从零实现深度学习框架——再探多层双向RNN的实现
来源:投稿 作者:175
编辑:学姐
往期内容:
从零实现深度学习框架1:RNN从理论到实战(理论篇)
从零实现深度学习框架2:RNN从理论到实战(实战篇)
从零实现深度学习框架3:再探多层双向RNN的实现(本篇)
在前面的文章中,我们实现了多层、双向RNN。但是这几天一直在思考,这种实现方式是不是有问题。因为RNN的实现关乎后面ELMo和seq2seq,所以不得不重视。
双向RNN的实现方式
以两层双向RNN为例。我们之前实现的方式类似如下图所示:
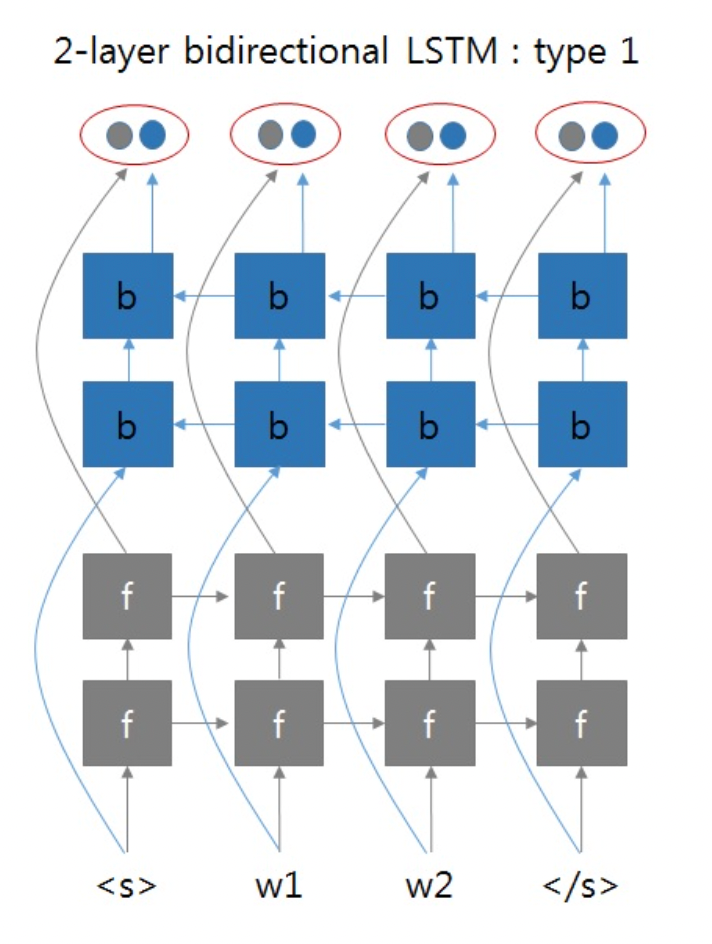
这两张图片来自于:https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/4930#issuecomment-361851298
就是正向RNN和反向RNN可以看成是两个独立的两层RNN网络,最终拼接了它们的输出。但是总感觉双向RNN不会这么简单,带着这个疑问去拜读了双向RNN的论文1,得到下面的这张图片:
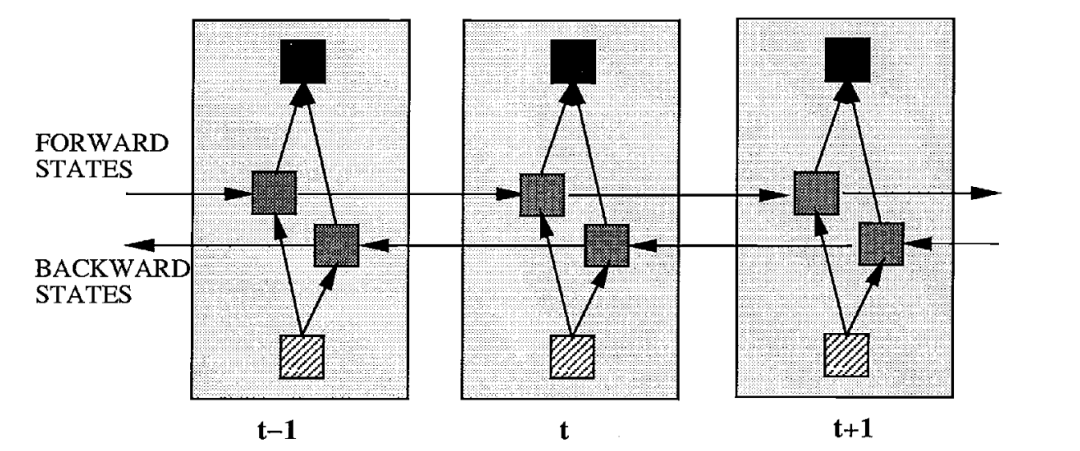
如果采用这种方式的话,那么两层双向RNN的实现应该像下图这样:
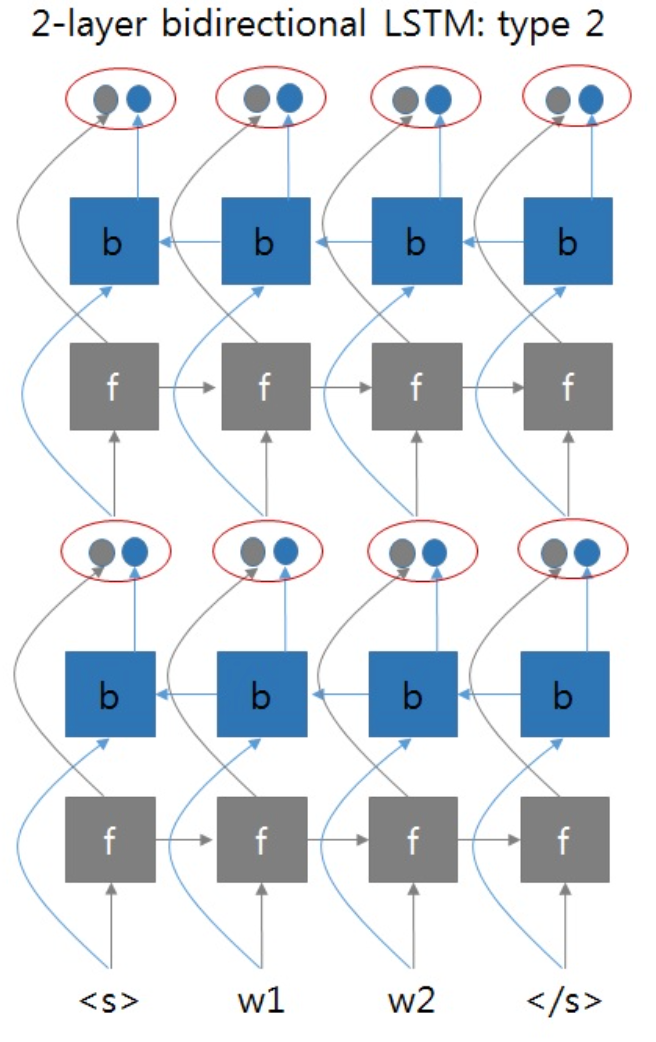
即第一层BRNN的输出同时考虑了正向和方向输出,将它们拼接在一起,作为第二层BRNN的输入。
但是这时遇到了一个问题,如果这样实现的话,那么输出的维度会怎样呢?BRNN中每层参数的维度会产生怎样的变化呢?
遇事不决找Torch,我们摸着PyTorch过河。
带着这个问题,我们去看PyTorch的文档,并查阅资料,梳理一下PyTorch实现的RNN(GRU、LSTM)中各种输入、输出、隐藏状态的维度。
理解RNN中的各种维度
以RNN为例,为什么不以最复杂的LSTM为例呢?因为LSTM参数过多,相比RNN太过复杂,不太容易理解。柿子要挑软的捏,我们理解了RNN,再去理解GRU或LSTM就会简单多了。
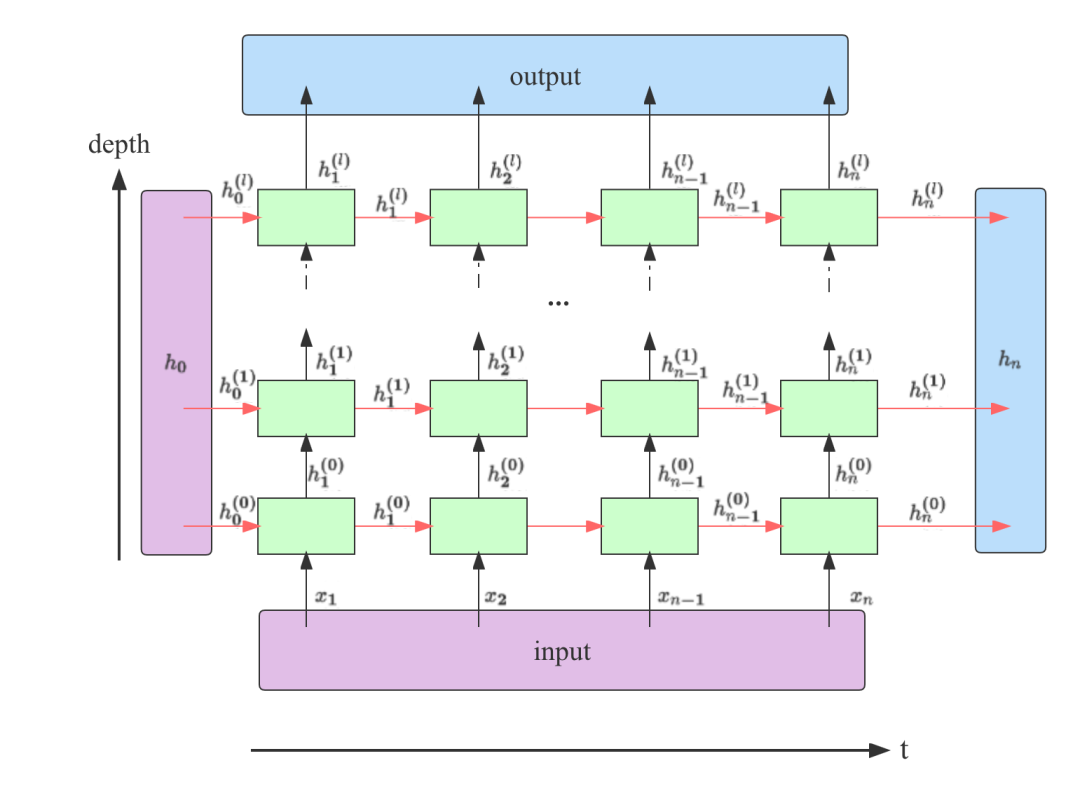
此图片参考了https://stackoverflow.com/a/48305882
从上图可以看出,在一个堆叠了l层的RNN中,output包含了最后一层RNN输出的所有隐藏状态;h_n包含了最后一个时间步上所有层的输出。
我们知道了它们的构成方式,下面看一下它们和上图中另外两个参数input和h_0在不同类型的RNN中维度如何2。
-
inputRNN的输入序列。若batch_first=False,则其大小为(seq_len, batch_size, input_size);若batch_first=True,则其大小为(batch_size, seq_len, input_size); -
h_0RNN的初始隐藏状态,可以为空。大小为(num_layers * num_directions, batch_size, hidden_size); -
outputRNN最后一层所有时间步的输出。若batch_first=False,则其大小为(seq_len, batch_size, num_directions * hidden_size);若batch_first=True,则其大小为(batch_size, seq_len, num_directions * hidden_size); -
h_nRNN中所有层最后一个时间步的隐藏状态。其大小为(num_layers * num_directions, batch_size, hidden_size)。不受batch_first的影响,其批次维度表现和batch_first=False一样。后面以代码实现的角度解释下为何这样,不代表官方的意图。
其中seq_len表示输入序列长度;batch_size表示批次大小;input_size表示输入的特征数量;num_layers表示层数;num_directions表示方向个数,单向RNN时为1,双向RNN时为2;hidden_size表示隐藏状态的特征数。
的形状应该和
是一致的。
下面我们进行验证,首先看一下初始参数:
# 输入大小
INPUT_SIZE = 2
# 序列长度
SEQ_LENGTH = 5
# 隐藏大小
HIDDEN_SIZE = 3
# 批大小
BATCH_SIZE = 4
以及输入:
inputs = Tensor.randn(BATCH_SIZE, SEQ_LENGTH, INPUT_SIZE)
简单RNN
简单RNN就是单向单层RNN:
rnn = nn.RNN(input_size=INPUT_SIZE, hidden_size=HIDDEN_SIZE, num_layers=1, batch_first=True)output, h_n = rnn(inputs)print(f'Input Shape: {inputs.shape} ')
print(f'Output Shape: {output.shape} ')
print(f'Hidden Shape: {h_n.shape} ')
-
inputs维度是我们预先定理好的,注意这里batch_first=True,所以inputs的第一个维度是批大小。 -
output来自最后一层所有时间步的输出,时间步长度为5,包含整个批次内4条数据,每条数据的输出维度为3,可以理解为3分类问题。 -
$h_n$来自单层最后一个时间步的隐藏状态,包含整个批次内4条数据,每条数据的输出维度为3。
Input Shape: (4, 5, 2)
Output Shape: (4, 5, 3)
Hidden Shape: (1, 4, 3)
堆叠RNN
如果将层数改成3,我们就得到了3层RNN堆叠在一起的架构,来看下此时output和h_n的维度会发生怎样的变化。
rnn = nn.RNN(input_size=INPUT_SIZE, hidden_size=HIDDEN_SIZE, num_layers=3, batch_first=True)output, h_n = rnn(inputs)print(f'Input Shape: {inputs.shape} ')
print(f'Output Shape: {output.shape} ')
print(f'Hidden Shape: {h_n.shape} ')
Input Shape: (4, 5, 2)
Output Shape: (4, 5, 3)
Hidden Shape: (3, 4, 3)
-
output来自最后一层所有时间步的输出,时间步长度为5,包含整个批次内4条数据,每条数据的输出维度为3。其维度保持不变。 -
h_n来自所有三层最后一个时间步的隐藏状态,包含整个批次内4条数据,每条数据的输出维度为3。可以看到,其输出的第一个维度大小由1变成了3,因为包含了3层的结果。
双向RNN
传入bidirectional=True,并将层数改回单层。
rnn = nn.RNN(input_size=INPUT_SIZE, hidden_size=HIDDEN_SIZE, num_layers=1, batch_first=True, bidirectional=True)output, h_n = rnn(inputs)print(f'Input Shape: {inputs.shape} ')
print(f'Output Shape: {output.shape} ')
print(f'Hidden Shape: {h_n.shape} ')
Input Shape: (4, 5, 2)
Output Shape: (4, 5, 6)
Hidden Shape: (2, 4, 3)
-
output来自最后一层所有时间步的输出,时间步长度为5,包含整个批次内4条数据,每条数据的输出维度为3,由于是双向,包含了两个方向上的结果,在此维度上进行堆叠,所以由3变成了6。 -
h_n最后一个时间步的隐藏状态,包含整个批次内4条数据,每条数据的输出维度为3。第一个维度由1变成了2,因为在此维度上堆叠了双向的结果。
它们都包含了双向的结果,那如果想分别得到每个方向上的结果,要怎么做呢?
对于output。若batch_first=True,将output按照out.reshape(shape=(batch_size, seq_len, num_directions, hidden_size))进行变形,正向和反向的维度值为别为0和1。
对于h_n,按照h_n.reshape(shape=(num_layers, num_directions, batch_size, hidden_size)),正向和反向的维度值为别为0和1。
我们来对output进行拆分:
# batch_first=True
output_reshaped = output.reshape((BATCH_SIZE, SEQ_LENGTH, 2, HIDDEN_SIZE))
print("Shape of the output after directions are separated: ", output_reshaped.shape)# 分别获取正向和反向的输出
output_forward = output_reshaped[:, :, 0, :]
output_backward = output_reshaped[:, :, 1, :]
print("Forward output Shape: ", output_forward.shape)
print("Backward output Shape: ", output_backward.shape)
Shape of the output after directions are separated: (4, 5, 2, 3)
Forward output Shape: (4, 5, 3)
Backward output Shape: (4, 5, 3)
对h_n进行拆分:
# 1: 层数 2: 方向数
h_n_reshaped = h_n.reshape((1, 2, BATCH_SIZE, HIDDEN_SIZE))
print("Shape of the hidden after directions are separated: ", h_n_reshaped.shape)h_n_forward = h_n_reshaped[:, 0, :, :]
h_n_backward = h_n_reshaped[:, 1, :, :]
print("Forward h_n Shape: ", h_n_forward.shape)
print("Backward h_n Shape: ", h_n_backward.shape)
Shape of the hidden after directions are separated: (1, 2, 4, 3)
Forward h_n Shape: (1, 4, 3)
Backward h_n Shape: (1, 4, 3)
堆叠双向RNN
设置bidirectional=True,并将层数设成3层。
rnn = nn.RNN(input_size=INPUT_SIZE, hidden_size=HIDDEN_SIZE, num_layers=3, batch_first=True, bidirectional=True)output, h_n = rnn(inputs)print(f'Input Shape: {inputs.shape} ')
print(f'Output Shape: {output.shape} ')
print(f'Hidden Shape: {h_n.shape} ')
Input Shape: (4, 5, 2)
Output Shape: (4, 5, 6)
Hidden Shape: (6, 4, 3)
-
output来自最后一层所有时间步的输出,时间步长度为5,包含整个批次内4条数据,每条数据的输出维度为3,由于是双向,包含了两个方向上的结果,在此维度上进行堆叠,所以由3变成了6。 -
h_n来自所有三层最后一个时间步的隐藏状态,包含整个批次内4条数据,每条数据的输出维度为3。第一个维度由变成了6,因为三层输出在此维度上堆叠了双向的结果。
如果我们也对它们按方向进行拆分的话。
首先对output拆分:
# batch_first=True
output_reshaped = output.reshape((BATCH_SIZE, SEQ_LENGTH, 2, HIDDEN_SIZE))
print("Shape of the output after directions are separated: ", output_reshaped.shape)# 分别获取正向和反向的输出
output_forward = output_reshaped[:, :, 0, :]
output_backward = output_reshaped[:, :, 1, :]
print("Forward output Shape: ", output_forward.shape)
print("Backward output Shape: ", output_backward.shape)
Shape of the output after directions are separated: (4, 5, 2, 3)
Forward output Shape: (4, 5, 3)
Backward output Shape: (4, 5, 3)
其次对h_out拆分:
# 3: 层数 2: 方向数
h_n_reshaped = h_n.reshape((3, 2, BATCH_SIZE, HIDDEN_SIZE))
print("Shape of the hidden after directions are separated: ", h_n_reshaped.shape)h_n_forward = h_n_reshaped[:, 0, :, :]
h_n_backward = h_n_reshaped[:, 1, :, :]
print("Forward h_n Shape: ", h_n_forward.shape)
print("Backward h_n Shape: ", h_n_backward.shape)
Shape of the hidden after directions are separated: (3, 2, 4, 3)
Forward h_n Shape: (3, 4, 3)
Backward h_n Shape: (3, 4, 3)
重构双向RNN的实现

我们按照对每层输出状态进行拼接的方式来重构多层双向RNN。
这里有一个问题是,由于我们对隐藏状态进行了拼接, 其维度变成了(n_steps, batch_size, num_directions * hidden_size)。
受到了PyTorch官网启发:
-
~RNN.weight_ih_l[k] – the learnable input-hidden weights of the k-th layer, of shape (hidden_size, input_size) for k = 0. Otherwise, the shape is (hidden_size, num_directions * hidden_size)
-
~RNN.weight_hh_l[k] – the learnable hidden-hidden weights of the k-th layer, of shape (hidden_size, hidden_size)
所以,我们相应地改变输入到隐藏状态的维度:(hidden_size, num_directions * hidden_size)。
我们说 h_n的输出维度不受batch_first的影响,其批次维度表现和batch_first=False一样。这是因为在实现时,为了统一,将input的时间步放到了第1个维度,将批大小放到中间,input就像batch_first=False一样,而隐藏状态的方式和它保持一致即可。
if self.batch_first:batch_size, n_steps, _ = input.shapeinput = input.transpose((1, 0, 2)) # 将batch放到中间维度
下面看具体实现:
RNNCellBase
class RNNCellBase(Module):def reset_parameters(self) -> None:stdv = 1.0 / math.sqrt(self.hidden_size) if self.hidden_size > 0 else 0for weight in self.parameters():init.uniform_(weight, -stdv, stdv)def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size: int, num_chunks: int, bias: bool = True, num_directions=1,reset_parameters=True, device=None, dtype=None) -> None:'''RNN单时间步的抽象:param input_size: 输入x的特征数:param hidden_size: 隐藏状态的特征数:param bias: 线性层是否包含偏置:param nonlinearity: 非线性激活函数 tanh | relu (mode = RNN)'''factory_kwargs = {'device': device, 'dtype': dtype}super(RNNCellBase, self).__init__()self.input_size = input_sizeself.hidden_size = hidden_size# 输入x的线性变换self.input_trans = Linear(num_directions * input_size, num_chunks * hidden_size, bias=bias, **factory_kwargs)# 隐藏状态的线性变换self.hidden_trans = Linear(hidden_size, num_chunks * hidden_size, bias=bias, **factory_kwargs)if reset_parameters:self.reset_parameters()def extra_repr(self) -> str:s = 'input_size={input_size}, hidden_size={hidden_size}'if 'bias' in self.__dict__ and self.bias is not True:s += ', bias={bias}'if 'nonlinearity' in self.__dict__ and self.nonlinearity != "tanh":s += ', nonlinearity={nonlinearity}'return s.format(**self.__dict__)
RNNCell
class RNNCell(RNNCellBase):def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size: int, bias: bool = True, nonlinearity: str = 'tanh', num_directions=1,reset_parameters=True, device=None, dtype=None):factory_kwargs = {'device': device, 'dtype': dtype, 'reset_parameters': reset_parameters}super(RNNCell, self).__init__(input_size, hidden_size, num_chunks=1, bias=bias, num_directions=num_directions,**factory_kwargs)if nonlinearity == 'tanh':self.activation = F.tanhelse:self.activation = F.reludef forward(self, x: Tensor, h: Tensor, c: Tensor = None) -> Tuple[Tensor, None]:h_next = self.activation(self.input_trans(x) + self.hidden_trans(h))return h_next, None
在RNNCell的forward中也返回了一个元组,元组中第二个元素代表了c_next,为了兼容LSTM的实现。
RNNBase
class RNNBase(Module):def __init__(self, cell: RNNCellBase, input_size: int, hidden_size: int, batch_first: bool = False,num_layers: int = 1, bidirectional: bool = False, bias: bool = True, dropout: float = 0,reset_parameters=True, device=None, dtype=None) -> None:''':param input_size: 输入x的特征数:param hidden_size: 隐藏状态的特征数:param batch_first: 批次维度是否在前面:param num_layers: 层数:param bidirectional: 是否为双向:param bias: 线性层是否包含偏置:param dropout: 用于多层堆叠RNN,默认为0代表不使用dropout:param reset_parameters: 是否执行reset_parameters:param device::param dtype:'''super(RNNBase, self).__init__()factory_kwargs = {'device': device, 'dtype': dtype, 'reset_parameters': reset_parameters}self.num_layers = num_layersself.hidden_size = hidden_sizeself.input_size = input_sizeself.batch_first = batch_firstself.bidirectional = bidirectionalself.bias = biasself.num_directions = 2 if self.bidirectional else 1# 支持多层self.cells = ModuleList([cell(input_size, hidden_size, bias, **factory_kwargs)] +[cell(hidden_size, hidden_size, bias, num_directions=self.num_directions,**factory_kwargs) for _ inrange(num_layers - 1)])if self.bidirectional:# 支持双向self.back_cells = copy.deepcopy(self.cells)self.dropout = dropoutif dropout != 0:# Dropout层self.dropout_layer = Dropout(dropout)def _one_directional_op(self, input, n_steps, cell, h, c) -> Tuple[Tensor, Tensor, Tensor]:hs = []# 沿着input时间步进行遍历for t in range(n_steps):inp = input[t]h, c = cell(inp, h, c)hs.append(h)return h, c, F.stack(hs)def _handle_hidden_state(self, input, state):assert input.ndim == 3 # 必须传入批数据,最小批大小为1if self.batch_first:batch_size, n_steps, _ = input.shapeinput = input.transpose((1, 0, 2)) # 将batch放到中间维度else:n_steps, batch_size, _ = input.shapeif state is None:h = Tensor.zeros((self.num_layers * self.num_directions, batch_size, self.hidden_size), dtype=input.dtype,device=input.device)else:h = state# 得到每层的状态hs = list(F.unbind(h)) # 按层数拆分hreturn hs, [None] * len(hs), input, n_steps, batch_sizedef forward(self, input: Tensor, state: Tensor) -> Tuple[Tensor, Tensor, Tensor]:'''RNN的前向传播:param input: 形状 [n_steps, batch_size, input_size] 若batch_first=False:param state: (隐藏状态,单元状态)元组, 每个元素形状 [num_layers, batch_size, hidden_size]:return:num_directions = 2 if self.bidirectional else 1output: (n_steps, batch_size, num_directions * hidden_size)若batch_first=False 或(batch_size, n_steps, num_directions * hidden_size)若batch_first=True包含每个时间步最后一层(多层RNN)的输出h_th_n: (num_directions * num_layers, batch_size, hidden_size) 包含最终隐藏状态c_n: (num_directions * num_layers, batch_size, hidden_size) 包含最终单元状态(LSTM);非LSTM为None'''hs, cs, input, n_steps, batch_size = self._handle_hidden_state(input, state)# 正向得到的h_n,反向得到的h_n,正向得到的c_n,反向得到的c_nh_n_f, h_n_b, c_n_f, c_n_b = [], [], [], []for layer in range(self.num_layers):h, c, hs_f = self._one_directional_op(input, n_steps, self.cells[layer], hs[layer], cs[layer])h_n_f.append(h) # 保存最后一个时间步的隐藏状态c_n_f.append(c)if self.bidirectional:h, c, hs_b = self._one_directional_op(F.flip(input, 0), n_steps, self.back_cells[layer],hs[layer + self.num_layers], cs[layer + self.num_layers])hs_b = F.flip(hs_b, 0) # 将输出时间步维度逆序,使得时间步t=0上,是看了整个序列的结果。# 拼接两个方向上的输入h_n_b.append(h)c_n_b.append(c)input = F.cat([hs_f, hs_b], 2) # (n_steps, batch_size, num_directions * hidden_size)else:input = hs_f # (n_steps, batch_size, num_directions * hidden_size)# 在第1层之后,最后一层之前需要经过dropoutif self.dropout and layer != self.num_layers - 1:input = self.dropout_layer(input)output = input # (n_steps, batch_size, num_directions * hidden_size) 最后一层最后计算的输入,就是它的输出c_n = Noneif self.bidirectional:h_n = F.cat([F.stack(h_n_f), F.stack(h_n_b)], 0)if c is not None:c_n = F.cat([F.stack(c_n_f), F.stack(c_n_b)], 0)else:h_n = F.stack(h_n_f)if c is not None:c_n = F.stack(c_n_f)if self.batch_first:output = output.transpose((1, 0, 2))return output, h_n, c_ndef extra_repr(self) -> str:s = 'input_size={input_size}, hidden_size={hidden_size}'if self.num_layers != 1:s += ', num_layers={num_layers}'if self.bias is not True:s += ', bias={bias}'if self.batch_first is not False:s += ', batch_first={batch_first}'if self.dropout:s += ', dropout={dropout}'if self.bidirectional is not False:s += ', bidirectional={bidirectional}'return s.format(**self.__dict__)
同样,做了兼容LSTM的实现,会多了一些if判断。
RNN
class RNN(RNNBase):def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs) -> None:''':param input_size: 输入x的特征数:param hidden_size: 隐藏状态的特征数:param batch_first::param num_layers: 层数:param bidirectional: 是否为双向:param bias: 线性层是否包含偏置:param dropout: 用于多层堆叠RNN,默认为0代表不使用dropout:param nonlinearity: 非线性激活函数 tanh | relu'''super(RNN, self).__init__(RNNCell, *args, **kwargs)def forward(self, input: Tensor, state: Tensor = None) -> Tuple[Tensor, Tensor]:output, h_n, _ = super().forward(input, state)return output, h_n
因为基类RNNBase的forward会返回output,h_n,c_n,所以RNN这里重写了forward方法,仅返回output和h_n。
通过这种方式实现GRU和RNN非常类似。
GRU
class GRU(RNNBase):def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):''':param input_size: 输入x的特征数:param hidden_size: 隐藏状态的特征数:param batch_first::param num_layers: 层数:param bidirectional: 是否为双向:param bias: 线性层是否包含偏置:param dropout: 用于多层堆叠RNN,默认为0代表不使用dropout'''super(GRU, self).__init__(GRUCell, *args, **kwargs)def forward(self, input: Tensor, state: Tensor = None) -> Tuple[Tensor, Tensor]:output, h_n, _ = super().forward(input, state)return output, h_n
实例测试
同样的配置下:
embedding_dim = 128
hidden_dim = 128
batch_size = 32
num_epoch = 10
n_layers = 2
dropout = 0.2model = RNN(len(vocab), embedding_dim, hidden_dim, num_class, n_layers, dropout, bidirectional=True, mode=mode)
两层双向RNN可以得到75%的准确率。
Training Epoch 0: 94it [01:16, 1.23it/s]
Loss: 220.78
Training Epoch 1: 94it [01:16, 1.24it/s]
Loss: 151.85
Training Epoch 2: 94it [01:14, 1.26it/s]
Loss: 125.62
Training Epoch 3: 94it [01:15, 1.25it/s]
Loss: 110.55
Training Epoch 4: 94it [01:14, 1.27it/s]
Loss: 100.75
Training Epoch 5: 94it [01:13, 1.28it/s]
Loss: 94.12
Training Epoch 6: 94it [01:12, 1.29it/s]
Loss: 88.64
Training Epoch 7: 94it [01:12, 1.29it/s]
Loss: 84.51
Training Epoch 8: 94it [01:13, 1.28it/s]
Loss: 80.83
Training Epoch 9: 94it [01:13, 1.27it/s]
Loss: 78.12
Testing: 29it [00:06, 4.79it/s]
Acc: 0.75
Cost:749.8793613910675
完整代码
https://github.com/nlp-greyfoss/metagrad
References
Bidirectional recurrent neural networkshttps://www.researchgate.net/publication/3316656_Bidirectional_recurrent_neural_networks
Pytorch [Basics] — Intro to
RNNhttps://towardsdatascience.com/pytorch-basics-how-to-train-your-neural-net-intro-to-rnn-cb6ebc594677
关注下方《学姐带你玩AI》🚀🚀🚀
220+篇AI必读论文免费领取
码字不易,欢迎大家点赞评论收藏!
相关文章:

从零实现深度学习框架——再探多层双向RNN的实现
来源:投稿 作者:175 编辑:学姐 往期内容: 从零实现深度学习框架1:RNN从理论到实战(理论篇) 从零实现深度学习框架2:RNN从理论到实战(实战篇) 从零实现深度…...
Flink 连接流详解
连接流 1 Union 最简单的合流操作,就是直接将多条流合在一起,叫作流的“联合”(union)。联合操作要求必须流中的数据类型必须相同,合并之后的新流会包括所有流中的元素,数据类型不变。这种合流方式非常简…...

分享112个HTML电子商务模板,总有一款适合您
分享112个HTML电子商务模板,总有一款适合您 112个HTML电子商务模板下载链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/13wf9C9NtaJz67ZqwQyo74w?pwdzt4a 提取码:zt4a Python采集代码下载链接:采集代码.zip - 蓝奏云 有机蔬菜水果食品商城网…...
)
2023备战金三银四,Python自动化软件测试面试宝典合集(八)
马上就又到了程序员们躁动不安,蠢蠢欲动的季节~这不,金三银四已然到了家门口,元宵节一过后台就有不少人问我:现在外边大厂面试都问啥想去大厂又怕面试挂面试应该怎么准备测试开发前景如何面试,一个程序员成长之路永恒绕…...

J-Link RTT Viewer使用教程(附代码)
目录 RTT(Real Time Transfer)简介 使用教程 常用API介绍 RTT缓冲大小修改 使用printf重定向 官方例程 RTT(Real Time Transfer)简介 平常调试代码中使用串口打印log,往往需要接出串口引脚,比较麻烦,并且串口打印速度较慢,串…...
C语言——指针、数组的经典笔试题目
文章目录前言1.一维数组2.字符数组3.二维数组4.经典指针试题前言 1、数组名通常表示首元素地址,sizeof(数组名)和&数组名两种情况下,数组名表示整个数组。 2、地址在内存中唯一标识一块空间,大小是4/8字节。32位平台4字节,64位…...
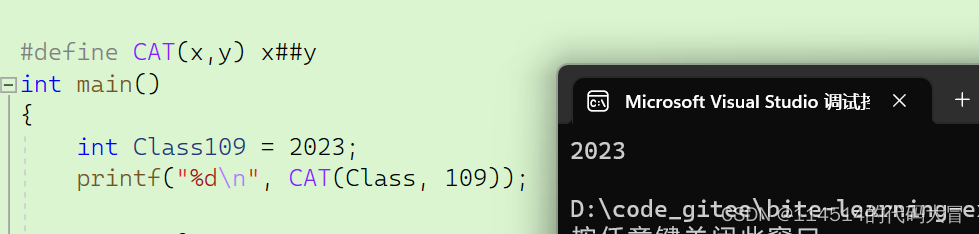
【C语言】程序环境和预处理|预处理详解|定义宏(上)
主页:114514的代码大冒险 qq:2188956112(欢迎小伙伴呀hi✿(。◕ᴗ◕。)✿ ) Gitee:庄嘉豪 (zhuang-jiahaoxxx) - Gitee.com 文章目录 目录 文章目录 前言 一、程序的翻译环境和执行环境 二、详解编译和链接 1.翻译环境 2.编…...

上海霄腾自动化装备盛装亮相2023生物发酵展
上海霄腾自动化携液体膏体粉剂颗粒等灌装生产线解决方案亮相2023生物发酵展BIO CHINA2023生物发酵展,作为生物发酵产业一年一度行业盛会,由中国生物发酵产业协会主办,上海信世展览服务有限公司承办,2023第10届国际生物发酵产品与技…...

python+flask开发mock服务
目录 什么是mock? 什么时候需要用到mock? 如何实现? pythonflask自定义mock服务的步骤 一、环境搭建 1、安装flask插件 2、验证插件 二、mock案例 1、模拟 返回结果 2、模拟 异常响应状态码 3、模拟登录,从jmeter中获取…...
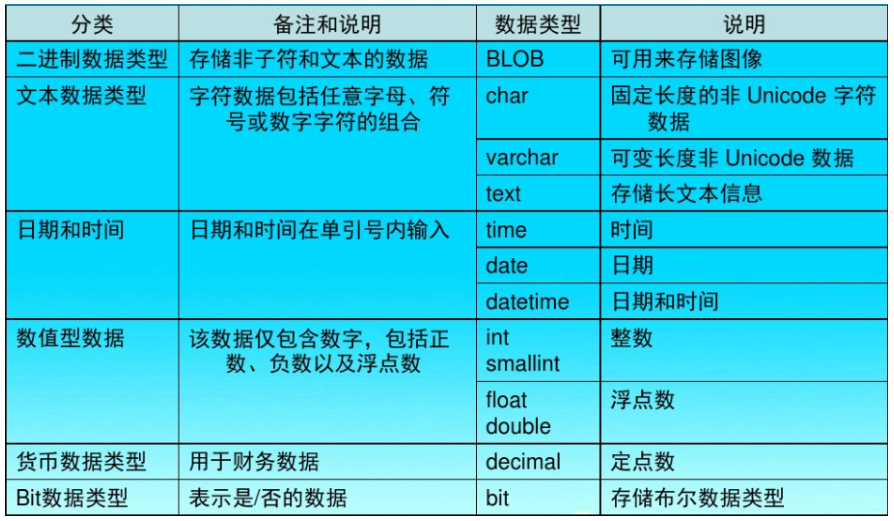
数据库(三)
第三章 MySQL库表操作 3.1 SQL语句基础 3.1.1 SQL简介 SQL:结构化查询语言(Structured Query Language),在关系型数据库上执行数据操作、数据检索以及数据维护的标准语言。使用SQL语句,程序员和数据库管理员可以完成如下的任务。 改变数据…...

2023软考纸质证书领取通知来了!
不少同学都在关注2022下半年软考证书领取时间,截止至目前,上海、湖北、江苏、南京、安徽、山东、浙江、宁波、江西、贵州、云南、辽宁、大连、吉林、广西地区的纸质证书可以领取了。将持续更新2022下半年软考纸质证书领取时间,请同学们在证书…...
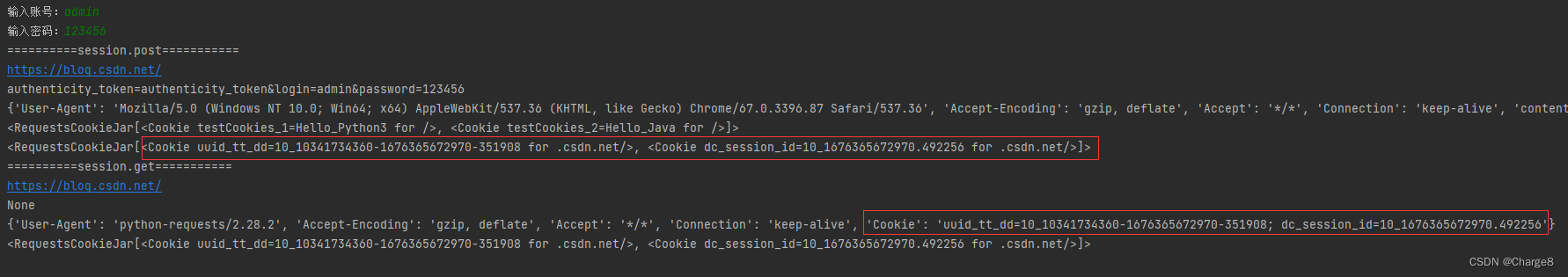
Python requests模块
一、requests模块简介 requests模块是一个第三方模块,需要在python环境中安装: pip install requests 该模块主要用来发送 HTTP 请求,requests 模块比 urllib 模块更简洁。 requests模块支持: 自动处理url编码自动处理post请求…...

工业智能网关解决方案:物联网仓储环境监测系统
仓储是连接生产、供应和销售的中转系统,对于促进生产、提高效率有着重要的辅助作用。对于很多大型工厂或食品厂来说,需要对仓储环境进行严控的控制,以确保产品或食品的质量,避免不必要的产品损耗,提高产品存管的水平。…...
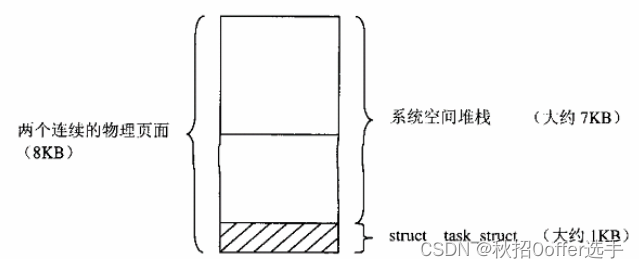
Linux进程线程管理
目录 存储管理 linux内存管理基本框架 系统空间管理和用户空间管理 进程与进程调度 进程四要素 用户堆栈的扩展 进程三部曲:创建,执行,消亡 系统调用exit(),wait() 内核中的互斥操作 存储管理 linux内存管理基本框架 系统空间管理…...

分享111个HTML电子商务模板,总有一款适合您
分享111个HTML电子商务模板,总有一款适合您 111个HTML电子商务模板下载链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1e8Wp1Rl9RaFrcW0bilIatg?pwdc97h 提取码:c97h Python采集代码下载链接:采集代码.zip - 蓝奏云 HTML5家居家具电子商务网…...

百度前端必会手写面试题整理
请实现一个 add 函数,满足以下功能 add(1); // 1 add(1)(2); // 3 add(1)(2)(3);// 6 add(1)(2, 3); // 6 add(1, 2)(3); // 6 add(1, 2, 3); // 6function add(...args) {// 在内部声明一个函数,利用闭包的特性保存并收集…...
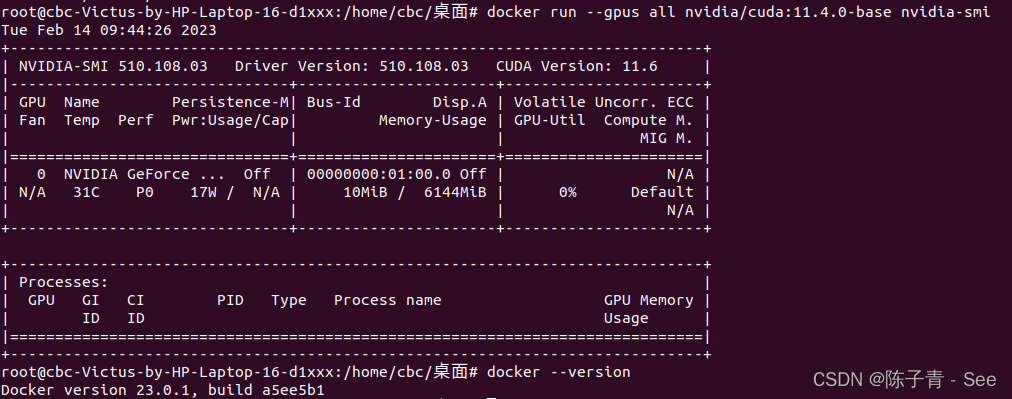
ubuntu 安装支持GPU的Docker详细步骤
安装依赖项 sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install -y apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl gnupg-agent software-properties-common 添加 Docker GPG 密钥 curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add - sudo apt-key fingerpr…...
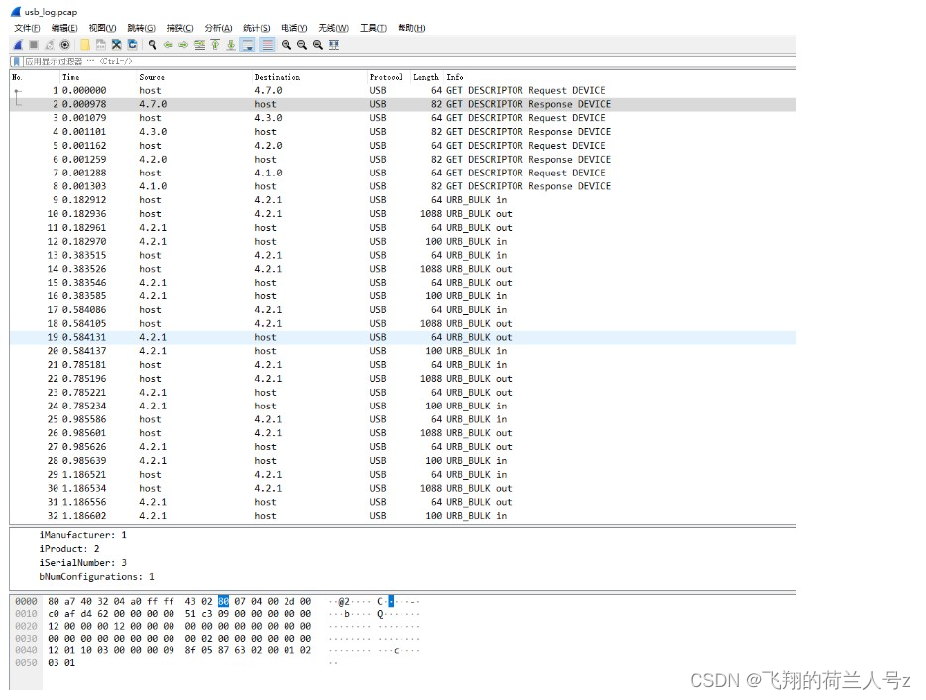
usbmon+tcpdump+wireshark USB抓包
文章目录usbmon抓包及配合wireshark解析usbmon抓包及配合wireshark解析 usbmon首先编译为内核模块,然后通过modprobe usbmon加载到linux sys文件系统中 rootroot-PC:~# modprobe usbmon 而后 linux系统下安装 tcpdump rootroot-PC:~# apt-get install tcpdump…...
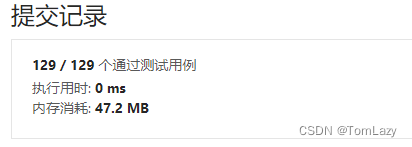
【LeetCode】剑指 Offer 04. 二维数组中的查找 p44 -- Java Version
题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/er-wei-shu-zu-zhong-de-cha-zhao-lcof/ 1. 题目介绍(04. 二维数组中的查找) 在一个 n * m 的二维数组中,每一行都按照从左到右 非递减 的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下 非递…...
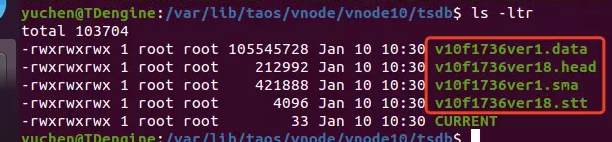
TDengine 3.0.2.5 查询再优化!揭秘索引文件的工作原理
TDengine 3.0 虽然对底层做了大规模的优化重构,但是相对于数据文件的工作逻辑和 2.0 相比是整体保持不变的。本系列文章的主旨在于帮助用户深入理解产品,并且拥有基本的性能调试思路,从而获得更好的产品体验。本期文章会在讲解 TDengine 时序…...

C++_核心编程_多态案例二-制作饮品
#include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;/*制作饮品的大致流程为:煮水 - 冲泡 - 倒入杯中 - 加入辅料 利用多态技术实现本案例,提供抽象制作饮品基类,提供子类制作咖啡和茶叶*//*基类*/ class AbstractDr…...
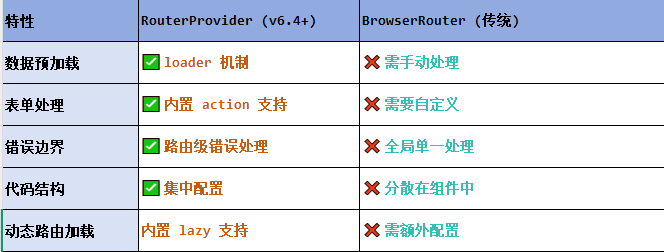
React第五十七节 Router中RouterProvider使用详解及注意事项
前言 在 React Router v6.4 中,RouterProvider 是一个核心组件,用于提供基于数据路由(data routers)的新型路由方案。 它替代了传统的 <BrowserRouter>,支持更强大的数据加载和操作功能(如 loader 和…...

vue3 字体颜色设置的多种方式
在Vue 3中设置字体颜色可以通过多种方式实现,这取决于你是想在组件内部直接设置,还是在CSS/SCSS/LESS等样式文件中定义。以下是几种常见的方法: 1. 内联样式 你可以直接在模板中使用style绑定来设置字体颜色。 <template><div :s…...

C# 类和继承(抽象类)
抽象类 抽象类是指设计为被继承的类。抽象类只能被用作其他类的基类。 不能创建抽象类的实例。抽象类使用abstract修饰符声明。 抽象类可以包含抽象成员或普通的非抽象成员。抽象类的成员可以是抽象成员和普通带 实现的成员的任意组合。抽象类自己可以派生自另一个抽象类。例…...

Python+ZeroMQ实战:智能车辆状态监控与模拟模式自动切换
目录 关键点 技术实现1 技术实现2 摘要: 本文将介绍如何利用Python和ZeroMQ消息队列构建一个智能车辆状态监控系统。系统能够根据时间策略自动切换驾驶模式(自动驾驶、人工驾驶、远程驾驶、主动安全),并通过实时消息推送更新车…...

区块链技术概述
区块链技术是一种去中心化、分布式账本技术,通过密码学、共识机制和智能合约等核心组件,实现数据不可篡改、透明可追溯的系统。 一、核心技术 1. 去中心化 特点:数据存储在网络中的多个节点(计算机),而非…...

Python实现简单音频数据压缩与解压算法
Python实现简单音频数据压缩与解压算法 引言 在音频数据处理中,压缩算法是降低存储成本和传输效率的关键技术。Python作为一门灵活且功能强大的编程语言,提供了丰富的库和工具来实现音频数据的压缩与解压。本文将通过一个简单的音频数据压缩与解压算法…...
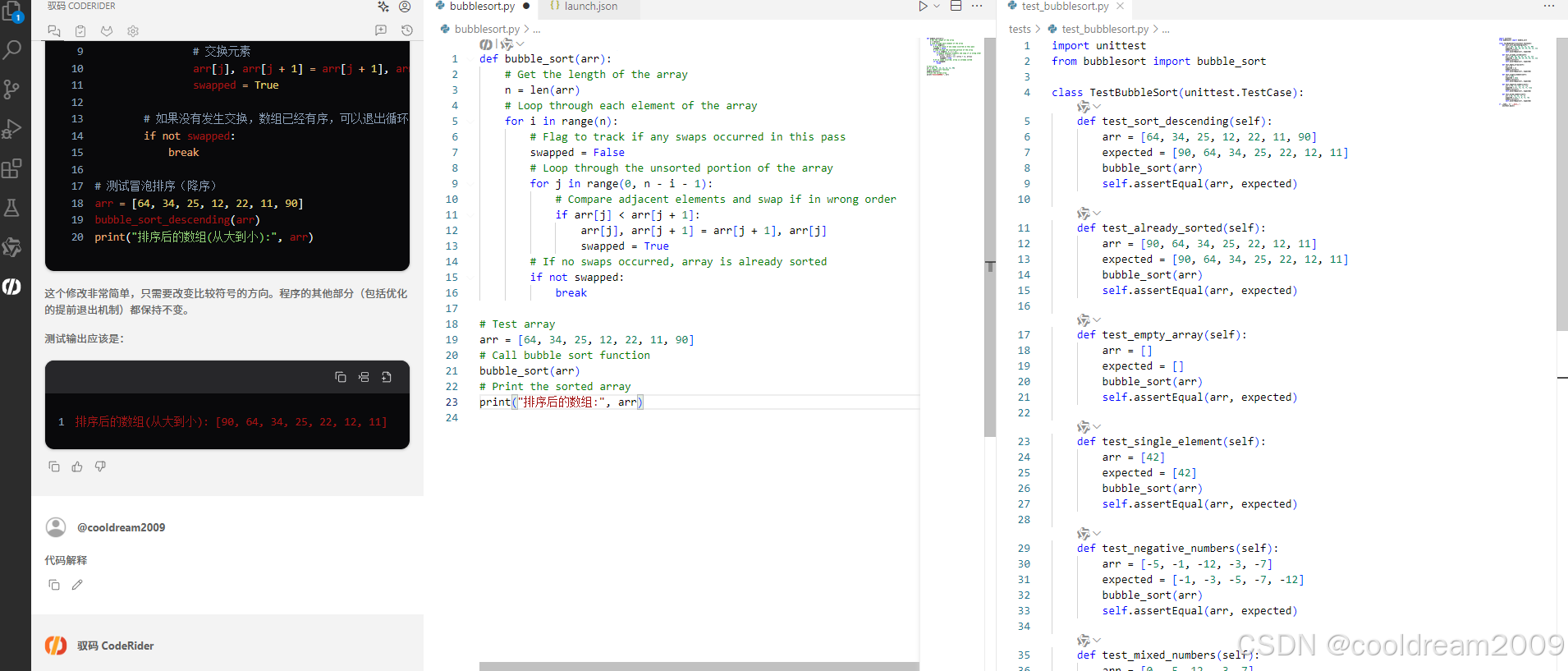
在 Visual Studio Code 中使用驭码 CodeRider 提升开发效率:以冒泡排序为例
目录 前言1 插件安装与配置1.1 安装驭码 CodeRider1.2 初始配置建议 2 示例代码:冒泡排序3 驭码 CodeRider 功能详解3.1 功能概览3.2 代码解释功能3.3 自动注释生成3.4 逻辑修改功能3.5 单元测试自动生成3.6 代码优化建议 4 驭码的实际应用建议5 常见问题与解决建议…...

TJCTF 2025
还以为是天津的。这个比较容易,虽然绕了点弯,可还是把CP AK了,不过我会的别人也会,还是没啥名次。记录一下吧。 Crypto bacon-bits with open(flag.txt) as f: flag f.read().strip() with open(text.txt) as t: text t.read…...

Django RBAC项目后端实战 - 03 DRF权限控制实现
项目背景 在上一篇文章中,我们完成了JWT认证系统的集成。本篇文章将实现基于Redis的RBAC权限控制系统,为系统提供细粒度的权限控制。 开发目标 实现基于Redis的权限缓存机制开发DRF权限控制类实现权限管理API配置权限白名单 前置配置 在开始开发权限…...
