Rust5.2 Generic Types, Traits, and Lifetimes
Rust学习笔记
Rust编程语言入门教程课程笔记
参考教材: The Rust Programming Language (by Steve Klabnik and Carol Nichols, with contributions from the Rust Community)
Lecture 10: Generic Types, Traits, and Lifetimes
lib.rs
use std::fmt::Display;//Traits: Defining Shared Behavior
pub trait Summary {fn summarize_author(&self) -> String;// fn summarize(&self) -> String;fn summarize(&self) -> String {//String::from("(Read more from...)")format!("(Read more from {}...)", self.summarize_author())}}pub struct NewsArticle {pub headline: String,pub location: String,pub author: String,pub content: String,
}impl Summary for NewsArticle {//implementing a trait on a type// fn summarize(&self) -> String {//implementing a trait method// format!("{}, by {} ({})", self.headline, self.author, self.location)// }fn summarize_author(&self) -> String {//implementing a trait methodformat!("{}", self.author)}}pub struct Tweet {pub username: String,pub content: String,pub reply: bool,pub retweet: bool,
}impl Summary for Tweet {//implementing a trait on a typefn summarize(&self) -> String {//implementing a trait methodformat!("{}: {}", self.username, self.content)}fn summarize_author(&self) -> String {//implementing a trait methodformat!("{}", self.username)}}pub fn notify(item: &impl Summary) {println!("Breaking news! {}", item.summarize());
}pub fn notify_trait_bound<T: Summary>(item: &T) {//trait bound syntaxprintln!("Breaking news! {}", item.summarize());
}pub fn notify_trait_bounds<T: Summary>(item1: &T, item2: &T) {//trait bound syntaxprintln!("Breaking news! {}", item1.summarize());println!("Breaking news! {}", item2.summarize());
}pub fn notify_multiple_trait_bounds<T: Summary + Display>(item1: &T, item2: &T) {//trait bound syntaxprintln!("Breaking news! {}", item1.summarize());println!("Breaking news! {}", item2.summarize());
}pub fn notify_where_clause<T, U>(item1: &T, item2: &U) where T: Summary + Display,U: Summary + Display
{println!("Breaking news! {}", item1.summarize());println!("Breaking news! {}", item2.summarize());
}//Returning Types that Implement Traits
fn _returns_summarizable() -> impl Summary {//returning a type that implements the Summary trait//cannot return different typesTweet {username: String::from("horse_ebooks"),content: String::from("of course, as you probably already know, people"),reply: false,retweet: false,}
}struct _Pair<T> {x: T,y: T,
}impl <T> _Pair<T> {fn _new(x: T, y: T) -> Self {Self {x,y,}}}impl <T: Display + PartialOrd> _Pair<T> {//trait bound syntaxfn _cmp_display(&self) {if self.x >= self.y {println!("The largest member is x = {}", self.x);} else {println!("The largest member is y = {}", self.y);}}}//blanket implementations
// impl<T: Display> ToString for T {
// // --snip--
// }
main.rs
use generic_types_traits_and_lifetimes::Summary;
use generic_types_traits_and_lifetimes::Tweet;
use std::fmt::Display;//Generic Data Types
fn largest_generic<T:std::cmp::PartialOrd + Clone>(list: &[T]) -> &T {let mut largest = &list[0];for item in list {if item > largest { //error: the trait `std::cmp::PartialOrd` is not implemented for `T`largest = item;}}largest
}struct Point<T> {x: T,y: T,
}impl Point<i32> {fn selfx(&self) -> &i32 {&self.x}}impl Point<f32> {fn distance_from_origin(&self) -> f32 {(self.x.powi(2) + self.y.powi(2)).sqrt()}
}impl Point<&str>{fn concatenate(&self) -> String {format!("{}{}", self.x, self.y)}
}#[derive(Debug)]
struct Point2<T, U> {x: T,y: U,
}impl<T, U> Point2<T, U> {fn mixup<V, W>(self, other: Point2<V, W>) -> Point2<T, W> {Point2 {x: self.x,y: other.y,}}
}//Lifetime Annotations in Struct Definitions
struct _ImportantExcerpt<'a> {_part: &'a str,
}fn main() {//remove duplication by extracting the match expression into a functionlet number_list = vec![34, 50, 25, 100, 65];// let mut largest = &number_list[0];// for number in &number_list {// if number > largest {// largest = number;// }// }//largest function with generic typelet result1 = largest(&number_list);println!("The largest number is {}", result1);//duplicationlet number_list = vec![102, 34, 6000, 89, 54, 2, 43, 8];// let mut largest = &number_list[0];// for number in &number_list {// if number > largest {// largest = number;// }// }//largest function with generic typelet result2 = largest(&number_list);println!("The largest number is {}", result2);let str_list = vec!["Hello", "Rust", "World"];let result3 = largest_generic(&str_list);println!("The largest string is {}", result3);//Generic Data Types in Struct Definitionslet integer = Point { x: 5, y: 10 };println!("x,y = {},{}", integer.x, integer.y);let float = Point { x: 1.0, y: 4.0 };println!("x,y = {},{}", float.x, float.y);//Generic Data Types in Enum Definitionslet integer = Option::Some(5);let float = Option::Some(5.0);let none: Option<i32> = None;println!("integer = {:?}, float = {:?}, none = {:?}", integer, float, none);println!("integer = {:?}, float = {:?}, none = {:?}", integer, float, none);//Generic Data Types in Method Definitionslet p1 = Point { x: 5, y: 10 };let p2 = Point { x: "Hello", y: " Rust" };let p3 = Point { x: 5.0, y: 10.0 };println!("p1:{}",p1.selfx());println!("p2:{}",p2.concatenate());println!("p3:{}",p3.distance_from_origin());//Generic Data Types in Struct Definitionslet p4 = Point2 { x: 5, y: 10.4 };let p5: Point2<&str, i32> = Point2 {x:"Hello", y:2};println!("p4:{:?}",p4.mixup(p5));//Traits: Defining Shared Behaviorlet tweet = Tweet {username: String::from("horse_ebooks"),content: String::from("of course, as you probably already know, people"),reply: false,retweet: false,};println!("1 new tweet: {}", tweet.summarize());//Lifetimes: Ensuring One Borrow Lasts as Long as the Other//avoiding dangling references// let r;// //let b = r;//error: use of possibly uninitialized `r`// {// let x = 5;// r = &x;// }// //borrow checker// //println!("r:{}",r);//error: `x` does not live long enoughlet x = 5;let r = &x;println!("r:{}",r);let string1 = String::from("abcd"); let string2 = "xyz";let result = longest(string1.as_str(), string2);println!("The longest string is {}", result);//Lifetime Annotations in Struct Definitionslet novel = String::from("Call me Ishmael. Some years ago...");let first_sentence = novel.split('.').next().expect("Could not find a '.'");let _i = _ImportantExcerpt { _part: first_sentence };//Lifetime Elision}fn largest(list: &[i32]) -> &i32 {//we need to return a reference to the valuelet mut largest = &list[0];for number in list {if number > largest {largest = number;}}largest
}//Lifetime Annotation Syntax
//'a is a generic lifetime parameter
//&'a str: a string slice that lives for the lifetime 'a
fn longest<'a>(x: &'a str, y: &'a str) -> &'a str {//we need to return a reference to the value//'a is the part of the scope of x that overlaps with the scope of yif x.len() > y.len() {x} else {y}
}fn _longest<'a>(x: &'a str, _y: &str) -> &'a str {//we need to return a reference to the value//'a is the part of the scope of x that overlaps with the scope of yx
}// fn error_longest<'a>(x: &str, _y: &str) -> &'a str {//we need to return a reference to the value
// let result = String::from("really long string");
// result.as_str()
// }fn _corroct_longest<'a>(_x: &'a str, _y: &str) -> String {//we need to return a reference to the valuelet result = String::from("really long string");result
}//Lifetime Elision
//The compiler uses three rules to figure out what lifetimes references have when there aren’t explicit annotations.
//The first rule applies to input lifetimes, and the second and third rules apply to output lifetimes.
//If the compiler gets to the end of the three rules and there are still references for which it can’t figure out lifetimes, the compiler will stop with an error.//1. Each parameter that is a reference gets its own lifetime parameter.
//2. If there is exactly one input lifetime parameter, that lifetime is assigned to all output lifetime parameters: fn foo<'a>(x: &'a i32) -> &'a i32.
//3. If there are multiple input lifetime parameters, but one of them is &self or &mut self because this is a method, the lifetime of self is assigned to all output lifetime parameters.fn _first_word(s: &str) -> &str {let bytes = s.as_bytes();for (i, &item) in bytes.iter().enumerate() {if item == b' ' {return &s[0..i];}}&s[..]
}fn _longest_with_an_announcement<'a, T>(x: &'a str,y: &'a str,ann: T,
) -> &'a str where T: Display
{println!("Announcement! {}", ann);if x.len() > y.len() {x} else {y}
}
相关文章:

Rust5.2 Generic Types, Traits, and Lifetimes
Rust学习笔记 Rust编程语言入门教程课程笔记 参考教材: The Rust Programming Language (by Steve Klabnik and Carol Nichols, with contributions from the Rust Community) Lecture 10: Generic Types, Traits, and Lifetimes lib.rs use std::fmt::Display;//Traits: …...
)
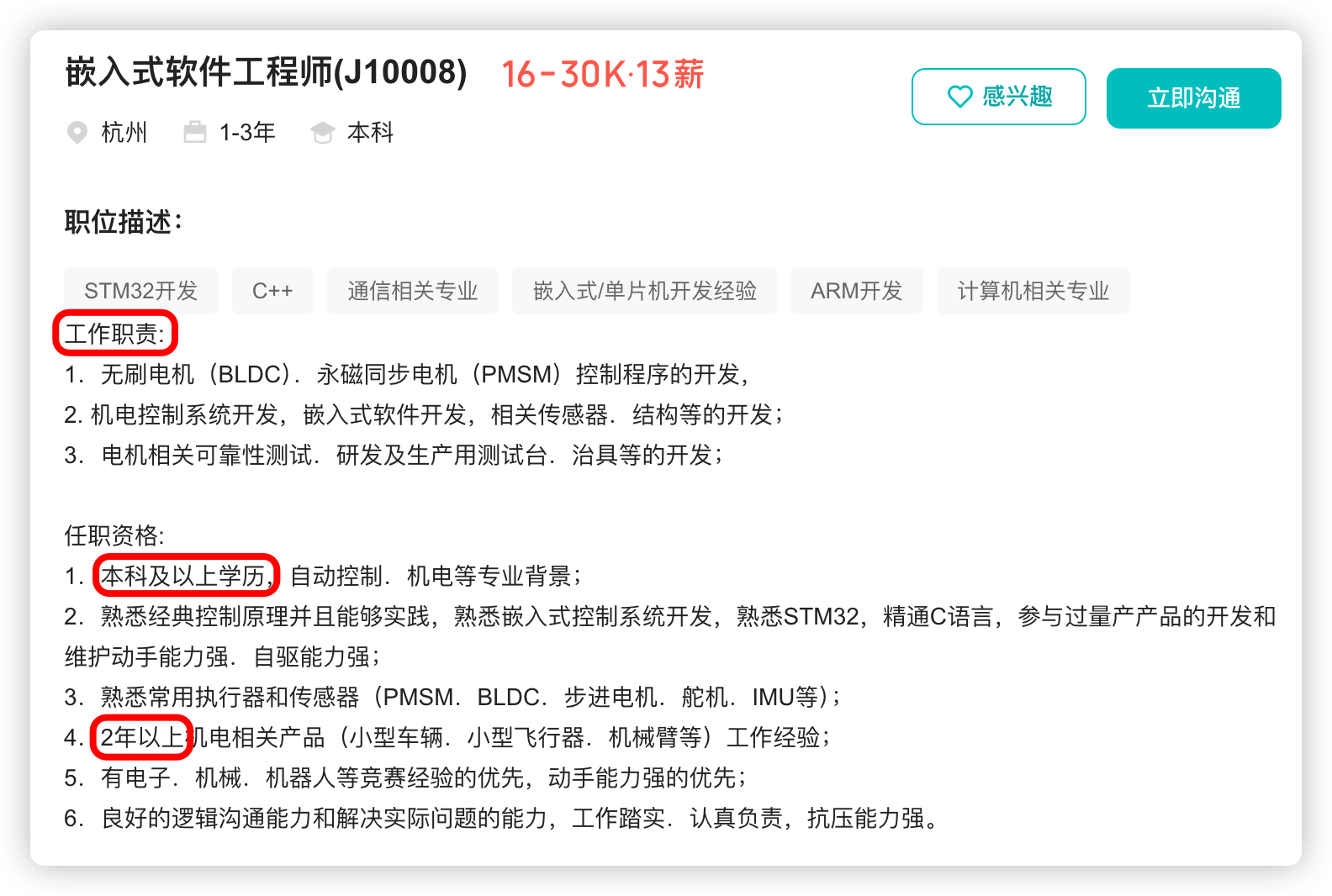
c 实用化的摄像头生成avi视频程序(加入精确的时间控制)
I时间控制是指:生成了n张图片帧用了多少时间m。帧率等于n/m。对应于头文件,m等于scale, n等于rate.为了精确,采用微秒计时。 I此程序生成的视频远好于ffmpeg,可能是此程序没有压缩数据原因吧。 现在的帧率不高,是因…...
Web后端开发_01
Web后端开发 请求响应 SpringBoot提供了一个非常核心的Servlet 》DispatcherServlet,DispatcherServlet实现了servlet中规范的接口 请求响应: 请求(HttpServletRequest):获取请求数据响应(HttpServletRe…...
二十、泛型(6)
本章概要 问题 任何基本类型都不能作为类型参数实现参数化接口转型和警告重载基类劫持接口 自限定的类型 古怪的循环泛型自限定参数协变 问题 本节将阐述在使用 Java 泛型时会出现的各类问题。 任何基本类型都不能作为类型参数 正如本章早先提到的,Java 泛型的…...

Java18新增特性
前言 前面的文章,我们对Java9、Java10、Java11、Java12 、Java13、Java14、Java15、Java16、Java17 的特性进行了介绍,对应的文章如下 Java9新增特性 Java10新增特性 Java11新增特性 Java12新增特性 Java13新增特性 Java14新增特性 Java15新增特性 Java…...

springboot容器
1.主要指的是servlet容器 servlet组件由sevlet Filter Listener等 2.自动配置原理 通过ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration 配置这些内容 (自动配置类开始分析功能) conditionalOnclass开启条件 ServletRequest类 import导入嵌入式的tomcat Jetty等 这些是配置类&…...
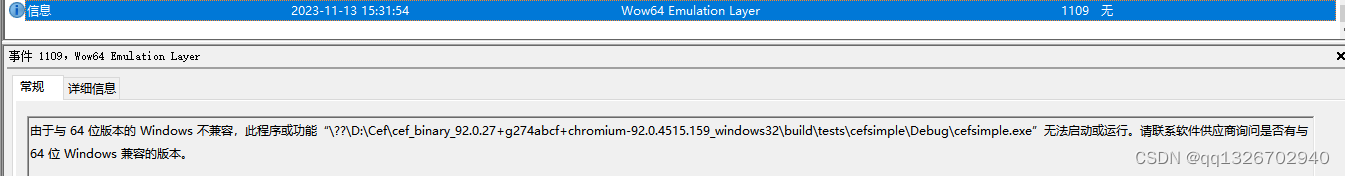
Windows 10 下使用Visual Studio 2017 编译CEF SDK
1.下载CEF SDK 由于需要跑在32位的机器,所以选择下载32位的SDKCEF Automated Builds 选择 Current Stable Build (Preferred) ,这是当前稳定版本,CEF版本118 下载成功解压 2.下载编译工具 CMake 下载地址:CMake 配置CMake指向…...

数字货币swap交易所逻辑系统开发分析方案
随着数字货币市场的快速发展, Swap交易所已成为一种重要的交易方式。本文将对数字货币Swap交易所逻辑系统开发进行分析,并探讨其优势、开发难点和解决方案。 一、数字货币Swap交易所逻辑系统开发的优势 数字货币Swap交易所是一种点对点的交易方式&#x…...
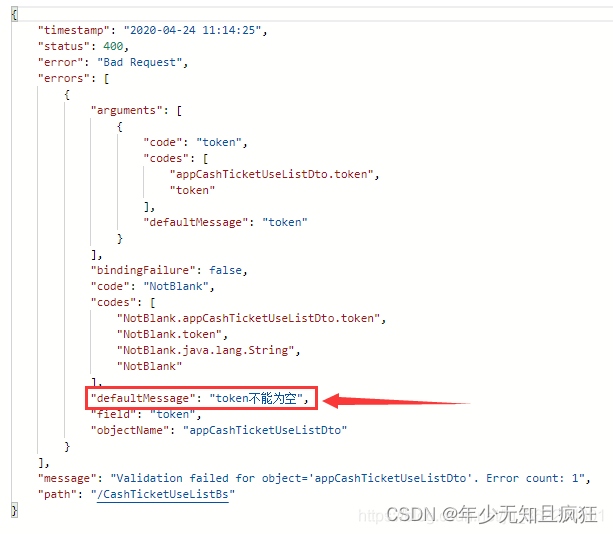
spring boot中使用Bean Validation做优雅的参数校验
一、Bean Validation简介 Bean Validation是Java定义的一套基于注解的数据校验规范,目前已经从JSR 303的1.0版本升级到JSR 349的1.1版本,再到JSR 380的2.0版本(2.0完成于2017.08),目前最新稳定版2.0.2(201…...

搜索引擎项目
认识搜索引擎 1、有一个主页、有搜索框。在搜索框中输入的内容 称为“查询词” 2、还有搜索结果页,包含了若干条搜索结果 3、针对每一个搜索结果,都会包含查询词或者查询词的一部分或者和查询词具有一定的相关性 4、每个搜索结果包含好几个部分&…...

7.外部存储器,Cache,虚拟存储器
目录 一. 外部存储器 (1)磁盘存储器 1.磁盘的组成 2.磁盘的性能指标 3.磁盘地址 4.硬盘的工作过程 5.磁盘阵列 (2)固态硬盘(SSD) 二. Cache基本概念与原理 三. Cache和主存的映射方式 ÿ…...
UITableView的style是UITableViewStyleGrouped
一般情况下,UITableViewStylePlain和UITableViewStyleGrouped是UITableView常用到的style, 之前都是用到的时候,遇到问题直接用度娘,差不多就够用了,今天在修复UI提出的间隙问题,来回改,总觉得…...

Java17新增特性
前言 前面的文章,我们对Java9、Java10、Java11、Java12 、Java13、Java14、Java15、Java16 的特性进行了介绍,对应的文章如下 Java9新增特性 Java10新增特性 Java11新增特性 Java12新增特性 Java13新增特性 Java14新增特性 Java15新增特性 Java16新增特…...

VR全景技术在城市园区发展中有哪些应用与帮助
引言: 在数字化时代的浪潮中,虚拟现实(VR)全景技术逐渐融入各个领域,也为城市园区展示带来了全新的可能性。 一.VR全景技术简介 虚拟现实全景技术是一种通过全景图像和视频模拟真实环境的技术。通过相关设…...
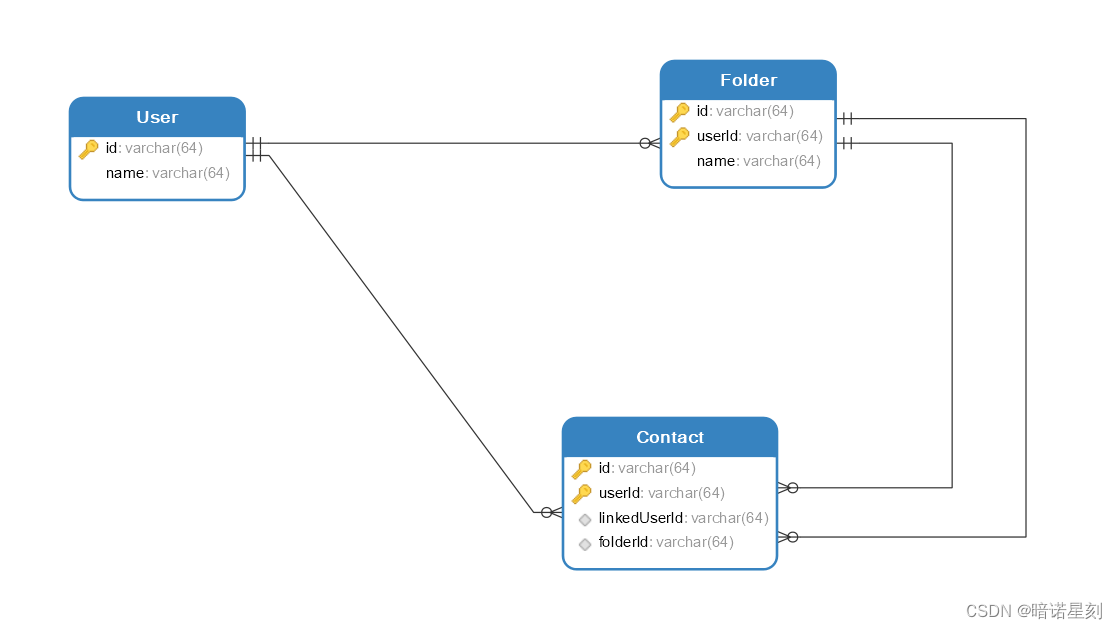
在 SQL 中,当复合主键成为外键时应该如何被其它表引用
文章目录 当研究一个问题慢慢深入时,一个看起来简单的问题也暗藏玄机。在 SQL 中,主键成为外键这是一个很平常的问题,乍一看没啥值得注意的。但如果这个主键是一种复合主键,而另一个表又引用这个键作为它的复合主键,问…...

Ps:通过显示大小了解图像的打印尺寸
在 Photoshop 中,如果想了解文档窗口中的图像打印出来之后的实质大小,只要知道两个数值即可。 第一个数值是图像分辨率(也称“文档分辨率”)的大小,可在Ps菜单:图像/图像大小 Image Size对话框中查询或设置…...

Linux - 驱动开发 - watchdog - SMP机制下多核确活
说明 理论上:不管IC是单核还是多核,只要watchdog有被循环feed,就不会触发超时重启,因此watchdog在SMP机制下的多核环境显得比较宽松,只要任意核存活(喂狗)就不会重启设备。 实际情况 有客户反…...

概念解析 | LoRA:低秩矩阵分解在神经网络微调中的魔力
注1:本文系“概念解析”系列之一,致力于简洁清晰地解释、辨析复杂而专业的概念。本次辨析的概念是:基于低秩矩阵分解的神经网络微调方法LoRA LoRA:低秩矩阵分解在神经网络微调中的魔力 Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models LoRA由如下论文提出,详细信息请参见论文原…...
量子计算和量子通信技术:引领潜力无限的未来
近年来,随着量子计算和量子通信技术的迅速发展,它们在各个领域的广泛应用前景引起了人们的极大兴趣。本文将深入探讨量子计算和量子通信技术的普遍应用,以及它们预示的未来,同时提出业内人士需要注意的事项。 介绍:量子…...
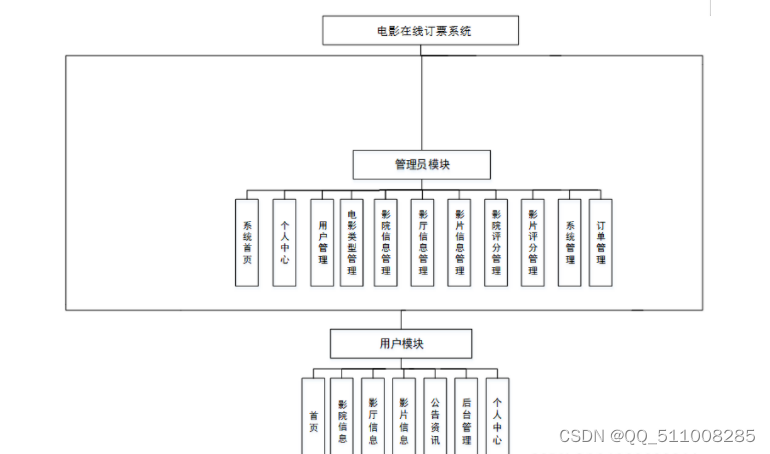
nodejs+vue+python+PHP+微信小程序-安卓- 电影在线订票系统的设计与实现-计算机毕业设计推荐
目 录 摘 要 I ABSTRACT II 目 录 II 第1章 绪论 1 1.1背景及意义 1 1.2 国内外研究概况 1 1.3 研究的内容 1 第2章 相关技术 3 2.1 nodejs简介 4 2.2 express框架介绍 6 2.4 MySQL数据库 4 第3章 系统分析 5 3.1 需求分析 5 3.2 系统可行性分析 5 3.2.1技术可行性:…...

深度学习在微纳光子学中的应用
深度学习在微纳光子学中的主要应用方向 深度学习与微纳光子学的结合主要集中在以下几个方向: 逆向设计 通过神经网络快速预测微纳结构的光学响应,替代传统耗时的数值模拟方法。例如设计超表面、光子晶体等结构。 特征提取与优化 从复杂的光学数据中自…...

在 Nginx Stream 层“改写”MQTT ngx_stream_mqtt_filter_module
1、为什么要修改 CONNECT 报文? 多租户隔离:自动为接入设备追加租户前缀,后端按 ClientID 拆分队列。零代码鉴权:将入站用户名替换为 OAuth Access-Token,后端 Broker 统一校验。灰度发布:根据 IP/地理位写…...

vue3 字体颜色设置的多种方式
在Vue 3中设置字体颜色可以通过多种方式实现,这取决于你是想在组件内部直接设置,还是在CSS/SCSS/LESS等样式文件中定义。以下是几种常见的方法: 1. 内联样式 你可以直接在模板中使用style绑定来设置字体颜色。 <template><div :s…...

什么是EULA和DPA
文章目录 EULA(End User License Agreement)DPA(Data Protection Agreement)一、定义与背景二、核心内容三、法律效力与责任四、实际应用与意义 EULA(End User License Agreement) 定义: EULA即…...

代码随想录刷题day30
1、零钱兑换II 给你一个整数数组 coins 表示不同面额的硬币,另给一个整数 amount 表示总金额。 请你计算并返回可以凑成总金额的硬币组合数。如果任何硬币组合都无法凑出总金额,返回 0 。 假设每一种面额的硬币有无限个。 题目数据保证结果符合 32 位带…...
【C++特殊工具与技术】优化内存分配(一):C++中的内存分配
目录 一、C 内存的基本概念 1.1 内存的物理与逻辑结构 1.2 C 程序的内存区域划分 二、栈内存分配 2.1 栈内存的特点 2.2 栈内存分配示例 三、堆内存分配 3.1 new和delete操作符 4.2 内存泄漏与悬空指针问题 4.3 new和delete的重载 四、智能指针…...
宇树科技,改名了!
提到国内具身智能和机器人领域的代表企业,那宇树科技(Unitree)必须名列其榜。 最近,宇树科技的一项新变动消息在业界引发了不少关注和讨论,即: 宇树向其合作伙伴发布了一封公司名称变更函称,因…...
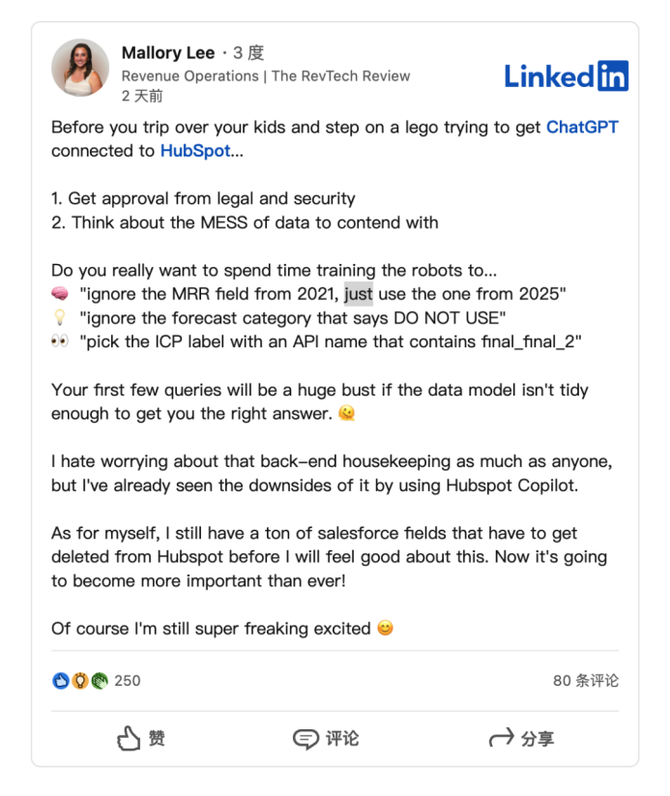
HubSpot推出与ChatGPT的深度集成引发兴奋与担忧
上周三,HubSpot宣布已构建与ChatGPT的深度集成,这一消息在HubSpot用户和营销技术观察者中引发了极大的兴奋,但同时也存在一些关于数据安全的担忧。 许多网络声音声称,这对SaaS应用程序和人工智能而言是一场范式转变。 但向任何技…...
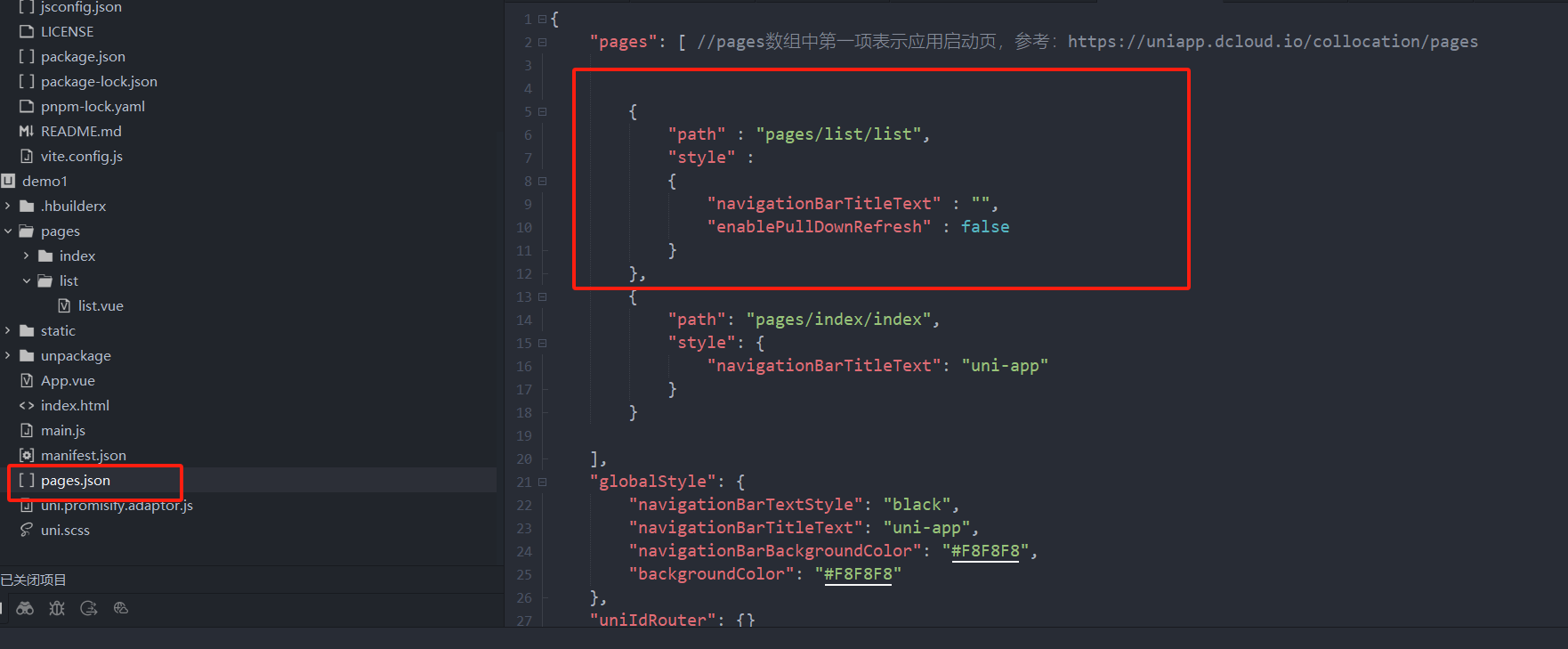
uniapp 小程序 学习(一)
利用Hbuilder 创建项目 运行到内置浏览器看效果 下载微信小程序 安装到Hbuilder 下载地址 :开发者工具默认安装 设置服务端口号 在Hbuilder中设置微信小程序 配置 找到运行设置,将微信开发者工具放入到Hbuilder中, 打开后出现 如下 bug 解…...

认识CMake并使用CMake构建自己的第一个项目
1.CMake的作用和优势 跨平台支持:CMake支持多种操作系统和编译器,使用同一份构建配置可以在不同的环境中使用 简化配置:通过CMakeLists.txt文件,用户可以定义项目结构、依赖项、编译选项等,无需手动编写复杂的构建脚本…...
