【Linux网络】TCP全连接队列
TCP 相关实验
理解 listen 的第二个参数
- 基于刚才封装的 TcpSocket 实现以下测试代码
- 对于服务器, listen 的第二个参数设置为 1, 并且不调用 accept
- 测试代码链接
test_server.cc
#include "tcp_socket.hpp"int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {if (argc != 3) {printf("Usage ./test_server [ip] [port]\n");return 1;}TcpSocket sock;bool ret = sock.Bind(argv[1], atoi(argv[2]));if (!ret) {return 1;}ret = sock.Listen(2);if (!ret) {return 1;}// 客户端不进行 acceptwhile (1) {sleep(1);}return 0;
}
test_client.cc
#include "tcp_socket.hpp"int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {if (argc != 3) {printf("Usage ./test_client [ip] [port]\n");return 1;}TcpSocket sock;bool ret = sock.Connect(argv[1], atoi(argv[2]));if (ret) {printf("connect ok\n");} else {printf("connect failed\n");}while (1) {sleep(1);}return 0;
}
此时启动 3 个客户端同时连接服务器, 用 netstat 查看服务器状态, 一切正常.
但是启动第四个客户端时, 发现服务器对于第四个连接的状态存在问题了
tcp 3 0 0.0.0.0:9090 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 9084/./test_server
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:9090 127.0.0.1:48178 SYN_RECV -
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:9090 127.0.0.1:48176 ESTABLISHED -
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:48178 127.0.0.1:9090 ESTABLISHED 9140/./test_client
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:48174 127.0.0.1:9090 ESTABLISHED 9087/./test_client
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:48176 127.0.0.1:9090 ESTABLISHED 9088/./test_client
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:48172 127.0.0.1:9090 ESTABLISHED 9086/./test_client
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:9090 127.0.0.1:48174 ESTABLISHED -
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:9090 127.0.0.1:48172 ESTABLISHED -
客户端状态正常, 但是服务器端出现了 SYN_RECV 状态, 而不是 ESTABLISHED 状态
这是因为, Linux 内核协议栈为一个 tcp 连接管理使用两个队列:
- 半连接队列 (用来保存处于 SYN_SENT 和 SYN_RECV 状态的请求)
- 全连接队列 (accpetd 队列) (用来保存处于 established 状态, 但是应用层没有调用 accept 取走的请求)
而全连接队列的长度会受到 listen 第二个参数的影响.
全连接队列满了的时候, 就无法继续让当前连接的状态进入 established 状态了.
这个队列的长度通过上述实验可知, 是 listen 的第二个参数 + 1.
使用 TCP dump 进行抓包,分析 TCP 过程
我们代码中故意在 close(sockfd)那里留了一个问题
TCPDump 是一款强大的网络分析工具, 主要用于捕获和分析网络上传输的数据包。
安装 tcpdump
tcpdump 通常已经预装在大多数 Linux 发行版中。如果没有安装, 可以使用包管理器进行安装。例如 Ubuntu, 可以使用以下命令安装:
sudo apt - get update
sudo apt - get install tcpdump
在 Red Hat 或 CentOS 系统中, 可以使用以下命令:
sudo yum install tcpdump
常见使用
- 捕获所有网络接口上的 TCP 报文
使用以下命令可以捕获所有网络接口上传输的 TCP 报文:
$ sudo tcpdump -i any tcp
注意: -i any 指定捕获所有网络接口上的数据包, tcp 指定捕获 TCP 协议的数据, -i 可以理解为 interface 的意思
2. 捕获指定网络接口上的 TCP 报文
如果你只想捕获某个特定网络接口 (如 eth0) 上的 TCP 报文, 可以使用以下命令:
$ sudo tcpdump -i eth0 tcp
eth0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500inet 172.18.45.153 netmask 255.255.192.0 broadcast 172.18.63.255inet6 fe80::216:3eff:fe03:059b prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>ether 00:16:3e:03:95:9b txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)RX packets 34378927 bytes 6954263239 (6.9 GB)RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0TX packets 34274797 bytes 6954263239 (6.9 GB)TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
- 捕获特定源或目的 IP 地址的 TCP 报文
使用 host 关键字可以指定源或目的 IP 地址。例如, 要捕获源 IP 地址为 192.168.1.100 的 TCP 报文, 可以使用以下命令:
$ sudo tcpdump src host 192.168.1.100 and tcp
要捕获目的 IP 地址为 192.168.1.200 的 TCP 报文, 可以使用以下命令:
$ sudo tcpdump dst host 192.168.1.200 and tcp
同时指定源和目的 IP 地址, 可以使用 and 关键字连接两个条件:
$ sudo tcpdump src host 192.168.1.100 and dst host 192.168.1.200 and tcp
- 捕获特定端口的 TCP 报文
使用 port 关键字可以指定端口号。例如, 要捕获端口号为 80 的 TCP 报文 (通常是 HTTP 请求), 可以使用以下命令:
$ sudo tcpdump port 80 and tcp
- 保存捕获的数据包到文件
使用 -w 选项可以将捕获的数据包保存到文件中, 以便后续分析。例如:
$ sudo tcpdump -i eth0 port 80 -w data.pcap
这将把捕获到的 HTTP 流量保存到名为 data.pcap 的文件中。
- 了解: pcap 后缀的文件通常与 PCAP (Packet Capture) 文件格式相关, 这是一种用于捕获网络数据包的文件格式
- 从文件中读取数据包进行分析
使用 -r 选项可以从文件中读取数据包进行分析。例如:
tcpdump -r data.pcap
这将读取 data.pcap 文件中的数据包并进行分析。
注意事项
- 使用 tcpdump 时, 请确保你有足够的权限来捕获网络接口上的数据。通常, 你需要以 root 用户身份运行 tcpdump。
- 使用 tcpdump 的时候, 有些主机名会被云服务器解释成为随机的主机名, 如果不想要, 就用-n 选项
- 主机观察三次握手的第三次握手, 不占序号
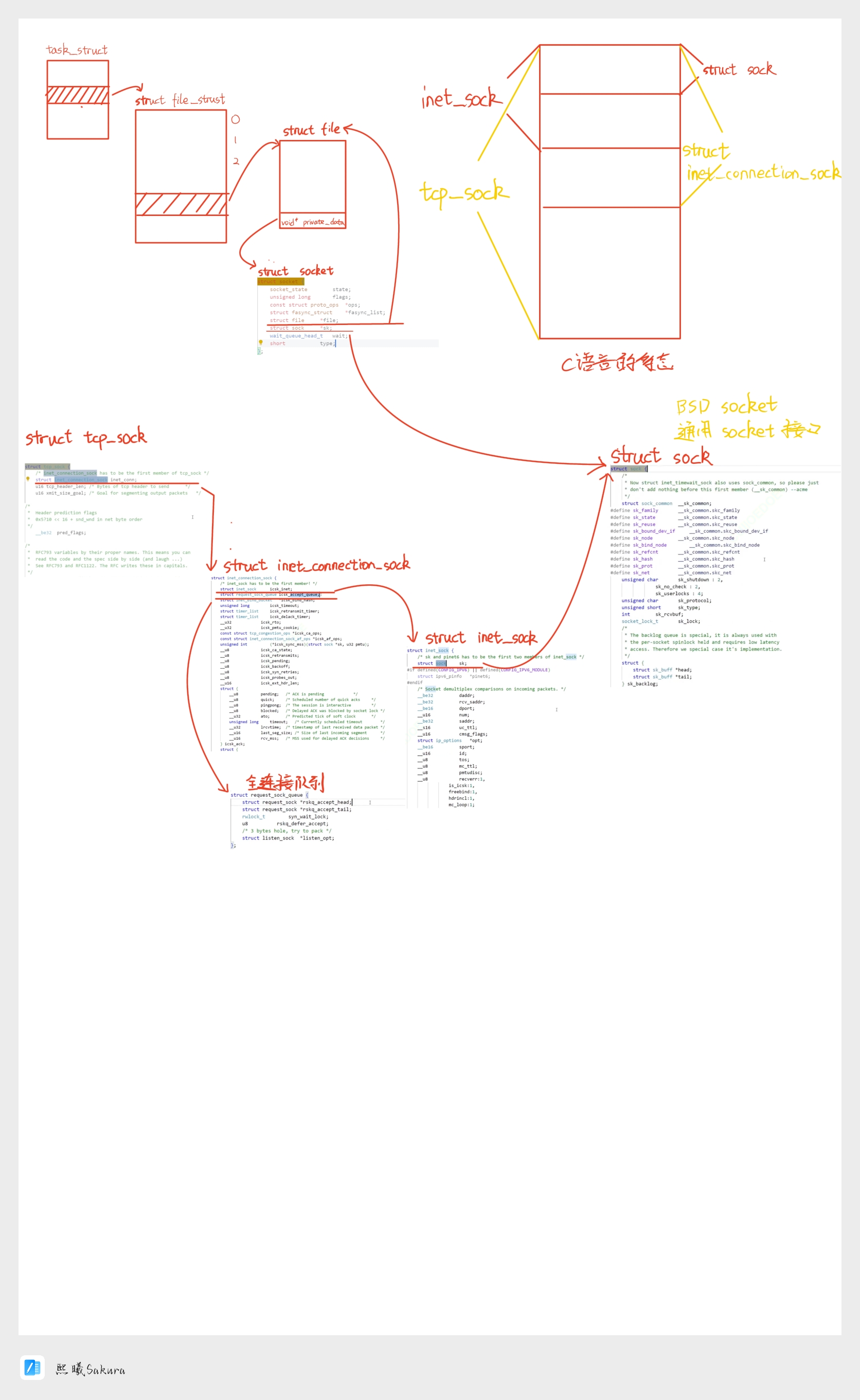
socket源码分析
相关源码
struct socket {socket_state state;unsigned long flags;const struct proto_ops *ops;struct fasync_struct *fasync_list;struct file *file;struct sock *sk;wait_queue_head_t wait;short type;
};
我们知道。在Linux系统下,一切皆文件。所以socket是如何与文件描述符相关联的?
struct task_struct {volatile long state; /* -1 unrunnable, 0 runnable, >0 stopped */void *stack;atomic_t usage;unsigned int flags; /* per process flags, defined below */unsigned int ptrace;int lock_depth; /* BKL lock depth */#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
#ifdef __ARCH_WANT_UNLOCKED_CTXSWint oncpu;
#endif
#endifint prio, static_prio, normal_prio;const struct sched_class *sched_class;struct sched_entity se;struct sched_rt_entity rt;#ifdef CONFIG_PREEMPT_NOTIFIERS/* list of struct preempt_notifier: */struct hlist_head preempt_notifiers;
#endif/** fpu_counter contains the number of consecutive context switches* that the FPU is used. If this is over a threshold, the lazy fpu* saving becomes unlazy to save the trap. This is an unsigned char* so that after 256 times the counter wraps and the behavior turns* lazy again; this to deal with bursty apps that only use FPU for* a short time*/unsigned char fpu_counter;s8 oomkilladj; /* OOM kill score adjustment (bit shift). */
#ifdef CONFIG_BLK_DEV_IO_TRACEunsigned int btrace_seq;
#endifunsigned int policy;cpumask_t cpus_allowed;#ifdef CONFIG_PREEMPT_RCUint rcu_read_lock_nesting;int rcu_flipctr_idx;
#endif /* #ifdef CONFIG_PREEMPT_RCU */#if defined(CONFIG_SCHEDSTATS) || defined(CONFIG_TASK_DELAY_ACCT)struct sched_info sched_info;
#endifstruct list_head tasks;/** ptrace_list/ptrace_children forms the list of my children* that were stolen by a ptracer.*/struct list_head ptrace_children;struct list_head ptrace_list;struct mm_struct *mm, *active_mm;/* task state */struct linux_binfmt *binfmt;int exit_state;int exit_code, exit_signal;int pdeath_signal; /* The signal sent when the parent dies *//* ??? */unsigned int personality;unsigned did_exec:1;pid_t pid;pid_t tgid;#ifdef CONFIG_CC_STACKPROTECTOR/* Canary value for the -fstack-protector gcc feature */unsigned long stack_canary;
#endif/* * pointers to (original) parent process, youngest child, younger sibling,* older sibling, respectively. (p->father can be replaced with * p->parent->pid)*/struct task_struct *real_parent; /* real parent process (when being debugged) */struct task_struct *parent; /* parent process *//** children/sibling forms the list of my children plus the* tasks I'm ptracing.*/struct list_head children; /* list of my children */struct list_head sibling; /* linkage in my parent's children list */struct task_struct *group_leader; /* threadgroup leader *//* PID/PID hash table linkage. */struct pid_link pids[PIDTYPE_MAX];struct list_head thread_group;struct completion *vfork_done; /* for vfork() */int __user *set_child_tid; /* CLONE_CHILD_SETTID */int __user *clear_child_tid; /* CLONE_CHILD_CLEARTID */unsigned int rt_priority;cputime_t utime, stime, utimescaled, stimescaled;cputime_t gtime;cputime_t prev_utime, prev_stime;unsigned long nvcsw, nivcsw; /* context switch counts */struct timespec start_time; /* monotonic time */struct timespec real_start_time; /* boot based time */
/* mm fault and swap info: this can arguably be seen as either mm-specific or thread-specific */unsigned long min_flt, maj_flt;cputime_t it_prof_expires, it_virt_expires;unsigned long long it_sched_expires;struct list_head cpu_timers[3];/* process credentials */uid_t uid,euid,suid,fsuid;gid_t gid,egid,sgid,fsgid;struct group_info *group_info;kernel_cap_t cap_effective, cap_inheritable, cap_permitted, cap_bset;unsigned securebits;struct user_struct *user;
#ifdef CONFIG_KEYSstruct key *request_key_auth; /* assumed request_key authority */struct key *thread_keyring; /* keyring private to this thread */unsigned char jit_keyring; /* default keyring to attach requested keys to */
#endifchar comm[TASK_COMM_LEN]; /* executable name excluding path- access with [gs]et_task_comm (which lockit with task_lock())- initialized normally by flush_old_exec */
/* file system info */int link_count, total_link_count;
#ifdef CONFIG_SYSVIPC
/* ipc stuff */struct sysv_sem sysvsem;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_DETECT_SOFTLOCKUP
/* hung task detection */unsigned long last_switch_timestamp;unsigned long last_switch_count;
#endif
/* CPU-specific state of this task */struct thread_struct thread;
/* filesystem information */struct fs_struct *fs;
/* open file information */struct files_struct *files; //重点!!!!!
/* namespaces */struct nsproxy *nsproxy;
/* signal handlers */struct signal_struct *signal;struct sighand_struct *sighand;sigset_t blocked, real_blocked;sigset_t saved_sigmask; /* restored if set_restore_sigmask() was used */struct sigpending pending;unsigned long sas_ss_sp;size_t sas_ss_size;int (*notifier)(void *priv);void *notifier_data;sigset_t *notifier_mask;
#ifdef CONFIG_SECURITYvoid *security;
#endifstruct audit_context *audit_context;
#ifdef CONFIG_AUDITSYSCALLuid_t loginuid;unsigned int sessionid;
#endifseccomp_t seccomp;/* Thread group tracking */u32 parent_exec_id;u32 self_exec_id;
/* Protection of (de-)allocation: mm, files, fs, tty, keyrings */spinlock_t alloc_lock;/* Protection of the PI data structures: */spinlock_t pi_lock;#ifdef CONFIG_RT_MUTEXES/* PI waiters blocked on a rt_mutex held by this task */struct plist_head pi_waiters;/* Deadlock detection and priority inheritance handling */struct rt_mutex_waiter *pi_blocked_on;
#endif#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_MUTEXES/* mutex deadlock detection */struct mutex_waiter *blocked_on;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_TRACE_IRQFLAGSunsigned int irq_events;int hardirqs_enabled;unsigned long hardirq_enable_ip;unsigned int hardirq_enable_event;unsigned long hardirq_disable_ip;unsigned int hardirq_disable_event;int softirqs_enabled;unsigned long softirq_disable_ip;unsigned int softirq_disable_event;unsigned long softirq_enable_ip;unsigned int softirq_enable_event;int hardirq_context;int softirq_context;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_LOCKDEP
# define MAX_LOCK_DEPTH 48ULu64 curr_chain_key;int lockdep_depth;struct held_lock held_locks[MAX_LOCK_DEPTH];unsigned int lockdep_recursion;
#endif/* journalling filesystem info */void *journal_info;/* stacked block device info */struct bio *bio_list, **bio_tail;/* VM state */struct reclaim_state *reclaim_state;struct backing_dev_info *backing_dev_info;struct io_context *io_context;unsigned long ptrace_message;siginfo_t *last_siginfo; /* For ptrace use. */
#ifdef CONFIG_TASK_XACCT
/* i/o counters(bytes read/written, #syscalls */u64 rchar, wchar, syscr, syscw;
#endifstruct task_io_accounting ioac;
#if defined(CONFIG_TASK_XACCT)u64 acct_rss_mem1; /* accumulated rss usage */u64 acct_vm_mem1; /* accumulated virtual memory usage */cputime_t acct_stimexpd;/* stime since last update */
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_NUMAstruct mempolicy *mempolicy;short il_next;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_CPUSETSnodemask_t mems_allowed;int cpuset_mems_generation;int cpuset_mem_spread_rotor;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_CGROUPS/* Control Group info protected by css_set_lock */struct css_set *cgroups;/* cg_list protected by css_set_lock and tsk->alloc_lock */struct list_head cg_list;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_FUTEXstruct robust_list_head __user *robust_list;
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPATstruct compat_robust_list_head __user *compat_robust_list;
#endifstruct list_head pi_state_list;struct futex_pi_state *pi_state_cache;
#endifatomic_t fs_excl; /* holding fs exclusive resources */struct rcu_head rcu;/** cache last used pipe for splice*/struct pipe_inode_info *splice_pipe;
#ifdef CONFIG_TASK_DELAY_ACCTstruct task_delay_info *delays;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_FAULT_INJECTIONint make_it_fail;
#endifstruct prop_local_single dirties;
#ifdef CONFIG_LATENCYTOPint latency_record_count;struct latency_record latency_record[LT_SAVECOUNT];
#endif
};/** Priority of a process goes from 0..MAX_PRIO-1, valid RT* priority is 0..MAX_RT_PRIO-1, and SCHED_NORMAL/SCHED_BATCH* tasks are in the range MAX_RT_PRIO..MAX_PRIO-1. Priority* values are inverted: lower p->prio value means higher priority.** The MAX_USER_RT_PRIO value allows the actual maximum* RT priority to be separate from the value exported to* user-space. This allows kernel threads to set their* priority to a value higher than any user task. Note:* MAX_RT_PRIO must not be smaller than MAX_USER_RT_PRIO.*/
struct files_struct {/** read mostly part*/atomic_t count;struct fdtable *fdt;struct fdtable fdtab;/** written part on a separate cache line in SMP*/spinlock_t file_lock ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;int next_fd;struct embedded_fd_set close_on_exec_init;struct embedded_fd_set open_fds_init;struct file * fd_array[NR_OPEN_DEFAULT];
};
struct file {/** fu_list becomes invalid after file_free is called and queued via* fu_rcuhead for RCU freeing*/union {struct list_head fu_list;struct rcu_head fu_rcuhead;} f_u;struct path f_path;
#define f_dentry f_path.dentry
#define f_vfsmnt f_path.mntconst struct file_operations *f_op;atomic_t f_count;unsigned int f_flags;mode_t f_mode;loff_t f_pos;struct fown_struct f_owner;unsigned int f_uid, f_gid;struct file_ra_state f_ra;u64 f_version;
#ifdef CONFIG_SECURITYvoid *f_security;
#endif/* needed for tty driver, and maybe others */void *private_data; //重点!!!!#ifdef CONFIG_EPOLL/* Used by fs/eventpoll.c to link all the hooks to this file */struct list_head f_ep_links;spinlock_t f_ep_lock;
#endif /* #ifdef CONFIG_EPOLL */struct address_space *f_mapping;
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_WRITECOUNTunsigned long f_mnt_write_state;
#endif
};
struct file 中成员void*private_data; ,将会指向struct socket;同时struct socket中的struct file *file同时也会指向管理他的文件描述符。
struct tcp_sock {/* inet_connection_sock has to be the first member of tcp_sock */struct inet_connection_sock inet_conn; //重点!!!!!u16 tcp_header_len; /* Bytes of tcp header to send */u16 xmit_size_goal; /* Goal for segmenting output packets *//** Header prediction flags* 0x5?10 << 16 + snd_wnd in net byte order*/__be32 pred_flags;/** RFC793 variables by their proper names. This means you can* read the code and the spec side by side (and laugh ...)* See RFC793 and RFC1122. The RFC writes these in capitals.*/u32 rcv_nxt; /* What we want to receive next */u32 copied_seq; /* Head of yet unread data */u32 rcv_wup; /* rcv_nxt on last window update sent */u32 snd_nxt; /* Next sequence we send */u32 snd_una; /* First byte we want an ack for */u32 snd_sml; /* Last byte of the most recently transmitted small packet */u32 rcv_tstamp; /* timestamp of last received ACK (for keepalives) */u32 lsndtime; /* timestamp of last sent data packet (for restart window) *//* Data for direct copy to user */struct {struct sk_buff_head prequeue;struct task_struct *task;struct iovec *iov;int memory;int len;
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_DMA/* members for async copy */struct dma_chan *dma_chan;int wakeup;struct dma_pinned_list *pinned_list;dma_cookie_t dma_cookie;
#endif} ucopy;u32 snd_wl1; /* Sequence for window update */u32 snd_wnd; /* The window we expect to receive */u32 max_window; /* Maximal window ever seen from peer */u32 mss_cache; /* Cached effective mss, not including SACKS */u32 window_clamp; /* Maximal window to advertise */u32 rcv_ssthresh; /* Current window clamp */u32 frto_highmark; /* snd_nxt when RTO occurred */u8 reordering; /* Packet reordering metric. */u8 frto_counter; /* Number of new acks after RTO */u8 nonagle; /* Disable Nagle algorithm? */u8 keepalive_probes; /* num of allowed keep alive probes *//* RTT measurement */u32 srtt; /* smoothed round trip time << 3 */u32 mdev; /* medium deviation */u32 mdev_max; /* maximal mdev for the last rtt period */u32 rttvar; /* smoothed mdev_max */u32 rtt_seq; /* sequence number to update rttvar */u32 packets_out; /* Packets which are "in flight" */u32 retrans_out; /* Retransmitted packets out */
/** Options received (usually on last packet, some only on SYN packets).*/struct tcp_options_received rx_opt;/** Slow start and congestion control (see also Nagle, and Karn & Partridge)*/u32 snd_ssthresh; /* Slow start size threshold */u32 snd_cwnd; /* Sending congestion window */u32 snd_cwnd_cnt; /* Linear increase counter */u32 snd_cwnd_clamp; /* Do not allow snd_cwnd to grow above this */u32 snd_cwnd_used;u32 snd_cwnd_stamp;struct sk_buff_head out_of_order_queue; /* Out of order segments go here */u32 rcv_wnd; /* Current receiver window */u32 write_seq; /* Tail(+1) of data held in tcp send buffer */u32 pushed_seq; /* Last pushed seq, required to talk to windows *//* SACKs data */struct tcp_sack_block duplicate_sack[1]; /* D-SACK block */struct tcp_sack_block selective_acks[4]; /* The SACKS themselves*/struct tcp_sack_block recv_sack_cache[4];struct sk_buff *highest_sack; /* highest skb with SACK received* (validity guaranteed only if* sacked_out > 0)*//* from STCP, retrans queue hinting */struct sk_buff* lost_skb_hint;struct sk_buff *scoreboard_skb_hint;struct sk_buff *retransmit_skb_hint;struct sk_buff *forward_skb_hint;int lost_cnt_hint;int retransmit_cnt_hint;u32 lost_retrans_low; /* Sent seq after any rxmit (lowest) */u16 advmss; /* Advertised MSS */u32 prior_ssthresh; /* ssthresh saved at recovery start */u32 lost_out; /* Lost packets */u32 sacked_out; /* SACK'd packets */u32 fackets_out; /* FACK'd packets */u32 high_seq; /* snd_nxt at onset of congestion */u32 retrans_stamp; /* Timestamp of the last retransmit,* also used in SYN-SENT to remember stamp of* the first SYN. */u32 undo_marker; /* tracking retrans started here. */int undo_retrans; /* number of undoable retransmissions. */u32 urg_seq; /* Seq of received urgent pointer */u16 urg_data; /* Saved octet of OOB data and control flags */u8 urg_mode; /* In urgent mode */u8 ecn_flags; /* ECN status bits. */u32 snd_up; /* Urgent pointer */u32 total_retrans; /* Total retransmits for entire connection */u32 bytes_acked; /* Appropriate Byte Counting - RFC3465 */unsigned int keepalive_time; /* time before keep alive takes place */unsigned int keepalive_intvl; /* time interval between keep alive probes */int linger2;unsigned long last_synq_overflow; u32 tso_deferred;/* Receiver side RTT estimation */struct {u32 rtt;u32 seq;u32 time;} rcv_rtt_est;/* Receiver queue space */struct {int space;u32 seq;u32 time;} rcvq_space;/* TCP-specific MTU probe information. */struct {u32 probe_seq_start;u32 probe_seq_end;} mtu_probe;#ifdef CONFIG_TCP_MD5SIG
/* TCP AF-Specific parts; only used by MD5 Signature support so far */struct tcp_sock_af_ops *af_specific;/* TCP MD5 Signagure Option information */struct tcp_md5sig_info *md5sig_info;
#endif
};
inet_connection_sock中request_sock_queue,既是全连接队列
struct inet_connection_sock {/* inet_sock has to be the first member! */struct inet_sock icsk_inet;struct request_sock_queue icsk_accept_queue;struct inet_bind_bucket *icsk_bind_hash;unsigned long icsk_timeout;struct timer_list icsk_retransmit_timer;struct timer_list icsk_delack_timer;__u32 icsk_rto;__u32 icsk_pmtu_cookie;const struct tcp_congestion_ops *icsk_ca_ops;const struct inet_connection_sock_af_ops *icsk_af_ops;unsigned int (*icsk_sync_mss)(struct sock *sk, u32 pmtu);__u8 icsk_ca_state;__u8 icsk_retransmits;__u8 icsk_pending;__u8 icsk_backoff;__u8 icsk_syn_retries;__u8 icsk_probes_out;__u16 icsk_ext_hdr_len;struct {__u8 pending; /* ACK is pending */__u8 quick; /* Scheduled number of quick acks */__u8 pingpong; /* The session is interactive */__u8 blocked; /* Delayed ACK was blocked by socket lock */__u32 ato; /* Predicted tick of soft clock */unsigned long timeout; /* Currently scheduled timeout */__u32 lrcvtime; /* timestamp of last received data packet */__u16 last_seg_size; /* Size of last incoming segment */__u16 rcv_mss; /* MSS used for delayed ACK decisions */ } icsk_ack;struct {int enabled;/* Range of MTUs to search */int search_high;int search_low;/* Information on the current probe. */int probe_size;} icsk_mtup;u32 icsk_ca_priv[16];
#define ICSK_CA_PRIV_SIZE (16 * sizeof(u32))
};
inet_sock首个成员struct sock sk
struct inet_sock {/* sk and pinet6 has to be the first two members of inet_sock */struct sock sk;
#if defined(CONFIG_IPV6) || defined(CONFIG_IPV6_MODULE)struct ipv6_pinfo *pinet6;
#endif/* Socket demultiplex comparisons on incoming packets. */__be32 daddr;__be32 rcv_saddr;__be16 dport;__u16 num;__be32 saddr;__s16 uc_ttl;__u16 cmsg_flags;struct ip_options *opt;__be16 sport;__u16 id;__u8 tos;__u8 mc_ttl;__u8 pmtudisc;__u8 recverr:1,is_icsk:1,freebind:1,hdrincl:1,mc_loop:1;int mc_index;__be32 mc_addr;struct ip_mc_socklist *mc_list;struct {unsigned int flags;unsigned int fragsize;struct ip_options *opt;struct dst_entry *dst;int length; /* Total length of all frames */__be32 addr;struct flowi fl;} cork;
};
相关文章:

【Linux网络】TCP全连接队列
TCP 相关实验 理解 listen 的第二个参数 基于刚才封装的 TcpSocket 实现以下测试代码对于服务器, listen 的第二个参数设置为 1, 并且不调用 accept测试代码链接 test_server.cc #include "tcp_socket.hpp"int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {if (argc ! 3) {pri…...
HTML 颜色全解析:从命名规则到 RGBA/HSL 值,附透明度设置与场景应用指南
一、HTML 颜色系统详解 HTML 中的颜色可以通过多种方式定义,包括颜色名称、RGB 值、十六进制值、HSL 值等,同时支持透明度调整。以下是详细分类及应用场景: 1. 颜色名称(预定义关键字) HTML 预定义了 140 个标准颜色名…...

蓝桥杯12届国B 完全日期
题目描述。 如果一个日期中年月日的各位数字之和是完全平方数,则称为一个完全日期。 例如:2021 年 6 月 5 日的各位数字之和为 20216516,而 16 是一个完全平方数,它是 4 的平方。所以 2021 年 6 月 5 日是一个完全日期。 例如&…...

深度剖析多模态大模型中的视频编码器算法
写在前面 随着多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)的兴起,AI 理解世界的能力从静态的文本和图像,进一步拓展到了动态的、包含丰富时空信息的视频。视频作为一种承载了动作、交互、场景变化和声音(虽然本文主要聚焦视觉部分)的复杂数据形式,为 MLLM 提供了理解真实世界动态和因果关…...

游戏引擎学习第282天:Z轴移动与摄像机运动
运行游戏,展示目前进展 我们目前正在进行一个游戏开发项目。昨天,我们实现了基于房间的角色移动系统,并且加入了摄像机的跟随滚动功能。这是我们首次进入“游戏逻辑设计”阶段,也就是说,我们开始构建游戏本身的行为和…...

C++中的std::allocator
C中的std::allocator 文章目录 C中的std::allocator1.std::allocator1.1C中的placement new 和operator new1.2一个custom allocator的实现1.3使用std::allocator_traits实现allocator 1.std::allocator C中的std::allocator默默工作在CSTL中的所有容器的内存分配上࿰…...

Git/GitLab日常使用的命令指南来了!
在 GitLab 中拉取并合并代码的常见流程是通过 Git 命令来完成的。以下是一个标准的 Git 工作流,适用于从远程仓库(如 GitLab)拉取代码、切换分支、合并更新等操作。 🌐 一、基础命令:拉取最新代码 # 拉取远程仓库的所…...
aws 实践创建policy + Role
今天Cyber 通过image 来创建EC2 的时候,要添加policy, 虽然是administrator 的role, 参考Cyber 提供的link: Imageshttps://docs.cyberark.com/pam-self-hosted/14.2/en/content/pas%20cloud/images.htm#Bring 1 Step1:...
)
[Java实战]Spring Boot 解决跨域问题(十四)
[Java实战]Spring Boot 解决跨域问题(十四) 一、CORS 问题背景 什么是跨域问题? 当浏览器通过 JavaScript 发起跨域请求(不同协议、域名、端口)时,会触发同源策略限制,导致请求被拦截。 示例场…...

【HarmonyOS 5】鸿蒙星闪NearLink详解
【HarmonyOS 5】鸿蒙星闪NearLink详解 一、前言 鸿蒙星闪NearLink Kit 是 HarmonyOS 提供的短距离通信服务,支持星闪设备间的连接、数据交互。例如,手机可作为中心设备与外围设备(如鼠标、手写笔、智能家电、车钥匙等)通过星闪进…...

Python高级进阶:Vim与Vi使用指南
李升伟 整理 在 Python 高级进阶中,使用 Vim 或 Vi 作为代码编辑器可以显著提升开发效率,尤其是在远程服务器开发或快速脚本编辑时。以下是关于它们在 Python 开发中的高级应用详解: 1. Vim/Vi 简介 Vi:经典的 Unix 文本编辑器…...

【Python】对象生命周期全解析
Python对象生命周期全解析 在Python中,一个对象从创建到销毁会经历一系列过程,理解这些过程对于编写高效、可靠的Python代码非常重要。下面我将详细讲解Python对象的完整生命周期。 1. 对象创建阶段 (1) 内存分配 当使用类实例化时(obj MyClass())&…...
在影评情感分析中的处理流程示例)
自然语言处理(NLP)在影评情感分析中的处理流程示例
自然语言处理(NLP)在影评情感分析中的处理流程示例 以影评情感分析为例,为你详细介绍自然语言处理的处理流程。在这个例子中,我们将使用 Python 和一些常用的 NLP 库,如nltk(自然语言工具包)和…...

WF24 wifi/蓝牙模块串口与手机蓝牙通信
usb-ttl ch340接线 打开串口工具SSCOM,端口号选择ch340接的那个口,波特率改成115200 DX-SMART_2.0.5.apk下载 手机打开DX-SMART软件 点击透传-搜索BLE-连接WF24-BLE 连接成功串口会收到消息 [14:37:10.591]收←◆ BLE_CONNECT_SUCCESS发送命令ATBLUFI…...

互联网大厂Java求职面试:优惠券服务架构设计与AI增强实践-3
互联网大厂Java求职面试:优惠券服务架构设计与AI增强实践-3 场景背景 面试场景设定在一家大型互联网公司,面试官为拥有10年以上经验的技术总监,专注于高并发、高可用系统的架构设计。候选人郑薪苦是一名技术潜力十足的程序员,擅…...

C++核心编程--1 内存分区模型
C程序执行时,内存可以划分为4部分 代码区:存放函数体的二进制代码 全局区:存放全局变量、静态变量、常量 栈区:局部变量、函数参数值,编译器自动分配和释放 堆区:程序员自己分配和释放 1.1 程序运行前…...
)
02_线性模型(回归分类模型)
用于分类的线性模型 线性模型也广泛应用于分类问题,可以利用下面的公式进行预测: $ \widehat y w[0]*x[0]w[1]*x[1]…w[p]*x[p]b > 0$ 公式看起来与线性回归的公式非常相似,但没有返回特征的加权求和,而是为预测设置了阈值…...

通义千问席卷日本!开源界“卷王”阿里通义千问成为日本AI发展新基石
据日本经济新闻(NIKKEI)报道,通义千问已成为日本AI开发的新基础,其影响力正逐步扩大,深刻改变着日本AI产业的格局。 同时,日本经济新闻将通义千问Qwen2.5-Max列为全球AI模型综合评测第六名,不仅…...

流程编辑器Bpmn与LogicFlow学习
工作流技术如何与用户交互结合(如动态表单、任务分配)处理过 XML 与 JSON 的转换自定义过 bpmn.js 的样式(如修改节点颜色、形状、图标)扩展过上下文菜单(Palette)或属性面板(Properties Panel&…...

Figma 新手教程学习笔记
📺 视频地址:Figma新手教程2025|30分钟高效掌握Figma基础操作与UI设计流程_哔哩哔哩_bilibili 🧭 课程结构 Figma 简介(00:38) 熟悉工作环境(01:49) 操作界面介绍(03:…...

RabbitMQ的工作队列模式和路由模式有什么区别?
RabbitMQ 的工作队列模式(Work Queues)和路由模式(Routing)是两种不同的消息传递模式,主要区别在于消息的分发逻辑和使用场景。以下是它们的核心差异: 1. 工作队列模式(Work Queues)…...

什么是 ANR 如何避免它
一、什么是 ANR? ANR(Application Not Responding) 是 Android 系统在应用程序主线程(UI 线程)被阻塞超过一定时间后触发的错误机制。此时系统会弹出一个对话框提示用户“应用无响应”,用户可以选择等待或强…...

配置Spark环境
1.上传spark安装包到某一台机器(自己在finaShell上的机器)。 2.解压。 把第一步上传的安装包解压到/opt/module下(也可以自己决定解压到哪里)。对应的命令是:tar -zxvf 安装包 -C /opt/module 3.重命名。进入/opt/mo…...

嵌入式硬件篇---IIC
文章目录 前言1. IC协议基础1.1 物理层特性两根信号线SCLSDA支持多主多从 标准模式电平 1.2 通信流程起始条件(Start Condition)从机地址(Slave Address)应答(ACK/NACK)数据传输:停止条件&#…...

Window下Jmeter多机压测方法
1.概述 Jmeter多机压测的原理,是通过单个jmeter客户端,控制多个远程的jmeter服务器,使他们同步的对服务器进行压力测试。 以此方式收集测试数据的好处在于: 保存测试采样数据到本地机器通过单台机器管理多个jmeter执行引擎测试…...

视频图像压缩领域中 DCT 的 DC 系数和 AC 系数详解
引言 在数字图像与视频压缩领域,离散余弦变换(Discrete Cosine Transform, DCT)凭借其卓越的能量集中特性,成为JPEG、MPEG等国际标准的核心技术。DCT通过将空域信号映射到频域,分离出DC系数(直流分量&…...

K8S cgroups详解
以下是 Kubernetes 中 cgroups(Control Groups) 的详细解析,涵盖其核心原理、在 Kubernetes 中的具体应用及实践操作: 一、cgroups 基础概念 1. 是什么? cgroups 是 Linux 内核提供的 资源隔离与控制机制,…...

能源设备数据采集
在全球可持续发展目标与环境保护理念日益深入人心的时代背景下,有效管理和优化能源使用已成为企业实现绿色转型、提升竞争力的关键路径。能源设备数据采集系统,作为能源管理的核心技术支撑,通过对各类能源生产设备运行数据的全面收集、深度分…...
Go语言安装proto并且使用gRPC服务(2025最新WINDOWS系统)
1.protobuf简介 protobuf 即 Protocol Buffers,是一种轻便高效的结构化数据存储格式,与语言、平台无关,可扩展可序列化。protobuf 性能和效率大幅度优于 JSON、XML 等其他的结构化数据格式。protobuf 是以二进制方式存储的,占用空…...

[Linux性能优化] 线程卡顿优化。Linux加入USB(HID)热插拔线程占用CPU优化。Linux中CPU使用率过高优化
文章目录 [Linux性能优化] 线程卡顿优化。0、省流版本一、问题定位:CPU 资源分析二、线程卡顿现场复现线程优化前图片 三、线程卡顿优化方向1.如果是轮询方式2.如果是事件驱动方式 四、修改方式线程优化后图片 [Linux性能优化] 线程卡顿优化。 0、省流版本 如果采…...
