JUC并发编程(二)ForkJoinPool、Future、CompletableFuture、CAS
文章目录
- ForkJoin
- 分治
- 工作窃取
- ForkJoinPool与ThreadPoolExecutor
- 使用案例
- 不带返回值的计算--RecursiveAction
- 带返回值的计算--RecursiveTask
- Future 异步回调
- 烧水案例
- join实现
- FutureTask实现
- CompletableFuture
- 为什么叫CompletableFuture?
- 创建异步任务
- supplyAsync
- runAsync
- 获取任务的方法
- 异步回调处理
- 1.thenApply和thenApplyAsync
- 2.thenAccept和thenAcceptAsync
- 3.thenRun和thenRunAsync
- 4、whenComplete和whenCompleteAsync
- 5、handle和handleAsync
- 多任务组合处理:thenCombine、thenAcceptBoth 和runAfterBoth
- CAS
- 原子类
- Unsafe类
- 原子引用解决ABA问题
ForkJoin
分治
ForkJoinPool线程池最大的特点就是分叉(fork)合并(join),将一个大任务拆分成多个小任务,并行执行,再结合**工作窃取模式(worksteal)**提高整体的执行效率,充分利用CPU资源。

工作窃取
工作窃取(work-stealing)是指当某个线程的任务队列中没有可执行任务的时候,从其他线程的任务队列中窃取任务来执行,以充分利用工作线程的计算能力,减少线程由于获取不到任务而造成的空闲浪费。
在ForkJoinpool中,工作任务的队列都采用双端队列Deque容器。我们知道,在通常使用队列的过程中,我们都在队尾插入,而在队头消费以实现FIFO。而为了实现工作窃取。一般我们会改成工作线程在工作队列上LIFO,而窃取其他线程的任务的时候,从队列头部取获取。示意图如下:
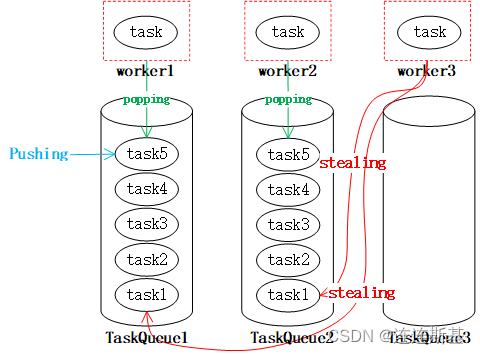
工作线程worker1、worker2以及worker3都从taskQueue的尾部popping获取task,而任务也从尾部Pushing,当worker3队列中没有任务的时候,就会从其他线程的队列中取stealing,这样就使得worker3不会由于没有任务而空闲。这就是工作窃取算法的基本原理。
可以想象,要是不使用工作窃取算法,那么我们在不断fork的过程中,可能某些worker就会一直处于join的等待中。工作窃取的思想,实际实在golang协程的底层处理中也是如此。
ForkJoinPool与ThreadPoolExecutor
ForkJoinPool和ThreadPoolExecutor都实现了Executor和ExecutorService接口,都可以通过构造函数设置线程数,threadFactory,可以查看ForkJoinPool.makeCommonPool()方法的源码查看通用线程池的构造细节。
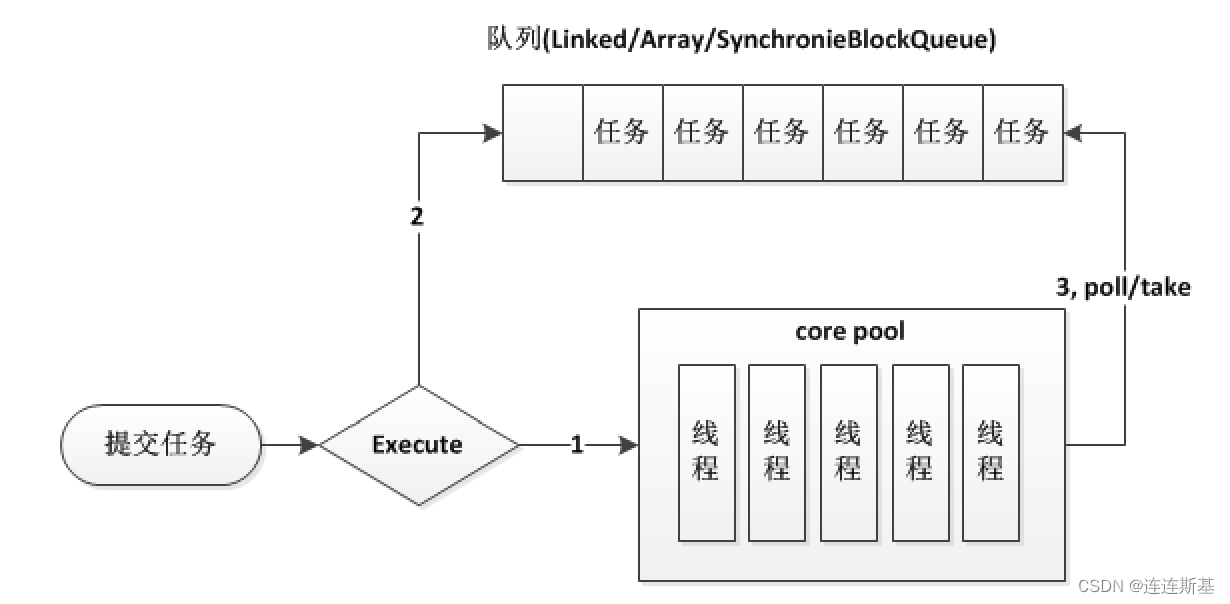
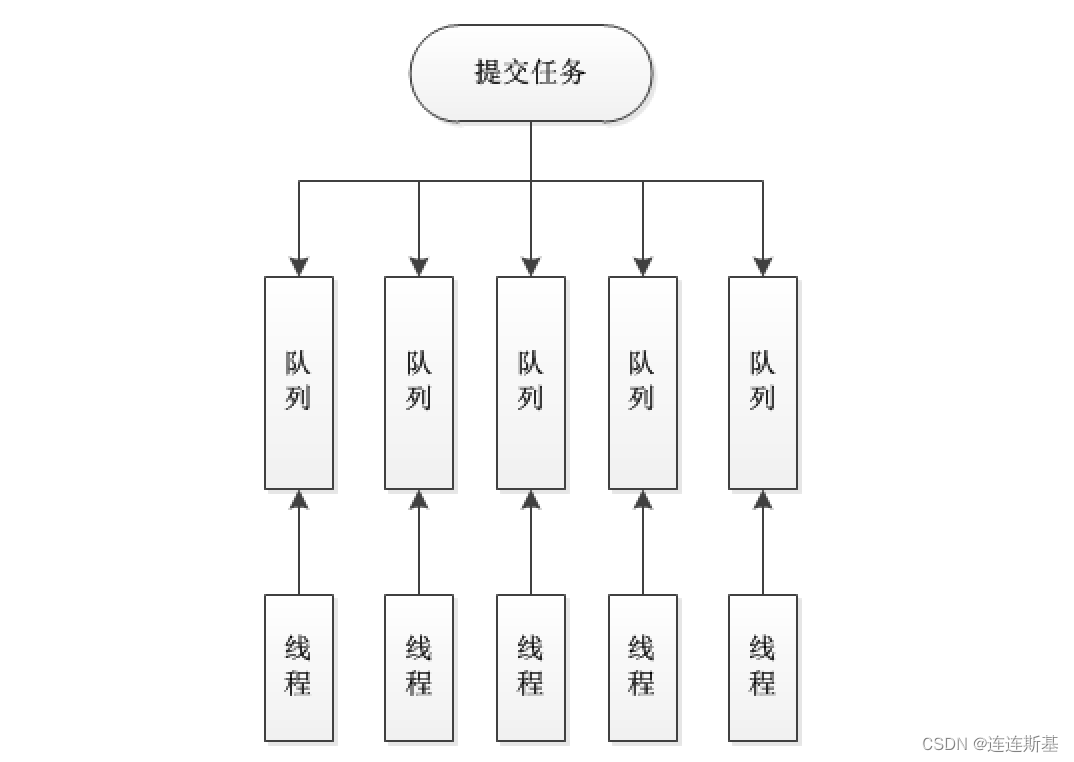
在内部结构上我觉得两个线程池最大的区别是在工作队列的设计上,如下图
ThreadPoolExecutor:
ForkJoinPool:
区别:
ForkJoinPool每个线程都有自己的队列
ThreadPoolExecutor共用一个队列
ForkJoinPool最适合计算密集型任务,而且最好是非阻塞任务。
使用案例
在JUC中,实现Fork-join框架有两个类,分别是ForkJoinPool以及提交的任务抽象类ForkJoinTask。对于ForkJoinTask,虽然有很多子类,但是我们在基本的使用中都是使用了带返回值的RecursiveTask和不带返回值的RecursiveAction类。
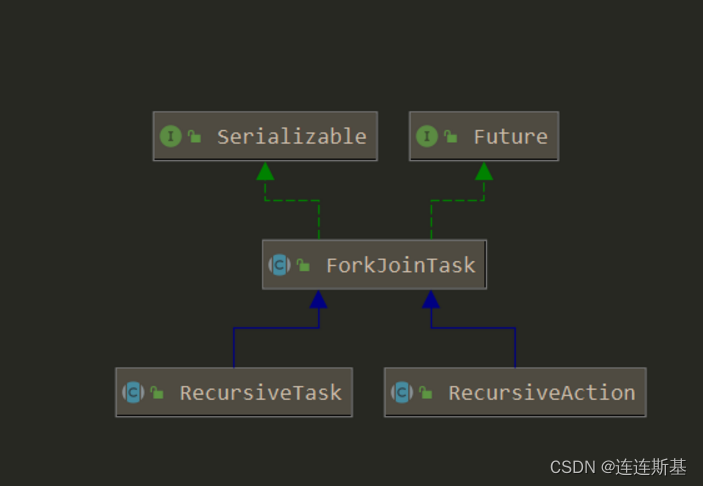
不带返回值的计算–RecursiveAction
案例:实现打印50个任务序列
- 第一步,构建要处理的printForkAction,继承自RecursiveAction:
- 第二步:重写compute()方法,Forkjoin分治的思路,体现在此,start为开始任务序号,en为结束任务序号,设置任务数阈值threshold。
- 当要处理的任务序列数,小于threshold,直接循环遍历,处理。
- 当要处理的任务序列数,大于等于threshold,将要处理的任务拆分(一般都是中分),构建两个新的printForkAction,随后
invokeAll(firstTask, secondTask);
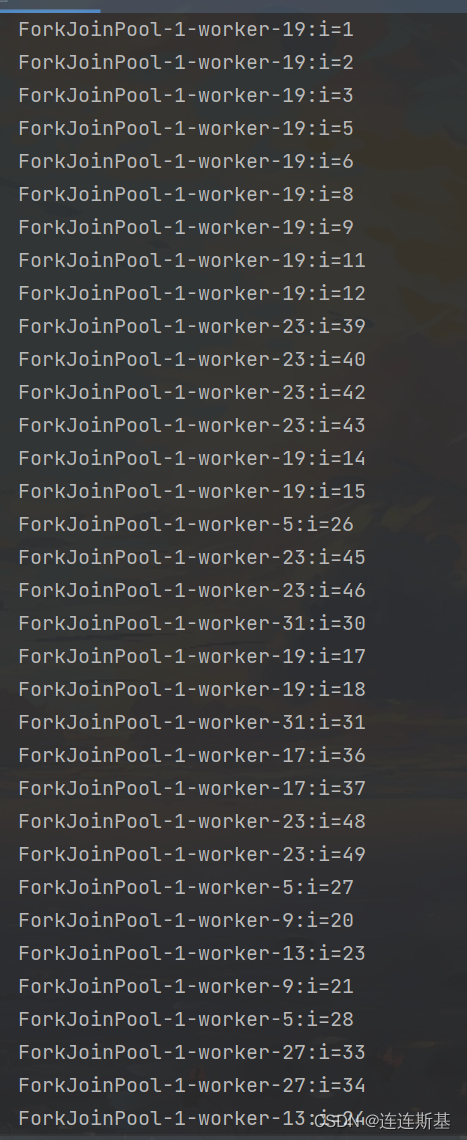
class printForkAction extends RecursiveAction {private static final int threshold = 5;private int start;private int end;public printForkAction(int start, int end) {this.start = start;this.end = end;}@Overrideprotected void compute() {if (end - start < threshold) {for (int i = start; i < end; ++i) {// 业务System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":i=" + i);}} else {int mid = start + ((end - start) / 2);printForkAction firstTask = new printForkAction(start, mid);printForkAction secondTask = new printForkAction(mid + 1, end);invokeAll(firstTask, secondTask);}}
}
第三步:创建ForkJoinPool,往里边提交printForkAction。
public static void main(String[] args) {ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();pool.submit(new printForkAction(1, 50));try {pool.awaitTermination(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}pool.shutdown();}
结果:实现了多个线程共同完成大于任务序列号的任务。
带返回值的计算–RecursiveTask
案例:计算1 - 1亿的和
步骤与上边类似,区别在于RecursiveTask有返回值:
- 1、继承RecursiveTask时,泛型为指定返回值类型
extends RecursiveTask<Long> - 2、
return firstTask.join() + secondTask.join();任务结果可以这里返回。 - 3、
ForkJoinTask<Long> task = pool.submit(new computeForkTask(1L, 100_000_00L));提交任务,返回一个ForkJoinTask对象,泛型任然是返回值类型 - 4、
Long ans = task.get();调用get(),获取结果。
public static void main(String[] args) {ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();ForkJoinTask<Long> task = pool.submit(new computeForkTask(1L, 100_000_00L));try {System.out.println("-------");Long ans = task.get();System.out.println("-------");System.out.println(ans);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}pool.shutdown();}
}class computeForkTask extends RecursiveTask<Long> {private Long start;private Long end;static final Long threshold = 100L;public computeForkTask(Long start, Long end) {this.start = start;this.end = end;}@Overrideprotected Long compute() {Long ans = 0L;if (end - start < threshold) {for (Long i = start; i < end; ++i) {// 业务ans += i;}return ans;} else {Long mid = start + ((end - start) / 2);computeForkTask firstTask = new computeForkTask(start, mid);computeForkTask secondTask = new computeForkTask(mid + 1, end);invokeAll(firstTask, secondTask);return firstTask.join() + secondTask.join();}}
}
Future 异步回调
Future表示一个可能还没有完成的异步任务的结果,针对这个结果可以添加Callback以便在任务执行成功或失败后作出相应的操作。
Future接口主要包括5个方法:
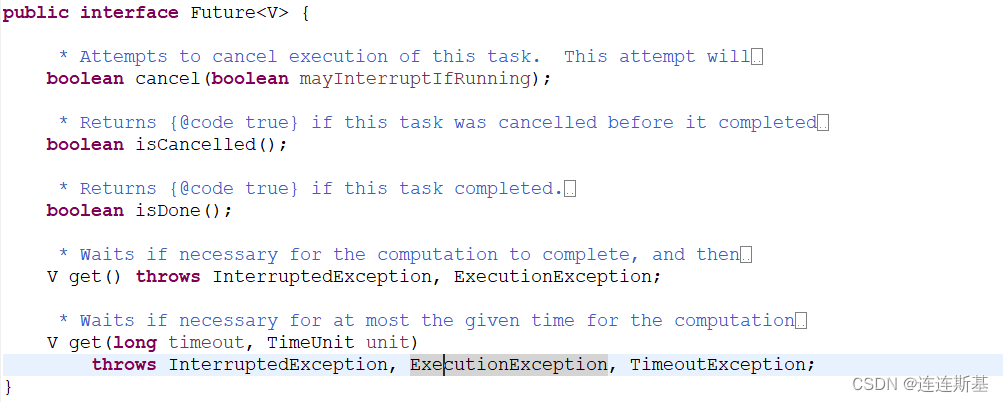
- get()方法可以当任务结束后返回一个结果,如果调用时,工作还没有结束,则会阻塞线程,直到任务执行完毕
- get(long timeout,TimeUnit unit)做多等待timeout的时间就会返回结果
- cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning)方法可以用来停止一个任务,如果任务可以停止(通过mayInterruptIfRunning来进行判断),则可以返回true,如果任务已经完成或者已经停止,或者这个任务无法停止,则会返回false.
- isDone()方法判断当前方法是否完成
- isCancel()方法判断当前方法是否取消
烧水案例
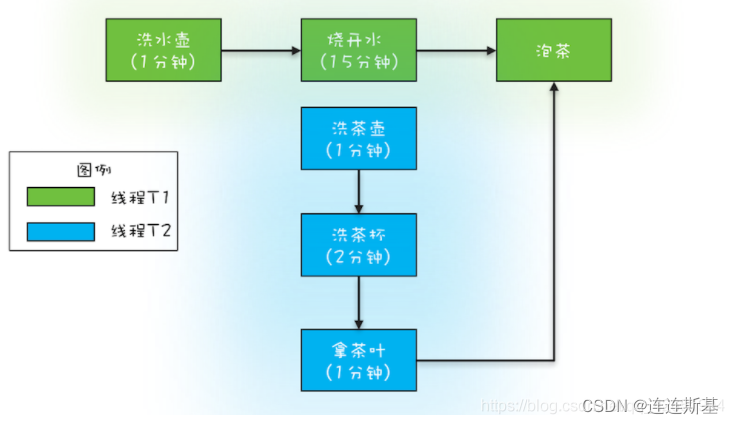
用两个线程 T1 和 T2 来完成烧水泡茶程序,T1 负责洗水壶、烧开水、泡茶这三道工序,T2 负责洗茶壶、洗茶杯、拿茶叶三道工序,其中 T1 在执行泡茶这道工序时需要等待 T2 完成拿茶叶的工序。
join实现
- A线程调用B线程的join方法,在B线程没有执行完成钱,A线程一直处于阻塞状态
- join是实例方法,需要用线程对象去调用
- 使用join线程合并线程无法获取到合并线程的返回值,即无法知道烧水线程执行的结果。只能一直阻塞等待烧水线程结束
那么我们可以构建两个线性,一个烧水,一个洗碗,将其加入(join)到主线程,然后泡茶:
public class JoinDemo {public static final int SLEEP_TIME = 1000;public static void main(String[] args) {Thread hThread = new Thread(() -> {try {Thread.currentThread().setName("烧水线程");System.out.println("洗好水壶");System.out.println("灌好凉水");System.out.println("放在火上");Thread.sleep(SLEEP_TIME);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("水烧开了");});hThread.start();Thread wThread = new Thread(() -> {try {Thread.currentThread().setName("清洗线程");System.out.println("洗茶壶");System.out.println("洗茶杯");System.out.println("拿茶叶");Thread.sleep(SLEEP_TIME);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("洗茶叶完成");});wThread.start();// 主线程 1. 合并烧水线程try {hThread.join();wThread.join();System.out.println("泡泡茶喝");} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}
FutureTask实现
烧水操作和洗碗操作分别构建为callable对象,装配FutureTask,在主线程中获取FutureTask的结果:
public class FutureTaskDemo {public static final int SLEEP_TIME = 1000;public static void main(String[] args) {Callable<Boolean> hotWaterJob = new HotWaterJob();FutureTask<Boolean> hotWaterTask = new FutureTask<>(hotWaterJob);Thread hotWaterThread = new Thread(hotWaterTask, "烧水线程");Callable<Boolean> washJob = new WashJob();FutureTask<Boolean> washTask = new FutureTask<>(washJob);Thread washThread = new Thread(washTask, "清洗线程");hotWaterThread.start();washThread.start();try {Boolean hotWaterFlag = hotWaterTask.get();Boolean washFlag = washTask.get();drinkTea(hotWaterFlag, washFlag);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}private static void drinkTea(Boolean hotWaterFlag, Boolean washFlag) {if (hotWaterFlag && washFlag) {System.out.println("喝茶");}}static class HotWaterJob implements Callable<Boolean> {@Overridepublic Boolean call() throws Exception {try {Thread.currentThread().setName("烧水线程");System.out.println("洗好水壶");System.out.println("灌好凉水");System.out.println("放在火上");Thread.sleep(SLEEP_TIME);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();return false;}System.out.println("水烧开了");return true;}}static class WashJob implements Callable<Boolean> {@Overridepublic Boolean call() throws Exception {try {Thread.currentThread().setName("清洗线程");System.out.println("洗茶壶");System.out.println("洗茶杯");System.out.println("拿茶叶");Thread.sleep(SLEEP_TIME);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();return false;}System.out.println("洗茶叶完成");return true;}}
}
CompletableFuture
CompletableFuture 与 FutureTask为例,同为Future的实现类。同传统的Future相比,其支持流式计算、函数式编程、完成通知、自定义异常处理等很多新的特性。由于函数式编程在java中越来越多的被使用到,熟练掌握CompletableFuture,对于更好的使用java 8后的主要新特性很重要。
为什么叫CompletableFuture?
CompletableFuture字面翻译过来,就是“可完成的Future”。同传统的Future相比较,CompletableFuture能够主动设置计算的结果值(主动终结计算过程,即completable),从而在某些场景下主动结束阻塞等待。而Future由于不能主动设置计算结果值,一旦调用get()进行阻塞等待,要么当计算结果产生,要么超时,才会返回。
下面的示例,比较简单的说明了,CompletableFuture是如何被主动完成的。在下面这段代码中,由于调用了complete方法,所以最终的打印结果是“manual test”,而不是"test"。
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{try{Thread.sleep(1000L);return "test";} catch (Exception e){return "failed test";}
});
future.complete("manual test");
System.out.println(future.join());
创建异步任务
supplyAsync
supplyAsync是创建带有返回值的异步任务。它有如下两个方法,一个是使用默认线程池(ForkJoinPool.commonPool())的方法,一个是带有自定义线程池的重载方法:
// 带返回值异步请求,默认线程池
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier)// 带返回值的异步请求,可以自定义线程池
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor)
具体使用:
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<String> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("do something....");return "result";});//等待任务执行完成System.out.println("结果->" + cf.get());
}public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {// 自定义线程池ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();CompletableFuture<String> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("do something....");return "result";}, executorService);//等待子任务执行完成System.out.println("结果->" + cf.get());
}
runAsync
runAsync是创建没有返回值的异步任务。它有如下两个方法,一个是使用默认线程池(ForkJoinPool.commonPool())的方法,一个是带有自定义线程池的重载方法
// 不带返回值的异步请求,默认线程池
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable)// 不带返回值的异步请求,可以自定义线程池
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor)
具体使用:
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<Void> cf = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {System.out.println("do something....");});//等待任务执行完成System.out.println("结果->" + cf.get());
}public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {// 自定义线程池ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();CompletableFuture<Void> cf = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {System.out.println("do something....");}, executorService);//等待任务执行完成System.out.println("结果->" + cf.get());
}
获取任务的方法
// 如果完成则返回结果,否则就抛出具体的异常
public T get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException // 最大时间等待返回结果,否则就抛出具体异常
public T get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException// 完成时返回结果值,否则抛出unchecked异常。为了更好地符合通用函数形式的使用,如果完成此 CompletableFuture所涉及的计算引发异常,则此方法将引发unchecked异常并将底层异常作为其原因
public T join()// 如果完成则返回结果值(或抛出任何遇到的异常),否则返回给定的 valueIfAbsent。
public T getNow(T valueIfAbsent)// 如果任务没有完成,返回的值设置为给定值
public boolean complete(T value)// 如果任务没有完成,就抛出给定异常
public boolean completeExceptionally(Throwable ex) 注意:
- join()与get()的区别:
- join()方法抛出的是uncheckException异常(即RuntimeException),不会强制开发者抛出
- get()方法抛出的是经过检查的异常,ExecutionException, InterruptedException 需要用户手动处理(抛出或者 try catch)
- complete()与getNow()的区别:
- complete() : 如果任务没有完成,将返回的值设置为给定值,提前结束。 complete()只是对结果提交结束的一种设置,并不返回任务结果。
- getNow():如果完成则返回结果值(或抛出任何遇到的异常),否则返回给定的 valueIfAbsent。
异步回调处理
1.thenApply和thenApplyAsync
thenApply 表示某个任务执行完成后执行的动作,即回调方法,会将该任务的执行结果即方法返回值作为入参传递到回调方法中,带有返回值。
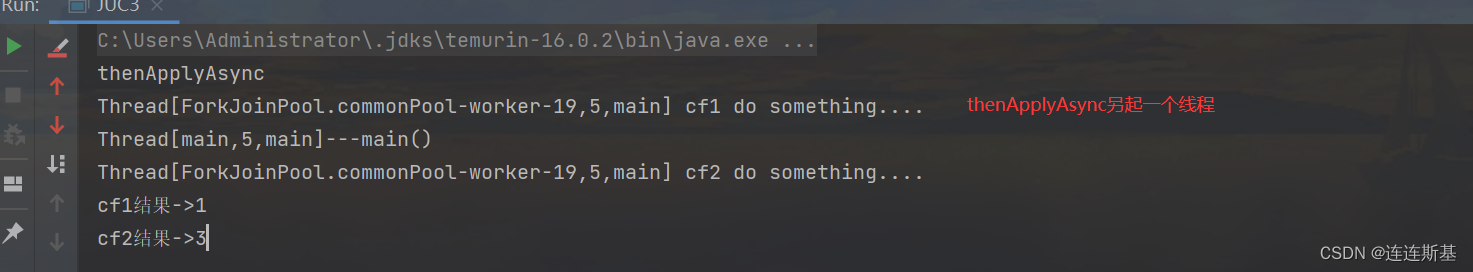
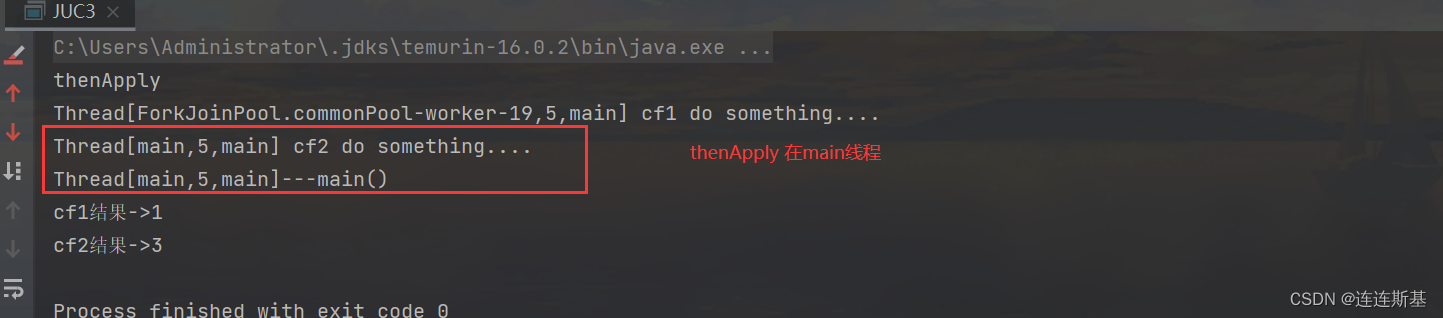
thenApply和thenApplyAsync区别在于,使用thenApply方法时子任务与父任务使用的是同一个线程,而thenApplyAsync在子任务中是另起一个线程执行任务,并且thenApplyAsync可以自定义线程池,默认的使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool()线程池。
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {System.out.println("thenApplyAsync");CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");return 1;});CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = cf1.thenApplyAsync((result) -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");result += 2;return result;});System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "---main()");//等待任务1执行完成System.out.println("cf1结果->" + cf1.get());//等待任务2执行完成System.out.println("cf2结果->" + cf2.get());
}public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {System.out.println("thenApply");CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");return 1;});CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = cf1.thenApply((result) -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");result += 2;return result;});System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "---main()");//等待任务1执行完成System.out.println("cf1结果->" + cf1.get());//等待任务2执行完成System.out.println("cf2结果->" + cf2.get());
}
2.thenAccept和thenAcceptAsync
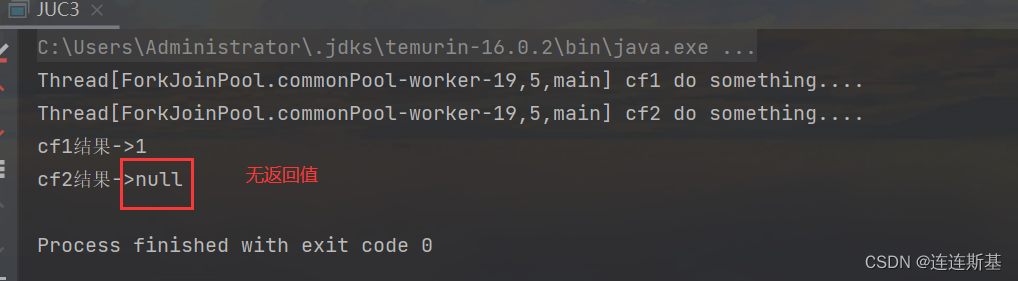
thenAccep表示某个任务执行完成后执行的动作,即回调方法,会将该任务的执行结果即方法返回值作为入参传递到回调方法中,无返回值。
thenAccept和thenAcceptAsync与thenApply和thenApplyAsync的区别在于accept无返回值,只接受有返回值的future的结果,自己本身无返回值
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");return 1;});CompletableFuture<Void> cf2 = cf1.thenAccept((result) -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");});//等待任务1执行完成System.out.println("cf1结果->" + cf1.get());//等待任务2执行完成System.out.println("cf2结果->" + cf2.get());
}public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");return 1;});CompletableFuture<Void> cf2 = cf1.thenAcceptAsync((result) -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");});//等待任务1执行完成System.out.println("cf1结果->" + cf1.get());//等待任务2执行完成System.out.println("cf2结果->" + cf2.get());
}
3.thenRun和thenRunAsync
thenRun表示某个任务执行完成后执行的动作,即回调方法,无入参,无返回值。
4、whenComplete和whenCompleteAsync
whenComplete是当某个任务执行完成后执行的回调方法,会将执行结果或者执行期间抛出的异常传递给回调方法,如果是正常执行则异常为null,回调方法对应的CompletableFuture的result和该任务一致,如果该任务正常执行,则get方法返回执行结果,如果是执行异常,则get方法抛出异常。
whenComplete 和 thenApply主要区别在于
whenComplete方法会传递异常,而thenApply不会传递异常。whenComplete也是没有返回值的
5、handle和handleAsync
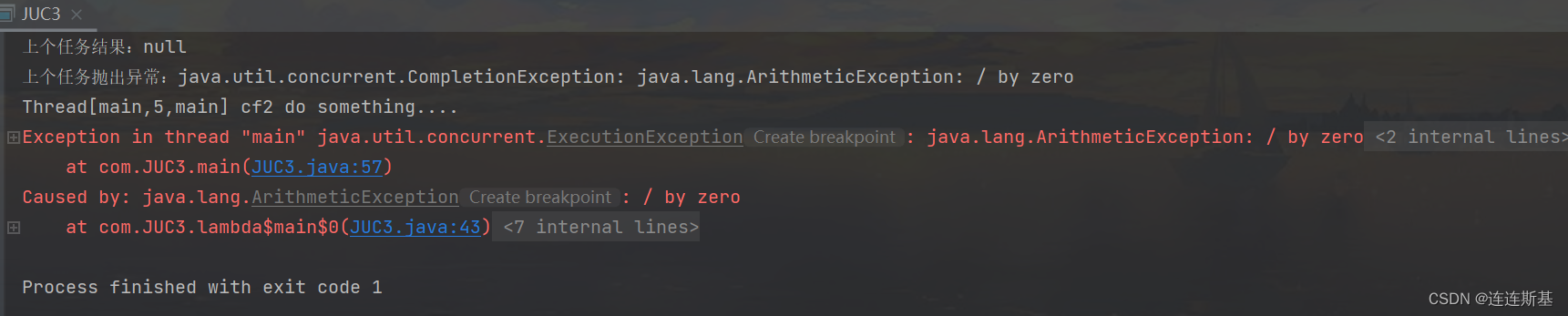
跟whenComplete基本一致,区别在于handle的回调方法有返回值。
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");// int a = 1/0;return 1;});CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = cf1.handle((result, e) -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");System.out.println("上个任务结果:" + result);System.out.println("上个任务抛出异常:" + e);return result+2;});//等待任务2执行完成System.out.println("cf2结果->" + cf2.get());
}
多任务组合处理:thenCombine、thenAcceptBoth 和runAfterBoth
1.thenCombine、thenAcceptBoth 和runAfterBoth
这三个方法都是将两个CompletableFuture组合起来处理,只有两个任务都正常完成时,才进行下阶段任务。
区别:
- thenCombine会将两个任务的执行结果作为所提供函数的参数,且该方法有返回值;
- thenAcceptBoth同样将两个任务的执行结果作为方法入参,但是无返回值;
- runAfterBoth没有入参,也没有返回值。注意两个任务中只要有一个执行异常,则将该异常信息作为指定任务的执行结果。
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");return 1;});CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");return 2;});CompletableFuture<Integer> cf3 = cf1.thenCombine(cf2, (a, b) -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf3 do something....");return a + b;});System.out.println("cf3结果->" + cf3.get());
}public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");return 1;});CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");return 2;});CompletableFuture<Void> cf3 = cf1.thenAcceptBoth(cf2, (a, b) -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf3 do something....");System.out.println(a + b);});System.out.println("cf3结果->" + cf3.get());
}public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");return 1;});CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");return 2;});CompletableFuture<Void> cf3 = cf1.runAfterBoth(cf2, () -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf3 do something....");});System.out.println("cf3结果->" + cf3.get());
}
CAS
CAS(Compare and Swap)名为比较交换, 通常是指一种原子操作: 针对一个变量,首先比较它的内存值与某个期望值是否相同,如果相同,就给它赋一个新值。 我们将原本的内存值举例为A, 期望值举例为B, 新值举例为C, CAS操作就是把A和B进行对比, 如果 A==B则将A的值替换为C; 如果A和B不相等, 那就说明有其他业务对数据A进行过修改, 于是A的值则不会更新为C.
我们通过上面的解释可以看出CAS是一种以乐观锁的思想实现的, 但是他本身却没有用到任何锁, 相对于synchronized悲观锁来说效率会高很多. Java原子类中的递增操作就通过CAS自旋实现的。
原子类
在J.U.C下的Atomic包提供了一系列的操作简单,性能高效,并能保证线程安全的类去更新基本类型变量,数组元素,引用类型以及更新对象中的字段类型。Atomic包下的这些类都是采用的是乐观锁策略去原子更新数据,在java中则是使用CAS操作具体实现。
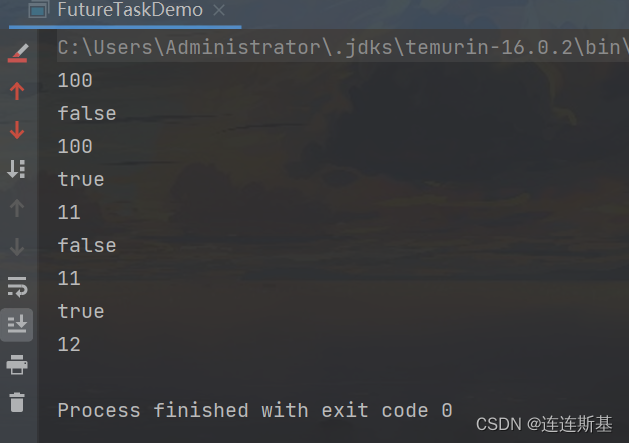
compareAndSet(V,A)
期望V,设置值为A,即仅在当前内存中原子变量a的值为V的情况,才会把变量更新为A。
AtomicInteger a = new AtomicInteger(100);
System.out.println(a.get());
System.out.println(a.compareAndSet(10, 11));
System.out.println(a.get());
System.out.println(a.compareAndSet(100, 11));
System.out.println(a.get());
System.out.println(a.compareAndSet(100, 12));
System.out.println(a.get());
System.out.println(a.compareAndSet(11, 12));
System.out.println(a.get());
结果:
其底层是调用的Unsafe类的compareAndSet()方法:

Unsafe类
Java无法直接访问底层操作系统,而是通过本地native方法来访问,但还是留了一个后门-Unsafe类,提供了一些低层次操作,如直接内存访问等,Unsafe类也提供了CAS操作的native方法:
/** 拿对象o在内存偏移offset处的对象与expected比较,如果相等,则设置o.offset=x并返回true,否则返回false */
public final native boolean compareAndSwapObject(Object o, long offset, Object expected, Object x);
/** 拿对象o在内存偏移offset处的long值与expected比较,如果相等则设置o.offset=x */
public final native boolean compareAndSwapLong(Object o, long offset, long expected, long x);
/** 拿对象o在内存偏移offset处的int值与expected比较,如果相等则设置o.offset=x */
public final native boolean compareAndSwapInt(Object o, long offset, int expected, int x);/** 获取字段f的偏移量 */
public native long objectFieldOffset(Field f);
/** 获取静态field在对象中的偏移量 */
public native long staticFieldOffset(Field f);
原子引用解决ABA问题
CAS锁的问题,当一个线程将期望值A修改为B,然后再将B改回A,那么我们的CAS锁就失效了。
为解决这个问题,采用AtomicStampedReference,原子引用类,给变量加上一个版本号,当拿到变量时,每次修改时,版本号 + 1,仅当版本号与初始一致时,才可以修改成功,这样就规避了ABA问题。
public static void main(String[] args) {AtomicStampedReference<Integer> as = new AtomicStampedReference<>(1,1000);new Thread(() ->{System.out.println("a1--" + as.getReference());System.out.println(as.compareAndSet(1, 2, as.getStamp(), as.getStamp() + 1));System.out.println("a2--" + as.getReference());System.out.println(as.compareAndSet(2, 1, as.getStamp(), as.getStamp() + 1));System.out.println("a3--" + as.getReference());}).start();new Thread(() -> {int stamp = as.getStamp();try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("b1:" + as.compareAndSet(1, 2, stamp, stamp + 1));System.out.println("b1--" + as.getReference());}).start();}
相关文章:

JUC并发编程(二)ForkJoinPool、Future、CompletableFuture、CAS
文章目录 ForkJoin分治工作窃取ForkJoinPool与ThreadPoolExecutor使用案例不带返回值的计算--RecursiveAction带返回值的计算--RecursiveTask Future 异步回调烧水案例join实现FutureTask实现 CompletableFuture为什么叫CompletableFuture?创建异步任务supplyAsyncrunAsync获取…...

大数据课程F2——HIve的安装操作
文章作者邮箱:yugongshiye@sina.cn 地址:广东惠州 ▲ 本章节目的 ⚪ 了解HIve的安装概念; ⚪ 掌握HIve安装步骤和Linux常用命令; ⚪ 掌握HIve安装的连接池jar包冲突和日志打印jar包冲突; ⚪ 掌握HIve安装的Hadoop安装配置; ⚪ 掌握HIve安装的JDK安装配…...
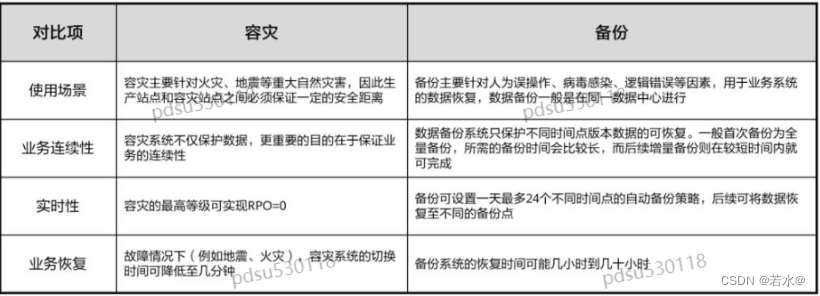
华为云hcip核心知识笔记(存储服务规划)
云上存储 : 云硬盘:基于分布式架构,可弹性扩展的虚拟块存储服务 注意事项 挂载云硬盘实例和云硬盘必须在同一区域,否则挂载失败文件存储服务:完全托管的共享文件存储 可以为多个实例实现共享访问,不同vpc中可以进行对…...

四、JVM-对象内存模型
Java对象内存模型 一个Java对象在内存中包括3个部分:对象头、实例数据和对齐填充 数据 内存 – CPU 寄存器 -127 补码 10000001 - 11111111 32位的处理器 一次能够去处理32个二进制位 4字节的数据 64位操作系统 8字节 2的64次方的寻址空间 指针压缩技术 JDK1.6出…...

2023-08-05 LeetCode每日一题(合并两个有序链表)
2023-08-05每日一题 一、题目编号 21. 合并两个有序链表二、题目链接 点击跳转到题目位置 三、题目描述 将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。 示例1: 示例2: 示例3: …...
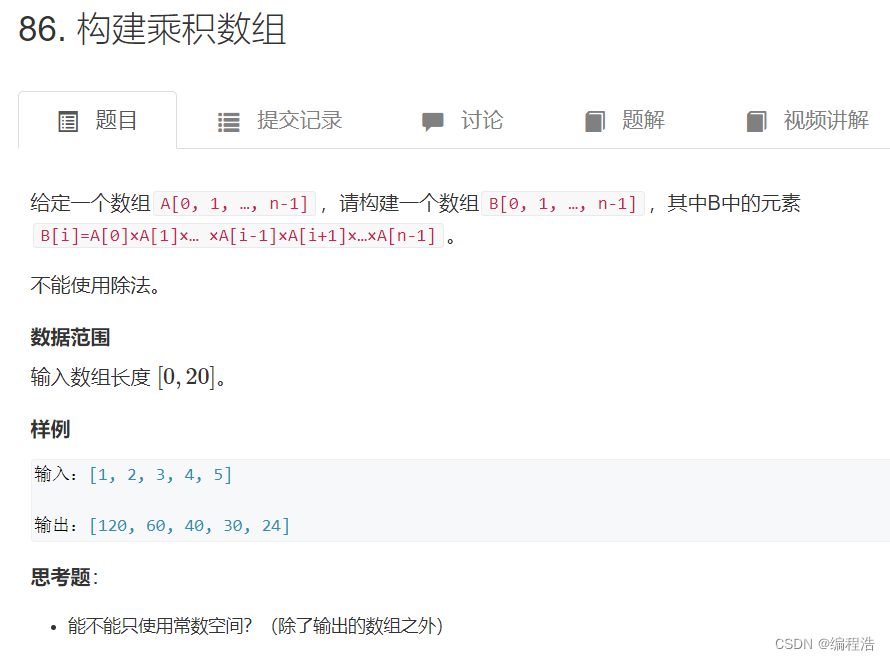
【每天40分钟,我们一起用50天刷完 (剑指Offer)】第四十七天 47/50
专注 效率 记忆 预习 笔记 复习 做题 欢迎观看我的博客,如有问题交流,欢迎评论区留言,一定尽快回复!(大家可以去看我的专栏,是所有文章的目录) 文章字体风格: 红色文字表示&#…...

离散型制造业生产管理云MES系统解决方案
典型的离散制造业主要包括机械、电子、航空、汽车等行业,这些企业既有按订单生产,也有按库存生产,既有批量生产,也有单件小批生产。那么,注重生产计划的制定,生产的快速响应是离散行业MES系统应用的关键。 …...

【Vue】全家桶介绍
文章目录 概述核心Vue.Js浏览器开发插件vue-devtools项目构建工具:vue-cli路由管理器 : vue-Router状态管理模式:vuex网络请求库:AxiosUI框架: iview、vant、elementUI打包工具: webpack来源 概述 Vue全家…...

【雕爷学编程】MicroPython动手做(33)——物联网之天气预报2
天气(自然现象) 是指某一个地区距离地表较近的大气层在短时间内的具体状态。而天气现象则是指发生在大气中的各种自然现象,即某瞬时内大气中各种气象要素(如气温、气压、湿度、风、云、雾、雨、闪、雪、霜、雷、雹、霾等ÿ…...

macOS 虚拟桌面黑屏(转)
转自:macOS重置虚拟桌面、macOS 虚拟桌面黑屏 有几次出现如图的情况,以为是iTerm的问题,但是在关闭软件,重启之后,依旧无效。 后面经过网友告知,才知道是虚拟桌面的问题。 为了清理这个问题,有以…...

查看gz文件 linux zcat file.gz mtx.gz
可以使用以下命令来查看 gz 压缩文件的内容: zcat file.gz 1 该命令会将 file.gz 文件解压并输出到标准输出,可以通过管道符将其与 grep 命令结合使用来查找需要的关键词,例如: zcat file.gz | grep keyword 1 该命令会将 file.gz…...

互联网——根服务器
说明 根服务器是互联网域名系统(DNS)中最高级别的服务器之一。它们负责管理整个DNS系统的顶级域名空间,例如.com、.org和.net等。 根服务器的主要功能是将用户的DNS查询转发到适当的顶级域名服务器。当用户在浏览器中输入一个域名ÿ…...

华为OD机试之报文回路(Java源码)
题目描述 IGMP 协议中响应报文和查询报文,是维系组播通路的两个重要报文,在一条已经建立的组播通路中两个相邻的 HOST 和 ROUTER,ROUTER 会给 HOST 发送查询报文,HOST 收到查询报文后给 ROUTER 回复一个响应报文,以维持…...

林大数据结构【2019】
关键字: 哈夫曼树权值最小、哈夫曼编码、邻接矩阵时间复杂度、二叉树后序遍历、二叉排序树最差时间复杂度、非连通无向图顶点数(完全图)、带双亲的孩子链表、平衡二叉树调整、AOE网关键路径 一、判断 二、单选 三、填空 四、应用题...

2023华数杯数学建模A题思路分析 - 隔热材料的结构优化控制研究
# 1 赛题 A 题 隔热材料的结构优化控制研究 新型隔热材料 A 具有优良的隔热特性,在航天、军工、石化、建筑、交通等 高科技领域中有着广泛的应用。 目前,由单根隔热材料 A 纤维编织成的织物,其热导率可以直接测出;但是 单根隔热…...

Linux常用命令——dos2unix命令
在线Linux命令查询工具 dos2unix 将DOS格式文本文件转换成Unix格式 补充说明 dos2unix命令用来将DOS格式的文本文件转换成UNIX格式的(DOS/MAC to UNIX text file format converter)。DOS下的文本文件是以\r\n作为断行标志的,表示成十六进…...
)
【NLP pytorch】基于BERT_TextCNN新闻文本分类实战(项目详解)
基于BERT_TextCNN新闻文本分类实战项目 1 数据集介绍2 模型介绍3 数据预处理3.1 数据集加载3.2 统计文本长度分布4 BERT模型4.1 HuggingFace介绍4.2 HuggingFace使用4.2.1 加载预训练模型4.2.2 预训练模型的使用4.3 BERT模型使用4.3.1 编码和解码4.3.2 批处理4.3.3 词向量处理5…...
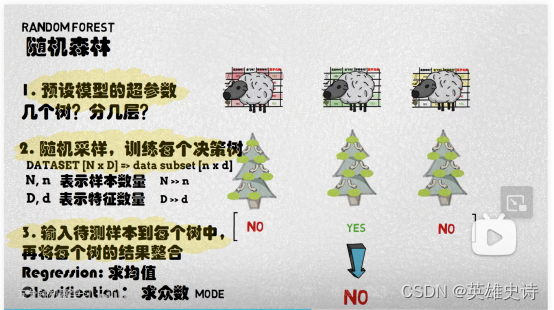
决策树与随机森林
目录 决策树是:Why:How:基本概念决策树生成举例决策树缺点参考 Demo 随机森林1.是:2.Why:3.How:参考 Demo 决策树 是: 1.一种有监督的分类(或预测)算法。 2.利用属性、…...

Nginx 网站服务
Nginx 稳定性高 (但是没有apache稳定) 版本号:1.12 1.20 1.22 系统资源消耗低 (处理http请求的并发能力很高,单台物理服务器可以处理30000-50000个并发请求) 稳定:一般在企业中,为了保持服务器稳定,并发量的…...

Python爬虫——爬虫时如何知道是否代理ip伪装成功?
前言 在进行爬虫时,我们可能需要使用代理IP来伪装自己的身份,以避免被网站封禁。如何判断代理IP是否伪装成功呢?本篇文章将围绕这个问题展开讲解,同时提供Python代码示例。 1. 确认代理IP地址 首先,我们需要确认代理…...
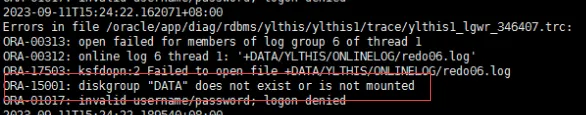
19c补丁后oracle属主变化,导致不能识别磁盘组
补丁后服务器重启,数据库再次无法启动 ORA01017: invalid username/password; logon denied Oracle 19c 在打上 19.23 或以上补丁版本后,存在与用户组权限相关的问题。具体表现为,Oracle 实例的运行用户(oracle)和集…...

ubuntu搭建nfs服务centos挂载访问
在Ubuntu上设置NFS服务器 在Ubuntu上,你可以使用apt包管理器来安装NFS服务器。打开终端并运行: sudo apt update sudo apt install nfs-kernel-server创建共享目录 创建一个目录用于共享,例如/shared: sudo mkdir /shared sud…...
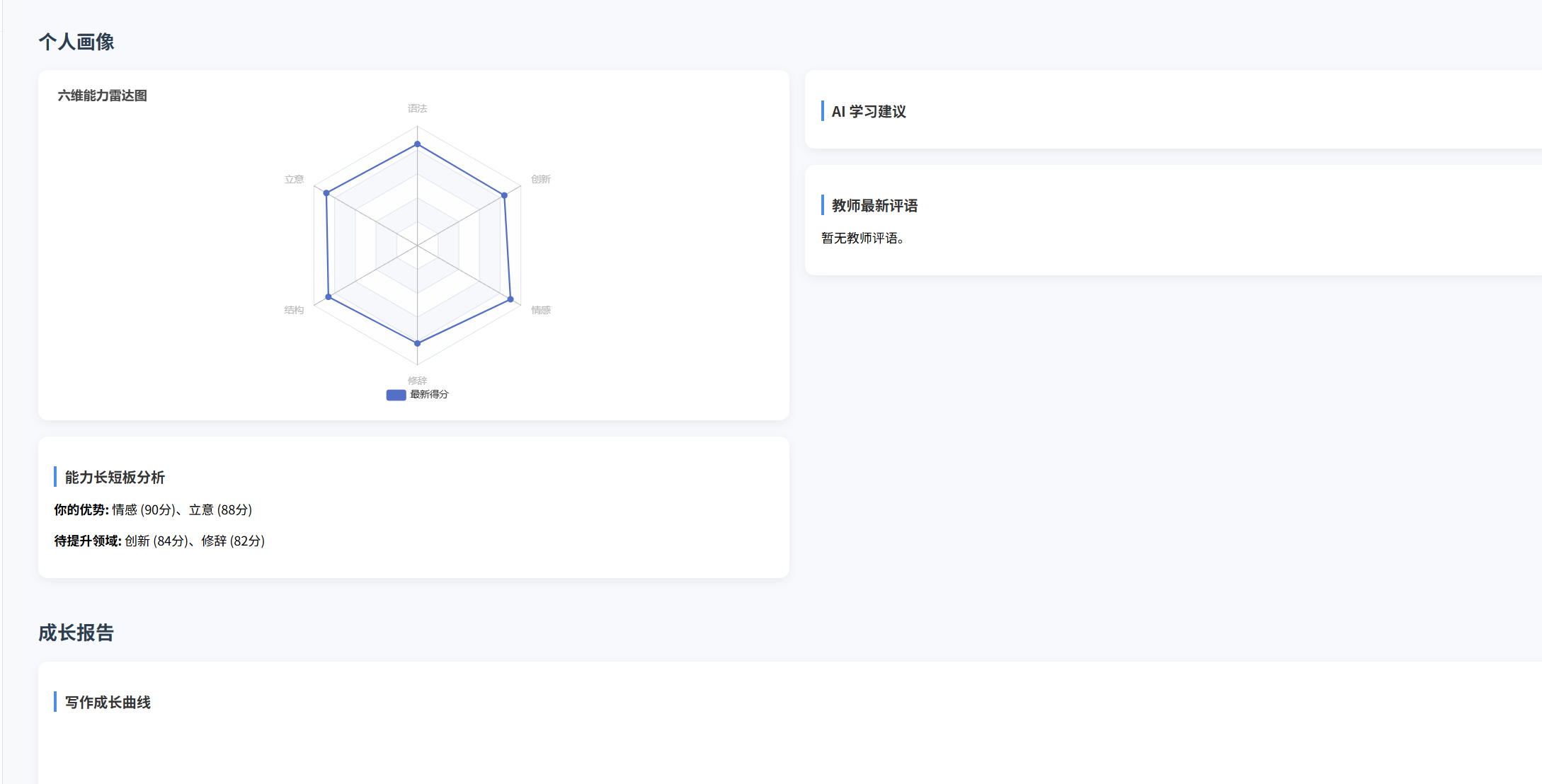
(十)学生端搭建
本次旨在将之前的已完成的部分功能进行拼装到学生端,同时完善学生端的构建。本次工作主要包括: 1.学生端整体界面布局 2.模拟考场与部分个人画像流程的串联 3.整体学生端逻辑 一、学生端 在主界面可以选择自己的用户角色 选择学生则进入学生登录界面…...

Qt Widget类解析与代码注释
#include "widget.h" #include "ui_widget.h"Widget::Widget(QWidget *parent): QWidget(parent), ui(new Ui::Widget) {ui->setupUi(this); }Widget::~Widget() {delete ui; }//解释这串代码,写上注释 当然可以!这段代码是 Qt …...
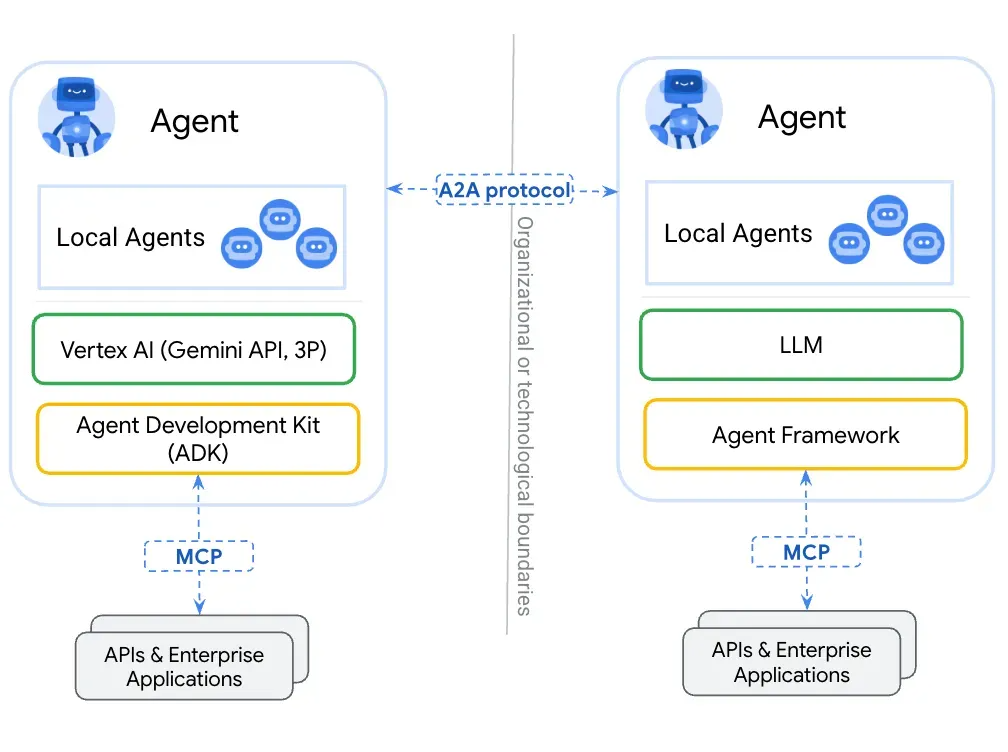
第一篇:Agent2Agent (A2A) 协议——协作式人工智能的黎明
AI 领域的快速发展正在催生一个新时代,智能代理(agents)不再是孤立的个体,而是能够像一个数字团队一样协作。然而,当前 AI 生态系统的碎片化阻碍了这一愿景的实现,导致了“AI 巴别塔问题”——不同代理之间…...
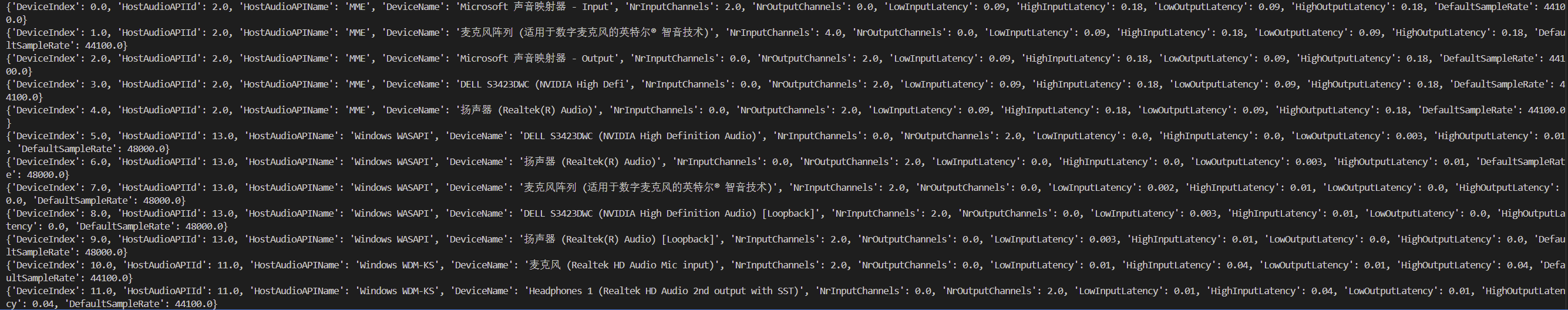
Psychopy音频的使用
Psychopy音频的使用 本文主要解决以下问题: 指定音频引擎与设备;播放音频文件 本文所使用的环境: Python3.10 numpy2.2.6 psychopy2025.1.1 psychtoolbox3.0.19.14 一、音频配置 Psychopy文档链接为Sound - for audio playback — Psy…...
的使用)
Go 并发编程基础:通道(Channel)的使用
在 Go 中,Channel 是 Goroutine 之间通信的核心机制。它提供了一个线程安全的通信方式,用于在多个 Goroutine 之间传递数据,从而实现高效的并发编程。 本章将介绍 Channel 的基本概念、用法、缓冲、关闭机制以及 select 的使用。 一、Channel…...

uniapp 字符包含的相关方法
在uniapp中,如果你想检查一个字符串是否包含另一个子字符串,你可以使用JavaScript中的includes()方法或者indexOf()方法。这两种方法都可以达到目的,但它们在处理方式和返回值上有所不同。 使用includes()方法 includes()方法用于判断一个字…...
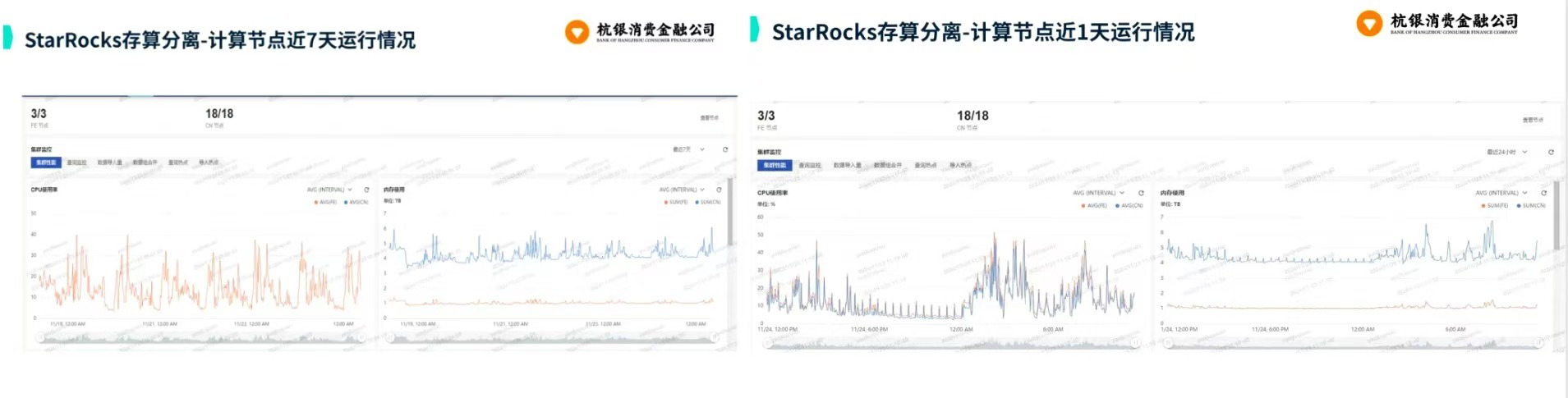
从 GreenPlum 到镜舟数据库:杭银消费金融湖仓一体转型实践
作者:吴岐诗,杭银消费金融大数据应用开发工程师 本文整理自杭银消费金融大数据应用开发工程师在StarRocks Summit Asia 2024的分享 引言:融合数据湖与数仓的创新之路 在数字金融时代,数据已成为金融机构的核心竞争力。杭银消费金…...

WebRTC从入门到实践 - 零基础教程
WebRTC从入门到实践 - 零基础教程 目录 WebRTC简介 基础概念 工作原理 开发环境搭建 基础实践 三个实战案例 常见问题解答 1. WebRTC简介 1.1 什么是WebRTC? WebRTC(Web Real-Time Communication)是一个支持网页浏览器进行实时语音…...
