qt-C++笔记之QStringList
qt-C++笔记之QStringList
—— 杭州 2023-12-03
文章目录
- qt-C++笔记之QStringList
- 1.1.《Qt官方文档》第一部分翻译:继承自QList\<QString\>-初始化-添加字符串
- 1.2.迭代字符串
- 1.3.join()和split()
- 1.4.filter()
- 1.5.lastIndexOf()
- 1.6.indexOf()
- 1.7.replaceInStrings()以及比较QString 类则提供了replace()函数
- 1.8.一些常用方法和操作
- 1.9.QStringList和QList<QString>关系
- 2.0.QStringList的append(),append(),operator+()
- 2.1.QStringLis:Public Functions
- 2.2.QStringLis:List of all members, including inherited members
- 2.3.Classes for String Data(Qt中字符串数据的类)
《Qt官方文档》链接:
https://doc.qt.io/qt-6/qstringlist.html
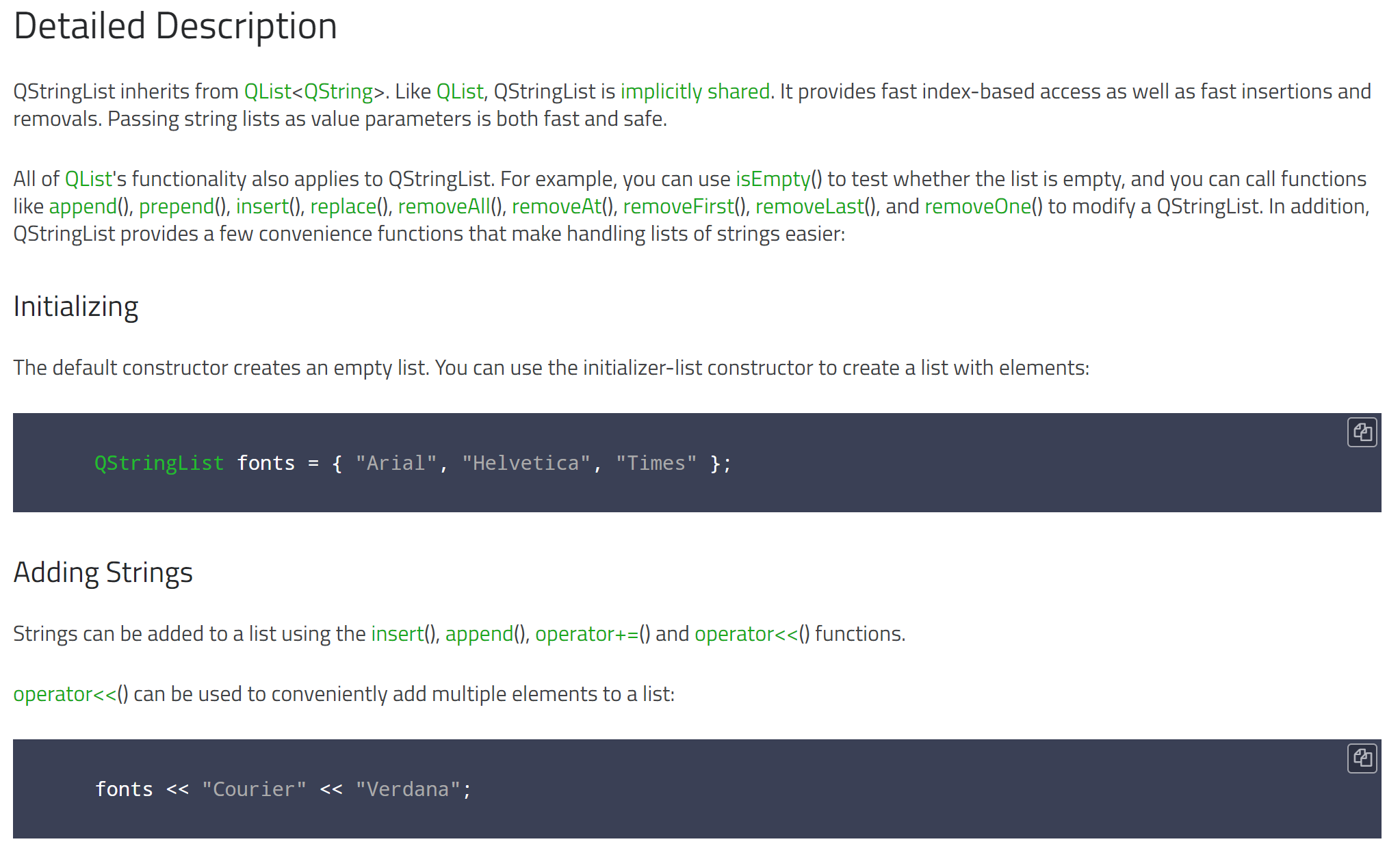
1.1.《Qt官方文档》第一部分翻译:继承自QList<QString>-初始化-添加字符串
原文:
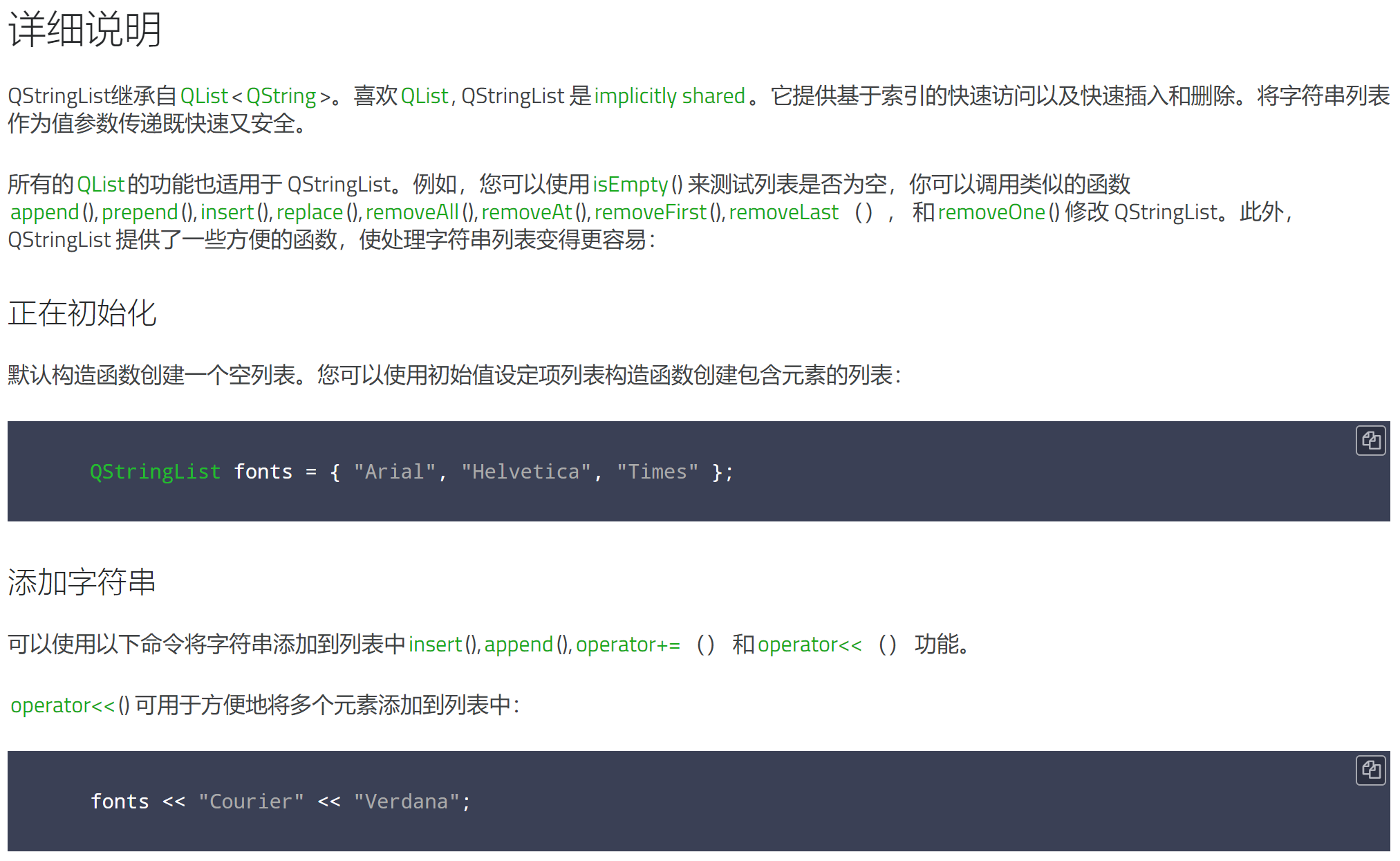
翻译:
1.2.迭代字符串
在Qt中,遍历 QStringList 可以使用迭代器、foreach 循环或基于索引的循环。下面是这些遍历方法的详细说明:
-
使用迭代器:
QStringList stringList; stringList << "Apple" << "Banana" << "Cherry";QStringList::iterator it; for (it = stringList.begin(); it != stringList.end(); ++it) {qDebug() << *it; } ```使用迭代器可遍历 `QStringList`,通过 `begin()` 获取迭代器的起始位置,通过 `end()` 获取迭代器的结束位置。在循环中,使用 `*it` 来访问迭代器当前指向的元素。 -
使用
foreach循环:QStringList stringList; stringList << "Apple" << "Banana" << "Cherry";foreach (const QString& str, stringList) {qDebug() << str; } `````foreach` 循环提供了一种简洁的方式来遍历 `QStringList`。在每次迭代中,变量 `str` 将依次引用列表中的元素。 -
基于索引的循环:
QStringList stringList; stringList << "Apple" << "Banana" << "Cherry";for (int i = 0; i < stringList.size(); ++i) {qDebug() << stringList.at(i); }基于索引的循环遍历
QStringList可以使用下标运算符[]或at()函数来访问列表中的元素。以下是基于索引的循环遍历的详细说明:QStringList stringList; stringList << "Apple" << "Banana" << "Cherry";for (int i = 0; i < stringList.size(); ++i) {QString str = stringList[i]; // 或者使用 stringList.at(i)qDebug() << str; }在上述示例中,我们创建了一个
QStringList对象stringList,其中包含多个字符串元素。然后,我们使用基于索引的循环遍历列表。在每次迭代中,我们使用下标运算符[]或at()函数来获取列表中的元素并将其存储在str变量中。最后,我们输出str的值。需要注意的是,索引从 0 开始,因此循环条件是
i < stringList.size()。我们使用size()函数获取列表的大小。
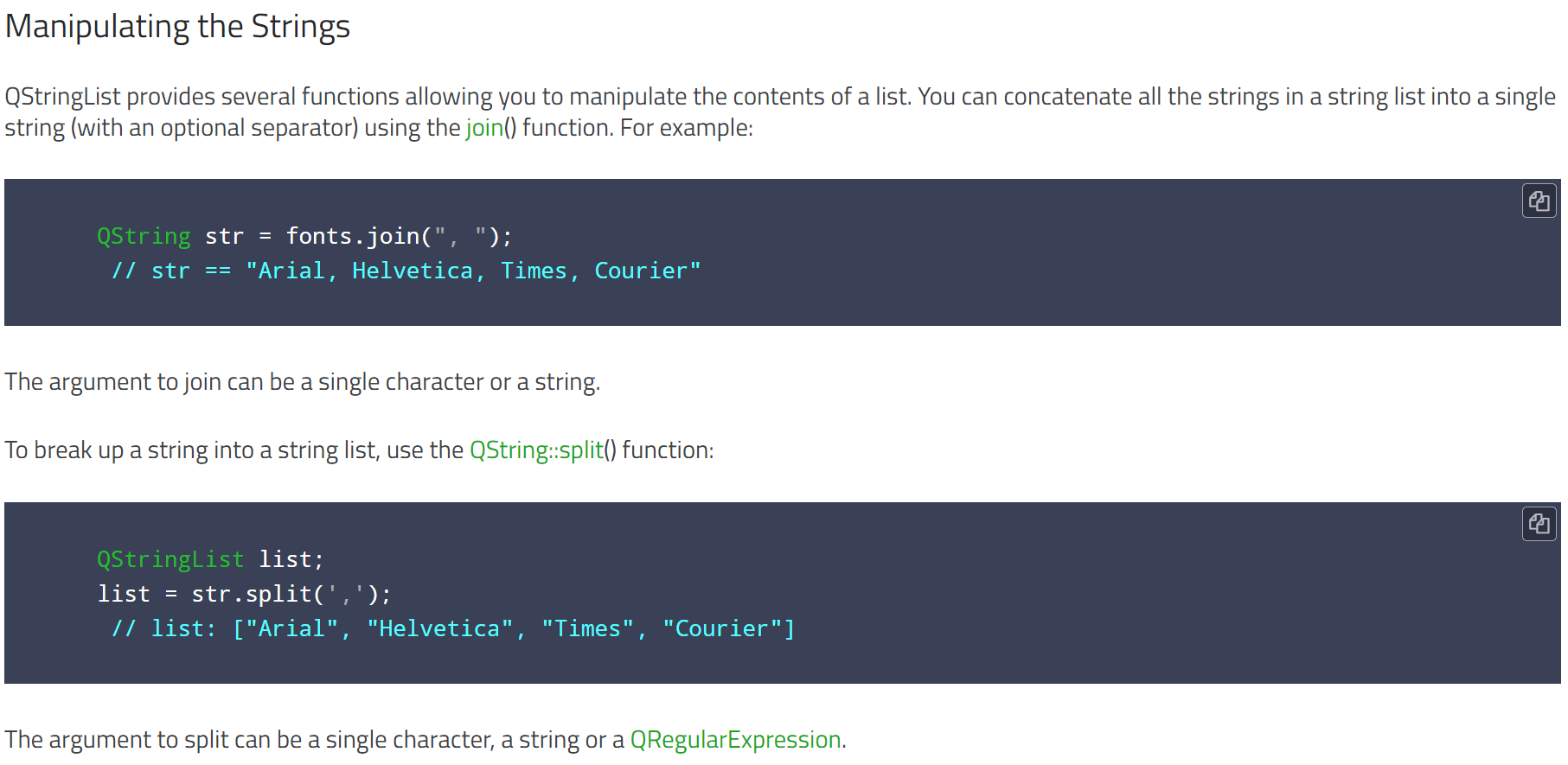
1.3.join()和split()
1.4.filter()

以下是一个完整的示例代码:
#include <QtCore>int main() {QStringList fonts;fonts << "Arial" << "Courier New" << "Times New Roman" << "Fixedsys";QStringList monospacedFonts = fonts.filter(QRegularExpression("Courier|Fixed"));qDebug() << "Monospaced Fonts:";for (const QString& font : monospacedFonts) {qDebug() << font;}return 0;
}
在这个示例中,我们先创建了一个 QStringList 对象 fonts,并向其添加了几个字体名称。然后,使用 filter() 函数结合正则表达式 "Courier|Fixed" 筛选出包含 “Courier” 或 “Fixed” 的字体名称,并将结果存储在 monospacedFonts 中。
最后,通过遍历 monospacedFonts,将筛选结果输出到调试输出中。
运行这段代码,你将得到如下输出结果:
Monospaced Fonts:
"Courier New"
"Fixedsys"
输出结果显示了满足条件的字体名称,即 “Courier New” 和 “Fixedsys”。这表明代码成功地筛选出了包含 “Courier” 或 “Fixed” 的字体名称。
1.5.lastIndexOf()
QStringList 类提供了 lastIndexOf() 函数用于查找指定字符串在列表中最后出现的位置(索引)。
函数原型如下:
int lastIndexOf(const QString& value, int from = -1) const;
参数说明:
value:要查找的字符串。from:可选参数,指定开始搜索的索引位置,默认值为 -1,表示从列表的末尾开始搜索。
函数返回值:
- 如果找到了指定的字符串,则返回最后一个匹配项的索引值。
- 如果没有找到匹配项,则返回 -1。
以下是一个示例,演示如何使用 lastIndexOf() 函数查找字符串在 QStringList 中最后出现的位置:
#include <QtCore>int main() {QStringList stringList;stringList << "Apple" << "Banana" << "Cherry" << "Banana" << "Apple";int lastIndex = stringList.lastIndexOf("Banana");if (lastIndex != -1) {qDebug() << "Last occurrence of 'Banana' found at index:" << lastIndex;} else {qDebug() << "No occurrence of 'Banana' found in the list.";}return 0;
}
在上述示例中,我们创建了一个 QStringList 对象 stringList,其中包含多个字符串元素。然后,我们使用 lastIndexOf() 函数查找字符串 “Banana” 在列表中最后出现的位置,并将结果存储在 lastIndex 中。
最后,我们根据 lastIndex 的值输出相应的信息。
运行这段代码,你将得到如下输出结果:
Last occurrence of 'Banana' found at index: 3
输出结果表明,字符串 “Banana” 在列表中最后出现的位置是索引 3。
1.6.indexOf()
QStringList 类提供了 indexOf() 函数用于查找指定字符串在列表中第一次出现的位置(索引)。
函数原型如下:
int indexOf(const QString& value, int from = 0) const;
参数说明:
value:要查找的字符串。from:可选参数,指定开始搜索的索引位置,默认值为 0,表示从列表的开头开始搜索。
函数返回值:
- 如果找到了指定的字符串,则返回第一个匹配项的索引值。
- 如果没有找到匹配项,则返回 -1。
以下是一个示例,演示如何使用 indexOf() 函数查找字符串在 QStringList 中第一次出现的位置:
#include <QtCore>int main() {QStringList stringList;stringList << "Apple" << "Banana" << "Cherry" << "Banana" << "Apple";int firstIndex = stringList.indexOf("Banana");if (firstIndex != -1) {qDebug() << "First occurrence of 'Banana' found at index:" << firstIndex;} else {qDebug() << "No occurrence of 'Banana' found in the list.";}return 0;
}
在上述示例中,我们创建了一个 QStringList 对象 stringList,其中包含多个字符串元素。然后,我们使用 indexOf() 函数查找字符串 “Banana” 在列表中第一次出现的位置,并将结果存储在 firstIndex 中。
最后,我们根据 firstIndex 的值输出相应的信息。
运行这段代码,你将得到如下输出结果:
First occurrence of 'Banana' found at index: 1
输出结果表明,字符串 “Banana” 在列表中第一次出现的位置是索引 1。
1.7.replaceInStrings()以及比较QString 类则提供了replace()函数
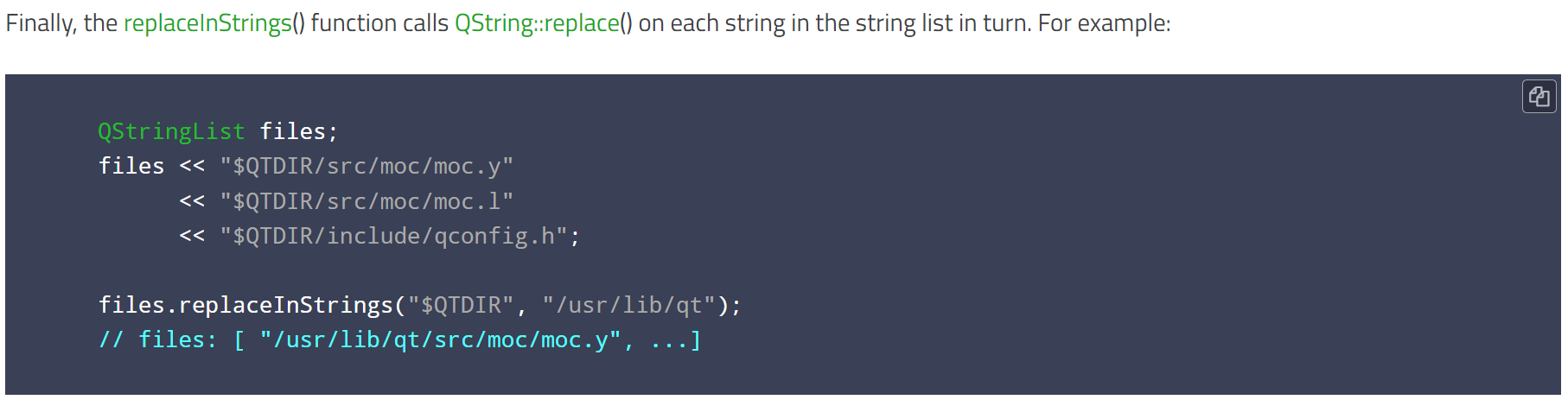
QStringList 类提供了一个成员函数 replaceInStrings(),用于在列表中的每个字符串中进行替换操作。而 QString 类则提供了 replace() 函数,用于执行单个字符串的替换操作。
-
QStringList::replaceInStrings(const QString& before, const QString& after):- 此函数用于在列表中的每个字符串中将
before替换为after。 - 它会修改原始的
QStringList对象,将所有匹配的字符串进行替换。 - 示例:
QStringList stringList; stringList << "apple" << "banana" << "cherry";stringList.replaceInStrings("a", "X");// 输出结果: "Xpple", "bXnXnX", "cherry" qDebug() << stringList; ``` - 此函数用于在列表中的每个字符串中将
-
QString::replace(const QString& before, const QString& after):- 此函数用于在单个字符串中将
before替换为after。 - 它返回一个新的字符串,不会修改原始的
QString对象。 - 示例:
QString str = "apple banana cherry"; QString replacedStr = str.replace("a", "X");// 输出结果: "Xpple bXnXnX cherry" qDebug() << replacedStr; ``` - 此函数用于在单个字符串中将
这两个函数都能执行字符串的替换操作,但 replaceInStrings() 是在 QStringList 对象的每个字符串中进行替换,而 replace() 是在单个字符串中进行替换。你可以根据自己的需求选择使用哪个函数。
1.8.一些常用方法和操作
QStringList是Qt框架中的一个类,用于存储字符串列表。它提供了一组方法和操作,方便对字符串列表进行处理、访问和修改。
以下是QStringList类的一些常用方法和操作的详细解释:
1. 构造函数和赋值操作符:
QStringList():默认构造函数,创建一个空的字符串列表。QStringList(const QStringList &other):拷贝构造函数,使用另一个字符串列表初始化当前列表。QStringList &operator=(const QStringList &other):赋值操作符,将另一个字符串列表赋值给当前列表。
2. 添加和移除元素:
void append(const QString &str):向列表末尾添加一个字符串。void prepend(const QString &str):向列表开头添加一个字符串。void insert(int i, const QString &str):在指定位置插入一个字符串。void removeAt(int i):移除指定位置的字符串。void removeOne(const QString &str):移除第一个匹配给定字符串的元素。void removeAll(const QString &str):移除所有匹配给定字符串的元素。void clear():清空列表,移除所有元素。
3. 获取和修改元素:
int size() const:返回列表中元素的数量。bool isEmpty() const:检查列表是否为空。QString at(int i) const:返回指定位置的字符串。QString &operator[](int i):访问指定位置的字符串,可用于修改该元素。const QString &operator[](int i) const:以只读方式访问指定位置的字符串。QStringList mid(int pos, int length = -1) const:返回从指定位置开始的指定长度子列表。QStringList &replace(int i, const QString &str):将指定位置的字符串替换为给定字符串。QStringList &replace(const QString &before, const QString &after):将所有匹配给定字符串的元素替换为新的字符串。
4. 其他常用方法:
bool contains(const QString &str) const:检查列表中是否包含给定字符串。int indexOf(const QString &str, int from = 0) const:返回第一个匹配给定字符串的位置。int lastIndexOf(const QString &str, int from = -1) const:返回最后一个匹配给定字符串的位置。QString join(const QString &separator) const:将列表中的所有元素连接为一个字符串,使用给定的分隔符分隔。
QStringList提供了方便的方法来处理字符串列表,如添加、移除、访问和修改元素等。它在Qt中广泛用于处理和操作字符串集合的场景,例如配置文件解析、日志记录、命令行参数处理等。
1.9.QStringList和QList关系
QStringList 和 QList<QString> 都是Qt中用于存储字符串的容器类,但它们在实现和使用上有一些区别。
-
类型差异:
QStringList是一个专门用于存储字符串的类,是QString类的派生类,可以直接使用QString的成员函数。QList<QString>是一个通用的列表类,可以存储任意类型的元素,其中的元素类型指定为QString。
-
头文件和命名空间:
QStringList类定义在<QStringList>头文件中,属于Qt命名空间。QList<QString>类定义在<QList>头文件中,同样属于Qt命名空间。
-
成员函数和使用:
QStringList类提供了一些特定于字符串列表的成员函数,如join()、split()、contains()等。QList<QString>类提供了通用的列表操作函数,如append()、insert()、remove()等。- 由于
QStringList是QString的派生类,可以直接使用QString类的成员函数。
-
隐式转换:
QStringList对象可以隐式转换为QList<QString>对象,即可以将QStringList类型的对象赋值给QList<QString>类型的变量。QList<QString>对象不能隐式转换为QStringList对象。
在实践中,QStringList 通常用于处理字符串的特定需求,如字符串的拆分和合并,而 QList<QString> 则更通用,适用于任意类型的元素的存储和操作。如果你只需要存储字符串,推荐使用 QStringList,如果需要存储其他类型的元素,可以使用 QList。
2.0.QStringList的append(),append(),operator+()
在Qt中,QStringList 提供了几种方法来添加和组合字符串:
append(const QString& str):该函数用于将指定的字符串添加到QStringList的末尾。例如:
QStringList stringList;
stringList.append("Apple");
stringList.append("Banana");
在上述示例中,我们使用 append() 函数将字符串 “Apple” 和 “Banana” 添加到 stringList 中。
operator<<(const QString& str):该运算符重载函数也可以用于将字符串添加到QStringList的末尾。例如:
QStringList stringList;
stringList << "Apple" << "Banana";
这个运算符的使用方式类似于使用 append() 函数。
operator+(const QStringList& other):该运算符重载函数用于将两个QStringList进行连接。它会返回一个新的QStringList,包含两个操作数的所有元素。例如:
QStringList list1;
list1 << "Apple" << "Banana";QStringList list2;
list2 << "Cherry" << "Durian";QStringList combinedList = list1 + list2;
在上述示例中,我们使用 operator+() 运算符将 list1 和 list2 进行连接,得到一个新的 combinedList,其中包含所有元素。
需要注意的是,operator+() 运算符返回的是一个新的 QStringList,原始的操作数 list1 和 list2 不会被修改。
这些函数和运算符提供了不同的方式来添加和组合字符串,可以根据具体的需求选择使用哪种方式。
2.1.QStringLis:Public Functions
QStringList(const QString &str)
QStringList(const QList<QString> &other)
QStringList(QList<QString> &&other)
bool contains(const QString &str, Qt::CaseSensitivity cs = Qt::CaseSensitive) const
bool contains(QLatin1StringView str, Qt::CaseSensitivity cs = Qt::CaseSensitive) const
bool contains(QStringView str, Qt::CaseSensitivity cs = Qt::CaseSensitive) const
QStringList filter(const QString &str, Qt::CaseSensitivity cs = Qt::CaseSensitive) const
QStringList filter(QStringView str, Qt::CaseSensitivity cs = Qt::CaseSensitive) const
QStringList filter(const QRegularExpression &re) const
qsizetype indexOf(const QRegularExpression &re, qsizetype from = 0) const
QString join(const QString &separator) const
QString join(QStringView separator) const
QString join(QLatin1StringView separator) const
QString join(QChar separator) const
qsizetype lastIndexOf(const QRegularExpression &re, qsizetype from = -1) const
qsizetype removeDuplicates()
QStringList & replaceInStrings(const QString &before, const QString &after, Qt::CaseSensitivity cs = Qt::CaseSensitive)
QStringList & replaceInStrings(QStringView before, QStringView after, Qt::CaseSensitivity cs = Qt::CaseSensitive)
QStringList & replaceInStrings(const QString &before, QStringView after, Qt::CaseSensitivity cs = Qt::CaseSensitive)
QStringList & replaceInStrings(QStringView before, const QString &after, Qt::CaseSensitivity cs = Qt::CaseSensitive)
QStringList & replaceInStrings(const QRegularExpression &re, const QString &after)
void sort(Qt::CaseSensitivity cs = Qt::CaseSensitive)
QStringList operator+(const QStringList &other) const
QStringList & operator<<(const QString &str)
QStringList & operator<<(const QStringList &other)
QStringList & operator<<(const QList<QString> &other)
QStringList & operator=(const QList<QString> &other)
QStringList & operator=(QList<QString> &&other)
2.2.QStringLis:List of all members, including inherited members
class const_iterator
class iterator
ConstIterator
Iterator
const_pointer
const_reference
const_reverse_iterator
difference_type
parameter_type
pointer
reference
reverse_iterator
rvalue_ref
size_type
value_type
QStringList(const QString &)
QStringList(const QList<QString> &)
QStringList(QList<QString> &&)
append(QList::parameter_type)
append(QList::rvalue_ref)
append(const QList<T> &)
append(QList<T> &&)
assign(qsizetype, QList::parameter_type) : QList<T> &
assign(InputIterator, InputIterator) : QList<T> &
assign(std::initializer_list<T>) : QList<T> &
at(qsizetype) const : QList::const_reference
back() : QList::reference
back() const : QList::const_reference
begin() : QList::iterator
begin() const : QList::const_iterator
capacity() const : qsizetype
cbegin() const : QList::const_iterator
cend() const : QList::const_iterator
clear()
constBegin() const : QList::const_iterator
constData() const : QList::const_pointer
constEnd() const : QList::const_iterator
constFirst() const : const T &
constLast() const : const T &
contains(const QString &, Qt::CaseSensitivity) const : bool
contains(const AT &) const : bool
contains(QLatin1StringView, Qt::CaseSensitivity) const : bool
contains(QStringView, Qt::CaseSensitivity) const : bool
count(const AT &) const : qsizetype
count() const : qsizetype
crbegin() const : QList::const_reverse_iterator
crend() const : QList::const_reverse_iterator
data() : QList::pointer
data() const : QList::const_pointer
emplace(qsizetype, Args &&...) : QList::iterator
emplace(QList::const_iterator, Args &&...) : QList::iterator
emplaceBack(Args &&...) : QList::reference
emplace_back(Args &&...) : QList::reference
empty() const : bool
end() : QList::iterator
end() const : QList::const_iterator
endsWith(QList::parameter_type) const : bool
erase(QList::const_iterator) : QList::iterator
erase(QList::const_iterator, QList::const_iterator) : QList::iterator
fill(QList::parameter_type, qsizetype) : QList<T> &
filter(const QString &, Qt::CaseSensitivity) const : QStringList
filter(QStringView, Qt::CaseSensitivity) const : QStringList
filter(const QRegularExpression &) const : QStringList
first() : T &
first() const : const T &
first(qsizetype) const : QList<T>
front() : QList::reference
front() const : QList::const_reference
indexOf(const AT &, qsizetype) const : qsizetype
indexOf(const QRegularExpression &, qsizetype) const : qsizetype
insert(qsizetype, QList::parameter_type) : QList::iterator
insert(qsizetype, qsizetype, QList::parameter_type) : QList::iterator
insert(QList::const_iterator, QList::parameter_type) : QList::iterator
insert(QList::const_iterator, qsizetype, QList::parameter_type) : QList::iterator
insert(QList::const_iterator, QList::rvalue_ref) : QList::iterator
insert(qsizetype, QList::rvalue_ref) : QList::iterator
isEmpty() const : bool
join(const QString &) const : QString
join(QStringView) const : QString
join(QLatin1StringView) const : QString
join(QChar) const : QString
last() : T &
last() const : const T &
last(qsizetype) const : QList<T>
lastIndexOf(const AT &, qsizetype) const : qsizetype
lastIndexOf(const QRegularExpression &, qsizetype) const : qsizetype
length() const : qsizetype
mid(qsizetype, qsizetype) const : QList<T>
move(qsizetype, qsizetype)
pop_back()
pop_front()
prepend(QList::rvalue_ref)
prepend(QList::parameter_type)
push_back(QList::parameter_type)
push_back(QList::rvalue_ref)
push_front(QList::rvalue_ref)
push_front(QList::parameter_type)
rbegin() : QList::reverse_iterator
rbegin() const : QList::const_reverse_iterator
remove(qsizetype, qsizetype)
removeAll(const AT &) : qsizetype
removeAt(qsizetype)
removeDuplicates() : qsizetype
removeFirst()
removeIf(Predicate) : qsizetype
removeLast()
removeOne(const AT &) : bool
rend() : QList::reverse_iterator
rend() const : QList::const_reverse_iterator
replace(qsizetype, QList::parameter_type)
replace(qsizetype, QList::rvalue_ref)
replaceInStrings(const QString &, const QString &, Qt::CaseSensitivity) : QStringList &
replaceInStrings(QStringView, QStringView, Qt::CaseSensitivity) : QStringList &
replaceInStrings(const QString &, QStringView, Qt::CaseSensitivity) : QStringList &
replaceInStrings(QStringView, const QString &, Qt::CaseSensitivity) : QStringList &
replaceInStrings(const QRegularExpression &, const QString &) : QStringList &
reserve(qsizetype)
resize(qsizetype)
resize(qsizetype, QList::parameter_type)
shrink_to_fit()
size() const : qsizetype
sliced(qsizetype, qsizetype) const : QList<T>
sliced(qsizetype) const : QList<T>
sort(Qt::CaseSensitivity)
squeeze()
startsWith(QList::parameter_type) const : bool
swap(QList<T> &)
swapItemsAt(qsizetype, qsizetype)
takeAt(qsizetype) : T
takeFirst() : QList::value_type
takeLast() : QList::value_type
value(qsizetype) const : T
value(qsizetype, QList::parameter_type) const : T
operator!=(const QList<T> &) const : bool
operator+(const QStringList &) const : QStringList
operator+(const QList<T> &) const : QList<T>
operator+(const QList<T> &) : QList<T>
operator+(QList<T> &&) const : QList<T>
operator+(QList<T> &&) : QList<T>
operator+=(const QList<T> &) : QList<T> &
operator+=(QList<T> &&) : QList<T> &
operator+=(QList::parameter_type) : QList<T> &
operator+=(QList::rvalue_ref) : QList<T> &
operator<(const QList<T> &) const : bool
operator<<(const QString &) : QStringList &
operator<<(QList::parameter_type) : QList<T> &
operator<<(const QStringList &) : QStringList &
operator<<(const QList<T> &) : QList<T> &
operator<<(const QList<QString> &) : QStringList &
operator<<(QList<T> &&) : QList<T> &
operator<<(QList::rvalue_ref) : QList<T> &
operator<=(const QList<T> &) const : bool
operator=(const QList<QString> &) : QStringList &
operator=(std::initializer_list<T>) : QList<T> &
operator=(QList<QString> &&) : QStringList &
operator=(const QList<T> &) : QList<T> &
operator=(QList<T> &&) : QList<T> &
operator==(const QList<T> &) const : bool
operator>(const QList<T> &) const : bool
operator>=(const QList<T> &) const : bool
operator[](qsizetype) : QList::reference
operator[](qsizetype) const : QList::const_reference
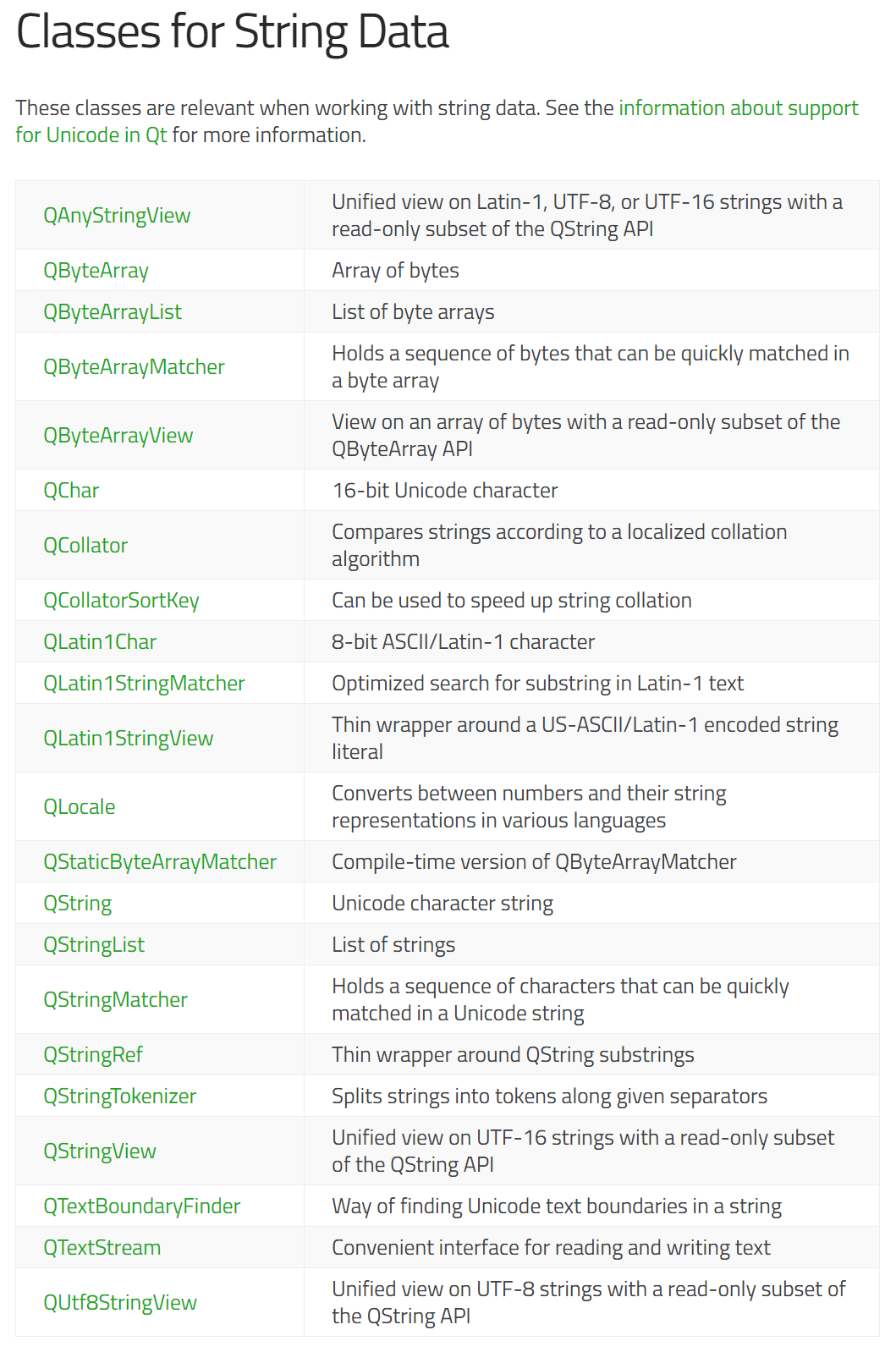
2.3.Classes for String Data(Qt中字符串数据的类)
相关文章:

qt-C++笔记之QStringList
qt-C笔记之QStringList —— 杭州 2023-12-03 文章目录 qt-C笔记之QStringList1.1.《Qt官方文档》第一部分翻译:继承自QList\<QString\>-初始化-添加字符串1.2.迭代字符串1.3.join()和split()1.4.filter()1.5.lastIndexOf()1.6.indexOf()1.7.replaceInString…...

ply前端
ply 是 eBPF 的 front-end 前端工具之一,专为 embedded Linux systems 开发,采用 C 语言编写,只需 libc 和内核支持 BPF 就可以运行,不需要外部 kernel 模块,不需要 LLVM,不需要 python。 ply 由瑞典工程师…...

U盘不仅能在电脑上使用,在手机上也可使用,包括安卓和苹果手机,但苹果的较特殊
许多最好的安卓手机都使用USB-C端口在电脑上充电和来回传输文件,但如果你需要给老板发电子邮件的文件放在闪存驱动器或全尺寸SD卡上呢? 幸运的是,使用廉价的适配器电缆,你可以将USB加密狗或读卡器直接连接到手机上。你甚至可以直接使用USB-C闪存驱动器,以实现更轻松的过程…...
面试数据库八股文十问十答第二期
面试数据库八股文十问十答第二期 作者:程序员小白条,个人博客 相信看了本文后,对你的面试是有一定帮助的! ⭐点赞⭐收藏⭐不迷路!⭐ 1.MySQL的主从复制 MySQL的主从复制是什么?MySQL主从复制是一种常见的…...

【LeetCode】每日一题 2023_12_2 拼车(模拟/差分)
文章目录 刷题前唠嗑题目:拼车题目描述代码与解题思路学习大佬题解 刷题前唠嗑 LeetCode?启动!!! 题目:拼车 题目链接:1094. 拼车 题目描述 代码与解题思路 func carPooling(trips [][]int…...
网络和Linux网络_7(传输层)UDP和TCP协议(端口号+确认应答+超时重传+三次握手四次挥手)
目录 1. 重看端口号 1.1 端口号的概念 1.2 端口号的划分 2. 重看UDP协议 2.1 UDP协议格式 2.2 UDP的特点 3. 重看TCP协议 3.1 TCP协议格式 3.2 TCP的解包分用 3.3 TCP的可靠性及机制 3.3.1 确认应答ACK机制 3.3.2 超时重传机制 3.3.3 连接管理机制(三次…...

KALI LINUX安全审核
预计更新 第一章 入门 1.1 什么是Kali Linux? 1.2 安装Kali Linux 1.3 Kali Linux桌面环境介绍 1.4 基本命令和工具 第二章 信息收集 1.1 网络扫描 1.2 端口扫描 1.3 漏洞扫描 1.4 社交工程学 第三章 攻击和渗透测试 1.1 密码破解 1.2 暴力破解 1.3 漏洞利用 1.4 …...

2023-12-03-解决libxkbcommon库编译完后图像界面不能使用键盘
layout: post # 使用的布局(不需要改) title: Ubuntu修复 # 标题 subtitle: 解决libxkbcommon库编译完图形界面不能使用键盘 #副标题 date: 2023-12-03 # 时间 author: BY ThreeStones1029 # 作者 header-img: img/about_bg.jpg #这篇文章标题背景图片 c…...
vue el-table表格中每行上传文件(上传简历)操作
1、HTML中 <el-table :data"formInfo.userListDto" border stripe max-height"400"><el-table-column type"index" label"序号" width"50"> </el-table-column><el-table-column prop"realName&q…...

Python批量图像处理--图片重命名、图片旋转
图像批量重命名: 使用batch_rename_images函数实现对多个文件夹下面的图片进行重命名操作 先检查文件名的后缀,使用了.endswith()方法来判断文件名是否以.jpg、.png或.JPG结尾,判断是否为图片文件 然后构造新的文件路径new_filepath&#…...

第五天 用Python批量处理Excel文件,实现自动化办公
用Python批量处理Excel文件,实现自动化办公 一、具体需求 有以下N个表,每个表的结构一样,如下: 需要把所有表数据汇总,把每个人的得分、积分分别加起来,然后按总积分排名,总积分一致时ÿ…...
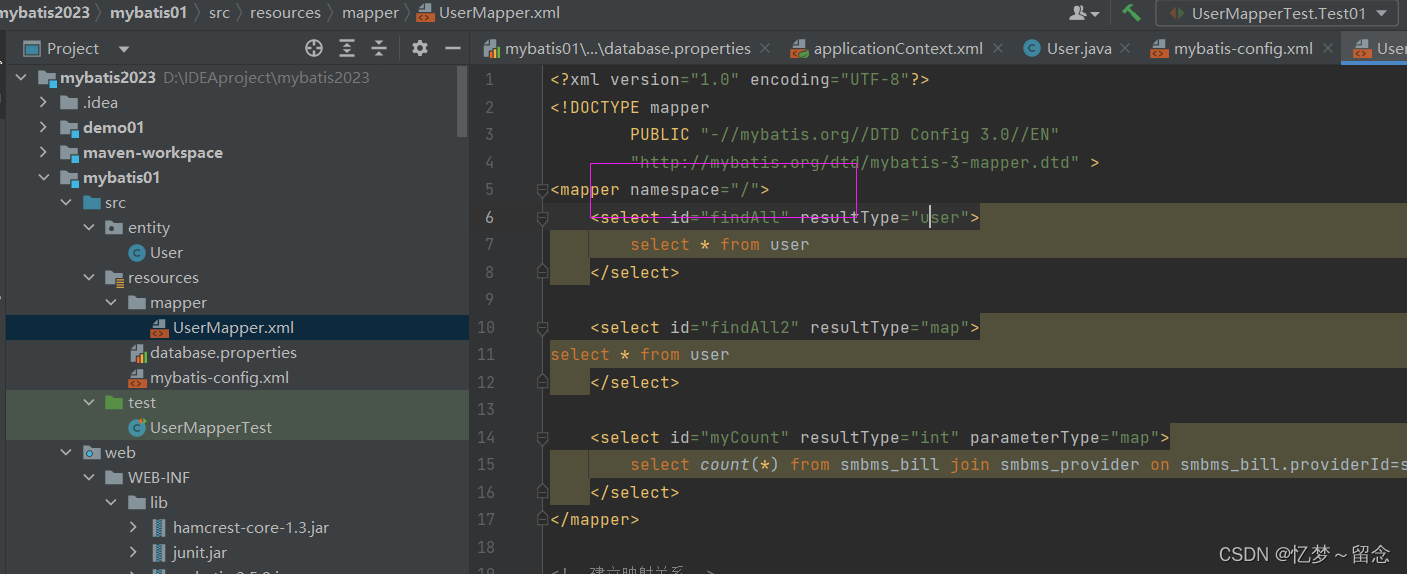
mybatis整合(手动添加jar包方式)
操作步骤 创建数据库 建立user表 放入数据 1、创建javaweb工程并添加Jar包 用到的jar包 junit 用于测试 mybatis框架:mybatis-3.5.9.jar mysql数据库:mysql-connector-java-8.0.28.jar 2、添加MyBatis核心配置文件 <?xml version"1.0"…...
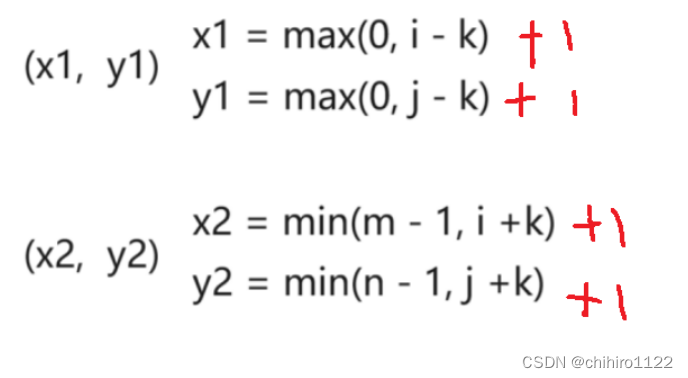
leetcode - 矩阵区域和
1314. 矩阵区域和 - 力扣(LeetCode) 给你一个 m x n 的矩阵 mat 和一个整数 k ,请你返回一个矩阵 answer ,其中每个 answer[i][j] 是所有满足下述条件的元素 mat[r][c] 的和: i - k < r < i k, j - k < c …...

头歌JUnit单元测试相关实验进阶
JUnit是一个由 Erich Gamma 和 Kent Beck 编写的一个回归测试框架(regression testing framework),主要供 Java 开发人员编写单元测试。Junit在极限编程和重构中被极力推荐使用,因为它可以大大地提高开发的效率。 Junit的特性&…...

【kafka实践】11|消费位移提交
消费者位移 消费者位移这一节介绍了消费者位移的基本概念和消息格式,本节我们来聊聊消费位移的提交。 Consumer 需要向 Kafka 汇报自己的位移数据,这个汇报过程被称为提交位移(Committing Offsets)。因为 Consumer 能够同时消费…...
Mac卸载、安装Python
卸载 说明 对于删除 Python,我们首先要知道其具体都安装了什么,实际上,在安装 Python 时,其自动生成: Python framework,即 Python 框架;Python 应用目录;指向 Python 的连接。 …...

算法——滑动窗口
滑动窗口大致分为两类:一类是窗口长度固定的,即left和right可以一起移动;另一种是窗口的长度变化(例如前五道题),即right疯狂移动,left没怎么动,这类题需要观察单调性(即指针)等各方…...
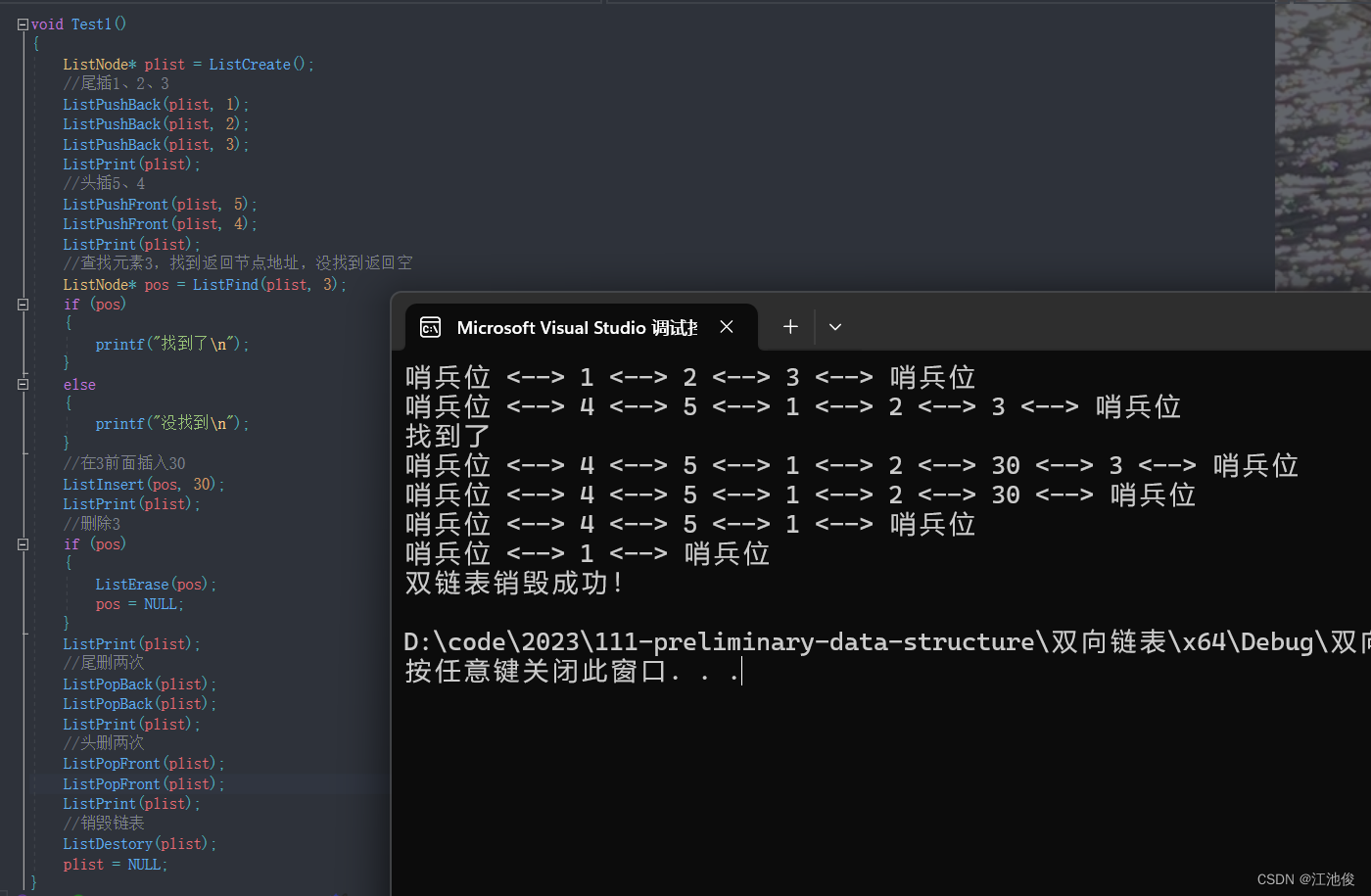
带头双向循环链表:一种高效的数据结构
💓 博客主页:江池俊的博客⏩ 收录专栏:数据结构探索👉专栏推荐:✅cpolar ✅C语言进阶之路💻代码仓库:江池俊的代码仓库🔥编译环境:Visual Studio 2022🎉欢迎大…...

C++基础 -34- 输入输出运算符重载
输出运算符重载格式 ostream & operator<<(ostream &out,person a) {cout << a.a << endl;return out; }举例输出运算符重载 #include "iostream"using namespace std;class person {public:person(int a):a(a){}int a; };ostream &…...

MimicGen论文分析与资料汇总
MimicGen论文分析与资料汇总 前言论文分析相关资料汇总 前言 论文分析 相关资料汇总 Paper:MimicGen: A Data Generation System for Scalable Robot Learning using Human Demonstrations mimicgen.github 破局利刃!英伟达合成数据新成果:为机器人造…...

(LeetCode 每日一题) 3442. 奇偶频次间的最大差值 I (哈希、字符串)
题目:3442. 奇偶频次间的最大差值 I 思路 :哈希,时间复杂度0(n)。 用哈希表来记录每个字符串中字符的分布情况,哈希表这里用数组即可实现。 C版本: class Solution { public:int maxDifference(string s) {int a[26]…...
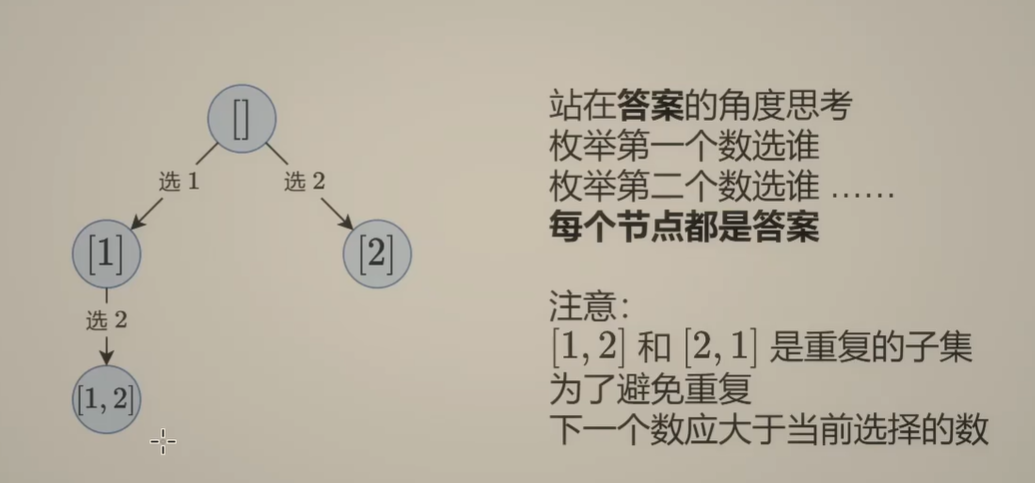
Day131 | 灵神 | 回溯算法 | 子集型 子集
Day131 | 灵神 | 回溯算法 | 子集型 子集 78.子集 78. 子集 - 力扣(LeetCode) 思路: 笔者写过很多次这道题了,不想写题解了,大家看灵神讲解吧 回溯算法套路①子集型回溯【基础算法精讲 14】_哔哩哔哩_bilibili 完…...
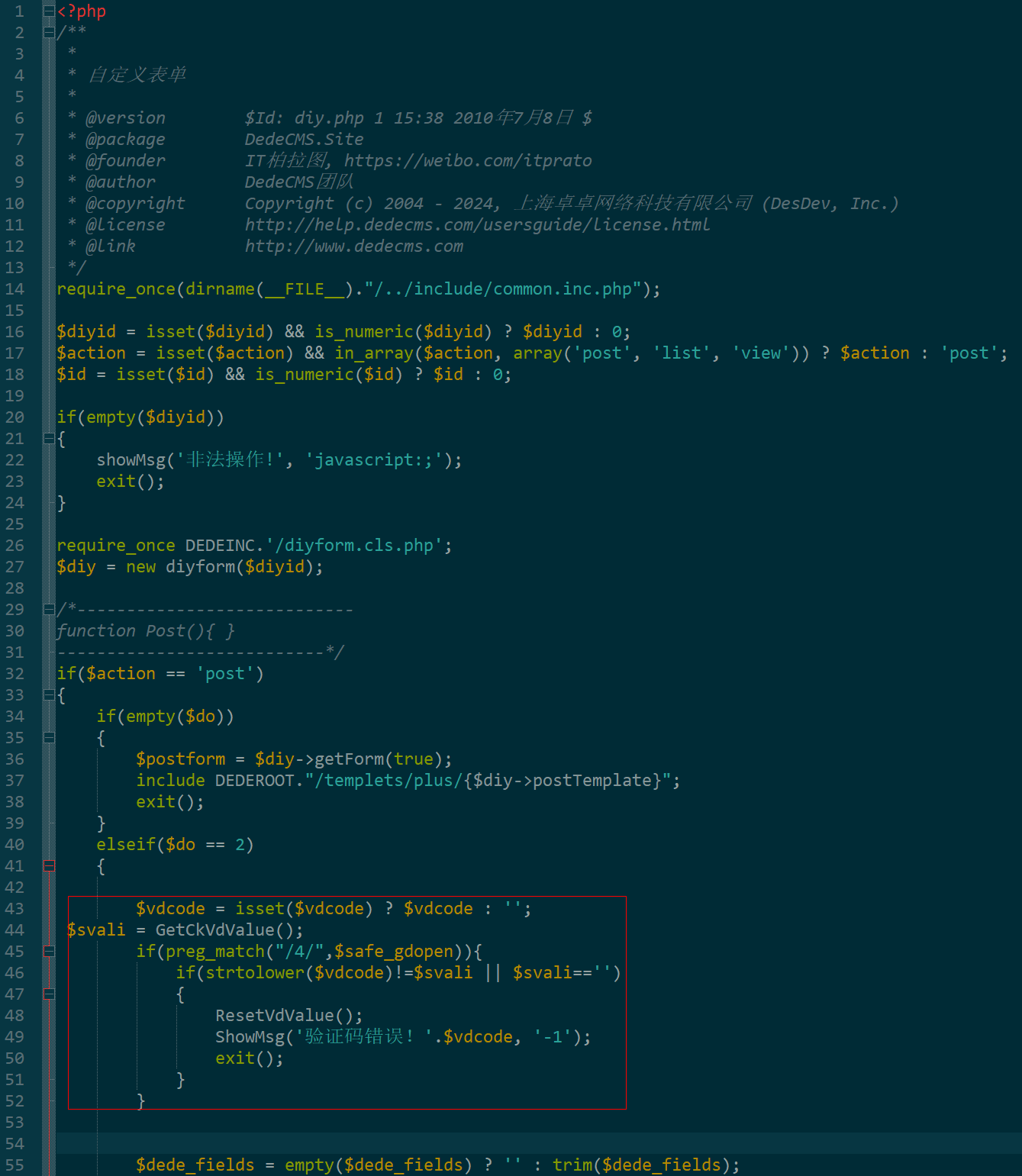
dedecms 织梦自定义表单留言增加ajax验证码功能
增加ajax功能模块,用户不点击提交按钮,只要输入框失去焦点,就会提前提示验证码是否正确。 一,模板上增加验证码 <input name"vdcode"id"vdcode" placeholder"请输入验证码" type"text&quo…...
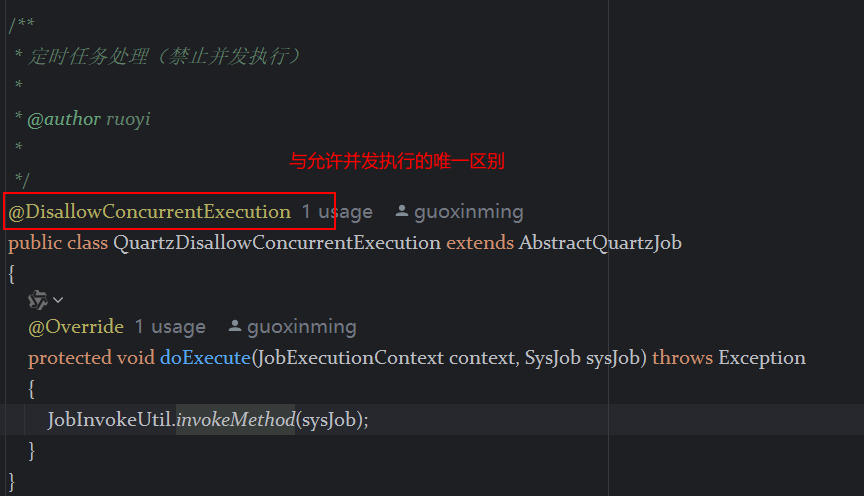
定时器任务——若依源码分析
分析util包下面的工具类schedule utils: ScheduleUtils 是若依中用于与 Quartz 框架交互的工具类,封装了定时任务的 创建、更新、暂停、删除等核心逻辑。 createScheduleJob createScheduleJob 用于将任务注册到 Quartz,先构建任务的 JobD…...
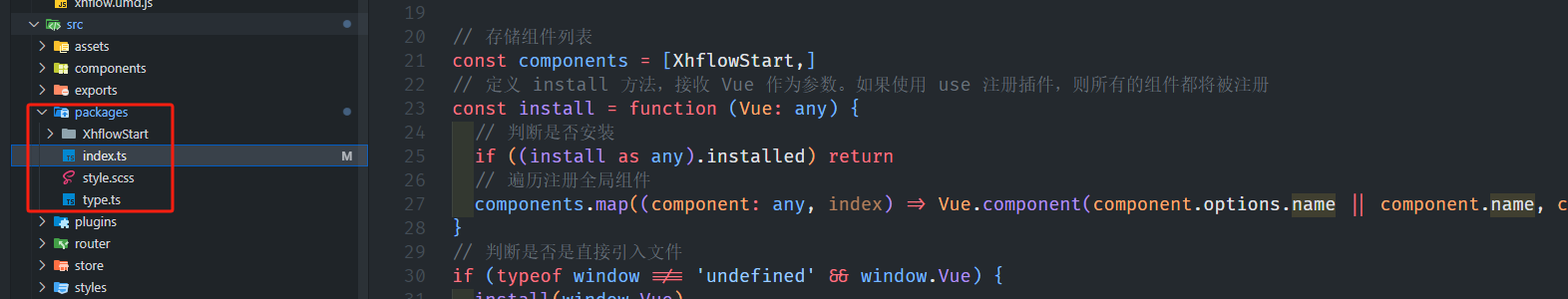
基于当前项目通过npm包形式暴露公共组件
1.package.sjon文件配置 其中xh-flowable就是暴露出去的npm包名 2.创建tpyes文件夹,并新增内容 3.创建package文件夹...

江苏艾立泰跨国资源接力:废料变黄金的绿色供应链革命
在华东塑料包装行业面临限塑令深度调整的背景下,江苏艾立泰以一场跨国资源接力的创新实践,重新定义了绿色供应链的边界。 跨国回收网络:废料变黄金的全球棋局 艾立泰在欧洲、东南亚建立再生塑料回收点,将海外废弃包装箱通过标准…...
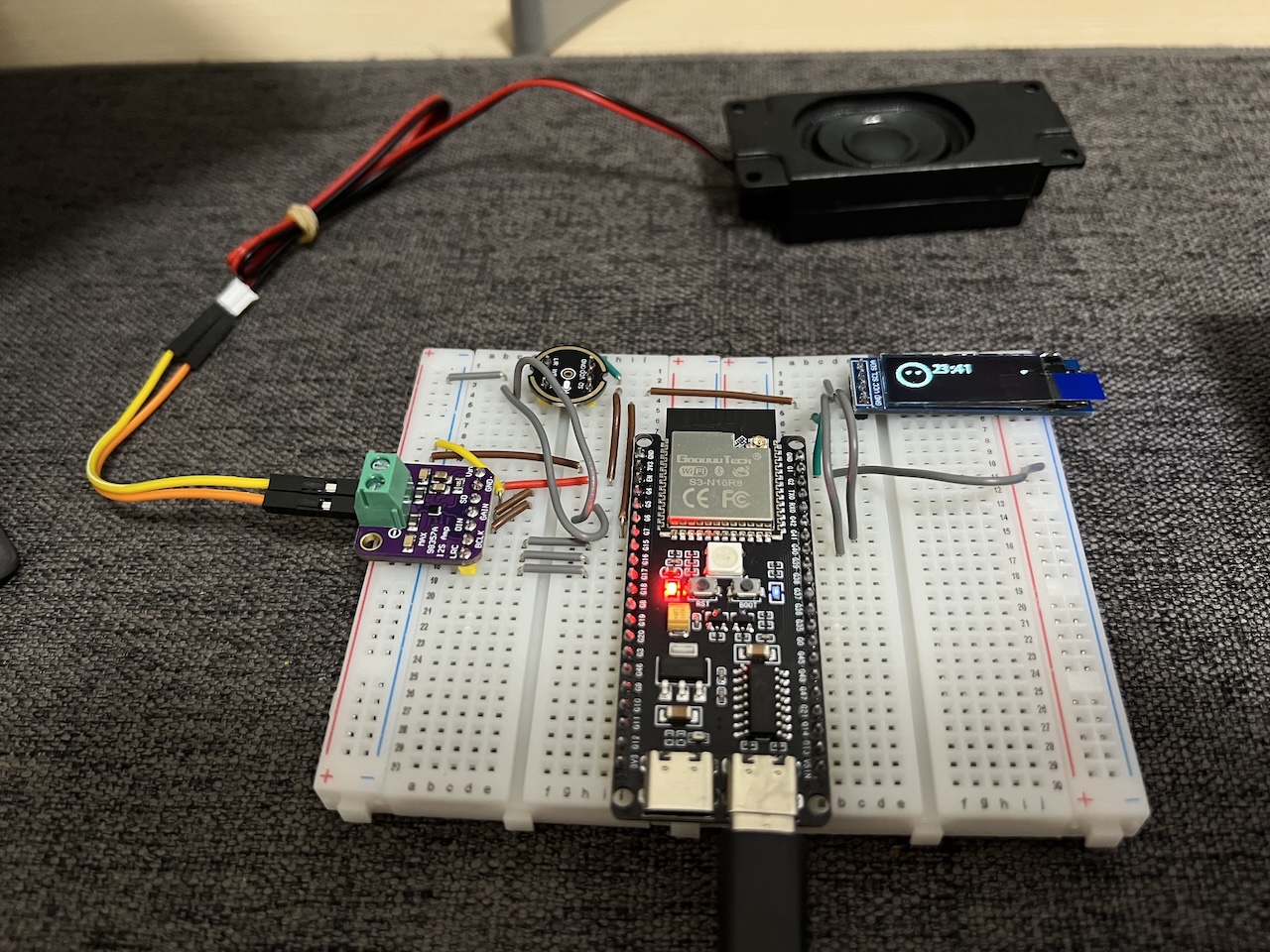
DIY|Mac 搭建 ESP-IDF 开发环境及编译小智 AI
前一阵子在百度 AI 开发者大会上,看到基于小智 AI DIY 玩具的演示,感觉有点意思,想着自己也来试试。 如果只是想烧录现成的固件,乐鑫官方除了提供了 Windows 版本的 Flash 下载工具 之外,还提供了基于网页版的 ESP LA…...
基础光照(Basic Lighting))
C++.OpenGL (10/64)基础光照(Basic Lighting)
基础光照(Basic Lighting) 冯氏光照模型(Phong Lighting Model) #mermaid-svg-GLdskXwWINxNGHso {font-family:"trebuchet ms",verdana,arial,sans-serif;font-size:16px;fill:#333;}#mermaid-svg-GLdskXwWINxNGHso .error-icon{fill:#552222;}#mermaid-svg-GLd…...
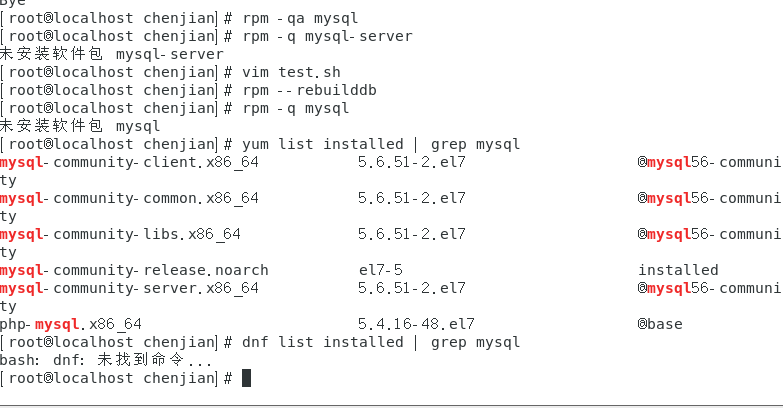
mysql已经安装,但是通过rpm -q 没有找mysql相关的已安装包
文章目录 现象:mysql已经安装,但是通过rpm -q 没有找mysql相关的已安装包遇到 rpm 命令找不到已经安装的 MySQL 包时,可能是因为以下几个原因:1.MySQL 不是通过 RPM 包安装的2.RPM 数据库损坏3.使用了不同的包名或路径4.使用其他包…...
selenium学习实战【Python爬虫】
selenium学习实战【Python爬虫】 文章目录 selenium学习实战【Python爬虫】一、声明二、学习目标三、安装依赖3.1 安装selenium库3.2 安装浏览器驱动3.2.1 查看Edge版本3.2.2 驱动安装 四、代码讲解4.1 配置浏览器4.2 加载更多4.3 寻找内容4.4 完整代码 五、报告文件爬取5.1 提…...
