Athena 执行引擎:在线服务计算的效率王者
引言
在在线服务领域,计算任务呈现出独特的特性:一方面,数据量通常不会过于庞大,因为在线服务对耗时和响应速度有着严苛要求;另一方面,计算任务具有可控性,其大多并非由用户实时输入动态生成,属于有限集合,因此能够进行预编译处理。在这样的背景下,传统的向量化引擎如 velox,可能会因数据在行存与列存之间转换产生的额外开销,导致性能不增反降;而解释性引擎也无法充分发挥预编译带来的效率优势。
athena 执行引擎正是为了在上述场景中实现极致性能而诞生。此前笔者介绍的 jitfusion 引擎:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34262582/article/details/145496431?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501。
在列表类型计算和优化方面存在不足,且缺乏便捷的类脚本语言描述执行过程。经过持续完善与优化,athena 应运而生,用户能够通过简洁的 DSL 描述执行逻辑。本文将深入剖析 athena 的设计架构、核心优化特性,并通过严谨的 benchmark 对比,展现其相较于 exprtk 和 gandiva 的性能优势。
设计架构:灵活接口与简洁 DSL
接口设计
首先 athena 提供的对外接口是这样的。
// Applicable to simple scenarios, the program will not actually use a custom store function to write data. Instead,// the result will be returned, similar to expression scenarios.// If you need to optimize the memory allocation issue of ExecContext, you can use the function passed to ExecContext.Status Compile(const std::string& code, const std::unique_ptr<FunctionRegistry>& func_registry);Status Execute(void* entry_arguments, RetType* result);Status Execute(ExecContext& exec_ctx, void* entry_arguments, RetType* result);// Applicable to complex scenarios where multiple pipelines are computed simultaneously. Each pipeline writes data// using a custom function, and results are not returned. This is similar to feature processing scenarios.// If you need to optimize the memory allocation issue of ExecContext, you can use the function passed to ExecContext.Status Compile(const std::vector<std::string>& code, const std::unique_ptr<FunctionRegistry>& func_registry);Status Execute(void* entry_arguments, void* result);Status Execute(ExecContext& exec_ctx, void* entry_arguments, void* result);其中,Compile接口负责编译 DSL 代码,只有完成编译后,才能通过 Execute 接口执行任务,且 Execute 接口具备线程安全特性。code 为 DSL 代码,func_registry 用于函数注册,entry_arguments 接收用户输入,result 存储输出结果,exec_ctx 则作为执行上下文,默认情况下即使不传入也会自动生成。
这个设计有几个好处。
1.通过传入 func_registry,可避免重复的函数注册操作,适用于函数注册相对固定的服务场景。
2.用户能够自由定义输入输出,无需按照引擎规则重组数据,从而有效降低执行成本。
3.用户可通过传入 exec_ctx,实现自定义的内存池化逻辑,减少频繁内存分配带来的性能损耗。
4.支持同时编译多个计算 pipeline,能够自动识别并优化重复计算路径,尤其适用于特征工程等复杂场景。
当用户使用第一组函数来执行时,result 会得到最后一行代码返回的结果。使用第二组函数来执行时,result 需要用户调用自定义的函数来把结果写到传入的 result 指针,此时无法通过最后一行代码返回得到结果。
DSL
athena 的 DSL 遵循简洁易用的设计原则,其核心规则如下:
1.执行过程由 statement 组成,每个 statement 的分隔符是’;'号。
2.statement 的格式必须按以下方式构造:{ID} = {Expression},其中 ID 表示变量名,Expression 是一个表达式。
3.除了支持各种运算操作外,表达式还支持几种特殊语法。函数语法:{function_name}({arg1}, {arg2}, …)。它还支持 switch 语句和 if 语句。遵循简洁原则,switch 语句和 if 语句的语法与函数语法类似:if({condition}, {true_expression}, {false_expression}),switch({case1}, {value1}, {case2}, {value2}…, {default_value})。
4.用户可通过 entry_arg 访问输入参数指针,exec_ctx 访问执行上下文,output 访问输出参数指针。
核心优化:性能提升的关键
athena 内部有很多优化,下面来一一讲解。
Constant folding
athena 会在编译阶段自动计算可确定的常量表达式。例如:
int main() {athena::Athena athena;std::unique_ptr<athena::FunctionRegistry> func_registry;athena::FunctionRegistryFactory::CreateFunctionRegistry(&func_registry);std::string code = R"(r = 2 * 3 + 4;)";std::vector<double> r(3);auto st = athena.Compile(code, func_registry);athena::RetType ret;athena.Execute(nullptr, &ret);std::cout << std::get<int32_t>(ret) << "\n";return 0;
}
计算 2 * 3 + 4, 得到的中间代码是这样的。
; ModuleID = 'module'
source_filename = "module"
target datalayout = "e-m:o-i64:64-i128:128-n32:64-S128-Fn32"; Function Attrs: mustprogress nofree norecurse nosync nounwind willreturn memory(none)
define noundef i32 @entry(ptr noalias nocapture readonly %0, ptr noalias nocapture readnone %1, ptr noalias nocapture readnone %2) local_unnamed_addr #0 {
entryBB:ret i32 10
}attributes #0 = { mustprogress nofree norecurse nosync nounwind willreturn memory(none) }
编译后的中间代码直接返回结果10,避免了运行时的重复计算。
Dead code elimination
引擎能够识别并删除对最终结果无影响的代码。比如:
int main() {athena::Athena athena;std::unique_ptr<athena::FunctionRegistry> func_registry;athena::FunctionRegistryFactory::CreateFunctionRegistry(&func_registry);std::string code = R"(a = 2 * 3 + 4;b = 100 * 100;c = a * 2;)";std::vector<double> r(3);auto st = athena.Compile(code, func_registry);athena::RetType ret;athena.Execute(nullptr, &ret);std::cout << std::get<int32_t>(ret) << "\n";return 0;
}
由于仅最后一行代码的结果被返回,“b = 100 * 100;” 被认定为死代码,编译时自动剔除。
; ModuleID = 'module'
source_filename = "module"
target datalayout = "e-m:o-i64:64-i128:128-n32:64-S128-Fn32"; Function Attrs: mustprogress nofree norecurse nosync nounwind willreturn memory(none)
define noundef i32 @entry(ptr noalias nocapture readonly %0, ptr noalias nocapture readnone %1, ptr noalias nocapture readnone %2) local_unnamed_addr #0 {
entryBB:ret i32 20
}attributes #0 = { mustprogress nofree norecurse nosync nounwind willreturn memory(none) }
Static Typing Language
athena 的 DSL 作为静态类型语言,athena 在编译期确定所有变量类型,能够进行严格的类型安全检查。
比如说除0。此时编译会失败,输出错误信息。
int main() {athena::Athena athena;std::unique_ptr<athena::FunctionRegistry> func_registry;athena::FunctionRegistryFactory::CreateFunctionRegistry(&func_registry);std::string code = R"(a = 1 / 0;)";std::vector<double> r(3);auto st = athena.Compile(code, func_registry);std::cout << st.ToString() << std::endl;return 0;
}
Parse Error: Cant no div/mod zero
或者是浮点数位运算。
int main() {athena::Athena athena;std::unique_ptr<athena::FunctionRegistry> func_registry;athena::FunctionRegistryFactory::CreateFunctionRegistry(&func_registry);std::string code = R"(a = 1.0 & 2.0;)";std::vector<double> r(3);auto st = athena.Compile(code, func_registry);std::cout << st.ToString() << std::endl;return 0;
}
Runtime Error: Module verification failed: Logical operators only work with integral types!%3 = and double 1.000000e+00, 2.000000e+00
又或者是函数调用的时候类型不匹配。
int main() {athena::Athena athena;std::unique_ptr<athena::FunctionRegistry> func_registry;athena::FunctionRegistryFactory::CreateFunctionRegistry(&func_registry);std::string code = R"(a = Len(1.0);)";std::vector<double> r(3);auto st = athena.Compile(code, func_registry);std::cout << st.ToString() << std::endl;return 0;
}
Runtime Error: function Len(f64) not found
这些都可以在编译期做检查来避免一些简单的错误。
Short-Circuit Evaluation
athena 优化条件语句实现,仅执行必要分支。举例:
double LoadF64(void* entry_arguments, int32_t index) {auto* args = reinterpret_cast<double*>(entry_arguments);return args[index];
}void bench_short_path(benchmark::State& state) {athena::Athena athena;std::unique_ptr<athena::FunctionRegistry> func_registry;athena::FunctionRegistryFactory::CreateFunctionRegistry(&func_registry);athena::FunctionSignature sign("load", {athena::ValueType::kPtr, athena::ValueType::kI32}, athena::ValueType::kF64);func_registry->RegisterReadOnlyCFunc(sign, reinterpret_cast<void*>(LoadF64));std::string code = R"(v1 = load(entry_arg, 0);v2 = load(entry_arg, 1);r = if(v1 + v2 < 100000000, floor(log2(1 + v1 + v2)), 27.0);)";athena.Compile(code, func_registry);athena::RetType ret;std::vector<double> value = {100000000, 100000000};for (auto _ : state) {athena.Execute(value.data(), &ret);}// std::cout << "ret=" << std::get<double>(ret) << '\n';
}void bench_run_all_path(benchmark::State& state) {athena::Athena athena;std::unique_ptr<athena::FunctionRegistry> func_registry;athena::FunctionRegistryFactory::CreateFunctionRegistry(&func_registry);athena::FunctionSignature sign("load", {athena::ValueType::kPtr, athena::ValueType::kI32}, athena::ValueType::kF64);func_registry->RegisterReadOnlyCFunc(sign, reinterpret_cast<void*>(LoadF64));std::string code = R"(v1 = load(entry_arg, 0);v2 = load(entry_arg, 1);r = max(floor(log2(1 + v1 + v2)), 27.0);)";athena.Compile(code, func_registry);athena::RetType ret;std::vector<double> value = {100000000, 100000000};for (auto _ : state) {athena.Execute(value.data(), &ret);}// std::cout << "ret=" << std::get<double>(ret) << '\n';
}
BENCHMARK(bench_short_path);
BENCHMARK(bench_run_all_path);
BENCHMARK_MAIN();
这段代码从逻辑上来说不能完全等价, 但我们关注的是 if 语句和 max 函数的区别, if 在 athena 里的实现只会执行其中一个分支, 而 max 需要把所有分支执行完后比较, 从这个case上来说第一个 benchmark 不会走 log 函数,会直接返回 27,第二个 benchmark 则要执行 log 函数,笔者找了一台执行 log 数学函数比较慢的机器上跑的结果如下:

Common Subexpression Elimination
自动识别并合并相同计算路径。无论是简单的变量计算,还是符合规则的函数调用,只要计算逻辑相同,athena 均会合并计算。
比如,下面这个例子里,显然 add1 和 add2 是一样的。
double LoadF64(void* entry_arguments, int32_t index) {auto* args = reinterpret_cast<double*>(entry_arguments);return args[index];
}int main() {athena::Athena athena;std::unique_ptr<athena::FunctionRegistry> func_registry;athena::FunctionRegistryFactory::CreateFunctionRegistry(&func_registry);athena::FunctionSignature sign("load", {athena::ValueType::kPtr, athena::ValueType::kI32}, athena::ValueType::kF64);func_registry->RegisterReadOnlyCFunc(sign, reinterpret_cast<void*>(LoadF64));std::string code = R"(v1 = load(entry_arg, 0);v2 = load(entry_arg, 1);add1 = v1 + v2;add2 = v1 + v2;add3 = add1 + add2;)";std::vector<double> value = {100000000, 100000000};auto st = athena.Compile(code, func_registry);std::cout << st.ToString() << '\n';return 0;
}
它编译出来的中间代码则只会计算一次 v1 + v2。
; ModuleID = 'module'
source_filename = "module"
target datalayout = "e-m:o-i64:64-i128:128-n32:64-S128-Fn32"; Function Attrs: nofree nounwind memory(read)
define double @entry(ptr noalias readonly %0, ptr noalias nocapture readnone %1, ptr noalias nocapture readnone %2) local_unnamed_addr #0 {
entryBB:%call_load = tail call double @"load(ptr, i32)"(ptr %0, i32 0)%call_load1 = tail call double @"load(ptr, i32)"(ptr %0, i32 1)%3 = fadd double %call_load, %call_load1%4 = fadd double %3, %3ret double %4
}; Function Attrs: nofree nounwind memory(read)
declare double @"load(ptr, i32)"(ptr, i32) local_unnamed_addr #0attributes #0 = { nofree nounwind memory(read) }
可能你会想知道如果是函数调用,是否可以合并。不考虑直接使用 LLVM API 实现的 intrinic function,只考虑 C 函数的话,在 athena 里遵循一定的规则就可以合并。
athena 推荐用户将函数分为两类,一种 read only function,一种是 store function,对应的注册接口如下:
// Register ReadOnlyCFuncStatus RegisterReadOnlyCFunc(const FunctionSignature &func_sign, void *c_func_ptr);// Register StoreCFunc// store_args_index is the index of the args in the function signature that is OuputNodeStatus RegisterStoreCFunc(const FunctionSignature &func_sign, void *c_func_ptr, uint32_t store_args_index);
在 athena 里只要函数不直接修改入参的变量,通过生成新的变量返回函数结果,堆内存分配通过 exec_ctx 分配(该行为不被认为是修改入参),则可以被认为是 read only function。把计算结果通过 output 指针写到用户定义的区域,以便用户在引擎执行完后可以获取到结果,这类函数被认为是 store function。在计算任务里,大体都可以被拆成这两种函数。假设执行过程中只会有这两种函数,则 athena 也会合并相同的计算。举例:
athena::I32ListStruct LoadI32List(void* entry_arguments, int32_t index) {auto* args = reinterpret_cast<std::vector<int32_t>*>(entry_arguments);athena::I32ListStruct result;result.data = args[index].data();result.len = args[index].size();return result;
}int32_t StoreI32List(void* output, int32_t index, athena::I32ListStruct value) {auto store_i = reinterpret_cast<std::vector<int32_t>*>(output)[index];store_i.resize(value.len);std::copy_n(value.data, value.len, store_i.begin());return 0;
}int main() {athena::Athena athena;std::unique_ptr<athena::FunctionRegistry> func_registry;athena::FunctionRegistryFactory::CreateFunctionRegistry(&func_registry);athena::FunctionSignature sign1("load", {athena::ValueType::kPtr, athena::ValueType::kI32},athena::ValueType::kI32List);func_registry->RegisterReadOnlyCFunc(sign1, reinterpret_cast<void*>(LoadI32List));athena::FunctionSignature sign2("store",{athena::ValueType::kPtr, athena::ValueType::kI32, athena::ValueType::kI32List},athena::ValueType::kI32);func_registry->RegisterStoreCFunc(sign2, reinterpret_cast<void*>(StoreI32List), 1);std::string code = R"(a = load(entry_arg, 0);b = GenLargeBitmap(a, 3, exec_ctx);c = load(entry_arg, 1);r1 = store(output, 0, FilterByBitmap(a, b, CountBits(b), exec_ctx));r2 = store(output, 1, FilterByBitmap(c, b, CountBits(b), exec_ctx));)";auto st = athena.Compile(std::vector<std::string>{code}, func_registry);std::cout << st.ToString() << '\n';return 0;
}
这段代码从 entry_arg 里加载了两个 i32list 命名为 a, c,然后生成一个 a > 3 的位图,根据这个位图过滤 a,c,得到的结果写入到 output 里。这段代码编译后的中间代码表示是这样的。
; ModuleID = 'module'
source_filename = "module"
target datalayout = "e-m:o-i64:64-i128:128-n32:64-S128-Fn32"%I32ListStruct = type { ptr, i32 }
%U8ListStruct = type { ptr, i32 }; Function Attrs: nounwind memory(read, argmem: readwrite)
define noundef i8 @entry(ptr noalias readonly %0, ptr noalias %1, ptr noalias nocapture %2) local_unnamed_addr #0 {
entryBB:%call_load = tail call %I32ListStruct @"load(ptr, i32)"(ptr %0, i32 0)%call_GenLargeBitmap = tail call %U8ListStruct @"GenLargeBitmap(i32list, i32, ptr)"(%I32ListStruct %call_load, i32 3, ptr %1)%call_CountBits = tail call i32 @"CountBits(u8list)"(%U8ListStruct %call_GenLargeBitmap)%call_FilterByBitmap = tail call %I32ListStruct @"FilterByBitmap(i32list, u8list, u32, ptr)"(%I32ListStruct %call_load, %U8ListStruct %call_GenLargeBitmap, i32 %call_CountBits, ptr %1)%call_store = tail call i32 @"store(ptr, i32, i32list)"(ptr %2, i32 0, %I32ListStruct %call_FilterByBitmap)%call_load4 = tail call %I32ListStruct @"load(ptr, i32)"(ptr %0, i32 1)%call_FilterByBitmap10 = tail call %I32ListStruct @"FilterByBitmap(i32list, u8list, u32, ptr)"(%I32ListStruct %call_load4, %U8ListStruct %call_GenLargeBitmap, i32 %call_CountBits, ptr %1)%call_store11 = tail call i32 @"store(ptr, i32, i32list)"(ptr %2, i32 1, %I32ListStruct %call_FilterByBitmap10)ret i8 0
}; Function Attrs: nofree nounwind memory(read)
declare %I32ListStruct @"load(ptr, i32)"(ptr, i32) local_unnamed_addr #1; Function Attrs: nofree nounwind memory(read)
declare %U8ListStruct @"GenLargeBitmap(i32list, i32, ptr)"(%I32ListStruct, i32, ptr) local_unnamed_addr #1; Function Attrs: nofree nounwind memory(read)
declare i32 @"CountBits(u8list)"(%U8ListStruct) local_unnamed_addr #1; Function Attrs: nofree nounwind memory(read)
declare %I32ListStruct @"FilterByBitmap(i32list, u8list, u32, ptr)"(%I32ListStruct, %U8ListStruct, i32, ptr) local_unnamed_addr #1; Function Attrs: nounwind memory(argmem: readwrite)
declare i32 @"store(ptr, i32, i32list)"(ptr noalias nocapture, i32, %I32ListStruct) local_unnamed_addr #2attributes #0 = { nounwind memory(read, argmem: readwrite) }
attributes #1 = { nofree nounwind memory(read) }
attributes #2 = { nounwind memory(argmem: readwrite) }
GenLargeBitmap 是相同的计算,所以只执行了一次,CountBits 也是相同的计算,也只执行了一次。
Vectorization
在 athena 中,对 list 类型的函数进行了大量优化,使得大部分代码都能很好地支持自动向量化,并且能够依赖编译器来适配多种平台。然而,对于某些数学函数,例如 log,编译器在大多数情况下无法实现自动向量化,因此需要依赖向量化数学库。为了解决多平台数学库向量化的问题,athena 引入了 xsimd。同样的, 我们拿一段代码举例:
static std::mt19937_64 rng(std::random_device{}());
static std::uniform_real_distribution<double> dist(0, 1e8);std::vector<double> GenInputs() {std::vector<double> inputs;inputs.reserve(1000);for (int i = 0; i < 1000; ++i) {inputs.emplace_back(dist(rng));}return inputs;
}static std::vector<double> inputs = GenInputs();athena::F64ListStruct Load(void* entry_arguments) {auto* args = reinterpret_cast<std::vector<double>*>(entry_arguments);athena::F64ListStruct result;result.data = args->data();result.len = args->size();return result;
}void bench_cpp_code(benchmark::State& state) {std::vector<double> result;result.resize(inputs.size());for (auto _ : state) {for (int i = 0; i < inputs.size(); i++) {result[i] = std::log(inputs[i]);}}// for (auto v : result) {// std::cout << v << '\n';// }
}void bench_athena_vectorization(benchmark::State& state) {athena::Athena athena;std::unique_ptr<athena::FunctionRegistry> func_registry;athena::FunctionRegistryFactory::CreateFunctionRegistry(&func_registry);athena::FunctionSignature sign1("load", {athena::ValueType::kPtr}, athena::ValueType::kF64List);func_registry->RegisterReadOnlyCFunc(sign1, reinterpret_cast<void*>(Load));std::string code = R"(r = ListLog(load(entry_arg), exec_ctx);)";auto st = athena.Compile(code, func_registry);athena::RetType ret;athena::ExecContext exec_ctx(4096);for (auto _ : state) {athena.Execute(exec_ctx, &inputs, &ret);}auto result = std::get<std::vector<double>>(ret);// for (auto v : result) {// std::cout << v << '\n';// }
}
BENCHMARK(bench_cpp_code);
BENCHMARK(bench_athena_vectorization);
BENCHMARK_MAIN();
这里是用的 gcc7 -O2 -ftree-vectorize 编译的,结果如下:

Benchmark
总的来说,athena 进行了许多优化,那么与其他开源执行引擎相比,它的性能如何呢?在这里,笔者选择了 exprtk 和 gandiva 进行测试。原本也计划加入 velox,但由于 velox 的依赖库较多,编译起来比较麻烦。有兴趣的朋友可以自行尝试进行对比。
我们选取了一个当前业务中使用的表达式进行测试:“if(v1 + v2 < 100000000, floor(log10(1 + v1 + v2)), 27.0)”。这个表达式涵盖了条件语句和数学运算。由于 gandiva 是列存引擎,我们将进行不同批次(batch)的测试。此外,由于 exprtk 仅支持浮点数运算,因此我们在测试中均使用 double 类型。代码如下:
#include "benchmark/benchmark.h"
#include <chrono>
#include <cstddef>
#include <iostream>
#include <random>
#include "arrow/array/array_base.h"
#include "arrow/array/builder_base.h"
#include "arrow/record_batch.h"
#include "arrow/status.h"
#include "arrow/type_fwd.h"
#include "athena/athena.h"
#include "exec_engine.h"
#include "gandiva/expression.h"
#include "gandiva/gandiva_aliases.h"
#include "gandiva/parser.h"
#include "gandiva/projector.h"
#include "gandiva/tree_expr_builder.h"
#include "riemann/3rd/exprtk/exprtk.hpp"
#include "type.h"namespace {
std::mt19937_64 rng(std::chrono::steady_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count());
std::uniform_real_distribution<double> eng_f64(0, 1e8);struct TestInput {double v1;double v2;
};constexpr size_t kBatchSize = 100000;
std::vector<TestInput> GenInputs() {std::vector<TestInput> inputs;for (int i = 0; i < kBatchSize; ++i) {TestInput input{.v1 = eng_f64(rng), .v2 = eng_f64(rng)};// std::cout << "v1=" << input.v1 << " v2=" << input.v2 << '\n';inputs.emplace_back(input);}return inputs;
}std::vector<TestInput> inputs = GenInputs();struct TestInputVec {std::vector<double> v1;std::vector<double> v2;
};void bench_exprtk_expr(benchmark::State &state) {typedef exprtk::symbol_table<double> symbol_table_t;typedef exprtk::expression<double> expression_t;typedef exprtk::parser<double> parser_t;typedef exprtk::parser_error::type error_t;std::string expression_str = "if(v1 + v2 < 100000000, floor(log10(1 + v1 + v2)), 27.0)";symbol_table_t symbol_table;symbol_table.add_constants();double s1;double s2;symbol_table.add_variable("v1", s1);symbol_table.add_variable("v2", s2);expression_t expression;expression.register_symbol_table(symbol_table);parser_t parser;parser.compile(expression_str, expression);double ans;const int batch_size = state.range(0);for (auto _ : state) {for (int i = 0; i < batch_size; i++) {s1 = inputs[i].v1;s2 = inputs[i].v2;ans = expression.value();}}// std::cout << ans << '\n';
}double LoadV1(void *entry_args) { return reinterpret_cast<TestInput *>(entry_args)->v1; }double LoadV2(void *entry_args) { return reinterpret_cast<TestInput *>(entry_args)->v2; }void bench_athena(benchmark::State &state) {athena::Athena athena;std::unique_ptr<jitfusion::FunctionRegistry> func_registry;jitfusion::FunctionRegistryFactory::CreateFunctionRegistry(&func_registry);jitfusion::FunctionSignature sign1("LoadV1", {jitfusion::ValueType::kPtr}, jitfusion::ValueType::kF64);func_registry->RegisterReadOnlyCFunc(sign1, reinterpret_cast<void *>(LoadV1));jitfusion::FunctionSignature sign2("LoadV2", {jitfusion::ValueType::kPtr}, jitfusion::ValueType::kF64);func_registry->RegisterReadOnlyCFunc(sign2, reinterpret_cast<void *>(LoadV2));std::string code = R"(v1 = LoadV1(entry_arg);v2 = LoadV2(entry_arg);r = if(v1 + v2 < 100000000, floor(log10(1 + v1 + v2)), 27.0);)";athena.Compile(code, func_registry);jitfusion::RetType ret;athena::ExecContext exec_ctx(4096);const int batch_size = state.range(0);for (auto _ : state) {for (int i = 0; i < batch_size; i++) {athena.Execute(exec_ctx, &inputs[i], &ret);}}// std::cout << std::get<double>(ret) << '\n';
}void PrintSimple(const std::vector<std::shared_ptr<arrow::Array>> &arrays) {// std::cout << arrays.size() << std::endl;for (const auto &i : arrays) {const auto &array = std::static_pointer_cast<arrow::DoubleArray>(i);for (int i = 0; i < array->length(); i++) {std::cout << "value " << i << "=" << array->raw_values()[i] << '\n';}}
}void bench_gandiva(benchmark::State &state) {std::string expr_str = "if(v1 + v2 < 100000000, floor(log10(1 + v1 + v2)), 27.0)";// prep gandivaauto field_v1_type = arrow::field("v1", arrow::float64());auto field_v2_type = arrow::field("v2", arrow::float64());auto v1 = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeField(field_v1_type);auto v2 = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeField(field_v2_type);auto v1_add_v2 = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeFunction("add", {v1, v2}, arrow::float64());auto literal_1 = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeLiteral(1.0);auto v1_add_v2_add_1 = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeFunction("add", {v1_add_v2, literal_1}, arrow::float64());auto log10_result = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeFunction("log10", {v1_add_v2_add_1}, arrow::float64());auto floor_result = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeFunction("floor", {log10_result}, arrow::float64());auto literal_100000000 = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeLiteral(100000000.0);auto literal_27 = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeLiteral(27.0);auto cmp = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeFunction("less_than", {v1_add_v2, literal_100000000}, arrow::boolean());auto conditional = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeIf(cmp, floor_result, literal_27, arrow::float64());// auto conditional = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeIf(cmp, v1_add_v2, literal_27, arrow::float64());auto field_result = arrow::field("result", arrow::float64());auto gandiva_expr = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeExpression(conditional, field_result);auto schema = arrow::schema({field_v1_type, field_v2_type});// std::cout << "expr: " << gandiva_expr->ToString() << '\n';// std::cout << "schema: " << schema->ToString() << std::endl;// std::cout << "schema metadata: " << schema->ToString(true) << std::endl;std::shared_ptr<gandiva::Projector> projector;auto status = gandiva::Projector::Make(schema, {gandiva_expr}, &projector);if (!status.ok()) {std::cout << status.ToString() << '\n';return;}std::vector<std::shared_ptr<arrow::Array>> input_arr(2);const int batch_size = state.range(0);arrow::DoubleBuilder builder;auto ret = builder.Reserve(batch_size);std::vector<double> v1s;v1s.reserve(batch_size);for (int i = 0; i < batch_size; i++) {v1s.emplace_back(inputs[i].v1);}ret = builder.AppendValues(v1s);ret = builder.Finish(input_arr.data());builder.Reset();std::vector<double> v2s;v2s.reserve(batch_size);for (int i = 0; i < batch_size; i++) {v2s.emplace_back(inputs[i].v2);}ret = builder.AppendValues(v2s);ret = builder.Finish(&input_arr[1]);auto *pool = arrow::default_memory_pool();// std::cout << pool->backend_name() << std::endl;auto in_batch = arrow::RecordBatch::Make(schema, batch_size, input_arr);arrow::ArrayVector outputs;for (auto _ : state) {projector->Evaluate(*in_batch, pool, &outputs);}// PrintSimple(input_arr);// PrintSimple(outputs);// std::cout << "value =" << std::static_pointer_cast<arrow::DoubleArray>(outputs[0])->raw_values()[batch_size - 1]// << '\n';
}BENCHMARK(bench_exprtk_expr)->RangeMultiplier(10)->Range(10, kBatchSize);
BENCHMARK(bench_athena)->RangeMultiplier(10)->Range(10, kBatchSize);
BENCHMARK(bench_gandiva)->RangeMultiplier(10)->Range(10, kBatchSize);} // namespaceBENCHMARK_MAIN();
在这次测试中,我们特别优待了 gandiva,没有将数据从行转列的重组过程开销计算在内,因为这个转换效率因人而异,并且在不同场景中表现也有所不同。以下是这次benchmark 的结果:

首先,athena 的性能全面优于 exprtk。随着批次(batch)规模的增加,gandiva 逐渐超过了 athena,但并没有拉开太大的差距。正如之前提到的,这里没有将数据转换的开销计算在内,那么如果将其考虑进去,结果会如何呢?
#include "benchmark/benchmark.h"
#include <chrono>
#include <cstddef>
#include <iostream>
#include <random>
#include "arrow/array/array_base.h"
#include "arrow/array/builder_base.h"
#include "arrow/record_batch.h"
#include "arrow/status.h"
#include "arrow/type_fwd.h"
#include "athena/athena.h"
#include "exec_engine.h"
#include "gandiva/expression.h"
#include "gandiva/gandiva_aliases.h"
#include "gandiva/parser.h"
#include "gandiva/projector.h"
#include "gandiva/tree_expr_builder.h"
#include "riemann/3rd/exprtk/exprtk.hpp"
#include "type.h"namespace {
std::mt19937_64 rng(std::chrono::steady_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count());
std::uniform_real_distribution<double> eng_f64(0, 1e8);struct TestInput {double v1;double v2;
};constexpr size_t kBatchSize = 100000;
std::vector<TestInput> GenInputs() {std::vector<TestInput> inputs;for (int i = 0; i < kBatchSize; ++i) {TestInput input{.v1 = eng_f64(rng), .v2 = eng_f64(rng)};// std::cout << "v1=" << input.v1 << " v2=" << input.v2 << '\n';inputs.emplace_back(input);}return inputs;
}std::vector<TestInput> inputs = GenInputs();struct TestInputVec {std::vector<double> v1;std::vector<double> v2;
};void bench_exprtk_expr(benchmark::State &state) {typedef exprtk::symbol_table<double> symbol_table_t;typedef exprtk::expression<double> expression_t;typedef exprtk::parser<double> parser_t;typedef exprtk::parser_error::type error_t;std::string expression_str = "if(v1 + v2 < 100000000, floor(log10(1 + v1 + v2)), 27.0)";symbol_table_t symbol_table;symbol_table.add_constants();double s1;double s2;symbol_table.add_variable("v1", s1);symbol_table.add_variable("v2", s2);expression_t expression;expression.register_symbol_table(symbol_table);parser_t parser;parser.compile(expression_str, expression);double ans;const int batch_size = state.range(0);for (auto _ : state) {for (int i = 0; i < batch_size; i++) {s1 = inputs[i].v1;s2 = inputs[i].v2;ans = expression.value();}}// std::cout << ans << '\n';
}double LoadV1(void *entry_args) { return reinterpret_cast<TestInput *>(entry_args)->v1; }double LoadV2(void *entry_args) { return reinterpret_cast<TestInput *>(entry_args)->v2; }void bench_athena(benchmark::State &state) {athena::Athena athena;std::unique_ptr<jitfusion::FunctionRegistry> func_registry;jitfusion::FunctionRegistryFactory::CreateFunctionRegistry(&func_registry);jitfusion::FunctionSignature sign1("LoadV1", {jitfusion::ValueType::kPtr}, jitfusion::ValueType::kF64);func_registry->RegisterReadOnlyCFunc(sign1, reinterpret_cast<void *>(LoadV1));jitfusion::FunctionSignature sign2("LoadV2", {jitfusion::ValueType::kPtr}, jitfusion::ValueType::kF64);func_registry->RegisterReadOnlyCFunc(sign2, reinterpret_cast<void *>(LoadV2));std::string code = R"(v1 = LoadV1(entry_arg);v2 = LoadV2(entry_arg);r = if(v1 + v2 < 100000000, floor(log10(1 + v1 + v2)), 27.0);)";athena.Compile(code, func_registry);jitfusion::RetType ret;athena::ExecContext exec_ctx(4096);const int batch_size = state.range(0);for (auto _ : state) {for (int i = 0; i < batch_size; i++) {athena.Execute(exec_ctx, &inputs[i], &ret);}}// std::cout << std::get<double>(ret) << '\n';
}void PrintSimple(const std::vector<std::shared_ptr<arrow::Array>> &arrays) {// std::cout << arrays.size() << std::endl;for (const auto &i : arrays) {const auto &array = std::static_pointer_cast<arrow::DoubleArray>(i);for (int i = 0; i < array->length(); i++) {std::cout << "value " << i << "=" << array->raw_values()[i] << '\n';}}
}void bench_gandiva(benchmark::State &state) {std::string expr_str = "if(v1 + v2 < 100000000, floor(log10(1 + v1 + v2)), 27.0)";// prep gandivaauto field_v1_type = arrow::field("v1", arrow::float64());auto field_v2_type = arrow::field("v2", arrow::float64());auto v1 = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeField(field_v1_type);auto v2 = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeField(field_v2_type);auto v1_add_v2 = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeFunction("add", {v1, v2}, arrow::float64());auto literal_1 = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeLiteral(1.0);auto v1_add_v2_add_1 = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeFunction("add", {v1_add_v2, literal_1}, arrow::float64());auto log10_result = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeFunction("log10", {v1_add_v2_add_1}, arrow::float64());auto floor_result = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeFunction("floor", {log10_result}, arrow::float64());auto literal_100000000 = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeLiteral(100000000.0);auto literal_27 = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeLiteral(27.0);auto cmp = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeFunction("less_than", {v1_add_v2, literal_100000000}, arrow::boolean());auto conditional = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeIf(cmp, floor_result, literal_27, arrow::float64());// auto conditional = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeIf(cmp, v1_add_v2, literal_27, arrow::float64());auto field_result = arrow::field("result", arrow::float64());auto gandiva_expr = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeExpression(conditional, field_result);auto schema = arrow::schema({field_v1_type, field_v2_type});// std::cout << "expr: " << gandiva_expr->ToString() << '\n';// std::cout << "schema: " << schema->ToString() << std::endl;// std::cout << "schema metadata: " << schema->ToString(true) << std::endl;std::shared_ptr<gandiva::Projector> projector;auto status = gandiva::Projector::Make(schema, {gandiva_expr}, &projector);if (!status.ok()) {std::cout << status.ToString() << '\n';return;}const int batch_size = state.range(0);// std::cout << pool->backend_name() << std::endl;arrow::ArrayVector outputs;for (auto _ : state) {std::vector<std::shared_ptr<arrow::Array>> input_arr(2);const int batch_size = state.range(0);arrow::DoubleBuilder builder;auto ret = builder.Reserve(batch_size);std::vector<double> v1s;v1s.reserve(batch_size);for (int i = 0; i < batch_size; i++) {v1s.emplace_back(inputs[i].v1);}ret = builder.AppendValues(v1s);ret = builder.Finish(input_arr.data());builder.Reset();std::vector<double> v2s;v2s.reserve(batch_size);for (int i = 0; i < batch_size; i++) {v2s.emplace_back(inputs[i].v2);}ret = builder.AppendValues(v2s);ret = builder.Finish(&input_arr[1]);auto *pool = arrow::default_memory_pool();// std::cout << pool->backend_name() << std::endl;auto in_batch = arrow::RecordBatch::Make(schema, batch_size, input_arr);projector->Evaluate(*in_batch, pool, &outputs);}// PrintSimple(input_arr);// PrintSimple(outputs);// std::cout << "value =" << std::static_pointer_cast<arrow::DoubleArray>(outputs[0])->raw_values()[batch_size - 1]// << '\n';
}void bench_athena_optimize(benchmark::State &state) {athena::Athena athena;std::unique_ptr<jitfusion::FunctionRegistry> func_registry;jitfusion::FunctionRegistryFactory::CreateFunctionRegistry(&func_registry);jitfusion::FunctionSignature sign1("LoadV1", {jitfusion::ValueType::kPtr}, jitfusion::ValueType::kF64);jitfusion::FunctionStructure func_struct1 = {jitfusion::FunctionType::kLLVMIntrinicFunc, nullptr, CallLoadV1Function};func_registry->RegisterFunc(sign1, func_struct1);jitfusion::FunctionSignature sign2("LoadV2", {jitfusion::ValueType::kPtr}, jitfusion::ValueType::kF64);jitfusion::FunctionStructure func_struct2 = {jitfusion::FunctionType::kLLVMIntrinicFunc, nullptr, CallLoadV2Function};func_registry->RegisterFunc(sign2, func_struct2);std::string code = R"(v1 = LoadV1(entry_arg);v2 = LoadV2(entry_arg);r = if(v1 + v2 < 100000000, floor(log10(1 + v1 + v2)), 27.0);)";athena.Compile(code, func_registry);jitfusion::RetType ret;const int batch_size = state.range(0);for (auto _ : state) {for (int i = 0; i < batch_size; i++) {athena.Execute(&inputs[i], &ret);}}// std::cout << std::get<double>(ret) << '\n';
}BENCHMARK(bench_exprtk_expr)->RangeMultiplier(10)->Range(10, kBatchSize);
BENCHMARK(bench_athena)->RangeMultiplier(10)->Range(10, kBatchSize);
BENCHMARK(bench_gandiva)->RangeMultiplier(10)->Range(10, kBatchSize);} // namespaceBENCHMARK_MAIN();
可以看到,对于这个表达式来说,只有在数据量达到10万级别时,gandiva 才显示出优势。然而,实际上这些数据已经是预先组装好的,在拷贝过程中有利于 cpu cache,因此开销并不特别大。如果在实际业务中使用,转换效率可能会更低一些。考虑到 athena 实际上支持 list 类型的计算,我们再来对比一下使用 athena 的 list 函数计算这个表达式的效果。
#include "benchmark/benchmark.h"
#include <chrono>
#include <cstddef>
#include <iostream>
#include <random>
#include "arrow/array/array_base.h"
#include "arrow/array/builder_base.h"
#include "arrow/record_batch.h"
#include "arrow/status.h"
#include "arrow/type_fwd.h"
#include "athena/athena.h"
#include "exec_engine.h"
#include "gandiva/expression.h"
#include "gandiva/gandiva_aliases.h"
#include "gandiva/parser.h"
#include "gandiva/projector.h"
#include "gandiva/tree_expr_builder.h"
#include "riemann/3rd/exprtk/exprtk.hpp"
#include "type.h"namespace {
std::mt19937_64 rng(std::chrono::steady_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count());
std::uniform_real_distribution<double> eng_f64(0, 1e8);struct TestInput {double v1;double v2;
};constexpr size_t kBatchSize = 100000;
std::vector<TestInput> GenInputs() {std::vector<TestInput> inputs;for (int i = 0; i < kBatchSize; ++i) {TestInput input{.v1 = eng_f64(rng), .v2 = eng_f64(rng)};// std::cout << "v1=" << input.v1 << " v2=" << input.v2 << '\n';inputs.emplace_back(input);}return inputs;
}std::vector<TestInput> inputs = GenInputs();struct TestInputVec {std::vector<double> v1;std::vector<double> v2;
};void bench_exprtk_expr(benchmark::State &state) {typedef exprtk::symbol_table<double> symbol_table_t;typedef exprtk::expression<double> expression_t;typedef exprtk::parser<double> parser_t;typedef exprtk::parser_error::type error_t;std::string expression_str = "if(v1 + v2 < 100000000, floor(log10(1 + v1 + v2)), 27.0)";symbol_table_t symbol_table;symbol_table.add_constants();double s1;double s2;symbol_table.add_variable("v1", s1);symbol_table.add_variable("v2", s2);expression_t expression;expression.register_symbol_table(symbol_table);parser_t parser;parser.compile(expression_str, expression);double ans;const int batch_size = state.range(0);for (auto _ : state) {for (int i = 0; i < batch_size; i++) {s1 = inputs[i].v1;s2 = inputs[i].v2;ans = expression.value();}}// std::cout << ans << '\n';
}double LoadV1(void *entry_args) { return reinterpret_cast<TestInput *>(entry_args)->v1; }double LoadV2(void *entry_args) { return reinterpret_cast<TestInput *>(entry_args)->v2; }void bench_athena(benchmark::State &state) {athena::Athena athena;std::unique_ptr<jitfusion::FunctionRegistry> func_registry;jitfusion::FunctionRegistryFactory::CreateFunctionRegistry(&func_registry);jitfusion::FunctionSignature sign1("LoadV1", {jitfusion::ValueType::kPtr}, jitfusion::ValueType::kF64);func_registry->RegisterReadOnlyCFunc(sign1, reinterpret_cast<void *>(LoadV1));jitfusion::FunctionSignature sign2("LoadV2", {jitfusion::ValueType::kPtr}, jitfusion::ValueType::kF64);func_registry->RegisterReadOnlyCFunc(sign2, reinterpret_cast<void *>(LoadV2));std::string code = R"(v1 = LoadV1(entry_arg);v2 = LoadV2(entry_arg);r = if(v1 + v2 < 100000000, floor(log10(1 + v1 + v2)), 27.0);)";athena.Compile(code, func_registry);jitfusion::RetType ret;athena::ExecContext exec_ctx(4096);const int batch_size = state.range(0);for (auto _ : state) {for (int i = 0; i < batch_size; i++) {athena.Execute(exec_ctx, &inputs[i], &ret);}}// std::cout << std::get<double>(ret) << '\n';
}void PrintSimple(const std::vector<std::shared_ptr<arrow::Array>> &arrays) {// std::cout << arrays.size() << std::endl;for (const auto &i : arrays) {const auto &array = std::static_pointer_cast<arrow::DoubleArray>(i);for (int i = 0; i < array->length(); i++) {std::cout << "value " << i << "=" << array->raw_values()[i] << '\n';}}
}void bench_gandiva(benchmark::State &state) {std::string expr_str = "if(v1 + v2 < 100000000, floor(log10(1 + v1 + v2)), 27.0)";// prep gandivaauto field_v1_type = arrow::field("v1", arrow::float64());auto field_v2_type = arrow::field("v2", arrow::float64());auto v1 = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeField(field_v1_type);auto v2 = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeField(field_v2_type);auto v1_add_v2 = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeFunction("add", {v1, v2}, arrow::float64());auto literal_1 = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeLiteral(1.0);auto v1_add_v2_add_1 = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeFunction("add", {v1_add_v2, literal_1}, arrow::float64());auto log10_result = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeFunction("log10", {v1_add_v2_add_1}, arrow::float64());auto floor_result = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeFunction("floor", {log10_result}, arrow::float64());auto literal_100000000 = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeLiteral(100000000.0);auto literal_27 = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeLiteral(27.0);auto cmp = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeFunction("less_than", {v1_add_v2, literal_100000000}, arrow::boolean());auto conditional = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeIf(cmp, floor_result, literal_27, arrow::float64());// auto conditional = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeIf(cmp, v1_add_v2, literal_27, arrow::float64());auto field_result = arrow::field("result", arrow::float64());auto gandiva_expr = gandiva::TreeExprBuilder::MakeExpression(conditional, field_result);auto schema = arrow::schema({field_v1_type, field_v2_type});// std::cout << "expr: " << gandiva_expr->ToString() << '\n';// std::cout << "schema: " << schema->ToString() << std::endl;// std::cout << "schema metadata: " << schema->ToString(true) << std::endl;std::shared_ptr<gandiva::Projector> projector;auto status = gandiva::Projector::Make(schema, {gandiva_expr}, &projector);if (!status.ok()) {std::cout << status.ToString() << '\n';return;}const int batch_size = state.range(0);// std::cout << pool->backend_name() << std::endl;arrow::ArrayVector outputs;for (auto _ : state) {std::vector<std::shared_ptr<arrow::Array>> input_arr(2);const int batch_size = state.range(0);arrow::DoubleBuilder builder;auto ret = builder.Reserve(batch_size);std::vector<double> v1s;v1s.reserve(batch_size);for (int i = 0; i < batch_size; i++) {v1s.emplace_back(inputs[i].v1);}ret = builder.AppendValues(v1s);ret = builder.Finish(input_arr.data());builder.Reset();std::vector<double> v2s;v2s.reserve(batch_size);for (int i = 0; i < batch_size; i++) {v2s.emplace_back(inputs[i].v2);}ret = builder.AppendValues(v2s);ret = builder.Finish(&input_arr[1]);auto *pool = arrow::default_memory_pool();// std::cout << pool->backend_name() << std::endl;auto in_batch = arrow::RecordBatch::Make(schema, batch_size, input_arr);projector->Evaluate(*in_batch, pool, &outputs);}// PrintSimple(input_arr);// PrintSimple(outputs);// std::cout << "value =" << std::static_pointer_cast<arrow::DoubleArray>(outputs[0])->raw_values()[batch_size - 1]// << '\n';
}jitfusion::F64ListStruct LoadV1List(void *entry_args, void *exec_ctx) {// 考虑到gandiva要组装一次数据,这里athena就复制一份数据测试比较公平。auto *inputs = reinterpret_cast<TestInputVec *>(entry_args);auto *ctx = reinterpret_cast<jitfusion::ExecContext *>(exec_ctx);jitfusion::F64ListStruct result;result.data = reinterpret_cast<double *>(ctx->arena.Allocate(sizeof(double) * inputs->v1.size()));for (size_t i = 0; i < inputs->v1.size(); i++) {result.data[i] = inputs->v1[i];}result.len = static_cast<uint32_t>(inputs->v1.size());return result;
}jitfusion::F64ListStruct LoadV2List(void *entry_args, void *exec_ctx) {auto *inputs = reinterpret_cast<TestInputVec *>(entry_args);auto *ctx = reinterpret_cast<jitfusion::ExecContext *>(exec_ctx);jitfusion::F64ListStruct result;result.data = reinterpret_cast<double *>(ctx->arena.Allocate(sizeof(double) * inputs->v2.size()));for (size_t i = 0; i < inputs->v2.size(); i++) {result.data[i] = inputs->v2[i];}result.len = static_cast<uint32_t>(inputs->v2.size());return result;
}void bench_athena_vectorization(benchmark::State &state) {athena::Athena athena;std::unique_ptr<jitfusion::FunctionRegistry> func_registry;jitfusion::FunctionRegistryFactory::CreateFunctionRegistry(&func_registry);jitfusion::FunctionSignature sign1("LoadV1", {jitfusion::ValueType::kPtr, jitfusion::ValueType::kPtr},jitfusion::ValueType::kF64List);func_registry->RegisterReadOnlyCFunc(sign1, reinterpret_cast<void *>(LoadV1List));jitfusion::FunctionSignature sign2("LoadV2", {jitfusion::ValueType::kPtr, jitfusion::ValueType::kPtr},jitfusion::ValueType::kF64List);func_registry->RegisterReadOnlyCFunc(sign2, reinterpret_cast<void *>(LoadV2List));std::string code = R"(v1 = LoadV1(entry_arg, exec_ctx);v2 = LoadV2(entry_arg, exec_ctx);v3 = ListAddWithMinSize(v1, v2, exec_ctx);condition = GenLessBitmap(v3, 100000000.0, exec_ctx);r = IfByBitmap(condition, ListFloor(ListLog10(ListAdd(v3, 1.0, exec_ctx), exec_ctx), exec_ctx), 27.0, exec_ctx);)";auto st = athena.Compile(code, func_registry);jitfusion::RetType ret;const int batch_size = state.range(0);TestInputVec input_vec;input_vec.v1.reserve(batch_size);input_vec.v2.reserve(batch_size);for (int i = 0; i < batch_size; i++) {input_vec.v1.emplace_back(inputs[i].v1);input_vec.v2.emplace_back(inputs[i].v2);}jitfusion::ExecContext exec_ctx(static_cast<int64_t>(batch_size * 10 * 8));for (auto _ : state) {athena.Execute(exec_ctx, &input_vec, &ret);}auto result = std::get<std::vector<double>>(ret);// std::cout << result[result.size() - 1] << '\n';
}BENCHMARK(bench_exprtk_expr)->RangeMultiplier(10)->Range(10, kBatchSize);
BENCHMARK(bench_athena)->RangeMultiplier(10)->Range(10, kBatchSize);
BENCHMARK(bench_gandiva)->RangeMultiplier(10)->Range(10, kBatchSize);
BENCHMARK(bench_athena_vectorization)->RangeMultiplier(10)->Range(10, kBatchSize);} // namespaceBENCHMARK_MAIN();

对于这个表达式而言,athena 的效率全面超越了 gandiva,提升幅度达到倍数级。然而,athena 并非专注于向量化计算,其支持的数据类型不如 gandiva 底层的 arrow 那样全面。之所以举这个例子,是为了说明 athena 在处理 list 类型运算时同样具备极高的效率。
结语
athena 执行引擎精准定位小 batch、可预编译的高性能计算场景,通过创新的设计架构、强大的优化策略,在众多执行引擎中脱颖而出。目前库已开源:https://github.com/viktorika/jitfusion/tree/main/athena。
相关文章:

Athena 执行引擎:在线服务计算的效率王者
引言 在在线服务领域,计算任务呈现出独特的特性:一方面,数据量通常不会过于庞大,因为在线服务对耗时和响应速度有着严苛要求;另一方面,计算任务具有可控性,其大多并非由用户实时输入动态生成&a…...

飞桨paddle ‘ParallelEnv‘ object has no attribute ‘_device_id‘【已解决】
书借上回,自从我反复重装paddle之后,我发现了,只要pip list中有库,但是代码报错,那就是飞桨没把代码更新完全,只能自己去改源代码 我又遇到报错了: 根据报错信息,找到ParallelEnv报…...

Bert预训练任务-MLM/NSP
MLM MLM:Masked Language Mode:在每一个训练序列中以15%的概率随机地选中某个token进行MASK,当一个token被选中后,有以下三种处理方式: 80%的概率被[MASK],如my dog is hairy->my dog is [MASK]10%的概率修改为随机的其他token,如my dog …...

微信小程序之Promise-Promise初始用
我们来尝试使用Promise。 1、需求,做个抽奖的按钮, 抽奖规则: 30%的几率中奖,中奖会提示恭喜恭喜,奖品为10万 RMB 劳斯莱斯优惠券,没中奖会提示再接再厉。 2、先搭界面: <view class&qu…...
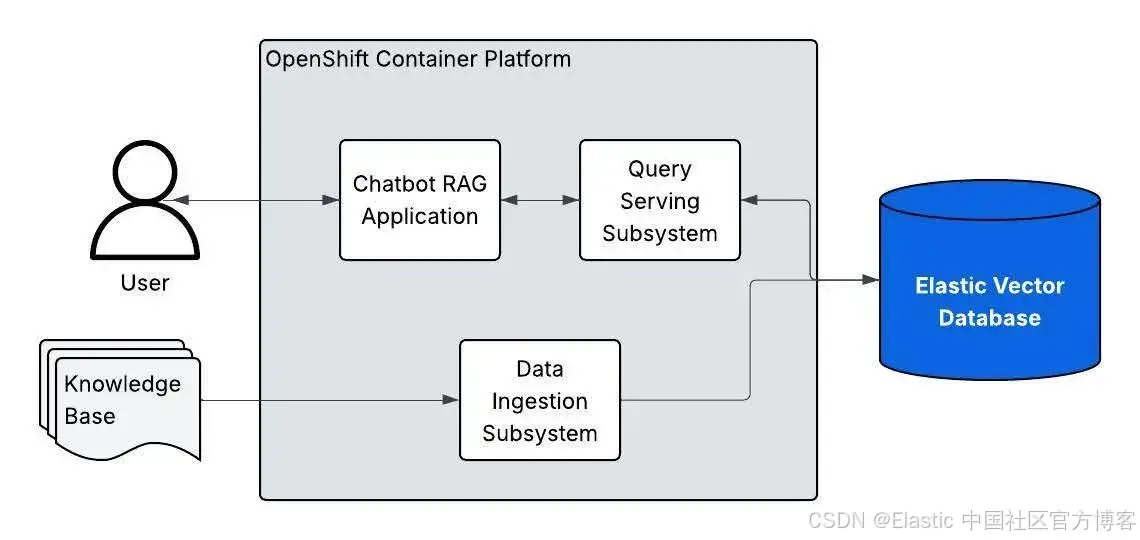
准备好,开始构建:由 Elasticsearch 向量数据库驱动的 Red Hat OpenShift AI 应用程序
作者:来自 Elastic Tom Potoma Elasticsearch 向量数据库现在被 “基于 LLM 和 RAG 的 AI 生成” 验证模式支持。本文将指导你如何开始使用。 Elasticsearch 已原生集成业内领先的生成式 AI 工具和服务提供商。欢迎观看我们的网络研讨会,了解如何突破 RA…...

spring的注入方式都有什么区别
目录 1. 构造器注入(Constructor Injection) 2. Setter 注入(Setter Injection) 3. 字段注入(Field Injection) 4. 接口注入(Interface Injection) 主要区别对比 最佳实践 总…...
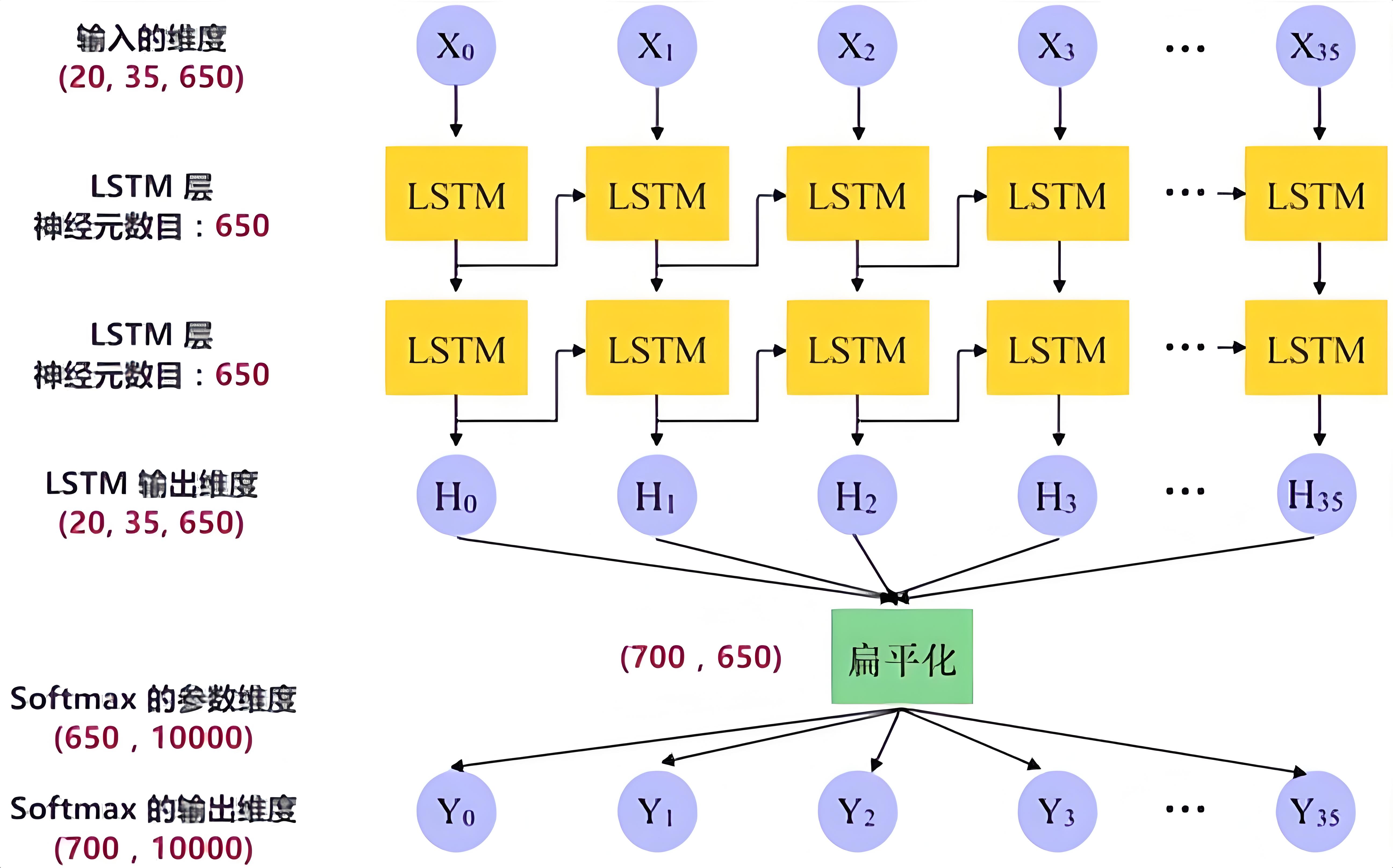
RNN神经网络
RNN神经网络 1-核心知识 1-解释RNN神经网络2-RNN和传统的神经网络有什么区别?3-RNN和LSTM有什么区别?4-transformer的归一化有哪几种实现方式 2-知识问答 1-解释RNN神经网络 Why:与我何干? 在我们的生活中,很多事情…...

Linux | 开机自启动设置多场景实现
注:本文为“Llinux 设置开机自启”相关文章合辑。 略作重排,未整理去重。 如有内容异常,请看原文。 Linux 设置开机自启动的三种方法 幽夜卡尔 2022-10-22 一、在 /etc/rc.local 文件中添加自启动命令 编辑文件:执行以下命令&a…...

杨校老师竞赛课之青科赛GOC3-4年级组模拟题
1.山峰(程序填空)程序填空题 题目描述 编程画出山峰。 要求:两个正三角形,三角形边长分别是200、100,山峰的颜色为8号色。 int main() {// 绘制等边三角形(边长100):右转30度调整…...

设计杂谈-工厂模式
“工厂”模式在各种框架中非常常见,包括 MyBatis,它是一种创建对象的设计模式。使用工厂模式有很多好处,尤其是在复杂的框架中,它可以带来更好的灵活性、可维护性和可配置性。 让我们以 MyBatis 为例,来理解工厂模式及…...

SC3000智能相机-自动存图
1、需求:SC3000智能相机开机自动存图。相机自带的相机存储空间有限,预留存图需要开启SCMVS、并手动点存图。如果工人忘了开启则不会存图,导致生产严重失误! 2、方法:利用相机提供的FTP协议,将图自动存到本地。 1、在本地建立FTP服务器。 (1)win10默认开启了FTP服务器…...
高级前端开发者指南:框架运用与综合实战)
(高级)高级前端开发者指南:框架运用与综合实战
当您已经掌握了HTML5、CSS3和JavaScript的基础知识后,接下来就是学习现代前端框架和性能优化的高级阶段。本文将重点介绍Vue.js/React的组件化开发、状态管理和路由配置,以及前端性能优化的核心技巧。通过丰富的代码示例和详细讲解,帮助您在实…...

【Java高阶面经:微服务篇】5.限流实战:高并发系统流量治理全攻略
一、限流阈值的三维度计算模型 1.1 系统容量基准线:压测驱动的安全水位 1.1.1 压力测试方法论 测试目标:确定系统在资源安全水位(CPU≤80%,内存≤70%,RT≤500ms)下的最大处理能力测试工具: 单机压测:JMeter(模拟10万并发)、wrk(低资源消耗)集群压测:LoadRunner …...

2025中青杯数学建模B题思路+模型+代码
本文将为大家带来2025年中青杯的选题建议,旨在十分钟内帮助大家快速了解每个题目具体难点、涉及模型等。初步预估赛题难度 A:B:C4:5:3初步预测选题人数 A:B:C2:1:0.6 首先是C题,忧郁症的双重防线:精准预测与有效治疗,这个题目涉及…...

记录:uniapp 上线部署到微信小程序vendorjs包过大的问题
问题: 在代码依赖分析图中,可以看到主包的容量已经超过了2M了,分包没有超! 根据网上的资料的解决方案,当前我已经做了以下相关的配置: 1.分包 2.在manifest.json的(mp-weixin)节点…...

如果教材这样讲--碳膜电阻、金属氧化膜电阻、金属膜电阻、保险丝电阻、绕线电阻的区别和用途
之前在设计一款电源时,参考手册上标明电阻选择为12Ω/3W,但是没有注明是什么类型的电阻,小白的我于是乎想当然的选了一款碳膜电阻,然后悲剧就这样形成了,电源在上电的瞬间,碳膜电阻竟然被烧坏了,比例还挺大…...

Vue 3.0中异步组件defineAsyncComponent
在大型项目中,组件的体积可能会随着项目规模的增加而变得庞大。为了优化性能,我们可以将应用拆分为更小的块,并仅在需要时从服务器加载相关组件,这样的组件称为异步组件。 在 Vue 3 中,可以使用 defineAsyncComponent…...

dedecms织梦全局变量调用方法总结
dedecms织梦的全局变量可以在/include/common.inc.php文件中看到,此文件内定义了大量的全局变量,详细自己去看看。 如果我们要实用dedeCMS织梦全局变量该如何调用: 第一种单独调用: {dede:global.变量名 /},注意闭合…...

新手到资深的Java开发编码规范
新手到资深的开发编码规范 一、前言二、命名规范:代码的 “第一印象”2.1 标识符命名原则2.2 命名的 “自描述性” 原则2.3 避免魔法值 三、代码格式规范:结构清晰的视觉美学3.1 缩进与空格3.2 代码块规范3.3 换行与断行 四、注释规范:代码的…...

asp.net core 添加 EntityFrame
1:Nuget 引入程序集 Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer.Design Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools 2:执行脚本 Scaffold-DbContext "Data Source.;Initial Ca…...

微软全新开源的Agentic Web网络项目:NLWeb,到底是什么 ?
目录 1、背景 2、NLWeb是什么? 3、NLWeb是如何工作的? 3.1 技术原理 3.2 对发布者的价值 3.3 核心团队与合作伙伴 4、快速入门指南 5、延伸阅读 Agentic:Agent的形容词,Agentic指系统由大型语言模型(LLM&#…...

Idea出现 100% classes 等
总是误点出来,每次又忘了怎么消除,在这里记录一下。 出现这样: 操作idea界面的:点击View->Tool Windows ->Coverage,然后关掉...

【学习笔记】计算机操作系统(五)—— 虚拟存储器
第五章 虚拟存储器 文章目录 第五章 虚拟存储器5.1 虚拟存储器概述5.1.1 常规存储管理方式的特征和局部性原理5.1.2 虚拟存储器的定义和特征5.1.3 虚拟存储器的实现方法 5.2 请求分页存储管理方式5.2.1 请求分页中的硬件支持5.2.2 请求分页中的内存分配5.2.3 页面调入策略 5.3 …...

构建基于全面业务数据的大数据与大模型企业护城河战略
引言:数据与AI驱动的专精企业未来 在数字化浪潮和人工智能技术飞速发展的今天,对于“专精特新”型企业而言,如何利用自身积累的深厚行业知识和独特的业务数据,结合大数据分析与大模型能力,构建难以被复制的竞争壁垒&a…...

centos系统redis-dump安装
1. Ruby 环境 Redis-dump 是一个 Ruby 工具,需先安装 Ruby 和 RubyGems。 安装依赖: sudo yum install -y curl gpg2 gcc-c patch readline readline-devel zlib zlib-devel libyaml-devel libffi-devel openssl-devel make bzip2 autoconf aut…...

乘最多水的容器 | 算法 | 给定一个整数数组。有n条垂线。找出其中的两条线,使得它们与 x 轴共同构成的容器可以容纳最多的水。
在我们日常生活中,蓄水似乎是一个极为朴素的物理行为:两堵墙之间,注入水,看谁能装得更多。可如果换个角度,从算法的视角去看这个问题,它会变得怎样?你是否意识到,这样一个简单的问题…...

Python项目文件组织与PyCharm实践:打造高效开发环境
# Python项目文件组织与PyCharm实践:打造高效开发环境 在Python编程的世界里,合理组织项目文件是提升代码质量、增强可维护性以及促进团队协作的关键。同时,借助强大的集成开发环境(IDE)——PyCharm,我们能…...

【Java高阶面经:数据库篇】19、分库分表查询困境:无分库分表键时的高效应对
一、分库分表下的无分片键查询困境 在分布式数据库架构中,分库分表通过分片键(如买家ID)将数据分散存储,显著提升了单表性能和系统扩展性。然而,当业务需要从非分片键维度(如卖家ID)进行查询时,传统架构暴露出以下核心问题: 1.1 跨分片扫描的性能灾难 数据分散性:以…...

spring中的BeanFactoryAware接口详解
一、接口定义与核心作用 BeanFactoryAware 是 Spring 框架提供的一个回调接口,允许 Bean 在初始化阶段获取其所属的 BeanFactory 实例。该接口定义如下: public interface BeanFactoryAware {void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws Bea…...

Unity Hub打不开项目一直在加载
Unity Hub打不开项目,一直在加载。 运行环境:win10 解决方法:退还个人许可证,退出UnityHub重新登录后,再次获取个人许可证 Tips: 国内连续超过三天不登陆就需要激活一次。(每天登陆一次会自动续时间吗&…...
