【C++】list的模拟实现
文章目录
- 1.list 底层
- 2. list的模拟实现
- 1. list_node 类设计
- 2. list类如何调用类型
- 3 .push_back(正常实现)
- 4. 迭代器的实现
- 第一个模板参数T
- const迭代器
- 第二个模板参数Ref
- 第三个模板参数Ptr
- 对list封装的理解
- 5. insert
- 6.push_back与 push_front(复用)
- 7. erase
- 8. pop_back与pop_front (复用)
- 9. clear 清空数据
- 10. 迭代器区间构造
- 12. 拷贝构造
- 传统写法
- 现代写法
- 13. 赋值
- 3.完整代码
1.list 底层
list为任意位置插入删除的容器,底层为带头双向循环链表
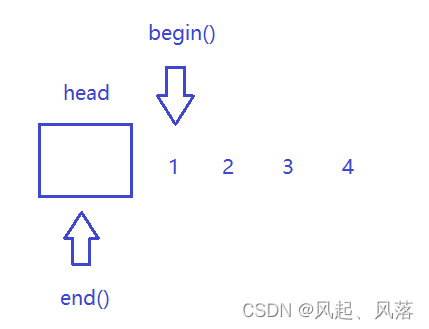
begin() 代表第一个结点,end()代表最后一个结点的下一个
2. list的模拟实现
1. list_node 类设计
template<class T>struct list_node{list_node<T>* _next;list_node<T>* _prev;T _data;};
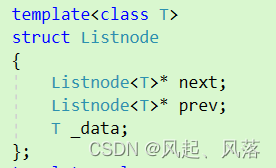
C++中,Listnode作为类名,而next和prev都是类指针,指针引用成员时使用->,而对象引用成员时使用 .
通过显示实例化,将两个类指针指定类型为T
2. list类如何调用类型
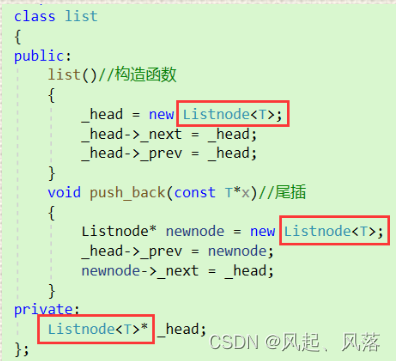
Listnode 代表类型
Listnode 代表类名 + 模板参数 才是类型
而_head 以及创建新节点前都需加上类型
3 .push_back(正常实现)
void push_back(const T&x)//尾插{node* newnode = new node(x);node* tail = _head->_prev;tail->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = tail;newnode->_next = _head;_head->_prev = newnode;}
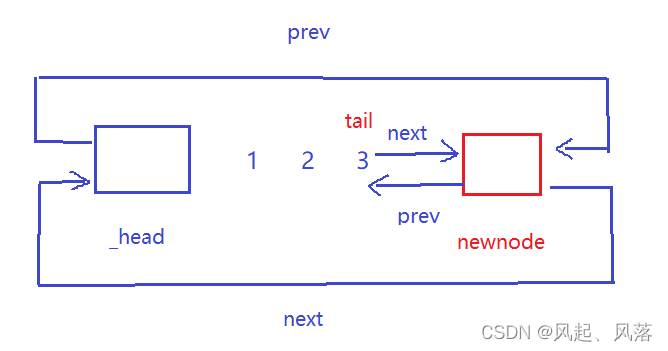
当我们想要创建一个节点时,需要调用node的构造函数
typedef list_node node ,node是由 list_node 类提供的
list_node(const T& x=T())//list类的构造函数:_next(nullptr), _prev(nullptr), _data(x){}
最好在构造函数处提供全缺省,对于内置类型int可以使用0,但对于自定义类型来说就不可以,所以为了满足泛型的要求,使用匿名对象调用默认构造函数
4. 迭代器的实现
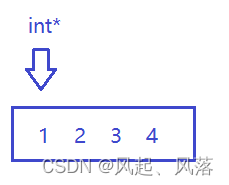
若在数组上有一个int类型的指针,解引用是int类型的数据,再++可以加载下一个位置,因为物理空间是连续的
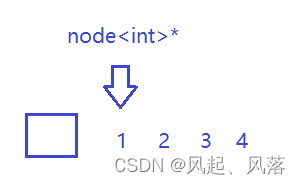
同样若在链表上,解引用类型为 node,再++不能到下一个节点,因为物理空间不连续
所以构造迭代器通过封装节点的指针来进行构造 (后面会讲)
第一个模板参数T
创建一个_list_iterator的类,来实现迭代器功能
template<class T>struct _list_iterator{typedef list_node<T> node;typedef _list_iterator<T> self;node* _node;_list_iterator(node* n):_node(n){}T& operator*()//解引用 {return _node->_data;}_list_iterator<T>& operator++()//返回迭代器{_node = _node->_next;//指向下一个节点return *this;}bool operator!=(const self&s){return _node != s._node;}};
在list类中,调用迭代器实现begin()和end()功能
typedef _list_iterator<T,T&,T*> iterator,
通过typedef 将_list_node类模板定义为iterator
iterator begin(){return iterator(_head->_next);//通过匿名对象访问第一个数据}iterator end(){return iterator(_head);//通过匿名对象访问最后一个数据的下一个}
在list类中实现begin()和end(),内部调用_list_node类的构造函数

const迭代器

假设第一个代表的是T * ,而第二个代表的 T * const,保护迭代器本身不可以被修改,而我们想要保护迭代器指向的内容不可被修改即 const T*
复制_list_iterator类中的内容,并将名字修改为const_list_iterator
只需修改*operator类型为cosnt T& ,说明解引用后的数据返回不能被修改
template<class T>struct _list_const_iterator{typedef list_node<T> node;typedef _list_const_iterator<T> self;node* _node;_list_const_iterator(node* n):_node(n){}const T& operator*()//解引用 {return _node->_data;}self& operator++()//前置++{_node = _node->_next;//指向下一个节点return *this;}self& operator++(int)//后置++{self ret = *this;_node = _node->_next;return ret;}self& operator--()//前置--{_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}self& operator--(int)//后置--{self ret = *this;_node = _node->_prev;return ret;}bool operator!=(const self& s)//!={return _node != s._node;}bool operator==(const self& s)//=={return _node == s._node;}};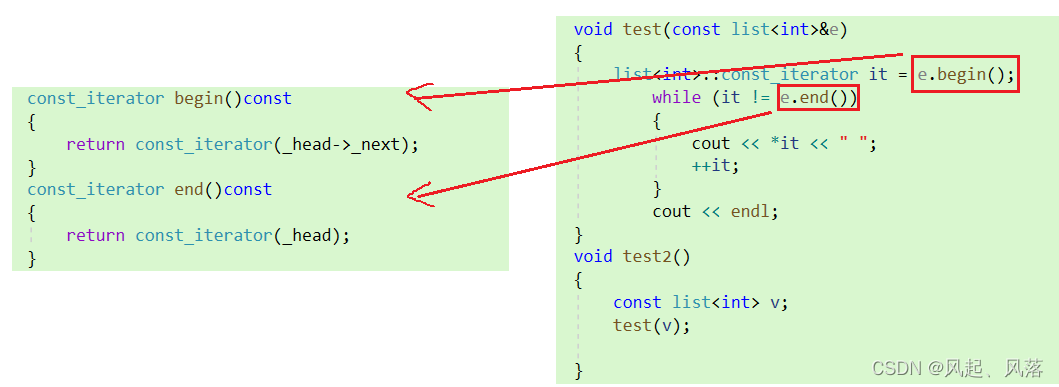
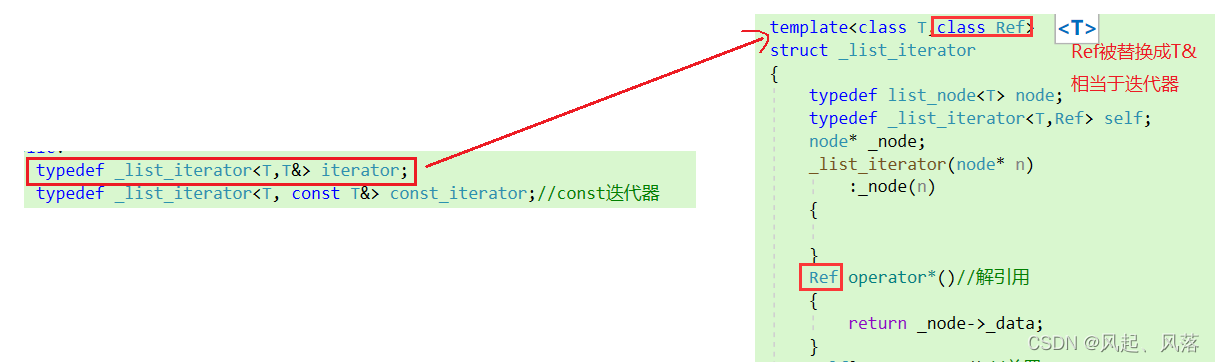
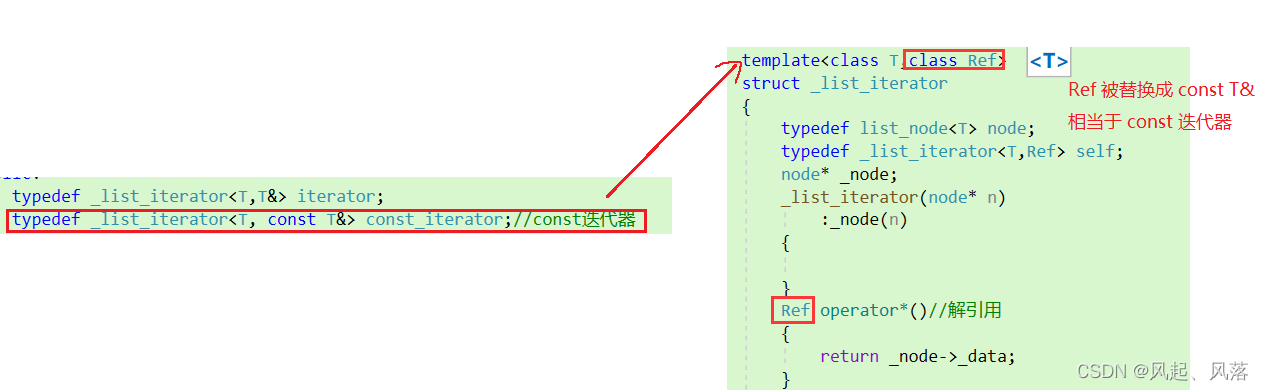
第二个模板参数Ref
迭代器和const迭代器只有 *operator 的返回值不同,
只需在模板中添加一个参数即可使用一个迭代器实现迭代器和const 迭代器的功能
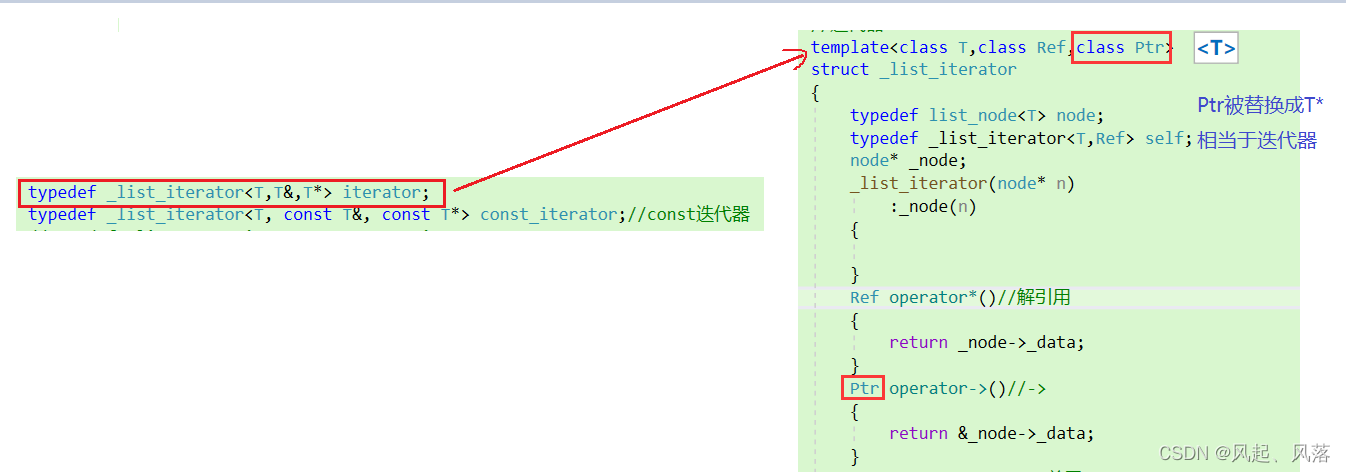
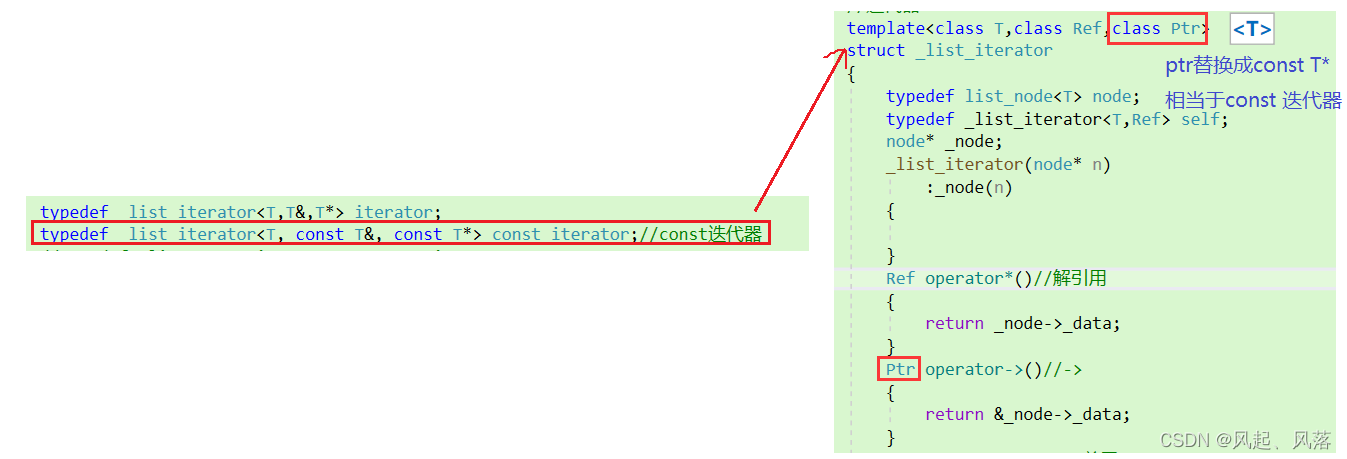
第三个模板参数Ptr
对于内置类型int使用解引用找到对应数据,而自定义类型需使用->寻找下一个节点
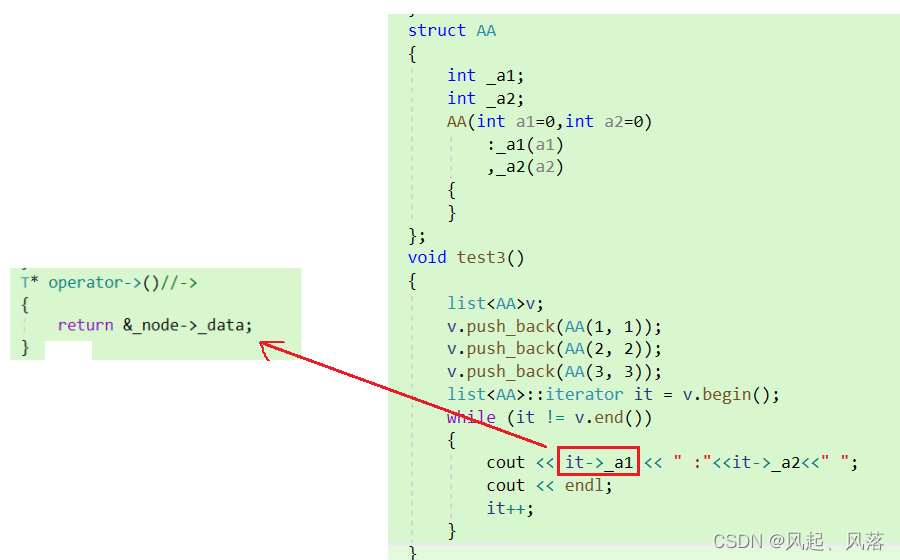
AA作为自定义类型,想要找到下一个节点需要使用->,在迭代器中 重载 - >
it->_a1,实际上是 it->->_a1,
it->返回值为AA* ,再通过这个指针使用->指向_a1
但是为了增强可读性,省略了一个->
it->_a1 实际上为 it.operator->()->._a1
对list封装的理解

在不考虑封装的情况下,两者等价
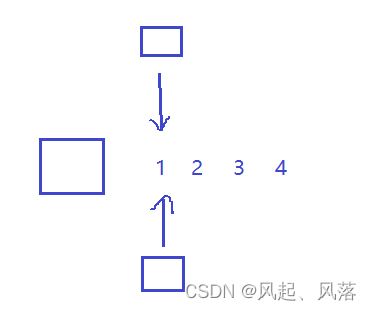
从物理空间上来看,it与pnode都是指向1的地址

pnode作为一个原生指针,解引用指针就会拿到这个地址,找到这个地址指向空间的内容
++pnode,找到下一个节点的地址,但是下一个节点不一定是要的节点
*it 识别成为自定义类型就会调用函数
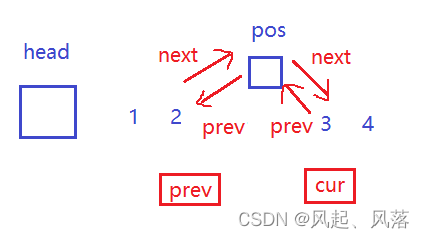
5. insert
void insert(iterator pos,const T&x)//在pos位置前插入x{node* cur = pos._node;node* prev = cur->_prev;node* newnode = new node(x);prev->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = prev;newnode->_next = cur;cur->_prev = newnode;}

6.push_back与 push_front(复用)
两者都可以通过复用 insert的方式实现
void push_back(const T&x)//尾插{/*node* tail = _head->_prev;node* newnode = new node(x);tail->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = tail;newnode->_next = _head;_head->_prev = newnode;*/insert(end(), x);}void push_front(const T&x)//头插{insert(begin(), x);}7. erase
void erase(iterator pos)//删除pos位置{//头节点不可以删除assert(pos != end());node* cur = pos._node;node* prev = cur->_prev;node* next = cur->_next;prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete cur;}
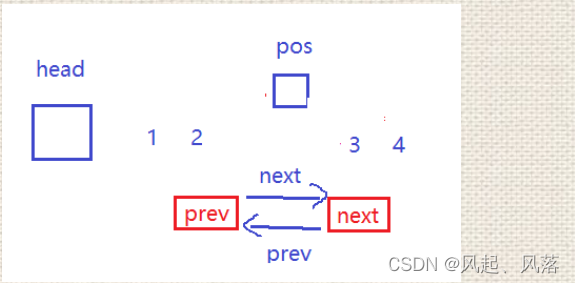
由于头节点不可以删除,所以使用assert断言的方式
8. pop_back与pop_front (复用)
void pop_back()//尾删{erase(--end());}void pop_front()//头删{erase(begin());}
9. clear 清空数据
void clear()//清空数据//但是要注意不要把head清掉{iterator it = begin();while (it != end()){it=erase(it);//为了防止迭代器失效设置返回值//返回值为当前节点的下一个}}
迭代器失效是指迭代器所指向的节点失效 即节点被删除了
erase函数执行后,it所指向的节点被删除,因此it无效,在下一次使用it时,必须先给it赋值
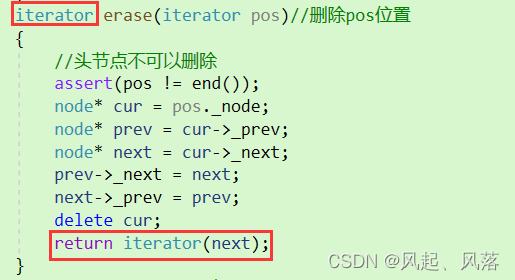
为了防止迭代器失效所以使erase设置返回值,返回值为当前节点的下一个
10. 迭代器区间构造
void empty_init(){_head = new node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;}
template <class Iterator>list(Iterator first, Iterator last){empty_init();while (first != last){push_back(*first);++first;}}
想要尾插的前提时,需要有头节点的存在,所以设置一个函数对头节点初始化
12. 拷贝构造
传统写法
void empty_init(){_head = new node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;}
list(const list<T>& It)//拷贝构造 传统写法{empty_init();//初始化头节点for (auto e : It){push_back(e);}}

现代写法
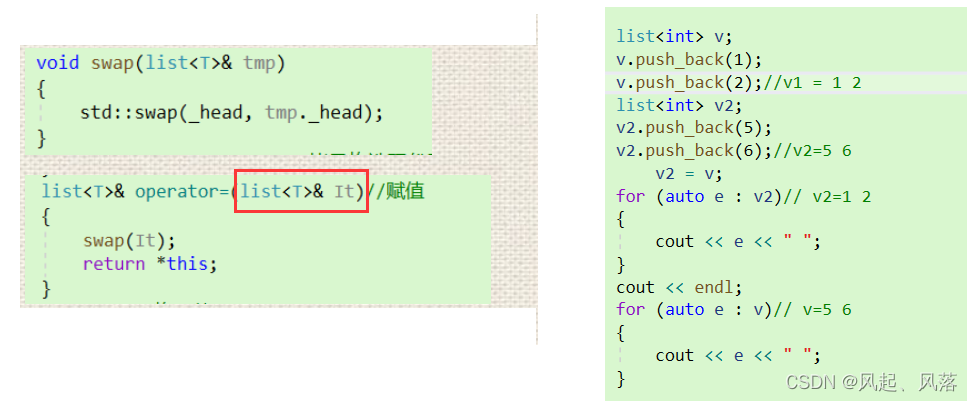
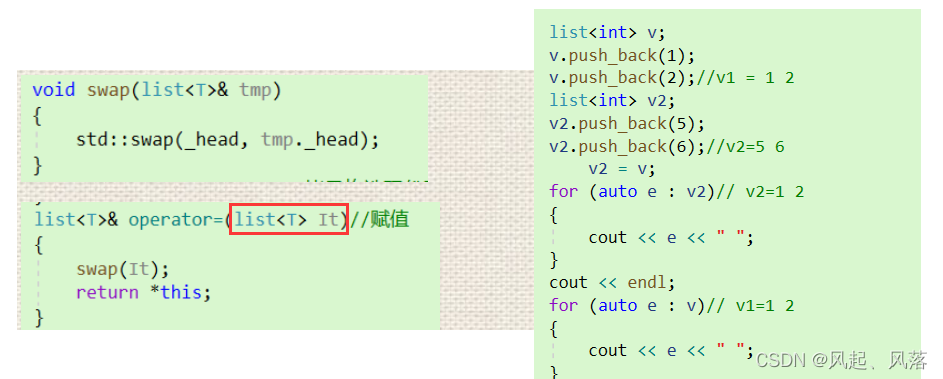
void swap(list<T>& tmp){std::swap(_head, tmp._head);}list(const list<T>& It)//拷贝构造现代写法{empty_init();//将头节点初始化list<T> tmp(It.begin(), It.end());swap(tmp);}
通过调用std中的swap来达到交换的目的
13. 赋值
void swap(list<T>& tmp){std::swap(_head, tmp._head);}
list<T>& operator=(list<T> It){swap(It);return *this;}
参数不可以使用 list &,虽然可以达到赋值的目的,但是It的值也会发生改变
3.完整代码
#include<iostream>
#include<list>
#include<assert.h>
using namespace std;
namespace yzq
{template<class T>struct list_node{list_node<T>* _next;list_node<T>* _prev;T _data;list_node(const T& x=T())//构造函数:_next(nullptr), _prev(nullptr), _data(x){}};//迭代器template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>struct _list_iterator{typedef list_node<T> node;typedef _list_iterator<T,Ref,Ptr> self;node* _node;_list_iterator(node* n):_node(n){}Ref operator*()//解引用 {return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->()//->{return &_node->_data;}self& operator++()//前置++{_node = _node->_next;//指向下一个节点return *this;}self& operator++(int)//后置++{self ret = *this;_node = _node->_next;return ret;}self& operator--()//前置--{_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}self& operator--(int)//后置--{self ret = *this;_node = _node->_prev;return ret;}bool operator!=(const self&s)//!={return _node != s._node;}bool operator==(const self& s)//=={return _node == s._node;}};//const迭代器//template<class T>//struct _list_const_iterator//{// typedef list_node<T> node;// typedef _list_const_iterator<T> self;// node* _node;// _list_const_iterator(node* n)// :_node(n)// {// }// const T& operator*()//解引用 // {// return _node->_data;// }// self& operator++()//前置++// {// _node = _node->_next;//指向下一个节点// return *this;// }// self& operator++(int)//后置++// {// self ret = *this;// _node = _node->_next;// return ret;// }// self& operator--()//前置--// {// _node = _node->_prev;// return *this;// }// self& operator--(int)//后置--// {// self ret = *this;// _node = _node->_prev;// return ret;// }// bool operator!=(const self& s)//!=// {// return _node != s._node;// }// bool operator==(const self& s)//==// {// return _node == s._node;// }//};template <class T>class list{typedef list_node<T> node;public:typedef _list_iterator<T,T&,T*> iterator;typedef _list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;//const迭代器//typedef _list_const_iterator<T> const_iterator;void empty_init(){_head = new node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;}list()//构造函数{empty_init();}template <class Iterator>list(Iterator first, Iterator last){empty_init();while (first != last){push_back(*first);++first;}}//list(const list<T>& It)//拷贝构造//{// empty_init();//初始化头节点// for (auto e : It)// {// push_back(e);// }//}void swap(list<T>& tmp){std::swap(_head, tmp._head);}list(const list<T>& It)//拷贝构造现代写法{empty_init();//将头节点初始化list<T> tmp(It.begin(), It.end());swap(tmp);}list<T>& operator=(list<T> It)//赋值{swap(It);return *this;}~list()//析构函数{//将头节点也要释放掉clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}void clear()//清空数据//但是要注意不要把head清掉{iterator it = begin();while (it != end()){it=erase(it);//为了防止迭代器失效设置返回值//返回值为当前节点的下一个}}void push_back(const T&x)//尾插{/*node* tail = _head->_prev;node* newnode = new node(x);tail->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = tail;newnode->_next = _head;_head->_prev = newnode;*/insert(end(), x);}void push_front(const T&x)//头插{insert(begin(), x);}void insert(iterator pos,const T&x)//在pos位置前插入x{node* cur = pos._node;node* prev = cur->_prev;node* newnode = new node(x);prev->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = prev;newnode->_next = cur;cur->_prev = newnode;}iterator erase(iterator pos)//删除pos位置{//头节点不可以删除assert(pos != end());node* cur = pos._node;node* prev = cur->_prev;node* next = cur->_next;prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete cur;return iterator(next);}void pop_back()//尾删{erase(--end());}void pop_front()//头删{erase(begin());}iterator begin(){return iterator(_head->_next);//通过匿名对象访问第一个数据}iterator end(){return iterator(_head);//通过匿名对象访问最后一个数据的下一个}const_iterator begin()const{return const_iterator(_head->_next);}const_iterator end()const{return const_iterator(_head);}private:node* _head;};/*void test(const list<int>&e){list<int>::const_iterator it = e.begin();while (it != e.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;}void test2(){const list<int> v;test(v);}*///void test1()//{// list<int> v;// v.push_back(1);// v.push_back(2);// v.push_back(3);// v.push_back(4);// list<int>::iterator it= v.begin();// while (it != v.end())// {// cout << *it << " ";// ++it;// }// cout << endl;//}/*struct AA{int _a1;int _a2;AA(int a1=0,int a2=0):_a1(a1),_a2(a2){}};*//*void test3(){list<AA>v;v.push_back(AA(1, 1));v.push_back(AA(2, 2));v.push_back(AA(3, 3));list<AA>::iterator it = v.begin();while (it != v.end()){cout << it->_a1 << " :"<<it->_a2<<" ";cout << endl;it++;}}*///void test4()//{// list<int> v;// v.push_back(1);// v.push_back(2);// v.push_back(3);// v.push_back(4);// 1 2 3 4// for (auto e : v)// {// cout << e << " ";// }// cout << endl;// v.clear();// v.push_back(4);// 4// for (auto e : v)// {// cout << e << " ";// }//}//void test4()//{// list<int> v;// v.push_back(1);// v.push_back(2);// v.push_back(3);// v.push_back(4);// 1 2 3 4// for (auto e : v)// {// cout << e << " ";// }// cout << endl;// list<int> v2(v);// for (auto e : v2)// 1 2 3 4// {// cout << e << " ";// }//}void test4(){list<int> v;v.push_back(1);v.push_back(2);//v1 = 1 2list<int> v2;v2.push_back(5);v2.push_back(6);//v2=5 6v2 = v;for (auto e : v2)// v2=1 2 {cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;for (auto e : v)// v1=1 2{cout << e << " ";}}
} int main()
{yzq::test4();return 0;
}
相关文章:

【C++】list的模拟实现
文章目录1.list 底层2. list的模拟实现1. list_node 类设计2. list类如何调用类型3 .push_back(正常实现)4. 迭代器的实现第一个模板参数Tconst迭代器第二个模板参数Ref第三个模板参数Ptr对list封装的理解5. insert6.push_back与 push_front(复用)7. erase8. pop_back与pop_fro…...

Python连接es笔记三之es更新操作
这一篇笔记介绍如何使用 Python 对数据进行更新操作。 对于 es 的更新的操作,不用到 Search() 方法,而是直接使用 es 的连接加上相应的函数来操作,本篇笔记目录如下: 获取连接update()update_by_query()批量更新UpdateByQuery()…...

哪个牌子的蓝牙耳机音质好?音质比较好的蓝牙耳机排名
蓝牙耳机经过多年发展,无论是在外观设计还是性能配置上都有很大的进步,越来越多的蓝牙耳机开始注重音质表现,逐渐有HIFI音质、无损音质出现在大众视野。那么哪个牌子的蓝牙耳机音质好?接下来,我来给大家分享几款音质比…...
Qt实用技巧:Qt中浮点数的相等比较方式(包括单精度和双精度)
若该文为原创文章,转载请注明原文出处 本文章博客地址:https://hpzwl.blog.csdn.net/article/details/129464152 红胖子(红模仿)的博文大全:开发技术集合(包含Qt实用技术、树莓派、三维、OpenCV、OpenGL、ffmpeg、OSG、单片机、软…...

【数据结构初阶】双向循环链表
目录一.链表的分类二.与单链表相比三.实现增删查改1.双向循环链表结构的创建2.创建新节点3.初始化链表4.头插和尾插5.判断链表是否为空6.头删和尾删7.打印函数8.查找函数9.删除pos位置节点10.在pos前位置插入数据11.优化升级一.链表的分类 链表可有根据单向双向、有无哨兵位、…...

0104BeanDefinition合并和BeanClass加载-Bean生命周期详解-spring
文章目录1 前言2 BeanDefinition合并2.1 BeanDefinition合并在做什么?2.2 BeanDefinition怎么合并2.3 示例演示3 Bean Class 加载后记1 前言 下面要介绍的阶段,都是在调用getBean()从容器中获取bean对象的过程中发生的操作,我们需要更多的去…...

Java集合进阶(三)
文章目录一、Map1. 概述2. 基本功能3. 遍历4. 遍历学生对象5. 集合嵌套6. 统计字符出现次数二、Collections1. 常用方法2. 学生对象排序三、模拟斗地主一、Map 1. 概述 Interface Map<K, V>:K 是键的类型,V 是值的类型。 将键映射到值的对象&…...
【网络】什么是RPC?RPC与HTTP有什么关系?
文章目录RPC是什么RPC和HTTP的关系和区别[附]关于REST论文中提到的"HTTP不是RPC"重点参考 凤凰架构-远程过程调用 既然有HTTP为什么还要有RPC? RPC是什么 RPC(Remote Procedure Call):即远程过程调用,目的是为了让计算机能够跟调用…...
[手撕数据结构]栈的深入学习-java实现
CSDN的各位uu们你们好,今天千泽带来了栈的深入学习,我们会简单的用代码实现一下栈, 接下来让我们一起进入栈的神奇小世界吧!0.速览文章一、栈的定义1. 栈的概念2. 栈的图解二、栈的模拟实现三.栈的经典使用场景-逆波兰表达式总结一、栈的定义 1. 栈的概念 栈:一种…...
2.线性表的顺序表示
数据结构很重要! 数据结构很重要!!! 数据结构很重要!!!! 思考 1.线性表的顺序表示内容有哪些?(What) 2.为什么要学线性表的顺序表示? ? (Why)…...
eps文件删除了能恢复吗?恢复误删eps文件的三种方法
eps文件格式专为矢量图像和图形而设计。虽然没有被广泛使用,但它仍然受到各种插画家和平面设计师的钟爱。eps文件十分适合创建徽标和商标设计,主要应用见于广告牌、海报和横幅。可是在使用设备过程中,难免会遇到数据丢失问题,如果…...

【C++】运算符重载练习——Date 类
文章目录👉日期类介绍👈👉日期类实现👈📕 成员变量📕 构造函数📕 对应月份天数📕 赋值重载📕 比较运算符重载📕 计算 运算符重载👉源代码…...
Redis学习(13)之Lua脚本【环境准备】
文章目录一 Lua入门环境准备1.1 Lua简介1.2 Linux 系统安装Lua1.2.1 Lua 下载1.2.2 Lua 安装1.3 Hello World1.3.1 命令行模式1.3.2 脚本文件模式1.3.3 两种脚本运行方式1.4 Win安装Lua1.4.1 LuaForWindows的安装1.4.2 SciTE修改字体大小1.4.3 SciTE中文乱码1.4.4 SciTE快捷键工…...
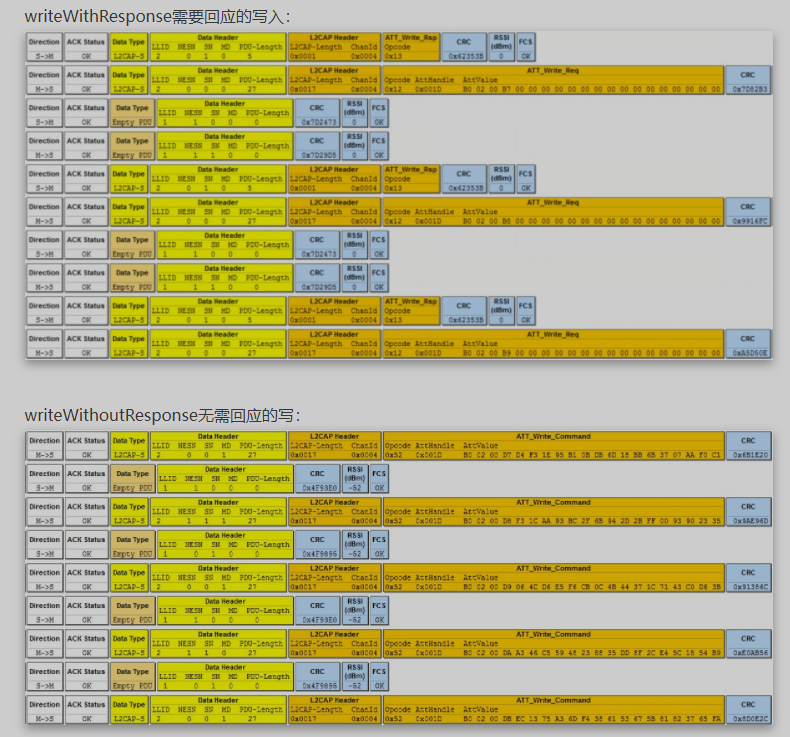
关于BLE的一些知识总结
数据包长度对于BLE4.0/4.1来说,一个数据包的有效载荷最大为20字节对于BLE4.2以上,数据包的有效载荷扩大为251字节传输速率在不考虑跳频间隔的情况下,最大传输速率为:1)BLE4.0/4.1的理论吞吐率为39kb/s;2&am…...
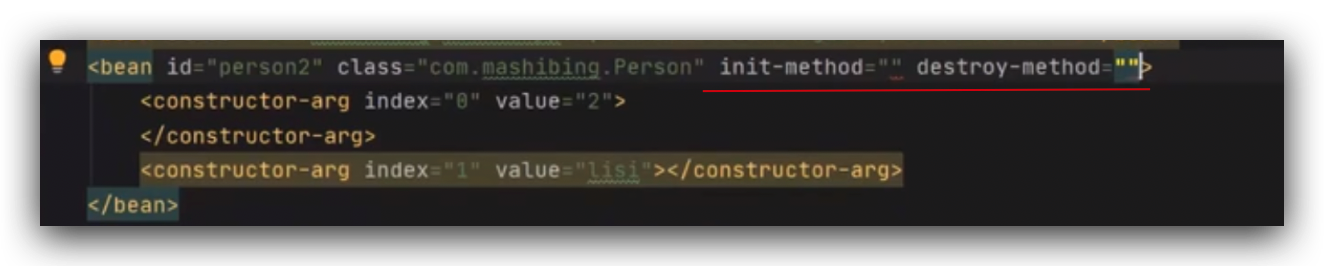
Spring框架源码分析一
如何看源码(方法论)不要忽略源码中的注释使用翻译工具先梳理脉络,然后梳理细节即总分总,先总体过一遍,再看细节,再做一个总结大胆猜测(8分靠猜),小心验证,再调…...
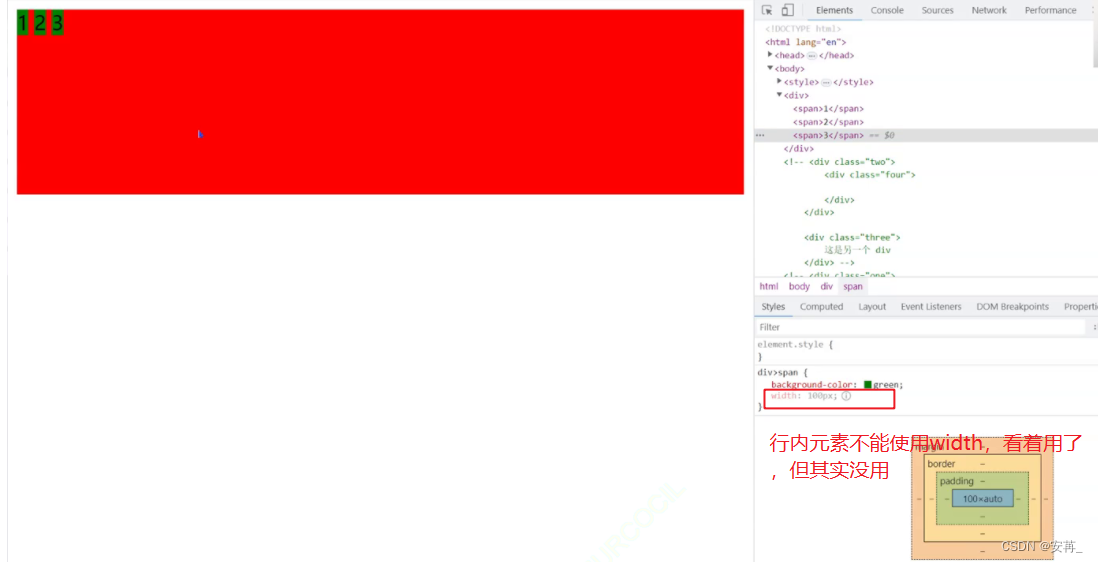
CSS常用内容总结(扫盲)
文章目录前言相关概念【了解】脚本语言什么是脚本语言脚本语言有什么特点常见的脚本语言什么是动态语言,什么是静态语言动态语言和静态语言两者之间有何区别CSSCSS是什么CSS的特点一、CSS代码怎么写基本语法规则引入方式内部样式内联样式表外部样式代码风格二、CSS的…...
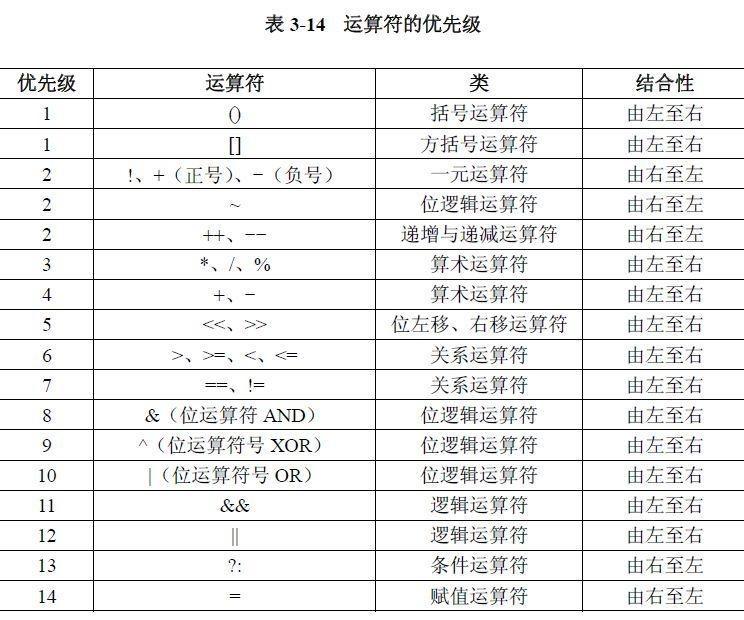
Java启蒙之语言基础
目录 一.Java标识符和关键字 1.1Java标识符 1.2Java关键字 二.数据类型和变量的概述和关系 2.1Java变量 2.2Java的数据类型 2.2.1数据类型的分类的概述 2.2.2数据类型的转换 3.Java运算符 总结 😽个人主页:tq02的博客_CSDN博客-领域博主 &#…...
)
数据库系统--T-SQL数据查询功能-多表查询(超详细/设计/实验/作业/练习)
目录课程名:数据库系统内容/作用:设计/实验/作业/练习学习:T-SQL数据查询功能-多表查询一、前言二、环境与设备三、内容四、内容练习题目:对应题目答案:五、总结课程名:数据库系统 内容/作用:设…...

Spring Boot 3.0系列【14】核心特性篇之Configuration相关注解汇总介绍
有道无术,术尚可求,有术无道,止于术。 本系列Spring Boot版本3.0.3 源码地址:https://gitee.com/pearl-organization/study-spring-boot3 文章目录 前言@Configuration@ConfigurationProperties@EnableConfigurationProperties@ConfigurationPropertiesScan@Configuratio…...

[ubuntu][jetson]给jetson增加swap空间类似于给windows加虚拟内存
具体操作如下: #打开性能模式 sudo nvpmodel -m 0 && sudo jetson_clocks #增加swap空间,防止爆内存 swapoff -a sudo fallocate -l 15G /swapfile sudo chmod 600 /var/swapfile sudo mkswap /swapfile sudo swapon /swapfile…...
第19节 Node.js Express 框架
Express 是一个为Node.js设计的web开发框架,它基于nodejs平台。 Express 简介 Express是一个简洁而灵活的node.js Web应用框架, 提供了一系列强大特性帮助你创建各种Web应用,和丰富的HTTP工具。 使用Express可以快速地搭建一个完整功能的网站。 Expre…...
)
Java 语言特性(面试系列1)
一、面向对象编程 1. 封装(Encapsulation) 定义:将数据(属性)和操作数据的方法绑定在一起,通过访问控制符(private、protected、public)隐藏内部实现细节。示例: public …...
通过Wrangler CLI在worker中创建数据库和表
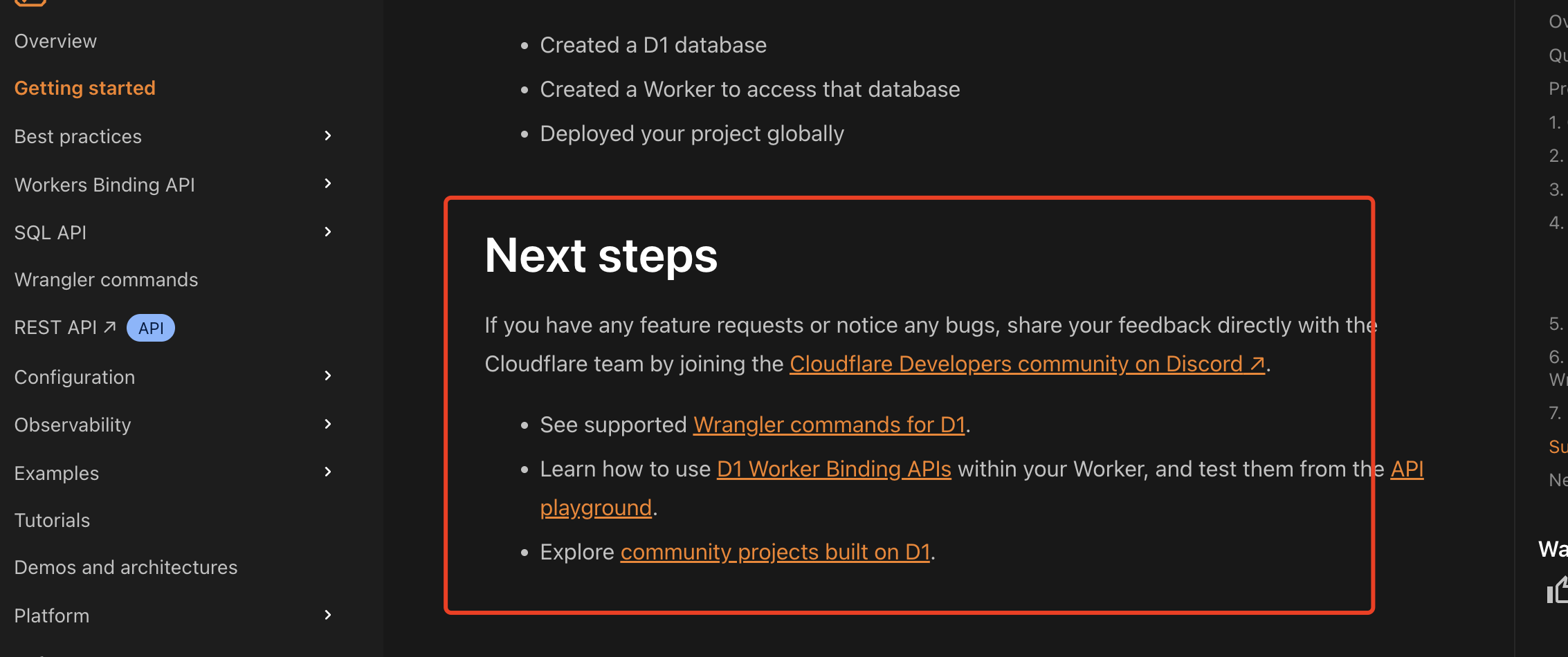
官方使用文档:Getting started Cloudflare D1 docs 创建数据库 在命令行中执行完成之后,会在本地和远程创建数据库: npx wranglerlatest d1 create prod-d1-tutorial 在cf中就可以看到数据库: 现在,您的Cloudfla…...

前端倒计时误差!
提示:记录工作中遇到的需求及解决办法 文章目录 前言一、误差从何而来?二、五大解决方案1. 动态校准法(基础版)2. Web Worker 计时3. 服务器时间同步4. Performance API 高精度计时5. 页面可见性API优化三、生产环境最佳实践四、终极解决方案架构前言 前几天听说公司某个项…...
)
【位运算】消失的两个数字(hard)
消失的两个数字(hard) 题⽬描述:解法(位运算):Java 算法代码:更简便代码 题⽬链接:⾯试题 17.19. 消失的两个数字 题⽬描述: 给定⼀个数组,包含从 1 到 N 所有…...

服务器硬防的应用场景都有哪些?
服务器硬防是指一种通过硬件设备层面的安全措施来防御服务器系统受到网络攻击的方式,避免服务器受到各种恶意攻击和网络威胁,那么,服务器硬防通常都会应用在哪些场景当中呢? 硬防服务器中一般会配备入侵检测系统和预防系统&#x…...

OkHttp 中实现断点续传 demo
在 OkHttp 中实现断点续传主要通过以下步骤完成,核心是利用 HTTP 协议的 Range 请求头指定下载范围: 实现原理 Range 请求头:向服务器请求文件的特定字节范围(如 Range: bytes1024-) 本地文件记录:保存已…...

【论文笔记】若干矿井粉尘检测算法概述
总的来说,传统机器学习、传统机器学习与深度学习的结合、LSTM等算法所需要的数据集来源于矿井传感器测量的粉尘浓度,通过建立回归模型来预测未来矿井的粉尘浓度。传统机器学习算法性能易受数据中极端值的影响。YOLO等计算机视觉算法所需要的数据集来源于…...
)
WEB3全栈开发——面试专业技能点P2智能合约开发(Solidity)
一、Solidity合约开发 下面是 Solidity 合约开发 的概念、代码示例及讲解,适合用作学习或写简历项目背景说明。 🧠 一、概念简介:Solidity 合约开发 Solidity 是一种专门为 以太坊(Ethereum)平台编写智能合约的高级编…...
)
【RockeMQ】第2节|RocketMQ快速实战以及核⼼概念详解(二)
升级Dledger高可用集群 一、主从架构的不足与Dledger的定位 主从架构缺陷 数据备份依赖Slave节点,但无自动故障转移能力,Master宕机后需人工切换,期间消息可能无法读取。Slave仅存储数据,无法主动升级为Master响应请求ÿ…...
