io基础入门
压缩的封装
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_29897369/article/details/120407125?utm_medium=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-2defaultbaidujs_baidulandingword~default-0-120407125-blog-120163063.235v38pc_relevant_sort_base3&spm=1001.2101.3001.4242.1&utm_relevant_index=3
Resource
Java的标准java.net.URL类和各种URL前缀的标准处理程序还不足以满足对所有低级资源的访问;Resource接口在Spring和Spring中被大量使用
用实用程序类:资源抽象不能取代功能。它尽可能地包装它。例如,UrlResource包装一个URL,并使用包装的URL来完成它的工作
Spring包括几个内置的资源实现:
UrlResource
UrlResource包装了一个java.net.URL,可用于访问通常可以通过URL访问的任何对象,如文件、HTTPS目标、FTP目标等
路径字符串包含一个众所周知的(对属性编辑器来说)前缀(例如classpath:),它将为该前缀创建一个适当的专门化资源;
如果它不识别前缀,则假定该字符串是标准URL字符串并创建UrlResource;
ClassPathResource
该类表示应该从类路径获得的资源
JavaBeans PropertyEditor识别字符串路径上的特殊前缀classpath:,并在这种情况下创建ClassPathResource;
/**
getPath: 返回此资源的路径:a.txt
getAbsolutePath: /Users/yyyyjinying/demo-file/git/backend/wx-project/wx-official-project/target/test-classes/a.txt
**/
@Test
public void demo3(){ClassPathResource classPathResource = new ClassPathResource("a.txt");System.out.println(classPathResource.getPath());try {System.out.println(classPathResource.getFile().getAbsolutePath());} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
}
test-classes和classes的区别:一个是@test资源resources和一个是项目资源resources
注意: 如果test-classes和classes资源不存在需要,maven重新install
FileSystemResource
这是java.io.File句柄的Resource实现
支持文件解析和URL解析;
PathResource
是一个纯粹的基于java.nio.path.Path的FileSystemResource替代品
ServletContextResource
这是ServletContext资源的Resource实现,用于解释相关web应用程序根目录中的相对路径。
InputStreamResource
InputStreamResource是给定InputStream的资源实现
ByteArrayResource
这是给定字节数组的Resource实现。它为给定的字节数组创建一个ByteArrayInputStream。
ResourceLoader
所有应用程序上下文实现ResourceLoader接口。因此,所有应用程序上下文都可以用于获取Resource实例。
会为每个上下文返回适当的对象。(ServletContextResource,FileSystemResource)
可以通过指定任何标准java.net.URL前缀来强制使用UrlResource。使用文件和https前缀的示例如下:
Resource template = ctx.getResource("file:///some/resource/path/myTemplate.txt");
Resource template = ctx.getResource("https://myhost.com/resource/path/myTemplate.txt");
classpath:
classpath:com/myapp/config.xml
file:
file:///data/config.xml
https:
https://myserver/logo.png
/data/config.xml:
取决于底层的ApplicationContext。
ResourcePatternResolver
Ant-style路径模式解析为资源对象
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver resourcePatternResolver = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();Resource[] resources = resourcePatternResolver.getResources(mapperLocations);sqlSessionFactoryBean.setMapperLocations(resources);
@Test
public void demo4() {PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver resource = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();Resource resource1 = resource.getResource("classpath:a.txt");try {System.out.println(resource1.getFile().getAbsolutePath());} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}try {Resource[] resources = resource.getResources("*.txt");for (Resource resource2 : resources) {System.out.println(resource2.getFile().getAbsolutePath());
// /Users/yyyyjinying/demo-file/git/backend/wx-project/wx-official-project/target/test-classes/a.txt
// /Users/yyyyjinying/demo-file/git/backend/wx-project/wx-official-project/target/test-classes/b.txt
// /Users/yyyyjinying/demo-file/git/backend/wx-project/wx-official-project/target/test-classes/c.txt}} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
}
classpath*:
classpath*:/config/beans.xml
您还可以依赖于ResourceLoader的自动装配,作为实现ResourceLoaderAware接口的替代方案。
资源路径没有前缀,根据应用程序上下文的确切类型;
如果需要强制使用特定的资源类型,可以使用前缀
@Component
public class MyBean {private final Resource template;public MyBean(@Value("${template.path}") Resource template) {this.template = template;}// ...
}
Ant-style Patterns
/WEB-INF/-context.xml
com/mycompany/**/applicationContext.xml
file:C:/some/path/-context.xml
classpath:com/mycompany/**/applicationContext.xml
通配符类路径依赖于底层ClassLoader的getResources()方法
相对路径相对于当前工作目录,而绝对路径相对于文件系统的根目录
hutool加载资源
import cn.hutool.setting.dialect.Props;Props props = new Props("demo.properties");
System.out.println(props.get("name"));
类加载器加载资源
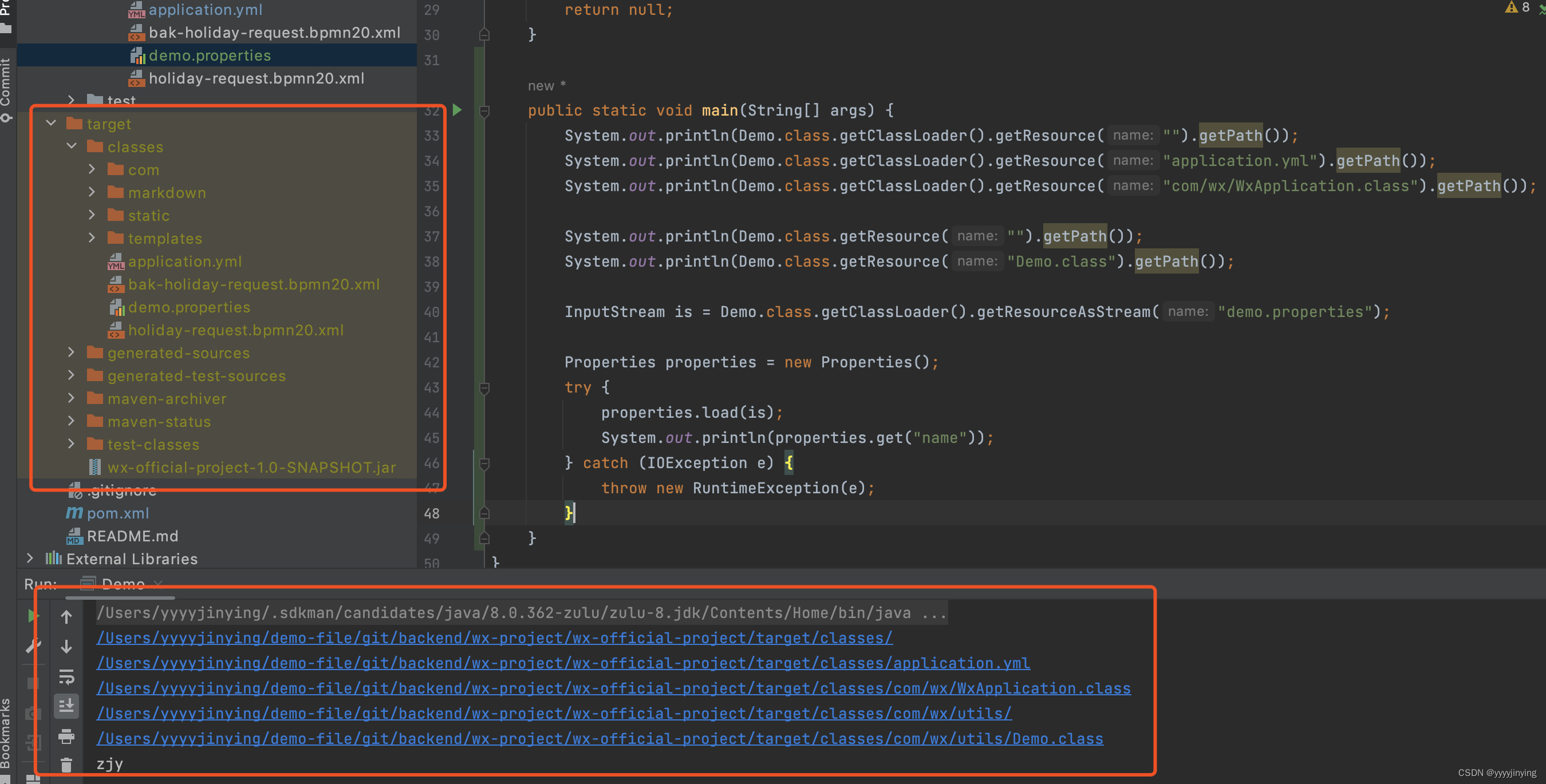
// 路径 /Users/yyyyjinying/demo-file/git/backend/wx-project/wx-official-project/src/main/java
package com.wx.utils.Demo
public class Demo {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(Demo.class.getClassLoader().getResource("").getPath());// /Users/yyyyjinying/demo-file/git/backend/wx-project/wx-official-project/target/classes/System.out.println(Demo.class.getClassLoader().getResource("application.yml").getPath());// /Users/yyyyjinying/demo-file/git/backend/wx-project/wx-official-project/target/classes/application.ymlSystem.out.println(Demo.class.getClassLoader().getResource("com/wx/WxApplication.class").getPath());// /Users/yyyyjinying/demo-file/git/backend/wx-project/wx-official-project/target/classes/com/wx/WxApplication.classSystem.out.println(Demo.class.getResource("").getPath());// /Users/yyyyjinying/demo-file/git/backend/wx-project/wx-official-project/target/classes/com/wx/utils/System.out.println(Demo.class.getResource("Demo.class").getPath());// /Users/yyyyjinying/demo-file/git/backend/wx-project/wx-official-project/target/classes/com/wx/utils/Demo.classInputStream is = Demo.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("demo.properties");Properties properties = new Properties();try {properties.load(is);System.out.println(properties.get("name"));} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}
}
demo.properties
name=zjy
File类
参考: https://www.ydlclass.com/doc21xnv/java/first/javase/12%E3%80%81IO%E6%B5%81/#_6%E3%80%81file%E7%B1%BB%E7%9A%84%E8%8E%B7%E5%8F%96%E5%8A%9F%E8%83%BD%E5%92%8C%E4%BF%AE%E6%94%B9%E5%90%8D%E5%AD%97%E5%8A%9F%E8%83%BD
在 Java 中,File 类是 java.io 包中唯一代表磁盘文件本身的对象。File 类定义了一些与平台无关的方法来操作文件,File类主要用来获取或处理与磁盘文件相关的信息,像文件名、 文件路径、访问权限和修改日期等,还可以浏览子目录层次结构。 File 类表示处理文件和文件系统的相关信息。也就是说,File 类不具有从文件读取信息和向文件写入信息的功能,它仅描述文件本身的属性。
File(String pathname)
File(File parent,String child)
File file = new File(“D:\code\a.txt”);
File file = new File(“D:\code”);
File child = new File(file,“a.txt”);
File类创建和删除功能
boolean createNewFile() 指定路径不存在该文件时创建文件,返回true 否则false
boolean mkdir() 当指定的单击文件夹不存在时创建文件夹并返回true 否则false
boolean mkdirs() 当指定的多级文件夹在某一级文件夹不存在时,创建多级文件夹并返回true 否则false
boolean delete() 删除文件或者删除单级文件夹
File类的判断功能
boolean exists() 判断指定路径的文件或文件夹是否为空
boolean isAbsolute() 判断当前路径是否是绝对路径
boolean isDirectory() 判断当前的目录是否存在
boolean isFile() 判断当前的目录是否是一个文件
boolean isHidden() 判断当前路径是否是一隐藏文件
File类的获取功能和修改名字功能
File getAbsoluteFile() 获取文件的绝对路径,返回File对象
String getAbsolutePath() 获取文件的绝对路径,返回路径的字符串
String getParent() 获取当前路径的父级路径,以字符串形式返回该父级路径
String getName() 获取文件或文件夹的名称
String getPath() 获取File对象中封装的路径
long lastModified() 以毫秒值返回最后修改时间
long length() 返回文件的字节数
boolean renameTo(File dest) 将当前File对象所指向的路径修改为指定File所指向的路径
文件夹列表操作
返回值 方法 描述
String list() 得到这个文件夹下的所有文件,返回路径数组
String[] list(FilenameFilter filter) 通过过滤器过滤文件,过滤通过文件名过滤,返回路径数组
File[] listFiles() 得到这个文件夹下的所有文件,返回文件数组
File[] listFiles(FileFilter filter) 通过过滤器过滤文件,过滤通过文件过滤,返回文件数组
File[] listFiles(FilenameFilter filter) 通过过滤器过滤文件,过滤通过文件名过滤,返回文件数组
public class FileTest {@Testpublic void demo(){getImageName(new File("/Users/yyyyjinying/Downloads"));}private void getImageName(File file) {if (file.isDirectory()) {File[] files = file.listFiles(new FilenameFilter() {@Overridepublic boolean accept(File dir, String name) {if (dir.isDirectory() || dir.getName().endsWith(".png")) {return true;}return false;}});for (File file1 : files) {getImageName(file1);}} else if(file.getName().endsWith(".png")) {System.out.println(file.getName());}}
}
IO流
输入流和输出流:是否写入程序内存;
字节流和字符流:是一个字节一个字节的读取或写入
| 分类 | 字节输入流 | 字节输出流 | 字符输入流 | 字符输出流 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 抽象基类 | InputStream | OutputStream | Reader | Writer |
| 访问文件 | FileInputStream | FileOutputStream | FileReader | FileWriter |
| 访问数组 | ByteArrayInputStream | ByteArrayOutputStream | CharArrayReader | CharArrayWriter |
| 访问字符串 | StringReader | StringWriter | ||
| 缓冲流(处理) | BufferedInputStream | BufferedOutputStream | BufferedReader | BufferedWriter |
| 操作对象 | ObjectInputStream | ObjectOutputStream |
一个流读完了就没有了,就不能在读了
字节流通过InputStreamReader转化为字符流
// 字节流通过InputStreamReader转化为字符流,通过BufferedReader处理流BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(tarArchiveInputStream));
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {list.add(line);
}
字符流通过ByteArrayInputStream转化为字节流
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("Hello", "world!");
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
list.forEach(item -> {builder.append(item);builder.append("\n");
});
String str = builder.toString();
byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(str.getBytes());
bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(byteArrayInputStream);
集合字符串输入文件中
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("Hello", "world!");String str = builder.toString();
File tempFile = File.createTempFile("demo8", ".txt");
// 第一种
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
list.forEach(item -> {builder.append(item);builder.append("\n");
});
try (BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(tempFile))) {writer.write(str);
}
// 第二种
FileUtil.writeLines(list, tempFile, Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
字节流和字符流的输入输出
public class IOUtilsTest {@Testpublic void demo() {try (InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(new File("/Users/yyyyjinying/demo-file/git/backend/wx-project/wx-official-project/src/test/resources/a.txt"));FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(new File("/Users/yyyyjinying/demo-file/git/backend/wx-project/wx-official-project/src/test/resources/b.txt"), true)) {byte[] buf = new byte[1024];int len;while ((len = inputStream.read(buf)) != -1) {
// write(b, off, len)的一般契约是数组b中的一些字节按顺序写入输出流;元素b[off]是写入的第一个字节,
// b[off+len-1]是该操作写入的最后一个字节。
// OutputStream的write方法在每个要写入的字节上调用一个参数的write方法fileOutputStream.write(buf, 0, len);}} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}@Testpublic void demo2(){File fileInput = new File("/Users/yyyyjinying/demo-file/git/backend/wx-project/wx-official-project/src/test/resources/a.txt");File fileOutput = new File("/Users/yyyyjinying/demo-file/git/backend/wx-project/wx-official-project/src/test/resources/c.txt");FileReader fileReader = null;FileWriter fileWriter = null;try {fileReader = new FileReader(fileInput);fileWriter = new FileWriter(fileOutput);char[] buf = new char[1024];int len;while((len = fileReader.read(buf)) != -1){fileWriter.write(buf, 0, len);}} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} finally {try {fileReader.close();} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}try {fileWriter.close();} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}}
IOUtils.closeQuietly
可以简化io关闭的代码,
import org.apache.tomcat.util.http.fileupload.IOUtils;
import java.io.StringReader;
import java.io.StringWriter;try {} catch (IOException e) { } finally {if (in != null) {try {in.close();} catch (IOException e) {}}if (out != null) {try {out.close();} catch (IOException e) {}}} try {} catch (IOException e) { } finally {IOUtils.closeQuietly(in);IOUtils.closeQuietly(out);}
String content = "字符串";
StringReader reader = new StringReader(content);
StringWriter sw = new StringWriter();
try {//渲染模板 模板名没有取默认值String templateName = map.getOrDefault("templateName", "generator").toString();Template template = new Template(templateName, reader, null, "utf-8");template.process(map, sw);
} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();throw new RenException("渲染模板失败,请检查模板语法", e);
}content = sw.toString();IOUtils.closeQuietly(reader);
IOUtils.closeQuietly(sw);
return content;
序列化和反序列化
序列化:将对象写入到IO流中,说的简单一点就是将内存模型的对象变成字节数字,可以进行存储和传输;
反序列化:从IO流中恢复对象,将存储在磁盘或者从网络接收的数据恢复成对象模型;
使用场景:所有可在网络上传输的对象都必须是可序列化的,否则会出错;所有需要保存到磁盘的Java对象都必须是可序列化的。
序列化版本号:我们知道,反序列化必须拥有class文件,但随着项目的升级,class文件也会升级,序列化怎么保证升级前后的兼容性呢? Java序列化提供了一个``private static final long serialVersionUID` 的序列化版本号,只要版本号相同,即使更改了序列化属性,对象也可以正确被反序列化回来。序列化版本号可自由指定,如果不指定,JVM会根据类信息自己计算一个版本号,这样随着class的升级、代码的修改等因素无法正确反序列化;不指定版本号另一个明显隐患是,不利于jvm间的移植,可能class文件没有更改,但不同jvm可能计算的规则不一样,这样也会导致无法反序列化。
所有需要网络传输的对象都需要实现序列化接口。
对象的类名、实例变量(包括基本类型,数组,对其他对象的引用)都会被序列化;方法、类变量、transient实例变量都不会被序列化。如果想让某个变量不被序列化,使用transient修饰。序列化对象的引用类型成员变量,也必须是可序列化的,否则,会报错。反序列化时必须有序列化对象的class文件。同一对象序列化多次,只有第一次序列化为二进制流,以后都只是保存序列化编号,不会重复序列化。建议所有可序列化的类加上serialVersionUID 版本号,方便项目升级。
/*** user对象通过字节流实现深拷贝* @throws CloneNotSupportedException*/@Testpublic void deepClone() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {User user = new User("aa", "bb");user.setDog(new Dog("dog"));// 写出缓存字节数组ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(byteArrayOutputStream);out.writeObject(user);byte[] bytes = byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray();// 将缓存字节数组写入程序对象ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes);ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(byteArrayInputStream);User user1 = (User) in.readObject();// 关闭资源byteArrayInputStream.close();in.close();out.close();byteArrayOutputStream.close();user.setName("xiugai");user.getDog().setName("xigou");System.out.println(user);System.out.println(user1);}@Testpublic void qianClone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {User user = new User("aa", "bb");user.setDog(new Dog("dog"));User user1 = (User) user.clone();user.setName("xiugai");user.getDog().setName("xigou");System.out.println(user);System.out.println(user1);}
相关文章:

io基础入门
压缩的封装 参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_29897369/article/details/120407125?utm_mediumdistribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-2defaultbaidujs_baidulandingword~default-0-120407125-blog-120163063.235v38pc_relevant_sort_base3&spm1001.2101.3001.…...
k8s ingress 无法找到端点
文章目录 ingress rule无法找到端点这个注解是什么意思呢?为何不生效呢?端点无法更新?如何确认ingressclass呢?修复端点无法发现的问题多个ingress controller 架构 ingress rule无法找到端点 在vnnox-cn集群创建ingress…...
properties转yml
目前搜索到的大部分代码都存在以下问题: 复杂结构解析丢失解析后顺序错乱 所以自己写了一个,经过不充分测试,基本满足使用。可以直接在线使用 在线地址 除了yml和properties互转之外,还可以生成代码、sql转json等,可…...
谈谈中间件设计的思路
前言 想要设计和真正理解中间件的架构理论和思想。对于开发来说需要具备三个关键的能力 1:基础通用技术的深入理解和运用2:了解和熟悉常见中间件的设计思想,且有自己的感悟,并且能按照自己的理解模仿写一写3:业务的高度理解能力…...

WT2605-24SS音频蓝牙录放语音芯片:标准蓝牙功能与多样化存储播放方式助力音频体验升级
在音频技术日新月异的今天,WT2605-24SS音频蓝牙录放语音芯片以其强大的功能和出色的性能,成为了音频市场的一颗璀璨明星。该芯片不仅具备标准音频蓝牙功能,还支持蓝牙电话本、录音功能以及多种存储和播放方式,为用户提供了更加便捷…...

openssl生成ssl证书
x509证书一般会用到三类文,key,csr,crt。 Key 是私用密钥openssl格,通常是rsa算法。 Csr 是证书请求文件,用于申请证书。在制作csr文件的时,必须使用自己的私钥来签署申,还可以设定一个密钥。…...
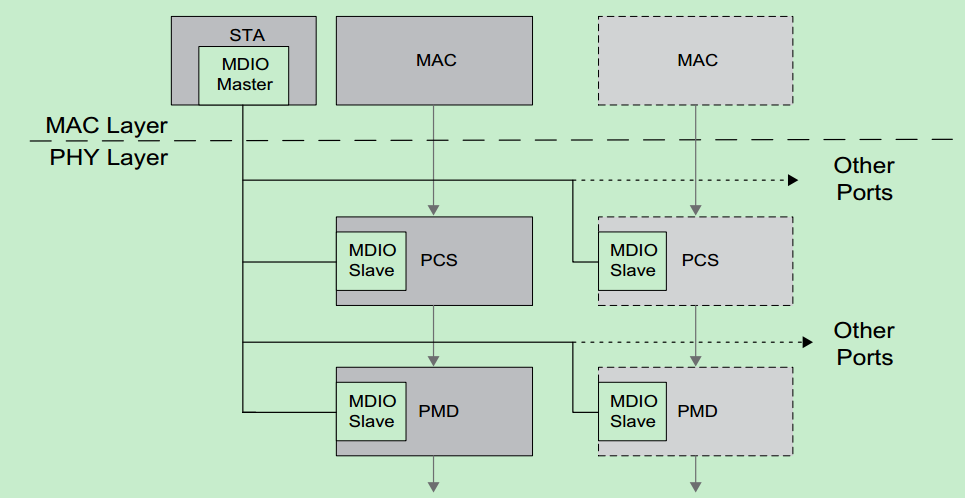
以太网PHY,MAC接口
本文主要介绍以太网的 MAC 和 PHY,以及之间的 MII(Media Independent Interface ,媒体独立接口)和 MII 的各种衍生版本——GMII、SGMII、RMII、RGMII等。 简介 从硬件的角度看,以太网接口电路主要由MAC(M…...

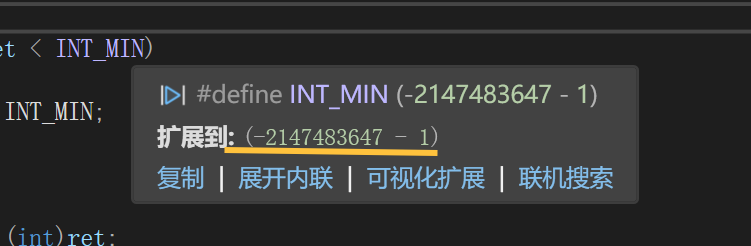
c语言中 , x++ 和 ++x的区别
一 c语言中 , x 和 x的区别 x 和 x 是 C 语言中的自增运算符,它们的区别在于它们的执行时机和返回值: 1. x (后缀自增): 先使用变量的值,然后再将变量的值加 1。这意味着,如果你在一个表达式中使用了 x,那么该表达式…...
DBeaver 社区版(免费版)下载、安装、解决驱动更新出错问题
DBeaver 社区版(免费版) DBeaver有简洁版,企业版,旗舰版,社区版(免费版)。除了社区版,其他几个版本都是需要付费的,当然相对来说,功能也要更完善些ÿ…...

景联文科技加入中国人工智能产业联盟(AIIA)数据委员会
近日,景联文科技加入中国人工智能产业联盟(AIIA)数据委员会,成为委员会成员单位。 中国人工智能产业发展联盟(简称AIIA)是在国家发改委、科技部、工信部、网信办指导下,由中国信息通信研究院等单…...

数据结构 / 结构体指针
1. 格式 struct 结构体名{数据类型 成员1;数据类型 成员2; .... };struct 结构体名 *指针变量名 2. 结构体指针指向普通变量的地址 struct CAR{char name[10];int price; };struct CAR car{"byd",160}; struct CAR *p&car; //p是指向结构体变量car的指针// p…...
P1 什么是链表 C语言简单易懂
目录 前言 01 什么是链表 02 数组的特点 03 数组的缺点 3.1 删除数组其中一个元素 3.2 数组增加某个节点 04 链表 前言 🎬 个人主页:ChenPi 🐻推荐专栏1: 《 C 》✨✨✨ 🔥 推荐专栏2: 《 Linux C应用编程(概念…...
Python实现FA萤火虫优化算法优化循环神经网络分类模型(LSTM分类算法)项目实战
说明:这是一个机器学习实战项目(附带数据代码文档视频讲解),如需数据代码文档视频讲解可以直接到文章最后获取。 1.项目背景 萤火虫算法(Fire-fly algorithm,FA)由剑桥大学Yang于2009年提出 , …...

Spring Task
Spring Task 是Spring框架提供的任务调度工具,可以按照约定的时间自动执行某个代码逻辑。 **定位:**定时任务框架 **作用:**定时自动执行某段Java代码 cron表达式 cron表达式其实就是一个字符串,通过cron表达式可以定义任务触…...

HttpServletRequest/Response视频笔记
学习地址:144-尚硅谷-Servlet-HttpServletRequest类的介绍_哔哩哔哩_bilibili 目录 1.HttpServletRequest 类 a.HttpServletRequest类有什么作用 b.HttpServletRequest类的常用方法 c.如何获取请求参数 d.解决post请求中文乱码问题 获取请求的参数值相关问题 …...
网上选课系统源码(Java)
JavaWebjsp网上选课系统源码 运行示意图:...

mac修改默认shell为bash
1. 打开系统偏好设置 2. 点击用户群组 3. 按住ctrl,点击用户名 4. 点击高级选项,修改登录shell 参考:在 Mac 上将 zsh 用作默认 Shell - 官方 Apple 支持 (中国)...

基于Java SSM小区物业管理系统
小区有多栋住宅,每栋楼有多套物业(房屋),物业管理公司提供物业管理服务,业主需要按月缴纳物业费。小区物业管理系统对物业公司的日常工作进行管理。系统管理的对象及操作有: 楼宇信息:楼号、户数、物业费标准。 房屋信…...

计算机网络408
一:计算机网络体系结构 1.计网的概念,组成,功能和分类 一:计算机网络的发展 (3)从功能组成视觉看:分为资源子网和通信子网 2.计网性能指标 注意:带宽影响链路入口处的发射速率—>从而影响了…...
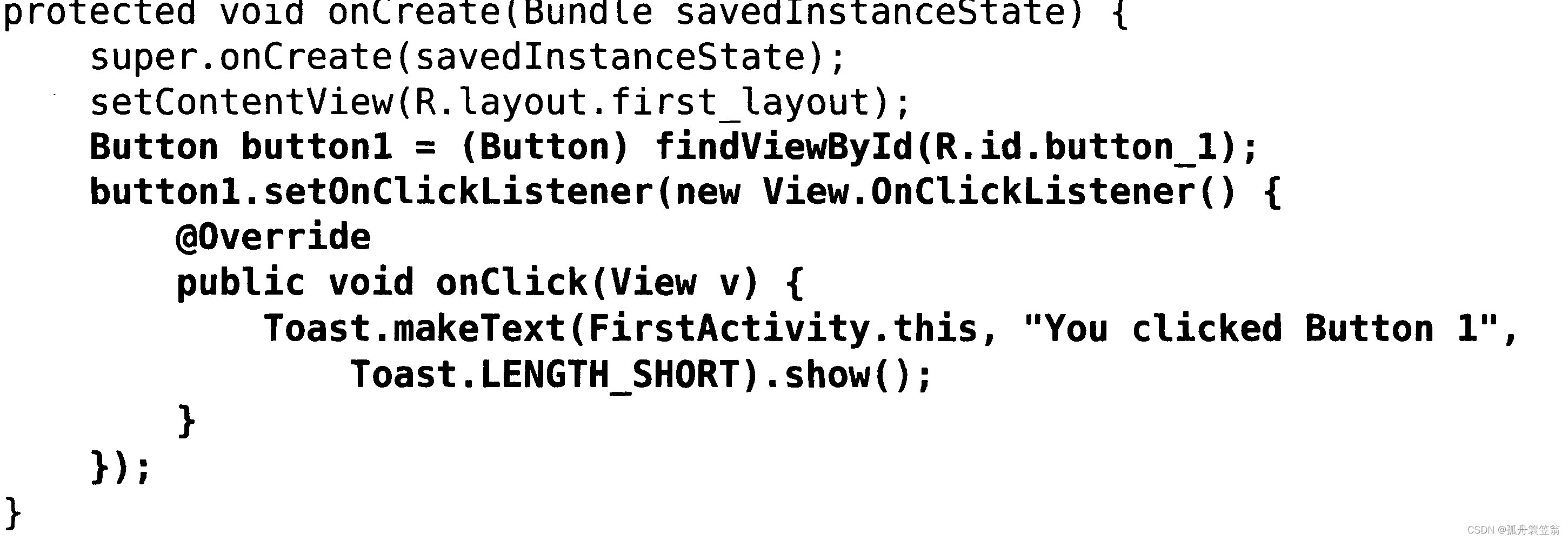
【android开发-01】android中toast的用法介绍
1,android中toast的作用 在Android开发中,Toast是一种用于向用户显示简短消息的轻量级对话框。它通常用于向用户提供一些即时的反馈信息,例如操作结果、提示或警告。 Toast的主要作用如下: 提供反馈:Toast可以在用户…...
SpringBoot-17-MyBatis动态SQL标签之常用标签
文章目录 1 代码1.1 实体User.java1.2 接口UserMapper.java1.3 映射UserMapper.xml1.3.1 标签if1.3.2 标签if和where1.3.3 标签choose和when和otherwise1.4 UserController.java2 常用动态SQL标签2.1 标签set2.1.1 UserMapper.java2.1.2 UserMapper.xml2.1.3 UserController.ja…...
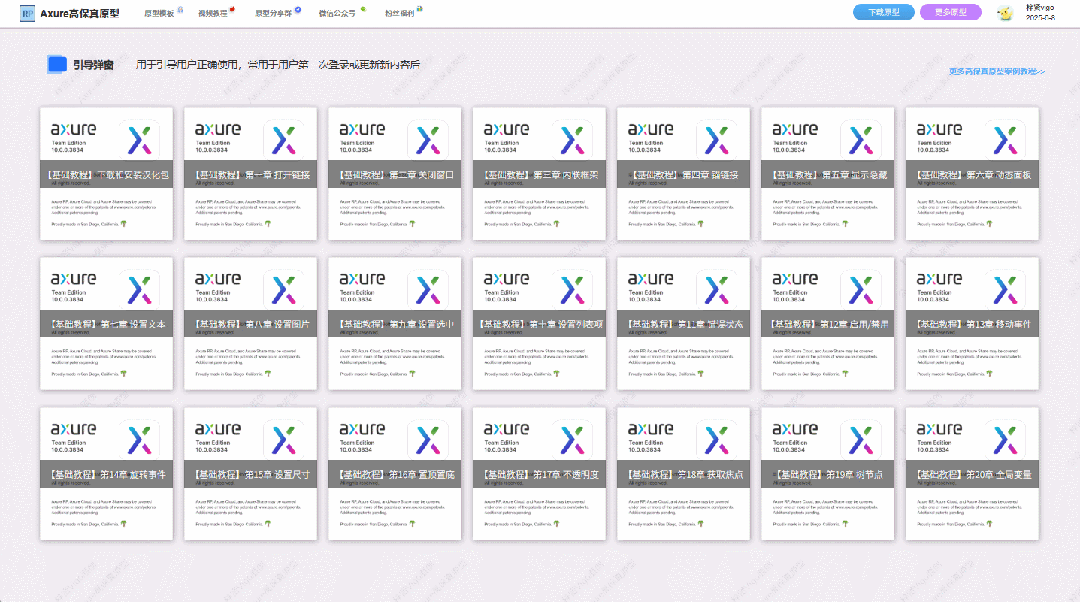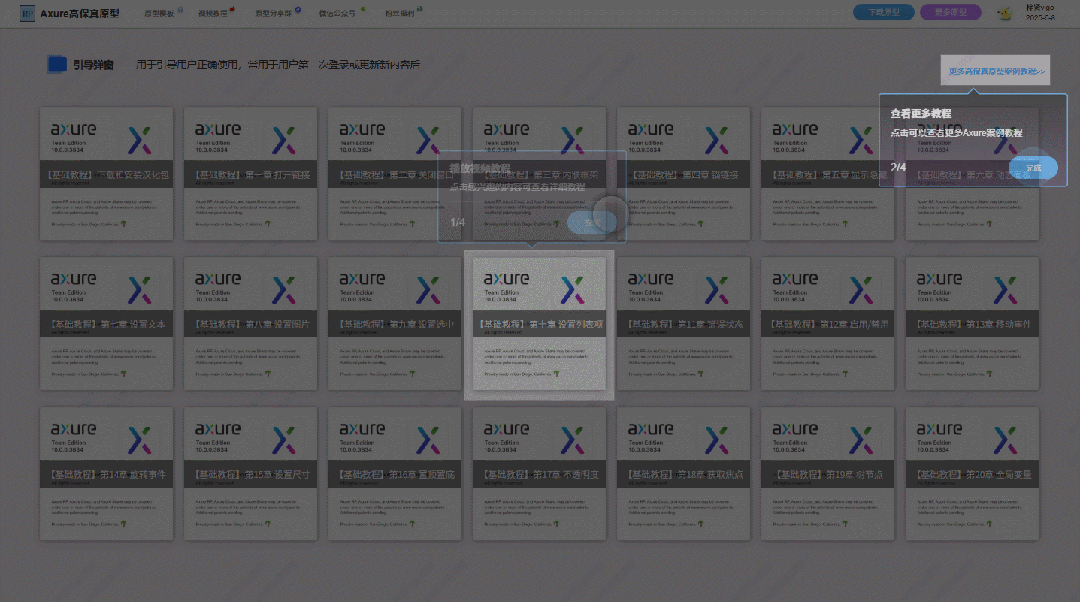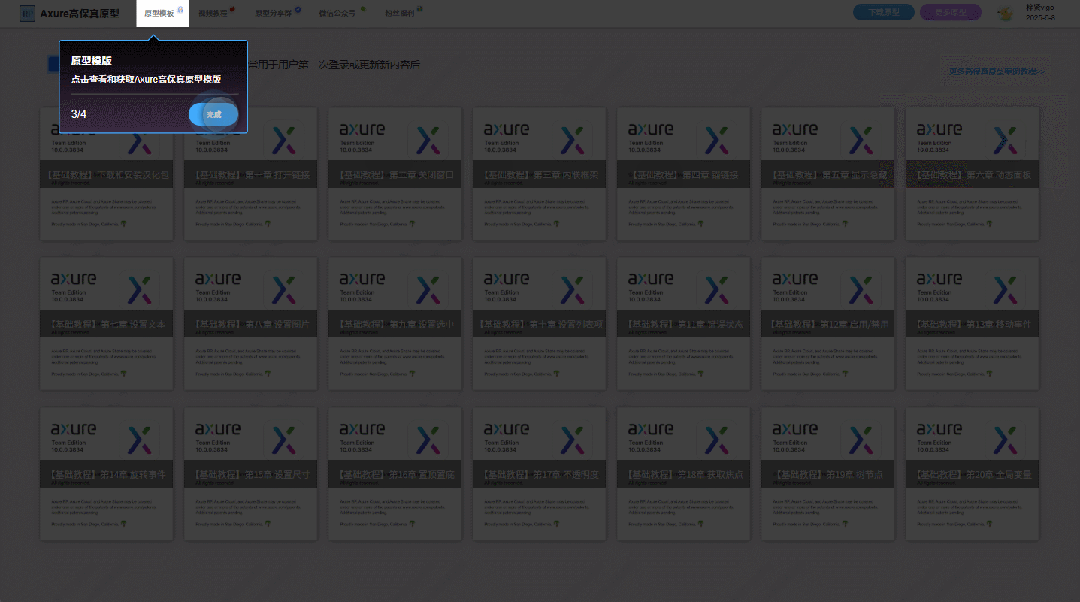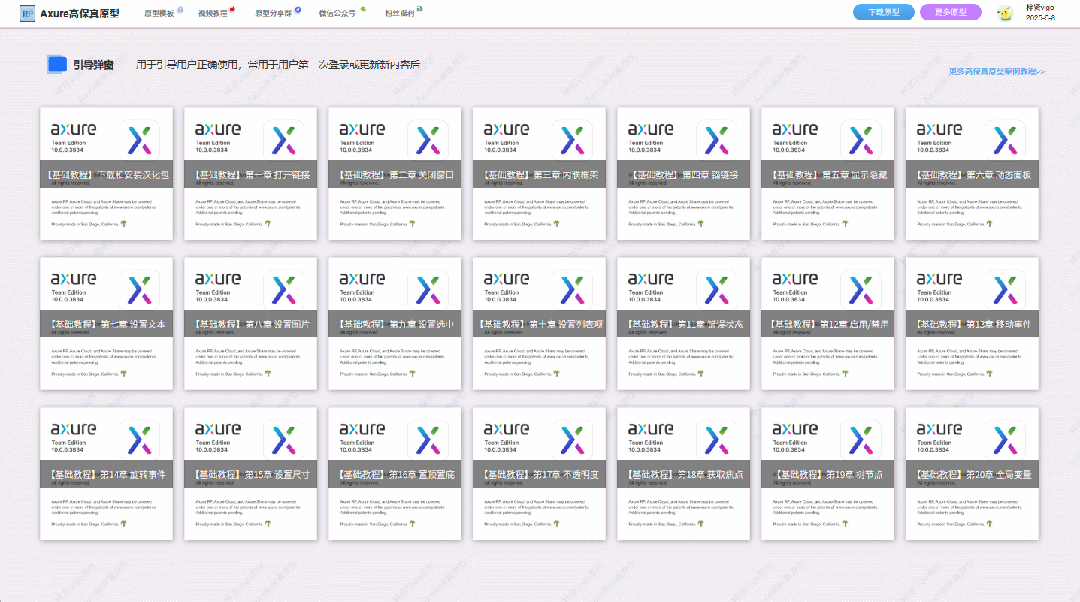
【Axure高保真原型】引导弹窗
今天和大家中分享引导弹窗的原型模板,载入页面后,会显示引导弹窗,适用于引导用户使用页面,点击完成后,会显示下一个引导弹窗,直至最后一个引导弹窗完成后进入首页。具体效果可以点击下方视频观看或打开下方…...
练习(含atoi的模拟实现,自定义类型等练习)
一、结构体大小的计算及位段 (结构体大小计算及位段 详解请看:自定义类型:结构体进阶-CSDN博客) 1.在32位系统环境,编译选项为4字节对齐,那么sizeof(A)和sizeof(B)是多少? #pragma pack(4)st…...

关于iview组件中使用 table , 绑定序号分页后序号从1开始的解决方案
问题描述:iview使用table 中type: "index",分页之后 ,索引还是从1开始,试过绑定后台返回数据的id, 这种方法可行,就是后台返回数据的每个页面id都不完全是按照从1开始的升序,因此百度了下,找到了…...
【第二十一章 SDIO接口(SDIO)】
第二十一章 SDIO接口 目录 第二十一章 SDIO接口(SDIO) 1 SDIO 主要功能 2 SDIO 总线拓扑 3 SDIO 功能描述 3.1 SDIO 适配器 3.2 SDIOAHB 接口 4 卡功能描述 4.1 卡识别模式 4.2 卡复位 4.3 操作电压范围确认 4.4 卡识别过程 4.5 写数据块 4.6 读数据块 4.7 数据流…...

高危文件识别的常用算法:原理、应用与企业场景
高危文件识别的常用算法:原理、应用与企业场景 高危文件识别旨在检测可能导致安全威胁的文件,如包含恶意代码、敏感数据或欺诈内容的文档,在企业协同办公环境中(如Teams、Google Workspace)尤为重要。结合大模型技术&…...
)
论文解读:交大港大上海AI Lab开源论文 | 宇树机器人多姿态起立控制强化学习框架(一)
宇树机器人多姿态起立控制强化学习框架论文解析 论文解读:交大&港大&上海AI Lab开源论文 | 宇树机器人多姿态起立控制强化学习框架(一) 论文解读:交大&港大&上海AI Lab开源论文 | 宇树机器人多姿态起立控制强化…...

【C语言练习】080. 使用C语言实现简单的数据库操作
080. 使用C语言实现简单的数据库操作 080. 使用C语言实现简单的数据库操作使用原生APIODBC接口第三方库ORM框架文件模拟1. 安装SQLite2. 示例代码:使用SQLite创建数据库、表和插入数据3. 编译和运行4. 示例运行输出:5. 注意事项6. 总结080. 使用C语言实现简单的数据库操作 在…...
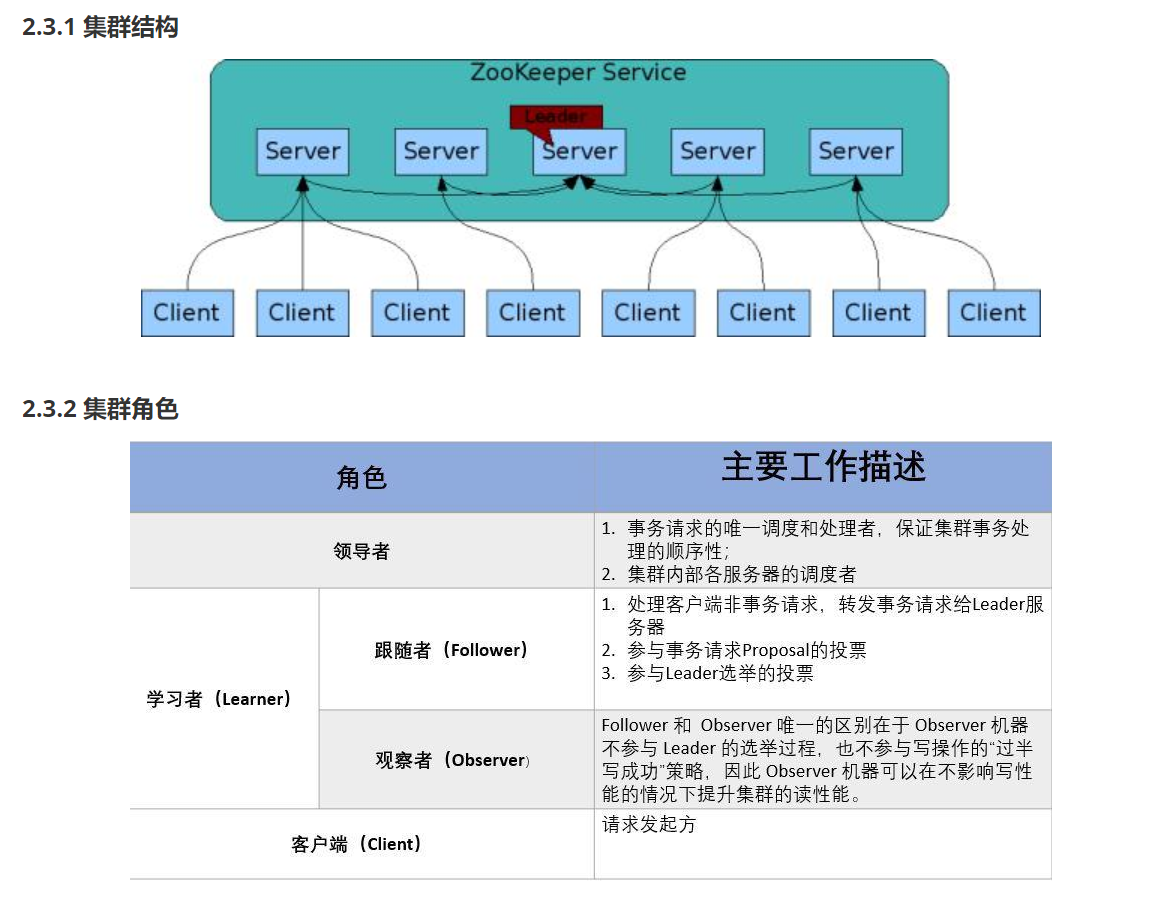
HDFS分布式存储 zookeeper
hadoop介绍 狭义上hadoop是指apache的一款开源软件 用java语言实现开源框架,允许使用简单的变成模型跨计算机对大型集群进行分布式处理(1.海量的数据存储 2.海量数据的计算)Hadoop核心组件 hdfs(分布式文件存储系统)&a…...

JavaScript基础-API 和 Web API
在学习JavaScript的过程中,理解API(应用程序接口)和Web API的概念及其应用是非常重要的。这些工具极大地扩展了JavaScript的功能,使得开发者能够创建出功能丰富、交互性强的Web应用程序。本文将深入探讨JavaScript中的API与Web AP…...
