Python网页自动化Selenium中文文档
1. 安装
1.1. 安装
Selenium Python bindings 提供了一个简单的API,让你使用Selenium WebDriver来编写功能/校验测试。 通过Selenium Python的API,你可以非常直观的使用Selenium WebDriver的所有功能。
Selenium Python bindings 使用非常简洁方便的API让你去使用像Firefox, IE, Chrome, Remote等等 这样的Selenium WebDrivers(Selenium web驱动器)。当前支持的版本为 2.7, 3.2及以上。
本文的用来讲解说明Selenium 2 WebDriver的API,此文档不包含Selenium 1 / Selenium RC的文档。
1.2. 下载 Python bindings for Selenium
可以从PyPI的官方库中下载该selenium支持库, 点此下载 当然, 更好的方法当然是使用 pip 命令来安装selenium包。 Python3.5的 `标准库 <Installing Python Modules — Python 3.5.10 documentation>`_中包含pip命令。 使用 `pip`命令,你可以像下面这样安装 selenium:
pip install selenium
Note
使用Python2.x版本的用户可以手动安装pip或者easy_install,下面是easy_install 的安装方法:
easy_install selenium
你可以考虑使用`virtualenv <http://www.virtualenv.org>`_ 创建独立的Python环境。Python3.5中`pyvenv <5. Additional Tools and Scripts — Python 3.5.10 documentation>`_ 可以提供几乎一样的功能。
1.3. Windows用户的详细说明
Note
请在有网的情况下执行该安装命令。
-
安装Python3.5:官方下载页.
-
从开始菜单点击运行(或者`Windows+R`)输入`cmd`,然后执行下列命令安装:
C:\Python35\Scripts\pip.exe install selenium
现在你可以使用Python运行测试脚本了。 例如:如果你创建了一个selenium的基本示例并且保存在了``C:my_selenium_script.py``,你可以如下执行:
C:\Python35\python.exe C:\my_selenium_script.py
1.4. 下载 Selenium 服务器
Note
如果你想使用一个远程的WebDriver,Selenium服务是唯一的依赖, 参见 使用远程 Selenium WebDriver 获得更多细节。 如果你只是刚刚开始学习使用Selenium,你可以忽略该章节直接开始下一节。
Selenium server是一个JAVA工程,Java Runtime Environment (JRE) 1.6或者更高的版本是推荐的运行环境。
你可以在 该下载页 下载2.x的Selenium server,这个文件大概长成这个样子:selenium-server-standalone-2.x.x.jar, 你可以去下载最新版本的2.x server。
如果你还没有安装Java Runtime Environment (JRE)的话, 呢,在这下载, 如果你是有的是GNU/Linux系统,并且巧了,你还有root权限,你还可以使用操作系统指令去安装JRE。
如果你把`java`命令放在了PATH(环境变量)中的话,使用下面命令安装:
java -jar selenium-server-standalone-2.x.x.jar
当然了,把``2.x.x``换成你下载的实际版本就可以了。
如果是不是root用户你或者没有把JAVA放到PATH中, 你可以使用绝对路径或者相对路径的方式来使用命令, 这个命令大概长这样子:
/path/to/java -jar /path/to/selenium-server-standalone-2.x.x.jar
2. 快速入门
2.1. 简单用例
如果你已经安装好了selenium,你可以把下面的python代码拷贝到你的编辑器中
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.keys import Keysdriver = webdriver.Firefox()
driver.get("http://www.python.org")
assert "Python" in driver.title
elem = driver.find_element_by_name("q")
elem.clear()
elem.send_keys("pycon")
elem.send_keys(Keys.RETURN)
assert "No results found." not in driver.page_source
driver.close()
上面的脚本可以保存到一个文件(如:- python_org_search.py),那么可以这样使用
python python_org_search.py
你运行的 python 环境中应该已经安装了 selenium 模块。
2.2. 示例详解
selenium.webdriver 模块提供了所有WebDriver的实现, 当前支持的WebDriver有: Firefox, Chrome, IE and Remote。 `Keys`类提供键盘按键的支持,比如:RETURN, F1, ALT等
from selenium import webdriver from selenium.webdriver.common.keys import Keys
接下来,创建一个Firefox WebDriver的实例
driver = webdriver.Firefox()
driver.get 方法将打开URL中填写的地址,WebDriver 将等待, 直到页面完全加载完毕(其实是等到”onload” 方法执行完毕),然后返回继续执行你的脚本。 值得注意的是,如果你的页面使用了大量的Ajax加载, WebDriver可能不知道什么时候页面已经完全加载:
driver.get("http://www.python.org")
下一行是用assert的方式确认标题是否包含“Python”一词。 (译注:assert 语句将会在之后的语句返回false后抛出异常,详细内容可以自行百度)
assert "Python" in driver.title
WebDriver 提供了大量的方法让你去查询页面中的元素,这些方法形如: find_element_by_*。 例如:包含 name 属性的input输入框可以通过 find_element_by_name 方法查找到, 详细的查找方法可以在第四节元素查找中查看:
elem = driver.find_element_by_name("q")
接下来,我们发送了一个关键字,这个方法的作用类似于你用键盘输入关键字。 特殊的按键可以使用Keys类来输入,该类继承自 selenium.webdriver.common.keys, 为了安全起见,我们先清除input输入框中的任何预填充的文本(例如:”Search”),从而避免我们的搜索结果受影响:
elem.clear()
elem.send_keys("pycon")
elem.send_keys(Keys.RETURN)
提交页面后,你会得到所有的结果。为了确保某些特定的结果被找到,使用`assert`如下:
assert "No results found." not in driver.page_source
最后,关闭浏览器窗口,你还可以使用quit方法代替close方法, quit将关闭整个浏览器,而_close——只会关闭一个标签页, 如果你只打开了一个标签页,大多数浏览器的默认行为是关闭浏览器:
driver.close()
2.3. 用Selenium写测试用例
Selenium 通常被用来写一些测试用例. selenium 包本身不提供测试工具或者框架. 你可以使用Python自带的模块unittest写测试用例。 The other options for a tool/framework are py.test and nose.
在本章中,我们使用 unittest 来编写测试代码,下面是一个已经写好的用例。 这是一个在 python.org 站点上搜索的案例:
import unittest
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.keys import Keysclass PythonOrgSearch(unittest.TestCase):def setUp(self):self.driver = webdriver.Firefox()def test_search_in_python_org(self):driver = self.driverdriver.get("http://www.python.org")self.assertIn("Python", driver.title)elem = driver.find_element_by_name("q")elem.send_keys("pycon")elem.send_keys(Keys.RETURN)assert "No results found." not in driver.page_sourcedef tearDown(self):self.driver.close()if __name__ == "__main__":unittest.main()
你可以在shell中运行下列代码:
python test_python_org_search.py . ---------------------------------------------------------------------- Ran 1 test in 15.566sOK
结果表明这个测试用例已经成功运行。
2.4. 逐步解释测试代码
一开始,我们引入了需要的模块, unittest 模块是基于JAVA JUnit的Python内置的模块。 该模块提供了一个框架去组织测试用例。 selenium.webdriver 模块提供了所有WebDriver的实现。 现在支持的WebDriver有:Firefox, Chrome, IE and Remote. Keys 类提供所有的键盘按键操作,比如像这样的:
RETURN, F1, ALT等。
import unittest from selenium import webdriver from selenium.webdriver.common.keys import Keys
该测试类继承自 unittest.TestCase. 继承 TestCase 类是告诉 unittest 模块该类是一个测试用例:
class PythonOrgSearch(unittest.TestCase):
setUp 方法是初始化的一部分, 该方法会在该测试类中的每一个测试方法被执行前都执行一遍。 下面创建了一个Firefox WebDriver的一个实例。
def setUp(self):self.driver = webdriver.Firefox()
这是一个测试用例实际的测试方法. 测试方法始终以 test`开头。 在该方法中的第一行创建了一个在 `setUp 方法中创建的驱动程序对象的本地引用。
def test_search_in_python_org(self):driver = self.driver
driver.get 方法将会根据方法中给出的URL地址打开该网站。 WebDriver 会等待整个页面加载完成(其实是等待”onload”事件执行完毕)之后把控制权交给测试程序。 如果你的页面使用大量的AJAX技术来加载页面,WebDriver可能不知道什么时候页面已经加载完成:
driver.get("http://www.python.org")
下面一行使用assert断言的方法判断在页面标题中是否包含 “Python”
self.assertIn("Python", driver.title)
WebDriver 提供很多方法去查找页面值的元素,这些方法都以 find_element_by_* 开头。 例如:包含 name 属性的input元素可以使用
find_element_by_name`方法查找到。详细的细节可以参照 :ref:`locating-elements 章节:
elem = driver.find_element_by_name("q")
接下来我们发送keys,这个和使用键盘输入keys类似。 特殊的按键可以通过引入`selenium.webdriver.common.keys`的 Keys 类来输入
elem.send_keys("pycon")
elem.send_keys(Keys.RETURN)
提交页面之后,无论如何你都会得到搜索结果,为了确保某些结果类检索到,可以使用下列断言 After submission of the page, you should get result as per search if
assert "No results found." not in driver.page_source
tearDown 方法会在每一个测试方法执行之后被执行。 该方法可以用来做一些清扫工作,比如关闭浏览器。 当然你也可以调用 quit 方法代替`close`方法,
quit 将关闭整个浏览器,而`close`只会关闭一个标签页, 如果你只打开了一个标签页,大多数浏览器的默认行为是关闭浏览器。
def tearDown(self):self.driver.close()
下面是入口函数:
if __name__ == "__main__":unittest.main()
2.5. 使用远程 Selenium WebDriver
为了使用远程 WebDriver, 你应该拥有一个正在运行的 Selenium 服务器。 通过下列命令运行服务器:
java -jar selenium-server-standalone-2.x.x.jar
Selenium 服务运行后, 你会看到这样的提示信息:
15:43:07.541 INFO - RemoteWebDriver instances should connect to: http://127.0.0.1:4444/wd/hub
上面一行告诉你,你可以通过这个URL连接到远程WebDriver, 下面是一些例子:
from selenium import webdriver from selenium.webdriver.common.desired_capabilities import DesiredCapabilitiesdriver = webdriver.Remote(command_executor='http://127.0.0.1:4444/wd/hub',desired_capabilities=DesiredCapabilities.CHROME)driver = webdriver.Remote(command_executor='http://127.0.0.1:4444/wd/hub',desired_capabilities=DesiredCapabilities.OPERA)driver = webdriver.Remote(command_executor='http://127.0.0.1:4444/wd/hub',desired_capabilities=DesiredCapabilities.HTMLUNITWITHJS)
`desired_capabilities`是一个字典,如果你不想使用默认的字典,你可以明确指定的值
driver = webdriver.Remote(command_executor='http://127.0.0.1:4444/wd/hub',desired_capabilities={'browserName': 'htmlunit','version': '2','javascriptEnabled': True})
3. 打开一个页面
你想做的第一件事也许是使用WebDriver打开一个链接。 常规的方法是调用 get 方法:
driver.get("http://www.google.com")
WebDriver 将等待,直到页面完全加载完毕(其实是等到 onload 方法执行完毕), 然后返回继续执行你的脚本。 值得注意的是,如果你的页面使用了大量的Ajax加载, WebDriver可能不知道什么时候页面已经完全加载。 如果你想确保也main完全加载完毕,可以使用:ref:waits <waits>
3.1. 与页面交互
只是打开页面其实并没有什么卵用。我们真正想要的是与页面做交互。 更具体地说,对于一个页面中的HTML元素,首先我们要找到他。WebDriver 提供了大量的方法帮助你去查找元素,例如:已知一个元素定义如下:
<input type="text" name="passwd" id="passwd-id" />
你可以通过下面的方法查找他:
element = driver.find_element_by_id("passwd-id")
element = driver.find_element_by_name("passwd")
element = driver.find_element_by_xpath("//input[@id='passwd-id']")
你还可以通过链接的文本查找他,需要注意的是,这个文本必须完全匹地配。 当你使用`XPATH`时,你必须注意,如果匹配超过一个元素,只返回第一个元素。 如果上面也没找到,将会抛出 ``NoSuchElementException``异常。
WebDriver有一个”基于对象”的API; 我们使用相同的接口表示所有类型的元素。 这就意味着,当你打开你的IDE的自动补全的时候,你会有很多可以调用的方法。 但是并不是所有的方法都是有意义或是有效的。不过不要担心! 当你调用一些毫无意义的方法时,WebDriver会尝试去做一些正确的事情(例如你对一个”meta” 元素调用”setSelected()”方法的时候)。
所以,当你拿到ige元素时,你能做什么呢?首先,你可能会想在文本框中输入一些内容:
element.send_keys("some text")
你还可以通过”Keys”类来模式输入方向键:
element.send_keys(" and some", Keys.ARROW_DOWN)
对于任何元素,他可能都叫 send_keys ,这就使得它可以测试键盘快捷键, 比如当你使用Gmail的时候。但是有一个副作用是当你输入一些文本时,这些 输入框中原有的文本不会被自动清除掉,相反,你的输入会继续添加到已存在文本之后。 你可以很方便的使用 clear 方法去清除input或者textarea元素中的内容:
element.clear()
3.2. 填写表格
我们已经知道如何在input或textarea元素中输入内容,但是其他元素怎么办? 你可以“切换”下拉框的状态,你可以使用``setSelected``方法去做一些事情,比如 选择下拉列表,处理`SELECT`元素其实没有那么麻烦:
element = driver.find_element_by_xpath("//select[@name='name']")
all_options = element.find_elements_by_tag_name("option")
for option in all_options:print("Value is: %s" % option.get_attribute("value"))option.click()
上面这段代码将会寻找页面第一个 “SELECT” 元素, 并且循环他的每一个OPTION元素, 打印从utamen的值,然后按顺序都选中一遍。
正如你说看到的那样,这不是处理 SELECT 元素最好的方法。WebDriver的支持类包括一个叫做 ``Select``的类,他提供有用的方法处理这些内容:
from selenium.webdriver.support.ui import Select
select = Select(driver.find_element_by_name('name'))
select.select_by_index(index)
select.select_by_visible_text("text")
select.select_by_value(value)
WebDriver 也提供一些有用的方法来取消选择已经选择的元素:
select = Select(driver.find_element_by_id('id'))
select.deselect_all()
这将取消选择所以的OPTION。
假设在一个案例中,我们需要列出所有已经选择的选项,Select类提供了方便的方法来实现这一点:
select = Select(driver.find_element_by_xpath("xpath"))
all_selected_options = select.all_selected_options
获得所以选项:
options = select.options
一旦你填写完整个表单,你应该想去提交它,有一个方法就是去找到一个“submit” 按钮然后点击它:
# Assume the button has the ID "submit" :)
driver.find_element_by_id("submit").click()
或者,WebDriver对每一个元素都有一个叫做 “submit” 的方法,如果你在一个表单内的 元素上使用该方法,WebDriver会在DOM树上就近找到最近的表单,返回提交它。 如果调用的元素不再表单内,将会抛出``NoSuchElementException``异常:
element.submit()
3.3. 拖放
您可以使用拖放,无论是移动一个元素,或放到另一个元素内:
element = driver.find_element_by_name("source")
target = driver.find_element_by_name("target")from selenium.webdriver import ActionChains
action_chains = ActionChains(driver)
action_chains.drag_and_drop(element, target).perform()
3.4. 在不同的窗口和框架之间移动
对于现在的web应用来说,没有任何frames或者只包含一个window窗口是比较罕见的。 WebDriver 支持在不同的窗口之间移动,只需要调用``switch_to_window``方法即可:
driver.switch_to_window("windowName")
所有的 driver 将会指向当前窗口,但是你怎么知道当前窗口的名字呢,查看打开他的javascript或者连接代码:
<a href="somewhere.html" target="windowName">Click here to open a new window</a>
或者,你可以在”switch_to_window()”中使用”窗口句柄”来打开它, 知道了这些,你就可以迭代所有已经打开的窗口了:
for handle in driver.window_handles:driver.switch_to_window(handle)
你还可以在不同的frame中切换 (or into iframes):
driver.switch_to_frame("frameName")
通过“.”操作符你还可以获得子frame,并通过下标指定任意frame,就像这样:
driver.switch_to_frame("frameName.0.child")
如何获取名叫“frameName”的frame中名叫 “child”的子frame呢? 来自*top*frame的所有的frame都会被评估 (All frames are evaluated as if from *top*.)
一旦我们完成了frame中的工作,我们可以这样返回父frame:
driver.switch_to_default_content()
3.5. 弹出对话框
Selenium WebDriver 内置了对处理弹出对话框的支持。 在你的某些动作之后可能会触发弹出对话框,你可以像下面这样访问对话框:
alert = driver.switch_to_alert()
它将返回当前打开的对话框对象。使用此对象,您现在可以接受、排除、读取其内容, 甚至可以在prompt对话框中输入(译注:prompt()是对话框的一种,不同于alert()对话框,不同点可以自行百度)。 这个接口对alert, confirm, prompt 对话框效果相同。 参考相关的API文档获取更多信息。
3.6. 访问浏览器历史记录
在之前的文章中,我们使用``get``命令打开一个页面, ( driver.get("http://www.example.com")),WebDriver有很多更小的,以任务为导向的接口, navigation就是一个有用的任务,打开一个页面你可以使用`get`:
driver.get("http://www.example.com")
在浏览历史中前进和后退你可以使用:
driver.forward() driver.back()
请注意,这个功能完全取决于底层驱动程序。当你调用这些方法的时候,很有可能会发生意想不到的事情, 如果你习惯了浏览器的这些行为于其他的不同。(原文:It’s just possible that something unexpected may happen when you call these methods if you’re used to the behaviour of one browser over another.)
3.7. 操作Cookies
在我们结束这一节之前,或许你对如何操作Cookies可能会很感兴趣。 首先,你需要打开一个也面,因为Cookie是在某个域名下才生效的:
::
# 打开一个页面 driver.get(“http://www.example.com”)
# 现在设置Cookies,这个cookie在域名根目录下(”/”)生效 cookie = {‘name’ : ‘foo’, ‘value’ : ‘bar’} driver.add_cookie(cookie)
# 现在获取所有当前URL下可获得的Cookies driver.get_cookies()
4. 查找元素
在一个页面中有很多不同的策略可以定位一个元素。在你的项目中, 你可以选择最合适的方法去查找元素。Selenium提供了下列的方法给你:
- find_element_by_id
- find_element_by_name
- find_element_by_xpath
- find_element_by_link_text
- find_element_by_partial_link_text
- find_element_by_tag_name
- find_element_by_class_name
- find_element_by_css_selector
一次查找多个元素 (这些方法会返回一个list列表):
- find_elements_by_name
- find_elements_by_xpath
- find_elements_by_link_text
- find_elements_by_partial_link_text
- find_elements_by_tag_name
- find_elements_by_class_name
- find_elements_by_css_selector
除了上述的公共方法,下面还有两个私有方法,在你查找也页面元素的时候也许有用。 他们是 find_element 和 find_elements 。
用法示例:
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import Bydriver.find_element(By.XPATH, '//button[text()="Some text"]') driver.find_elements(By.XPATH, '//button')
下面是 By 类的一些可用属性:
ID = "id" XPATH = "xpath" LINK_TEXT = "link text" PARTIAL_LINK_TEXT = "partial link text" NAME = "name" TAG_NAME = "tag name" CLASS_NAME = "class name" CSS_SELECTOR = "css selector"
4.1. 通过ID查找元素
当你知道一个元素的 id 时,你可以使用本方法。在该策略下,页面中第一个该 id 元素 会被匹配并返回。如果找不到任何元素,会抛出 NoSuchElementException 异常。
作为示例,页面元素如下所示:
<html><body><form id="loginForm"><input name="username" type="text" /><input name="password" type="password" /><input name="continue" type="submit" value="Login" /></form></body> <html>
可以这样查找表单(form)元素:
login_form = driver.find_element_by_id('loginForm')
4.2. 通过Name查找元素
当你知道一个元素的 name 时,你可以使用本方法。在该策略下,页面中第一个该 name 元素 会被匹配并返回。如果找不到任何元素,会抛出 NoSuchElementException 异常。
作为示例,页面元素如下所示:
<html><body><form id="loginForm"><input name="username" type="text" /><input name="password" type="password" /><input name="continue" type="submit" value="Login" /><input name="continue" type="button" value="Clear" /></form> </body> <html>
name属性为 username & password 的元素可以像下面这样查找:
username = driver.find_element_by_name('username')
password = driver.find_element_by_name('password')
这会得到 “Login” 按钮,因为他在 “Clear” 按钮之前:
continue = driver.find_element_by_name('continue')
4.3. 通过XPath查找元素
XPath是XML文档中查找结点的语法。因为HTML文档也可以被转换成XML(XHTML)文档, Selenium的用户可以利用这种强大的语言在web应用中查找元素。 XPath扩展了(当然也支持)这种通过id或name属性获取元素的简单方式,同时也开辟了各种新的可能性, 例如获取页面上的第三个复选框。
使用XPath的主要原因之一就是当你想获取一个既没有id属性也没有name属性的元素时, 你可以通过XPath使用元素的绝对位置来获取他(这是不推荐的),或相对于有一个id或name属性的元素 (理论上的父元素)的来获取你想要的元素。XPath定位器也可以通过非id和name属性查找元素。
绝对的XPath是所有元素都从根元素的位置(HTML)开始定位,只要应用中有轻微的调整,会就导致你的定位失败。 但是通过就近的包含id或者name属性的元素出发定位你的元素,这样相对关系就很靠谱, 因为这种位置关系很少改变,所以可以使你的测试更加强大。
作为示例,页面元素如下所示:
<html><body><form id="loginForm"><input name="username" type="text" /><input name="password" type="password" /><input name="continue" type="submit" value="Login" /><input name="continue" type="button" value="Clear" /></form> </body> <html>
可以这样查找表单(form)元素:
login_form = driver.find_element_by_xpath("/html/body/form[1]")
login_form = driver.find_element_by_xpath("//form[1]")
login_form = driver.find_element_by_xpath("//form[@id='loginForm']")
- 绝对定位 (页面结构轻微调整就会被破坏)
- HTML页面中的第一个form元素
- 包含 id 属性并且其值为 loginForm 的form元素
username元素可以如下获取:
username = driver.find_element_by_xpath("//form[input/@name='username']")
username = driver.find_element_by_xpath("//form[@id='loginForm']/input[1]")
username = driver.find_element_by_xpath("//input[@name='username']")
- 第一个form元素中包含name属性并且其值为 username 的input元素
- id为 loginForm 的form元素的第一个input子元素
- 第一个name属性为 username 的input元素
“Clear” 按钮可以如下获取:
clear_button = driver.find_element_by_xpath("//input[@name='continue'][@type='button']")
clear_button = driver.find_element_by_xpath("//form[@id='loginForm']/input[4]")
- Input with attribute named name and the value continue and attribute named type and the value button
- Fourth input child element of the form element with attribute named id and value loginForm
这些实例都是一些举出用法, 为了学习更多有用的东西,下面这些参考资料推荐给你:
- W3Schools XPath Tutorial
- W3C XPath Recommendation
- XPath Tutorial - with interactive examples.
还有一些非常有用的插件,可以协助发现元素的XPath:
- XPath Checker - suggests XPath and can be used to test XPath results.
- Firebug - XPath suggestions are just one of the many powerful features of this very useful add-on.
- XPath Helper - for Google Chrome
4.4. 通过链接文本获取超链接
当你知道在一个锚标签中使用的链接文本时使用这个。 在该策略下,页面中第一个匹配链接内容锚标签 会被匹配并返回。如果找不到任何元素,会抛出 NoSuchElementException 异常。
作为示例,页面元素如下所示:
<html><body><p>Are you sure you want to do this?</p><a href="continue.html">Continue</a><a href="cancel.html">Cancel</a> </body> <html>
continue.html 超链接可以被这样查找到:
continue_link = driver.find_element_by_link_text('Continue')
continue_link = driver.find_element_by_partial_link_text('Conti')
4.5. 通过标签名查找元素
当你向通过标签名查找元素时使用这个。 在该策略下,页面中第一个匹配该标签名的元素 会被匹配并返回。如果找不到任何元素,会抛出 NoSuchElementException 异常。
作为示例,页面元素如下所示:
<html><body><h1>Welcome</h1><p>Site content goes here.</p> </body> <html>
h1 元素可以如下查找:
heading1 = driver.find_element_by_tag_name('h1')
4.6. 通过Class name 定位元素
当你向通过class name查找元素时使用这个。 在该策略下,页面中第一个匹配该class属性的元素 会被匹配并返回。如果找不到任何元素,会抛出 NoSuchElementException 异常。
作为示例,页面元素如下所示:
<html><body><p class="content">Site content goes here.</p> </body> <html>
p 元素可以如下查找:
content = driver.find_element_by_class_name('content')
4.7. 通过CSS选择器查找元素
当你向通过CSS选择器查找元素时使用这个。 在该策略下,页面中第一个匹配该CSS 选择器的元素 会被匹配并返回。如果找不到任何元素,会抛出 NoSuchElementException 异常。
作为示例,页面元素如下所示:
<html><body><p class="content">Site content goes here.</p> </body> <html>
p 元素可以如下查找:
content = driver.find_element_by_css_selector('p.content')
5. 等待页面加载完成(Waits)
现在的大多数的Web应用程序是使用Ajax技术。当一个页面被加载到浏览器时, 该页面内的元素可以在不同的时间点被加载。这使得定位元素变得困难, 如果元素不再页面之中,会抛出 ElementNotVisibleException 异常。 使用 waits, 我们可以解决这个问题。waits提供了一些操作之间的时间间隔- 主要是定位元素或针对该元素的任何其他操作。
Selenium Webdriver 提供两种类型的waits - 隐式和显式。 显式等待会让WebDriver等待满足一定的条件以后再进一步的执行。 而隐式等待让Webdriver等待一定的时间后再才是查找某元素。
5.1. 显式等待
显式等待是你在代码中定义等待一定条件发生后再进一步执行你的代码。 最糟糕的案例是使用time.sleep(),它将条件设置为等待一个确切的时间段。 这里有一些方便的方法让你只等待需要的时间。WebDriverWait结合ExpectedCondition 是实现的一种方式。
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from selenium.webdriver.support.ui import WebDriverWait
from selenium.webdriver.support import expected_conditions as ECdriver = webdriver.Firefox()
driver.get("http://somedomain/url_that_delays_loading")
try:element = WebDriverWait(driver, 10).until(EC.presence_of_element_located((By.ID, "myDynamicElement")))
finally:driver.quit()
在抛出TimeoutException异常之前将等待10秒或者在10秒内发现了查找的元素。 WebDriverWait 默认情况下会每500毫秒调用一次ExpectedCondition直到结果成功返回。 ExpectedCondition成功的返回结果是一个布尔类型的true或是不为null的返回值。
预期的条件
自动化的Web浏览器中一些常用的预期条件,下面列出的是每一个实现, Selenium Python binding都提供了一些方便的方法,这样你就不用去编写 expected_condition类或是创建至今的工具包去实现他们。 - title_is - title_contains - presence_of_element_located - visibility_of_element_located - visibility_of - presence_of_all_elements_located - text_to_be_present_in_element - text_to_be_present_in_element_value - frame_to_be_available_and_switch_to_it - invisibility_of_element_located - element_to_be_clickable - 显示并可用. - staleness_of - element_to_be_selected - element_located_to_be_selected - element_selection_state_to_be - element_located_selection_state_to_be - alert_is_present
from selenium.webdriver.support import expected_conditions as ECwait = WebDriverWait(driver, 10) element = wait.until(EC.element_to_be_clickable((By.ID,'someid')))
expected_conditions 模块提供了一组预定义的条件供WebDriverWait使用。
5.2. 隐式等待
如果某些元素不是立即可用的,隐式等待是告诉WebDriver去等待一定的时间后去查找元素。 默认等待时间是0秒,一旦设置该值,隐式等待是设置该WebDriver的实例的生命周期。
from selenium import webdriverdriver = webdriver.Firefox()
driver.implicitly_wait(10) # seconds
driver.get("http://somedomain/url_that_delays_loading")
myDynamicElement = driver.find_element_by_id("myDynamicElement")
6. 页面对象
本章是一个针对页面对象设计模式的教程引导。 一个页面对象表示在你测试的WEB应用程序的用户界面上的区域。
使用页面对象模式的好处:
- 创建可复用的代码以便于在多个测试用例间共享
- 减少重复的代码量
- 如果用户界面变化,只需要修改一处
6.1. 测试用例
下面是一个在python.org网站搜索一个词并保证一些结果可以找到的测试用例。
import unittest
from selenium import webdriver
import pageclass PythonOrgSearch(unittest.TestCase):"""A sample test class to show how page object works"""def setUp(self):self.driver = webdriver.Firefox()self.driver.get("http://www.python.org")def test_search_in_python_org(self):"""Tests python.org search feature. Searches for the word "pycon" then verified that some results show up.Note that it does not look for any particular text in search results page. This test verifies thatthe results were not empty."""#Load the main page. In this case the home page of Python.org.main_page = page.MainPage(self.driver)#Checks if the word "Python" is in titleassert main_page.is_title_matches(), "python.org title doesn't match."#Sets the text of search textbox to "pycon"main_page.search_text_element = "pycon"main_page.click_go_button()search_results_page = page.SearchResultsPage(self.driver)#Verifies that the results page is not emptyassert search_results_page.is_results_found(), "No results found."def tearDown(self):self.driver.close()if __name__ == "__main__":unittest.main()
6.2. 页面对象类
页面对象为每个网页模拟创建出一个对象。 按照此技术,在测试代码和技术实施之间的一个分离层被创建。
这个 page.py 看起来像这样:
from element import BasePageElement from locators import MainPageLocatorsclass SearchTextElement(BasePageElement):"""This class gets the search text from the specified locator"""#The locator for search box where search string is enteredlocator = 'q'class BasePage(object):"""Base class to initialize the base page that will be called from all pages"""def __init__(self, driver):self.driver = driverclass MainPage(BasePage):"""Home page action methods come here. I.e. Python.org"""#Declares a variable that will contain the retrieved textsearch_text_element = SearchTextElement()def is_title_matches(self):"""Verifies that the hardcoded text "Python" appears in page title"""return "Python" in self.driver.titledef click_go_button(self):"""Triggers the search"""element = self.driver.find_element(*MainPageLocators.GO_BUTTON)element.click()class SearchResultsPage(BasePage):"""Search results page action methods come here"""def is_results_found(self):# Probably should search for this text in the specific page# element, but as for now it works finereturn "No results found." not in self.driver.page_source
6.3. 页面元素
这个 element.py 看起来像这样:
from selenium.webdriver.support.ui import WebDriverWaitclass BasePageElement(object):"""Base page class that is initialized on every page object class."""def __set__(self, obj, value):"""Sets the text to the value supplied"""driver = obj.driverWebDriverWait(driver, 100).until(lambda driver: driver.find_element_by_name(self.locator))driver.find_element_by_name(self.locator).send_keys(value)def __get__(self, obj, owner):"""Gets the text of the specified object"""driver = obj.driverWebDriverWait(driver, 100).until(lambda driver: driver.find_element_by_name(self.locator))element = driver.find_element_by_name(self.locator)return element.get_attribute("value")
6.4. 定位器
其中一个做法是,从它们正在使用的地方分离定位字符。在这个例子中,同一页面的定位器属于同一个类。
这个 locators.py 看起来像这样:
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import Byclass MainPageLocators(object):"""A class for main page locators. All main page locators should come here"""GO_BUTTON = (By.ID, 'submit')class SearchResultsPageLocators(object):"""A class for search results locators. All search results locators should come here"""pass
7. WebDriver API
Note
这不是一个官方的文档. 但是你可以在这访问官方文档: 官方文档.
这一章包含所有的 Selenium WebDriver 接口.
Recommended Import Style
The API definitions in this chapter shows the absolute location of classes. However the recommended import style is as given below:
from selenium import webdriver
Then, you can access the classes like this:
webdriver.Firefox webdriver.FirefoxProfile webdriver.Chrome webdriver.ChromeOptions webdriver.Ie webdriver.Opera webdriver.PhantomJS webdriver.Remote webdriver.DesiredCapabilities webdriver.ActionChains webdriver.TouchActions webdriver.Proxy
The special keys class (Keys) can be imported like this:
from selenium.webdriver.common.keys import Keys
The exception classes can be imported like this (Replace the TheNameOfTheExceptionClass with actual class name given below):
from selenium.common.exceptions import [TheNameOfTheExceptionClass]
Conventions used in the API
Some attributes are callable (or methods) and others are non-callable (properties). All the callable attributes are ending with round brackets.
Here is an example for property:
current_url
URL of the current loaded page.
Usage:
driver.current_url
Here is an example for a method:
close()
Closes the current window.
Usage:
driver.close()
7.1. Exceptions
Exceptions that may happen in all the webdriver code.
exceptionselenium.common.exceptions.ElementNotInteractableException(msg=None, screen=None, stacktrace=None)
Bases: selenium.common.exceptions.InvalidElementStateException
Thrown when an element is present in the DOM but interactions with that element will hit another element do to paint order
exceptionselenium.common.exceptions.ElementNotSelectableException(msg=None, screen=None, stacktrace=None)
Bases: selenium.common.exceptions.InvalidElementStateException
Thrown when trying to select an unselectable element.
For example, selecting a ‘script’ element.
exceptionselenium.common.exceptions.ElementNotVisibleException(msg=None, screen=None, stacktrace=None)
Bases: selenium.common.exceptions.InvalidElementStateException
Thrown when an element is present on the DOM, but it is not visible, and so is not able to be interacted with.
Most commonly encountered when trying to click or read text of an element that is hidden from view.
exceptionselenium.common.exceptions.ErrorInResponseException(response, msg)
Bases: selenium.common.exceptions.WebDriverException
Thrown when an error has occurred on the server side.
This may happen when communicating with the firefox extension or the remote driver server.
exceptionselenium.common.exceptions.ImeActivationFailedException(msg=None, screen=None, stacktrace=None)
Bases: selenium.common.exceptions.WebDriverException
Thrown when activating an IME engine has failed.
exceptionselenium.common.exceptions.ImeNotAvailableException(msg=None, screen=None, stacktrace=None)
Bases: selenium.common.exceptions.WebDriverException
Thrown when IME support is not available. This exception is thrown for every IME-related method call if IME support is not available on the machine.
exceptionselenium.common.exceptions.InvalidArgumentException(msg=None, screen=None, stacktrace=None)
Bases: selenium.common.exceptions.WebDriverException
The arguments passed to a command are either invalid or malformed.
exceptionselenium.common.exceptions.InvalidCookieDomainException(msg=None, screen=None, stacktrace=None)
Bases: selenium.common.exceptions.WebDriverException
Thrown when attempting to add a cookie under a different domain than the current URL.
exceptionselenium.common.exceptions.InvalidElementStateException(msg=None, screen=None, stacktrace=None)
Bases: selenium.common.exceptions.WebDriverException
exceptionselenium.common.exceptions.InvalidSelectorException(msg=None, screen=None, stacktrace=None)
Bases: selenium.common.exceptions.NoSuchElementException
Thrown when the selector which is used to find an element does not return a WebElement. Currently this only happens when the selector is an xpath expression and it is either syntactically invalid (i.e. it is not a xpath expression) or the expression does not select WebElements (e.g. “count(//input)”).
exceptionselenium.common.exceptions.InvalidSwitchToTargetException(msg=None, screen=None, stacktrace=None)
Bases: selenium.common.exceptions.WebDriverException
Thrown when frame or window target to be switched doesn’t exist.
exceptionselenium.common.exceptions.MoveTargetOutOfBoundsException(msg=None, screen=None, stacktrace=None)
Bases: selenium.common.exceptions.WebDriverException
Thrown when the target provided to the ActionsChains move() method is invalid, i.e. out of document.
exceptionselenium.common.exceptions.NoAlertPresentException(msg=None, screen=None, stacktrace=None)
Bases: selenium.common.exceptions.WebDriverException
Thrown when switching to no presented alert.
This can be caused by calling an operation on the Alert() class when an alert is not yet on the screen.
exceptionselenium.common.exceptions.NoSuchAttributeException(msg=None, screen=None, stacktrace=None)
Bases: selenium.common.exceptions.WebDriverException
Thrown when the attribute of element could not be found.
You may want to check if the attribute exists in the particular browser you are testing against. Some browsers may have different property names for the same property. (IE8’s .innerText vs. Firefox .textContent)
exceptionselenium.common.exceptions.NoSuchElementException(msg=None, screen=None, stacktrace=None)
Bases: selenium.common.exceptions.WebDriverException
Thrown when element could not be found.
If you encounter this exception, you may want to check the following:
- Check your selector used in your find_by...
- Element may not yet be on the screen at the time of the find operation, (webpage is still loading) see selenium.webdriver.support.wait.WebDriverWait() for how to write a wait wrapper to wait for an element to appear.
exceptionselenium.common.exceptions.NoSuchFrameException(msg=None, screen=None, stacktrace=None)
Bases: selenium.common.exceptions.InvalidSwitchToTargetException
Thrown when frame target to be switched doesn’t exist.
exceptionselenium.common.exceptions.NoSuchWindowException(msg=None, screen=None, stacktrace=None)
Bases: selenium.common.exceptions.InvalidSwitchToTargetException
Thrown when window target to be switched doesn’t exist.
To find the current set of active window handles, you can get a list of the active window handles in the following way:
print driver.window_handles
exceptionselenium.common.exceptions.RemoteDriverServerException(msg=None, screen=None, stacktrace=None)
Bases: selenium.common.exceptions.WebDriverException
exceptionselenium.common.exceptions.StaleElementReferenceException(msg=None, screen=None, stacktrace=None)
Bases: selenium.common.exceptions.WebDriverException
Thrown when a reference to an element is now “stale”.
Stale means the element no longer appears on the DOM of the page.
Possible causes of StaleElementReferenceException include, but not limited to:
- You are no longer on the same page, or the page may have refreshed since the element was located.
- The element may have been removed and re-added to the screen, since it was located. Such as an element being relocated. This can happen typically with a javascript framework when values are updated and the node is rebuilt.
- Element may have been inside an iframe or another context which was refreshed.
exceptionselenium.common.exceptions.TimeoutException(msg=None, screen=None, stacktrace=None)
Bases: selenium.common.exceptions.WebDriverException
Thrown when a command does not complete in enough time.
exceptionselenium.common.exceptions.UnableToSetCookieException(msg=None, screen=None, stacktrace=None)
Bases: selenium.common.exceptions.WebDriverException
Thrown when a driver fails to set a cookie.
exceptionselenium.common.exceptions.UnexpectedAlertPresentException(msg=None, screen=None, stacktrace=None, alert_text=None)
Bases: selenium.common.exceptions.WebDriverException
Thrown when an unexpected alert is appeared.
Usually raised when when an expected modal is blocking webdriver form executing any more commands.
exceptionselenium.common.exceptions.UnexpectedTagNameException(msg=None, screen=None, stacktrace=None)
Bases: selenium.common.exceptions.WebDriverException
Thrown when a support class did not get an expected web element.
exceptionselenium.common.exceptions.WebDriverException(msg=None, screen=None, stacktrace=None)
Bases: exceptions.Exception
Base webdriver exception.
7.2. Action Chains
The ActionChains implementation,
classselenium.webdriver.common.action_chains.ActionChains(driver)
Bases: object
ActionChains are a way to automate low level interactions such as mouse movements, mouse button actions, key press, and context menu interactions. This is useful for doing more complex actions like hover over and drag and drop.
Generate user actions.
When you call methods for actions on the ActionChains object, the actions are stored in a queue in the ActionChains object. When you call perform(), the events are fired in the order they are queued up.
ActionChains can be used in a chain pattern:
menu = driver.find_element_by_css_selector(".nav")
hidden_submenu = driver.find_element_by_css_selector(".nav #submenu1")ActionChains(driver).move_to_element(menu).click(hidden_submenu).perform()
Or actions can be queued up one by one, then performed.:
menu = driver.find_element_by_css_selector(".nav")
hidden_submenu = driver.find_element_by_css_selector(".nav #submenu1")actions = ActionChains(driver)
actions.move_to_element(menu)
actions.click(hidden_submenu)
actions.perform()
Either way, the actions are performed in the order they are called, one after another.
click(on_element=None)
Clicks an element.
| Args: |
|
|---|
click_and_hold(on_element=None)
Holds down the left mouse button on an element.
| Args: |
|
|---|
context_click(on_element=None)
Performs a context-click (right click) on an element.
| Args: |
|
|---|
double_click(on_element=None)
Double-clicks an element.
| Args: |
|
|---|
drag_and_drop(source, target)
Holds down the left mouse button on the source element,
then moves to the target element and releases the mouse button.
| Args: |
|
|---|
drag_and_drop_by_offset(source, xoffset, yoffset)
Holds down the left mouse button on the source element,
then moves to the target offset and releases the mouse button.
| Args: |
|
|---|
key_down(value, element=None)
Sends a key press only, without releasing it.
Should only be used with modifier keys (Control, Alt and Shift).
| Args: |
|
|---|
Example, pressing ctrl+c:
ActionChains(driver).key_down(Keys.CONTROL).send_keys('c').key_up(Keys.CONTROL).perform()
key_up(value, element=None)
Releases a modifier key.
| Args: |
|
|---|
Example, pressing ctrl+c:
ActionChains(driver).key_down(Keys.CONTROL).send_keys('c').key_up(Keys.CONTROL).perform()
move_by_offset(xoffset, yoffset)
Moving the mouse to an offset from current mouse position.
| Args: |
|
|---|
move_to_element(to_element)
Moving the mouse to the middle of an element.
| Args: |
|
|---|
move_to_element_with_offset(to_element, xoffset, yoffset)
Move the mouse by an offset of the specified element.
Offsets are relative to the top-left corner of the element.
| Args: |
|
|---|
pause(seconds)
Pause all inputs for the specified duration in seconds
perform()
Performs all stored actions.
release(on_element=None)
Releasing a held mouse button on an element.
| Args: |
|
|---|
reset_actions()
Clears actions that are already stored on the remote end.
send_keys(*keys_to_send)
Sends keys to current focused element.
| Args: |
|
|---|
send_keys_to_element(element, *keys_to_send)
Sends keys to an element.
| Args: |
|
|---|
7.3. Alerts
The Alert implementation.
classselenium.webdriver.common.alert.Alert(driver)
Bases: object
Allows to work with alerts.
Use this class to interact with alert prompts. It contains methods for dismissing, accepting, inputting, and getting text from alert prompts.
Accepting / Dismissing alert prompts:
Alert(driver).accept() Alert(driver).dismiss()
Inputting a value into an alert prompt:
name_prompt = Alert(driver) name_prompt.send_keys(“Willian Shakesphere”) name_prompt.accept()
Reading a the text of a prompt for verification:
alert_text = Alert(driver).text self.assertEqual(“Do you wish to quit?”, alert_text)
accept()
Accepts the alert available.
Usage:: Alert(driver).accept() # Confirm a alert dialog.
authenticate(username, password)
Send the username / password to an Authenticated dialog (like with Basic HTTP Auth). Implicitly ‘clicks ok’
Usage:: driver.switch_to.alert.authenticate(‘cheese’, ‘secretGouda’)
| Args: | -username: string to be set in the username section of the dialog -password: string to be set in the password section of the dialog |
|---|
dismiss()
Dismisses the alert available.
send_keys(keysToSend)
Send Keys to the Alert.
| Args: |
|
|---|
text
Gets the text of the Alert.
7.4. Special Keys
The Keys implementation.
classselenium.webdriver.common.keys.Keys
Bases: object
Set of special keys codes.
ADD= u'\ue025'
ALT= u'\ue00a'
ARROW_DOWN= u'\ue015'
ARROW_LEFT= u'\ue012'
ARROW_RIGHT= u'\ue014'
ARROW_UP= u'\ue013'
BACKSPACE= u'\ue003'
BACK_SPACE= u'\ue003'
CANCEL= u'\ue001'
CLEAR= u'\ue005'
COMMAND= u'\ue03d'
CONTROL= u'\ue009'
DECIMAL= u'\ue028'
DELETE= u'\ue017'
DIVIDE= u'\ue029'
DOWN= u'\ue015'
END= u'\ue010'
ENTER= u'\ue007'
EQUALS= u'\ue019'
ESCAPE= u'\ue00c'
F1= u'\ue031'
F10= u'\ue03a'
F11= u'\ue03b'
F12= u'\ue03c'
F2= u'\ue032'
F3= u'\ue033'
F4= u'\ue034'
F5= u'\ue035'
F6= u'\ue036'
F7= u'\ue037'
F8= u'\ue038'
F9= u'\ue039'
HELP= u'\ue002'
HOME= u'\ue011'
INSERT= u'\ue016'
LEFT= u'\ue012'
LEFT_ALT= u'\ue00a'
LEFT_CONTROL= u'\ue009'
LEFT_SHIFT= u'\ue008'
META= u'\ue03d'
MULTIPLY= u'\ue024'
NULL= u'\ue000'
NUMPAD0= u'\ue01a'
NUMPAD1= u'\ue01b'
NUMPAD2= u'\ue01c'
NUMPAD3= u'\ue01d'
NUMPAD4= u'\ue01e'
NUMPAD5= u'\ue01f'
NUMPAD6= u'\ue020'
NUMPAD7= u'\ue021'
NUMPAD8= u'\ue022'
NUMPAD9= u'\ue023'
PAGE_DOWN= u'\ue00f'
PAGE_UP= u'\ue00e'
PAUSE= u'\ue00b'
RETURN= u'\ue006'
RIGHT= u'\ue014'
SEMICOLON= u'\ue018'
SEPARATOR= u'\ue026'
SHIFT= u'\ue008'
SPACE= u'\ue00d'
SUBTRACT= u'\ue027'
TAB= u'\ue004'
UP= u'\ue013'
7.5. Locate elements By
These are the attributes which can be used to locate elements. See the 查找元素 chapter for example usages.
The By implementation.
classselenium.webdriver.common.by.By
Bases: object
Set of supported locator strategies.
CLASS_NAME= 'class name'
CSS_SELECTOR= 'css selector'
ID= 'id'
LINK_TEXT= 'link text'
NAME= 'name'
PARTIAL_LINK_TEXT= 'partial link text'
TAG_NAME= 'tag name'
XPATH= 'xpath'
7.6. Desired Capabilities
See the 使用远程 Selenium WebDriver section for example usages of desired capabilities.
The Desired Capabilities implementation.
classselenium.webdriver.common.desired_capabilities.DesiredCapabilities
Bases: object
Set of default supported desired capabilities.
Use this as a starting point for creating a desired capabilities object for requesting remote webdrivers for connecting to selenium server or selenium grid.
Usage Example:
from selenium import webdriverselenium_grid_url = "http://198.0.0.1:4444/wd/hub"# Create a desired capabilities object as a starting point. capabilities = DesiredCapabilities.FIREFOX.copy() capabilities['platform'] = "WINDOWS" capabilities['version'] = "10"# Instantiate an instance of Remote WebDriver with the desired capabilities. driver = webdriver.Remote(desired_capabilities=capabilities,command_executor=selenium_grid_url)
Note: Always use ‘.copy()’ on the DesiredCapabilities object to avoid the side effects of altering the Global class instance.
ANDROID= {'platform': 'ANDROID', 'browserName': 'android', 'version': ''}
CHROME= {'platform': 'ANY', 'browserName': 'chrome', 'version': ''}
EDGE= {'platform': 'WINDOWS', 'browserName': 'MicrosoftEdge', 'version': ''}
FIREFOX= {'acceptInsecureCerts': True, 'browserName': 'firefox', 'marionette': True}
HTMLUNIT= {'platform': 'ANY', 'browserName': 'htmlunit', 'version': ''}
HTMLUNITWITHJS= {'platform': 'ANY', 'browserName': 'htmlunit', 'version': 'firefox', 'javascriptEnabled': True}
INTERNETEXPLORER= {'platform': 'WINDOWS', 'browserName': 'internet explorer', 'version': ''}
IPAD= {'platform': 'MAC', 'browserName': 'iPad', 'version': ''}
IPHONE= {'platform': 'MAC', 'browserName': 'iPhone', 'version': ''}
OPERA= {'platform': 'ANY', 'browserName': 'opera', 'version': ''}
PHANTOMJS= {'platform': 'ANY', 'browserName': 'phantomjs', 'version': '', 'javascriptEnabled': True}
SAFARI= {'platform': 'MAC', 'browserName': 'safari', 'version': ''}
7.7. Utilities
The Utils methods.
selenium.webdriver.common.utils.find_connectable_ip(host, port=None)
Resolve a hostname to an IP, preferring IPv4 addresses.
We prefer IPv4 so that we don’t change behavior from previous IPv4-only implementations, and because some drivers (e.g., FirefoxDriver) do not support IPv6 connections.
If the optional port number is provided, only IPs that listen on the given port are considered.
| Args: |
|
|---|---|
| Returns: | A single IP address, as a string. If any IPv4 address is found, one is returned. Otherwise, if any IPv6 address is found, one is returned. If neither, then None is returned. |
selenium.webdriver.common.utils.free_port()
Determines a free port using sockets.
selenium.webdriver.common.utils.is_connectable(port, host='localhost')
Tries to connect to the server at port to see if it is running.
| Args: |
|
|---|
selenium.webdriver.common.utils.is_url_connectable(port)
Tries to connect to the HTTP server at /status path and specified port to see if it responds successfully.
| Args: |
|
|---|
selenium.webdriver.common.utils.join_host_port(host, port)
Joins a hostname and port together.
This is a minimal implementation intended to cope with IPv6 literals. For example, _join_host_port(‘::1’, 80) == ‘[::1]:80’.
| Args: |
|
|---|
selenium.webdriver.common.utils.keys_to_typing(value)
Processes the values that will be typed in the element.
7.8. Firefox WebDriver
classselenium.webdriver.firefox.webdriver.WebDriver(firefox_profile=None, firefox_binary=None, timeout=30, capabilities=None, proxy=None, executable_path='geckodriver', firefox_options=None, log_path='geckodriver.log')
Bases: selenium.webdriver.remote.webdriver.WebDriver
context(*args, **kwds)
Sets the context that Selenium commands are running in using a with statement. The state of the context on the server is saved before entering the block, and restored upon exiting it.
| Parameters: | context – Context, may be one of the class properties CONTEXT_CHROME or CONTEXT_CONTENT. |
|---|
Usage example:
with selenium.context(selenium.CONTEXT_CHROME):# chrome scope... do stuff ...
install_addon(path, temporary=None)
Installs Firefox addon.
Returns identifier of installed addon. This identifier can later be used to uninstall addon.
| Parameters: | path – Absolute path to the addon that will be installed. |
|---|---|
| Usage: | driver.install_addon(‘/path/to/firebug.xpi’) |
quit()
Quits the driver and close every associated window.
set_context(context)
uninstall_addon(identifier)
Uninstalls Firefox addon using its identifier.
| Usage: | driver.uninstall_addon('addon@foo.com‘) |
|---|
CONTEXT_CHROME= 'chrome'
CONTEXT_CONTENT= 'content'
NATIVE_EVENTS_ALLOWED= True
firefox_profile
7.9. Chrome WebDriver
classselenium.webdriver.chrome.webdriver.WebDriver(executable_path='chromedriver', port=0, chrome_options=None, service_args=None, desired_capabilities=None, service_log_path=None)
Bases: selenium.webdriver.remote.webdriver.WebDriver
Controls the ChromeDriver and allows you to drive the browser.
You will need to download the ChromeDriver executable from http://chromedriver.storage.googleapis.com/index.html
create_options()
get_network_conditions()
Gets Chrome network emulation settings.
| Returns: | A dict. For example: {‘latency’: 4, ‘download_throughput’: 2, ‘upload_throughput’: 2, ‘offline’: False} |
|---|
launch_app(id)
Launches Chrome app specified by id.
quit()
Closes the browser and shuts down the ChromeDriver executable that is started when starting the ChromeDriver
set_network_conditions(**network_conditions)
Sets Chrome network emulation settings.
| Args: |
|
|---|---|
| Usage: | driver.set_network_conditions( offline=False, latency=5, # additional latency (ms) download_throughput=500 * 1024, # maximal throughput upload_throughput=500 * 1024) # maximal throughput Note: ‘throughput’ can be used to set both (for download and upload). |
7.10. Remote WebDriver
The WebDriver implementation.
classselenium.webdriver.remote.webdriver.WebDriver(command_executor='http://127.0.0.1:4444/wd/hub', desired_capabilities=None, browser_profile=None, proxy=None, keep_alive=False, file_detector=None)
Bases: object
Controls a browser by sending commands to a remote server. This server is expected to be running the WebDriver wire protocol as defined at https://github.com/SeleniumHQ/selenium/wiki/JsonWireProtocol
| Attributes: |
|
|---|
add_cookie(cookie_dict)
Adds a cookie to your current session.
| Args: |
|
|---|
Usage:
driver.add_cookie({‘name’ : ‘foo’, ‘value’ : ‘bar’}) driver.add_cookie({‘name’ : ‘foo’, ‘value’ : ‘bar’, ‘path’ : ‘/’}) driver.add_cookie({‘name’ : ‘foo’, ‘value’ : ‘bar’, ‘path’ : ‘/’, ‘secure’:True})
back()
Goes one step backward in the browser history.
| Usage: | driver.back() |
|---|
close()
Closes the current window.
| Usage: | driver.close() |
|---|
create_web_element(element_id)
Creates a web element with the specified element_id.
delete_all_cookies()
Delete all cookies in the scope of the session.
| Usage: | driver.delete_all_cookies() |
|---|
delete_cookie(name)
Deletes a single cookie with the given name.
| Usage: | driver.delete_cookie(‘my_cookie’) |
|---|
execute(driver_command, params=None)
Sends a command to be executed by a command.CommandExecutor.
| Args: |
|
|---|---|
| Returns: | The command’s JSON response loaded into a dictionary object. |
execute_async_script(script, *args)
Asynchronously Executes JavaScript in the current window/frame.
| Args: |
|
|---|---|
| Usage: | driver.execute_async_script(‘document.title’) |
execute_script(script, *args)
Synchronously Executes JavaScript in the current window/frame.
| Args: |
|
|---|---|
| Usage: | driver.execute_script(‘document.title’) |
file_detector_context(*args, **kwds)
Overrides the current file detector (if necessary) in limited context. Ensures the original file detector is set afterwards.
Example:
with webdriver.file_detector_context(UselessFileDetector):
someinput.send_keys(‘/etc/hosts’)
| Args: |
|
|---|
find_element(by='id', value=None)
‘Private’ method used by the find_element_by_* methods.
| Usage: | Use the corresponding find_element_by_* instead of this. |
|---|---|
| Return type: | WebElement |
find_element_by_class_name(name)
Finds an element by class name.
| Args: |
|
|---|---|
| Usage: | driver.find_element_by_class_name(‘foo’) |
find_element_by_css_selector(css_selector)
Finds an element by css selector.
| Args: |
|
|---|---|
| Usage: | driver.find_element_by_css_selector(‘#foo’) |
find_element_by_id(id_)
Finds an element by id.
| Args: |
|
|---|---|
| Usage: | driver.find_element_by_id(‘foo’) |
find_element_by_link_text(link_text)
Finds an element by link text.
| Args: |
|
|---|---|
| Usage: | driver.find_element_by_link_text(‘Sign In’) |
find_element_by_name(name)
Finds an element by name.
| Args: |
|
|---|---|
| Usage: | driver.find_element_by_name(‘foo’) |
find_element_by_partial_link_text(link_text)
Finds an element by a partial match of its link text.
| Args: |
|
|---|---|
| Usage: | driver.find_element_by_partial_link_text(‘Sign’) |
find_element_by_tag_name(name)
Finds an element by tag name.
| Args: |
|
|---|---|
| Usage: | driver.find_element_by_tag_name(‘foo’) |
find_element_by_xpath(xpath)
Finds an element by xpath.
| Args: |
|
|---|---|
| Usage: | driver.find_element_by_xpath(‘//div/td[1]’) |
find_elements(by='id', value=None)
‘Private’ method used by the find_elements_by_* methods.
| Usage: | Use the corresponding find_elements_by_* instead of this. |
|---|---|
| Return type: | list of WebElement |
find_elements_by_class_name(name)
Finds elements by class name.
| Args: |
|
|---|---|
| Usage: | driver.find_elements_by_class_name(‘foo’) |
find_elements_by_css_selector(css_selector)
Finds elements by css selector.
| Args: |
|
|---|---|
| Usage: | driver.find_elements_by_css_selector(‘.foo’) |
find_elements_by_id(id_)
Finds multiple elements by id.
| Args: |
|
|---|---|
| Usage: | driver.find_elements_by_id(‘foo’) |
find_elements_by_link_text(text)
Finds elements by link text.
| Args: |
|
|---|---|
| Usage: | driver.find_elements_by_link_text(‘Sign In’) |
find_elements_by_name(name)
Finds elements by name.
| Args: |
|
|---|---|
| Usage: | driver.find_elements_by_name(‘foo’) |
find_elements_by_partial_link_text(link_text)
Finds elements by a partial match of their link text.
| Args: |
|
|---|---|
| Usage: | driver.find_element_by_partial_link_text(‘Sign’) |
find_elements_by_tag_name(name)
Finds elements by tag name.
| Args: |
|
|---|---|
| Usage: | driver.find_elements_by_tag_name(‘foo’) |
find_elements_by_xpath(xpath)
Finds multiple elements by xpath.
| Args: |
|
|---|---|
| Usage: | driver.find_elements_by_xpath(“//div[contains(@class, ‘foo’)]”) |
forward()
Goes one step forward in the browser history.
| Usage: | driver.forward() |
|---|
fullscreen_window()
Invokes the window manager-specific ‘full screen’ operation
get(url)
Loads a web page in the current browser session.
get_cookie(name)
Get a single cookie by name. Returns the cookie if found, None if not.
| Usage: | driver.get_cookie(‘my_cookie’) |
|---|
get_cookies()
Returns a set of dictionaries, corresponding to cookies visible in the current session.
| Usage: | driver.get_cookies() |
|---|
get_log(log_type)
Gets the log for a given log type
| Args: |
|
|---|---|
| Usage: | driver.get_log(‘browser’) driver.get_log(‘driver’) driver.get_log(‘client’) driver.get_log(‘server’) |
get_screenshot_as_base64()
Gets the screenshot of the current window as a base64 encoded string
which is useful in embedded images in HTML.
| Usage: | driver.get_screenshot_as_base64() |
|---|
get_screenshot_as_file(filename)
Saves a screenshot of the current window to a PNG image file. Returns
False if there is any IOError, else returns True. Use full paths in your filename.
| Args: |
|
|---|---|
| Usage: | driver.get_screenshot_as_file(‘/Screenshots/foo.png’) |
get_screenshot_as_png()
Gets the screenshot of the current window as a binary data.
| Usage: | driver.get_screenshot_as_png() |
|---|
get_window_position(windowHandle='current')
Gets the x,y position of the current window.
| Usage: | driver.get_window_position() |
|---|
get_window_rect()
Gets the x, y coordinates of the window as well as height and width of the current window.
| Usage: | driver.get_window_rect() |
|---|
get_window_size(windowHandle='current')
Gets the width and height of the current window.
| Usage: | driver.get_window_size() |
|---|
implicitly_wait(time_to_wait)
Sets a sticky timeout to implicitly wait for an element to be found,
or a command to complete. This method only needs to be called one time per session. To set the timeout for calls to execute_async_script, see set_script_timeout.
| Args: |
|
|---|---|
| Usage: | driver.implicitly_wait(30) |
maximize_window()
Maximizes the current window that webdriver is using
minimize_window()
Invokes the window manager-specific ‘minimize’ operation
quit()
Quits the driver and closes every associated window.
| Usage: | driver.quit() |
|---|
refresh()
Refreshes the current page.
| Usage: | driver.refresh() |
|---|
save_screenshot(filename)
Saves a screenshot of the current window to a PNG image file. Returns
False if there is any IOError, else returns True. Use full paths in your filename.
| Args: |
|
|---|---|
| Usage: | driver.save_screenshot(‘/Screenshots/foo.png’) |
set_page_load_timeout(time_to_wait)
Set the amount of time to wait for a page load to complete
before throwing an error.
| Args: |
|
|---|---|
| Usage: | driver.set_page_load_timeout(30) |
set_script_timeout(time_to_wait)
Set the amount of time that the script should wait during an
execute_async_script call before throwing an error.
| Args: |
|
|---|---|
| Usage: | driver.set_script_timeout(30) |
set_window_position(x, y, windowHandle='current')
Sets the x,y position of the current window. (window.moveTo)
| Args: |
|
|---|---|
| Usage: | driver.set_window_position(0,0) |
set_window_rect(x=None, y=None, width=None, height=None)
Sets the x, y coordinates of the window as well as height and width of the current window.
| Usage: | driver.set_window_rect(x=10, y=10) driver.set_window_rect(width=100, height=200) driver.set_window_rect(x=10, y=10, width=100, height=200) |
|---|
set_window_size(width, height, windowHandle='current')
Sets the width and height of the current window. (window.resizeTo)
| Args: |
|
|---|---|
| Usage: | driver.set_window_size(800,600) |
start_client()
Called before starting a new session. This method may be overridden to define custom startup behavior.
start_session(capabilities, browser_profile=None)
Creates a new session with the desired capabilities.
| Args: |
|
|---|
stop_client()
Called after executing a quit command. This method may be overridden to define custom shutdown behavior.
switch_to_active_element()
Deprecated use driver.switch_to.active_element
switch_to_alert()
Deprecated use driver.switch_to.alert
switch_to_default_content()
Deprecated use driver.switch_to.default_content
switch_to_frame(frame_reference)
Deprecated use driver.switch_to.frame
switch_to_window(window_name)
Deprecated use driver.switch_to.window
application_cache
Returns a ApplicationCache Object to interact with the browser app cache
current_url
Gets the URL of the current page.
| Usage: | driver.current_url |
|---|
current_window_handle
Returns the handle of the current window.
| Usage: | driver.current_window_handle |
|---|
desired_capabilities
returns the drivers current desired capabilities being used
file_detector
log_types
Gets a list of the available log types
| Usage: | driver.log_types |
|---|
mobile
name
Returns the name of the underlying browser for this instance.
| Usage: |
|
|---|
orientation
Gets the current orientation of the device
| Usage: | orientation = driver.orientation |
|---|
page_source
Gets the source of the current page.
| Usage: | driver.page_source |
|---|
switch_to
title
Returns the title of the current page.
| Usage: | driver.title |
|---|
window_handles
Returns the handles of all windows within the current session.
| Usage: | driver.window_handles |
|---|
7.11. WebElement
classselenium.webdriver.remote.webelement.WebElement(parent, id_, w3c=False)
Bases: object
Represents a DOM element.
Generally, all interesting operations that interact with a document will be performed through this interface.
All method calls will do a freshness check to ensure that the element reference is still valid. This essentially determines whether or not the element is still attached to the DOM. If this test fails, then an StaleElementReferenceException is thrown, and all future calls to this instance will fail.
clear()
Clears the text if it’s a text entry element.
click()
Clicks the element.
find_element(by='id', value=None)
find_element_by_class_name(name)
Finds element within this element’s children by class name.
| Args: |
|
|---|
find_element_by_css_selector(css_selector)
Finds element within this element’s children by CSS selector.
| Args: |
|
|---|
find_element_by_id(id_)
Finds element within this element’s children by ID.
| Args: |
|
|---|
find_element_by_link_text(link_text)
Finds element within this element’s children by visible link text.
| Args: |
|
|---|
find_element_by_name(name)
Finds element within this element’s children by name.
| Args: |
|
|---|
find_element_by_partial_link_text(link_text)
Finds element within this element’s children by partially visible link text.
| Args: |
|
|---|
find_element_by_tag_name(name)
Finds element within this element’s children by tag name.
| Args: |
|
|---|
find_element_by_xpath(xpath)
Finds element by xpath.
| Args: | xpath - xpath of element to locate. “//input[@class=’myelement’]” |
|---|
Note: The base path will be relative to this element’s location.
This will select the first link under this element.
myelement.find_elements_by_xpath(".//a")
However, this will select the first link on the page.
myelement.find_elements_by_xpath("//a")
find_elements(by='id', value=None)
find_elements_by_class_name(name)
Finds a list of elements within this element’s children by class name.
| Args: |
|
|---|
find_elements_by_css_selector(css_selector)
Finds a list of elements within this element’s children by CSS selector.
| Args: |
|
|---|
find_elements_by_id(id_)
Finds a list of elements within this element’s children by ID.
| Args: |
|
|---|
find_elements_by_link_text(link_text)
Finds a list of elements within this element’s children by visible link text.
| Args: |
|
|---|
find_elements_by_name(name)
Finds a list of elements within this element’s children by name.
| Args: |
|
|---|
find_elements_by_partial_link_text(link_text)
Finds a list of elements within this element’s children by link text.
| Args: |
|
|---|
find_elements_by_tag_name(name)
Finds a list of elements within this element’s children by tag name.
| Args: |
|
|---|
find_elements_by_xpath(xpath)
Finds elements within the element by xpath.
| Args: |
|
|---|
Note: The base path will be relative to this element’s location.
This will select all links under this element.
myelement.find_elements_by_xpath(".//a")
However, this will select all links in the page itself.
myelement.find_elements_by_xpath("//a")
get_attribute(name)
Gets the given attribute or property of the element.
This method will first try to return the value of a property with the given name. If a property with that name doesn’t exist, it returns the value of the attribute with the same name. If there’s no attribute with that name, None is returned.
Values which are considered truthy, that is equals “true” or “false”, are returned as booleans. All other non-None values are returned as strings. For attributes or properties which do not exist, None is returned.
| Args: |
|
|---|
Example:
# Check if the "active" CSS class is applied to an element.
is_active = "active" in target_element.get_attribute("class")
get_property(name)
Gets the given property of the element.
| Args: |
|
|---|
Example:
# Check if the "active" CSS class is applied to an element.
text_length = target_element.get_property("text_length")
is_displayed()
Whether the element is visible to a user.
is_enabled()
Returns whether the element is enabled.
is_selected()
Returns whether the element is selected.
Can be used to check if a checkbox or radio button is selected.
screenshot(filename)
Saves a screenshot of the current element to a PNG image file. Returns
False if there is any IOError, else returns True. Use full paths in your filename.
| Args: |
|
|---|---|
| Usage: | element.screenshot(‘/Screenshots/foo.png’) |
send_keys(*value)
Simulates typing into the element.
| Args: |
|
|---|
Use this to send simple key events or to fill out form fields:
form_textfield = driver.find_element_by_name('username')
form_textfield.send_keys("admin")
This can also be used to set file inputs.
file_input = driver.find_element_by_name('profilePic')
file_input.send_keys("path/to/profilepic.gif")
# Generally it's better to wrap the file path in one of the methods
# in os.path to return the actual path to support cross OS testing.
# file_input.send_keys(os.path.abspath("path/to/profilepic.gif"))
submit()
Submits a form.
value_of_css_property(property_name)
The value of a CSS property.
id
Internal ID used by selenium.
This is mainly for internal use. Simple use cases such as checking if 2 webelements refer to the same element, can be done using ==:
if element1 == element2:print("These 2 are equal")
location
The location of the element in the renderable canvas.
location_once_scrolled_into_view
THIS PROPERTY MAY CHANGE WITHOUT WARNING. Use this to discover where on the screen an element is so that we can click it. This method should cause the element to be scrolled into view.
Returns the top lefthand corner location on the screen, or None if the element is not visible.
parent
Internal reference to the WebDriver instance this element was found from.
rect
A dictionary with the size and location of the element.
screenshot_as_base64
Gets the screenshot of the current element as a base64 encoded string.
| Usage: | img_b64 = element.screenshot_as_base64 |
|---|
screenshot_as_png
Gets the screenshot of the current element as a binary data.
| Usage: | element_png = element.screenshot_as_png |
|---|
size
The size of the element.
tag_name
This element’s tagName property.
text
The text of the element.
7.12. UI Support
classselenium.webdriver.support.select.Select(webelement)
Bases: object
deselect_all()
Clear all selected entries. This is only valid when the SELECT supports multiple selections. throws NotImplementedError If the SELECT does not support multiple selections
deselect_by_index(index)
Deselect the option at the given index. This is done by examing the “index” attribute of an element, and not merely by counting.
| Args: |
throws NoSuchElementException If there is no option with specisied index in SELECT |
|---|
deselect_by_value(value)
Deselect all options that have a value matching the argument. That is, when given “foo” this would deselect an option like:
<option value=”foo”>Bar</option>
| Args: |
throws NoSuchElementException If there is no option with specisied value in SELECT |
|---|
deselect_by_visible_text(text)
Deselect all options that display text matching the argument. That is, when given “Bar” this would deselect an option like:
<option value=”foo”>Bar</option>
| Args: |
|
|---|
select_by_index(index)
Select the option at the given index. This is done by examing the “index” attribute of an element, and not merely by counting.
| Args: |
|
|---|
throws NoSuchElementException If there is no option with specisied index in SELECT
select_by_value(value)
Select all options that have a value matching the argument. That is, when given “foo” this would select an option like:
<option value=”foo”>Bar</option>
| Args: |
|
|---|
throws NoSuchElementException If there is no option with specisied value in SELECT
select_by_visible_text(text)
Select all options that display text matching the argument. That is, when given “Bar” this would select an option like:
<option value=”foo”>Bar</option>
| Args: |
throws NoSuchElementException If there is no option with specisied text in SELECT |
|---|
all_selected_options
Returns a list of all selected options belonging to this select tag
first_selected_option
The first selected option in this select tag (or the currently selected option in a normal select)
options
Returns a list of all options belonging to this select tag
classselenium.webdriver.support.wait.WebDriverWait(driver, timeout, poll_frequency=0.5, ignored_exceptions=None)
Bases: object
until(method, message='')
Calls the method provided with the driver as an argument until the return value is not False.
until_not(method, message='')
Calls the method provided with the driver as an argument until the return value is False.
7.13. Color Support
classselenium.webdriver.support.color.Color(red, green, blue, alpha=1)
Bases: object
Color conversion support class
Example:
from selenium.webdriver.support.color import Colorprint(Color.from_string('#00ff33').rgba)
print(Color.from_string('rgb(1, 255, 3)').hex)
print(Color.from_string('blue').rgba)
staticfrom_string(str_)
hex
rgb
rgba
7.14. Expected conditions Support
classselenium.webdriver.support.expected_conditions.alert_is_present
Bases: object
Expect an alert to be present.
classselenium.webdriver.support.expected_conditions.element_located_selection_state_to_be(locator, is_selected)
Bases: object
An expectation to locate an element and check if the selection state specified is in that state. locator is a tuple of (by, path) is_selected is a boolean
classselenium.webdriver.support.expected_conditions.element_located_to_be_selected(locator)
Bases: object
An expectation for the element to be located is selected. locator is a tuple of (by, path)
classselenium.webdriver.support.expected_conditions.element_selection_state_to_be(element, is_selected)
Bases: object
An expectation for checking if the given element is selected. element is WebElement object is_selected is a Boolean.”
classselenium.webdriver.support.expected_conditions.element_to_be_clickable(locator)
Bases: object
An Expectation for checking an element is visible and enabled such that you can click it.
classselenium.webdriver.support.expected_conditions.element_to_be_selected(element)
Bases: object
An expectation for checking the selection is selected. element is WebElement object
classselenium.webdriver.support.expected_conditions.frame_to_be_available_and_switch_to_it(locator)
Bases: object
An expectation for checking whether the given frame is available to switch to. If the frame is available it switches the given driver to the specified frame.
classselenium.webdriver.support.expected_conditions.invisibility_of_element_located(locator)
Bases: object
An Expectation for checking that an element is either invisible or not present on the DOM.
locator used to find the element
classselenium.webdriver.support.expected_conditions.new_window_is_opened(current_handles)
Bases: object
An expectation that a new window will be opened and have the number of windows handles increase
classselenium.webdriver.support.expected_conditions.number_of_windows_to_be(num_windows)
Bases: object
An expectation for the number of windows to be a certain value.
classselenium.webdriver.support.expected_conditions.presence_of_all_elements_located(locator)
Bases: object
An expectation for checking that there is at least one element present on a web page. locator is used to find the element returns the list of WebElements once they are located
classselenium.webdriver.support.expected_conditions.presence_of_element_located(locator)
Bases: object
An expectation for checking that an element is present on the DOM of a page. This does not necessarily mean that the element is visible. locator - used to find the element returns the WebElement once it is located
classselenium.webdriver.support.expected_conditions.staleness_of(element)
Bases: object
Wait until an element is no longer attached to the DOM. element is the element to wait for. returns False if the element is still attached to the DOM, true otherwise.
classselenium.webdriver.support.expected_conditions.text_to_be_present_in_element(locator, text_)
Bases: object
An expectation for checking if the given text is present in the specified element. locator, text
classselenium.webdriver.support.expected_conditions.text_to_be_present_in_element_value(locator, text_)
Bases: object
An expectation for checking if the given text is present in the element’s locator, text
classselenium.webdriver.support.expected_conditions.title_contains(title)
Bases: object
An expectation for checking that the title contains a case-sensitive substring. title is the fragment of title expected returns True when the title matches, False otherwise
classselenium.webdriver.support.expected_conditions.title_is(title)
Bases: object
An expectation for checking the title of a page. title is the expected title, which must be an exact match returns True if the title matches, false otherwise.
classselenium.webdriver.support.expected_conditions.url_changes(url)
Bases: object
An expectation for checking the current url. url is the expected url, which must not be an exact match returns True if the url is different, false otherwise.
classselenium.webdriver.support.expected_conditions.url_contains(url)
Bases: object
An expectation for checking that the current url contains a case-sensitive substring. url is the fragment of url expected, returns True when the title matches, False otherwise
classselenium.webdriver.support.expected_conditions.url_matches(pattern)
Bases: object
An expectation for checking the current url. pattern is the expected pattern, which must be an exact match returns True if the title matches, false otherwise.
classselenium.webdriver.support.expected_conditions.url_to_be(url)
Bases: object
An expectation for checking the current url. url is the expected url, which must be an exact match returns True if the title matches, false otherwise.
classselenium.webdriver.support.expected_conditions.visibility_of(element)
Bases: object
An expectation for checking that an element, known to be present on the DOM of a page, is visible. Visibility means that the element is not only displayed but also has a height and width that is greater than 0. element is the WebElement returns the (same) WebElement once it is visible
classselenium.webdriver.support.expected_conditions.visibility_of_all_elements_located(locator)
Bases: object
An expectation for checking that all elements are present on the DOM of a page and visible. Visibility means that the elements are not only displayed but also has a height and width that is greater than 0. locator - used to find the elements returns the list of WebElements once they are located and visible
classselenium.webdriver.support.expected_conditions.visibility_of_any_elements_located(locator)
Bases: object
An expectation for checking that there is at least one element visible on a web page. locator is used to find the element returns the list of WebElements once they are located
classselenium.webdriver.support.expected_conditions.visibility_of_element_located(locator)
Bases: object
An expectation for checking that an element is present on the DOM of a page and visible. Visibility means that the element is not only displayed but also has a height and width that is greater than 0. locator - used to find the element returns the WebElement once it is located and visible
相关文章:

Python网页自动化Selenium中文文档
1. 安装 1.1. 安装 Selenium Python bindings 提供了一个简单的API,让你使用Selenium WebDriver来编写功能/校验测试。 通过Selenium Python的API,你可以非常直观的使用Selenium WebDriver的所有功能。 Selenium Python bindings 使用非常简洁方便的A…...

区块链技术概述
区块链技术是一种去中心化、分布式账本技术,通过密码学、共识机制和智能合约等核心组件,实现数据不可篡改、透明可追溯的系统。 一、核心技术 1. 去中心化 特点:数据存储在网络中的多个节点(计算机),而非…...

comfyui 工作流中 图生视频 如何增加视频的长度到5秒
comfyUI 工作流怎么可以生成更长的视频。除了硬件显存要求之外还有别的方法吗? 在ComfyUI中实现图生视频并延长到5秒,需要结合多个扩展和技巧。以下是完整解决方案: 核心工作流配置(24fps下5秒120帧) #mermaid-svg-yP…...

数据结构:递归的种类(Types of Recursion)
目录 尾递归(Tail Recursion) 什么是 Loop(循环)? 复杂度分析 头递归(Head Recursion) 树形递归(Tree Recursion) 线性递归(Linear Recursion)…...

保姆级【快数学会Android端“动画“】+ 实现补间动画和逐帧动画!!!
目录 补间动画 1.创建资源文件夹 2.设置文件夹类型 3.创建.xml文件 4.样式设计 5.动画设置 6.动画的实现 内容拓展 7.在原基础上继续添加.xml文件 8.xml代码编写 (1)rotate_anim (2)scale_anim (3)translate_anim 9.MainActivity.java代码汇总 10.效果展示 逐帧…...
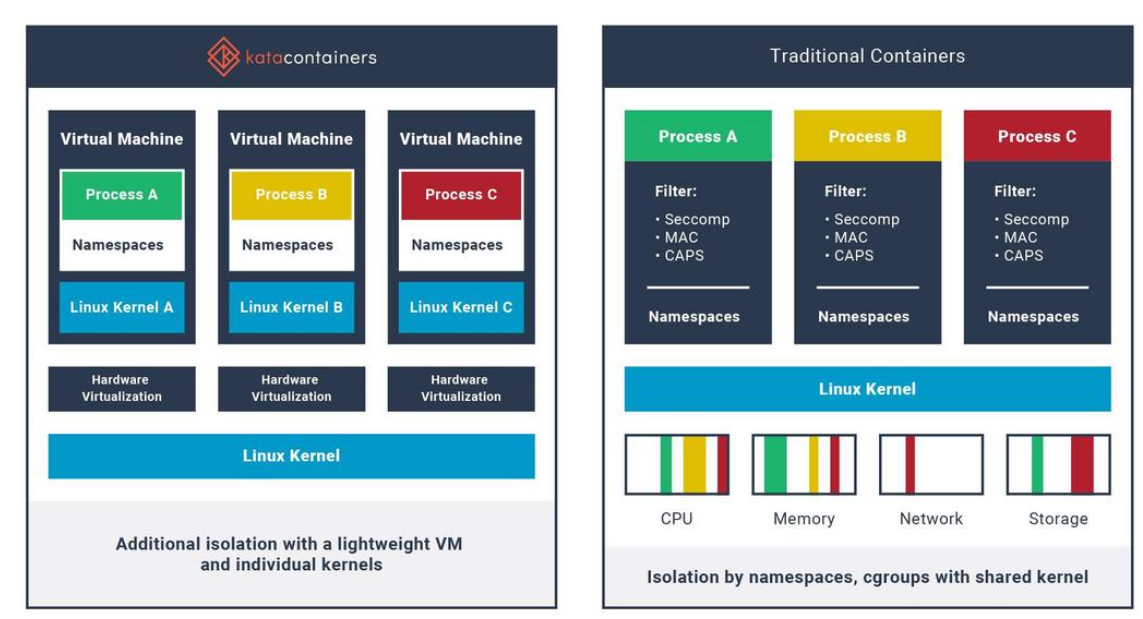
沙箱虚拟化技术虚拟机容器之间的关系详解
问题 沙箱、虚拟化、容器三者分开一一介绍的话我知道他们各自都是什么东西,但是如果把三者放在一起,它们之间到底什么关系?又有什么联系呢?我不是很明白!!! 就比如说: 沙箱&#…...
实现跳一跳小游戏)
鸿蒙(HarmonyOS5)实现跳一跳小游戏
下面我将介绍如何使用鸿蒙的ArkUI框架,实现一个简单的跳一跳小游戏。 1. 项目结构 src/main/ets/ ├── MainAbility │ ├── pages │ │ ├── Index.ets // 主页面 │ │ └── GamePage.ets // 游戏页面 │ └── model │ …...
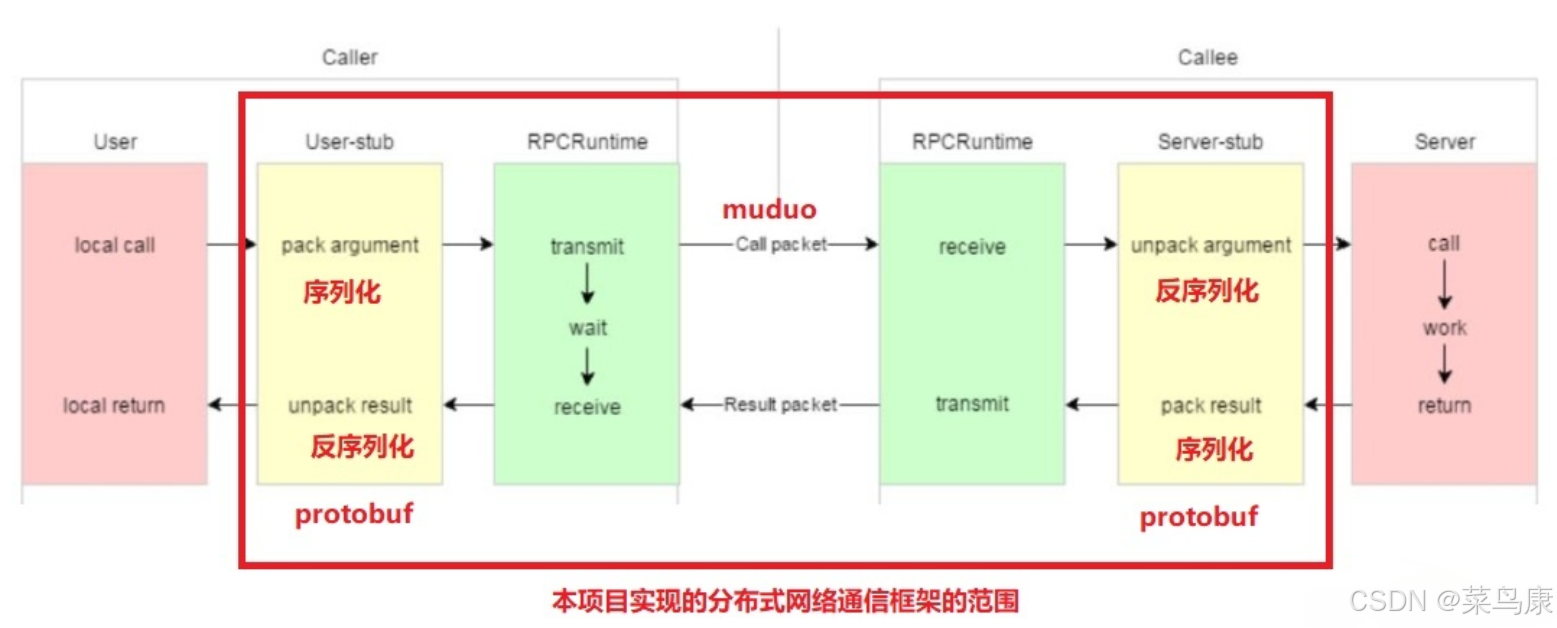
C++实现分布式网络通信框架RPC(2)——rpc发布端
有了上篇文章的项目的基本知识的了解,现在我们就开始构建项目。 目录 一、构建工程目录 二、本地服务发布成RPC服务 2.1理解RPC发布 2.2实现 三、Mprpc框架的基础类设计 3.1框架的初始化类 MprpcApplication 代码实现 3.2读取配置文件类 MprpcConfig 代码实现…...
的打车小程序)
基于鸿蒙(HarmonyOS5)的打车小程序
1. 开发环境准备 安装DevEco Studio (鸿蒙官方IDE)配置HarmonyOS SDK申请开发者账号和必要的API密钥 2. 项目结构设计 ├── entry │ ├── src │ │ ├── main │ │ │ ├── ets │ │ │ │ ├── pages │ │ │ │ │ ├── H…...

消防一体化安全管控平台:构建消防“一张图”和APP统一管理
在城市的某个角落,一场突如其来的火灾打破了平静。熊熊烈火迅速蔓延,滚滚浓烟弥漫开来,周围群众的生命财产安全受到严重威胁。就在这千钧一发之际,消防救援队伍迅速行动,而豪越科技消防一体化安全管控平台构建的消防“…...
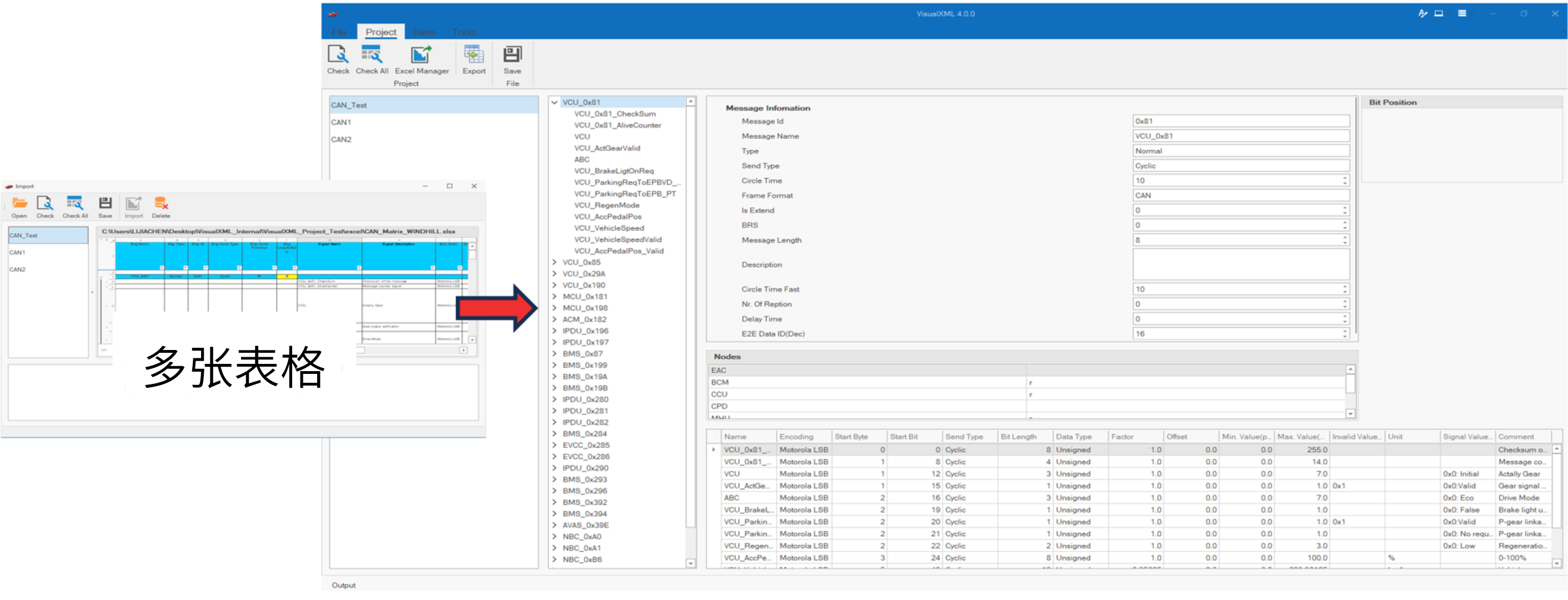
VisualXML全新升级 | 新增数据库编辑功能
VisualXML是一个功能强大的网络总线设计工具,专注于简化汽车电子系统中复杂的网络数据设计操作。它支持多种主流总线网络格式的数据编辑(如DBC、LDF、ARXML、HEX等),并能够基于Excel表格的方式生成和转换多种数据库文件。由此&…...

Sklearn 机器学习 缺失值处理 获取填充失值的统计值
💖亲爱的技术爱好者们,热烈欢迎来到 Kant2048 的博客!我是 Thomas Kant,很开心能在CSDN上与你们相遇~💖 本博客的精华专栏: 【自动化测试】 【测试经验】 【人工智能】 【Python】 使用 Scikit-learn 处理缺失值并提取填充统计信息的完整指南 在机器学习项目中,数据清…...
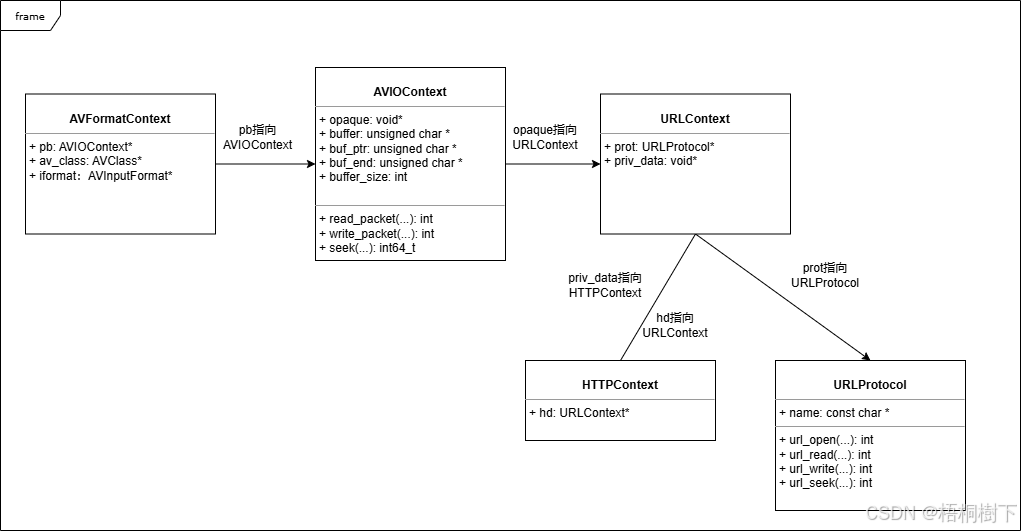
FFmpeg avformat_open_input函数分析
函数内部的总体流程如下: avformat_open_input 精简后的代码如下: int avformat_open_input(AVFormatContext **ps, const char *filename,ff_const59 AVInputFormat *fmt, AVDictionary **options) {AVFormatContext *s *ps;int i, ret 0;AVDictio…...

如何配置一个sql server使得其它用户可以通过excel odbc获取数据
要让其他用户通过 Excel 使用 ODBC 连接到 SQL Server 获取数据,你需要完成以下配置步骤: ✅ 一、在 SQL Server 端配置(服务器设置) 1. 启用 TCP/IP 协议 打开 “SQL Server 配置管理器”。导航到:SQL Server 网络配…...
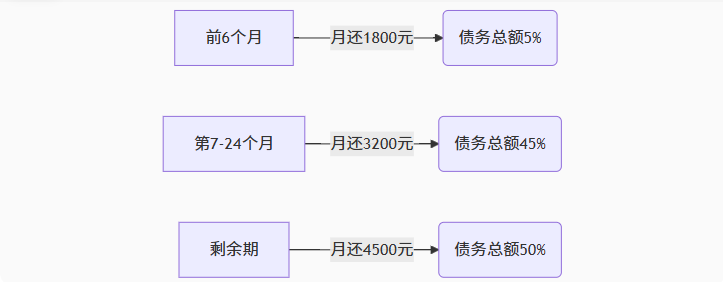
【无标题】湖北理元理律师事务所:债务优化中的生活保障与法律平衡之道
文/法律实务观察组 在债务重组领域,专业机构的核心价值不仅在于减轻债务数字,更在于帮助债务人在履行义务的同时维持基本生活尊严。湖北理元理律师事务所的服务实践表明,合法债务优化需同步实现三重平衡: 法律刚性(债…...
嵌入式学习之系统编程(九)OSI模型、TCP/IP模型、UDP协议网络相关编程(6.3)
目录 一、网络编程--OSI模型 二、网络编程--TCP/IP模型 三、网络接口 四、UDP网络相关编程及主要函数 编辑编辑 UDP的特征 socke函数 bind函数 recvfrom函数(接收函数) sendto函数(发送函数) 五、网络编程之 UDP 用…...
从物理机到云原生:全面解析计算虚拟化技术的演进与应用
前言:我的虚拟化技术探索之旅 我最早接触"虚拟机"的概念是从Java开始的——JVM(Java Virtual Machine)让"一次编写,到处运行"成为可能。这个软件层面的虚拟化让我着迷,但直到后来接触VMware和Doc…...
五子棋测试用例
一.项目背景 1.1 项目简介 传统棋类文化的推广 五子棋是一种古老的棋类游戏,有着深厚的文化底蕴。通过将五子棋制作成网页游戏,可以让更多的人了解和接触到这一传统棋类文化。无论是国内还是国外的玩家,都可以通过网页五子棋感受到东方棋类…...
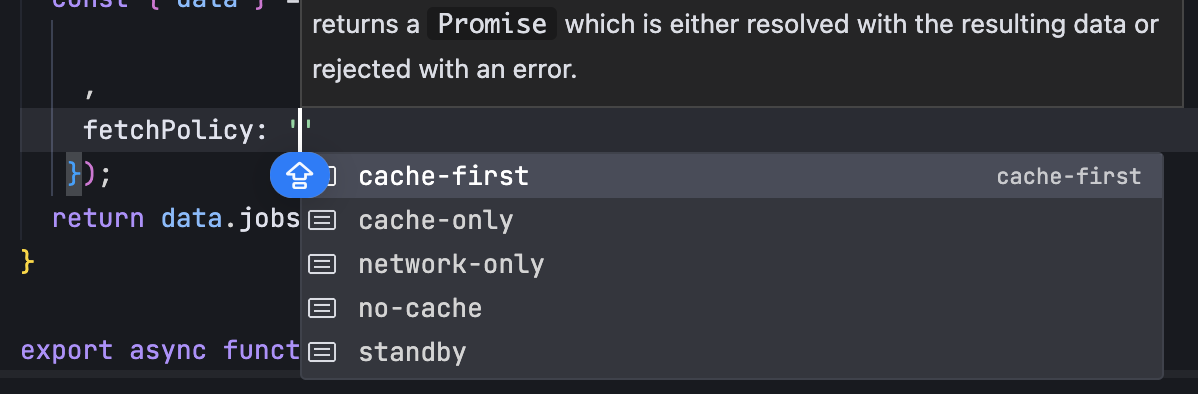
GraphQL 实战篇:Apollo Client 配置与缓存
GraphQL 实战篇:Apollo Client 配置与缓存 上一篇:GraphQL 入门篇:基础查询语法 依旧和上一篇的笔记一样,主实操,没啥过多的细节讲解,代码具体在: https://github.com/GoldenaArcher/graphql…...

微服务通信安全:深入解析mTLS的原理与实践
🔥「炎码工坊」技术弹药已装填! 点击关注 → 解锁工业级干货【工具实测|项目避坑|源码燃烧指南】 一、引言:微服务时代的通信安全挑战 随着云原生和微服务架构的普及,服务间的通信安全成为系统设计的核心议题。传统的单体架构中&…...
【Post-process】【VBA】ETABS VBA FrameObj.GetNameList and write to EXCEL
ETABS API实战:导出框架元素数据到Excel 在结构工程师的日常工作中,经常需要从ETABS模型中提取框架元素信息进行后续分析。手动复制粘贴不仅耗时,还容易出错。今天我们来用简单的VBA代码实现自动化导出。 🎯 我们要实现什么? 一键点击,就能将ETABS中所有框架元素的基…...

Python实现简单音频数据压缩与解压算法
Python实现简单音频数据压缩与解压算法 引言 在音频数据处理中,压缩算法是降低存储成本和传输效率的关键技术。Python作为一门灵活且功能强大的编程语言,提供了丰富的库和工具来实现音频数据的压缩与解压。本文将通过一个简单的音频数据压缩与解压算法…...

Axure 下拉框联动
实现选省、选完省之后选对应省份下的市区...
【UE5 C++】通过文件对话框获取选择文件的路径
目录 效果 步骤 源码 效果 步骤 1. 在“xxx.Build.cs”中添加需要使用的模块 ,这里主要使用“DesktopPlatform”模块 2. 添加后闭UE编辑器,右键点击 .uproject 文件,选择 "Generate Visual Studio project files",重…...

全面解析数据库:从基础概念到前沿应用
在数字化时代,数据已成为企业和社会发展的核心资产,而数据库作为存储、管理和处理数据的关键工具,在各个领域发挥着举足轻重的作用。从电商平台的商品信息管理,到社交网络的用户数据存储,再到金融行业的交易记录处理&a…...

热烈祝贺埃文科技正式加入可信数据空间发展联盟
2025年4月29日,在福州举办的第八届数字中国建设峰会“可信数据空间分论坛”上,可信数据空间发展联盟正式宣告成立。国家数据局党组书记、局长刘烈宏出席并致辞,强调该联盟是推进全国一体化数据市场建设的关键抓手。 郑州埃文科技有限公司&am…...
rknn toolkit2搭建和推理
安装Miniconda Miniconda - Anaconda Miniconda 选择一个 新的 版本 ,不用和RKNN的python版本保持一致 使用 ./xxx.sh进行安装 下面配置一下载源 # 清华大学源(最常用) conda config --add channels https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn…...
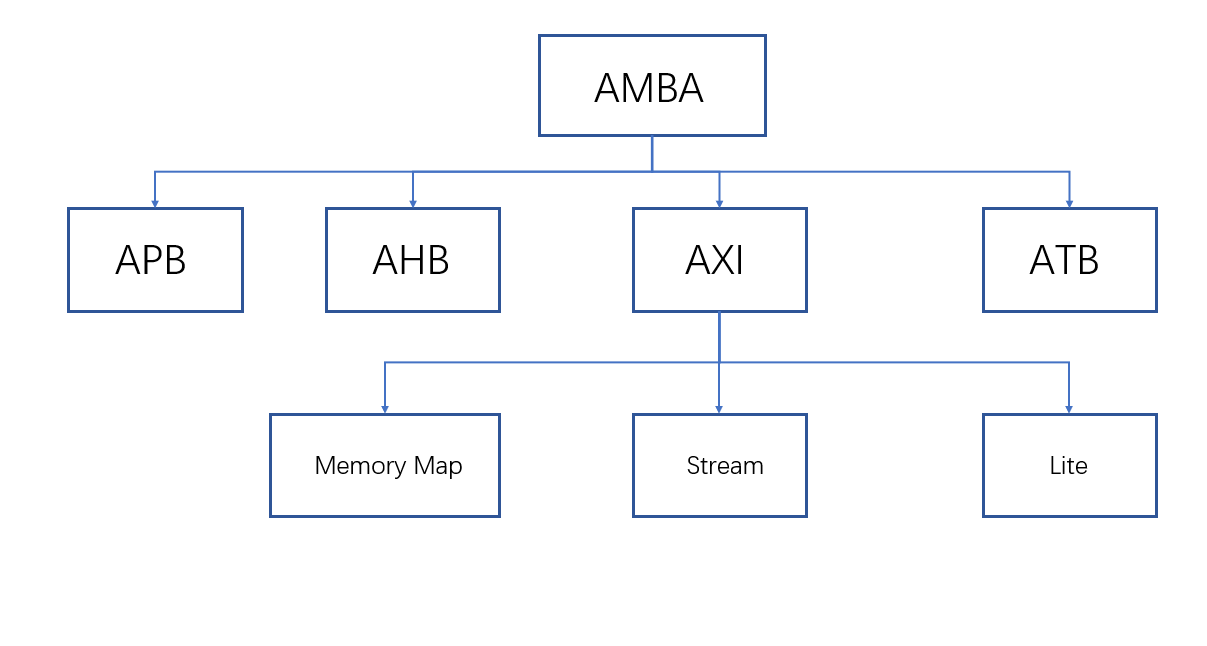
ZYNQ学习记录FPGA(一)ZYNQ简介
一、知识准备 1.一些术语,缩写和概念: 1)ZYNQ全称:ZYNQ7000 All Pgrammable SoC 2)SoC:system on chips(片上系统),对比集成电路的SoB(system on board) 3)ARM:处理器…...

ubuntu22.04 安装docker 和docker-compose
首先你要确保没有docker环境或者使用命令删掉docker sudo apt-get remove docker docker-engine docker.io containerd runc安装docker 更新软件环境 sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade下载docker依赖和GPG 密钥 # 依赖 apt-get install ca-certificates curl gnupg lsb-rel…...

DiscuzX3.5发帖json api
参考文章:PHP实现独立Discuz站外发帖(直连操作数据库)_discuz 发帖api-CSDN博客 简单改造了一下,适配我自己的需求 有一个站点存在多个采集站,我想通过主站拿标题,采集站拿内容 使用到的sql如下 CREATE TABLE pre_forum_post_…...
