【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之SPEED_BOUNDS_PRIORI_DECIDERSPEED_BOUNDS_FINAL_DECIDER
文章目录
- 前言
- SPEED_BOUNDS_PRIORI_DECIDER功能简介
- SPEED_BOUNDS_FINAL_DECIDER功能简介
- SPEED_BOUNDS_PRIORI_DECIDER相关配置
- SPEED_BOUNDS_FINAL_DECIDER相关配置
- SPEED_BOUNDS_DECIDER流程
- 将障碍物映射到ST图中
- ComputeSTBoundary(PathDecision* path_decision)
- ComputeSTBoundary(Obstacle* obstacle)
- GetOverlapBoundaryPoints
- ComputeSTBoundaryWithDecision
- SetSpeedFallbackDistance
- 创建速度限制
- GetSpeedLimits
- GetSpeedLimitFromS
- 参考
前言
在Apollo星火计划学习笔记——Apollo路径规划算法原理与实践与【Apollo学习笔记】——Planning模块讲到……Stage::Process的PlanOnReferenceLine函数会依次调用task_list中的TASK,本文将会继续以LaneFollow为例依次介绍其中的TASK部分究竟做了哪些工作。由于个人能力所限,文章可能有纰漏的地方,还请批评斧正。
在modules/planning/conf/scenario/lane_follow_config.pb.txt配置文件中,我们可以看到LaneFollow所需要执行的所有task。
stage_config: {stage_type: LANE_FOLLOW_DEFAULT_STAGEenabled: truetask_type: LANE_CHANGE_DECIDERtask_type: PATH_REUSE_DECIDERtask_type: PATH_LANE_BORROW_DECIDERtask_type: PATH_BOUNDS_DECIDERtask_type: PIECEWISE_JERK_PATH_OPTIMIZERtask_type: PATH_ASSESSMENT_DECIDERtask_type: PATH_DECIDERtask_type: RULE_BASED_STOP_DECIDERtask_type: SPEED_BOUNDS_PRIORI_DECIDERtask_type: SPEED_HEURISTIC_OPTIMIZERtask_type: SPEED_DECIDERtask_type: SPEED_BOUNDS_FINAL_DECIDERtask_type: PIECEWISE_JERK_SPEED_OPTIMIZER# task_type: PIECEWISE_JERK_NONLINEAR_SPEED_OPTIMIZERtask_type: RSS_DECIDER
本文将继续介绍LaneFollow的第9个TASK——SPEED_BOUNDS_PRIORI_DECIDER以及第12个TASK——SPEED_BOUNDS_FINAL_DECIDER
SPEED_BOUNDS_PRIORI_DECIDER功能简介
产生速度可行驶边界

所形成的区域是非凸的,不能用之前凸优化的方法去做,需要用动态规划的方法去做。
SPEED_BOUNDS_FINAL_DECIDER功能简介
产生速度规划边界

 在障碍物的上方或下方确定可行使区域。
在障碍物的上方或下方确定可行使区域。
SPEED_BOUNDS_PRIORI_DECIDER相关配置
modules/planning/proto/task_config.proto
// SpeedBoundsDeciderConfigmessage SpeedBoundsDeciderConfig {optional double total_time = 1 [default = 7.0];optional double boundary_buffer = 2 [default = 0.1];optional double max_centric_acceleration_limit = 3 [default = 2.0];optional double minimal_kappa = 4 [default = 0.00001];optional double point_extension = 5 [default = 1.0];optional double lowest_speed = 6 [default = 2.5];optional double collision_safety_range = 7 [default = 1.0];optional double static_obs_nudge_speed_ratio = 8;optional double dynamic_obs_nudge_speed_ratio = 9;
}modules/planning/conf/planning_config.pb.txt
default_task_config: {task_type: ST_BOUNDS_DECIDERst_bounds_decider_config {total_time: 7.0}
}
SPEED_BOUNDS_FINAL_DECIDER相关配置
modules/planning/conf/planning_config.pb.txt
default_task_config: {task_type: SPEED_BOUNDS_FINAL_DECIDERspeed_bounds_decider_config {total_time: 7.0boundary_buffer: 0.1max_centric_acceleration_limit: 2.0point_extension: 0.0lowest_speed: 2.5static_obs_nudge_speed_ratio: 0.6dynamic_obs_nudge_speed_ratio: 0.8}
}
SpeedBoundsFinalDecider对应的Decider同样是SpeedBoundsDecider,和SpeedBoundsPrioriDecider不同的是配置参数,从Apollo中的默认配置参数来看,SpeedBoundsFinalDecider会根据DP过程生成的决策结果和更小的boundary_buffer生成更加精确的STBoundary。
SPEED_BOUNDS_DECIDER流程
通过modules/planning/tasks/task_factory.cc,我们可以看到SPEED_BOUNDS_PRIORI_DECIDER和SPEED_BOUNDS_FINAL_DECIDER按以下方式进行注册:
task_factory_.Register(TaskConfig::SPEED_BOUNDS_PRIORI_DECIDER,[](const TaskConfig& config,const std::shared_ptr<DependencyInjector>& injector) -> Task* {return new SpeedBoundsDecider(config, injector);});task_factory_.Register(TaskConfig::SPEED_BOUNDS_FINAL_DECIDER,[](const TaskConfig& config,const std::shared_ptr<DependencyInjector>& injector) -> Task* {return new SpeedBoundsDecider(config, injector);});
也据此可知,SPEED_BOUNDS_PRIORI_DECIDER、SPEED_BOUNDS_FINAL_DECIDER代码实现的部分在modules/planning/tasks/deciders/speed_bounds_decider/speed_bounds_decider.cc中。
Speed bounds decider 主要完成以下任务:
- 将障碍物映射到ST图中
- 创建速度限制
- 获取路径长度以及时间长度作为ST边界
SpeedBoundsDecider是一个继承自Decider的派生类。当task_list中运行task::Execute()时,SpeedBoundsDecider中的Process部分开始运行。
-
输入:frame 和reference_line_info。通过计算PathData/ReferenceLine/PathDecision/PlanningStartPoint等等信息,来得到ST_Graph。
-
Process:
- 将障碍物映射到ST图中。
(boundary_mapper.ComputeSTBoundary(path_decision).code() == ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR) {}此处将会遍历所有的障碍物去生成ST graph。当有纵向决策产生时,会对边界进行细微调整。再此之后,所有的障碍物的st_boundary会送入一个boundaries vector之中进行保存。 - 创建速度限制。
if (!speed_limit_decider.GetSpeedLimits(path_decision->obstacles(), &speed_limit).ok())此处会遍历每一个离散的路径点并且找到其速度限制。在每一个循环中,基本速度会取决于map/path_curvature/nudge obstacles等因素。对于nudge obstacles,需要找到最近的障碍物。 - 获取路径长度以及时间长度作为搜索边界。时间长度来自于配置文件
total_time: 7.0(配置部分已有介绍)
- 将障碍物映射到ST图中。
-
输出:boundaries/speed_limit 会存储在reference_line_info的st_graph_data中。

Status SpeedBoundsDecider::Process(Frame *const frame, ReferenceLineInfo *const reference_line_info) {// retrieve data from frame and reference_line_infoconst PathData &path_data = reference_line_info->path_data();const TrajectoryPoint &init_point = frame->PlanningStartPoint();const ReferenceLine &reference_line = reference_line_info->reference_line();PathDecision *const path_decision = reference_line_info->path_decision();// 1. Map obstacles into st graphauto time1 = std::chrono::system_clock::now();// 构造一个STBoundary映射对象STBoundaryMapper boundary_mapper(speed_bounds_config_, reference_line, path_data,path_data.discretized_path().Length(), speed_bounds_config_.total_time(),injector_);// FLAGS_use_st_drivable_boundary: True to use st_drivable boundary in speed planning// default: false// 清除STBoundaryif (!FLAGS_use_st_drivable_boundary) {path_decision->EraseStBoundaries();}// 将障碍物投影到ST Gragh上if (boundary_mapper.ComputeSTBoundary(path_decision).code() ==ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR) {const std::string msg = "Mapping obstacle failed.";AERROR << msg;return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, msg);}auto time2 = std::chrono::system_clock::now();std::chrono::duration<double> diff = time2 - time1;ADEBUG << "Time for ST Boundary Mapping = " << diff.count() * 1000<< " msec.";// 所有的障碍物的st_boundary送入到一个boundaries vector之中进行保存std::vector<const STBoundary *> boundaries;for (auto *obstacle : path_decision->obstacles().Items()) {const auto &id = obstacle->Id();const auto &st_boundary = obstacle->path_st_boundary();if (!st_boundary.IsEmpty()) {if (st_boundary.boundary_type() == STBoundary::BoundaryType::KEEP_CLEAR) {path_decision->Find(id)->SetBlockingObstacle(false);} else {path_decision->Find(id)->SetBlockingObstacle(true);}boundaries.push_back(&st_boundary);}}const double min_s_on_st_boundaries = SetSpeedFallbackDistance(path_decision);// 2. Create speed limit along pathSpeedLimitDecider speed_limit_decider(speed_bounds_config_, reference_line,path_data);SpeedLimit speed_limit;if (!speed_limit_decider.GetSpeedLimits(path_decision->obstacles(), &speed_limit).ok()) {const std::string msg = "Getting speed limits failed!";AERROR << msg;return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, msg);}// 3. Get path_length as s axis search bound in st graphconst double path_data_length = path_data.discretized_path().Length();// 4. Get time duration as t axis search bound in st graphconst double total_time_by_conf = speed_bounds_config_.total_time();// Load generated st graph data back to frameStGraphData *st_graph_data = reference_line_info_->mutable_st_graph_data();// Add a st_graph debug info and save the pointer to st_graph_data for// optimizer loggingauto *debug = reference_line_info_->mutable_debug();STGraphDebug *st_graph_debug = debug->mutable_planning_data()->add_st_graph();st_graph_data->LoadData(boundaries, min_s_on_st_boundaries, init_point,speed_limit, reference_line_info->GetCruiseSpeed(),path_data_length, total_time_by_conf, st_graph_debug);// Create and record st_graph debug infoRecordSTGraphDebug(*st_graph_data, st_graph_debug);return Status::OK();
}
将障碍物映射到ST图中
由Process部分代码可知,(boundary_mapper.ComputeSTBoundary(path_decision).code() == ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR) {}此处是函数的入口。
该部分的流程示意图如下图所示:
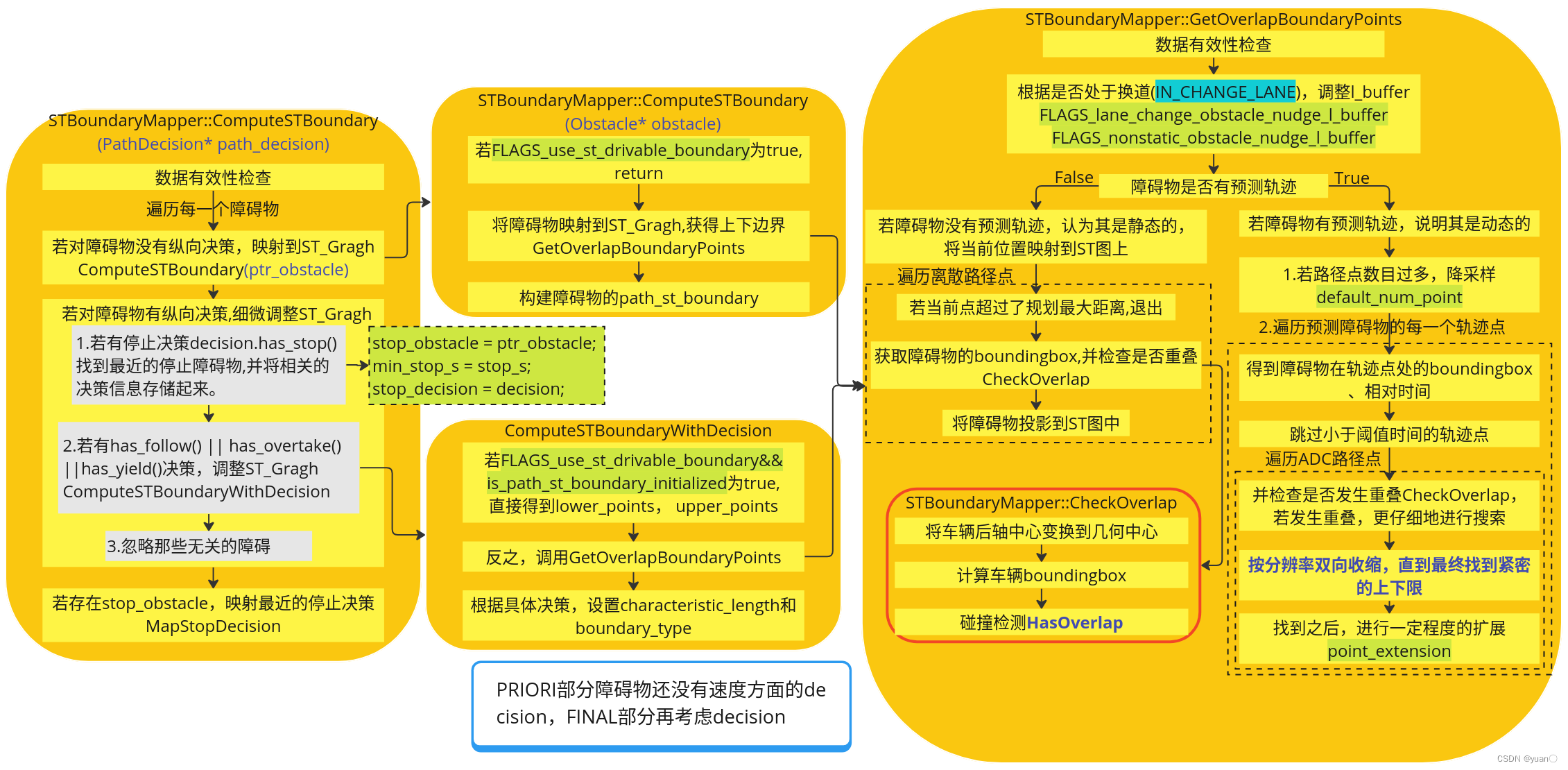
ComputeSTBoundary(PathDecision* path_decision)
ComputeSTBoundary将会遍历所有的障碍物去生成ST graph。当有纵向决策产生时,会对边界进行细微调整。再此之后,所有的障碍物的st_boundary会送入一个boundaries vector之中进行保存。
Status STBoundaryMapper::ComputeSTBoundary(PathDecision* path_decision) const {// Sanity checks.CHECK_GT(planning_max_time_, 0.0);if (path_data_.discretized_path().size() < 2) {AERROR << "Fail to get params because of too few path points. path points ""size: "<< path_data_.discretized_path().size() << ".";return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR,"Fail to get params because of too few path points");}// Go through every obstacle.Obstacle* stop_obstacle = nullptr;ObjectDecisionType stop_decision;double min_stop_s = std::numeric_limits<double>::max();for (const auto* ptr_obstacle_item : path_decision->obstacles().Items()) {Obstacle* ptr_obstacle = path_decision->Find(ptr_obstacle_item->Id());ACHECK(ptr_obstacle != nullptr);// If no longitudinal decision has been made, then plot it onto ST-graph.if (!ptr_obstacle->HasLongitudinalDecision()) {ComputeSTBoundary(ptr_obstacle);continue;}// If there is a longitudinal decision, then fine-tune boundary.const auto& decision = ptr_obstacle->LongitudinalDecision();if (decision.has_stop()) {// 1. Store the closest stop fence info.// TODO(all): store ref. s value in stop decision; refine the code then.common::SLPoint stop_sl_point;reference_line_.XYToSL(decision.stop().stop_point(), &stop_sl_point);const double stop_s = stop_sl_point.s();if (stop_s < min_stop_s) {stop_obstacle = ptr_obstacle;min_stop_s = stop_s;stop_decision = decision;}} else if (decision.has_follow() || decision.has_overtake() ||decision.has_yield()) {// 2. Depending on the longitudinal overtake/yield decision,// fine-tune the upper/lower st-boundary of related obstacles.ComputeSTBoundaryWithDecision(ptr_obstacle, decision);} else if (!decision.has_ignore()) {// 3. Ignore those unrelated obstacles.AWARN << "No mapping for decision: " << decision.DebugString();}}if (stop_obstacle) {bool success = MapStopDecision(stop_obstacle, stop_decision);if (!success) {const std::string msg = "Fail to MapStopDecision.";AERROR << msg;return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, msg);}}return Status::OK();
}
ComputeSTBoundary(Obstacle* obstacle)
调用GetOverlapBoundaryPoints来获取给定障碍物的上下点,然后在此基础上制定STBoundary。它还根据以前记录的决策标记边界类型。
void STBoundaryMapper::ComputeSTBoundary(Obstacle* obstacle) const {if (FLAGS_use_st_drivable_boundary) {return;}std::vector<STPoint> lower_points;std::vector<STPoint> upper_points;// Map the given obstacle onto the ST-Graph.if (!GetOverlapBoundaryPoints(path_data_.discretized_path(), *obstacle,&upper_points, &lower_points)) {return;}// 构建障碍物的boundaryauto boundary = STBoundary::CreateInstance(lower_points, upper_points);boundary.set_id(obstacle->Id());// TODO(all): potential bug here.const auto& prev_st_boundary = obstacle->path_st_boundary();const auto& ref_line_st_boundary = obstacle->reference_line_st_boundary();if (!prev_st_boundary.IsEmpty()) {boundary.SetBoundaryType(prev_st_boundary.boundary_type());} else if (!ref_line_st_boundary.IsEmpty()) {boundary.SetBoundaryType(ref_line_st_boundary.boundary_type());}obstacle->set_path_st_boundary(boundary);
}
GetOverlapBoundaryPoints
将给定的障碍物映射到ST图中。
// Map the given obstacle onto the ST-Graph.
// The boundary is represented as upper and lower points for every s of interests.
// Note that upper_points.size() = lower_points.size()
bool STBoundaryMapper::GetOverlapBoundaryPoints(const std::vector<PathPoint>& path_points, const Obstacle& obstacle,std::vector<STPoint>* upper_points,std::vector<STPoint>* lower_points) const {// Sanity checks.DCHECK(upper_points->empty());DCHECK(lower_points->empty());if (path_points.empty()) {AERROR << "No points in path_data_.discretized_path().";return false;}const auto* planning_status = injector_->planning_context()->mutable_planning_status()->mutable_change_lane();// lane_change_obstacle_nudge_l_buffer: minimum l-distance to nudge when changing lane (meters);0.3// nonstatic_obstacle_nudge_l_buffer: minimum l-distance to nudge a non-static obstacle (meters);0.4double l_buffer =planning_status->status() == ChangeLaneStatus::IN_CHANGE_LANE? FLAGS_lane_change_obstacle_nudge_l_buffer: FLAGS_nonstatic_obstacle_nudge_l_buffer;// Draw the given obstacle on the ST-graph.const auto& trajectory = obstacle.Trajectory();if (trajectory.trajectory_point().empty()) {// For those with no predicted trajectories, just map the obstacle's// current position to ST-graph and always assume it's static.if (!obstacle.IsStatic()) {AWARN << "Non-static obstacle[" << obstacle.Id()<< "] has NO prediction trajectory."<< obstacle.Perception().ShortDebugString();}// 遍历离散路径点for (const auto& curr_point_on_path : path_points) {// planning_max_distance_ = path_data.discretized_path().Length()// 若当前点超过了规划最大距离,退出if (curr_point_on_path.s() > planning_max_distance_) {break;}// 获取障碍物的boundingboxconst Box2d& obs_box = obstacle.PerceptionBoundingBox();if (CheckOverlap(curr_point_on_path, obs_box, l_buffer)) {// If there is overlapping, then plot it on ST-graph.const double backward_distance = -vehicle_param_.front_edge_to_center();const double forward_distance = obs_box.length();double low_s =std::fmax(0.0, curr_point_on_path.s() + backward_distance);double high_s = std::fmin(planning_max_distance_,curr_point_on_path.s() + forward_distance);// It is an unrotated rectangle appearing on the ST-graph.// 静止的障碍物在ST图中就是一个矩形// TODO(jiacheng): reconsider the backward_distance, it might be// unnecessary, but forward_distance is indeed meaningful though.lower_points->emplace_back(low_s, 0.0);lower_points->emplace_back(low_s, planning_max_time_);upper_points->emplace_back(high_s, 0.0);upper_points->emplace_back(high_s, planning_max_time_);break;}}} else {// For those with predicted trajectories (moving obstacles):// 1. Subsample to reduce computation time.const int default_num_point = 50;DiscretizedPath discretized_path;if (path_points.size() > 2 * default_num_point) {const auto ratio = path_points.size() / default_num_point;std::vector<PathPoint> sampled_path_points;for (size_t i = 0; i < path_points.size(); ++i) {if (i % ratio == 0) {sampled_path_points.push_back(path_points[i]);}}discretized_path = DiscretizedPath(std::move(sampled_path_points));} else {discretized_path = DiscretizedPath(path_points);}// 2. Go through every point of the predicted obstacle trajectory.for (int i = 0; i < trajectory.trajectory_point_size(); ++i) {const auto& trajectory_point = trajectory.trajectory_point(i);// 得到障碍物在轨迹点处的boundingboxconst Box2d obs_box = obstacle.GetBoundingBox(trajectory_point);// 得到障碍物在轨迹点处的相对时间double trajectory_point_time = trajectory_point.relative_time();static constexpr double kNegtiveTimeThreshold = -1.0;// 跳过小于阈值时间的轨迹点if (trajectory_point_time < kNegtiveTimeThreshold) {continue;}// 步长const double step_length = vehicle_param_.front_edge_to_center();// FLAGS_max_trajectory_len: (unit: meter) max possible trajectory length. 1000.0auto path_len =std::min(FLAGS_max_trajectory_len, discretized_path.Length());// Go through every point of the ADC's path.for (double path_s = 0.0; path_s < path_len; path_s += step_length) {// 估计当前车辆的位置const auto curr_adc_path_point =discretized_path.Evaluate(path_s + discretized_path.front().s());if (CheckOverlap(curr_adc_path_point, obs_box, l_buffer)) {// Found overlap, start searching with higher resolutionconst double backward_distance = -step_length;const double forward_distance = vehicle_param_.length() +vehicle_param_.width() +obs_box.length() + obs_box.width();const double default_min_step = 0.1; // in metersconst double fine_tuning_step_length = std::fmin(default_min_step, discretized_path.Length() / default_num_point);bool find_low = false;bool find_high = false;double low_s = std::fmax(0.0, path_s + backward_distance);double high_s =std::fmin(discretized_path.Length(), path_s + forward_distance);// Keep shrinking by the resolution bidirectionally until finally// locating the tight upper and lower bounds.while (low_s < high_s) {if (find_low && find_high) {break;}if (!find_low) {const auto& point_low = discretized_path.Evaluate(low_s + discretized_path.front().s());if (!CheckOverlap(point_low, obs_box, l_buffer)) {low_s += fine_tuning_step_length;} else {find_low = true;}}if (!find_high) {const auto& point_high = discretized_path.Evaluate(high_s + discretized_path.front().s());if (!CheckOverlap(point_high, obs_box, l_buffer)) {high_s -= fine_tuning_step_length;} else {find_high = true;}}}if (find_high && find_low) {lower_points->emplace_back(low_s - speed_bounds_config_.point_extension(),trajectory_point_time);upper_points->emplace_back(high_s + speed_bounds_config_.point_extension(),trajectory_point_time);}break;}}}}// Sanity checks and return.DCHECK_EQ(lower_points->size(), upper_points->size());return (lower_points->size() > 1 && upper_points->size() > 1);
}
ComputeSTBoundaryWithDecision
对于产生纵向决策的障碍物产生的ST boundary进行调整。
// Fine-tune the boundary for yielding or overtaking obstacles.
// Increase boundary on the s-dimension or set the boundary type, etc., when necessary.
void STBoundaryMapper::ComputeSTBoundaryWithDecision(Obstacle* obstacle, const ObjectDecisionType& decision) const {DCHECK(decision.has_follow() || decision.has_yield() ||decision.has_overtake())<< "decision is " << decision.DebugString()<< ", but it must be follow or yield or overtake.";std::vector<STPoint> lower_points;std::vector<STPoint> upper_points;if (FLAGS_use_st_drivable_boundary &&obstacle->is_path_st_boundary_initialized()) {const auto& path_st_boundary = obstacle->path_st_boundary();lower_points = path_st_boundary.lower_points();upper_points = path_st_boundary.upper_points();} else {if (!GetOverlapBoundaryPoints(path_data_.discretized_path(), *obstacle,&upper_points, &lower_points)) {return;}}auto boundary = STBoundary::CreateInstance(lower_points, upper_points);// get characteristic_length and boundary_type.STBoundary::BoundaryType b_type = STBoundary::BoundaryType::UNKNOWN;double characteristic_length = 0.0;if (decision.has_follow()) {characteristic_length = std::fabs(decision.follow().distance_s());b_type = STBoundary::BoundaryType::FOLLOW;} else if (decision.has_yield()) {characteristic_length = std::fabs(decision.yield().distance_s());boundary = STBoundary::CreateInstance(lower_points, upper_points).ExpandByS(characteristic_length);b_type = STBoundary::BoundaryType::YIELD;} else if (decision.has_overtake()) {characteristic_length = std::fabs(decision.overtake().distance_s());b_type = STBoundary::BoundaryType::OVERTAKE;} else {DCHECK(false) << "Obj decision should be either yield or overtake: "<< decision.DebugString();}boundary.SetBoundaryType(b_type);boundary.set_id(obstacle->Id());boundary.SetCharacteristicLength(characteristic_length);obstacle->set_path_st_boundary(boundary);
}
SetSpeedFallbackDistance
找到障碍物路径上最低的 s 值,该 s 值将用作速度回退的距离。
double SpeedBoundsDecider::SetSpeedFallbackDistance(PathDecision *const path_decision) {// Set min_s_on_st_boundaries to guide speed fallback.static constexpr double kEpsilon = 1.0e-6;double min_s_non_reverse = std::numeric_limits<double>::infinity();double min_s_reverse = std::numeric_limits<double>::infinity();// 遍历障碍物for (auto *obstacle : path_decision->obstacles().Items()) {const auto &st_boundary = obstacle->path_st_boundary();// 障碍物ST边界为空,跳过if (st_boundary.IsEmpty()) {continue;}// 获取st边界底部左侧点和右侧点的s值,并选择较小的值作为最低的s值const auto left_bottom_point_s = st_boundary.bottom_left_point().s();const auto right_bottom_point_s = st_boundary.bottom_right_point().s();const auto lowest_s = std::min(left_bottom_point_s, right_bottom_point_s);// 如果左侧点的 s 值减去右侧点的 s 值大于 kEpsilon(即左侧点在右侧点之后),则说明这是一个反向行驶的边界if (left_bottom_point_s - right_bottom_point_s > kEpsilon) {// 更新 min_s_reverse,将其设置为最低的 s 值if (min_s_reverse > lowest_s) {min_s_reverse = lowest_s;}} else if (min_s_non_reverse > lowest_s) {// 更新 min_s_non_reverse,将其设置为最低的 s 值。min_s_non_reverse = lowest_s;}}min_s_reverse = std::max(min_s_reverse, 0.0);min_s_non_reverse = std::max(min_s_non_reverse, 0.0);return min_s_non_reverse > min_s_reverse ? 0.0 : min_s_non_reverse;
}
创建速度限制
SpeedLimits来源于三个部分:
- 来自于地图的速度限制
- 来自于道路曲率的速度限制
- 来自于Nudge障碍物的速度限制
该部分流程图如下所示:
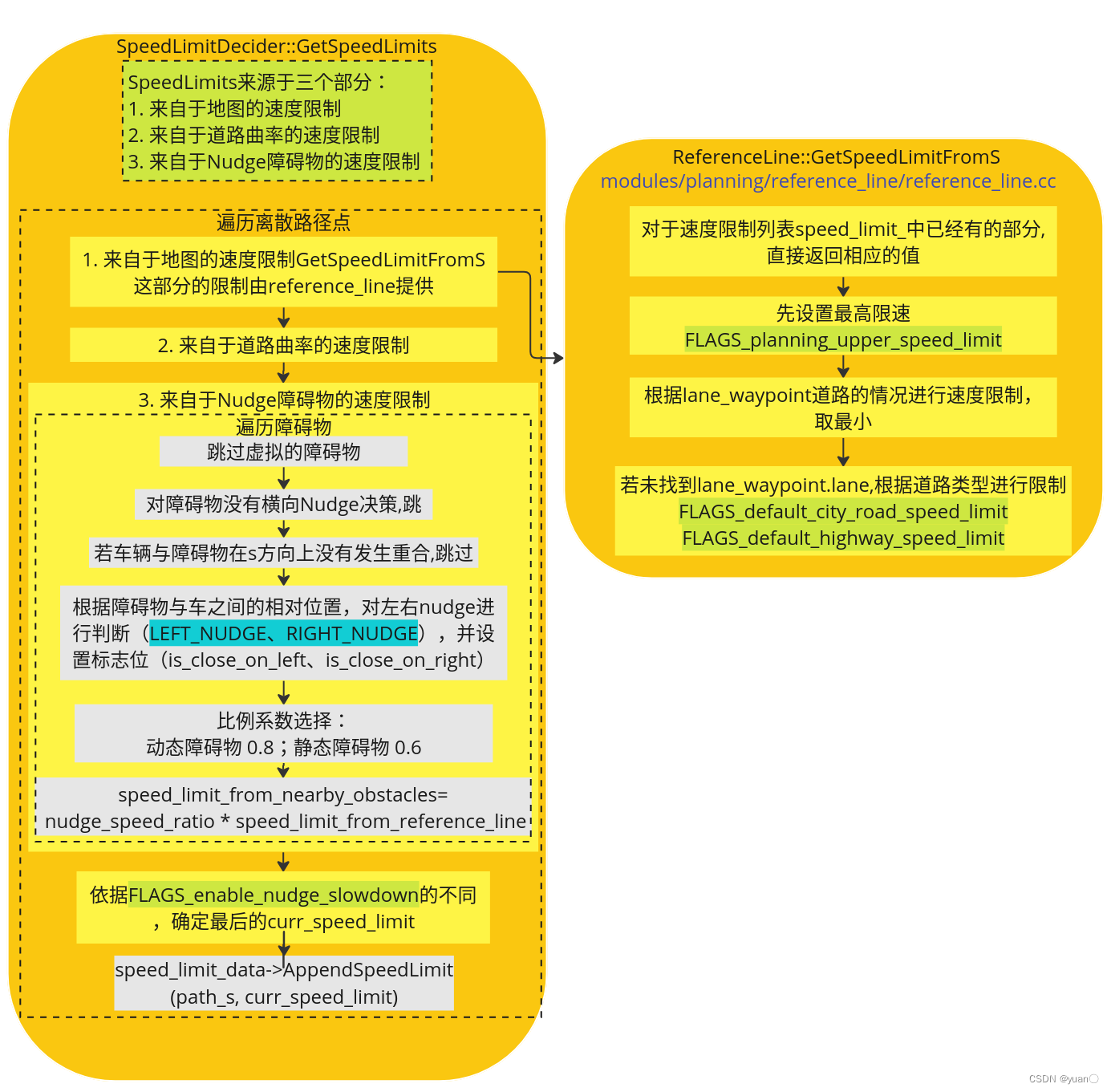
GetSpeedLimits
Status SpeedLimitDecider::GetSpeedLimits(const IndexedList<std::string, Obstacle>& obstacles,SpeedLimit* const speed_limit_data) const {CHECK_NOTNULL(speed_limit_data);const auto& discretized_path = path_data_.discretized_path();const auto& frenet_path = path_data_.frenet_frame_path();// 遍历离散路径点for (uint32_t i = 0; i < discretized_path.size(); ++i) {const double path_s = discretized_path.at(i).s();const double reference_line_s = frenet_path.at(i).s();if (reference_line_s > reference_line_.Length()) {AWARN << "path w.r.t. reference line at [" << reference_line_s<< "] is LARGER than reference_line_ length ["<< reference_line_.Length() << "]. Please debug before proceeding.";break;}// (1) speed limit from mapdouble speed_limit_from_reference_line =reference_line_.GetSpeedLimitFromS(reference_line_s);// (2) speed limit from path curvature// -- 2.1: limit by centripetal force (acceleration)const double speed_limit_from_centripetal_acc =// max_centric_acceleration_limit default = 2.0std::sqrt(speed_bounds_config_.max_centric_acceleration_limit() /std::fmax(std::fabs(discretized_path.at(i).kappa()),speed_bounds_config_.minimal_kappa()));// (3) speed limit from nudge obstacles// TODO(all): in future, expand the speed limit not only to obstacles with// nudge decisions.double speed_limit_from_nearby_obstacles =std::numeric_limits<double>::max();const double collision_safety_range =speed_bounds_config_.collision_safety_range();// default = 1.0// 遍历障碍物for (const auto* ptr_obstacle : obstacles.Items()) {// 跳过虚拟的障碍物if (ptr_obstacle->IsVirtual()) {continue;}// 障碍物没有横向Nudge决策,跳过if (!ptr_obstacle->LateralDecision().has_nudge()) {continue;}/* ref line:* -------------------------------* start_s end_s* ------| adc |---------------* ------------| obstacle |------*/// TODO(all): potential problem here;// frenet and cartesian coordinates are mixed.const double vehicle_front_s =reference_line_s + vehicle_param_.front_edge_to_center();const double vehicle_back_s =reference_line_s - vehicle_param_.back_edge_to_center();const double obstacle_front_s =ptr_obstacle->PerceptionSLBoundary().end_s();const double obstacle_back_s =ptr_obstacle->PerceptionSLBoundary().start_s();// 若车辆与障碍物在s方向上没有发生重合,跳过if (vehicle_front_s < obstacle_back_s ||vehicle_back_s > obstacle_front_s) {continue;}const auto& nudge_decision = ptr_obstacle->LateralDecision().nudge();// Please notice the differences between adc_l and frenet_point_lconst double frenet_point_l = frenet_path.at(i).l();// obstacle is on the right of ego vehicle (at path point i)bool is_close_on_left =(nudge_decision.type() == ObjectNudge::LEFT_NUDGE) &&(frenet_point_l - vehicle_param_.right_edge_to_center() -collision_safety_range <ptr_obstacle->PerceptionSLBoundary().end_l());// obstacle is on the left of ego vehicle (at path point i)bool is_close_on_right =(nudge_decision.type() == ObjectNudge::RIGHT_NUDGE) &&(ptr_obstacle->PerceptionSLBoundary().start_l() -collision_safety_range <frenet_point_l + vehicle_param_.left_edge_to_center());// TODO(all): dynamic obstacles do not have nudge decisionif (is_close_on_left || is_close_on_right) {double nudge_speed_ratio = 1.0;// 静态障碍物 x 0.6if (ptr_obstacle->IsStatic()) {nudge_speed_ratio =speed_bounds_config_.static_obs_nudge_speed_ratio(); // static_obs_nudge_speed_ratio: 0.6} else {// 动态障碍物 x 0.8nudge_speed_ratio =speed_bounds_config_.dynamic_obs_nudge_speed_ratio(); // dynamic_obs_nudge_speed_ratio: 0.8}speed_limit_from_nearby_obstacles =nudge_speed_ratio * speed_limit_from_reference_line;break;}}double curr_speed_limit = 0.0;// FLAGS_enable_nudge_slowdown: True to slow down when nudge obstaclesif (FLAGS_enable_nudge_slowdown) {curr_speed_limit =std::fmax(speed_bounds_config_.lowest_speed(), // lowest_speed:2.5std::min({speed_limit_from_reference_line,speed_limit_from_centripetal_acc,speed_limit_from_nearby_obstacles}));} else {curr_speed_limit =std::fmax(speed_bounds_config_.lowest_speed(),std::min({speed_limit_from_reference_line,speed_limit_from_centripetal_acc}));}speed_limit_data->AppendSpeedLimit(path_s, curr_speed_limit);}return Status::OK();
}
设置标志位(is_close_on_left、is_close_on_right)部分的示意图如下:

GetSpeedLimitFromS
double ReferenceLine::GetSpeedLimitFromS(const double s) const {// 对于速度限制列表speed_limit_中已经有的部分,直接返回相应的值。for (const auto& speed_limit : speed_limit_) {if (s >= speed_limit.start_s && s <= speed_limit.end_s) {return speed_limit.speed_limit;}}const auto& map_path_point = GetReferencePoint(s);// FLAGS_planning_upper_speed_limit: Maximum speed (m/s) in planning;31.3double speed_limit = FLAGS_planning_upper_speed_limit;bool speed_limit_found = false;// 根据lane_waypoint道路的情况进行速度限制for (const auto& lane_waypoint : map_path_point.lane_waypoints()) {if (lane_waypoint.lane == nullptr) {AWARN << "lane_waypoint.lane is nullptr.";continue;}speed_limit_found = true;speed_limit =std::fmin(lane_waypoint.lane->lane().speed_limit(), speed_limit);}// 若未找到lane_waypoint.lane,根据道路类型进行限制if (!speed_limit_found) {// use default speed limit based on road_type// FLAGS_default_city_road_speed_limit: default speed limit (m/s) for city road. 35 mphspeed_limit = FLAGS_default_city_road_speed_limit;hdmap::Road::Type road_type = GetRoadType(s);if (road_type == hdmap::Road::HIGHWAY) {// FLAGS_default_highway_speed_limit: default speed limit (m/s) for highway. 65 mphspeed_limit = FLAGS_default_highway_speed_limit;}}return speed_limit;
}
参考
[1] Planning Piecewise Jerk Nonlinear Speed Optimizer Introduction
[2] Apollo规划控制学习笔记
[3] 1.10 Speed Bounds Prior Decider
相关文章:

【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之SPEED_BOUNDS_PRIORI_DECIDERSPEED_BOUNDS_FINAL_DECIDER
文章目录 前言SPEED_BOUNDS_PRIORI_DECIDER功能简介SPEED_BOUNDS_FINAL_DECIDER功能简介SPEED_BOUNDS_PRIORI_DECIDER相关配置SPEED_BOUNDS_FINAL_DECIDER相关配置SPEED_BOUNDS_DECIDER流程将障碍物映射到ST图中ComputeSTBoundary(PathDecision* path_decision)ComputeSTBounda…...

score_inverse_problems运行环境,pycharm重新安装,jax,jaxlib的GPU版本安装-230831
尝试运行https://github.com/yang-song/score_inverse_problems pycharm2019不支持python3.10,其实后来我用来3.8…… pycharm2022.3.3的安装,涉及激活(淘宝5元),搜狗拼音输入(shift不能切换输入法&#x…...

VSC++: 奇怪的风吹
void 奇怪的风吹() {//缘由https://ask.csdn.net/questions/1062454int aa[]{15, 30, 12, 36, 11, 20, 19, 17, 16, 18, 38, 15, 30, 12, 36, 11, 20, 19, 17, 16, 18, 38, -1},j 0, a 0, y 0, z 0;while (aa[j] > 0){if (j && aa[j] > 35 || aa[j] < 15)…...

被动操作系统指纹识别的强大功能可实现准确的物联网设备识别
到 2030 年,企业网络和互联网上的物联网设备数量预计将达到290 亿。这种指数级增长无意中增加了攻击面。 每个互连设备都可能为网络攻击和安全漏洞创造新的途径。Mirai 僵尸网络通过使用数千个易受攻击的 IoT 设备对关键互联网基础设施和热门网站发起大规模 DDoS 攻…...
QT/C++获取电脑系统,主板型号,CPU型号,硬盘型号,内存大小等相关信息(二)通过Windows Server (WMI)查询
Qt/C调用windows Api库通过wmi的方式查询电脑能获取更多详细信息,也更加合理有技术性。 建议使用MSCV编译器,如MSCV 2017 ,Qt版本 : 5.13.1 目录导读 关于 WMI示例:创建 WMI 应用程序示例:打印Wmi执行的查询项的所有属性头文件引用…...
自建音乐服务器Navidrome之一
这里写自定义目录标题 1.1 官方网站 2. Navidrome 简介2.1 简介2.2 特性 3. 准备工作4. 视频教程5. 界面演示5.1 初始化页5.2 专辑页 前言 之前给大家介绍过 Koel 音频流服务,就是为了解决大家的这个问题:下载下来的音乐,只能在本机欣赏&…...

ACL 访问控制 过滤数据 维护网络安全(第七课)
一 ACL 简介 ACL是Access Control List(访问控制列表)的缩写,是一种用于控制文件、目录、网络设备等资源访问权限的方法。ACL可以对每个用户或用户组设置不同的访问权,即在访问控制清单中为每个用户或用户组指定允许或禁止访问该资源的权限。它通常由一系列规则组成,规则…...

3D视觉测量:面对面的对称度 点对(附源码)
文章目录 0. 测试效果1. 基本内容2. 3D视觉测量对称度测量思路3. 代码实现4. 参考文章目录:3D视觉测量目录微信:dhlddxB站: Non-Stop_目标:通过3D视觉方法计算面对面的对称度0. 测试效果 数据说明:此测试点云是通过UG建模,Meshlab降采样得到,数据比较理想,仅作为测试使用…...

无涯教程-JavaScript - RANK函数
RANK函数取代了Excel 2010中的RANK.EQ函数。 描述 该函数返回数字列表中数字的等级。数字的等级是其相对于列表中其他值的大小。 如果对列表进行排序,则数字的排名将是其位置。 语法 RANK (number,ref,[order])争论 Argument描述Required/OptionalNumberThe number whose…...
蓝牙发展现状
目录 一、产品分类1、Bluetooth经典2、Bluetooth低能耗(LE)3、二者差异 二、出货量三、未来需要加强的方向四、技术行业细分五、学习资料1、蓝牙官网2、大神博客——于忠军 一、产品分类 1、Bluetooth经典 Bluetooth Classic无线电,也被称为Bluetooth 基本速率/增强…...
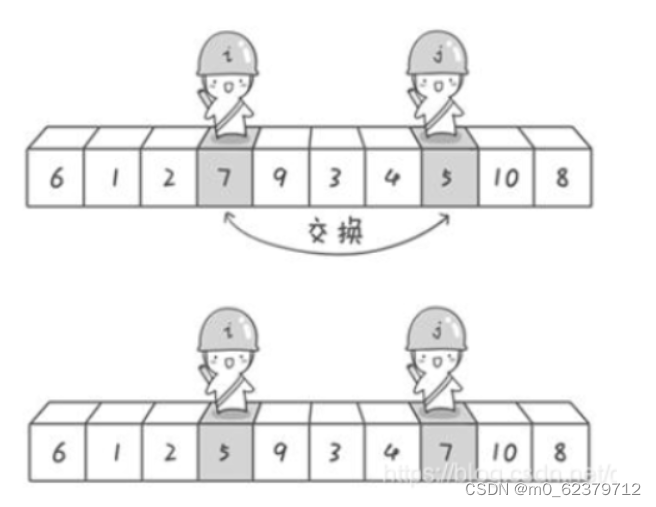
排序算法问题
给你一个整数数组 nums,请你将该数组升序排列。 示例 1: 输入:nums [5,2,3,1] 输出:[1,2,3,5] 示例 2: 输入:nums [5,1,1,2,0,0] 输出:[0,0,1,1,2,5] 代码如下: 1.插入排序(简…...

PlotlyJs 指定画布的宽度并页面居中
可以通过CSS样式来实现指定画布的宽度并使其在页面居中。具体方法如下: 在HTML文件中定义一个div,用来包含PlotlyJs画布。如下所示: <div id"plotly-div"></div>在CSS样式中指定该div的宽度和居中方式。如下所示&…...
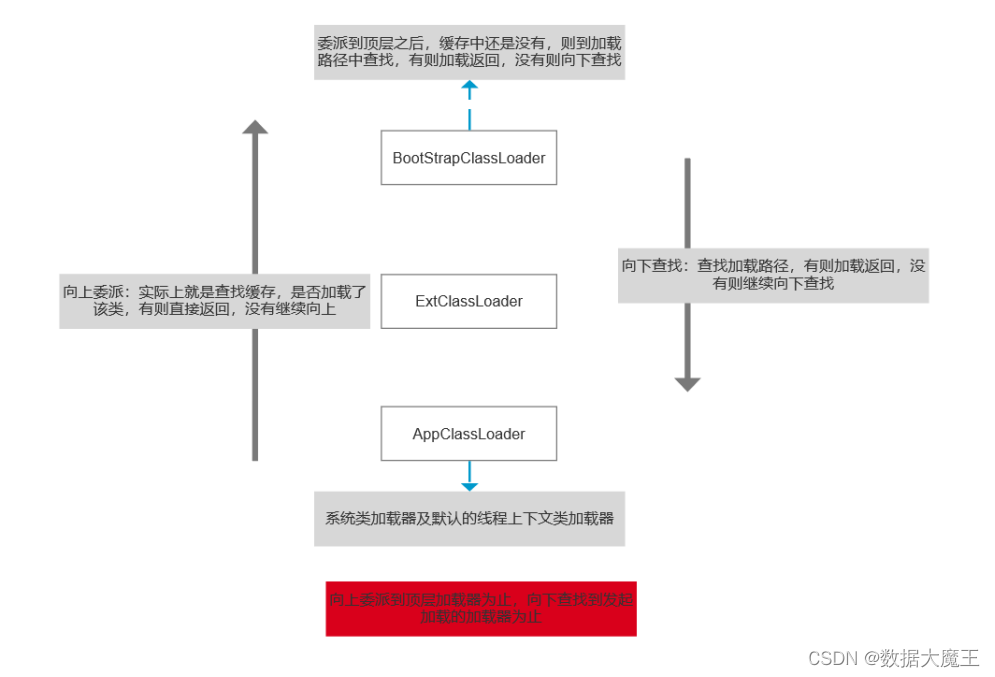
java基础-----第八篇
系列文章目录 文章目录 系列文章目录一、Java类加载器二、双亲委托模型 一、Java类加载器 JDK自带有三个类加载器:bootstrap ClassLoader、ExtClassLoader、AppClassLoader。 BootStrapClassLoader是ExtClassLoader的父类加载器,默认负责加载%JAVA_HOME…...

【Java 基础篇】StringBuilder的魔力:Java字符串处理探究
在Java编程中,字符串是一个常见的数据类型,用于存储文本信息。然而,与字符串相关的操作可能会导致性能问题,因为字符串是不可变的,每次对字符串进行操作都会创建一个新的字符串对象。为了解决这个问题,Java…...

Shell 编程技巧:批量转换Markdown文件
由于一些原因,需要将以前编写的所有markdown文件转成docx文件,以便做一个备份,特别是原文档中引用的图片需要嵌入docx文件,作本地化保存。先上脚本吧: sudo yum -y install pandoc # set new line char as IFS IFS$\…...
EasyAVFilter的初衷:把ffmpeg.c当做SDK来用,而不是当做EXE来用
之前我们做一个视频点播的功能,大概的流程就是将上传上来的各种格式的视频,用FFmpeg统一进行一次转码,如果probe到视频的编码格式是H.264就调用-vcodec copy,如果probe到视频的编码格式不是H.264就调用-vcodec libx264,…...

内存管理之:内存空间分布和栈攻击(黑客常用攻击手段)
目录 C语言内存管理及栈攻击 内存管理 Linux虚拟内存空间分布(重要) 栈溢出(栈攻击) 堆栈的特点 栈攻击 栈攻击的实现 原理 编译器选项 实现案例 linux修改栈空间大小方式 内存泄漏 如何避免野指针? 如何…...

一米facebook功能点
用户信息批量修改 可批量修改已登录用户的头像、密码、个人说明等信息。 小号批量刷赞、评论 可以批量用facebook小号给帖子、主页等刷赞或评论。 直播帖刷人气/评论/分享 可以直接刷直播帖子的人气、评论,并可一键分享到小组或个人时间线、公共主页等。 小组成员…...
)
uni-app:监听数据变化(watch监听、@input事件)
方法一:文本框监听,使用input事件 <template><view><input type"text" v-model"wip_entity_name" input"handleInputChange" /></view> </template><script> export default {data() {return {…...

提升C语言的方法?
我个人的习惯,学一门新的编程语言一定是需要目的的。 也就是学这个语言是干什么? 单纯的上学学习C语言一般都是工科的专业作为专业课而开设的学科,这种很多都是使用谭浩强的教材,很多同学也基本没听,所以学习效果也是…...
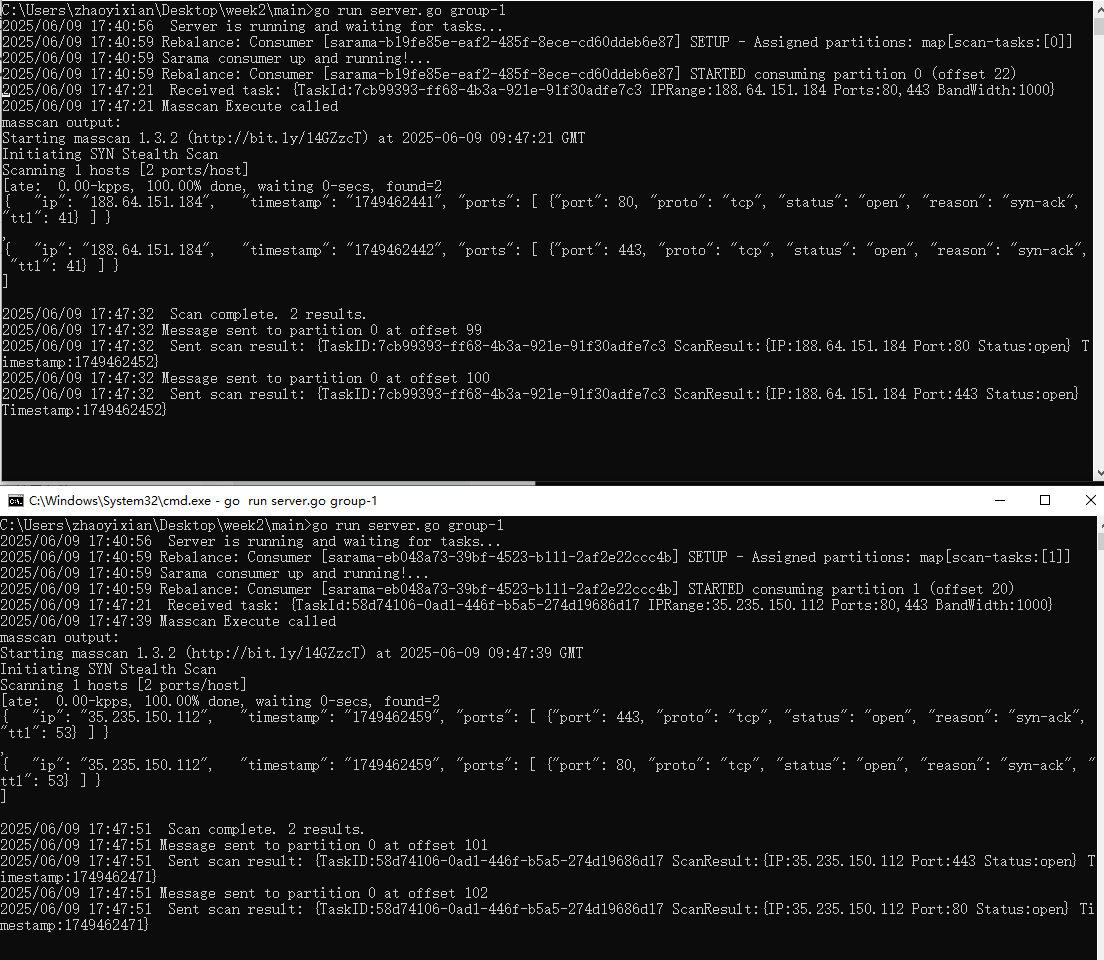
【kafka】Golang实现分布式Masscan任务调度系统
要求: 输出两个程序,一个命令行程序(命令行参数用flag)和一个服务端程序。 命令行程序支持通过命令行参数配置下发IP或IP段、端口、扫描带宽,然后将消息推送到kafka里面。 服务端程序: 从kafka消费者接收…...
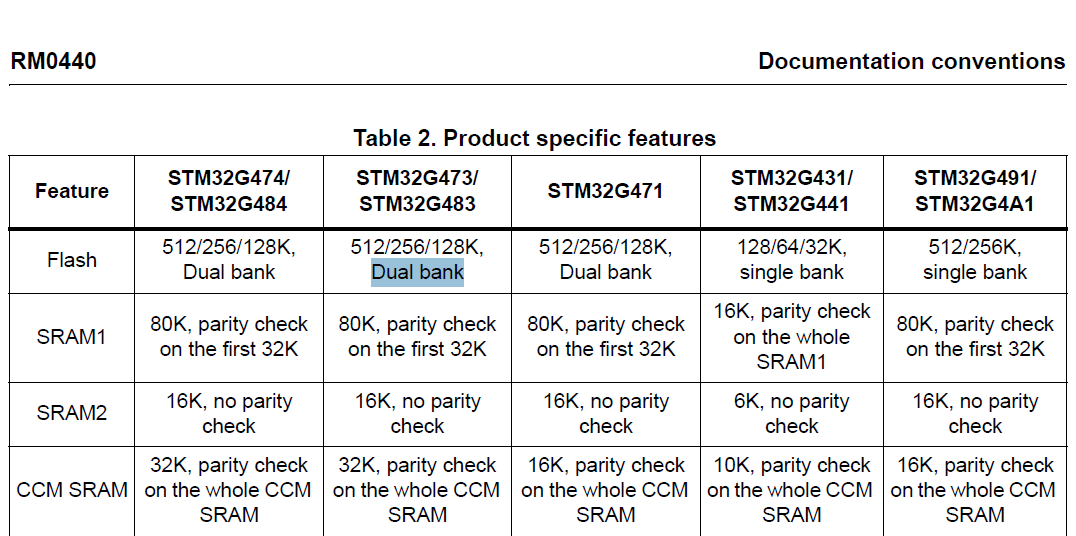
stm32G473的flash模式是单bank还是双bank?
今天突然有人stm32G473的flash模式是单bank还是双bank?由于时间太久,我真忘记了。搜搜发现,还真有人和我一样。见下面的链接:https://shequ.stmicroelectronics.cn/forum.php?modviewthread&tid644563 根据STM32G4系列参考手…...
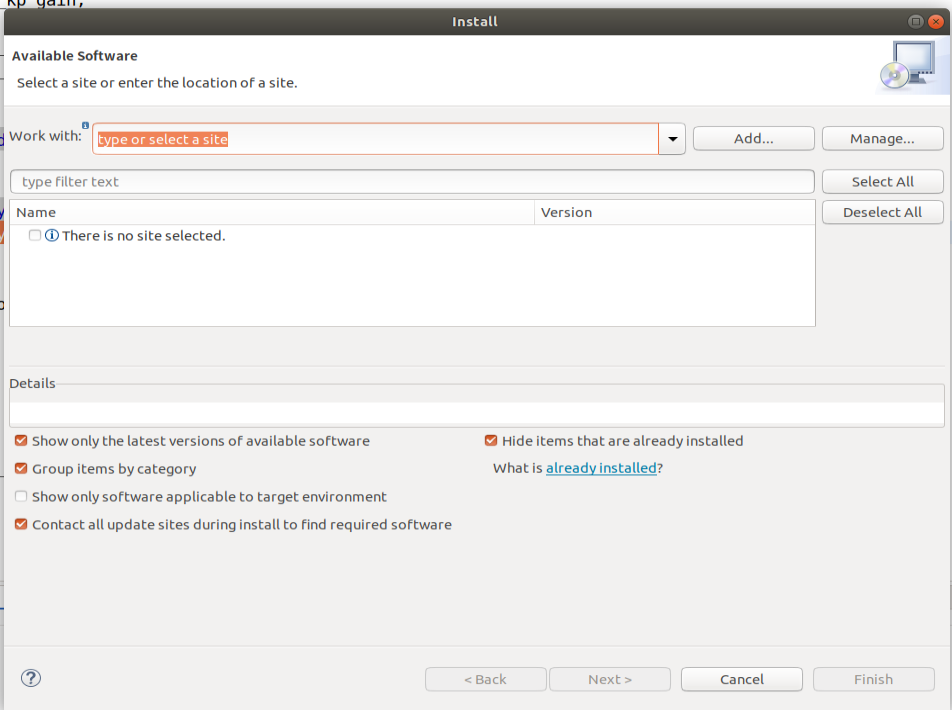
ardupilot 开发环境eclipse 中import 缺少C++
目录 文章目录 目录摘要1.修复过程摘要 本节主要解决ardupilot 开发环境eclipse 中import 缺少C++,无法导入ardupilot代码,会引起查看不方便的问题。如下图所示 1.修复过程 0.安装ubuntu 软件中自带的eclipse 1.打开eclipse—Help—install new software 2.在 Work with中…...
可以参考以下方法:)
根据万维钢·精英日课6的内容,使用AI(2025)可以参考以下方法:
根据万维钢精英日课6的内容,使用AI(2025)可以参考以下方法: 四个洞见 模型已经比人聪明:以ChatGPT o3为代表的AI非常强大,能运用高级理论解释道理、引用最新学术论文,生成对顶尖科学家都有用的…...
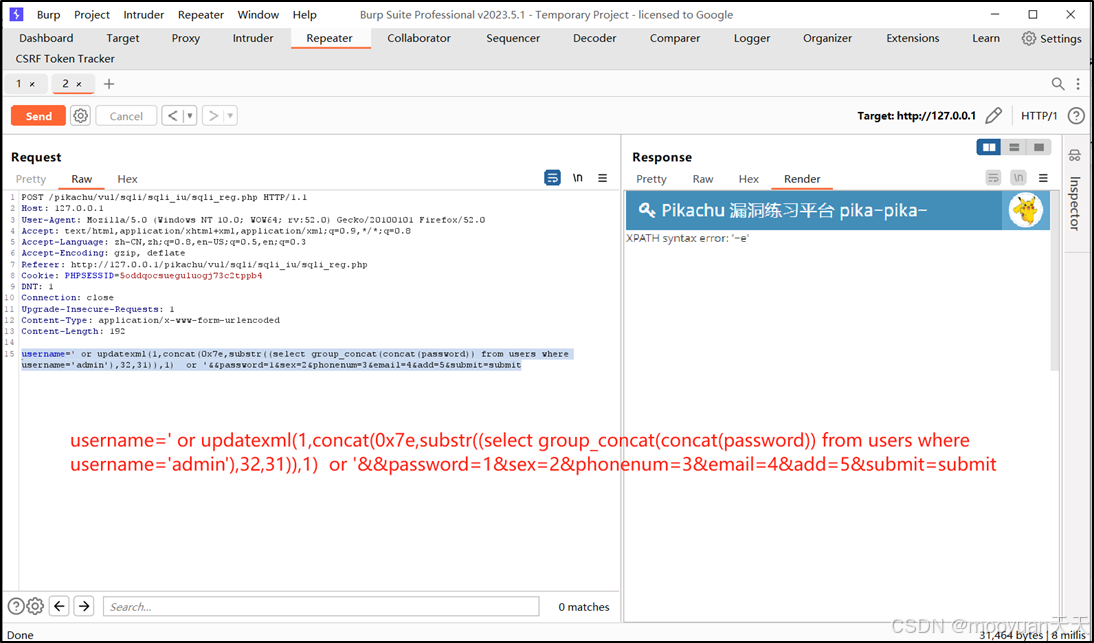
pikachu靶场通关笔记22-1 SQL注入05-1-insert注入(报错法)
目录 一、SQL注入 二、insert注入 三、报错型注入 四、updatexml函数 五、源码审计 六、insert渗透实战 1、渗透准备 2、获取数据库名database 3、获取表名table 4、获取列名column 5、获取字段 本系列为通过《pikachu靶场通关笔记》的SQL注入关卡(共10关࿰…...

DeepSeek 技术赋能无人农场协同作业:用 AI 重构农田管理 “神经网”
目录 一、引言二、DeepSeek 技术大揭秘2.1 核心架构解析2.2 关键技术剖析 三、智能农业无人农场协同作业现状3.1 发展现状概述3.2 协同作业模式介绍 四、DeepSeek 的 “农场奇妙游”4.1 数据处理与分析4.2 作物生长监测与预测4.3 病虫害防治4.4 农机协同作业调度 五、实际案例大…...

Spring Cloud Gateway 中自定义验证码接口返回 404 的排查与解决
Spring Cloud Gateway 中自定义验证码接口返回 404 的排查与解决 问题背景 在一个基于 Spring Cloud Gateway WebFlux 构建的微服务项目中,新增了一个本地验证码接口 /code,使用函数式路由(RouterFunction)和 Hutool 的 Circle…...
微软PowerBI考试 PL300-在 Power BI 中清理、转换和加载数据
微软PowerBI考试 PL300-在 Power BI 中清理、转换和加载数据 Power Query 具有大量专门帮助您清理和准备数据以供分析的功能。 您将了解如何简化复杂模型、更改数据类型、重命名对象和透视数据。 您还将了解如何分析列,以便知晓哪些列包含有价值的数据,…...
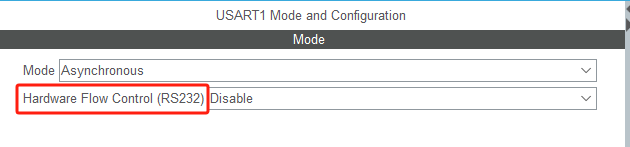
STM32HAL库USART源代码解析及应用
STM32HAL库USART源代码解析 前言STM32CubeIDE配置串口USART和UART的选择使用模式参数设置GPIO配置DMA配置中断配置硬件流控制使能生成代码解析和使用方法串口初始化__UART_HandleTypeDef结构体浅析HAL库代码实际使用方法使用轮询方式发送使用轮询方式接收使用中断方式发送使用中…...

深度剖析 DeepSeek 开源模型部署与应用:策略、权衡与未来走向
在人工智能技术呈指数级发展的当下,大模型已然成为推动各行业变革的核心驱动力。DeepSeek 开源模型以其卓越的性能和灵活的开源特性,吸引了众多企业与开发者的目光。如何高效且合理地部署与运用 DeepSeek 模型,成为释放其巨大潜力的关键所在&…...
