机器学习样本数据划分的典型Python方法
机器学习样本数据划分的典型Python方法
| Date | Author | Version | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023.08.16 | Dog Tao | V1.0 | 完成文档撰写。 |
文章目录
- 机器学习样本数据划分的典型Python方法
- 样本数据的分类
- Training Data
- Validation Data
- Test Data
- numpy.ndarray类型数据
- 直接划分
- 交叉验证
- 基于`KFold`
- 基于`RepeatedKFold`
- 基于`cross_val_score`
- torch.tensor类型数据
- 直接划分
- 基于TensorDataset
- 基于切片方法
- 交叉验证
样本数据的分类
In machine learning and deep learning, the data used to develop a model can be divided into three distinct sets: training data, validation data, and test data. Understanding the differences among them and their distinct roles is crucial for effective model development and evaluation.
Training Data
- Purpose: The training data is used to train the model. It’s the dataset the algorithm will learn from.
- Usage: The model parameters are adjusted or “learned” using this data. For example, in a neural network, weights are adjusted using backpropagation on this data.
- Fraction: Typically, a significant majority of the dataset is allocated to training (e.g., 60%-80%).
- Issues: Overfitting can be a concern if the model becomes too specialized to the training data, leading it to perform poorly on unseen data.
Validation Data
- Purpose: The validation data is used to tune the model’s hyperparameters and make decisions about the model’s structure (e.g., choosing the number of hidden units in a neural network or the depth of a decision tree).
- Usage: After training on the training set, the model is evaluated on the validation set, and adjustments to the model (like changing hyperparameters) are made based on this evaluation. The process might be iterative.
- Fraction: Often smaller than the training set, typically 10%-20% of the dataset.
- Issues: Overfitting to the validation set can happen if you make too many adjustments based on the validation performance. This phenomenon is sometimes called “validation set overfitting” or “leakage.”
Test Data
- Purpose: The test data is used to evaluate the model’s final performance after training and validation. It provides an unbiased estimate of model performance in real-world scenarios.
- Usage: Only for evaluation. The model does not “see” this data during training or hyperparameter tuning. Once the model is finalized, it is tested on this dataset to gauge its predictive performance.
- Fraction: Typically, 10%-20% of the dataset.
- Issues: To preserve the unbiased nature of the test set, it should never be used to make decisions about the model. If it’s used in this way, it loses its purpose, and one might need a new test set.
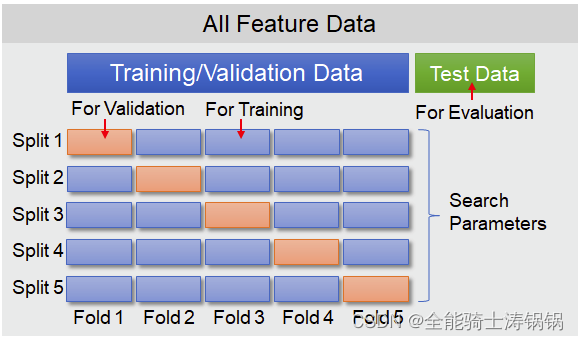
Note: The exact percentages mentioned can vary based on the domain, dataset size, and specific methodologies. In practice, strategies like k-fold cross-validation might be used, where the dataset is split into k subsets, and the model is trained and validated multiple times, each time using a different subset as the validation set and the remaining data as the training set.
In summary, the distinction among training, validation, and test data sets is crucial for robust model development, avoiding overfitting, and ensuring that the model will generalize well to new, unseen data.
numpy.ndarray类型数据
直接划分
To split numpy.ndarray data into a training set and validation set, you can use the train_test_split function provided by the sklearn.model_selection module.
Here’s a brief explanation followed by an example:
-
Function Name:
train_test_split() -
Parameters:
- arrays: Sequence of indexables with the same length. Can be any data type.
- test_size: If float, should be between 0.0 and 1.0, representing the proportion of the dataset to include in the test split. If int, represents the absolute number of test samples.
- train_size: Complement to
test_size. If not provided, the value is set to the complement of the test size. - random_state: Seed for reproducibility.
- shuffle: Whether to shuffle before splitting. Default is True.
- stratify: If not None, the data is split in a stratified fashion using this as the class labels.
-
Returns: Split arrays.
Example:
Let’s split an example dataset into a training set (80%) and a validation set (20%):
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split# Sample data
X = np.random.rand(100, 5) # 100 samples, 5 features
y = np.random.randint(0, 2, 100) # 100 labels, binary classification# Split the data
X_train, X_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)print("Training set size:", len(X_train))
print("Validation set size:", len(X_val))
- If you want the split to be reproducible (i.e., get the same split each time you run the code), set the
random_stateto any integer value. - If you’re working with imbalanced datasets and want to ensure that the class distribution is the same in both the training and validation sets, you can use the
stratifyparameter. Settingstratify=ywill ensure that the splits have the same class distribution as the original dataset.
交叉验证
基于KFold
For performing ( n )-fold cross-validation on numpy.ndarray data, you can use the KFold class from the sklearn.model_selection module.
Here’s how you can use ( n )-fold cross-validation:
-
Class Name:
KFold -
Parameters of
KFold:- n_splits: Number of folds.
- shuffle: Whether to shuffle the data before splitting into batches.
- random_state: Seed used by the random number generator for reproducibility.
Example:
Let’s say you want 5-fold cross-validation:
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold# Sample data
X = np.random.rand(100, 5) # 100 samples, 5 features
y = np.random.randint(0, 2, 100) # 100 labels, binary classificationkf = KFold(n_splits=5, shuffle=True, random_state=42)for train_index, val_index in kf.split(X):X_train, X_val = X[train_index], X[val_index]y_train, y_val = y[train_index], y[val_index]print("Training set size:", len(X_train))print("Validation set size:", len(X_val))print("---")
- Each iteration in the loop gives you a different split of training and validation data.
- The training and validation indices are generated based on the size of
X. - If you want the split to be reproducible (i.e., get the same split each time you run the code), set the
random_stateparameter. - In case you want stratified k-fold cross-validation (where the folds are made by preserving the percentage of samples for each class), use
StratifiedKFoldinstead ofKFold. This can be particularly useful for imbalanced datasets.
基于RepeatedKFold
RepeatedKFold repeats K-Fold cross-validator. For each repetition, it splits the dataset into k-folds and then the k-fold cross-validation is performed. This results in having multiple scores for multiple runs, which might give a more comprehensive evaluation of the model’s performance.
Parameters:
- n_splits: Number of folds.
- n_repeats: Number of times cross-validator needs to be repeated.
- random_state: Random seed for reproducibility.
Example:
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import RepeatedKFoldX = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6], [7, 8]])
y = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4])rkf = RepeatedKFold(n_splits=2, n_repeats=2, random_state=42)for train_index, test_index in rkf.split(X):print("TRAIN:", train_index, "TEST:", test_index)X_train, X_test = X[train_index], X[test_index]y_train, y_test = y[train_index], y[test_index]
基于cross_val_score
cross_val_score evaluates a score by cross-validation. It’s a quick utility that wraps both the steps of splitting the dataset and evaluating the estimator’s performance.
Parameters:
- estimator: The object to use to fit the data.
- X: The data to fit.
- y: The target variable for supervised learning problems.
- cv: Cross-validation strategy.
- scoring: A string (see model evaluation documentation) or a scorer callable object/function.
Example:
Here’s an example using RepeatedKFold with cross_val_score for a simple regression model:
from sklearn.datasets import make_regression
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score, RepeatedKFold# Generate a sample dataset
X, y = make_regression(n_samples=1000, n_features=20, noise=0.1)# Define the model
model = LinearRegression()# Define the evaluation procedure
cv = RepeatedKFold(n_splits=10, n_repeats=3, random_state=1)# Evaluate the model
scores = cross_val_score(model, X, y, scoring='neg_mean_absolute_error', cv=cv, n_jobs=-1)# Summary of performance
print('Mean MAE: %.3f (%.3f)' % (np.mean(scores), np.std(scores)))
In the above example:
cross_val_scoreis used to evaluate the performance of aLinearRegressionmodel using the mean absolute error (MAE) metric.- We employ a 10-fold cross-validation strategy that is repeated 3 times, as specified by
RepeatedKFold. - The scores from all these repetitions and folds are aggregated into the
scoresarray.
Note:
- In the scoring parameter, the ‘neg_mean_absolute_error’ is used because in
sklearn, the convention is to maximize the score, so loss functions are represented with negative values (the closer to 0, the better).
torch.tensor类型数据
直接划分
基于TensorDataset
To split a tensor into training and validation sets, you can use the random_split method from torch.utils.data. This is particularly handy when you’re dealing with Dataset objects, but it can also be applied directly to tensors with a bit of wrapping.
Here’s how you can do it:
-
Wrap your tensor in a TensorDataset:
Before usingrandom_split, you might need to wrap your tensors in aTensorDatasetso they can be treated as a dataset. -
Use
random_splitto divide the dataset:
Therandom_splitfunction requires two arguments: the dataset you’re splitting and a list of lengths for each resulting subset.
Here’s an example using random_split:
import torch
from torch.utils.data import TensorDataset, random_split# Sample tensor data
X = torch.randn(1000, 10) # 1000 samples, 10 features each
Y = torch.randint(0, 2, (1000,)) # 1000 labels# Wrap tensors in a dataset
dataset = TensorDataset(X, Y)# Split into 80% training (800 samples) and 20% validation (200 samples)
train_size = int(0.8 * len(dataset))
val_size = len(dataset) - train_size
train_dataset, val_dataset = random_split(dataset, [train_size, val_size])print(len(train_dataset)) # 800
print(len(val_dataset)) # 200
Once you’ve split your data into training and validation sets, you can easily load them in batches using DataLoader if needed.
-
The
random_splitmethod does not actually make a deep copy of the dataset. Instead, it returnsSubsetobjects that internally have indices to access the original dataset. This makes the splitting operation efficient in terms of memory. -
Each time you call
random_split, the split will be different because the method shuffles the indices. If you want reproducibility, you should set the random seed usingtorch.manual_seed()before callingrandom_split.
The resulting subsets from random_split can be directly passed to DataLoader to create training and validation loaders:
from torch.utils.data import DataLoadertrain_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=32, shuffle=True)
val_loader = DataLoader(val_dataset, batch_size=32, shuffle=False)
This allows you to efficiently iterate over the batches of data during training and validation.
If you have a TensorDataset and you want to retrieve all the data pairs from it, you can simply iterate over the dataset. Each iteration will give you a tuple where each element of the tuple corresponds to a tensor in the TensorDataset.
Here’s an example:
import torch
from torch.utils.data import TensorDataset# Sample tensor data
X = torch.randn(100, 10) # 100 samples, 10 features each
Y = torch.randint(0, 2, (100,)) # 100 labels# Wrap tensors in a dataset
dataset = TensorDataset(X, Y)# Get all data pairs
data_pairs = [data for data in dataset]# If you want to get them separately
X_data, Y_data = zip(*data_pairs)# Convert back to tensors if needed
X_data = torch.stack(X_data)
Y_data = torch.stack(Y_data)print(X_data.shape) # torch.Size([100, 10])
print(Y_data.shape) # torch.Size([100])
In the code above:
- We first create a
TensorDatasetfrom sample data. - Then, we use list comprehension to retrieve all data pairs from the dataset.
- Finally, we separate the features and labels using the
zipfunction, and then convert them back to tensors.
The zip(*data_pairs) expression is a neat Python trick that involves unpacking and transposing pairs (or tuples) of data.
To break it down:
-
zipfunction: This is a built-in Python function that allows you to iterate over multiple lists (or other iterable objects) in parallel. For example, if you have two listsa = [1,2,3]andb = [4,5,6], callingzip(a,b)will yield pairs(1,4),(2,5), and(3,6). -
The
*unpacking operator: When used in a function call, it unpacks a list (or tuple) into individual elements. For instance, if you havefunc(*[1,2,3]), it’s the same as callingfunc(1,2,3).
When you use them together as in zip(*data_pairs), you’re doing the following:
- Unpacking the
data_pairs: This treats the list of tuples indata_pairsas separate arguments tozip. - Transposing with
zip: Since each element ofdata_pairsis a tuple of (X, Y), usingzipeffectively transposes the data, separating all the X’s from the Y’s.
Here’s a simple example to illustrate:
data_pairs = [(1, 'a'), (2, 'b'), (3, 'c')]
x_data, y_data = zip(*data_pairs)
print(x_data) # Outputs: (1, 2, 3)
print(y_data) # Outputs: ('a', 'b', 'c')
In the context of our previous discussion, this operation allowed us to efficiently separate the feature tensors from the label tensors in the TensorDataset.
基于切片方法
To split a PyTorch tensor into training and validation sets, you can use simple slicing. Here’s a straightforward way to do this:
- Decide on a split ratio (e.g., 80% training and 20% validation).
- Shuffle the tensor (optional, but often a good idea).
- Split the tensor based on the desired ratio.
Here’s an example using a 80-20 split:
import torch# Sample data
X = torch.randn(1000, 10) # 1000 samples, 10 features each
Y = torch.randint(0, 2, (1000,))# Shuffle data
indices = torch.randperm(X.size(0))
X = X[indices]
Y = Y[indices]# Split ratios
train_size = int(0.8 * X.size(0))
val_size = X.size(0) - train_size# Split data
X_train = X[:train_size]
Y_train = Y[:train_size]
X_val = X[train_size:]
Y_val = Y[train_size:]print(X_train.size())
print(Y_train.size())
print(X_val.size())
print(Y_val.size())
In this example:
- We first shuffled the data by generating a permutation of indices with
torch.randperm(). - We then split the data based on the desired ratio (in this case, 80-20).
- The resulting tensors (
X_train,Y_train,X_val,Y_val) represent the training and validation sets respectively.
This method works well when you have independent and identically distributed data. If you need to perform stratified sampling (e.g., you want to ensure the training and validation sets have similar class distributions), consider using utilities from libraries like scikit-learn to generate the splits, and then index into the PyTorch tensor using those splits.
The torch.randperm(n) function generates a random permutation of integers from 0 to n-1. This is particularly useful for shuffling data. Let’s break down the function torch.randperm(X.size(0)):
-
X.size(0):- This retrieves the size of the first dimension of tensor
X. - If
Xis a 2D tensor with shape[samples, features], thenX.size(0)will return the number of samples.
- This retrieves the size of the first dimension of tensor
-
torch.randperm(...):- This generates a tensor of random permutations of integers from
0ton-1, wherenis the input argument. - The result is effectively a shuffled sequence of integers in the range
[0, n-1].
- This generates a tensor of random permutations of integers from
In the context of splitting data into training and validation sets, the random permutation ensures that the data is shuffled randomly before the split, so that the training and validation sets are likely to be representative of the overall dataset.
交叉验证
To perform n-fold cross-validation on PyTorch tensor data, you can use the KFold class from sklearn.model_selection. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Convert the PyTorch tensor to numpy arrays using the
.numpy()method. - Use
KFoldfromsklearn.model_selectionto generate training and validation indices. - Use these indices to split your PyTorch tensor data into training and validation sets.
- Train and validate your model using these splits.
Let’s see a practical example:
import torch
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold# Sample tensor data
X = torch.randn(100, 10) # 100 samples, 10 features each
Y = torch.randint(0, 2, (100,)) # 100 labels# Convert tensor to numpy
X_np = X.numpy()
Y_np = Y.numpy()# Number of splits
n_splits = 5
kf = KFold(n_splits=n_splits)for train_index, val_index in kf.split(X_np):# Convert indices to tensortrain_index = torch.tensor(train_index)val_index = torch.tensor(val_index)X_train, X_val = X[train_index], X[val_index]Y_train, Y_val = Y[train_index], Y[val_index]# Now, you can train and validate your model using X_train, X_val, Y_train, Y_val
Note:
- The
KFoldclass provides indices which we then use to slice our tensor and obtain the respective training and validation sets. - In the example above, we’re performing a 5-fold cross-validation on the data. Each iteration provides a new training-validation split.
If you want to shuffle the data before splitting, you can set the shuffle parameter of KFold to True.
相关文章:

机器学习样本数据划分的典型Python方法
机器学习样本数据划分的典型Python方法 DateAuthorVersionNote2023.08.16Dog TaoV1.0完成文档撰写。 文章目录 机器学习样本数据划分的典型Python方法样本数据的分类Training DataValidation DataTest Data numpy.ndarray类型数据直接划分交叉验证基于KFold基于RepeatedKFold基…...

重建与突破,探讨全链游戏的现在与未来
全链游戏(On-Chain Game)是指将游戏内资产通过虚拟货币或 NFT 形式记录上链的游戏类型。除此以外,游戏的状态存储、计算与执行等皆被部署在链上,目的是为用户打造沉浸式、全方位的游戏体验,超越传统游戏玩家被动控制的…...
[C++] 模板template
目录 1、函数模板 1.1 函数模板概念 1.2 函数模板格式 1.3 函数模板的原理 1.4 函数模板的实例化 1.4.1 隐式实例化 1.4.2 显式实例化 1.5 模板参数的匹配原则 2、类模板 2.1 类模板的定义格式 2.2 类模板的实例化 讲模板之前呢,我们先来谈谈泛型编程&am…...
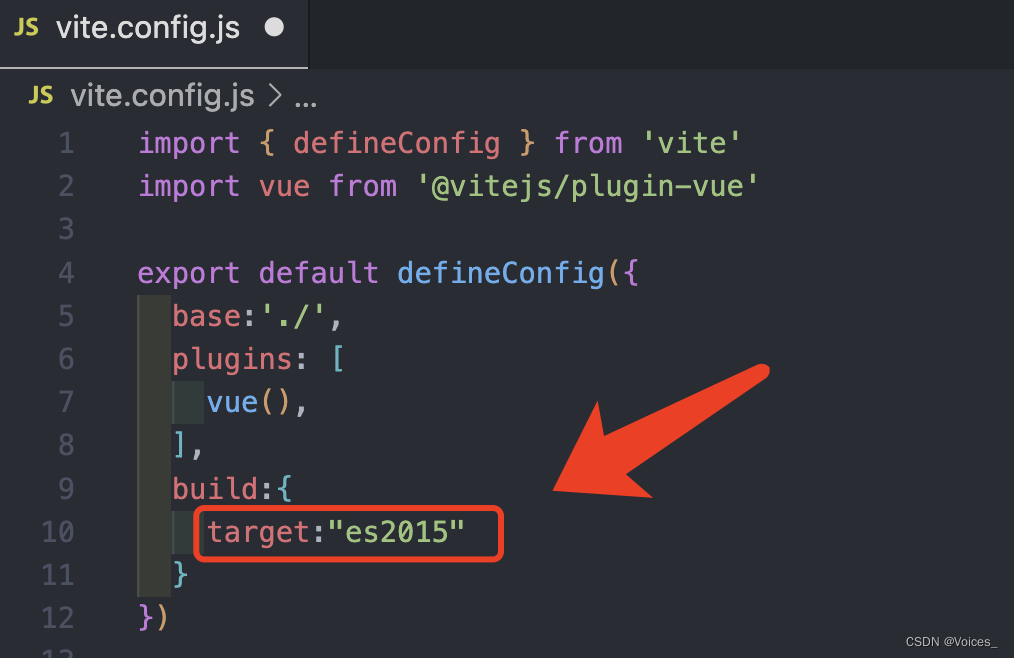
[vite] 项目打包后页面空白,配置了base后也不生效
记录下解决问题的过程和思路 首先打开看打包后的 dist/index.html 文件,和页面上的报错 这里就发现了第一个问题 报错的意思是 index.html中引用的 css文件 和 js文件 找不到 为了解决这个问题,在vite.config.js配置中,增加一项 base:./ …...

springboot整合kafka-笔记
springboot整合kafka-笔记 配置pom.xml 这里我的springboot版本是2.3.8.RELEASE,使用的kafka-mq的版本是2.12 <dependencyManagement><dependencies><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>s…...

Rust软件外包开发语言的特点
Rust 是一种系统级编程语言,强调性能、安全性和并发性的编程语言,适用于广泛的应用领域,特别是那些需要高度可靠性和高性能的场景。下面和大家分享 Rust 语言的一些主要特点以及适用的场合,希望对大家有所帮助。北京木奇移动技术有…...
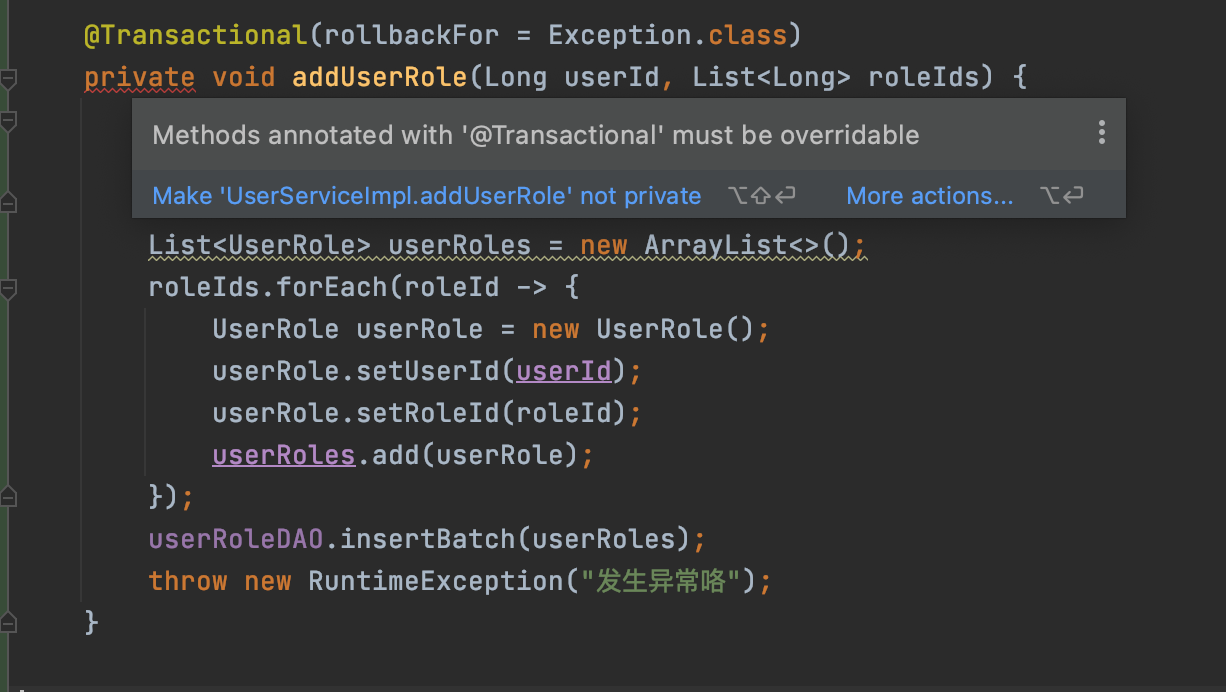
Spring Boot业务代码中使用@Transactional事务失效踩坑点总结
1.概述 接着之前我们对Spring AOP以及基于AOP实现事务控制的上文,今天我们来看看平时在项目业务开发中使用声明式事务Transactional的失效场景,并分析其失效原因,从而帮助开发人员尽量避免踩坑。 我们知道 Spring 声明式事务功能提供了极其…...
知识体系总结(九)设计原则、设计模式、分布式、高性能、高可用
文章目录 架构设计为什么要进行技术框架的设计 六大设计原则一、单一职责原则二、开闭原则三、依赖倒置原则四、接口分离原则五、迪米特法则(又称最小知道原则)六、里氏替换原则案例诠释 常见设计模式构造型单例模式工厂模式简单工厂工厂方法 生成器模式…...
Springboot 集成Beetl模板
一、在启动类下的pom.xml中导入依赖: <!--beetl模板引擎--><dependency><groupId>com.ibeetl</groupId><artifactId>beetl</artifactId><version>2.9.8</version></dependency> 二、 配置 beetl需要的Beetl…...

RabbitMQ查询队列使用情况和消费者详情实现
spring-boot-starter-amqp spring-boot-starter-amqp是Spring Boot框架中与AMQP(高级消息队列协议)相关的自动配置启动器。它提供了使用AMQP进行消息传递和异步通信的功能。 以下是spring-boot-starter-amqp的主要特性和功能: 自动配置:spring-boot-starter-amqp通过自动…...
Spark第二课RDD的详解
1.前言 RDD JAVA中的IO 1.小知识点穿插 1. 装饰者设计模式 装饰者设计模式:本身功能不变,扩展功能. 举例: 数据流的读取 一层一层的包装,进而将功能进行进一步的扩展 2.sleep和wait的区别 本质区别是字体不一样,sleep斜体,wait正常 斜体是静态方法…...
人工智能学习框架—飞桨Paddle人工智能
1.人工智能框架 机器学习的三要素:模型、学习策略、优化算法。 当我们用机器学习来解决一些模式识别任务时,一般的流程包含以下几个步骤: 1.1.浅层学习和深度学习 浅层学习(Shallow Learning):不涉及特征学习,其特征…...
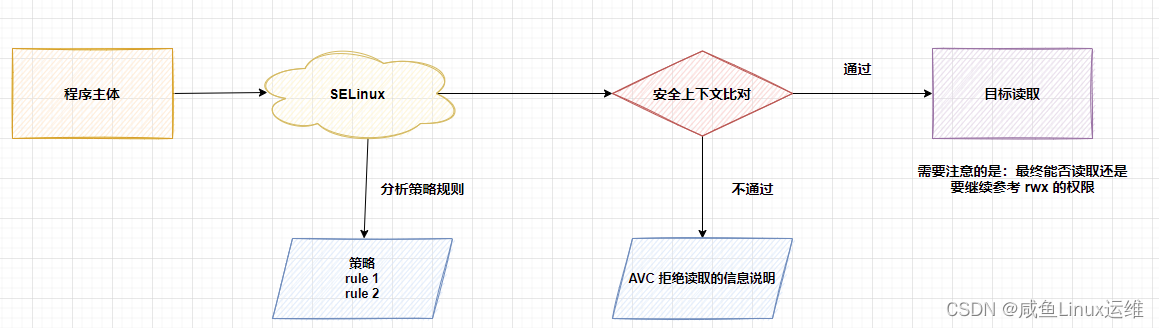
SElinux 导致 Keepalived 检测脚本无法执行
哈喽大家好,我是咸鱼 今天我们来看一个关于 Keepalived 检测脚本无法执行的问题 一位粉丝后台私信我,说他部署的 keepalived 集群 vrrp_script 模块中的脚本执行失败了,但是手动执行这个脚本却没有任何问题 这个问题也是咸鱼第一次遇到&…...
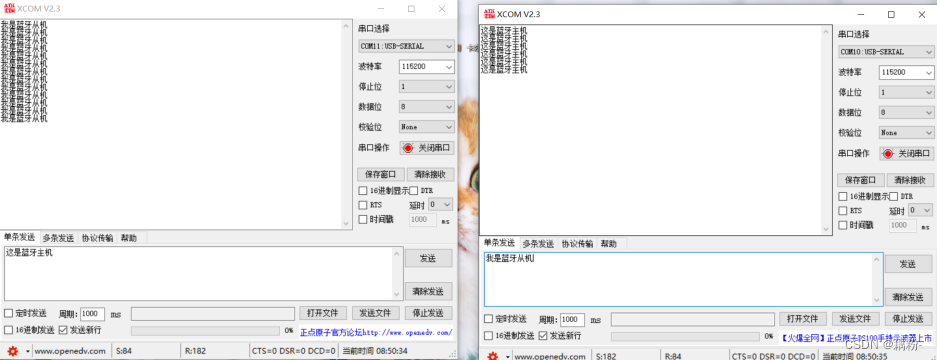
2022年电赛C题——小车跟随行驶系统——做题记录以及经验分享
前言 自己打算将做过的电赛真题,主要包含控制组的,近几年出现的小车控制题目,自己做过的真题以及在准备电赛期间刷真题出现的问题以及经验分享给大家 这次带来的是22年电赛C题——小车跟随行驶系统,这道题目指定使用的是TI的单片…...
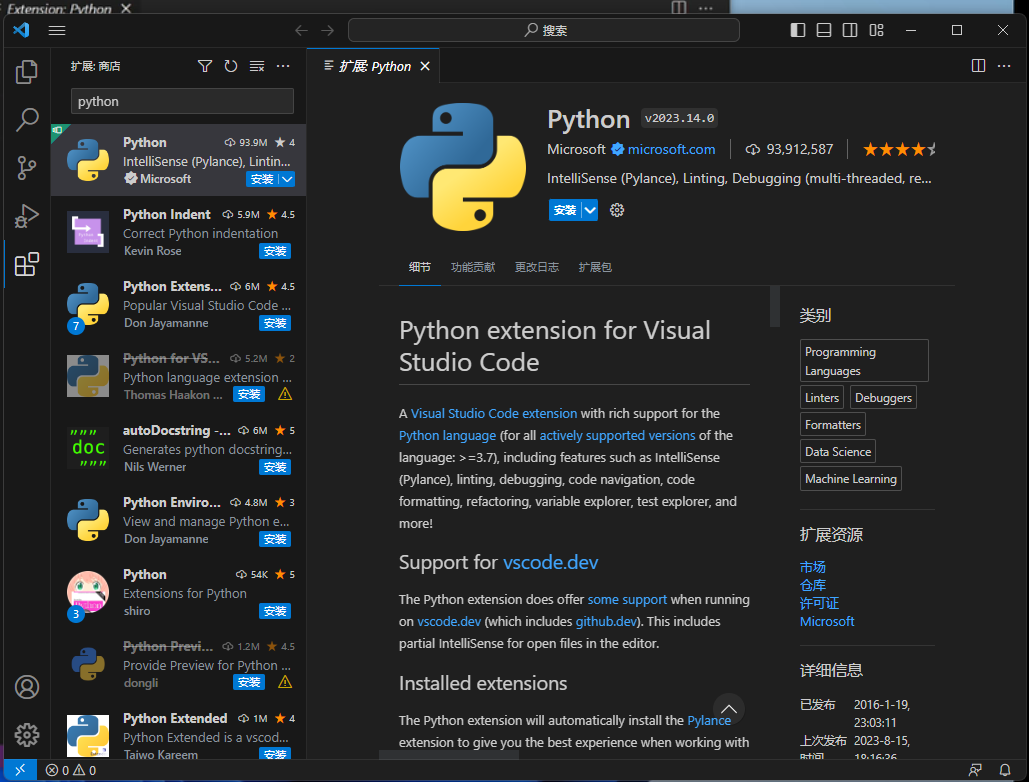
vscode + python
序 参考链接: 【教程】VScode中配置Python运行环境_哔哩哔哩_bilibili Python部分 Python Releases for Windows | Python.org vscode部分 Visual Studio Code - Code Editing. Redefined 一路next,全部勾上: 就可以了: 安装插…...
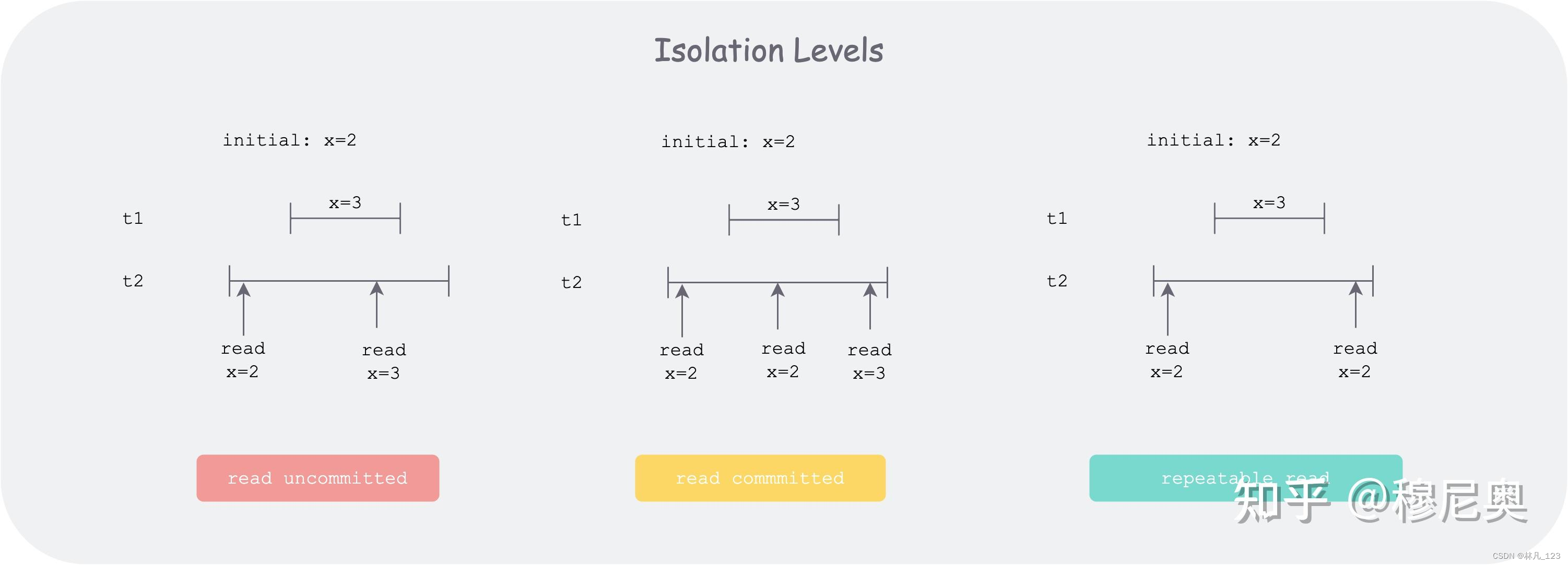
badgerdb里面的事务
事务的ACID A 原子性(Atomicity) 多步骤操作,只能是两种状态,要么所有的步骤都成功执行,要么所有的步骤都不执行,举例说明就是小明向小红转账30元的场景,拆分成两个步骤,步骤1&#…...
 => { /* some code */ }))用法说明)
C# this.Invoke(new Action(() => { /* some code */ }))用法说明
在 C# 中,this.Invoke(new Action(() > { /* some code */ })) 是一种用于在 UI 线程上执行代码的方法,通常用于在后台线程中更新 UI 控件的值或执行其他需要在 UI 线程上执行的操作。 在 Windows Forms 或 WPF 等图形界面应用程序中,UI …...

MongoDB:MySQL,Redis,ES,MongoDB的应用场景
简单明了说明MySQL,ES,MongoDB的各自特点,应用场景,以及MongoDB如何使用的第一章节. 一. SQL与NoSQL SQL被称为结构化查询语言.是传统意义上的数据库,数据之间存在很明确的关联关系,例如主外键关联,这种结构可以确保数据的完整性(数据没有缺失并且正确).但是正因为这种严密的结…...

leetcode每日一题_2682.找出转圈游戏输家
2682.找出转圈游戏输家 题目: n 个朋友在玩游戏。这些朋友坐成一个圈,按 顺时针方向 从 1 到 n 编号。从第 i 个朋友的位置开始顺时针移动 1 步会到达第 (i 1) 个朋友的位置(1 < i < n),而从第 n 个朋友的位置开始顺时针移…...
)
OpenCV之薄板样条插值(ThinPlateSpline)
官方文档:OpenCV: cv::ThinPlateSplineShapeTransformer Class Reference 使用方法: 头文件:#include <opencv2/shape/shape_transformer.hpp> (1)点匹配 一般根据有多少个样本(或者点)…...

基于大模型的 UI 自动化系统
基于大模型的 UI 自动化系统 下面是一个完整的 Python 系统,利用大模型实现智能 UI 自动化,结合计算机视觉和自然语言处理技术,实现"看屏操作"的能力。 系统架构设计 #mermaid-svg-2gn2GRvh5WCP2ktF {font-family:"trebuchet ms",verdana,arial,sans-…...
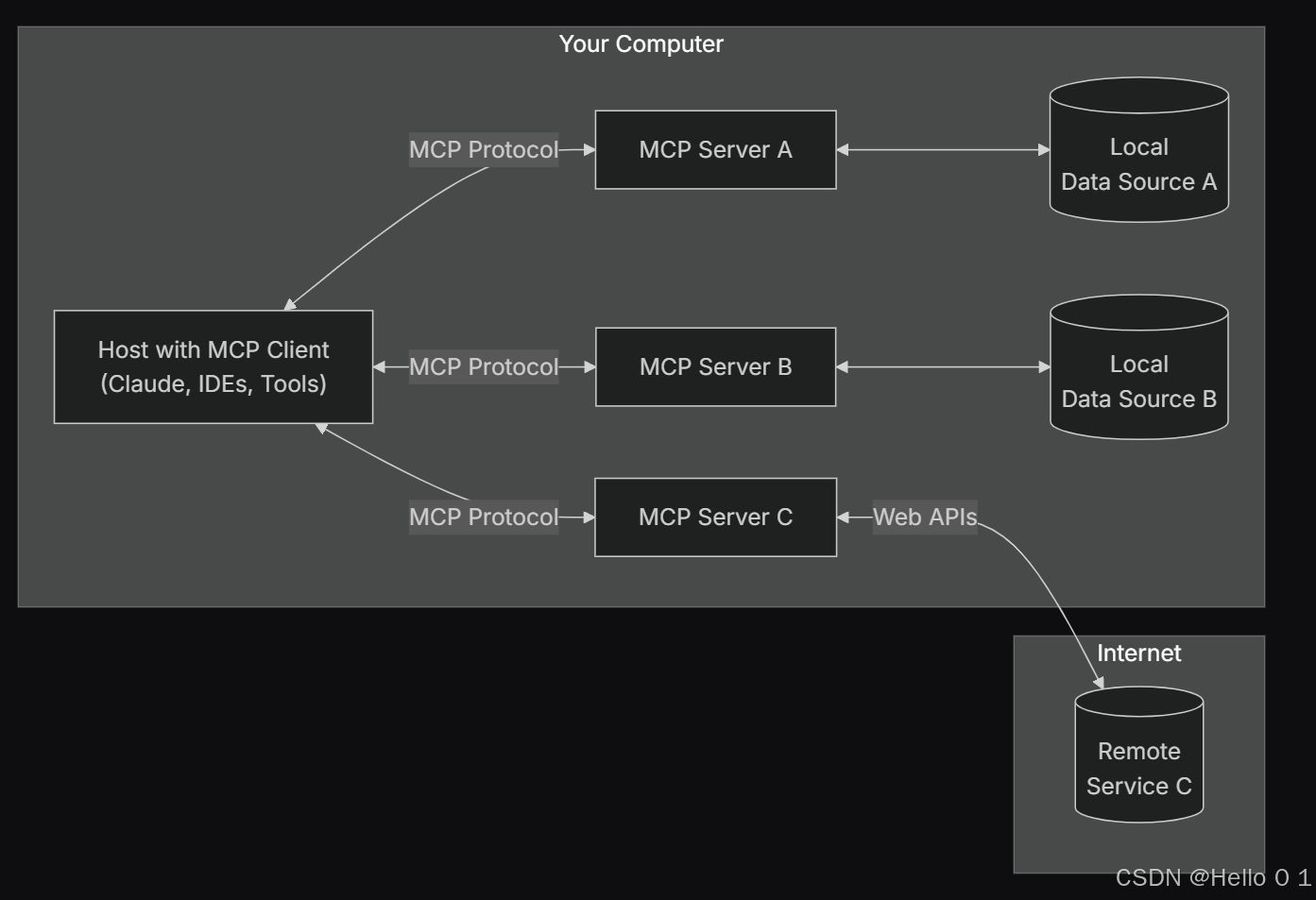
让AI看见世界:MCP协议与服务器的工作原理
让AI看见世界:MCP协议与服务器的工作原理 MCP(Model Context Protocol)是一种创新的通信协议,旨在让大型语言模型能够安全、高效地与外部资源进行交互。在AI技术快速发展的今天,MCP正成为连接AI与现实世界的重要桥梁。…...

安宝特案例丨Vuzix AR智能眼镜集成专业软件,助力卢森堡医院药房转型,赢得辉瑞创新奖
在Vuzix M400 AR智能眼镜的助力下,卢森堡罗伯特舒曼医院(the Robert Schuman Hospitals, HRS)凭借在无菌制剂生产流程中引入增强现实技术(AR)创新项目,荣获了2024年6月7日由卢森堡医院药剂师协会࿰…...

【JVM】Java虚拟机(二)——垃圾回收
目录 一、如何判断对象可以回收 (一)引用计数法 (二)可达性分析算法 二、垃圾回收算法 (一)标记清除 (二)标记整理 (三)复制 (四ÿ…...

【堆垛策略】设计方法
堆垛策略的设计是积木堆叠系统的核心,直接影响堆叠的稳定性、效率和容错能力。以下是分层次的堆垛策略设计方法,涵盖基础规则、优化算法和容错机制: 1. 基础堆垛规则 (1) 物理稳定性优先 重心原则: 大尺寸/重量积木在下…...
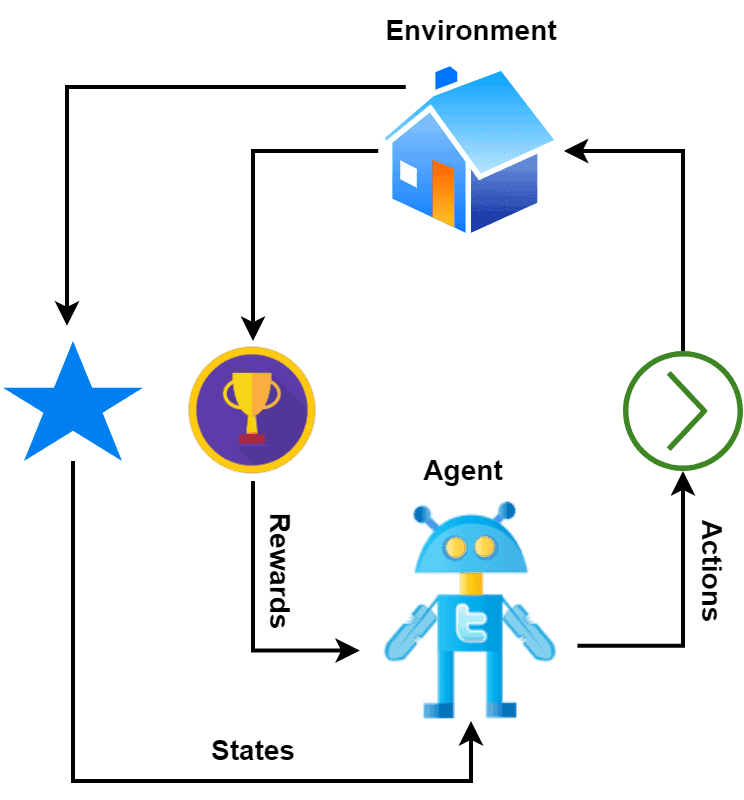
【深度学习新浪潮】什么是credit assignment problem?
Credit Assignment Problem(信用分配问题) 是机器学习,尤其是强化学习(RL)中的核心挑战之一,指的是如何将最终的奖励或惩罚准确地分配给导致该结果的各个中间动作或决策。在序列决策任务中,智能体执行一系列动作后获得一个最终奖励,但每个动作对最终结果的贡献程度往往…...
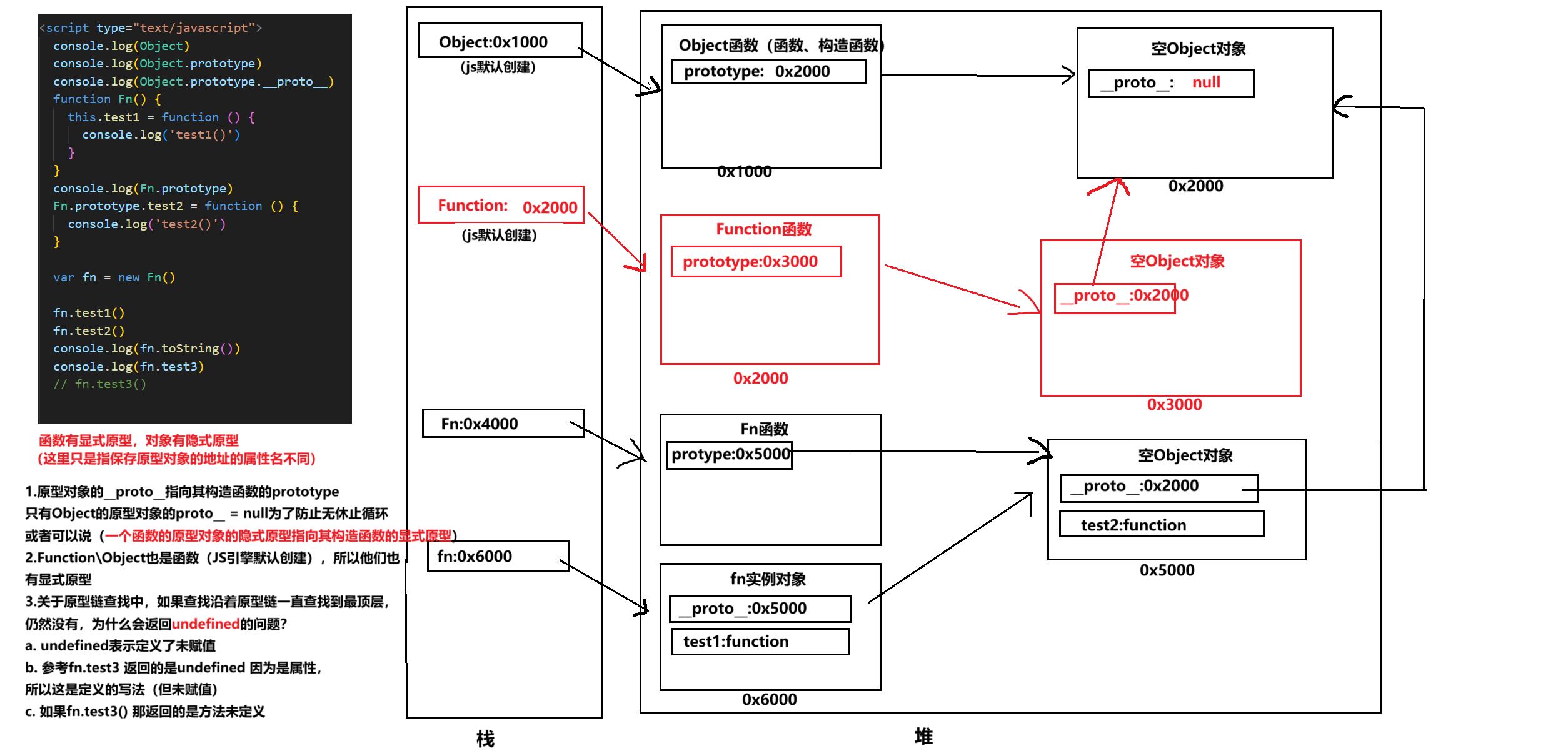
图解JavaScript原型:原型链及其分析 | JavaScript图解
忽略该图的细节(如内存地址值没有用二进制) 以下是对该图进一步的理解和总结 1. JS 对象概念的辨析 对象是什么:保存在堆中一块区域,同时在栈中有一块区域保存其在堆中的地址(也就是我们通常说的该变量指向谁&…...

密码学基础——SM4算法
博客主页:christine-rr-CSDN博客 专栏主页:密码学 📌 【今日更新】📌 对称密码算法——SM4 目录 一、国密SM系列算法概述 二、SM4算法 2.1算法背景 2.2算法特点 2.3 基本部件 2.3.1 S盒 2.3.2 非线性变换 编辑…...
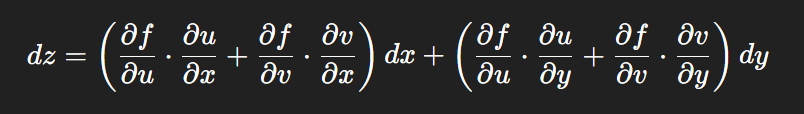
链式法则中 复合函数的推导路径 多变量“信息传递路径”
非常好,我们将之前关于偏导数链式法则中不能“约掉”偏导符号的问题,统一使用 二重复合函数: z f ( u ( x , y ) , v ( x , y ) ) \boxed{z f(u(x,y),\ v(x,y))} zf(u(x,y), v(x,y)) 来全面说明。我们会展示其全微分形式(偏导…...

命令行关闭Windows防火墙
命令行关闭Windows防火墙 引言一、防火墙:被低估的"智能安检员"二、优先尝试!90%问题无需关闭防火墙方案1:程序白名单(解决软件误拦截)方案2:开放特定端口(解决网游/开发端口不通)三、命令行极速关闭方案方法一:PowerShell(推荐Win10/11)方法二:CMD命令…...
