);tail->_next = p;p->_prev = tail;p->_next = head;head->_prev = p;}void pop_back(){assert(_head != _head->_next);node* head = _head;node* tail = head->_prev;node* newtail = tail->_prev;newtail->_next = head;head->_prev = newtail;delete[] tail;}private:node* _head;};list的头插头删
template<class T>class list{public: typedef ListNode<T> node;list():_head(new node){_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;}void push_front(const T& x){node* newnode = new node(x);node* head = _head;node* tail = _head->_next;head->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = head;newnode->_next = tail;tail->_prev = newnode;}void pop_front(){assert(_head != _head->_next);node* head = _head;node* tail = _head->_next;head->_next = tail->_next;tail->_next->_prev = head;delete[]tail;}private:node* _head;};迭代器
迭代器有两种实现方式,具体应根据容器底层数据结构实现:
- 原生态指针,比如:vector和string ->物理空间是连续的,因为string和vector对象都将其数据存储在了一块连续的内存空间,我们通过指针进行自增、自减以及解引用等操作,就可以对相应位置的数据进行一系列操作,因此string和vector当中的迭代器就是原生指针。
- .将原生态指针进行封装,因迭代器使用形式与指针完全相同,因此在自定义的类中必须实现以下方法:
指针可以解引用,迭代器的类中必须重载operator*()
指针可以通过->访问其所指空间成员,迭代器类中必须重载oprator->()
指针可以++向后移动,迭代器类中必须重载operator++()与operator++(int)
至于operator--()/operator--(int) 是否需要重载,根据具体的结构来抉择,双向链表可
以向前 移动,所以需要重载,如果是forward_list就不需要重载–
迭代器需要进行是否相等的比较,因此还需要重载operator==()与operator!=()
但是对于list来说,其各个结点在内存当中的位置是随机的,并不是连续的,我们不能仅通过结点指针的自增、自减以及解引用等操作对相应结点的数据进行操作,
总结:list的迭代器 实际上就是对结点指针进行了封装,对其各种运算符进行了重载,使得结点指针的各种行为看起来和普通指针一样,(例如,对结点指针自增就能指向下一个结点 p = p->next)
template<class T1, class T2>struct Reverse_iterator{typedef Reverse_iterator<T1, T2> self;typedef ListNode<T1> node;node* _it;Reverse_iterator(node* pos);self& operator++();self operator++(int);self& operator--();self operator--(int);T2& operator*();T2* operator->();bool operator!=(const self& pos);bool operator==(const self& pos);};迭代器模板参数说明: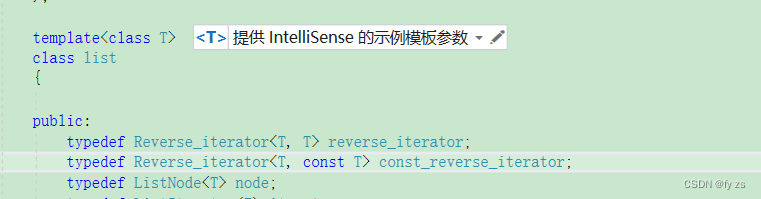
构造函数
迭代器类实际上就是对结点指针进行了封装
其成员变量就是结点指针,所以其构造函数直接根据所给结点指针构造一个迭代器对象即可,
Reverse_iterator(node* pos){_it = pos;}拷贝构造,operator,析构函数我们都不需要写,因为成员变量是内置类型(指针), 用编译器默认生成的就可以。
++运算符重载
self& operator++()//前置{_it =_it->_prev;return *this;}self operator++(int)//后置{self tmp(_it);_it = _it->_prev;return tmp;}前置++原本的作用是将数据自增,然后返回自增后的数据,
而对于结点迭代器的前置++:应该先让结点指针指向后一个结点.然后再返回“自增”后的结点迭代器即可
后置++,先拷贝构造当前迭代器结点, 然后让当前迭代器结点的指针自增指向下一个结点,最后返回“自增”前的结点迭代器即可,
--运算符重载
self& operator--()//前置{_it = _it->_next;return *this;}self operator--(int)//后置{self tmp(_it);_it = _it->_next;return tmp;}前置- -:当前迭代器结点中的指针指向前一个结点,然后再返回“自减”后的结点迭代器即可,
后置--:拷贝构造当前迭代器对象 -> 当前迭代器结点中的指针自减指向前一个结点 ->返回自减前的迭代器。
==和!= 运算符重载
bool operator!=(const self& pos){return _it != pos._it;}bool operator==(const self& pos){return _it == pos._it;}这里注意形参别写错就好了。
* 和 -> 运算符重载
使用解引用操作符时,是想得到该指针指向的数据内容
因此,我们直接返回当前结点指针所指结点的数据即可,这里需要使用引用返回,因为解引用后可能需要对数据进行修改,
T2& operator*(){return _it->_date;}->返回当前迭代器结点的指针所指结点的数据的地址
T2* operator->(){return &_it->_date;}使用场景:

list 的insert
insert函数可以在所给迭代器pos之前插入一个新结点,
1.先根据所给迭代器pos得到该位置处的结点指针
2.然后通过该指针找到前一个位置的结点指针last
根据所给数据x构造一个新结点
iterator insert(iterator pos,const T& x){node* newnode = new node(x);node* next = pos._node;node* last = next->_prev;last->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = last;newnode->_next = next;next->_prev = newnode;return iterator(newnode);}list的erase
erase函数可以删除所给迭代器位置的结点,
注意**:pos不可以是哨兵位的迭代器,即不能删除哨兵位 pos迭代器结点中的指针不能为空**
1.根据所给迭代器得到该位置处的结点指针self
2.通过self指针找到前一个位置的结点指针last,以及后一个位置的结点指针next
3.紧接着释放cur结点,最后prev和next结点进行链接
iterator erase(iterator pos){assert(pos._node);assert(_head != _head->_next);node* self = pos._node;node* next = self->_next;node* last = self->_prev;last->_next = next;next->_prev = last;delete[] self;return iterator(next);}关于insert 和 erase 迭代器失效的问题:
insert不会导致迭代器失效,因为pos迭代器中的节点指针仍然指向原来的节点。
问:erase之后, pos迭代器是否失效:
一定失效,因为此时pos迭代器中的节点指针指向的节点已经被释放了,该指针相当于是野指针。
最后所有代码如下:
namespace bit
{template<class T>struct ListNode{ListNode<T>* _next;ListNode<T>* _prev;T _date;ListNode(const T& pos = T()){_next = nullptr;_prev = nullptr;_date = pos;}};template<class T1,class T2 = T1>struct ListIterator{typedef ListIterator<T1,T2> iterator;typedef ListNode<T1> node;node* _node;ListIterator(node* pos){_node = pos;}T2& operator*(){return _node->_date;}iterator& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;} iterator operator++(int){iterator tmp(_node);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}iterator& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}iterator operator--(int){iterator tmp(_node);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}T2* operator->(){return &_node->_date;}bool operator!=(const iterator& pos){return _node != pos._node;}bool operator==(const iterator& pos){return _node == pos._node;}};template<class T1, class T2>struct Reverse_iterator{typedef Reverse_iterator<T1, T2> self;typedef ListNode<T1> node;node* _it;Reverse_iterator(node* pos){_it = pos;}self& operator++(){_it =_it->_prev;return *this;}self operator++(int){self tmp(_it);_it = _it->_prev;return tmp;}self& operator--(){_it = _it->_next;return *this;}self operator--(int){self tmp(_it);_it = _it->_next;return tmp;}T2& operator*(){return _it->_date;}T2* operator->(){return &_it->_date;}bool operator!=(const self& pos){return _it != pos._it;}bool operator==(const self& pos){return _it == pos._it;}};template<class T>class list{public:typedef Reverse_iterator<T, T> reverse_iterator;typedef Reverse_iterator<T, const T> const_reverse_iterator;typedef ListNode<T> node;typedef ListIterator<T> iterator;typedef ListIterator<T,const T> const_iterator;list():_head(new node){_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;}list(const list& pos){_head = new node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;for (auto e : pos){push_back(e);}}list(initializer_list<T> il){_head = new node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;for (auto e : il){push_back(e);}}void push_back(const T& x){node* head = _head;node* tail = _head->_prev;node* p = new node(x);tail->_next = p;p->_prev = tail;p->_next = head;head->_prev = p;}void pop_back(){assert(_head != _head->_next);node* head = _head;node* tail = head->_prev;node* newtail = tail->_prev;newtail->_next = head;head->_prev = newtail;delete[] tail;}reverse_iterator rbegin(){return reverse_iterator(_head->_prev);}reverse_iterator rend(){return reverse_iterator(_head);}const_reverse_iterator crbegin()const{return const_reverse_iterator(_head->_prev);}const_reverse_iterator crend()const{return const_reverse_iterator(_head);}iterator begin(){return iterator(_head->_next);}const_iterator begin()const{return const_iterator(_head->_next);}iterator end(){return iterator(_head);}const_iterator end()const{return const_iterator(_head);}void push_front(const T& x){node* newnode = new node(x);node* head = _head;node* tail = _head->_next;head->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = head;newnode->_next = tail;tail->_prev = newnode;}void pop_front(){assert(_head != _head->_next);node* head = _head;node* tail = _head->_next;head->_next = tail->_next;tail->_next->_prev = head;delete[]tail;}iterator insert(iterator pos,const T& x){node* newnode = new node(x);node* next = pos._node;node* last = next->_prev;last->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = last;newnode->_next = next;next->_prev = newnode;return iterator(newnode);}iterator erase(iterator pos){assert(pos._node);assert(_head != _head->_next);node* self = pos._node;node* next = self->_next;node* last = self->_prev;last->_next = next;next->_prev = last;delete[] self;return iterator(next);}~list(){iterator it1 = begin();while (it1 != end()){it1 = erase(it1);}delete _head;_head = nullptr;}private:node* _head;};相关文章:

list 的实现
目录 list 结点类 结点类的构造函数 list的尾插尾删 list的头插头删 迭代器 运算符重载 --运算符重载 和! 运算符重载 * 和 -> 运算符重载 list 的insert list的erase list list实际上是一个带头双向循环链表,要实现list,则首先需要实现一个结点类,而一个结点需要…...
学法)
一个程序员的牢狱生涯(47)学法
星期一 学法 二铺不知道什么时候走到了我的身边,向我说道,这是二铺在我进来号子后主动过来和我说话。 我听到二铺这声突兀的说话后,抬起头。这时我才看到,除了二铺,还有六子、棍子都围在我的身边,看着我。虽然六子和棍子依旧一副‘吊儿郎当’的样子,但我从他们几个的眼神…...
微信小程序-页面导航
一、页面导航 页面导航指的是页面之间的相互跳转,例如:浏览器中实现页面导航的方式有如下两种: 1.<a>链接 2.location.href 二、小程序中实现页面导航的两种方式 1.声明式导航 在页面上声明一个<navigator>导航组件 通过点击…...
 服务质量(Quality of Service, QoS))
计算机网络- 特定服务类型(Type of Service, TOS) 服务质量(Quality of Service, QoS)
特定服务类型(Type of Service, TOS) 具有特定服务类型(Type of Service, TOS)的数据包是指在IP头部中包含特定TOS字段设置的数据包。TOS字段用于指示数据包的服务质量要求,如延迟、吞吐量、可靠性等。现代IP网络通常…...
2.6 Docker部署多个前端项目
2.6 Docker部署多个项目 三. 部署前端项目 1.将前端项目打包到同一目录下(tcm-ui) 2. 部署nginx容器 docker run --namenginx -p 9090:9090 -p 9091:9091 -d nginx3. 复制nginx.conf文件到主机目录 docker cp nginx:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf /root/ja…...
如何格式化只读U盘?
U盘只读无法格式化,该怎么处理?别担心!本文将向你提供一些实用方法,助你解决U盘写保护的难题。这些方法能有效帮助你解除U盘的只读状态,从而可以顺利进行格式化和其他操作。 不能格式化只读U盘 “我购买了一个U盘&…...

【并查集】专题练习
题目列表 - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn) 模板 836. 合并集合 - AcWing题库 #include<bits/stdc.h> using lllong long; //#define int ll const int N1e510,mod1e97; int n,m; int p[N],sz[N]; int find(int a) {if(p[a]!a) p[a]find(p[a]);return p[a…...
服装连锁店收银系统需要具备的五大功能
当今服装连锁店在市场竞争中需要拥有高效的收银系统来提升业务效率和顾客满意度。以下是服装连锁店收银系统需要具备的五大功能: 首先,完善的商品管理功能是至关重要的。这包括商品信息的录入、管理、更新和查询。收银系统应该能够快速而准确地识别商品&…...
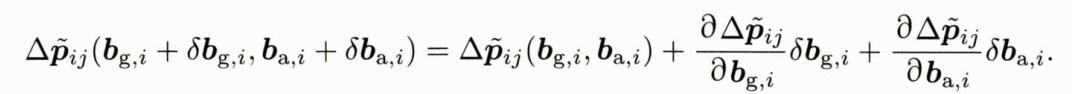
IMU状态预积分代码实现 —— IMU状态预积分类
IMU状态预积分代码实现 —— IMU状态预积分类 实现IMU状态预积分类 实现IMU状态预积分类 首先,实现预积分自身的结构。一个预积分类应该存储一下数据: 预积分的观测量 △ R ~ i j , △ v ~ i j , △ p ~ i j \bigtriangleup \tilde{R} _{ij},\bigtrian…...

C语言编程:探索最小公倍数的奥秘
C语言编程:探索最小公倍数的奥秘 在编程的世界中,计算两个数的最小公倍数(LCM)是一个常见的数学问题。C语言作为一种基础且强大的编程语言,为我们提供了实现这一功能的工具。本文将从四个方面、五个方面、六个方面和七…...
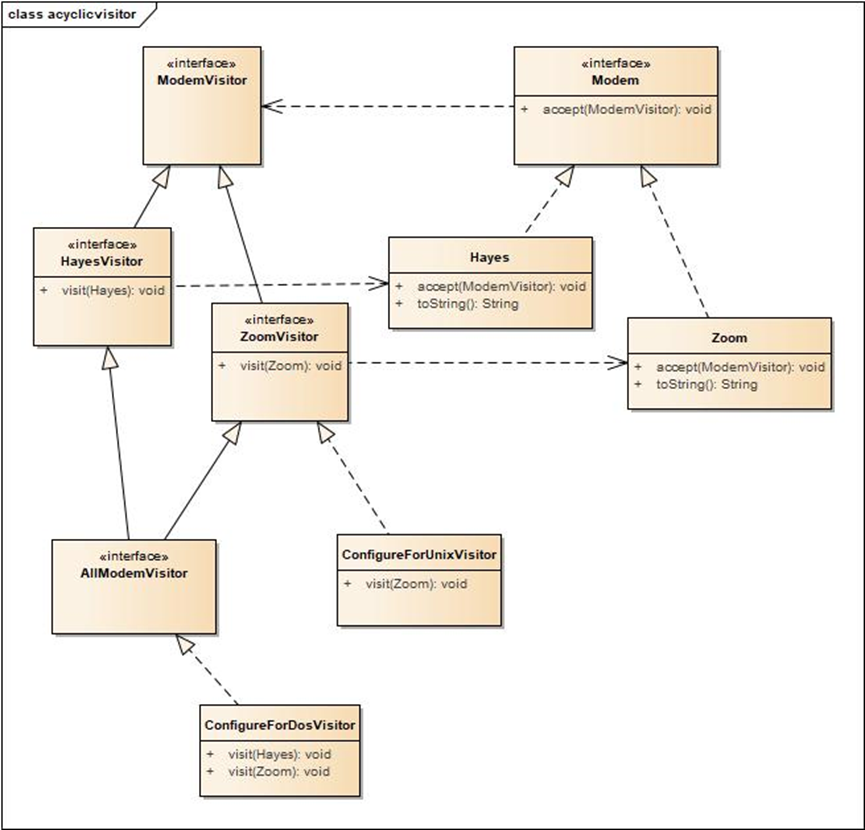
Java设计模式-活动对象与访问者
活动对象 Java设计模式中,活动对象是指一个对象始终处于活动的状态,该对象包括一个线程安全的数据结构以及一个活跃的执行线程。 如上所示,ActiveCreature类的构造函数初始化一个线程安全的数据结构(阻塞队列)、初始化…...
用HAL库改写江科大的stm32入门-6-3 PWM驱动LED呼吸灯
接线图: 2 :实验目的: 利用pwm实现呼吸灯。 关键PWM定时器设置: 代码部分: int main(void) {/* USER CODE BEGIN 1 *//* USER CODE END 1 *//* MCU Configuration--------------------------------------------------------*…...

[数据集][目标检测]喝水检测数据集VOC+YOLO格式995张3类别
数据集格式:Pascal VOC格式YOLO格式(不包含分割路径的txt文件,仅仅包含jpg图片以及对应的VOC格式xml文件和yolo格式txt文件) 图片数量(jpg文件个数):995 标注数量(xml文件个数):995 标注数量(txt文件个数):995 标注类别…...

【C++】开源:RabbitMQ安装与配置使用(SimpleAmqpClient)
😏★,:.☆( ̄▽ ̄)/$:.★ 😏 这篇文章主要介绍。 无专精则不能成,无涉猎则不能通。——梁启超 欢迎来到我的博客,一起学习,共同进步。 喜欢的朋友可以关注一下,下次更新不迷路…...
git使用流程与规范
原文网址:git代码提交流程与规范-CSDN博客 简介 本文git提交流程与规范是宝贵靠谱的经验,它能解决如下问题: 分支差距过大,导致合代码无数的冲突合完代码后发现代码丢失分支不清晰,无法追溯问题合代码耗时很长&…...

力扣 264. 丑数 II python AC
堆 from heapq import heappop, heappushclass Solution:def nthUglyNumber(self, n):q [1]vis {1}for _ in range(n - 1):now heappop(q)for i in [2, 3, 5]:if now * i not in vis:vis.add(now * i)heappush(q, now * i)return heappop(q)...

resetlogs强制拉库失败并使用备份system文件还原数据库故障处理---惜分飞
接手一个库,在open的过程中遭遇到ORA-600 2662错误 Sun May 26 10:15:54 2024 alter database open RESETLOGS RESETLOGS is being done without consistancy checks. This may result in a corrupted database. The database should be recreated. RESETLOGS after incomplete…...

解析Java中1000个常用类:Error类,你学会了吗?
在 Java 编程中,异常处理是一个至关重要的部分。Java 提供了丰富的异常处理机制,包括 Exception 和 Error。 本文将深入探讨 Error 类的功能、用法、实际应用中的注意事项,以及如何处理和预防这些错误。 什么是 Error 类? Error 类是 Java 中 Throwable 类的一个子类,用…...

【C++】——string模拟实现
前言 string的模拟实现其实就是增删改查,只不过加入了类的概念。 为了防止与std里面的string冲突,所以这里统一用String。 目录 前言 一 初始化和销毁 1.1 构造函数 1.2 析构函数 二 迭代器实现 三 容量大小及操作 四 运算符重载 4.1 bool…...
unity2D跑酷游戏
项目成果 项目网盘 导入资源包 放入Assets文件Assets资源文件 游戏流程分析 摄像机size调小,让图片占满屏幕 人跑本质,相对运动,图片无限向右滚动 图片720,缩小100倍第二个图片x为7.2每unit px100两张图片刚好挨着连贯 空对象Bg…...
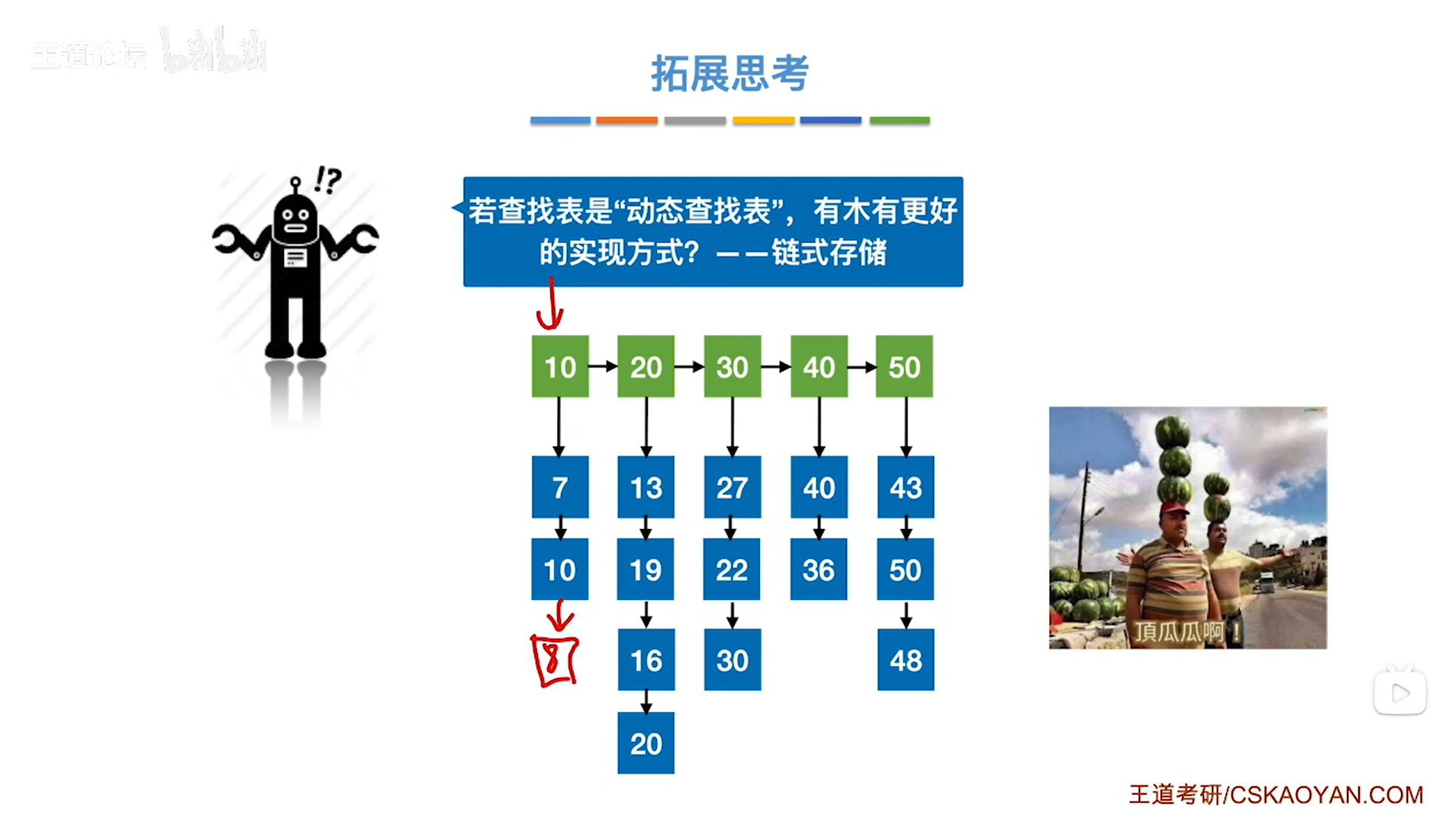
7.4.分块查找
一.分块查找的算法思想: 1.实例: 以上述图片的顺序表为例, 该顺序表的数据元素从整体来看是乱序的,但如果把这些数据元素分成一块一块的小区间, 第一个区间[0,1]索引上的数据元素都是小于等于10的, 第二…...

基于大模型的 UI 自动化系统
基于大模型的 UI 自动化系统 下面是一个完整的 Python 系统,利用大模型实现智能 UI 自动化,结合计算机视觉和自然语言处理技术,实现"看屏操作"的能力。 系统架构设计 #mermaid-svg-2gn2GRvh5WCP2ktF {font-family:"trebuchet ms",verdana,arial,sans-…...
:OpenBCI_GUI:从环境搭建到数据可视化(下))
脑机新手指南(八):OpenBCI_GUI:从环境搭建到数据可视化(下)
一、数据处理与分析实战 (一)实时滤波与参数调整 基础滤波操作 60Hz 工频滤波:勾选界面右侧 “60Hz” 复选框,可有效抑制电网干扰(适用于北美地区,欧洲用户可调整为 50Hz)。 平滑处理&…...
【第二十一章 SDIO接口(SDIO)】
第二十一章 SDIO接口 目录 第二十一章 SDIO接口(SDIO) 1 SDIO 主要功能 2 SDIO 总线拓扑 3 SDIO 功能描述 3.1 SDIO 适配器 3.2 SDIOAHB 接口 4 卡功能描述 4.1 卡识别模式 4.2 卡复位 4.3 操作电压范围确认 4.4 卡识别过程 4.5 写数据块 4.6 读数据块 4.7 数据流…...

2021-03-15 iview一些问题
1.iview 在使用tree组件时,发现没有set类的方法,只有get,那么要改变tree值,只能遍历treeData,递归修改treeData的checked,发现无法更改,原因在于check模式下,子元素的勾选状态跟父节…...
)
【RockeMQ】第2节|RocketMQ快速实战以及核⼼概念详解(二)
升级Dledger高可用集群 一、主从架构的不足与Dledger的定位 主从架构缺陷 数据备份依赖Slave节点,但无自动故障转移能力,Master宕机后需人工切换,期间消息可能无法读取。Slave仅存储数据,无法主动升级为Master响应请求ÿ…...

CRMEB 框架中 PHP 上传扩展开发:涵盖本地上传及阿里云 OSS、腾讯云 COS、七牛云
目前已有本地上传、阿里云OSS上传、腾讯云COS上传、七牛云上传扩展 扩展入口文件 文件目录 crmeb\services\upload\Upload.php namespace crmeb\services\upload;use crmeb\basic\BaseManager; use think\facade\Config;/*** Class Upload* package crmeb\services\upload* …...

Mac下Android Studio扫描根目录卡死问题记录
环境信息 操作系统: macOS 15.5 (Apple M2芯片)Android Studio版本: Meerkat Feature Drop | 2024.3.2 Patch 1 (Build #AI-243.26053.27.2432.13536105, 2025年5月22日构建) 问题现象 在项目开发过程中,提示一个依赖外部头文件的cpp源文件需要同步,点…...

稳定币的深度剖析与展望
一、引言 在当今数字化浪潮席卷全球的时代,加密货币作为一种新兴的金融现象,正以前所未有的速度改变着我们对传统货币和金融体系的认知。然而,加密货币市场的高度波动性却成为了其广泛应用和普及的一大障碍。在这样的背景下,稳定…...
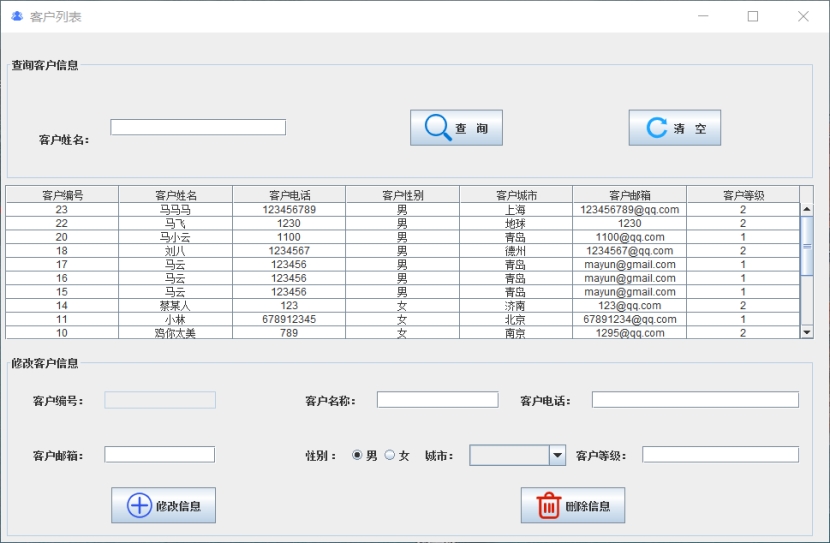
基于Java+MySQL实现(GUI)客户管理系统
客户资料管理系统的设计与实现 第一章 需求分析 1.1 需求总体介绍 本项目为了方便维护客户信息为了方便维护客户信息,对客户进行统一管理,可以把所有客户信息录入系统,进行维护和统计功能。可通过文件的方式保存相关录入数据,对…...
