【稀疏矩阵】使用torch.sparse模块
文章目录
- 稀疏矩阵的格式
- coo
- csr
- csc
- Construction of Sparse COO tensors
- Construction of CSR tensors
- Linear Algebra operations(稀疏与稠密之间混合运算)
- Tensor methods and sparse(与稀疏有关的tensor成员函数)
- coo张量可用的tensor成员函数(经实测,csr也有一些可以用,比如dim())
- Torch functions specific to sparse Tensors(与稀疏有关的torch函数)
- 支持稀疏张量的常规torch函数
- 支持稀疏张量的一元函数
稀疏矩阵的格式
目前,torch.sparse和scipy.sparse模块比较支持的主流的稀疏矩阵格式有coo格式、csr格式和csc格式,这三种格式中可供使用的API也最多。
coo
将矩阵中非零元素的坐标和值分开存储在3个数组中,3个数组长度必须相同,表示有n个非零元素。

csr
分 Index Pointers、Indices、Data3个数组存储。
Index Pointers:第i个元素记录这个矩阵的第i行的第1个非零值在Data数组的起始位置,第i+1个元素记录这个矩阵的第i行的最后一个非零值在Data数组的终止位置(不包含右边界)。因此,这个矩阵的行数等于len(Index Pointers)-1,第i行非零值的个数等于Index Pointers[i+1]-Index Pointers[i]。Indices:第i个元素记录这个矩阵的第i个非零值的列坐标。Data:第i个元素记录这个矩阵的第i个非零值的具体数值,排列顺序严格按照行优先,列次先。

csc
与csr唯一的不同在于列优先,其他规则一模一样。

Construction of Sparse COO tensors
- 常规构建
>>> i = [[0, 1, 1],[2, 0, 2]]
>>> v = [3, 4, 5]
>>> s = torch.sparse_coo_tensor(i, v, (2, 3))
>>> s
tensor(indices=tensor([[0, 1, 1],[2, 0, 2]]),values=tensor([3, 4, 5]),size=(2, 3), nnz=3, layout=torch.sparse_coo)
>>> s.to_dense()
tensor([[0, 0, 3],[4, 0, 5]])
torch中,稀疏矩阵的存储方式记录在 tensor.layout中,可以通过检查 torch.layout == torch.sparse_coo来判断是否是coo张量。此外,稠密张量的 layout等于 strided。
- 稠密混合的coo张量
>>> i = [[0, 1, 1],[2, 0, 2]]
>>> v = [[3, 4], [5, 6], [7, 8]]
>>> s = torch.sparse_coo_tensor(i, v, (2, 3, 2))
>>> s
tensor(indices=tensor([[0, 1, 1],[2, 0, 2]]),values=tensor([[3, 4],[5, 6],[7, 8]]),size=(2, 3, 2), nnz=3, layout=torch.sparse_coo)
此方案与常规的coo构建方式不同,values中每个元素可以是一个向量,表示对应坐标的稠密张量,因此,创建出的coo张量也多出了一个维度。
- 带有重复坐标的coo张量
>>> i = [[1, 1]]
>>> v = [3, 4]
>>> s=torch.sparse_coo_tensor(i, v, (3,))
>>> s
tensor(indices=tensor([[1, 1]]),values=tensor( [3, 4]),size=(3,), nnz=2, layout=torch.sparse_coo)
>>> s.to_dense()
tensor([0, 7, 0])
如果输入的坐标有重复,则创建出的coo张量会自动把坐标重复的元素值相加。此外,可以通过成员函数 .coalesce()把重复坐标的元素值相加,将这个coo转换成一个不重复的张量;也可以通过 .is_coalesced()检查这个coo是否存在重复的坐标。
Construction of CSR tensors
按照 Index Pointers、Indices、Data三个数组的定义构建即可。
>>> crow_indices = torch.tensor([0, 2, 4])
>>> col_indices = torch.tensor([0, 1, 0, 1])
>>> values = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3, 4])
>>> csr = torch.sparse_csr_tensor(crow_indices, col_indices, values, dtype=torch.float64)
>>> csr
tensor(crow_indices=tensor([0, 2, 4]),col_indices=tensor([0, 1, 0, 1]),values=tensor([1., 2., 3., 4.]), size=(2, 2), nnz=4,dtype=torch.float64)
>>> csr.to_dense()
tensor([[1., 2.],[3., 4.]], dtype=torch.float64)
Linear Algebra operations(稀疏与稠密之间混合运算)
M表示2-D张量,V表示1-D张量,f表示标量,*表示逐元素乘法,@表示矩阵乘法。M[SparseSemiStructured]表示一种半结构化的稀疏矩阵,此处不再展开,可以自行去torch官网察看。
| PyTorch operation | Sparse grad | Layout signature |
|---|---|---|
| torch.mv() | no | M[sparse_coo] @ V[strided] -> V[strided] |
| torch.mv() | no | M[sparse_csr] @ V[strided] -> V[strided] |
| torch.matmul() | no | M[sparse_coo] @ M[strided] -> M[strided] |
| torch.matmul() | no | M[sparse_csr] @ M[strided] -> M[strided] |
| torch.matmul() | no | M[SparseSemiStructured] @ M[strided] -> M[strided] |
| torch.matmul() | no | M[strided] @ M[SparseSemiStructured] -> M[strided] |
| torch.mm() | no | M[strided] @ M[SparseSemiStructured] -> M[strided] |
| torch.mm() | no | M[sparse_coo] @ M[strided] -> M[strided] |
| torch.mm() | no | M[SparseSemiStructured] @ M[strided] -> M[strided] |
| torch.sparse.mm() | yes | M[sparse_coo] @ M[strided] -> M[strided] |
| torch.smm() | no | M[sparse_coo] @ M[strided] -> M[sparse_coo] |
| torch.hspmm() | no | M[sparse_coo] @ M[strided] -> M[hybrid sparse_coo] |
| torch.bmm() | no | T[sparse_coo] @ T[strided] -> T[strided] |
| torch.addmm() | no | f * M[strided] + f * (M[sparse_coo] @ M[strided]) -> M[strided] |
| torch.addmm() | no | f * M[strided] + f * (M[SparseSemiStructured] @ M[strided]) -> M[strided] |
| torch.addmm() | no | f * M[strided] + f * (M[strided] @ M[SparseSemiStructured]) -> M[strided] |
| torch.sparse.addmm() | yes | f * M[strided] + f * (M[sparse_coo] @ M[strided]) -> M[strided] |
| torch.sspaddmm() | no | f * M[sparse_coo] + f * (M[sparse_coo] @ M[strided]) -> M[sparse_coo] |
| torch.lobpcg() | no | GENEIG(M[sparse_coo]) -> M[strided], M[strided] |
| torch.pca_lowrank() | yes | PCA(M[sparse_coo]) -> M[strided], M[strided], M[strided] |
| torch.svd_lowrank() | yes | SVD(M[sparse_coo]) -> M[strided], M[strided], M[strided] |
以上API中,如果 Layout signature中提供了 @或者 *操作符,就不需要记住API,直接通过操作符即可隐式调用对应的API。如:
>>> a = torch.tensor([[0, 0, 1, 0], [1, 2, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0]], dtype=torch.float64)
>>> sp = a.to_sparse_csr()
>>> vec = torch.randn(4, 1, dtype=torch.float64)
>>> sp.matmul(vec)
tensor([[ 0.4788],[-3.2338],[ 0.0000]], dtype=torch.float64)
>>> sp @ vec
tensor([[ 0.4788],[-3.2338],[ 0.0000]], dtype=torch.float64)
需要注意的是,使用操作符在稀疏张量和稠密张量之间乘法运算时,返回的都是稠密张量。如果想要返回稀疏张量,需要显式使用torch.smm()。
torch同样支持稀疏与稀疏之间的运算,但要求输入的稀疏张量必须具有相同的稀疏结构,否则会报错,返回的稀疏张量的稀疏结构也与输入相同。
乘法运算:
>>> a = torch.tensor([[0, 0, 1, 0], [1, 2, 0, 0], [0, 1, 0, 0], [1, 0, 0, 0]], dtype=torch.float64)
>>> b = torch.tensor([[0, 0, 2, 0], [3, 1, 0, 0], [0, 0, 4, 0], [1, 0, 0, 1]], dtype=torch.float64)
>>> sp1 = a.to_sparse_coo()
>>> sp2 = b.to_sparse_coo()
>>> sp1 @ sp2
tensor(indices=tensor([[0, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3],[2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2]]),values=tensor([4., 6., 2., 2., 3., 1., 2.]),size=(4, 4), nnz=7, dtype=torch.float64, layout=torch.sparse_coo)
加法运算
>>> a = torch.tensor([[0, 0, 1, 0], [1, 2, 0, 0], [0, 1, 0, 0], [1, 0, 0, 0]], dtype=torch.float64)
>>> b = torch.tensor([[0, 0, 2, 0], [3, 1, 0, 0], [0, 0, 4, 0], [1, 0, 0, 1]], dtype=torch.float64)
>>> sp1 = a.to_sparse_coo()
>>> sp2 = b.to_sparse_coo()
>>> sp3 = b.to_sparse_csr()
>>> sp1 + sp2
tensor(indices=tensor([[0, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3],[2, 0, 1, 1, 2, 0, 3]]),values=tensor([3., 4., 3., 1., 4., 2., 1.]),size=(4, 4), nnz=7, dtype=torch.float64, layout=torch.sparse_coo)
>>> sp1 + sp3
UserWarning: Sparse CSR tensor support is in beta state. If you miss a functionality in the sparse tensor support, please submit a feature request to https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues. (Triggered internally at C:\actions-runner\_work\pytorch\pytorch\builder\windows\pytorch\aten\src\ATen\SparseCsrTensorImpl.cpp:55.)sp3 = b.to_sparse_csr()
Traceback (most recent call last):File "C:\Users\Xu Han\Desktop\pycharm-projects\MD_notes\main.py", line 18, in <module>print(sp1 + sp3)
RuntimeError: memory format option is only supported by strided tensors
Tensor methods and sparse(与稀疏有关的tensor成员函数)
| PyTorch operation | return |
|---|---|
| Tensor.is_sparse | IsTrue if the Tensor uses sparse COO storage layout, False otherwise. |
| Tensor.is_sparse_csr | IsTrue if the Tensor uses sparse CSR storage layout, False otherwise. |
| Tensor.dense_dim | Return the number of dense dimensions in a sparse tensorself. |
| Tensor.sparse_dim | Return the number of sparse dimensions in a sparse tensorself. |
这里打断一下表格,讲解一下dense_dim和sparse_dim的含义。上文中,我们曾构建过稠密混合的coo张量,如下:
>>> i = [[0, 1, 1],[2, 0, 2]]
>>> v = [[3, 4], [5, 6], [7, 8]]
>>> s = torch.sparse_coo_tensor(i, v, (2, 3, 2))
>>> s
tensor(indices=tensor([[0, 1, 1],[2, 0, 2]]),values=tensor([[3, 4],[5, 6],[7, 8]]),size=(2, 3, 2), nnz=3, layout=torch.sparse_coo)
那么,对于这个tensor,它的dense_dim为1,sparse_dim为2。
此外,在进行稀疏与稀疏之间的数学运算时,一定要保证稀疏张量的sparse_dim等于2.
继续表格。
| PyTorch operation | return |
|---|---|
| Tensor.sparse_mask | Returns a new sparse tensor with values from a strided tensorself filtered by the indices of the sparse tensor mask. |
| Tensor.to_sparse | Returns a sparse copy of the tensor. |
| Tensor.to_sparse_coo | Convert a tensor to coordinate format. |
| Tensor.to_sparse_csr | Convert a tensor to compressed row storage format (CSR). |
| Tensor.to_sparse_csc | Convert a tensor to compressed column storage (CSC) format. |
| Tensor.to_sparse_bsr | Convert a tensor to a block sparse row (BSR) storage format of given blocksize. |
| Tensor.to_sparse_bsc | Convert a tensor to a block sparse column (BSC) storage format of given blocksize. |
| Tensor.to_dense | Creates a strided copy ofself if self is not a strided tensor, otherwise returns self. |
| Tensor.values | Return the values tensor of a sparse COO tensor. |
以下是仅限coo张量的成员:
| PyTorch operation | return |
|---|---|
| Tensor.coalesce | Returns a coalesced copy ofself if self is an uncoalesced tensor. |
| Tensor.sparse_resize_ | Resizesself sparse tensor to the desired size and the number of sparse and dense dimensions. |
| Tensor.sparse_resize_and_clear_ | Removes all specified elements from a sparse tensorself and resizes self to the desired size and the number of sparse and dense dimensions. |
| Tensor.is_coalesced | ReturnsTrue if self is a sparse COO tensor that is coalesced, False otherwise. |
| Tensor.indices | Return the indices tensor of a sparse COO tensor. |
以下是仅限csr和bsr张量的成员:
| PyTorch operation | return |
|---|---|
| Tensor.crow_indices | Returns the tensor containing the compressed row indices of theself tensor when self is a sparse CSR tensor of layout sparse_csr. |
| Tensor.col_indices | Returns the tensor containing the column indices of theself tensor when self is a sparse CSR tensor of layout sparse_csr. |
以下是仅限csc和bsc张量的成员:
| PyTorch operation | return |
|---|---|
| Tensor.row_indices | … |
| Tensor.ccol_indices | … |
coo张量可用的tensor成员函数(经实测,csr也有一些可以用,比如dim())
add() add_() addmm() addmm_() any() asin() asin_() arcsin() arcsin_() bmm() clone() deg2rad() deg2rad_() detach() detach_() dim() div() div_() floor_divide() floor_divide_() get_device() index_select() isnan() log1p() log1p_() mm() mul() mul_() mv() narrow_copy() neg() neg_() negative() negative_() numel() rad2deg() rad2deg_() resize_as_() size() pow() sqrt() square() smm() sspaddmm() sub() sub_() t() t_() transpose() transpose_() zero_()
Torch functions specific to sparse Tensors(与稀疏有关的torch函数)
| PyTorch operation | return |
|---|---|
| sparse_coo_tensor | Constructs a sparse tensor in COO(rdinate) format with specified values at the givenindices. |
| sparse_csr_tensor | Constructs a sparse tensor in CSR (Compressed Sparse Row) with specified values at the givencrow_indices and col_indices. |
| sparse_csc_tensor | Constructs a sparse tensor in CSC (Compressed Sparse Column) with specified values at the givenccol_indices and row_indices. |
| sparse_bsr_tensor | Constructs a sparse tensor in BSR (Block Compressed Sparse Row)) with specified 2-dimensional blocks at the givencrow_indices and col_indices. |
| sparse_bsc_tensor | Constructs a sparse tensor in BSC (Block Compressed Sparse Column)) with specified 2-dimensional blocks at the givenccol_indices and row_indices. |
| sparse_compressed_tensor | Constructs a sparse tensor in Compressed Sparse format - CSR, CSC, BSR, or BSC - with specified values at the givencompressed_indices and plain_indices. |
| sparse.sum | Return the sum of each row of the given sparse tensor. |
| sparse.addmm | This function does exact same thing as torch.addmm() in the forward, except that it supports backward for sparse COO matrixmat1. |
| sparse.sampled_addmm | Performs a matrix multiplication of the dense matricesmat1 and mat2 at the locations specified by the sparsity pattern of input. |
| sparse.mm | Performs a matrix multiplication of the sparse matrixmat1 |
| sspaddmm | Matrix multiplies a sparse tensormat1 with a dense tensor mat2, then adds the sparse tensor input to the result. |
| hspmm | Performs a matrix multiplication of a sparse COO matrixmat1 and a strided matrix mat2. |
| smm | Performs a matrix multiplication of the sparse matrixinput with the dense matrix mat. |
| sparse.softmax | Applies a softmax function. |
| sparse.log_softmax | Applies a softmax function followed by logarithm. |
| sparse.spdiags | Creates a sparse 2D tensor by placing the values from rows ofdiagonals along specified diagonals of the output |
支持稀疏张量的常规torch函数
cat() dstack() empty() empty_like() hstack() index_select() is_complex() is_floating_point() is_nonzero() is_same_size() is_signed() is_tensor() lobpcg() mm() native_norm() pca_lowrank() select() stack() svd_lowrank() unsqueeze() vstack() zeros() zeros_like()
支持稀疏张量的一元函数
The following operators currently support sparse COO/CSR/CSC/BSR tensor inputs.
abs() asin() asinh() atan() atanh() ceil() conj_physical() floor() log1p() neg() round() sin() sinh() sign() sgn() signbit() tan() tanh() trunc() expm1() sqrt() angle() isinf() isposinf() isneginf() isnan() erf() erfinv()
相关文章:

【稀疏矩阵】使用torch.sparse模块
文章目录 稀疏矩阵的格式coocsrcsc Construction of Sparse COO tensorsConstruction of CSR tensorsLinear Algebra operations(稀疏与稠密之间混合运算)Tensor methods and sparse(与稀疏有关的tensor成员函数)coo张量可用的ten…...

如何增加谷歌网站曝光率?
增加谷歌网站曝光率其实就是让更多的人在搜索相关内容时,能看到你的网站。首先你就要搞清楚用户在搜索什么,这样才能把正确的内容呈现在他们面前。首先,你得站在用户的角度思考,想想他们在搜索与你网站相关的信息时,可…...
)
虚幻中的c++(持续更新)
文章目录 虚幻中的cUPROPERTY参数 UFUNCTION参数 虚幻中的c UPROPERTY 是虚幻中用于声明属性的宏,它用于标记某个属性是一个虚幻托管的属性,并且可以在编辑器中进行访问和操作。其提供了一系列参数,用于定义属性的各种行为,例如是…...

83-MySQL 索引有几种
MySQL中的索引主要有以下几种: 普通索引:最基本的索引类型,没有唯一性的限制,可以通过多个字段创建复合索引。 唯一索引:与普通索引类似,但区别在于唯一索引的每一个索引值只对应唯一的数据记录。 主键索…...

文献解读-The trans-omics landscape of COVID-19
关键词:流行病学;基因测序;变异检测; 文献简介 标题(英文):The trans-omics landscape of COVID-19 标题(中文):COVID-19的跨组学全景 发表期刊:…...

Unity核心实践小项目
要源码包的私信我。 简介 衔接Unity核心学习后的实操小项目 需求分析 准备工作 面板基类 为了能够控制一画布整体的透明度,所以需要给每个面板都添加一个 CanvasGroup组件 UI管理器 UGUI方面的参数设置 开始场景 场景搭建 直接用资源包搭建好的场景:…...
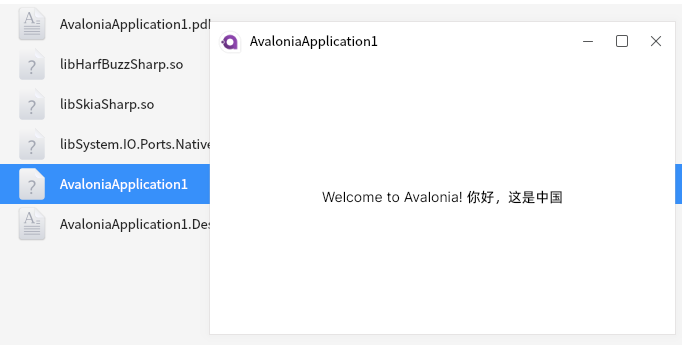
Avaloia 实现国产麒麟系统中文显示界面
最近在搞一个国产麒麟系统的接口对接,因为,接口内含复杂的签名验证,而且还是离线环境,所以,postman不是很好用。 就想着哪个方式好一些,主要是有选择图片的操作,所以,在Electron和A…...

pytest 生成allure测试报告
allure的安装 github地址 allure资产列表 windows下载.zip,解压并配置环境变量PATH;linux下载tar.gz,解压配置; allure作为pytest插件 # 安装 pip install allure-pytest# 执行单元测试,生成allure测试数据&…...

查询GPU版本以及PyTorch中使用单GPU和多GPU
文章目录 多GPU介绍GPU可用性及版本检查使用单个GPU使用多个GPU多GPU介绍 多GPU是指使用多个显卡来同时进行计算,以加速深度学习模型的训练和推断。每个GPU都有自己的内存和计算能力,通过同时利用多个GPU可以并行地执行模型的计算,从而提高整体的计算效率。 GPU可用性及版…...

基于SpringBoot+Vue的线上考试系统
作者:计算机学姐 开发技术:SpringBoot、SSM、Vue、MySQL、JSP、ElementUI、小程序等,“文末源码”。 专栏推荐:前后端分离项目源码、SpringBoot项目源码、SSM项目源码 系统展示 【2025最新】基于JavaSpringBootVueMySQL的线上考试…...

动手学深度学习(pytorch土堆)-02TensorBoard的使用
1.可视化 代码使用了 torch.utils.tensorboard 将数据记录到 TensorBoard 以便可视化。具体来说,它将标量数据记录到目录 logs 中,使用的是 SummaryWriter 类。 代码分解如下: SummaryWriter("logs"):初始化一个 Ten…...

STM3学习记录
一、串口 1.串口定义,将串口相关寄存器的首地址强制转化为串口结构体,方便通过结果体访问串口的寄存器 #define __IO volatile /*!< Defines read / write permissions */ typedef struct {__IO uint32_t SR; /*!< US…...
【网络】应用层协议-http协议
应用层协议-http协议 文章目录 1.Http协议1.1什么是http协议1.2认识URL1.3urlencode和urldecode1.4HTTP请求协议格式1.5HTTP响应协议格式1.6HTTP常见的Header1.7HTTP常见状态码1.8HTTP的方法1.8根据url调取对应的服务 2.cookie和session2.1cookie2.2session 3.HTTPS协议3.1对称…...

【python】OpenCV—Mask RCNN for Object Detection and Instance Segmentation
文章目录 1、任务描述2、MASR RCNN 网络结构3、方法实现4、结果展示5、涉及到的库getPerfProfile 6、参考 1、任务描述 利用 mask rcnn 网络,进行图片和视频的目标检测和实例分割 2、MASR RCNN 网络结构 3、方法实现 # Copyright (C) 2018-2019, BigVision LLC (L…...

通过 Python 使用 Pexels图片库 API 打造个性化壁纸应用
在数字时代,照片不仅仅是回忆的载体,它们还是我们生活的美丽装饰品。想象一下,如果你能轻松地将世界上最美的免费图片应用到你的应用程序中,岂不是让你的程序立刻闪亮起来?好消息是,这不仅仅是一个梦想。今…...
多线程篇(其它容器- CopyOnWriteArrayList)(持续更新迭代)
一、CopyOnWriteArrayList(一) 1. 简介 并发包中的并发List只有CopyOnWriteArrayList。 CopyOnWriteArrayList是一个线程安全的ArrayList,对其进行的修改操作都是在底层的一个复制的数 组(快照)上进行的࿰…...

OPENAIGC开发者大赛高校组金奖 | 知洞—基于大模型的智慧题库
在第二届拯救者杯OPENAIGC开发者大赛中,涌现出一批技术突出、创意卓越的作品。为了让这些优秀项目被更多人看到,我们特意开设了优秀作品报道专栏,旨在展示其独特之处和开发者的精彩故事。 无论您是技术专家还是爱好者,希望能带给您…...

java服务CPU使用率高排查
第一步 使用top命令进行查看 如果是死锁,cpu使用率不会很高,但不会响应,这时这样排查。 第二步 使用jps查看到进程id,再使用jstack pid查看线程堆栈信息 jstack pid会出现如图所示的信息,表示发生死锁,然后去排查这…...

聚焦:clicOH 借助 NVIDIA cuOpt 实现最后一英里交付速度 20 倍提升
受消费者行为转变和疫情影响,电子商务继续呈爆炸式增长和转型。因此,物流和运输公司发现自己处于包裹配送革命的前沿。这新的现实情况在最后一英里配送中尤为明显,而后者现在已经成为供应链物流中成本最高的要素,占从零售到制造等…...
)
从头开始嵌入式第三十八天(数据结构 双向链表)
目录 双向链表 一、结构特点 二、操作优势 三、应用场景 1.创建链表 2.头插数据 3.打印数据 4.查找数据 5.删除数据 6.更改数据 7.清空数据 8.尾插数据 9.按位插入 10.获取长度 11.是否为空 双向链表 双向链表是一种链表结构。 一、结构特点 1. 每个节点包含两个…...

HTML 语义化
目录 HTML 语义化HTML5 新特性HTML 语义化的好处语义化标签的使用场景最佳实践 HTML 语义化 HTML5 新特性 标准答案: 语义化标签: <header>:页头<nav>:导航<main>:主要内容<article>&#x…...

pam_env.so模块配置解析
在PAM(Pluggable Authentication Modules)配置中, /etc/pam.d/su 文件相关配置含义如下: 配置解析 auth required pam_env.so1. 字段分解 字段值说明模块类型auth认证类模块,负责验证用户身份&am…...

HTML 列表、表格、表单
1 列表标签 作用:布局内容排列整齐的区域 列表分类:无序列表、有序列表、定义列表。 例如: 1.1 无序列表 标签:ul 嵌套 li,ul是无序列表,li是列表条目。 注意事项: ul 标签里面只能包裹 li…...
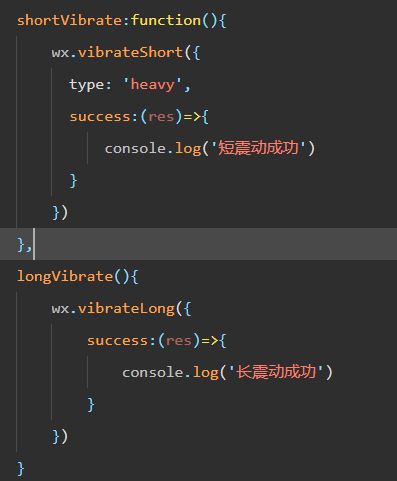
微信小程序 - 手机震动
一、界面 <button type"primary" bindtap"shortVibrate">短震动</button> <button type"primary" bindtap"longVibrate">长震动</button> 二、js逻辑代码 注:文档 https://developers.weixin.qq…...
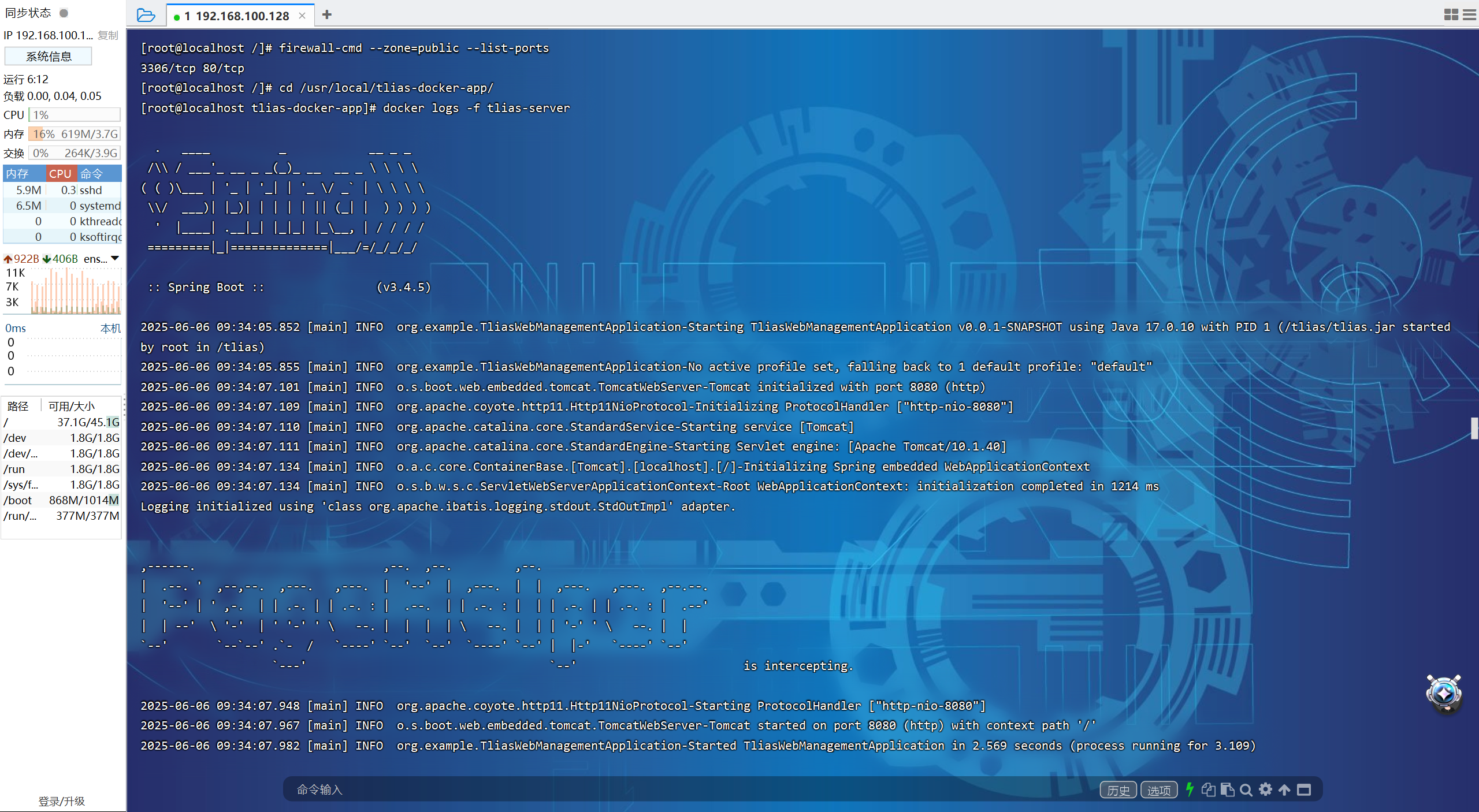
【JavaWeb】Docker项目部署
引言 之前学习了Linux操作系统的常见命令,在Linux上安装软件,以及如何在Linux上部署一个单体项目,大多数同学都会有相同的感受,那就是麻烦。 核心体现在三点: 命令太多了,记不住 软件安装包名字复杂&…...

今日学习:Spring线程池|并发修改异常|链路丢失|登录续期|VIP过期策略|数值类缓存
文章目录 优雅版线程池ThreadPoolTaskExecutor和ThreadPoolTaskExecutor的装饰器并发修改异常并发修改异常简介实现机制设计原因及意义 使用线程池造成的链路丢失问题线程池导致的链路丢失问题发生原因 常见解决方法更好的解决方法设计精妙之处 登录续期登录续期常见实现方式特…...

2023赣州旅游投资集团
单选题 1.“不登高山,不知天之高也;不临深溪,不知地之厚也。”这句话说明_____。 A、人的意识具有创造性 B、人的认识是独立于实践之外的 C、实践在认识过程中具有决定作用 D、人的一切知识都是从直接经验中获得的 参考答案: C 本题解…...

2025季度云服务器排行榜
在全球云服务器市场,各厂商的排名和地位并非一成不变,而是由其独特的优势、战略布局和市场适应性共同决定的。以下是根据2025年市场趋势,对主要云服务器厂商在排行榜中占据重要位置的原因和优势进行深度分析: 一、全球“三巨头”…...
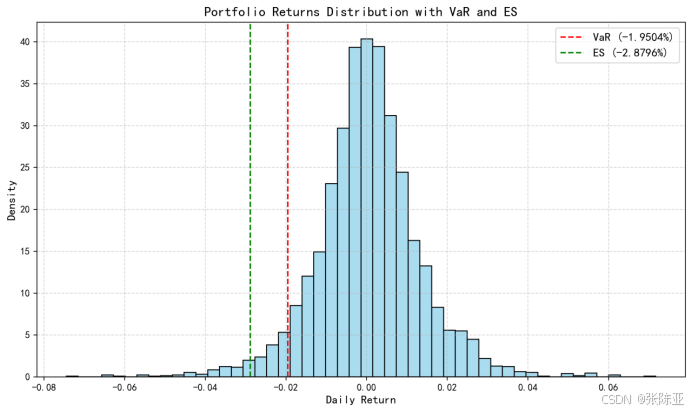
Python基于历史模拟方法实现投资组合风险管理的VaR与ES模型项目实战
说明:这是一个机器学习实战项目(附带数据代码文档),如需数据代码文档可以直接到文章最后关注获取。 1.项目背景 在金融市场日益复杂和波动加剧的背景下,风险管理成为金融机构和个人投资者关注的核心议题之一。VaR&…...
push [特殊字符] present
push 🆚 present 前言present和dismiss特点代码演示 push和pop特点代码演示 前言 在 iOS 开发中,push 和 present 是两种不同的视图控制器切换方式,它们有着显著的区别。 present和dismiss 特点 在当前控制器上方新建视图层级需要手动调用…...
