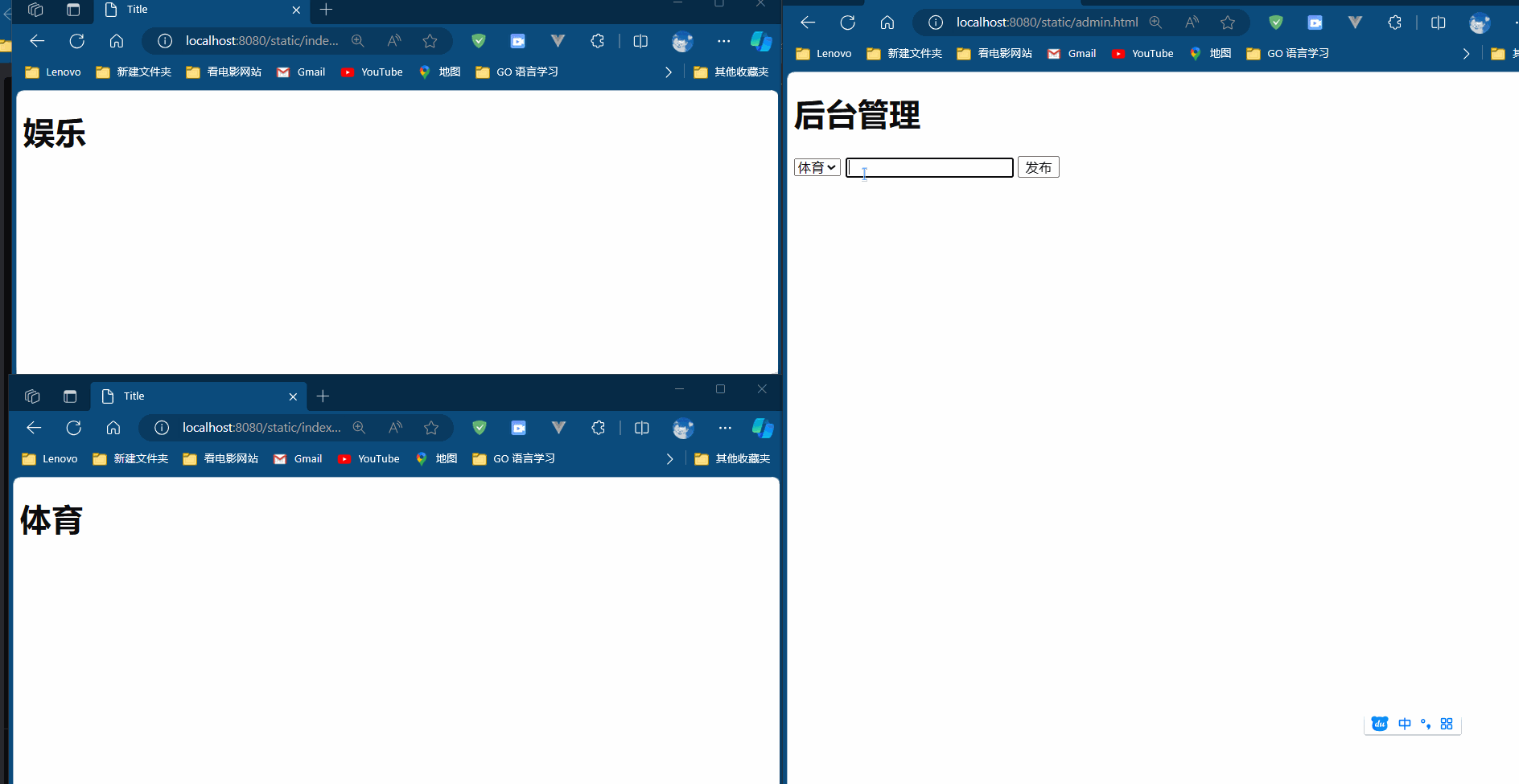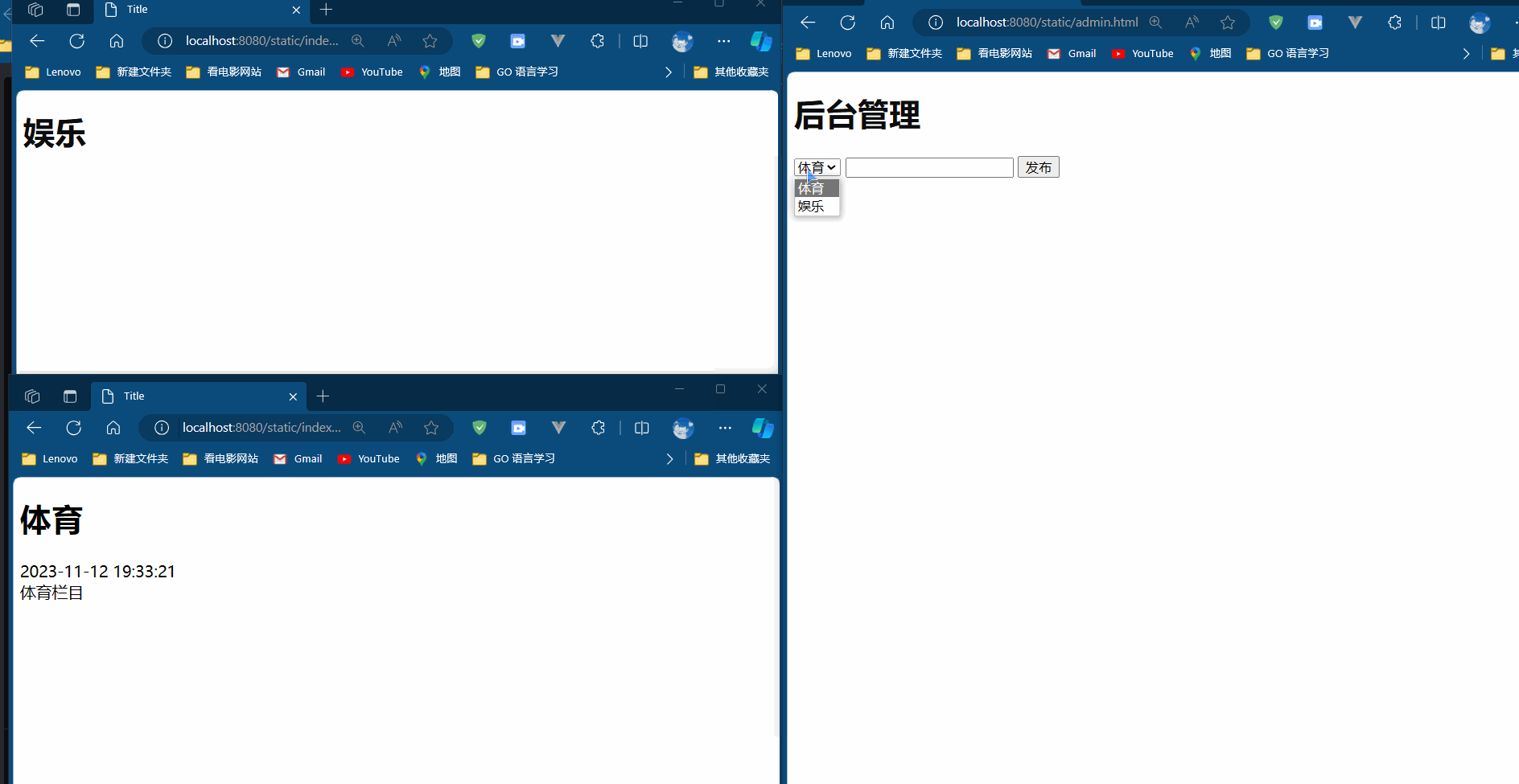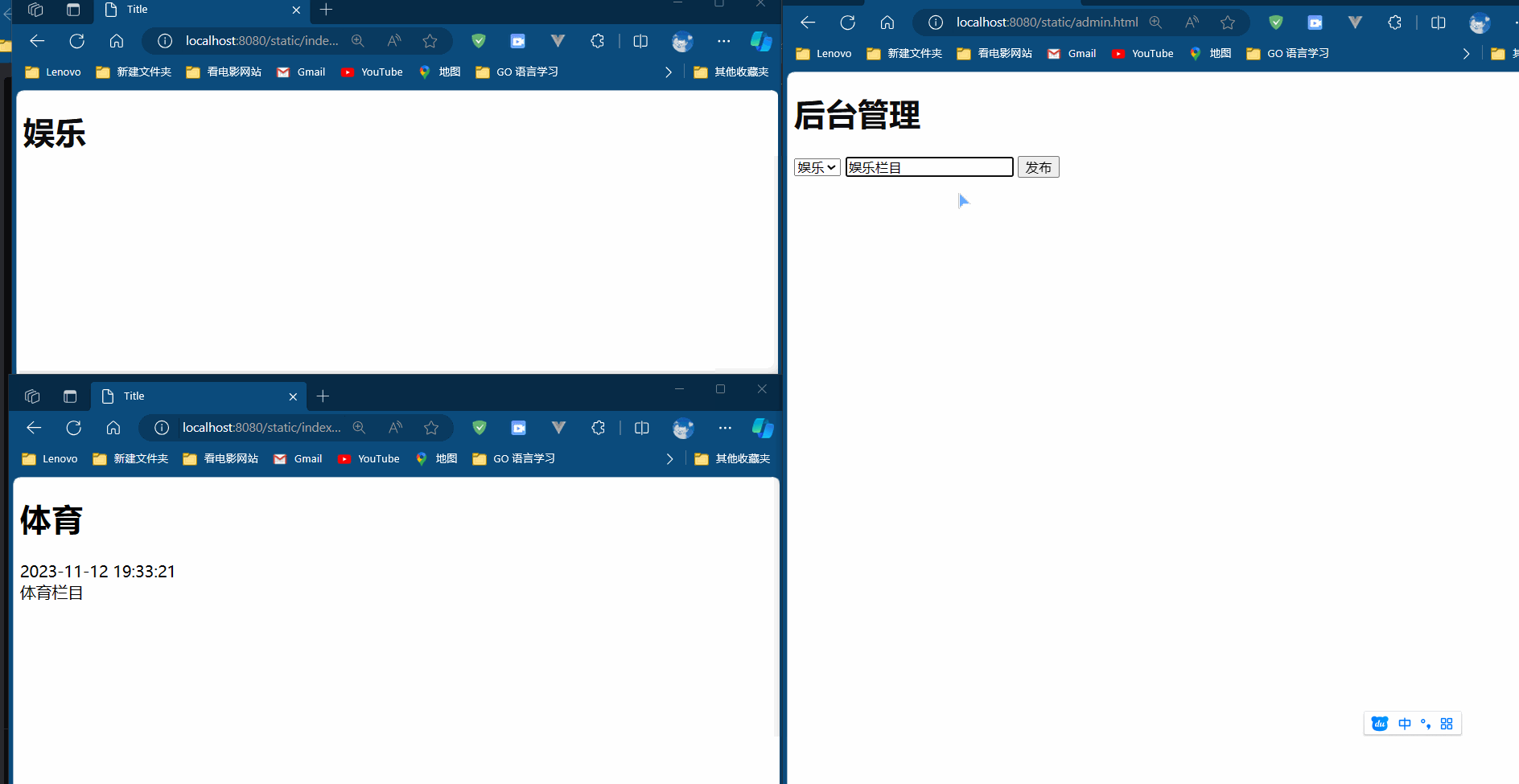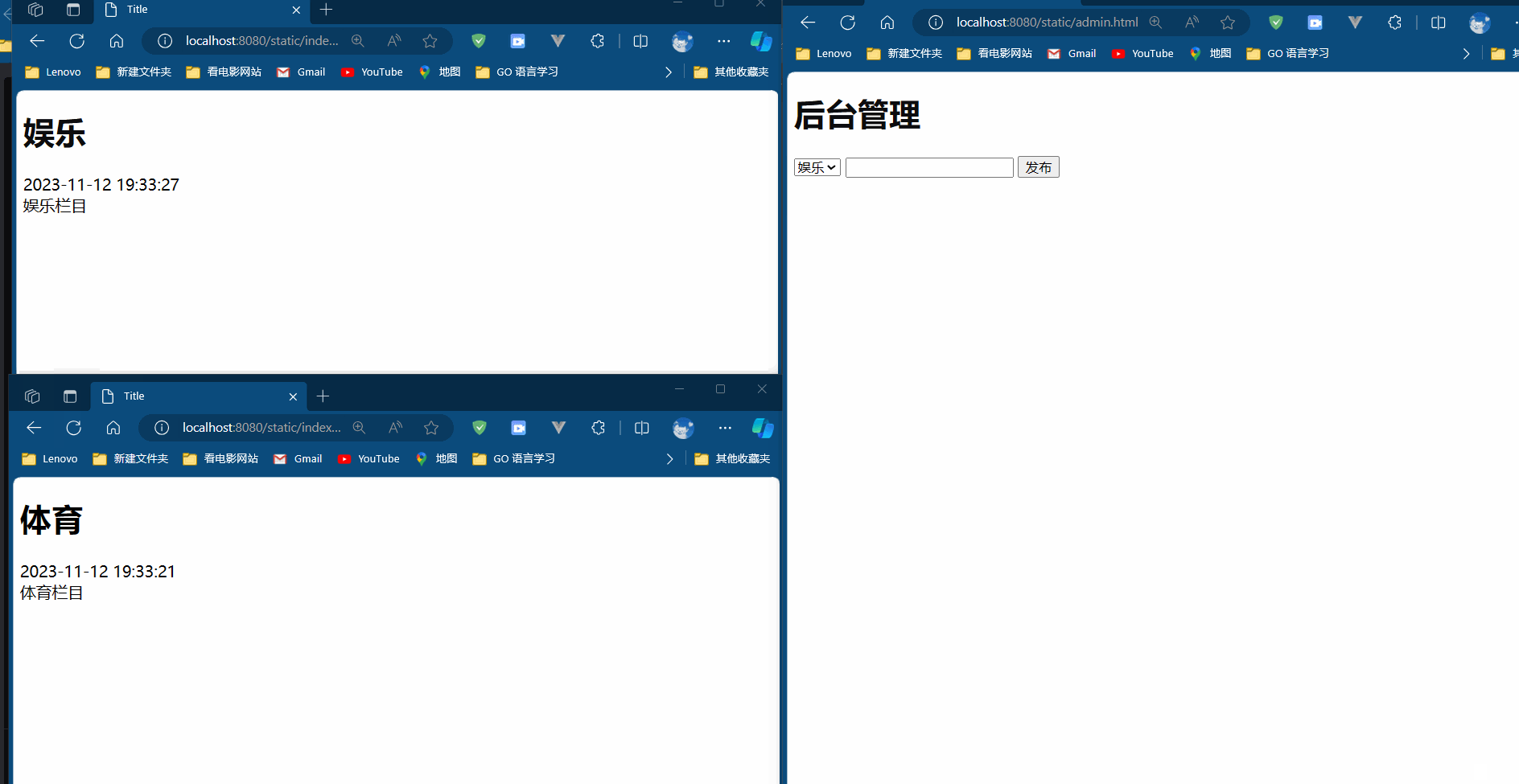
Java Stream 的常用API
Java Stream 的常用API
遍历(forEach)
package com.liudashuai;import java.util.ArrayList;
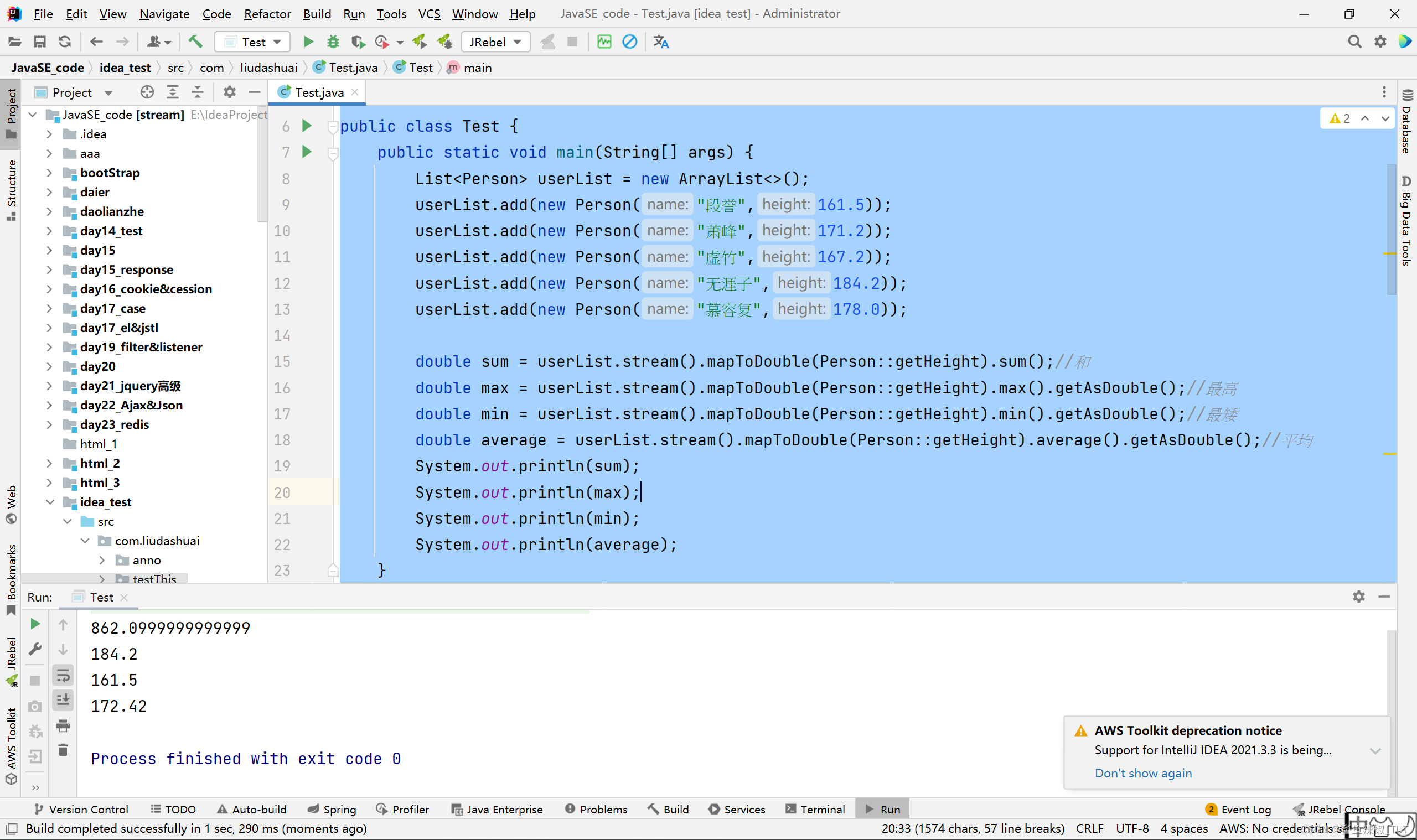
import java.util.List;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {List<Person> userList = new ArrayList<>();userList.add(new Person("段誉",25));userList.add(new Person("萧峰",40));userList.add(new Person("虚竹",30));userList.add(new Person("无涯子",100));userList.add(new Person("慕容复",35));userList.add(new Person("云中鹤",45));System.out.println(userList);System.out.println("---------------");userList.stream().forEach(u -> {u.setName("天龙八部-" + u.getName());});System.out.println(userList);}
}
class Person{private String name;private int age;public Person(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Person{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}
}
筛选(filter)
package com.liudashuai;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {List<Person> userList = new ArrayList<>();userList.add(new Person("段誉",25));userList.add(new Person("萧峰",40));userList.add(new Person("虚竹",30));userList.add(new Person("无涯子",100));userList.add(new Person("慕容复",35));userList.add(new Person("云中鹤",45));List<Person> collect =userList.stream().filter(user -> (user.getAge() > 30 && user.getName().length() >2)).collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println(collect);}
}
class Person{private String name;private int age;public Person(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Person{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}
}

查找(findAny/findFirst)
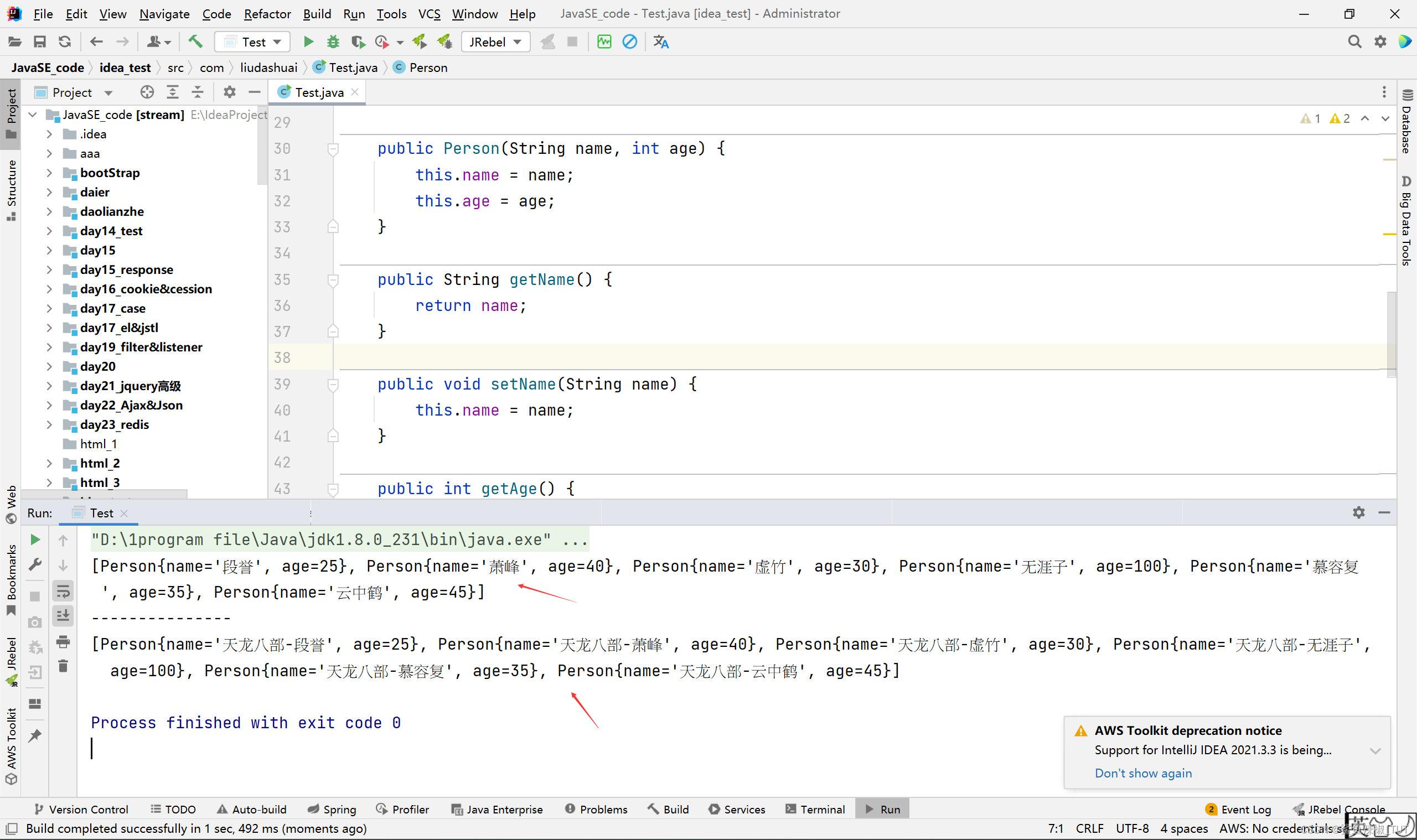
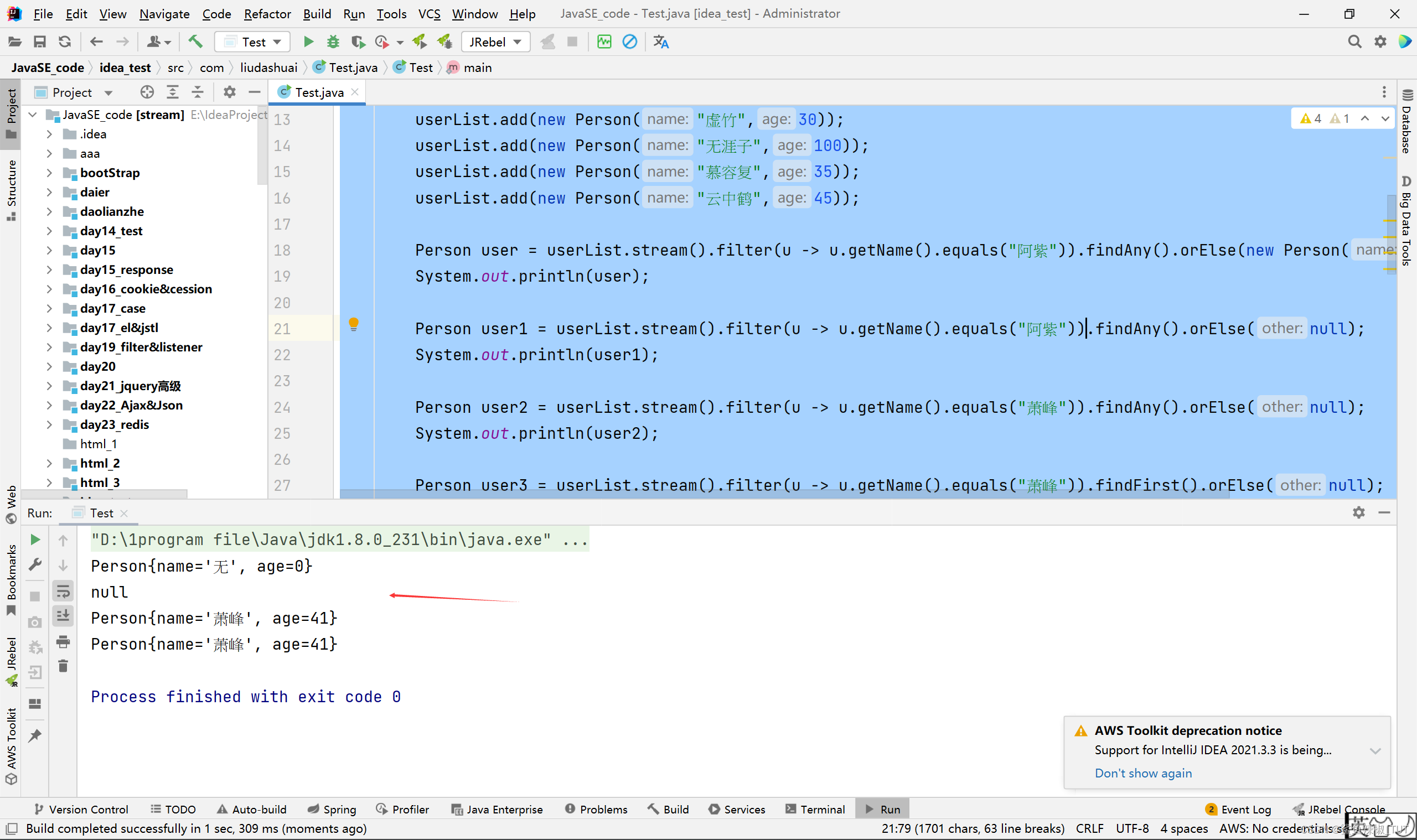
package com.liudashuai;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {List<Person> userList = new ArrayList<>();userList.add(new Person("段誉",25));userList.add(new Person("萧峰",41));userList.add(new Person("萧峰",42));userList.add(new Person("萧峰",43));userList.add(new Person("虚竹",30));userList.add(new Person("无涯子",100));userList.add(new Person("慕容复",35));userList.add(new Person("云中鹤",45));Person user = userList.stream().filter(u -> u.getName().equals("阿紫")).findAny().orElse(new Person("无",0));System.out.println(user);Person user1 = userList.stream().filter(u -> u.getName().equals("阿紫")).findAny().orElse(null);System.out.println(user1);Person user2 = userList.stream().filter(u -> u.getName().equals("萧峰")).findAny().orElse(null);System.out.println(user2);Person user3 = userList.stream().filter(u -> u.getName().equals("萧峰")).findFirst().orElse(null);System.out.println(user3);}
}
class Person{private String name;private int age;public Person(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Person{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}
}
- findFirst() 方法根据命名,我们可以大致知道是获取Optional流中的第一个元素。
- findAny() 方法是获取Optional 流中任意一个,存在随机性,其实这里也是获取元素中的第一个,因为是并行流。
注意:在串行流中,findFirst和findAny返回同样的结果;但在并行流中,由于多个线程同时处理,findFirst可能会返回处理结果中的第一个元素,而findAny会返回最先处理完的元素。所以并行流里面使用findAny会更高效。这里并行下findFirst可能返回的不是第一个符合条件的元素吗?我不知道,但是,不重要,因为用得场景不多,因为多线程下,谁是处理结果中的第一个元素一般不重要,因为谁都可能是第一个,所以这里我不去了解findFirst是否可能返回的不是第一个符合条件的元素了。
总之就是串行流下,findFirst和findAny结果一样,并行流下,findAny效率更高,且并行流一般不在意谁是第一个,所以我建议平时使用findAny。
.orElse(null)表示如果一个都没找到返回null。
orElse()中可以塞默认值。如果找不到就会返回orElse中你自己设置的默认值。比如:上面的.orElse(new Person(“无”,0))
转换/去重(map/distinct)
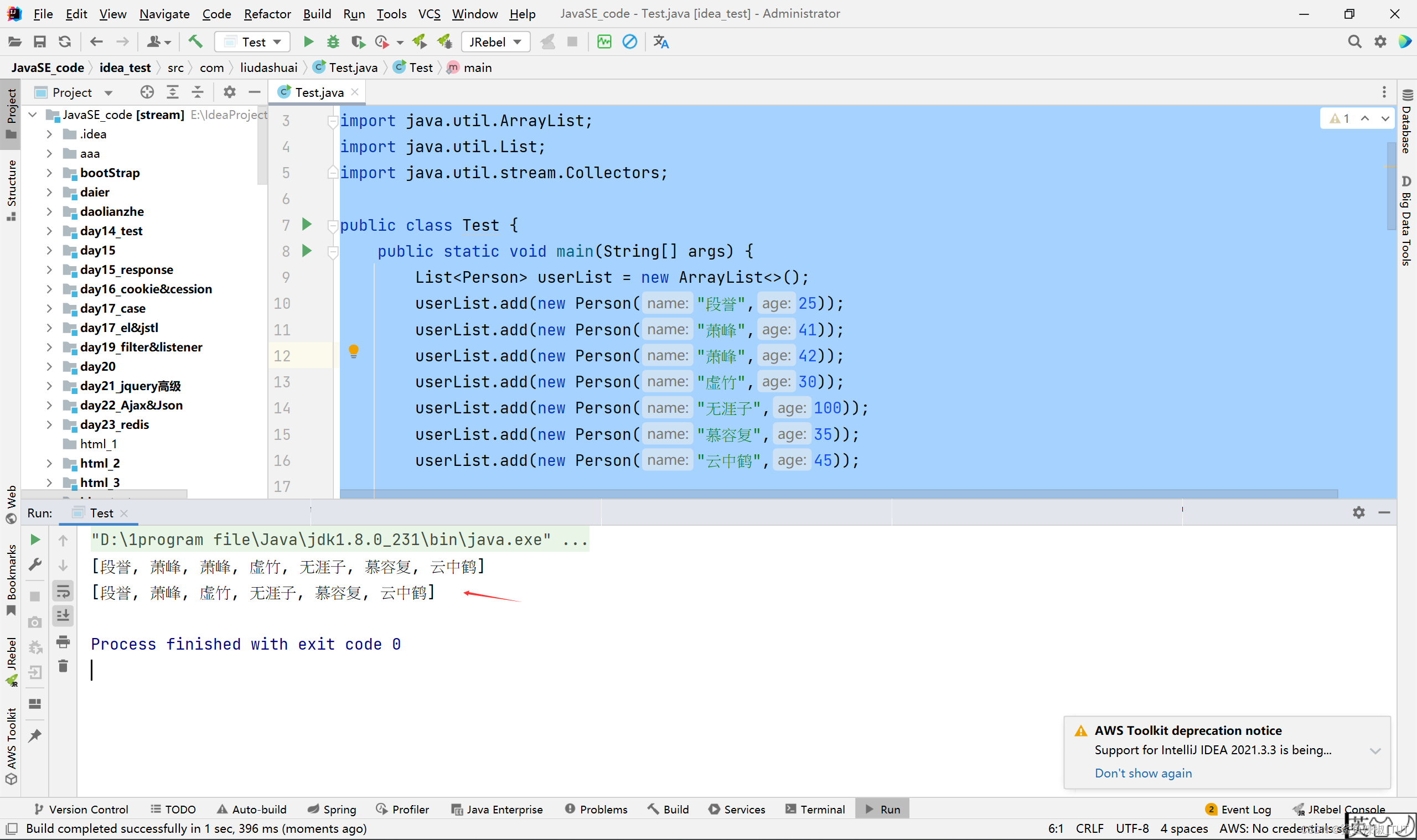
package com.liudashuai;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {List<Person> userList = new ArrayList<>();userList.add(new Person("段誉",25));userList.add(new Person("萧峰",41));userList.add(new Person("萧峰",42));userList.add(new Person("虚竹",30));userList.add(new Person("无涯子",100));userList.add(new Person("慕容复",35));userList.add(new Person("云中鹤",45));List<String> nameList = userList.stream().map(Person::getName).collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println(nameList);List<String> nameList2 = userList.stream().map(Person::getName).distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println(nameList2);}
}
class Person{private String name;private int age;public Person(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Person{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}
}
map的作用:是将输入一种类型,转化为另一种类型,通俗来说:就是将输入类型变成另一个类型。
跳过(limit/skip)
package com.liudashuai;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {List<Person> userList = new ArrayList<>();userList.add(new Person("段誉",25));userList.add(new Person("萧峰",41));userList.add(new Person("虚竹",30));userList.add(new Person("无涯子",100));userList.add(new Person("慕容复1",35));userList.add(new Person("慕容复2",35));userList.add(new Person("慕容复3",35));//跳过第一个List<Person> collect = userList.stream().skip(1).collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println(collect);//只输出前两个元素List<Person> collect2 = userList.stream().limit(2).collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println(collect2);//跳过前3个元素,然后输出3个元素。可以代替sql中的limit。List<Person> collect3 = userList.stream().skip(3).limit(3).collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println(collect3);}
}
class Person{private String name;private int age;public Person(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Person{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}
}
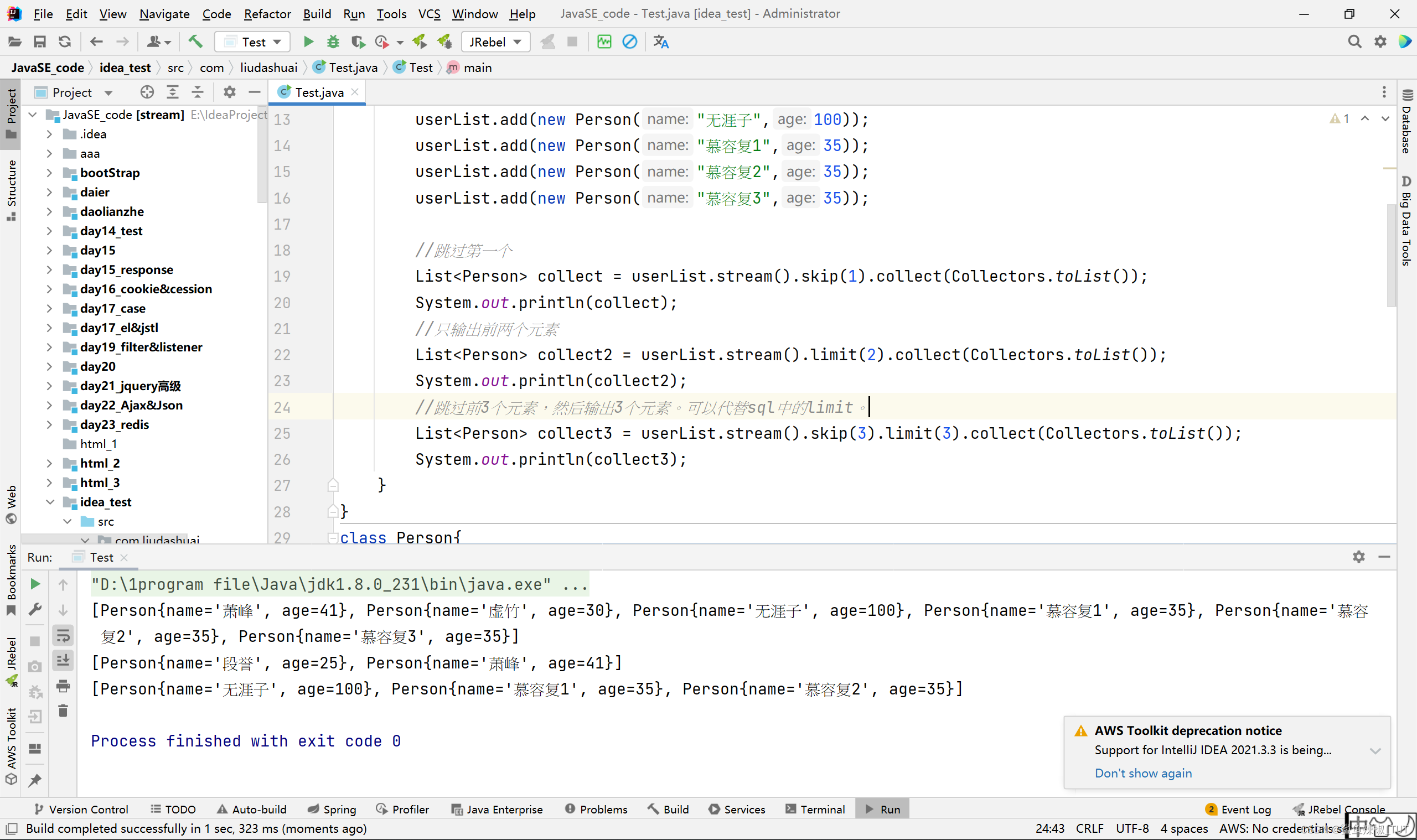
最大值/最小值/平均值(reduce)
package com.liudashuai;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
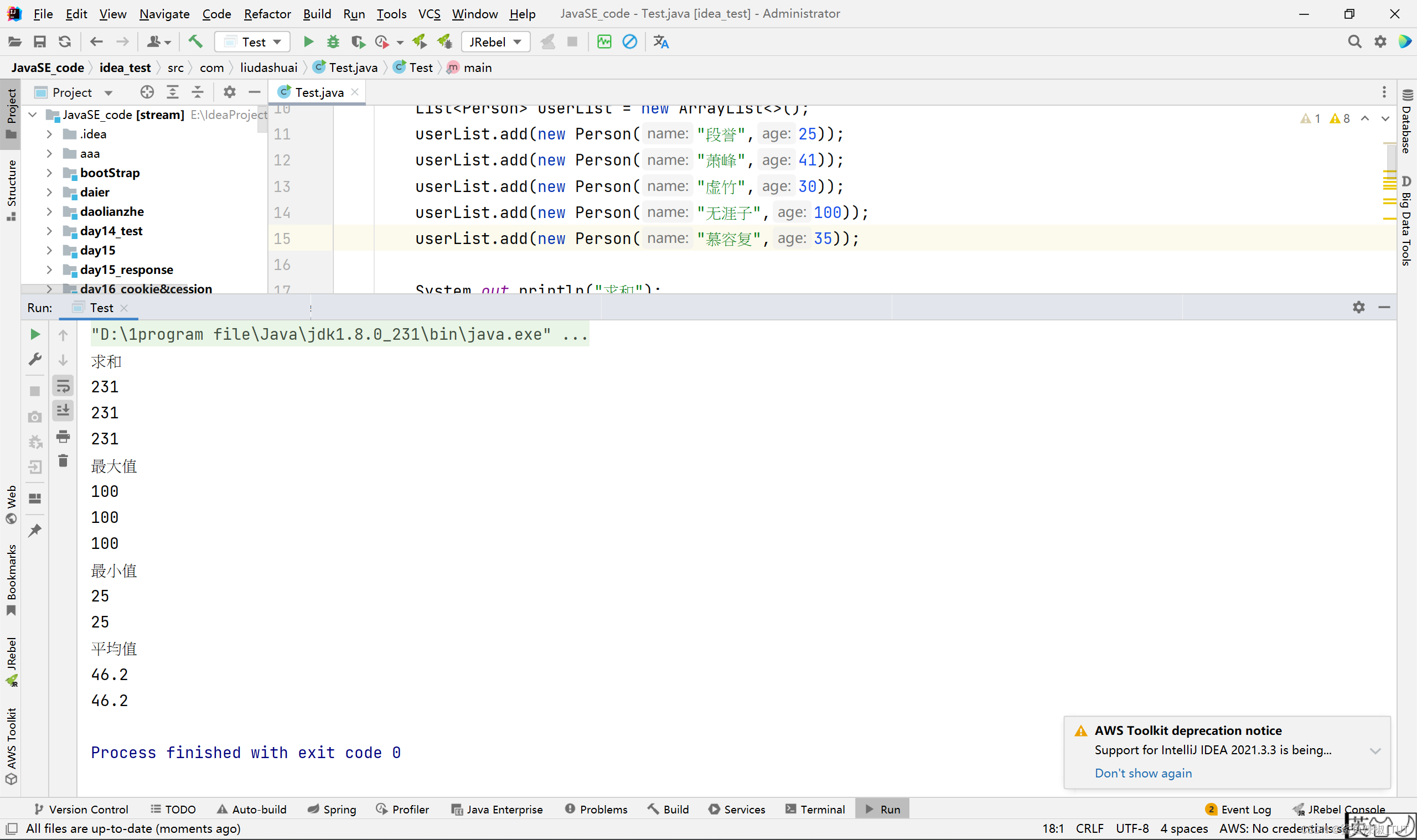
import java.util.stream.Collectors;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {List<Person> userList = new ArrayList<>();userList.add(new Person("段誉",25));userList.add(new Person("萧峰",41));userList.add(new Person("虚竹",30));userList.add(new Person("无涯子",100));userList.add(new Person("慕容复",35));System.out.println("求和");Integer sum1 = userList.stream().map(Person::getAge).reduce(0, Integer::sum);System.out.println(sum1);int sum2 = userList.stream().mapToInt(Person::getAge).sum();System.out.println(sum2);Integer sum3 = userList.stream().collect(Collectors.summingInt(Person::getAge));System.out.println(sum3);System.out.println("最大值");Optional<Integer> max1 = userList.stream().map(Person::getAge).collect(Collectors.toList()).stream().reduce((v1, v2) -> v1 > v2 ? v1 : v2);System.out.println(max1.get());Optional<Integer> max2 = userList.stream().map(Person::getAge).collect(Collectors.toList()).stream().reduce(Integer::max);System.out.println(max2.get());int max3 = userList.stream().mapToInt(Person::getAge).max().getAsInt();System.out.println(max3);System.out.println("最小值");Optional<Integer> min = userList.stream().map(Person::getAge).collect(Collectors.toList()).stream().reduce(Integer::min);System.out.println(min.get());int min2 = userList.stream().mapToInt(Person::getAge).min().getAsInt();System.out.println(min2);System.out.println("平均值");Double averaging1 = userList.stream().collect(Collectors.averagingDouble(Person::getAge));System.out.println(averaging1);double averaging2 = userList.stream().mapToInt(Person::getAge).average().getAsDouble();System.out.println(averaging2);}
}
class Person{private String name;private int age;public Person(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Person{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}
}
mapToInt是 Stream API中一个非常有用的方法。它的主要作用是将一个 Stream 转换成一个IntStream,使得可以更加方便地对数字流进行处理。
IntStream中的一些常用方法如下:
- sum()
- max()
- min()
- average()
这些方法上面案例里面也有演示。
如果要操作的元素不是int,是double,我们也可以用mapToDouble也行。
package com.liudashuai;import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {List<Person> userList = new ArrayList<>();userList.add(new Person("段誉",161.5));userList.add(new Person("萧峰",171.2));userList.add(new Person("虚竹",167.2));userList.add(new Person("无涯子",184.2));userList.add(new Person("慕容复",178.0));double sum = userList.stream().mapToDouble(Person::getHeight).sum();//和double max = userList.stream().mapToDouble(Person::getHeight).max().getAsDouble();//最高double min = userList.stream().mapToDouble(Person::getHeight).min().getAsDouble();//最矮double average = userList.stream().mapToDouble(Person::getHeight).average().getAsDouble();//平均System.out.println(sum);System.out.println(max);System.out.println(min);System.out.println(average);} } class Person{private String name;private double height;public Person(String name, double height) {this.name = name;this.height = height;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public double getHeight() {return height;}public void setHeight(double height) {this.height = height;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Person{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", height=" + height +'}';} }
统计(count/counting)
package com.liudashuai;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
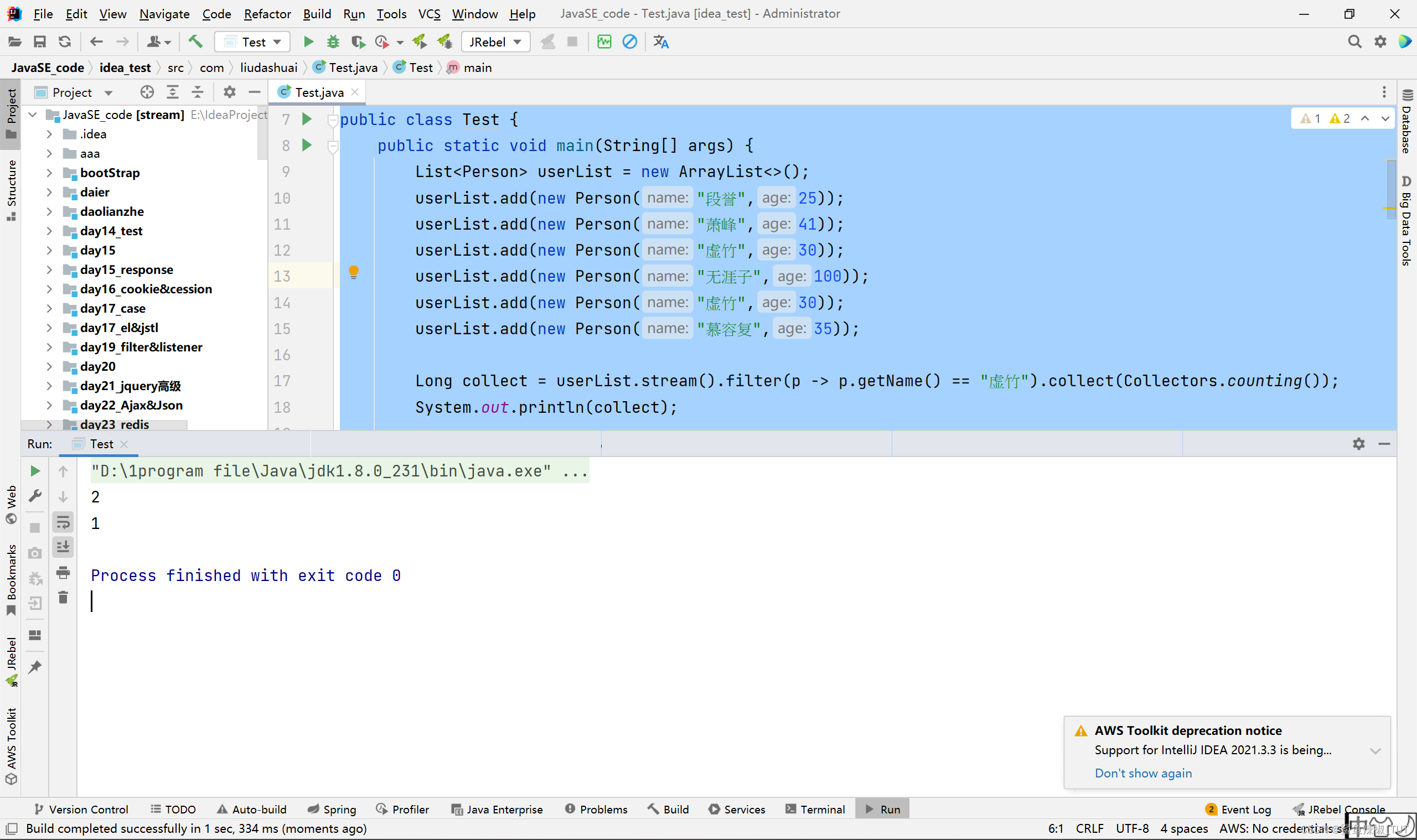
import java.util.stream.Collectors;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {List<Person> userList = new ArrayList<>();userList.add(new Person("段誉",25));userList.add(new Person("萧峰",41));userList.add(new Person("虚竹",30));userList.add(new Person("无涯子",100));userList.add(new Person("虚竹",30));userList.add(new Person("慕容复",35));Long collect = userList.stream().filter(p -> p.getName() == "虚竹").collect(Collectors.counting());System.out.println(collect);long count = userList.stream().filter(p -> p.getAge() >= 50).count();System.out.println(count);}
}
class Person{private String name;private int age;public Person(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Person{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}
}
排序(sorted)
package com.liudashuai;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
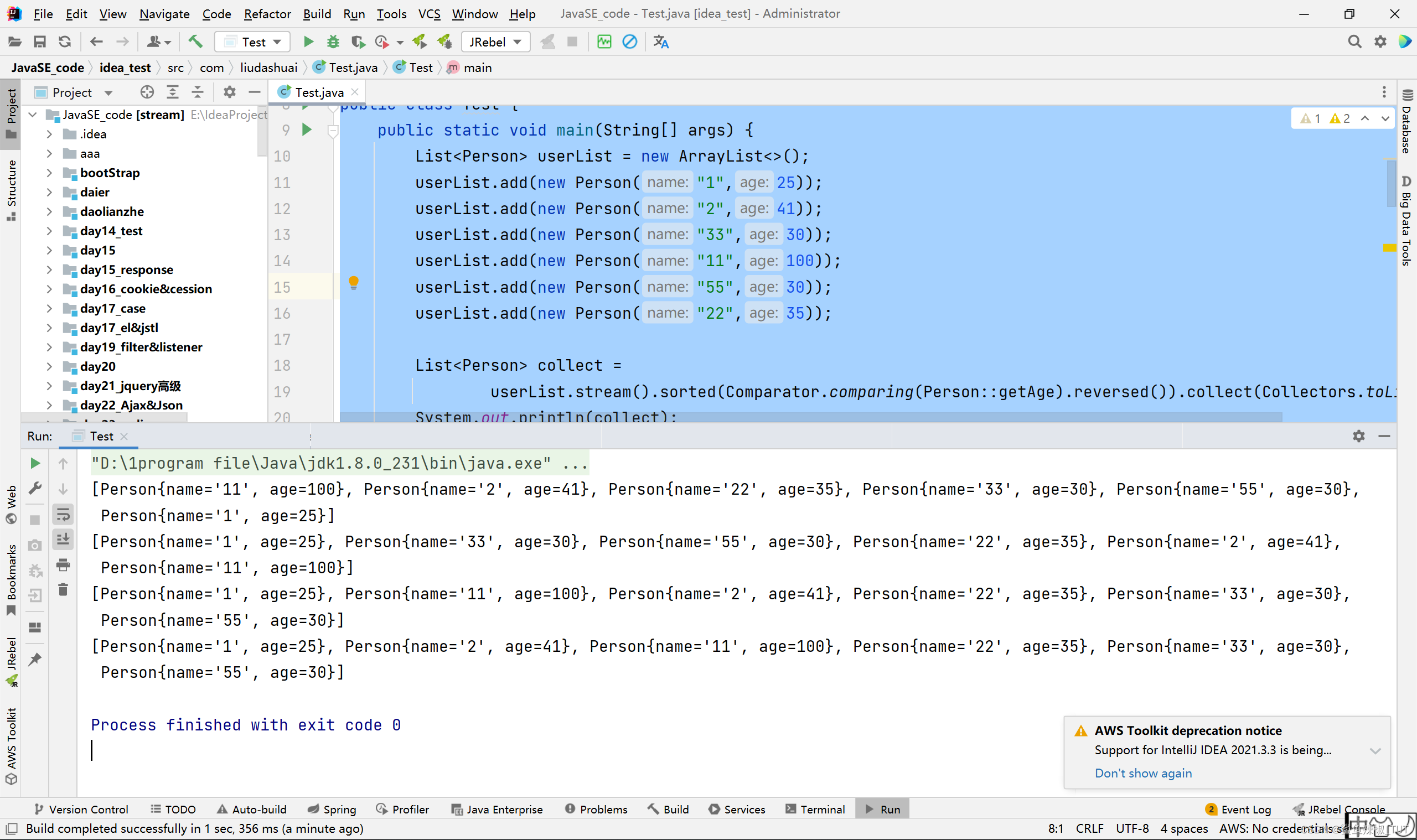
import java.util.stream.Collectors;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {List<Person> userList = new ArrayList<>();userList.add(new Person("1",25));userList.add(new Person("2",41));userList.add(new Person("33",30));userList.add(new Person("11",100));userList.add(new Person("55",30));userList.add(new Person("22",35));List<Person> collect =userList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Person::getAge).reversed()).collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println(collect);List<Person> collect2 =userList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Person::getAge)).collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println(collect2);List<Person> collect3 =userList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Person::getName)).collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println(collect3);List<Person> collect4 = userList.stream().sorted((e1, e2) -> {return Integer.compare(Integer.parseInt(e1.getName()), Integer.parseInt(e2.getName()));}).collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println(collect4);}
}
class Person{private String name;private int age;public Person(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Person{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}
}
相关文章:

Java Stream 的常用API
Java Stream 的常用API 遍历(forEach) package com.liudashuai;import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {List<Person> userList new ArrayList<>();userList.ad…...

代驾预约小程序系统源码 :提起预约,避免排队 带完整搭建教程
大家好啊,又到罗峰来给大家分享好用的源码系统的时间了。今天要给大家分享的第一款代驾预约小程序源码系统。传统的代驾服务中,用户往往需要在酒后代驾、长途驾驶等场景下,面对排队等待代驾司机空闲时间的繁琐过程。这不仅浪费了用户的时间和…...

es 报错 Data too large 触发断路器
文章目录 [toc]事出有因解决思路效果展示关于重启课外扩展 事出有因 报错原因是 es 在 full GC 之前触发了默认的断路器,导致报错 [parent] Data too large,相似的报错内容如下: Caused by: org.elasticsearch.common.breaker.CircuitBreakin…...
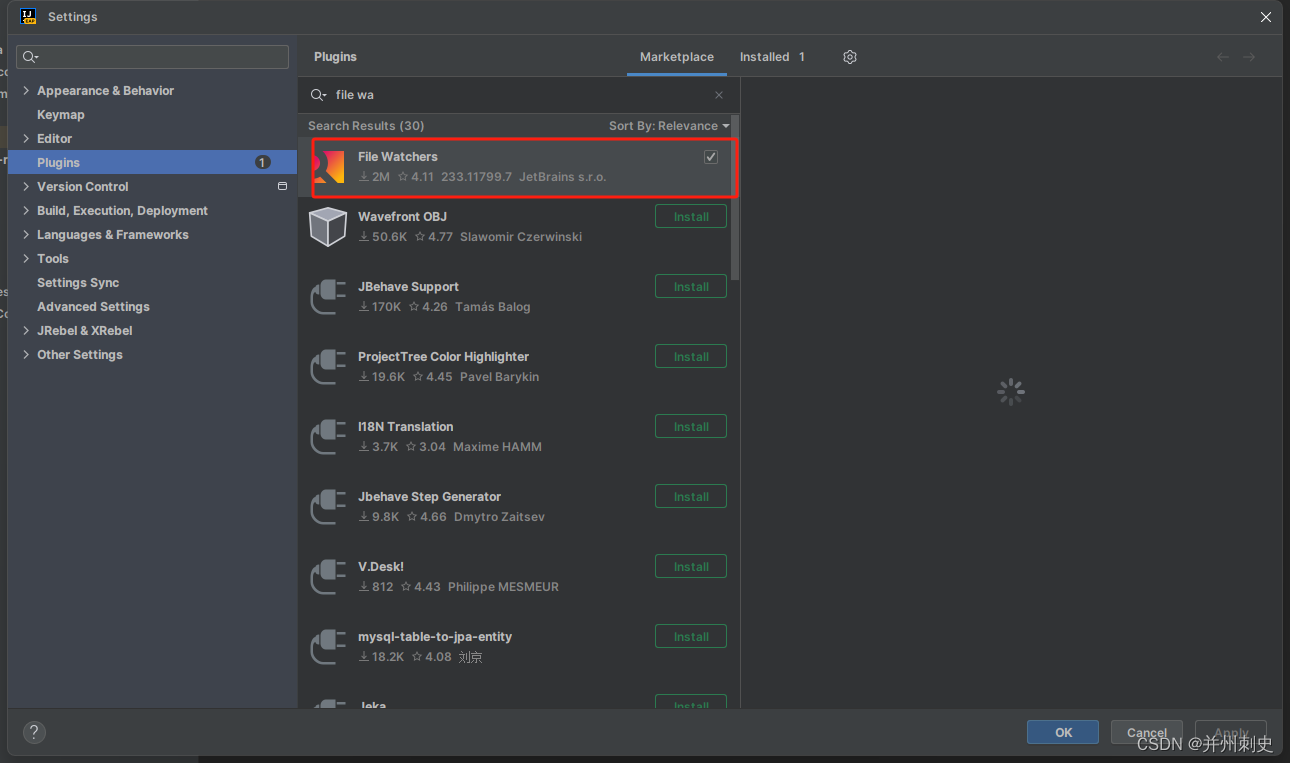
idea报[Ubuntu] File watcher failed repeatedly and has been disabled
1.安装File Watchers 2.restart idea解决...
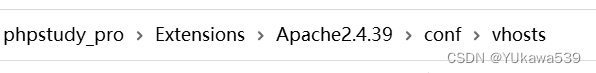
phpstudy 开启目录浏览功能
(1)在该目录下: (2)选择对应网站的配置文件; (3)修改: # Options FollowSymLinks ExecCGI Options Indexes FollowSymLinks ExecCGI...

【前端开发】图例宽度根据数值自适应
前端开发 先看结果图 图例的宽度会随数值的改变而变化。 HTML部分 <!-- 数值部分 --> <ul class"tuli" ref"num"><listyle"margin-top: 5px;padding: 0 5px;text-align: center;"v-for"item of itemArr":key"i…...

AOMedia发布免版税沉浸音频规范IAMF
11月10日,开放媒体联盟(AOMedia)发布了旗下首个沉浸式音频规范IAMF(https://aomediacodec.github.io/iamf/),IAMF是一种编解码器无关的容器规范,可以携带回放时间渲染算法和音频混音的信息&…...

Linux C 进程编程
进程编程 进程介绍进程的定义进程和线程以及程序的区别进程块PCB进程的状态相关指令 进程调度算法先来先服务调度算法 FCFS短作业(进程)优先调度算法 SJF优先权调度算法 FPF优先权调度算法的类型非抢占式优先权算法抢占式优先权算法 优先权类型静态优先权动态优先权 高响应比优…...
Spring Boot (三)
1、热部署 热部署可以替我们节省大把花在重启项目本身上的时间。热部署原理上,一个springboot项目在运行时实际上是分两个过程进行的,根据加载的东西不同,划分成base类加载器与restart类加载器。 base类加载器:用来加载jar包中的类…...

第五章:抽象类
系列文章目录 文章目录 系列文章目录前言一、抽象类二、模板设计模式总结 前言 当我们想让子类来实现方法时,我们需要抽象类与抽象方法。 一、抽象类 当父类的某些方法,需要声明,但是又不确定如何实现时,可以将其声明为抽象方法…...
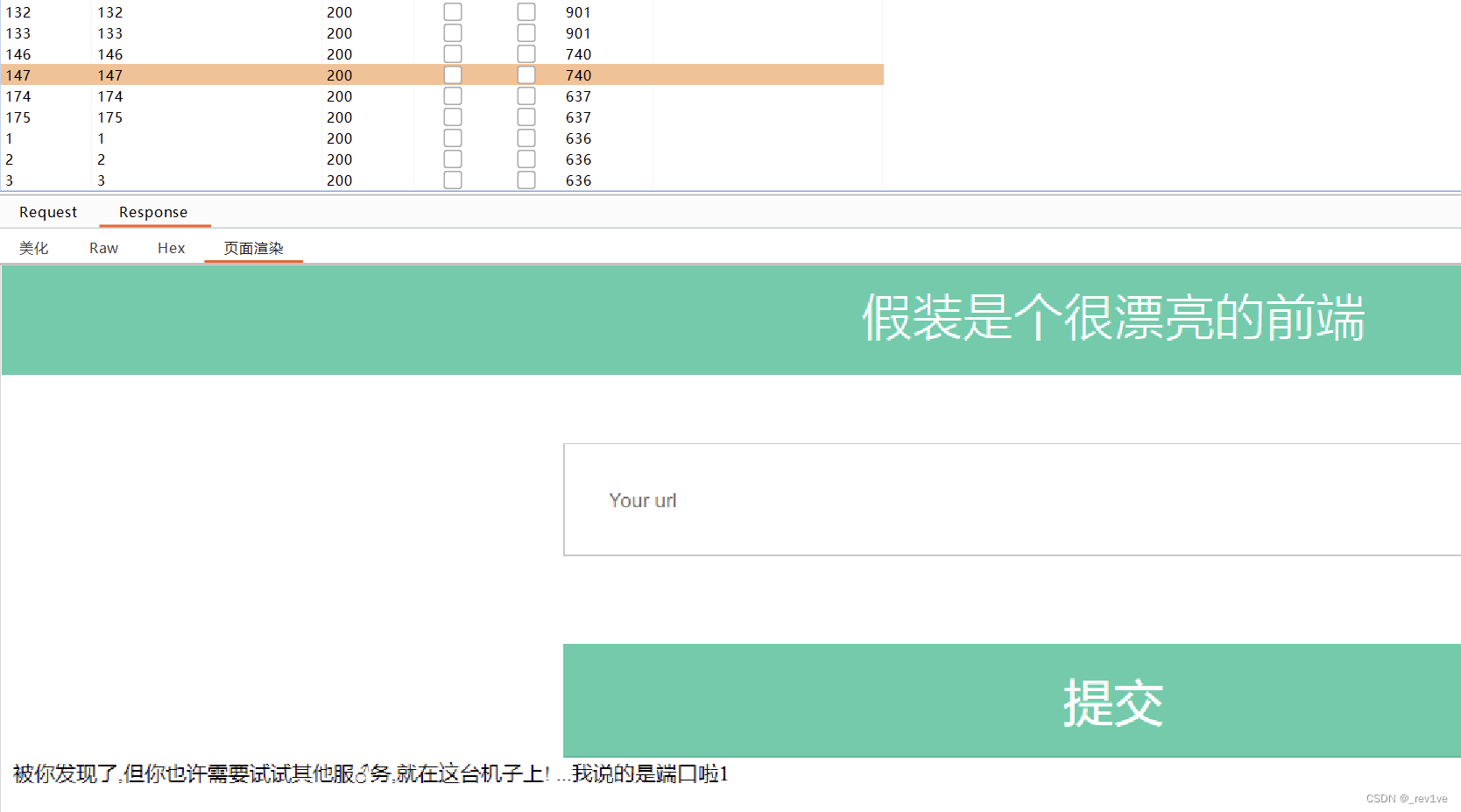
NSSCTF web刷题记录5
文章目录 [HZNUCTF 2023 preliminary]ezlogin[MoeCTF 2021]地狱通讯[NSSRound#7 Team]0o0[ISITDTU 2019]EasyPHP[极客大挑战 2020]greatphp[安洵杯 2020]Validator[GKCTF 2020]ez三剑客-ezweb [HZNUCTF 2023 preliminary]ezlogin 考点:时间盲注 打开题目,…...

Spark SQL 每年的1月1日算当年的第一个自然周, 给出日期,计算是本年的第几周
一、问题 按每年的1月1日算当年的第一个自然周 (遇到跨年也不管,如果1月1日是周三,那么到1月5号(周日)算是本年的第一个自然周, 如果按周一是一周的第一天) 计算是本年的第几周,那么 spark sql 如何写 ? 二、分析 …...
WebSocket Day04 : 消息推送
前言 随着Web应用程序的不断发展,实时性和交互性成为了用户体验中至关重要的一部分。传统的HTTP协议在处理实时数据传输方面存在一些局限性,而WebSocket作为一种全双工通信协议,为实现实时、高效的消息推送提供了全新的解决方案。 在Web开发…...

【Hadoop】MapReduce详解
🦄 个人主页——🎐开着拖拉机回家_大数据运维-CSDN博客 🎐✨🍁 🪁🍁🪁🍁🪁🍁🪁🍁 🪁🍁🪁…...
ctf之流量分析学习
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1e3ZcfioIOmebbUs-xGRnUA?pwd9jmc 提取码:9jmc 前几道比较简单,是经常见、常考到的类型 1.pcap——zip里 流量分析里有压缩包 查字符串或者正则表达式,在包的最底层找到flag的相关内容 我们追踪…...
Linux——vim简介、配置方案(附带超美观的配置方案)、常用模式的基本操作
vim简介、配置方案、常用模式的基本操作 本章思维导图: 注:本章思维导图对应的xmind和.png文件都已同步导入至资源 1. vim简介 vim是Linux常用的文本编辑器,每个Linux账户都独有一个vim编辑器 本篇我们介绍vim最常用的三种模式:…...

在线预览编辑PDF::RAD PDF for ASP.NET
RAD PDF for ASP.NET作为功能最齐全的基于 HTML 的 PDF 查看器、编辑器和 ASP.NET 表单填充器,RAD PDF 为传统 PDF 解决方案提供了灵活而强大的替代方案。与 Adobe Acrobat Reader 不同,RAD PDF 几乎可以在任何现代网络浏览器中运行,…...

【赠书第4期】机器学习与人工智能实战:基于业务场景的工程应用
文章目录 前言 1 机器学习基础知识 2 人工智能基础知识 3 机器学习和人工智能的实战案例 4 总结 5 推荐图书 6 粉丝福利 前言 机器学习与人工智能是当前最热门的领域之一,也是未来发展的方向。随着科技的不断进步,越来越多的企业开始关注和投入机…...
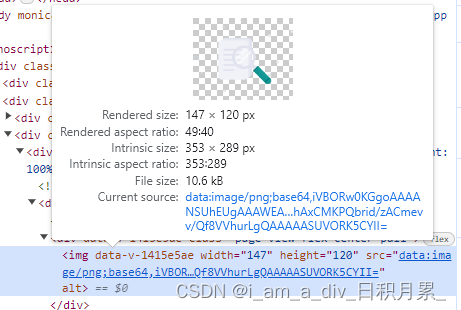
npm封装插件打包上传后图片资源错误
问题: npm封装插件:封装的组件页面涉及使用图片资源,在封装的项目里调用图片显示正常;但是打包上传后,其他项目引入使用报错找不到图片资源;图片路径也不对 获取图片的base64方法 解决方案: 将…...
[云原生案例2.3 ] Kubernetes的部署安装 【多master集群架构高可用 ---- (二进制安装部署)】
文章目录 1. Kubernetes多Master集群高可用方案1.1 多节点Master高可用的实现过程1.2 实现高可用方法 2. 新Master节点的部署2.1 前置准备2.2 系统初始化操作2.2.1 关闭防火墙、selinux和swap分区2.2.2 修改主机名,添加域名映射2.2.3 修改内核参数2.2.4 时间同步 2.…...

React hook之useRef
React useRef 详解 useRef 是 React 提供的一个 Hook,用于在函数组件中创建可变的引用对象。它在 React 开发中有多种重要用途,下面我将全面详细地介绍它的特性和用法。 基本概念 1. 创建 ref const refContainer useRef(initialValue);initialValu…...
【Oracle APEX开发小技巧12】
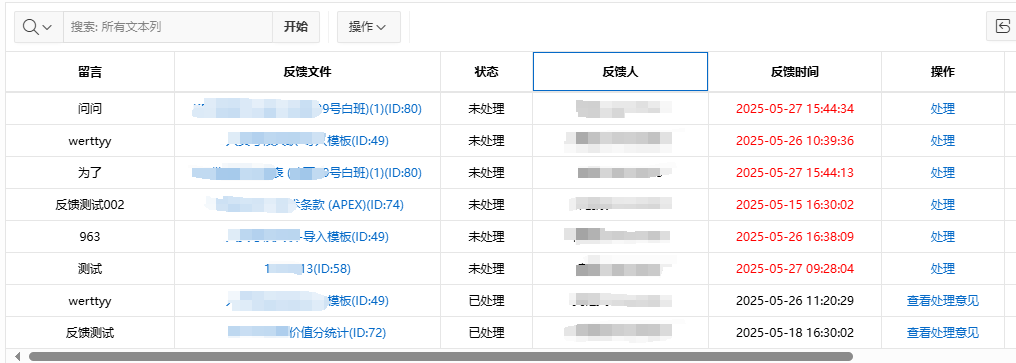
有如下需求: 有一个问题反馈页面,要实现在apex页面展示能直观看到反馈时间超过7天未处理的数据,方便管理员及时处理反馈。 我的方法:直接将逻辑写在SQL中,这样可以直接在页面展示 完整代码: SELECTSF.FE…...
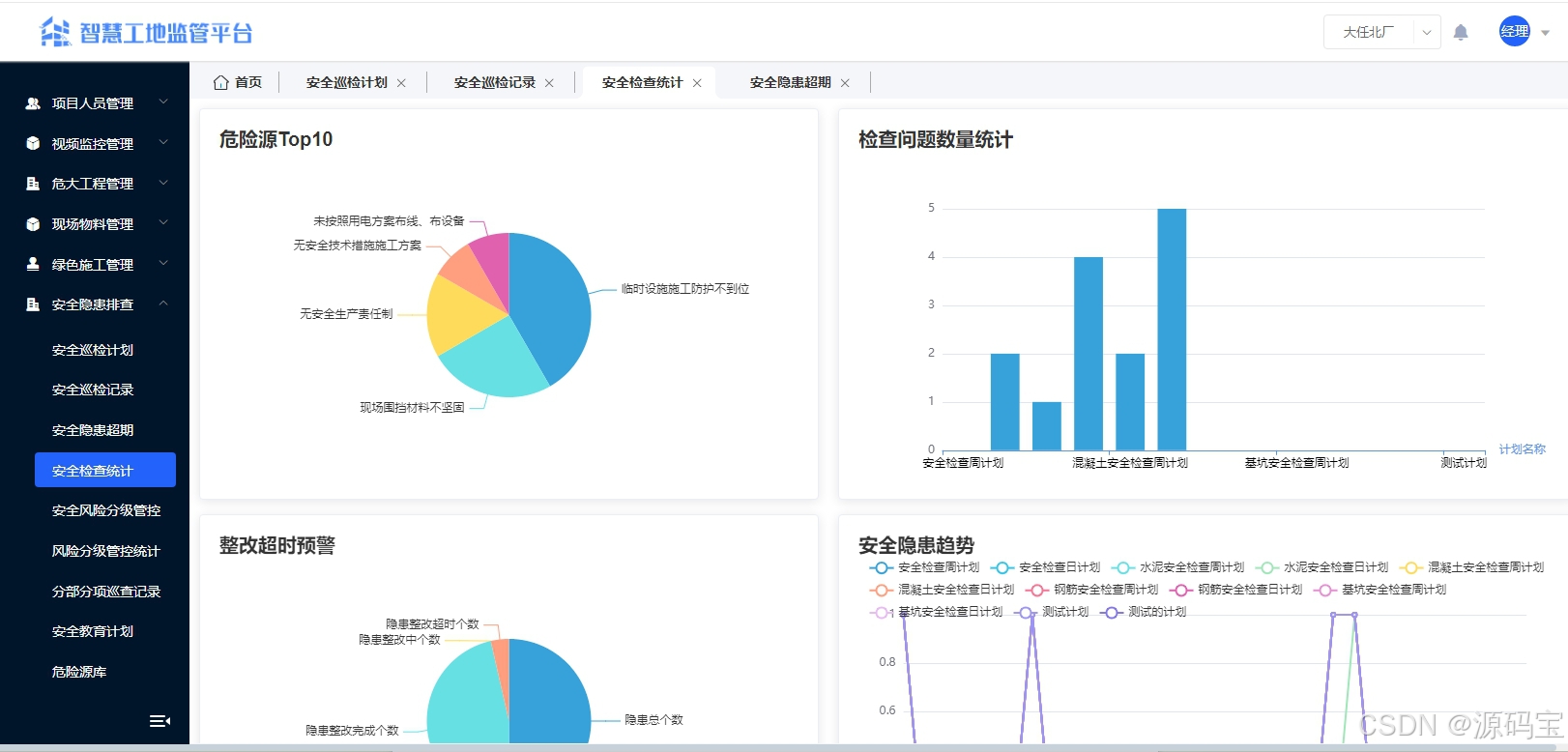
智慧工地云平台源码,基于微服务架构+Java+Spring Cloud +UniApp +MySql
智慧工地管理云平台系统,智慧工地全套源码,java版智慧工地源码,支持PC端、大屏端、移动端。 智慧工地聚焦建筑行业的市场需求,提供“平台网络终端”的整体解决方案,提供劳务管理、视频管理、智能监测、绿色施工、安全管…...
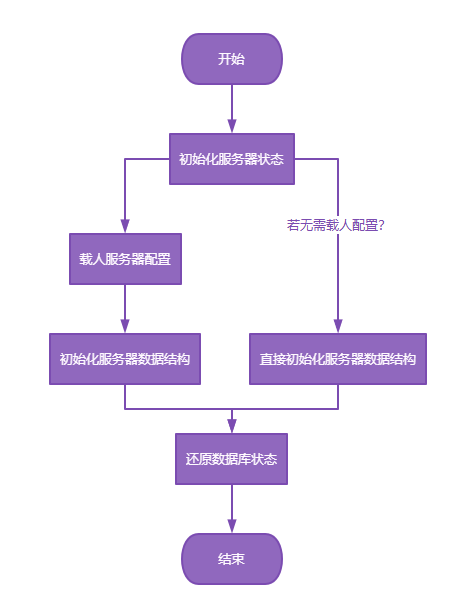
【Redis技术进阶之路】「原理分析系列开篇」分析客户端和服务端网络诵信交互实现(服务端执行命令请求的过程 - 初始化服务器)
服务端执行命令请求的过程 【专栏简介】【技术大纲】【专栏目标】【目标人群】1. Redis爱好者与社区成员2. 后端开发和系统架构师3. 计算机专业的本科生及研究生 初始化服务器1. 初始化服务器状态结构初始化RedisServer变量 2. 加载相关系统配置和用户配置参数定制化配置参数案…...

vue3 字体颜色设置的多种方式
在Vue 3中设置字体颜色可以通过多种方式实现,这取决于你是想在组件内部直接设置,还是在CSS/SCSS/LESS等样式文件中定义。以下是几种常见的方法: 1. 内联样式 你可以直接在模板中使用style绑定来设置字体颜色。 <template><div :s…...
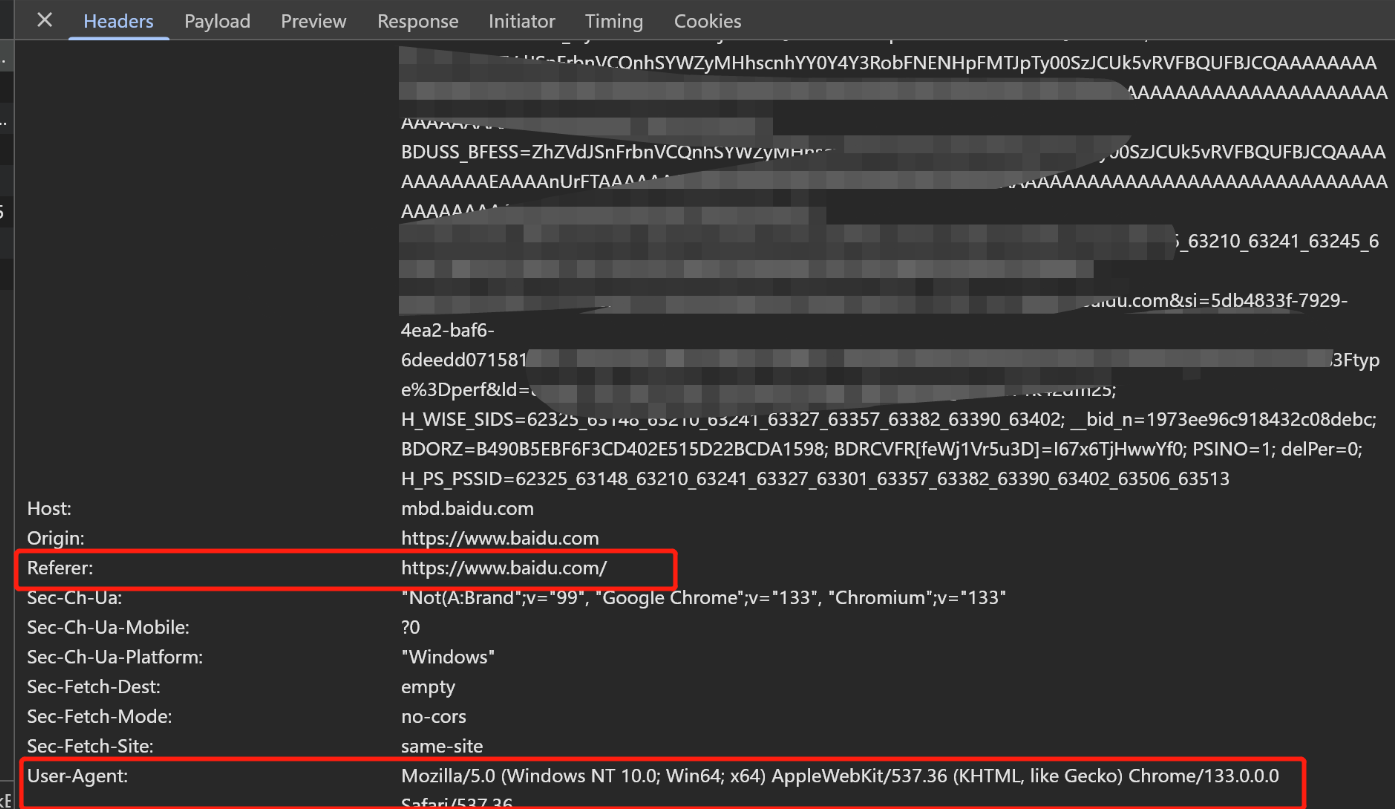
Python爬虫(一):爬虫伪装
一、网站防爬机制概述 在当今互联网环境中,具有一定规模或盈利性质的网站几乎都实施了各种防爬措施。这些措施主要分为两大类: 身份验证机制:直接将未经授权的爬虫阻挡在外反爬技术体系:通过各种技术手段增加爬虫获取数据的难度…...
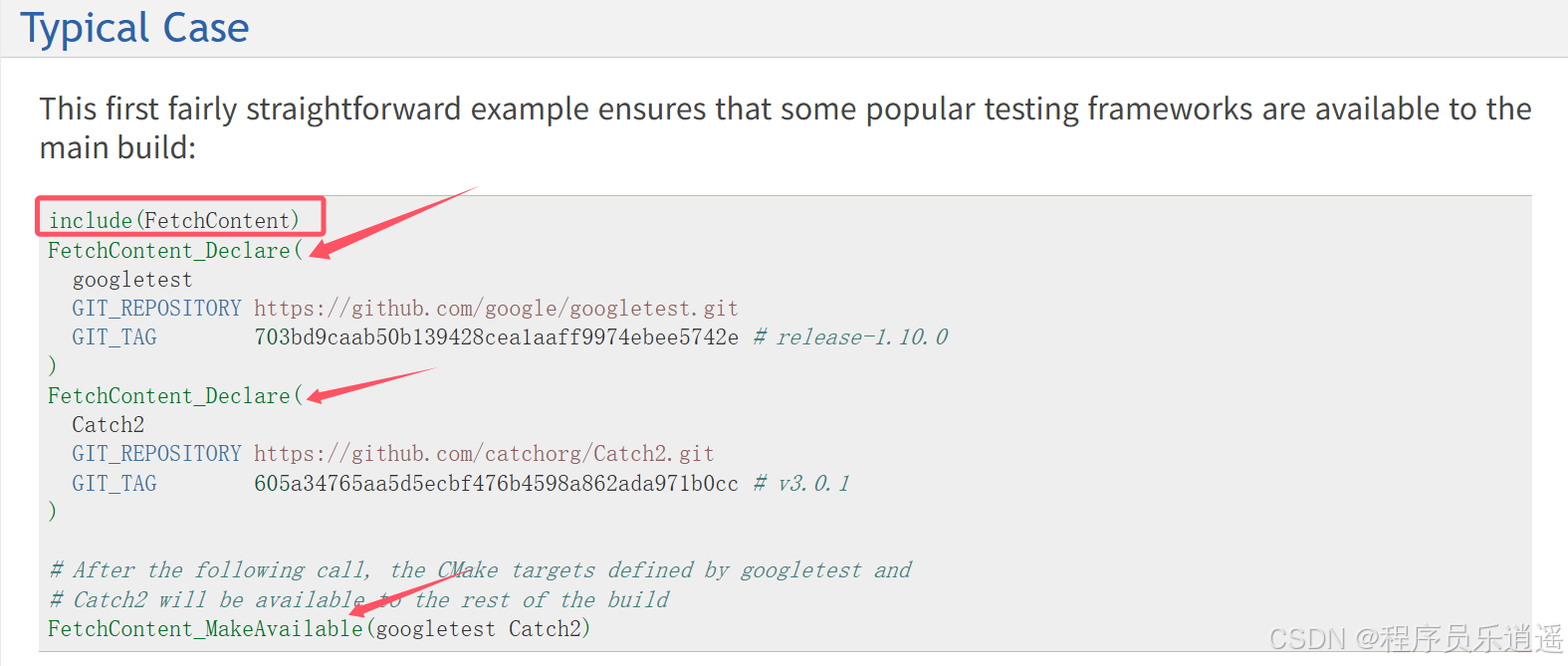
CMake 从 GitHub 下载第三方库并使用
有时我们希望直接使用 GitHub 上的开源库,而不想手动下载、编译和安装。 可以利用 CMake 提供的 FetchContent 模块来实现自动下载、构建和链接第三方库。 FetchContent 命令官方文档✅ 示例代码 我们将以 fmt 这个流行的格式化库为例,演示如何: 使用 FetchContent 从 GitH…...

laravel8+vue3.0+element-plus搭建方法
创建 laravel8 项目 composer create-project --prefer-dist laravel/laravel laravel8 8.* 安装 laravel/ui composer require laravel/ui 修改 package.json 文件 "devDependencies": {"vue/compiler-sfc": "^3.0.7","axios": …...

面向无人机海岸带生态系统监测的语义分割基准数据集
描述:海岸带生态系统的监测是维护生态平衡和可持续发展的重要任务。语义分割技术在遥感影像中的应用为海岸带生态系统的精准监测提供了有效手段。然而,目前该领域仍面临一个挑战,即缺乏公开的专门面向海岸带生态系统的语义分割基准数据集。受…...
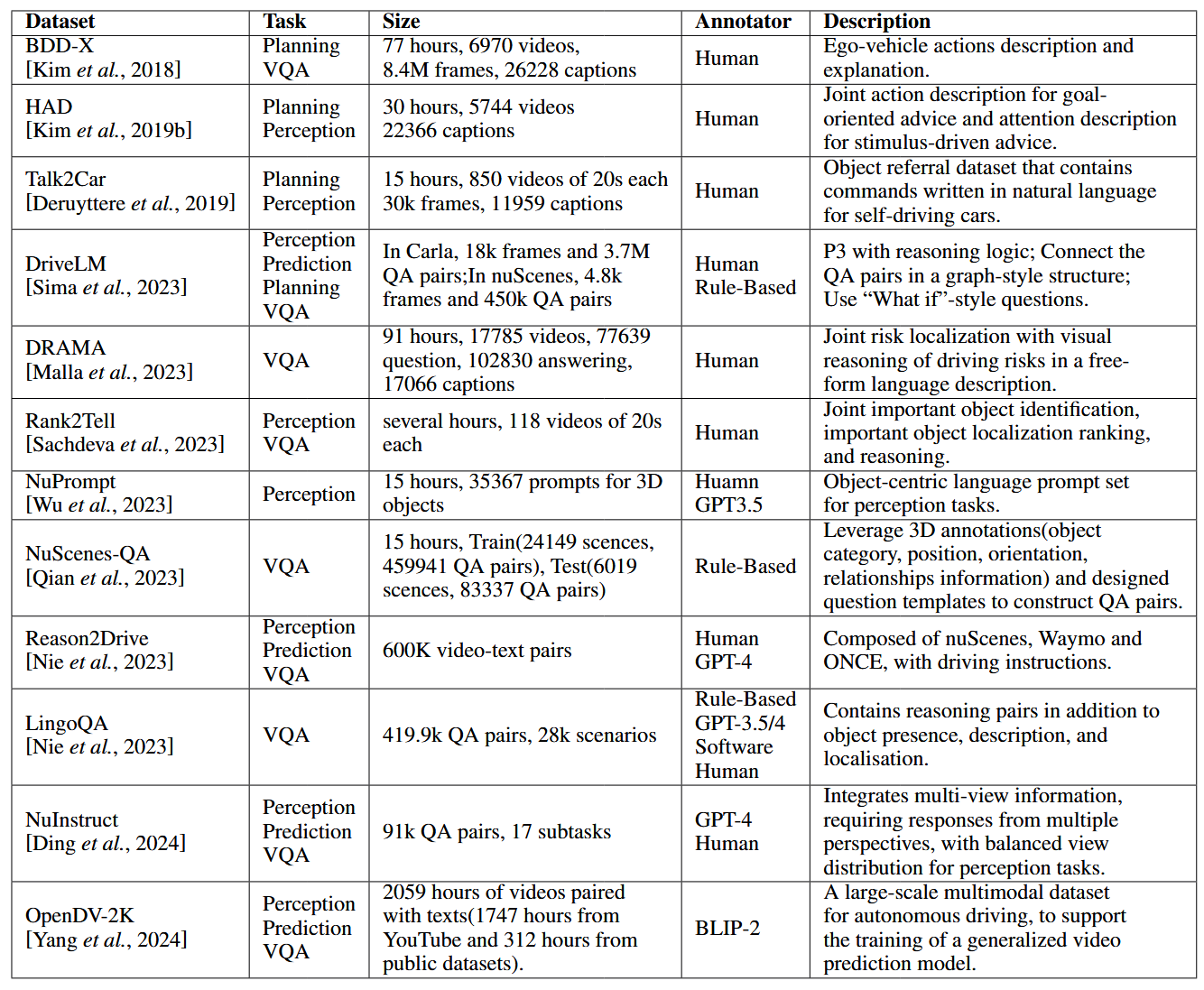
论文阅读:LLM4Drive: A Survey of Large Language Models for Autonomous Driving
地址:LLM4Drive: A Survey of Large Language Models for Autonomous Driving 摘要翻译 自动驾驶技术作为推动交通和城市出行变革的催化剂,正从基于规则的系统向数据驱动策略转变。传统的模块化系统受限于级联模块间的累积误差和缺乏灵活性的预设规则。…...