02-C++数据类型-高级
数据类型-高级
4、复合类型
4.4、结构简介
struct inflatable
{char name[20];float vol;double price;
};inflatable vincent; //C++
struct inflatable goose; //C
例子
// structur.cpp -- a simple structure
#include <iostream>
struct inflatable // structure declaration
{char name[20];float volume;double price;
};int main()
{using namespace std;inflatable guest ={"Glorious Gloria", // name value1.88, // volume value29.99 // price value}; // guest is a structure variable of type inflatable
// It's initialized to the indicated valuesinflatable pal ={"Audacious Arthur",3.12,32.99}; // pal is a second variable of type inflatable
// NOTE: some implementations require using
// static inflatable guest =cout << "Expand your guest list with " << guest.name;cout << " and " << pal.name << "!\n";
// pal.name is the name member of the pal variablecout << "You can have both for $";cout << guest.price + pal.price << "!\n";// cin.get();return 0;
}
/*
Expand your guest list with Glorious Gloria and Audacious Arthur!
You can have both for $62.98!
*/
外部声明可以被其后面的任何函数使用,而内部声明只能被该声明所属的函数使用。通常使用外部声明,这样所有函数都可以使用这种类型的结构。

变量也可以在函数内部和外部定义,外部变量由所有的函数共享。C++不提倡使用外部变量,但提倡使用外部结构的声明。
结构的赋值
可以使用赋值运算符(=)将结构A赋给另一个同类型的结构B。这样结构中每个成员都将被设置成另一个结构中相应成员的值,即使成员是数组。这种赋值被称为成员赋值。
// assgn_st.cpp -- assigning structures
#include <iostream>struct inflatable {char name[20];float volume;double price;
};int main() {using namespace std;inflatable bouquet = {"sunflowers",0.20,12.49};inflatable choice;cout << "bouquet: " << bouquet.name << " for $";cout << bouquet.price << endl;choice = bouquet; // assign one structure to anothercout << "choice: " << choice.name << " for $";cout << choice.price << endl;// cin.get();return 0;
}
/*
bouquet: sunflowers for $12.49
choice: sunflowers for $12.49
*/
结构体数组
// arrstruc.cpp -- an array of structures
#include <iostream>struct inflatable {char name[20];float volume;double price;
};int main() {using namespace std;inflatable guests[2] = { // initializing an array of structs{"Bambi", 0.5, 21.99}, // first structure in array{"Godzilla", 2000, 565.99} // next structure in array};cout << "The guests " << guests[0].name << " and " << guests[1].name<< "\nhave a combined volume of "<< guests[0].volume + guests[1].volume << " cubic feet.\n";// cin.get();return 0;
}
/*
The guests Bambi and Godzilla
have a combined volume of 2000.5 cubic feet.
*/
结构中的位字段
与C语言一样,C++也允许指定占用特定位数的结构成员,这使得创建于某个硬件设备上的寄存器对应的数据结构非常方便。
struct torgle_register
{unsigned int SN :4;unsigned int :4;bool goodIn:1bool goodTorgle:1;
}
4.5、共用体
共同体是一种数据格式,它能够存储不同的数据类型,但只能同时存储其中的一种类型。也就是说,结构可以同时存储int、long、double,共用体只能存储int、long或double。
union one4all
{int int_val;long long_val;double double_val;
};struct widget
{char brand[20];int type;union id{long id_num;char id_char[20];}id_val;
};
widget prize;
if(prize.type==1)cin>>prize.id_val.id_num;
elsecin>>prize.id_val.id_char;//匿名共用体没有名称,其成员将成为位于相同地址处的变量
struct widget
{char brand[20];int type;union {long id_num;char id_char[20];};
};
widget prize;
if(prize.type==1)cin>>prize.id_num;
elsecin>>prize.id_char;
4.6、枚举
enum spectnum{red, orange, yellow, green, blue, violet, indigo, yyuu};spectnum band;
band=blue; //valid
band=2000; //invalidband=orange; //valid
++band; //invalid
band=orange + red; //invalidint color =blue; //valid
band =3; //invalid
color=3+red; //valid, red converted to intband = spectnum(3); //强转
枚举的取值范围
enum bits{one=1, two=2, four=4, eight=8};
bits myflag;
myflag=bits(6); //valid,because 6 is in bits range
范围,最大值、最小值所对应的2次幂-1(负数:+1)
4.7、指针和自由存储空间
// address.cpp -- using the & operator to find addresses
#include <iostream>int main() {using namespace std;int donuts = 6;double cups = 4.5;cout << "donuts value = " << donuts;cout << " and donuts address = " << &donuts << endl;
// NOTE: you may need to use unsigned (&donuts)
// and unsigned (&cups)cout << "cups value = " << cups;cout << " and cups address = " << &cups << endl;// cin.get();return 0;
}
/*
donuts value = 6 and donuts address = 0x62fe1c
cups value = 4.5 and cups address = 0x62fe10
*/
指针与C++基本原理
面向对象编程与传统的过程性编程的区别在于,OOP强调的是在运行阶段(而不是编译阶段)进行决策。运行阶段指的是程序正在运行时,编译阶段指的是编译器将程序组合起来时。运行阶段觉得就好比度假时,选择参观哪些景点取决于天气和当时的心情;而编译阶段决策更像不管在什么条件下,都坚持预先设定的日程安排。总之,使用OOP时,可能在运行阶段吧确定数组的长度。为使用这种方法,语言必须允许在程序运行时创建数组。C++采用的方法是,使用关键字new请求正确数量的农村以及使用指针来跟踪新分配的内存的位置。在运行阶段做决策并非OOP独有的,但使用C++编写这样的代码比使用C语言要简单很多。
指针表示的是地址。*运算符被称为间接值或解除引用运算符,将其应用与指针,可以得到该地址处存储的值。
// pointer.cpp -- our first pointer variable
#include <iostream>int main() {using namespace std;int updates = 6; // declare a variableint *p_updates; // declare pointer to an intp_updates = &updates; // assign address of int to pointer// express values two wayscout << "Values: updates = " << updates;cout << ", *p_updates = " << *p_updates << endl;// express address two wayscout << "Addresses: &updates = " << &updates;cout << ", p_updates = " << p_updates << endl;// use pointer to change value*p_updates = *p_updates + 1;cout << "Now updates = " << updates << endl;// cin.get();return 0;
}
/*
Values: updates = 6, *p_updates = 6
Addresses: &updates = 0x62fe14, p_updates = 0x62fe14
Now updates = 7
*/
对于指针,&取地址运算符;*解除引用运算符。有以下的图
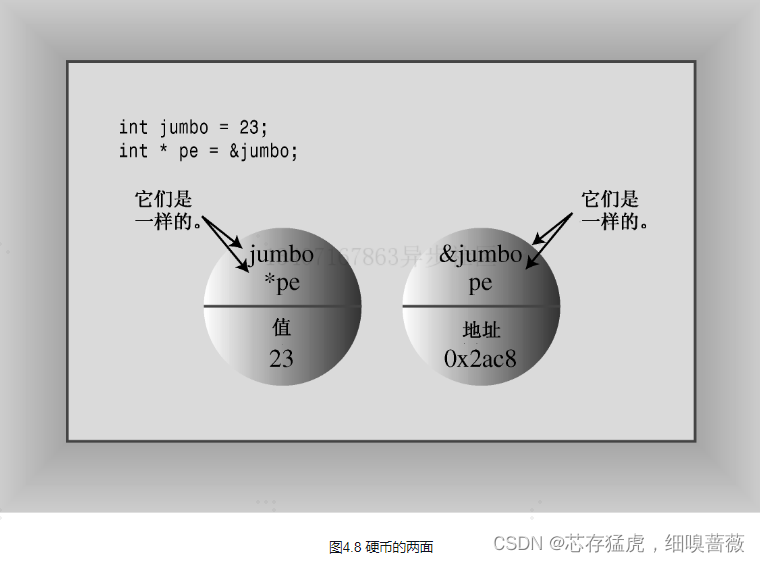
指针初始化
int * p_updates;int *ptr; //*ptr是一个int类型的值
int* ptr; //指针ptr指向int类型;ptr的类型是指针int的指针int* p1,p2; //一个指针(p1)和一个int变量(p2)double* tax_ptr;//指向double的指针
char* str; //指向char的指针
**注意:**在C++中,int*是一种复合类型,是指向int的指针
和数组一样,指针都是基于其他类型的。虽然tax_ptr和str指向两种长度不同的数据类型,但这两个变量本身的长度通常是相同的。也就是说,char的地址和double的地址的长度相同。
可以在声明语句中初始化指针。
//被初始化的是指针,而不是它指向的值
int higgens=5;
int* pt=&higgens;
// init_ptr.cpp -- initialize a pointer
#include <iostream>int main() {using namespace std;int higgens = 5;int *pt = &higgens;cout << "Value of higgens = " << higgens<< "; Address of higgens = " << &higgens << endl;cout << "Value of *pt = " << *pt<< "; Value of pt = " << pt << endl;// cin.get();return 0;
}/*
Value of higgens = 5; Address of higgens = 0x62fe14
Value of *pt = 5; Value of pt = 0x62fe14
*/
指针的危险
在C++中创建指针时,计算机将分配用来存储地址的内存,但不会分配用来存储指针所指向的数据的内存。为数据提供空间是一个独立的步骤。
long *fwllow;
*fwllow=23455556; //invalid
警告
一定要在对指针应用解除引用运算符(*)之前,将指针初始化为一个确定的、适当的地址。
int* pt;
pt=0xB8000000; //type mismatch
//要将数字值作为地址来使用,应通过强制类型转换将数字转换为适当的地址类型
pt=(int*)0xB8000000; //type now match
new&delete
- 可以使用new来分配内存
//方式1
int* pn=new int;//方式2
int higgens;
int* pt=&higgens;
都是将一个int变量的地址赋给了指针。第2种情况下,可以通过名称higgens来访问该int,在第1种情况下,只能通过该指针进行访问。
// use_new.cpp -- using the new operator
#include <iostream>
int main()
{using namespace std;int nights = 1001;int *pt = new int; // allocate space for an int*pt = 1001; // store a value therecout << "nights value = ";cout << nights << ": location " << &nights << endl;cout << "int ";cout << "value = " << *pt << ": location = " << pt << endl;double *pd = new double; // allocate space for a double*pd = 10000001.0; // store a double therecout << "double ";cout << "value = " << *pd << ": location = " << pd << endl;cout << "location of pointer pd: " << &pd << endl;cout << "size of pt = " << sizeof(pt);cout << ": size of *pt = " << sizeof(*pt) << endl;cout << "size of pd = " << sizeof pd;cout << ": size of *pd = " << sizeof(*pd) << endl;// cin.get();return 0;
}
/*
nights value = 1001: location 0x62fe14
int value = 1001: location = 0x26d6710
double value = 1e+07: location = 0x26d6cf0
location of pointer pd: 0x62fe08
size of pt = 8: size of *pt = 4
size of pd = 8: size of *pd = 8
*/
- 使用delete释放内存
int* ps= new int; //allocate memory with new
.... //use the memory
delete ps; //free memory with delete when done
这将释放ps指向的内存,但不会删除指针ps本身。例如,可以将ps重新指向另一个新分配的内存块。一定要配对得使用new和delete。
不要尝试释放已经释放的内存块。另外,不能使用delete来释放声明变量所获得的内存:
int *ps=new int;
delete ps;
delete ps; //not ok nowint jugs=5;
int* pi=&jugs; //ok
delete pi; //not allowed
警告:
智能用delete来释放使用new分配的内存。然而,对空指针使用delete是安全的。
int* ps=new int;
int* pq=ps;
delete pq;
一般来说,不要创建两个指向同一个内存块的指针,因为这将增加错误地删除同一个内存块两次的可能性。
- 使用new来创建动态数组
int* psome=new int[10];
delete [] psome;
//分配内存的通用格式
type_name* pointer_name =new type_name[size];
使用new和delete时,应遵守以下规则
- 不要使用delete来释放不是new分配的内存
- 不要使用delete释放同一个内存块两次
- 如果使用new[]为数组分配内存,则应使用delete[]来释放
- 如果使用new为一个实体分配内存,则应使用delete(没有方括号)来释放
- 对空指针应用delete是安全的
// arraynew.cpp -- using the new operator for arrays
#include <iostream>int main() {using namespace std;double *p3 = new double [3]; // space for 3 doublesp3[0] = 0.2; // treat p3 like an array namep3[1] = 0.5;p3[2] = 0.8;cout << "p3[1] is " << p3[1] << ".\n";p3 = p3 + 1; // increment the pointercout << "Now p3[0] is " << p3[0] << " and ";cout << "p3[1] is " << p3[1] << ".\n";p3 = p3 - 1; // point back to beginningdelete [] p3; // free the memory// cin.get();return 0;
}
/*
p3[1] is 0.5.
Now p3[0] is 0.5 and p3[1] is 0.8.
*/
不能修改数组名的值,但指针时变量,可以修改它的值。
4.8、指针、数组和指针算术
指针和数组等价的原因在于指针算术和C++内部处理数组的方式。
C++将数组名解释为地址。
// addpntrs.cpp -- pointer addition
#include <iostream>int main() {using namespace std;double wages[3] = {10000.0, 20000.0, 30000.0};short stacks[3] = {3, 2, 1};// Here are two ways to get the address of an arraydouble *pw = wages; // name of an array = addressshort *ps = &stacks[0]; // or use address operator =stacks
// with array elementcout << "pw = " << pw << ", *pw = " << *pw << endl;pw = pw + 1;cout << "add 1 to the pw pointer:\n";cout << "pw = " << pw << ", *pw = " << *pw << "\n\n";cout << "ps = " << ps << ", *ps = " << *ps << endl;ps = ps + 1;cout << "add 1 to the ps pointer:\n";cout << "ps = " << ps << ", *ps = " << *ps << "\n\n";cout << "access two elements with array notation\n";cout << "stacks[0] = " << stacks[0]<< ", stacks[1] = " << stacks[1] << endl;cout << "access two elements with pointer notation\n";cout << "*stacks = " << *stacks<< ", *(stacks + 1) = " << *(stacks + 1) << endl;cout << sizeof(wages) << " = size of wages array\n";cout << sizeof(pw) << " = size of pw pointer\n";// cin.get();return 0;
}
/*
pw = 0x62fdf0, *pw = 10000
add 1 to the pw pointer:
pw = 0x62fdf8, *pw = 20000ps = 0x62fdea, *ps = 3
add 1 to the ps pointer:
ps = 0x62fdec, *ps = 2access two elements with array notation
stacks[0] = 3, stacks[1] = 2
access two elements with pointer notation
*stacks = 3, *(stacks + 1) = 2
24 = size of wages array
8 = size of pw pointer
*/
对于指针的加法
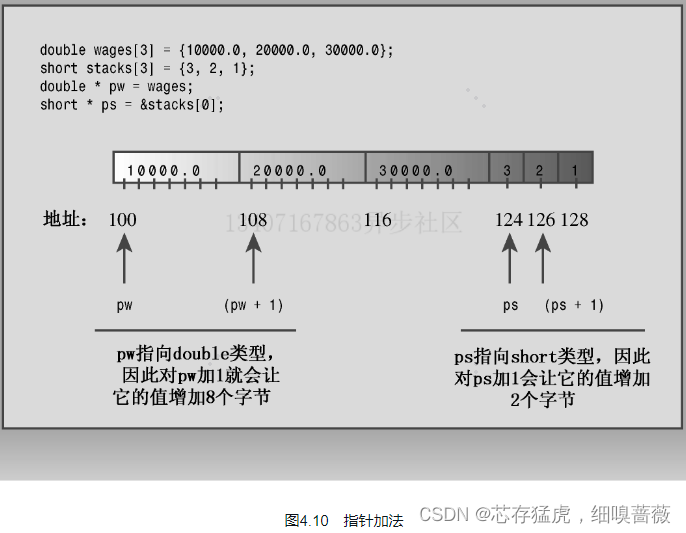
注意:
将指针变量加1后,其增加的值等于指向的类型占用的字节数。
通常,使用数组表示法时,C++都执行下面的转换
arrayname[i] becomes *(arrayname+i)
如果使用的指针,而不是数组名,则C++也将执行同样的转换
pointername[i] becomes *(pointername+i)
因此,在很多情况下,可以相同的方式使用指针名和数组名。对于它们,可以使用数组方括号表示法,也可以使用解除引用运算符(*)。在多数表达式中,它们都表示地址。区别之一是,可以修改指针的值,而数组名是常量:
pointername=pointername+1; //valid
arrayname=arrayname+1; //not allow
另一个区别是,对数组应用sizeof运算符得到的是数组的长度,而对指针应用sizeof得到的是指针的长度,即使指针指向的是一个数组。
数组的指针
short tell[10];
cout<<tell; //displays &tell[0]
cout<<&tell; //displays address of whole array
从数字上说,两个地址是相同的;但从概念上说,&tell[0](即tell)是一个2字节内存块的地址,而&tell是一个20字节内存块的地址。换句话说,tell是一个short指针(short*),而&tell是一个这样的指针,即指向包含10个元素的short数组(short( * )[10])。
short(*pas)[10]=&tell;
指针小结
- 声明指针
typeName* pointerName;
double* pn;
char* pc;
- 给指针赋值
应将内存地址赋给指针。可以对变量名应用 &运算符,来获得被命名的内存的地址,new运算符返回未命名的内存的地址。
double* pn;
double* pa;
char *pc;
double bubble=3.2;pn=&bubble;
pc=new char;
pa=new double[30];
- 对指针解除引用
cout<< *pn; //3.2
*pc='s';
另一种对指针解除引用的方法是使用数组表示法,例如,pn[0]与*pn是一样的。决不要对未被初始化为适当地址的指针解除引用。
- 区分指针和指针所指向的值
int* pt=new int; //assigns an address to the pointer pt
*pt=5; //stores the value 5 at that address
- 数组名
在多数情况下,C++将数组名视为数组的第1个元素的地址
int tacos[10];
- 指针算术
C++允许将指针和整数相加。加1的结果等于原来的地址值加上指向的对象占用的总字节数。还可以将一个指针减去另一个指针,获得两个指针的差。
仅当两个指针指向同一个数组(也可以指向超出结尾的一个位置)时,这种运算才有意义。
int tacos[10]={5,2,8,2,3,4,5,5,6,7};
int* pt=tacos;
pt=pt+1;
int* pe=&tacos[9];
pe=pe-1;
int diff=pe-pt;
- 数组的动态联编和静态联编
//static
int tacos[10];//dynamic
int size;
cin>>size;
int *pz=new int[size];
...
delete[]pz;
- 数组表示法和指针表示法
使用方括号数组表示法等同于对指针解除引用
tacos[0]
tacos[3]
数组名和指针变量都是如此。因此对于指针和数组名,即可以使用指针表示法,也可以使用数组表示法
int *pt=new int[10];
*pt=5;
pt[0]=6;
pt[9]=44;int coats[10];
*(coats+4)=12;
指针和字符串
注意:
在cout和多数C++表达式中,char数组名、char指针以及用括号扩起来的字符串常量都被解释为字符串第一个字符的地址。
// ptrstr.cpp -- using pointers to strings
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring> // declare strlen(), strcpy()int main() {using namespace std;char animal[20] = "bear"; // animal holds bearconst char *bird = "wren"; // bird holds address of stringchar *ps; // uninitializedcout << animal << " and "; // display bearcout << bird << "\n"; // display wren// cout << ps << "\n"; //may display garbage, may cause a crashcout << "Enter a kind of animal: ";cin >> animal; // ok if input < 20 chars// cin >> ps; Too horrible a blunder to try; ps doesn't// point to allocated spaceps = animal; // set ps to point to stringcout << ps << "!\n"; // ok, same as using animalcout << "Before using strcpy():\n";cout << animal << " at " << (int *) animal << endl;cout << ps << " at " << (int *) ps << endl;ps = new char[strlen(animal) + 1]; // get new storagestrcpy(ps, animal); // copy string to new storagecout << "After using strcpy():\n";cout << animal << " at " << (int *) animal << endl;cout << ps << " at " << (int *) ps << endl;delete [] ps;// cin.get();// cin.get();return 0;
}
/*
bear and wren
Enter a kind of animal: fox
fox!
Before using strcpy():
fox at 0x62fdf0
fox at 0x62fdf0
After using strcpy():
fox at 0x62fdf0
fox at 0x2576cd0
*/
通过使用strcpy()和new,将获得"fox"的两个独立副本
经常需要将字符串放到数组中。初始化数组时,请使用=运算符;否则应使用strcpy()或strncpy()。
char food[20]="carrots"; //initalization
strcpy(food,"flan"); //otherwise
对于strncpy()
strncpy(food,"a picnic basket filled with many goodies",19);
food[19]='\0';
这样最多将19个字符复制到数组中,然后将最后一个元素设置成空字符。如果该字符串少于19个字符,则strncpy()将在复制完该字符串之后加上空字符,以 标记该字符串的结尾。
使用new创建动态结构
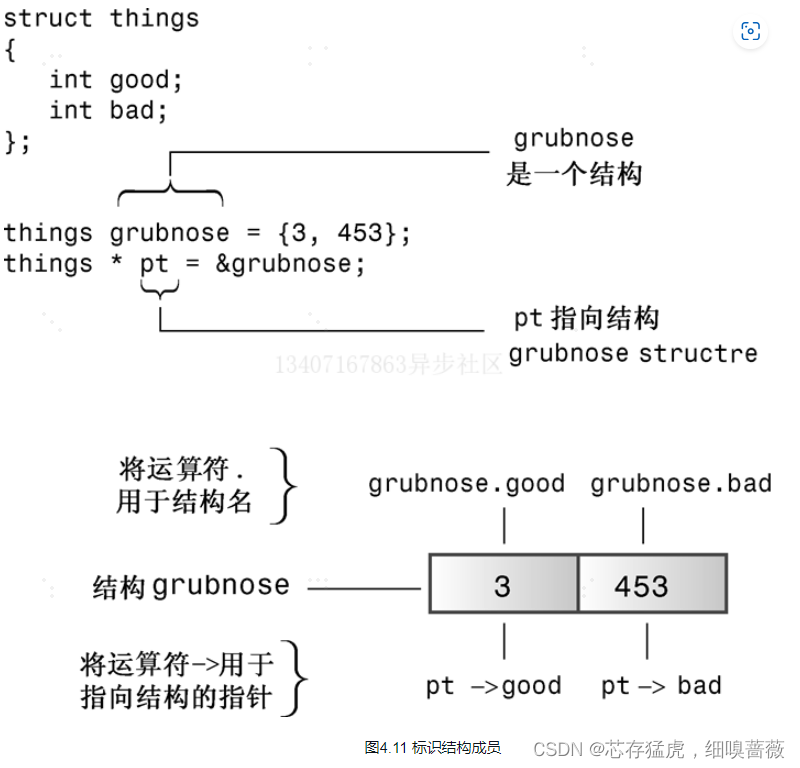
提示
如果结构标识符时结构名,则使用句点运算符;如果标识符是指向结构的指针,则使用箭头运算符。
另一种访问结构成员的方法是,如果ps是指向结构的指针,则*ps就是被指向的值——结构本身。由于*ps是一个结构,因此(*ps).price是该结构的price成员。
// newstrct.cpp -- using new with a structure
#include <iostream>struct inflatable { // structure definitionchar name[20];float volume;double price;
};int main() {using namespace std;inflatable *ps = new inflatable; // allot memory for structurecout << "Enter name of inflatable item: ";cin.get(ps->name, 20); // method 1 for member accesscout << "Enter volume in cubic feet: ";cin >> (*ps).volume; // method 2 for member accesscout << "Enter price: $";cin >> ps->price;cout << "Name: " << (*ps).name << endl; // method 2cout << "Volume: " << ps->volume << " cubic feet\n"; // method 1cout << "Price: $" << ps->price << endl; // method 1delete ps; // free memory used by structure// cin.get();// cin.get();return 0;
}
/*
Enter name of inflatable item: Fab
Enter volume in cubic feet: 1.4
Enter price: $27.99
Name: Fab
Volume: 1.4 cubic feet
Price: $27.99
*/
- 使用new和delete
// delete.cpp -- using the delete operator
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring> // or string.h
using namespace std;
char *getname(void); // function prototypeint main() {char *name; // create pointer but no storagename = getname(); // assign address of string to namecout << name << " at " << (int *) name << "\n";delete [] name; // memory freedname = getname(); // reuse freed memorycout << name << " at " << (int *) name << "\n";delete [] name; // memory freed again// cin.get();// cin.get();return 0;
}char *getname() { // return pointer to new stringchar temp[80]; // temporary storagecout << "Enter last name: ";cin >> temp;char *pn = new char[strlen(temp) + 1];strcpy(pn, temp); // copy string into smaller spacereturn pn; // temp lost when function ends
}/*
Enter last name: Fredlkin
Fredlkin at 0x726cd0
Enter last name: Pook
Pook at 0x726cd0
*/
自动存储、静态存储和动态存储
- 自动存储
在函数内部定义的常规变量使用自动存储空间,被称为自动变量,这以为着它们在所属的函数被调用时自动产生,在该函数结束时消亡。
实际上,自动变量是一个局部变量,其作用域为包含它的代码块。
自动变量通常存储在栈中。这意味着执行代码块时,其中的变量依次加入到栈中,而离开代码块时,将按相反的顺序释放这些变量。这被称为后进先出(LIFO)。因此,在程序执行的过程中,栈不断地增大和缩小。
- 静态存储
静态存储是整个程序执行期间都存在的存储方式。使变量称为静态的方式有两种:一种是在函数外面定义它;另一种是在声明变量时使用关键字static:
static double fee=56.50;
- 动态存储
new和delete运算符提供了一种比自动变量和静态变量更灵活的方法。它们管理了一个内存池,这在C++中被称为自由存储空间(free store)或堆(heap)。该内存池同用于静态变量和自动变量的内存时分开的。
new和delete让我们能够在一个函数中分配内存,在另一个函数中释放它。因此,数据的生命周期不完全受程序或函数的生存时间控制。
栈、堆和内存泄漏
如果使用了new运算符在自由存储空间(或堆)上创建变量后,没有调用delete,将会发生什么?
如果没有调用delete,则即使包含指针的内存由于作用域规则和对象生命周期的原因而被释放,在自由存储空间上动态分配的变量或结构也将继续存在。实际上,将会无法访问自由存储空间中的结构,因为指向这些内存的指针无效。这将导致内存泄漏。被泄漏的内存将在程序的整个生命周期内都不可使用;这些内存被分配出去,但无法收回。
4.9、类型组合
//结构定义
struct antarctica_year_end
{int year;
};antarctica_year_end s01,s02,s03; //创建变量
s01.year=1998; //使用成员运算符访问成员antarctica_year_end=&s02; //创建指向这种结构的指针
pa->year=1999; //使用间接成员运算符访问成员antarctica_year_end trio[3]; //创建结构数组
trio[0].year=2003; //使用成员运算符访问成员
(trio+1)->year=2004; //使用间接成员运算符const antarctica_year_end* arp[3]={&s01,&s02,&s03}; //创建指针数组
std::cout<<arp[1]->year<<std::endl; //使用间接运算符const antarctica_year_end** ppa=arp; //创建上面数组的指针 ppa=arp
std::cout<<(*ppa)->year<<std::endl; //*ppa为&s01,式子为s01的year成员
std::cout<<(*(ppb+1))->year<<std::endl;
例子
// mixtypes.cpp --some type combinations
#include <iostream>struct antarctica_years_end
{int year;/* some really interesting data, etc. */
};int main()
{antarctica_years_end s01, s02, s03; s01.year = 1998;antarctica_years_end * pa = &s02;pa->year = 1999;antarctica_years_end trio[3]; // array of 3 structurestrio[0].year = 2003;std::cout << trio->year << std::endl;const antarctica_years_end * arp[3] = {&s01, &s02, &s03};std::cout << arp[1]->year << std::endl;const antarctica_years_end ** ppa = arp; auto ppb = arp; // C++0x automatic type deduction
// or else use const antarctica_years_end ** ppb = arp; std::cout << (*ppa)->year << std::endl;std::cout << (*(ppb+1))->year << std::endl;// std::cin.get();return 0;
}
/*
2003
1999
1998
1999
*/
4.10、vector、array
vector
模板类vector类似于string类,也是一种动态数组。可以在运行阶段设置vector对象的长度,可以在末尾附加新数据,还可以再中间插入新数据。
声明创建一个名为vt的vector对象,它可以存储n_elem个类型为typeName的元素
vector<typeName> vt(n_elem)
//其中参数n_elem可以是整型常量,也可以是整型变量。#include<vector>
using namespace std;
vector<int>vi;
int n;
cin>>n;
vector<double> vd(n);
array
vector类的功能比数组强大,但代价是效率较低。如果需要长度固定的数组,使用数组是更佳的选择,但代价是不那么方便和安全。array,也位于名称空间std中。
与数组一样,array对象的长度也是固定的,也使用栈(静态内存分配),而不是自由存储区,因此其效率与数组相同,但更方便、安全。
array<typeName,n_elem> arr;
//声明创建一个名为arr的array对象,它包含n_elem个类型为typeName的元素。
//n_elem不能是变量#include<array>
....
using namespace std;
array<int,5> ai;
array<double,4>ad={1.2, 2.1, 3.43, 4.3};
对比
// choices.cpp -- array variations
#include <iostream>
#include <vector> // STL C++98
#include <array> // C++0xint main() {using namespace std;
// C, original C++double a1[4] = {1.2, 2.4, 3.6, 4.8};
// C++98 STLvector<double> a2(4); // create vector with 4 elements
// no simple way to initialize in C98a2[0] = 1.0 / 3.0;a2[1] = 1.0 / 5.0;a2[2] = 1.0 / 7.0;a2[3] = 1.0 / 9.0;
// C++0x -- create and initialize array objectarray<double, 4> a3 = {3.14, 2.72, 1.62, 1.41};array<double, 4> a4;a4 = a3; // valid for array objects of same size
// use array notationcout << "a1[2]: " << a1[2] << " at " << &a1[2] << endl;cout << "a2[2]: " << a2[2] << " at " << &a2[2] << endl;cout << "a3[2]: " << a3[2] << " at " << &a3[2] << endl;cout << "a4[2]: " << a4[2] << " at " << &a4[2] << endl;
// misdeeda1[-2] = 20.2;cout << "a1[-2]: " << a1[-2] << " at " << &a1[-2] << endl;cout << "a3[2]: " << a3[2] << " at " << &a3[2] << endl;cout << "a4[2]: " << a4[2] << " at " << &a4[2] << endl;// cin.get();return 0;
}/*
a1[2]: 3.6 at 0x62fdf0
a2[2]: 0.142857 at 0x25b6720
a3[2]: 1.62 at 0x62fdb0
a4[2]: 1.62 at 0x62fd90
a1[-2]: 20.2 at 0x62fdd0
a3[2]: 1.62 at 0x62fdb0
a4[2]: 1.62 at 0x62fd90
*/
首先,无论是数组、vector对象还是array对象,都可以使用标准数组表示法来访问各个元素。
其次,从地址中可知,array对象和数组存储在相同的内存区域(即栈)中,而vector对象存储在另一个区域(自由存储区或堆)中。
第三,可以将一个array对象赋给另一个array对象;对于数组,必须逐个元素复制数据。
数组越界无法禁止。对于vector和array对象,可以禁止,但仍然不安全。
相关文章:

02-C++数据类型-高级
数据类型-高级 4、复合类型 4.4、结构简介 struct inflatable {char name[20];float vol;double price; };inflatable vincent; //C struct inflatable goose; //C例子 // structur.cpp -- a simple structure #include <iostream> struct inflatable // structu…...
Kotlin实战之获取本地配置文件、远程Apollo配置失败问题排查
背景 Kotlin作为一门JVM脚本语言,收到很多Java开发者的青睐。 项目采用JavaKotlin混合编程。Spring Boot应用开发,不会发生变动的配置放在本地配置文件,可能会变化的配置放在远程Apollo Server。 问题 因为业务需要,需要增加一…...
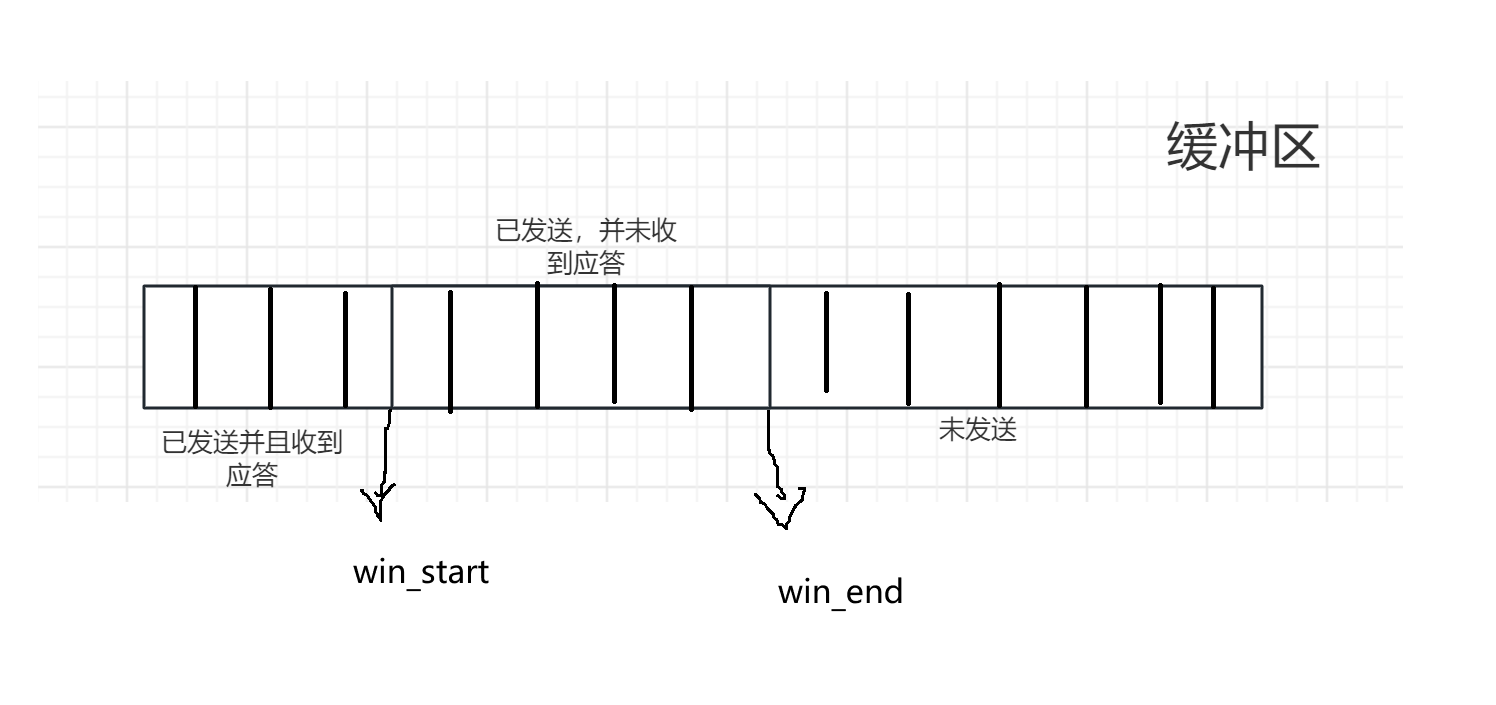
TCP协议的报头格式和滑动窗口
文章目录 TCP报头格式端口号序号和确认序号确认应答(ACK)机制超时重传机制 首部长度窗口大小报文类型URGACKSYNPSHFINRST 滑动窗口滑动窗口的大小怎么设定怎么变化滑动窗口变化问题 TCP报头格式 端口号 两个端口号比较好理解,通过端口号来找…...
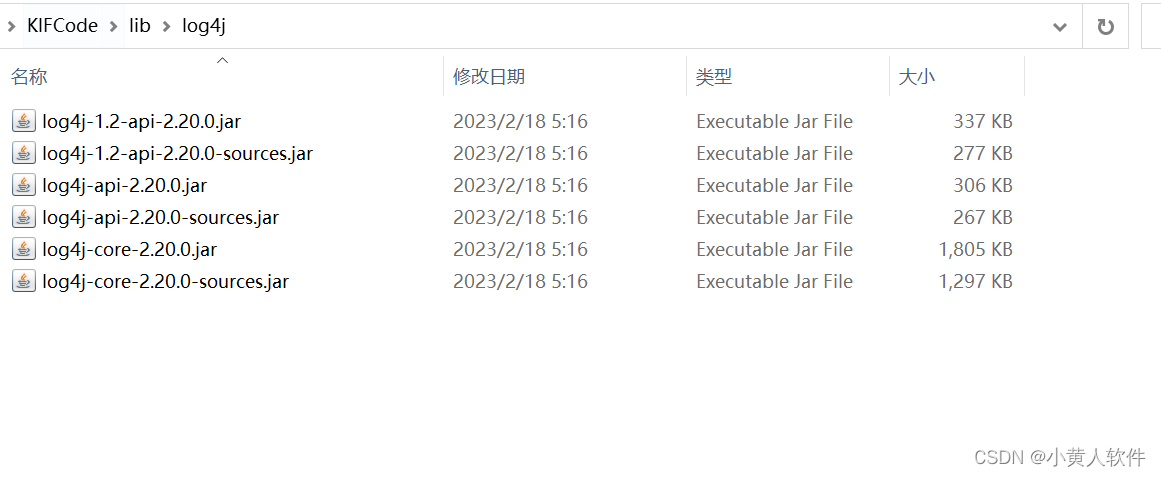
java 使用log4j显示到界面和文件 并格式化
1.下载log4j jar包https://dlcdn.apache.org/logging/log4j/2.20.0/apache-log4j-2.20.0-bin.zip 2. 我只要到核心包 ,看需要 sources是源码包,可以看到说明。在IDEA里先加入class jar后,再双击这个class jar包或或右键选Navigate ,Add ,…...

【js】链接中有多余的怎么取出参数值
https://pq.equalearning.net/assessment/379208869278126080?userId23ebb&originhttps://www.equalearning.net&fnameIm&lnamehappy在上面的例子中,fnameI’m,其中单引号’被转义为, 而如果使用下面的代码,因为在UR…...
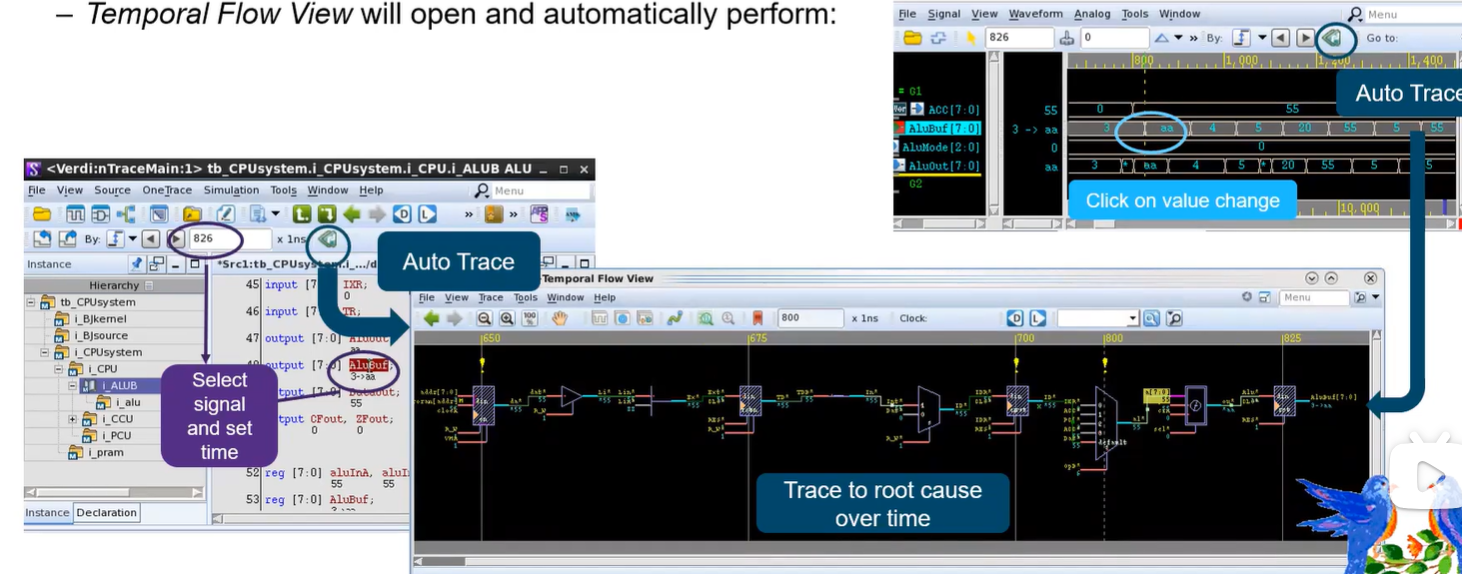
Verdi_traceX and autotrace
Verdi_traceX and autotrace Trace X From nWave/nTrace of from the Teporal Flow View. Show Paths on Flow ViewShow Paths on nWave 若Waveform中有X态,鼠标右键会有Trace X的选项; 会自动打开Temporal Flow View窗口,展示对应路径&am…...
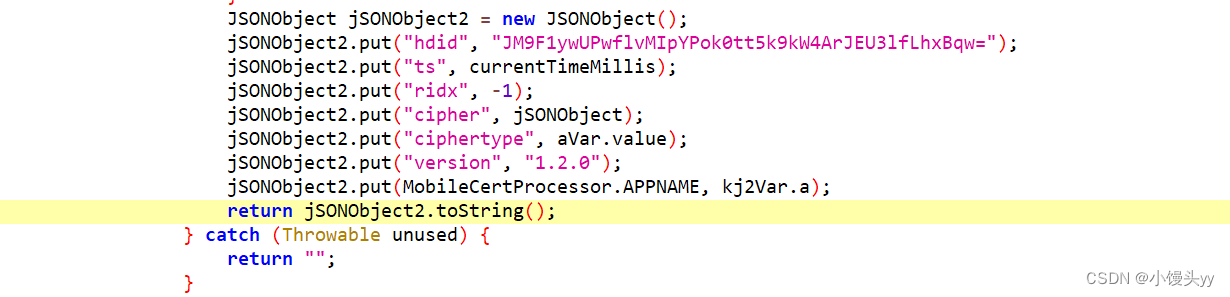
安卓逆向 - 某严选app sign算法还原
本文仅供学习交流,只提供关键思路不会给出完整代码,严禁用于非法用途,若有侵权请联系我删除! 目标app: 5ouN5ouN5Lil6YCJMy45LjY 目标接口:aHR0cHM6Ly9hcGkubS5qZC5jb20vYXBp 一、引言 1、本篇分析某二手交易平台 …...
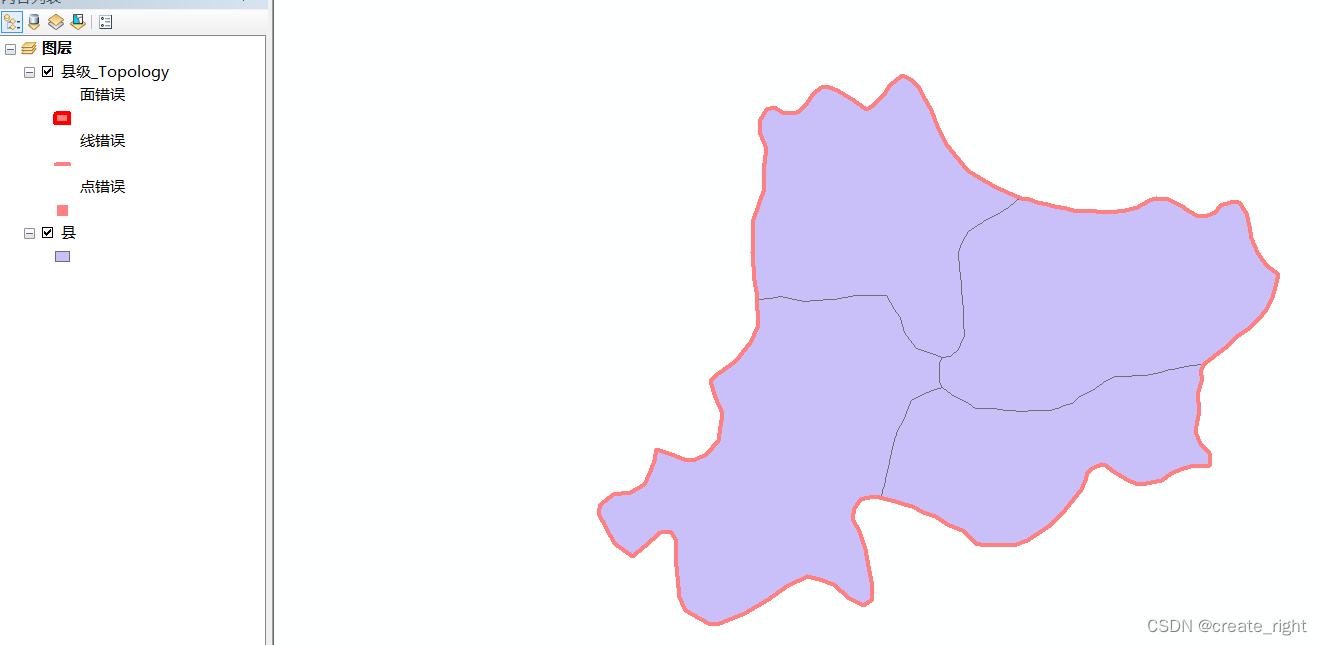
arcgis数据采集与拓扑检查
1、已准备好一张配准好的浙江省行政区划图,如下: 2、现在需要绘制湖州市县级行政区划。需要右击文件夹新建文件地理数据库,如下: 其余步骤均默认即可。 创建好县级要素数据集后,再新建要素类,命名为县。 为…...
【前端 | CSS】滚动到底部加载,滚动监听、懒加载
背景 在日常开发过程中,我们会遇到图片懒加载的功能,基本原理是,滚动条滚动到底部后再次获取数据进行渲染。 那怎么判断滚动条是否滚动到底部呢?滚动条滚动到底部触发时间的时机和方法又该怎样定义? 针对以上问题我…...

word将mathtype公式批量转为latex公式
最近,由于工作学习需要,要将word里面的mathype公式转为latex公式。 查了查资料,有alt\的操作,这样太慢了。通过下面链接的操作,结合起来可以解决问题。 某乎:https://www.zhihu.com/question/532353646 csd…...
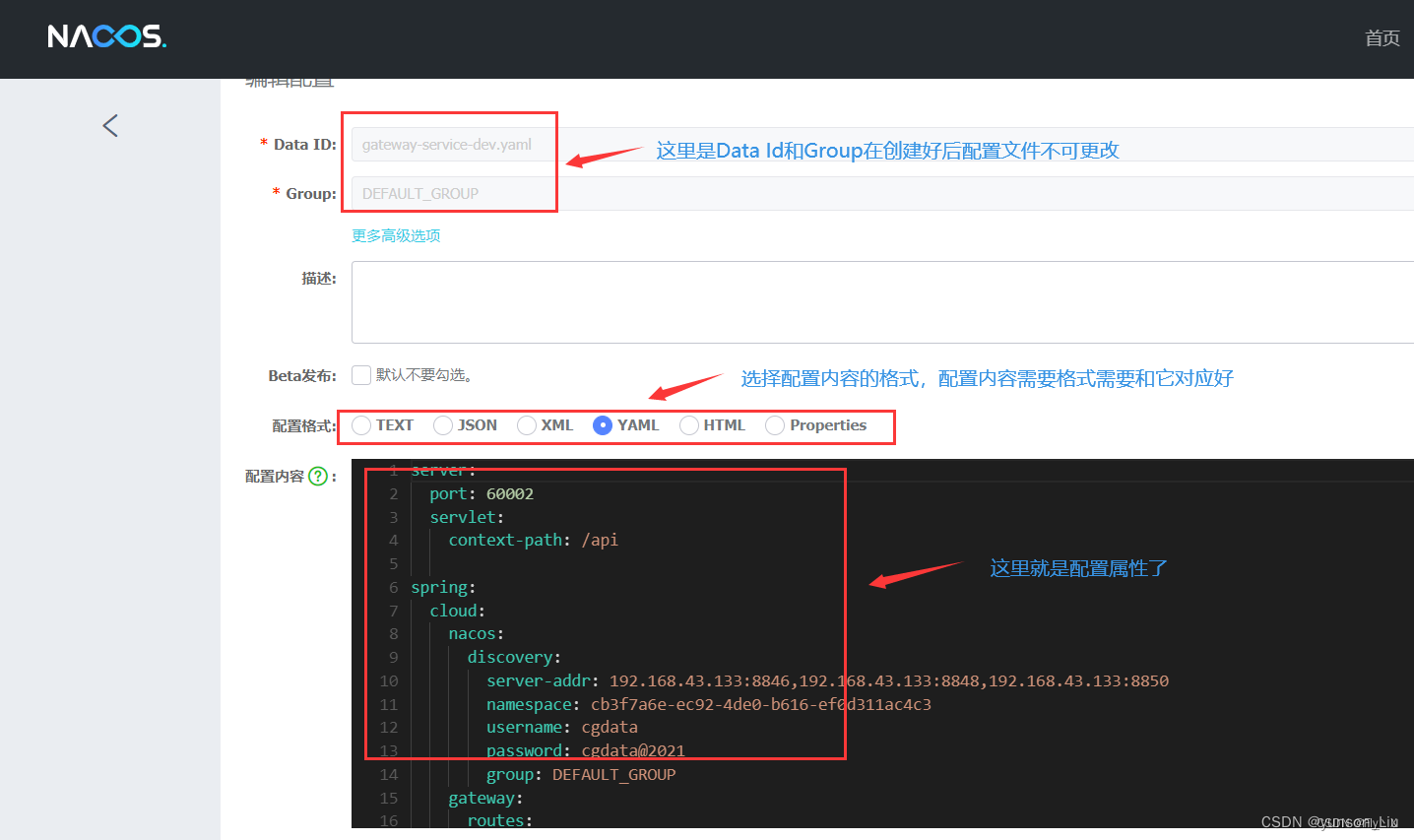
docker-compose部署nacos 2.2.3
1、编写docker-compose.yml文件 version: "3.1" services:nacos:restart: alwaysimage: nacos/nacos-server:v2.2.3container_name: nacosenvironment:- NACOS_AUTH_ENABLEtrue- MODEstandalone- NACOS_AUTH_TOKEN8b92c609089f74db3c5ee04bd7d4d89e8b92c609089f74db…...
软件测试52讲-学习笔记
测试基础知识篇(11讲) 01 你真的懂测试吗?从“用户登录”测试谈起 测试用例设计框架 基于功能性需求和非功能性需求思考: 功能性需求使用等价类划分、边界值分析、错误推断法设计用例 非功能性需求考虑安全(信息的保存…...

【ARM 嵌入式 编译系列 4 -- GCC 编译属性 __read_mostly 详细介绍】
文章目录 __read_mostly 介绍__read_mostly 在 linux 中的使用.data.read_mostly 介绍 __read_mostly 介绍 __read_mostly 是一个在Linux内核编程中用到的宏定义,这是一个gcc编译器的属性,用于告诉编译器此变量主要用于读取,很少进行写入&am…...
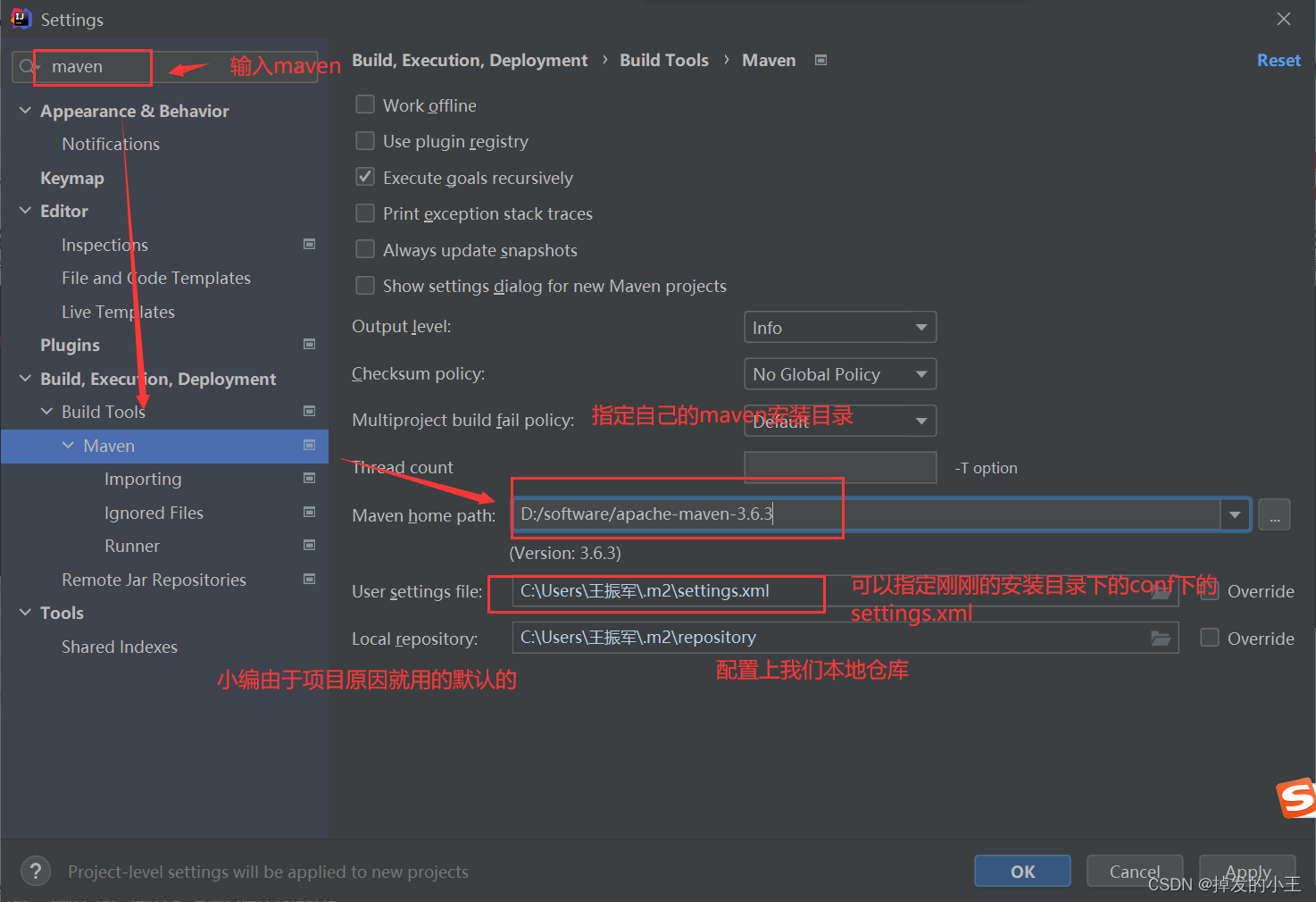
Maven在IDEA2021版本中全局配置(一次配置处处生效)
前言 我们在开发中,Maven是必不可少的,但是每次都需要设置一遍Maven的仓库和settings.xml。真的是心累,今天教大家全局配置一下。再也不要每次项目都配了,Maven还经常出问题。 解决方案 友情提示:小编的IDEA版本为2…...

名侦探番外——Arduino“炸弹”引爆摩天大楼
名侦探番外——Arduino“炸弹”引爆摩天大楼 硬件准备1.材料准备2.模块介绍 电路设计1.硬件接线 程序设计1.设计思路2.部分程序3.功能优化 总结 好久不见,童鞋们!小编突然想到很久以前看的柯南剧场版——计时引爆摩天大楼的情景,对剧里的“炸…...
自适应AI chatgpt智能聊天创作官网html源码
我们致力于开发先进的自适应AI智能聊天技术,旨在为用户提供前所未有的聊天体验。通过融合自然语言处理、机器学习和深度学习等领域的顶尖技术,我们的智能聊天系统能够准确理解用户的需求并给出相应的回应。 我们的自适应AI智能聊天系统具备以下核心特点…...

防抖,节流
概念 防抖(debounce):类似法师技能读条,读条没完再按技能就会重新读条,在触发后的n秒内只会执行一次,若在这n秒内重复触发则重新计算 节流(throttle):连续发生的事件在n秒内只执行一次函数 参考 【前端面试必问】—…...
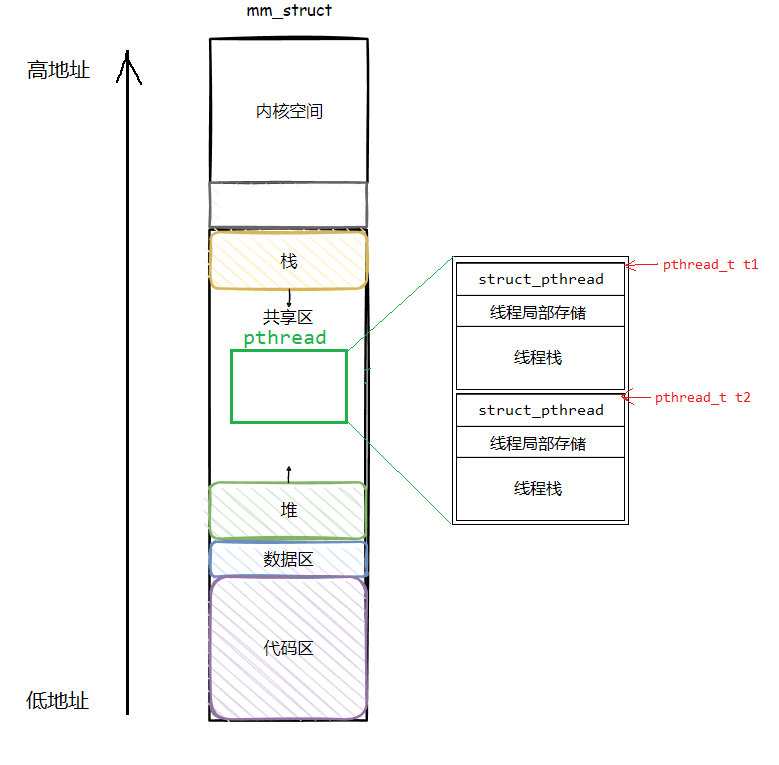
【Linux】多线程1——线程概念与线程控制
文章目录 1. 线程概念什么是线程Linux中的线程线程的优点线程的缺点线程的独立资源和共享资源 2. 线程控制Linux的pthread库用户级线程 📝 个人主页 :超人不会飞)📑 本文收录专栏:《Linux》💭 如果本文对您有帮助&…...
【Maven】SpringBoot项目使用maven-assembly-plugin插件多环境打包
SpringBoot项目使用maven-assembly-plugin插件多环境打包 1.创建SpringBoot项目并在pom.xml文件中添加maven-assembly-plugin配置 <!-- 多环境配置 --><profiles><!-- 开发环境 --><profile><id>dev</id><properties><prof…...

指令集_基础
指令集-基础 一、提示过程1,文章摘要2,数学问题求解 二、角色提示三、多范例提示 一、提示过程 指导人工智能,执行任务的过程,称为提示过程。向AI 提供一组指令(提示),然后它执行任务 1,文章摘要 例如&a…...
eNSP-Cloud(实现本地电脑与eNSP内设备之间通信)
说明: 想象一下,你正在用eNSP搭建一个虚拟的网络世界,里面有虚拟的路由器、交换机、电脑(PC)等等。这些设备都在你的电脑里面“运行”,它们之间可以互相通信,就像一个封闭的小王国。 但是&#…...

conda相比python好处
Conda 作为 Python 的环境和包管理工具,相比原生 Python 生态(如 pip 虚拟环境)有许多独特优势,尤其在多项目管理、依赖处理和跨平台兼容性等方面表现更优。以下是 Conda 的核心好处: 一、一站式环境管理:…...
【Oracle APEX开发小技巧12】
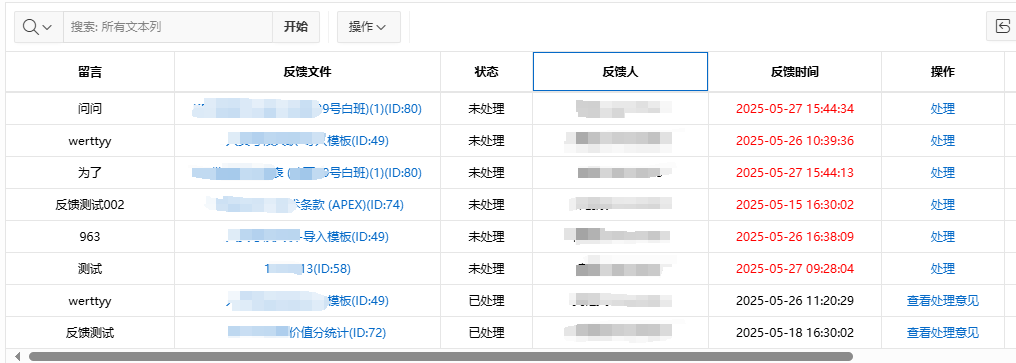
有如下需求: 有一个问题反馈页面,要实现在apex页面展示能直观看到反馈时间超过7天未处理的数据,方便管理员及时处理反馈。 我的方法:直接将逻辑写在SQL中,这样可以直接在页面展示 完整代码: SELECTSF.FE…...

Auto-Coder使用GPT-4o完成:在用TabPFN这个模型构建一个预测未来3天涨跌的分类任务
通过akshare库,获取股票数据,并生成TabPFN这个模型 可以识别、处理的格式,写一个完整的预处理示例,并构建一个预测未来 3 天股价涨跌的分类任务 用TabPFN这个模型构建一个预测未来 3 天股价涨跌的分类任务,进行预测并输…...

Qwen3-Embedding-0.6B深度解析:多语言语义检索的轻量级利器
第一章 引言:语义表示的新时代挑战与Qwen3的破局之路 1.1 文本嵌入的核心价值与技术演进 在人工智能领域,文本嵌入技术如同连接自然语言与机器理解的“神经突触”——它将人类语言转化为计算机可计算的语义向量,支撑着搜索引擎、推荐系统、…...

C++ 基础特性深度解析
目录 引言 一、命名空间(namespace) C 中的命名空间 与 C 语言的对比 二、缺省参数 C 中的缺省参数 与 C 语言的对比 三、引用(reference) C 中的引用 与 C 语言的对比 四、inline(内联函数…...

Python如何给视频添加音频和字幕
在Python中,给视频添加音频和字幕可以使用电影文件处理库MoviePy和字幕处理库Subtitles。下面将详细介绍如何使用这些库来实现视频的音频和字幕添加,包括必要的代码示例和详细解释。 环境准备 在开始之前,需要安装以下Python库:…...
c#开发AI模型对话
AI模型 前面已经介绍了一般AI模型本地部署,直接调用现成的模型数据。这里主要讲述讲接口集成到我们自己的程序中使用方式。 微软提供了ML.NET来开发和使用AI模型,但是目前国内可能使用不多,至少实践例子很少看见。开发训练模型就不介绍了&am…...

A2A JS SDK 完整教程:快速入门指南
目录 什么是 A2A JS SDK?A2A JS 安装与设置A2A JS 核心概念创建你的第一个 A2A JS 代理A2A JS 服务端开发A2A JS 客户端使用A2A JS 高级特性A2A JS 最佳实践A2A JS 故障排除 什么是 A2A JS SDK? A2A JS SDK 是一个专为 JavaScript/TypeScript 开发者设计的强大库ÿ…...

Golang——6、指针和结构体
指针和结构体 1、指针1.1、指针地址和指针类型1.2、指针取值1.3、new和make 2、结构体2.1、type关键字的使用2.2、结构体的定义和初始化2.3、结构体方法和接收者2.4、给任意类型添加方法2.5、结构体的匿名字段2.6、嵌套结构体2.7、嵌套匿名结构体2.8、结构体的继承 3、结构体与…...
