Collection-LinkedList源码解析
文章目录
- 概述
- LinkedList实现
- 底层数据结构
- 构造函数
- getFirst(), getLast()
- removeFirst(), removeLast(), remove(e), remove(index)
- add()
- addAll()
- clear()
- Positional Access 方法
- 查找操作
概述
LinkedList同时实现了List接口和Deque接口,也就是说它既可以看作一个顺序容器,又可以看作一个队列(Queue),同时又可以看作一个栈(Stack)。这样看来,LinkedList简直就是个全能冠军。当你需要使用栈或者队列时,可以考虑使用LinkedList,一方面是因为Java官方已经声明不建议使用Stack类,更遗憾的是,Java里根本没有一个叫做Queue的类(它是个接口名字)。关于栈或队列,现在的首选是ArrayDeque,它有着比LinkedList(当作栈或队列使用时)有着更好的性能。
LinkedList实现
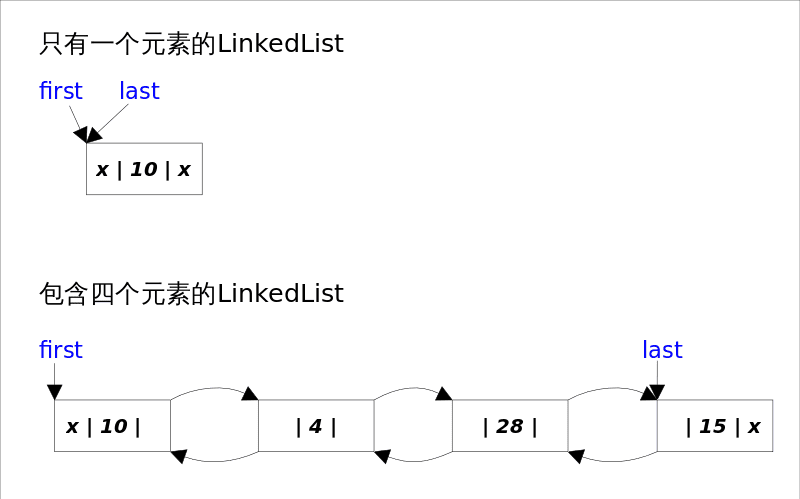
底层数据结构
LinkedList底层通过双向链表实现,本节将着重讲解插入和删除元素时双向链表的维护过程。双向链表的每个节点用内部类Node表示。LinkedList通过first和last引用分别指向链表的第一个和最后一个元素。当链表为空的时候first和last都指向null。
transient int size = 0;/*** Pointer to first node.* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||* (first.prev == null && first.item != null)*/transient Node<E> first;/*** Pointer to last node.* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||* (last.next == null && last.item != null)*/transient Node<E> last;
其中Node是私有的内部类:
private static class Node<E> {E item;Node<E> next;Node<E> prev;Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {this.item = element;this.next = next;this.prev = prev;}}
构造函数
/*** Constructs an empty list.*/public LinkedList() {}/*** Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's* iterator.** @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null*/public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {this();addAll(c);}
getFirst(), getLast()
获取第一个元素, 和获取最后一个元素:
/*** Returns the first element in this list.** @return the first element in this list* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty*/public E getFirst() {final Node<E> f = first;if (f == null)throw new NoSuchElementException();return f.item;}/*** Returns the last element in this list.** @return the last element in this list* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty*/public E getLast() {final Node<E> l = last;if (l == null)throw new NoSuchElementException();return l.item;}
removeFirst(), removeLast(), remove(e), remove(index)
remove()方法也有两个版本,一个是删除跟指定元素相等的第一个元素remove(Object o),另一个是删除指定下标处的元素remove(int index)。
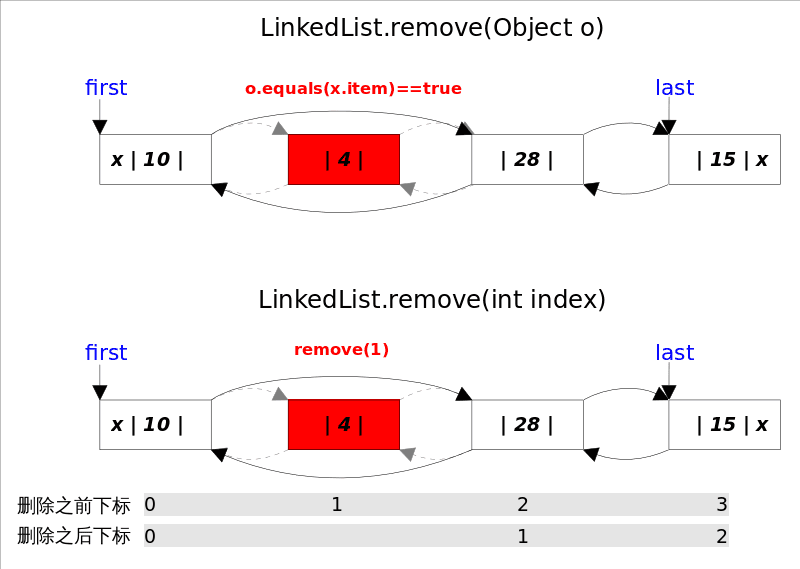
删除元素 - 指的是删除第一次出现的这个元素, 如果没有这个元素,则返回false;判断的依据是equals方法, 如果equals,则直接unlink这个node;由于LinkedList可存放null元素,故也可以删除第一次出现null的元素;
/*** Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list,* if it is present. If this list does not contain the element, it is* unchanged. More formally, removes the element with the lowest index* {@code i} such that* <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>* (if such an element exists). Returns {@code true} if this list* contained the specified element (or equivalently, if this list* changed as a result of the call).** @param o element to be removed from this list, if present* @return {@code true} if this list contained the specified element*/public boolean remove(Object o) {if (o == null) {for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {if (x.item == null) {unlink(x);return true;}}} else {for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {if (o.equals(x.item)) {unlink(x);return true;}}}return false;}/*** Unlinks non-null node x.*/E unlink(Node<E> x) {// assert x != null;final E element = x.item;final Node<E> next = x.next;final Node<E> prev = x.prev;if (prev == null) {// 第一个元素first = next;} else {prev.next = next;x.prev = null;}if (next == null) {// 最后一个元素last = prev;} else {next.prev = prev;x.next = null;}x.item = null; // GCsize--;modCount++;return element;}
remove(int index)使用的是下标计数, 只需要判断该index是否有元素即可,如果有则直接unlink这个node。
/*** Removes the element at the specified position in this list. Shifts any* subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their indices).* Returns the element that was removed from the list.** @param index the index of the element to be removed* @return the element previously at the specified position* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}*/public E remove(int index) {checkElementIndex(index);return unlink(node(index));}
删除head元素:
/*** Removes and returns the first element from this list.** @return the first element from this list* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty*/public E removeFirst() {final Node<E> f = first;if (f == null)throw new NoSuchElementException();return unlinkFirst(f);}/*** Unlinks non-null first node f.*/private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) {// assert f == first && f != null;final E element = f.item;final Node<E> next = f.next;f.item = null;f.next = null; // help GCfirst = next;if (next == null)last = null;elsenext.prev = null;size--;modCount++;return element;}
删除last元素:
/*** Removes and returns the last element from this list.** @return the last element from this list* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty*/public E removeLast() {final Node<E> l = last;if (l == null)throw new NoSuchElementException();return unlinkLast(l);}/*** Unlinks non-null last node l.*/private E unlinkLast(Node<E> l) {// assert l == last && l != null;final E element = l.item;final Node<E> prev = l.prev;l.item = null;l.prev = null; // help GClast = prev;if (prev == null)first = null;elseprev.next = null;size--;modCount++;return element;}
add()
add()*方法有两个版本,一个是add(E e),该方法在*LinkedList的末尾插入元素,因为有last指向链表末尾,在末尾插入元素的花费是常数时间。只需要简单修改几个相关引用即可;另一个是add(int index, E element),该方法是在指定下表处插入元素,需要先通过线性查找找到具体位置,然后修改相关引用完成插入操作。
/*** Appends the specified element to the end of this list.** <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addLast}.** @param e element to be appended to this list* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})*/public boolean add(E e) {linkLast(e);return true;}/*** Links e as last element.*/void linkLast(E e) {final Node<E> l = last;final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);last = newNode;if (l == null)first = newNode;elsel.next = newNode;size++;modCount++;}
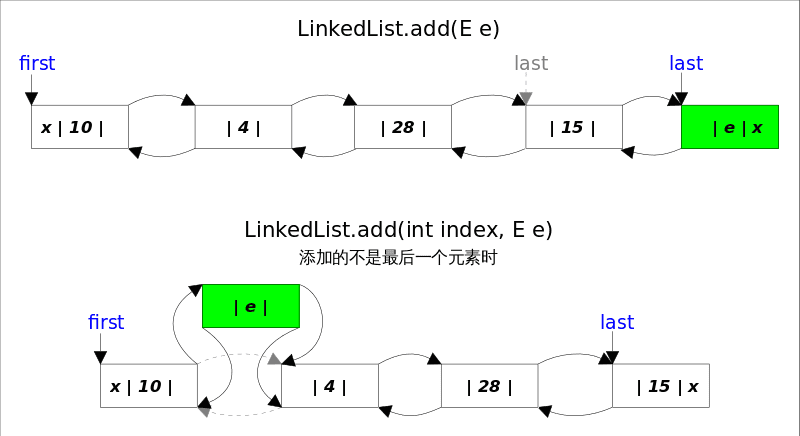
add(int index, E element), 当index==size时,等同于add(E e); 如果不是,则分两步: 1.先根据index找到要插入的位置,即node(index)方法;2.修改引用,完成插入操作。
/*** Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list.* Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and any* subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).** @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted* @param element element to be inserted* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}*/public void add(int index, E element) {checkPositionIndex(index);if (index == size)linkLast(element);elselinkBefore(element, node(index));}
addAll()
addAll(index, c) 实现方式并不是直接调用add(index,e)来实现,主要是因为效率的问题,另一个是fail-fast中modCount只会增加1次;
/*** Appends all of the elements in the specified collection to the end of* this list, in the order that they are returned by the specified* collection's iterator. The behavior of this operation is undefined if* the specified collection is modified while the operation is in* progress. (Note that this will occur if the specified collection is* this list, and it's nonempty.)** @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null*/public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {return addAll(size, c);}/*** Inserts all of the elements in the specified collection into this* list, starting at the specified position. Shifts the element* currently at that position (if any) and any subsequent elements to* the right (increases their indices). The new elements will appear* in the list in the order that they are returned by the* specified collection's iterator.** @param index index at which to insert the first element* from the specified collection* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null*/public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {checkPositionIndex(index);Object[] a = c.toArray();int numNew = a.length;if (numNew == 0)return false;Node<E> pred, succ;if (index == size) {succ = null;pred = last;} else {succ = node(index);pred = succ.prev;}for (Object o : a) {@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o;Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null);if (pred == null)first = newNode;elsepred.next = newNode;pred = newNode;}if (succ == null) {last = pred;} else {pred.next = succ;succ.prev = pred;}size += numNew;modCount++;return true;}
clear()
为了让GC更快可以回收放置的元素,需要将node之间的引用关系赋空。
/*** Removes all of the elements from this list.* The list will be empty after this call returns.*/public void clear() {// Clearing all of the links between nodes is "unnecessary", but:// - helps a generational GC if the discarded nodes inhabit// more than one generation// - is sure to free memory even if there is a reachable Iteratorfor (Node<E> x = first; x != null; ) {Node<E> next = x.next;x.item = null;x.next = null;x.prev = null;x = next;}first = last = null;size = 0;modCount++;}
Positional Access 方法
通过index获取元素
/*** Returns the element at the specified position in this list.** @param index index of the element to return* @return the element at the specified position in this list* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}*/public E get(int index) {checkElementIndex(index);return node(index).item;}
将某个位置的元素重新赋值:
/*** Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with the* specified element.** @param index index of the element to replace* @param element element to be stored at the specified position* @return the element previously at the specified position* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}*/public E set(int index, E element) {checkElementIndex(index);Node<E> x = node(index);E oldVal = x.item;x.item = element;return oldVal;}
将元素插入到指定index位置:
/*** Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list.* Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and any* subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).** @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted* @param element element to be inserted* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}*/public void add(int index, E element) {checkPositionIndex(index);if (index == size)linkLast(element);elselinkBefore(element, node(index));}
删除指定位置的元素:
/*** Removes the element at the specified position in this list. Shifts any* subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their indices).* Returns the element that was removed from the list.** @param index the index of the element to be removed* @return the element previously at the specified position* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}*/public E remove(int index) {checkElementIndex(index);return unlink(node(index));}
查找操作
查找操作的本质是查找元素的下标:
查找第一次出现的index, 如果找不到返回-1;
/*** Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element* in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.* More formally, returns the lowest index {@code i} such that* <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>,* or -1 if there is no such index.** @param o element to search for* @return the index of the first occurrence of the specified element in* this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element*/public int indexOf(Object o) {int index = 0;if (o == null) {for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {if (x.item == null)return index;index++;}} else {for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {if (o.equals(x.item))return index;index++;}}return -1;}
查找最后一次出现的index, 如果找不到返回-1;
/*** Returns the index of the last occurrence of the specified element* in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.* More formally, returns the highest index {@code i} such that* <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>,* or -1 if there is no such index.** @param o element to search for* @return the index of the last occurrence of the specified element in* this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element*/public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {int index = size;if (o == null) {for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {index--;if (x.item == null)return index;}} else {for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {index--;if (o.equals(x.item))return index;}}return -1;}
相关文章:

Collection-LinkedList源码解析
文章目录 概述LinkedList实现底层数据结构构造函数getFirst(), getLast()removeFirst(), removeLast(), remove(e), remove(index)add()addAll()clear()Positional Access 方法查找操作 概述 LinkedList同时实现了List接口和Deque接口,也就是说它既可以看作一个顺序…...

vue判断对象数组里是否有重复数据
TOCvue判断对象数组里是否有重复数据 try {//通过产品编码赛选出新的数组 在比较let names this.goodsJson.map(item > item["productCode"]);let nameSet new Set(names)if (nameSet.size ! names.length) {this.$message({message: 警告!产品选项…...

CSS 3D转换
在 CSS 中,除了可以对页面中的元素进行 2D 转换外,您也可以对象元素进行 3D转换(将页面看作是一个三维空间来对页面中的元素进行移动、旋转、缩放和倾斜等操作)。与 2D 转换相同,3D 转换同样不会影响周围的元素&#x…...

51单片机数码管循环显示0~f
原理图: #include <reg52.h>sbit dulaP2^6;//段选信号 sbit welaP2^7;//位选信号unsigned char num;//数码管显示的数字0~funsigned char code table[]{ 0x3f,0x06,0x5b,0x4f, 0x66,0x6d,0x7d,0x07, 0x7f,0x6f,0x77,0x7c, 0x39,0x5e,0x79,0x71};//定义数码管显…...

【编程进阶知识】Java NIO:掌握高效的I/O多路复用技术
Java NIO:掌握高效的I/O多路复用技术 摘要: 本文将带你深入了解Java NIO(New I/O)中的Selector类,探索如何利用它实现高效的I/O多路复用,类似于Linux中的select和epoll系统调用。文章将提供详细的代码示例…...

vscode创建flutter项目,运行flutter项目
打开View(查看) > Command Palette...(命令面板)。 可以按下 Ctrl / Cmd Shift P 输入 flutter 选择Flutter: New Project 命令 按下 Enter 。选择Application 选择项目地址 输入项目名称 。按下 Enter 等待项目初始化完成 …...

STM32之CAN外设
相信大家在学习STM32系列的单片机时,在翻阅芯片的数据手册时,都会看到这么一个寄存器外设——CAN外设寄存器。那么,大家知道这个外设的工作原理以及该如何使用吗?这节的内容将会详细介绍STM32上的CAN外设,文章结尾附有…...

【阅读笔记】水果轻微损伤的无损检测技术应用
一、水果轻微损伤检测技术以及应用 无损检测技术顾名思义就是指在不破坏水果样品完整性的情况下对样品进行品质鉴定。目前比较常用的农产品水果类无损检测法有:基于红外热成像、机器视觉技术的图像处理方法、光谱检测技术、介电特性技术检测法等。 1.1 基于红外热…...

忘记7-zip密码,如何解压文件?
7z压缩包设置了密码,解压的时候就需要输入正确对密码才能顺利解压出文件,正常当我们解压文件或者删除密码的时候,虽然方法多,但是都需要输入正确的密码才能完成。忘记密码就无法进行操作。 那么,忘记了7z压缩包的密码…...
)
SpringBoot基础(一)
1.SpringBoot简介 Spring Boot是Spring社区发布的一个开源项目,旨在帮助开发者快速并且更简单的构建项目。它 使用习惯优于配置的理念让你的项目快速运行起来,使用Spring Boot很容易创建一个独立运行 (运行jar,内置Servlet容器&am…...

Java智能匹配灵活用工高效人力资源管理系统小程序源码
智能匹配灵活用工高效人力资源管理系统 💼🚀 🚀 开篇:职场新风尚,智能匹配引领变革 在这个瞬息万变的时代,职场也在经历着前所未有的变革。传统的用工模式已难以满足现代企业的需求,而“智能匹…...
openpdf
1、简介 2、示例 2.1 引入依赖 <dependency><groupId>com.github.librepdf</groupId><artifactId>openpdf</artifactId><version>1.3.34</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>com.github.librepdf</…...

C#垃圾回收机制详解
本文详解C#垃圾回收机制。 目录 一、C#垃圾收集器定义 二、C#中的垃圾收集器特点 三、垃圾回收触发条件 四、常见的内存泄漏情况 五、高性能应用程序的垃圾回收策略 六、最佳实践和建议 七、实例 一、C#垃圾收集器定义 int、string变量,这些数据都存储在内存中,如果…...

身份证二要素核验操作指南
身份证二要素核验主要涉及验证身份证上的姓名和身份证号码这两个关键信息,以下是详细的操作指南: 一、核验流程 输入信息:用户在客户端(如APP、网站等)输入自己的姓名和身份证号码。 信息加密与传输:客户端…...
量子数字签名概述
我们都知道,基于量子力学原理研究密钥生成和使用的学科称为量子密码学。其内容包括了量子密钥分发、量子秘密共享、量子指纹识别、量子比特承诺、量子货币、秘密通信扩展量子密钥、量子安全计算、量子数字签名、量子隐性传态等。虽然各种技术发展的状态不同…...

算法题——合并 k 个升序的链表
题目描述: 合并 k 个升序的链表并将结果作为一个升序的链表返回其头节点。 数据范围:节点总数 0≤n≤50000≤n≤5000,每个节点的val满足 ∣val∣<1000∣val∣<1000 要求:时间复杂度 O(nlogn) 一、常见解法 (…...
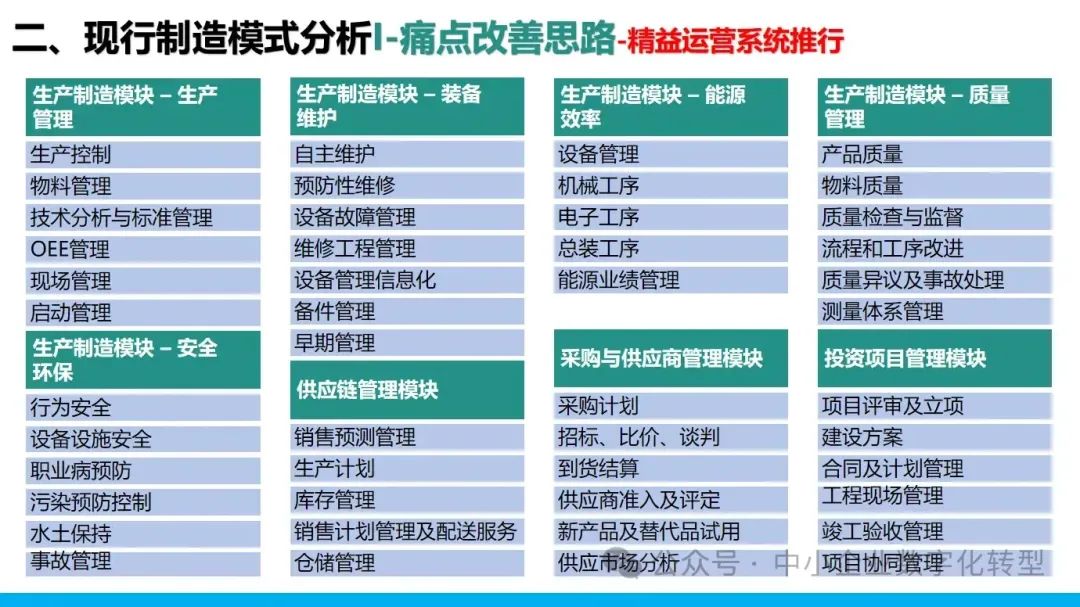
智能制造与精益制造的模型搭建
现行制造模式分析I-痛点改善思路-管控省优四化推行...

快速生成生产级Go应用的利器——Cgapp
简介 CGAPP是一个强大的命令行工具,开发者通过简单的命令就可以快速搭建起一个完整的Go项目框架。这个框架不仅包括后端服务,还可以集成前端代码和数据库配置,大大简化了项目的初始化过程。 安装 安装CGAPP的过程非常简单。首先࿰…...

MySQL基本语法、高级语法知识总结以及常用语法案例
MySQL基本语法总结 MySQL是一种广泛使用的关系型数据库管理系统,其基本语法涵盖了数据库和数据表的创建、查询、修改和删除等操作。 一、数据库操作 创建数据库(CREATE DATABASE) 语法:CREATE DATABASE [IF NOT EXISTS] databa…...

单片机(学习)2024.10.11
目录 按键 按键原理 按键消抖 1.延时消抖 2.抬手检测 通信 1.通信是什么 2.电平信号和差分信号 3.通信的分类 (1)时钟信号划分 同步通信 异步通信 (2)通信方式划分 串行通信 并行通信 (3)通信方向划分 单工 半双工 全双工 4.USART和UART(串口通信&a…...

利用最小二乘法找圆心和半径
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <cmath> #include <Eigen/Dense> // 需安装Eigen库用于矩阵运算 // 定义点结构 struct Point { double x, y; Point(double x_, double y_) : x(x_), y(y_) {} }; // 最小二乘法求圆心和半径 …...

深度学习在微纳光子学中的应用
深度学习在微纳光子学中的主要应用方向 深度学习与微纳光子学的结合主要集中在以下几个方向: 逆向设计 通过神经网络快速预测微纳结构的光学响应,替代传统耗时的数值模拟方法。例如设计超表面、光子晶体等结构。 特征提取与优化 从复杂的光学数据中自…...
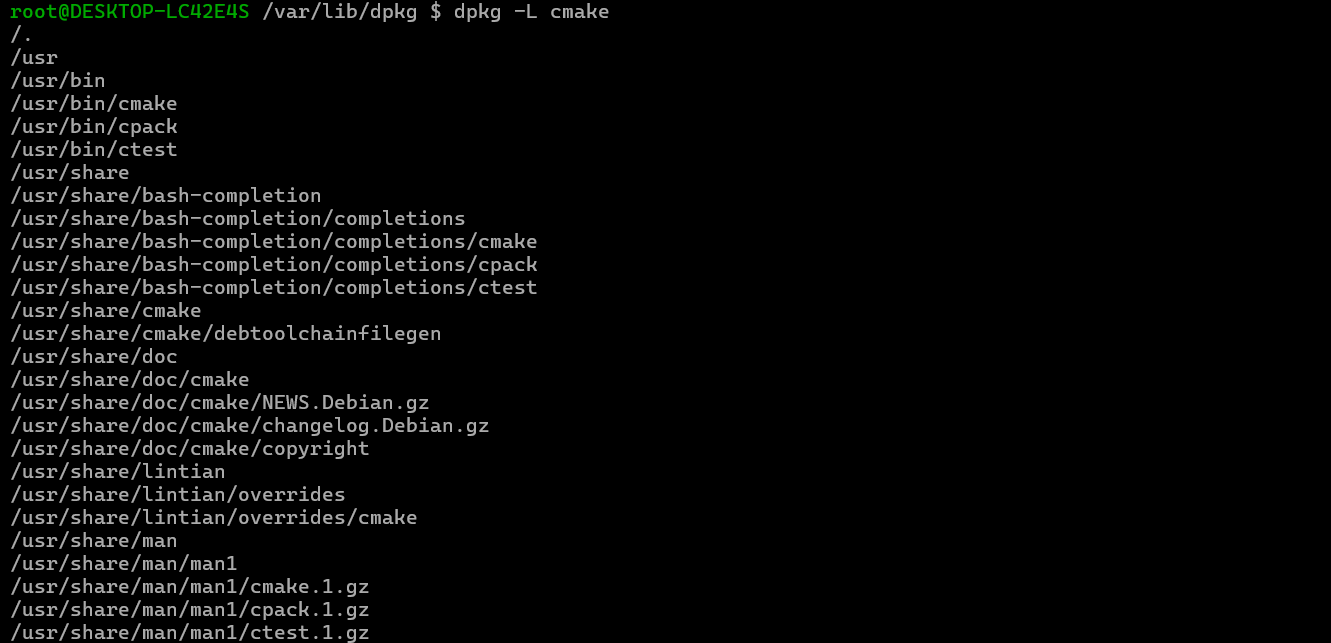
Debian系统简介
目录 Debian系统介绍 Debian版本介绍 Debian软件源介绍 软件包管理工具dpkg dpkg核心指令详解 安装软件包 卸载软件包 查询软件包状态 验证软件包完整性 手动处理依赖关系 dpkg vs apt Debian系统介绍 Debian 和 Ubuntu 都是基于 Debian内核 的 Linux 发行版ÿ…...
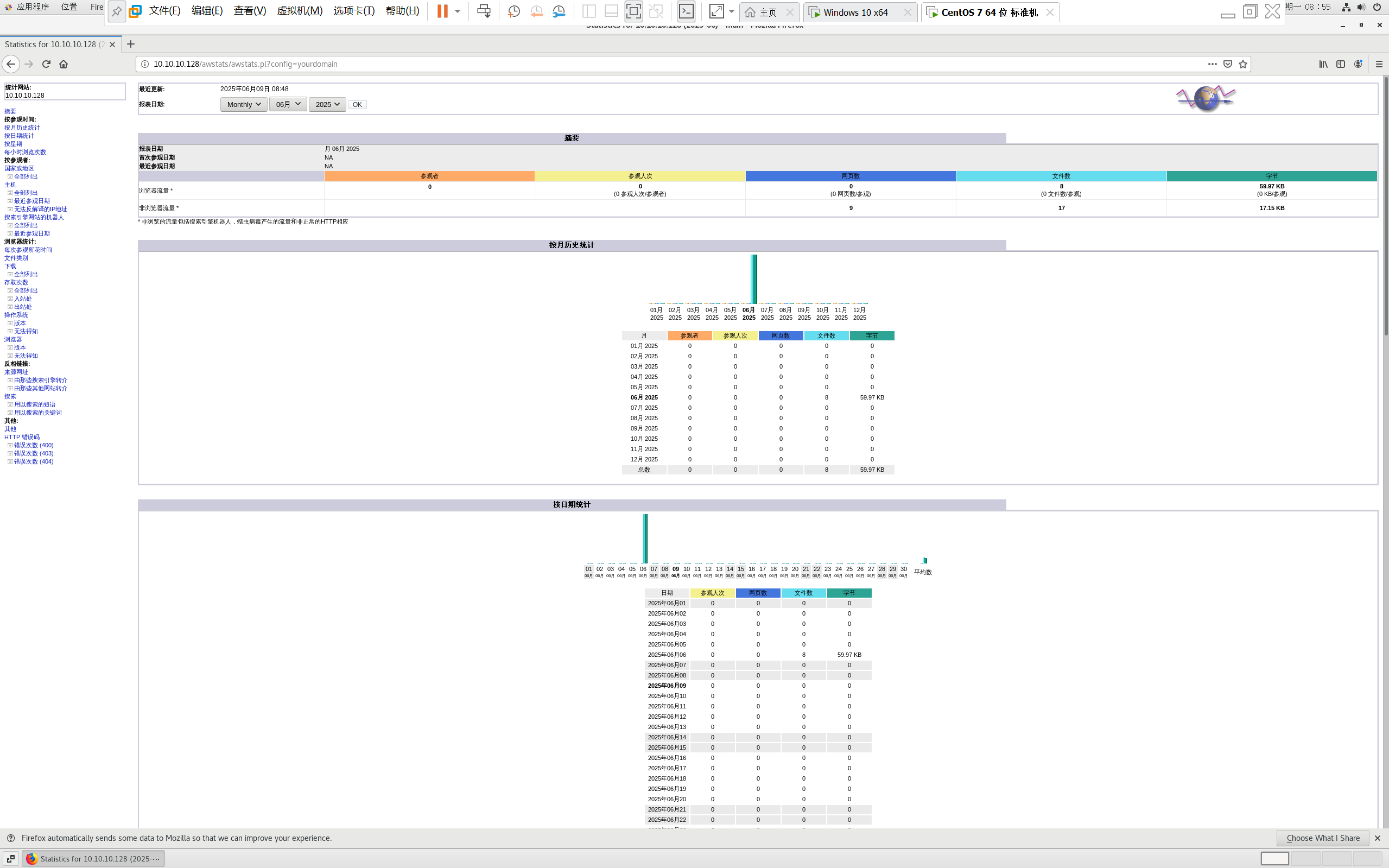
centos 7 部署awstats 网站访问检测
一、基础环境准备(两种安装方式都要做) bash # 安装必要依赖 yum install -y httpd perl mod_perl perl-Time-HiRes perl-DateTime systemctl enable httpd # 设置 Apache 开机自启 systemctl start httpd # 启动 Apache二、安装 AWStats࿰…...

系统设计 --- MongoDB亿级数据查询优化策略
系统设计 --- MongoDB亿级数据查询分表策略 背景Solution --- 分表 背景 使用audit log实现Audi Trail功能 Audit Trail范围: 六个月数据量: 每秒5-7条audi log,共计7千万 – 1亿条数据需要实现全文检索按照时间倒序因为license问题,不能使用ELK只能使用…...

【Web 进阶篇】优雅的接口设计:统一响应、全局异常处理与参数校验
系列回顾: 在上一篇中,我们成功地为应用集成了数据库,并使用 Spring Data JPA 实现了基本的 CRUD API。我们的应用现在能“记忆”数据了!但是,如果你仔细审视那些 API,会发现它们还很“粗糙”:有…...
佰力博科技与您探讨热释电测量的几种方法
热释电的测量主要涉及热释电系数的测定,这是表征热释电材料性能的重要参数。热释电系数的测量方法主要包括静态法、动态法和积分电荷法。其中,积分电荷法最为常用,其原理是通过测量在电容器上积累的热释电电荷,从而确定热释电系数…...
android RelativeLayout布局
<?xml version"1.0" encoding"utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android"http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"android:layout_width"match_parent"android:layout_height"match_parent"android:gravity&…...
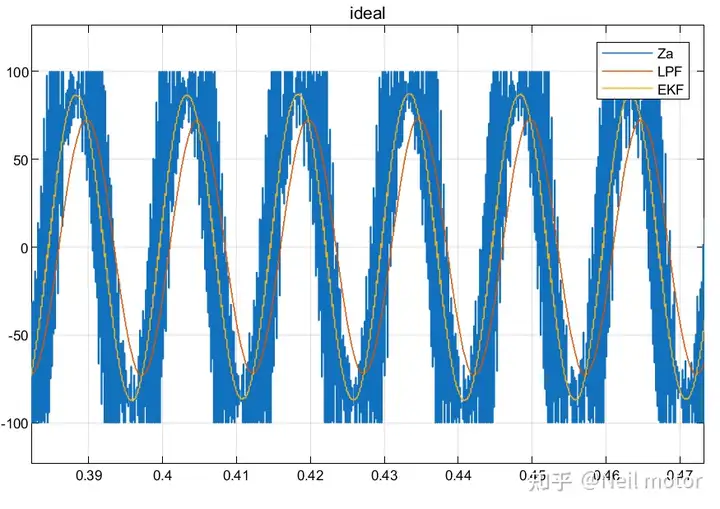
永磁同步电机无速度算法--基于卡尔曼滤波器的滑模观测器
一、原理介绍 传统滑模观测器采用如下结构: 传统SMO中LPF会带来相位延迟和幅值衰减,并且需要额外的相位补偿。 采用扩展卡尔曼滤波器代替常用低通滤波器(LPF),可以去除高次谐波,并且不用相位补偿就可以获得一个误差较小的转子位…...
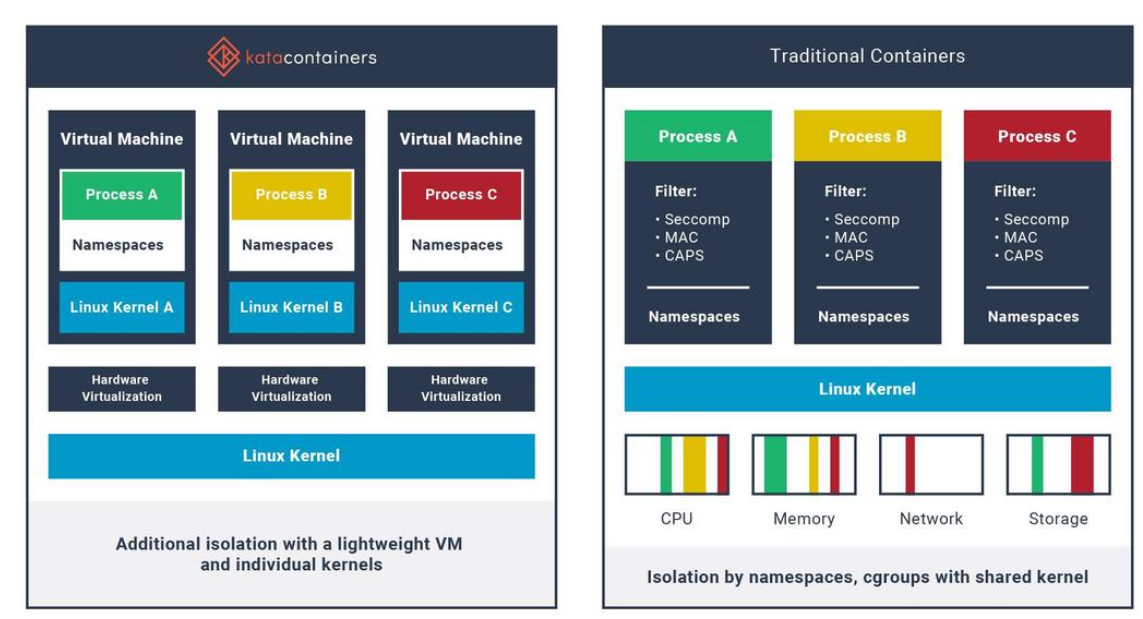
沙箱虚拟化技术虚拟机容器之间的关系详解
问题 沙箱、虚拟化、容器三者分开一一介绍的话我知道他们各自都是什么东西,但是如果把三者放在一起,它们之间到底什么关系?又有什么联系呢?我不是很明白!!! 就比如说: 沙箱&#…...
