[论文阅读] Knowledge Fusion of Large Language Models
Knowledge Fusion of Large Language Models (FuseLLM)
Methodology
整体Pipeline如下图所示

不同的动物代表不同的LLM。左边第一,第二分别是Ensemble以及Weight Merging方法。最右侧为本文提出的FuseLLM。
- Ensemble: 融合多个models的预测结果,比如求加权平均等。
- Weight Merging:在权重/参数层面融合,但通常仅限于相同架构的模型。
- FuseLLM 主要思想为:融合多个LLMs(可以是不同架构的)的probabilistic matrices,得到Fused Matrix后,喂给Target Model,起到知识蒸馏的作用。
这里面会涉及到一个关键:
- 不同LLM,使用的Tokenizer可能不同,设置也可能不一样(如 model_max_length ),分词结果可能不一样(比如对同一个句子分词,tokens总数不同),使用的Vocabulary也可能不一样,因此生成的probabilistic matrix在维度上可能有所不同,如何解决对齐问题?这个实际上就是 token alignment 问题,本文中着重描述了解决方案。
Definition of Problem
假设我们有一个语料库 C \mathcal{C} C, K K K个source LLMs, 对于文本 t ∈ C t \in \mathcal{C} t∈C,经过 K K K个LLM处理,可以得到对应的概率分布矩阵 probabilistic distribution matrix: { P t θ j } j = 1 K \{\mathbf{P}^{\theta_j}_t\}^K_{j=1} {Ptθj}j=1K,其中 θ j \theta_j θj表示第 j j j个LLM的参数。我们要做的就是将这 K K K个概率分布矩阵融合,然后送入Target LLM中辅助训练:
P t = F u s i o n ( P t θ 1 , P t θ 2 , … , P t θ K ) , \begin{align} \mathbf{P}_t=\mathbb{F}\mathrm{usion}(\mathbf{P}_t^{\theta_1},\mathbf{P}_t^{\theta_2},\ldots,\mathbf{P}_t^{\theta_K}), \end{align} Pt=Fusion(Ptθ1,Ptθ2,…,PtθK),
P t \mathbf{P}_t Pt即得到的融合概率分布矩阵(Fused Representation Matrix)。
为了将 P t \mathbf{P}_t Pt迁移至target model中,我们假设 Q t \mathbf{Q}_t Qt为其输出的representation matrix,则Knowledge Fusion的训练目标为:
L F u s i o n = − E t ∼ C [ D ( Q t , P t ) ] . \begin{align} \mathcal{L}_{\mathrm{Fusion}}=-\mathbb{E}_{t\sim\mathcal{C}}\left[\mathbb{D}(\mathbf{Q}_t,\mathbf{P}_t)\right]. \end{align} LFusion=−Et∼C[D(Qt,Pt)].
其中 D ( ⋅ , ⋅ ) \mathbb{D}(\cdot, \cdot) D(⋅,⋅)表示差异性函数,具体实现可以是KL散度。
整体的模型损失如下:
L = λ L C L M + ( 1 − λ ) L F u s i o n . \begin{align}\mathcal{L}=\lambda\mathcal{L}_{\mathrm{CLM}}+(1-\lambda)\mathcal{L}_{\mathrm{Fusion}}.\end{align} L=λLCLM+(1−λ)LFusion.
其中 L C L M \mathcal{L}_{\mathrm{CLM}} LCLM表示最原始的ground-truth之间的损失, λ \lambda λ为系数。
实现细节
Token Alignment
我们假设有两个LLM,使用不同的tokenizer。对同一段文本分词,得到的token序列不同,长度也不同:

如上图,用DeepSeek和TinyLlama各自的分词器分词,得到的结果完全不一样。最终预测的概率分布矩阵也不一样。
Token-Level Alignment
为了解决这个问题,FuseLLM采用基于最小编辑距离Minimal Edit Distance(MinED)的动态规划策略,在token-level实现对齐,以下图为例:

具体实现的源代码other.py如下:
def dtw(series_1, series_2, norm_func=np.linalg.norm):"""Use dynamic time wrapping to align to tokenizers, modified from:https://github.com/talcs/simpledtw/blob/master/simpledtw.py""""""Parameters----------series_1: List[str]blending_input_tokensseries_2: List[str]base_input_tokensnorm_func: functionedit distance evaluation between 2 tokensReturn Values----------matches: List[Tuple]matched pairs between a base token and a blending tokenmatrix[-1, -1]: int the total cost for mapping the two series of tokensmappings_series_1: List[List]mapping from blending tokens to base tokenseg: [0], [1, 2], [3, 4, 5], [6], ...mappings_series_2: List[List]mapping from base tokens to blending tokensmatrix: List[int]the dtw matrix"""matrix = np.zeros((len(series_1) + 1, len(series_2) + 1))matrix[0, :] = np.infmatrix[:, 0] = np.infmatrix[0, 0] = 0for i, vec1 in enumerate(series_1):for j, vec2 in enumerate(series_2):cost = norm_func(vec1, vec2)matrix[i + 1, j + 1] = cost + min(matrix[i, j + 1], matrix[i + 1, j], matrix[i, j])matrix = matrix[1:, 1:]i = matrix.shape[0] - 1j = matrix.shape[1] - 1matches = []mappings_series_1 = [list() for v in range(matrix.shape[0])]mappings_series_2 = [list() for v in range(matrix.shape[1])]while i > 0 or j > 0:matches.append((i, j))mappings_series_1[i].append(j)mappings_series_2[j].append(i)option_diag = matrix[i - 1, j - 1] if i > 0 and j > 0 else np.infoption_up = matrix[i - 1, j] if i > 0 else np.infoption_left = matrix[i, j - 1] if j > 0 else np.infmove = np.argmin([option_diag, option_up, option_left])if move == 0:i -= 1j -= 1elif move == 1:i -= 1else:j -= 1matches.append((0, 0))mappings_series_1[0].append(0)mappings_series_2[0].append(0)matches.reverse()for mp in mappings_series_1:mp.reverse()for mp in mappings_series_2:mp.reverse()return matches, matrix[-1, -1], mappings_series_1, mappings_series_2, matrixLogit-Level Alignment
利用该对齐结果,将不同LLMs得到的representation matrix对齐。关键代码other.py如下:
def transform_step_logits(base_model_tokenizer: transformers.tokenization_utils_base.PreTrainedTokenizerBase,blending_model_tokenizer: transformers.tokenization_utils_base.PreTrainedTokenizerBase,base_model_vocab: Dict[str, int],base_model_input_ids: List[int],blending_model_input_ids: List[int],blending_model_per_step_logits: List[List[float]],blending_model_per_step_indices: List[List[int]],vocab_align_type: str = "hard",blending_to_base_mapping: Dict[str, str] = None,
):"""Align blending model per step logits & indices with base model.""""""Parameters----------base_model_tokenizer: transformers.tokenization_utils_base.PreTrainedTokenizerBaseblending_model_tokenizer: transformers.tokenization_utils_base.PreTrainedTokenizerBasebase_model_vocab: Dict[str, int]mapping token to id using vocabulary of base modelbase_model_input_ids: List[int]ids of base_model_input_tokensblending_model_input_ids: List[int]ids of blending_model_input_tokensblending_model_per_step_logits: List[List[float]]logits for each token in blending_model_input_tokens blending_model_per_step_indices: List[List[int]]indices corresponding to logits for each token in blending_model_input_tokens vocab_align_type: str = "hard"blending_to_base_mapping: Dict[str, str] = Nonemapping each blending token to its corresponding base token Return Values----------aligned_blending_model_per_step_logits: List[List[float]]aligned logits for each token in base_model_input_tokens for the FuseLLM trainingaligned_blending_model_per_step_indices: List[List[int]]aligned indices corresponding aligned logits for each token in base_model_input_tokens for the FuseLLM training. Use the base model vocabulary to look up the token."""base_model_tokens = base_model_tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens(base_model_input_ids)blending_model_tokens = blending_model_tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens(blending_model_input_ids)base_model_special_token = TOKENIZER_TO_SPECIAL_TOKEN[base_model_tokenizer.__class__]blending_model_special_token = TOKENIZER_TO_SPECIAL_TOKEN[blending_model_tokenizer.__class__]def dist_fn(a, b):"""Calculate editdistance between two tokens, a is from blending model, b is from base model."""aa = a.replace(blending_model_special_token, "")bb = b.replace(base_model_special_token, "")dist = editdistance.eval(aa, bb)return dist_, _, _, base_to_blending, _ = dtw(blending_model_tokens, base_model_tokens, norm_func=dist_fn)aligned_blending_model_per_step_logits, aligned_blending_model_per_step_indices = ([],[],)for i, blending_idx in enumerate(base_to_blending):aligned_blending_model_per_step_logit = []aligned_blending_model_per_step_index = []if len(blending_idx) == 1: # one base token map to one blending tokenj = blending_idx[0]base_token = base_model_tokens[i]blending_token = blending_model_tokens[j].replace(blending_model_special_token, base_model_special_token)if ((blending_model_tokenizer.__class__== transformers.GPTNeoXTokenizerFastor blending_model_tokenizer.__class__== transformers.GPT2TokenizerFast)and i == 0and base_token.startswith(base_model_special_token)and not blending_token.startswith(base_model_special_token)):blending_token = (base_model_special_token + blending_token) # special case for mptif vocab_align_type == "hard":if (base_token == blending_token): # find the aligned mapping, use the corresponding logits# the logits and indices at this stepfor blending_logit, blending_index in zip(blending_model_per_step_logits[j],blending_model_per_step_indices[j],):# the token corresponds to the logit and indicesblending_t = blending_model_tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens([blending_index])[0].replace(blending_model_special_token, base_model_special_token)if blending_t in base_model_vocab:aligned_index = base_model_vocab[blending_t] # the index of the token in base model vocabif (aligned_indexnot in aligned_blending_model_per_step_index):aligned_blending_model_per_step_index.append(aligned_index)aligned_blending_model_per_step_logit.append(blending_logit)else: # find error aligned mapping, use the one-hot logitsaligned_blending_model_per_step_index.append(base_model_vocab[base_token])aligned_blending_model_per_step_logit.append(1.0)elif vocab_align_type == "soft":if (base_token == blending_token) or (blending_token in blending_to_base_mappingand base_token == blending_to_base_mapping[blending_token]): # find the aligned mapping, use the corresponding logits# the logits and indices at this stepfor blending_logit, blending_index in zip(blending_model_per_step_logits[j],blending_model_per_step_indices[j],):# the token corresponds to the logit and indicesblending_t = blending_model_tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens([blending_index])[0].replace(blending_model_special_token, base_model_special_token)blending_t = blending_to_base_mapping[blending_t]if blending_t in base_model_vocab:aligned_index = base_model_vocab[blending_t] # the index of the token in base model vocabif (aligned_indexnot in aligned_blending_model_per_step_index):aligned_blending_model_per_step_index.append(aligned_index)aligned_blending_model_per_step_logit.append(blending_logit)else:logger.warning(f"blending_t: {blending_t} not in base_model_vocab!")else: # find error aligned mapping, use the one-hot logitsaligned_blending_model_per_step_index.append(base_model_vocab[base_token])aligned_blending_model_per_step_logit.append(1.0)else:logger.warning(f"The vocab_align_type: '{vocab_align_type}' is not support!")raise NotImplementedErrorelse: # one base token map to multiple blending token, in this case only fit base token. use the one-hot logitsbase_token = base_model_tokens[i]aligned_blending_model_per_step_index.append(base_model_vocab[base_token])aligned_blending_model_per_step_logit.append(1.0)aligned_blending_model_per_step_indices.append(aligned_blending_model_per_step_index)aligned_blending_model_per_step_logits.append(aligned_blending_model_per_step_logit)return (aligned_blending_model_per_step_logits,aligned_blending_model_per_step_indices,)Fusion Strategies:
得到对其的representation matrix以后,由于不同的LLM具有不同的性能,可以使用概率分布矩阵与ground-truth之间的交叉熵损失(CE loss)评估LLM的优劣,再根据此判断选择哪些LLM参与知识融合。CE loss越低,证明模型效果更好。具体而言,作者提出了两种Fusion Strategy:
- MinCE: 仅选择CE loss最小的representation matrix用于知识融合。
- AvgCE: 基于各个模型的CE loss,采用多个representation matrices的加权平均,用于知识融合。
整体的算法流程如下:

- 注:这里Eq.5实际是本文中上述的Eq.3
一些思考
本文的思路是将多个LLMs输出的概率分布矩阵视为知识,将知识融合后,送入target LLM进行训练,以达到融合多种模型知识,提升目标模型性能的目的。但在实际的实现当中我们会发现,logit-level的alignment,要么是直接采用blending_model_per_step_logits/indices,要么直接用ground-truth one-hot作为融合后的知识,而没有充分评估logit-level中,blending/base_model_per_step_logits之间的差异性。为此,Probabilistic Token Alignment for Large Language Model Fusion提出采用Probabilistic Token Alignment方法,在logit-level实现alignment。
相关文章:

[论文阅读] Knowledge Fusion of Large Language Models
Knowledge Fusion of Large Language Models (FuseLLM) Methodology 整体Pipeline如下图所示 不同的动物代表不同的LLM。左边第一,第二分别是Ensemble以及Weight Merging方法。最右侧为本文提出的FuseLLM。 Ensemble: 融合多个models的预测结果,比如…...

deepseek来讲lua
Lua 是一种轻量级、高效、可嵌入的脚本语言,广泛应用于游戏开发、嵌入式系统、Web 服务器等领域。以下是 Lua 的主要特点和一些基本概念: 1. 特点 轻量级:Lua 的核心非常小,适合嵌入到其他应用程序中。高效:Lua 的执…...

探索 Spring Cloud Alibaba:开启微服务架构新时代
一、引言 在当今数字化浪潮中,软件系统的规模和复杂度不断攀升,传统的单体架构逐渐难以满足快速迭代、高并发处理以及灵活扩展的需求。微服务架构应运而生,它将一个大型的应用拆分成多个小型、自治的服务,每个服务专注于特定的业务…...

【数据结构】(6) LinkedList 链表
一、什么是链表 1、链表与顺序表对比 不同点LinkedListArrayList物理存储上不连续连续随机访问效率O(N)O(1)插入、删除效率O(1)O(N) 3、链表的分类 链表根据结构分类,可分为单向/双向、无头结点/有头节点、非循环/循环链表,这三组每组各取…...

【工具变量】上市公司企业渐进式创新程度及渐进式创新锁定数据(1991-2023年)
测算方式: 参考顶刊《经济研究》孙雅慧(2024)老师的做法,用当期创新和往期创新的内容重叠度作为衡量渐进式创新程度的合理指标。通过搜集海量专利摘要,测算当前专利申请和既有专利的内容相似度,反映企业在…...

07_任务状态——改进播放控制
一、声明 在05和06的程序里面可以达到的一个效果就是很完美的播放音乐,并且不会影响到其它任务的运行,但是这个代码有一个弊端就是要么创建任务从头开始播放要么就直接删除任务。 我们现在的程序就增加了音乐的暂停和恢复的功能,那么能够达到…...

【R语言】apply函数族
在R语言中使用循环操作时是使用自身来实现的,效率较低。所以R语言有一个符合其统计语言出身的特点:向量化。R语言中的向量化运用了底层的C语言,而C语言的效率比高层的R语言的效率高。 apply函数族主要是为了解决数据向量化运算的问题&#x…...

Retrieval-Augmented Generation,检索增强生成流程
RAG流程 用户输入接收 系统接收用户输入的查询问题或文本内容,例如“李白有哪些著名的作品?”用户输入可以通过自然语言处理(NLP)模型的输入端口或用户交互界面(如聊天应用、搜索引擎输入框等)接收。 查询…...

[AI][本地部署]离线升级后报ChromeDb错误
【背景】 升级了OpenWebUI,在离线环境下补足了很多需要的Package后终于成功启动了Backend的服务,但是一旦上传文件,就会报ChromaDb错误,少了Collection这一列云云。 【分析】 两个环境ChromaDb的版本不同,所以怀疑是…...

Pinocchio: 刚体动力学算法库介绍
Pinocchio 是一个高性能的开源刚体动力学计算库,广泛应用于机器人学研究与开发。它主要致力于提供高效、精确的运动学和动力学算法,实现机器人模型的建模、前向运动学、反向动力学、力动力学计算等功能。下面将详细介绍该库的一些关键特点和应用场景。 基…...

电商平台的设计与实现(代码+数据库+LW)
摘 要 如今社会上各行各业,都喜欢用自己行业的专属软件工作,互联网发展到这个时候,人们已经发现离不开了互联网。新技术的产生,往往能解决一些老技术的弊端问题。因为传统商品交易信息管理难度大,容错率低࿰…...

c#对接deepseek 聊天AI接口
注意:不是免费 对接文档:对话补全 | DeepSeek API Docs 注册地址:DeepSeek 申请key 在线请求示例 apifox deepseek - deepseek...
)
Node.js中http模块(二)
一、http模块 http 模块是 Node.js 官方提供的、用来创建 web 服务器的模块。通过 http 模块提供的 http.createServer0) 方法,就能方便的把一台普通的电脑,变成一台 Web 服务器,从而对外提供 Web 资源服务。 二、域名和域名服务器 尽管 I…...

主流顶级域名服务商ZDNS连续十余年跟进国际顶级域名政策制定
顶级域名(TLD,Top-Level Domain)是域名层次结构中的最高层,位于域名最后一段,也即最右边的点(.)之后的字符。品牌顶级域名是顶级域名的一种,以品牌相关名称命名,由品牌所属企业申请、运营、并自由分配二级域名,能够直接反映企业或品牌的形象和特色,如.citic、.中信、.baidu、.联…...

低至3折,百度智能云千帆宣布全面支持DeepSeek-R1/V3调用
DeepSeek-R1和 DeepSeek-V3模型已在百度智能云千帆平台上架 。 出品|产业家 新年伊始,百度智能云又传来新动作 。 2月3日百度智能云宣布, DeepSeek-R1和 DeepSeek-V3模型已在百度智能云千帆平台上架,同步推出超低价格方案,并…...

解释一下数据库中的事务隔离级别,在 Java 中如何通过 JDBC设置事务隔离级别?
数据库中的事务隔离级别是用于控制并发事务之间相互影响的一种机制。 它定义了事务之间的可见性和影响范围,常见的隔离级别包括: 读未提交(Read Uncommitted):最低的隔离级别,事务中的修改即使没有提交也…...

【自动化测试】使用Python selenium类库模拟手人工操作网页
使用Python selenium类库模拟手人工操作网页 背景准备工作安装Python版本安装selenium类库下载selenium驱动配置本地环境变量 自动化脚本输出页面表单自动化填充相关代码 背景 待操作网页必须使用IE浏览器登录访问用户本地只有edge浏览器,通过edge浏览器IE模式访问…...

【Apache Paimon】-- 15 -- 利用 paimon-flink-action 同步 postgresql 表数据
利用 Paimon Schema Evolution 核心特性同步变更的 postgresql 表结构和数据 1、背景信息 在Paimon 诞生以前,若 mysql/pg 等数据源的表结构发生变化时,我们有几种处理方式 (1)人工消息通知,然后手动同步到数据仓库中(2)使用 flink 消费 DDL binlog ,然后自动更新 Hi…...

PostgreSql-COALESCE函数、NULLIF函数、NVL函数使用
COALESCE函数 COALESCE函数是返回参数中的第一个非null的值,它要求参数中至少有一个是非null的; select coalesce(1,null,2),coalesce(null,2,1),coalesce(null,null,null); NULLIF(ex1,ex2)函数 如果ex1与ex2相等则返回Null,不相等返回第一个表达式的值…...

springboot+vue导入ruoyi项目的框架
一、介绍 RuoYi-Vue版本,采用了前后端分离的单体架构设计软件环境:JDK、Mysql、Redis、Maven、Node技术选型: Spring Boot、Spring Security、MyBatis、Jwt、Vue3、Element-Plus官方地址: https://gitee.com/y_project/RuoYi-Vue 官方推荐的版本如下&a…...
c#开发AI模型对话
AI模型 前面已经介绍了一般AI模型本地部署,直接调用现成的模型数据。这里主要讲述讲接口集成到我们自己的程序中使用方式。 微软提供了ML.NET来开发和使用AI模型,但是目前国内可能使用不多,至少实践例子很少看见。开发训练模型就不介绍了&am…...

MySQL用户和授权
开放MySQL白名单 可以通过iptables-save命令确认对应客户端ip是否可以访问MySQL服务: test: # iptables-save | grep 3306 -A mp_srv_whitelist -s 172.16.14.102/32 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 3306 -j ACCEPT -A mp_srv_whitelist -s 172.16.4.16/32 -p tcp -m tcp -…...
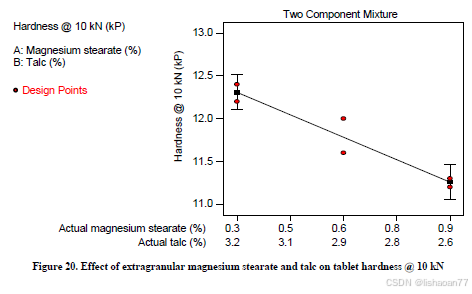
R语言速释制剂QBD解决方案之三
本文是《Quality by Design for ANDAs: An Example for Immediate-Release Dosage Forms》第一个处方的R语言解决方案。 第一个处方研究评估原料药粒径分布、MCC/Lactose比例、崩解剂用量对制剂CQAs的影响。 第二处方研究用于理解颗粒外加硬脂酸镁和滑石粉对片剂质量和可生产…...

Unity VR/MR开发-VR开发与传统3D开发的差异
视频讲解链接:【XR马斯维】VR/MR开发与传统3D开发的差异【UnityVR/MR开发教程--入门】_哔哩哔哩_bilibili...

React父子组件通信:Props怎么用?如何从父组件向子组件传递数据?
系列回顾: 在上一篇《React核心概念:State是什么?》中,我们学习了如何使用useState让一个组件拥有自己的内部数据(State),并通过一个计数器案例,实现了组件的自我更新。这很棒&#…...

深入解析 ReentrantLock:原理、公平锁与非公平锁的较量
ReentrantLock 是 Java 中 java.util.concurrent.locks 包下的一个重要类,用于实现线程同步,支持可重入性,并且可以选择公平锁或非公平锁的实现方式。下面将详细介绍 ReentrantLock 的实现原理以及公平锁和非公平锁的区别。 ReentrantLock 实现原理 基本架构 ReentrantLo…...

基于小程序老人监护管理系统源码数据库文档
摘 要 近年来,随着我国人口老龄化问题日益严重,独居和居住养老机构的的老年人数量越来越多。而随着老年人数量的逐步增长,随之而来的是日益突出的老年人问题,尤其是老年人的健康问题,尤其是老年人产生健康问题后&…...

HTML版英语学习系统
HTML版英语学习系统 这是一个完全免费、无需安装、功能完整的英语学习工具,使用HTML CSS JavaScript实现。 功能 文本朗读练习 - 输入英文文章,系统朗读帮助练习听力和发音,适合跟读练习,模仿学习;实时词典查询 - 双…...

使用VMware克隆功能快速搭建集群
自己搭建的虚拟机,后续不管是学习java还是大数据,都需要集群,java需要分布式的微服务,大数据Hadoop的计算集群,如果从头开始搭建虚拟机会比较费时费力,这里分享一下如何使用克隆功能快速搭建一个集群 先把…...

python打卡day47
昨天代码中注意力热图的部分顺移至今天 知识点回顾: 热力图 作业:对比不同卷积层热图可视化的结果 import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.optim as optim from torchvision import datasets, transforms from torch.utils.data import D…...
