PK Nounique CASCADE DROP INDEX keep index
| Explicit Control Over Indexes when Creating, Disabling, or Dropping PK/Unique Constraints (Doc ID 139666.1) | 编辑To Bottom |
|
![]()
PURPOSEIn Oracle 9i, the DBA has an explicit control over how indexes are affectedwhile creating, disabling, or dropping Primary Key (PK) and unique constraints.This bulletin explains the different behaviours of indexes associated withPrimary Key or UNIQUE constraints according to the new clauses used when you execute one of the following commands:CREATE TABLE ... PRIMARY KEY/UNIQUEALTER TABLE ... DISABLE PRIMARY KEY/UNIQUEALTER TABLE ... DROP PRIMARY KEY/UNIQUESCOPE & APPLICATIONIt is important for DBAs to know what happens to the indexes when creating,disabling or dropping a constraint relying on an index, since indexes may have to be rebuilt after these operations. This can have two consequences:- Indexes may be missing for the Cost Based Optimizer (CBO) if the DBA thinks that the index was not dropped. This can have a major impact on performance.- Index rebuilding takes time.Explicit control over INDEXES when DISABLING/DROPPING PK, Unique constraints:
=============================================================================A. Creation of Primary Key/Unique constraints and associated index ----------------------------------------------------------------In the following views, depending on the way you created the Primary Key (PK)or UNIQUE constraint and its associated index, you get these different combinations:+-----------------+ +------------+| DBA_CONSTRAINTS | | DBA_INDEXES|+-----------------+ +------------+----------------------------- ------------Constraint_name Index_name Index_name--------------- ------------- ------------
Case 1: Create constraint, and index PK_EMP_ID EMP_ID_IX EMP_ID_IX explicitely within the samestatement.Case 2: Create constraint, and index PK_EMP_ID PK_EMP_ID PK_EMP_ID implicitely within the same statement.Case 3: Create constraint and index PK_EMP_ID - EMP_ID_IX separately within twostatements.Enable the constraint. PK_EMP_ID EMP_ID_IX EMP_ID_IX-------------------------------------------------------------------------
Case 1: Create constraint and index explicitely within the same statement
-------------------------------------------------------------------------SQL> drop table <OWNER>.<TABLE_NAME>
Table dropped.SQL> create table <OWNER>.<TABLE_NAME>(emp_id NUMBERCONSTRAINT pk_emp_id PRIMARY KEY USING INDEX(CREATE INDEX <OWNER>.emp_id_ix ON <OWNER>.<TABLE_NAME>(emp_id)TABLESPACE indx),ename VARCHAR2(12),sal number);Table created.SQL> select index_name,uniqueness from dba_indexes where table_name='<TABLE_NAME>';INDEX_NAME UNIQUENES------------------------------ ---------EMP_ID_IX NONUNIQUESQL> select constraint_name,index_name, constraint_type from dba_constraintswhere table_name='<TABLE_NAME>' and constraint_type='P';CONSTRAINT_NAME INDEX_NAME C------------------------------ ------------------------------ -PK_EMP_ID EMP_ID_IX P-------------------------------------------------------------------------
Case 2: Create constraint and index implicitely within the same statement
-------------------------------------------------------------------------SQL> drop table <OWNER>.<TABLE_NAME>
Table dropped.SQL> create table <OWNER>.<TABLE_NAME>(emp_id NUMBERCONSTRAINT pk_emp_id PRIMARY KEY USING INDEX TABLESPACE indx,ename VARCHAR2(12),sal number);Table created.SQL> select index_name,uniqueness from dba_indexes where table_name='<TABLE_NAME>';INDEX_NAME UNIQUENES------------------------------ ---------PK_EMP_ID UNIQUESQL> select constraint_name,index_name, constraint_type from dba_constraintswhere table_name='<TABLE_NAME>' and constraint_type='P';CONSTRAINT_NAME INDEX_NAME C------------------------------ ------------------------------ -PK_EMP_ID PK_EMP_ID P--------------------------------------------------------------------
Case 3: Create constraint and index separately within two statements
--------------------------------------------------------------------SQL> drop table <OWNER>.<TABLE_NAME>
Table dropped.SQL> create table <OWNER>.<TABLE_NAME>(emp_id NUMBERCONSTRAINT pk_emp_id PRIMARY KEY DISABLE,ename VARCHAR2(12),sal number);Table created.SQL> create index <OWNER>.emp_id_ix on <OWNER>.<TABLE_NAME>(emp_id)tablespace indx;
Index created.SQL> select index_name,uniqueness from dba_indexes where table_name='<TABLE_NAME>';INDEX_NAME UNIQUENES------------------------------ ---------EMP_ID_IX NONUNIQUESQL> select constraint_name,index_name, constraint_type from dba_constraintswhere table_name='<TABLE_NAME>' and constraint_type='P';CONSTRAINT_NAME INDEX_NAME C------------------------------ ------------------------------ -PK_EMP_ID PSQL> alter table <OWNER>.<TABLE_NAME> ENABLE constraint pk_emp_id;
Table altered.SQL> select index_name,uniqueness from dba_indexes where table_name='<TABLE_NAME>';INDEX_NAME UNIQUENES------------------------------ ---------EMP_ID_IX NONUNIQUESQL> select constraint_name,index_name, constraint_type from dba_constraintswhere table_name='<TABLE_NAME>' and constraint_type='P';CONSTRAINT_NAME INDEX_NAME C------------------------------ ------------------------------ -PK_EMP_ID EMP_ID_IX PB. Disabling PK/UNIQUE constraints: what happens to the associated index ---------------------------------------------------------------------In Case 1 where the index was created explicitely within the same statementas the constraint, the index is in both cases disassociated from the constraint; depending on the clause "CASCADE DROP INDEX" usage, the index is dropped or not.In traditionnal Case 2, the behavior remains the same: using the clause "CASCADE DROP INDEX" or not does not influence the usual behavior: it automatically drops the relying index.In case 3, disabling the constraint drops the index or not: * if the constraint has never been enabled, it never drops the index.* but in most cases, the constraint has been enabled for some time. In this case, the clause "CASCADE DROP INDEX" drops the index.+-----------------+ +------------+| DBA_CONSTRAINTS | | DBA_INDEXES|+-----------------+ +------------+----------------------------- ------------Constraint_name Index_name Index_name--------------- ------------- ------------
Case 1: ALTER TABLE ... DISABLE PK PK_EMP_ID - - CASCADE DROP INDEX;orALTER TABLE ... DISABLE PK; PK_EMP_ID - EMP_ID_IX Case 2: ALTER TABLE ... DISABLE PK PK_EMP_ID - - CASCADE DROP INDEX;or ALTER TABLE ... DISABLE PK; PK_EMP_ID - - Case 3: ALTER TABLE ... DISABLE PK PK_EMP_ID - - CASCADE DROP INDEX;or ALTER TABLE ... DISABLE PK; PK_EMP_ID - EMP_ID_IXC. Dropping PK/UNIQUE constraints: what happens to the associated index ---------------------------------------------------------------------In Case 1, where the index was created explicitely within the same statementas the constraint, the index is by default KEPT when the constraint is dropped.If you want the index to be dropped, you have to explicitely ask for it through the "DROP INDEX" clause.In case 2, the behavior is the opposite: if you want the index to be kept and the constraint dropped, you have to explicitly ask for it with the "KEEP INDEX" clause; otherwise the index is DROPPED by default.In Case 3, dropping the constraint drops the index or not: * if the constraint has never been enabled, it never drops the index.* but in most cases, the constraint has been enabled for some time. Then the index is by default KEPT when the constraint is dropped. If you want the index to be dropped, you have to explicitly ask for it with the "DROP INDEX" clause.+-----------------+ +-----------+| DBA_CONSTRAINTS | |DBA_INDEXES|+-----------------+ +-----------+----------------------- ------------Constraint Index_name Index_name----------- ----------- ------------
Case 1: ALTER TABLE ... DROP PK DROP INDEX; - - -
Case 1: ALTER TABLE ... DROP PK KEEP INDEX; - - EMP_ID_IX
Case 1: ALTER TABLE ... DROP PK; - - EMP_ID_IX Case 2: ALTER TABLE ... DROP PK DROP INDEX; - - -
Case 2: ALTER TABLE ... DROP PK KEEP INDEX; - - PK_EMP_ID
Case 2: ALTER TABLE ... DROP PK; - - - Case 3: ALTER TABLE ... DROP PK DROP INDEX; - - -
Case 3: ALTER TABLE ... DROP PK KEEP INDEX; - - EMP_ID_IX
Case 3: ALTER TABLE ... DROP PK; - - EMP_ID_IX |
相关文章:

PK Nounique CASCADE DROP INDEX keep index
Explicit Control Over Indexes when Creating, Disabling, or Dropping PK/Unique Constraints (Doc ID 139666.1)编辑To Bottom PURPOSEIn Oracle 9i, the DBA has an explicit control over how indexes are affectedwhile creating, disabling, or dropping Primary Ke…...

【Antd】实现Table组件行点击,解决某一列不触发行点击
今天有个新需求,点击table行,执行一些操作。实现过程中遇到了:点击操作列、操作列内按钮会冒泡触发行点击。antd版本:1.7.8 一、解决方案 customRow <a-table :customRow"handleClickRow" :data-source"data_li…...
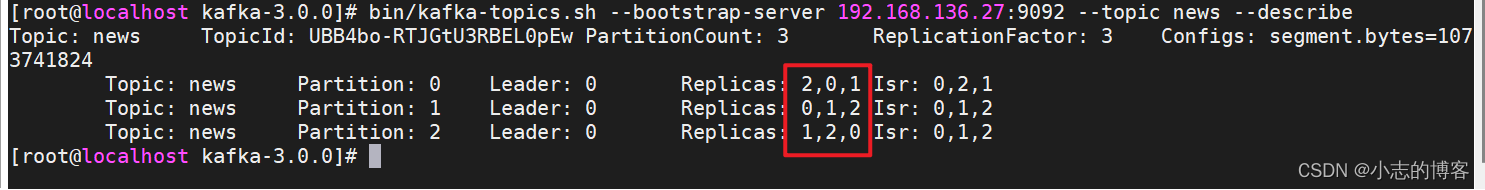
Kafka3.0.0版本——Broker( 退役旧节点)示例
目录 一、服务器信息二、先启动4台zookeeper,再启动4台kafka三、通过PrettyZoo工具验证启动的kafka是否ok四、查看4台kafka集群节点上是否存在创建的名称为news的主题五、退役旧节点5.1、执行负载均衡操作5.2、 执行停止命令5.3、再次查看kafka中的创建过的名称为ne…...
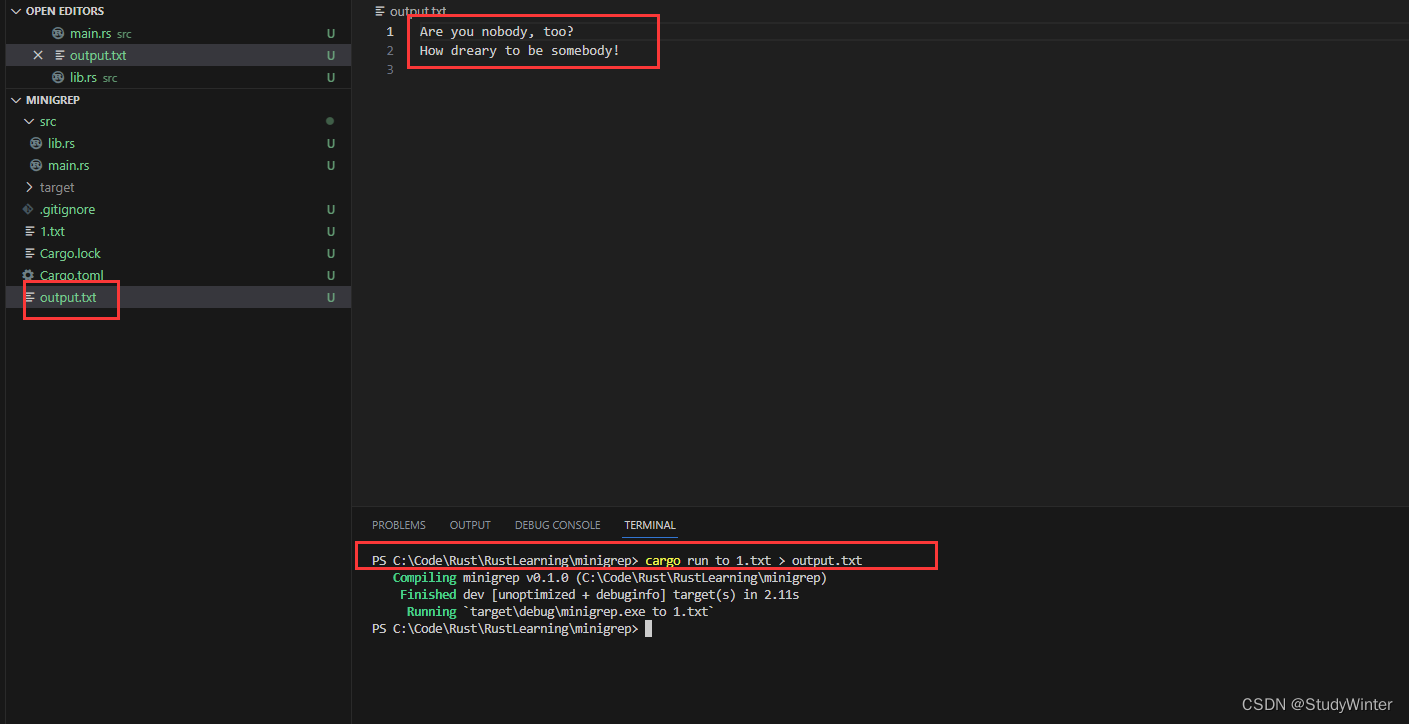
【Rust】Rust学习 第十二章一个 I/O 项目:构建一个命令行程序
本章既是一个目前所学的很多技能的概括,也是一个更多标准库功能的探索。我们将构建一个与文件和命令行输入/输出交互的命令行工具来练习现在一些你已经掌握的 Rust 技能。 Rust 的运行速度、安全性、单二进制文件输出和跨平台支持使其成为创建命令行程序的绝佳选择…...
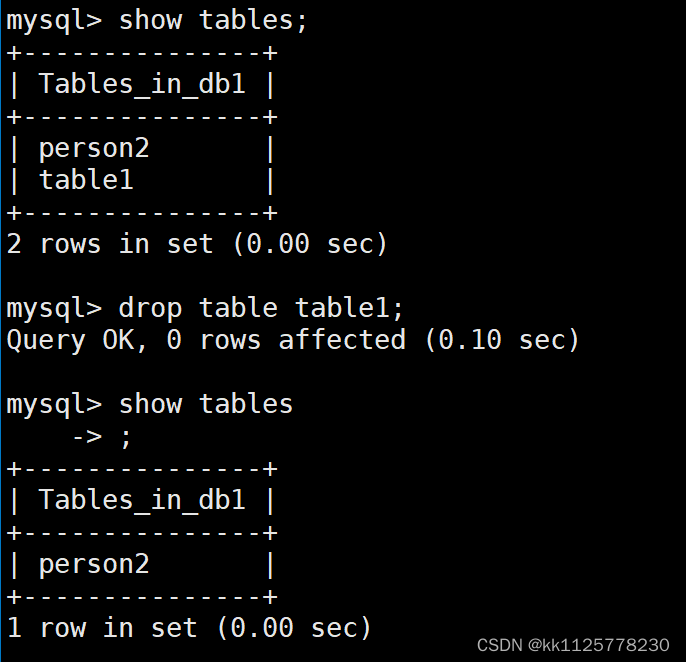
【MySQL--->表的操作】
文章目录 [TOC](文章目录) 一、创建表二、查看表三、修改表四、删除表drop table 表名;  一、创建表 语句格式:create table 表名(列名 类型,…)字符集 校验规则 存储引擎;字符集和校…...
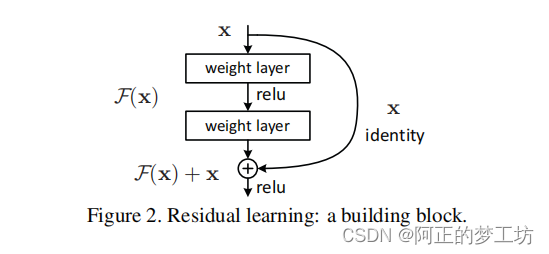
PyTorch从零开始实现ResNet
文章目录 代码实现参考 代码实现 本文实现 ResNet原论文 Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition 中的50层,101层和152层残差连接。 代码中使用基础残差块这个概念,这里的基础残差块指的是上图中红色矩形圈出的内容:从上到下分别使用…...
企业微信 企业内部开发 学习笔记
官方文档 文档 术语介绍 引入pom <dependency><groupId>com.github.binarywang</groupId><artifactId>wx-java-cp-spring-boot-starter</artifactId><version>4.5.3.B</version></dependency>核心代码 推送消息 final WxCp…...

03 QT基本控件和功能类
一 进度条 、水平滑动条 垂直滑动条 当在QT中,在已知类名的情况下,要了解类的构造函数 常用属性 及 信号和槽 常用api 特征:可以获取当前控件的值和设置它的当值 ---- int ui->progressBar->setValue(value); //给进度条设置一个整型值 ui->progressBar->value…...
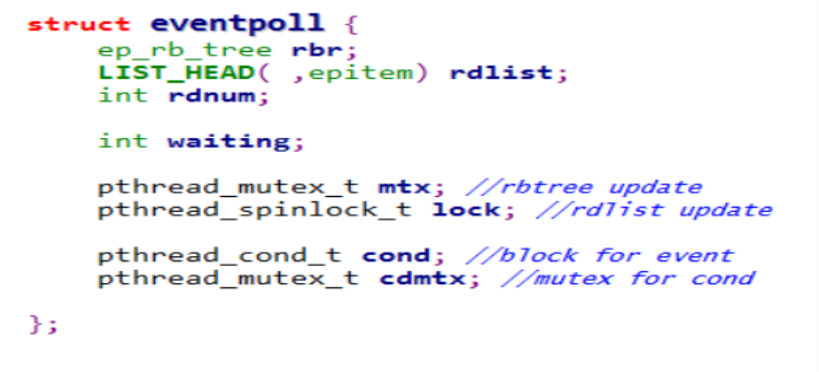
epoll数据结构
目录 1.大量的fd 集合。选择什么数据结构?2、Epoll 数据结构Epitem 的定义Eventpoll 的定义 1.大量的fd 集合。选择什么数据结构? 查找频率很高的数据结构 1.红黑树 2.哈希(扩容缩容) 3. b/btree (降低树的高度&#…...

LINUX学习笔记_GIT操作命令
LINUX学习笔记 GIT操作命令 基本命令 git init:初始化仓库git status:查看文件状态git add:添加文件到暂存区(index)git commit -m “注释”:提交文件到仓库(repository)git log&a…...

第一百二十九天学习记录:数据结构与算法基础:栈和队列(中)(王卓教学视频)
栈的表示和实现 顺序栈的初始化 ##入栈 链栈的表示...
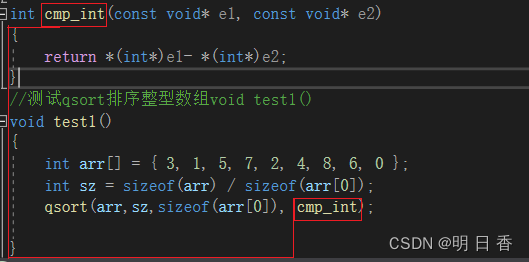
C语言 — qsort 函数
介绍:qsort是一个库函数,用来对数据进行排序,可以排序任意类型的数据。 void qsort (void*base, size_t num, size_t size, int(*compart)(const void*,constvoid*) ) qsort 具有四个参数: …...

开放式耳机哪个好一点?推荐几款优秀的开放式耳机
在追求更广阔的音场和更真实的音质时,开放式耳机是绝对值得考虑的选择。它们以其通透感和自然的音质而备受推崇,带来更逼真的音乐体验。下面我来推荐几款优秀的开放式耳机,满足你对音质和舒适度的要求,可尽情享受音乐的魅力。 一…...
vue-cli前端工程化——创建vue-cli工程 router版本的创建 目录结构 案例初步
目录 引出创建vue-cli前端工程vue-cli是什么自动构建创建vue-cli项目选择Vue的版本号 手动安装进行选择创建成功 手动创建router版多了一个router 运行测试bug解决 Vue项目结构main.jspackage.jsonvue.config.js Vue项目初步hello案例 总结 引出 1.vue-cli是啥,创建…...

Go和Java实现外观模式
Go和Java实现外观模式 下面我们通过一个构造各种形状的案例来说明外观模式的使用。 1、外观模式 外观模式隐藏系统的复杂性,并向客户端提供了一个客户端可以访问系统的接口。这种类型的设计模式属于结构型 模式,它向现有的系统添加一个接口ÿ…...

人工智能(一)基本概念
人工智能之基本概念 常见问题什么是人工智能?人工智能应用在那些地方?人工智能的三种形态图灵测试是啥?人工智能、机器学习和深度学习之间是什么关系?为什么人工智能计算会用到GPU? 机器学习什么是机器学习?…...

〔AI 绘画〕Stable Diffusion 之 解决绘制多人或面部很小的人物时面部崩坏问题 篇
✨ 目录 🎈 脸部崩坏🎈 下载脸部修复插件🎈 启用脸部修复插件🎈 插件生成效果🎈 插件功能详解 🎈 脸部崩坏 相信很多人在画图时候,特别是画 有多个人物 图片或者 人物在图片中很小 的时候&…...
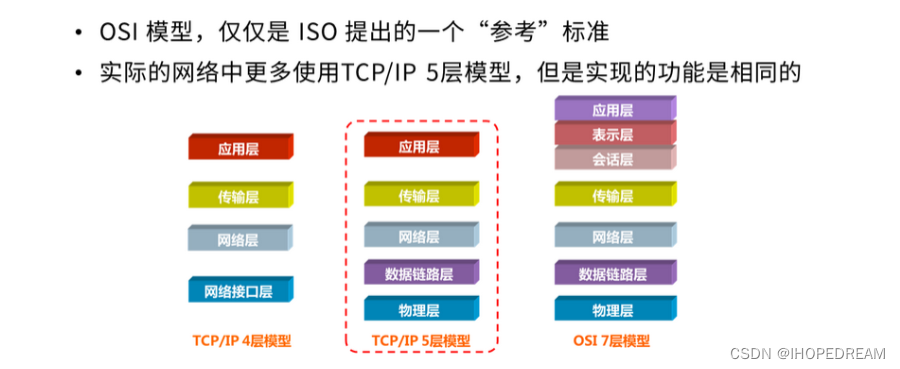
初步认识OSI/TCP/IP一(第三十八课)
1 初始OSI模型 OSI参考模型(Open Systems Interconnection Reference Model)是一个由国际标准化组织(ISO)和国际电报电话咨询委员会(CCITT)联合制定的网络通信协议规范,它将网络通信分为七个不同的层次,每个层次负责不同的功能和任务。 2 网络功能 数据通信、资源共享…...

英伟达结构化剪枝工具Nvidia Apex Automatic Sparsity [ASP](2)——代码分析
伟达结构化剪枝工具Nvidia Apex Automatic Sparsity [ASP](2)——代码分析 ASP整个模块的结果如下: . ├── COPYRIGHT ├── README.md ├── __init__.py ├── asp.py ├── permutation_lib.py ├── permutation_search_kernels…...

FileNotFoundError: [WinError 2] 系统找不到指定的文件。
pyspark demo程序创建spark上下文 完整报错如下: sc SparkContext(“local”, “Partition ID Example”) File “C:\ProgramData\anaconda3\envs\python36\lib\site-packages\pyspark\context.py”, line 133, in init SparkContext._ensure_initialized(self, ga…...
结构体的进阶应用)
基于算法竞赛的c++编程(28)结构体的进阶应用
结构体的嵌套与复杂数据组织 在C中,结构体可以嵌套使用,形成更复杂的数据结构。例如,可以通过嵌套结构体描述多层级数据关系: struct Address {string city;string street;int zipCode; };struct Employee {string name;int id;…...
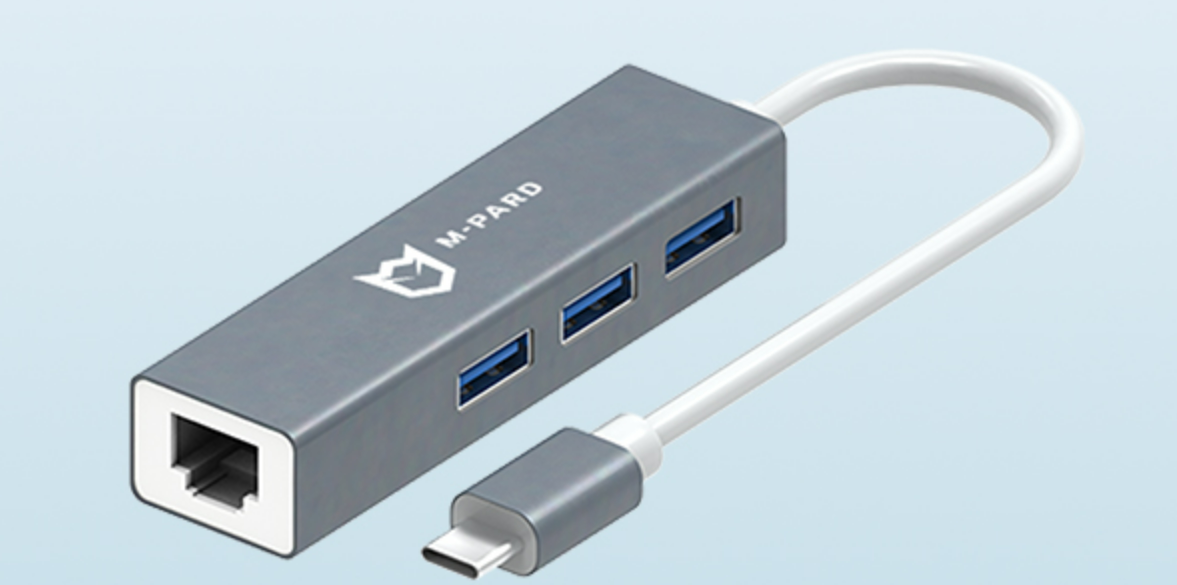

铭豹扩展坞 USB转网口 突然无法识别解决方法
当 USB 转网口扩展坞在一台笔记本上无法识别,但在其他电脑上正常工作时,问题通常出在笔记本自身或其与扩展坞的兼容性上。以下是系统化的定位思路和排查步骤,帮助你快速找到故障原因: 背景: 一个M-pard(铭豹)扩展坞的网卡突然无法识别了,扩展出来的三个USB接口正常。…...
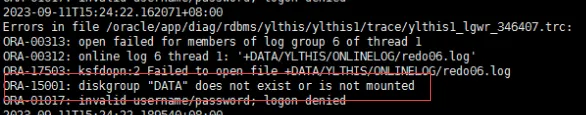
19c补丁后oracle属主变化,导致不能识别磁盘组
补丁后服务器重启,数据库再次无法启动 ORA01017: invalid username/password; logon denied Oracle 19c 在打上 19.23 或以上补丁版本后,存在与用户组权限相关的问题。具体表现为,Oracle 实例的运行用户(oracle)和集…...

内存分配函数malloc kmalloc vmalloc
内存分配函数malloc kmalloc vmalloc malloc实现步骤: 1)请求大小调整:首先,malloc 需要调整用户请求的大小,以适应内部数据结构(例如,可能需要存储额外的元数据)。通常,这包括对齐调整,确保分配的内存地址满足特定硬件要求(如对齐到8字节或16字节边界)。 2)空闲…...

QMC5883L的驱动
简介 本篇文章的代码已经上传到了github上面,开源代码 作为一个电子罗盘模块,我们可以通过I2C从中获取偏航角yaw,相对于六轴陀螺仪的yaw,qmc5883l几乎不会零飘并且成本较低。 参考资料 QMC5883L磁场传感器驱动 QMC5883L磁力计…...

uni-app学习笔记二十二---使用vite.config.js全局导入常用依赖
在前面的练习中,每个页面需要使用ref,onShow等生命周期钩子函数时都需要像下面这样导入 import {onMounted, ref} from "vue" 如果不想每个页面都导入,需要使用node.js命令npm安装unplugin-auto-import npm install unplugin-au…...

工业自动化时代的精准装配革新:迁移科技3D视觉系统如何重塑机器人定位装配
AI3D视觉的工业赋能者 迁移科技成立于2017年,作为行业领先的3D工业相机及视觉系统供应商,累计完成数亿元融资。其核心技术覆盖硬件设计、算法优化及软件集成,通过稳定、易用、高回报的AI3D视觉系统,为汽车、新能源、金属制造等行…...

【C++从零实现Json-Rpc框架】第六弹 —— 服务端模块划分
一、项目背景回顾 前五弹完成了Json-Rpc协议解析、请求处理、客户端调用等基础模块搭建。 本弹重点聚焦于服务端的模块划分与架构设计,提升代码结构的可维护性与扩展性。 二、服务端模块设计目标 高内聚低耦合:各模块职责清晰,便于独立开发…...
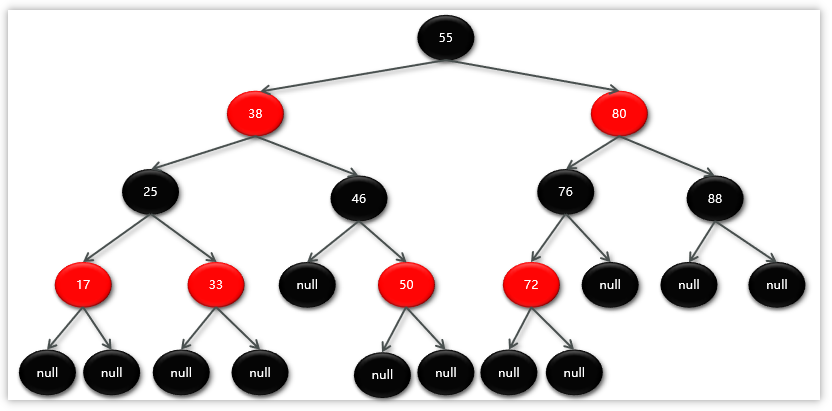
Map相关知识
数据结构 二叉树 二叉树,顾名思义,每个节点最多有两个“叉”,也就是两个子节点,分别是左子 节点和右子节点。不过,二叉树并不要求每个节点都有两个子节点,有的节点只 有左子节点,有的节点只有…...

Java线上CPU飙高问题排查全指南
一、引言 在Java应用的线上运行环境中,CPU飙高是一个常见且棘手的性能问题。当系统出现CPU飙高时,通常会导致应用响应缓慢,甚至服务不可用,严重影响用户体验和业务运行。因此,掌握一套科学有效的CPU飙高问题排查方法&…...
