Integer源码
介绍
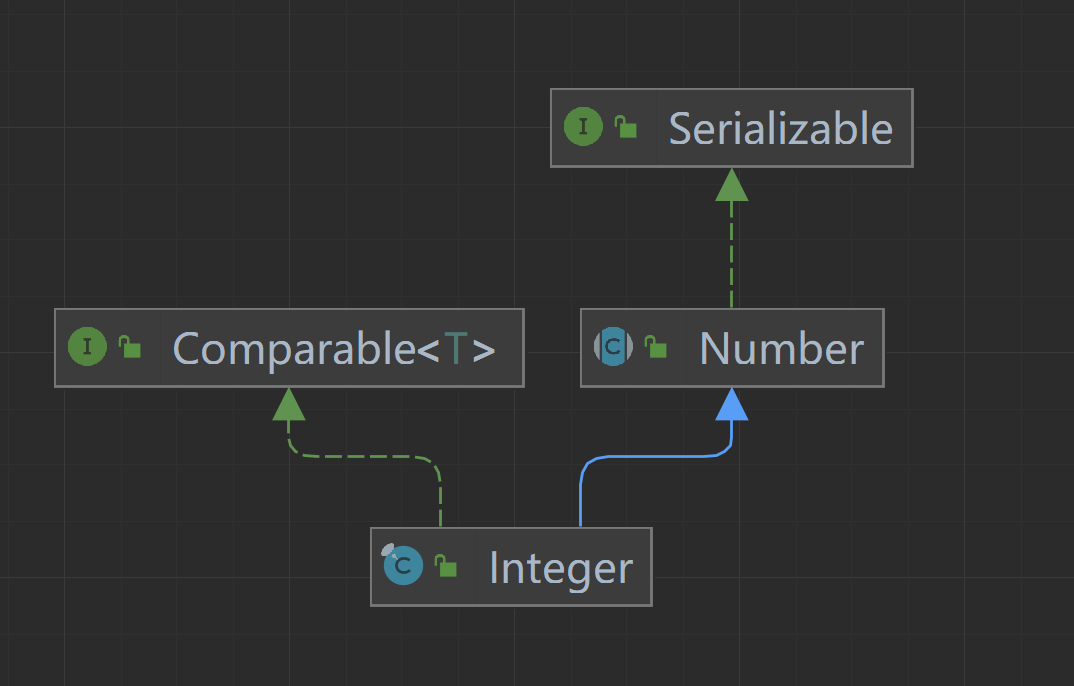
Integer是int类型的包装类,继承自Number抽象类,实现了Comparable接口。提供了一些处理int类型的方法,比如int到String类型的转换方法或String类型到int类型的转换方法,当然也包含与其他类型之间的转换方法。
- Comparable提供了比较大小的功能
- Number抽象类主要抽象出了对数值类型的转换方法。
public final class Integer extends Number implements Comparable<Integer>
常量&变量
/*** A constant holding the minimum value an {@code int} can* have, -2<sup>31</sup>.*最小值0x80000000*/@Native public static final int MIN_VALUE = 0x80000000;/*** A constant holding the maximum value an {@code int} can* have, 2<sup>31</sup>-1.* 最大值0x7fffffff*/@Native public static final int MAX_VALUE = 0x7fffffff;/*** The {@code Class} instance representing the primitive type* {@code int}.** @since JDK1.1* int的原始类型*/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public static final Class<Integer> TYPE = (Class<Integer>) Class.getPrimitiveClass("int");/*** All possible chars for representing a number as a String* 数字表示为字符串的所有可能字符*/final static char[] digits = {'0' , '1' , '2' , '3' , '4' , '5' ,'6' , '7' , '8' , '9' , 'a' , 'b' ,'c' , 'd' , 'e' , 'f' , 'g' , 'h' ,'i' , 'j' , 'k' , 'l' , 'm' , 'n' ,'o' , 'p' , 'q' , 'r' , 's' , 't' ,'u' , 'v' , 'w' , 'x' , 'y' , 'z'};//使用DigitOnes和DigitTens来确定一个两位数int对应的char//十位数final static char [] DigitTens = {'0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0','1', '1', '1', '1', '1', '1', '1', '1', '1', '1','2', '2', '2', '2', '2', '2', '2', '2', '2', '2','3', '3', '3', '3', '3', '3', '3', '3', '3', '3','4', '4', '4', '4', '4', '4', '4', '4', '4', '4','5', '5', '5', '5', '5', '5', '5', '5', '5', '5','6', '6', '6', '6', '6', '6', '6', '6', '6', '6','7', '7', '7', '7', '7', '7', '7', '7', '7', '7','8', '8', '8', '8', '8', '8', '8', '8', '8', '8','9', '9', '9', '9', '9', '9', '9', '9', '9', '9',} ;//个位数final static char [] DigitOnes = {'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9','0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9','0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9','0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9','0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9','0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9','0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9','0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9','0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9','0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',} ;//位数上限的数组final static int [] sizeTable = { 9, 99, 999, 9999, 99999, 999999, 9999999,99999999, 999999999, Integer.MAX_VALUE };/*** The value of the {@code Integer}.** @serial* 存储的int值*/private final int value;/*** The number of bits used to represent an {@code int} value in two's* complement binary form.** @since 1.5* 占用bit位*/@Native public static final int SIZE = 32;/*** The number of bytes used to represent a {@code int} value in two's* complement binary form.** @since 1.8* 占用字节数*/public static final int BYTES = SIZE / Byte.SIZE;/** use serialVersionUID from JDK 1.0.2 for interoperability *///序列化版本号@Native private static final long serialVersionUID = 1360826667806852920L;
-
value:表示Integer对应的int值。
-
MIN_VALUE:定义一个常量,表示int类型的最小值,-2^31,@Native 表示被注解的内容是原生,不影响java代码的本身逻辑。
-
MAX_VALUE:定义一个常量,表示int类型的最大值,2^31-1。
-
TYPE:表示这个包装类包装的是基本类型int。
-
Size:定义常量,用于以二进制补码形式表示int值的位数。
-
BYTES:定义常量,用于以二进制补码形式表示int值的字节数。
-
digits:表示所有可能用来表示数字的字符,因为int是支持2-36进制,所以需要36个字符在表示不同的数字。
-
DigitOnes和DigitTens:使用DigitOnes和DigitTens来确定一个两位数int对应的char。如65,DigitOnes[65]=5,DigitTens[65]=6。
-
sizeTable:主要用来计算一个int类型对应字符串的长度。如下的stringSize方法
构造方法
/*** Constructs a newly allocated {@code Integer} object that* represents the specified {@code int} value.** @param value the value to be represented by the* {@code Integer} object.*/public Integer(int value) {this.value = value;}/*** Constructs a newly allocated {@code Integer} object that* represents the {@code int} value indicated by the* {@code String} parameter. The string is converted to an* {@code int} value in exactly the manner used by the* {@code parseInt} method for radix 10.** @param s the {@code String} to be converted to an* {@code Integer}.* @exception NumberFormatException if the {@code String} does not* contain a parsable integer.* @see java.lang.Integer#parseInt(java.lang.String, int)*/public Integer(String s) throws NumberFormatException {this.value = parseInt(s, 10);}
常用方法
toString
将int转成字符串
/*** Returns a {@code String} object representing this* {@code Integer}'s value. The value is converted to signed* decimal representation and returned as a string, exactly as if* the integer value were given as an argument to the {@link* java.lang.Integer#toString(int)} method.** @return a string representation of the value of this object in* base 10.*/public String toString() {return toString(value);}
/*** Returns a {@code String} object representing the* specified integer. The argument is converted to signed decimal* representation and returned as a string, exactly as if the* argument and radix 10 were given as arguments to the {@link* #toString(int, int)} method.** @param i an integer to be converted.* @return a string representation of the argument in base 10.*/public static String toString(int i) {//int的最小值if (i == Integer.MIN_VALUE)return "-2147483648";//调用stringSize计算int值对应字符串的长度,负数有一个符号位所以要+1int size = (i < 0) ? stringSize(-i) + 1 : stringSize(i);//新建一个临时数组,用来存放int值每一位转成char后的值char[] buf = new char[size];//将int值每一位转成char放到buf中getChars(i, size, buf);return new String(buf, true);}
/*** Returns a string representation of the first argument in the* radix specified by the second argument.** <p>If the radix is smaller than {@code Character.MIN_RADIX}* or larger than {@code Character.MAX_RADIX}, then the radix* {@code 10} is used instead.** <p>If the first argument is negative, the first element of the* result is the ASCII minus character {@code '-'}* ({@code '\u005Cu002D'}). If the first argument is not* negative, no sign character appears in the result.** <p>The remaining characters of the result represent the magnitude* of the first argument. If the magnitude is zero, it is* represented by a single zero character {@code '0'}* ({@code '\u005Cu0030'}); otherwise, the first character of* the representation of the magnitude will not be the zero* character. The following ASCII characters are used as digits:** <blockquote>* {@code 0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz}* </blockquote>** These are {@code '\u005Cu0030'} through* {@code '\u005Cu0039'} and {@code '\u005Cu0061'} through* {@code '\u005Cu007A'}. If {@code radix} is* <var>N</var>, then the first <var>N</var> of these characters* are used as radix-<var>N</var> digits in the order shown. Thus,* the digits for hexadecimal (radix 16) are* {@code 0123456789abcdef}. If uppercase letters are* desired, the {@link java.lang.String#toUpperCase()} method may* be called on the result:** <blockquote>* {@code Integer.toString(n, 16).toUpperCase()}* </blockquote>** @param i an integer to be converted to a string.* @param radix the radix to use in the string representation.* @return a string representation of the argument in the specified radix.* @see java.lang.Character#MAX_RADIX* @see java.lang.Character#MIN_RADIX*/public static String toString(int i, int radix) {//当基数小于2或大于36,radix默认为10进制if (radix < Character.MIN_RADIX || radix > Character.MAX_RADIX)radix = 10;/* Use the faster version *///当基数为10时,直接调用toString方法后返回if (radix == 10) {return toString(i);}//因为int最大为32位(2进制占的位数),所以只需要33位就可以存储int+符号位char buf[] = new char[33];boolean negative = (i < 0);int charPos = 32;//将正数转换为负数if (!negative) {i = -i;}//循环 当负值i 依然小于 负值radixwhile (i <= -radix) {//buf[32] = digits[]buf[charPos--] = digits[-(i % radix)];i = i / radix;}buf[charPos] = digits[-i];//i小于0,符号标志位为'-'if (negative) {buf[--charPos] = '-';}return new String(buf, charPos, (33 - charPos));}
stringSize
获取一个int值对应字符串的长度
// Requires positive x//返回位数 利用sizeTable属性,可以高效的获取一个int值对应字符串你的长度,不用过多的除法或取模运算static int stringSize(int x) {for (int i=0; ; i++)if (x <= sizeTable[i])return i+1;}
getChars
在toString方法中调用,主要作用是,将int值的每一位转成char后放到buf中。
/*** Places characters representing the integer i into the* character array buf. The characters are placed into* the buffer backwards starting with the least significant* digit at the specified index (exclusive), and working* backwards from there.** Will fail if i == Integer.MIN_VALUE*/static void getChars(int i, int index, char[] buf) {int q, r;//buf数组的长度int charPos = index;//符号标志位char sign = 0;//当i小于0时,if (i < 0) {//定义符号位‘-’sign = '-';//将负值i取反i = -i;}// Generate two digits per iteration//①如果i大于65536(两个字节的长度)那么就去除i的后两位while (i >= 65536) {//去除i的后两位赋值给q 比如i为65536,那么q为655q = i / 100;// really: r = i - (q * 100);//②计算后两位的值,如果i为65537,那么r为37,公式 r = 65537 - (655 * 100)r = i - ((q << 6) + (q << 5) + (q << 2));//去除后两位重新赋值ii = q;//通过DigitOnes和DigitTens获取r的个位和十位对应的char。buf [--charPos] = DigitOnes[r];buf [--charPos] = DigitTens[r];}// Fall thru to fast mode for smaller numbers// assert(i <= 65536, i);//经过上面循环,i小于等于65536for (;;) {//③就是q = i/10,如果i=655,那么q=65q = (i * 52429) >>> (16+3);//取i的最后一位 r= 655 - (65 * 10) = 5r = i - ((q << 3) + (q << 1)); // r = i-(q*10) ...//通过digits数组获取对应的charbuf [--charPos] = digits [r];// q=65,并赋值给i,进入下一个循环i = q;if (i == 0) break;}//符号标志为不为0 即为‘-’if (sign != 0) {//数组下标为0的char为‘-’buf [--charPos] = sign;}}
parseInt
/*** Parses the string argument as a signed integer in the radix* specified by the second argument. The characters in the string* must all be digits of the specified radix (as determined by* whether {@link java.lang.Character#digit(char, int)} returns a* nonnegative value), except that the first character may be an* ASCII minus sign {@code '-'} ({@code '\u005Cu002D'}) to* indicate a negative value or an ASCII plus sign {@code '+'}* ({@code '\u005Cu002B'}) to indicate a positive value. The* resulting integer value is returned.** <p>An exception of type {@code NumberFormatException} is* thrown if any of the following situations occurs:* <ul>* <li>The first argument is {@code null} or is a string of* length zero.** <li>The radix is either smaller than* {@link java.lang.Character#MIN_RADIX} or* larger than {@link java.lang.Character#MAX_RADIX}.** <li>Any character of the string is not a digit of the specified* radix, except that the first character may be a minus sign* {@code '-'} ({@code '\u005Cu002D'}) or plus sign* {@code '+'} ({@code '\u005Cu002B'}) provided that the* string is longer than length 1.** <li>The value represented by the string is not a value of type* {@code int}.* </ul>** <p>Examples:* <blockquote><pre>* parseInt("0", 10) returns 0* parseInt("473", 10) returns 473* parseInt("+42", 10) returns 42* parseInt("-0", 10) returns 0* parseInt("-FF", 16) returns -255* parseInt("1100110", 2) returns 102* parseInt("2147483647", 10) returns 2147483647* parseInt("-2147483648", 10) returns -2147483648* parseInt("2147483648", 10) throws a NumberFormatException* parseInt("99", 8) throws a NumberFormatException* parseInt("Kona", 10) throws a NumberFormatException* parseInt("Kona", 27) returns 411787* </pre></blockquote>** @param s the {@code String} containing the integer* representation to be parsed* @param radix the radix to be used while parsing {@code s}.* @return the integer represented by the string argument in the* specified radix.* @exception NumberFormatException if the {@code String}* does not contain a parsable {@code int}.* 将radix进制的String类型整数转换为int类型。*/public static int parseInt(String s, int radix)throws NumberFormatException{/** WARNING: This method may be invoked early during VM initialization* before IntegerCache is initialized. Care must be taken to not use* the valueOf method.*/if (s == null) {throw new NumberFormatException("null");}if (radix < Character.MIN_RADIX) {throw new NumberFormatException("radix " + radix +" less than Character.MIN_RADIX");}if (radix > Character.MAX_RADIX) {throw new NumberFormatException("radix " + radix +" greater than Character.MAX_RADIX");}int result = 0;boolean negative = false;int i = 0, len = s.length();int limit = -Integer.MAX_VALUE;int multmin;int digit;if (len > 0) {char firstChar = s.charAt(0);// 若firstChar < '0' 说明第一个字符是+或—。if (firstChar < '0') { // Possible leading "+" or "-"if (firstChar == '-') {negative = true;limit = Integer.MIN_VALUE;} else if (firstChar != '+')throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);if (len == 1) // Cannot have lone "+" or "-"throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);i++;}// 这个变量是为了防止超过最大整数multmin = limit / radix;while (i < len) {// Accumulating negatively avoids surprises near MAX_VALUE// 获取进制为radix的字符i的整数int类型digit = Character.digit(s.charAt(i++),radix);if (digit < 0) {throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);}// 乘以radix之前先判断是否越界if (result < multmin) {throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);}result *= radix;if (result < limit + digit) {throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);}// 这里使用负数进行计算,因为最小负数比最大正数多一个,不然可能出现溢出result -= digit;}} else {throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);}return negative ? result : -result;}/*** Parses the string argument as a signed decimal integer. The* characters in the string must all be decimal digits, except* that the first character may be an ASCII minus sign {@code '-'}* ({@code '\u005Cu002D'}) to indicate a negative value or an* ASCII plus sign {@code '+'} ({@code '\u005Cu002B'}) to* indicate a positive value. The resulting integer value is* returned, exactly as if the argument and the radix 10 were* given as arguments to the {@link #parseInt(java.lang.String,* int)} method.** @param s a {@code String} containing the {@code int}* representation to be parsed* @return the integer value represented by the argument in decimal.* @exception NumberFormatException if the string does not contain a* parsable integer.* 默认十进制*/public static int parseInt(String s) throws NumberFormatException {return parseInt(s,10);}
parseUnsignedInt
/*** Parses the string argument as an unsigned integer in the radix* specified by the second argument. An unsigned integer maps the* values usually associated with negative numbers to positive* numbers larger than {@code MAX_VALUE}.** The characters in the string must all be digits of the* specified radix (as determined by whether {@link* java.lang.Character#digit(char, int)} returns a nonnegative* value), except that the first character may be an ASCII plus* sign {@code '+'} ({@code '\u005Cu002B'}). The resulting* integer value is returned.** <p>An exception of type {@code NumberFormatException} is* thrown if any of the following situations occurs:* <ul>* <li>The first argument is {@code null} or is a string of* length zero.** <li>The radix is either smaller than* {@link java.lang.Character#MIN_RADIX} or* larger than {@link java.lang.Character#MAX_RADIX}.** <li>Any character of the string is not a digit of the specified* radix, except that the first character may be a plus sign* {@code '+'} ({@code '\u005Cu002B'}) provided that the* string is longer than length 1.** <li>The value represented by the string is larger than the* largest unsigned {@code int}, 2<sup>32</sup>-1.** </ul>*** @param s the {@code String} containing the unsigned integer* representation to be parsed* @param radix the radix to be used while parsing {@code s}.* @return the integer represented by the string argument in the* specified radix.* @throws NumberFormatException if the {@code String}* does not contain a parsable {@code int}.* @since 1.8* 将String类型的无符号数转换为int类型。*/public static int parseUnsignedInt(String s, int radix)throws NumberFormatException {if (s == null) {throw new NumberFormatException("null");}int len = s.length();if (len > 0) {char firstChar = s.charAt(0);if (firstChar == '-') {throw newNumberFormatException(String.format("Illegal leading minus sign " +"on unsigned string %s.", s));} else {// 这里先判断String长度是否小于等于5,这是因为最大整数用36进制表示为6位,越界了if (len <= 5 || // Integer.MAX_VALUE in Character.MAX_RADIX is 6 digits// 因为10进制比较常用,所以这里它专门判断是不是10进制(radix == 10 && len <= 9) ) { // Integer.MAX_VALUE in base 10 is 10 digitsreturn parseInt(s, radix);} else {// 如果无法用parseInt来转换就需要使用长整型longlong ell = Long.parseLong(s, radix);// 若转换后的long高32位有数字说明越界了if ((ell & 0xffff_ffff_0000_0000L) == 0) {return (int) ell;} else {throw newNumberFormatException(String.format("String value %s exceeds " +"range of unsigned int.", s));}}}} else {throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);}}/*** Parses the string argument as an unsigned decimal integer. The* characters in the string must all be decimal digits, except* that the first character may be an an ASCII plus sign {@code* '+'} ({@code '\u005Cu002B'}). The resulting integer value* is returned, exactly as if the argument and the radix 10 were* given as arguments to the {@link* #parseUnsignedInt(java.lang.String, int)} method.** @param s a {@code String} containing the unsigned {@code int}* representation to be parsed* @return the unsigned integer value represented by the argument in decimal.* @throws NumberFormatException if the string does not contain a* parsable unsigned integer.* @since 1.8*/public static int parseUnsignedInt(String s) throws NumberFormatException {return parseUnsignedInt(s, 10);}
valueOf
/*** Returns an {@code Integer} object holding the value* extracted from the specified {@code String} when parsed* with the radix given by the second argument. The first argument* is interpreted as representing a signed integer in the radix* specified by the second argument, exactly as if the arguments* were given to the {@link #parseInt(java.lang.String, int)}* method. The result is an {@code Integer} object that* represents the integer value specified by the string.** <p>In other words, this method returns an {@code Integer}* object equal to the value of:** <blockquote>* {@code new Integer(Integer.parseInt(s, radix))}* </blockquote>** @param s the string to be parsed.* @param radix the radix to be used in interpreting {@code s}* @return an {@code Integer} object holding the value* represented by the string argument in the specified* radix.* @exception NumberFormatException if the {@code String}* does not contain a parsable {@code int}.* 调用ParseInt方法将String转换为Integer。*/public static Integer valueOf(String s, int radix) throws NumberFormatException {return Integer.valueOf(parseInt(s,radix));}/*** Returns an {@code Integer} object holding the* value of the specified {@code String}. The argument is* interpreted as representing a signed decimal integer, exactly* as if the argument were given to the {@link* #parseInt(java.lang.String)} method. The result is an* {@code Integer} object that represents the integer value* specified by the string.** <p>In other words, this method returns an {@code Integer}* object equal to the value of:** <blockquote>* {@code new Integer(Integer.parseInt(s))}* </blockquote>** @param s the string to be parsed.* @return an {@code Integer} object holding the value* represented by the string argument.* @exception NumberFormatException if the string cannot be parsed* as an integer.*/public static Integer valueOf(String s) throws NumberFormatException {return Integer.valueOf(parseInt(s, 10));}/*** Returns an {@code Integer} instance representing the specified* {@code int} value. If a new {@code Integer} instance is not* required, this method should generally be used in preference to* the constructor {@link #Integer(int)}, as this method is likely* to yield significantly better space and time performance by* caching frequently requested values.** This method will always cache values in the range -128 to 127,* inclusive, and may cache other values outside of this range.** @param i an {@code int} value.* @return an {@code Integer} instance representing {@code i}.* @since 1.5* 首先判断缓存里有没有,如果有就从缓存里面拿,没有就创建一个。*/public static Integer valueOf(int i) {if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];return new Integer(i);}IntegerCache
/*** Cache to support the object identity semantics of autoboxing for values between* -128 and 127 (inclusive) as required by JLS.** The cache is initialized on first usage. The size of the cache* may be controlled by the {@code -XX:AutoBoxCacheMax=<size>} option.* During VM initialization, java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high property* may be set and saved in the private system properties in the* sun.misc.VM class.* 缓存静态内部类 -128 ,127*/private static class IntegerCache {static final int low = -128;static final int high;static final Integer cache[];static {// high value may be configured by propertyint h = 127;// 这个是启动虚拟机的时候带的参数,可以自行设置表示缓存的最大整数String integerCacheHighPropValue =sun.misc.VM.getSavedProperty("java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high");if (integerCacheHighPropValue != null) {try {int i = parseInt(integerCacheHighPropValue);i = Math.max(i, 127);// Maximum array size is Integer.MAX_VALUE// 缓存的最大整数h = Math.min(i, Integer.MAX_VALUE - (-low) -1);} catch( NumberFormatException nfe) {// If the property cannot be parsed into an int, ignore it.}}high = h;cache = new Integer[(high - low) + 1];int j = low;for(int k = 0; k < cache.length; k++)cache[k] = new Integer(j++);// range [-128, 127] must be interned (JLS7 5.1.7)assert IntegerCache.high >= 127;}private IntegerCache() {}}
decode
/*** Decodes a {@code String} into an {@code Integer}.* Accepts decimal, hexadecimal, and octal numbers given* by the following grammar:** <blockquote>* <dl>* <dt><i>DecodableString:</i>* <dd><i>Sign<sub>opt</sub> DecimalNumeral</i>* <dd><i>Sign<sub>opt</sub></i> {@code 0x} <i>HexDigits</i>* <dd><i>Sign<sub>opt</sub></i> {@code 0X} <i>HexDigits</i>* <dd><i>Sign<sub>opt</sub></i> {@code #} <i>HexDigits</i>* <dd><i>Sign<sub>opt</sub></i> {@code 0} <i>OctalDigits</i>** <dt><i>Sign:</i>* <dd>{@code -}* <dd>{@code +}* </dl>* </blockquote>** <i>DecimalNumeral</i>, <i>HexDigits</i>, and <i>OctalDigits</i>* are as defined in section 3.10.1 of* <cite>The Java™ Language Specification</cite>,* except that underscores are not accepted between digits.** <p>The sequence of characters following an optional* sign and/or radix specifier ("{@code 0x}", "{@code 0X}",* "{@code #}", or leading zero) is parsed as by the {@code* Integer.parseInt} method with the indicated radix (10, 16, or* 8). This sequence of characters must represent a positive* value or a {@link NumberFormatException} will be thrown. The* result is negated if first character of the specified {@code* String} is the minus sign. No whitespace characters are* permitted in the {@code String}.** @param nm the {@code String} to decode.* @return an {@code Integer} object holding the {@code int}* value represented by {@code nm}* @exception NumberFormatException if the {@code String} does not* contain a parsable integer.* @see java.lang.Integer#parseInt(java.lang.String, int)* 将String类型的nm解码为Integer类型*/public static Integer decode(String nm) throws NumberFormatException {int radix = 10;int index = 0;boolean negative = false;Integer result;if (nm.isEmpty())throw new NumberFormatException("Zero length string");char firstChar = nm.charAt(0);// Handle sign, if present// 首先判断是否有符号if (firstChar == '-') {negative = true;index++;} else if (firstChar == '+')index++;// Handle radix specifier, if present// 查看字符串表示的整数的进制// 是否是16进制if (nm.startsWith("0x", index) || nm.startsWith("0X", index)) {index += 2;radix = 16;}// 是否是16进制else if (nm.startsWith("#", index)) {index ++;radix = 16;}// 是否是8进制else if (nm.startsWith("0", index) && nm.length() > 1 + index) {index ++;radix = 8;}// 判断符号是否写错地方了if (nm.startsWith("-", index) || nm.startsWith("+", index))throw new NumberFormatException("Sign character in wrong position");try {// 将相应进制的字符串转换为对应的Integer类型// 这里如果是最小负数会出错进入到下面的catch语句中处理// 这里有点操作麻烦了,如果是我就会在这里将nm的符号一起传入result = Integer.valueOf(nm.substring(index), radix);// 将符号赋值给resultresult = negative ? Integer.valueOf(-result.intValue()) : result;} catch (NumberFormatException e) {// If number is Integer.MIN_VALUE, we'll end up here. The next line// handles this case, and causes any genuine format error to be// rethrown.String constant = negative ? ("-" + nm.substring(index)): nm.substring(index);result = Integer.valueOf(constant, radix);}return result;}
github:Integer源码
如文章有问题请留言,谢谢~
相关文章:

Integer源码
介绍 Integer是int类型的包装类,继承自Number抽象类,实现了Comparable接口。提供了一些处理int类型的方法,比如int到String类型的转换方法或String类型到int类型的转换方法,当然也包含与其他类型之间的转换方法。 Comparable提供…...
【四】设计模式~~~创建型模式~~~建造者模式(Java)
【学习难度:★★★★☆,使用频率:★★☆☆☆】 4.1. 模式动机 无论是在现实世界中还是在软件系统中,都存在一些复杂的对象,它们拥有多个组成部分,如汽车,它包括车轮、方向盘、发送机等各种部件…...
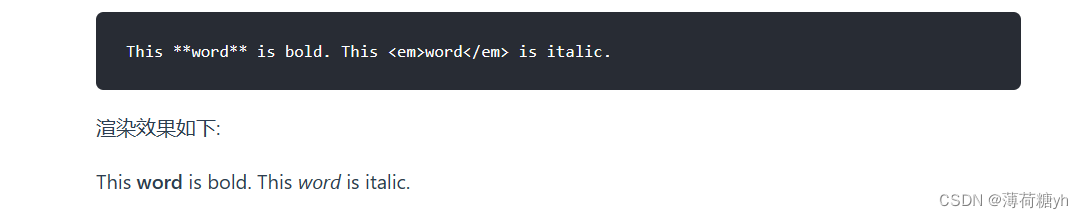
MarkDown的基本使用方法
为了给官方的文档知识总结:Markdown 基本语法 | Markdown 官方教程 #空格内容:‘#’表示标题的等级,越少表示标题级别越高(字越大) 在一行的末尾加两个或多个空格再回车,就是我们普通的文本回车。【还有一…...

IDEA 安装配置步骤详解
引言 IntelliJ IDEA 是一款功能强大的集成开发环境,它具有许多优势,适用于各种开发过程。本文将介绍 IDEA 的主要优势,并提供详细的安装配置步骤。 介绍 IntelliJ IDEA(以下简称 IDEA)之所以被广泛使用,…...
【网络】· 路由器中配置单臂路由和DHCP,VTP原理
目录 🍉单臂路由的工作原理 🥝交换机配置 🥝路由器配置 🍉路由器配置DHCP 🥝配置实例 🥝路由器配置 🥝验证 🍉VTP工作原理 🥝VTP模式 🥝VTP通告 🥝…...

Python 子域名扫描工具:使用多线程优化
部分数据来源:ChatGPT 本文仅用于信息安全的学习,请遵守相关法律法规,严禁用于非法途径。若观众因此作出任何危害网络安全的行为,后果自负,与本人无关。 摘要:子域名扫描是一个重要的安全工作,它可以发现目标网站的更多威胁和漏洞。本文介绍了如何使用 Python 来编写一…...
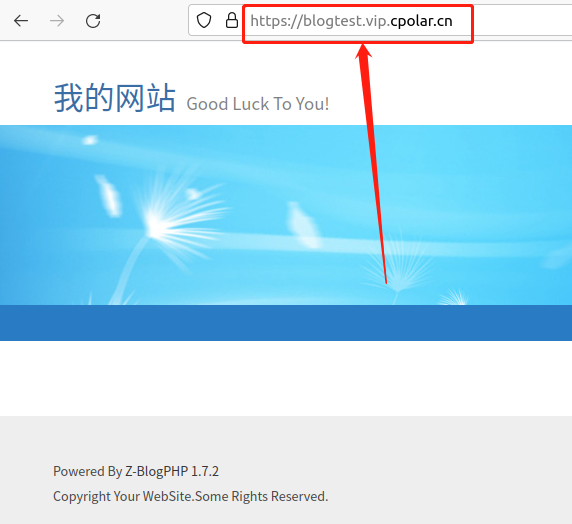
宝塔面板一键部署Z-Blog博客 - 内网穿透实现公网访问
文章目录 1.前言2.网站搭建2.1. 网页下载和安装2.2.网页测试2.3.cpolar的安装和注册 3.本地网页发布3.1.Cpolar临时数据隧道3.2.Cpolar稳定隧道(云端设置)3.3.Cpolar稳定隧道(本地设置) 4.公网访问测试5.结语 转发自cpolar极点云的…...

深入理解设计原则之单一职责原则(SRP)
系列文章目录 C高性能优化编程系列 深入理解设计原则系列 深入理解设计模式系列 高级C并发线程编程 SRP:单一职责原则 系列文章目录1、单一职责原则的定义和解读2、单一职责原则案例解读2.1、违背单一职责原则反面案例2.2、违背单一职责原则反面案例 - 解决方案 3…...

钉钉群通过短信转发器接收手机短信消息
1.短信转发器官网下载 下载地址 首发地址:https://github.com/pppscn/SmsForwarder/releases国内镜像:https://gitee.com/pp/SmsForwarder/releases网盘下载:https://wws.lanzoui.com/b025yl86h 访问密码:pppscn 使用文档 首发…...
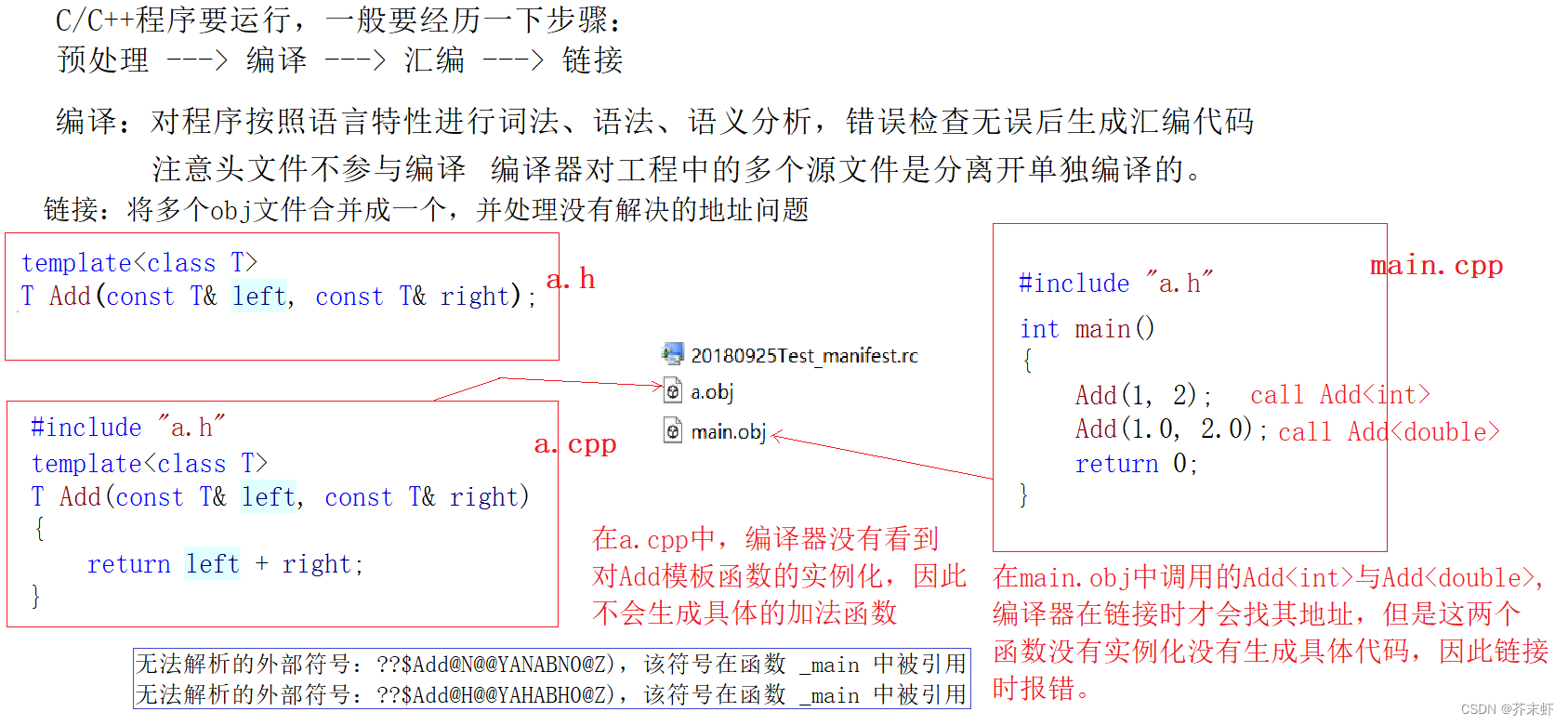
【C++模版】模版进阶 {非类型模版参数; 模版的特化; 模版的分离编译; 模版总结}
一、非类型模版参数 模板参数分类型形参与非类型形参。 类型形参:出现在模板参数列表中,跟在class或者typename之后的参数类型名称。非类型形参:就是用一个常量作为类(函数)模板的一个参数,在类(函数)模板中可将该参数当成常量来…...
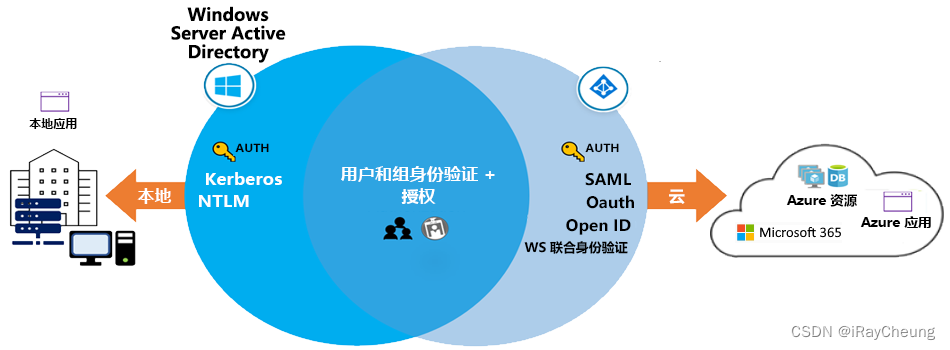
Azure Active Directory 的功能和优势
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) 是 Microsoft 基于云的多租户目录和标识管理服务。 Azure AD 有助于支持用户访问资源和应用程序,例如: 位于企业网络上的内部资源和应用。 Microsoft 365、Azure 门户和 SaaS 应用程序等外部资源。 为组织开发的云应…...
mysql查询语句执行过程及运行原理命令
Mysql查询语句执行原理 数据库查询语句如何执行? DML语句首先进行语法分析,对使用sql表示的查询进行语法分析,生成查询语法分析树。语义检查:检查sql中所涉及的对象以及是否在数据库中存在,用户是否具有操作权限等视…...

可视化探索开源项目的 contributor 关系
引语:作为国内外最大的代码托管平台,根据最新的 GitHub 数据,它拥有超 372,000,000 个仓库,其中有 28,000,000 是公开仓。分布式图数据库 NebulaGraph 便是其中之一,同其他开源项目一样,NebulaGrpah 也有自…...

SpringBoot 实现启动项目后立即执行方法的几种方式
在项目开发中某些场景必须要用到启动项目后立即执行方式的功能,如我们需要去初始化数据到redis缓存,或者启动后读取相应的字典配置等,这篇文章主要聊聊实现立即执行的几种方法。 一、CommandLineRunner和ApplicationRunner 这两者的实现方法…...

2021第十二届蓝桥杯Python组国赛【真题+解析+代码】
🎁2021第十二届蓝桥杯python组国赛真题 🚀 真题练习,冲刺国赛 🚀 2021第十二届蓝桥杯python组国赛真题解析代码 博观而约取,厚积而薄发 🏆国赛真题目录 文章目录 🎁2021第十二届蓝桥杯python组国…...

3D引擎渲染管理系统概览
3D引擎渲染管理系统, 目前由: RendererScene, RendererSubScene, RendererSceneGraph, RenderProcess, RenderingCacheProcess/FBOProcess, (Material)PassGraph, (Material)PassNode, Material(Shader)Pipeline, RenderingFlowContainer, RenderableEnti…...
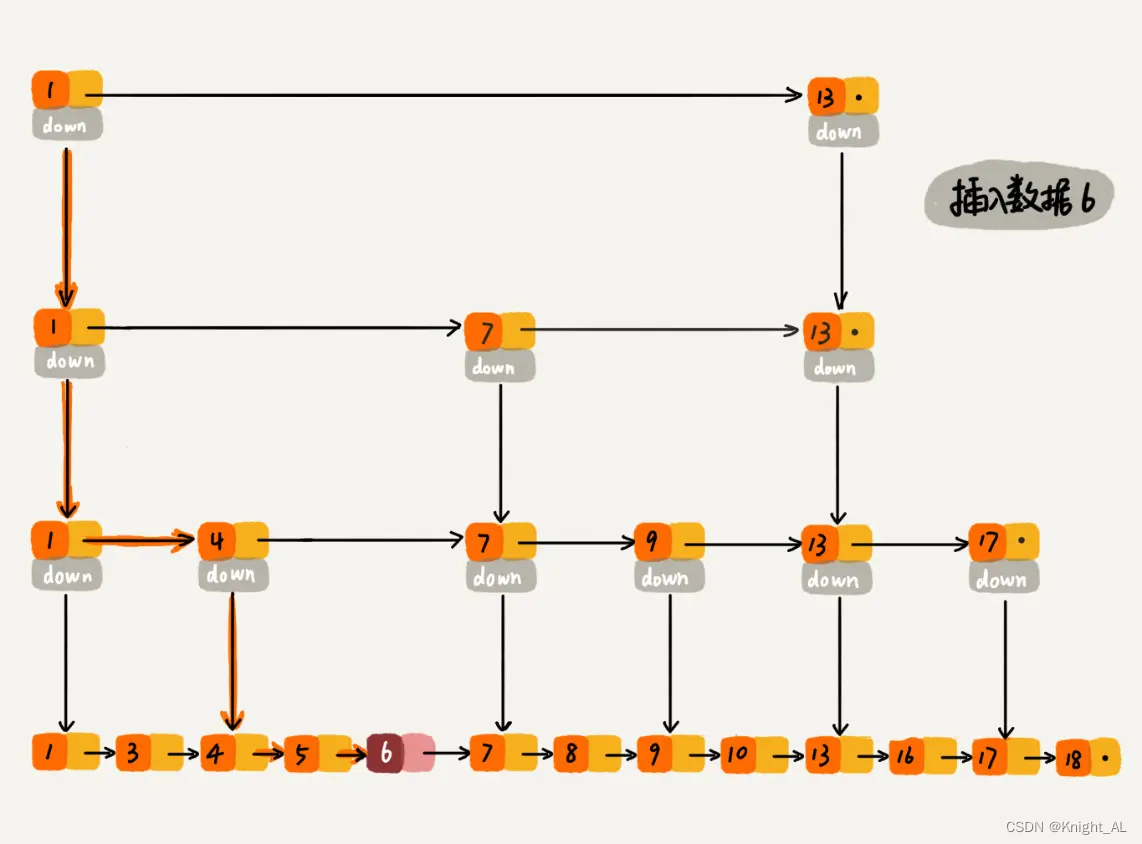
蔚来Java实习面经
目录 1.解释一下MySQL中脏读、不可重复读、幻读2.索引失效的场景有哪些?3.Explain执行计划用过吗4.Type字段有哪一些5.binlog和redolog的区别6.Redis基本数据类型7.有序集合的底层数据结构使用的是?8.跳表插入数据的过程能描述一下吗9.线程池,…...
流媒体的一次尝试)
nginx 搭建http-flv(rtmp)流媒体的一次尝试
nginx 搭建http-flv(rtmp)流媒体的一次尝试 项目需要通过调用海康摄像头实现远程监控,但是由于网络限制,只能通过代理来调用,因此只能放弃海康官网提供的视频插件,经过一番搜索,决定采用此种方式:nginx 搭…...
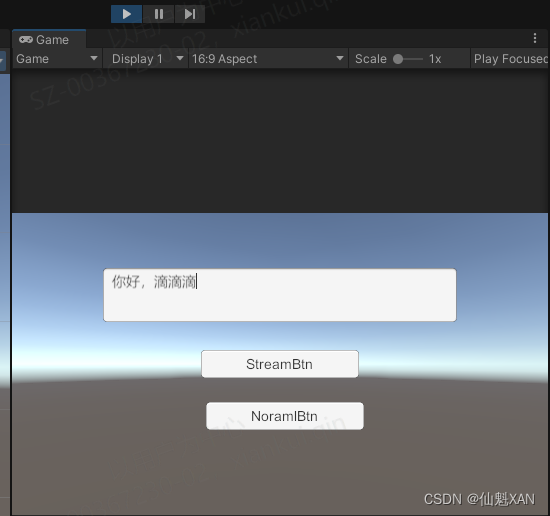
Unity 工具 之 Azure 微软语音合成普通方式和流式获取音频数据的简单整理
Unity 工具 之 Azure 微软语音合成普通方式和流式获取音频数据的简单整理 目录 Unity 工具 之 Azure 微软语音合成普通方式和流式获取音频数据的简单整理 一、简单介绍 二、实现原理 三、注意实现 四、实现步骤 六、关键脚本 附加: 声音设置相关 一、简单介绍…...

【A卡,Windows】stable diffusion webui下载安装避坑指南
观前提醒 本文内容都是本人亲身经历的,一个一个安装下载测试所感,当然如果你更想用傻瓜式集成包的,那还是跳过这篇文章吧。 当然我不推荐这篇文章的操作,因为我用了差不多1h才有一副图,有N卡,就用N卡&…...
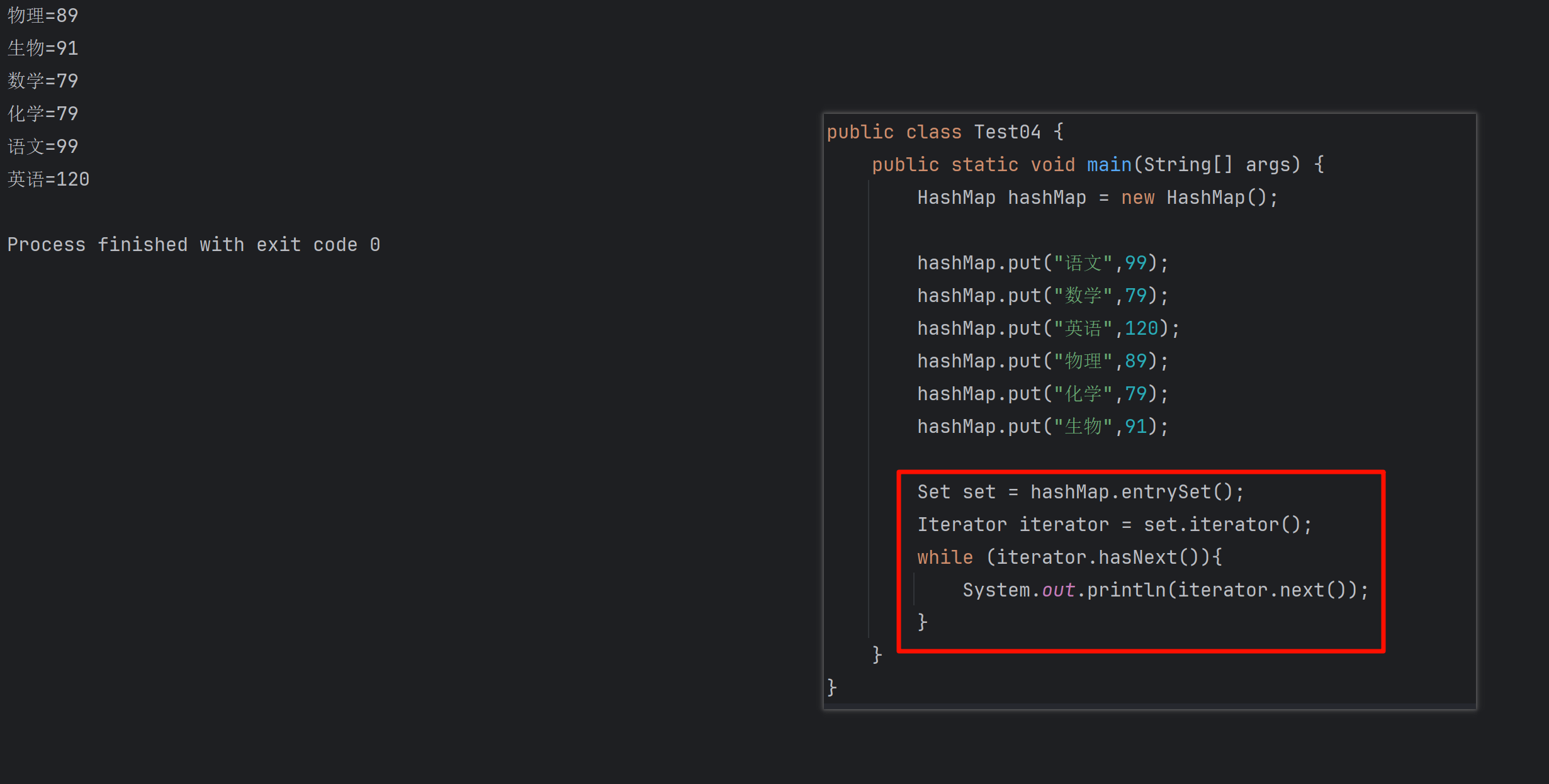
遍历 Map 类型集合的方法汇总
1 方法一 先用方法 keySet() 获取集合中的所有键。再通过 gey(key) 方法用对应键获取值 import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Set;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {HashMap hashMap new HashMap();hashMap.put("语文",99);has…...
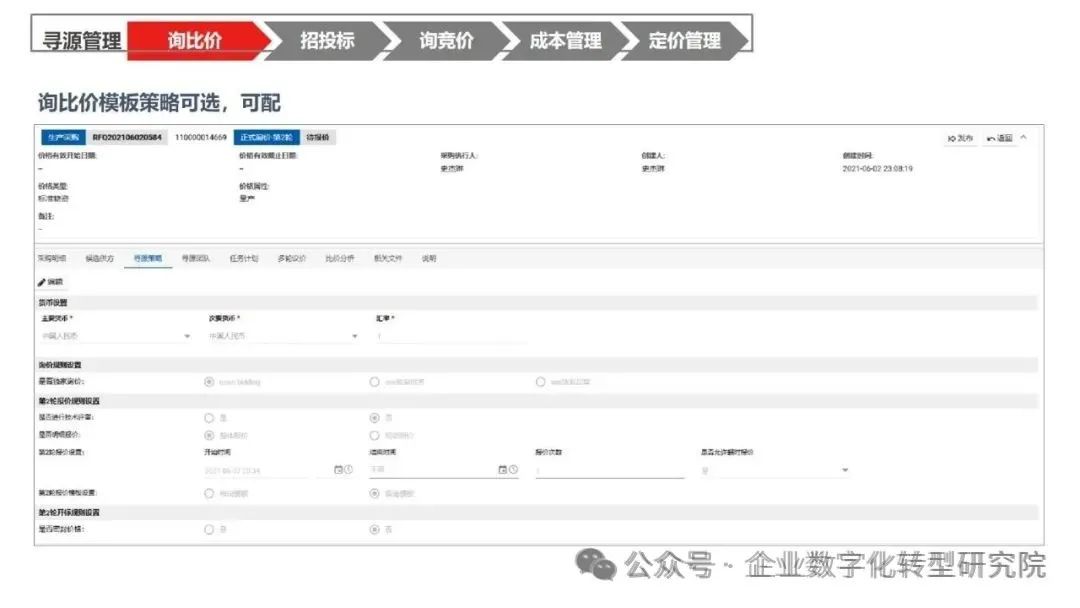
PPT|230页| 制造集团企业供应链端到端的数字化解决方案:从需求到结算的全链路业务闭环构建
制造业采购供应链管理是企业运营的核心环节,供应链协同管理在供应链上下游企业之间建立紧密的合作关系,通过信息共享、资源整合、业务协同等方式,实现供应链的全面管理和优化,提高供应链的效率和透明度,降低供应链的成…...
视觉slam十四讲实践部分记录——ch2、ch3
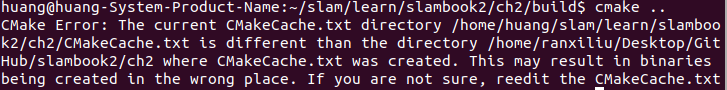
ch2 一、使用g++编译.cpp为可执行文件并运行(P30) g++ helloSLAM.cpp ./a.out运行 二、使用cmake编译 mkdir build cd build cmake .. makeCMakeCache.txt 文件仍然指向旧的目录。这表明在源代码目录中可能还存在旧的 CMakeCache.txt 文件,或者在构建过程中仍然引用了旧的路…...

根目录0xa0属性对应的Ntfs!_SCB中的FileObject是什么时候被建立的----NTFS源代码分析--重要
根目录0xa0属性对应的Ntfs!_SCB中的FileObject是什么时候被建立的 第一部分: 0: kd> g Breakpoint 9 hit Ntfs!ReadIndexBuffer: f7173886 55 push ebp 0: kd> kc # 00 Ntfs!ReadIndexBuffer 01 Ntfs!FindFirstIndexEntry 02 Ntfs!NtfsUpda…...

LOOI机器人的技术实现解析:从手势识别到边缘检测
LOOI机器人作为一款创新的AI硬件产品,通过将智能手机转变为具有情感交互能力的桌面机器人,展示了前沿AI技术与传统硬件设计的完美结合。作为AI与玩具领域的专家,我将全面解析LOOI的技术实现架构,特别是其手势识别、物体识别和环境…...
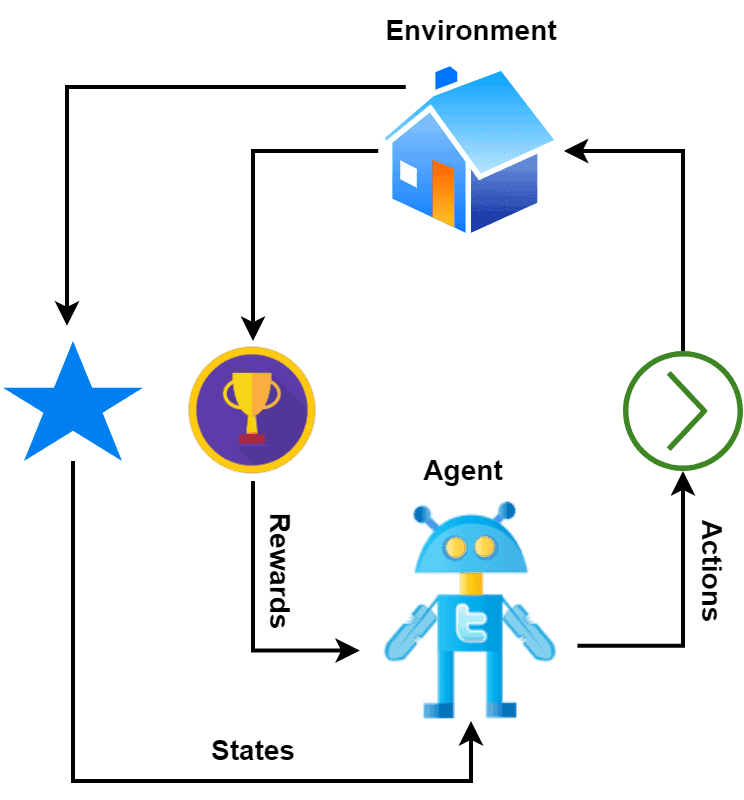
【深度学习新浪潮】什么是credit assignment problem?
Credit Assignment Problem(信用分配问题) 是机器学习,尤其是强化学习(RL)中的核心挑战之一,指的是如何将最终的奖励或惩罚准确地分配给导致该结果的各个中间动作或决策。在序列决策任务中,智能体执行一系列动作后获得一个最终奖励,但每个动作对最终结果的贡献程度往往…...
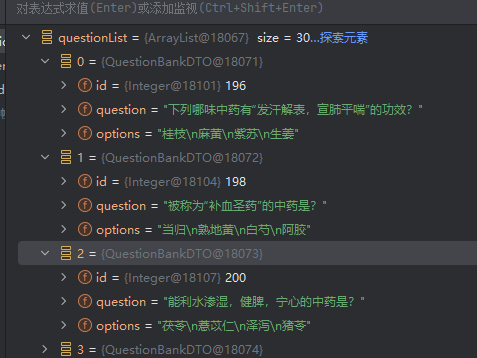
jdbc查询mysql数据库时,出现id顺序错误的情况
我在repository中的查询语句如下所示,即传入一个List<intager>的数据,返回这些id的问题列表。但是由于数据库查询时ID列表的顺序与预期不一致,会导致返回的id是从小到大排列的,但我不希望这样。 Query("SELECT NEW com…...

React核心概念:State是什么?如何用useState管理组件自己的数据?
系列回顾: 在上一篇《React入门第一步》中,我们已经成功创建并运行了第一个React项目。我们学会了用Vite初始化项目,并修改了App.jsx组件,让页面显示出我们想要的文字。但是,那个页面是“死”的,它只是静态…...

渗透实战PortSwigger Labs指南:自定义标签XSS和SVG XSS利用
阻止除自定义标签之外的所有标签 先输入一些标签测试,说是全部标签都被禁了 除了自定义的 自定义<my-tag onmouseoveralert(xss)> <my-tag idx onfocusalert(document.cookie) tabindex1> onfocus 当元素获得焦点时(如通过点击或键盘导航&…...

第22节 Node.js JXcore 打包
Node.js是一个开放源代码、跨平台的、用于服务器端和网络应用的运行环境。 JXcore是一个支持多线程的 Node.js 发行版本,基本不需要对你现有的代码做任何改动就可以直接线程安全地以多线程运行。 本文主要介绍JXcore的打包功能。 JXcore 安装 下载JXcore安装包&a…...
