Debian11 Crontab
Crontab用户命令
可执行文件
crontab命令的可执行文件在哪儿?
$ which -a crontab
/usr/bin/crontab
/bin/crontab
crontab命令的可执行文件有2个:/usr/bin/crontab 和 /bin/crontab
$ diff /usr/bin/crontab /bin/crontab
$
diff 发现这两个文件并无区别。那么,执行时使用的是哪个文件呢?
$ echo $PATH
/usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/bin:/usr/local/games:/usr/games
打印环境变量PATH,发现/usr/bin排在/bin之前,所以,执行的是/usr/bin/crontab吗?
$ strace crontab -l
execve("/usr/bin/crontab", ["crontab", "-l"], 0x7ffdf7c19ce8 /* 21 vars */) = 0
...
strace 跟踪一下crontab的执行过程,发现实际执行的的确是/usr/bin/crontab。
cronatb命令使用手册
man 1 cronatb
CRONTAB(1) General Commands Manual CRONTAB(1)NAMEcrontab - maintain crontab files for individual users (Vixie Cron)SYNOPSIScrontab [ -u user ] filecrontab [ -u user ] [ -i ] { -e | -l | -r }DESCRIPTIONcrontab is the program used to install, deinstall or list the tables used to drive the cron(8) daemon in Vixie Cron. Eachuser can have their own crontab, and though these are files in /var/spool/cron/crontabs, they are not intended to be editeddirectly.If the /etc/cron.allow file exists, then you must be listed (one user per line) therein in order to be allowed to use thiscommand. If the /etc/cron.allow file does not exist but the /etc/cron.deny file does exist, then you must not be listed inthe /etc/cron.deny file in order to use this command.If neither of these files exists, then depending on site-dependent configuration parameters, only the super user will be al‐lowed to use this command, or all users will be able to use this command.If both files exist then /etc/cron.allow takes precedence. Which means that /etc/cron.deny is not considered and your usermust be listed in /etc/cron.allow in order to be able to use the crontab.Regardless of the existence of any of these files, the root administrative user is always allowed to setup a crontab. Forstandard Debian systems, all users may use this command.If the -u option is given, it specifies the name of the user whose crontab is to be used (when listing) or modified (whenediting). If this option is not given, crontab examines "your" crontab, i.e., the crontab of the person executing the com‐mand. Note that su(8) can confuse crontab and that if you are running inside of su(8) you should always use the -u optionfor safety's sake.The first form of this command is used to install a new crontab from some named file or standard input if the pseudo-filename``-'' is given.The -l option causes the current crontab to be displayed on standard output. See the note under DEBIAN SPECIFIC below.The -r option causes the current crontab to be removed.The -e option is used to edit the current crontab using the editor specified by the VISUAL or EDITOR environment variables.After you exit from the editor, the modified crontab will be installed automatically. If neither of the environment vari‐ables is defined, then the default editor /usr/bin/editor is used.The -i option modifies the -r option to prompt the user for a 'y/Y' response before actually removing the crontab.DEBIAN SPECIFICThe "out-of-the-box" behaviour for crontab -l is to display the three line "DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE" header that is placed atthe beginning of the crontab when it is installed. The problem is that it makes the sequencecrontab -l | crontab -non-idempotent — you keep adding copies of the header. This causes pain to scripts that use sed to edit a crontab. There‐fore, the default behaviour of the -l option has been changed to not output such header. You may obtain the original behav‐iour by setting the environment variable CRONTAB_NOHEADER to 'N', which will cause the crontab -l command to emit the extra‐neous header.SEE ALSOcrontab(5), cron(8)FILES/etc/cron.allow/etc/cron.deny/var/spool/cron/crontabsThe files /etc/cron.allow and /etc/cron.deny if, they exist, must be either world-readable, or readable by group ``crontab''.If they are not, then cron will deny access to all users until the permissions are fixed.There is one file for each user's crontab under the /var/spool/cron/crontabs directory. Users are not allowed to edit thefiles under that directory directly to ensure that only users allowed by the system to run periodic tasks can add them, andonly syntactically correct crontabs will be written there. This is enforced by having the directory writable only by thecrontab group and configuring crontab command with the setgid bid set for that specific group.STANDARDSThe crontab command conforms to IEEE Std1003.2-1992 (``POSIX''). This new command syntax differs from previous versions ofVixie Cron, as well as from the classic SVR3 syntax.DIAGNOSTICSA fairly informative usage message appears if you run it with a bad command line.cron requires that each entry in a crontab end in a newline character. If the last entry in a crontab is missing the new‐line, cron will consider the crontab (at least partially) broken and refuse to install it.The files under /var/spool/cron/crontabs are named based on the user's account name. Crontab jobs will not be run for userswhose accounts have been renamed either due to changes in the local system or because they are managed through a central userdatabase (external to the system, for example an LDAP directory).AUTHORPaul Vixie <paul@vix.com> is the author of cron and original creator of this manual page. This page has also been modifiedfor Debian by Steve Greenland, Javier Fernandez-Sanguino and Christian Kastner.4th Berkeley Distribution 19 April 2010 CRONTAB(1)
crontab配置文件
man 5 crontab
CRONTAB(5) File Formats Manual CRONTAB(5)NAMEcrontab - tables for driving cronDESCRIPTIONA crontab file contains instructions to the cron(8) daemon of the general form: ``run this command at this time on thisdate''. Each user has their own crontab, and commands in any given crontab will be executed as the user who owns thecrontab. Uucp and News will usually have their own crontabs, eliminating the need for explicitly running su(1) as part of acron command.Blank lines and leading spaces and tabs are ignored. Lines whose first non-space character is a hash-sign (#) are comments,and are ignored. Note that comments are not allowed on the same line as cron commands, since they will be taken to be partof the command. Similarly, comments are not allowed on the same line as environment variable settings.An active line in a crontab will be either an environment setting or a cron command. The crontab file is parsed from top tobottom, so any environment settings will affect only the cron commands below them in the file. An environment setting is ofthe form,name = valuewhere the spaces around the equal-sign (=) are optional, and any subsequent non-leading spaces in value will be part of thevalue assigned to name. The value string may be placed in quotes (single or double, but matching) to preserve leading ortrailing blanks. To define an empty variable, quotes must be used.The value string is not parsed for environmental substitutions or replacement of variables or tilde(~) expansion, thus lineslikePATH = $HOME/bin:$PATHPATH = ~/bin:/usr/bin:/binwill not work as you might expect. And neither will this workA=1B=2C=$A $BThere will not be any substitution for the defined variables in the last value.Several environment variables are set up automatically by the cron(8) daemon. SHELL is set to /bin/sh, and LOGNAME and HOMEare set from the /etc/passwd line of the crontab's owner. PATH is set to "/usr/bin:/bin". HOME, SHELL, and PATH may beoverridden by settings in the crontab; LOGNAME is the user that the job is running from, and may not be changed.(Another note: the LOGNAME variable is sometimes called USER on BSD systems... on these systems, USER will be set also.)In addition to LOGNAME, HOME, and SHELL, cron(8) will look at MAILTO and MAILFROM if it has any reason to send mail as a re‐sult of running commands in ``this'' crontab.If MAILTO is defined (and non-empty), mail is sent to the user so named. MAILTO may also be used to direct mail to multiplerecipients by separating recipient users with a comma. If MAILTO is defined but empty (MAILTO=""), no mail will be sent.Otherwise mail is sent to the owner of the crontab.If MAILFROM is defined, the sender email address is set to MAILFROM. Otherwise mail is sent as "root (Cron Daemon)".On the Debian GNU/Linux system, cron supports the pam_env module, and loads the environment specified by /etc/environment and/etc/security/pam_env.conf. It also reads locale information from /etc/default/locale. However, the PAM settings do NOToverride the settings described above nor any settings in the crontab file itself. Note in particular that if you want aPATH other than "/usr/bin:/bin", you will need to set it in the crontab file.By default, cron will send mail using the mail "Content-Type:" header of "text/plain" with the "charset=" parameter set tothe charmap / codeset of the locale in which crond(8) is started up – i.e. either the default system locale, if no LC_* envi‐ronment variables are set, or the locale specified by the LC_* environment variables ( see locale(7)). You can use differentcharacter encodings for mailed cron job output by setting the CONTENT_TYPE and CONTENT_TRANSFER_ENCODING variables incrontabs, to the correct values of the mail headers of those names.The format of a cron command is very much the V7 standard, with a number of upward-compatible extensions. Each line has fivetime and date fields, followed by a command, followed by a newline character ('\n'). The system crontab (/etc/crontab) usesthe same format, except that the username for the command is specified after the time and date fields and before the command.The fields may be separated by spaces or tabs. The maximum permitted length for the command field is 998 characters.Commands are executed by cron(8) when the minute, hour, and month of year fields match the current time, and when at leastone of the two day fields (day of month, or day of week) match the current time (see ``Note'' below). cron(8) examines cronentries once every minute. The time and date fields are:field allowed values----- --------------minute 0–59hour 0–23day of month 1–31month 1–12 (or names, see below)day of week 0–7 (0 or 7 is Sun, or use names)A field may be an asterisk (*), which always stands for ``first-last''.Ranges of numbers are allowed. Ranges are two numbers separated with a hyphen. The specified range is inclusive. For exam‐ple, 8-11 for an ``hours'' entry specifies execution at hours 8, 9, 10 and 11.Lists are allowed. A list is a set of numbers (or ranges) separated by commas. Examples: ``1,2,5,9'', ``0-4,8-12''.Step values can be used in conjunction with ranges. Following a range with ``/<number>'' specifies skips of the number'svalue through the range. For example, ``0-23/2'' can be used in the hours field to specify command execution every otherhour (the alternative in the V7 standard is ``0,2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16,18,20,22''). Steps are also permitted after an asterisk,so if you want to say ``every two hours'', just use ``*/2''.Names can also be used for the ``month'' and ``day of week'' fields. Use the first three letters of the particular day ormonth (case doesn't matter). Ranges or lists of names are not allowed.The ``sixth'' field (the rest of the line) specifies the command to be run. The entire command portion of the line, up to anewline or % character, will be executed by /bin/sh or by the shell specified in the SHELL variable of the crontab file.Percent-signs (%) in the command, unless escaped with backslash (\), will be changed into newline characters, and all dataafter the first % will be sent to the command as standard input. There is no way to split a single command line onto multi‐ple lines, like the shell's trailing "\".Note: The day of a command's execution can be specified by two fields — day of month, and day of week. If both fields arerestricted (i.e., don't start with *), the command will be run when either field matches the current time. For example,``30 4 1,15 * 5'' would cause a command to be run at 4:30 am on the 1st and 15th of each month, plus every Friday. One can,however, achieve the desired result by adding a test to the command (see the last example in EXAMPLE CRON FILE below).Instead of the first five fields, one of eight special strings may appear:string meaning------ -------@reboot Run once, at startup.@yearly Run once a year, "0 0 1 1 *".@annually (same as @yearly)@monthly Run once a month, "0 0 1 * *".@weekly Run once a week, "0 0 * * 0".@daily Run once a day, "0 0 * * *".@midnight (same as @daily)@hourly Run once an hour, "0 * * * *".Please note that startup, as far as @reboot is concerned, is the time when the cron(8) daemon startup. In particular, it maybe before some system daemons, or other facilities, were startup. This is due to the boot order sequence of the machine.EXAMPLE CRON FILEThe following lists an example of a user crontab file.# use /bin/bash to run commands, instead of the default /bin/shSHELL=/bin/bash# mail any output to `paul', no matter whose crontab this isMAILTO=paul## run five minutes after midnight, every day5 0 * * * $HOME/bin/daily.job >> $HOME/tmp/out 2>&1# run at 2:15pm on the first of every month — output mailed to paul15 14 1 * * $HOME/bin/monthly# run at 10 pm on weekdays, annoy Joe0 22 * * 1-5 mail -s "It's 10pm" joe%Joe,%%Where are your kids?%23 0-23/2 * * * echo "run 23 minutes after midn, 2am, 4am ..., everyday"5 4 * * sun echo "run at 5 after 4 every Sunday"0 */4 1 * mon echo "run every 4th hour on the 1st and on every Monday"0 0 */2 * sun echo "run at midn on every Sunday that's an uneven date"# Run on every second Saturday of the month0 4 8-14 * * test $(date +\%u) -eq 6 && echo "2nd Saturday"All the above examples run non-interactive programs. If you wish to run a program that interacts with the user's desktop youhave to make sure the proper environment variable DISPLAY is set.# Execute a program and run a notification every day at 10:00 am0 10 * * * $HOME/bin/program | DISPLAY=:0 notify-send "Program run" "$(cat)"EXAMPLE SYSTEM CRON FILEThe following lists the content of a regular system-wide crontab file. Unlike a user's crontab, this file has the usernamefield, as used by /etc/crontab.# /etc/crontab: system-wide crontab# Unlike any other crontab you don't have to run the `crontab'# command to install the new version when you edit this file# and files in /etc/cron.d. These files also have username fields,# that none of the other crontabs do.SHELL=/bin/shPATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin# Example of job definition:# .---------------- minute (0 - 59)# | .------------- hour (0 - 23)# | | .---------- day of month (1 - 31)# | | | .------- month (1 - 12) OR jan,feb,mar,apr ...# | | | | .---- day of week (0 - 6) (Sunday=0 or 7) OR sun,mon,tue,wed,thu,fri,sat# | | | | |# m h dom mon dow usercommand17 * * * * root cd / && run-parts --report /etc/cron.hourly25 6 * * * root test -x /usr/sbin/anacron || ( cd / && run-parts --report /etc/cron.daily )47 6 * * 7 root test -x /usr/sbin/anacron || ( cd / && run-parts --report /etc/cron.weekly )52 6 1 * * root test -x /usr/sbin/anacron || ( cd / && run-parts --report /etc/cron.monthly )#Note that all the system-wide tasks will run, by default, from 6 am to 7 am. In the case of systems that are not powered onduring that period of time, only the hourly tasks will be executed unless the defaults above are changed.SEE ALSOcron(8), crontab(1)EXTENSIONSWhen specifying day of week, both day 0 and day 7 will be considered Sunday. BSD and AT&T seem to disagree about this.Lists and ranges are allowed to co-exist in the same field. "1-3,7-9" would be rejected by AT&T or BSD cron — they want tosee "1-3" or "7,8,9" ONLY.Ranges can include "steps", so "1-9/2" is the same as "1,3,5,7,9".Months or days of the week can be specified by name.Environment variables can be set in the crontab. In BSD or AT&T, the environment handed to child processes is basically theone from /etc/rc.Command output is mailed to the crontab owner (BSD can't do this), can be mailed to a person other than the crontab owner(SysV can't do this), or the feature can be turned off and no mail will be sent at all (SysV can't do this either).All of the `@' commands that can appear in place of the first five fields are extensions.LIMITATIONSThe cron daemon runs with a defined timezone. It currently does not support per-user timezones. All the tasks: system's anduser's will be run based on the configured timezone. Even if a user specifies the TZ environment variable in his crontabthis will affect only the commands executed in the crontab, not the execution of the crontab tasks themselves.POSIX specifies that the day of month and the day of week fields both need to match the current time if either of them is a*. However, this implementation only checks if the first character is a *. This is why "0 0 */2 * sun" runs every Sundaythat's an uneven date while the POSIX standard would have it run every Sunday and on every uneven date.The crontab syntax does not make it possible to define all possible periods one can imagine. For example, it is notstraightforward to define the last weekday of a month. To have a task run in a time period that cannot be defined usingcrontab syntax, the best approach would be to have the program itself check the date and time information and continue execu‐tion only if the period matches the desired one.If the program itself cannot do the checks then a wrapper script would be required. Useful tools that could be used for dateanalysis are ncal or calendar For example, to run a program the last Saturday of every month you could use the followingwrapper code:0 4 * * Sat [ "$(date +\%e)" = "$(LANG=C ncal | sed -n 's/^Sa .* \([0-9]\+\) *$/\1/p')" ] && echo "Last Saturday" && program_to_runDIAGNOSTICScron requires that each entry in a crontab end in a newline character. If the last entry in a crontab is missing a newline(i.e. terminated by EOF), cron will consider the crontab (at least partially) broken. A warning will be written to syslog.AUTHORPaul Vixie <paul@vix.com> is the author of cron and original creator of this manual page. This page has also been modifiedfor Debian by Steve Greenland, Javier Fernandez-Sanguino, Christian Kastner and Christian Pekeler.4th Berkeley Distribution 19 April 2010 CRONTAB(5)
附录
Linux man 手册分类:
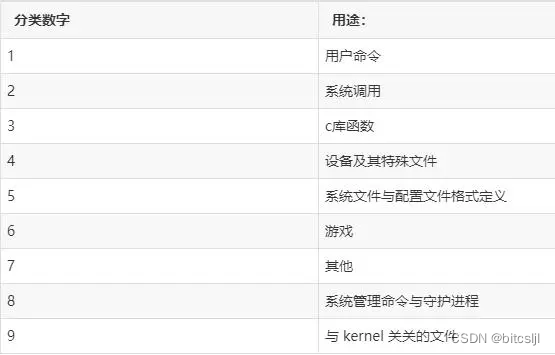
相关文章:

Debian11 Crontab
Crontab用户命令 可执行文件 crontab命令的可执行文件在哪儿? $ which -a crontab /usr/bin/crontab /bin/crontabcrontab命令的可执行文件有2个:/usr/bin/crontab 和 /bin/crontab $ diff /usr/bin/crontab /bin/crontab $diff 发现这两个文件并无区…...

css 文字排版-平铺
序: 1、表格的宽度要有!!!!! 2、容器不能是display:inline 3、扩展---》node全栈框架 代码 text-align-last: justify; width: 70px; display: inline-block; 主要是用于表单左侧文字排序!...
把握潮流:服装定制小程序的发展与趋势
随着互联网的快速发展,小程序成为了人们生活中不可或缺的一部分。尤其在服装行业,定制化已经成为了一种趋势。为了满足消费者个性化的需求,服装定制小程序应运而生。 为了方便开发者的设计和制作,我们可以使用第三方的制作平台来创…...
Go 安装配置
介绍Ubuntu20.04 安装和配置Go 可以参考官网的这个为 Go 开发配置Visual Studio Code - Go on Azure | Microsoft Learn 1.安装Go 去这个地方下载Go https://go.dev/doc/install 如果之前安装过,可以参考这个(没有可以忽略) 下载完成后执…...
镜像底层原理详解和基于Docker file创建镜像
目录 一、镜像底层原理 1.联合文件系统(UnionFS) 2.镜像加载原理 3.为什么Docker里的centos的大小才200M? 二、Dockerfile 1.简介 2.Dockerfile操作常用命令 (1)FORM 镜像 (2)MAINTAINER 维护人信息 (3&…...

k8s扩缩容与滚动更新
使用kubectl run创建应用 kubectl run kubernetes-bootcamp \> --imagedocker.io/jocatalin/kubernetes-bootcamp:v1 \> --port8080 端口暴露出去 kubectl expose pod kubernetes-bootcamp --type"NodePort" --port 8080 使用kubectl create创建应用 kubect…...

4.小程序的运行机制
启动过程 把小程序的代码包下载到本地解析app.json全局配置文件执行app.js小程序入口文件,调用App()创建小程序的实例渲染小程序首页小程序启动完成 页面渲染过程 加载解析页面的.json配置文件加载页面.wxml模板和.scss样式执行页面的.ts文件,调用Pag…...
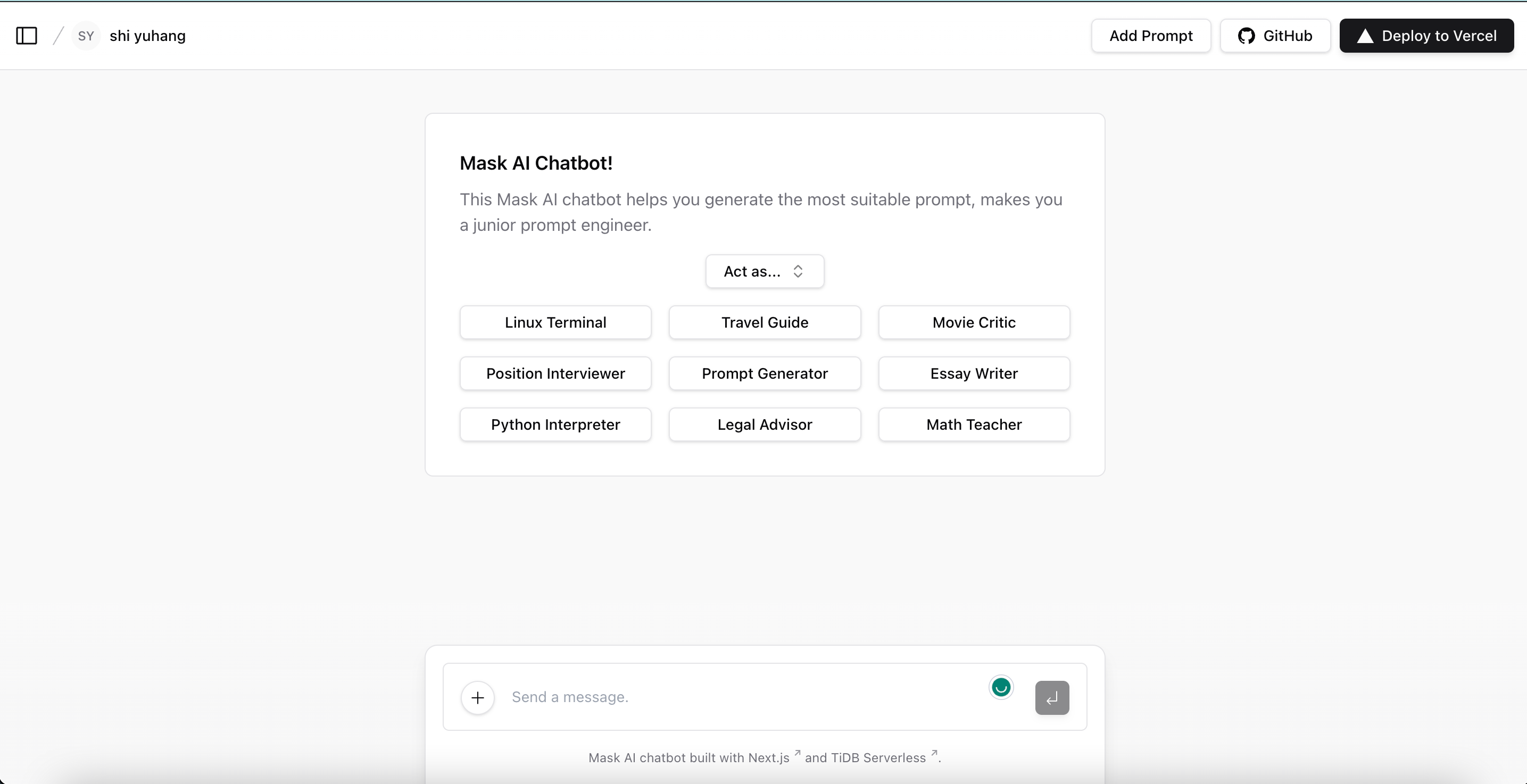
基于 Vercel TiDB Serverless 的 chatbot
作者: shiyuhang0 原文来源: https://tidb.net/blog/7b5fcdc9 # 前言 TiDB Serverless 去年就有和 Vercel 的集成了,同时还有一个 bookstore template 方便大家体验。但个人感觉 bookstore 不够炫酷,借 2023 TiDB hackthon 的…...
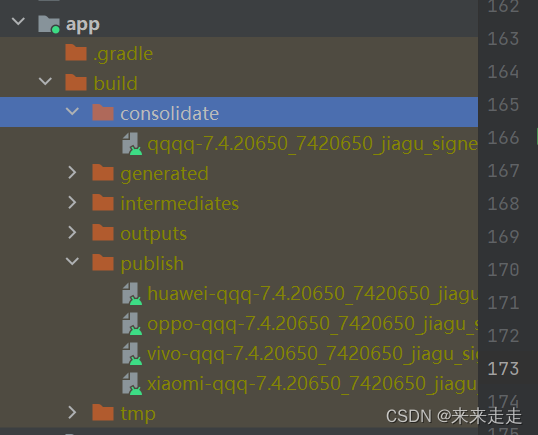
Android 多渠道打包及VasDolly使用
目录 1.添加productFlavors的配置buildConfigFieldmanifestPlaceholdersresValue 2.设置apk文件的名称,便于识别3.添加vasdolly、添加gradle脚本(windows) 作用:一次性可以打多个apk包,名字、包名、logo等可以不相同。…...

LeetCode 42题:接雨水
题目 给定 n 个非负整数表示每个宽度为 1 的柱子的高度图,计算按此排列的柱子,下雨之后能接多少雨水。 示例 1: 输入:height [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1] 输出:6 解释:上面是由数组 [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,…...

spring boot 提示:程序包不存在,解决方法总结
背景: 之前出现过这样的问题,打包安装父项目就好了,今天改了一下代码,重新编译的时候,又出现了这样的情况,决定深度挖掘一下这里面的问题 spring boot 提示:程序包不存在,解决方法总…...
docker项目实战
1、使用mysql:5.6和 owncloud 镜像,构建一个个人网盘 1)拉取mysql:5.6和owncloud镜像 [rootmaster ~]# docker pull mysql:5.6 5.6: Pulling from library/mysql 35b2232c987e: Pull complete fc55c00e48f2: Pull complete 0030405130e3: Pull compl…...

银行客户关系管理系统springboot财务金融进销存java jsp源代码
本项目为前几天收费帮学妹做的一个项目,Java EE JSP项目,在工作环境中基本使用不到,但是很多学校把这个当作编程入门的项目来做,故分享出本项目供初学者参考。 一、项目描述 银行客户关系管理系统springboot 系统有1权限&#x…...

Maven 插件 maven-antrun-plugin 执行 ant 脚本
Ant 相信大家都不陌生,你可以把它理解为使用 xml 格式描述的一系列命令处理工具。它是一种基于Java的build工具。理论上来说,它有些类似于(Unix)C中的make、有些类似于基于shell命令编写的sh脚本文件。Ant 用 Java 的类来扩展。&a…...
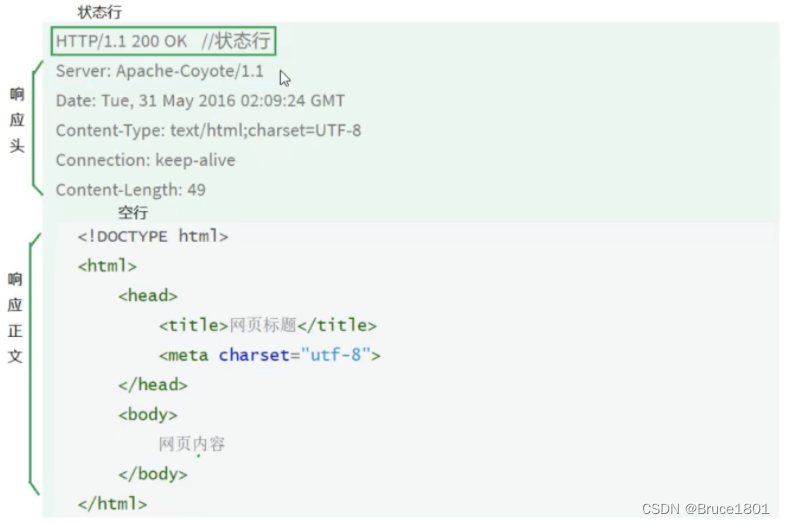
【仿写框架之仿写Tomact】四、封装HttpRequest对象(属性映射http请求报文)、HttpResponse对象(属性映射http响应报文)
文章目录 1、创建HttpRequest对象2、创建HttpResponse对象 1、创建HttpRequest对象 HttpRequest对象中的属性与HTTP协议中的内容对应,用于后序servlet从request中获取请求中的参数。 参照http请求报文: import java.io.BufferedReader; import java…...

LeetCode 41题:缺失的第一个正数
目录 题目 思路 代码 题目 给你一个未排序的整数数组 nums ,请你找出其中没有出现的最小的正整数。 请你实现时间复杂度为 O(n) 并且只使用常数级别额外空间的解决方案。 示例 1: 输入:nums [1,2,0] 输出:3示例 2ÿ…...

学单片机有什么用?
单片机简而言之就是一个小计算机系统,它已经应用到了我们生活中的方方面面。单片机比专用处理器适合应用于嵌入式系统,因此它得到了多的应用,事实上单片机是世界上数量多的计算机。 现代人类生活中所用的几乎每件电子和机械产品中都会集成有单…...
)
Go 1.21新增的 slices 包详解(二)
Go 1.21新增的 slices 包提供了很多和切片相关的函数,可以用于任何类型的切片。 slices.Delete 定义如下: func Delete[S ~[]E, E any](s S, i, j int) S 从 s 中删除元素 s[i:j],返回修改后的切片。如果 s[i:j] 不是 s 的有效切片&#…...
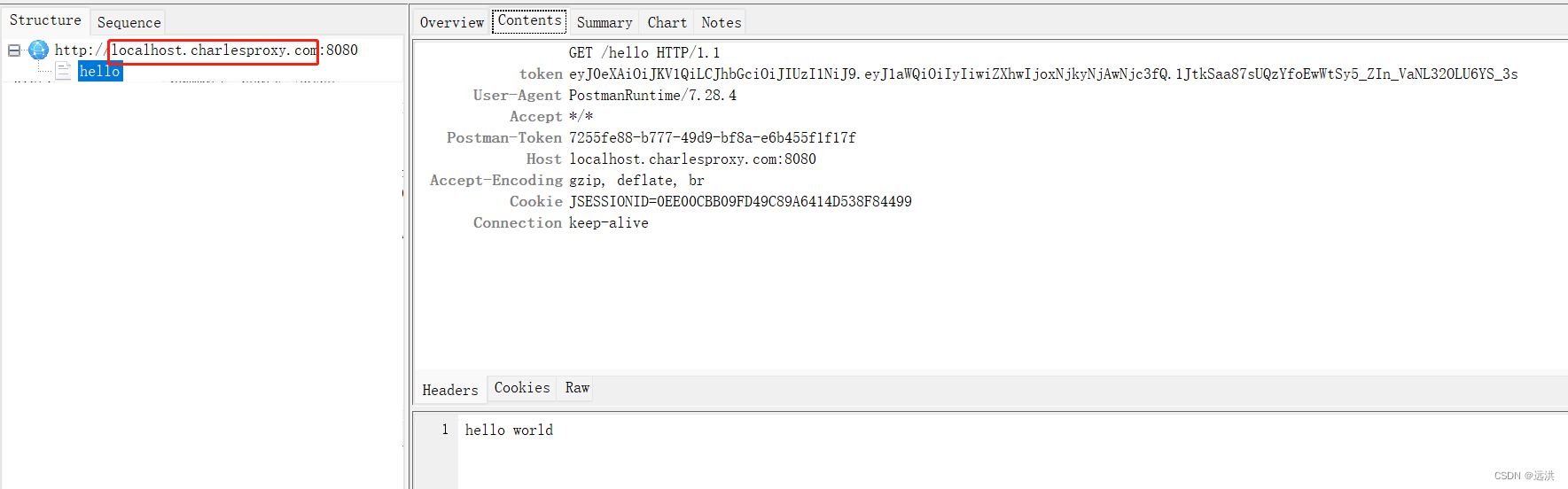
解决charles无法抓取localhost数据包
我们有时候在本地调试的时候,使用charles抓取向本地服务发送的请求的,发现无法抓取。 charles官方也作了相应说明: 大概意思就是 某些系统使用的是硬编码不能使用localhost进行传输,所以当我们连接到 localhost的时候,…...

基于注解优雅的实现接口幂等性
一、什么是幂等性 简单来说,就是对一个接口执行重复的多次请求,与一次请求所产生的结果是相同的,听起来非常容易理解,但要真正的在系统中要始终保持这个目标,是需要很严谨的设计的,在实际的生产环境下&…...
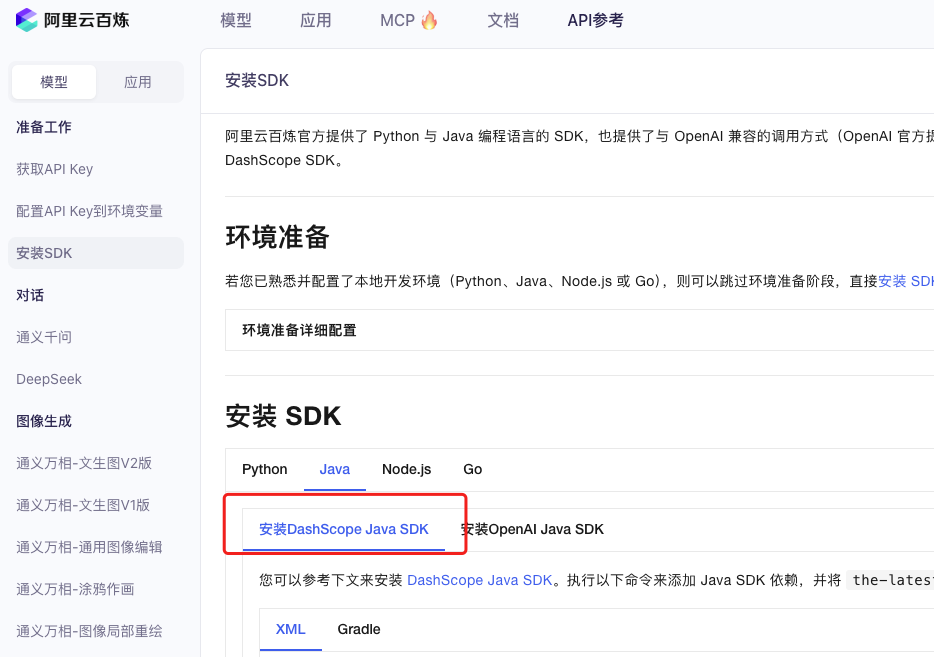
业务系统对接大模型的基础方案:架构设计与关键步骤
业务系统对接大模型:架构设计与关键步骤 在当今数字化转型的浪潮中,大语言模型(LLM)已成为企业提升业务效率和创新能力的关键技术之一。将大模型集成到业务系统中,不仅可以优化用户体验,还能为业务决策提供…...

OpenLayers 可视化之热力图
注:当前使用的是 ol 5.3.0 版本,天地图使用的key请到天地图官网申请,并替换为自己的key 热力图(Heatmap)又叫热点图,是一种通过特殊高亮显示事物密度分布、变化趋势的数据可视化技术。采用颜色的深浅来显示…...

C++:std::is_convertible
C++标志库中提供is_convertible,可以测试一种类型是否可以转换为另一只类型: template <class From, class To> struct is_convertible; 使用举例: #include <iostream> #include <string>using namespace std;struct A { }; struct B : A { };int main…...

《Qt C++ 与 OpenCV:解锁视频播放程序设计的奥秘》
引言:探索视频播放程序设计之旅 在当今数字化时代,多媒体应用已渗透到我们生活的方方面面,从日常的视频娱乐到专业的视频监控、视频会议系统,视频播放程序作为多媒体应用的核心组成部分,扮演着至关重要的角色。无论是在个人电脑、移动设备还是智能电视等平台上,用户都期望…...
Python实现prophet 理论及参数优化
文章目录 Prophet理论及模型参数介绍Python代码完整实现prophet 添加外部数据进行模型优化 之前初步学习prophet的时候,写过一篇简单实现,后期随着对该模型的深入研究,本次记录涉及到prophet 的公式以及参数调优,从公式可以更直观…...

将对透视变换后的图像使用Otsu进行阈值化,来分离黑色和白色像素。这句话中的Otsu是什么意思?
Otsu 是一种自动阈值化方法,用于将图像分割为前景和背景。它通过最小化图像的类内方差或等价地最大化类间方差来选择最佳阈值。这种方法特别适用于图像的二值化处理,能够自动确定一个阈值,将图像中的像素分为黑色和白色两类。 Otsu 方法的原…...
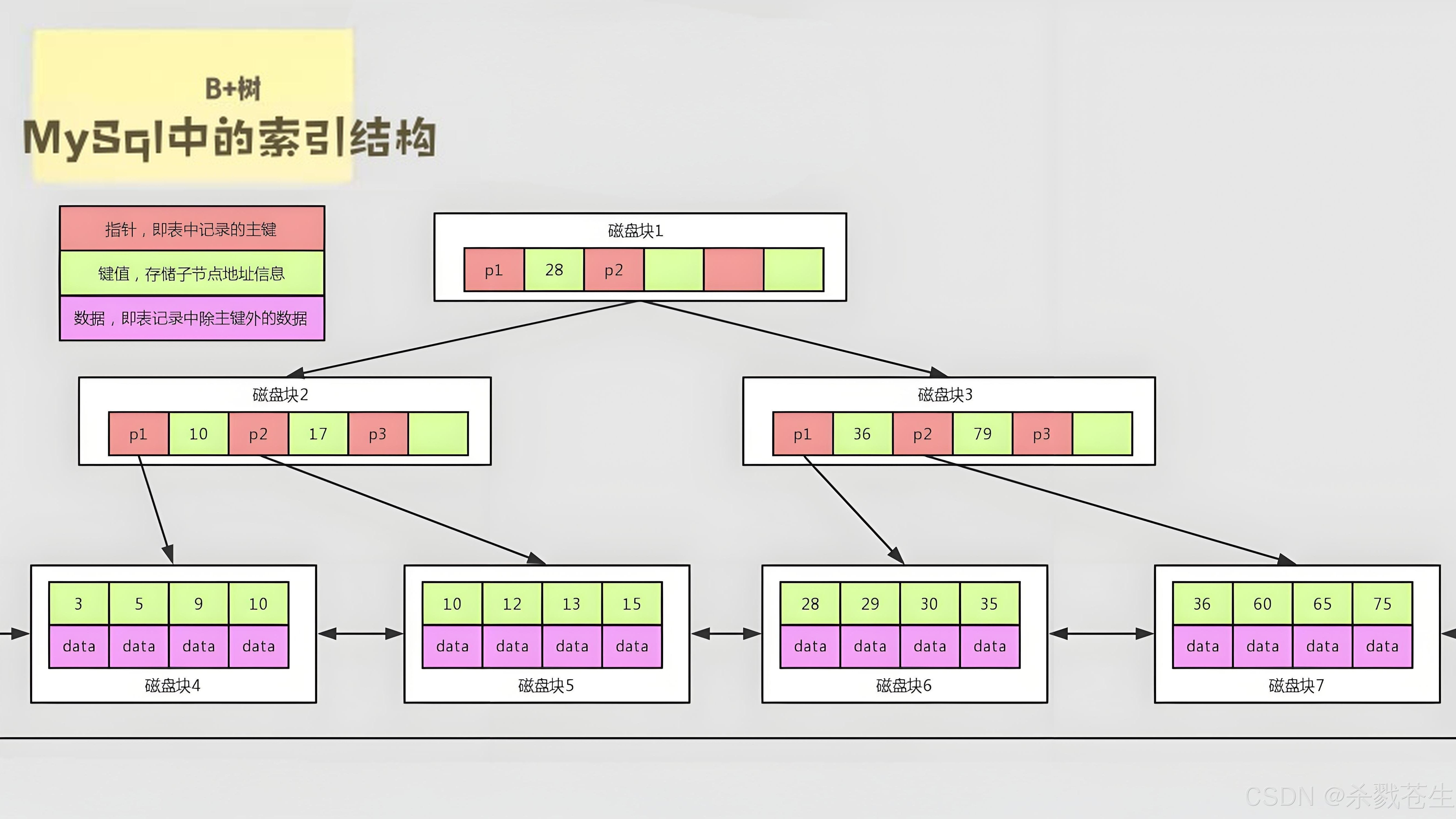
ElasticSearch搜索引擎之倒排索引及其底层算法
文章目录 一、搜索引擎1、什么是搜索引擎?2、搜索引擎的分类3、常用的搜索引擎4、搜索引擎的特点二、倒排索引1、简介2、为什么倒排索引不用B+树1.创建时间长,文件大。2.其次,树深,IO次数可怕。3.索引可能会失效。4.精准度差。三. 倒排索引四、算法1、Term Index的算法2、 …...

【OSG学习笔记】Day 16: 骨骼动画与蒙皮(osgAnimation)
骨骼动画基础 骨骼动画是 3D 计算机图形中常用的技术,它通过以下两个主要组件实现角色动画。 骨骼系统 (Skeleton):由层级结构的骨头组成,类似于人体骨骼蒙皮 (Mesh Skinning):将模型网格顶点绑定到骨骼上,使骨骼移动…...
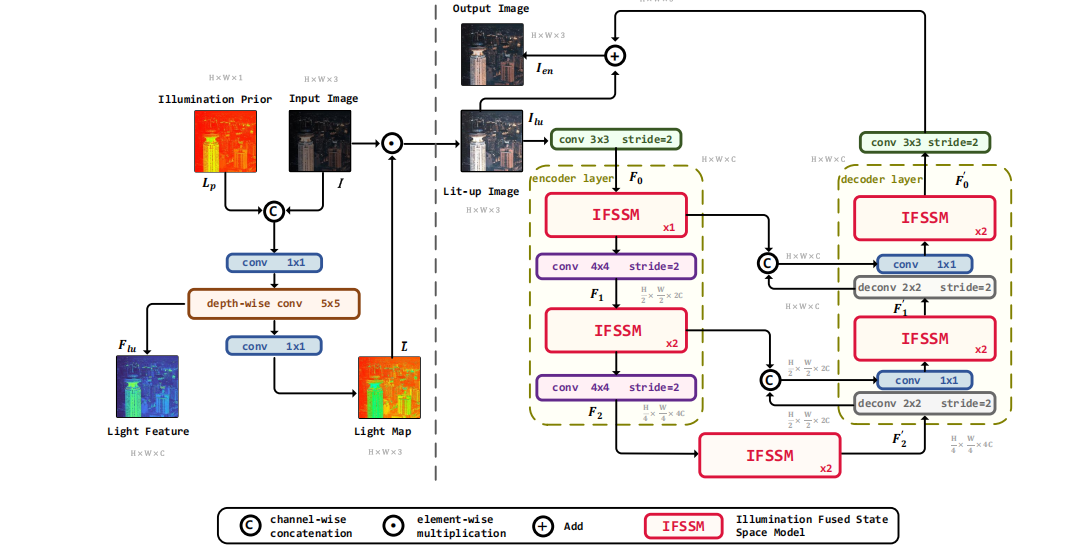
深度学习水论文:mamba+图像增强
🧀当前视觉领域对高效长序列建模需求激增,对Mamba图像增强这方向的研究自然也逐渐火热。原因在于其高效长程建模,以及动态计算优势,在图像质量提升和细节恢复方面有难以替代的作用。 🧀因此短时间内,就有不…...
集成 Mybatis-Plus 和 Mybatis-Plus-Join)
纯 Java 项目(非 SpringBoot)集成 Mybatis-Plus 和 Mybatis-Plus-Join
纯 Java 项目(非 SpringBoot)集成 Mybatis-Plus 和 Mybatis-Plus-Join 1、依赖1.1、依赖版本1.2、pom.xml 2、代码2.1、SqlSession 构造器2.2、MybatisPlus代码生成器2.3、获取 config.yml 配置2.3.1、config.yml2.3.2、项目配置类 2.4、ftl 模板2.4.1、…...
