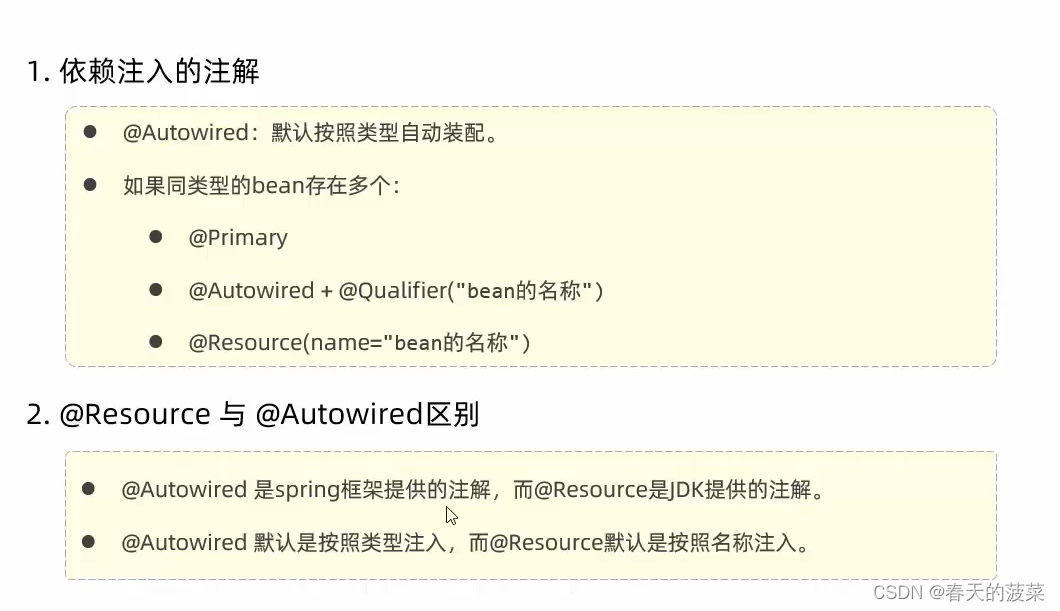
目标检测(Object Detection)
文章目录
- 1. 目标检测
- 1.1 目标检测简要概述及名词解释
- 1.2 IOU
- 1.3 TP TN FP FN
- 1.4 precision(精确度)和recall(召回率)
- 2. 边框回归Bounding-Box regression
- 3. Faster R-CNN
- 3.1 Faster-RCNN:conv layer
- 3.2 Faster-RCNN:Region Proposal Networks(RPN)
- 3.2.1 anchors
- 3.2.2 softmax判定positive与negative
- 3.2.3 对proposals进行bounding box regression
- 3.2.4 Proposal Layer
- 3.3 Faster-RCNN:Roi pooling
- 3.4 Faster-RCNN: Classification
- 3.5 网络对比
- 3.6 代码示例
- 3.6.1 网络搭建
- 3.6.2 训练脚本
- 3.6.3 预测脚本
- 4. One stage和two stage
- 5. Yolo
- 5.1 Yolo-You Only Look Once
- 5.2 Yolo2
- 5.2.1 Yolo2 -- 采用anchor boxes
- 5.2.2 Yolo2 -- Dimension Clusters(维度聚类)
- 5.3 Yolo3
- 5.4 代码示例(yolo v3)
- 5.4.1 模型搭建
- 5.4.2 配置文件
- 5.4.3 detect文件
- 5.4.4 gen_anchors.py
- 5.4.5 utils.py
- 5.4.6 预测脚本
- 6. 拓展-SSD
1. 目标检测
计算机视觉的五大应用
1.1 目标检测简要概述及名词解释
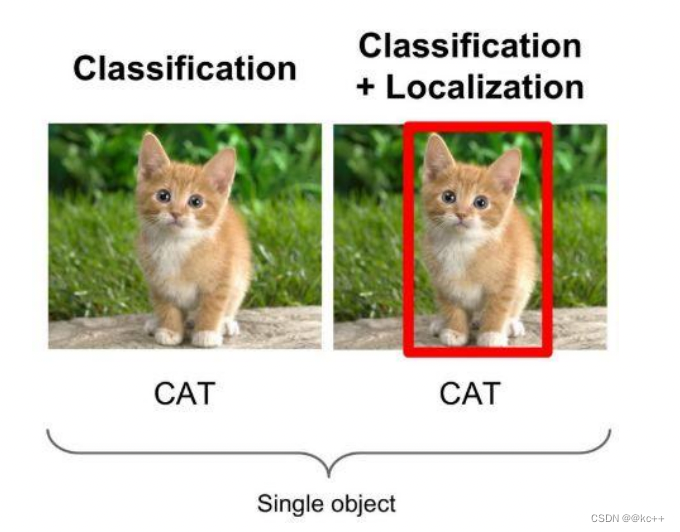
- 物体识别是要分辨出图片中有什么物体,输入是图片,输出是类别标签和概率。物体检测算法不仅要检测图片中有什么物体,还要输出物体的外框(x, y, width, height)来定位物体的位置。
- object detection,就是在给定的图片中精确找到物体所在位置,并标注出物体的类别。
- object detection要解决的问题就是物体在哪里以及是什么的整个流程问题。
- 然而,这个问题可不是那么容易解决的,物体的尺寸变化范围很大,摆放物体的角度,姿态不定,而且可以出现在图片的任何地方,更何况物体还可以是多个类别。
目前学术和工业界出现的目标检测算法分成3类:
- 传统的目标检测算法:Cascade + HOG/DPM + Haar/SVM以及上述方法的诸多改进、优化;
- 候选区域/框 + 深度学习分类:通过提取候选区域,并对相应区域进行以深度学习方法为主的分类的方案,如:
- R-CNN(Selective Search + CNN + SVM)
- SPP-net(ROI Pooling)
- Fast R-CNN(Selective Search + CNN + ROI)
- Faster R-CNN(RPN + CNN + ROI)
- 基于深度学习的回归方法:YOLO/SSD 等方法
1.2 IOU
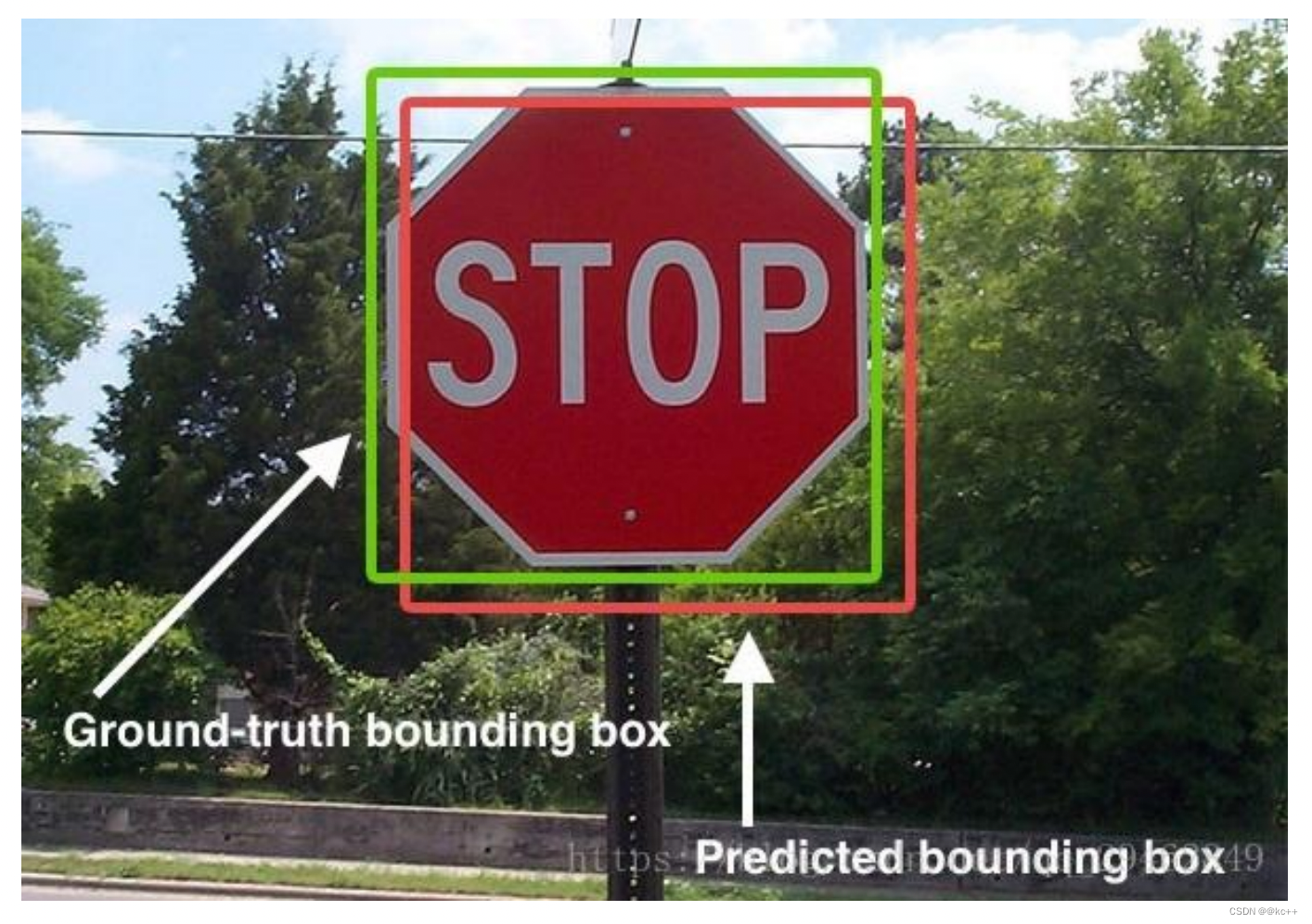
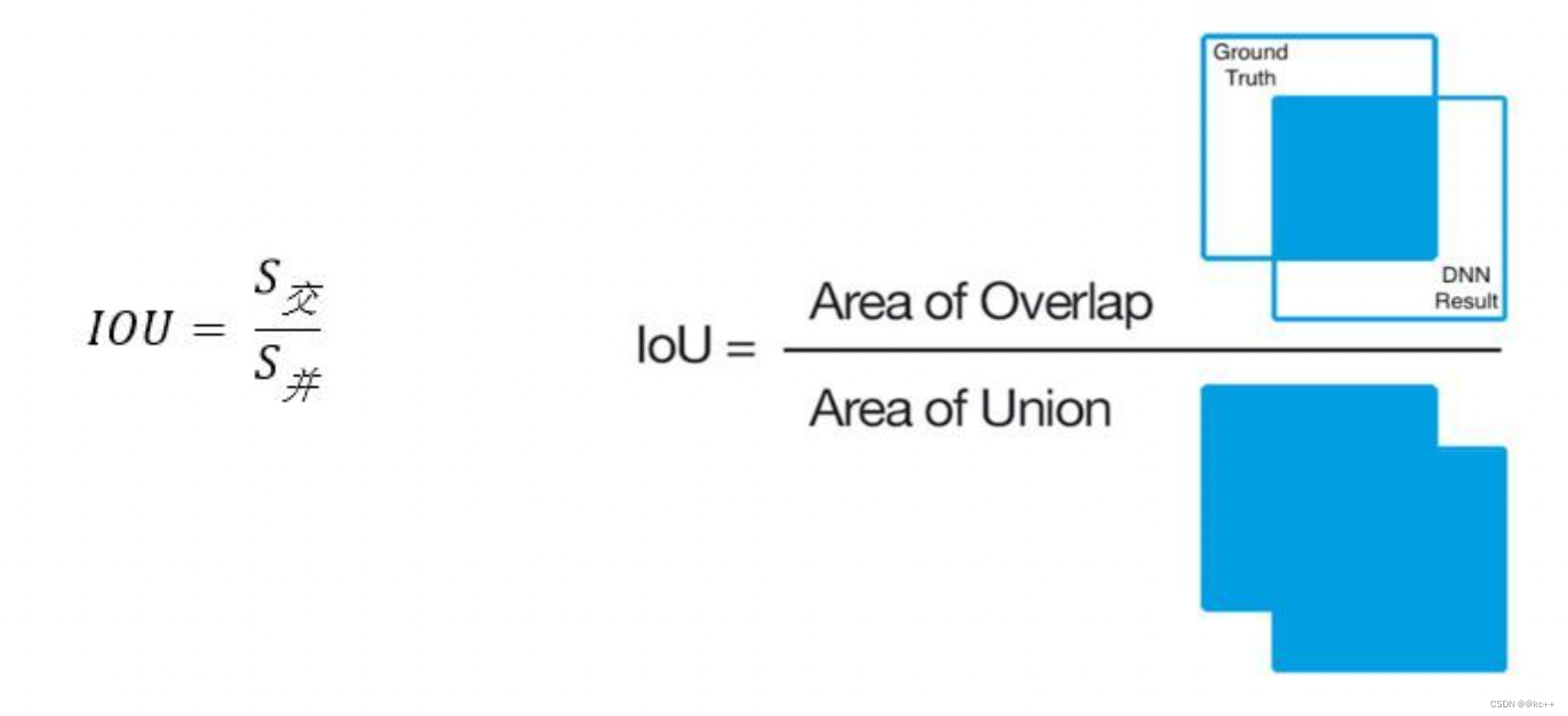
Intersection over Union是一种测量在特定数据集中检测相应物体准确度的一个标准。
IoU是一个简单的测量标准,只要是在输出中得出一个预测范围(bounding boxex)的任务都可以用IoU来进行测量。
为了可以使IoU用于测量任意大小形状的物体检测,我们需要:
- ground-truth bounding boxes(人为在训练集图像中标出要检测物体的大概范围);
- 我们的算法得出的结果范围。
也就是说,这个标准用于测量真实和预测之间的相关度,相关度越高,该值越高。
1.3 TP TN FP FN
TP TN FP FN里面一共出现了4个字母,分别是T F P N。
T是True;
F是False;
P是Positive;
N是Negative。
T或者F代表的是该样本 是否被正确分类。
P或者N代表的是该样本 原本是正样本还是负样本。
TP(True Positives)意思就是被分为了正样本,而且分对了。
TN(True Negatives)意思就是被分为了负样本,而且分对了,
FP(False Positives)意思就是被分为了正样本,但是分错了(事实上这个样本是负样本)。
FN(False Negatives)意思就是被分为了负样本,但是分错了(事实上这个样本是正样本)。
在mAP计算的过程中主要用到了,TP、FP、FN这三个概念。
1.4 precision(精确度)和recall(召回率)
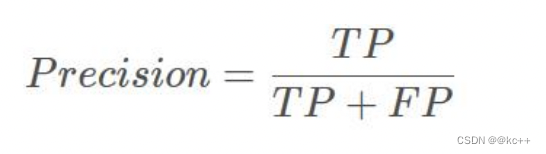
TP是分类器认为是正样本而且确实是正样本的例子,FP是分类器认为是正样本但实际上不是正样本的例子,Precision翻译成中文就是“分类器认为是正类并且确实是正类的部分占所有分类器认为是正类的比例”。
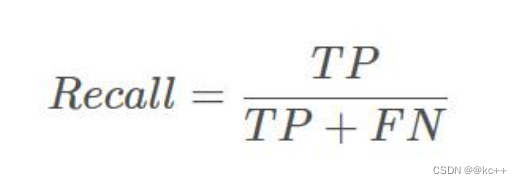
TP是分类器认为是正样本而且确实是正样本的例子,FN是分类器认为是负样本但实际上不是负样本的例子,Recall翻译成中文就是“分类器认为是正类并且确实是正类的部分占所有确实是正类的比例”。
精度就是找得对,召回率就是找得全。
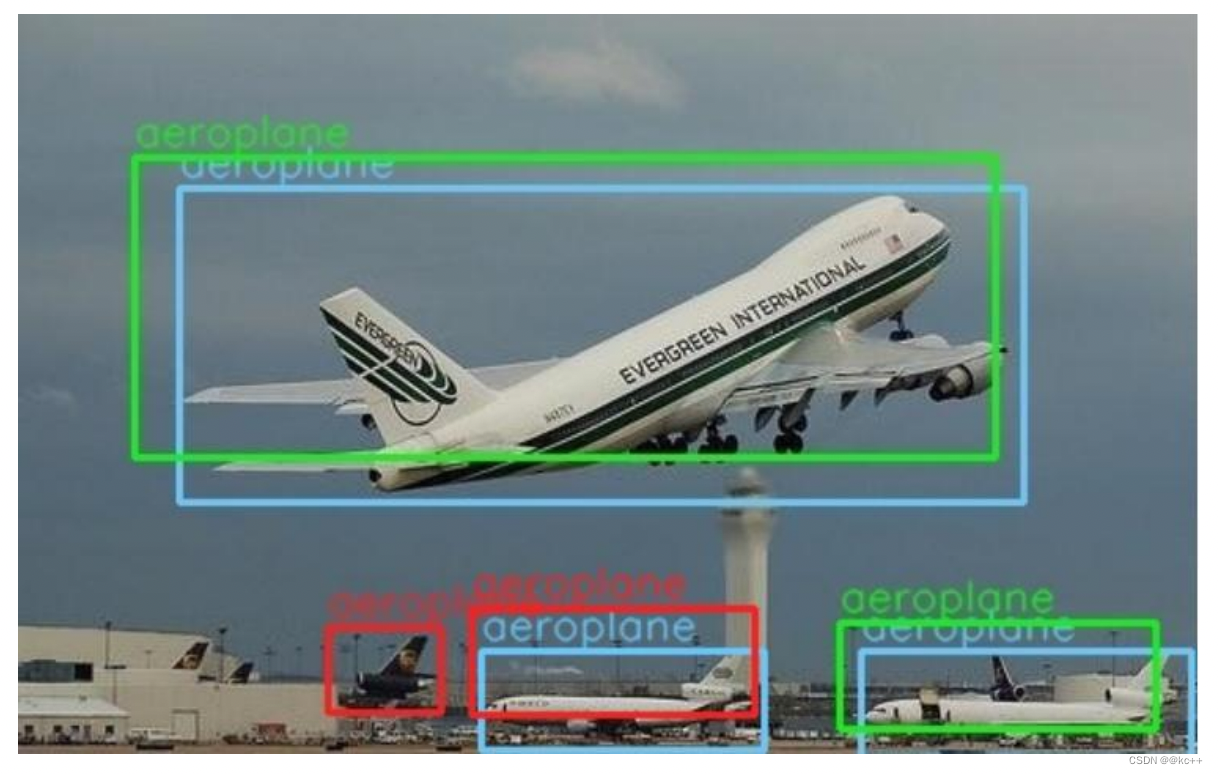
- 蓝色的框是真实框。绿色和红色的框是预测框,绿色的框是正样本,红色的框是负样本。
- 一般来讲,当预测框和真实框IOU>=0.5时,被认为是正样本。
2. 边框回归Bounding-Box regression
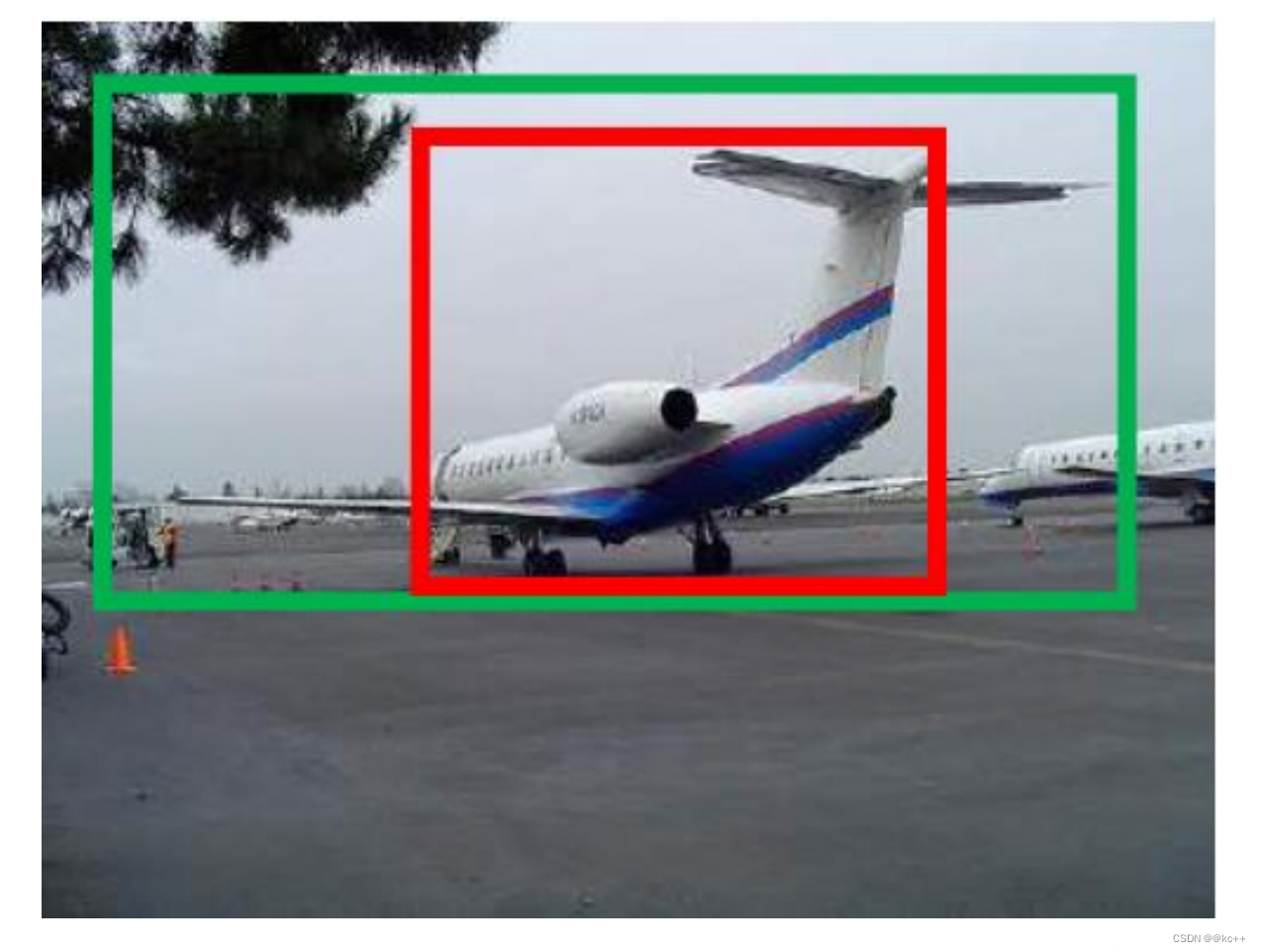

边框回归是什么?
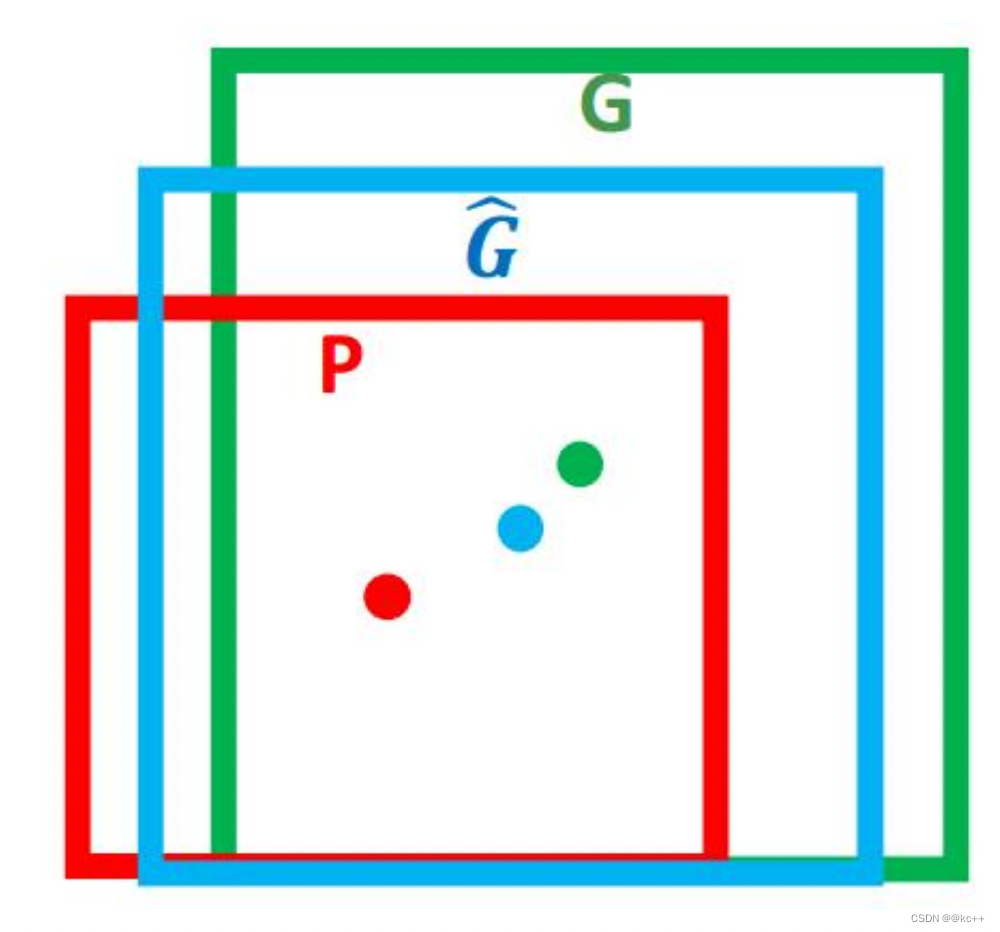
- 对于窗口一般使用四维向量(x,y,w,h) 来表示, 分别表示窗口的中心点坐标和宽高。
- 红色的框 P 代表原始的Proposal,;
- 绿色的框 G 代表目标的 Ground Truth;
我们的目标是寻找一种关系使得输入原始的窗口 P 经过映射得到一个跟真实窗口 G 更接近的回归窗口G^。
所以,边框回归的目的即是:
给定(Px,Py,Pw,Ph)寻找一种映射f, 使得:f(Px,Py,Pw,Ph)=(Gx,Gy,Gw,Gh)并且 (Gx,Gy,Gw,Gh)≈(Gx,Gy,Gw,Gh)
边框回归怎么做?
比较简单的思路就是: 平移+尺度缩放
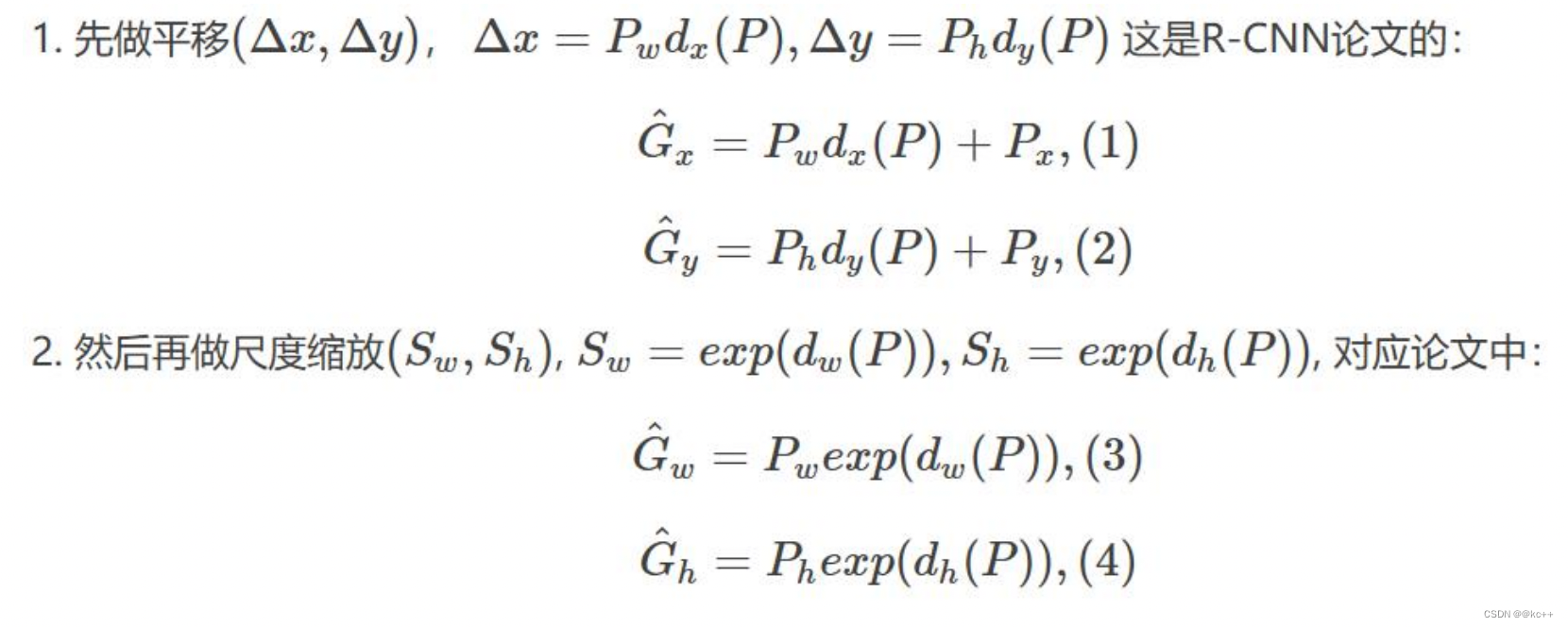
Input:
P=(Px,Py,Pw,Ph)
(注:训练阶段输入还包括 Ground Truth)
Output:
需要进行的平移变换和尺度缩放 dx,dy,dw,dh ,或者说是Δx,Δy,Sw,Sh 。
有了这四个变换我们就可以直接得到 Ground Truth。
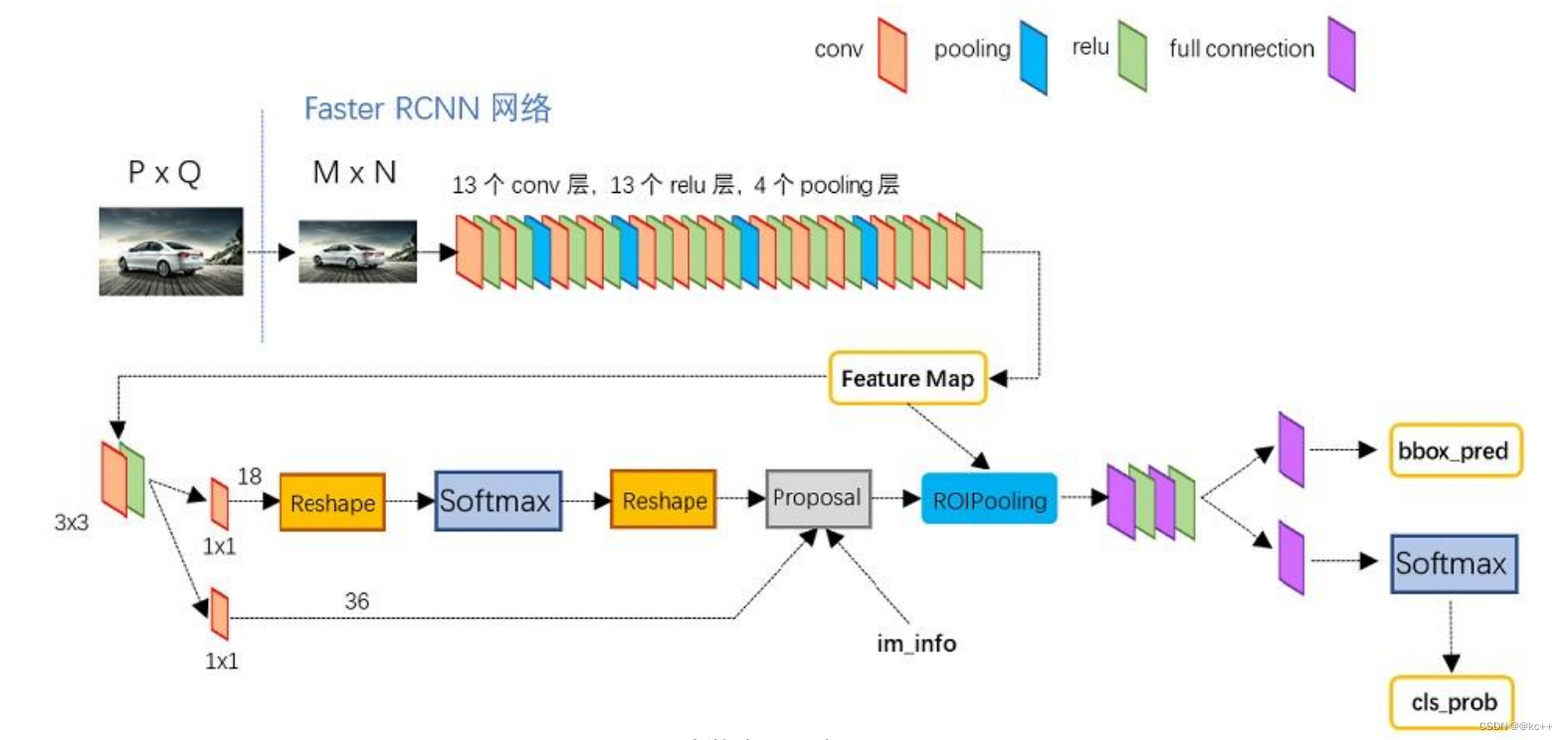
3. Faster R-CNN
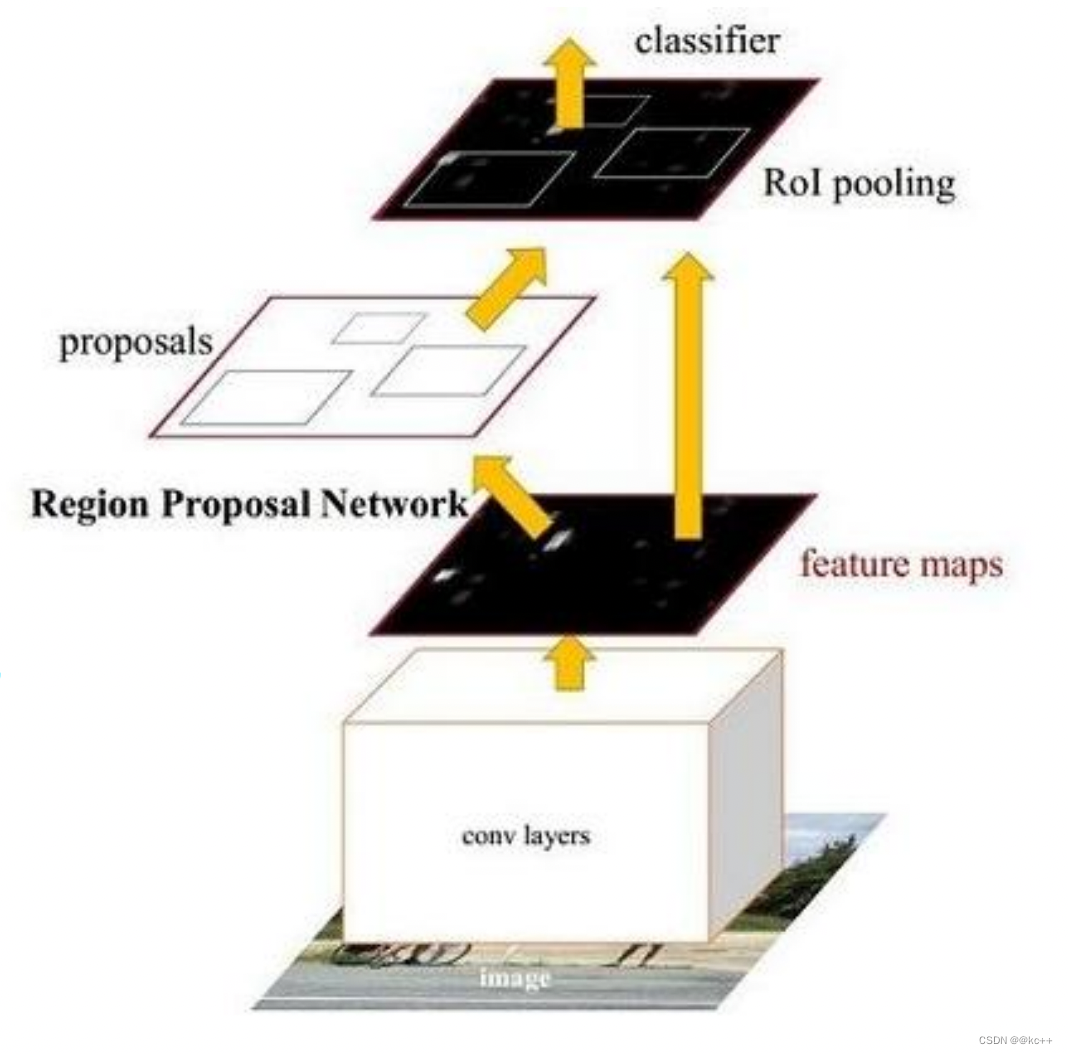
Faster RCNN可以分为4个主要内容:
- Conv layers:作为一种CNN网络目标检测方法,Faster RCNN首先使用一组基础的conv+relu+pooling层提取image的feature maps。该feature maps被共享用于后续RPN层和全连接层。
- Region Proposal Networks(RPN):RPN网络用于生成region proposals。通过softmax判断anchors属于positive或者negative,再利用bounding box regression修正anchors获得精确的proposals。
- Roi Pooling:该层收集输入的feature maps和proposals,综合这些信息后提取proposal feature maps,送入后续全连接层判定目标类别。
- Classification:利用proposal feature maps计算proposal的类别,同时再次bounding box regression获得检测框最终的精确位置。
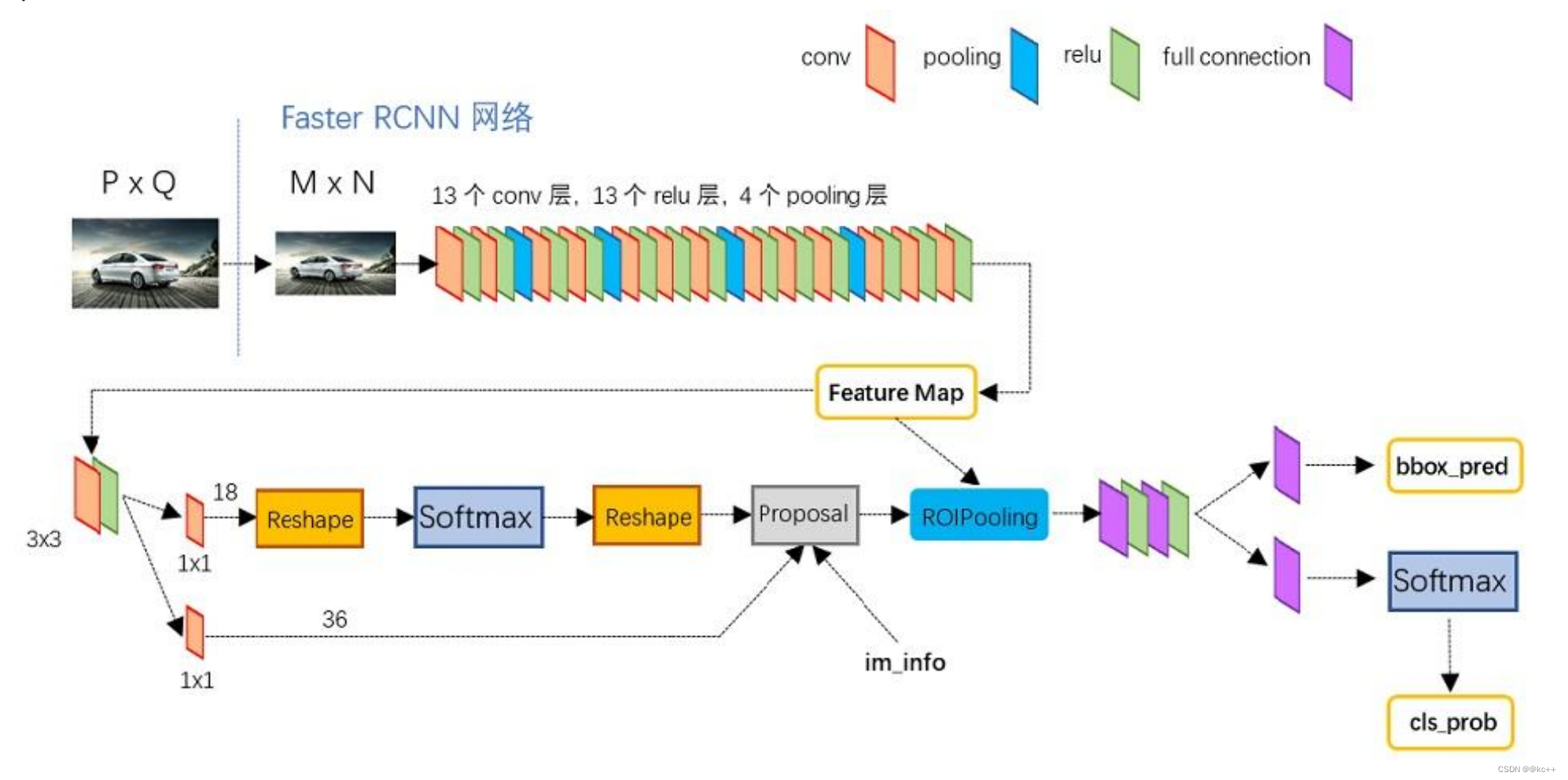
3.1 Faster-RCNN:conv layer
1 Conv layers
Conv layers包含了conv,pooling,relu三种层。共有13个conv层,13个relu层,4个pooling层。
在Conv layers中:
- 所有的conv层都是:kernel_size=3,pad=1,stride=1
- 所有的pooling层都是:kernel_size=2,pad=1,stride=2
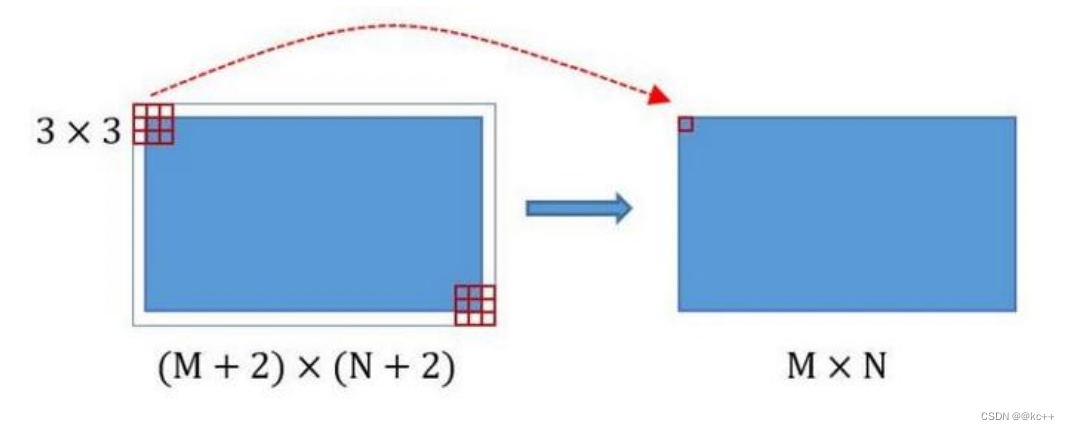
在Faster RCNN Conv layers中对所有的卷积都做了pad处理( pad=1,即填充一圈0),导致原图变为 (M+2)x(N+2)大小,再做3x3卷积后输出MxN 。正是这种设置,导致Conv layers中的conv层不改变输入和输出矩阵大小。
类似的是,Conv layers中的pooling层kernel_size=2,stride=2。
这样每个经过pooling层的MxN矩阵,都会变为(M/2)x(N/2)大小。
综上所述,在整个Conv layers中,conv和relu层不改变输入输出大小,只有pooling层使输出长宽都变为输入的1/2。
那么,一个MxN大小的矩阵经过Conv layers固定变为(M/16)x(N/16)。
这样Conv layers生成的feature map都可以和原图对应起来。
3.2 Faster-RCNN:Region Proposal Networks(RPN)
2. 区域生成网络Region Proposal Networks(RPN)
经典的检测方法生成检测框都非常耗时。直接使用RPN生成检测框,是Faster R-CNN的巨大优势,能极大提升检测框的生成速度。
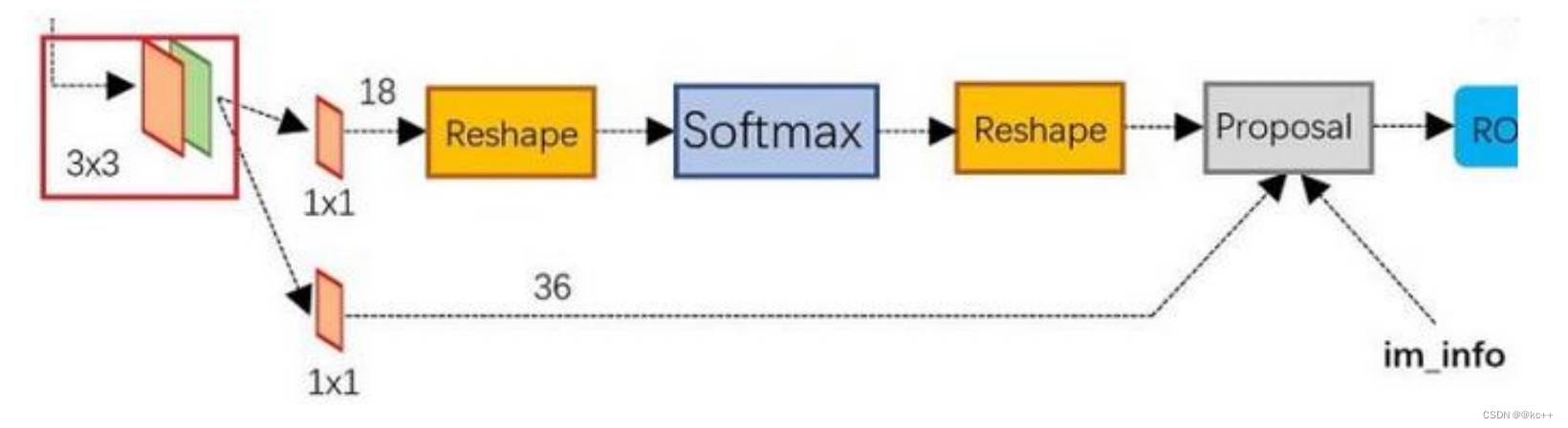
- 可以看到RPN网络实际分为2条线:
- 上面一条通过softmax分类anchors,获得positive和negative分类;
- 下面一条用于计算对于anchors的bounding box regression偏移量,以获得精确的proposal。
- 而最后的Proposal层则负责综合positive anchors和对应bounding box regression偏移量获取 proposals,同时剔除太小和超出边界的proposals。
- 其实整个网络到了Proposal Layer这里,就完成了相当于目标定位的功能。
3.2.1 anchors
RPN网络在卷积后,对每个像素点,上采样映射到原始图像一个区域,找到这个区域的中心位置,然后基于这个中心位置按规则选取9种anchor box。
9个矩形共有3种面积:128,256,512; 3种形状:长宽比大约为1:1, 1:2, 2:1。 (不是固定比例,可调)
每行的4个值表示矩形左上和右下角点坐标。
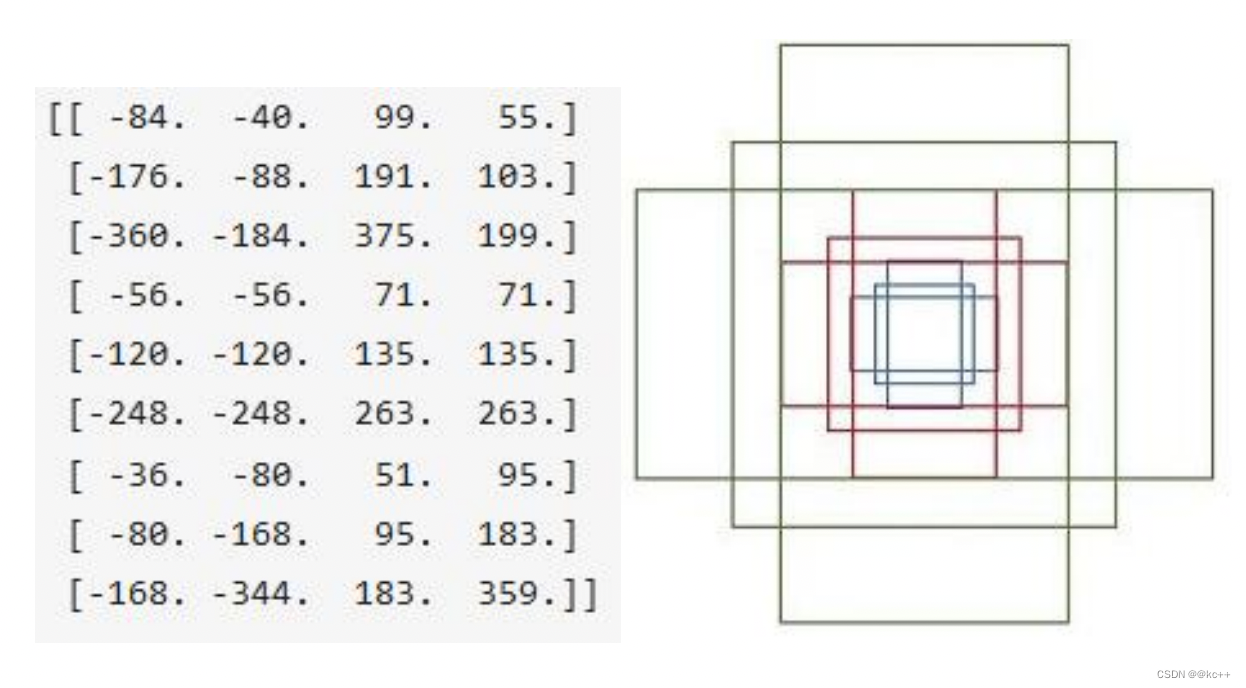
遍历Conv layers获得的feature maps,为每一个点都配备这9种anchors作为初始的检测框。
3.2.2 softmax判定positive与negative
其实RPN最终就是在原图尺度上,设置了密密麻麻的候选Anchor。然后用cnn去判断哪些Anchor是里面有目标的positive anchor,哪些是没目标的negative anchor。所以,仅仅是个二分类而已。
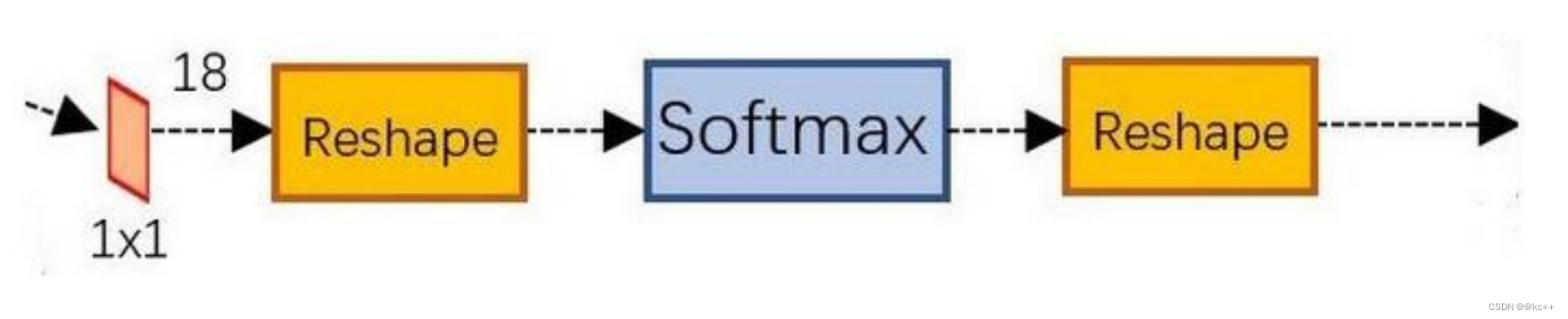
可以看到其conv的num_output=18,也就是经过该卷积的输出图像为WxHx18大小。
这也就刚好对应了feature maps每一个点都有9个anchors,同时每个anchors又有可能是positive和negative,所有这些信息都保存在WxHx(9*2)大小的矩阵。
为何这样做?后面接softmax分类获得positive anchors,也就相当于初步提取了检测目标候选区域box(一般认为目标在positive anchors中)。
那么为何要在softmax前后都接一个reshape layer?其实只是为了便于softmax分类。
前面的positive/negative anchors的矩阵,其在caffe中的存储形式为[1, 18, H, W]。而在softmax分类时需要进行positive/negative二分类,所以reshape layer会将其变为[1, 2, 9xH, W]大小,即单独“腾空”出来一个维度以便softmax分类,之后再reshape回复原状。
综上所述,RPN网络中利用anchors和softmax初步提取出positive anchors作为候选区域。
3.2.3 对proposals进行bounding box regression

可以看到conv的 num_output=36,即经过该卷积输出图像为WxHx36。这里相当于feature maps每个点都有9个anchors,每个anchors又都有4个用于回归的变换量:
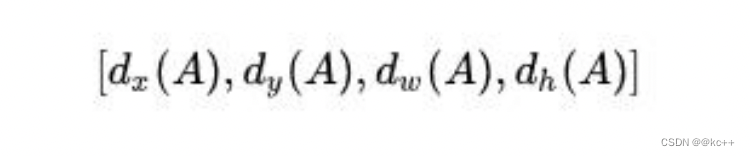
3.2.4 Proposal Layer
Proposal Layer负责综合所有变换量和positive anchors,计算出精准的proposal,送入后续RoI Pooling Layer。
Proposal Layer有4个输入:
- positive vs negative anchors分类器结果rpn_cls_prob_reshape,
- 对应的bbox reg的变换量rpn_bbox_pred,
- im_info
- 参数feature_stride=16
im_info:对于一副任意大小PxQ图像,传入Faster RCNN前首先reshape到固定MxN,im_info=[M, N, scale_factor]则保存了此次缩放的所有信息。
输入图像经过Conv Layers,经过4次pooling变为WxH=(M/16)x(N/16)大小,其中feature_stride=16则保存了该信息,用于计算anchor偏移量。
Proposal Layer 按照以下顺序依次处理:
- 利用变换量对所有的positive anchors做bbox regression回归
- 按照输入的positive softmax scores由大到小排序anchors,提取前pre_nms_topN(e.g. 6000)个anchors,即提取修正位置后的positive anchors。
- 对剩余的positive anchors进行NMS(non-maximum suppression)。
- 之后输出proposal。
严格意义上的检测应该到此就结束了,后续部分应该属于识别了。
RPN网络结构,总结起来:生成anchors -> softmax分类器提取positvie anchors -> bbox reg回归positive anchors -> Proposal Layer生成proposals
3.3 Faster-RCNN:Roi pooling
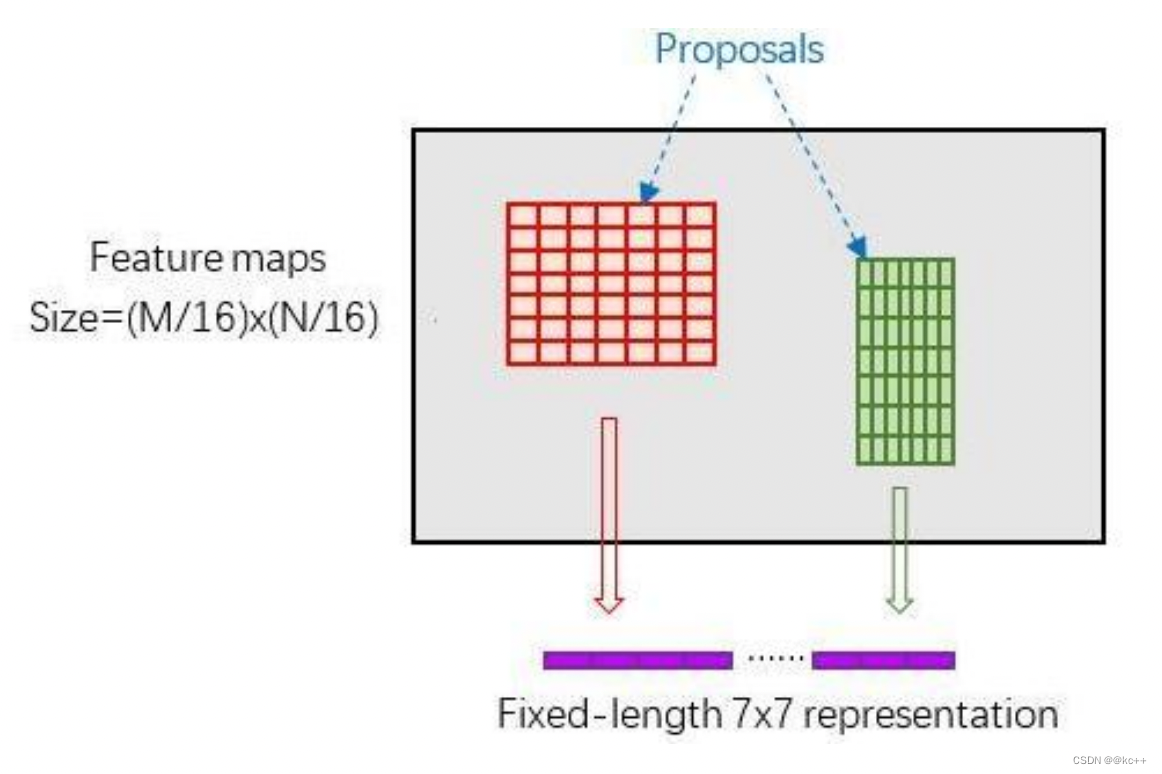
RoI Pooling层则负责收集proposal,并计算出proposal feature maps,送入后续网络。
Rol pooling层有2个输入:
- 原始的feature maps
- RPN输出的proposal boxes(大小各不相同)
为何需要RoI Pooling?
对于传统的CNN(如AlexNet和VGG),当网络训练好后输入的图像尺寸必须是固定值,同时网络输出也是固定大小的vector or matrix。如果输入图像大小不定,这个问题就变得比较麻烦。
有2种解决办法:
- 从图像中crop一部分传入网络将图像(破坏了图像的完整结构)
- warp成需要的大小后传入网络(破坏了图像原始形状信息)
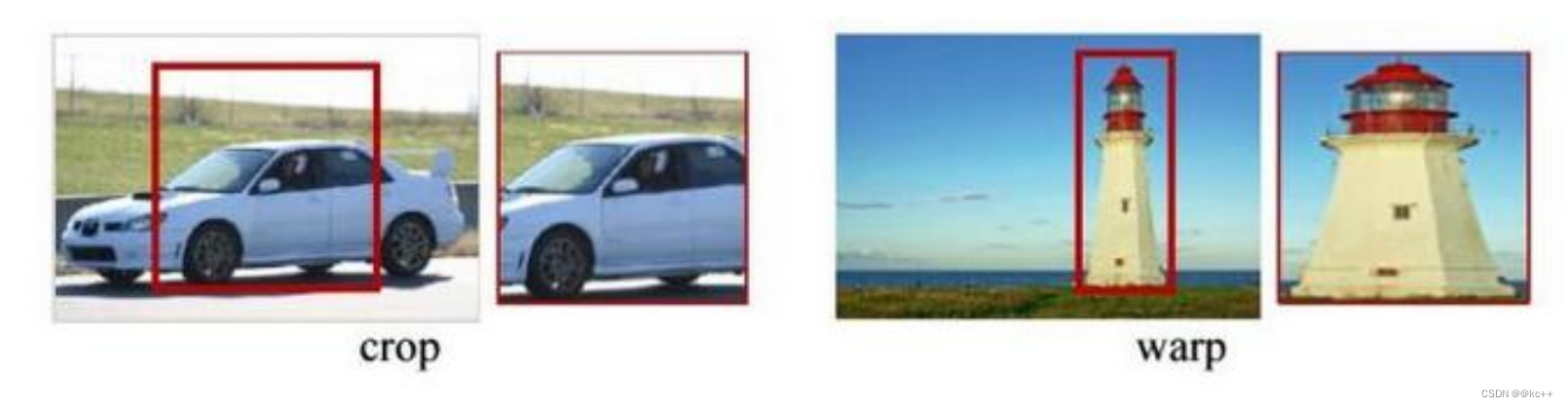

RoI Pooling原理
新参数pooled_w、pooled_h和spatial_scale(1/16)
RoI Pooling layer forward过程:
- 由于proposal是对应MN尺度的,所以首先使用spatial_scale参数将其映射回(M/16)(N/16)大小的feature map尺度;
- 再将每个proposal对应的feature map区域水平分为pooled_w * pooled_h的网格;
- 对网格的每一份都进行max pooling处理。
这样处理后,即使大小不同的proposal输出结果都是pooled_w * pooled_h固定大小,实现了固定长度输出。
再将每个proposal对应的feature map区 域水平分为pooled_w * pooled_h的网格;
对网格的每一份都进行max pooling处 理。
这样处理后,即使大小不同的proposal输 出结果都是pooled_w * pooled_h固定大小,实现了固定长度输出。
3.4 Faster-RCNN: Classification
Classification部分利用已经获得的proposal feature maps,通过full connect层与softmax计算每个proposal具体属于那个类别(如人,车,电视等),输出cls_prob概率向量;
同时再次利用bounding box regression获得每个proposal的位置偏移量bbox_pred,用于回归更加精确的目标检测框。
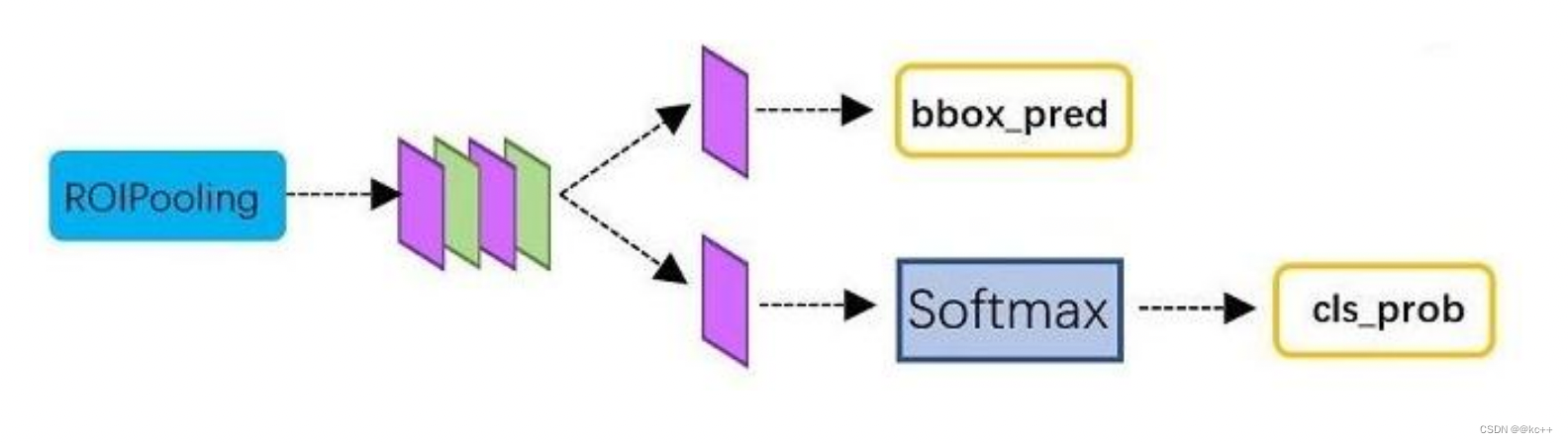
从RoI Pooling获取到pooled_w * pooled_h大小的proposal feature maps后,送入后续网络,做了如下2件事:
- 通过全连接和softmax对proposals进行分类,这实际上已经是识别的范畴了
- 再次对proposals进行bounding box regression,获取更高精度的预测框
全连接层InnerProduct layers:

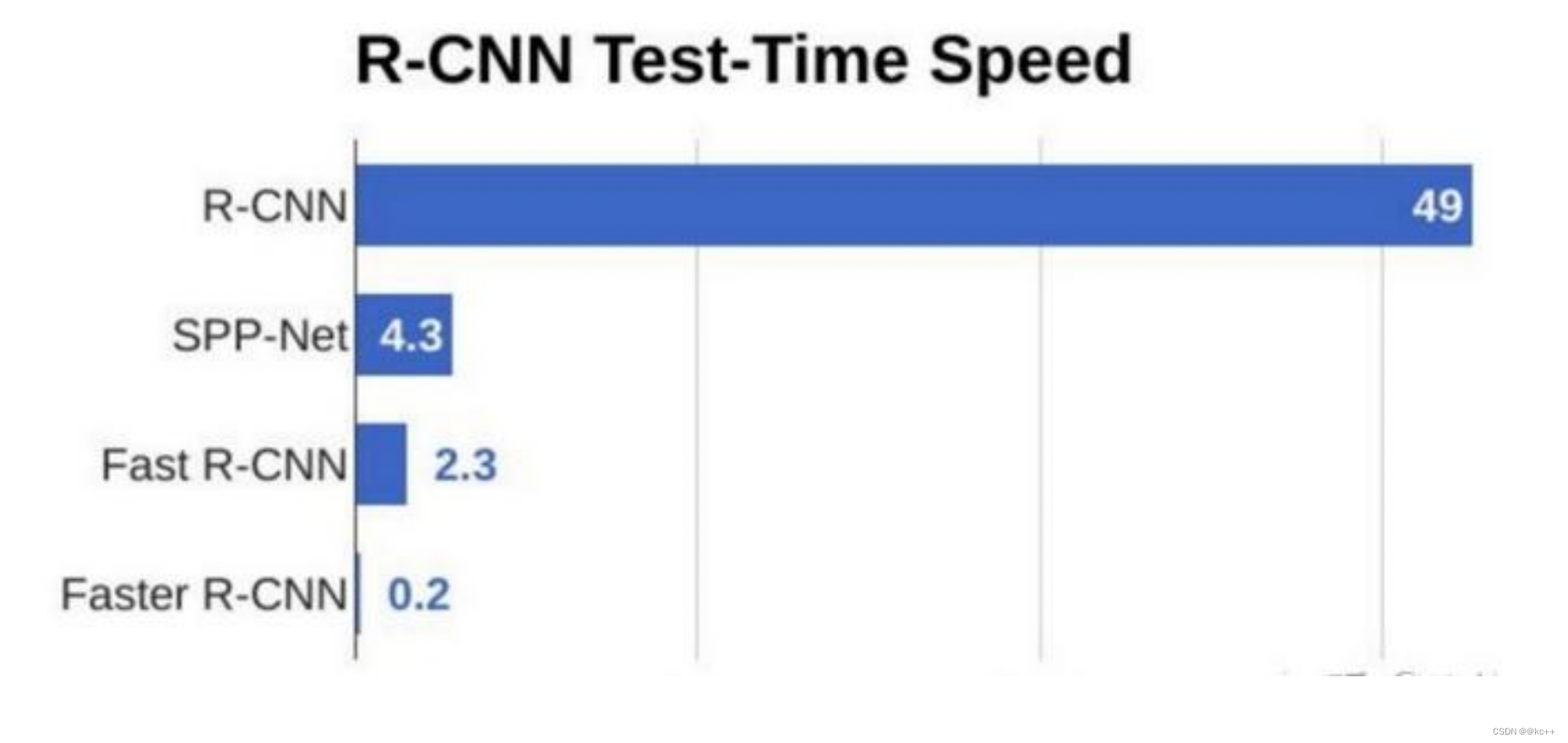
3.5 网络对比
3.6 代码示例
3.6.1 网络搭建
import cv2
import keras
import numpy as np
import colorsys
import pickle
import os
import nets.frcnn as frcnn
from nets.frcnn_training import get_new_img_size
from keras import backend as K
from keras.layers import Input
from keras.applications.imagenet_utils import preprocess_input
from PIL import Image,ImageFont, ImageDraw
from utils.utils import BBoxUtility
from utils.anchors import get_anchors
from utils.config import Config
import copy
import math
class FRCNN(object):_defaults = {"model_path": 'model_data/voc_weights.h5',"classes_path": 'model_data/voc_classes.txt',"confidence": 0.7,}@classmethoddef get_defaults(cls, n):if n in cls._defaults:return cls._defaults[n]else:return "Unrecognized attribute name '" + n + "'"#---------------------------------------------------## 初始化faster RCNN#---------------------------------------------------#def __init__(self, **kwargs):self.__dict__.update(self._defaults)self.class_names = self._get_class()self.sess = K.get_session()self.config = Config()self.generate()self.bbox_util = BBoxUtility()#---------------------------------------------------## 获得所有的分类#---------------------------------------------------#def _get_class(self):classes_path = os.path.expanduser(self.classes_path)with open(classes_path) as f:class_names = f.readlines()class_names = [c.strip() for c in class_names]return class_names#---------------------------------------------------## 获得所有的分类#---------------------------------------------------#def generate(self):model_path = os.path.expanduser(self.model_path)assert model_path.endswith('.h5'), 'Keras model or weights must be a .h5 file.'# 计算总的种类self.num_classes = len(self.class_names)+1# 载入模型,如果原来的模型里已经包括了模型结构则直接载入。# 否则先构建模型再载入self.model_rpn,self.model_classifier = frcnn.get_predict_model(self.config,self.num_classes)self.model_rpn.load_weights(self.model_path,by_name=True)self.model_classifier.load_weights(self.model_path,by_name=True,skip_mismatch=True)print('{} model, anchors, and classes loaded.'.format(model_path))# 画框设置不同的颜色hsv_tuples = [(x / len(self.class_names), 1., 1.)for x in range(len(self.class_names))]self.colors = list(map(lambda x: colorsys.hsv_to_rgb(*x), hsv_tuples))self.colors = list(map(lambda x: (int(x[0] * 255), int(x[1] * 255), int(x[2] * 255)),self.colors))def get_img_output_length(self, width, height):def get_output_length(input_length):# input_length += 6filter_sizes = [7, 3, 1, 1]padding = [3,1,0,0]stride = 2for i in range(4):# input_length = (input_length - filter_size + stride) // strideinput_length = (input_length+2*padding[i]-filter_sizes[i]) // stride + 1return input_lengthreturn get_output_length(width), get_output_length(height) #---------------------------------------------------## 检测图片#---------------------------------------------------#def detect_image(self, image):image_shape = np.array(np.shape(image)[0:2])old_width = image_shape[1]old_height = image_shape[0]old_image = copy.deepcopy(image)width,height = get_new_img_size(old_width,old_height)image = image.resize([width,height])photo = np.array(image,dtype = np.float64)# 图片预处理,归一化photo = preprocess_input(np.expand_dims(photo,0))preds = self.model_rpn.predict(photo)# 将预测结果进行解码anchors = get_anchors(self.get_img_output_length(width,height),width,height)rpn_results = self.bbox_util.detection_out(preds,anchors,1,confidence_threshold=0)R = rpn_results[0][:, 2:]R[:,0] = np.array(np.round(R[:, 0]*width/self.config.rpn_stride),dtype=np.int32)R[:,1] = np.array(np.round(R[:, 1]*height/self.config.rpn_stride),dtype=np.int32)R[:,2] = np.array(np.round(R[:, 2]*width/self.config.rpn_stride),dtype=np.int32)R[:,3] = np.array(np.round(R[:, 3]*height/self.config.rpn_stride),dtype=np.int32)R[:, 2] -= R[:, 0]R[:, 3] -= R[:, 1]base_layer = preds[2]delete_line = []for i,r in enumerate(R):if r[2] < 1 or r[3] < 1:delete_line.append(i)R = np.delete(R,delete_line,axis=0)bboxes = []probs = []labels = []for jk in range(R.shape[0]//self.config.num_rois + 1):ROIs = np.expand_dims(R[self.config.num_rois*jk:self.config.num_rois*(jk+1), :], axis=0)if ROIs.shape[1] == 0:breakif jk == R.shape[0]//self.config.num_rois:#pad Rcurr_shape = ROIs.shapetarget_shape = (curr_shape[0],self.config.num_rois,curr_shape[2])ROIs_padded = np.zeros(target_shape).astype(ROIs.dtype)ROIs_padded[:, :curr_shape[1], :] = ROIsROIs_padded[0, curr_shape[1]:, :] = ROIs[0, 0, :]ROIs = ROIs_padded[P_cls, P_regr] = self.model_classifier.predict([base_layer,ROIs])for ii in range(P_cls.shape[1]):if np.max(P_cls[0, ii, :]) < self.confidence or np.argmax(P_cls[0, ii, :]) == (P_cls.shape[2] - 1):continuelabel = np.argmax(P_cls[0, ii, :])(x, y, w, h) = ROIs[0, ii, :]cls_num = np.argmax(P_cls[0, ii, :])(tx, ty, tw, th) = P_regr[0, ii, 4*cls_num:4*(cls_num+1)]tx /= self.config.classifier_regr_std[0]ty /= self.config.classifier_regr_std[1]tw /= self.config.classifier_regr_std[2]th /= self.config.classifier_regr_std[3]cx = x + w/2.cy = y + h/2.cx1 = tx * w + cxcy1 = ty * h + cyw1 = math.exp(tw) * wh1 = math.exp(th) * hx1 = cx1 - w1/2.y1 = cy1 - h1/2.x2 = cx1 + w1/2y2 = cy1 + h1/2x1 = int(round(x1))y1 = int(round(y1))x2 = int(round(x2))y2 = int(round(y2))bboxes.append([x1,y1,x2,y2])probs.append(np.max(P_cls[0, ii, :]))labels.append(label)if len(bboxes)==0:return old_image# 筛选出其中得分高于confidence的框labels = np.array(labels)probs = np.array(probs)boxes = np.array(bboxes,dtype=np.float32)boxes[:,0] = boxes[:,0]*self.config.rpn_stride/widthboxes[:,1] = boxes[:,1]*self.config.rpn_stride/heightboxes[:,2] = boxes[:,2]*self.config.rpn_stride/widthboxes[:,3] = boxes[:,3]*self.config.rpn_stride/heightresults = np.array(self.bbox_util.nms_for_out(np.array(labels),np.array(probs),np.array(boxes),self.num_classes-1,0.4))top_label_indices = results[:,0]top_conf = results[:,1]boxes = results[:,2:]boxes[:,0] = boxes[:,0]*old_widthboxes[:,1] = boxes[:,1]*old_heightboxes[:,2] = boxes[:,2]*old_widthboxes[:,3] = boxes[:,3]*old_heightfont = ImageFont.truetype(font='model_data/simhei.ttf',size=np.floor(3e-2 * np.shape(image)[1] + 0.5).astype('int32'))thickness = (np.shape(old_image)[0] + np.shape(old_image)[1]) // widthimage = old_imagefor i, c in enumerate(top_label_indices):predicted_class = self.class_names[int(c)]score = top_conf[i]left, top, right, bottom = boxes[i]top = top - 5left = left - 5bottom = bottom + 5right = right + 5top = max(0, np.floor(top + 0.5).astype('int32'))left = max(0, np.floor(left + 0.5).astype('int32'))bottom = min(np.shape(image)[0], np.floor(bottom + 0.5).astype('int32'))right = min(np.shape(image)[1], np.floor(right + 0.5).astype('int32'))# 画框框label = '{} {:.2f}'.format(predicted_class, score)draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image)label_size = draw.textsize(label, font)label = label.encode('utf-8')print(label)if top - label_size[1] >= 0:text_origin = np.array([left, top - label_size[1]])else:text_origin = np.array([left, top + 1])for i in range(thickness):draw.rectangle([left + i, top + i, right - i, bottom - i],outline=self.colors[int(c)])draw.rectangle([tuple(text_origin), tuple(text_origin + label_size)],fill=self.colors[int(c)])draw.text(text_origin, str(label,'UTF-8'), fill=(0, 0, 0), font=font)del drawreturn imagedef close_session(self):self.sess.close()3.6.2 训练脚本
from __future__ import division
from nets.frcnn import get_model
from nets.frcnn_training import cls_loss,smooth_l1,Generator,get_img_output_length,class_loss_cls,class_loss_regrfrom utils.config import Config
from utils.utils import BBoxUtility
from utils.roi_helpers import calc_ioufrom keras.utils import generic_utils
from keras.callbacks import TensorBoard, ModelCheckpoint, ReduceLROnPlateau, EarlyStopping
import keras
import numpy as np
import time
import tensorflow as tf
from utils.anchors import get_anchorsdef write_log(callback, names, logs, batch_no):for name, value in zip(names, logs):summary = tf.Summary()summary_value = summary.value.add()summary_value.simple_value = valuesummary_value.tag = namecallback.writer.add_summary(summary, batch_no)callback.writer.flush()if __name__ == "__main__":config = Config()NUM_CLASSES = 21EPOCH = 100EPOCH_LENGTH = 2000bbox_util = BBoxUtility(overlap_threshold=config.rpn_max_overlap,ignore_threshold=config.rpn_min_overlap)annotation_path = '2007_train.txt'model_rpn, model_classifier,model_all = get_model(config,NUM_CLASSES)base_net_weights = "model_data/voc_weights.h5"model_all.summary()model_rpn.load_weights(base_net_weights,by_name=True)model_classifier.load_weights(base_net_weights,by_name=True)with open(annotation_path) as f: lines = f.readlines()np.random.seed(10101)np.random.shuffle(lines)np.random.seed(None)gen = Generator(bbox_util, lines, NUM_CLASSES, solid=True)rpn_train = gen.generate()log_dir = "logs"# 训练参数设置logging = TensorBoard(log_dir=log_dir)callback = loggingcallback.set_model(model_all)model_rpn.compile(loss={'regression' : smooth_l1(),'classification': cls_loss()},optimizer=keras.optimizers.Adam(lr=1e-5))model_classifier.compile(loss=[class_loss_cls, class_loss_regr(NUM_CLASSES-1)], metrics={'dense_class_{}'.format(NUM_CLASSES): 'accuracy'},optimizer=keras.optimizers.Adam(lr=1e-5))model_all.compile(optimizer='sgd', loss='mae')# 初始化参数iter_num = 0train_step = 0losses = np.zeros((EPOCH_LENGTH, 5))rpn_accuracy_rpn_monitor = []rpn_accuracy_for_epoch = [] start_time = time.time()# 最佳lossbest_loss = np.Inf# 数字到类的映射print('Starting training')for i in range(EPOCH):if i == 20:model_rpn.compile(loss={'regression' : smooth_l1(),'classification': cls_loss()},optimizer=keras.optimizers.Adam(lr=1e-6))model_classifier.compile(loss=[class_loss_cls, class_loss_regr(NUM_CLASSES-1)], metrics={'dense_class_{}'.format(NUM_CLASSES): 'accuracy'},optimizer=keras.optimizers.Adam(lr=1e-6))print("Learning rate decrease")progbar = generic_utils.Progbar(EPOCH_LENGTH) print('Epoch {}/{}'.format(i + 1, EPOCH))while True:if len(rpn_accuracy_rpn_monitor) == EPOCH_LENGTH and config.verbose:mean_overlapping_bboxes = float(sum(rpn_accuracy_rpn_monitor))/len(rpn_accuracy_rpn_monitor)rpn_accuracy_rpn_monitor = []print('Average number of overlapping bounding boxes from RPN = {} for {} previous iterations'.format(mean_overlapping_bboxes, EPOCH_LENGTH))if mean_overlapping_bboxes == 0:print('RPN is not producing bounding boxes that overlap the ground truth boxes. Check RPN settings or keep training.')X, Y, boxes = next(rpn_train)loss_rpn = model_rpn.train_on_batch(X,Y)write_log(callback, ['rpn_cls_loss', 'rpn_reg_loss'], loss_rpn, train_step)P_rpn = model_rpn.predict_on_batch(X)height,width,_ = np.shape(X[0])anchors = get_anchors(get_img_output_length(width,height),width,height)# 将预测结果进行解码results = bbox_util.detection_out(P_rpn,anchors,1, confidence_threshold=0)R = results[0][:, 2:]X2, Y1, Y2, IouS = calc_iou(R, config, boxes[0], width, height, NUM_CLASSES)if X2 is None:rpn_accuracy_rpn_monitor.append(0)rpn_accuracy_for_epoch.append(0)continueneg_samples = np.where(Y1[0, :, -1] == 1)pos_samples = np.where(Y1[0, :, -1] == 0)if len(neg_samples) > 0:neg_samples = neg_samples[0]else:neg_samples = []if len(pos_samples) > 0:pos_samples = pos_samples[0]else:pos_samples = []rpn_accuracy_rpn_monitor.append(len(pos_samples))rpn_accuracy_for_epoch.append((len(pos_samples)))if len(neg_samples)==0:continueif len(pos_samples) < config.num_rois//2:selected_pos_samples = pos_samples.tolist()else:selected_pos_samples = np.random.choice(pos_samples, config.num_rois//2, replace=False).tolist()try:selected_neg_samples = np.random.choice(neg_samples, config.num_rois - len(selected_pos_samples), replace=False).tolist()except:selected_neg_samples = np.random.choice(neg_samples, config.num_rois - len(selected_pos_samples), replace=True).tolist()sel_samples = selected_pos_samples + selected_neg_samplesloss_class = model_classifier.train_on_batch([X, X2[:, sel_samples, :]], [Y1[:, sel_samples, :], Y2[:, sel_samples, :]])write_log(callback, ['detection_cls_loss', 'detection_reg_loss', 'detection_acc'], loss_class, train_step)losses[iter_num, 0] = loss_rpn[1]losses[iter_num, 1] = loss_rpn[2]losses[iter_num, 2] = loss_class[1]losses[iter_num, 3] = loss_class[2]losses[iter_num, 4] = loss_class[3]train_step += 1iter_num += 1progbar.update(iter_num, [('rpn_cls', np.mean(losses[:iter_num, 0])), ('rpn_regr', np.mean(losses[:iter_num, 1])),('detector_cls', np.mean(losses[:iter_num, 2])), ('detector_regr', np.mean(losses[:iter_num, 3]))])if iter_num == EPOCH_LENGTH:loss_rpn_cls = np.mean(losses[:, 0])loss_rpn_regr = np.mean(losses[:, 1])loss_class_cls = np.mean(losses[:, 2])loss_class_regr = np.mean(losses[:, 3])class_acc = np.mean(losses[:, 4])mean_overlapping_bboxes = float(sum(rpn_accuracy_for_epoch)) / len(rpn_accuracy_for_epoch)rpn_accuracy_for_epoch = []if config.verbose:print('Mean number of bounding boxes from RPN overlapping ground truth boxes: {}'.format(mean_overlapping_bboxes))print('Classifier accuracy for bounding boxes from RPN: {}'.format(class_acc))print('Loss RPN classifier: {}'.format(loss_rpn_cls))print('Loss RPN regression: {}'.format(loss_rpn_regr))print('Loss Detector classifier: {}'.format(loss_class_cls))print('Loss Detector regression: {}'.format(loss_class_regr))print('Elapsed time: {}'.format(time.time() - start_time))curr_loss = loss_rpn_cls + loss_rpn_regr + loss_class_cls + loss_class_regriter_num = 0start_time = time.time()write_log(callback,['Elapsed_time', 'mean_overlapping_bboxes', 'mean_rpn_cls_loss', 'mean_rpn_reg_loss','mean_detection_cls_loss', 'mean_detection_reg_loss', 'mean_detection_acc', 'total_loss'],[time.time() - start_time, mean_overlapping_bboxes, loss_rpn_cls, loss_rpn_regr,loss_class_cls, loss_class_regr, class_acc, curr_loss],i)if config.verbose:print('The best loss is {}. The current loss is {}. Saving weights'.format(best_loss,curr_loss))if curr_loss < best_loss:best_loss = curr_lossmodel_all.save_weights(log_dir+"/epoch{:03d}-loss{:.3f}-rpn{:.3f}-roi{:.3f}".format(i,curr_loss,loss_rpn_cls+loss_rpn_regr,loss_class_cls+loss_class_regr)+".h5")break3.6.3 预测脚本
from keras.layers import Input
from frcnn import FRCNN
from PIL import Imagefrcnn = FRCNN()while True:img = input('img/street.jpg')try:image = Image.open('img/street.jpg')except:print('Open Error! Try again!')continueelse:r_image = frcnn.detect_image(image)r_image.show()
frcnn.close_session()4. One stage和two stage
two-stage:two-stage算法会先使用一个网络生成proposal,如selective search和RPN网络, RPN出现后,ss方法基本就被摒弃了。RPN网络接在图像特征提取网络backbone后,会设置RPN loss(bbox regression loss+classification loss)对RPN网络进行训练,RPN生成的proposal再送到 后面的网络中进行更精细的bbox regression和classification。
one-stage :One-stage追求速度舍弃了two-stage架构,即不再设置单独网络生成proposal,而 是直接在feature map上进行密集抽样,产生大量的先验框,如YOLO的网格方法。这些先验框没 有经过两步处理,且框的尺寸往往是人为规定。
two-stage算法主要是RCNN系列,包括RCNN, Fast-RCNN,Faster-RCNN。之后的Mask-RCNN 融合了Faster-RCNN架构、ResNet和FPN(Feature Pyramid Networks)backbone,以及FCN里的 segmentation方法,在完成了segmentation的同时也提高了detection的精度。
one-stage算法最典型的是YOLO,该算法速度极快。
5. Yolo
行人检测-Yolo3
5.1 Yolo-You Only Look Once
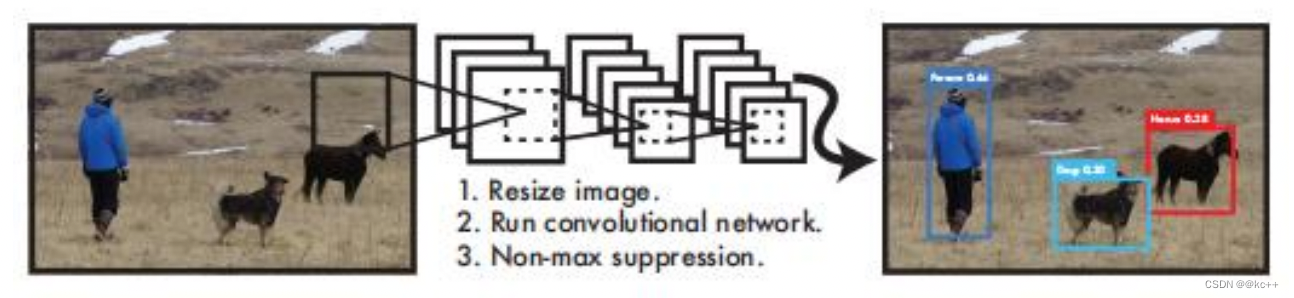
YOLO算法采用一个单独的CNN模型实现end-to-end的目标检测:
- Resize成448448,图片分割得到77网格(cell)
- CNN提取特征和预测:卷积部分负责提取特征,全连接部分负责预测。
- 过滤bbox(通过nms)
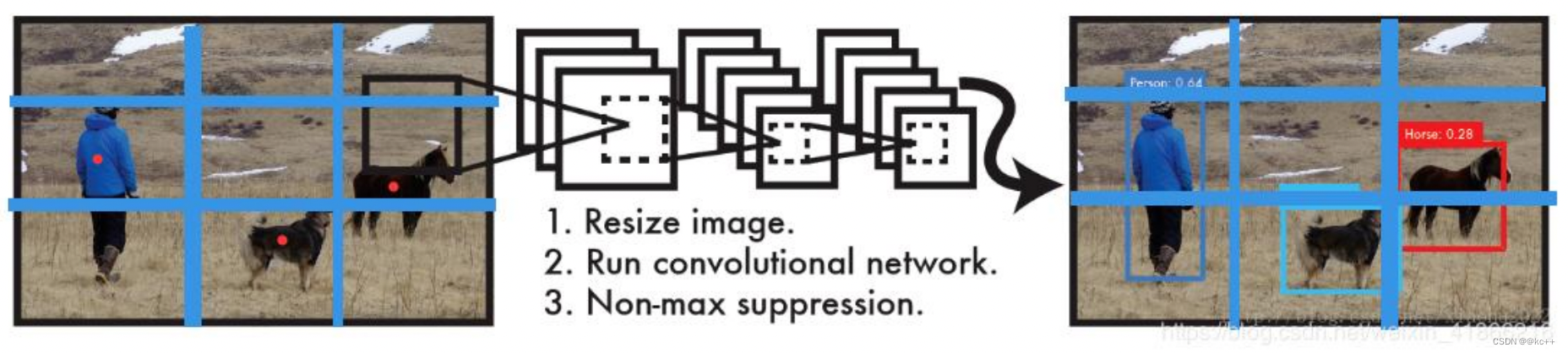
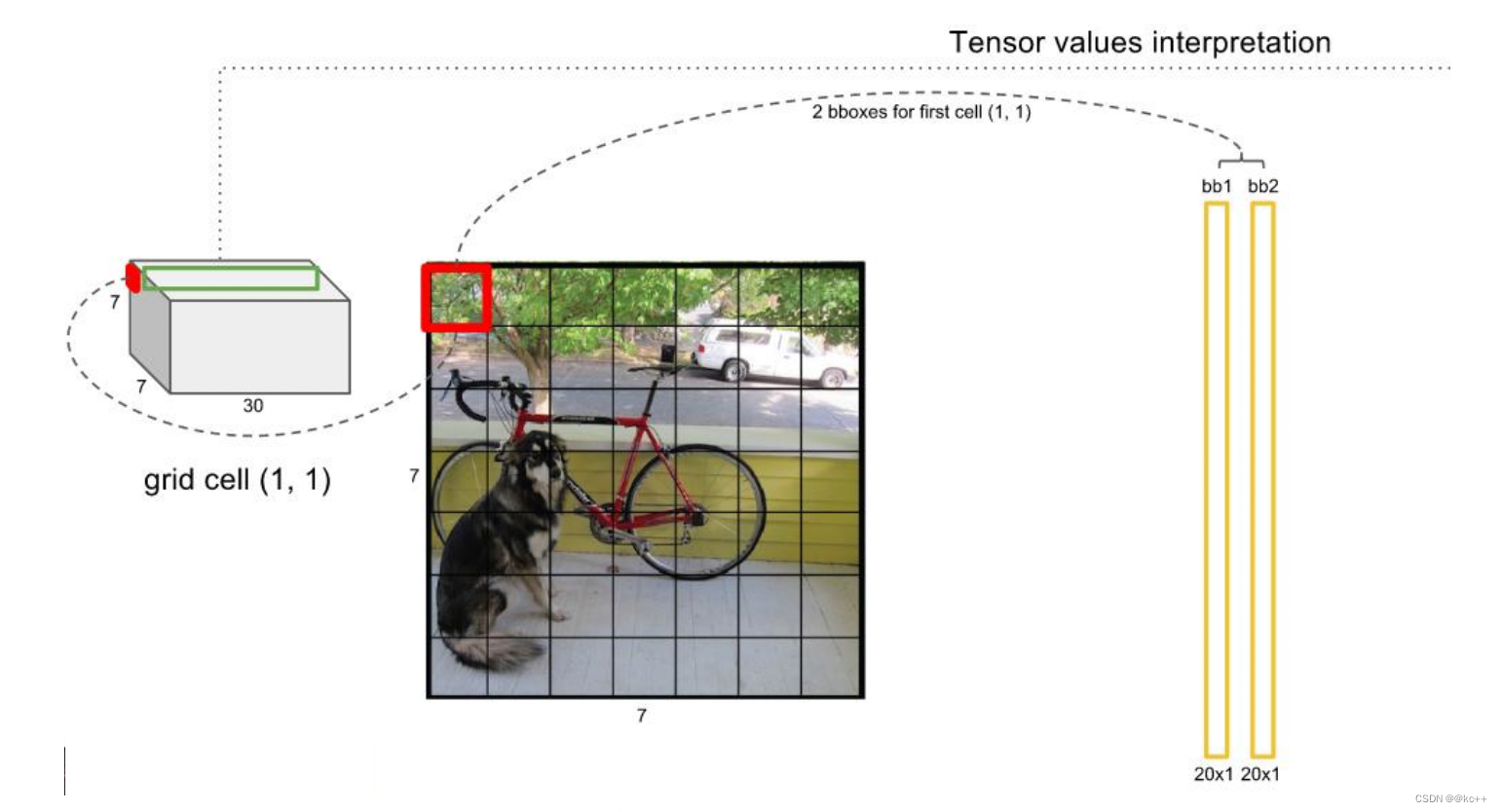
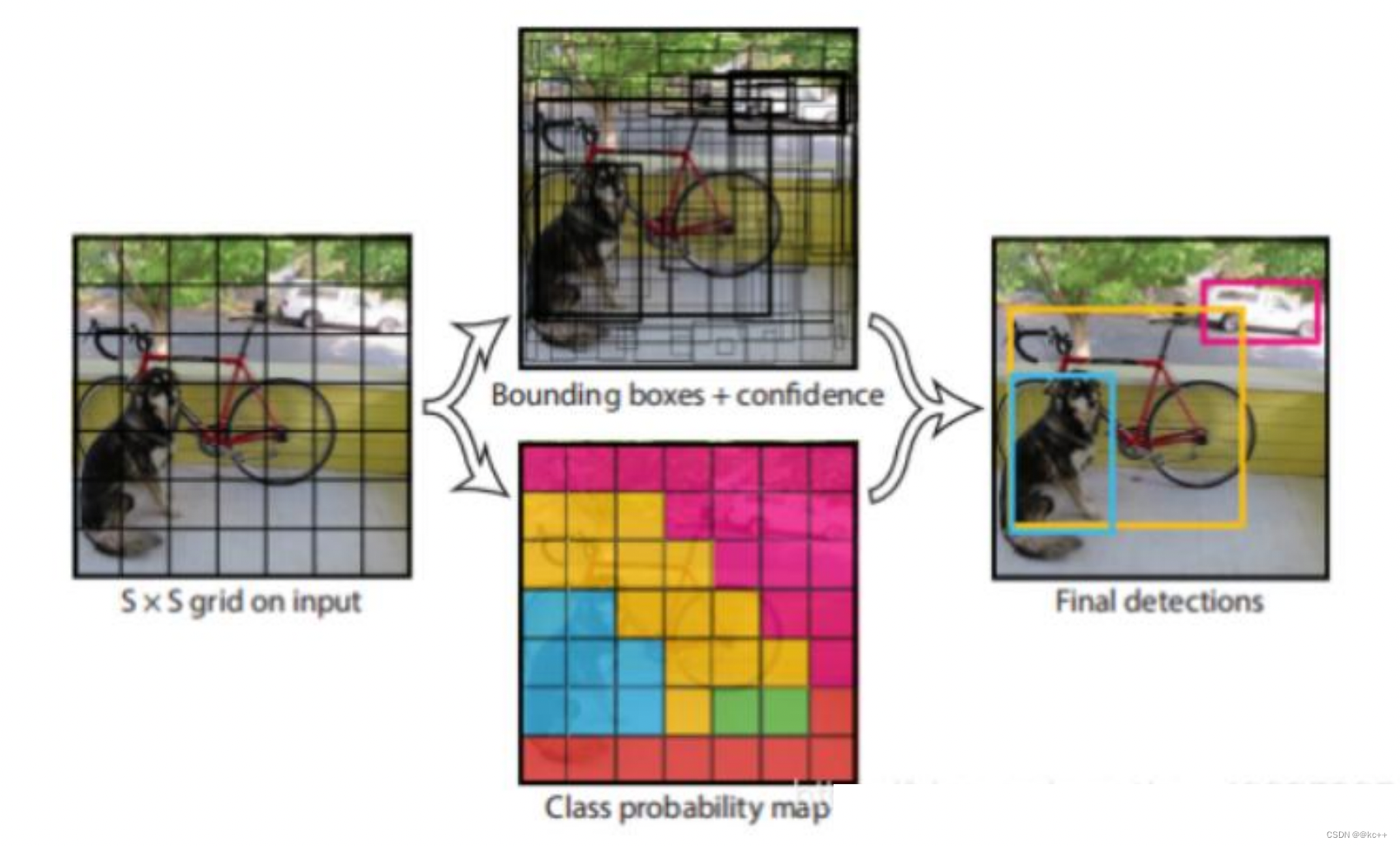
- YOLO算法整体来说就是把输入的图片划分为SS格子,这里是33个格子。
- 当被检测的目标的中心点落入这个格子时,这个格子负责检测这个目标,如图中的人。
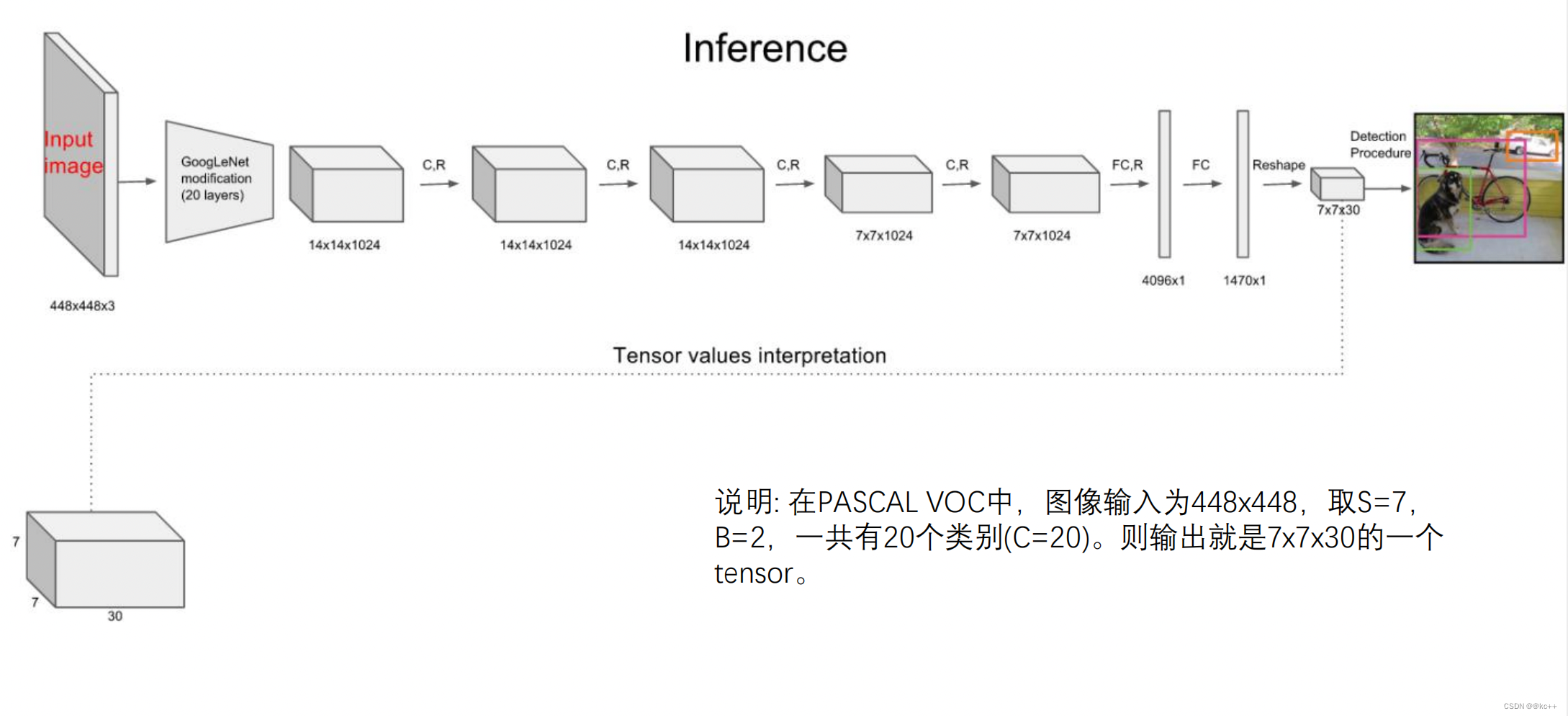
- 我们把这个图片输入到网络中,最后输出的尺寸也是SSn(n是通道数),这个输出的SS与原输入图片SS相对应(都是3*3)。
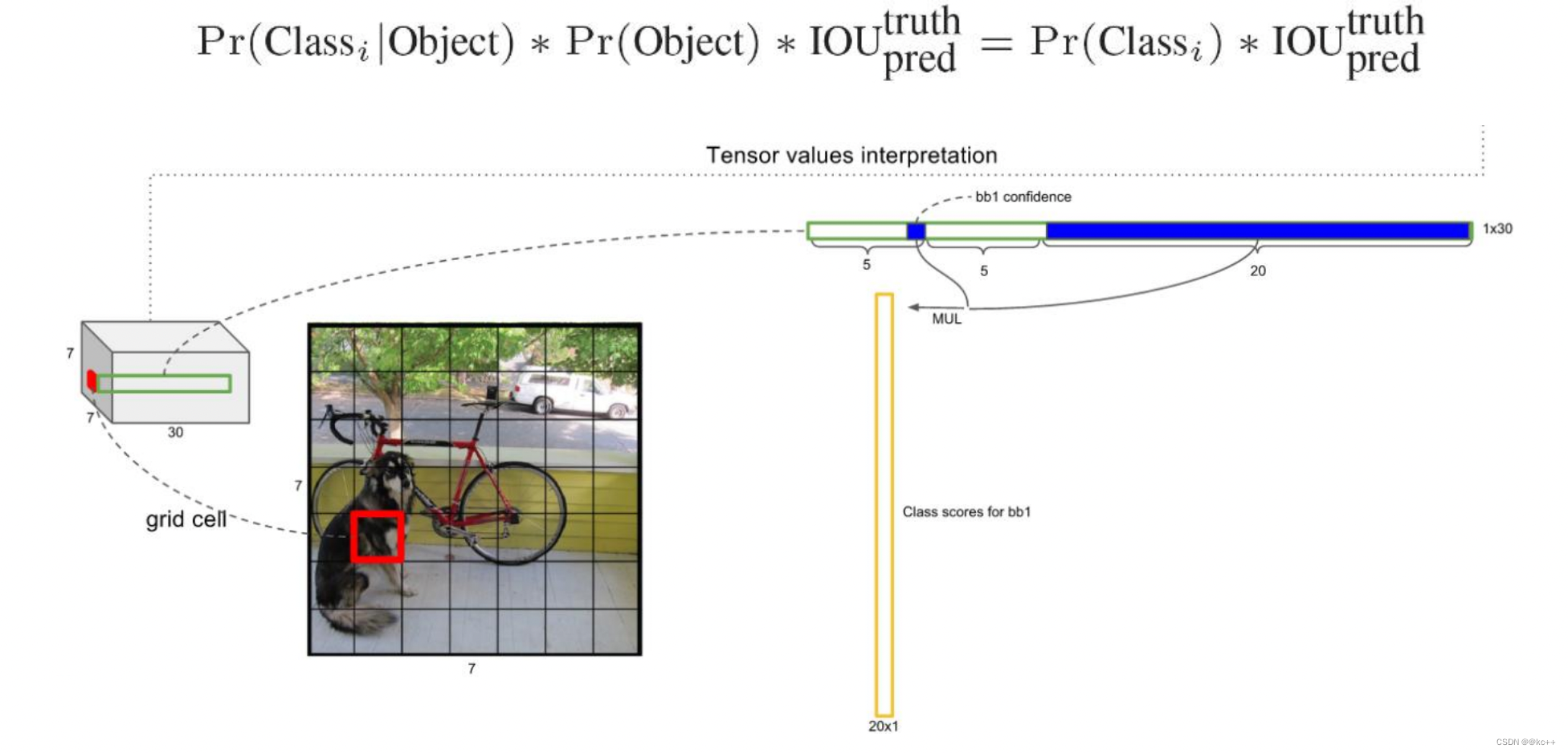
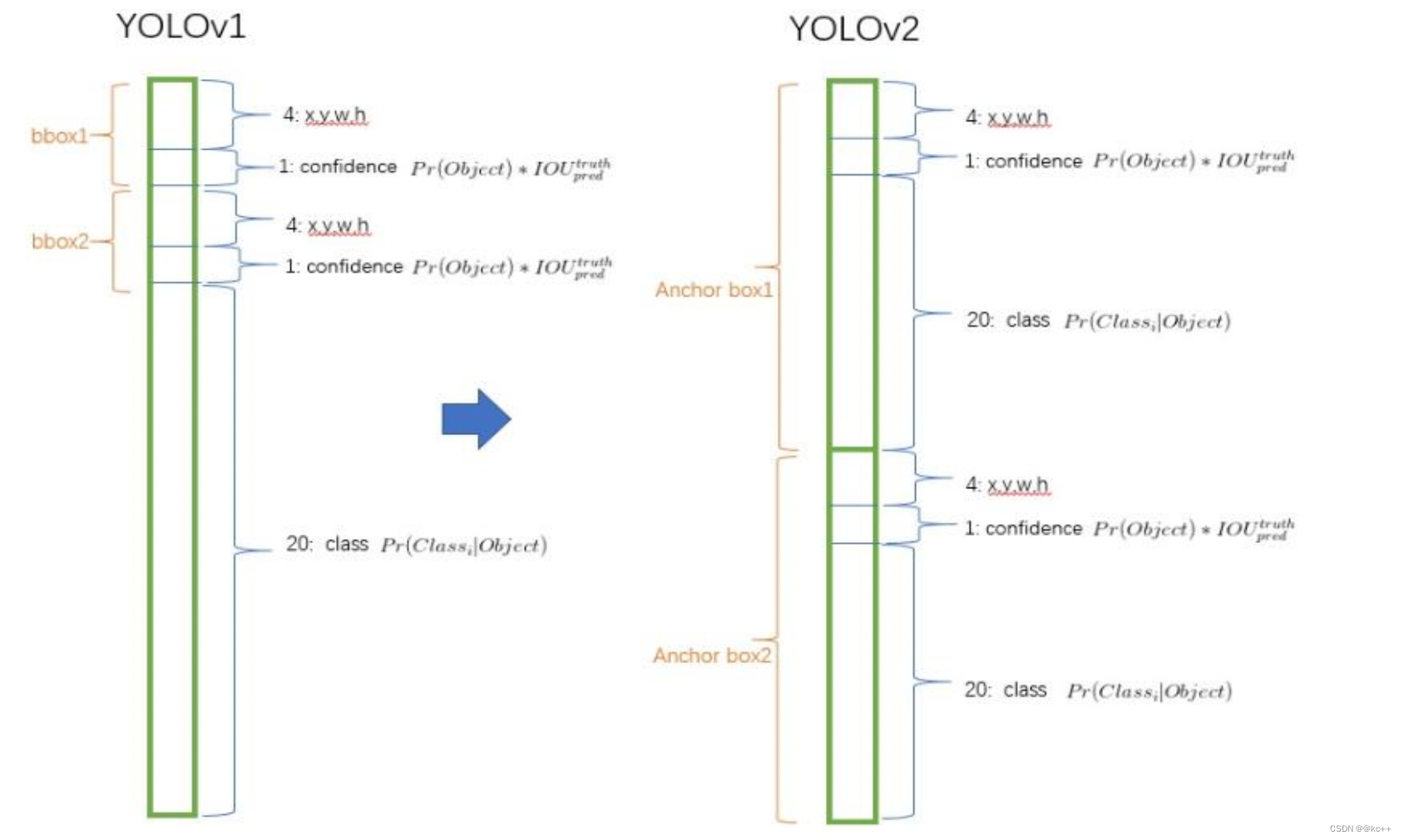
- 假如我们网络一共能检测20个类别的目标,那么输出的通道数n=2*(4+1)+20=30。这里的2指的是每个格子有两个标定框(论文指出的),4代表标定框的坐标信息,1代表标定框的置信度, 20是检测目标的类别数。
- 所以网络最后输出结果的尺寸是SSn=3330。
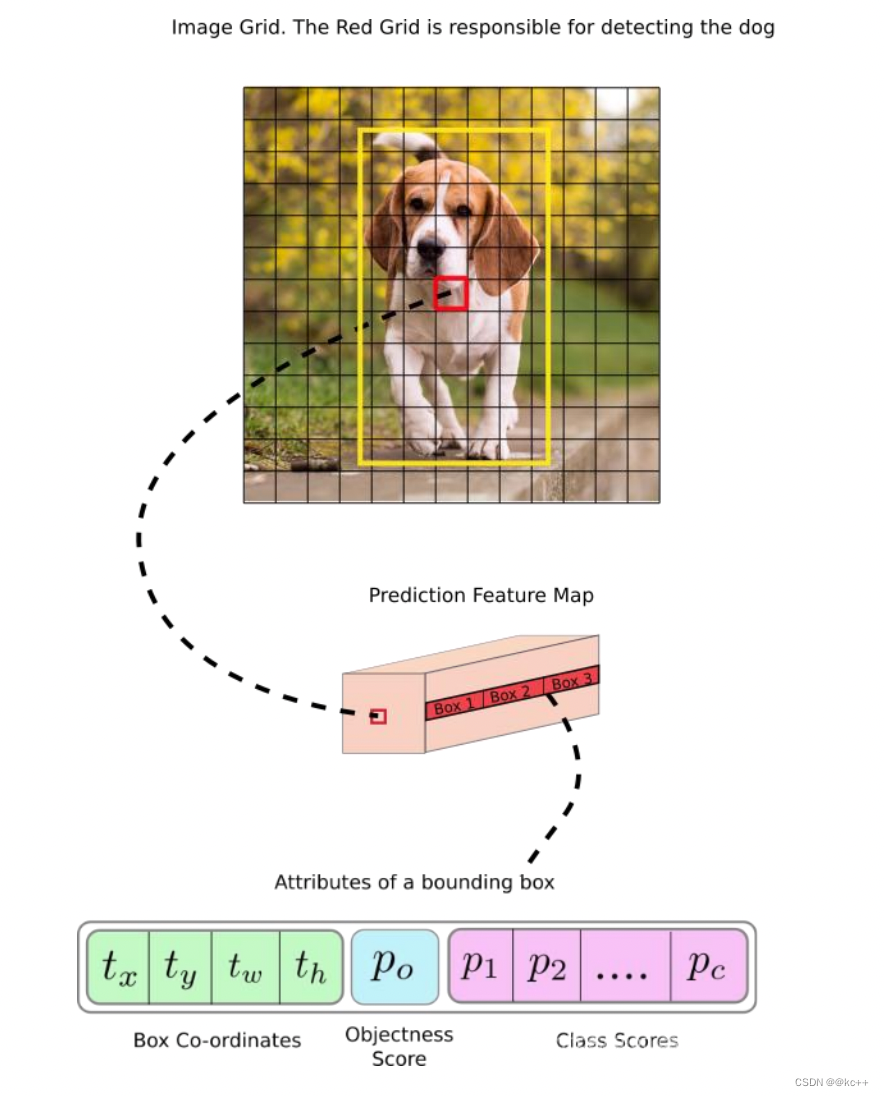
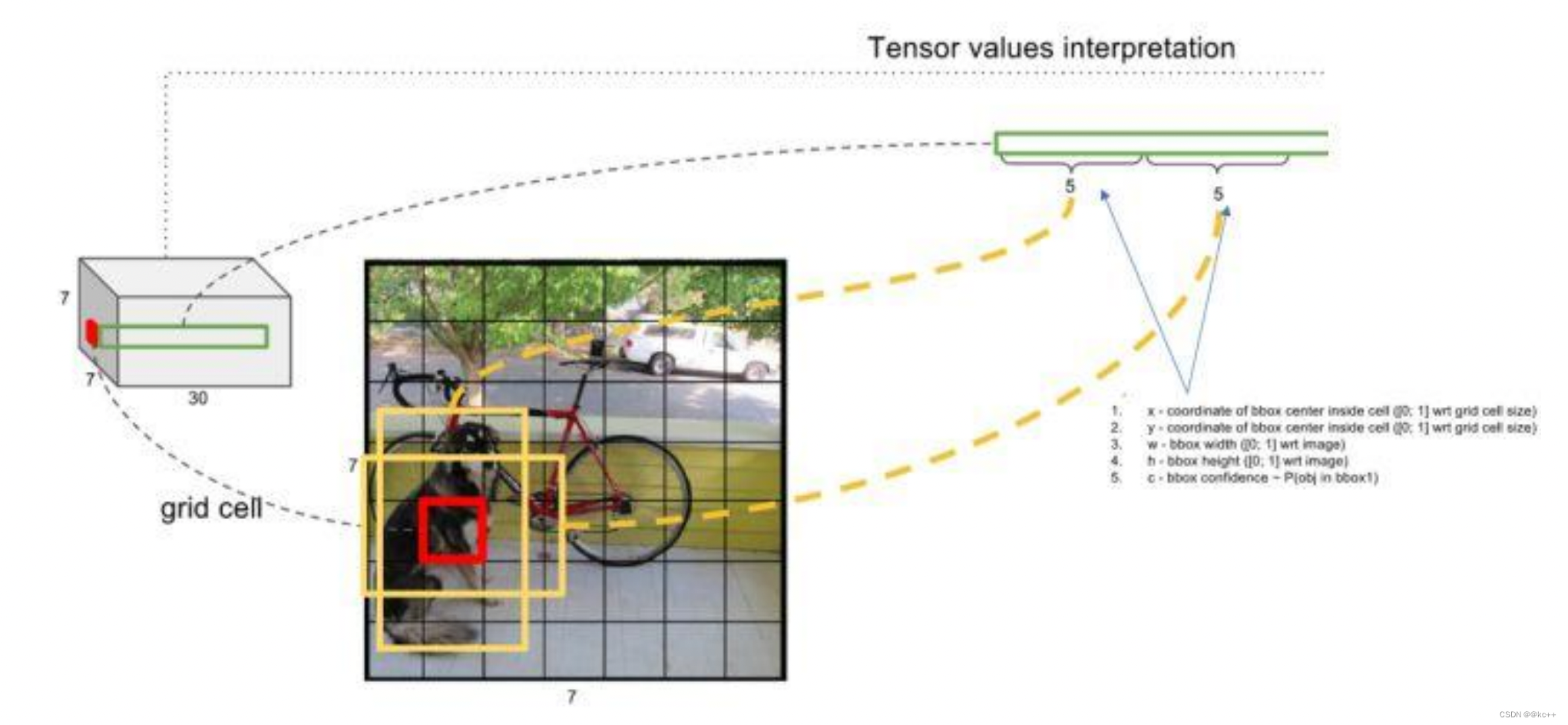
关于标定框
- 网络的输出是S x S x (5*B+C) 的一个 tensor(S-尺寸,B- 标定框个数,C-检测类别数,5-标定框的信息)。
- 5分为4+1:
- 4代表标定框的位置信息。框的中心点(x,y),框的高宽 h,w。
- 1表示每个标定框的置信度以及标定框的准确度信息。
一般情况下,YOLO 不会预测边界框中心的确切坐标。它预测:
- 与预测目标的网格单元左上角相关的偏移;
- 使用特征图单元的维度进行归一化的偏移。
例如:
以上图为例,如果中心的预测是 (0.4, 0.7),则中心在 13 x 13 特征图上的坐标是 (6.4, 6.7)(红色单元的左上角坐标是 (6,6))。
但是,如果预测到的 x,y 坐标大于 1,比如 (1.2, 0.7)。那么预测的中心坐标是 (7.2, 6.7)。注意该中心在红色单元右侧的单元中。这打破了 YOLO 背后的理论,因为如果我们假设红色框负责预测目标狗,那么狗的中心必须在红色单元中,不应该在它旁边的网格单元中。
因此,为了解决这个问题,我们对输出执行 sigmoid 函数,将输出压缩到区间 0 到 1 之间,有效确保中心处于执行预测的网格单元中。
每个标定框的置信度以及标定框的准确度信息:
左边代表包含这个标定框的格子里是否有目标。有=1没有=0。
右边代表标定框的准确程度, 右边的部分是把两个标定框(一个是Ground truth,一个是预测的标定框)进行一个IOU操作,即两个标定框的交集比并集,数值越大,即标定框重合越多,越准确。
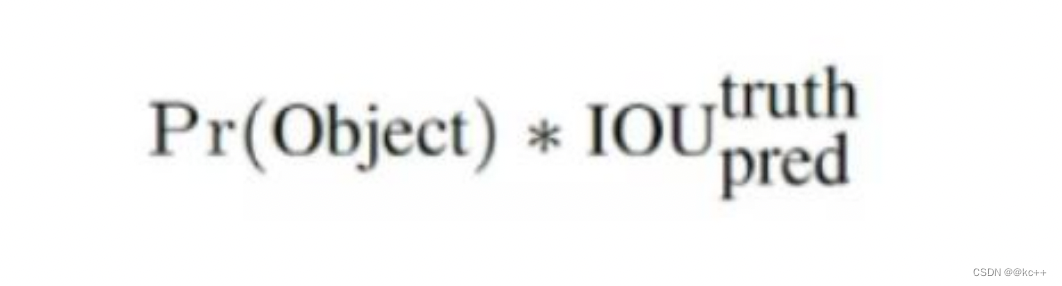
我们可以计算出各个标定框的类别置信度(class-specific confidence scores/ class scores): 表达的是该标定框中目标属于各个类别的可能性大小以及标定框匹配目标的好坏。
每个网格预测的class信息和bounding box预测的confidence信息相乘,就得到每个bounding box 的class-specific confidence score。
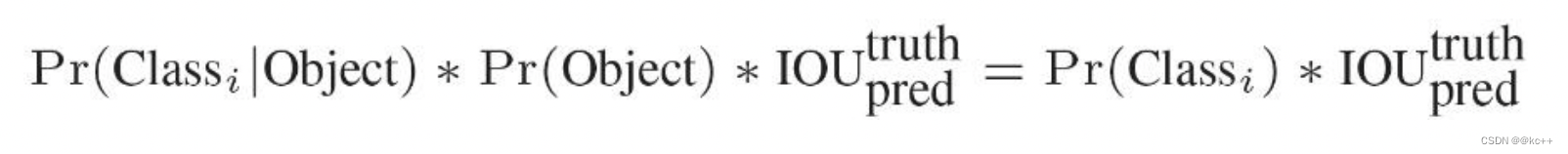
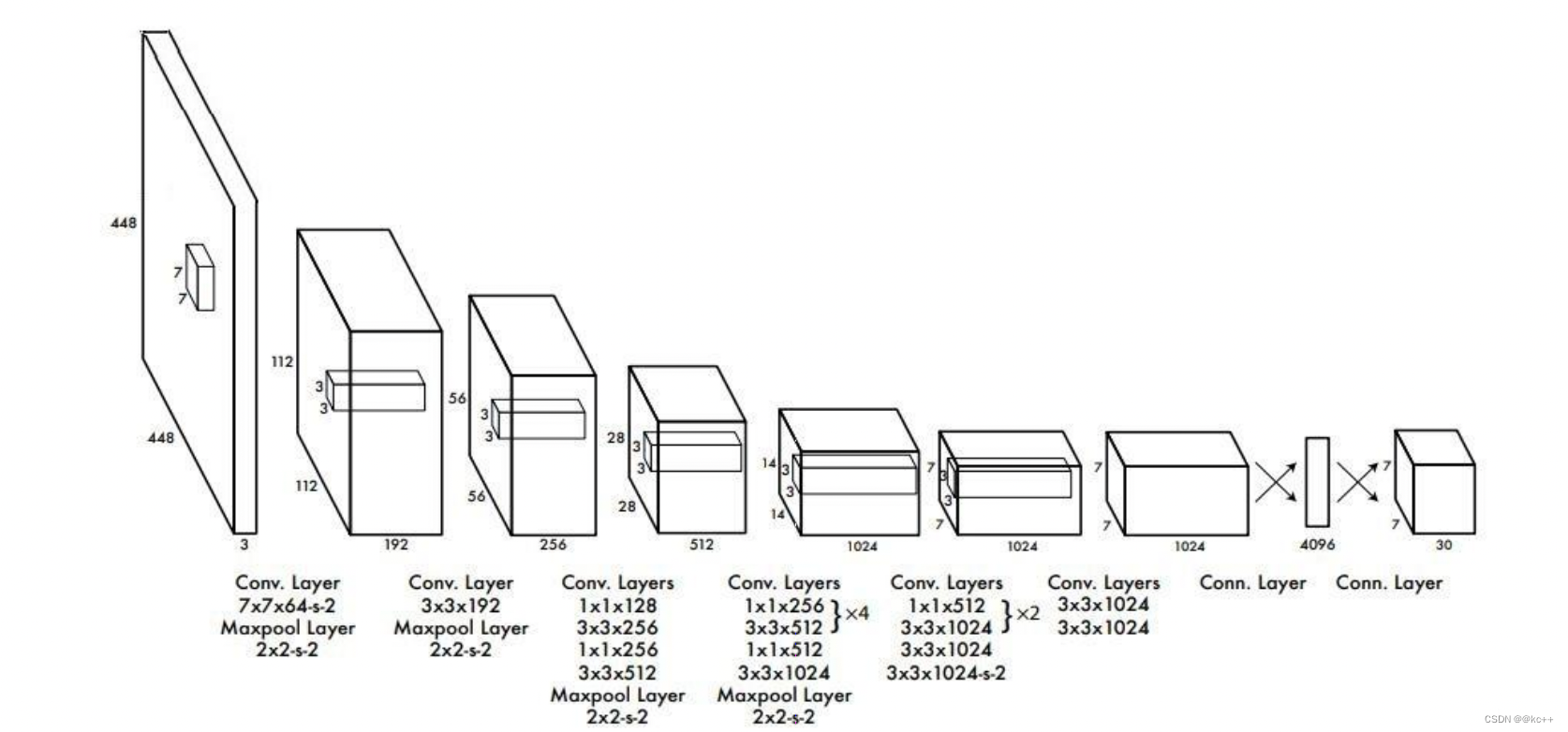
- 其进行了二十多次卷积还有四次最大池化。其中3x3卷积用于提取特征,1x1卷积用于压缩特征,最后将图像压缩到7x7xfilter的大小,相当于将整个图像划分为7x7的网格,每个网格负责自己这一块区域的目标检测。
- 整个网络最后利用全连接层使其结果的size为(7x7x30),其中7x7代表的是7x7的网格,30前20个代表的是预测的种类,后10代表两个预测框及其置信度(5x2)。
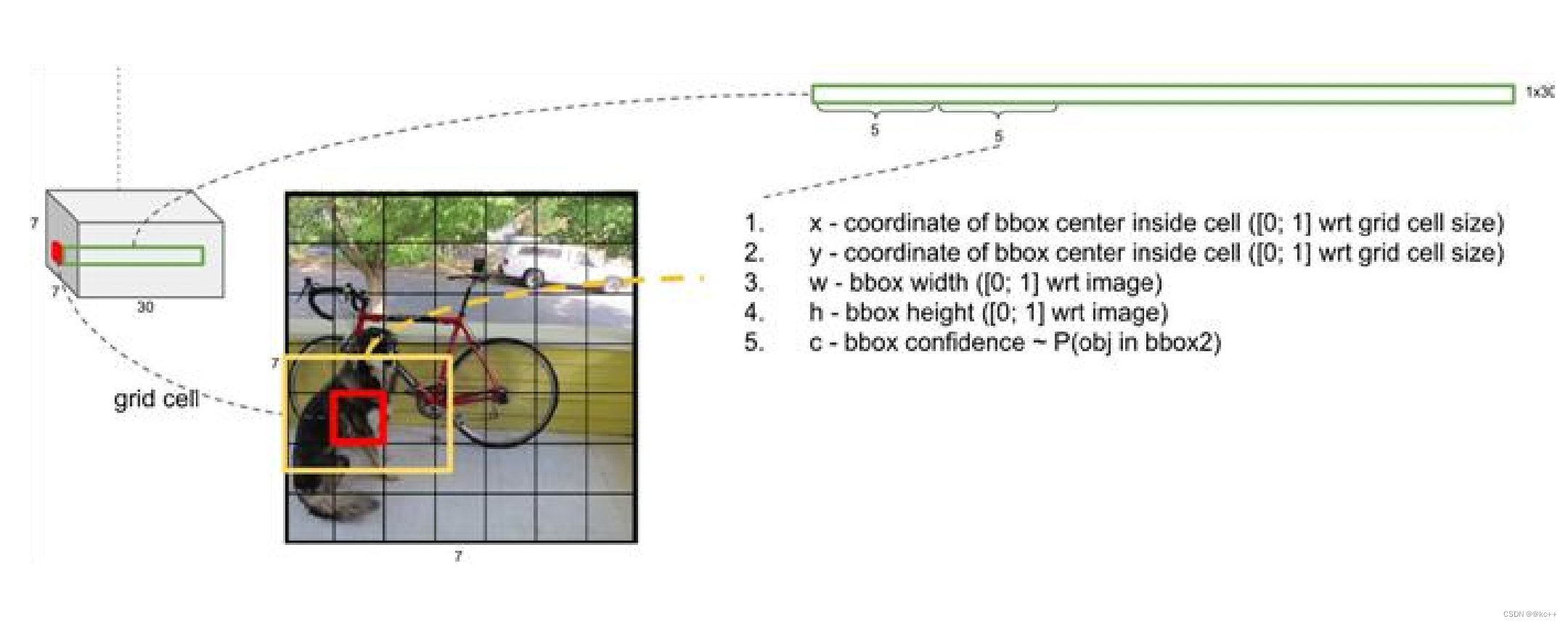

对每一个网格的每一个bbox执行同样操作: 7x7x2 = 98 bbox (每个bbox既有对应的class信息又有坐标信息)
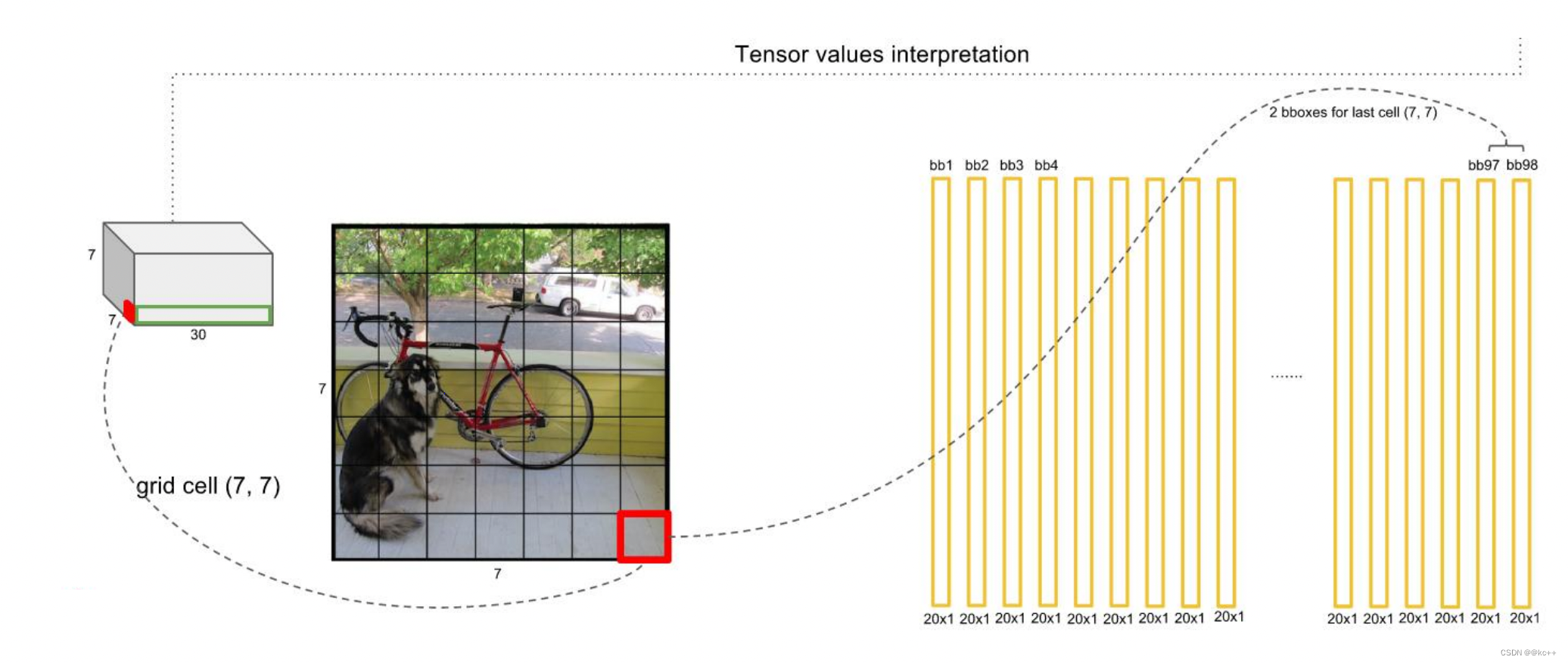
得到每个bbox的class-specific confidence score以后,设置阈值,滤掉得分低的boxes,对保留的boxes进行NMS处理,就得到最终的检测结果。
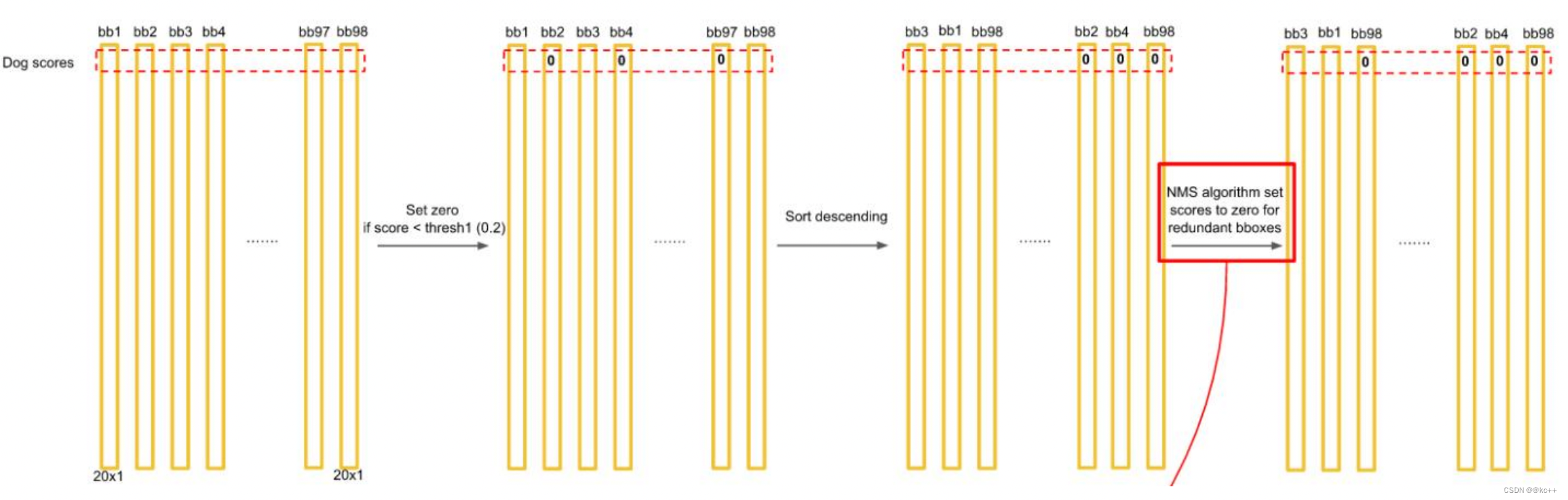
排序后,不同位置的框内,概率不同:
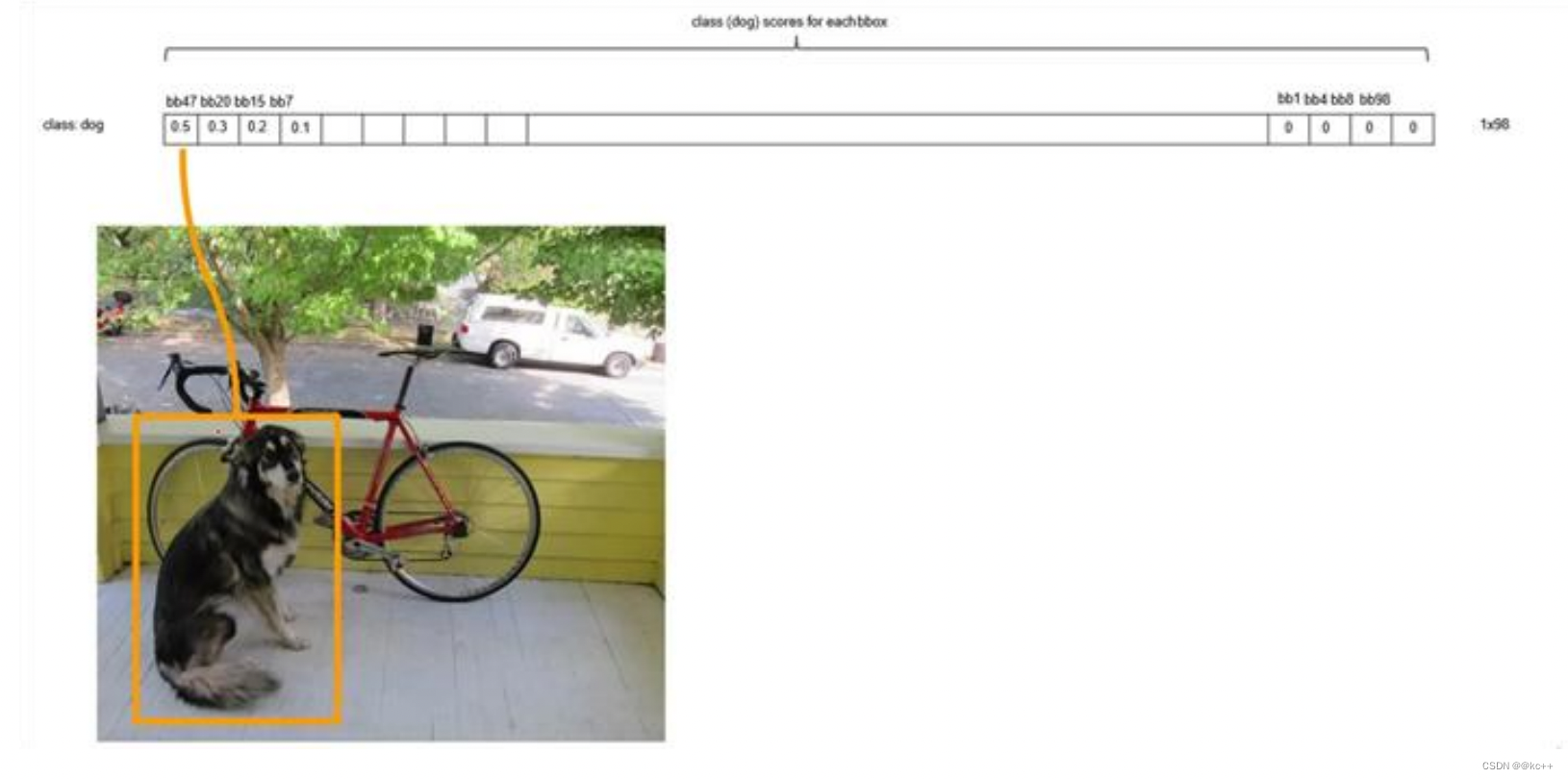
以最大值作为bbox_max,并与比它小的非0值(bbox_cur)做比较:IOU
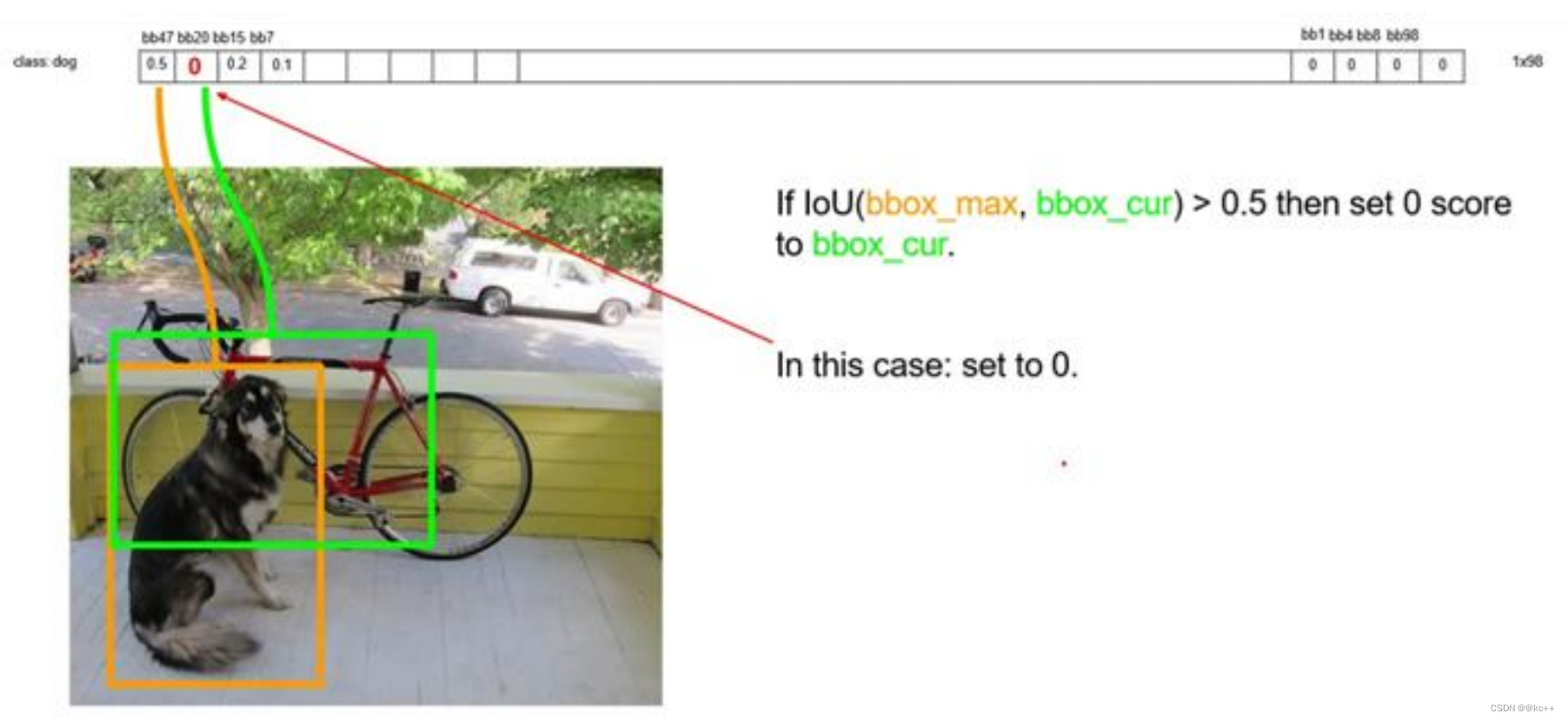
递归,以下一个非0 bbox_cur(0.2)作为bbox_max继续比较IOU:
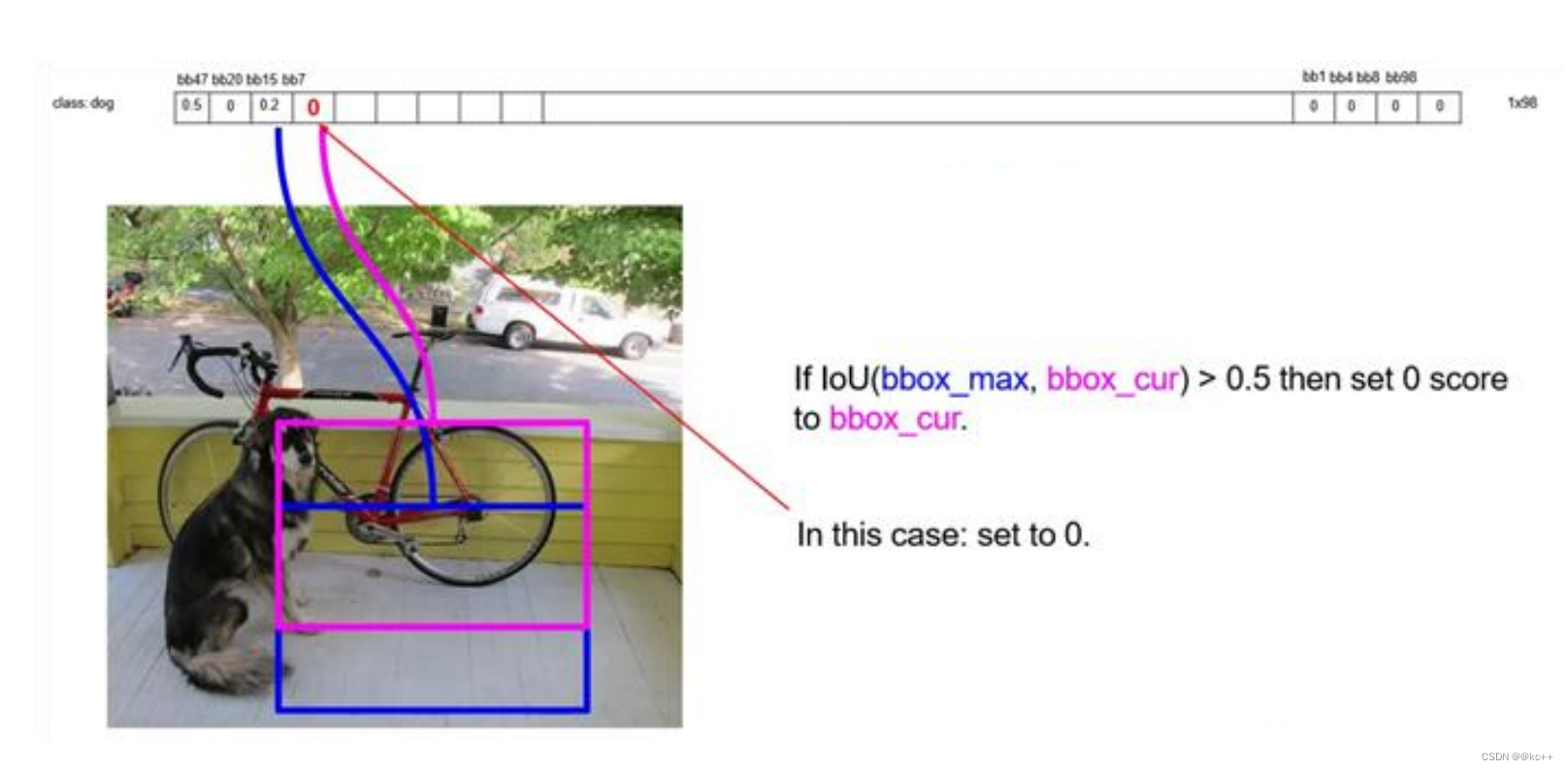
最终,剩下n个框
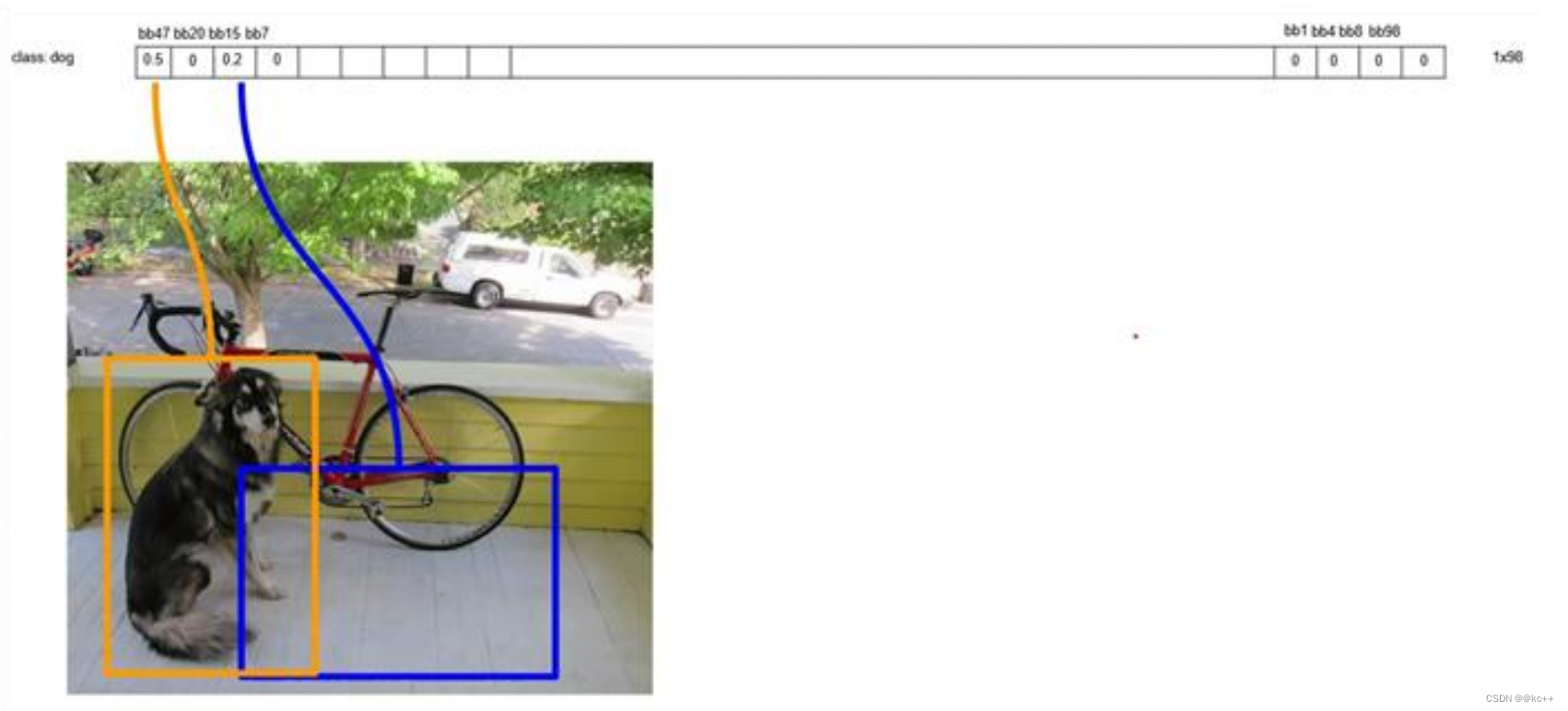
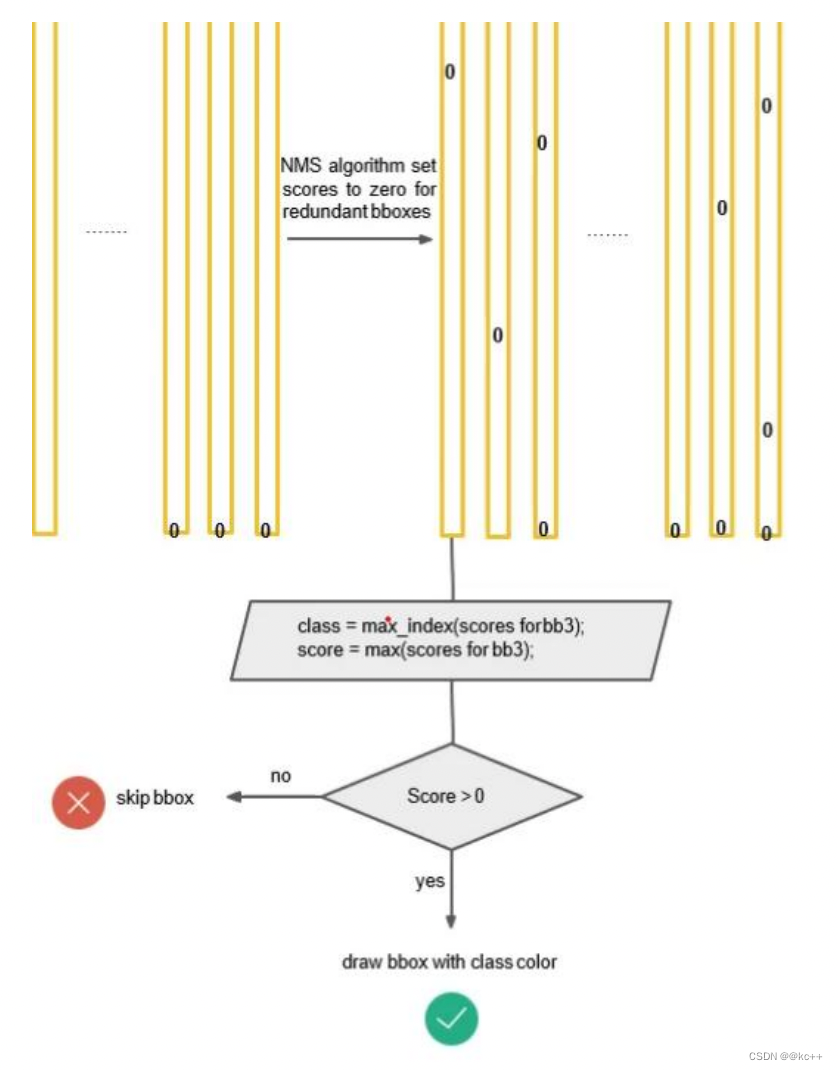
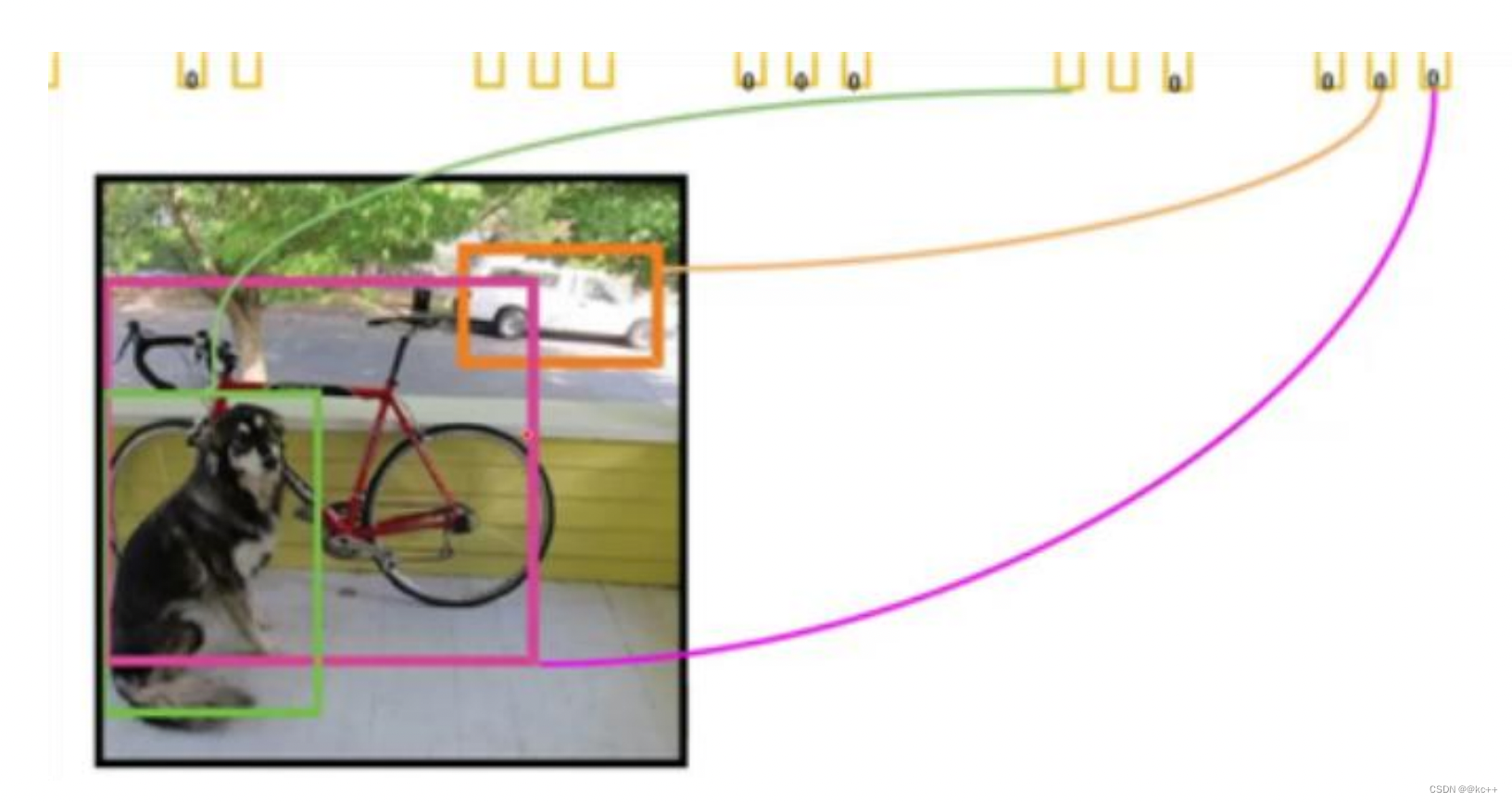
得到每个bbox的class-specific confidence score以后,设置阈值,滤掉得分低的boxes,对保留的boxes进行NMS处理,就得到最终的检测结果。
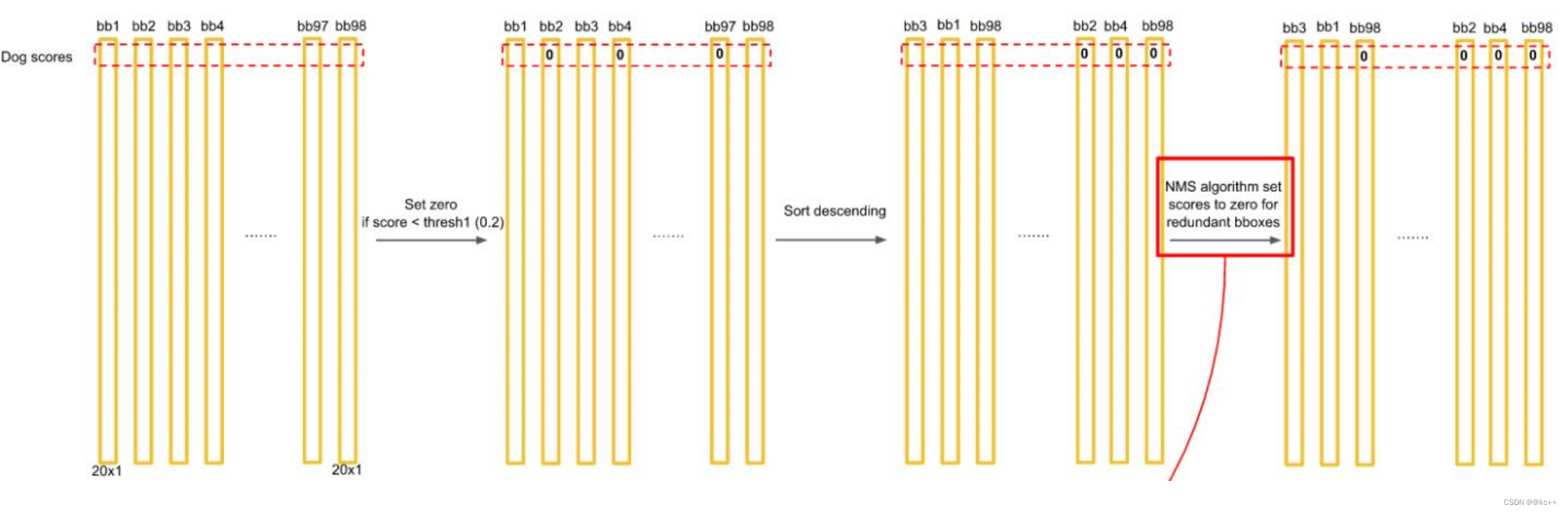
对bb3(20×1)类别的分数,找分数对应最大类别的索引.---->class bb3(20×1)中最大的分---->score
Yolo的缺点:
- YOLO对相互靠的很近的物体(挨在一起且中点都落在同一个格子上的情况),还有很小 的群体检测效果不好,这是因为一个网格中只预测了两个框,并且只属于一类。
- 测试图像中,当同一类物体出现不常见的长宽比和其他情况时泛化能力偏弱。
5.2 Yolo2
- Yolo2使用了一个新的分类网络作为特征提取部分。
- 网络使用了较多的3 x 3卷积核,在每一次池化操作后把通道数翻倍。
- 把1 x 1的卷积核置于3 x 3的卷积核之间,用来压缩特征。
- 使用batch normalization稳定模型训练,加速收敛。
- 保留了一个shortcut用于存储之前的特征。
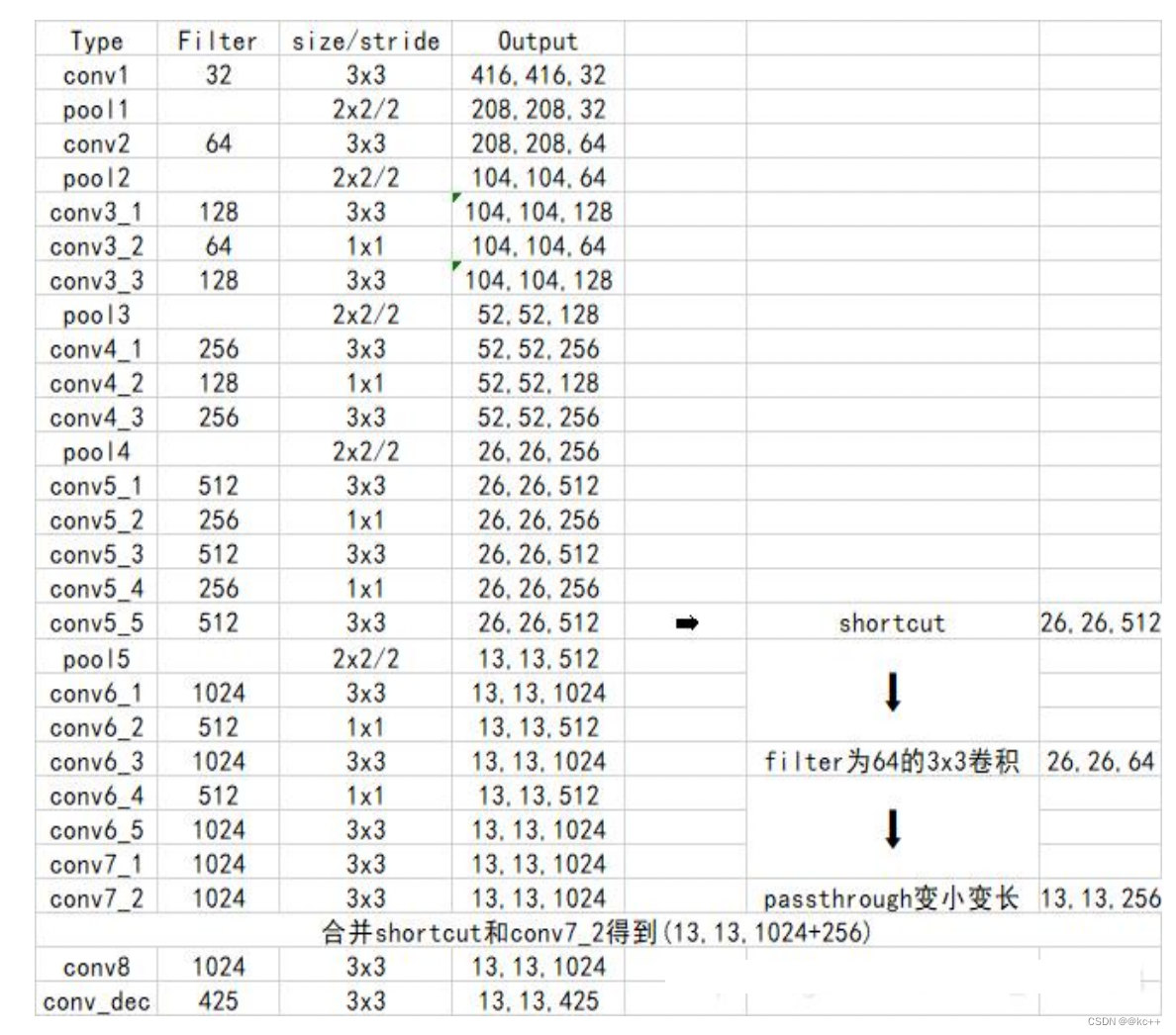
- yolo2相比于yolo1加入了先验框部分,最后输出的conv_dec的shape为(13,13,425):
- 13x13是把整个图分为13x13的网格用于预测。
- 425可以分解为(85x5)。在85中,由于yolo2常用的是coco数据集,其中具有80个类;剩余的5指的是x、y、w、h和其置信度。x5意味着预测结果包含5个框,分别对应5个先验框。
5.2.1 Yolo2 – 采用anchor boxes
5.2.2 Yolo2 – Dimension Clusters(维度聚类)
使用kmeans聚类获取先验框的信息:
之前先验框都是手工设定的,YOLO2尝试统计出更符合样本中对象尺寸的先验框,这样就可以减少网络微调先验框到实际位置的难度。YOLO2的做法是对训练集中标注的边框进行聚类分析,以寻找尽可能匹配样本的边框尺寸。
聚类算法最重要的是选择如何计算两个边框之间的“距离”,对于常用的欧式距离,大边框会产生更大的误差,但我们关心的是边框的IOU。所以,YOLO2在聚类时采用以下公式来计算两个边框之间的“距离”。
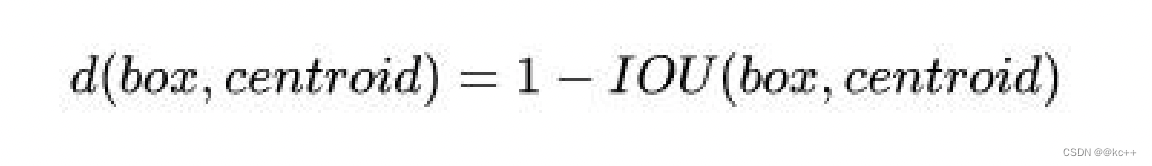
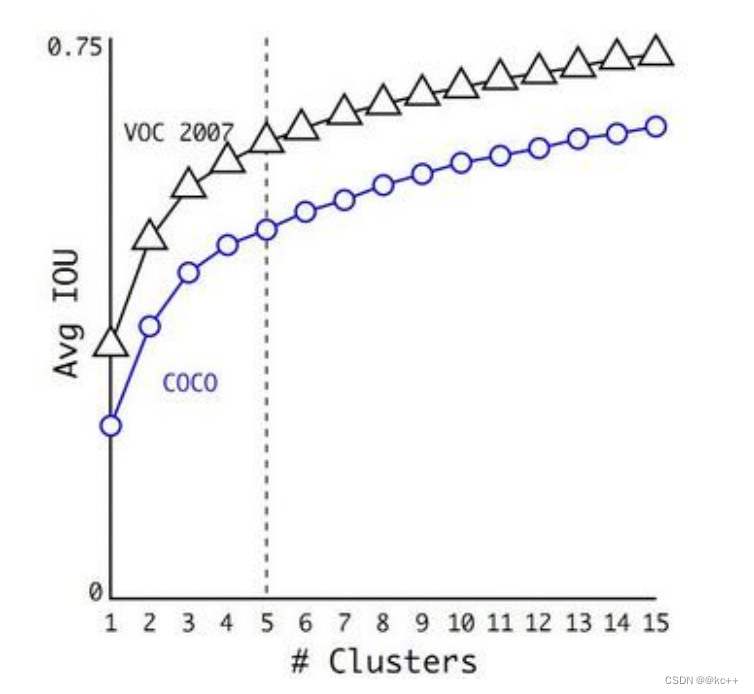
在选择不同的聚类k值情况下,得到的k个centroid边框,计算样本中标注的边框与各centroid的Avg IOU。
显然,边框数k越多,Avg IOU越大。
YOLO2选择k=5作为边框数量与IOU的折中。对比手工选择的先验框,使用5个聚类框即可达到61 Avg IOU,相当于9个手工设置的先验框60.9 Avg IOU
作者最终选取5个聚类中心作为先验框。对于两个数据集,5个先验框的width和height如下:
COCO: (0.57273, 0.677385), (1.87446, 2.06253), (3.33843, 5.47434), (7.88282, 3.52778), (9.77052, 9.16828)
VOC: (1.3221, 1.73145), (3.19275, 4.00944), (5.05587, 8.09892), (9.47112, 4.84053), (11.2364, 10.0071)
5.3 Yolo3
YOLOv3相比于之前的yolo1和yolo2,改进较大,主要改进方向有:
- 使用了残差网络Residual
- 提取多特征层进行目标检测,一共提取三个特征层,它的shape分别为(13,13,75),(26,26,75), (52,52,75)。最后一个维度为75是因为该图是基于voc数据集的,它的类为20种。yolo3针对每一个特征层存在3个先验框,所以最后维度为3x25。
- 其采用了UpSampling2d设计
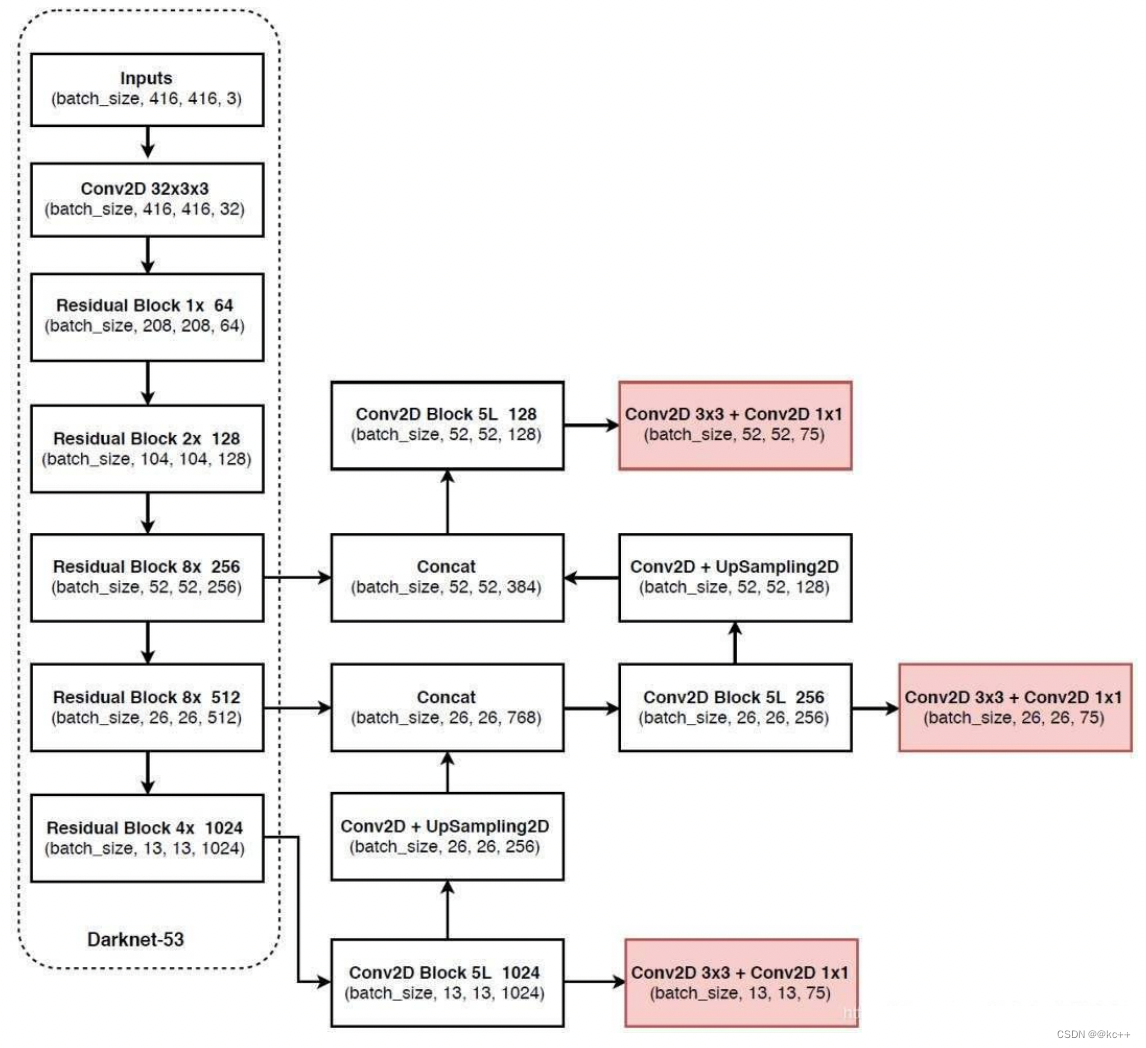
5.4 代码示例(yolo v3)
5.4.1 模型搭建
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import osclass yolo:def __init__(self, norm_epsilon, norm_decay, anchors_path, classes_path, pre_train):"""Introduction------------初始化函数Parameters----------norm_decay: 在预测时计算moving average时的衰减率norm_epsilon: 方差加上极小的数,防止除以0的情况anchors_path: yolo anchor 文件路径classes_path: 数据集类别对应文件pre_train: 是否使用预训练darknet53模型"""self.norm_epsilon = norm_epsilonself.norm_decay = norm_decayself.anchors_path = anchors_pathself.classes_path = classes_pathself.pre_train = pre_trainself.anchors = self._get_anchors()self.classes = self._get_class()#---------------------------------------## 获取种类和先验框#---------------------------------------#def _get_class(self):"""Introduction------------获取类别名字Returns-------class_names: coco数据集类别对应的名字"""classes_path = os.path.expanduser(self.classes_path)with open(classes_path) as f:class_names = f.readlines()class_names = [c.strip() for c in class_names]return class_namesdef _get_anchors(self):"""Introduction------------获取anchors"""anchors_path = os.path.expanduser(self.anchors_path)with open(anchors_path) as f:anchors = f.readline()anchors = [float(x) for x in anchors.split(',')]return np.array(anchors).reshape(-1, 2)#---------------------------------------## 用于生成层#---------------------------------------## l2 正则化def _batch_normalization_layer(self, input_layer, name = None, training = True, norm_decay = 0.99, norm_epsilon = 1e-3):'''Introduction------------对卷积层提取的feature map使用batch normalizationParameters----------input_layer: 输入的四维tensorname: batchnorm层的名字trainging: 是否为训练过程norm_decay: 在预测时计算moving average时的衰减率norm_epsilon: 方差加上极小的数,防止除以0的情况Returns-------bn_layer: batch normalization处理之后的feature map'''bn_layer = tf.layers.batch_normalization(inputs = input_layer,momentum = norm_decay, epsilon = norm_epsilon, center = True,scale = True, training = training, name = name)return tf.nn.leaky_relu(bn_layer, alpha = 0.1)# 这个就是用来进行卷积的def _conv2d_layer(self, inputs, filters_num, kernel_size, name, use_bias = False, strides = 1):"""Introduction------------使用tf.layers.conv2d减少权重和偏置矩阵初始化过程,以及卷积后加上偏置项的操作经过卷积之后需要进行batch norm,最后使用leaky ReLU激活函数根据卷积时的步长,如果卷积的步长为2,则对图像进行降采样比如,输入图片的大小为416*416,卷积核大小为3,若stride为2时,(416 - 3 + 2)/ 2 + 1, 计算结果为208,相当于做了池化层处理因此需要对stride大于1的时候,先进行一个padding操作, 采用四周都padding一维代替'same'方式Parameters----------inputs: 输入变量filters_num: 卷积核数量strides: 卷积步长name: 卷积层名字trainging: 是否为训练过程use_bias: 是否使用偏置项kernel_size: 卷积核大小Returns-------conv: 卷积之后的feature map"""conv = tf.layers.conv2d(inputs = inputs, filters = filters_num,kernel_size = kernel_size, strides = [strides, strides], kernel_initializer = tf.glorot_uniform_initializer(),padding = ('SAME' if strides == 1 else 'VALID'), kernel_regularizer = tf.contrib.layers.l2_regularizer(scale = 5e-4), use_bias = use_bias, name = name)return conv# 这个用来进行残差卷积的# 残差卷积就是进行一次3X3的卷积,然后保存该卷积layer# 再进行一次1X1的卷积和一次3X3的卷积,并把这个结果加上layer作为最后的结果def _Residual_block(self, inputs, filters_num, blocks_num, conv_index, training = True, norm_decay = 0.99, norm_epsilon = 1e-3):"""Introduction------------Darknet的残差block,类似resnet的两层卷积结构,分别采用1x1和3x3的卷积核,使用1x1是为了减少channel的维度Parameters----------inputs: 输入变量filters_num: 卷积核数量trainging: 是否为训练过程blocks_num: block的数量conv_index: 为了方便加载预训练权重,统一命名序号weights_dict: 加载预训练模型的权重norm_decay: 在预测时计算moving average时的衰减率norm_epsilon: 方差加上极小的数,防止除以0的情况Returns-------inputs: 经过残差网络处理后的结果"""# 在输入feature map的长宽维度进行paddinginputs = tf.pad(inputs, paddings=[[0, 0], [1, 0], [1, 0], [0, 0]], mode='CONSTANT')layer = self._conv2d_layer(inputs, filters_num, kernel_size = 3, strides = 2, name = "conv2d_" + str(conv_index))layer = self._batch_normalization_layer(layer, name = "batch_normalization_" + str(conv_index), training = training, norm_decay = norm_decay, norm_epsilon = norm_epsilon)conv_index += 1for _ in range(blocks_num):shortcut = layerlayer = self._conv2d_layer(layer, filters_num // 2, kernel_size = 1, strides = 1, name = "conv2d_" + str(conv_index))layer = self._batch_normalization_layer(layer, name = "batch_normalization_" + str(conv_index), training = training, norm_decay = norm_decay, norm_epsilon = norm_epsilon)conv_index += 1layer = self._conv2d_layer(layer, filters_num, kernel_size = 3, strides = 1, name = "conv2d_" + str(conv_index))layer = self._batch_normalization_layer(layer, name = "batch_normalization_" + str(conv_index), training = training, norm_decay = norm_decay, norm_epsilon = norm_epsilon)conv_index += 1layer += shortcutreturn layer, conv_index#---------------------------------------## 生成_darknet53#---------------------------------------#def _darknet53(self, inputs, conv_index, training = True, norm_decay = 0.99, norm_epsilon = 1e-3):"""Introduction------------构建yolo3使用的darknet53网络结构Parameters----------inputs: 模型输入变量conv_index: 卷积层数序号,方便根据名字加载预训练权重weights_dict: 预训练权重training: 是否为训练norm_decay: 在预测时计算moving average时的衰减率norm_epsilon: 方差加上极小的数,防止除以0的情况Returns-------conv: 经过52层卷积计算之后的结果, 输入图片为416x416x3,则此时输出的结果shape为13x13x1024route1: 返回第26层卷积计算结果52x52x256, 供后续使用route2: 返回第43层卷积计算结果26x26x512, 供后续使用conv_index: 卷积层计数,方便在加载预训练模型时使用"""with tf.variable_scope('darknet53'):# 416,416,3 -> 416,416,32conv = self._conv2d_layer(inputs, filters_num = 32, kernel_size = 3, strides = 1, name = "conv2d_" + str(conv_index))conv = self._batch_normalization_layer(conv, name = "batch_normalization_" + str(conv_index), training = training, norm_decay = norm_decay, norm_epsilon = norm_epsilon)conv_index += 1# 416,416,32 -> 208,208,64conv, conv_index = self._Residual_block(conv, conv_index = conv_index, filters_num = 64, blocks_num = 1, training = training, norm_decay = norm_decay, norm_epsilon = norm_epsilon)# 208,208,64 -> 104,104,128conv, conv_index = self._Residual_block(conv, conv_index = conv_index, filters_num = 128, blocks_num = 2, training = training, norm_decay = norm_decay, norm_epsilon = norm_epsilon)# 104,104,128 -> 52,52,256conv, conv_index = self._Residual_block(conv, conv_index = conv_index, filters_num = 256, blocks_num = 8, training = training, norm_decay = norm_decay, norm_epsilon = norm_epsilon)# route1 = 52,52,256route1 = conv# 52,52,256 -> 26,26,512conv, conv_index = self._Residual_block(conv, conv_index = conv_index, filters_num = 512, blocks_num = 8, training = training, norm_decay = norm_decay, norm_epsilon = norm_epsilon)# route2 = 26,26,512route2 = conv# 26,26,512 -> 13,13,1024conv, conv_index = self._Residual_block(conv, conv_index = conv_index, filters_num = 1024, blocks_num = 4, training = training, norm_decay = norm_decay, norm_epsilon = norm_epsilon)# route3 = 13,13,1024return route1, route2, conv, conv_index# 输出两个网络结果# 第一个是进行5次卷积后,用于下一次逆卷积的,卷积过程是1X1,3X3,1X1,3X3,1X1# 第二个是进行5+2次卷积,作为一个特征层的,卷积过程是1X1,3X3,1X1,3X3,1X1,3X3,1X1def _yolo_block(self, inputs, filters_num, out_filters, conv_index, training = True, norm_decay = 0.99, norm_epsilon = 1e-3):"""Introduction------------yolo3在Darknet53提取的特征层基础上,又加了针对3种不同比例的feature map的block,这样来提高对小物体的检测率Parameters----------inputs: 输入特征filters_num: 卷积核数量out_filters: 最后输出层的卷积核数量conv_index: 卷积层数序号,方便根据名字加载预训练权重training: 是否为训练norm_decay: 在预测时计算moving average时的衰减率norm_epsilon: 方差加上极小的数,防止除以0的情况Returns-------route: 返回最后一层卷积的前一层结果conv: 返回最后一层卷积的结果conv_index: conv层计数"""conv = self._conv2d_layer(inputs, filters_num = filters_num, kernel_size = 1, strides = 1, name = "conv2d_" + str(conv_index))conv = self._batch_normalization_layer(conv, name = "batch_normalization_" + str(conv_index), training = training, norm_decay = norm_decay, norm_epsilon = norm_epsilon)conv_index += 1conv = self._conv2d_layer(conv, filters_num = filters_num * 2, kernel_size = 3, strides = 1, name = "conv2d_" + str(conv_index))conv = self._batch_normalization_layer(conv, name = "batch_normalization_" + str(conv_index), training = training, norm_decay = norm_decay, norm_epsilon = norm_epsilon)conv_index += 1conv = self._conv2d_layer(conv, filters_num = filters_num, kernel_size = 1, strides = 1, name = "conv2d_" + str(conv_index))conv = self._batch_normalization_layer(conv, name = "batch_normalization_" + str(conv_index), training = training, norm_decay = norm_decay, norm_epsilon = norm_epsilon)conv_index += 1conv = self._conv2d_layer(conv, filters_num = filters_num * 2, kernel_size = 3, strides = 1, name = "conv2d_" + str(conv_index))conv = self._batch_normalization_layer(conv, name = "batch_normalization_" + str(conv_index), training = training, norm_decay = norm_decay, norm_epsilon = norm_epsilon)conv_index += 1conv = self._conv2d_layer(conv, filters_num = filters_num, kernel_size = 1, strides = 1, name = "conv2d_" + str(conv_index))conv = self._batch_normalization_layer(conv, name = "batch_normalization_" + str(conv_index), training = training, norm_decay = norm_decay, norm_epsilon = norm_epsilon)conv_index += 1route = convconv = self._conv2d_layer(conv, filters_num = filters_num * 2, kernel_size = 3, strides = 1, name = "conv2d_" + str(conv_index))conv = self._batch_normalization_layer(conv, name = "batch_normalization_" + str(conv_index), training = training, norm_decay = norm_decay, norm_epsilon = norm_epsilon)conv_index += 1conv = self._conv2d_layer(conv, filters_num = out_filters, kernel_size = 1, strides = 1, name = "conv2d_" + str(conv_index), use_bias = True)conv_index += 1return route, conv, conv_index# 返回三个特征层的内容def yolo_inference(self, inputs, num_anchors, num_classes, training = True):"""Introduction------------构建yolo模型结构Parameters----------inputs: 模型的输入变量num_anchors: 每个grid cell负责检测的anchor数量num_classes: 类别数量training: 是否为训练模式"""conv_index = 1# route1 = 52,52,256、route2 = 26,26,512、route3 = 13,13,1024conv2d_26, conv2d_43, conv, conv_index = self._darknet53(inputs, conv_index, training = training, norm_decay = self.norm_decay, norm_epsilon = self.norm_epsilon)with tf.variable_scope('yolo'):#--------------------------------------## 获得第一个特征层#--------------------------------------## conv2d_57 = 13,13,512,conv2d_59 = 13,13,255(3x(80+5))conv2d_57, conv2d_59, conv_index = self._yolo_block(conv, 512, num_anchors * (num_classes + 5), conv_index = conv_index, training = training, norm_decay = self.norm_decay, norm_epsilon = self.norm_epsilon)#--------------------------------------## 获得第二个特征层#--------------------------------------#conv2d_60 = self._conv2d_layer(conv2d_57, filters_num = 256, kernel_size = 1, strides = 1, name = "conv2d_" + str(conv_index))conv2d_60 = self._batch_normalization_layer(conv2d_60, name = "batch_normalization_" + str(conv_index),training = training, norm_decay = self.norm_decay, norm_epsilon = self.norm_epsilon)conv_index += 1# unSample_0 = 26,26,256unSample_0 = tf.image.resize_nearest_neighbor(conv2d_60, [2 * tf.shape(conv2d_60)[1], 2 * tf.shape(conv2d_60)[1]], name='upSample_0')# route0 = 26,26,768route0 = tf.concat([unSample_0, conv2d_43], axis = -1, name = 'route_0')# conv2d_65 = 52,52,256,conv2d_67 = 26,26,255conv2d_65, conv2d_67, conv_index = self._yolo_block(route0, 256, num_anchors * (num_classes + 5), conv_index = conv_index, training = training, norm_decay = self.norm_decay, norm_epsilon = self.norm_epsilon)#--------------------------------------## 获得第三个特征层#--------------------------------------# conv2d_68 = self._conv2d_layer(conv2d_65, filters_num = 128, kernel_size = 1, strides = 1, name = "conv2d_" + str(conv_index))conv2d_68 = self._batch_normalization_layer(conv2d_68, name = "batch_normalization_" + str(conv_index), training=training, norm_decay=self.norm_decay, norm_epsilon = self.norm_epsilon)conv_index += 1# unSample_1 = 52,52,128unSample_1 = tf.image.resize_nearest_neighbor(conv2d_68, [2 * tf.shape(conv2d_68)[1], 2 * tf.shape(conv2d_68)[1]], name='upSample_1')# route1= 52,52,384route1 = tf.concat([unSample_1, conv2d_26], axis = -1, name = 'route_1')# conv2d_75 = 52,52,255_, conv2d_75, _ = self._yolo_block(route1, 128, num_anchors * (num_classes + 5), conv_index = conv_index, training = training, norm_decay = self.norm_decay, norm_epsilon = self.norm_epsilon)return [conv2d_59, conv2d_67, conv2d_75]5.4.2 配置文件
num_parallel_calls = 4
input_shape = 416
max_boxes = 20
jitter = 0.3
hue = 0.1
sat = 1.0
cont = 0.8
bri = 0.1
norm_decay = 0.99
norm_epsilon = 1e-3
pre_train = True
num_anchors = 9
num_classes = 80
training = True
ignore_thresh = .5
learning_rate = 0.001
train_batch_size = 10
val_batch_size = 10
train_num = 2800
val_num = 5000
Epoch = 50
obj_threshold = 0.5
nms_threshold = 0.5
gpu_index = "0"
log_dir = './logs'
data_dir = './model_data'
model_dir = './test_model/model.ckpt-192192'
pre_train_yolo3 = True
yolo3_weights_path = './model_data/yolov3.weights'
darknet53_weights_path = './model_data/darknet53.weights'
anchors_path = './model_data/yolo_anchors.txt'
classes_path = './model_data/coco_classes.txt'image_file = "./img/img.jpg"5.4.3 detect文件
import os
import config
import argparse
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from yolo_predict import yolo_predictor
from PIL import Image, ImageFont, ImageDraw
from utils import letterbox_image, load_weights# 指定使用GPU的Index
os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = config.gpu_indexdef detect(image_path, model_path, yolo_weights = None):"""Introduction------------加载模型,进行预测Parameters----------model_path: 模型路径,当使用yolo_weights无用image_path: 图片路径"""#---------------------------------------## 图片预处理#---------------------------------------#image = Image.open(image_path)# 对预测输入图像进行缩放,按照长宽比进行缩放,不足的地方进行填充resize_image = letterbox_image(image, (416, 416))image_data = np.array(resize_image, dtype = np.float32)# 归一化image_data /= 255.# 转格式,第一维度填充image_data = np.expand_dims(image_data, axis = 0)#---------------------------------------## 图片输入#---------------------------------------## input_image_shape原图的sizeinput_image_shape = tf.placeholder(dtype = tf.int32, shape = (2,))# 图像input_image = tf.placeholder(shape = [None, 416, 416, 3], dtype = tf.float32)# 进入yolo_predictor进行预测,yolo_predictor是用于预测的一个对象predictor = yolo_predictor(config.obj_threshold, config.nms_threshold, config.classes_path, config.anchors_path)with tf.Session() as sess:#---------------------------------------## 图片预测#---------------------------------------#if yolo_weights is not None:with tf.variable_scope('predict'):boxes, scores, classes = predictor.predict(input_image, input_image_shape)# 载入模型load_op = load_weights(tf.global_variables(scope = 'predict'), weights_file = yolo_weights)sess.run(load_op)# 进行预测out_boxes, out_scores, out_classes = sess.run([boxes, scores, classes],feed_dict={# image_data这个resize过input_image: image_data,# 以y、x的方式传入input_image_shape: [image.size[1], image.size[0]]})else:boxes, scores, classes = predictor.predict(input_image, input_image_shape)saver = tf.train.Saver()saver.restore(sess, model_path)out_boxes, out_scores, out_classes = sess.run([boxes, scores, classes],feed_dict={input_image: image_data,input_image_shape: [image.size[1], image.size[0]]})#---------------------------------------## 画框#---------------------------------------## 找到几个box,打印print('Found {} boxes for {}'.format(len(out_boxes), 'img'))font = ImageFont.truetype(font = 'font/FiraMono-Medium.otf', size = np.floor(3e-2 * image.size[1] + 0.5).astype('int32'))# 厚度thickness = (image.size[0] + image.size[1]) // 300for i, c in reversed(list(enumerate(out_classes))):# 获得预测名字,box和分数predicted_class = predictor.class_names[c]box = out_boxes[i]score = out_scores[i]# 打印label = '{} {:.2f}'.format(predicted_class, score)# 用于画框框和文字draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image)# textsize用于获得写字的时候,按照这个字体,要多大的框label_size = draw.textsize(label, font)# 获得四个边top, left, bottom, right = boxtop = max(0, np.floor(top + 0.5).astype('int32'))left = max(0, np.floor(left + 0.5).astype('int32'))bottom = min(image.size[1]-1, np.floor(bottom + 0.5).astype('int32'))right = min(image.size[0]-1, np.floor(right + 0.5).astype('int32'))print(label, (left, top), (right, bottom))print(label_size)if top - label_size[1] >= 0:text_origin = np.array([left, top - label_size[1]])else:text_origin = np.array([left, top + 1])# My kingdom for a good redistributable image drawing library.for i in range(thickness):draw.rectangle([left + i, top + i, right - i, bottom - i],outline = predictor.colors[c])draw.rectangle([tuple(text_origin), tuple(text_origin + label_size)],fill = predictor.colors[c])draw.text(text_origin, label, fill=(0, 0, 0), font=font)del drawimage.show()image.save('./img/result1.jpg')if __name__ == '__main__':# 当使用yolo3自带的weights的时候if config.pre_train_yolo3 == True:detect(config.image_file, config.model_dir, config.yolo3_weights_path)# 当使用模型的时候else:detect(config.image_file, config.model_dir)5.4.4 gen_anchors.py
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltdef convert_coco_bbox(size, box):"""Introduction------------计算box的长宽和原始图像的长宽比值Parameters----------size: 原始图像大小box: 标注box的信息Returnsx, y, w, h 标注box和原始图像的比值"""dw = 1. / size[0]dh = 1. / size[1]x = (box[0] + box[2]) / 2.0 - 1y = (box[1] + box[3]) / 2.0 - 1w = box[2]h = box[3]x = x * dww = w * dwy = y * dhh = h * dhreturn x, y, w, hdef box_iou(boxes, clusters):"""Introduction------------计算每个box和聚类中心的距离值Parameters----------boxes: 所有的box数据clusters: 聚类中心"""box_num = boxes.shape[0]cluster_num = clusters.shape[0]box_area = boxes[:, 0] * boxes[:, 1]#每个box的面积重复9次,对应9个聚类中心box_area = box_area.repeat(cluster_num)box_area = np.reshape(box_area, [box_num, cluster_num])cluster_area = clusters[:, 0] * clusters[:, 1]cluster_area = np.tile(cluster_area, [1, box_num])cluster_area = np.reshape(cluster_area, [box_num, cluster_num])#这里计算两个矩形的iou,默认所有矩形的左上角坐标都是在原点,然后计算iou,因此只需取长宽最小值相乘就是重叠区域的面积boxes_width = np.reshape(boxes[:, 0].repeat(cluster_num), [box_num, cluster_num])clusters_width = np.reshape(np.tile(clusters[:, 0], [1, box_num]), [box_num, cluster_num])min_width = np.minimum(clusters_width, boxes_width)boxes_high = np.reshape(boxes[:, 1].repeat(cluster_num), [box_num, cluster_num])clusters_high = np.reshape(np.tile(clusters[:, 1], [1, box_num]), [box_num, cluster_num])min_high = np.minimum(clusters_high, boxes_high)iou = np.multiply(min_high, min_width) / (box_area + cluster_area - np.multiply(min_high, min_width))return ioudef avg_iou(boxes, clusters):"""Introduction------------计算所有box和聚类中心的最大iou均值作为准确率Parameters----------boxes: 所有的boxclusters: 聚类中心Returns-------accuracy: 准确率"""return np.mean(np.max(box_iou(boxes, clusters), axis =1))def Kmeans(boxes, cluster_num, iteration_cutoff = 25, function = np.median):"""Introduction------------根据所有box的长宽进行Kmeans聚类Parameters----------boxes: 所有的box的长宽cluster_num: 聚类的数量iteration_cutoff: 当准确率不再降低多少轮停止迭代function: 聚类中心更新的方式Returns-------clusters: 聚类中心box的大小"""boxes_num = boxes.shape[0]best_average_iou = 0best_avg_iou_iteration = 0best_clusters = []anchors = []np.random.seed()# 随机选择所有boxes中的box作为聚类中心clusters = boxes[np.random.choice(boxes_num, cluster_num, replace = False)]count = 0while True:distances = 1. - box_iou(boxes, clusters)boxes_iou = np.min(distances, axis=1)# 获取每个box距离哪个聚类中心最近current_box_cluster = np.argmin(distances, axis=1)average_iou = np.mean(1. - boxes_iou)if average_iou > best_average_iou:best_average_iou = average_ioubest_clusters = clustersbest_avg_iou_iteration = count# 通过function的方式更新聚类中心for cluster in range(cluster_num):clusters[cluster] = function(boxes[current_box_cluster == cluster], axis=0)if count >= best_avg_iou_iteration + iteration_cutoff:breakprint("Sum of all distances (cost) = {}".format(np.sum(boxes_iou)))print("iter: {} Accuracy: {:.2f}%".format(count, avg_iou(boxes, clusters) * 100))count += 1for cluster in best_clusters:anchors.append([round(cluster[0] * 416), round(cluster[1] * 416)])return anchors, best_average_ioudef load_cocoDataset(annfile):"""Introduction------------读取coco数据集的标注信息Parameters----------datasets: 数据集名字列表"""data = []coco = COCO(annfile)cats = coco.loadCats(coco.getCatIds())coco.loadImgs()base_classes = {cat['id'] : cat['name'] for cat in cats}imgId_catIds = [coco.getImgIds(catIds = cat_ids) for cat_ids in base_classes.keys()]image_ids = [img_id for img_cat_id in imgId_catIds for img_id in img_cat_id ]for image_id in image_ids:annIds = coco.getAnnIds(imgIds = image_id)anns = coco.loadAnns(annIds)img = coco.loadImgs(image_id)[0]image_width = img['width']image_height = img['height']for ann in anns:box = ann['bbox']bb = convert_coco_bbox((image_width, image_height), box)data.append(bb[2:])return np.array(data)def process(dataFile, cluster_num, iteration_cutoff = 25, function = np.median):"""Introduction------------主处理函数Parameters----------dataFile: 数据集的标注文件cluster_num: 聚类中心数目iteration_cutoff: 当准确率不再降低多少轮停止迭代function: 聚类中心更新的方式"""last_best_iou = 0last_anchors = []boxes = load_cocoDataset(dataFile)box_w = boxes[:1000, 0]box_h = boxes[:1000, 1]plt.scatter(box_h, box_w, c = 'r')anchors = Kmeans(boxes, cluster_num, iteration_cutoff, function)plt.scatter(anchors[:,0], anchors[:, 1], c = 'b')plt.show()for _ in range(100):anchors, best_iou = Kmeans(boxes, cluster_num, iteration_cutoff, function)if best_iou > last_best_iou:last_anchors = anchorslast_best_iou = best_iouprint("anchors: {}, avg iou: {}".format(last_anchors, last_best_iou))print("final anchors: {}, avg iou: {}".format(last_anchors, last_best_iou))if __name__ == '__main__':process('./annotations/instances_train2014.json', 9)5.4.5 utils.py
import json
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from PIL import Image
from collections import defaultdictdef load_weights(var_list, weights_file):"""Introduction------------加载预训练好的darknet53权重文件Parameters----------var_list: 赋值变量名weights_file: 权重文件Returns-------assign_ops: 赋值更新操作"""with open(weights_file, "rb") as fp:_ = np.fromfile(fp, dtype=np.int32, count=5)weights = np.fromfile(fp, dtype=np.float32)ptr = 0i = 0assign_ops = []while i < len(var_list) - 1:var1 = var_list[i]var2 = var_list[i + 1]# do something only if we process conv layerif 'conv2d' in var1.name.split('/')[-2]:# check type of next layerif 'batch_normalization' in var2.name.split('/')[-2]:# load batch norm paramsgamma, beta, mean, var = var_list[i + 1:i + 5]batch_norm_vars = [beta, gamma, mean, var]for var in batch_norm_vars:shape = var.shape.as_list()num_params = np.prod(shape)var_weights = weights[ptr:ptr + num_params].reshape(shape)ptr += num_paramsassign_ops.append(tf.assign(var, var_weights, validate_shape=True))# we move the pointer by 4, because we loaded 4 variablesi += 4elif 'conv2d' in var2.name.split('/')[-2]:# load biasesbias = var2bias_shape = bias.shape.as_list()bias_params = np.prod(bias_shape)bias_weights = weights[ptr:ptr + bias_params].reshape(bias_shape)ptr += bias_paramsassign_ops.append(tf.assign(bias, bias_weights, validate_shape=True))# we loaded 1 variablei += 1# we can load weights of conv layershape = var1.shape.as_list()num_params = np.prod(shape)var_weights = weights[ptr:ptr + num_params].reshape((shape[3], shape[2], shape[0], shape[1]))# remember to transpose to column-majorvar_weights = np.transpose(var_weights, (2, 3, 1, 0))ptr += num_paramsassign_ops.append(tf.assign(var1, var_weights, validate_shape=True))i += 1return assign_opsdef letterbox_image(image, size):"""Introduction------------对预测输入图像进行缩放,按照长宽比进行缩放,不足的地方进行填充Parameters----------image: 输入图像size: 图像大小Returns-------boxed_image: 缩放后的图像"""image_w, image_h = image.sizew, h = sizenew_w = int(image_w * min(w*1.0/image_w, h*1.0/image_h))new_h = int(image_h * min(w*1.0/image_w, h*1.0/image_h))resized_image = image.resize((new_w,new_h), Image.BICUBIC)boxed_image = Image.new('RGB', size, (128, 128, 128))boxed_image.paste(resized_image, ((w-new_w)//2,(h-new_h)//2))return boxed_imagedef draw_box(image, bbox):"""Introduction------------通过tensorboard把训练数据可视化Parameters----------image: 训练数据图片bbox: 训练数据图片中标记box坐标"""xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, label = tf.split(value = bbox, num_or_size_splits = 5, axis=2)height = tf.cast(tf.shape(image)[1], tf.float32)weight = tf.cast(tf.shape(image)[2], tf.float32)new_bbox = tf.concat([tf.cast(ymin, tf.float32) / height, tf.cast(xmin, tf.float32) / weight, tf.cast(ymax, tf.float32) / height, tf.cast(xmax, tf.float32) / weight], 2)new_image = tf.image.draw_bounding_boxes(image, new_bbox)tf.summary.image('input', new_image)def voc_ap(rec, prec):"""--- Official matlab code VOC2012---mrec=[0 ; rec ; 1];mpre=[0 ; prec ; 0];for i=numel(mpre)-1:-1:1mpre(i)=max(mpre(i),mpre(i+1));endi=find(mrec(2:end)~=mrec(1:end-1))+1;ap=sum((mrec(i)-mrec(i-1)).*mpre(i));"""rec.insert(0, 0.0) # insert 0.0 at begining of listrec.append(1.0) # insert 1.0 at end of listmrec = rec[:]prec.insert(0, 0.0) # insert 0.0 at begining of listprec.append(0.0) # insert 0.0 at end of listmpre = prec[:]for i in range(len(mpre) - 2, -1, -1):mpre[i] = max(mpre[i], mpre[i + 1])i_list = []for i in range(1, len(mrec)):if mrec[i] != mrec[i - 1]:i_list.append(i)ap = 0.0for i in i_list:ap += ((mrec[i] - mrec[i - 1]) * mpre[i])return ap, mrec, mpre
5.4.6 预测脚本
import os
import config
import random
import colorsys
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from model.yolo3_model import yoloclass yolo_predictor:def __init__(self, obj_threshold, nms_threshold, classes_file, anchors_file):"""Introduction------------初始化函数Parameters----------obj_threshold: 目标检测为物体的阈值nms_threshold: nms阈值"""self.obj_threshold = obj_thresholdself.nms_threshold = nms_threshold# 预读取self.classes_path = classes_fileself.anchors_path = anchors_file# 读取种类名称self.class_names = self._get_class()# 读取先验框self.anchors = self._get_anchors()# 画框框用hsv_tuples = [(x / len(self.class_names), 1., 1.)for x in range(len(self.class_names))]self.colors = list(map(lambda x: colorsys.hsv_to_rgb(*x), hsv_tuples))self.colors = list(map(lambda x: (int(x[0] * 255), int(x[1] * 255), int(x[2] * 255)), self.colors))random.seed(10101)random.shuffle(self.colors)random.seed(None)def _get_class(self):"""Introduction------------读取类别名称"""classes_path = os.path.expanduser(self.classes_path)with open(classes_path) as f:class_names = f.readlines()class_names = [c.strip() for c in class_names]return class_namesdef _get_anchors(self):"""Introduction------------读取anchors数据"""anchors_path = os.path.expanduser(self.anchors_path)with open(anchors_path) as f:anchors = f.readline()anchors = [float(x) for x in anchors.split(',')]anchors = np.array(anchors).reshape(-1, 2)return anchors#---------------------------------------## 对三个特征层解码# 进行排序并进行非极大抑制#---------------------------------------#def boxes_and_scores(self, feats, anchors, classes_num, input_shape, image_shape):"""Introduction------------将预测出的box坐标转换为对应原图的坐标,然后计算每个box的分数Parameters----------feats: yolo输出的feature mapanchors: anchor的位置class_num: 类别数目input_shape: 输入大小image_shape: 图片大小Returns-------boxes: 物体框的位置boxes_scores: 物体框的分数,为置信度和类别概率的乘积"""# 获得特征box_xy, box_wh, box_confidence, box_class_probs = self._get_feats(feats, anchors, classes_num, input_shape)# 寻找在原图上的位置boxes = self.correct_boxes(box_xy, box_wh, input_shape, image_shape)boxes = tf.reshape(boxes, [-1, 4])# 获得置信度box_confidence * box_class_probsbox_scores = box_confidence * box_class_probsbox_scores = tf.reshape(box_scores, [-1, classes_num])return boxes, box_scores# 获得在原图上框的位置def correct_boxes(self, box_xy, box_wh, input_shape, image_shape):"""Introduction------------计算物体框预测坐标在原图中的位置坐标Parameters----------box_xy: 物体框左上角坐标box_wh: 物体框的宽高input_shape: 输入的大小image_shape: 图片的大小Returns-------boxes: 物体框的位置"""box_yx = box_xy[..., ::-1]box_hw = box_wh[..., ::-1]# 416,416input_shape = tf.cast(input_shape, dtype = tf.float32)# 实际图片的大小image_shape = tf.cast(image_shape, dtype = tf.float32)new_shape = tf.round(image_shape * tf.reduce_min(input_shape / image_shape))offset = (input_shape - new_shape) / 2. / input_shapescale = input_shape / new_shapebox_yx = (box_yx - offset) * scalebox_hw *= scalebox_mins = box_yx - (box_hw / 2.)box_maxes = box_yx + (box_hw / 2.)boxes = tf.concat([box_mins[..., 0:1],box_mins[..., 1:2],box_maxes[..., 0:1],box_maxes[..., 1:2]], axis = -1)boxes *= tf.concat([image_shape, image_shape], axis = -1)return boxes# 其实是解码的过程def _get_feats(self, feats, anchors, num_classes, input_shape):"""Introduction------------根据yolo最后一层的输出确定bounding boxParameters----------feats: yolo模型最后一层输出anchors: anchors的位置num_classes: 类别数量input_shape: 输入大小Returns-------box_xy, box_wh, box_confidence, box_class_probs"""num_anchors = len(anchors)anchors_tensor = tf.reshape(tf.constant(anchors, dtype=tf.float32), [1, 1, 1, num_anchors, 2])grid_size = tf.shape(feats)[1:3]predictions = tf.reshape(feats, [-1, grid_size[0], grid_size[1], num_anchors, num_classes + 5])# 这里构建13*13*1*2的矩阵,对应每个格子加上对应的坐标grid_y = tf.tile(tf.reshape(tf.range(grid_size[0]), [-1, 1, 1, 1]), [1, grid_size[1], 1, 1])grid_x = tf.tile(tf.reshape(tf.range(grid_size[1]), [1, -1, 1, 1]), [grid_size[0], 1, 1, 1])grid = tf.concat([grid_x, grid_y], axis = -1)grid = tf.cast(grid, tf.float32)# 将x,y坐标归一化,相对网格的位置box_xy = (tf.sigmoid(predictions[..., :2]) + grid) / tf.cast(grid_size[::-1], tf.float32)# 将w,h也归一化box_wh = tf.exp(predictions[..., 2:4]) * anchors_tensor / tf.cast(input_shape[::-1], tf.float32)box_confidence = tf.sigmoid(predictions[..., 4:5])box_class_probs = tf.sigmoid(predictions[..., 5:])return box_xy, box_wh, box_confidence, box_class_probsdef eval(self, yolo_outputs, image_shape, max_boxes = 20):"""Introduction------------根据Yolo模型的输出进行非极大值抑制,获取最后的物体检测框和物体检测类别Parameters----------yolo_outputs: yolo模型输出image_shape: 图片的大小max_boxes: 最大box数量Returns-------boxes_: 物体框的位置scores_: 物体类别的概率classes_: 物体类别"""# 每一个特征层对应三个先验框anchor_mask = [[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]]boxes = []box_scores = []# inputshape是416x416# image_shape是实际图片的大小input_shape = tf.shape(yolo_outputs[0])[1 : 3] * 32# 对三个特征层的输出获取每个预测box坐标和box的分数,score = 置信度x类别概率#---------------------------------------## 对三个特征层解码# 获得分数和框的位置#---------------------------------------#for i in range(len(yolo_outputs)):_boxes, _box_scores = self.boxes_and_scores(yolo_outputs[i], self.anchors[anchor_mask[i]], len(self.class_names), input_shape, image_shape)boxes.append(_boxes)box_scores.append(_box_scores)# 放在一行里面便于操作boxes = tf.concat(boxes, axis = 0)box_scores = tf.concat(box_scores, axis = 0)mask = box_scores >= self.obj_thresholdmax_boxes_tensor = tf.constant(max_boxes, dtype = tf.int32)boxes_ = []scores_ = []classes_ = []#---------------------------------------## 1、取出每一类得分大于self.obj_threshold# 的框和得分# 2、对得分进行非极大抑制#---------------------------------------## 对每一个类进行判断for c in range(len(self.class_names)):# 取出所有类为c的boxclass_boxes = tf.boolean_mask(boxes, mask[:, c])# 取出所有类为c的分数class_box_scores = tf.boolean_mask(box_scores[:, c], mask[:, c])# 非极大抑制nms_index = tf.image.non_max_suppression(class_boxes, class_box_scores, max_boxes_tensor, iou_threshold = self.nms_threshold)# 获取非极大抑制的结果class_boxes = tf.gather(class_boxes, nms_index)class_box_scores = tf.gather(class_box_scores, nms_index)classes = tf.ones_like(class_box_scores, 'int32') * cboxes_.append(class_boxes)scores_.append(class_box_scores)classes_.append(classes)boxes_ = tf.concat(boxes_, axis = 0)scores_ = tf.concat(scores_, axis = 0)classes_ = tf.concat(classes_, axis = 0)return boxes_, scores_, classes_#---------------------------------------## predict用于预测,分三步# 1、建立yolo对象# 2、获得预测结果# 3、对预测结果进行处理#---------------------------------------#def predict(self, inputs, image_shape):"""Introduction------------构建预测模型Parameters----------inputs: 处理之后的输入图片image_shape: 图像原始大小Returns-------boxes: 物体框坐标scores: 物体概率值classes: 物体类别"""model = yolo(config.norm_epsilon, config.norm_decay, self.anchors_path, self.classes_path, pre_train = False)# yolo_inference用于获得网络的预测结果output = model.yolo_inference(inputs, config.num_anchors // 3, config.num_classes, training = False)boxes, scores, classes = self.eval(output, image_shape, max_boxes = 20)return boxes, scores, classes
6. 拓展-SSD
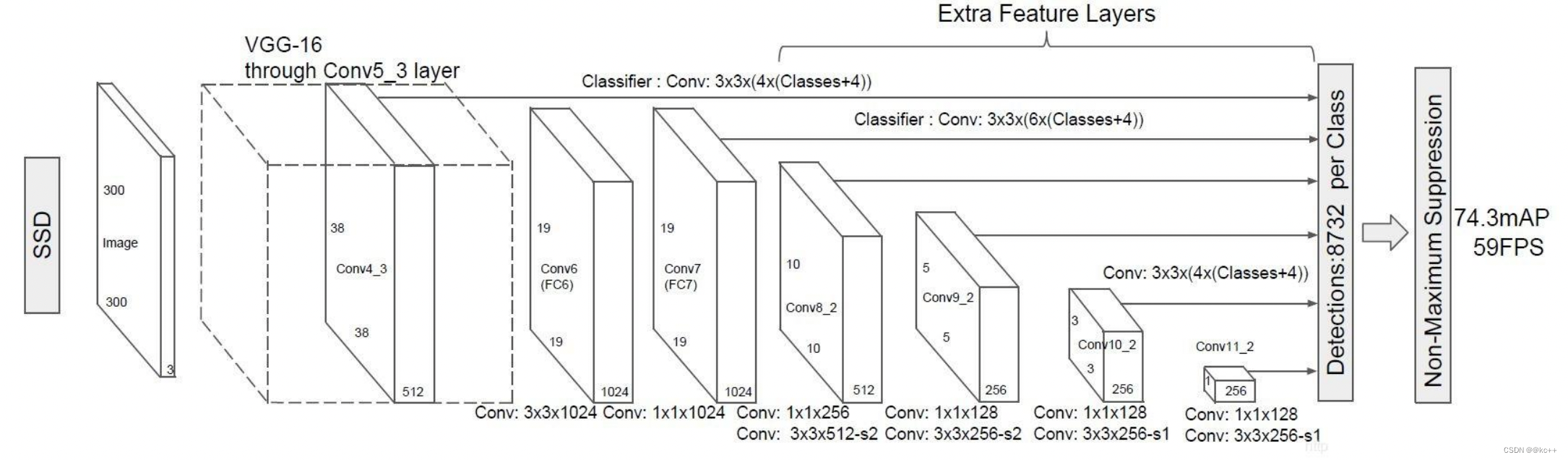
SSD也是一个多特征层网络,其一共具有11层,前半部分结构是VGG16:
- 首先通过了多个3X3卷积层、5次步长为2的最大池化取出特征,形成了5个Block,其中第四个Block用于提取小目标(多次卷积后大目标的特征保存的更好,小目标特征会消失,需要在比较靠前的层提取小目标特征)。
- 进行一次卷积核膨胀dilate。
- 读取第七个Block7的特征。
- 分别利用1x1和3x3卷积提取特征,在3x3卷积的时候使用步长2,缩小特征数,获取第八个Block8的特征。
- 重复步骤4,获得9、10、11卷积层的特征。
相关文章:

目标检测(Object Detection)
文章目录 1. 目标检测1.1 目标检测简要概述及名词解释1.2 IOU1.3 TP TN FP FN1.4 precision(精确度)和recall(召回率) 2. 边框回归Bounding-Box regression3. Faster R-CNN3.1 Faster-RCNN:conv layer3.2 Faster-RCNN&…...
vue中实现文字检索时候将搜索内容标红
实现结果 html: <div class"searchBox"><span class"bt">标  题</span><div class"search"><div class"shuru"><!-- <span class"title">生产经营<…...

PCL protocol composition logic
PCL 协议组合逻辑 一 主体(principal)和线程(thread)的区分 1.主体:指 **协议的参与者,用X^来表示。**每个主体可以扮演一个或多个角色,如 InitCR和RespCR ; 2.线程:主…...
聊聊看React和Vue的区别
Vue 更适合小项目,React 更适合大公司大项目; Vue 的学习成本较低,很容易上手,但项目质量不能保证...... 真的是这样吗?借助本篇文章,我们来从一些方面的比较来客观的去看这个问题。 论文档的丰富性 从两个…...
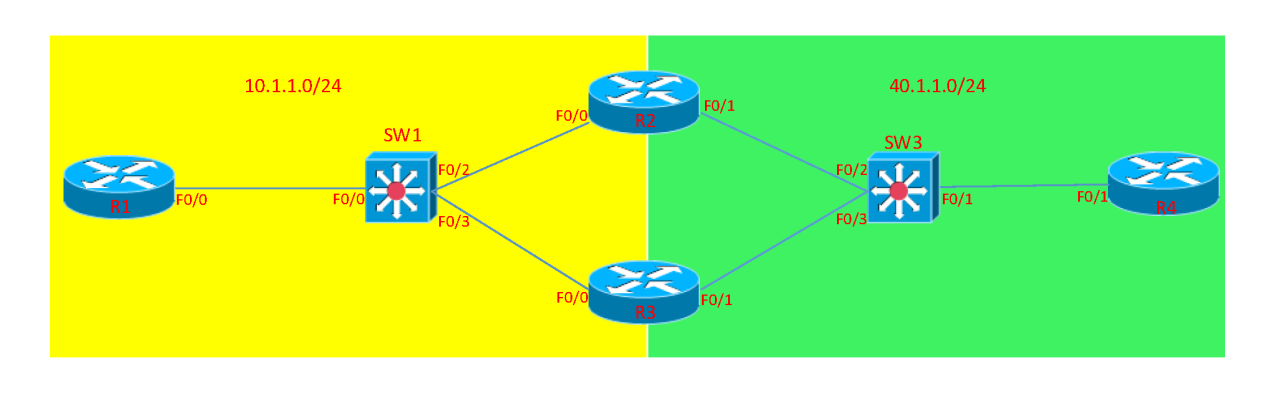
OSPF在广播类型的网络拓扑中DR和BDR的选举
指定路由器(DR): 一个网段上的其他路由器都和指定路由器(DR)构成邻接关系,而不是它们互相之间构成邻接关系。 备份指定路由器(BDR): 当DR出现问题,由BDR接…...
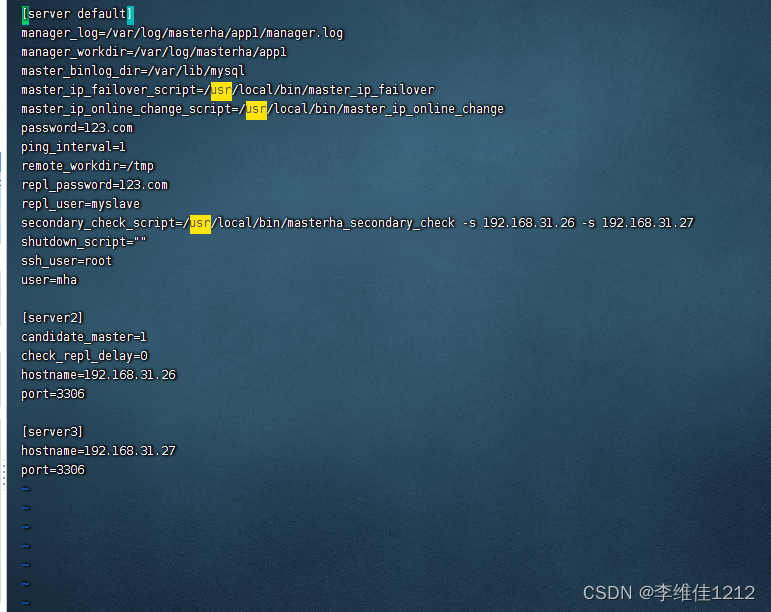
系统学习Linux-Mariadb高可用MHA
概念 MHA(MasterHigh Availability)是一套优秀的MySQL高可用环境下故障切换和主从复制的软件。 MHA 的出现就是解决MySQL 单点的问题。 MySQL故障切换过程中,MHA能做到0-30秒内自动完成故障切换操作。 MHA能在故障切换的过程中最大程度上…...

慢SQL的原因
如何排查慢SQL问题 识别慢SQL:使用数据库性能监控工具,如慢SQL日志,识别耗时较长的查询。执行计划分析:使用数据库提供的分析工具,例如EXPLAIN来查看查询的执行计划,判断是否存在全表扫描,索引…...

php正则替换文章的图片
要使用正则表达式替换文章中的图片链接,可以按照以下步骤进行操作: 1. 获取文章内容:首先,你需要获取包含图片链接的文章内容。你可以从文件中读取文章,或者从数据库中检索文章内容。 2. 使用正则表达式匹配图片链接…...

57 | TAPTAP客户端分析
TAPTAP客户端分析 一、用户群分析 首先,TapTap用户群可分为三大类: 游戏爱好者游戏发烧者游戏开发者(次要用户,有开发者后台,可以显示数据,不重点分析)注:爱好者与发烧者区别在于,前者是用空余时间来玩游戏,时间不如后者充足,且后者更执着于游戏,游戏种类更多。 …...
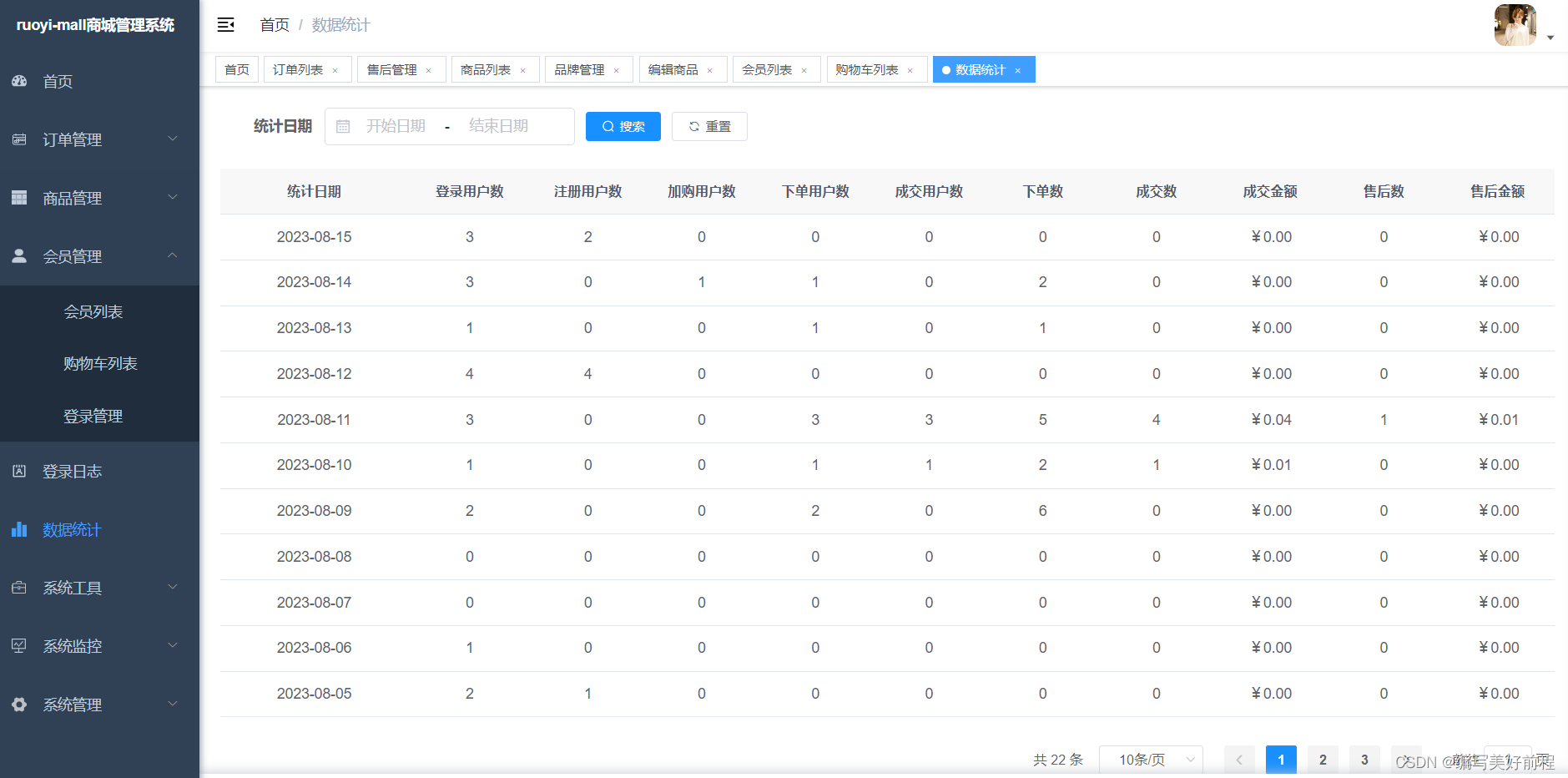
开源了一套基于springboot+vue+uniapp的商城,包含分类、sku、商户管理、分销、会员、适合企业或个人二次开发
RuoYi-Mall-JAVA商城-电商系统简介 开源了一套基于若依框架,SringBoot2MybatisPlusSpringSecurityjwtredisVueUniapp的前后端分离的商城系统, 包含分类、sku、商户管理、分销、会员、适合企业或个人二次开发。 前端采用Vue、Element UI(ant…...
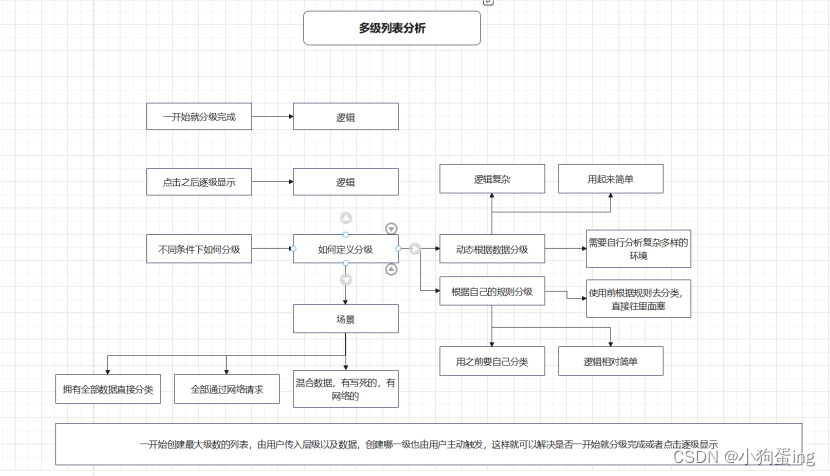
Android进阶之多级列表
遇到一个需求需要显示多级列表,因为界面是在平板上的,所以层级是从左向右往下排的,类似于 我当时的写法是在xml布局里一个个RecyclerView往下排的 当然前提是已经规定好最大的层级我才敢如此去写界面,如果已经明确规定只有两级或…...

Stochastic: Distribution-Expectation-Inequalities
见:https://www.math.hkust.edu.hk/~makchen/MATH5411/Chap1Sec2.pdf...
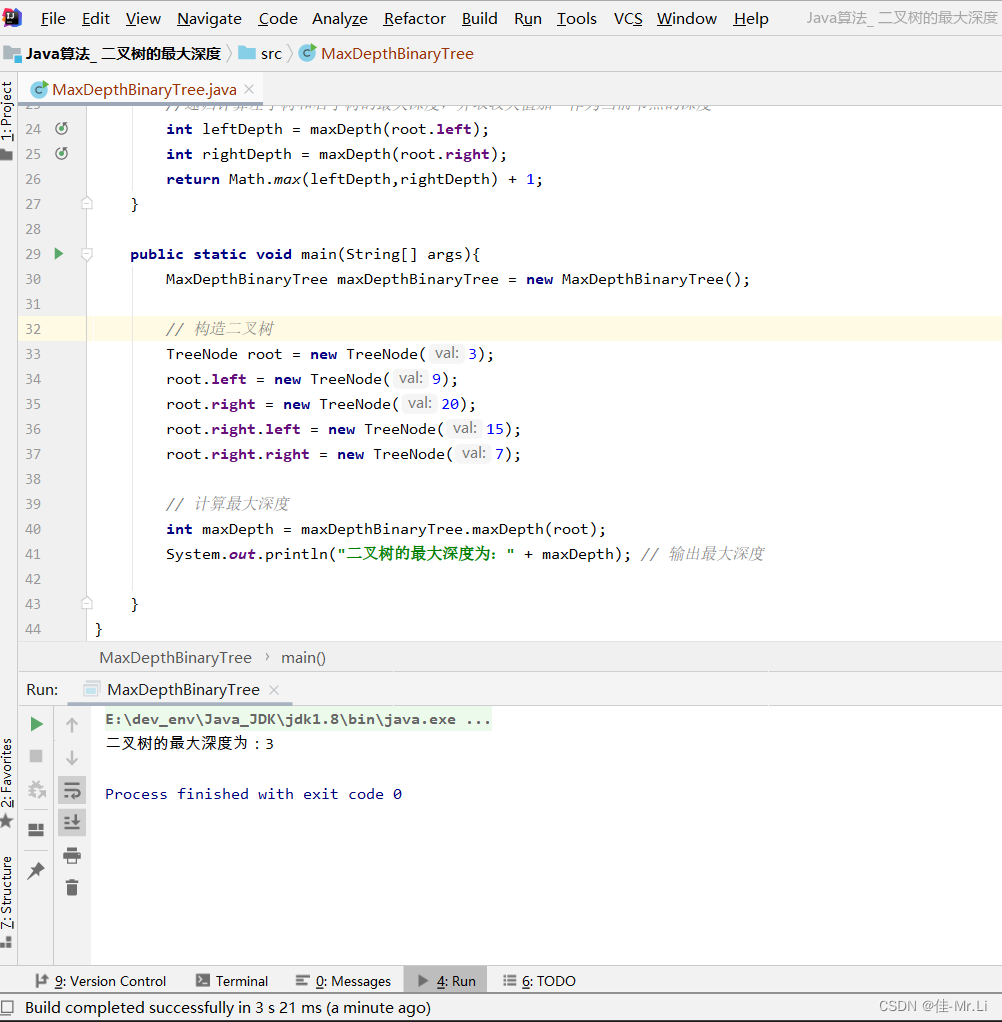
Java算法_ 二叉树的最大深度(LeetCode_Hot100)
题目描述:给定一个二叉树 ,返回其最大深度。root 二叉树的 最大深度 是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。 获得更多?算法思路:代码文档,算法解析的私得。 运行效果 完整代码 /*** 2 * Author: LJJ* 3 * Date: 2023/…...
行业追踪,2023-08-18
自动复盘 2023-08-18 凡所有相,皆是虚妄。若见诸相非相,即见如来。 k 线图是最好的老师,每天持续发布板块的rps排名,追踪板块,板块来开仓,板块去清仓,丢弃自以为是的想法,板块去留让…...

js将项目中的图片上传到服务器
项目上有时候会有奇怪的需求,比如前端有一些示例,想点击按钮就能上传图片,而这个图片是在前端的项目中的,如果不上传吧,又获取不到一些业务数据的id,但后端又不想为这块功能做特殊的处理,这时想通过前端直接上传到后端,需要file对象才可以。 这个时候我们需要将img转换…...
【C语言】指针的进阶
目录 一、字符指针 二、指针数组 三、数组指针 1.数组指针的定义 2.&数组名和数组名区别 3.数组指针的使用 四、数组参数与指针参数 1.一维数组传参 2.二维数组传参 3.一级指针传参 4.二级指针传参 五、函数指针 六、函数指针数组 七、指向函数指针数组的指针…...
【Windows系统编程】03.远线程注入ShellCode
shellcode:本质上也是一段普通的代码,只不过特殊的编程手法,可以在任意环境下,不依赖于原有的依赖库执行。 远程线程 #include <iostream> #include <windows.h> #include <TlHelp32.h>int main(){HANDLE hPr…...

第1天----验证一个字符串是否是另一个字符串的子串
本文我们将学习如何去验证一个字符串是否是另一个字符串的子串。 一、小试牛刀: 题目描述 输入两个字符串,验证其中一个串是否为另一个串的子串。 输入格式 两行,每行一个字符串。 输出格式 若第一个串 s 1 是第二个串 s 2 的子串,…...

项目实战第四十三讲:使用模版模式优雅实现财务编辑费用
项目实战第四十三讲:财务编辑费用 本文是项目实战第43讲:使用模版模式优雅实现财务编辑费用。支持查看司机填写费用信息,并且附件管理支持展示司机上传费用照片。 文章目录 项目实战第四十三讲:财务编辑费用1、项目背景2、主要技术3、项目职责4、项目实现4.1、表结构4.2、流…...
[JavaWeb]【六】web后端开发-请求响应
前言:请求响应 目录 一 引子 二 请求 2.1 Postman 2.1.1 安装 2.1.2 创建工作空间 2.1.3 添加接口 2.2 简单参数 2.2.1 原始方式(不推荐) 2.2.2 SpringBoot方式-GET(参数名与形参变量名相同) 2.2.3 SpringBoot方式-POST(参数名与形参…...

Cursor实现用excel数据填充word模版的方法
cursor主页:https://www.cursor.com/ 任务目标:把excel格式的数据里的单元格,按照某一个固定模版填充到word中 文章目录 注意事项逐步生成程序1. 确定格式2. 调试程序 注意事项 直接给一个excel文件和最终呈现的word文件的示例,…...
Linux 文件类型,目录与路径,文件与目录管理
文件类型 后面的字符表示文件类型标志 普通文件:-(纯文本文件,二进制文件,数据格式文件) 如文本文件、图片、程序文件等。 目录文件:d(directory) 用来存放其他文件或子目录。 设备…...

逻辑回归:给不确定性划界的分类大师
想象你是一名医生。面对患者的检查报告(肿瘤大小、血液指标),你需要做出一个**决定性判断**:恶性还是良性?这种“非黑即白”的抉择,正是**逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)** 的战场&a…...
UE5 学习系列(三)创建和移动物体
这篇博客是该系列的第三篇,是在之前两篇博客的基础上展开,主要介绍如何在操作界面中创建和拖动物体,这篇博客跟随的视频链接如下: B 站视频:s03-创建和移动物体 如果你不打算开之前的博客并且对UE5 比较熟的话按照以…...

高频面试之3Zookeeper
高频面试之3Zookeeper 文章目录 高频面试之3Zookeeper3.1 常用命令3.2 选举机制3.3 Zookeeper符合法则中哪两个?3.4 Zookeeper脑裂3.5 Zookeeper用来干嘛了 3.1 常用命令 ls、get、create、delete、deleteall3.2 选举机制 半数机制(过半机制࿰…...
视频字幕质量评估的大规模细粒度基准
大家读完觉得有帮助记得关注和点赞!!! 摘要 视频字幕在文本到视频生成任务中起着至关重要的作用,因为它们的质量直接影响所生成视频的语义连贯性和视觉保真度。尽管大型视觉-语言模型(VLMs)在字幕生成方面…...

鸿蒙中用HarmonyOS SDK应用服务 HarmonyOS5开发一个生活电费的缴纳和查询小程序
一、项目初始化与配置 1. 创建项目 ohpm init harmony/utility-payment-app 2. 配置权限 // module.json5 {"requestPermissions": [{"name": "ohos.permission.INTERNET"},{"name": "ohos.permission.GET_NETWORK_INFO"…...

Caliper 配置文件解析:config.yaml
Caliper 是一个区块链性能基准测试工具,用于评估不同区块链平台的性能。下面我将详细解释你提供的 fisco-bcos.json 文件结构,并说明它与 config.yaml 文件的关系。 fisco-bcos.json 文件解析 这个文件是针对 FISCO-BCOS 区块链网络的 Caliper 配置文件,主要包含以下几个部…...
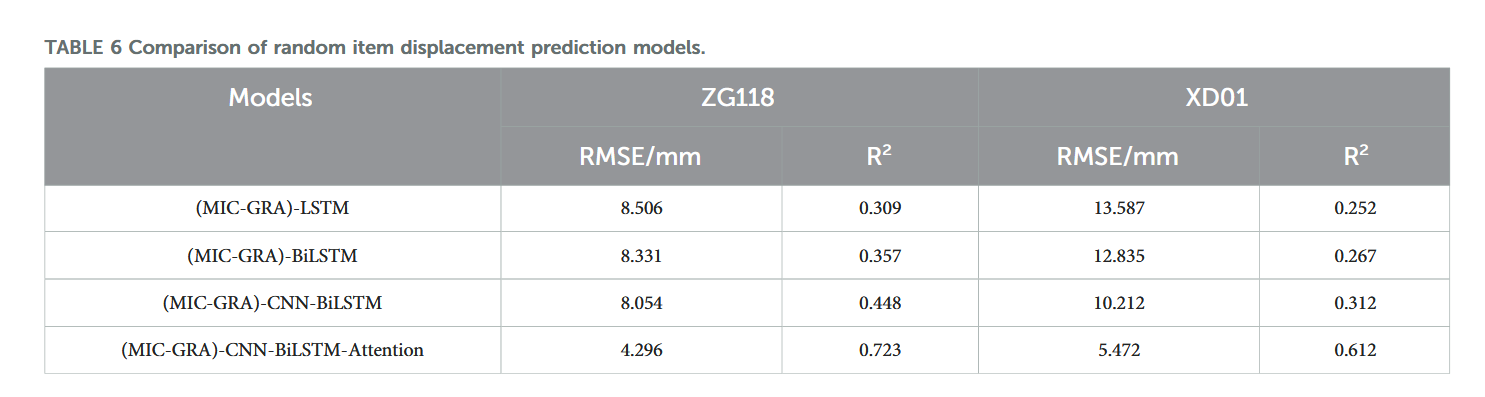
【论文阅读28】-CNN-BiLSTM-Attention-(2024)
本文把滑坡位移序列拆开、筛优质因子,再用 CNN-BiLSTM-Attention 来动态预测每个子序列,最后重构出总位移,预测效果超越传统模型。 文章目录 1 引言2 方法2.1 位移时间序列加性模型2.2 变分模态分解 (VMD) 具体步骤2.3.1 样本熵(S…...
C++ 设计模式 《小明的奶茶加料风波》
👨🎓 模式名称:装饰器模式(Decorator Pattern) 👦 小明最近上线了校园奶茶配送功能,业务火爆,大家都在加料: 有的同学要加波霸 🟤,有的要加椰果…...
