【0803作业】创建两个线程:其中一个线程拷贝图片的前半部分,另一个线程拷贝后半部分(4种方法)
方法一:使用pthread_create、pthread_exit、pthread_join函数【两个线程不共用同一份资源】
先在主函数创建并清空拷贝的目标文件,再创建两个线程,在两个线程内部同时打开要读取的文件以及要拷贝的目标文件(两个线程不共用同一份资源)。
使用到的函数:
- 标准IO函数(fprintf)【用于打印错误信息】
- 文件IO函数(open、close、lseek)
- 有关线程的函数(pthread_create、pthread_exit、pthread_join)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <head.h>
//线程的执行体
void* callback_1(void* arg) //void* arg = (void*)&c
{umask(0);int fp_r=open("./1.png",O_RDONLY); if(fp_r < 0){ERR_MSG("open");}int fp_w=open("./copy.png",O_WRONLY);if(fp_w <0){ERR_MSG("open");}char c = 0;off_t len=lseek(fp_r,0,SEEK_END);int i=0;lseek(fp_r,0,SEEK_SET);lseek(fp_w,0,SEEK_SET);for(i=0;i<len/2;i++){bzero(&c,sizeof(c));read(fp_r,&c,1);write(fp_w,&c,1);}close(fp_r);close(fp_w);printf("前半部分拷贝完毕\n");pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void* callback_2(void* arg)
{umask(0);int fp_r=open("./1.png",O_RDONLY);if(fp_r < 0){ERR_MSG("open");}int fp_w=open("./copy.png",O_WRONLY);if(fp_w < 0){ERR_MSG("open");}char c = 0;off_t len=lseek(fp_r,0,SEEK_END);int i=0;lseek(fp_r,len/2,SEEK_SET);lseek(fp_w,len/2,SEEK_SET);for(i=0;i<len/2;i++){bzero(&c,sizeof(c));read(fp_r,&c,sizeof(c));write(fp_w,&c,sizeof(c));}close(fp_r);close(fp_w);printf("后半部分拷贝完毕\n");pthread_exit(NULL);}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{//两个线程在拷贝前,确保文件w存在,且是清空状态int fp_w=open("./copy.png",O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC,0664);if(fp_w <0){ERR_MSG("open");}close(fp_w);pthread_t tid_1,tid_2;if(pthread_create(&tid_1,NULL,callback_1,NULL) != 0){fprintf(stderr, "pthread_create failed __%d__\n",__LINE__);return -1;}pthread_join(tid_1,NULL);if(pthread_create(&tid_2,NULL,callback_2,NULL)!=0){fprintf(stderr, "pthread_create failed __%d__\n",__LINE__);return -1;}pthread_join(tid_2,NULL);printf("主线程准备退出... ...\n");return 0;
}
方法二:使用结构体【两个线程共享同一份资源】
创建一个结构体用于存放需要打开的两个文件文件标识符、需要拷贝的字节大小。
在主函数中打开两个文件,计算好需要拷贝的字节大小,再创建两个线程,将结构体fileinfo的地址传递到线程中(强转成(void*)类型再传,否则报错),线程中用指针void* arg接fileinfo的地址。线程中需要将指针arg的地址转为struct Msg类型。
PS:两个线程共享同一份资源,使用pthread_exit函数使线程1先完成拷贝(与sleep达到的效果一致)。
使用到的函数:
- 结构体struct
- 标准IO函数(fprintf)【用于打印错误信息】
- 文件IO函数(open、close、lseek)
- 有关线程的函数(pthread_create、pthread_exit、pthread_join)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <head.h>
struct Msg
{int fp_r;int fp_w;off_t size;
};
//线程1的执行体:拷贝前半部分
void* callback_1(void* arg) //void* arg = &fileinfo
{struct Msg *tp=(struct Msg*)arg;int fp_r=tp->fp_r;int fp_w=tp->fp_w;off_t size=tp->size;//将光标偏移到开头,拷贝size/2个字节到目标文件中lseek(fp_r,0,SEEK_SET);lseek(fp_w,0,SEEK_SET);char c = 0;for(int i=0;i<size/2;i++){bzero(&c,sizeof(c));read(fp_r,&c,1);write(fp_w,&c,1);}printf("前半部分拷贝完毕\n");pthread_exit(NULL);//退出分支线程
}
//线程2的执行体
void* callback_2(void* arg) //void* arg = &fileinfo
{//sleep(5);//主动放弃cpu资源,让线程1先执行struct Msg *tp=(struct Msg*)arg;int fp_r=tp->fp_r;int fp_w=tp->fp_w;off_t size=tp->size;//将光标偏移到size/2的位置,拷贝size/2个字节到目标文件中lseek(fp_r,size/2,SEEK_SET);lseek(fp_w,size/2,SEEK_SET);char c = 0;for(int i=0;i<size/2;i++){bzero(&c,sizeof(c));read(fp_r,&c,sizeof(c));write(fp_w,&c,sizeof(c));}printf("后半部分拷贝完毕\n");pthread_exit(NULL);//退出分支线程
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{struct Msg fileinfo;//以读的方式打开1.pngfileinfo.fp_r=open("./1.png",O_RDONLY);if(fileinfo.fp_r < 0){ERR_MSG("open");return -1;}//以写的方式打开并创建(若存在则清空)copy.pngfileinfo.fp_w=open("./copy.png",O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC,0664);if(fileinfo.fp_w <0){ERR_MSG("open");return -1;}//计算需要拷贝的字节大小fileinfo.size=lseek(fileinfo.fp_r,0,SEEK_END);//创建2个线程pthread_t tid_1,tid_2;if(pthread_create(&tid_1,NULL,callback_1,(void *)&fileinfo) != 0){fprintf(stderr, "pthread_create failed __%d__\n",__LINE__);return -1;}pthread_join(tid_1,NULL);//阻塞等待线程1完成if(pthread_create(&tid_2,NULL,callback_2,(void *)&fileinfo) !=0){fprintf(stderr, "pthread_create failed __%d__\n",__LINE__);return -1;}pthread_join(tid_2,NULL);//阻塞等待线程2完成//关闭文件close(fileinfo.fp_r);close(fileinfo.fp_w);printf("主线程准备退出\n");return 0;
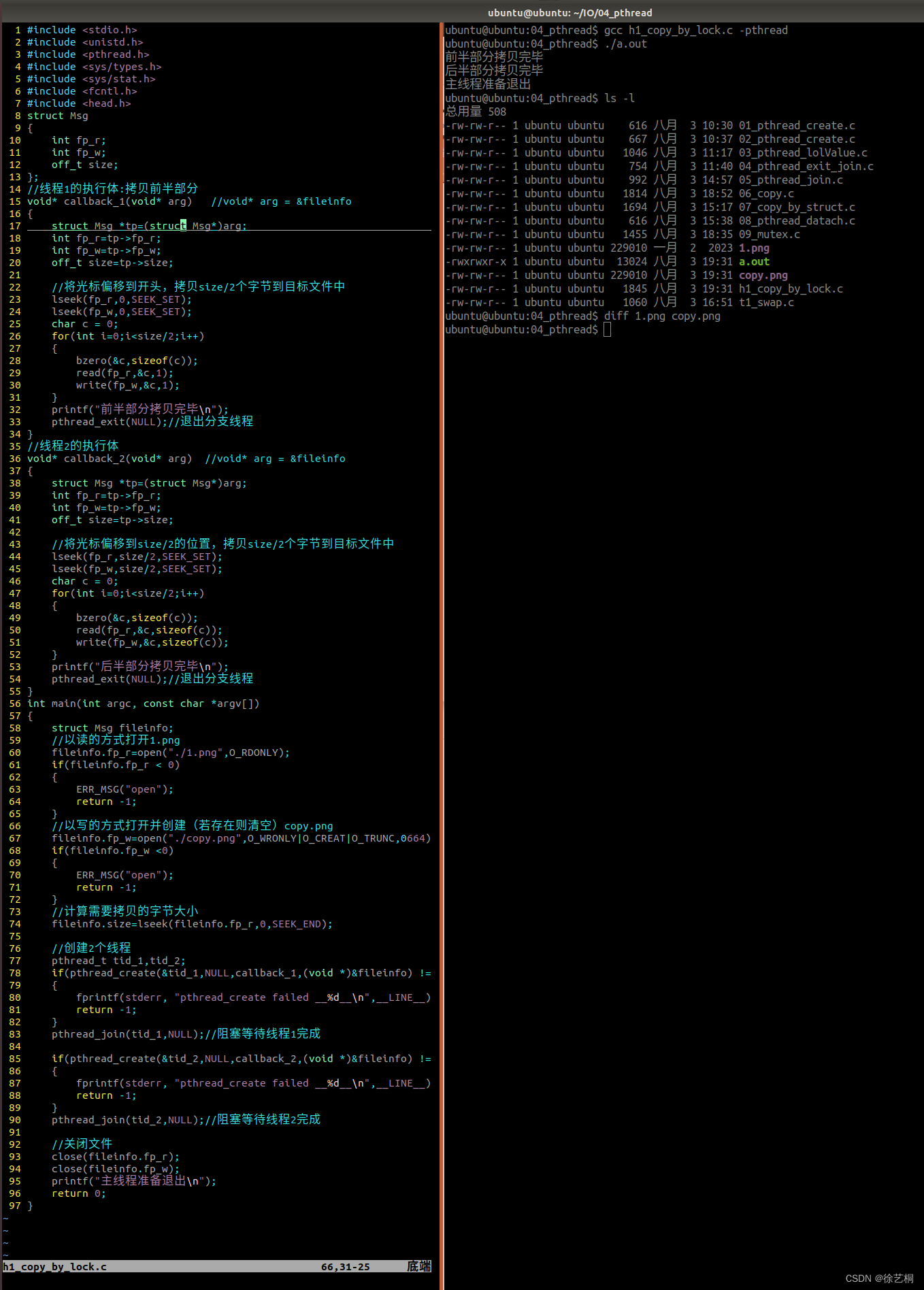
}
方法三:互斥锁【两个线程共享同一份资源】
创建一个结构体用于存放需要打开的两个文件文件标识符、需要拷贝的字节大小;将互斥锁初始化。
达到的效果:
- 拷贝完前半部分或后半部分解锁
PS:两个线程共享同一份资源,利用互斥锁完成任务。
使用到的函数:
- 结构体struct
- 标准IO函数(fprintf)【用于打印错误信息】
- 文件IO函数(open、close、lseek)
- 有关线程的函数(pthread_create、pthread_exit、pthread_join)
- 互斥锁(创建互斥锁pthread_mutex_init、上锁pthread_mutex_lock、解锁pthread_mutex_unlock、销毁互斥锁pthread_mutex_destroy)
修改后:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <head.h>pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
//临界资源
struct Msg
{int fp_r;int fp_w;off_t size;pthread_mutex_t mutex;//互斥锁
};
//线程1的执行体:拷贝前半部分
void* callback_1(void* arg) //void* arg = &fileinfo
{struct Msg *fileinfo=(struct Msg*)arg;int fp_r=fileinfo->fp_r;int fp_w=fileinfo->fp_w;off_t size=fileinfo->size;char c = 0;/************************临界区***************************///上锁pthread_mutex_lock(&fileinfo->mutex);//将光标偏移到开头,拷贝size/2个字节到目标文件中lseek(fp_r,0,SEEK_SET);lseek(fp_w,0,SEEK_SET);for(int i=0;i<size/2;i++){//bzero(&c,sizeof(c));read(fp_r,&c,1);write(fp_w,&c,1);}printf("前半部分拷贝完毕\n");//解锁pthread_mutex_unlock(&fileinfo->mutex);/************************临界区***************************/pthread_exit(NULL);//退出分支线程
}
//线程2的执行体
void* callback_2(void* arg) //void* arg = &fileinfo
{struct Msg *fileinfo=(struct Msg*)arg;int fp_r=fileinfo->fp_r;int fp_w=fileinfo->fp_w;off_t size=fileinfo->size;char c = 0;/************************临界区***************************///上锁pthread_mutex_lock(&fileinfo->mutex);//将光标偏移到size/2的位置,拷贝size/2个字节到目标文件中lseek(fp_r,size/2,SEEK_SET);lseek(fp_w,size/2,SEEK_SET);for(int i=0;i<size/2;i++){//bzero(&c,sizeof(c));read(fp_r,&c,1);write(fp_w,&c,1);}printf("后半部分拷贝完毕\n");//解锁pthread_mutex_unlock(&fileinfo->mutex);/************************临界区***************************/pthread_exit(NULL);//退出分支线程
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{struct Msg fileinfo;//以读的方式打开1.pngfileinfo.fp_r=open("./1.png",O_RDONLY);if(fileinfo.fp_r < 0){ERR_MSG("open");return -1;}//以写的方式打开并创建(若存在则清空)copy.pngfileinfo.fp_w=open("./copy.png",O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC,0664);if(fileinfo.fp_w <0){ERR_MSG("open");return -1;}//计算需要拷贝的字节大小fileinfo.size=lseek(fileinfo.fp_r,0,SEEK_END);//申请一个互斥锁pthread_mutex_init(&fileinfo.mutex,NULL);//创建2个线程pthread_t tid_1,tid_2;if(pthread_create(&tid_1,NULL,callback_1,(void *)&fileinfo) != 0){fprintf(stderr, "pthread_create failed __%d__\n",__LINE__);return -1;}//pthread_detach(tid_1); //分离线程1if(pthread_create(&tid_2,NULL,callback_2,(void *)&fileinfo) !=0){fprintf(stderr, "pthread_create failed __%d__\n",__LINE__);return -1;}pthread_join(tid_1,NULL);//阻塞等待线程1完成pthread_join(tid_2,NULL);//阻塞等待线程2完成//销毁互斥锁pthread_mutex_destroy(&fileinfo.mutex);//关闭文件close(fileinfo.fp_r);close(fileinfo.fp_w);printf("主线程准备退出\n");return 0;
}
错误:将线程1分离
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <head.h>
//临界资源
struct Msg
{int fp_r;int fp_w;off_t size;pthread_mutex_t mutex;//互斥锁
};
//线程1的执行体:拷贝前半部分
void* callback_1(void* arg) //void* arg = &fileinfo
{struct Msg *fileinfo=(struct Msg*)arg;/************************临界区***************************///上锁pthread_mutex_lock(&fileinfo->mutex);int fp_r=fileinfo->fp_r;int fp_w=fileinfo->fp_w;off_t size=fileinfo->size;//将光标偏移到开头,拷贝size/2个字节到目标文件中lseek(fp_r,0,SEEK_SET);lseek(fp_w,0,SEEK_SET);char c = 0;for(int i=0;i<size/2;i++){bzero(&c,sizeof(c));read(fp_r,&c,1);write(fp_w,&c,1);}printf("前半部分拷贝完毕\n");//解锁pthread_mutex_unlock(&fileinfo->mutex);/************************临界区***************************/pthread_exit(NULL);//退出分支线程
}
//线程2的执行体
void* callback_2(void* arg) //void* arg = &fileinfo
{struct Msg *fileinfo=(struct Msg*)arg;/************************临界区***************************///上锁pthread_mutex_lock(&fileinfo->mutex);int fp_r=fileinfo->fp_r;int fp_w=fileinfo->fp_w;off_t size=fileinfo->size;//将光标偏移到size/2的位置,拷贝size/2个字节到目标文件中lseek(fp_r,size/2,SEEK_SET);lseek(fp_w,size/2,SEEK_SET);char c = 0;for(int i=0;i<size/2;i++){bzero(&c,sizeof(c));read(fp_r,&c,sizeof(c));write(fp_w,&c,sizeof(c));}printf("后半部分拷贝完毕\n");//解锁pthread_mutex_unlock(&fileinfo->mutex);/************************临界区***************************/pthread_exit(NULL);//退出分支线程
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{struct Msg fileinfo;//以读的方式打开1.pngfileinfo.fp_r=open("./1.png",O_RDONLY);if(fileinfo.fp_r < 0){ERR_MSG("open");return -1;}//以写的方式打开并创建(若存在则清空)copy.pngfileinfo.fp_w=open("./copy.png",O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC,0664);if(fileinfo.fp_w <0){ERR_MSG("open");return -1;}//计算需要拷贝的字节大小fileinfo.size=lseek(fileinfo.fp_r,0,SEEK_END);//申请一个互斥锁pthread_mutex_init(&fileinfo.mutex,NULL);//创建2个线程pthread_t tid_1,tid_2;if(pthread_create(&tid_1,NULL,callback_1,(void *)&fileinfo) != 0){fprintf(stderr, "pthread_create failed __%d__\n",__LINE__);return -1;}pthread_detach(tid_1); //分离线程1if(pthread_create(&tid_2,NULL,callback_2,(void *)&fileinfo) !=0){fprintf(stderr, "pthread_create failed __%d__\n",__LINE__);return -1;}pthread_join(tid_2,NULL);//阻塞等待线程2完成//关闭文件close(fileinfo.fp_r);close(fileinfo.fp_w);printf("主线程准备退出\n");//销毁互斥锁pthread_mutex_destroy(&fileinfo.mutex);return 0;
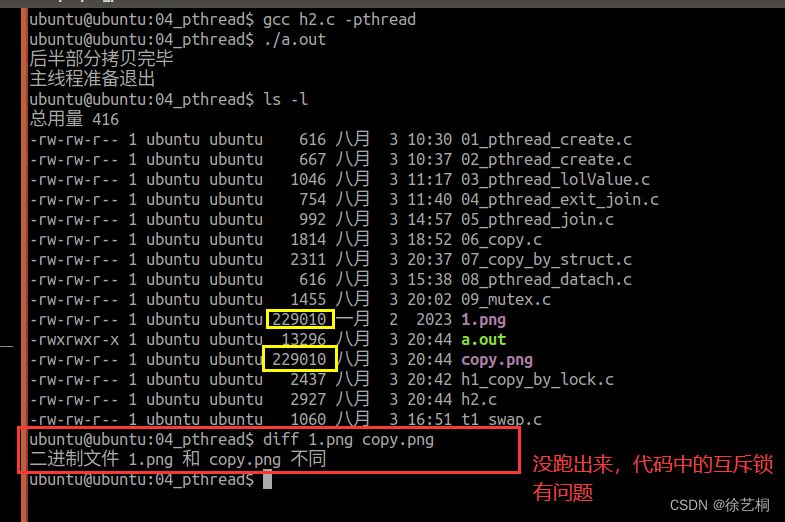
}
方法四:互斥锁【两个线程共享同一份资源】
创建一个结构体用于存放需要打开的两个文件文件标识符、需要拷贝的字节大小;将互斥锁初始化。
达到的效果:
- 记录拷贝的位置,给偏移量和offset上锁。记录完fooset的数据后解锁
- 可两个线程切换拷贝
PS:两个线程共享同一份资源,利用互斥锁完成任务。
使用到的函数:
- 结构体struct
- 标准IO函数(fprintf)【用于打印错误信息】
- 文件IO函数(open、close、lseek)
- 有关线程的函数(pthread_create、pthread_exit、pthread_join)
- 互斥锁(创建互斥锁pthread_mutex_init、上锁pthread_mutex_lock、解锁pthread_mutex_unlock、销毁互斥锁pthread_mutex_destroy)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <head.h>pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
//临界资源
struct Msg
{int fp_r;int fp_w;off_t size;pthread_mutex_t mutex;//互斥锁
};
//线程1的执行体:拷贝前半部分
void* callback_1(void* arg) //void* arg = &fileinfo
{struct Msg *fileinfo=(struct Msg*)arg;int fp_r=fileinfo->fp_r;int fp_w=fileinfo->fp_w;off_t size=fileinfo->size;char c = 0;off_t offset=0;for(int i=0;i<size/2;i++){/******************临界区*******************///上锁pthread_mutex_lock(&fileinfo->mutex);//将光标偏移到开头,拷贝size/2个字节到目标文件中lseek(fp_r,offset,SEEK_SET);lseek(fp_w,offset,SEEK_SET);read(fp_r,&c,1);write(fp_w,&c,1);offset=lseek(fp_r,0,SEEK_CUR);//解锁pthread_mutex_unlock(&fileinfo->mutex);/****** ************临界区*******************/}printf("前半部分拷贝完毕\n");pthread_exit(NULL);//退出分支线程
}
//线程2的执行体
void* callback_2(void* arg) //void* arg = &fileinfo
{struct Msg *fileinfo=(struct Msg*)arg;int fp_r=fileinfo->fp_r;int fp_w=fileinfo->fp_w;off_t size=fileinfo->size;char c = 0;off_t offset=size/2;for(int i=0;i<size/2;i++){/*******************临界区*******************///上锁pthread_mutex_lock(&fileinfo->mutex);//将光标偏移到size/2的位置,拷贝size/2个字节到目标文件中lseek(fp_r,offset,SEEK_SET);lseek(fp_w,offset,SEEK_SET);read(fp_r,&c,1);write(fp_w,&c,1);offset=lseek(fp_r,0,SEEK_CUR);//解锁pthread_mutex_unlock(&fileinfo->mutex); /******************临界区*********************/}printf("后半部分拷贝完毕\n");pthread_exit(NULL);//退出分支线程
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{struct Msg fileinfo;//以读的方式打开1.pngfileinfo.fp_r=open("./1.png",O_RDONLY);if(fileinfo.fp_r < 0){ERR_MSG("open");return -1;}//以写的方式打开并创建(若存在则清空)copy.pngfileinfo.fp_w=open("./copy.png",O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC,0664);if(fileinfo.fp_w <0){ERR_MSG("open");return -1;}//计算需要拷贝的字节大小fileinfo.size=lseek(fileinfo.fp_r,0,SEEK_END);//申请一个互斥锁pthread_mutex_init(&fileinfo.mutex,NULL);//创建2个线程pthread_t tid_1,tid_2;if(pthread_create(&tid_1,NULL,callback_1,(void *)&fileinfo) != 0){fprintf(stderr, "pthread_create failed __%d__\n",__LINE__);return -1;}if(pthread_create(&tid_2,NULL,callback_2,(void *)&fileinfo) !=0){fprintf(stderr, "pthread_create failed __%d__\n",__LINE__);return -1;}pthread_join(tid_1,NULL);//阻塞等待线程2完成pthread_join(tid_2,NULL);//阻塞等待线程2完成//销毁互斥锁pthread_mutex_destroy(&fileinfo.mutex);//关闭文件close(fileinfo.fp_r);close(fileinfo.fp_w);printf("主线程准备退出\n");return 0;
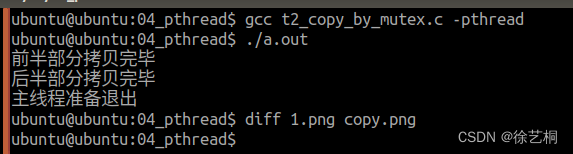
} 
相关文章:

【0803作业】创建两个线程:其中一个线程拷贝图片的前半部分,另一个线程拷贝后半部分(4种方法)
方法一:使用pthread_create、pthread_exit、pthread_join函数【两个线程不共用同一份资源】 先在主函数创建并清空拷贝的目标文件,再创建两个线程,在两个线程内部同时打开要读取的文件以及要拷贝的目标文件(两个线程不共用同一份资…...

php运算符的短路特性
php运算符的短路特性 1、逻辑运算符:逻辑与(&&)和逻辑或(||),存在着短路特性 PHP中有以下两个运算符具有短路的特性,他们是逻辑运算符的逻辑与(&&)和逻辑或(||&am…...
C语言假期作业 DAY 13
一、选择题 1、如果 x2014 ,下面函数的返回值是( ) int fun(unsigned int x) { int n 0; while(x 1) { n; x x | (x 1); } return n; } A: 20 B: 21 C: 23 D 25 答案解析 正确答案:C 这个作用是对整型中0的个数进行统计&…...
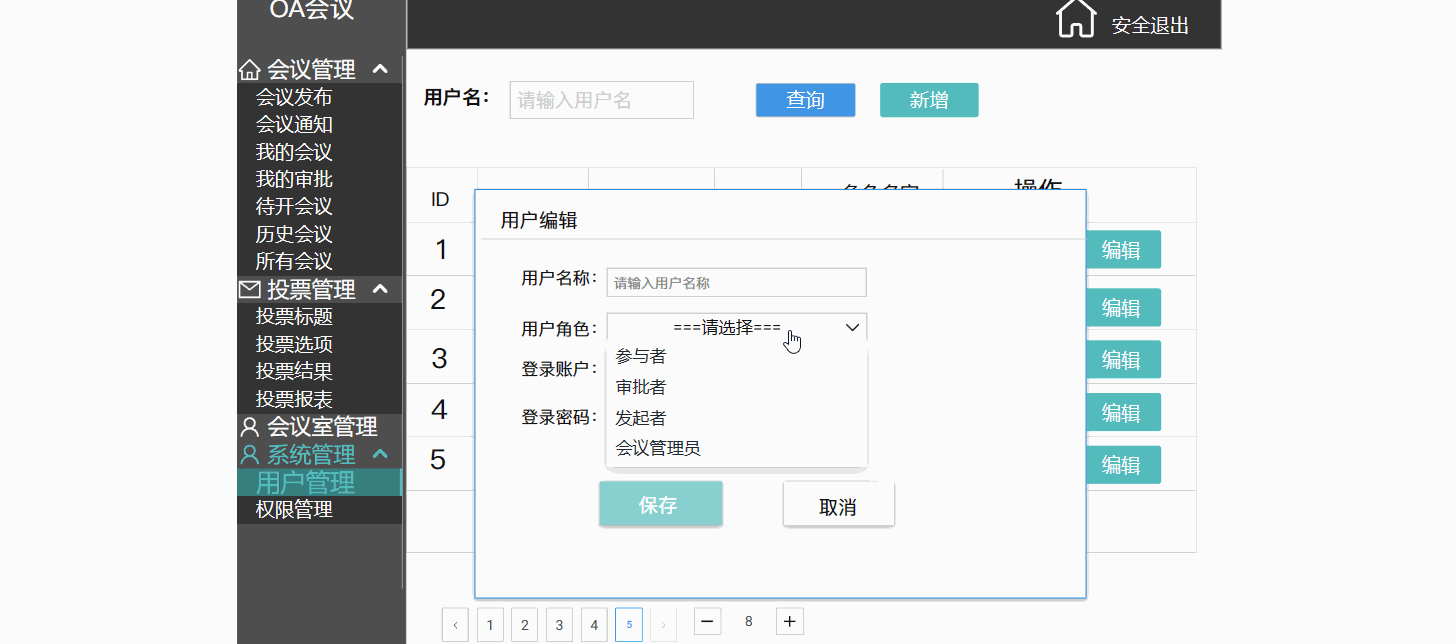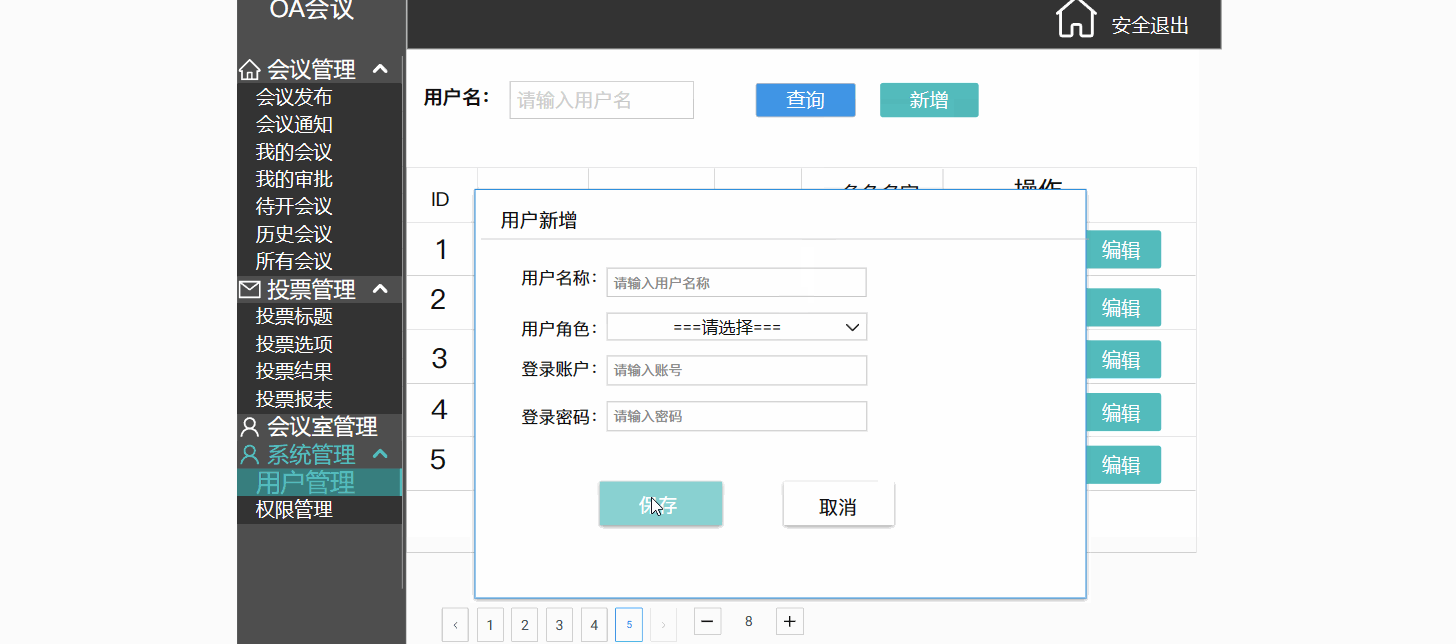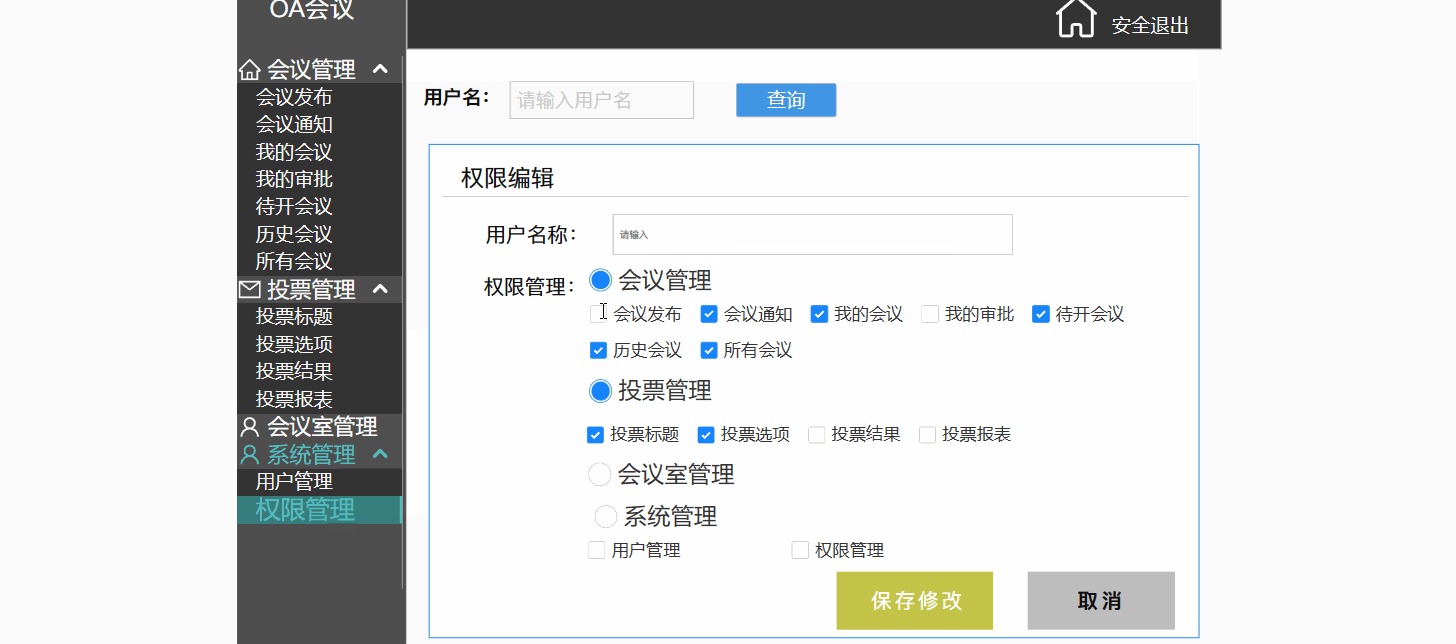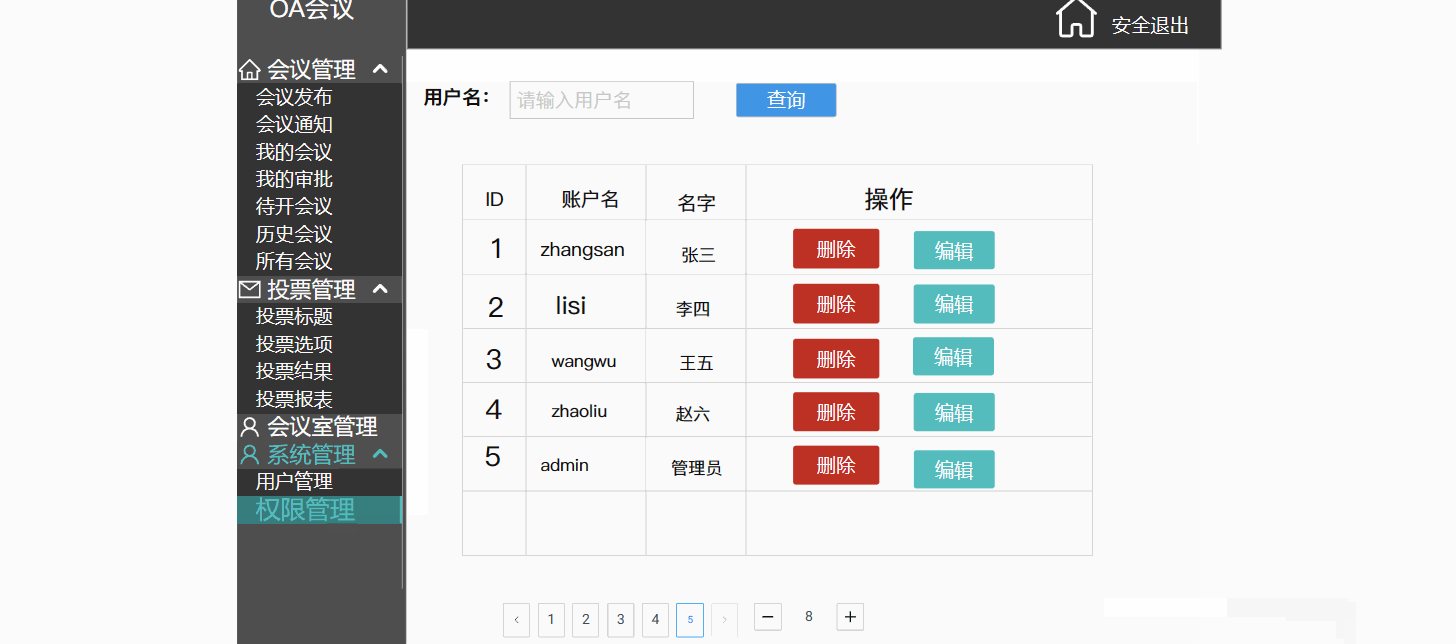
以产品经理的角度去讲解原型图---会议OA项目
目录 一.前言 二.原型图 2.1 原型图是什么 3.1 原型图的作用 三.演示讲解 3.1 项目背景 3.2 项目介绍 3.2.1 会议管理(会议的发起,通知) 3.2.2 投票管理(会议的流程重大决策记录) 3.2.3 会议室管理 3.2.4 系统管…...

C++ 外部变量和外部函数
1.外部变量 如果一个变量除了在定义它的源文件中可以使用外,还能被其他文件使用,那么就称这个变量为外部变量。命名空间作用域中定义的变量,默认情况下都是外部变量,但在其他文件中如果需要使用这一变量,需要用extern…...
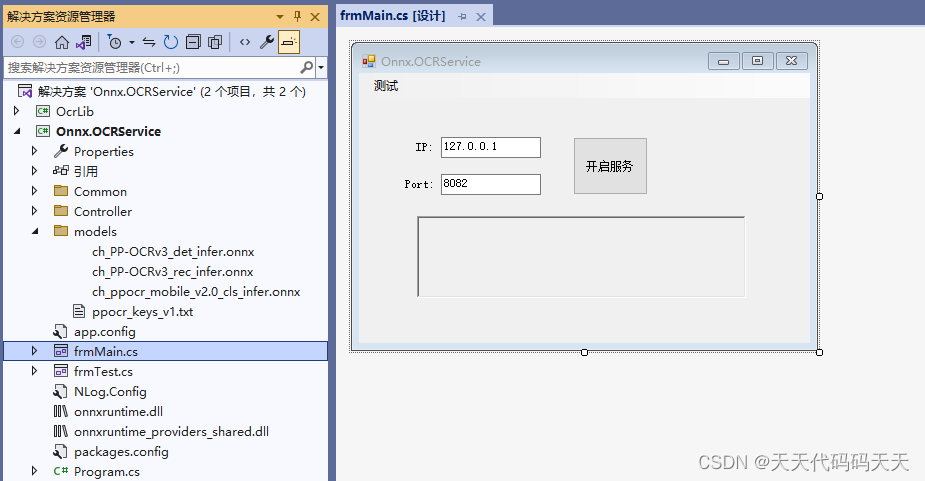
C# Onnx Paddle模型 OCR识别服务
效果 项目 可运行程序exe下载 Demo(完整源码)下载...
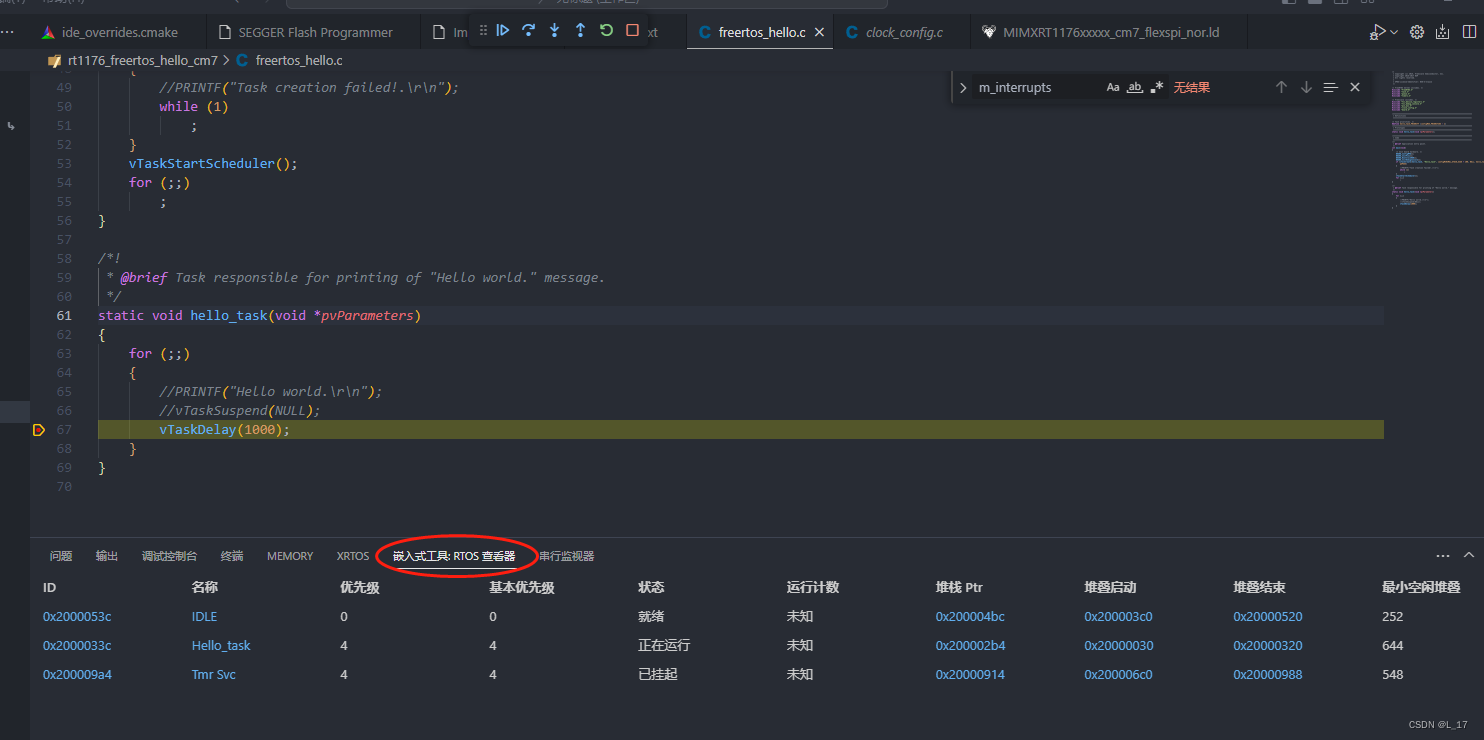
MCUXpresso for VS Code -- 基于VSCode开发RT1176
MCUXpresso for VS Code 是nxp推出插件,旗下MCX LPC, Kinetis和i.MX rt等MCU,都能在VS Code平台进行嵌入式开发。功能框图如下: 前期准备: 软件环境: windows(实际可以跨系统,linux和mac没有测试) VS Code ninja CMa…...

MySQL的使用——【初识MySQL】第二节
MySQL的使用——【初识MySQL】第二节 文章目录 MySQL环境变量的配置(如使用Navicat可忽略)使用命令行连接MySQL(如使用Navicat可忽略)步骤注意 NavicatNavicat的下载Navicat的使用连接MySQL新建表 总结总结 MySQL环境变量的配置&a…...

MySQL最终弹-并发(脏读,不可重复读,幻读及区别),JDBC的使用和安装,最全万字
一、💛并发基本概念 并发的基本意思: 什么是并发呢?简单的理解就是同一时间执行 服务器同一时刻,给多个客户端提供服务~~,这两个客户端都可以给服务器提交事务。 如果提交两个事务,改…...
⌈C++⌋从无到有了解并掌握C++面向对象三大特性——封装、继承、多态
前置知识:类和对象 参考书籍:《C Primer 第五版》 目录 什么是面向过程?什么是面向对象? 一、封装 1、封装的含义以及如何实现封装 1.1 访问限定符(访问说明符) 1.2 什么是封装? 2、封装的优点…...

Element的el-select下拉框多选添加全选功能
先看效果图 全选: 没有选中时: 选中部分: 作者项目使用的是vue3写法,如果是vue2的自己转换一下 html代码: js代码: 拓展 另一种方法,如果不想使用勾选框,可以试试下面的方…...
python调用pytorch的clip模型时报错
使用python调用pytorch中的clip模型时报错:AttributeError: partially initialized module ‘clip’ has no attribute ‘load’ (most likely due to a circular import) 目录 现象解决方案一、查看项目中是否有为clip名的文件二、查看clip是否安装成功 现象 clip…...

MySQL 数据库 binLog 日志的使用
一、概念与作用 binlog(二进制日志)是MySQL数据库中的一种日志类型。它记录了数据库中的所有更改操作,例如插入、更新、删除操作。binlog以二进制形式存储,因此可以更高效地进行读取和解析。 binlog通常用于以下几个方面&#x…...
Apache Storm入门介绍之三分钟看懂Apache Storm
文章目录 0.前言1. 什么是 Apache Storm?1.1. Nimbus1.2. Zookeeper1.3. Supervisor1.4. Worker1.5 集群模式下各组件职责 2. 核心概念2.1基本架构和任务模型2.2 工作流程 3. 源码地址3.1. 代码结构3.1. 核心模块介绍 4. Storm入门实例0.创建java工程并引入依赖1. 创…...

RF手机天线仿真介绍(三):调谐开关分析
目录 简介调谐开关RON、COFF的影响分析不同位置的调谐器件coff影响分析不同位置的调谐器件Ron影响分析Coff引起谐振的解决示例 调谐开关VPEAK分析调谐开关Vpeak示例 简介 孔径调谐能调节天线的电长度,可将其谐振点切换到所需支持的工作频段。天线孔径调谐器通过改变…...
Ubuntu20.04 + QT5.14.2 + VTK8.2.0 + PCL 1.10 环境配置
目录 Ubuntu20.04 QT5.14.2 VTK8.2.0 PCL 1.10 环境配置一、VTK 编译和安装1、库依赖:2、下载资源:[下载VTK8.2.0](https://www.vtk.org/files/release/8.2/VTK-8.2.0.tar.gz)3、编译:4、安装5、qtcreator 配置编译的libQVTKWidgetPlugin.…...

GPT Prompt编写的艺术:如何提高AI模型的表现力
随着AI技术的迅速发展,人工智能模型变得越来越强大,能够协助我们完成各种任务。然而,如何更好地利用AI的能力仍然存在很大的探索空间。在与AI进行交互的过程中,我们主要依赖于Prompt,不管是直接与大模型交互࿰…...
Ubuntu18.04 安装opencv 4.8.0教程(亲测可用)
1. 安装准备 安装前需要下载一些必须的依赖项。 不同版本opencv依赖会有不同,具体见官网opencv安装 sudo apt-get install build-essential sudo apt-get install cmake git libgtk2.0-dev pkg-config libavcodec-dev libavformat-dev libswscale-dev sudo apt-…...
【腾讯云Cloud Studio实战训练营】React 快速构建点餐页面
前言: Cloud Studio是一个在线的云集成开发环境(IDE),可以让开发人员在浏览器中轻松地开发、测试、调试和部署应用程序。它提供了基于云的计算资源和工具,例如代码编辑器、编译器、调试器、版本控制系统和项目管理工具…...

自监督去噪:Noise2Self原理分析及实现 (Pytorch)
文章地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.11365 代码地址: https://github.com/czbiohub-sf/noise2self 要点 Noise2Self方法不需要信号先验信息、噪声估计信息和干净的训练数据。唯一的假设就是噪声在测量的不同维度上表现出的统计独立性,而真实信号表现出一定的…...
)
uniapp 对接腾讯云IM群组成员管理(增删改查)
UniApp 实战:腾讯云IM群组成员管理(增删改查) 一、前言 在社交类App开发中,群组成员管理是核心功能之一。本文将基于UniApp框架,结合腾讯云IM SDK,详细讲解如何实现群组成员的增删改查全流程。 权限校验…...

DeepSeek 赋能智慧能源:微电网优化调度的智能革新路径
目录 一、智慧能源微电网优化调度概述1.1 智慧能源微电网概念1.2 优化调度的重要性1.3 目前面临的挑战 二、DeepSeek 技术探秘2.1 DeepSeek 技术原理2.2 DeepSeek 独特优势2.3 DeepSeek 在 AI 领域地位 三、DeepSeek 在微电网优化调度中的应用剖析3.1 数据处理与分析3.2 预测与…...
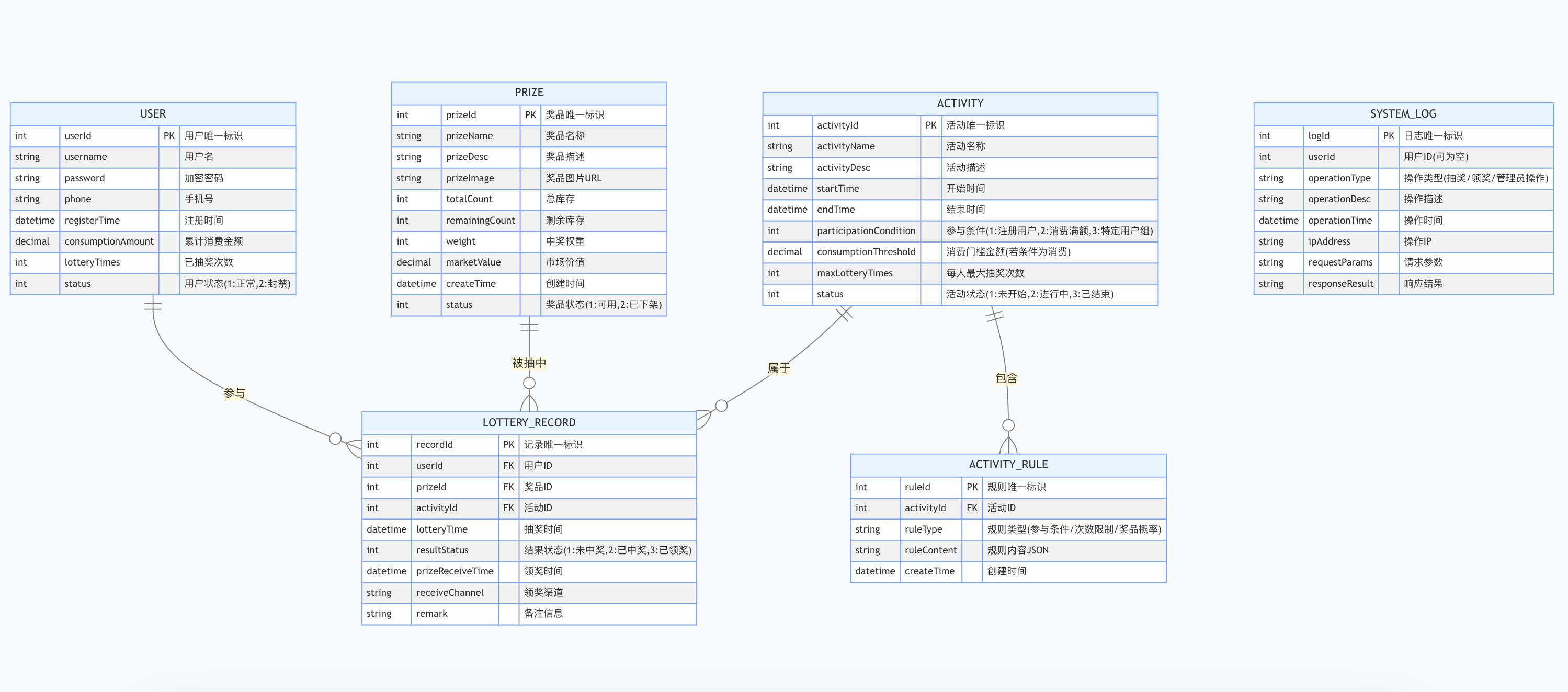
简易版抽奖活动的设计技术方案
1.前言 本技术方案旨在设计一套完整且可靠的抽奖活动逻辑,确保抽奖活动能够公平、公正、公开地进行,同时满足高并发访问、数据安全存储与高效处理等需求,为用户提供流畅的抽奖体验,助力业务顺利开展。本方案将涵盖抽奖活动的整体架构设计、核心流程逻辑、关键功能实现以及…...
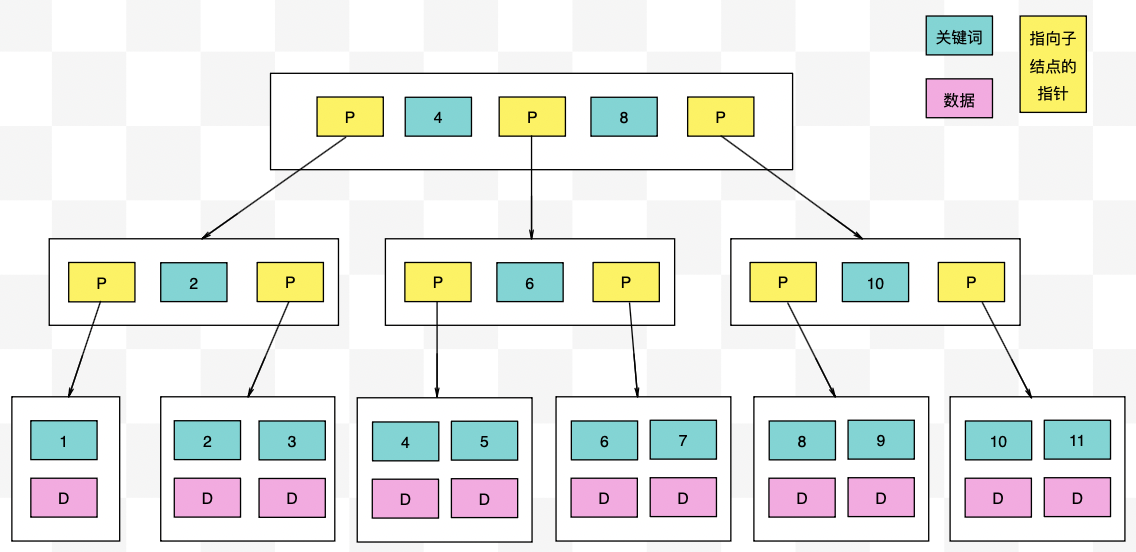
【力扣数据库知识手册笔记】索引
索引 索引的优缺点 优点1. 通过创建唯一性索引,可以保证数据库表中每一行数据的唯一性。2. 可以加快数据的检索速度(创建索引的主要原因)。3. 可以加速表和表之间的连接,实现数据的参考完整性。4. 可以在查询过程中,…...
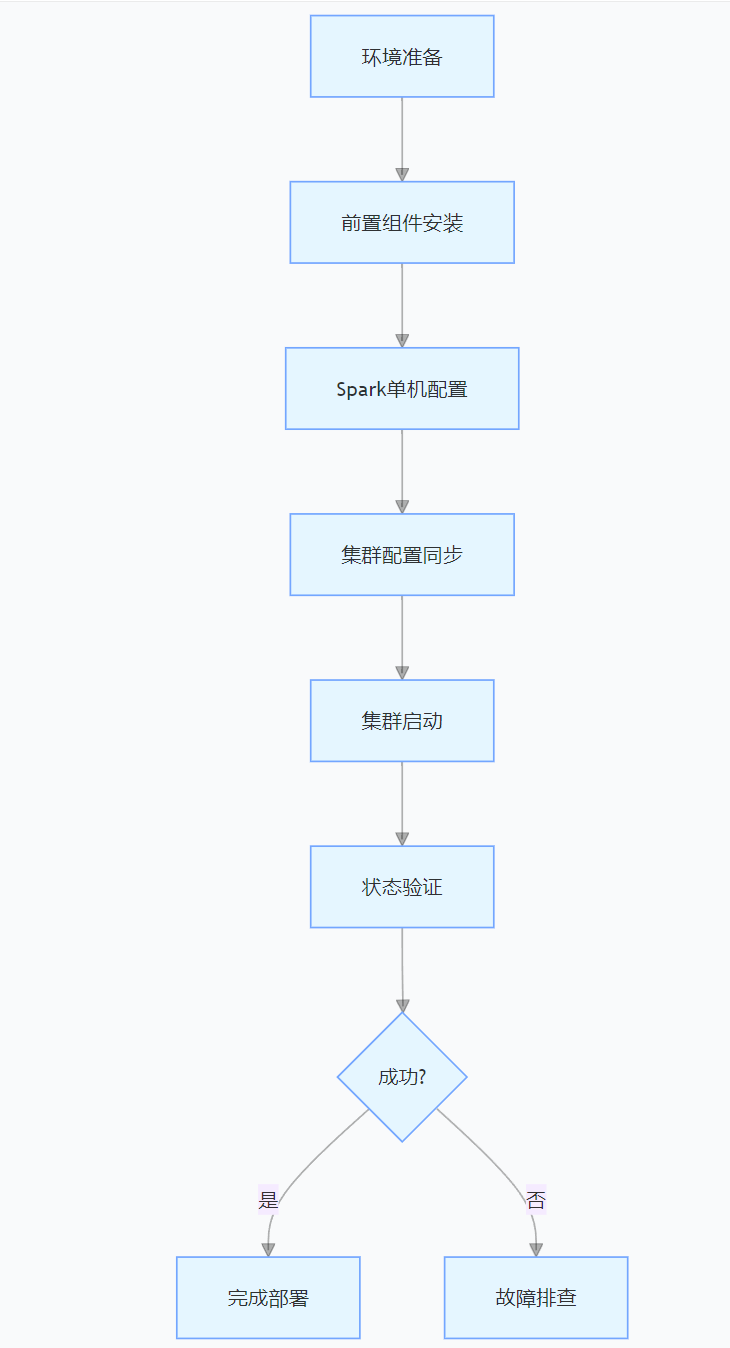
CentOS下的分布式内存计算Spark环境部署
一、Spark 核心架构与应用场景 1.1 分布式计算引擎的核心优势 Spark 是基于内存的分布式计算框架,相比 MapReduce 具有以下核心优势: 内存计算:数据可常驻内存,迭代计算性能提升 10-100 倍(文档段落:3-79…...
Mac软件卸载指南,简单易懂!
刚和Adobe分手,它却总在Library里给你写"回忆录"?卸载的Final Cut Pro像电子幽灵般阴魂不散?总是会有残留文件,别慌!这份Mac软件卸载指南,将用最硬核的方式教你"数字分手术"࿰…...
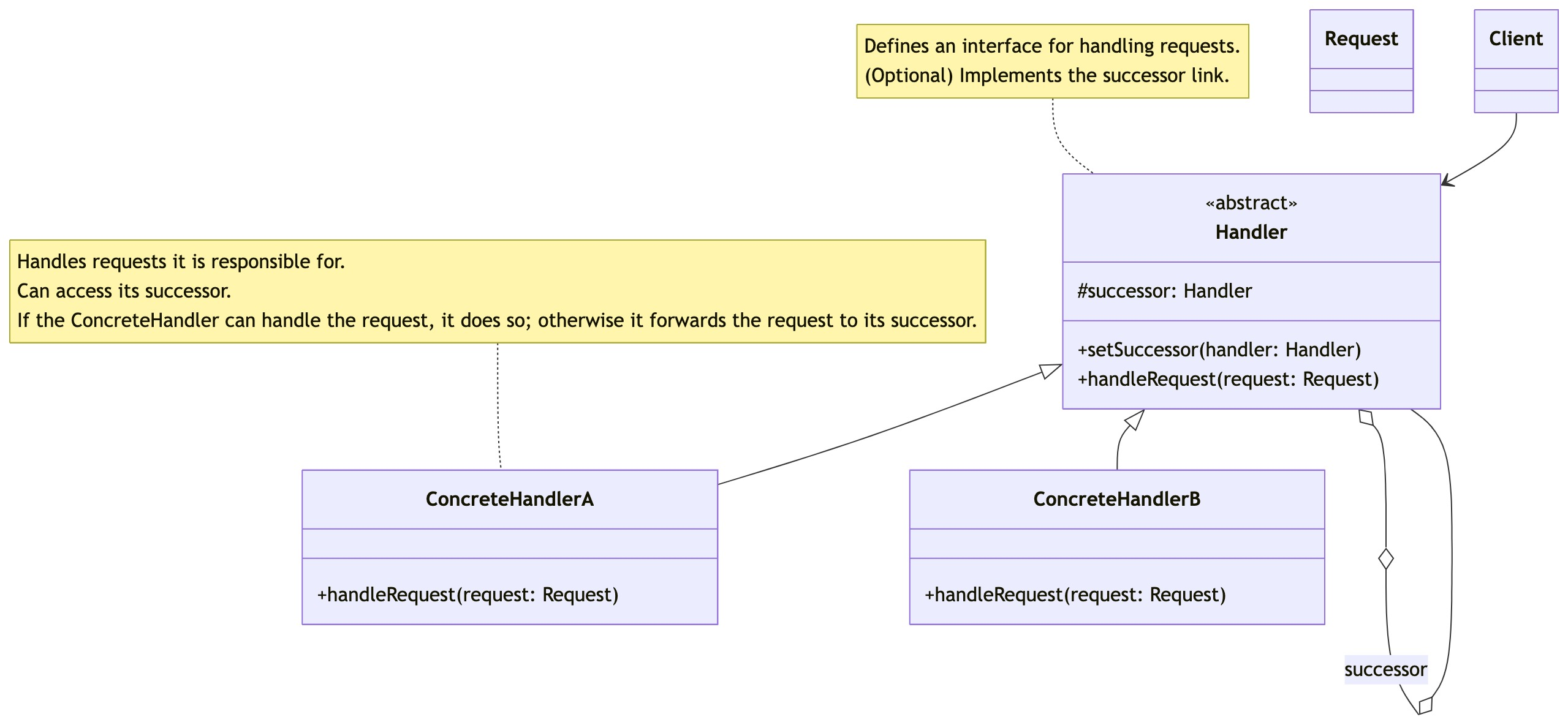
零基础设计模式——行为型模式 - 责任链模式
第四部分:行为型模式 - 责任链模式 (Chain of Responsibility Pattern) 欢迎来到行为型模式的学习!行为型模式关注对象之间的职责分配、算法封装和对象间的交互。我们将学习的第一个行为型模式是责任链模式。 核心思想:使多个对象都有机会处…...
python执行测试用例,allure报乱码且未成功生成报告
allure执行测试用例时显示乱码:‘allure’ �����ڲ����ⲿ���Ҳ���ǿ�&am…...

docker 部署发现spring.profiles.active 问题
报错: org.springframework.boot.context.config.InvalidConfigDataPropertyException: Property spring.profiles.active imported from location class path resource [application-test.yml] is invalid in a profile specific resource [origin: class path re…...

在Ubuntu24上采用Wine打开SourceInsight
1. 安装wine sudo apt install wine 2. 安装32位库支持,SourceInsight是32位程序 sudo dpkg --add-architecture i386 sudo apt update sudo apt install wine32:i386 3. 验证安装 wine --version 4. 安装必要的字体和库(解决显示问题) sudo apt install fonts-wqy…...
