Kubernetes 通过 Deployment 部署Jupyterlab
概要
在Kubernetes上部署jupyterlab服务,链接Kubernetes集群内的MySQL,实现简单的数据开发功能。
前置条件
镜像准备:自定义Docker镜像--Jupyterlab-CSDN博客
MySQL-Statefulset准备:StatefulSet 简单实践 Kubernetes-CSDN博客
步骤
1-namespace.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:name: jupyterlablabels:app1: jupyterlabapp.kubernetes.io/name: jupyterlab
2-jupyter-config.yaml
关键配置:
- c.ServerApp.allow_remote_access = True
- c.ServerApp.ip = '*'
- c.ServerApp.open_browser = False
- c.ServerApp.password = ''
- c.ServerApp.port = 8888
c.ServerApp.ip = '' 默认事localhost,配置 "*" 便于访问,便于nodeport的访问
如何生成password,参考:
jupyter-lab 设置密码(password) - 简书 (jianshu.com)
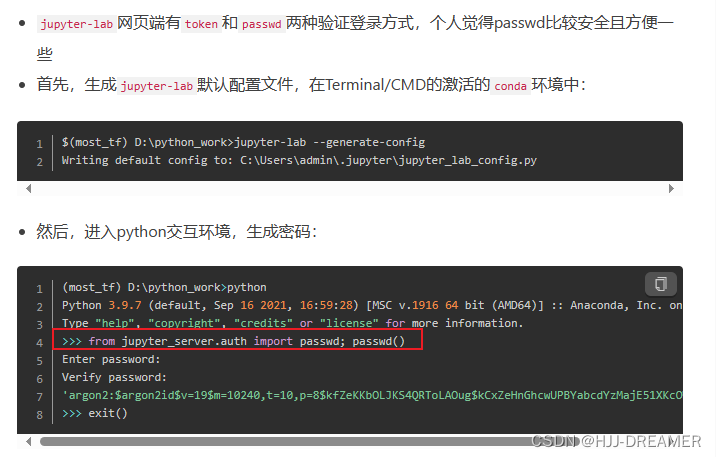
详细内容:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:labels:app1: jupyterlabapp.kubernetes.io/name: jupyterlabname: jupyter-confignamespace: jupyterlab
data:jupyter_lab_config.py: |-# Configuration file for lab.#------------------------------------------------------------------------------# Application(SingletonConfigurable) configuration#------------------------------------------------------------------------------## This is an application.## The date format used by logging formatters for %(asctime)s#c.Application.log_datefmt = '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'## The Logging format template#c.Application.log_format = '[%(name)s]%(highlevel)s %(message)s'## Set the log level by value or name.#c.Application.log_level = 30#------------------------------------------------------------------------------# JupyterApp(Application) configuration#------------------------------------------------------------------------------## Base class for Jupyter applications## Answer yes to any prompts.#c.JupyterApp.answer_yes = False## Full path of a config file.c.JupyterApp.config_file = '/root/.jupyter/jupyter_lab_config.py'## Specify a config file to load.#c.JupyterApp.config_file_name = ''## Generate default config file.#c.JupyterApp.generate_config = False#------------------------------------------------------------------------------# ExtensionApp(JupyterApp) configuration#------------------------------------------------------------------------------## Base class for configurable Jupyter Server Extension Applications.# # ExtensionApp subclasses can be initialized two ways:# 1. Extension is listed as a jpserver_extension, and ServerApp calls# its load_jupyter_server_extension classmethod. This is the# classic way of loading a server extension.# 2. Extension is launched directly by calling its `launch_instance`# class method. This method can be set as a entry_point in# the extensions setup.py## #c.ExtensionApp.default_url = ''## Handlers appended to the server.#c.ExtensionApp.handlers = []## Whether to open in a browser after starting. The specific browser used is# platform dependent and determined by the python standard library `webbrowser`# module, unless it is overridden using the --browser (ServerApp.browser)# configuration option.#c.ExtensionApp.open_browser = False## Settings that will passed to the server.#c.ExtensionApp.settings = {}## paths to search for serving static files.# # This allows adding javascript/css to be available from the notebook server# machine, or overriding individual files in the IPython#c.ExtensionApp.static_paths = []## Url where the static assets for the extension are served.#c.ExtensionApp.static_url_prefix = ''## Paths to search for serving jinja templates.# # Can be used to override templates from notebook.templates.#c.ExtensionApp.template_paths = []#------------------------------------------------------------------------------# LabServerApp(ExtensionAppJinjaMixin,LabConfig,ExtensionApp) configuration#------------------------------------------------------------------------------## A Lab Server Application that runs out-of-the-box## "A list of comma-separated URIs to get the allowed extensions list# # .. versionchanged:: 2.0.0# `LabServerApp.whitetlist_uris` renamed to `allowed_extensions_uris`#c.LabServerApp.allowed_extensions_uris = ''## Deprecated, use `LabServerApp.blocked_extensions_uris`#c.LabServerApp.blacklist_uris = ''## A list of comma-separated URIs to get the blocked extensions list# # .. versionchanged:: 2.0.0# `LabServerApp.blacklist_uris` renamed to `blocked_extensions_uris`#c.LabServerApp.blocked_extensions_uris = ''## The interval delay in seconds to refresh the lists#c.LabServerApp.listings_refresh_seconds = 3600## The optional kwargs to use for the listings HTTP requests as# described on https://2.python-requests.org/en/v2.7.0/api/#requests.request#c.LabServerApp.listings_request_options = {}## Deprecated, use `LabServerApp.allowed_extensions_uris`#c.LabServerApp.whitelist_uris = ''#------------------------------------------------------------------------------# LabApp(NBClassicConfigShimMixin,LabServerApp) configuration#------------------------------------------------------------------------------## The app directory to launch JupyterLab from.#c.LabApp.app_dir = None## Whether to enable collaborative mode.#c.LabApp.collaborative = False## Whether to start the app in core mode. In this mode, JupyterLab will run using# the JavaScript assets that are within the installed JupyterLab Python package.# In core mode, third party extensions are disabled. The `--dev-mode` flag is an# alias to this to be used when the Python package itself is installed in# development mode (`pip install -e .`).#c.LabApp.core_mode = False## The default URL to redirect to from `/`#c.LabApp.default_url = '/lab'## Whether to start the app in dev mode. Uses the unpublished local JavaScript# packages in the `dev_mode` folder. In this case JupyterLab will show a red# stripe at the top of the page. It can only be used if JupyterLab is installed# as `pip install -e .`.#c.LabApp.dev_mode = False## Whether to expose the global app instance to browser via window.jupyterlab#c.LabApp.expose_app_in_browser = False## Whether to load prebuilt extensions in dev mode. This may be useful to run and# test prebuilt extensions in development installs of JupyterLab. APIs in a# JupyterLab development install may be incompatible with published packages, so# prebuilt extensions compiled against published packages may not work# correctly.#c.LabApp.extensions_in_dev_mode = False## The override url for static lab assets, typically a CDN.#c.LabApp.override_static_url = ''## The override url for static lab theme assets, typically a CDN.#c.LabApp.override_theme_url = ''## Splice source packages into app directory.#c.LabApp.splice_source = False## The directory for user settings.#c.LabApp.user_settings_dir = '/root/.jupyter/lab/user-settings'## Whether to serve the app in watch mode#c.LabApp.watch = False## The directory for workspaces#c.LabApp.workspaces_dir = '/root/.jupyter/lab/workspaces'#------------------------------------------------------------------------------# ServerApp(JupyterApp) configuration#------------------------------------------------------------------------------## Set the Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true header#c.ServerApp.allow_credentials = False## Set the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header# # Use '*' to allow any origin to access your server.# # Takes precedence over allow_origin_pat.#c.ServerApp.allow_origin = ''## Use a regular expression for the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header# # Requests from an origin matching the expression will get replies with:# # Access-Control-Allow-Origin: origin# # where `origin` is the origin of the request.# # Ignored if allow_origin is set.#c.ServerApp.allow_origin_pat = ''## Allow password to be changed at login for the Jupyter server.# # While logging in with a token, the Jupyter server UI will give the opportunity# to the user to enter a new password at the same time that will replace the# token login mechanism.# # This can be set to false to prevent changing password from the UI/API.#c.ServerApp.allow_password_change = True## Allow requests where the Host header doesn't point to a local server# # By default, requests get a 403 forbidden response if the 'Host' header shows# that the browser thinks it's on a non-local domain. Setting this option to# True disables this check.# # This protects against 'DNS rebinding' attacks, where a remote web server# serves you a page and then changes its DNS to send later requests to a local# IP, bypassing same-origin checks.# # Local IP addresses (such as 127.0.0.1 and ::1) are allowed as local, along# with hostnames configured in local_hostnames.c.ServerApp.allow_remote_access = True## Whether to allow the user to run the server as root.c.ServerApp.allow_root = True## " Require authentication to access prometheus metrics.#c.ServerApp.authenticate_prometheus = True## Reload the webapp when changes are made to any Python src files.#c.ServerApp.autoreload = False## The base URL for the Jupyter server.# # Leading and trailing slashes can be omitted, and will automatically be added.#c.ServerApp.base_url = '/'## Specify what command to use to invoke a web browser when starting the server.# If not specified, the default browser will be determined by the `webbrowser`# standard library module, which allows setting of the BROWSER environment# variable to override it.#c.ServerApp.browser = ''## The full path to an SSL/TLS certificate file.#c.ServerApp.certfile = ''## The full path to a certificate authority certificate for SSL/TLS client# authentication.#c.ServerApp.client_ca = ''## The config manager class to use#c.ServerApp.config_manager_class = 'jupyter_server.services.config.manager.ConfigManager'## The content manager class to use.#c.ServerApp.contents_manager_class = 'jupyter_server.services.contents.largefilemanager.LargeFileManager'## Extra keyword arguments to pass to `set_secure_cookie`. See tornado's# set_secure_cookie docs for details.#c.ServerApp.cookie_options = {}## The random bytes used to secure cookies. By default this is a new random# number every time you start the server. Set it to a value in a config file to# enable logins to persist across server sessions.# # Note: Cookie secrets should be kept private, do not share config files with# cookie_secret stored in plaintext (you can read the value from a file).#c.ServerApp.cookie_secret = b''## The file where the cookie secret is stored.#c.ServerApp.cookie_secret_file = ''## Override URL shown to users.# # Replace actual URL, including protocol, address, port and base URL, with the# given value when displaying URL to the users. Do not change the actual# connection URL. If authentication token is enabled, the token is added to the# custom URL automatically.# # This option is intended to be used when the URL to display to the user cannot# be determined reliably by the Jupyter server (proxified or containerized# setups for example).#c.ServerApp.custom_display_url = ''## The default URL to redirect to from `/`#c.ServerApp.default_url = '/'## Disable cross-site-request-forgery protection# # Jupyter notebook 4.3.1 introduces protection from cross-site request# forgeries, requiring API requests to either:# # - originate from pages served by this server (validated with XSRF cookie and# token), or - authenticate with a token# # Some anonymous compute resources still desire the ability to run code,# completely without authentication. These services can disable all# authentication and security checks, with the full knowledge of what that# implies.#c.ServerApp.disable_check_xsrf = False## handlers that should be loaded at higher priority than the default services#c.ServerApp.extra_services = []## Extra paths to search for serving static files.# # This allows adding javascript/css to be available from the Jupyter server# machine, or overriding individual files in the IPython#c.ServerApp.extra_static_paths = []## Extra paths to search for serving jinja templates.# # Can be used to override templates from jupyter_server.templates.#c.ServerApp.extra_template_paths = []## Open the named file when the application is launched.#c.ServerApp.file_to_run = ''## The URL prefix where files are opened directly.#c.ServerApp.file_url_prefix = 'notebooks'## Extra keyword arguments to pass to `get_secure_cookie`. See tornado's# get_secure_cookie docs for details.#c.ServerApp.get_secure_cookie_kwargs = {}## (bytes/sec) Maximum rate at which stream output can be sent on iopub before# they are limited.#c.ServerApp.iopub_data_rate_limit = 1000000## (msgs/sec) Maximum rate at which messages can be sent on iopub before they are# limited.#c.ServerApp.iopub_msg_rate_limit = 1000## The IP address the Jupyter server will listen on.c.ServerApp.ip = '*'## Supply extra arguments that will be passed to Jinja environment.#c.ServerApp.jinja_environment_options = {}## Extra variables to supply to jinja templates when rendering.#c.ServerApp.jinja_template_vars = {}## Dict of Python modules to load as Jupyter server extensions.Entry values can# be used to enable and disable the loading ofthe extensions. The extensions# will be loaded in alphabetical order.#c.ServerApp.jpserver_extensions = {}## The kernel manager class to use.#c.ServerApp.kernel_manager_class = 'jupyter_server.services.kernels.kernelmanager.AsyncMappingKernelManager'## The kernel spec manager class to use. Should be a subclass of# `jupyter_client.kernelspec.KernelSpecManager`.# # The Api of KernelSpecManager is provisional and might change without warning# between this version of Jupyter and the next stable one.#c.ServerApp.kernel_spec_manager_class = 'jupyter_client.kernelspec.KernelSpecManager'## The full path to a private key file for usage with SSL/TLS.#c.ServerApp.keyfile = ''## Hostnames to allow as local when allow_remote_access is False.# # Local IP addresses (such as 127.0.0.1 and ::1) are automatically accepted as# local as well.#c.ServerApp.local_hostnames = ['localhost']## The login handler class to use.#c.ServerApp.login_handler_class = 'jupyter_server.auth.login.LoginHandler'## The logout handler class to use.#c.ServerApp.logout_handler_class = 'jupyter_server.auth.logout.LogoutHandler'## Sets the maximum allowed size of the client request body, specified in the# Content-Length request header field. If the size in a request exceeds the# configured value, a malformed HTTP message is returned to the client.# # Note: max_body_size is applied even in streaming mode.#c.ServerApp.max_body_size = 536870912## Gets or sets the maximum amount of memory, in bytes, that is allocated for use# by the buffer manager.#c.ServerApp.max_buffer_size = 536870912## Gets or sets a lower bound on the open file handles process resource limit.# This may need to be increased if you run into an OSError: [Errno 24] Too many# open files. This is not applicable when running on Windows.#c.ServerApp.min_open_files_limit = 0## DEPRECATED, use root_dir.#c.ServerApp.notebook_dir = ''## Whether to open in a browser after starting. The specific browser used is# platform dependent and determined by the python standard library `webbrowser`# module, unless it is overridden using the --browser (ServerApp.browser)# configuration option.#c.ServerApp.open_browser = False## Hashed password to use for web authentication.# # To generate, type in a python/IPython shell:# # from jupyter_server.auth import passwd; passwd()# # The string should be of the form type:salt:hashed-password.# password = 1c.ServerApp.password = 'argon2:$argon2id$v=19$m=10240,t=10,p=8$3SVwOn5jZCsVPToRwHfo6A$/Q67MolIfT+ztoV26F6eeuE0NxfhFFsyzLV//9IV+J4'## Forces users to use a password for the Jupyter server. This is useful in a# multi user environment, for instance when everybody in the LAN can access each# other's machine through ssh.# # In such a case, serving on localhost is not secure since any user can connect# to the Jupyter server via ssh.#c.ServerApp.password_required = False## The port the server will listen on (env: JUPYTER_PORT).c.ServerApp.port = 8888## The number of additional ports to try if the specified port is not available# (env: JUPYTER_PORT_RETRIES).#c.ServerApp.port_retries = 50## Preferred starting directory to use for notebooks and kernels.#c.ServerApp.preferred_dir = ''## DISABLED: use %pylab or %matplotlib in the notebook to enable matplotlib.#c.ServerApp.pylab = 'disabled'## If True, display controls to shut down the Jupyter server, such as menu items# or buttons.#c.ServerApp.quit_button = True## (sec) Time window used to check the message and data rate limits.#c.ServerApp.rate_limit_window = 3## Reraise exceptions encountered loading server extensions?#c.ServerApp.reraise_server_extension_failures = False## The directory to use for notebooks and kernels.c.ServerApp.root_dir = '/home/jupyterlab'## The session manager class to use.#c.ServerApp.session_manager_class = 'jupyter_server.services.sessions.sessionmanager.SessionManager'## Shut down the server after N seconds with no kernels or terminals running and# no activity. This can be used together with culling idle kernels# (MappingKernelManager.cull_idle_timeout) to shutdown the Jupyter server when# it's not in use. This is not precisely timed: it may shut down up to a minute# later. 0 (the default) disables this automatic shutdown.#c.ServerApp.shutdown_no_activity_timeout = 0## The UNIX socket the Jupyter server will listen on.#c.ServerApp.sock = ''## The permissions mode for UNIX socket creation (default: 0600).#c.ServerApp.sock_mode = '0600'## Supply SSL options for the tornado HTTPServer. See the tornado docs for# details.#c.ServerApp.ssl_options = {}## Supply overrides for terminado. Currently only supports "shell_command".#c.ServerApp.terminado_settings = {}## Set to False to disable terminals.# # This does *not* make the server more secure by itself. Anything the user can# in a terminal, they can also do in a notebook.# # Terminals may also be automatically disabled if the terminado package is not# available.#c.ServerApp.terminals_enabled = True## Token used for authenticating first-time connections to the server.# # The token can be read from the file referenced by JUPYTER_TOKEN_FILE or set# directly with the JUPYTER_TOKEN environment variable.# # When no password is enabled, the default is to generate a new, random token.# # Setting to an empty string disables authentication altogether, which is NOT# RECOMMENDED.#c.ServerApp.token = '<generated>'## Supply overrides for the tornado.web.Application that the Jupyter server uses.#c.ServerApp.tornado_settings = {}## Whether to trust or not X-Scheme/X-Forwarded-Proto and X-Real-Ip/X-Forwarded-# For headerssent by the upstream reverse proxy. Necessary if the proxy handles# SSL#c.ServerApp.trust_xheaders = False## Disable launching browser by redirect file For versions of notebook > 5.7.2, a# security feature measure was added that prevented the authentication token# used to launch the browser from being visible. This feature makes it difficult# for other users on a multi-user system from running code in your Jupyter# session as you. However, some environments (like Windows Subsystem for Linux# (WSL) and Chromebooks), launching a browser using a redirect file can lead the# browser failing to load. This is because of the difference in file# structures/paths between the runtime and the browser.# # Disabling this setting to False will disable this behavior, allowing the# browser to launch by using a URL and visible token (as before).#c.ServerApp.use_redirect_file = True## Specify where to open the server on startup. This is the `new` argument passed# to the standard library method `webbrowser.open`. The behaviour is not# guaranteed, but depends on browser support. Valid values are:# # - 2 opens a new tab,# - 1 opens a new window,# - 0 opens in an existing window.# # See the `webbrowser.open` documentation for details.#c.ServerApp.webbrowser_open_new = 2## Set the tornado compression options for websocket connections.# # This value will be returned from# :meth:`WebSocketHandler.get_compression_options`. None (default) will disable# compression. A dict (even an empty one) will enable compression.# # See the tornado docs for WebSocketHandler.get_compression_options for details.#c.ServerApp.websocket_compression_options = None## The base URL for websockets, if it differs from the HTTP server (hint: it# almost certainly doesn't).# # Should be in the form of an HTTP origin: ws[s]://hostname[:port]#c.ServerApp.websocket_url = ''
3-jupyter-class.yaml
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:name: nfs-jupyterlabnamespace: jupyterlabannotations:storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class: "false" ## 是否设置为默认的storageclass
provisioner: k8s-sigs.io/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner # or choose another name, must match deployment's env PROVISIONER_NAME'
#provisioner: nfs-subdir-external-provisioner # or choose another name, must match deployment's env PROVISIONER_NAME'
parameters:archiveOnDelete: "true"pathPattern: "${.PVC.namespace}/${.PVC.name}/${.PVC.annotations.nfs.io/storage-path}"# pathPattern: "${.PVC.namespace}/${.PVC.annotations.nfs.io/storage-path}"# pathPattern: "${.PVC.namespace}-${.PVC.name}"
5-pvc.yaml
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:name: nfs-jupyterlabnamespace: jupyterlabannotations:volume.beta.kubernetes.io/storage-class: "nfs-jupyterlab"
spec:accessModes:- ReadWriteManyresources:requests:storage: 50Mi6-jupyter-deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:name: jupyterlab-deploymentnamespace: jupyterlablabels:app1: jupyterlabapp.kubernetes.io/name: jupyterlab
spec:replicas: 1selector:matchLabels:app1: jupyterlabapp.kubernetes.io/name: jupyterlabtemplate:metadata:labels:app1: jupyterlabapp.kubernetes.io/name: jupyterlabspec:affinity:nodeAffinity:requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:nodeSelectorTerms:- matchExpressions:- key: kubernetes.io/hostnameoperator: NotInvalues:- master01- master02- master03hostNetwork: truecontainers:- name: jupyterlabimage: reporsitory:5000/jupyterlab:1.1imagePullPolicy: Alwaysports:- name: jupyterlabcontainerPort: 8888command:- bash- "-c"- |set -ex/usr/local/bin/jupyter-labresources:requests:cpu: 250mmemory: 500Milimits:cpu: 250mmemory: 500MivolumeMounts:- name: datamountPath: "/home/jupyterlab/data"- name: jupyter-configmountPath: /root/.jupyter/- name: jupytermountPath: /home/jupyterlabvolumes:- name: datapersistentVolumeClaim:claimName: nfs-jupyter-mysql- name: jupyterpersistentVolumeClaim:claimName: nfs-jupyterlab- name: jupyter-configconfigMap:name: jupyter-config
7-services.yaml
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:name: jupyterlab-svcnamespace: jupyterlablabels:app1: jupyterlabapp.kubernetes.io/name: jupyterlab
spec:ports:- name: jupyterlabport: 8888selector:app1: jupyterlabtype: NodePort
成功
后端状况:

网页访问:
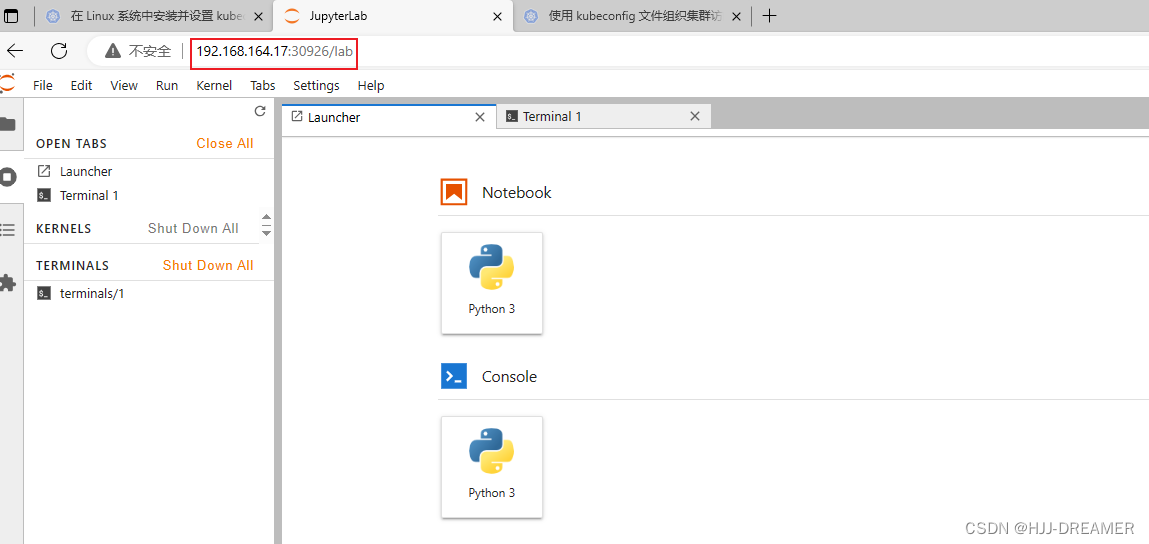
Jupyterlab服务的Pod提升
部署kubectl + bash-completion
在 Linux 系统中安装并设置 kubectl | Kubernetes
使用 kubeconfig 文件组织集群访问 | Kubernetes

更新数据库使用者权限
grant all privileges on *.* to 'root'@'%' identified by '1' with grant option;
flush privileges;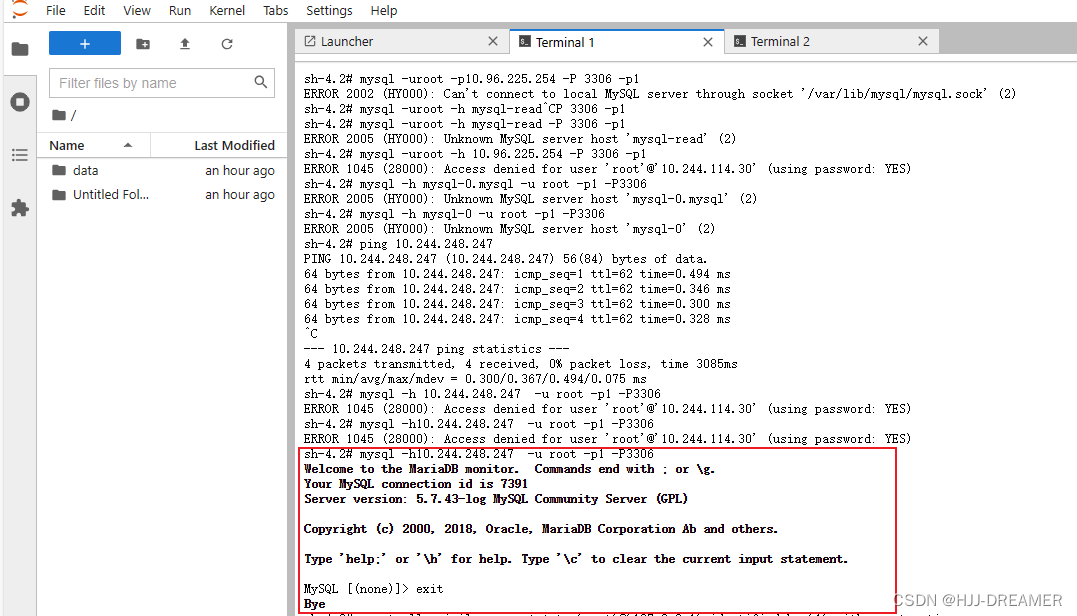
参考文档
https://developer.aliyun.com/article/857365
https://www.jianshu.com/p/743ed2209a8c
https://www.runoob.com/linux/linux-comm-nohup.html
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1783227
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/468585680
相关文章:

Kubernetes 通过 Deployment 部署Jupyterlab
概要 在Kubernetes上部署jupyterlab服务,链接Kubernetes集群内的MySQL,实现简单的数据开发功能。 前置条件 镜像准备:自定义Docker镜像--Jupyterlab-CSDN博客 MySQL-Statefulset准备:StatefulSet 简单实践 Kubernetes-CSDN博客…...

【Linux常用命令15】shell脚本
shell概述:shell是一个命令行解释器,它接收应用程序或用户的命令,然后调用操作系统内核 Linux Shell 种类非常多, 常见的有: Bourne Shell (/usr/bin/sh 或/bin/sh)、 Bourne Again Shell (/bin/bash)、 C Shell (/us…...

LTE系统TDD无线帧结构特点
LTE系统TDD无线帧结构的特点主要表现在以下几个方面: 无线帧结构时间描述的最小单位是采样周期Ts。在LTE中,每个子载波为2048阶IFFT采样,△f15kHz,因此采样周期Ts1/(204815000)0.033us。 TDD的帧结构包括两个5ms的半帧࿰…...

微信小程序OA会议系统数据交互
前言 经过我们所写的上一文章:微信小程序会议OA系统其他页面-CSDN博客 在我们的是基础面板上面,可以看到出来我们的数据是死数据,今天我们就完善我们的是数据 后台 在我们去完成项目之前我们要把我们的项目后台准备好资源我放在我资源中&…...

TypeScript环境安装
一、windows环境 安装node,附带自动安装npm工具 安装tsc npm install -g typescript 对于不支持 Nuget 的项目类型,你可以使用 TypeScript Visual Studio 扩展。 你可以使用 Visual Studio 中的 Extensions > Manage Extensions 安装扩展。 安装下…...

连接Mumu模拟器使用ADB
要连接Mumu模拟器使用ADB,您可以按照以下详细步骤进行操作: 安装ADB驱动程序:在您的计算机上安装ADB驱动程序。ADB是Android Debug Bridge的缩写,它允许您与Android设备进行通信。您可以从Android开发者网站(https://d…...

springboot缓存篇之mybatis一级缓存和二级缓存
前言 相信很多人都用过mybatis,这篇文章主要是介绍mybatis的缓存,了解一下mybatis缓存是如何实现,以及它在实际中的应用 一级缓存 什么是mybatis一级缓存?我们先看一个例子: GetMapping("/list") public…...

云计算认证有哪些?认证考了有什么用?
云计算作为一项快速发展的技术,对人才的需求持续增长。无论是男生还是女生,只要具备相关的技能和知识,都可以在云计算领域找到就业机会。 目前入行云计算最好最便捷的方式就是考证,拿到一个云计算相关的证书,就能开启…...

[ 云计算 | AWS 实践 ] Java 如何重命名 Amazon S3 中的文件和文件夹
本文收录于【#云计算入门与实践 - AWS】专栏中,收录 AWS 入门与实践相关博文。 本文同步于个人公众号:【云计算洞察】 更多关于云计算技术内容敬请关注:CSDN【#云计算入门与实践 - AWS】专栏。 本系列已更新博文: [ 云计算 | …...
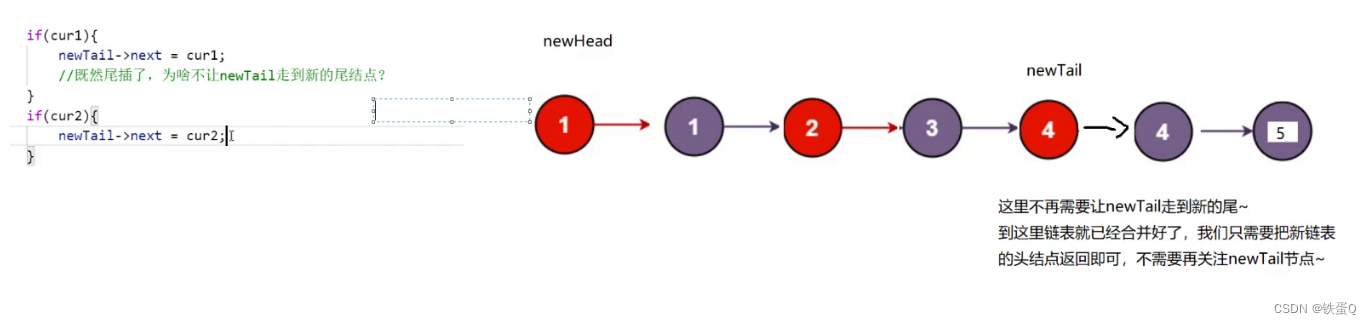
c语言练习91:合并两个有序链表
合并两个有序链表 力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台 代码1: /*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/typedef struct ListNode ListNode; struct Li…...
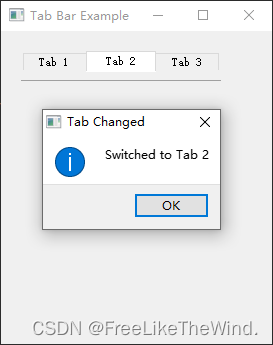
【Qt控件之QTabBar】介绍及使用
概述 QTabBar类提供了一个选项卡栏,例如用于选项卡对话框。 QTabBar非常简单易用,它使用预定义的形状绘制选项卡,并在选择选项卡时发出信号。它可以被子类化以调整外观和感觉。Qt还提供了一个实现好的QTabWidget。 每个选项卡具有一个tabT…...
最新Tuxera NTFS2023最新版Mac读写NTFS磁盘工具 更新详情介绍
Tuxera NTFS for Mac是一款Mac系统NTFS磁盘读写软件。在系统默认状态下,MacOSX只能实现对NTFS的读取功能,Tuxera NTFS可以帮助MacOS 系统的电脑顺利实现对NTFS分区的读/写功能。Tuxera NTFS 2023完美兼容最新版本的MacOS 11 Big Sur,在M1芯片…...

AndroidX使用Paho MQTT报找不到android/support/v4/content/LocalBroadcastManager
网上有直接引用support-v4包的,但我用的AndroidX,不能为这个类再引用support-v4 直接自己创建这个类,把androidx.localbroadcastmanager.content.LocalBroadcastManager改改就行。 虽然奇葩但能解决问题 package android.support.v4.content…...
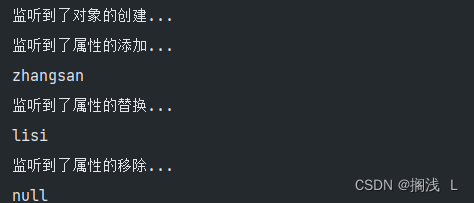
Filter与Listener(过滤器与监听器)
1.Filter 1.过滤器概述 过滤器——Filter,它是JavaWeb三大组件之一。另外两个是Servlet和Listener 它可以对web应用中的所有资源进行拦截,并且在拦截之后进行一些特殊的操作 在程序中访问服务器资源时,当一个请求到来,服务器首…...
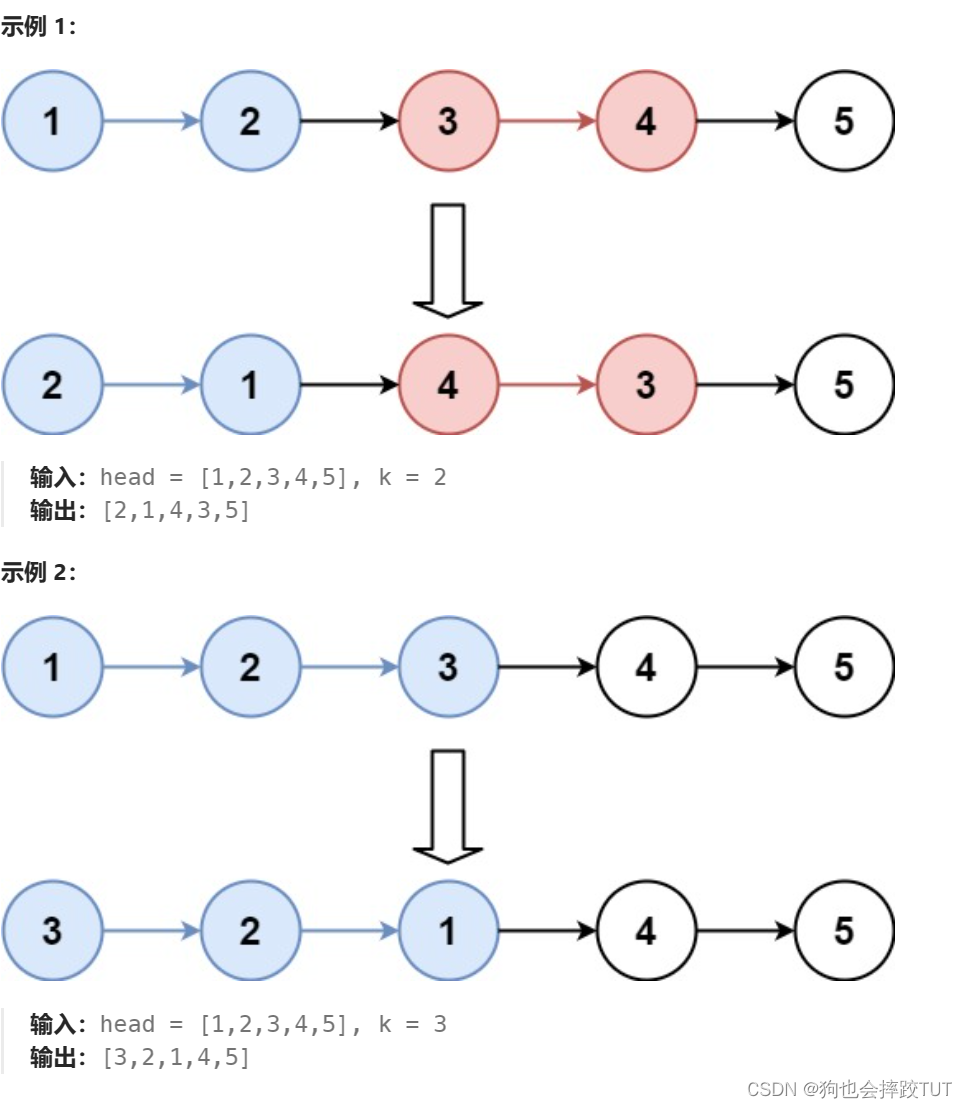
【刷题篇】反转链表
文章目录 一、206.反转链表二、92.反转链表 ||三、25. K 个一组翻转链表 一、206.反转链表 class Solution { public://使用头插//三个指针也可以ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {if(headnullptr)return nullptr;ListNode* curhead;ListNode* newheadnew ListNode(0);L…...

【C语言小游戏--猜数字】
文章目录 前言1.游戏描述2.代码实现2.1打印菜单2.2构建基础框架2.3玩游戏2.3.1生成随机数2.3.1.1rand()2.3.1.2srand()2.3.1.3time() 2.3.2game() 2.4自己设定猜的次数 3.完整代码 前言 猜数字小游戏是我们大多数人学习C语言时都会了解到的一个有趣的C语言小游戏,下…...

Vue计算属性computed和监听watch
1.计算属性 初衷:为了解决模块里面有太多的计算逻辑让模版难以维护。 计算属性可以依赖一个数据也可以依赖多个数据的变化 使用场景: 商品单价和数量改变时,商品总价更改。如果写在方法里面,那么每次修改商品单价和数量时都会…...
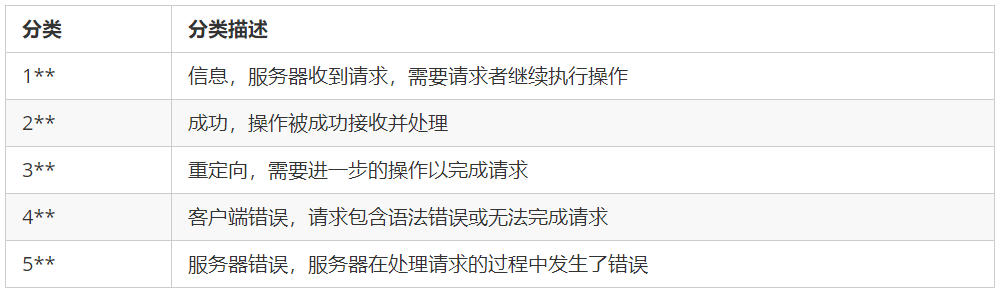
HTTP介绍 原理 消息结构 客户端请求 服务器响应 HTTP状态码
一、HTTP介绍二、HTTP工作原理HTTP三点注意事项 三、HTTP消息结构四、客户端请求消息五、服务器响应消息HTTP请求方法 七、HTTP响应头信息八、HTTP状态码(HTTP Status Code)下面是常见的HTTP状态码:HTTP状态码分类HTTP状态码列表 一、HTTP介绍…...

linux性能分析(五)如何学习linux性能优化
一 如何学习linux性能优化 强调: 由于知识记忆曲线以及某些知识点不常用,所以一定要注重复习思考: 如何进行能力转义以及能力嫁接? --> 真正站在巨人的肩膀上性能调优的目的: 不影响系统稳定性的资源最大利用化补充: 性能…...

1402. 做菜顺序 --力扣 --JAVA
题目 一个厨师收集了他 n 道菜的满意程度 satisfaction ,这个厨师做出每道菜的时间都是 1 单位时间。 一道菜的 「 like-time 系数 」定义为烹饪这道菜结束的时间(包含之前每道菜所花费的时间)乘以这道菜的满意程度,也就是 time[i…...
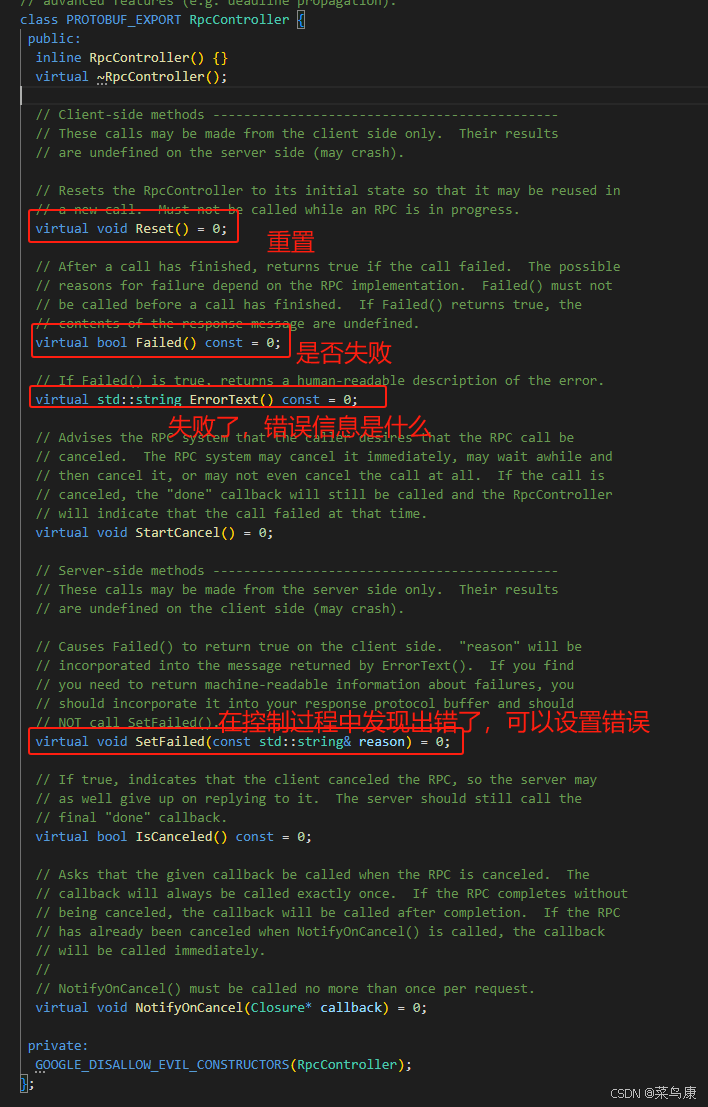
C++实现分布式网络通信框架RPC(3)--rpc调用端
目录 一、前言 二、UserServiceRpc_Stub 三、 CallMethod方法的重写 头文件 实现 四、rpc调用端的调用 实现 五、 google::protobuf::RpcController *controller 头文件 实现 六、总结 一、前言 在前边的文章中,我们已经大致实现了rpc服务端的各项功能代…...
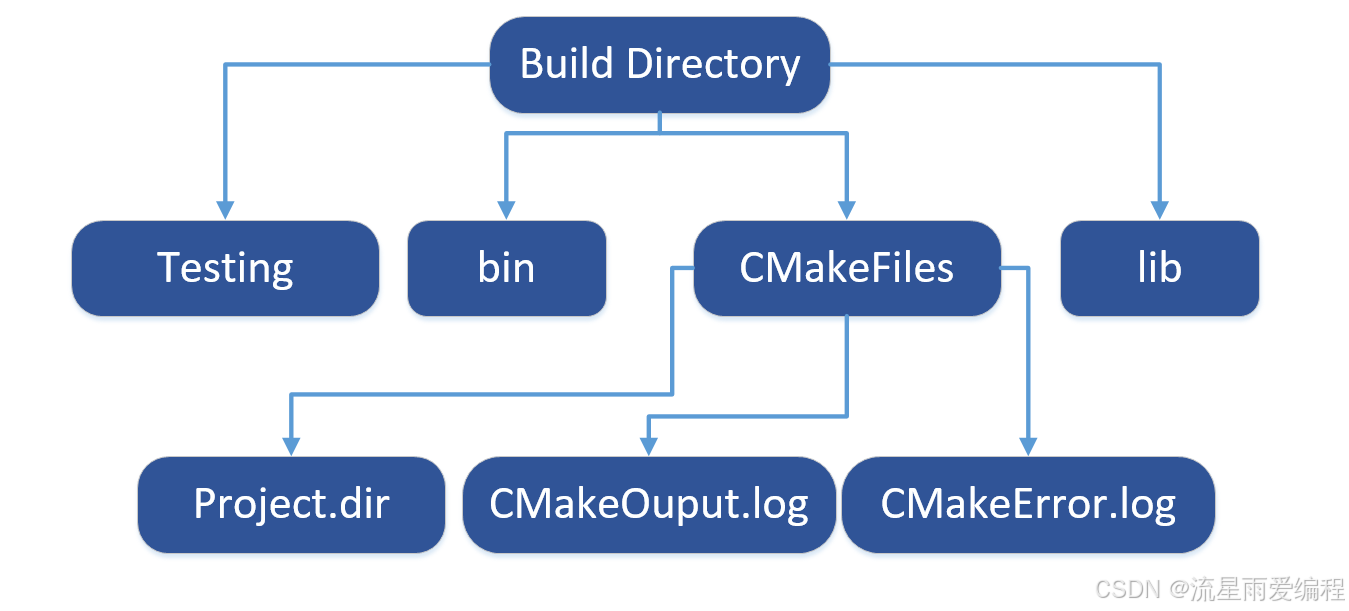
CMake基础:构建流程详解
目录 1.CMake构建过程的基本流程 2.CMake构建的具体步骤 2.1.创建构建目录 2.2.使用 CMake 生成构建文件 2.3.编译和构建 2.4.清理构建文件 2.5.重新配置和构建 3.跨平台构建示例 4.工具链与交叉编译 5.CMake构建后的项目结构解析 5.1.CMake构建后的目录结构 5.2.构…...

关于iview组件中使用 table , 绑定序号分页后序号从1开始的解决方案
问题描述:iview使用table 中type: "index",分页之后 ,索引还是从1开始,试过绑定后台返回数据的id, 这种方法可行,就是后台返回数据的每个页面id都不完全是按照从1开始的升序,因此百度了下,找到了…...
ABAP设计模式之---“简单设计原则(Simple Design)”
“Simple Design”(简单设计)是软件开发中的一个重要理念,倡导以最简单的方式实现软件功能,以确保代码清晰易懂、易维护,并在项目需求变化时能够快速适应。 其核心目标是避免复杂和过度设计,遵循“让事情保…...
c++第七天 继承与派生2
这一篇文章主要内容是 派生类构造函数与析构函数 在派生类中重写基类成员 以及多继承 第一部分:派生类构造函数与析构函数 当创建一个派生类对象时,基类成员是如何初始化的? 1.当派生类对象创建的时候,基类成员的初始化顺序 …...

【Linux】自动化构建-Make/Makefile
前言 上文我们讲到了Linux中的编译器gcc/g 【Linux】编译器gcc/g及其库的详细介绍-CSDN博客 本来我们将一个对于编译来说很重要的工具:make/makfile 1.背景 在一个工程中源文件不计其数,其按类型、功能、模块分别放在若干个目录中,mak…...

什么是VR全景技术
VR全景技术,全称为虚拟现实全景技术,是通过计算机图像模拟生成三维空间中的虚拟世界,使用户能够在该虚拟世界中进行全方位、无死角的观察和交互的技术。VR全景技术模拟人在真实空间中的视觉体验,结合图文、3D、音视频等多媒体元素…...
协议转换利器,profinet转ethercat网关的两大派系,各有千秋
随着工业以太网的发展,其高效、便捷、协议开放、易于冗余等诸多优点,被越来越多的工业现场所采用。西门子SIMATIC S7-1200/1500系列PLC集成有Profinet接口,具有实时性、开放性,使用TCP/IP和IT标准,符合基于工业以太网的…...
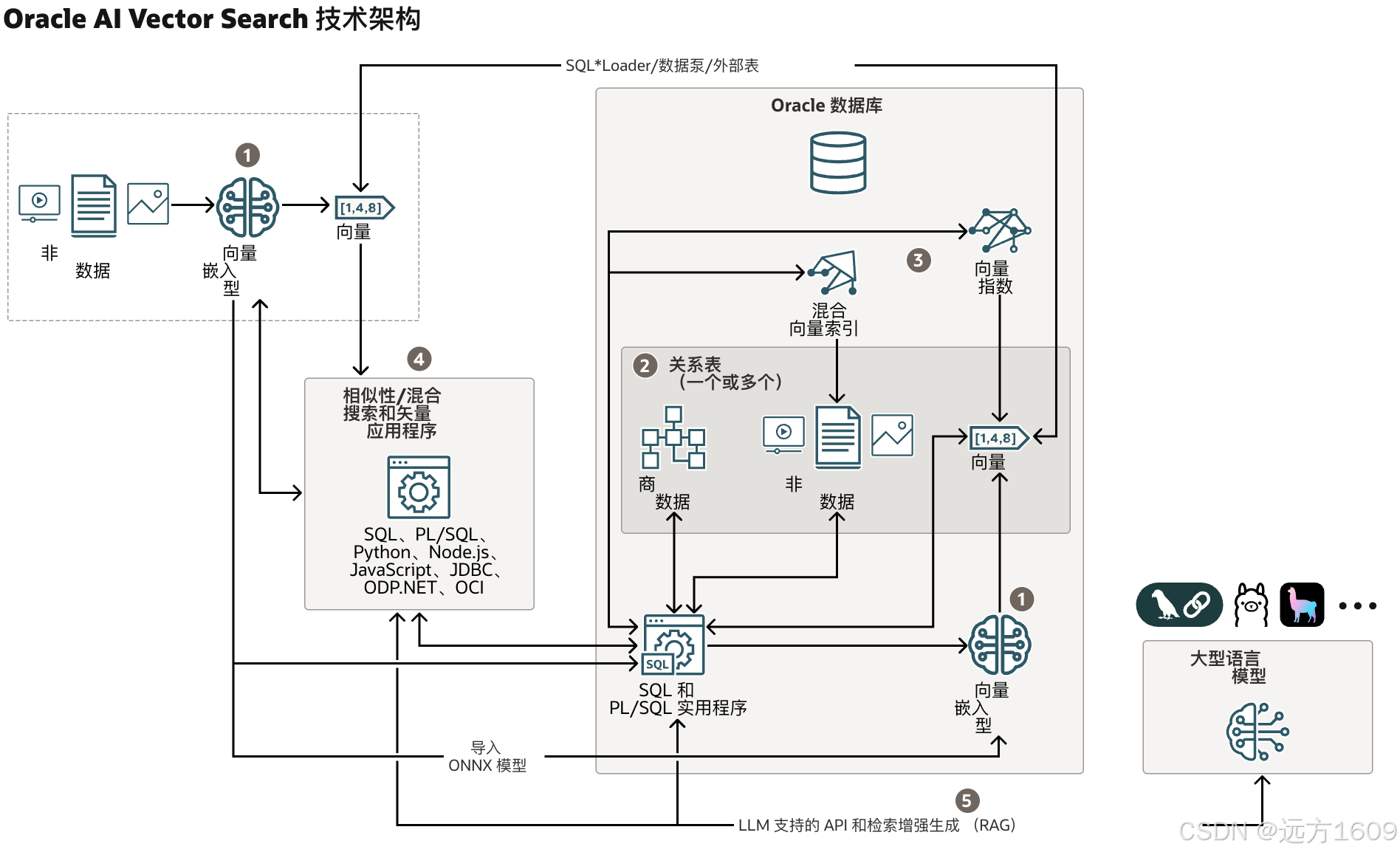
9-Oracle 23 ai Vector Search 特性 知识准备
很多小伙伴是不是参加了 免费认证课程(限时至2025/5/15) Oracle AI Vector Search 1Z0-184-25考试,都顺利拿到certified了没。 各行各业的AI 大模型的到来,传统的数据库中的SQL还能不能打,结构化和非结构的话数据如何和…...

【堆垛策略】设计方法
堆垛策略的设计是积木堆叠系统的核心,直接影响堆叠的稳定性、效率和容错能力。以下是分层次的堆垛策略设计方法,涵盖基础规则、优化算法和容错机制: 1. 基础堆垛规则 (1) 物理稳定性优先 重心原则: 大尺寸/重量积木在下…...
