STL常用遍历,查找,算法
目录
1.遍历算法
1.1for_earch
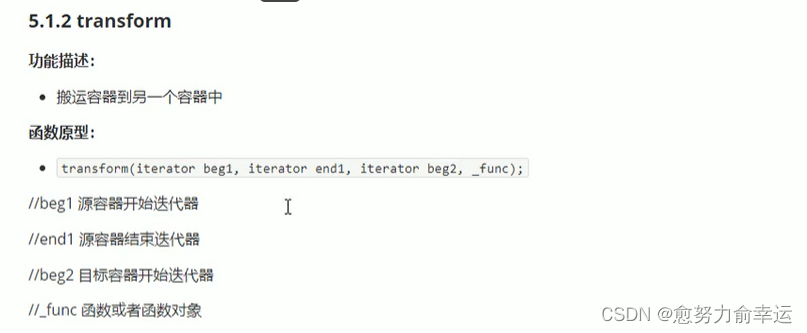
1.2transform
2.常用查找算法
2.1find,返回值是迭代器
2.1.1查找内置数据类型
2.1.2查找自定义数据类型
2.2fin_if 按条件查找元素
2.2.1查找内置的数据类型
2.2.2查找内置数据类型
2.3查找相邻元素adjeacent_find
2.4查找指定元素是否存在binarary_search
2.5统计元素的个数count
2.5.1统计内置数据类型
2.5.2统计自定义数据类型
2.6按条件统计元素个数
2.6.1统计内置数据类型
2.6.2统计自定义的数据类型
3.常用排序算法
3.1sort
1.遍历算法

1.1for_earch

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
//常用遍历算法 for_each//利用普通函数实现
void print01(int val)
{cout << val << " ";
}//仿函数(函数对象)本身是个类。不是一个函数
class print02
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};
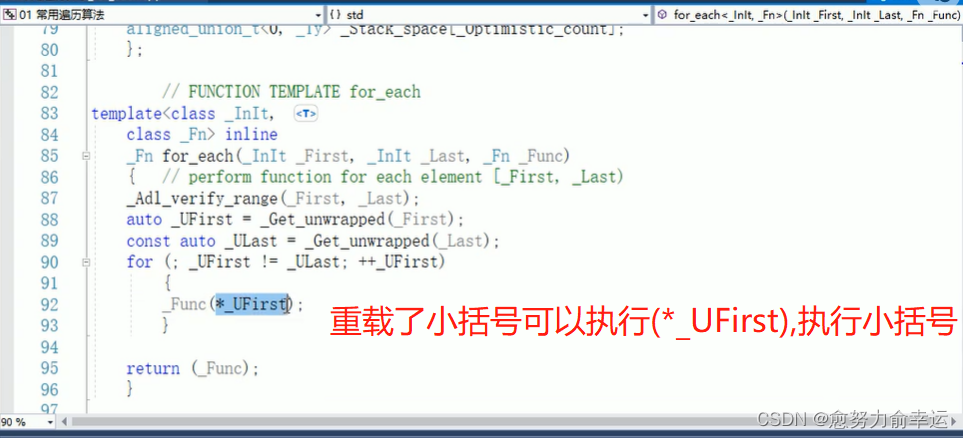
void test01()
{vector<int>v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print01);//第三个位置,普通函数是把函数名放过来cout << endl;for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print02());//第三个位置需要传入函数对象//类名加小括号,创建出匿名对象
}
int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}
1.2transform
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
//常用遍历算法 transform//仿函数(函数对象)本身是个类。不是一个函数
class Transform
{
public://搬运过程中把每个元素取出来在返回回去,由于操作的是int型,所以返回intint operator()(int val){return val+100;//+100在搬到容器中}
};
class Myprint
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};
void test01()
{vector<int>v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}vector<int>vTarget;//目标容器vTarget.resize(v.size());//目标容器 需要提前开辟空间,不然报错transform(v.begin(), v.end(), vTarget.begin(), Transform());//最后一个位置函数对象for_each(vTarget.begin(), vTarget.end(), Myprint());//最后一个位置函数对象cout << endl;
}
int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}2.常用查找算法

2.1find,返回值是迭代器

2.1.1查找内置数据类型
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
//常用查找算法
//find//查找 内置数据类型
void test01()
{vector<int>v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}//查找 容器中 是否有 5 这个元素vector<int>::iterator it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 50);if (it == v.end()){cout << "没有找到!" << endl;}else{cout << "找到:" << *it << endl;}
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}2.1.2查找自定义数据类型
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
//常用查找算法
//findclass Person
{
public:Person(string name, int age){m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}//重载== 让底层find知道如何对比person数据类型bool operator ==(const Person& p)//const防止修改p{if (this->m_Name == p.m_Name && this->m_Age == p.m_Age){return true;}else{return false;}}string m_Name;int m_Age;
};
//查找 自定义数据类型
void test02()
{vector<Person>v;//创建数据Person p1("aaa", 10);Person p2("bbb", 20);Person p3("ccc", 30);Person p4("ddd", 40);//放到容器中v.push_back(p1);v.push_back(p2);v.push_back(p3);v.push_back(p4);Person p("bbb", 20);//查找是否有和p一样的vector<Person>::iterator it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), p);if (it == v.end()){cout << "没有找到" << endl;}else{cout << "找到元素:姓名:" << (*it).m_Name << " 年龄:" << it->m_Age << endl;}}
int main()
{test02();system("pause");return 0;
}2.2fin_if 按条件查找元素

2.2.1查找内置的数据类型
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
//常用查找算法
//find_if//1.查找内置数据类型
class GreaterFive
{
public://谓词返回boolbool operator()(int val)//find_if的底层也是取出每个元素并解引用,放到重载小括号里去操纵{return val > 5;//大于5 的时候就返回真}
};
void test01()
{vector<int>v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}//返回一个迭代器vector<int>::iterator it=find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), GreaterFive());//第三个位置是匿名函数对象if (it == v.end()){cout << "没有找到大于5的元素" << endl;}else{cout << "找到大于5的数字为:" << *it << endl;}
}//2.查找自定义数据类型int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}2.2.2查找内置数据类型
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
//常用查找算法
//find_if//2.查找自定义数据类型
class Person
{
public:Person(string name, int age){m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}string m_Name;int m_Age;
};
class Great20
{
public:bool operator()(Person &p)//每个数据类型都是Perosn的数据类型用引用的方式传进来{return p.m_Age > 20;}
};
bool G2(Person& p)
{return p.m_Age > 20;
}
void test02()
{vector<Person>v;//创建数据Person p1("aaa", 10);Person p2("bbb", 20);Person p3("ccc", 30);Person p4("ddd", 40);v.push_back(p1);v.push_back(p2);v.push_back(p3);v.push_back(p4);//找年龄大于20的人vector<Person>::iterator it = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Great20());if (it == v.end()){cout << "没有找到" << endl;}else{cout << "找到姓名:" << (*it).m_Name << "年龄:" << it->m_Age << endl;}vector<Person>::iterator it1 = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Great20());if (it1 == v.end()){cout << "没有找到" << endl;}else{cout << "找到姓名:" << (*it1).m_Name << "年龄:" << it1->m_Age << endl;}
}
int main()
{test02();system("pause");return 0;
}2.3查找相邻元素adjeacent_find

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
//常用查找算法
//adjacent_find
void test01()
{vector<int>v;v.push_back(0);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(0);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(1);v.push_back(4);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(3);vector<int>::iterator it=adjacent_find(v.begin(), v.end());if (it == v.end()){cout << "未找到相邻重复元素" << endl;}else{cout << "找到相邻重复元素:" << *it << endl;}
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}2.4查找指定元素是否存在binarary_search

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
//常用查找算法
//binary_search 二分查找法,在无序的序列中不可以用
void test01()
{vector<int>v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}//查找容器中是否有9//注意容器必须是有序的序列//如果无序结果未知bool ret = binary_search(v.begin(), v.end(), 9);if (ret){cout << "找到了元素" << endl;}else{cout << "没找到" << endl;}
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}2.5统计元素的个数count

2.5.1统计内置数据类型
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
//常用查找算法
//count//1.统计内置数据类型
void test01()
{vector<int>v;v.push_back(10);v.push_back(40);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(40);v.push_back(20);v.push_back(40);int num=count(v.begin(), v.end(), 40);cout << "40的元素个数为:" <<num<< endl;int num1 = count(v.begin(), v.end(), 1);cout << "1的元素个数为:" << num1 << endl;//输出0
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}2.5.2统计自定义数据类型
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
//常用查找算法
//count//2.统计自定义数据类型
class Person
{
public:Person(string name, int age){m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}bool operator==(const Person& p)//底层要加const,{if (m_Age==p.m_Age){return true;}else{return false;}}string m_Name;int m_Age;
};
void test02()
{vector<Person>v;Person p1("刘备", 35);Person p2("关羽", 35);Person p3("张飞", 35);Person p4("赵云", 30);Person p5("曹操", 40);//将人员插入到容器中v.push_back(p1);v.push_back(p2);v.push_back(p3);v.push_back(p4);v.push_back(p5);Person p("诸葛亮", 35);//统计与诸葛亮年龄相同的有几人int num = count(v.begin(), v.end(), p);cout << "和诸葛亮同岁数的人员个数为:" << num << endl;
}int main()
{test02();system("pause");return 0;
}2.6按条件统计元素个数

2.6.1统计内置数据类型
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
//常用查找算法
//count_if//1.统计内置数据类型
class Greater20
{
public:bool operator()(int val){return val > 20;}
};
void test01()
{vector<int>v;v.push_back(10);v.push_back(40);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(20);v.push_back(40);v.push_back(20);int num = count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Greater20());cout << "大于20的元素个数为:" << num << endl;
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}2.6.2统计自定义的数据类型
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
//常用查找算法
//count_if//2.统计自定义的数据类型
class Person
{
public:Person(string name, int age){m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}string m_Name;int m_Age;
};class AgeGreater20
{
public:bool operator()(Person &p){return p.m_Age > 20;}
};void test02()
{vector<Person>v;Person p1("刘备", 35);Person p2("关羽", 35);Person p3("张飞", 35);Person p4("赵云", 40);Person p5("曹操", 20);v.push_back(p1);v.push_back(p2);v.push_back(p3);v.push_back(p4);v.push_back(p5);//统计 大于20岁人员个数int num = count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), AgeGreater20());cout << "大于20的元素个数为:" << num << endl;
}int main()
{test02();system("pause");return 0;
}3.常用排序算法

3.1sort

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
//常用排序算法
//sort
void myPrint(int val)
{cout << val << " ";
}
void test01()
{vector<int>v;v.push_back(10);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(50);v.push_back(20);v.push_back(40);//利用sort进行升序,默认情况下升序sort(v.begin(), v.end());for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;//改变为降序sort(v.begin(), v.end(), greater<int>());//greater<int>()内建函数对象,需要包含functional头文件,编译器高的不包含functional头文件也不会出错for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++){cout << v[i] << " ";}cout << endl;
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}bool compare(int a,int b)
{ return a < b; //升序排列,如果改为return a>b,则为降序
}
int a[20]={2,4,1,23,5,76,0,43,24,65},i;
for(i=0;i<20;i++) cout<< a[i]<< endl;
sort(a,a+20,compare);
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<stack>
#include<algorithm>
#include<bitset>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<map>struct Point
{int x;int y;//Point(int xx, int yy) :x(xx), y(yy) {};bool operator < (Point& p) {if (x != p.x) {return x < p.x;} else {return y < p.y;}}
};int main()
{vector<Point> p;p.push_back(Point{ 1,2 });p.push_back(Point{ 1,3 });Point p1;p1.x = 2;p1.y = 1;p.push_back(p1);sort(p.begin(), p.end());for (int i = 0; i < p.size(); i++) {cout << p[i].x << " " << p[i].y << endl;}/*输出:1 21 32 1*/system("pause");return 0;
}--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------struct Point
{int x;int y;
};
bool Cmp(Point& p1, Point& p2) {if (p1.x != p2.x) {return p1.x < p2.x;} else {return p1.y < p2.y;}
}int main()
{vector<Point> p;p.push_back(Point{ 1,2 });p.push_back(Point{ 1,3 });Point p1;p1.x = 2;p1.y = 1;p.push_back(p1);sort(p.begin(), p.end(),Cmp);for (int i = 0; i < p.size(); i++) {cout << p[i].x << " " << p[i].y << endl;}/*输出:1 21 32 1*/system("pause");return 0;
}
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------struct Point
{int x;int y;
};
class cmp
{
public:bool operator()(Point& p1, Point& p2)const {if (p1.x != p2.x) {return p1.x < p2.x;} else {return p1.y < p2.y;}}
};int main()
{vector<Point> p;p.push_back(Point{ 1,2 });p.push_back(Point{ 1,3 });Point p1;p1.x = 2;p1.y = 1;p.push_back(p1);sort(p.begin(), p.end(), cmp());for (int i = 0; i < p.size(); i++) {cout << p[i].x << " " << p[i].y << endl;}/*输出:1 21 32 1*/system("pause");return 0;
}相关文章:

STL常用遍历,查找,算法
目录 1.遍历算法 1.1for_earch 1.2transform 2.常用查找算法 2.1find,返回值是迭代器 2.1.1查找内置数据类型 2.1.2查找自定义数据类型 2.2fin_if 按条件查找元素 2.2.1查找内置的数据类型 2.2.2查找内置数据类型 2.3查找相邻元素adjeacent_find 2.4查找指…...
)
BCC源码内容概览(1)
接前一篇文章:BCC源码编译和安装 本文参考官网中的Contents部分的介绍。 BCC源码根目录的文件,其中一些是同时包含C和Python的单个文件,另一些是.c和.py的成对文件,还有一些是目录。 跟踪(Tracing) exam…...
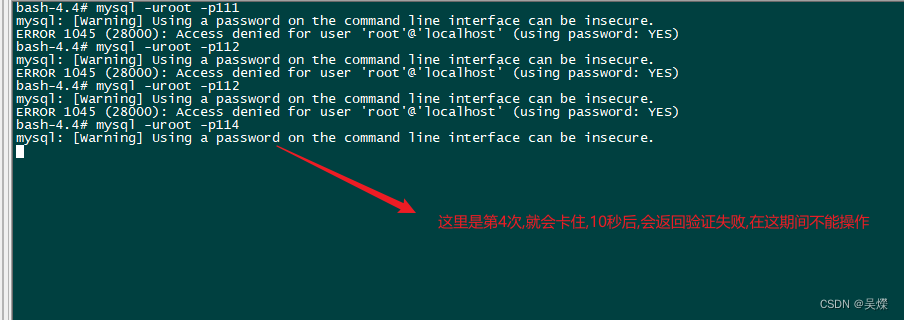
mysql限制用户登录失败次数,限制时间
mysql用户登录限制设置 mysql 需要进行用户登录次数限制,当使用密码登录超过 3 次认证链接失败之后,登录锁住一段时间,禁止登录这里使用的 mysql: 8.1.0 这种方式不用重启数据库. 配置: 首先进入到 mysql 命令行:然后需要安装两个插件: 在 mysql 命令行中执行: mysql> INS…...
)
从利用Arthas排查线上Fastjson问题到Java动态字节码技术(下)
上一篇从Arthas的源码引出了Java动态字节码技术,那么这一篇就从几种Java字节码技术出发,看看Arthas是如何通过动态字节码技术做到无侵入的源码增强; Java大部分情况下都是解释执行的,也就是解释.class文件,所以如果我们…...

Ubuntu中安装Anaconda 如何将 路径导入为全局变量
第一步:将你的anaconda 路径复制下来,在终端输入对应路径。 echo export PATH"/home/你的用户名/anaconda3/bin:$PATH" >> ~/.bashrc 第二步:在终端输入下面命令或者重启系统。 source ~/.bashrc 在对应的anaconda安装目…...
【QT】Qt的随身笔记(持续更新...)
目录 Qt 获取当前电脑桌面的路径Qt 获取当前程序运行路径Qt 创建新的文本文件txt,并写入内容如何向QPlainTextEdit 写入内容QTimerQMessageBox的使用QLatin1StringQLayoutC在c头文件中写#include类的头文件与直接写class加类名有何区别mutable关键字前向声明 QFontQ…...
【LeetCode-简单题】589. N 叉树的前序遍历
文章目录 题目方法一:单循环栈做法方法二:递归 题目 方法一:单循环栈做法 关键在于子节点的入栈顺序,决定了子节点的出栈顺序, 因为是前序遍历 所以压栈顺序先让右边的入栈 依次往左 这样左边的节点会在栈顶 这样下次…...

Linphone3.5.2 ARM RV1109音视频对讲开发记录
Linphone3.5.2 ARM RV1109音视频对讲开发记录 说明 这是一份事后记录,主要记录的几个核心关键点,有可能很多细节没有记上,主要是方便后面自己再找回来! 版本 3.5.2 一些原因选的是这样一个旧的版本! 新的开发最好选新一些的版…...
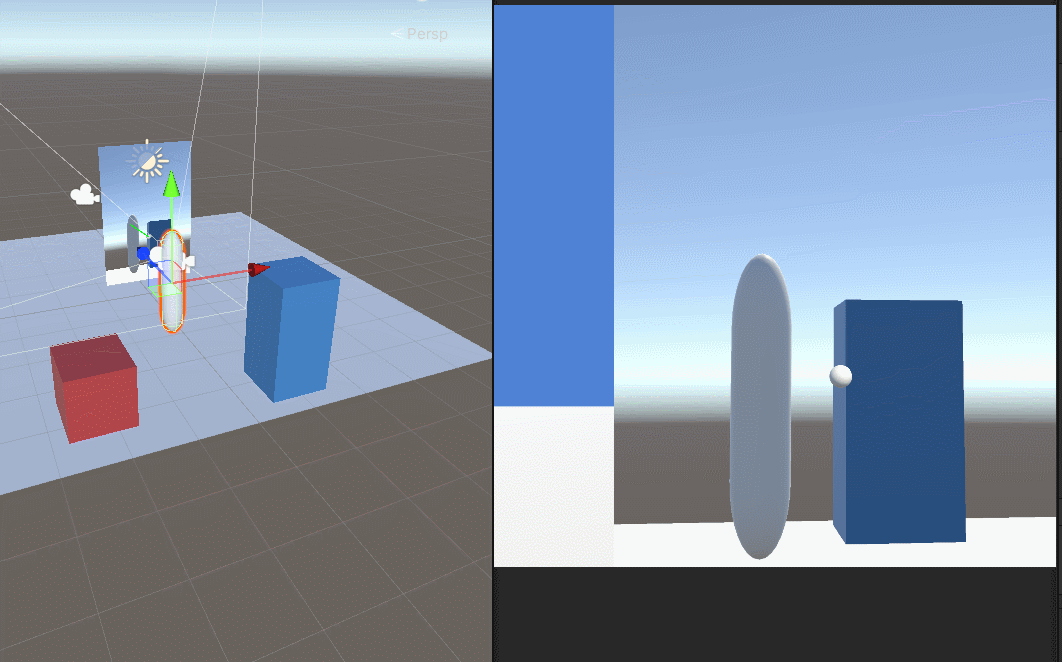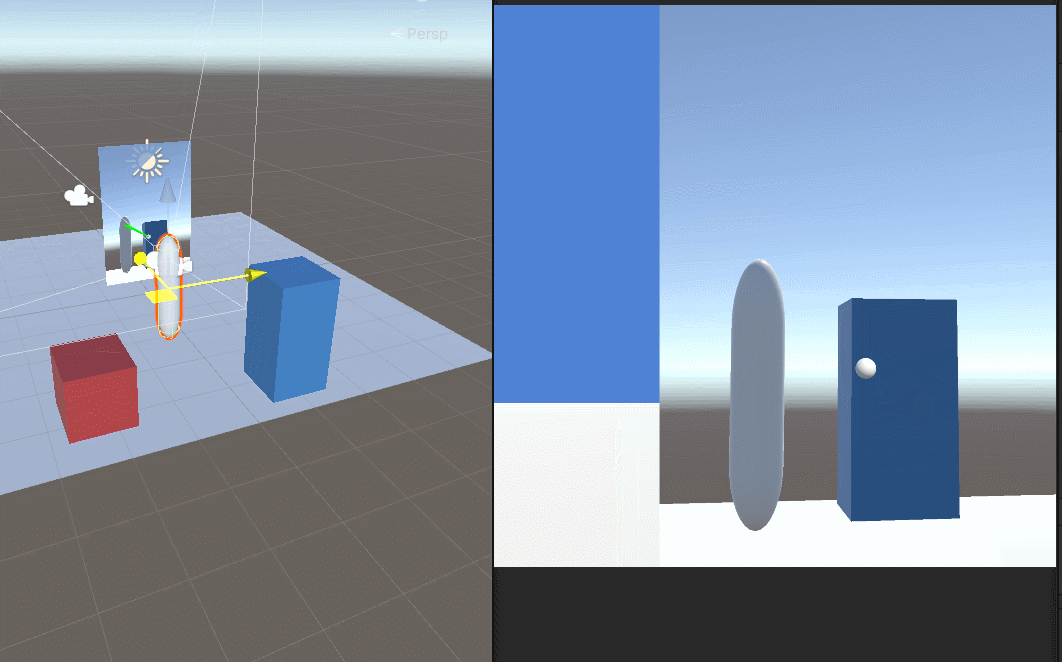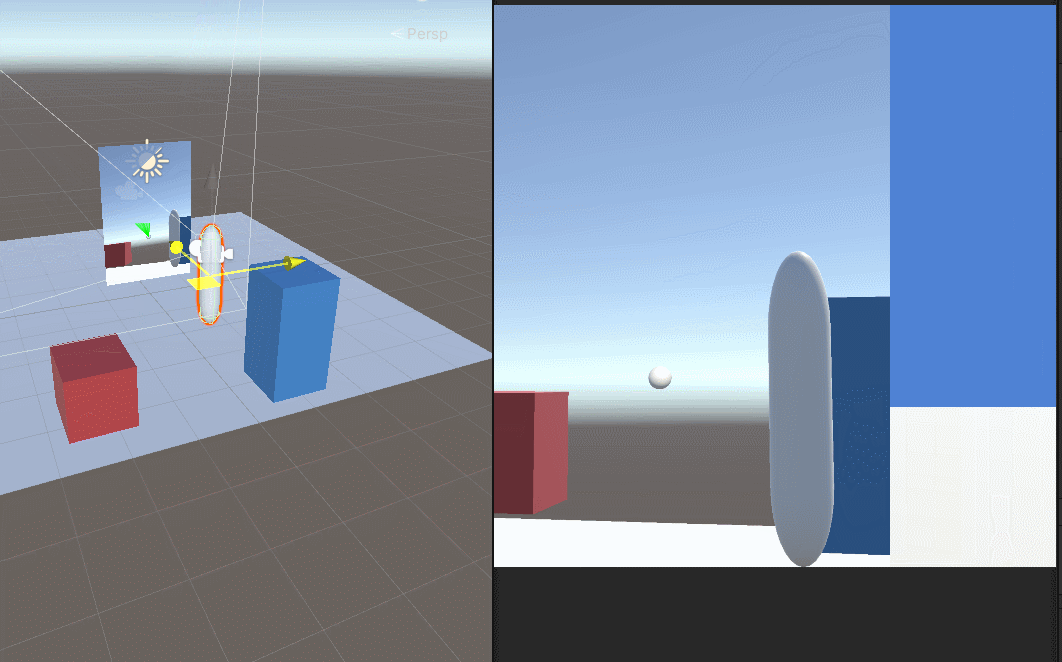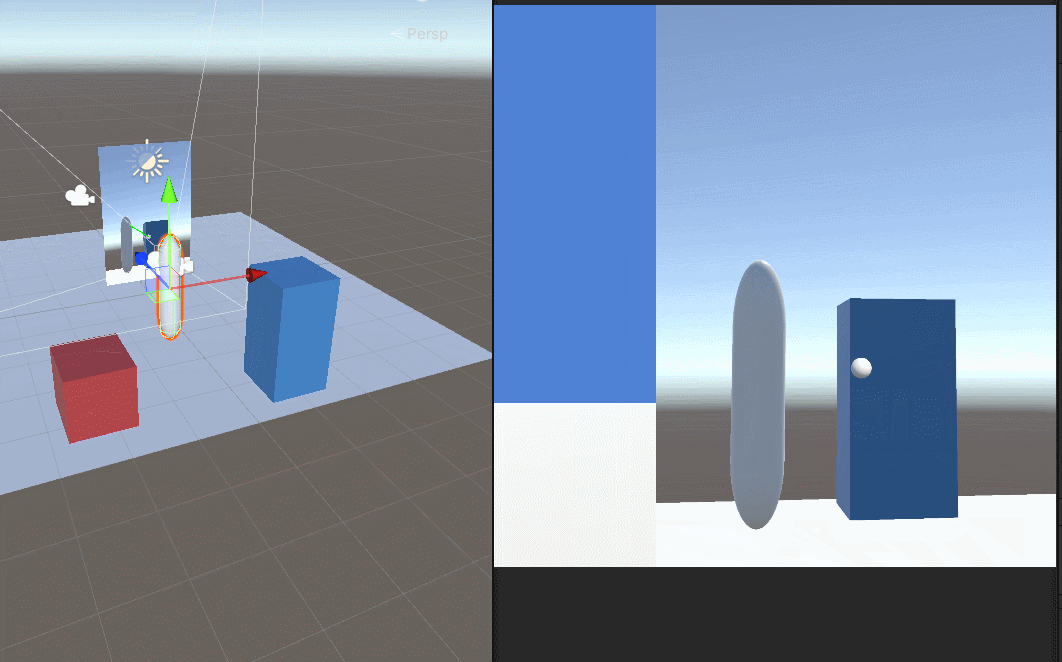
Unity用相机实现的镜子效果
首先登场 场景中的元素 mirror是镜子,挂着我们的脚本,Quad是一个面片。Camera是用来生成RenderTexture给面片的。里面的test1是我用来调试位置的球。 镜子size是大小,x是-2,为了反转一下贴图 相机直接可以禁用掉,用…...
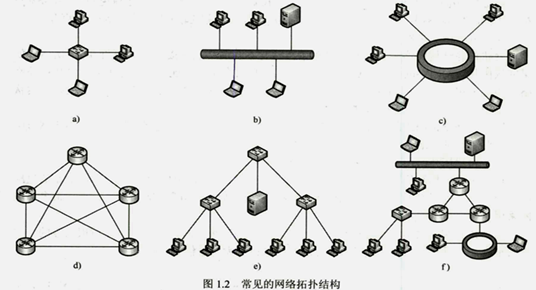
计算机网络分类
按照覆盖范围分类 (1)个域网:通常覆盖范围在1~10m。 (2)局域网:通常覆盖范围在10m~1km。 (3)城域网:覆盖范围通常在5~50 km 。 &…...
AI AIgents时代 - (三.) AutoGPT和AgentGPT
前两篇讲解了Agent的原理和组件,这节我将给大家介绍两个agent项目,给出它们的工作原理和区别,并教大家亲手尝试使用 Agents🎉 🟢 AutoGPT🤖️ 我们的老朋友,之前文章也专门写过。AutoGPT 是一…...

Jmeter接口自动化和Python接口自动化,如何选择?
选择Jmeter或Python进行接口自动化测试取决于您的具体需求和环境。以下是一些可以考虑的因素: 1. 语言熟悉度:如果您对Java更熟悉,那么Jmeter可能是更好的选择。而如果您的团队或个人对Python更熟悉,那么Python可能是更好的选择。…...

Sqilte3初步教程
文章目录 安装创建数据库创建和删除表插入行数据 安装 Windows下安装,首先到下载页面,下载Windows安装软件,一般是 sqlite-dll-win32-*.zip sqlite-tools-win32-*.zip下载之后将其内容解压到同一个文件夹下,我把它们都放在了D:\…...

详解Python中的json库
目录 1. json简介2. dumps/loads3. dump/load4. jsonl格式 1. json简介 JSON(JavaScript Object Notation)是一种轻量级的数据交换格式,用于在不同应用程序之间传递数据。它是一种文本格式,易于阅读和编写,同时也易于…...

【Spring Boot】Spring Boot源码解读与原理剖析
这里写目录标题 前言精进Spring Boot首选读物“小册”变“大书”,彻底弄懂Spring Boot全方位配套资源,学不会来找我!技术新赛道,2023领先抢跑 前言 承载着作者的厚望,掘金爆火小册同名读物《Spring Boot源码解读与原理…...
)
C++学习(1)
一、C概述(了解) C在C语言的基础上添加了面向对象编程和泛型编程的支持 二、helloword程序(掌握) #define _CET_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS//在开发软件visual studio编译 c文件时, visual studio认为strcpy,scanf等函数不安全的导致报…...
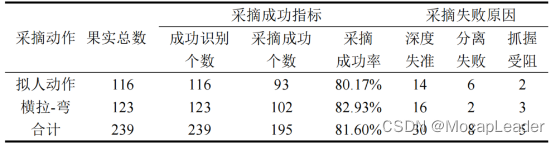
机器人如何有效采摘苹果?
摘要:本文利用动捕数据构建拟人运动模型,对比观察两种苹果采摘模式,并对系统性能进行全面评估,为提高机器人采摘效率提供创新方法。 近期,一项关于苹果采摘机器人的有趣研究—— "Design and evaluation of a rob…...
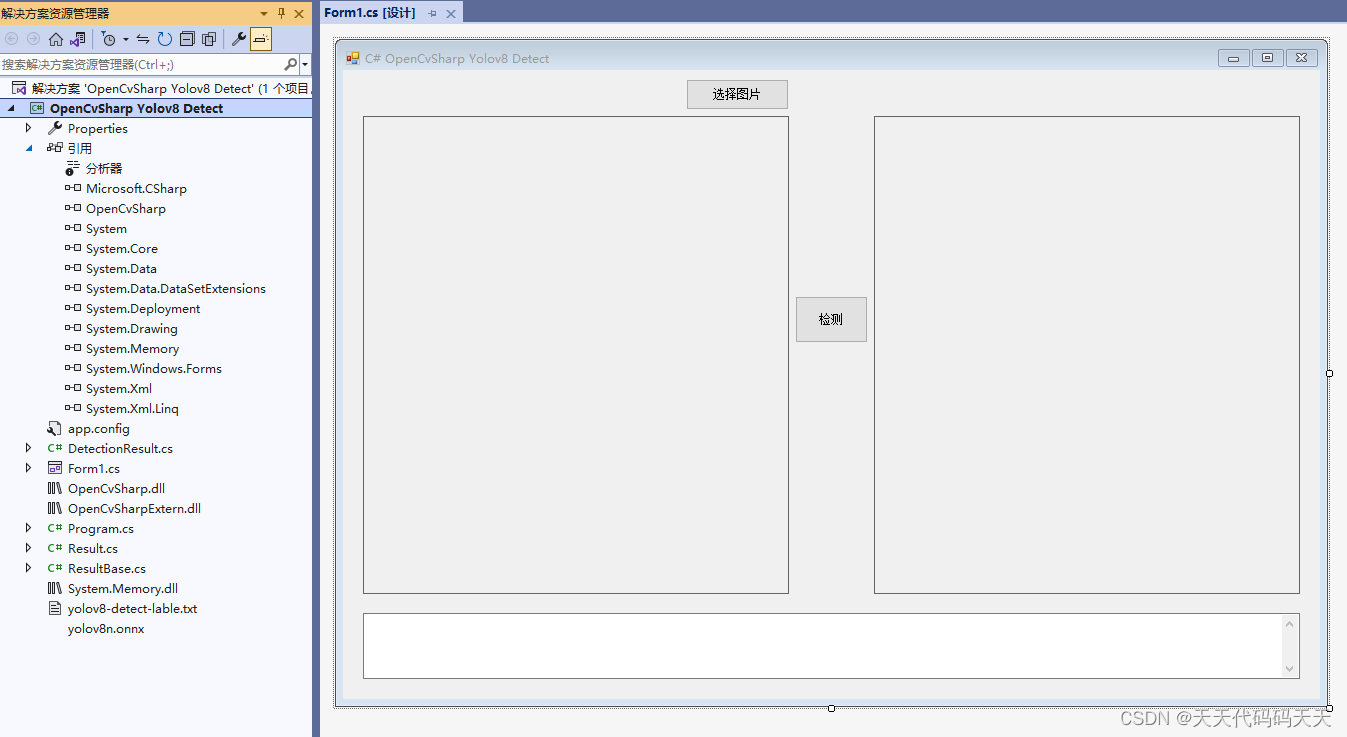
C# OpenCvSharp Yolov8 Detect 目标检测
效果 项目 代码 using OpenCvSharp; using OpenCvSharp.Dnn; using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Data; using System.Drawing; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Windows.Forms;namespace Open…...

rust数组
一、定义数组 (一)一维数组 1.指定所有元素 语法格式 let variable_name: [dataType; size] [value1,value2,value3];例如 let arr: [i32; 4] [10,20,30,40];2.指定初始值和长度 所有元素具有相同的值 语法格式 let variable_name: [dataType; siz…...

ubuntu | 安装NVIDIA套件:驱动、CUDA、cuDNN
CUDA 查看支持最高的cuda版本 nvidia-smiCUDA Version:12.2 区官网下在12.2.x最新的版本即可CUDA Toolkit Archive | NVIDIA Developer 下载安装 wget https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/12.2.2/local_installers/cuda_12.2.2_535.104.05_linux.run sudo…...

手游刚开服就被攻击怎么办?如何防御DDoS?
开服初期是手游最脆弱的阶段,极易成为DDoS攻击的目标。一旦遭遇攻击,可能导致服务器瘫痪、玩家流失,甚至造成巨大经济损失。本文为开发者提供一套简洁有效的应急与防御方案,帮助快速应对并构建长期防护体系。 一、遭遇攻击的紧急应…...

TDengine 快速体验(Docker 镜像方式)
简介 TDengine 可以通过安装包、Docker 镜像 及云服务快速体验 TDengine 的功能,本节首先介绍如何通过 Docker 快速体验 TDengine,然后介绍如何在 Docker 环境下体验 TDengine 的写入和查询功能。如果你不熟悉 Docker,请使用 安装包的方式快…...
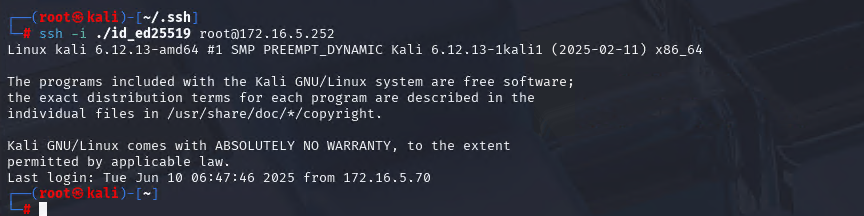
Xshell远程连接Kali(默认 | 私钥)Note版
前言:xshell远程连接,私钥连接和常规默认连接 任务一 开启ssh服务 service ssh status //查看ssh服务状态 service ssh start //开启ssh服务 update-rc.d ssh enable //开启自启动ssh服务 任务二 修改配置文件 vi /etc/ssh/ssh_config //第一…...

前端倒计时误差!
提示:记录工作中遇到的需求及解决办法 文章目录 前言一、误差从何而来?二、五大解决方案1. 动态校准法(基础版)2. Web Worker 计时3. 服务器时间同步4. Performance API 高精度计时5. 页面可见性API优化三、生产环境最佳实践四、终极解决方案架构前言 前几天听说公司某个项…...

【ROS】Nav2源码之nav2_behavior_tree-行为树节点列表
1、行为树节点分类 在 Nav2(Navigation2)的行为树框架中,行为树节点插件按照功能分为 Action(动作节点)、Condition(条件节点)、Control(控制节点) 和 Decorator(装饰节点) 四类。 1.1 动作节点 Action 执行具体的机器人操作或任务,直接与硬件、传感器或外部系统…...

使用van-uploader 的UI组件,结合vue2如何实现图片上传组件的封装
以下是基于 vant-ui(适配 Vue2 版本 )实现截图中照片上传预览、删除功能,并封装成可复用组件的完整代码,包含样式和逻辑实现,可直接在 Vue2 项目中使用: 1. 封装的图片上传组件 ImageUploader.vue <te…...
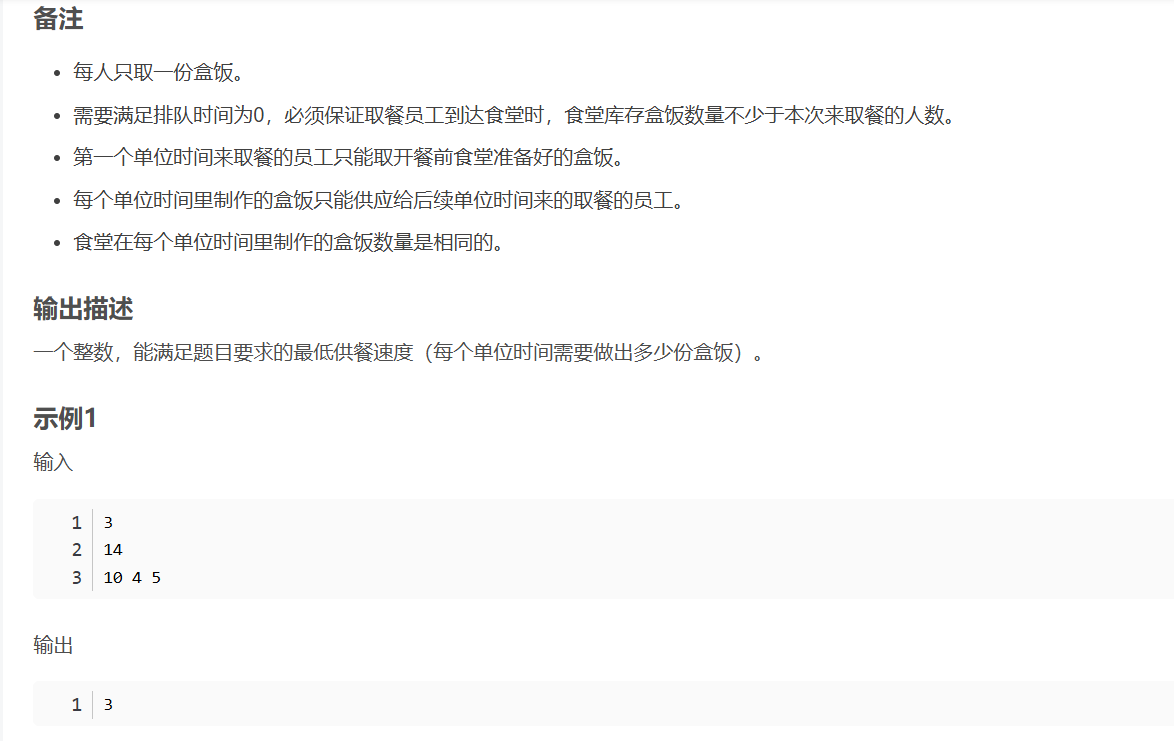
华为OD机试-食堂供餐-二分法
import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Scanner;public class DemoTest3 {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner in new Scanner(System.in);// 注意 hasNext 和 hasNextLine 的区别while (in.hasNextLine()) { // 注意 while 处理多个 caseint a in.nextIn…...
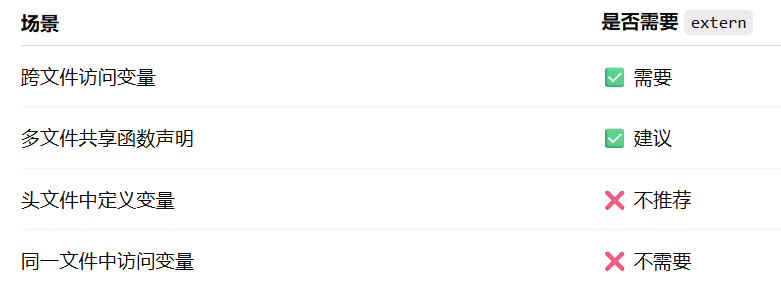
深入解析C++中的extern关键字:跨文件共享变量与函数的终极指南
🚀 C extern 关键字深度解析:跨文件编程的终极指南 📅 更新时间:2025年6月5日 🏷️ 标签:C | extern关键字 | 多文件编程 | 链接与声明 | 现代C 文章目录 前言🔥一、extern 是什么?&…...
ABAP设计模式之---“简单设计原则(Simple Design)”
“Simple Design”(简单设计)是软件开发中的一个重要理念,倡导以最简单的方式实现软件功能,以确保代码清晰易懂、易维护,并在项目需求变化时能够快速适应。 其核心目标是避免复杂和过度设计,遵循“让事情保…...

中医有效性探讨
文章目录 西医是如何发展到以生物化学为药理基础的现代医学?传统医学奠基期(远古 - 17 世纪)近代医学转型期(17 世纪 - 19 世纪末)现代医学成熟期(20世纪至今) 中医的源远流长和一脉相承远古至…...
