Ardusub源码剖析——control_althold.cpp
代码
#include "Sub.h"/** control_althold.pde - init and run calls for althold, flight mode*/// althold_init - initialise althold controller
bool Sub::althold_init()
{if(!control_check_barometer()) {return false;}// initialize vertical maximum speeds and acceleration// sets the maximum speed up and down returned by position controllerpos_control.set_max_speed_accel_z(-get_pilot_speed_dn(), g.pilot_speed_up, g.pilot_accel_z);pos_control.set_correction_speed_accel_z(-get_pilot_speed_dn(), g.pilot_speed_up, g.pilot_accel_z);// initialise position and desired velocitypos_control.init_z_controller();last_pilot_heading = ahrs.yaw_sensor;return true;
}// althold_run - runs the althold controller
// should be called at 100hz or more
void Sub::althold_run()
{uint32_t tnow = AP_HAL::millis();// initialize vertical speeds and accelerationpos_control.set_max_speed_accel_z(-get_pilot_speed_dn(), g.pilot_speed_up, g.pilot_accel_z);if (!motors.armed()) {motors.set_desired_spool_state(AP_Motors::DesiredSpoolState::GROUND_IDLE);// Sub vehicles do not stabilize roll/pitch/yaw when not auto-armed (i.e. on the ground, pilot has never raised throttle)attitude_control.set_throttle_out(0,true,g.throttle_filt);attitude_control.relax_attitude_controllers();pos_control.relax_z_controller(motors.get_throttle_hover());last_pilot_heading = ahrs.yaw_sensor;return;}motors.set_desired_spool_state(AP_Motors::DesiredSpoolState::THROTTLE_UNLIMITED);// get pilot desired lean anglesfloat target_roll, target_pitch;// Check if set_attitude_target_no_gps is validif (tnow - sub.set_attitude_target_no_gps.last_message_ms < 5000) {float target_yaw;Quaternion(set_attitude_target_no_gps.packet.q).to_euler(target_roll,target_pitch,target_yaw);target_roll = degrees(target_roll);target_pitch = degrees(target_pitch);target_yaw = degrees(target_yaw);attitude_control.input_euler_angle_roll_pitch_yaw(target_roll * 1e2f, target_pitch * 1e2f, target_yaw * 1e2f, true);return;}get_pilot_desired_lean_angles(channel_roll->get_control_in(), channel_pitch->get_control_in(), target_roll, target_pitch, attitude_control.get_althold_lean_angle_max());// get pilot's desired yaw ratefloat target_yaw_rate = get_pilot_desired_yaw_rate(channel_yaw->get_control_in());// call attitude controllerif (!is_zero(target_yaw_rate)) { // call attitude controller with rate yaw determined by pilot inputattitude_control.input_euler_angle_roll_pitch_euler_rate_yaw(target_roll, target_pitch, target_yaw_rate);last_pilot_heading = ahrs.yaw_sensor;last_pilot_yaw_input_ms = tnow; // time when pilot last changed heading} else { // hold current heading// this check is required to prevent bounce back after very fast yaw maneuvers// the inertia of the vehicle causes the heading to move slightly past the point when pilot input actually stoppedif (tnow < last_pilot_yaw_input_ms + 250) { // give 250ms to slow down, then set target headingtarget_yaw_rate = 0; // Stop rotation on yaw axis// call attitude controller with target yaw rate = 0 to decelerate on yaw axisattitude_control.input_euler_angle_roll_pitch_euler_rate_yaw(target_roll, target_pitch, target_yaw_rate);last_pilot_heading = ahrs.yaw_sensor; // update heading to hold} else { // call attitude controller holding absolute absolute bearingattitude_control.input_euler_angle_roll_pitch_yaw(target_roll, target_pitch, last_pilot_heading, true);}}control_depth();motors.set_forward(channel_forward->norm_input());motors.set_lateral(channel_lateral->norm_input());
}void Sub::control_depth() {// Hold actual position until zero derivative is detectedstatic bool engageStopZ = true;// Get last user velocity direction to check for zero derivative pointsstatic bool lastVelocityZWasNegative = false;if (fabsf(channel_throttle->norm_input()-0.5f) > 0.05f) { // Throttle input above 5%// output pilot's throttleattitude_control.set_throttle_out(channel_throttle->norm_input(), false, g.throttle_filt);// reset z targets to current valuespos_control.relax_z_controller(channel_throttle->norm_input());engageStopZ = true;lastVelocityZWasNegative = is_negative(inertial_nav.get_velocity_z());} else { // hold zif (ap.at_bottom) {pos_control.init_z_controller();pos_control.set_pos_target_z_cm(inertial_nav.get_altitude() + 10.0f); // set target to 10 cm above bottom}// Detects a zero derivative// When detected, move the altitude set point to the actual position// This will avoid any problem related to joystick delays// or smaller input signalsif(engageStopZ && (lastVelocityZWasNegative ^ is_negative(inertial_nav.get_velocity_z()))) {engageStopZ = false;pos_control.init_z_controller();}pos_control.update_z_controller();}
}剖析
Sub::althold_init()
#include "Sub.h"
包含 Sub 类的定义,以便在这个源文件中使用 Sub 类及其成员。
// althold_init - initialise althold controller
bool Sub::althold_init()
{
这是 althold_init 函数的声明。它不接受任何参数,返回一个布尔值,表示初始化是否成功。
if(!control_check_barometer()) {return false;}
这行代码检查气压计是否正常工作。control_check_barometer 用于验证气压计的读数是否有效。如果气压计检查失败,则初始化过程无法继续,函数返回 false。
// initialize vertical maximum speeds and acceleration// sets the maximum speed up and down returned by position controllerpos_control.set_max_speed_accel_z(-get_pilot_speed_dn(), g.pilot_speed_up, g.pilot_accel_z);pos_control.set_correction_speed_accel_z(-get_pilot_speed_dn(), g.pilot_speed_up, g.pilot_accel_z);
这些行设置了垂直方向上的最大速度和加速度。它们定义了位置控制器可以返回的最大上升和下降速度,以及用于纠正位置的速度和加速度。
pos_control.set_max_speed_accel_z(): 设置最大速度和加速度。get_pilot_speed_dn(): 获取飞行员设定的下降速度。g.pilot_speed_up: 飞行员设定的上升速度。g.pilot_accel_z: 飞行员设定的垂直加速度。
// initialise position and desired velocitypos_control.init_z_controller();
初始化垂直位置控制器,设置当前位置和期望的速度。这确保了潜水器在进入高度保持模式时能够从当前状态平滑过渡。
last_pilot_heading = ahrs.yaw_sensor;
记录当前的航向(yaw)作为最后飞行员指定的航向。ahrs 是一个姿态和航向参考系统(Attitude and Heading Reference System)对象,yaw_sensor 是其航向传感器的读数。
return true;
如果所有的初始化步骤都成功完成,则返回 true。
Sub::althold_run()
// althold_run - runs the althold controller
// should be called at 100hz or more
void Sub::althold_run()
{
这是 althold_run 函数的声明和注释。注释说明了这个函数的作用是运行高度保持控制器,并且建议该函数应该以至少100Hz的频率被调用。
uint32_t tnow = AP_HAL::millis();
获取当前系统时间(以毫秒为单位)。tnow 变量存储当前时间
// initialize vertical speeds and accelerationpos_control.set_max_speed_accel_z(-get_pilot_speed_dn(), g.pilot_speed_up, g.pilot_accel_z);
设置垂直方向上的最大速度和加速度。这些值决定了潜水器在垂直方向上响应指令的速度和加速度。
get_pilot_speed_dn(): 获取飞行员设定的下降速度。g.pilot_speed_up: 全局变量,代表飞行员设定的上升速度。g.pilot_accel_z: 全局变量,代表飞行员设定的垂直加速度。
if (!motors.armed()) {motors.set_desired_spool_state(AP_Motors::DesiredSpoolState::GROUND_IDLE);
如果电机未启动(armed),则将电机设置为地面空闲状态。
// Sub vehicles do not stabilize roll/pitch/yaw when not auto-armed (i.e. on the ground, pilot has never raised throttle)attitude_control.set_throttle_out(0,true,g.throttle_filt);attitude_control.relax_attitude_controllers();pos_control.relax_z_controller(motors.get_throttle_hover());
如果潜水器未启动,它不会稳定横滚(roll)、俯仰(pitch)和偏航(yaw)。因此,以下操作会被执行:
- 设置油门输出为0,并应用滤波器。
- 放松姿态控制器,以防止不必要的控制动作。
- 放松垂直位置控制器,并将其设置到悬停油门值。
last_pilot_heading = ahrs.yaw_sensor;
记录当前的航向作为最后飞行员指定的航向。
return;}
如果电机未启动,则退出函数。
motors.set_desired_spool_state(AP_Motors::DesiredSpoolState::THROTTLE_UNLIMITED);
如果电机已启动,则设置电机为油门无限制状态,这意味着潜水器可以根据控制输入全速运行。
// get pilot desired lean angles
float target_roll, target_pitch;
声明两个浮点变量 target_roll 和 target_pitch,用于存储飞行员期望的横滚和俯仰角度。
// Check if set_attitude_target_no_gps is valid
if (tnow - sub.set_attitude_target_no_gps.last_message_ms < 5000) {
检查 set_attitude_target_no_gps 消息是否在最近5秒内收到。set_attitude_target_no_gps 是一个结构体,包含一个四元数(quaternion)用于表示姿态和一个时间戳(last_message_ms)。如果该消息是有效的(即在5秒之内收到的),则执行以下代码块。
float target_yaw;Quaternion(set_attitude_target_no_gps.packet.q).to_euler(target_roll,target_pitch,target_yaw);
使用 Quaternion 类将收到的四元数转换为欧拉角(Euler angles),即横滚(roll)、俯仰(pitch)和偏航(yaw)角度。这些角度存储在 target_roll、target_pitch 和 target_yaw 变量中。
target_roll = degrees(target_roll);target_pitch = degrees(target_pitch);target_yaw = degrees(target_yaw);
将欧拉角从弧度转换为度。degrees() 函数是用来执行这个转换的。
attitude_control.input_euler_angle_roll_pitch_yaw(target_roll * 1e2f, target_pitch * 1e2f, target_yaw * 1e2f, true);return;
将转换后的角度(乘以100,转换成期望的单位)输入到姿态控制器中,并立即返回,结束 althold_run 函数的执行。true 参数表示这是一个直接设置姿态的请求,而不是一个增量变化。
get_pilot_desired_lean_angles(channel_roll->get_control_in(), channel_pitch->get_control_in(), target_roll, target_pitch, attitude_control.get_althold_lean_angle_max());
如果 set_attitude_target_no_gps 消息不是在最近5秒内收到的,则调用 get_pilot_desired_lean_angles 函数来获取飞行员的期望倾斜角度。这个函数基于遥控器的输入来计算期望的横滚和俯仰角度。
channel_roll->get_control_in(): 获取遥控器横滚通道的输入值。channel_pitch->get_control_in(): 获取遥控器俯仰通道的输入值。attitude_control.get_althold_lean_angle_max(): 获取高度保持模式下的最大倾斜角度。
// get pilot's desired yaw rate
float target_yaw_rate = get_pilot_desired_yaw_rate(channel_yaw->get_control_in());
获取飞行员期望的偏航速率(围绕垂直轴的旋转速率)。get_pilot_desired_yaw_rate 函数接收来自遥控器偏航通道的输入值,并返回期望的偏航速率。
// call attitude controller
if (!is_zero(target_yaw_rate)) { // call attitude controller with rate yaw determined by pilot inputattitude_control.input_euler_angle_roll_pitch_euler_rate_yaw(target_roll, target_pitch, target_yaw_rate);last_pilot_heading = ahrs.yaw_sensor;last_pilot_yaw_input_ms = tnow; // time when pilot last changed heading
如果期望的偏航速率不为零(即飞行员正在请求改变朝向),则调用姿态控制器,使用飞行员指定的横滚、俯仰和偏航速率。同时记录当前航向作为最后飞行员指定的航向,并更新最后飞行员偏航输入的时间戳。
} else { // hold current heading
如果期望的偏航速率为零(即飞行员没有请求改变朝向),则尝试保持当前的朝向。
// this check is required to prevent bounce back after very fast yaw maneuvers// the inertia of the vehicle causes the heading to move slightly past the point when pilot input actually stoppedif (tnow < last_pilot_yaw_input_ms + 250) { // give 250ms to slow down, then set target headingtarget_yaw_rate = 0; // Stop rotation on yaw axis// call attitude controller with target yaw rate = 0 to decelerate on yaw axisattitude_control.input_euler_angle_roll_pitch_euler_rate_yaw(target_roll, target_pitch, target_yaw_rate);last_pilot_heading = ahrs.yaw_sensor; // update heading to hold
如果自上次飞行员请求偏航以来不到250毫秒,则设置偏航速率为零以停止偏航轴的旋转,并调用姿态控制器来减速偏航轴。同时更新最后飞行员指定的航向。
} else { // call attitude controller holding absolute headingattitude_control.input_euler_angle_roll_pitch_yaw(target_roll, target_pitch, last_pilot_heading, true);}
如果自上次飞行员请求偏航以来已经超过250毫秒,则调用姿态控制器以保持绝对航向(即最后飞行员指定的航向)。
control_depth();
调用 control_depth 函数来控制潜水器的深度
motors.set_forward(channel_forward->norm_input());
motors.set_lateral(channel_lateral->norm_input());
设置潜水器的前进和侧向动力。channel_forward->norm_input() 和 channel_lateral->norm_input() 分别获取飞行员指定的前进和侧向通道的标准化输入值,并使用这些值来设置电机的推力方向。
Sub::control_depth()
void Sub::control_depth() {
定义 Sub 类的成员函数 control_depth,没有返回值。
// Hold actual position until zero derivative is detectedstatic bool engageStopZ = true;
声明一个静态布尔变量 engageStopZ,用于确定是否激活深度保持。当检测到速度的零导数时,它将保持实际位置。
// Get last user velocity direction to check for zero derivative pointsstatic bool lastVelocityZWasNegative = false;
声明一个静态布尔变量 lastVelocityZWasNegative,用于记录用户上一次的垂直速度方向(正或负),以检测速度的零导数点。
if (fabsf(channel_throttle->norm_input()-0.5f) > 0.05f) { // Throttle input above 5%
检查遥控器油门通道的标准化输入是否大于5%(即飞行员是否在请求垂直移动)。norm_input() 返回一个介于0和1之间的值,其中0.5代表中立位置。如果输入与0.5的差值的绝对值大于0.05,表示油门输入超过了5%。
// output pilot's throttleattitude_control.set_throttle_out(channel_throttle->norm_input(), false, g.throttle_filt);
如果飞行员请求垂直移动,则将飞行员的油门输入输出到姿态控制器。set_throttle_out 函数用于设置油门输出,g.throttle_filt 是一个滤波参数。
// reset z targets to current valuespos_control.relax_z_controller(channel_throttle->norm_input());
重置Z轴的目标位置到当前值,这是为了在新的油门输入下重新开始深度控制。
engageStopZ = true;lastVelocityZWasNegative = is_negative(inertial_nav.get_velocity_z());} else { // hold z
如果油门输入低于5%,则进入保持深度的模式。同时更新 engageStopZ 和 lastVelocityZWasNegative 变量。
if (ap.at_bottom) {pos_control.init_z_controller();pos_control.set_pos_target_z_cm(inertial_nav.get_altitude() + 10.0f); // set target to 10 cm above bottom}
如果潜水器到达了底部,初始化Z轴控制器,并将目标深度设置为当前高度加上10厘米,以保持潜水器在底部上方10厘米的位置。
// Detects a zero derivative// When detected, move the altitude set point to the actual position// This will avoid any problem related to joystick delays// or smaller input signalsif(engageStopZ && (lastVelocityZWasNegative ^ is_negative(inertial_nav.get_velocity_z()))) {engageStopZ = false;pos_control.init_z_controller();}
检测速度的零导数。如果检测到(即速度从正变为负或从负变为正),则将 engageStopZ 设置为 false 并重新初始化Z轴控制器,将目标深度设置为当前深度。
pos_control.update_z_controller();}
无论是否检测到零导数,都会更新Z轴控制器,以维持或改变潜水器的深度。
相关文章:

Ardusub源码剖析——control_althold.cpp
代码 #include "Sub.h"/** control_althold.pde - init and run calls for althold, flight mode*/// althold_init - initialise althold controller bool Sub::althold_init() {if(!control_check_barometer()) {return false;}// initialize vertical maximum sp…...

Vue前端开发-路由的基本配置
在传统的 Web 页面开发过程中,可以借助超级链接标签实现站内多个页面间的相互跳转,而在现代的工程化、模块化下开发的Web页面只有一个,在一个页面中需要实现站内各功能页面渲染,相互跳转,这时些功能的实现,…...

HarmonyOS JSON解析与生成 常用的几个方法
HarmonyOS 使用 JSON解析与生成 的好处 一、轻量级与高效性 易于阅读和编写:JSON格式的数据易于人类阅读和编写,降低了数据处理的复杂性。高效解析与生成:HarmonyOS的JSON解析库提供了一系列高效的函数和类,能够快速地将JSON字符串…...

Docker 进阶指南:常用命令、最佳实践与资源管理
Docker 进阶指南:常用命令、最佳实践与资源管理 Docker 作为一种轻量级的容器化技术,已经成为现代软件开发和部署不可或缺的工具。本文将为您深入介绍 Docker 的常用命令、最佳实践以及如何有效管理容器资源,帮助您更好地在 Ubuntu 22.04 或…...

【前端】特殊案例分析深入理解 JavaScript 中的词法作用域
博客主页: [小ᶻ☡꙳ᵃⁱᵍᶜ꙳] 本文专栏: 前端 文章目录 💯前言💯案例代码💯词法作用域(Lexical Scope)与静态作用域什么是词法作用域?代码执行的详细分析 💯函数定义与调用的…...
AI+性能测试领域场景落地)
Jmeter进阶篇(29)AI+性能测试领域场景落地
🏝️关于我:我是綦枫。一个顺手写写代码的音乐制作人。 前言 随着2022年GPT3.5的问世,我们的社会已经进入了AI时代,这是一个全新的风口,也会迎来全新的挑战和机遇。如果能抓住新时代的风口,你将会在进步的路上越走越快。今天让我们来一起探究一下,在软件性能测试领域,…...
 方法:详细解析与示例)
理解和应用 Python Requests 库中的 .json() 方法:详细解析与示例
理解和应用 Python Requests 库中的 .json() 方法:详细解析与示例 在使用 Python 的 requests 库进行网络请求时,.json() 方法是一种非常实用的功能,用于将从 API 获取的 JSON 格式的字符串响应转换为 Python 可操作的字典或列表。这一功能的…...

docker 运行my-redis命令
CREATE TABLE orders ( order_id bigint NOT NULL COMMENT "订单ID", dt date NOT NULL COMMENT "日期", merchant_id int NOT NULL COMMENT "商家ID", user_id int NOT NULL COMMENT "用户ID", good_id int NOT NULL COMMENT "商…...

cloudstack概要及单节点安装部署
概要 Apache CloudStack 是一个开源的云计算管理平台,用于管理和部署大规模的虚拟化环境,支持 IaaS(基础设施即服务)模型。它广泛应用于私有云、公共云和混合云场景。 核心功能 多租户支持 提供隔离的虚拟网络、计算资源和存储资…...

Android Gradle 相关
JDK环境配置: 1、Gradle运行时的JDK,即Gradle需要用到的JDK,配置如下: 如需修改现有项目的 Gradle JDK 配置,请依次点击 File(或者 macOS 上的 Android Studio)> Settings > Build, Exe…...

SpringMVC:入门案例
从此开始,我们步入SpringMVC的学习。 SpringMVC是一种基于Java实现MVC模型的轻量级Web框架 先来看一下web程序是如何工作的: 因为是异步调用,所以后端不需要返回view视图,将其去除前端如果通过异步调用的方式进行交互࿰…...

LuaForWindows_v5.1.5-52.exe
Releases rjpcomputing/luaforwindows GitHub #lua C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\test.lua print("Hello lua!") print("ZengWenFeng 13805029595")...

密码学实验工具--Cryptool2
一、 Cryptool2的下载与安装 请参考我的另一篇笔记 二、 Caesar密码 2.1 Caesar密码加解密 1. 在Starcenter中直接搜索caesar的模板。 2. 打开caesar Cipher的模板后,工作区上面已经有了输入框,密钥框,输出框 输入框:要加密…...

量化交易系统开发-实时行情自动化交易-8.1.TradingView平台
19年创业做过一年的量化交易但没有成功,作为交易系统的开发人员积累了一些经验,最近想重新研究交易系统,一边整理一边写出来一些思考供大家参考,也希望跟做量化的朋友有更多的交流和合作。 接下来会对于TradingView平台介绍。 T…...

Vue2 常见知识点(二)
使用简单的代码逻辑,理一理实现逻辑 为了方便理解,案例中,没有使用虚拟dom和抽象语法树,是通过直接操作dom来实现的 1.模板语法 先看一个简单的实现: this.compile( this.$el ); 执行模板编译,如果是文本…...

SAP-ABAP开发-第二代增强示例
CUSTOMER EXIT 以VA01为例 目录 一、查找出口 二、出口对象 三、销售订单的增强 一、查找出口 ①查找事务代码的主程序 ②搜索CALL CUSTOMER-FUNCTION SE37下查看函数 函数名称命名规则:EXIT_<程序名>_<序号> ③使用函数查找:MODX_FU…...

UDP 协议与端口绑定行为解析:理解 IP 地址和端口的绑定规则
UDP 协议与端口绑定行为解析:理解 IP 地址和端口的绑定规则 1. UDP 协议与端口绑定基础2. UDP 端口绑定行为与示例3. 关键结论:占有权与消息接收权4. 异常现象:多个程序绑定 0.0.0.0:80805. 端口共享与操作系统的行为差异6. 实践建议与最佳实践7. 总结在网络通信中,UDP(用…...

【Vue3】【Naive UI】<n-message>标签
【Vue3】【Naive UI】标签 content (String | VNode) 【VUE3】【Naive UI】<NCard> 标签 【VUE3】【Naive UI】<n-button> 标签 【VUE3】【Naive UI】<a> 标签 【VUE3】【Naive UI】<NDropdown&…...

C++ 变量和常量:开启程序构建之门的关键锁钥与永恒灯塔
目录 一、变量 1.1 变量的创建 1.2 变量的初始化 1.3 变量的分类 1.4 变量的初始化 二、常量 2.1 字面常量 2.2 #define定义常量 2.3 const 定义常量 一、变量 1.1 变量的创建 data_type name; | | | | 数据类型 变量名 ------------- int age; //整型变量 char ch; …...
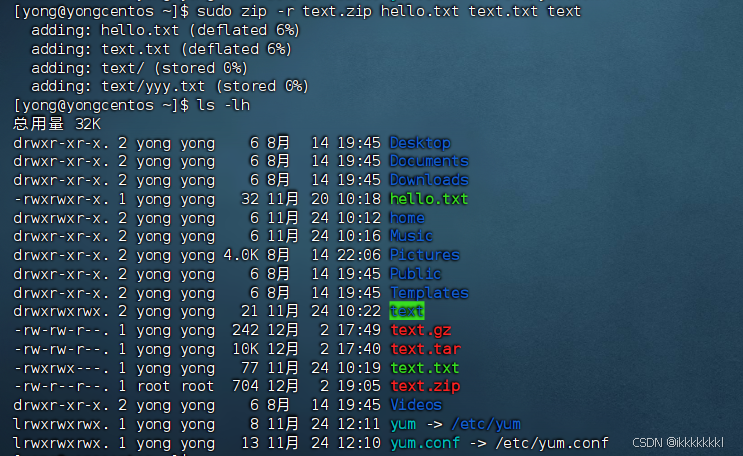
Linux部分实用操作
目录 1、快捷键 2、软件安装 3、systemctl 4、ln命令创建软连接 5、IP地址 6、主机名 7、域名解析 8、网络传输 ping wget curl命令 9、端口 10、进程 11、主机状态 查看系统资源占用--top 磁盘信息监控--df--iostat 网络状态监控--sar -n DEV 12、环境…...
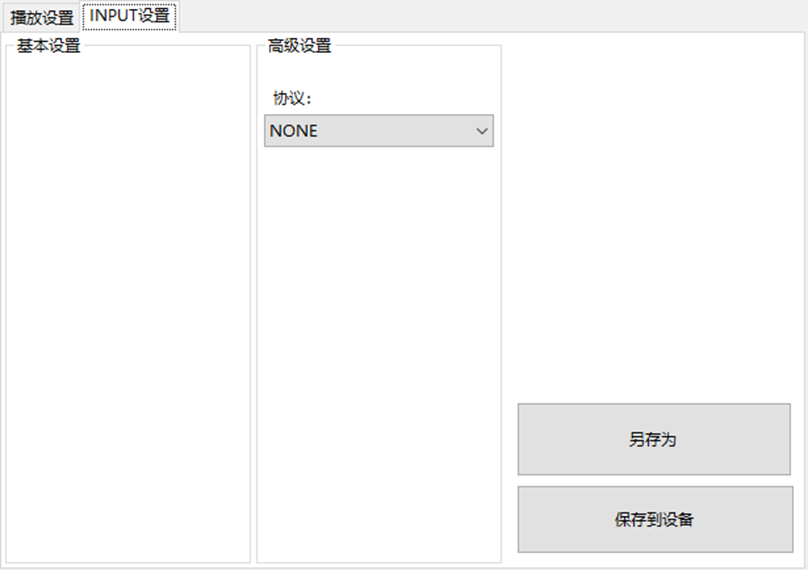
LBE-LEX系列工业语音播放器|预警播报器|喇叭蜂鸣器的上位机配置操作说明
LBE-LEX系列工业语音播放器|预警播报器|喇叭蜂鸣器专为工业环境精心打造,完美适配AGV和无人叉车。同时,集成以太网与语音合成技术,为各类高级系统(如MES、调度系统、库位管理、立库等)提供高效便捷的语音交互体验。 L…...
: K8s 核心概念白话解读(上):Pod 和 Deployment 究竟是什么?)
云原生核心技术 (7/12): K8s 核心概念白话解读(上):Pod 和 Deployment 究竟是什么?
大家好,欢迎来到《云原生核心技术》系列的第七篇! 在上一篇,我们成功地使用 Minikube 或 kind 在自己的电脑上搭建起了一个迷你但功能完备的 Kubernetes 集群。现在,我们就像一个拥有了一块崭新数字土地的农场主,是时…...

在鸿蒙HarmonyOS 5中实现抖音风格的点赞功能
下面我将详细介绍如何使用HarmonyOS SDK在HarmonyOS 5中实现类似抖音的点赞功能,包括动画效果、数据同步和交互优化。 1. 基础点赞功能实现 1.1 创建数据模型 // VideoModel.ets export class VideoModel {id: string "";title: string ""…...
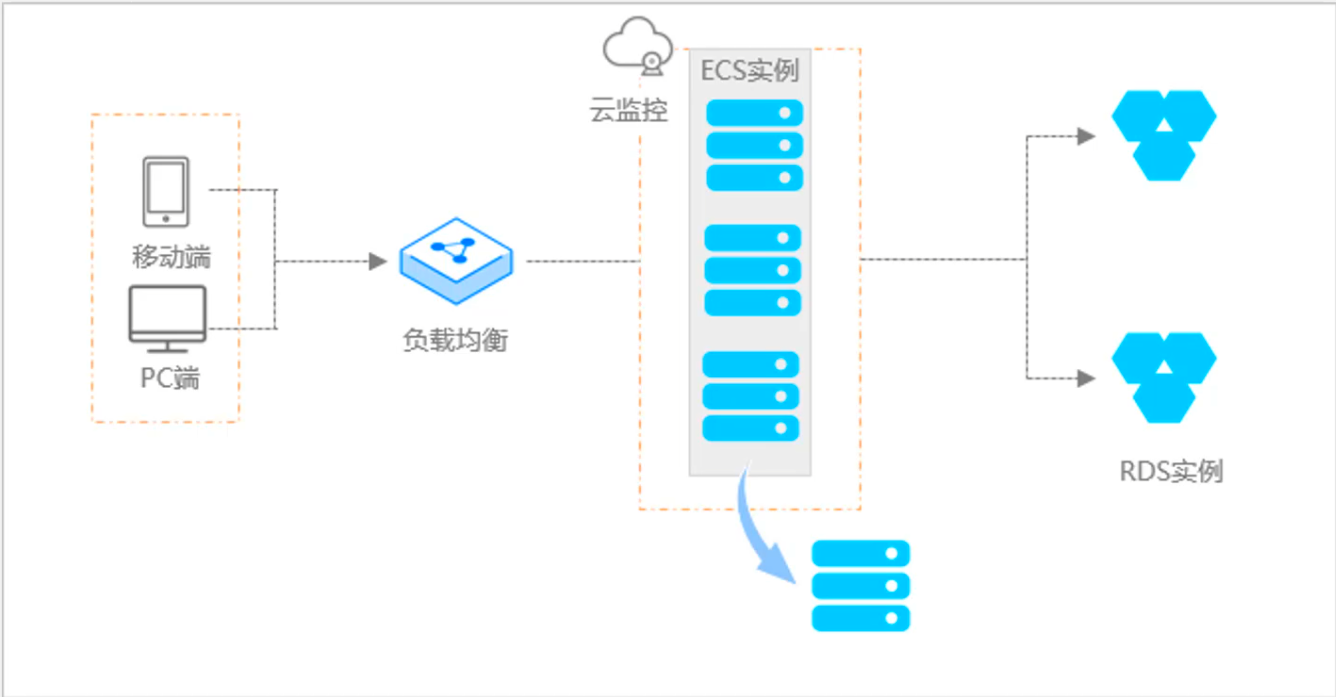
阿里云ACP云计算备考笔记 (5)——弹性伸缩
目录 第一章 概述 第二章 弹性伸缩简介 1、弹性伸缩 2、垂直伸缩 3、优势 4、应用场景 ① 无规律的业务量波动 ② 有规律的业务量波动 ③ 无明显业务量波动 ④ 混合型业务 ⑤ 消息通知 ⑥ 生命周期挂钩 ⑦ 自定义方式 ⑧ 滚的升级 5、使用限制 第三章 主要定义 …...
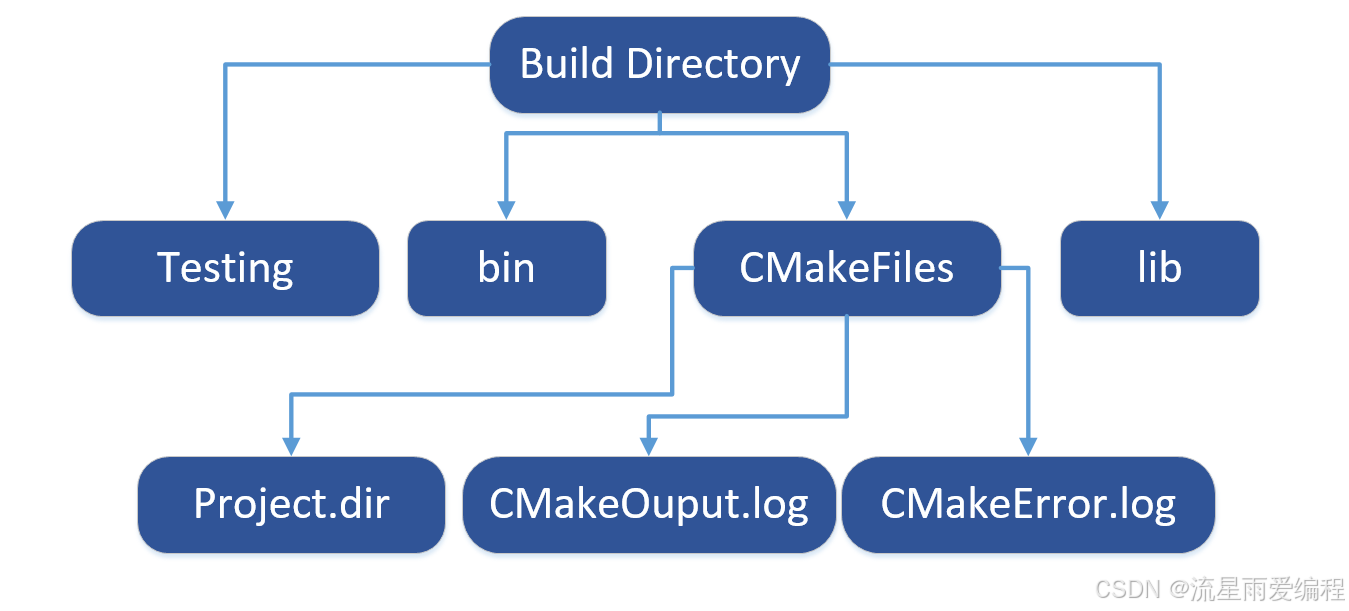
CMake基础:构建流程详解
目录 1.CMake构建过程的基本流程 2.CMake构建的具体步骤 2.1.创建构建目录 2.2.使用 CMake 生成构建文件 2.3.编译和构建 2.4.清理构建文件 2.5.重新配置和构建 3.跨平台构建示例 4.工具链与交叉编译 5.CMake构建后的项目结构解析 5.1.CMake构建后的目录结构 5.2.构…...

Linux简单的操作
ls ls 查看当前目录 ll 查看详细内容 ls -a 查看所有的内容 ls --help 查看方法文档 pwd pwd 查看当前路径 cd cd 转路径 cd .. 转上一级路径 cd 名 转换路径 …...

macOS多出来了:Google云端硬盘、YouTube、表格、幻灯片、Gmail、Google文档等应用
文章目录 问题现象问题原因解决办法 问题现象 macOS启动台(Launchpad)多出来了:Google云端硬盘、YouTube、表格、幻灯片、Gmail、Google文档等应用。 问题原因 很明显,都是Google家的办公全家桶。这些应用并不是通过独立安装的…...
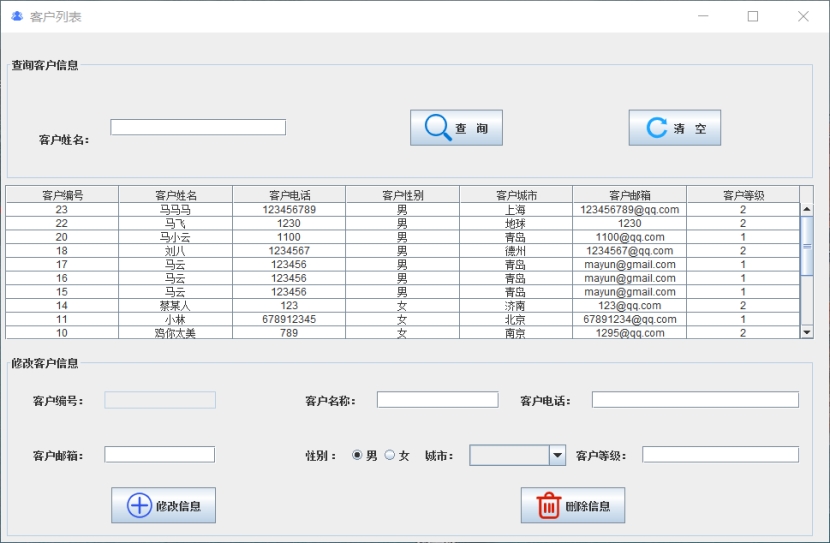
基于Java+MySQL实现(GUI)客户管理系统
客户资料管理系统的设计与实现 第一章 需求分析 1.1 需求总体介绍 本项目为了方便维护客户信息为了方便维护客户信息,对客户进行统一管理,可以把所有客户信息录入系统,进行维护和统计功能。可通过文件的方式保存相关录入数据,对…...
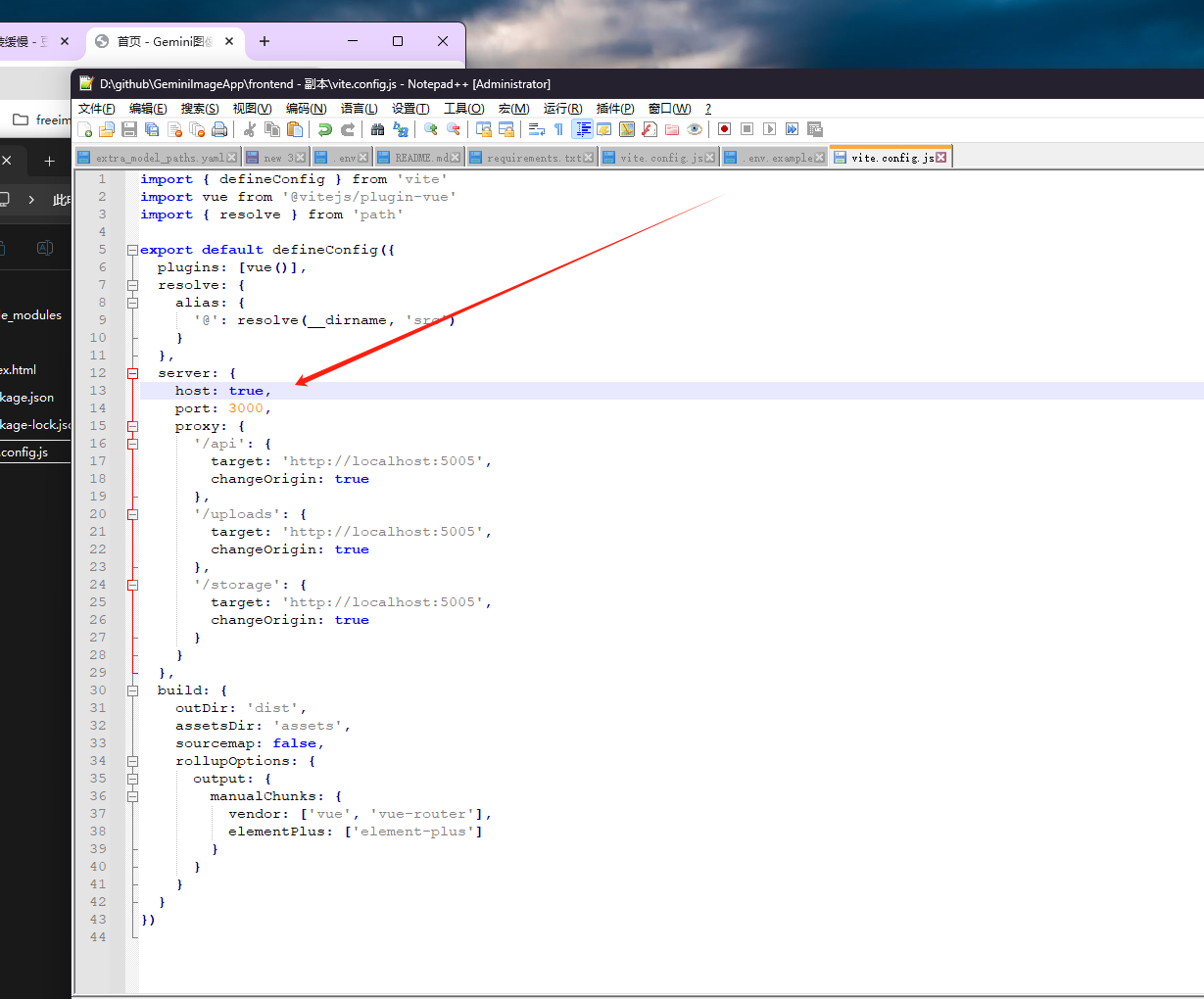
推荐 github 项目:GeminiImageApp(图片生成方向,可以做一定的素材)
推荐 github 项目:GeminiImageApp(图片生成方向,可以做一定的素材) 这个项目能干嘛? 使用 gemini 2.0 的 api 和 google 其他的 api 来做衍生处理 简化和优化了文生图和图生图的行为(我的最主要) 并且有一些目标检测和切割(我用不到) 视频和 imagefx 因为没 a…...

Git常用命令完全指南:从入门到精通
Git常用命令完全指南:从入门到精通 一、基础配置命令 1. 用户信息配置 # 设置全局用户名 git config --global user.name "你的名字"# 设置全局邮箱 git config --global user.email "你的邮箱example.com"# 查看所有配置 git config --list…...
