无人机避障——4D毫米波雷达Octomap从点云建立三维栅格地图
Octomap安装
sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-octomap-ros
sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-octomap-msgs
sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-octomap-server
sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-octomap-rviz-plugins
# map_server安装
sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-map-server启动rviz
roscore
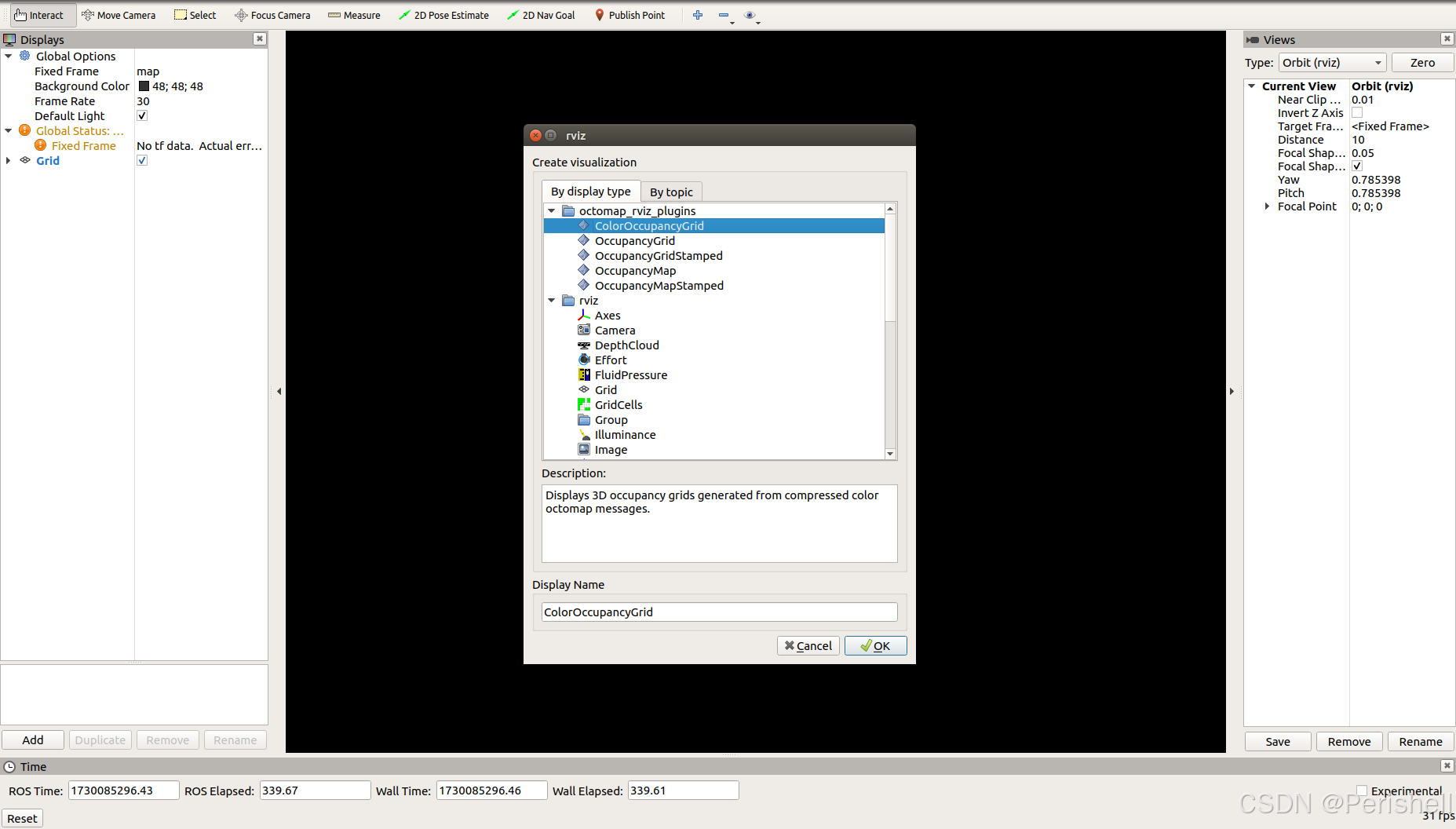
rosrun rviz rviz点击add,可以看到多了Octomap_rviz_plugins模组:
OccupancyGrid是显示三维概率地图,也就是octomap地图。OccupancyMap是显示二维占据栅格地图
从PCD创建PointCloud2点云话题并发布出去:
参考资料:
测试的test数据采用以下第一条博客的pcd测试数据
Octomap 在ROS环境下实时显示_octomap在ros环境下实时显示-飞天熊猫-CSDN博客
学习笔记:使用Octomap将点云地图pcd转换为三维栅格地图,并在rviz中可视化_octomap功能包-CSDN博客
创建点云发布话题的工作空间:
mkdir -p ~/publish_pointcloudtest/src #使用系统命令创建工作空间目录
cd ~/publish_pointcloudtest/src
catkin_init_workspace # ROS的工作空间初始化命令
在工作空间下放入以下两个文件:
octomap_mapping
octomap_server
资源下载:
https://github.com/OctoMap/octomap_mapping
src下创建cpp文件pointcloud_publisher.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>#include <ros/ros.h>
#include <pcl/point_cloud.h>
#include <pcl_conversions/pcl_conversions.h>
#include <sensor_msgs/PointCloud2.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>#include <octomap_msgs/OctomapWithPose.h>
#include <octomap_msgs/Octomap.h>
#include <geometry_msgs/Pose.h>#include <octomap/octomap.h>
#include <octomap_msgs/Octomap.h>
#include <octomap_msgs/conversions.h>#include <geometry_msgs/TransformStamped.h>#define TESTCLOUDPOINTS 1 // 设置为 1 以测试点云发布,设置为 0 不测试
#define TESTOCTOTREE 0 // 设置为 1 以测试OctoMap发布,设置为 0 不测试int main (int argc, char **argv)
{ std::string topic, path, frame_id;int hz = 5; // 发布频率,单位 Hzros::init(argc, argv, "publish_pointcloud"); // 初始化ROS节点ros::NodeHandle nh; // 创建节点句柄// 从参数服务器获取参数nh.param<std::string>("path", path, "/home/nvidia/publish_pointcloudtest/data/test.pcd");nh.param<std::string>("frame_id", frame_id, "map");nh.param<std::string>("topic", topic, "pointcloud_topic");nh.param<int>("hz", hz, 5);// 加载点云数据到pcl::PointCloud对象中pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> pcl_cloud; pcl::io::loadPCDFile(path, pcl_cloud); // 从文件加载点云数据#if TESTCLOUDPOINTS // 如果 TESTCLOUDPOINTS 定义为 1,则执行这部分代码ros::Publisher pcl_pub = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>(topic, 10); // 创建Publisher对象,将点云数据发布到指定话题// 转换PCL点云到ROS下的 PointCloud2 类型sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 output; pcl::toROSMsg(pcl_cloud, output);output.header.stamp = ros::Time::now(); // 设置时间戳output.header.frame_id = frame_id; // 设置坐标系框架// 打印参数信息std::cout << "path = " << path << std::endl;std::cout << "frame_id = " << frame_id << std::endl;std::cout << "topic = " << topic << std::endl;std::cout << "hz = " << hz << std::endl;ros::Rate loop_rate(hz); // 设置发布频率 while (ros::ok()) { pcl_pub.publish(output); // 发布 PointCloud2 数据ros::spinOnce(); // 处理所有回调函数loop_rate.sleep(); // 按照指定频率睡眠}
#endif#if TESTOCTOTREE // 如果 TESTOCTOTREE 定义为 1,则执行这部分代码ros::Publisher octomap_pub = nh.advertise<octomap_msgs::Octomap>(topic, 1); // 创建Publisher对象,将OctoMap数据发布到指定话题// 创建 octomap 对象,并设置其分辨率octomap::OcTree tree(0.1); // 你可以根据需要调整分辨率// 将点云数据插入到 octomap 中for (const auto& point : pcl_cloud.points) {tree.updateNode(point.x, point.y, point.z, true);}// 发布OctoMap消息octomap_msgs::Octomap octomap_msg;octomap_msgs::fullMapToMsg(tree, octomap_msg); // 转换为 OctoMap 消息// 设置 OctoMap 消息的头信息octomap_msg.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();octomap_msg.header.frame_id = frame_id;// 打印参数信息std::cout << "path = " << path << std::endl;std::cout << "frame_id = " << frame_id << std::endl;std::cout << "topic = " << topic << std::endl;std::cout << "hz = " << hz << std::endl;ros::Rate loop_rate(hz); // 设置发布频率 while (ros::ok()) { octomap_pub.publish(octomap_msg); // 发布 OctoMap 数据ros::spinOnce(); // 处理所有回调函数loop_rate.sleep(); // 按照指定频率睡眠}
#endifreturn 0; // 主函数返回值
}代码中需要进行修改为自己的点云,后续相应都需要修改为自己的路径(自行修改):
nh.param<std::string>("path", path, "/home/nvidia/publish_pointcloudtest/data/test.pcd");CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.0.2)
project(publish_pointcloud)## Compile as C++11, supported in ROS Kinetic and newer
# add_compile_options(-std=c++11)## Find catkin macros and libraries
## if COMPONENTS list like find_package(catkin REQUIRED COMPONENTS xyz)
## is used, also find other catkin packagesset(octomap_ros_DIR "/opt/ros/melodic/share/octomap_ros/cmake")find_package(catkin REQUIRED COMPONENTSroscppstd_msgssensor_msgsoctomap_msgsgeometry_msgsoctomap_ros
)
find_package(PCL REQUIRED)
find_package(octomap REQUIRED)## System dependencies are found with CMake's conventions
# find_package(Boost REQUIRED COMPONENTS system)## Uncomment this if the package has a setup.py. This macro ensures
## modules and global scripts declared therein get installed
## See http://ros.org/doc/api/catkin/html/user_guide/setup_dot_py.html
# catkin_python_setup()################################################
## Declare ROS messages, services and actions ##
################################################## To declare and build messages, services or actions from within this
## package, follow these steps:
## * Let MSG_DEP_SET be the set of packages whose message types you use in
## your messages/services/actions (e.g. std_msgs, actionlib_msgs, ...).
## * In the file package.xml:
## * add a build_depend tag for "message_generation"
## * add a build_depend and a exec_depend tag for each package in MSG_DEP_SET
## * If MSG_DEP_SET isn't empty the following dependency has been pulled in
## but can be declared for certainty nonetheless:
## * add a exec_depend tag for "message_runtime"
## * In this file (CMakeLists.txt):
## * add "message_generation" and every package in MSG_DEP_SET to
## find_package(catkin REQUIRED COMPONENTS ...)
## * add "message_runtime" and every package in MSG_DEP_SET to
## catkin_package(CATKIN_DEPENDS ...)
## * uncomment the add_*_files sections below as needed
## and list every .msg/.srv/.action file to be processed
## * uncomment the generate_messages entry below
## * add every package in MSG_DEP_SET to generate_messages(DEPENDENCIES ...)## Generate messages in the 'msg' folder
# add_message_files(
# FILES
# Message1.msg
# Message2.msg
# )## Generate services in the 'srv' folder
# add_service_files(
# FILES
# Service1.srv
# Service2.srv
# )## Generate actions in the 'action' folder
# add_action_files(
# FILES
# Action1.action
# Action2.action
# )## Generate added messages and services with any dependencies listed here
# generate_messages(
# DEPENDENCIES
# std_msgs
# )################################################
## Declare ROS dynamic reconfigure parameters ##
################################################## To declare and build dynamic reconfigure parameters within this
## package, follow these steps:
## * In the file package.xml:
## * add a build_depend and a exec_depend tag for "dynamic_reconfigure"
## * In this file (CMakeLists.txt):
## * add "dynamic_reconfigure" to
## find_package(catkin REQUIRED COMPONENTS ...)
## * uncomment the "generate_dynamic_reconfigure_options" section below
## and list every .cfg file to be processed## Generate dynamic reconfigure parameters in the 'cfg' folder
# generate_dynamic_reconfigure_options(
# cfg/DynReconf1.cfg
# cfg/DynReconf2.cfg
# )###################################
## catkin specific configuration ##
###################################
## The catkin_package macro generates cmake config files for your package
## Declare things to be passed to dependent projects
## INCLUDE_DIRS: uncomment this if your package contains header files
## LIBRARIES: libraries you create in this project that dependent projects also need
## CATKIN_DEPENDS: catkin_packages dependent projects also need
## DEPENDS: system dependencies of this project that dependent projects also need
catkin_package(
# INCLUDE_DIRS include
# LIBRARIES my_pkg
# CATKIN_DEPENDS roscpp std_msgs
# DEPENDS system_lib
)###########
## Build ##
############# Specify additional locations of header files
## Your package locations should be listed before other locations
include_directories(
# include${catkin_INCLUDE_DIRS}${PCL_INCLUDE_DIRS}${OCTOMAP_INCLUDE_DIRS}
)## Declare a C++ library
# add_library(${PROJECT_NAME}
# src/${PROJECT_NAME}/my_pkg.cpp
# )## Add cmake target dependencies of the library
## as an example, code may need to be generated before libraries
## either from message generation or dynamic reconfigure
# add_dependencies(${PROJECT_NAME} ${${PROJECT_NAME}_EXPORTED_TARGETS} ${catkin_EXPORTED_TARGETS})## Declare a C++ executable
## With catkin_make all packages are built within a single CMake context
## The recommended prefix ensures that target names across packages don't collide
add_executable(publish_pointcloud src/pointcloud_publisher.cpp)## Rename C++ executable without prefix
## The above recommended prefix causes long target names, the following renames the
## target back to the shorter version for ease of user use
## e.g. "rosrun someones_pkg node" instead of "rosrun someones_pkg someones_pkg_node"
# set_target_properties(${PROJECT_NAME}_node PROPERTIES OUTPUT_NAME node PREFIX "")## Add cmake target dependencies of the executable
## same as for the library above
# add_dependencies(${PROJECT_NAME}_node ${${PROJECT_NAME}_EXPORTED_TARGETS} ${catkin_EXPORTED_TARGETS})## Specify libraries to link a library or executable target against
target_link_libraries(publish_pointcloud${catkin_LIBRARIES}${PCL_LIBRARIES}${OCTOMAP_LIBRARIES}
)#############
## Install ##
############## all install targets should use catkin DESTINATION variables
# See http://ros.org/doc/api/catkin/html/adv_user_guide/variables.html## Mark executable scripts (Python etc.) for installation
## in contrast to setup.py, you can choose the destination
# catkin_install_python(PROGRAMS
# scripts/my_python_script
# DESTINATION ${CATKIN_PACKAGE_BIN_DESTINATION}
# )## Mark executables for installation
## See http://docs.ros.org/melodic/api/catkin/html/howto/format1/building_executables.html
# install(TARGETS ${PROJECT_NAME}_node
# RUNTIME DESTINATION ${CATKIN_PACKAGE_BIN_DESTINATION}
# )## Mark libraries for installation
## See http://docs.ros.org/melodic/api/catkin/html/howto/format1/building_libraries.html
# install(TARGETS ${PROJECT_NAME}
# ARCHIVE DESTINATION ${CATKIN_PACKAGE_LIB_DESTINATION}
# LIBRARY DESTINATION ${CATKIN_PACKAGE_LIB_DESTINATION}
# RUNTIME DESTINATION ${CATKIN_GLOBAL_BIN_DESTINATION}
# )## Mark cpp header files for installation
# install(DIRECTORY include/${PROJECT_NAME}/
# DESTINATION ${CATKIN_PACKAGE_INCLUDE_DESTINATION}
# FILES_MATCHING PATTERN "*.h"
# PATTERN ".svn" EXCLUDE
# )## Mark other files for installation (e.g. launch and bag files, etc.)
# install(FILES
# # myfile1
# # myfile2
# DESTINATION ${CATKIN_PACKAGE_SHARE_DESTINATION}
# )#############
## Testing ##
############### Add gtest based cpp test target and link libraries
# catkin_add_gtest(${PROJECT_NAME}-test test/test_my_pkg.cpp)
# if(TARGET ${PROJECT_NAME}-test)
# target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME}-test ${PROJECT_NAME})
# endif()## Add folders to be run by python nosetests
# catkin_add_nosetests(test)package.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<package format="2"><name>publish_pointcloud</name><version>0.0.0</version><description>The publish_pointcloud package</description><!-- One maintainer tag required, multiple allowed, one person per tag --><!-- Example: --><!-- <maintainer email="jane.doe@example.com">Jane Doe</maintainer> --><maintainer email="nvidia@todo.todo">nvidia</maintainer><!-- One license tag required, multiple allowed, one license per tag --><!-- Commonly used license strings: --><!-- BSD, MIT, Boost Software License, GPLv2, GPLv3, LGPLv2.1, LGPLv3 --><license>TODO</license><!-- Url tags are optional, but multiple are allowed, one per tag --><!-- Optional attribute type can be: website, bugtracker, or repository --><!-- Example: --><!-- <url type="website">http://wiki.ros.org/point_publish</url> --><!-- Author tags are optional, multiple are allowed, one per tag --><!-- Authors do not have to be maintainers, but could be --><!-- Example: --><!-- <author email="jane.doe@example.com">Jane Doe</author> --><!-- The *depend tags are used to specify dependencies --><!-- Dependencies can be catkin packages or system dependencies --><!-- Examples: --><!-- Use depend as a shortcut for packages that are both build and exec dependencies --><!-- <depend>roscpp</depend> --><!-- Note that this is equivalent to the following: --><!-- <build_depend>roscpp</build_depend> --><!-- <exec_depend>roscpp</exec_depend> --><!-- Use build_depend for packages you need at compile time: --><!-- <build_depend>message_generation</build_depend> --><!-- Use build_export_depend for packages you need in order to build against this package: --><!-- <build_export_depend>message_generation</build_export_depend> --><!-- Use buildtool_depend for build tool packages: --><!-- <buildtool_depend>catkin</buildtool_depend> --><!-- Use exec_depend for packages you need at runtime: --><!-- <exec_depend>message_runtime</exec_depend> --><!-- Use test_depend for packages you need only for testing: --><!-- <test_depend>gtest</test_depend> --><!-- Use doc_depend for packages you need only for building documentation: --><!-- <doc_depend>doxygen</doc_depend> --><buildtool_depend>catkin</buildtool_depend><build_depend>roscpp</build_depend><build_depend>std_msgs</build_depend><build_export_depend>roscpp</build_export_depend><build_export_depend>std_msgs</build_export_depend><exec_depend>roscpp</exec_depend><exec_depend>std_msgs</exec_depend><!-- The export tag contains other, unspecified, tags --><export><!-- Other tools can request additional information be placed here --></export>
</package>编译通过
记得在devel那边进行source
source devel/setup.bash
roscore
rosrun publish_pointcloud publish_pointcloud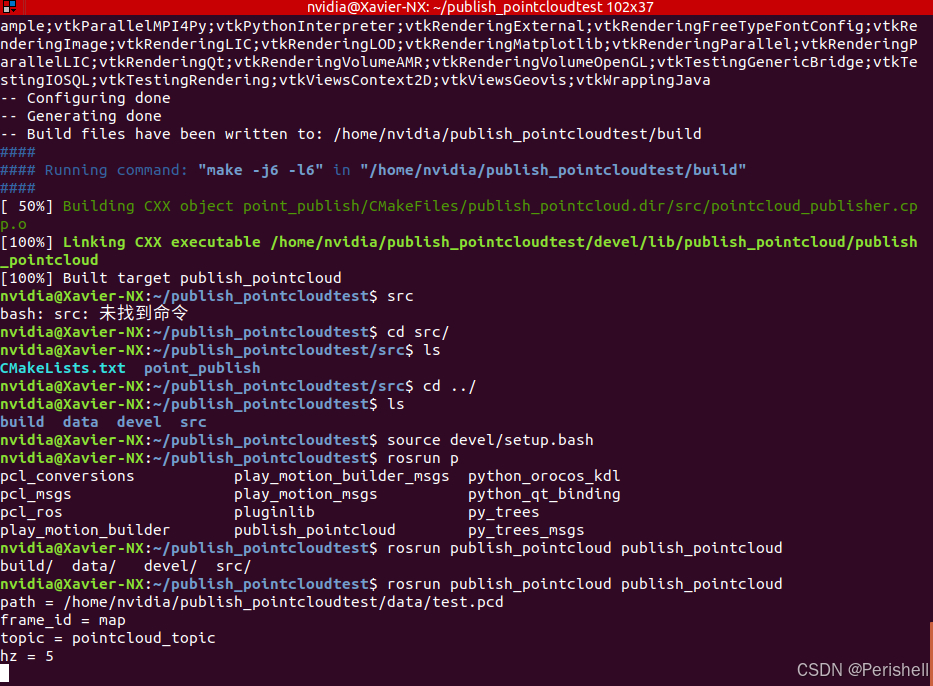
查看下是否有话题,且可以打印出来
rostopic list
rostopic echo /pointcloud_topic 
然后打开终端打开rviz
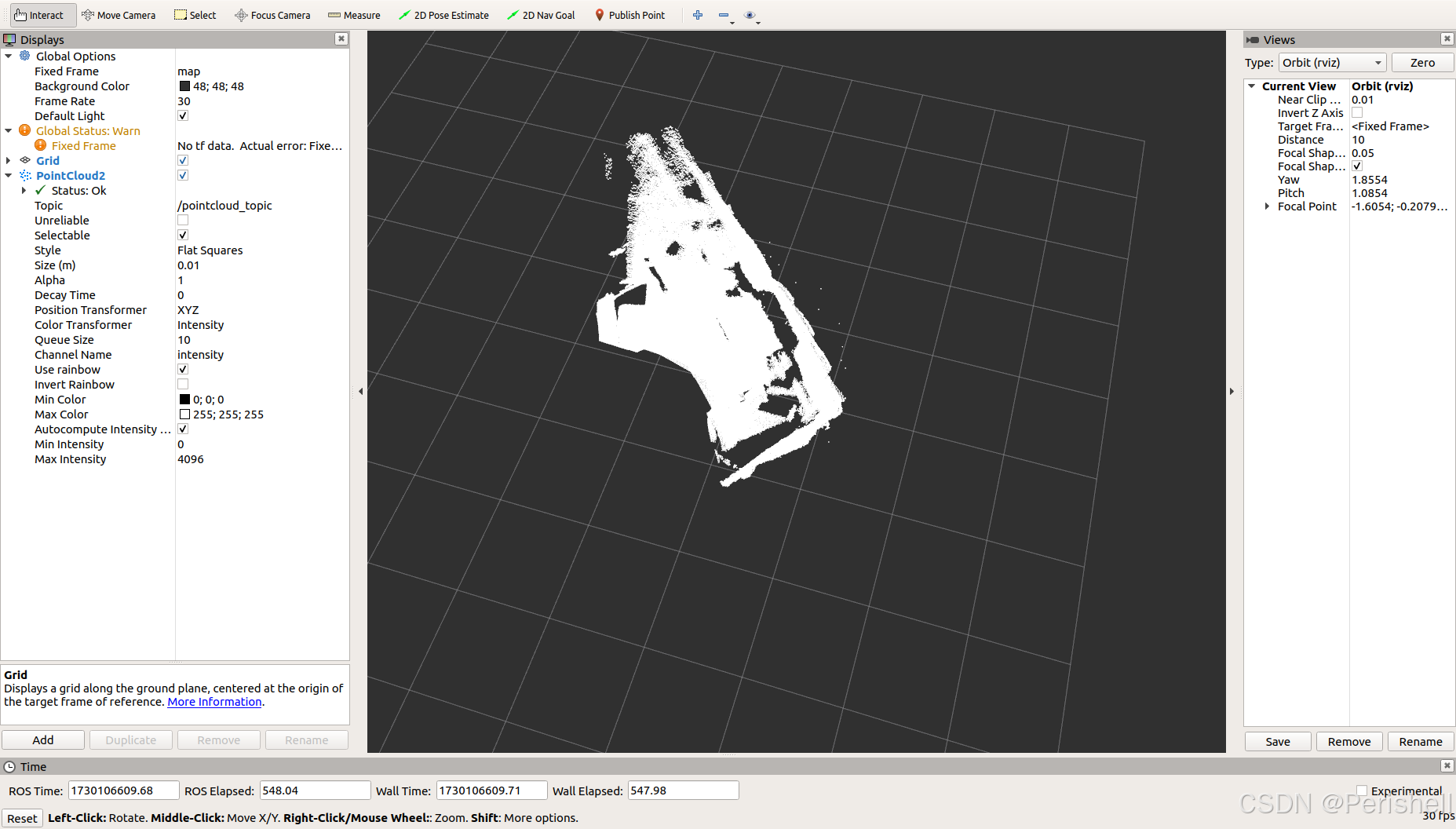
rviz将PointCloud2 添加进来,话题选择之前的点云话题
编写octomap_mapping.launch文件,launch文件在:
将frameid修改即可
<launch><node pkg="octomap_server" type="octomap_server_node" name="octomap_server"><param name="resolution" value="0.05" /><!-- fixed map frame (set to 'map' if SLAM or localization running!) --><param name="frame_id" type="string" value="map" /><!-- maximum range to integrate (speedup!) --><param name="sensor_model/max_range" value="5.0" /><!-- data source to integrate (PointCloud2) --><remap from="cloud_in" to="/pointcloud_topic" /></node>
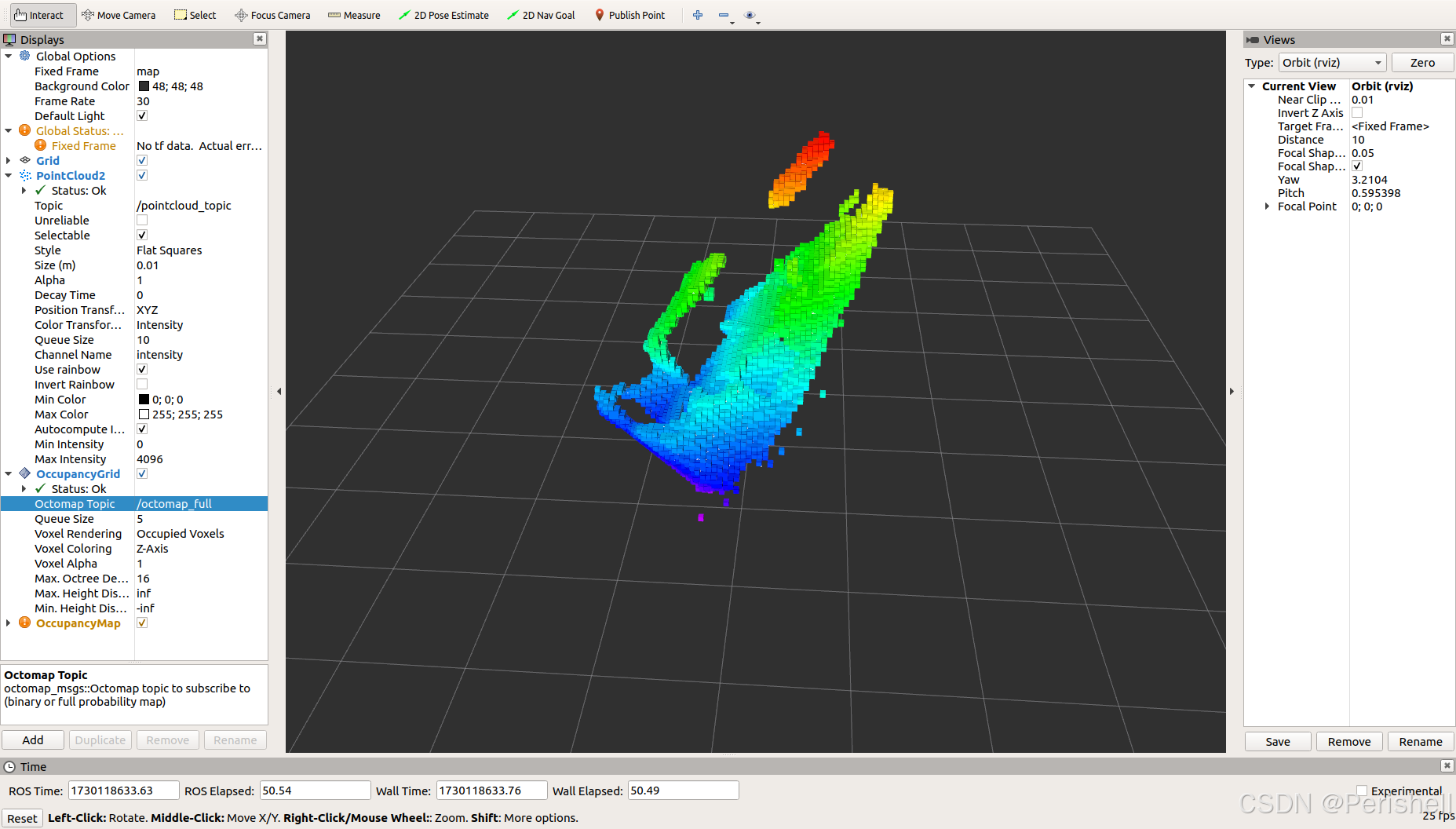
</launch>然后就可以运行launch文件了:
roslaunch octomap_server octomap_mapping.launch总结上面所有的过程 :
1、改完代码后编译nvidia@Xavier-NX:~/publish_pointcloudtest$ catkin_make2、编译完后roscorenvidia@Xavier-NX:~$ roscore3、运行点云发布代码nvidia@Xavier-NX:~/publish_pointcloudtest$ rosrun publish_pointcloud publish_pointcloud4、运行rviz使其显示白色的点云nvidia@Xavier-NX:~$ rviz5、运行octomapnvidia@Xavier-NX:~/publish_pointcloudtest$ roslaunch octomap_server octomap_mapping.launch上面的点云也是可以测试出来的,如第一张的图,最后用的自己4D毫米波雷达生成的点云也进行了测试,不过有些点云没能显示,后续还需要改进,估计跟坐标系的范围也有关系:
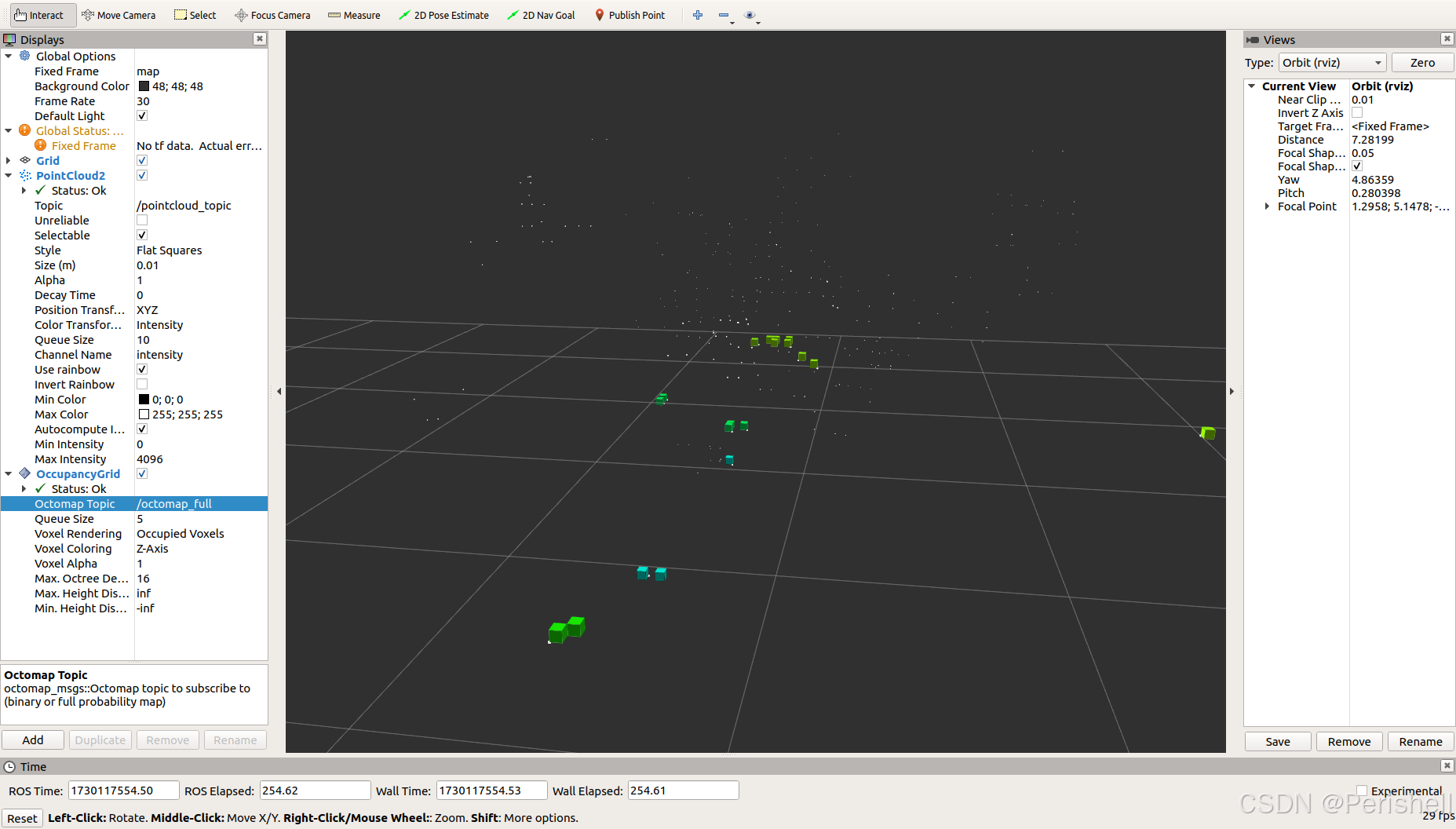
后续考虑实时动态,以及将其转换为二维栅格地图作为无人机的导航地图。
相关文章:

无人机避障——4D毫米波雷达Octomap从点云建立三维栅格地图
Octomap安装 sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-octomap-ros sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-octomap-msgs sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-octomap-server sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-octomap-rviz-plugins # map_server安装 sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-…...

Python(数据结构2)
常见数据结构 队列 队列(Queue),它是一种运算受限的线性表,先进先出(FIFO First In First Out) Python标准库中的queue模块提供了多种队列实现,包括普通队列、双端队列、优先队列等。 1 普通队列 queue.Queue 是 Python 标准库 queue 模块中的一个类…...
深入解析HTTP与HTTPS的区别及实现原理
文章目录 引言HTTP协议基础HTTP响应 HTTPS协议SSL/TLS协议 总结参考资料 引言 HTTP(HyperText Transfer Protocol)超文本传输协议是用于从Web服务器传输超文本到本地浏览器的主要协议。随着网络安全意识的提高,HTTPS(HTTP Secure…...

Java IO 模型
I/O 何为 I/O? I/O(Input/Output) 即输入/输出 。 我们先从计算机结构的角度来解读一下 I/O。 根据冯.诺依曼结构,计算机结构分为 5 大部分:运算器、控制器、存储器、输入设备、输出设备。 输入设备(比…...

安装双系统后ubuntu无法联网(没有wifi标识)网卡驱动为RTL8852BE
安装双系统后ubuntu没有办法联网,(本篇博客适用的版本为ubuntu20.04)且针对情况为无线网卡驱动未安装的情况 此时没有网络,可以使用手机数据线连接,使用USB共享网络便可解决无法下载的问题。 打开终端使用命令lshw -C …...

Sqoop的安装配置及使用
Sqoop安装前需要检查之前是否安装了Tez,否则会产生版本或依赖冲突,我们需要移除tez-site.xml,并将hadoop中的mapred-site.xml配置文件中的mapreduce驱动改回成yarn,然后分发到其他节点,hive里面配置的tez也要移除,然后…...

R语言机器学习算法实战系列(十三)随机森林生存分析构建预后模型 (Random Survival Forest)
禁止商业或二改转载,仅供自学使用,侵权必究,如需截取部分内容请后台联系作者! 文章目录 介绍教程加载R包案例数据数据预处理数据描述构建randomForestSRC模型评估模型C-indexBrier score特征重要性构建新的随机森林生存模型风险打分高低风险分组的生存分析时间依赖的ROC(Ti…...

三款计算服务器配置→如何选择科学计算服务器?
科学计算在众多领域都扮演着关键角色,无论是基础科学研究还是实际工程应用,强大的计算能力都是不可或缺的。而选择一台合适的科学计算服务器,对于确保科研和工作的顺利进行至关重要。 首先,明确自身需求是重中之重。要仔细考虑计算…...

Oracle 19c RAC删除多余的PDB的方式
文章目录 一、删除PDB并删除数据文件二、删除PDB并保留数据文件三、插拔PDB 一、删除PDB并删除数据文件 所删除的pdb必须是mount的状态才可以删除: #1、关闭pdb alter pluggable database pdb_name close immediate instancesall; #2、删除pdb以及数据文件 drop p…...
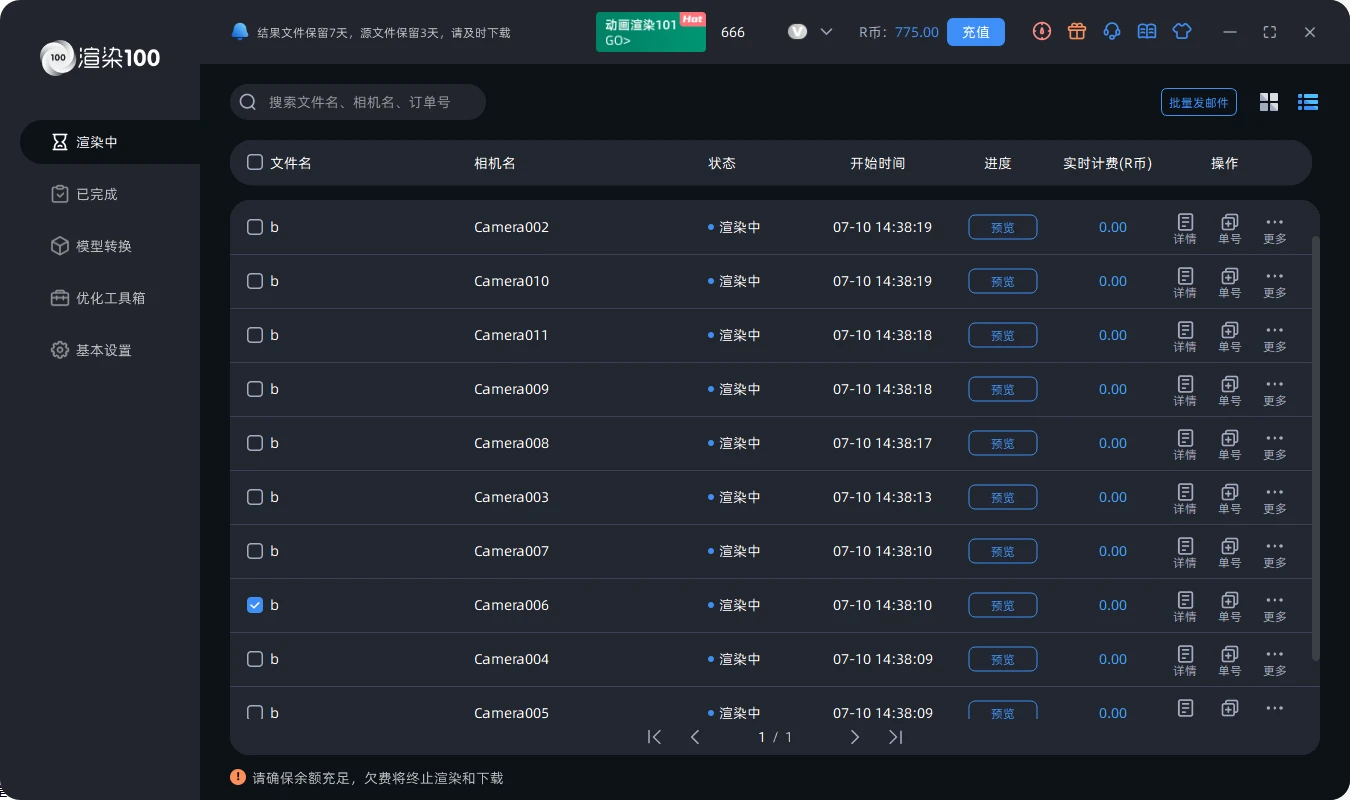
什么是云渲染?云渲染有什么用?一篇看懂云渲染意思
你知道云渲染是怎么回事吗? 其实就是把3D模型变成2D图像的过程,只不过这个过程是在云端完成的。我们在本地啥都不用做,只需要等结果就行。 现在云渲染主要有两种类型:一种是物理机房云渲染,另一种是服务器机房云渲染。…...

MATLAB中 exist函数用法
目录 语法 说明 示例 检查工作区变量是否存在 检查文件夹是否存在 检查 MATLAB 函数是否为内置函数 exist函数的功能是检查变量、脚本、函数、文件夹或类的存在情况。 语法 exist name exist name searchType A exist(___) 说明 exist name 以数字形式返回 name 的类…...

在银河麒麟系统中Qt连接达梦数据库
解决在银河麒麟系统中使用Qt连接达梦数据库提示:project Error library odbc is not defined问题 一、编译ODBC 下载解压unixODBC(http://www.unixodbc.org/unixODBC-2.3.1.tar.gz) 打开终端,切换到unixODBC-2.3.1目录下&#x…...

nodejs 服务器实现负载均衡
server.js const express require(express); const { createProxyMiddleware } require(http-proxy-middleware); const axios require(axios);const app express();// 定义后端服务列表 const services [{ target: http://localhost:3001 },{ target: http://localhost:…...

今日总结10.29
常见序列化协议有哪些 序列化(serialization)是将对象序列化为二进制形式(字节数组),一般也将序列化称为编码(Encode),主要用于网络传输、数据持久化等。常见的序列化协议包括以下几…...

使用 FastGPT 工作流实现 AI 赛博算卦,一键生成卦象图
最近那个男人写的汉语新解火遍了全网,那个男人叫李继刚,国内玩 AI 的同学如果不知道这个名字,可以去面壁思过了。 这个汉语新解的神奇之处就在于它只是一段几百字的提示词,效果却顶得上几千行代码写出来的应用程序。 这段提示词…...

vue3+ts实时播放视频,视频分屏
使用vue3以及播放视频组件Jessibuca Jessibuca地址 使用循环个数来实现分屏 效果图,四屏 九屏 dom代码 <div class"icon"><div class"icon-box"><span class"text">分屏:</span><el-icon …...

【网页设计】学成在线案例
Demo 典型的企业级网站,目的是为了整体感知企业级网站的布局流程,复习以前知识。 集合代码见文章最后。 5.1 准备素材和工具 学成在线 PSD 源文件。开发工具 PS(切图) sublime(代码) chrome࿰…...

一篇文章总结 SQL 基础知识点
1. 官方文档 MySQL:https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.4/en/ SQL Server:What is SQL Server? - SQL Server | Microsoft Learn Oracle:https://docs.oracle.com/en/database/oracle/oracle-database/23/lnpls/loe.html 2. 术语 SQL S…...

vue Element U 解决表格数据不更新问题
最近在使用 Vue 和 Element UI 开发后台管理系统时,操作表单数据重新请求表格接口后遇到表格数据不更新的问题。后面查阅了些资料,这通常是由于 Vue 的响应式系统没有检测到数据的变化,或者数据更新后没有正确地触发视图的重新渲染。以下是一…...

PeView 命令行PE文件解析工具
PeView 是一款基于C/C开发的命令行版PE文件解析工具,专门用于解析Windows可执行文件并提供详尽的文件结构和交互式查询功能,帮助用户理解和分析目标程序的内部构成,是逆向分析和软件调试中的重要工具,本次分享工具源代码及使用方法…...

React 第五十五节 Router 中 useAsyncError的使用详解
前言 useAsyncError 是 React Router v6.4 引入的一个钩子,用于处理异步操作(如数据加载)中的错误。下面我将详细解释其用途并提供代码示例。 一、useAsyncError 用途 处理异步错误:捕获在 loader 或 action 中发生的异步错误替…...

C++:std::is_convertible
C++标志库中提供is_convertible,可以测试一种类型是否可以转换为另一只类型: template <class From, class To> struct is_convertible; 使用举例: #include <iostream> #include <string>using namespace std;struct A { }; struct B : A { };int main…...
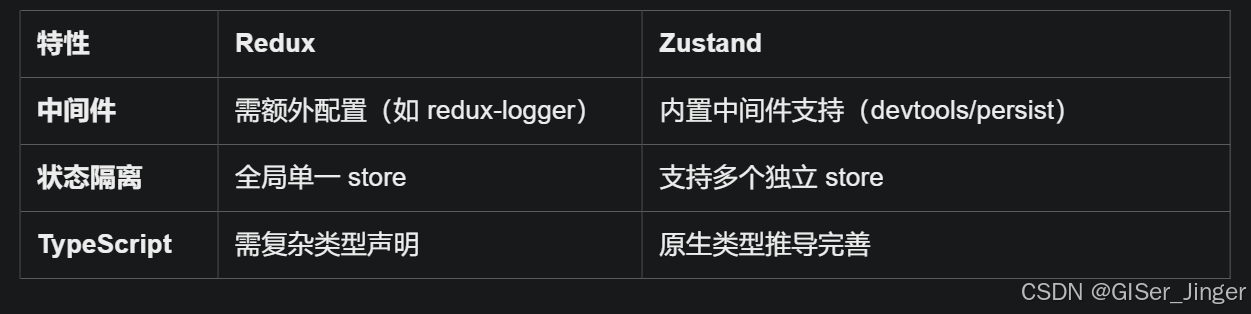
Zustand 状态管理库:极简而强大的解决方案
Zustand 是一个轻量级、快速和可扩展的状态管理库,特别适合 React 应用。它以简洁的 API 和高效的性能解决了 Redux 等状态管理方案中的繁琐问题。 核心优势对比 基本使用指南 1. 创建 Store // store.js import create from zustandconst useStore create((set)…...

DockerHub与私有镜像仓库在容器化中的应用与管理
哈喽,大家好,我是左手python! Docker Hub的应用与管理 Docker Hub的基本概念与使用方法 Docker Hub是Docker官方提供的一个公共镜像仓库,用户可以在其中找到各种操作系统、软件和应用的镜像。开发者可以通过Docker Hub轻松获取所…...
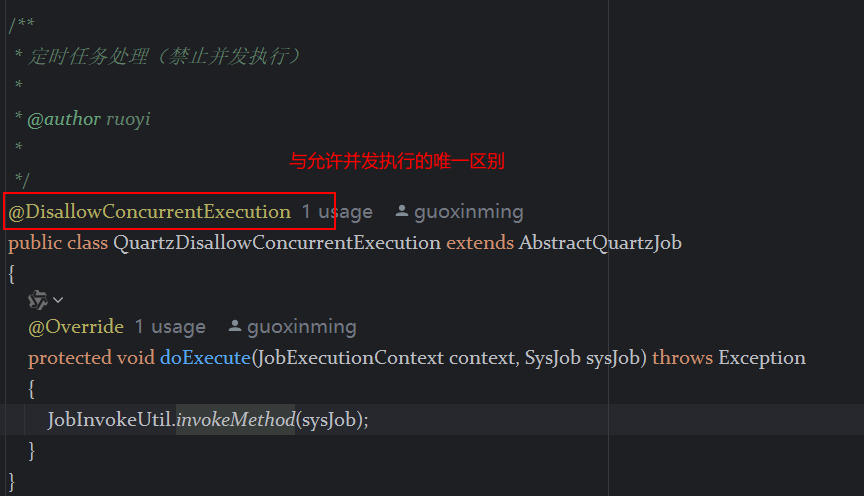
定时器任务——若依源码分析
分析util包下面的工具类schedule utils: ScheduleUtils 是若依中用于与 Quartz 框架交互的工具类,封装了定时任务的 创建、更新、暂停、删除等核心逻辑。 createScheduleJob createScheduleJob 用于将任务注册到 Quartz,先构建任务的 JobD…...
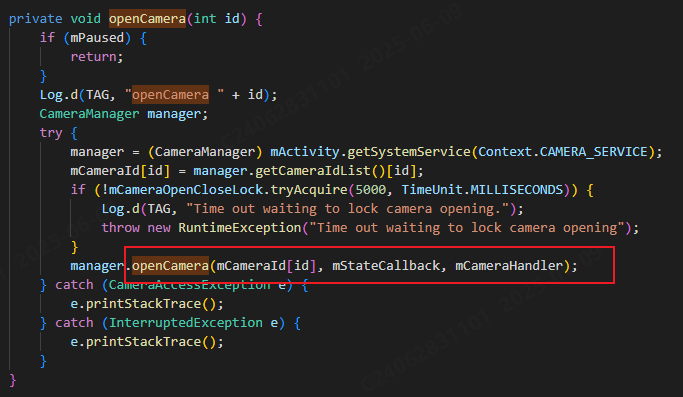
相机从app启动流程
一、流程框架图 二、具体流程分析 1、得到cameralist和对应的静态信息 目录如下: 重点代码分析: 启动相机前,先要通过getCameraIdList获取camera的个数以及id,然后可以通过getCameraCharacteristics获取对应id camera的capabilities(静态信息)进行一些openCamera前的…...
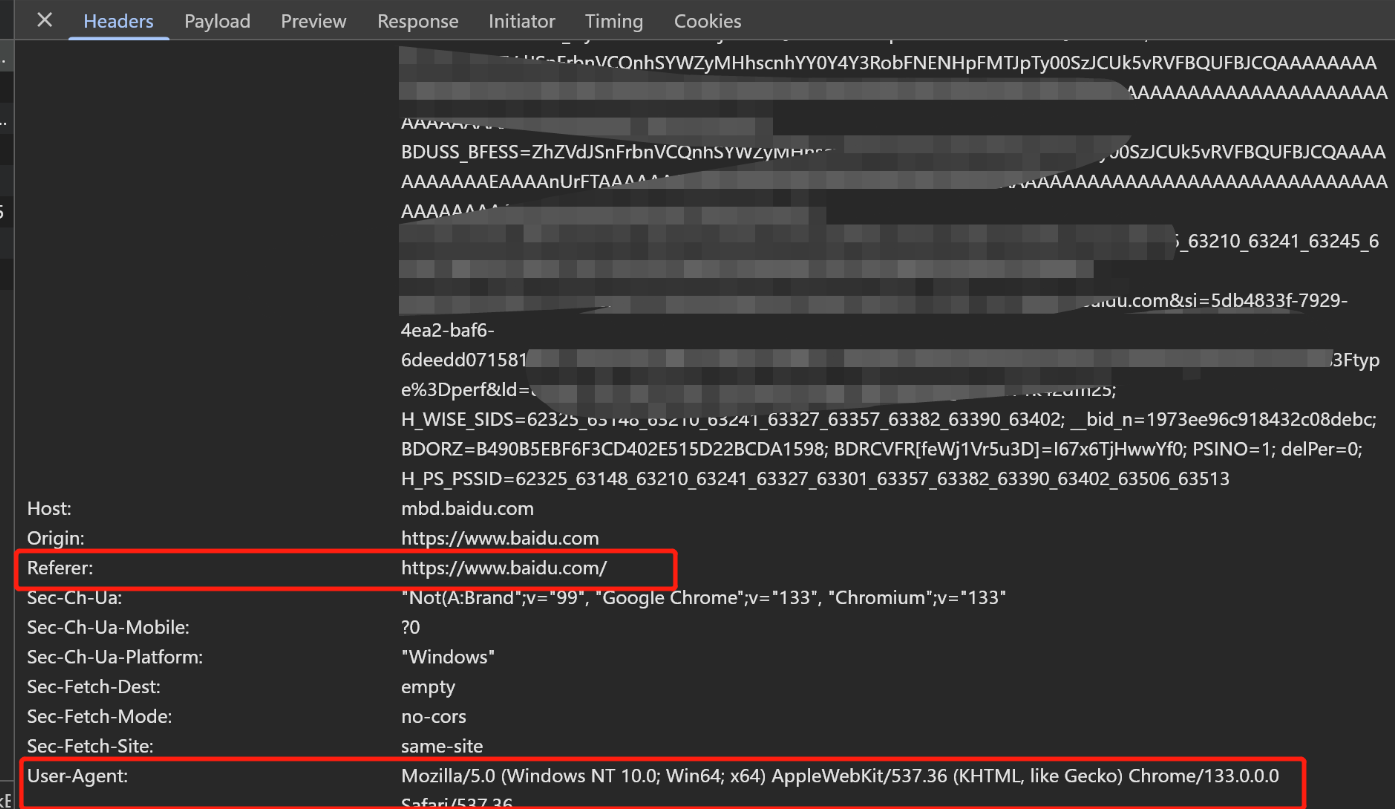
Python爬虫(一):爬虫伪装
一、网站防爬机制概述 在当今互联网环境中,具有一定规模或盈利性质的网站几乎都实施了各种防爬措施。这些措施主要分为两大类: 身份验证机制:直接将未经授权的爬虫阻挡在外反爬技术体系:通过各种技术手段增加爬虫获取数据的难度…...

leetcodeSQL解题:3564. 季节性销售分析
leetcodeSQL解题:3564. 季节性销售分析 题目: 表:sales ---------------------- | Column Name | Type | ---------------------- | sale_id | int | | product_id | int | | sale_date | date | | quantity | int | | price | decimal | -…...
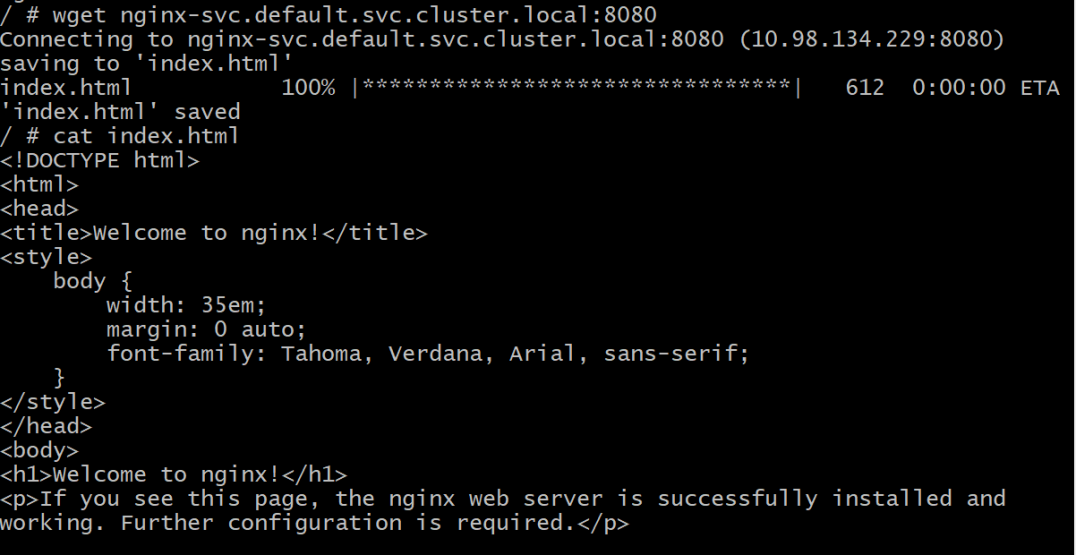
初探Service服务发现机制
1.Service简介 Service是将运行在一组Pod上的应用程序发布为网络服务的抽象方法。 主要功能:服务发现和负载均衡。 Service类型的包括ClusterIP类型、NodePort类型、LoadBalancer类型、ExternalName类型 2.Endpoints简介 Endpoints是一种Kubernetes资源…...
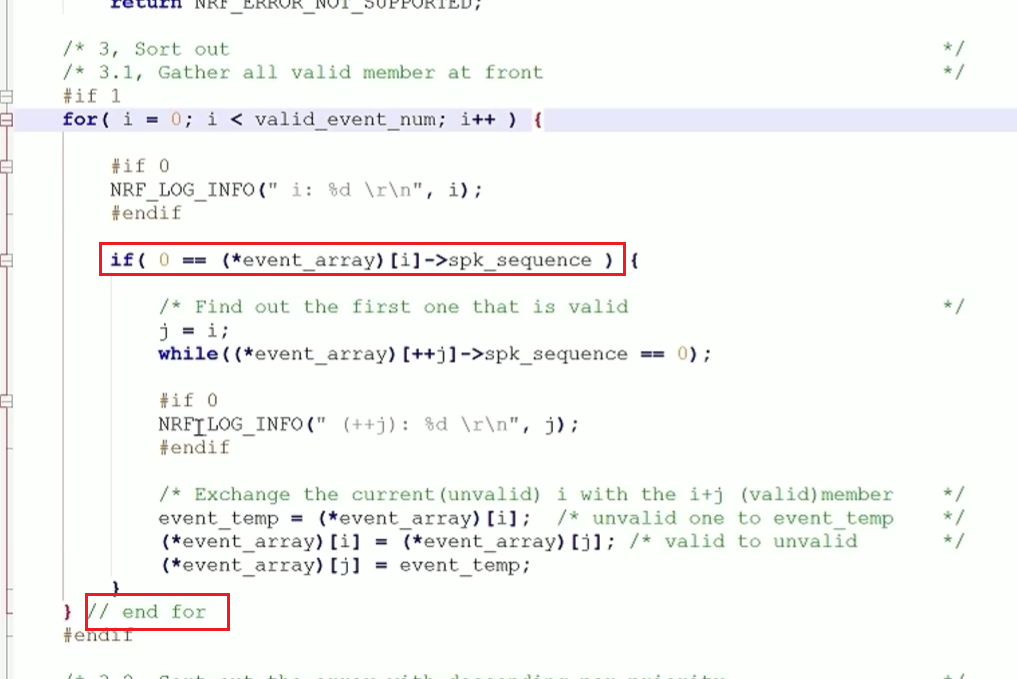
代码规范和架构【立芯理论一】(2025.06.08)
1、代码规范的目标 代码简洁精炼、美观,可持续性好高效率高复用,可移植性好高内聚,低耦合没有冗余规范性,代码有规可循,可以看出自己当时的思考过程特殊排版,特殊语法,特殊指令,必须…...

