C/C++每日一练(20230223)

目录
1. 数据合并
2. 回文链表
3. 完美矩形
1. 数据合并
题目描述
将两个从小到大排列的一维数组 (维长分别为 m,n , 其中 m,n≤100) 仍按从小到大的排列顺序合并到一个新的一维数组中,输出新的数组.
输入描述
第 1 行一个正整数 m , 表示第一个要合并的一维数组中的元素个数
第 2 行一个正整数 n , 表示第二个要合并的一维数组中的元素个数
第 3 行输入 m 个整数 (每个数用空格分开) , 表示第一个数组元素的值.
第 4 行输入 n 个整数 (每个数用空格分开) , 表示第二个数组元素的值.
输出描述
一行,表示合并后的数据,共 m +n 个数
样例输入
3
4
1 3 5
2 4 6 8样例输出
1 2 3 4 5 6 8代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;void merge(int * a1, int m, int * a2, int n)
{int m1 = m - 1;int n1 = n - 1;for (int i = m + n - 1; i >= 0; i--){if (m1 < 0) a1[i] = a2[n1--];else if (n1 < 0) a1[i] = a1[m1--];else if (a1[m1] < a2[n1]) a1[i] = a2[n1--];else a1[i] = a1[m1--];}
}int main()
{int m;int n;cin >> m;cin >> n;int a1[201];int a2[101];for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) cin >> a1[i];for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin >> a2[i];merge(a1, m, a2, n);for (int i = 0; i < m + n; i++) cout << a1[i] << " ";return 0;
}输入输出:
3
4
1 3 5
2 4 6 8
1 2 3 4 5 6 8
--------------------------------
Process exited after 5.567 seconds with return value 0
请按任意键继续. . .
2. 回文链表
给你一个单链表的头节点 head ,请你判断该链表是否为回文链表。如果是,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:

输入:head = [1,2,2,1] 输出:true
示例 2:

输入:head = [1,2] 输出:false
提示:
- 链表中节点数目在范围
[1, 105]内 0 <= Node.val <= 9
进阶:你能否用 O(n) 时间复杂度和 O(1) 空间复杂度解决此题?
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;struct ListNode
{int val;ListNode *next;ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};class Solution
{
public:bool isPalindrome(ListNode *head){vector<int> v;while (head != NULL){v.push_back(head->val);head = head->next;}for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++){if (v[i] != v[v.size() - i - 1])return false;}return true;}
};int CreateList(ListNode*& p, vector<int>& nums)
{ListNode* q = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));q = p;for (const auto& data : nums){ListNode* temp = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));if (q != NULL) {q->val = data;q->next = temp;q = temp;}}if(q != NULL){q->next = NULL;}}void PrintList(ListNode* p)
{while(p->next != NULL){cout << p->val << "->";p = p->next;}cout << "null" << endl;
}int main()
{Solution s;ListNode* head = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));vector <int> nums = {1,2,3,2,1};CreateList(head, nums); PrintList(head);cout << s.isPalindrome(head) << endl;return 0;}3. 完美矩形
我们有 N 个与坐标轴对齐的矩形, 其中 N > 0, 判断它们是否能精确地覆盖一个矩形区域。
每个矩形用左下角的点和右上角的点的坐标来表示。例如, 一个单位正方形可以表示为 [1,1,2,2]。 ( 左下角的点的坐标为 (1, 1) 以及右上角的点的坐标为 (2, 2) )。

示例 1:
rectangles = [ [1,1,3,3], [3,1,4,2], [3,2,4,4], [1,3,2,4], [2,3,3,4] ]
返回 true。5个矩形一起可以精确地覆盖一个矩形区域。

示例 2:
rectangles = [ [1,1,2,3], [1,3,2,4], [3,1,4,2], [3,2,4,4] ]
返回 false。两个矩形之间有间隔,无法覆盖成一个矩形。

示例 3:
rectangles = [ [1,1,3,3], [3,1,4,2], [1,3,2,4], [3,2,4,4] ]
返回 false。图形顶端留有间隔,无法覆盖成一个矩形。

示例 4:
rectangles = [ [1,1,3,3], [3,1,4,2], [1,3,2,4], [2,2,4,4] ]
返回 false。因为中间有相交区域,虽然形成了矩形,但不是精确覆盖。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;class Solution
{
public:bool isRectangleCover(vector<vector<int>> &ret){set<pair<int, int>> s;int x1 = INT_MAX, y1 = INT_MAX, x2 = INT_MIN, y2 = INT_MIN, area = 0;for (int i = 0; i < ret.size(); ++i){x1 = min(ret[i][0], x1);x2 = max(ret[i][2], x2);y1 = min(ret[i][1], y1);y2 = max(ret[i][3], y2);area += (ret[i][2] - ret[i][0]) * (ret[i][3] - ret[i][1]);if (s.find({ret[i][0], ret[i][1]}) == s.end())s.insert({ret[i][0], ret[i][1]});elses.erase({ret[i][0], ret[i][1]});if (s.find({ret[i][2], ret[i][3]}) == s.end())s.insert({ret[i][2], ret[i][3]});elses.erase({ret[i][2], ret[i][3]});if (s.find({ret[i][0], ret[i][3]}) == s.end())s.insert({ret[i][0], ret[i][3]});elses.erase({ret[i][0], ret[i][3]});if (s.find({ret[i][2], ret[i][1]}) == s.end())s.insert({ret[i][2], ret[i][1]});elses.erase({ret[i][2], ret[i][1]});}if (s.size() != 4 || !s.count({x1, y1}) || !s.count({x1, y2}) || !s.count({x2, y1}) || !s.count({x2, y2}))return false;return area == (x2 - x1) * (y2 - y1);}
};int main()
{Solution s;vector<vector<int>> rect = {{1,1,3,3},{3,1,4,2},{3,2,4,4},{1,3,2,4},{2,3,3,4}};cout << s.isRectangleCover(rect) << endl;rect = {{1,1,2,3}, {1,3,2,4}, {3,1,4,2}, {3,2,4,4}};cout << s.isRectangleCover(rect) << endl;return 0;
}附: 单链表的操作
基本操作:
1、单链表的初始化
2、单链表的创建
3、单链表的插入
4、单链表的删除
5、单链表的取值
6、单链表的查找
7、单链表的判空
8、单链表的求长
9、单链表的清空
10、单链表的销毁
11、单链表的打印
线性表链式存储结构的优点:
1、结点空间可以动态申请和释放;
2、数据元素的逻辑次序靠结点的指针来指示,插入和删除时不需要移动数据元素。
线性表链式存储结构的缺点:
1、存储密度小,每个结点的指针域需额外占用存储空间。当每个结点的数据域所占字节不多时,指针域所占存储空间的比重显得很大;
2、链式存储结构是非随机存取结构。对任一结点的操作都要从头指针依指针链查找到该结点,这增加了算法的复杂度。
以下为单链表的常用操作代码,来源于网络未经测试,仅供参考。
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
struct ListNode
{int data;ListNode* next;//结构体指针
};
void Listprintf(ListNode* phead)
{ListNode* cur=phead;while (cur != NULL){cout << cur->data << "->";cur = cur->next;}
}
void Listpushback(ListNode** pphead, int x)
{ListNode* newnode = new ListNode{ x,NULL };if (*pphead == NULL){*pphead = newnode;}else{ListNode* tail= *pphead;while(tail->next != NULL){tail = tail->next;}tail->next = newnode;}
}
void test_1()
{ListNode* phead = NULL;Listpushback(&phead, 1);Listpushback(&phead, 2);Listpushback(&phead, 3); Listprintf(phead);
}
int main()
{test_1();return 0;
}#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
struct ListNode
{int data;ListNode* next;//结构体指针
};
void Listprintf(ListNode* phead)
{ListNode* cur=phead;while (cur != NULL){cout << cur->data << "->";cur = cur->next;}cout << "NULL" << endl;
}
//尾插
void Listpushback(ListNode** pphead, int x)
{ListNode* newnode = new ListNode{ x,NULL };if (*pphead == NULL){*pphead = newnode;}else{ListNode* tail= *pphead;while(tail->next != NULL){tail = tail->next;}tail->next = newnode;}
}
//头插
void Listpushfront(ListNode** pphead, int x)
{ListNode* newnode = new ListNode{ x,NULL };newnode->next = *pphead;*pphead = newnode;
}
//尾删
void Listpopback(ListNode** pphead)
{if (*pphead == NULL){return;}if ((*pphead)->next == NULL){delete(*pphead);*pphead = NULL;}else{ListNode* tail = *pphead;ListNode* prev = NULL;while (tail->next){prev = tail;tail = tail->next;}delete(tail);tail = NULL;prev->next = NULL;}
}
//头删
void Listpopfront(ListNode** pphead)
{if (*pphead == NULL){return;}else{ListNode* newnode = (*pphead)->next;delete(*pphead);*pphead = newnode;}
}
//查找元素,返回值是地址
ListNode* Listfind(ListNode* phead, int x)
{ListNode* cur = phead;while (cur){if (cur->data == x){return cur;}else{cur = cur->next;}}return NULL;
}
//插入元素,在pos的前一个位置插入
//配合Listfind使用,具体使用见test_insert函数
void Listinsert(ListNode** phead, ListNode* pos, int x)
{ListNode* newnode = new ListNode{ x,NULL };if (*phead == pos){newnode->next = (*phead);*phead = newnode;}else{ListNode* posprev = *phead;while (posprev->next != pos){posprev = posprev->next;}posprev->next = newnode;newnode->next = pos;}
}
//单链表并不适合在前一个位置插入,因为运算较麻烦,会损失效率
//包括c++中为单链表提供的库函数也只有一个insert_after而没有前一个位置插入
//在后一个位置插入相对简单
void Listinsert_after(ListNode** phead, ListNode* pos, int x)
{ListNode* newnode = new ListNode{ x,NULL };newnode->next = pos->next;pos->next = newnode;
}
//删除指定位置的节点
void Listerase(ListNode** pphead, ListNode* pos)
{if (*pphead == pos){*pphead = pos->next;delete(pos);}else{ListNode* prev = *pphead;while (prev->next!=pos){prev = prev->next;}prev->next = pos->next;delete(pos);}
}
//释放链表
void Listdestory(ListNode** pphead)
{ListNode* cur = *pphead;while(cur){ListNode* next = cur->next;delete(cur);cur = next;}*pphead = NULL;
}
void test_insert()
{ListNode* phead = NULL;Listpushback(&phead, 1);Listpushback(&phead, 2);Listpushback(&phead, 3);Listprintf(phead);ListNode* pos = Listfind(phead, 2);if (pos != NULL){Listinsert(&phead, pos, 20);}Listprintf(phead);pos = Listfind(phead, 2);if (pos != NULL){Listinsert_after(&phead, pos, 20);}Listprintf(phead);Listdestory(&phead);
}
void test_find()
{ListNode* phead = NULL;Listpushback(&phead, 1);Listpushback(&phead, 2);Listpushback(&phead, 3);Listprintf(phead);ListNode* pos = Listfind(phead, 2);if (pos != NULL){pos->data = 20;//Listfind不仅能查找,也能借此修改,这也是函数返回地址的原因}Listprintf(phead);Listdestory(&phead);
}
void test_erase()
{ListNode* phead = NULL;Listpushback(&phead, 1);Listpushback(&phead, 2);Listpushback(&phead, 3);Listprintf(phead);ListNode* pos = Listfind(phead, 2);if (pos != NULL){Listerase(&phead, pos);}Listprintf(phead);Listdestory(&phead);
}
void test_pop_and_push()
{ListNode* phead = NULL;Listpushback(&phead, 1);Listpushback(&phead, 2);Listpushback(&phead, 3);Listprintf(phead);Listpushfront(&phead, 1);Listpushfront(&phead, 2);Listpushfront(&phead, 3);Listprintf(phead);Listpopback(&phead);Listpopfront(&phead);Listprintf(phead);Listdestory(&phead);
}
int main()
{//test_pop_and_push();test_find();//test_insert();//test_erase();return 0;
}
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
struct ListNode
{int data;ListNode* next;//结构体指针
};
void Listprintf(ListNode* phead)
{ListNode* cur=phead;while (cur != NULL){cout << cur->data << "->";cur = cur->next;}cout << "NULL" << endl;
}
void Listpushback(ListNode** pphead, int x)
{ListNode* newnode = new ListNode{ x,NULL };if (*pphead == NULL){*pphead = newnode;}else{ListNode* tail= *pphead;while(tail->next != NULL){tail = tail->next;}tail->next = newnode;}
}
ListNode* creatlist()
{ListNode* phead = NULL;Listpushback(&phead, 1);Listpushback(&phead, 9);Listpushback(&phead, 6);Listpushback(&phead, 8);Listpushback(&phead, 6);Listpushback(&phead, 2);Listpushback(&phead, 3);return phead;
}
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int x)
{ListNode* prev = NULL;ListNode* cur = head;while (cur){if (cur->data == x){if (cur == head)//如果第一个元素就是要删除的,进行头删{head = cur->next;delete(cur);cur = head;}else{prev->next = cur->next;delete(cur);cur = prev->next;}}else{prev = cur;cur = cur->next;}}return head;
}
int main()
{ListNode*phead = creatlist();//先创建一条链表Listprintf(phead);phead = removeElements(phead, 6);//删除值为6的节点Listprintf(phead);return 0;
}ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head)
{if (head == NULL){return NULL;}ListNode* prev, * cur, * next;prev = NULL;cur = head;next = cur->next;while (cur){cur->next = prev;//翻转指针//往后迭代prev = cur;cur = next;if (next)//这里是因为当cur指向最后一个节点的时候,next就已经是NULL了,这个时候如果再执行next=next->next则会出现错误{next = next->next;}}return prev;
}ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head)
{ListNode* cur = head;ListNode* newlist = NULL;ListNode* next = NULL;while (cur){next = cur->next;//头插cur->next = newlist;newlist = cur;//往后迭代cur = next;}return newlist;
}ListNode* middleNode(ListNode* head)
{ListNode* slow, * fast;slow = fast = head;while (fast && fast->next){slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;}return slow;
}ListNode* findK(ListNode* head, int k)
{ListNode* fast, * slow;fast = slow = head;while(k--){if (fast == NULL)//如果当fast等于NULL时k仍不为0,则k大于链表长度{return NULL;}fast = fast->next;}while (fast){fast = fast->next;slow = slow->next;}return slow;
}
ListNode* mergeTwoList(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2)
{if (l1 == NULL)//如果一个链表为空,则返回另一个{return l2;}if (l2 == NULL){return l1;}ListNode* head = NULL;ListNode* tail = NULL;while (l1 && l2){if (l1->data < l2->data){if (head == NULL){head = tail =l1;}else{tail->next = l1;tail = l1;}l1 = l1->next;}else{if (head == NULL){head = tail = l2;}else{tail->next = l2;tail = l2;}l2 = l2->next;}}if (l1){tail->next = l1;}if(l2){tail->next = l2;}return head;
}ListNode* mergeTwoList(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2)
{if (l1 == NULL)//如果一个链表为空,则返回另一个{return l2;}if (l2 == NULL){return l1;}ListNode* head = NULL, * tail = NULL;head = tail = new ListNode;//哨兵位的头结点while (l1 && l2){if (l1->data < l2->data){tail->next = l1;tail = l1;l1 = l1->next;}else{tail->next = l2;tail = l2;l2 = l2->next;}}if (l1){tail->next = l1;}if (l2){tail->next = l2;}ListNode* list = head->next;delete(head);return list;
}
ListNode* partition(ListNode* phead, int x)
{ListNode* lesshead, * lesstail, * greaterhead, * greatertail;lesshead = lesstail = new ListNode;//定义一个哨兵位头结点,方便尾插lesstail->next = NULL;greaterhead = greatertail = new ListNode;greatertail->next = NULL;ListNode* cur = phead;while (cur){if (cur->data < x){lesstail->next = cur;lesstail = cur;}else{greatertail->next = cur;greatertail = cur;}cur = cur->next;}lesstail->next = greaterhead->next;greatertail->next = NULL;//举个例子,这样一条链表:1->4->15->5,现在给的x是6,那么排序后15应该在最后,正因如此,重新排序后15的next是没变的,仍然指向5,不手动将next改为NULL,就会成环,无限排下去。ListNode* newhead = lesshead->next;delete(lesshead);delete(greaterhead);return newhead;
}ListNode* middleNode(ListNode* head)
{ListNode* slow, * fast;slow = fast = head;while (fast && fast->next){slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;}return slow;
}
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head)
{ListNode* cur = head;ListNode* newlist = NULL;ListNode* next = NULL;while (cur){next = cur->next;//头插cur->next = newlist;newlist = cur;//往后迭代cur = next;}return newlist;
}
bool check(ListNode* head)
{ListNode* mid = middleNode(head);ListNode* rhead = reverseList(mid);ListNode* curHead = head;ListNode* curRhead = rhead;while(curHead&&curRhead){if (curHead->data != curRhead->data)return false;else{curHead = curHead->next;curRhead = curRhead->next;}}return true;
}相关文章:

C/C++每日一练(20230223)
目录 1. 数据合并 2. 回文链表 3. 完美矩形 1. 数据合并 题目描述 将两个从小到大排列的一维数组 (维长分别为 m,n , 其中 m,n≤100) 仍按从小到大的排列顺序合并到一个新的一维数组中,输出新的数组. 输入描述 第 1 行一个正整数 m , 表示第一个要合并的一维…...
)
c语言中const 是什么意思?(面试)
const关键字使用非常的灵活,在c中,const因位置不同有不同的作用,因情景不同有不同的角色,使用起来也是非常的灵活。 可以定义const常量,具有不可变性。 例如:const int Max100; Max会产生错误; 便于进行类…...

网络工程(三)ensp配置静态路由
配置静态路由 这里选择的路由器是AR2220 因为有三个GE接口 下面说拓扑图 一、定义AR路由ip地址和下一条 AR1system-viewsysname AR1interface g0/0/0ip address 10.0.0.254 8interface g0/0/1ip address 50.0.0.1 8下一条代码[AR1]ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 50.0.0.2AR2 s…...
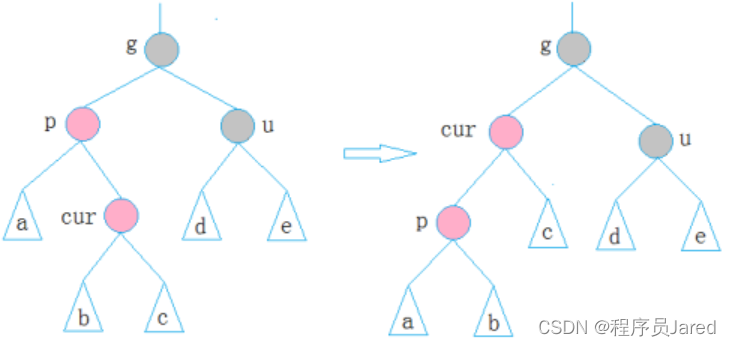
深入浅出C++ ——手撕红黑树
文章目录一、红黑树的概念二、红黑树的性质三、红黑树节点的定义四、红黑树的插入操作五、红黑树的验证五、红黑树的删除六、红黑树与AVL树的比较七、红黑树的应用八、红黑树模拟实现一、红黑树的概念 红黑树,是一种二叉搜索树,但在每个结点上增加一个存…...
Linux服务:Nginx服务重写功能
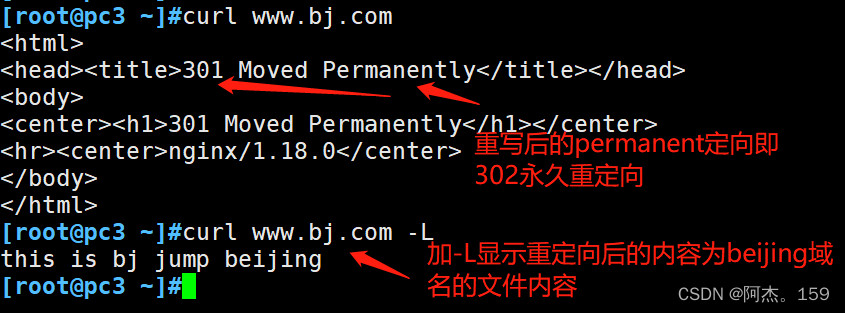
目录 一、重写功能 1、重写功能作用 2、rewrite指令 ①if指令 ②return指令 ③ set指令 ④break指令 3、rewrite标志 ①redirect标志 ②permanent标志 ③break标志 ④last标志 ⑤rewrite标志实验 一、重写功能 1、重写功能作用 重写功能(rewrite)用于实现URL的重…...

3.知识图谱概念和相关技术简介[知识抽取、知识融合、知识推理方法简述],典型应用案例介绍国内落地产品介绍。一份完整的入门指南,带你快速掌握KG知识,芜湖起飞!
1. 知识图谱(KG)的概念 知识图谱(KG)得益于Web的发展(更多的是数据层面),有着来源于KR、NLP、Web、AI多个方面的基因。知识图谱是2012年后的提法,基础还是语义网和本体论。 知识图谱的本质包含: 知识表示——Knowledge Representation基于知识表示的知识库——Knowledge…...

iOS 绿幕技术
绿幕(green screen)技术,又称 chroma key effect,实际上是将图片上指定颜色设置为透明的图形处理技术,这些透明区域也可以被任意背景图片替换。 这种技术在 视频合成中被广泛使用。iOS 中,通过 CoreImage …...
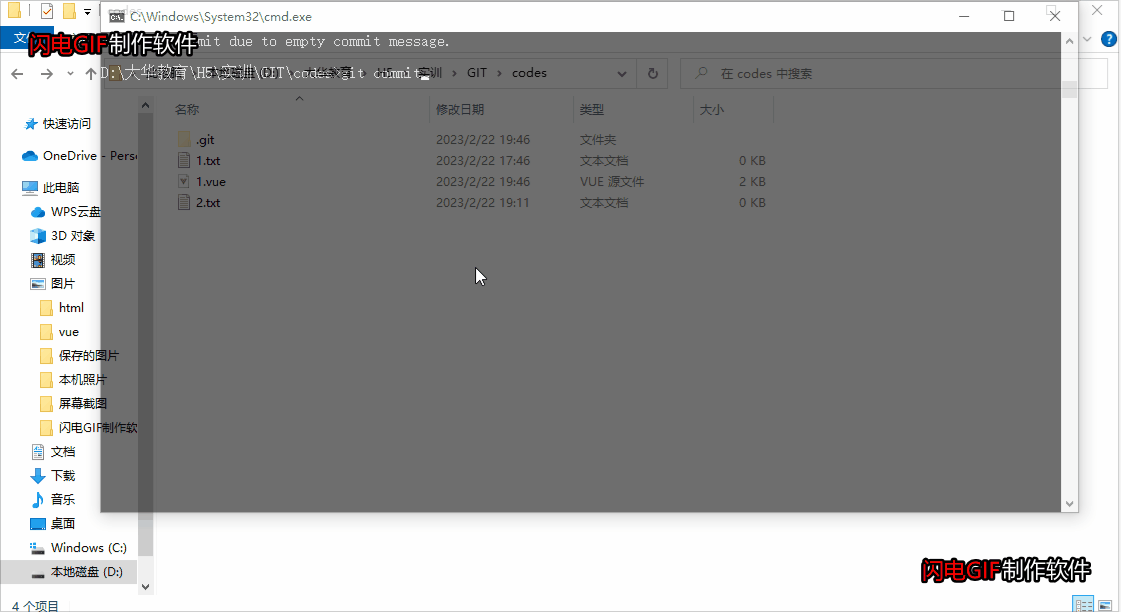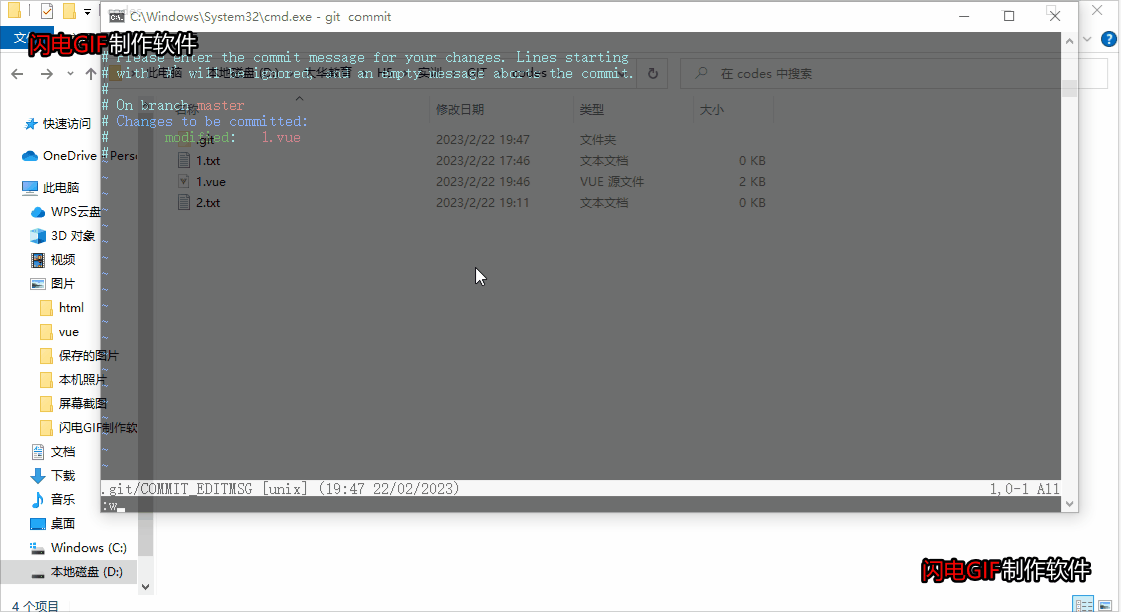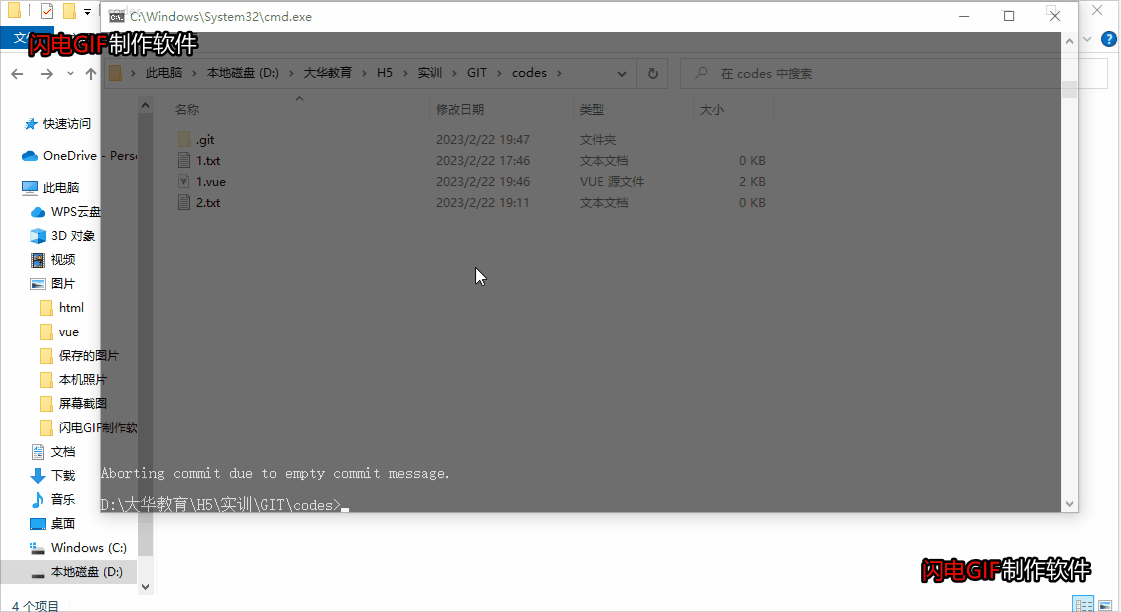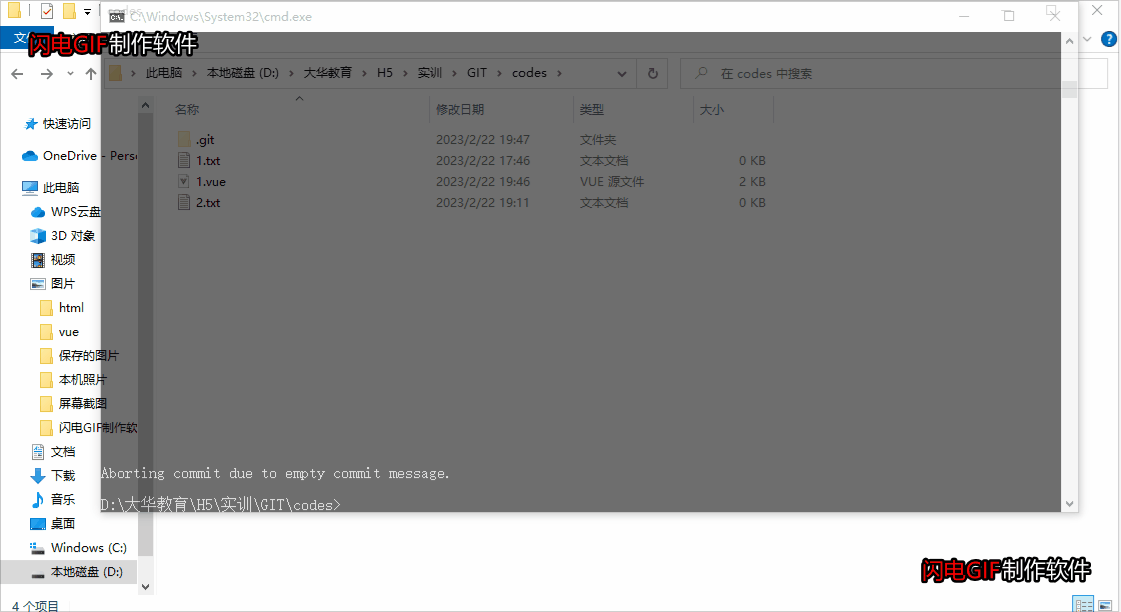
git 的使用方法(上 - 指令)
目录前言:一、Git 是什么?二、SVN与Git的最主要的区别?三、Git 安装四、git 配置1. 创建仓库 - repository2. 配置3. 工作流与基本操作五、Git 的使用流程1. 仓库中创建 1.txt文件2. 查看工作区的文件状态3. 添加工作区文件到暂存区4. 创建版…...

Windows 平台 oracle11g 单机 打补丁(33883353)
一、从oracle官网下载最新补丁包和打包工具 二、 对数据库及软件作全备 略 三、解压p33883353_112040_MSWIN-x86-64.zip 在33883353文件夹中打开README.html 2.1 OPatch Utility You must use the OPatch utility version 11.2.0.3.34 or later to apply this patch. 必须…...

1个寒假能学会多少网络安全技能?
现在可以看到很多标题都声称三个月内就可以转行网络安全领域,并且成为月入15K的网络工程师。那么,这个寒假的时间能学多少网络安全知识?是否能入门网络安全工程师呢? 答案是肯定的。 虽然网络完全知识是一门广泛的学科ÿ…...

六、肺癌检测-训练指标和数据增强
上一篇文章讲了训练过程和tensorboard可视化,这一篇文章记录下训练指标和数据增强的东西。 五、肺癌检测-数据集训练 training.py model.py_wxyczhyza的博客-CSDN博客 一、目标 1. 记录精度、召回率、F1分数 2. 样本均衡和样本随机化 3. 数据增强 二、要点 1…...

儿童饰品发夹发卡出口美国办理什么认证?
亚马逊美国站上传新产品,很多时候都是需要类目审核的,后台给出要求提供认证,产品类目不同,所需要提供的认证证书是不一样,儿童产品需要提交的是CPC认证,玩具,母婴用品,儿童书包&…...

Hive---Hive语法(一)
Hive语法(一) 文章目录Hive语法(一)Hive数据类型基本数据类型(与SQL类似)集合数据类型Hive数据结构数据库操作创建库使用库删除库表操作创建表指定分隔符默认分隔符(可省略 row formatÿ…...

微信小程序日记、微信小程序个人空间、个人日记
一.简述 个人比较喜欢微信小程序,因为小程序所追求的用户体验、代码质量、美观的样式,简单方便丰富的api、样式封装等,同时又与普通的前端开发非常相似,让人很容易就上手。 这篇博客介绍的是一款记录个人/家庭日常记录的微信小程…...
CentOS 8利用Apache安装部署下载服务器
1:部署的目的是做一个类似下面开源镜像网站,把一些软件或者资料上传到服务器上面,减少用户在互联网上下载资料,提高效率,减少病毒。 2:使用下面的命令配置本机的IP地址主机名等信息。后期使用IP地址进行访问…...

【数据结构与算法】顺序表增删查改的实现(动态版本+文件操作)附源码
目录 一.前言 二.顺序表 1.概念及结构 2.顺序表结构体的定义 3.初始化顺序表,销毁顺序表和打印 3.接口 a.尾插 SepListpushback 头插 SepListpushfront b.尾删 SepListpopback 头删 SepListpopfront c.查询 SepListsearch d.修改 SepListmodify 三…...
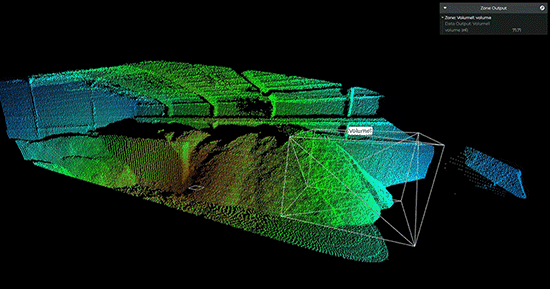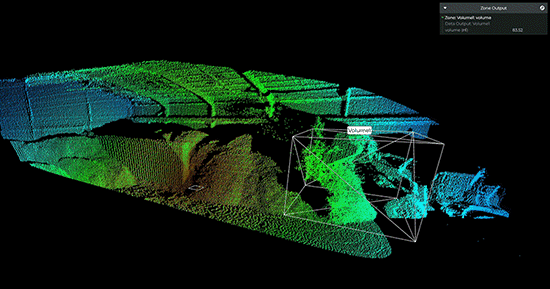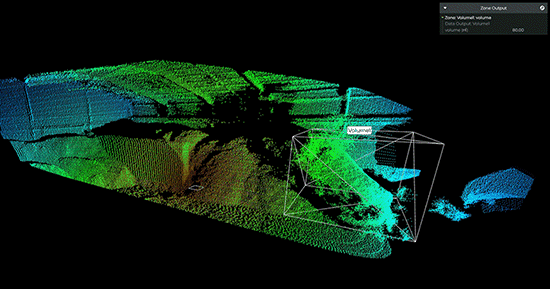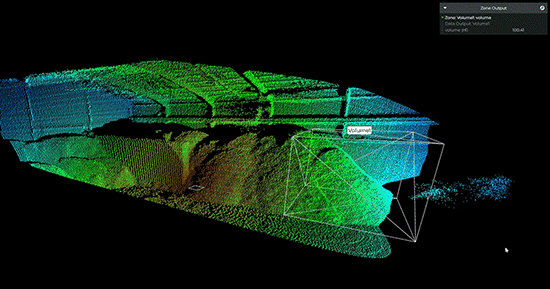
【虹科】基于Lidar的体积监控实现高效的库存管理
迄今为止,很多物料厂家测量库存的结果数据仍然不准确,会存在很大的误差,导致供应链效率低下——这个问题可以通过Lidar技术轻松解决。近年来,全球供应链的脆弱性已经多次得到证明。无论是油轮被困在苏伊士运河,阻塞海峡…...

一口吃不成ChatGPT,复旦版MOSS服务器被挤崩后续
ChatGPT 是目前最先进的 AI,由于 ChatGPT 的训练过程所需算力资源大、标注成本高,此前国内暂未出现对大众开放的同类产品。 适逢ChatGPT概念正火,2 月 21 日,复旦团队发布首个中国版类 ChatGPT 模型「MOSS」,没想到瞬时…...
html初识
HTML认知 文章目录HTML认知语法规范注释标签组成和关系标签的关系标签学习排版系列标签**标题标签****段落标签**换行标签水平线标签文本格式化标签媒体标签图片标签src 目标图片的路径alt 替换文本title 图片的标题width 宽度 / height 高度路径绝对路径相对路径(常…...
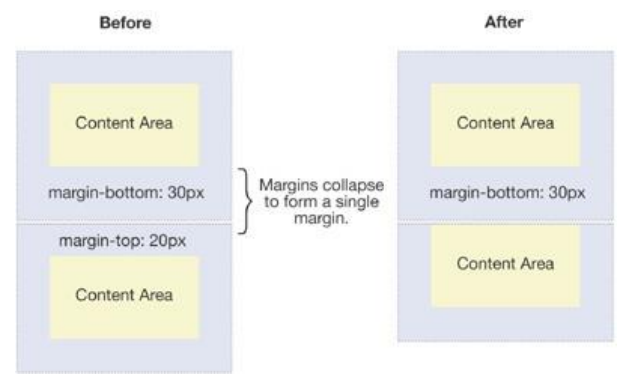
BFC的概念与作用
本篇详细介绍FC的概念,以及BFC的作用:FC的全称是Formatting Context,元素在标准流里面都是属于一个FC的.块级元素的布局属于Block Formatting Context(BFC) -也就是block level box都是在BFC中布局的; 行内…...

反向工程与模型迁移:打造未来商品详情API的可持续创新体系
在电商行业蓬勃发展的当下,商品详情API作为连接电商平台与开发者、商家及用户的关键纽带,其重要性日益凸显。传统商品详情API主要聚焦于商品基本信息(如名称、价格、库存等)的获取与展示,已难以满足市场对个性化、智能…...
)
React Native 导航系统实战(React Navigation)
导航系统实战(React Navigation) React Navigation 是 React Native 应用中最常用的导航库之一,它提供了多种导航模式,如堆栈导航(Stack Navigator)、标签导航(Tab Navigator)和抽屉…...
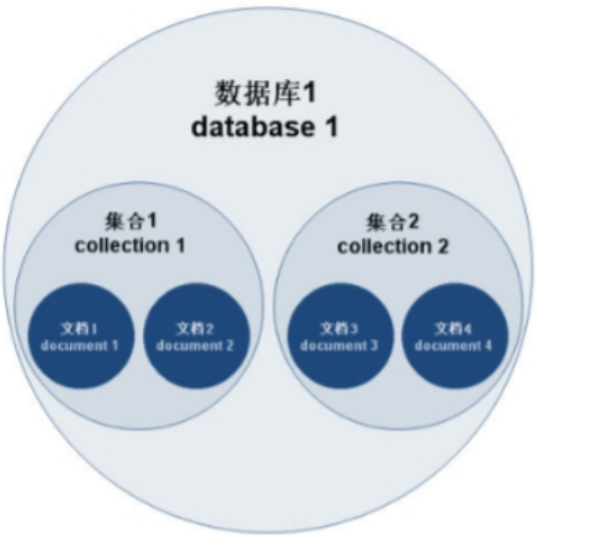
MongoDB学习和应用(高效的非关系型数据库)
一丶 MongoDB简介 对于社交类软件的功能,我们需要对它的功能特点进行分析: 数据量会随着用户数增大而增大读多写少价值较低非好友看不到其动态信息地理位置的查询… 针对以上特点进行分析各大存储工具: mysql:关系型数据库&am…...

基于Uniapp开发HarmonyOS 5.0旅游应用技术实践
一、技术选型背景 1.跨平台优势 Uniapp采用Vue.js框架,支持"一次开发,多端部署",可同步生成HarmonyOS、iOS、Android等多平台应用。 2.鸿蒙特性融合 HarmonyOS 5.0的分布式能力与原子化服务,为旅游应用带来…...

数据库分批入库
今天在工作中,遇到一个问题,就是分批查询的时候,由于批次过大导致出现了一些问题,一下是问题描述和解决方案: 示例: // 假设已有数据列表 dataList 和 PreparedStatement pstmt int batchSize 1000; // …...

scikit-learn机器学习
# 同时添加如下代码, 这样每次环境(kernel)启动的时候只要运行下方代码即可: # Also add the following code, # so that every time the environment (kernel) starts, # just run the following code: import sys sys.path.append(/home/aistudio/external-libraries)机…...
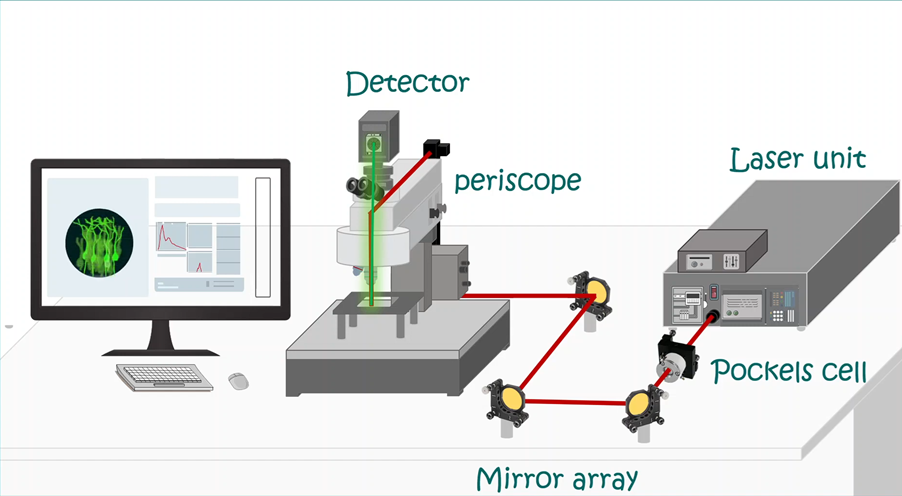
LabVIEW双光子成像系统技术
双光子成像技术的核心特性 双光子成像通过双低能量光子协同激发机制,展现出显著的技术优势: 深层组织穿透能力:适用于活体组织深度成像 高分辨率观测性能:满足微观结构的精细研究需求 低光毒性特点:减少对样本的损伤…...

【从零开始学习JVM | 第四篇】类加载器和双亲委派机制(高频面试题)
前言: 双亲委派机制对于面试这块来说非常重要,在实际开发中也是经常遇见需要打破双亲委派的需求,今天我们一起来探索一下什么是双亲委派机制,在此之前我们先介绍一下类的加载器。 目录 编辑 前言: 类加载器 1. …...
android RelativeLayout布局
<?xml version"1.0" encoding"utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android"http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"android:layout_width"match_parent"android:layout_height"match_parent"android:gravity&…...

pycharm 设置环境出错
pycharm 设置环境出错 pycharm 新建项目,设置虚拟环境,出错 pycharm 出错 Cannot open Local Failed to start [powershell.exe, -NoExit, -ExecutionPolicy, Bypass, -File, C:\Program Files\JetBrains\PyCharm 2024.1.3\plugins\terminal\shell-int…...
