boost::graph学习
boost::graph API简单小结
boost::graph是boost为图算法提供的API,简单易用。
API说明
-
boost::add_vertex
创建一个顶点。 -
boost::add_edge
创建一条边。 -
boost::edges
获取所有的边。 -
boost::vertices
获取所有的顶点。 -
graph.operator[vertex_descriptor]
获取顶点的属性Property。 -
graph.operator[edge_descriptor]
获取边的属性Property。 -
boost::out_edges
获取顶点的“出边”(out edges),即以当前顶点为出发点的边。
参考文档:
https://theboostcpplibraries.com/boost.graph-algorithms
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/338279100
https://www.boost.org/doc/libs/1_83_0/libs/graph/doc/quick_tour.html
https://www.boost.org/doc/libs/1_83_0/libs/graph/doc/adjacency_list.html
https://www.technical-recipes.com/2015/getting-started-with-the-boost-graph-library/
https://blog.csdn.net/Augusdi/article/details/105757441
代码示例:
#include "PSParametricModelingEngine.h"#include <QDebug>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <iterator>
#include <utility>using namespace std;
using namespace boost;namespace
{struct VertexProperty{int id;string name;};struct EdgeProperty{int id;int weight;};typedef boost::adjacency_list<vecS, // 使用数组来存储vertex vecS,vecS, // 使用数组来存储vertex vecS,directedS, // 申明为有向图,可以访问其out-edge,若要都能访问VertexProperty, // 定义顶点属性EdgeProperty // 定义边的属性>PSGraph;typedef graph_traits<PSGraph>::vertex_descriptor vertex_descriptor_t;void printVertices(){boost::adjacency_list<> g;boost::adjacency_list<>::vertex_descriptor v1 = boost::add_vertex(g);boost::adjacency_list<>::vertex_descriptor v2 = boost::add_vertex(g);boost::adjacency_list<>::vertex_descriptor v3 = boost::add_vertex(g);boost::adjacency_list<>::vertex_descriptor v4 = boost::add_vertex(g);std::cout << v1 << ", " << v2 << ", " << v3 << ", " << v4 << '\n';}void printEdgeVector(){boost::adjacency_list<> g;boost::adjacency_list<>::vertex_descriptor v1 = boost::add_vertex(g);boost::adjacency_list<>::vertex_descriptor v2 = boost::add_vertex(g);boost::add_vertex(g);boost::add_vertex(g);std::pair<boost::adjacency_list<>::edge_descriptor, bool> p = boost::add_edge(v1, v2, g);std::cout.setf(std::ios::boolalpha);std::cout << p.second << '\n';p = boost::add_edge(v1, v2, g);std::cout << p.second << '\n';p = boost::add_edge(v2, v1, g);std::cout << p.second << '\n';std::pair<boost::adjacency_list<>::edge_iterator, boost::adjacency_list<>::edge_iterator> es = boost::edges(g);std::copy(es.first, es.second, std::ostream_iterator<boost::adjacency_list<>::edge_descriptor>{std::cout, "\n"});for (boost::adjacency_list<>::edge_iterator iterator = es.first; iterator != es.second; iterator++){std::stringstream ss;ss << (*iterator);qDebug() << QString::fromUtf8(ss.str().c_str());}}void printEdgeSet(){typedef boost::adjacency_list<boost::setS, boost::vecS, boost::undirectedS> graph;graph g;boost::adjacency_list<>::vertex_descriptor v1 = boost::add_vertex(g);boost::adjacency_list<>::vertex_descriptor v2 = boost::add_vertex(g);boost::add_vertex(g);boost::add_vertex(g);std::pair<graph::edge_descriptor, bool> p = boost::add_edge(v1, v2, g);std::cout.setf(std::ios::boolalpha);std::cout << p.second << '\n';p = boost::add_edge(v1, v2, g);std::cout << p.second << '\n';p = boost::add_edge(v2, v1, g);std::cout << p.second << '\n';std::pair<graph::edge_iterator, graph::edge_iterator> es = boost::edges(g);std::copy(es.first, es.second, std::ostream_iterator<graph::edge_descriptor>{std::cout, "\n"});for (graph::edge_iterator iterator = es.first; iterator != es.second; iterator++){std::stringstream ss;ss << (*iterator);qDebug() << QString::fromUtf8(ss.str().c_str());}}int printDirectedGraph(){// 定义图类型,使用vector存放顶点和边,有向图typedef adjacency_list<vecS, vecS, directedS> graph_t;// 产生图对象,有6个顶点graph_t g(6);// 加入边add_edge(1, 2, g);add_edge(1, 5, g);add_edge(2, 2, g);add_edge(2, 0, g);add_edge(3, 4, g);add_edge(4, 3, g);add_edge(5, 0, g);// 显示所有的顶点// 顶点迭代器类型typedef graph_traits<graph_t>::vertex_iterator vertex_iter;// 得到所有顶点,vrange中的一对迭代器分别指向第一个顶点和最后的一个顶点之后。std::pair<vertex_iter, vertex_iter> vrange = vertices(g);for (vertex_iter itr = vrange.first; itr != vrange.second; ++itr)qDebug() << *itr;// 显示所有的边// 边迭代器类型typedef graph_traits<graph_t>::edge_iterator edge_iter;// 得到所有边,erange中的一对迭代器分别指向第一条边和最后的一条边之后std::pair<edge_iter, edge_iter> erange = edges(g);for (edge_iter itr = erange.first; itr != erange.second; ++itr)qDebug() << source(*itr, g) << "-->" << target(*itr, g);return 0;};void printPSGraph(){PSGraph g; // 声明一个图VertexProperty vertex1{101, "Vertex 1"};VertexProperty vertex2{102, "Vertex 2"};VertexProperty vertex3{103, "Vertex 3"};VertexProperty vertex4{104, "Vertex 4"};EdgeProperty edge1{101, 1};EdgeProperty edge2{102, 2};EdgeProperty edge3{103, 3};EdgeProperty edge4{104, 4};EdgeProperty edge5{105, 5};EdgeProperty edge6{106, 6};vertex_descriptor_t vert1 = boost::add_vertex(vertex1, g);vertex_descriptor_t vert2 = boost::add_vertex(vertex2, g);vertex_descriptor_t vert3 = boost::add_vertex(vertex3, g);vertex_descriptor_t vert4 = boost::add_vertex(vertex4, g);auto e1 = boost::add_edge(vert1, vert2, edge1, g);auto e2 = boost::add_edge(vert2, vert3, edge2, g);auto e3 = boost::add_edge(vert3, vert4, edge3, g);auto e4 = boost::add_edge(vert4, vert1, edge4, g);auto e5 = boost::add_edge(vert4, vert2, edge5, g);auto e6 = boost::add_edge(vert4, vert3, edge6, g);typedef graph_traits<PSGraph>::vertex_iterator vertex_iter;std::pair<vertex_iter, vertex_iter> vrange = vertices(g);for (vertex_iter itr = vrange.first; itr != vrange.second; ++itr){auto prop = g[*itr];qDebug() << *itr << ": {" << prop.id << ", " << QString::fromUtf8(prop.name.c_str()) << "}";typedef graph_traits<PSGraph> GraphTraits;typename GraphTraits::out_edge_iterator out_i, out_end;typename GraphTraits::edge_descriptor e;for (boost::tie(out_i, out_end) = out_edges(*itr, g); out_i != out_end; ++out_i){e = *out_i;auto prop = g[e];qDebug() << source(e, g) << "-->" << target(e, g) << ": {" << prop.id << ", " << prop.weight << "}";}}typedef graph_traits<PSGraph>::edge_iterator edge_iter;std::pair<edge_iter, edge_iter> erange = edges(g);for (edge_iter itr = erange.first; itr != erange.second; ++itr){auto prop = g[*itr];qDebug() << source(*itr, g) << "-->" << target(*itr, g) << ": {" << prop.id << ", " << prop.weight << "}";}}
} // namespacevoid main()
{// printEdgeSet();// printDirectedGraph();printPSGraph();
}
相关文章:

boost::graph学习
boost::graph API简单小结 boost::graph是boost为图算法提供的API,简单易用。 API说明 boost::add_vertex 创建一个顶点。 boost::add_edge 创建一条边。 boost::edges 获取所有的边。 boost::vertices 获取所有的顶点。 graph.operator[vertex_descriptor] 获…...

【C语言:动态内存管理】
文章目录 前言1.malloc2.free3.calloc4.realloc5.动态内存常见错误6.动态内存经典笔试题分析7.柔性数组8.C/C中的内存区域划分 前言 文章的标题是动态内存管理,那什么是动态内存管理?为什么有动态内存管理呢? 回顾一下以前学的知识ÿ…...

【Python基础】迭代器
文章目录 [toc]什么是迭代可迭代对象判断数据类型是否是可迭代类型 迭代器对可迭代对象进行迭代的本质获取可迭代对象的迭代器通过迭代器获取数据StopIteration异常 自定义迭代器__iter__()方法__next__()方法判断数据类型是否是可迭代类型自定义迭代器案例分离模式整合模式 fo…...
QVTK 可视化
#ifndef MAINWINDOW_H #define MAINWINDOW_H#include <QMainWindow>#include <vtkNew.h> // 智能指针 #include <QVTKOpenGLNativeWidget.h> #include <vtkCylinderSource.h> // 圆柱#include <vtkPolyDataMapper.h&g…...

【初阶C++】入门(超详解)
C入门 前言1. C关键字(C98)2. 命名空间2.1 命名空间定义2.2 命名空间使用2.3嵌套命名空间 3. C输入&输出4. 缺省参数4.1 缺省参数概念4.2 缺省参数分类 5. 函数重载5.1 函数重载概念5.2 C支持函数重载的原理--名字修饰(name Mangling) 6. 引用6.1 引用概念6.2 引用特性6.3 …...

Java正则表达式的使用
标题:Java正则表达式的使用 介绍: 正则表达式是一种强大的文本匹配模式和搜索工具。在Java中,通过使用正则表达式,我们可以快速有效地进行字符串的匹配、查找和替换。本文将介绍Java正则表达式的基本使用方法,并提供相…...
Collecting Application Engine Performance Data 收集应用程序引擎性能数据
You can collect performance data of any specific SQL action of an Application Engine program to address any performance issue. 您可以收集应用程序引擎程序的任何特定SQL操作的性能数据,以解决任何性能问题。 You can collect performance data of the S…...

C Primer Plus阅读--章节16
C Primer Plus阅读–章节16 翻译程序的第一步 预处理之前,编译器必须对该程序进行一些翻译处理。 首先,编译器将源代码中出现的字符映射到源字符集。第二,编译器定位每个反斜杠后面跟着换行符的实力,并删除他们。物理行的合并。…...
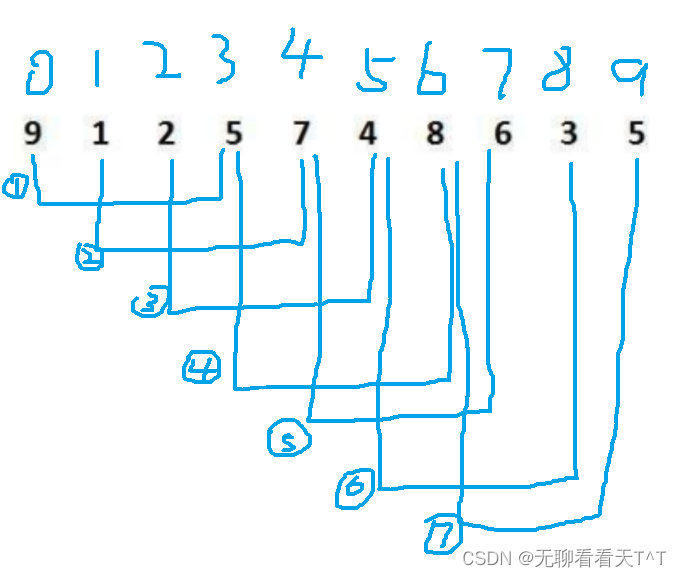
直接插入排序与希尔排序
目录 前言 插入排序 直接插入排序 时空复杂度 直接插入排序的特性 希尔排序(缩小增量排序) 预排序 顺序排序 多组并排 小总结 直接插入排序 时空复杂度 希尔排序的特性 前言 字可能有点多,但是真的理解起来真的没那么难&#…...
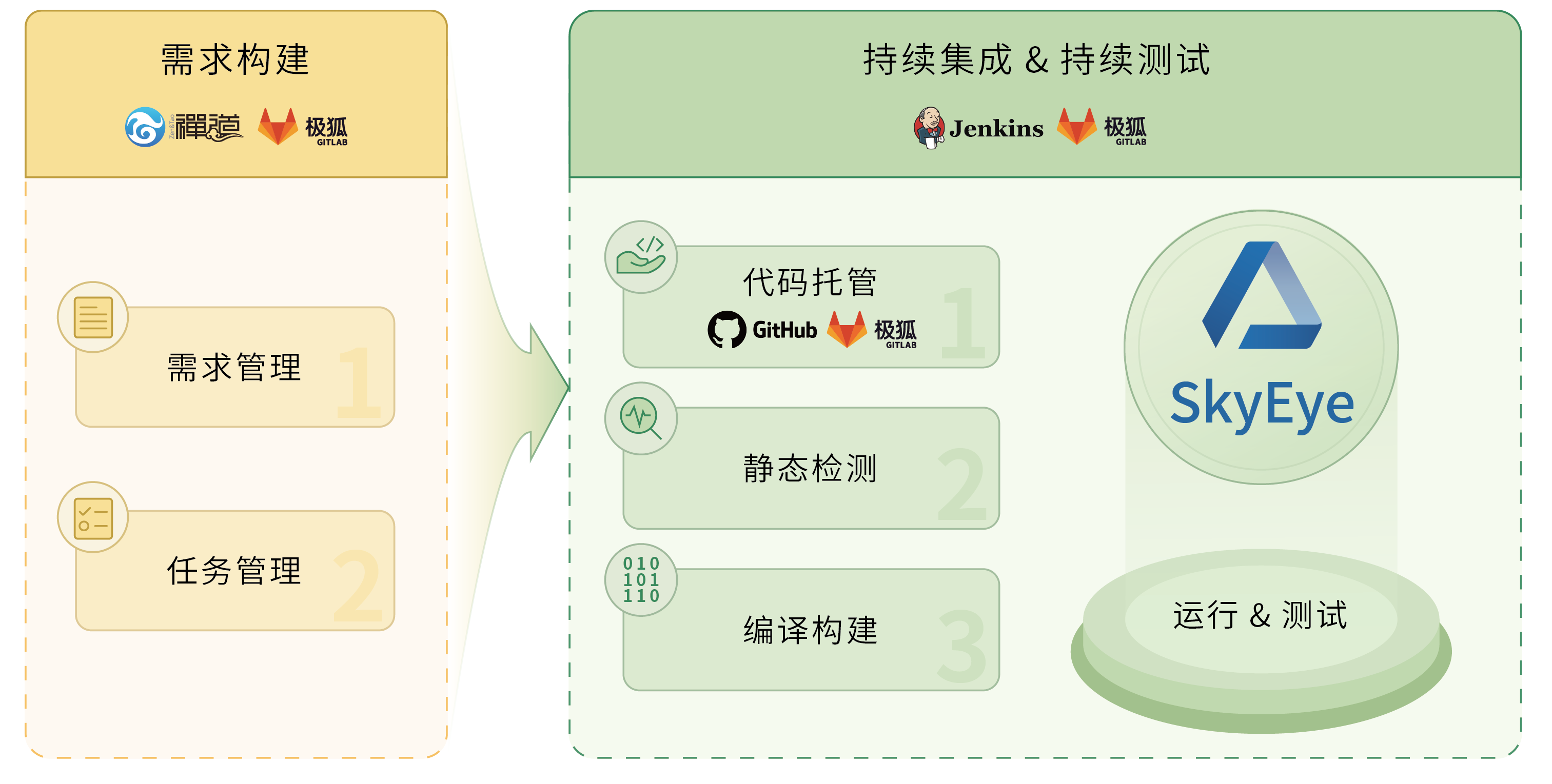
敏捷:应对软件定义汽车时代的开发模式变革
随着软件定义汽车典型应用场景的落地,汽车从交通工具转向智能移动终端的趋势愈发明显。几十年前,一台好车的定义主要取决于高性能的底盘操稳与动力系统;几年前,一台好车的定义主要取决于智能化系统与智能交互能否满足终端用户的用…...

做题笔记:SQL Sever 方式做牛客SQL的题目--查询每天刷题通过数最多的前二名用户
----查询每天刷题通过数最多的前二名用户id和刷题数 现有牛客刷题表questions_pass_record,请查询每天刷题通过数最多的前二名用户id和刷题数,输出按照日期升序排序,查询返回结果名称和顺序为: date|user_id|pass_count 表单创建…...

Vue3 用 Proxy API 替代 defineProperty API 的那些事
一、Object.defineProperty 定义:Object.defineProperty() 方法会直接在一个对象上定义一个新属性,或者修改一个对象的现有属性,并返回此对象 1.1 为什么能实现响应式 通过defineProperty 两个属性,get及set get 属性的 gett…...
成都工业学院Web技术基础(WEB)实验五:CSS3动画制作
写在前面 1、基于2022级计算机大类实验指导书 2、代码仅提供参考,前端变化比较大,按照要求,只能做到像,不能做到一模一样 3、图片和文字仅为示例,需要自行替换 4、如果代码不满足你的要求,请寻求其他的…...
三剑客之 docker-compose文件书写项目多服务容器运行)
【Docker】学习笔记(三)三剑客之 docker-compose文件书写项目多服务容器运行
简介 引言(需求) 为了完成一个完整项目势必用到N多个容器配合完成项目中的业务开发,一旦引入N多个容器,N个容器之间就会形成某种依赖,也就意味着某个容器的运行需要其他容器优先启动之后才能正常运行; 容…...

node.js基础
node.js基础 🍓什么是node.js🍓node.js模块🍒🍒 内置模块🍅🍅🍅fs模块🍅🍅🍅path模块🍅🍅🍅http模块 🍒&#…...

fastapi实现websocket在线聊天
最近要实现一个在线聊天功能,基于fastapi的websocket实现了这个功能。下面介绍一下遇到的技术问题 1.问题难点 在线上环境部署时,一般是多进程的方式进行部署启动fastapi服务,而每个启动的进程都有自己的独立存储空间。导致存储的连接对象分…...
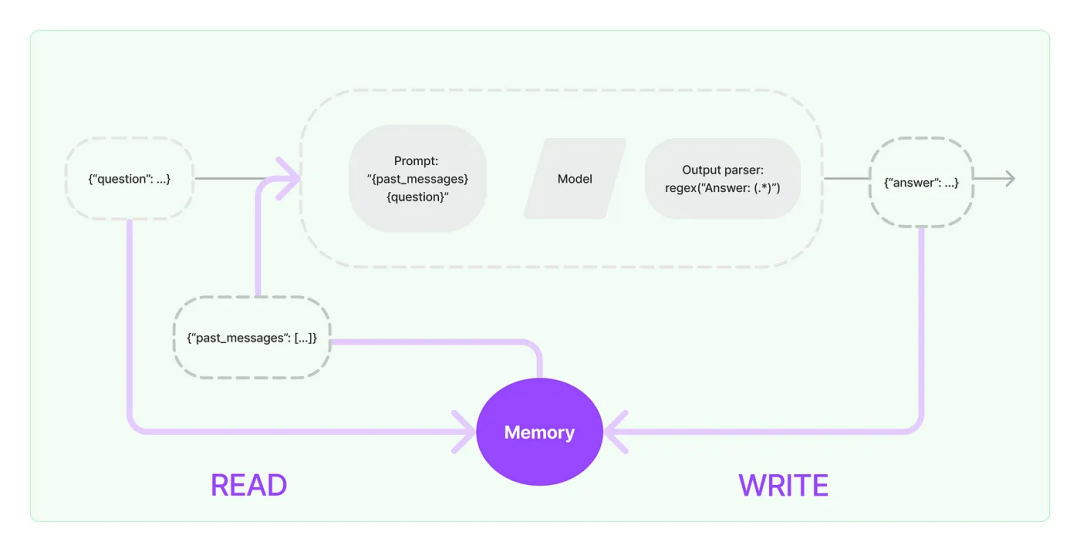
LLM推理部署(六):TogetherAI推出世界上LLM最快推理引擎,性能超过vLLM和TGI三倍
LLM能有多快?答案在于LLM推理的最新突破。 TogetherAI声称,他们在CUDA上构建了世界上最快的LLM推理引擎,该引擎运行在NVIDIA Tensor Core GPU上。Together推理引擎可以支持100多个开源大模型,比如Llama-2,并在Llama-2–…...
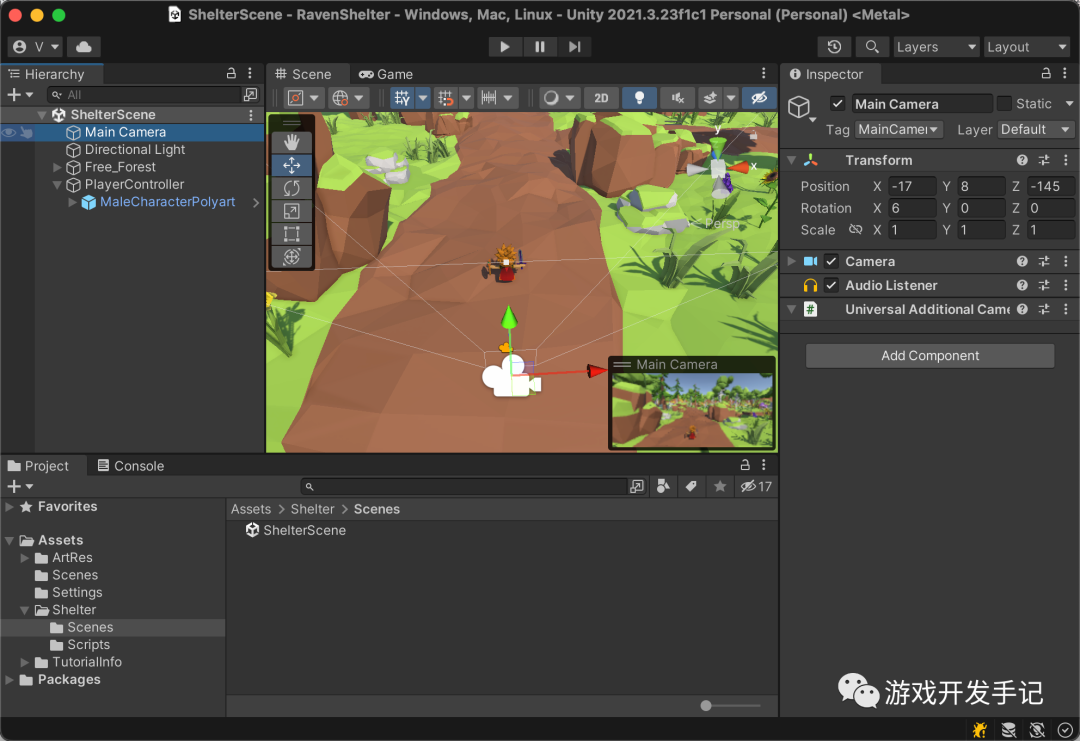
Unity | 渡鸦避难所-2 | 搭建场景并添加碰撞器
1 规范项目结构 上期中在导入一系列的商店资源包后,Assets 目录已经变的混乱不堪 开发过程中,随着资源不断更新,遵循一定的项目结构和设计规范是非常必要的。这可以增加项目的可读性、维护性、扩展性以及提高团队协作效率 这里先做下简单的…...
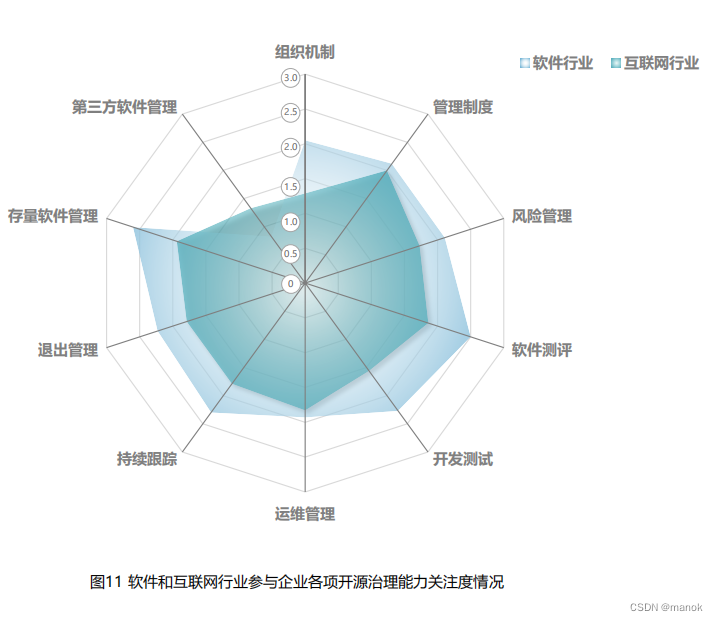
展望2024年供应链安全
2023年是开展供应链安全,尤其是开源治理如火如荼的一年,开源治理是供应链安全最重要的一个方面,所以我们从开源治理谈起。我们先回顾一下2023的开源治理情况。我们从信通院《2023年中国企业开源治理全景观察》发布的信息。信通院调研了来自七…...

React 列表页实现
一、介绍 列表页是常用的功能,从后端获取列表数据,刷新到页面上。开发列表页需要考虑以下技术要点:1.如何翻页;2.如何进行内容搜索;3.何时进行页面刷新。 二、使用教程 1.user-service 根据用户id获取用户列表,返回…...

HTML 语义化
目录 HTML 语义化HTML5 新特性HTML 语义化的好处语义化标签的使用场景最佳实践 HTML 语义化 HTML5 新特性 标准答案: 语义化标签: <header>:页头<nav>:导航<main>:主要内容<article>&#x…...
Cesium相机控制)
三维GIS开发cesium智慧地铁教程(5)Cesium相机控制
一、环境搭建 <script src"../cesium1.99/Build/Cesium/Cesium.js"></script> <link rel"stylesheet" href"../cesium1.99/Build/Cesium/Widgets/widgets.css"> 关键配置点: 路径验证:确保相对路径.…...

Rust 异步编程
Rust 异步编程 引言 Rust 是一种系统编程语言,以其高性能、安全性以及零成本抽象而著称。在多核处理器成为主流的今天,异步编程成为了一种提高应用性能、优化资源利用的有效手段。本文将深入探讨 Rust 异步编程的核心概念、常用库以及最佳实践。 异步编程基础 什么是异步…...

学习STC51单片机32(芯片为STC89C52RCRC)OLED显示屏2
每日一言 今天的每一份坚持,都是在为未来积攒底气。 案例:OLED显示一个A 这边观察到一个点,怎么雪花了就是都是乱七八糟的占满了屏幕。。 解释 : 如果代码里信号切换太快(比如 SDA 刚变,SCL 立刻变&#…...
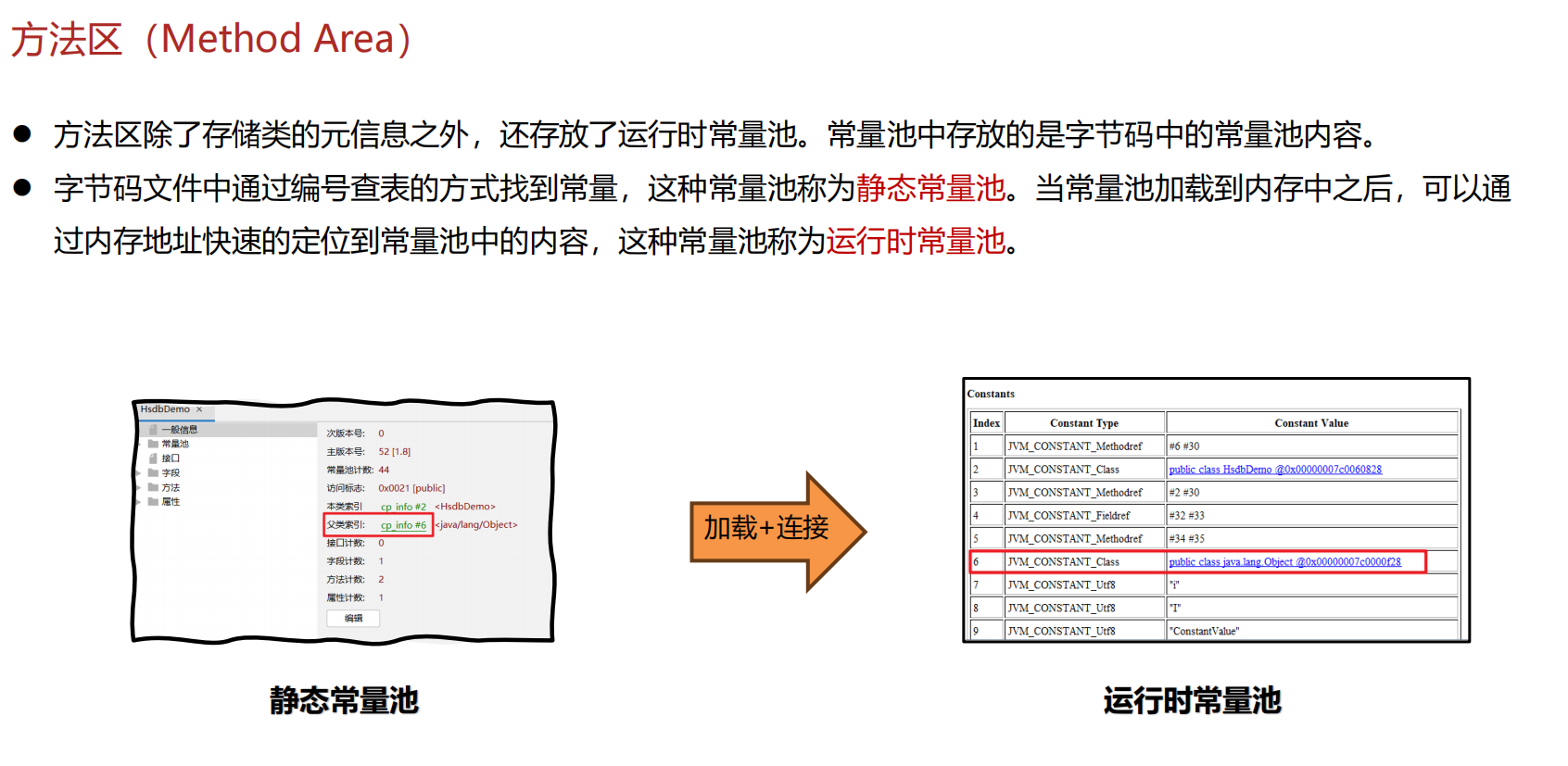
JVM 内存结构 详解
内存结构 运行时数据区: Java虚拟机在运行Java程序过程中管理的内存区域。 程序计数器: 线程私有,程序控制流的指示器,分支、循环、跳转、异常处理、线程恢复等基础功能都依赖这个计数器完成。 每个线程都有一个程序计数…...
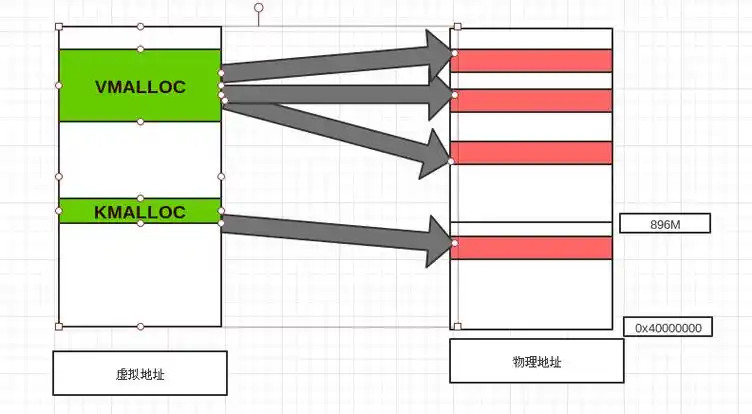
Linux 内存管理实战精讲:核心原理与面试常考点全解析
Linux 内存管理实战精讲:核心原理与面试常考点全解析 Linux 内核内存管理是系统设计中最复杂但也最核心的模块之一。它不仅支撑着虚拟内存机制、物理内存分配、进程隔离与资源复用,还直接决定系统运行的性能与稳定性。无论你是嵌入式开发者、内核调试工…...
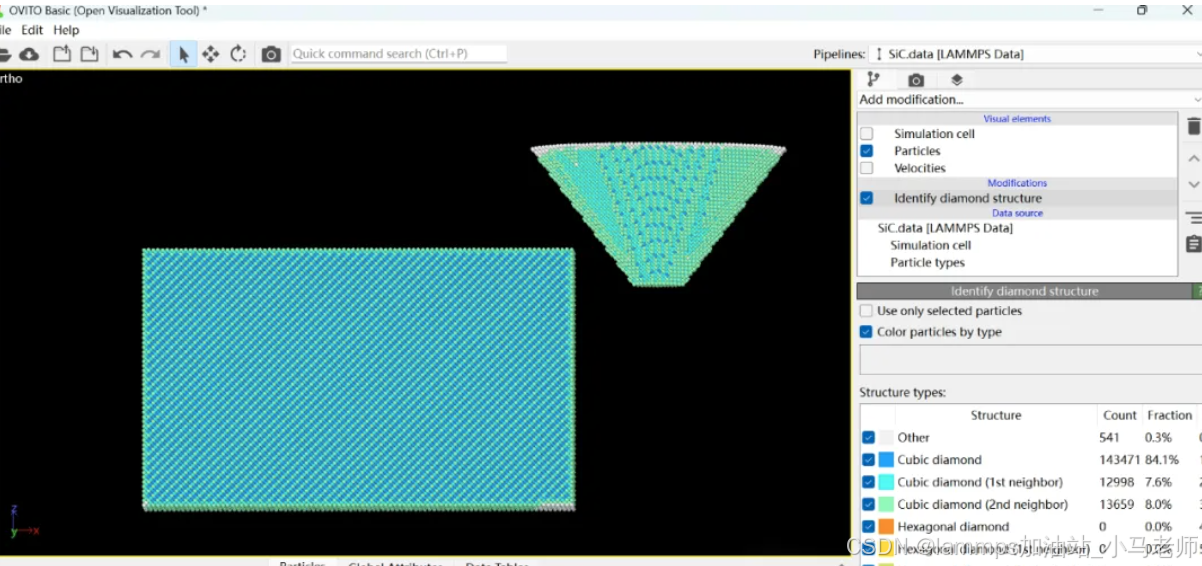
Python Ovito统计金刚石结构数量
大家好,我是小马老师。 本文介绍python ovito方法统计金刚石结构的方法。 Ovito Identify diamond structure命令可以识别和统计金刚石结构,但是无法直接输出结构的变化情况。 本文使用python调用ovito包的方法,可以持续统计各步的金刚石结构,具体代码如下: from ovito…...
 + 力扣解决)
LRU 缓存机制详解与实现(Java版) + 力扣解决
📌 LRU 缓存机制详解与实现(Java版) 一、📖 问题背景 在日常开发中,我们经常会使用 缓存(Cache) 来提升性能。但由于内存有限,缓存不可能无限增长,于是需要策略决定&am…...

4. TypeScript 类型推断与类型组合
一、类型推断 (一) 什么是类型推断 TypeScript 的类型推断会根据变量、函数返回值、对象和数组的赋值和使用方式,自动确定它们的类型。 这一特性减少了显式类型注解的需要,在保持类型安全的同时简化了代码。通过分析上下文和初始值,TypeSc…...

wpf在image控件上快速显示内存图像
wpf在image控件上快速显示内存图像https://www.cnblogs.com/haodafeng/p/10431387.html 如果你在寻找能够快速在image控件刷新大图像(比如分辨率3000*3000的图像)的办法,尤其是想把内存中的裸数据(只有图像的数据,不包…...
