点云配准方法原理(NDT、ICP)
配准是点云处理中的一个基础问题,众多学者此问题进行了广泛而深入的研究,也出现了一系列优秀成熟的算法,在三维建模、自动驾驶等领域发挥着重要的作用。
本文主要介绍粗配准NDT (Normal Distribution Transform) 与 精配准ICP (Iterative Closest Point)两种经典算法。
NDT (Normal Distribution Transform)点云配准
在去年曾经对NDT原理进行了简单总结,大家可以参考链接:点云配准NDT (P2D)算法详解。
ICP (Iterative Closest Point)点云配准
参考:
基于SVD求解 3D-3D 点对匹配
该如何学习三维点云配准的相关知识?
ICP是经典的精配准算法,其以“点”为配准基元,不断迭代求得最优的位姿,最终使得目标函数最小。
点云集合
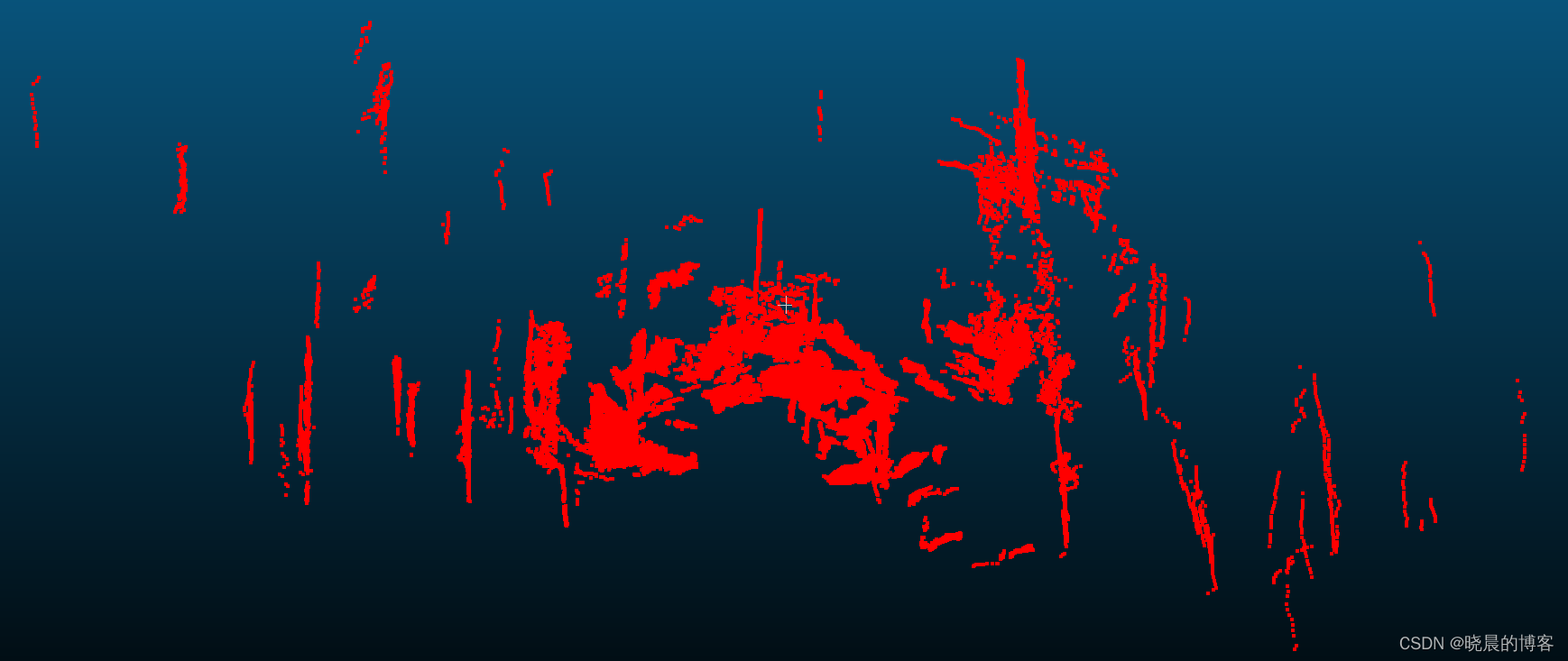
假设存在两个点云集合,
目标点云 (target cloud ):P={p1,p2,p3,...,pn}P=\{p_1, p_2, p_3,..., p_n\}P={p1,p2,p3,...,pn}
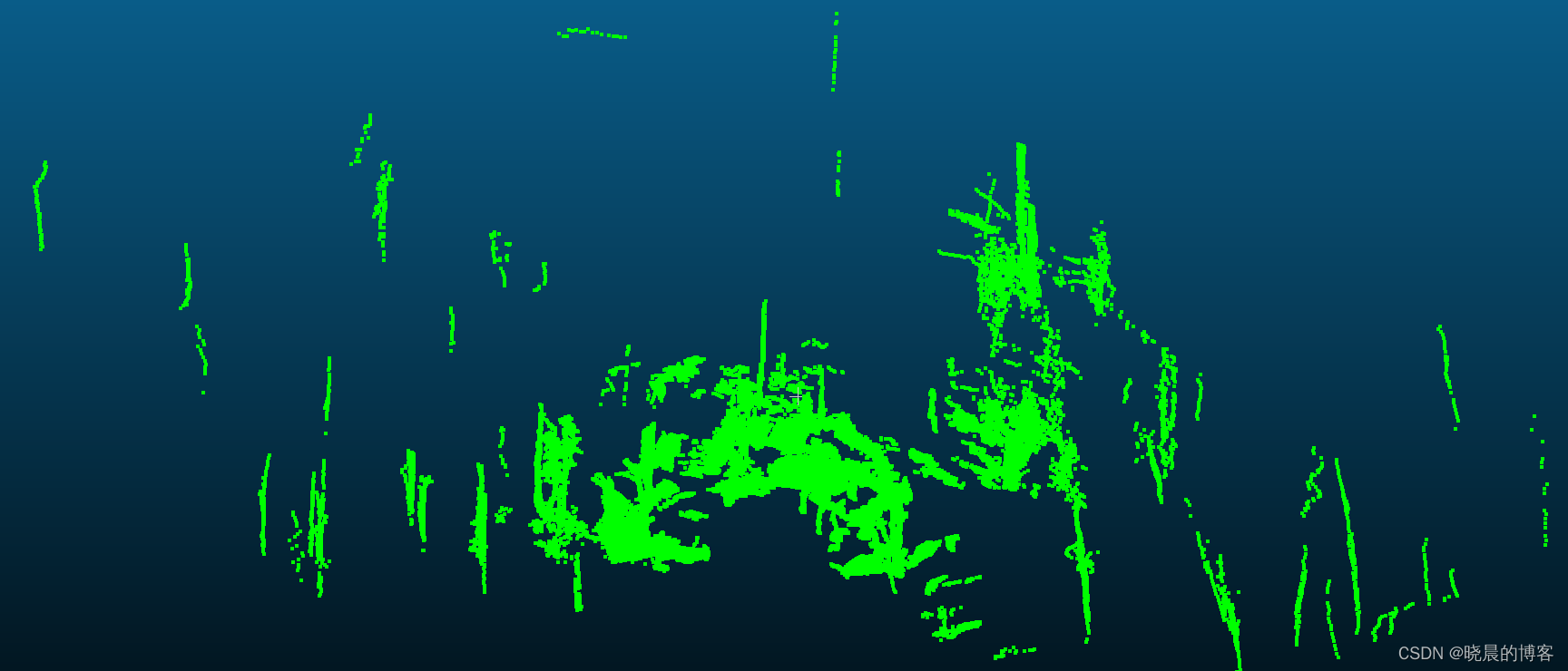
源点云 (source cloud):Q={q1,q2,q3,...,qn}Q=\{q_1, q_2, q_3,..., q_n\}Q={q1,q2,q3,...,qn}
两者叠加显示:
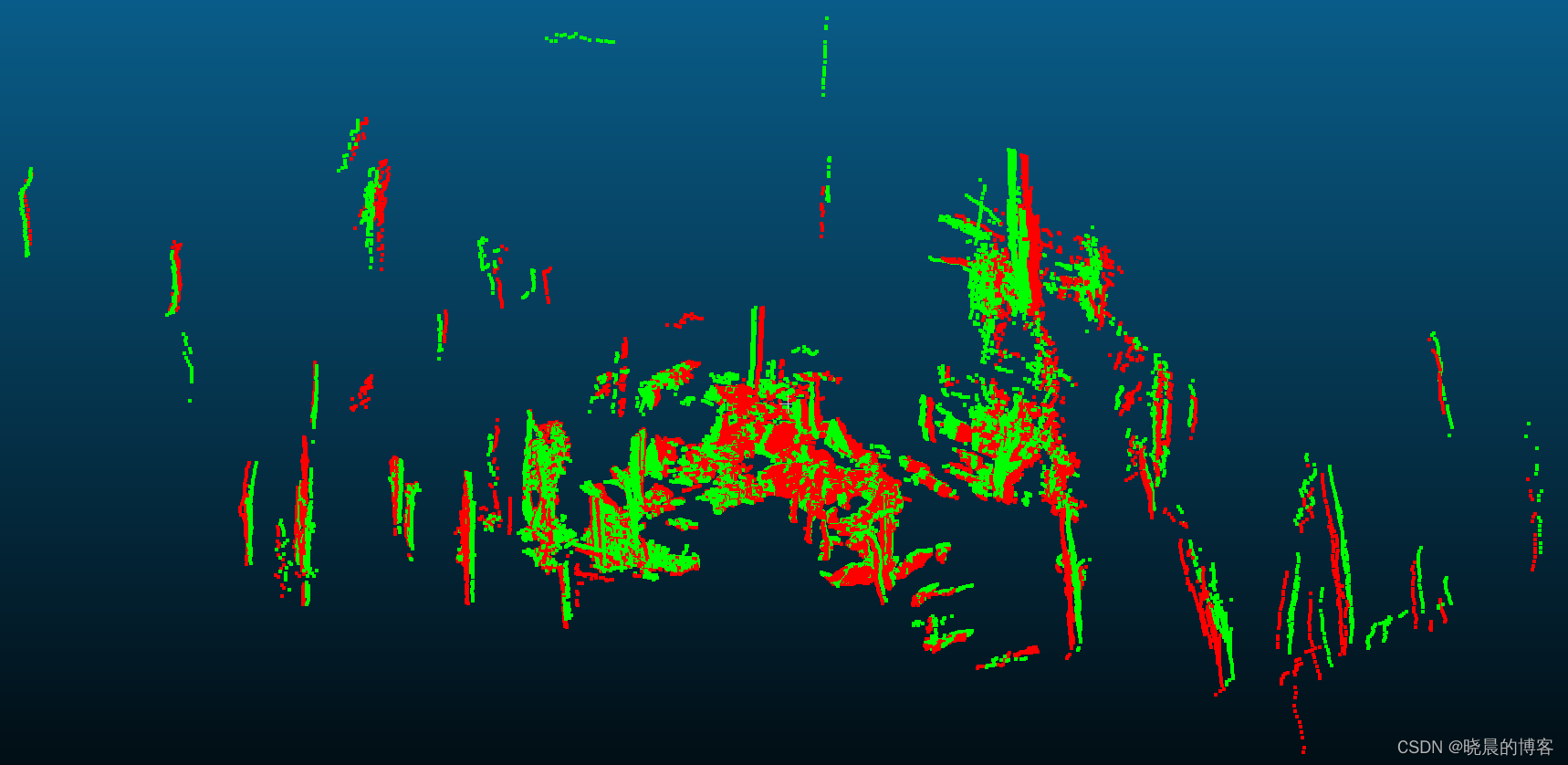
可以看到上图中的两帧点云之间存在一个偏差,这个偏差需要一个位姿变换(R,t)(R, t)(R,t)进行转换。
构造目标函数
ICP算法则希望得到一个最优的位姿变换(R∗,t∗)(R^*, t^*)(R∗,t∗)使得下式目标函数最小:
f(R∗,t∗)=MIN(1Np∑i=1Np∣pit−(R∗qis+t∗)∣2)f(R^*, t^*)=MIN(\frac{1}{N_p}{\textstyle \sum_{i=1}^{N_p}\left | p_{i}^{t}-(R^*q_{i}^{s}+t^*) \right |^2 } )f(R∗,t∗)=MIN(Np1∑i=1Np∣pit−(R∗qis+t∗)∣2)
其中NpN_pNp为配对点云个数,pitp_{i}^{t}pit与qisq_{i}^{s}qis是目标点云与源点云中的一对配对点。
寻找对应点对
起始步骤中,我们只有一系列无序的三维点,并没有对应的pitp_{i}^{t}pit与qisq_{i}^{s}qis点对。ICP中定义了“最近邻点”的定义。
- 使用一个初始位姿(R0,t0)(R^0, t^0)(R0,t0)对源点云QQQ进行变换,得到一个变换后的点云Q′Q'Q′。
- 对变换后的点云Q′Q'Q′中的点qi′q_{i}^{'}qi′在目标点云中查找最近邻点pjp_{j}pj,如果两点之间的距离小于预先设置的阈值,则认为点qi′q_{i}^{'}qi′与点pjp_{j}pj为对应的点对。
优化位姿变换(R,t)(R, t)(R,t)
找到所有合理的最近邻点对之后,则每一个点对都可以构建一个函数(每个点对类似于一个观测),而待求变量(R,t)(R, t)(R,t)只有6个自由度。所以我们有了NpN_pNp个观测,6个待求变量。使用最小二乘进行优化求解。
这样我们就更新了初始位姿(R0,t0)(R^0, t^0)(R0,t0)为新的(R1,t1)(R^1, t^1)(R1,t1)
迭代优化
得到新的位姿变换(R1,t1)(R^1, t^1)(R1,t1)之后,我们再次回到寻找对应点对步骤中,重新转换源点云QQQ为Q2Q^2Q2,查找Q2Q^2Q2与PPP新的点对。
接着,进行新的 “优化位姿变换(R,t)(R, t)(R,t)” 步骤,重复得到新的优化位姿(R2,t2)(R^2, t^2)(R2,t2)
直到达到迭代停止条件,如:1)达到最大迭代次数,或2)位姿变化量小于阈值,或3)最近邻点对不再变化等则终止迭代。
调用PCL库
参考链接:Interactive Iterative Closest Point
1#include <iostream>2#include <string>34#include <pcl/io/ply_io.h>5#include <pcl/point_types.h>6#include <pcl/registration/icp.h>7#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>8#include <pcl/console/time.h> // TicToc910typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointT;11typedef pcl::PointCloud<PointT> PointCloudT;1213bool next_iteration = false;1415void16print4x4Matrix (const Eigen::Matrix4d & matrix)17{18 printf ("Rotation matrix :\n");19 printf (" | %6.3f %6.3f %6.3f | \n", matrix (0, 0), matrix (0, 1), matrix (0, 2));20 printf ("R = | %6.3f %6.3f %6.3f | \n", matrix (1, 0), matrix (1, 1), matrix (1, 2));21 printf (" | %6.3f %6.3f %6.3f | \n", matrix (2, 0), matrix (2, 1), matrix (2, 2));22 printf ("Translation vector :\n");23 printf ("t = < %6.3f, %6.3f, %6.3f >\n\n", matrix (0, 3), matrix (1, 3), matrix (2, 3));24}2526void27keyboardEventOccurred (const pcl::visualization::KeyboardEvent& event,28 void*)29{30 if (event.getKeySym () == "space" && event.keyDown ())31 next_iteration = true;32}3334int35main (int argc,36 char* argv[])37{38 // The point clouds we will be using39 PointCloudT::Ptr cloud_in (new PointCloudT); // Original point cloud40 PointCloudT::Ptr cloud_tr (new PointCloudT); // Transformed point cloud41 PointCloudT::Ptr cloud_icp (new PointCloudT); // ICP output point cloud4243 // Checking program arguments44 if (argc < 2)45 {46 printf ("Usage :\n");47 printf ("\t\t%s file.ply number_of_ICP_iterations\n", argv[0]);48 PCL_ERROR ("Provide one ply file.\n");49 return (-1);50 }5152 int iterations = 1; // Default number of ICP iterations53 if (argc > 2)54 {55 // If the user passed the number of iteration as an argument56 iterations = atoi (argv[2]);57 if (iterations < 1)58 {59 PCL_ERROR ("Number of initial iterations must be >= 1\n");60 return (-1);61 }62 }6364 pcl::console::TicToc time;65 time.tic ();66 if (pcl::io::loadPLYFile (argv[1], *cloud_in) < 0)67 {68 PCL_ERROR ("Error loading cloud %s.\n", argv[1]);69 return (-1);70 }71 std::cout << "\nLoaded file " << argv[1] << " (" << cloud_in->size () << " points) in " << time.toc () << " ms\n" << std::endl;7273 // Defining a rotation matrix and translation vector74 Eigen::Matrix4d transformation_matrix = Eigen::Matrix4d::Identity ();7576 // A rotation matrix (see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rotation_matrix)77 double theta = M_PI / 8; // The angle of rotation in radians78 transformation_matrix (0, 0) = std::cos (theta);79 transformation_matrix (0, 1) = -sin (theta);80 transformation_matrix (1, 0) = sin (theta);81 transformation_matrix (1, 1) = std::cos (theta);8283 // A translation on Z axis (0.4 meters)84 transformation_matrix (2, 3) = 0.4;8586 // Display in terminal the transformation matrix87 std::cout << "Applying this rigid transformation to: cloud_in -> cloud_icp" << std::endl;88 print4x4Matrix (transformation_matrix);8990 // Executing the transformation91 pcl::transformPointCloud (*cloud_in, *cloud_icp, transformation_matrix);92 *cloud_tr = *cloud_icp; // We backup cloud_icp into cloud_tr for later use9394 // The Iterative Closest Point algorithm95 time.tic ();96 pcl::IterativeClosestPoint<PointT, PointT> icp;97 icp.setMaximumIterations (iterations);98 icp.setInputSource (cloud_icp);99 icp.setInputTarget (cloud_in);
100 icp.align (*cloud_icp);
101 icp.setMaximumIterations (1); // We set this variable to 1 for the next time we will call .align () function
102 std::cout << "Applied " << iterations << " ICP iteration(s) in " << time.toc () << " ms" << std::endl;
103
104 if (icp.hasConverged ())
105 {
106 std::cout << "\nICP has converged, score is " << icp.getFitnessScore () << std::endl;
107 std::cout << "\nICP transformation " << iterations << " : cloud_icp -> cloud_in" << std::endl;
108 transformation_matrix = icp.getFinalTransformation ().cast<double>();
109 print4x4Matrix (transformation_matrix);
110 }
111 else
112 {
113 PCL_ERROR ("\nICP has not converged.\n");
114 return (-1);
115 }
116
117 // Visualization
118 pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer ("ICP demo");
119 // Create two vertically separated viewports
120 int v1 (0);
121 int v2 (1);
122 viewer.createViewPort (0.0, 0.0, 0.5, 1.0, v1);
123 viewer.createViewPort (0.5, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, v2);
124
125 // The color we will be using
126 float bckgr_gray_level = 0.0; // Black
127 float txt_gray_lvl = 1.0 - bckgr_gray_level;
128
129 // Original point cloud is white
130 pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointT> cloud_in_color_h (cloud_in, (int) 255 * txt_gray_lvl, (int) 255 * txt_gray_lvl,
131 (int) 255 * txt_gray_lvl);
132 viewer.addPointCloud (cloud_in, cloud_in_color_h, "cloud_in_v1", v1);
133 viewer.addPointCloud (cloud_in, cloud_in_color_h, "cloud_in_v2", v2);
134
135 // Transformed point cloud is green
136 pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointT> cloud_tr_color_h (cloud_tr, 20, 180, 20);
137 viewer.addPointCloud (cloud_tr, cloud_tr_color_h, "cloud_tr_v1", v1);
138
139 // ICP aligned point cloud is red
140 pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointT> cloud_icp_color_h (cloud_icp, 180, 20, 20);
141 viewer.addPointCloud (cloud_icp, cloud_icp_color_h, "cloud_icp_v2", v2);
142
143 // Adding text descriptions in each viewport
144 viewer.addText ("White: Original point cloud\nGreen: Matrix transformed point cloud", 10, 15, 16, txt_gray_lvl, txt_gray_lvl, txt_gray_lvl, "icp_info_1", v1);
145 viewer.addText ("White: Original point cloud\nRed: ICP aligned point cloud", 10, 15, 16, txt_gray_lvl, txt_gray_lvl, txt_gray_lvl, "icp_info_2", v2);
146
147 std::stringstream ss;
148 ss << iterations;
149 std::string iterations_cnt = "ICP iterations = " + ss.str ();
150 viewer.addText (iterations_cnt, 10, 60, 16, txt_gray_lvl, txt_gray_lvl, txt_gray_lvl, "iterations_cnt", v2);
151
152 // Set background color
153 viewer.setBackgroundColor (bckgr_gray_level, bckgr_gray_level, bckgr_gray_level, v1);
154 viewer.setBackgroundColor (bckgr_gray_level, bckgr_gray_level, bckgr_gray_level, v2);
155
156 // Set camera position and orientation
157 viewer.setCameraPosition (-3.68332, 2.94092, 5.71266, 0.289847, 0.921947, -0.256907, 0);
158 viewer.setSize (1280, 1024); // Visualiser window size
159
160 // Register keyboard callback :
161 viewer.registerKeyboardCallback (&keyboardEventOccurred, (void*) NULL);
162
163 // Display the visualiser
164 while (!viewer.wasStopped ())
165 {
166 viewer.spinOnce ();
167
168 // The user pressed "space" :
169 if (next_iteration)
170 {
171 // The Iterative Closest Point algorithm
172 time.tic ();
173 icp.align (*cloud_icp);
174 std::cout << "Applied 1 ICP iteration in " << time.toc () << " ms" << std::endl;
175
176 if (icp.hasConverged ())
177 {
178 printf ("\033[11A"); // Go up 11 lines in terminal output.
179 printf ("\nICP has converged, score is %+.0e\n", icp.getFitnessScore ());
180 std::cout << "\nICP transformation " << ++iterations << " : cloud_icp -> cloud_in" << std::endl;
181 transformation_matrix *= icp.getFinalTransformation ().cast<double>(); // WARNING /!\ This is not accurate! For "educational" purpose only!
182 print4x4Matrix (transformation_matrix); // Print the transformation between original pose and current pose
183
184 ss.str ("");
185 ss << iterations;
186 std::string iterations_cnt = "ICP iterations = " + ss.str ();
187 viewer.updateText (iterations_cnt, 10, 60, 16, txt_gray_lvl, txt_gray_lvl, txt_gray_lvl, "iterations_cnt");
188 viewer.updatePointCloud (cloud_icp, cloud_icp_color_h, "cloud_icp_v2");
189 }
190 else
191 {
192 PCL_ERROR ("\nICP has not converged.\n");
193 return (-1);
194 }
195 }
196 next_iteration = false;
197 }
198 return (0);
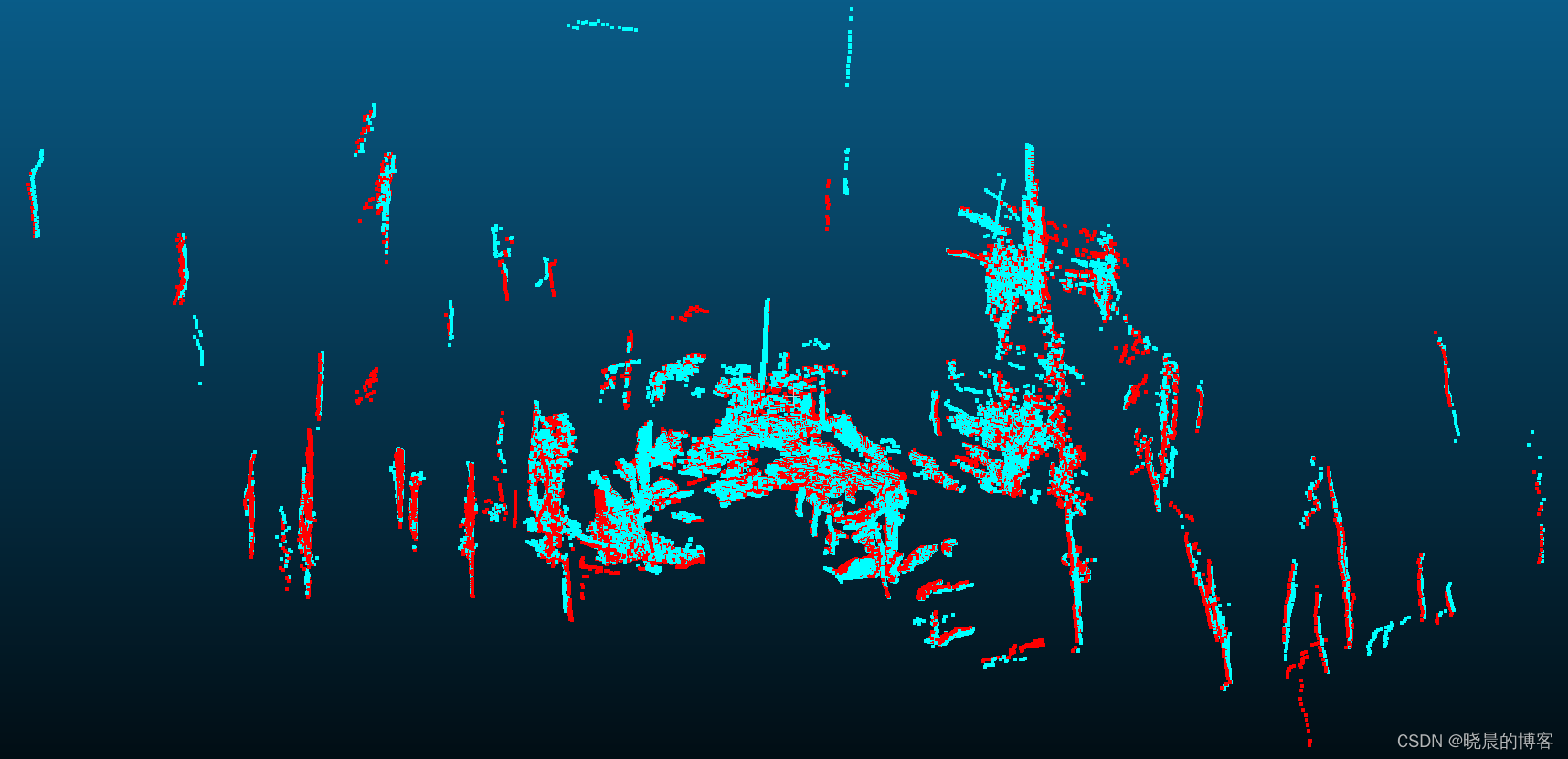
199}配准结果
图中红色为目标帧点云,蓝色为转换后的源点云。
相关文章:

点云配准方法原理(NDT、ICP)
配准是点云处理中的一个基础问题,众多学者此问题进行了广泛而深入的研究,也出现了一系列优秀成熟的算法,在三维建模、自动驾驶等领域发挥着重要的作用。 本文主要介绍粗配准NDT (Normal Distribution Transform) 与 精配准ICP (Iterative Cl…...

大规模 IoT 边缘容器集群管理的几种架构-0-边缘容器及架构简介
📚️Reference: IoT 边缘计算系列文章 什么是边缘容器? 边缘容器的概念 边缘容器是分散的计算资源,尽可能靠近最终用户或设备,以减少延迟、节省带宽并增强整体数字体验。 可以访问互联网的设备数量每天都在增加。有包括但不限于…...
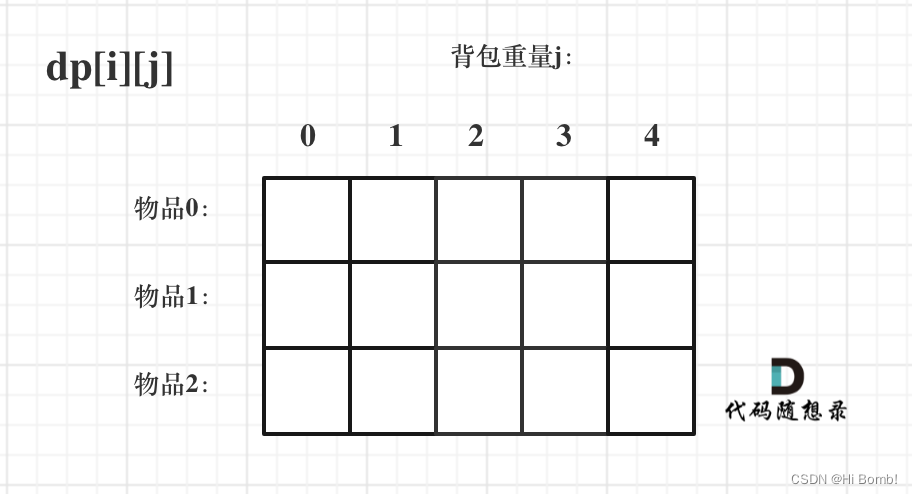
代码随想录算法训练营第45天动态规划 背包基础 1 2、 416. 分割等和子集
文章目录01背包基础 (二维数组)思路递推公式初始化遍历顺序一维dp数组(滚动数组)一维数组的递推公式遍历顺序LeetCode 416. 分割等和子集思路总结01背包基础 (二维数组) 思路 根据动态规划五部进行分析&a…...
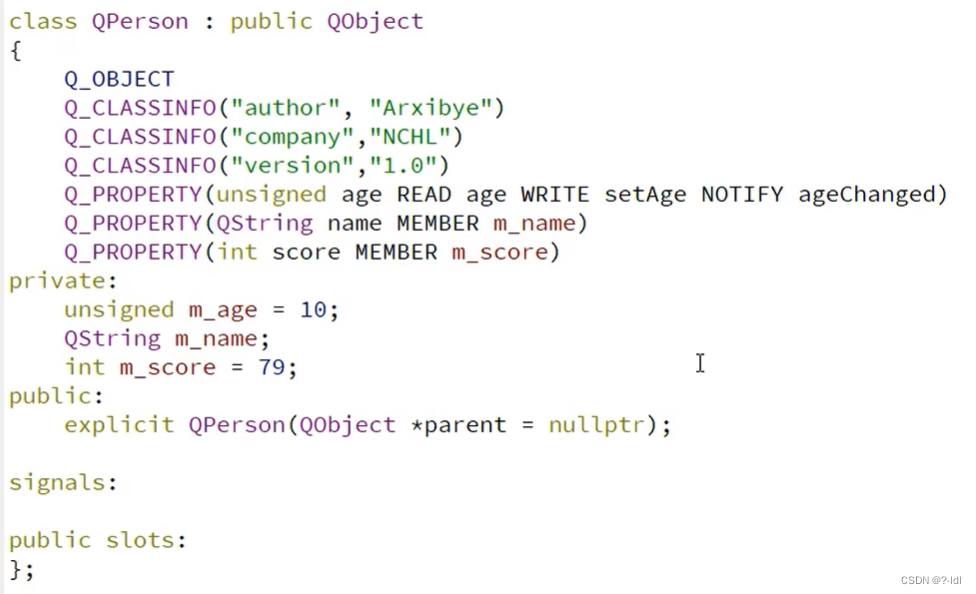
QT学习记录(六)类对象属性
类对象属性用来描述类对象的一些信息和当前的状态。类对象属性可以由类的编写者在编写类的时候定义,也可以由类的使用者在使用对象的时候定义。 由类的编写者定义 QPROPERTY()宏就是用来定义一个对象属性。 以第二行属性举例 QPROPERTY(bool enabled READ isEnabl…...

Spring Cloud Alibaba从搭建到源码完整进阶教程
微服务简介 Spring Cloud Alibaba 微服务简介 Nacos注册中心配置中心 Spring Cloud Nacos实战(一)- 下载和安装 Spring Cloud Nacos实战(二)- 服务提供者注册 Spring Cloud Nacos实战(三)- 服务消费者…...
Spring Cloud Nacos实战(一)- 下载和安装
Spring Cloud Alibaba Nacos下载和安装 Nacos介绍 Nacos(Naming Configuration Service) 是一个易于使用的动态服务发现、配置和服务管理平台,用于构建云原生应用程序 服务发现是微服务架构中的关键组件之一。Nacos 致力于帮助您发现…...
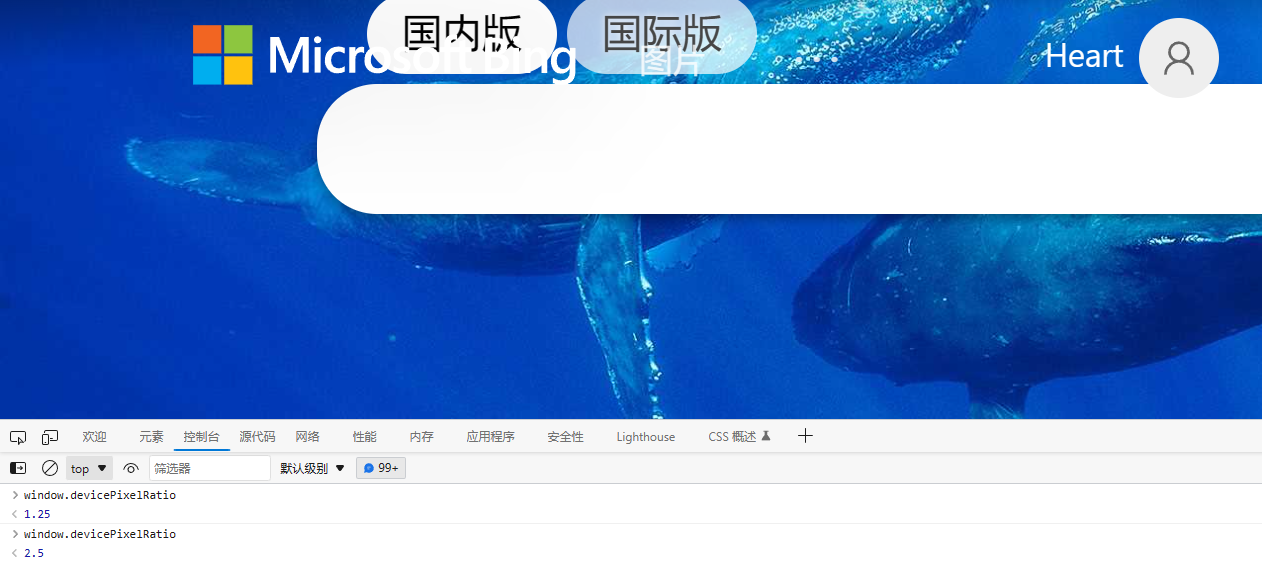
深入理解设备像素比
文章目录参考描述像素分辨率显示分辨率图像分辨率物理分辨率分辨率单位(仅部分)DPIPPI设备像素比设备物理像素设备独立像素设备像素比产生放大与缩小尾声参考 项目描述关于物理像素、逻辑像素(css像素)、分辨率、像素比的超详细讲…...
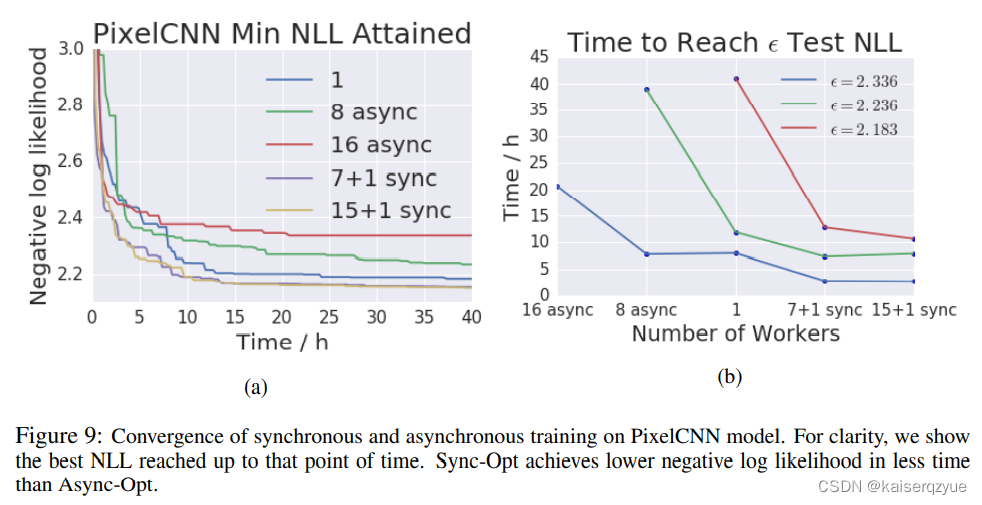
Revisiting Distributed Synchronous SGD 带有Back-up机制的分布式同步SGD方法 论文精读
论文链接:Revisiting Distributed Synchronous SGD ABS 本文介绍了用于分布式机器学习的同步和异步SGDSGDSGD,同时指出各自的缺点:stragglersstragglersstragglers和stalenessstalenessstaleness。 同时为了解决同步SGDSGDSGD存在straggle…...
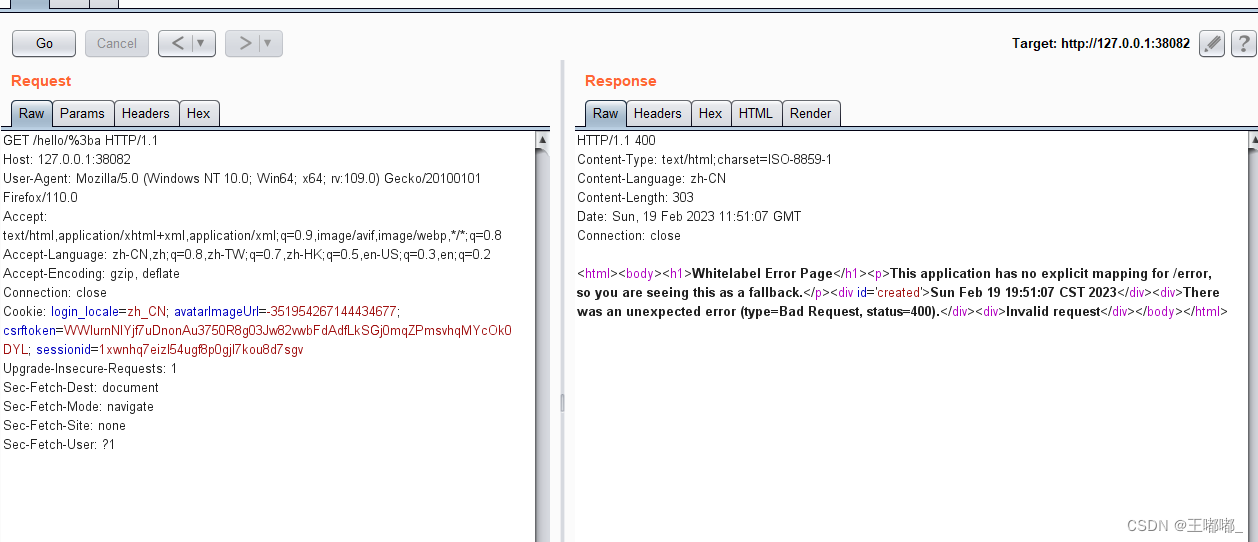
shiro CVE-2020-13933
0x00 前言 同CVE-2020-1957,补充一下笔记,在CVE-2020-1957的基础上进行了绕过。 影响版本:Apache Shiro < 1.6.0 环境搭建参考:shiro CVE-2020-1957 0x01 漏洞复现 CVE-2020-13933中使用%3b绕过了shiro /*的检测方式&…...

斐波那契数列(递归+迭代)
目录什么是斐波那契数列递归写法使用递归写法的缺点迭代写法(效率高)什么是斐波那契数列 斐波那契数列(Fibonacci sequence),又称黄金分割数列,因数学家莱昂纳多斐波那契(Leonardo Fibonacci)以兔子繁殖为例…...
2022黑马Redis跟学笔记.实战篇(六)
2022黑马Redis跟学笔记.实战篇 六4.7.达人探店功能4.7.1.分享探店图文1. 达人探店-发布探店笔记2. 达人探店-查看探店笔记4.7.2.点赞功能4.7.3.基于List实现点赞用户列表TOP104.7.4.基于SortedSet实现点赞排行榜4.8.关注列表4.8.1.关注列表实现原理4.8.2.添加关注1. 好友关注-关…...
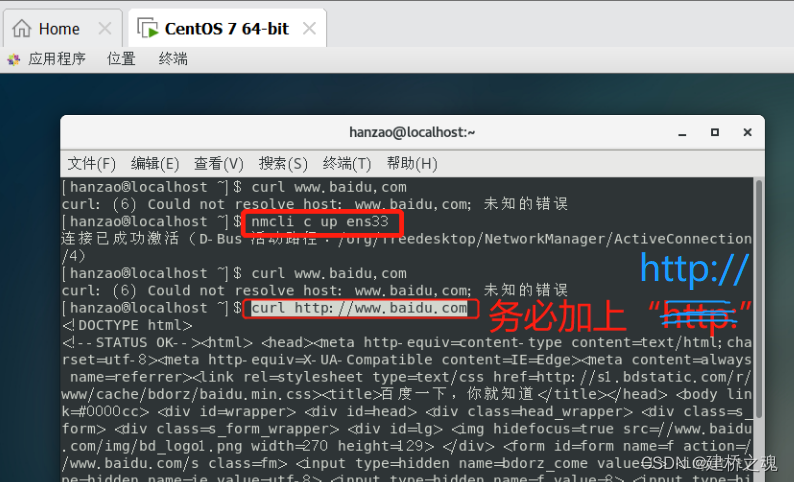
Linux-VMware常用设置(时间+网络)及网络连接激活失败解决方法-基础篇②
目录一、设置时间二、网络设置1. 激活网卡方法一:直接启动网卡(仅限当此)方法二:修改配置文件(永久)2. 将NAT模式改为桥接模式什么是是NAT模式?如何改为桥接模式?三、虚拟机网络连接…...

vue3学习总结1
一.vue3与vue2相比带来哪些变化?a.性能的提升(包括打包大小减少,初次渲染的速度加快,更新渲染速度加快,内存减少)b.源码的升级(响应式的原理发生了变化,由原来的defineProperty变成了…...
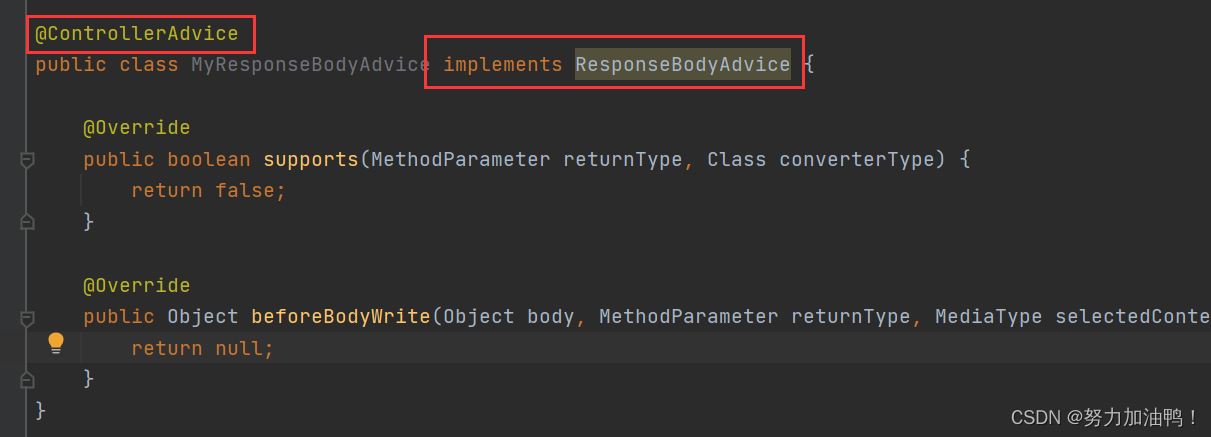
SpringBoot统一功能处理
一、统一用户登录权限验证 1.1Spring拦截器 实现拦截器需要以下两步: 1.创建自定义拦截器,实现 HandlerInterceptor 接⼝的 preHandle(执行具体方法之前的预处理)方法。 2.将⾃定义拦截器加⼊ WebMvcConfigurer 的 addIntercept…...
答案解析)
2022年3月电子学会Python等级考试试卷(五级)答案解析
目录 一、单选题(共25题,共50分) 二、判断题(共10题,共20分) 三、编程题(共3题,共30分) 青少年软件编程(Python)等级考试试卷(五级&#...

【C++】智能指针
目录 一、先来看一下什么是智能指针 二、 auto_ptr 1、C98版本 2、C11的auto_ptr 三、boost 库中的智能指针 1. scoped_ptr 2、shared_ptr(最好的智能指针) 四、C11中新提供的智能指针 unique_ptr shared_ptr std::shared_ptr的循环引用问题…...
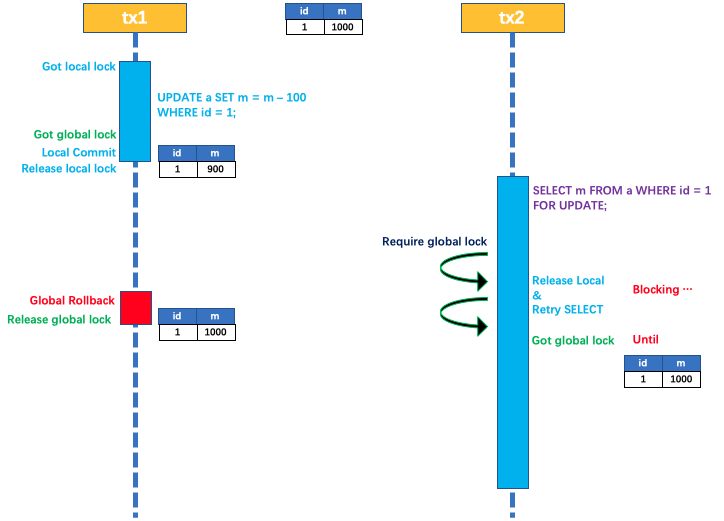
Seata架构篇 - AT模式
AT 模式 概述 Seata AT 模式是一种非侵入式的分布式事务解决方案,Seata 在内部做了对数据库操作的代理层,我们使用 Seata AT 模式时,实际上用的是 Seata 自带的数据源代理 DataSourceProxy,Seata 在这层代理中加入了很多逻辑&am…...
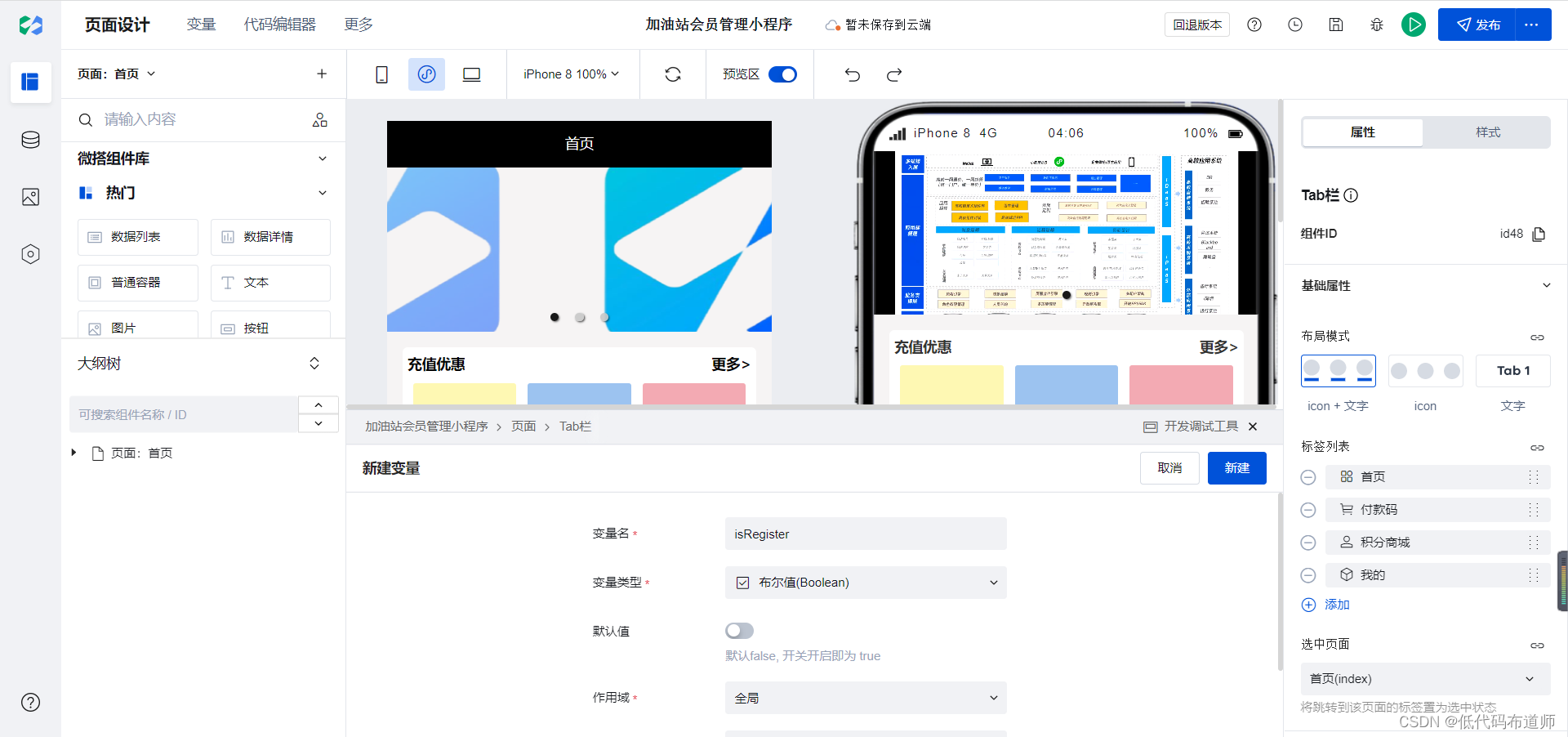
加油站会员管理小程序实战开发教程12
我们上一篇介绍了会员数据源的开发,本节我们介绍一下会员注册功能。 首先呢梳理一下会员注册的业务逻辑,如果用户是首次登录,那他肯定还没有给我们的小程序提交任何的信息。那么我们就在我的页面给他显示一个注册的按钮,如果他已经注册过了,那么就正常显示会员的信息,他…...
用腾讯云同步Obsidian笔记
介绍 之前用gitee同步OB笔记,同时做图床。但由于git系产品设置起来相对复杂,且后续可能有外链过审等问题。周五被同事小姐姐安利了用腾讯云COS,试了一下,果然不错。其主要优点如下: 设置简单,学习成本低&…...
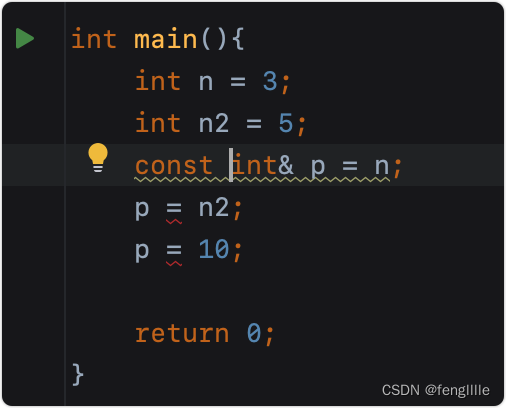
浅析C++指针与引用,栈传递的关系
目录 前言 C 堆指针 栈指针 常量指针 指针常量 引用 常量引用 总结 前言 目前做了很多项目,接触到各种语言,基本上用什么学什么,语言的边际就会很模糊,实际上语言的设计大同小异,只是语言具备各自的特性区别。…...
UE5 学习系列(二)用户操作界面及介绍
这篇博客是 UE5 学习系列博客的第二篇,在第一篇的基础上展开这篇内容。博客参考的 B 站视频资料和第一篇的链接如下: 【Note】:如果你已经完成安装等操作,可以只执行第一篇博客中 2. 新建一个空白游戏项目 章节操作,重…...

AI-调查研究-01-正念冥想有用吗?对健康的影响及科学指南
点一下关注吧!!!非常感谢!!持续更新!!! 🚀 AI篇持续更新中!(长期更新) 目前2025年06月05日更新到: AI炼丹日志-28 - Aud…...

模型参数、模型存储精度、参数与显存
模型参数量衡量单位 M:百万(Million) B:十亿(Billion) 1 B 1000 M 1B 1000M 1B1000M 参数存储精度 模型参数是固定的,但是一个参数所表示多少字节不一定,需要看这个参数以什么…...

Qt Widget类解析与代码注释
#include "widget.h" #include "ui_widget.h"Widget::Widget(QWidget *parent): QWidget(parent), ui(new Ui::Widget) {ui->setupUi(this); }Widget::~Widget() {delete ui; }//解释这串代码,写上注释 当然可以!这段代码是 Qt …...
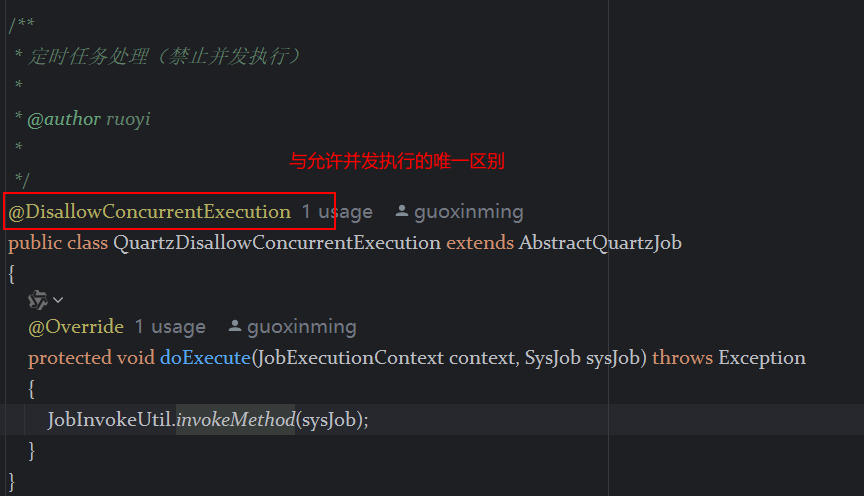
定时器任务——若依源码分析
分析util包下面的工具类schedule utils: ScheduleUtils 是若依中用于与 Quartz 框架交互的工具类,封装了定时任务的 创建、更新、暂停、删除等核心逻辑。 createScheduleJob createScheduleJob 用于将任务注册到 Quartz,先构建任务的 JobD…...
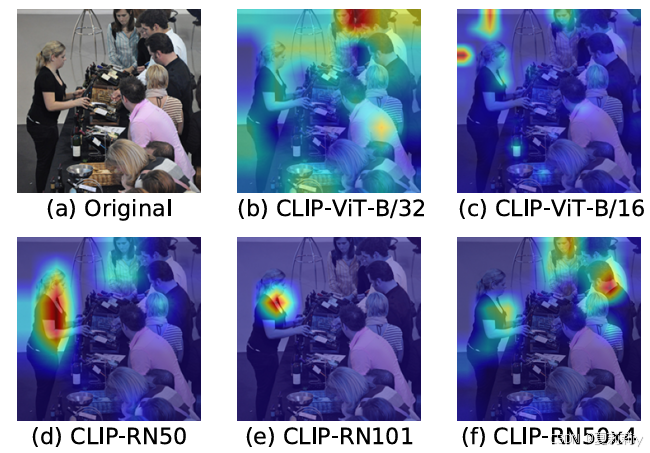

[ICLR 2022]How Much Can CLIP Benefit Vision-and-Language Tasks?
论文网址:pdf 英文是纯手打的!论文原文的summarizing and paraphrasing。可能会出现难以避免的拼写错误和语法错误,若有发现欢迎评论指正!文章偏向于笔记,谨慎食用 目录 1. 心得 2. 论文逐段精读 2.1. Abstract 2…...
2025盘古石杯决赛【手机取证】
前言 第三届盘古石杯国际电子数据取证大赛决赛 最后一题没有解出来,实在找不到,希望有大佬教一下我。 还有就会议时间,我感觉不是图片时间,因为在电脑看到是其他时间用老会议系统开的会。 手机取证 1、分析鸿蒙手机检材&#x…...

EtherNet/IP转DeviceNet协议网关详解
一,设备主要功能 疆鸿智能JH-DVN-EIP本产品是自主研发的一款EtherNet/IP从站功能的通讯网关。该产品主要功能是连接DeviceNet总线和EtherNet/IP网络,本网关连接到EtherNet/IP总线中做为从站使用,连接到DeviceNet总线中做为从站使用。 在自动…...

NFT模式:数字资产确权与链游经济系统构建
NFT模式:数字资产确权与链游经济系统构建 ——从技术架构到可持续生态的范式革命 一、确权技术革新:构建可信数字资产基石 1. 区块链底层架构的进化 跨链互操作协议:基于LayerZero协议实现以太坊、Solana等公链资产互通,通过零知…...
SpringCloudGateway 自定义局部过滤器
场景: 将所有请求转化为同一路径请求(方便穿网配置)在请求头内标识原来路径,然后在将请求分发给不同服务 AllToOneGatewayFilterFactory import lombok.Getter; import lombok.Setter; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; impor…...
