【C++】POCO学习总结(十六):随机数、密码、时间戳、日期和时间(格式化与解析)、时区、本地时间
【C++】郭老二博文之:C++目录
1、Poco::Random 随机数
1.1 说明
POCO包括一个伪随机数生成器(PRNG),使用非线性加性反馈算法,具有256位状态信息和长达269的周期。
PRNG可以生成31位的伪随机数。
它可以生成UInt32, char, bool, float和double随机值。
还可以提供随机字节流(使用/dev/random或Windows加密api)。
1.2 用法
Poco:::Random实现了一个伪随机数生成器(PRNG)。
头文件:#include “Poco/Random.h”
- void seed(Poco::UInt32 seed)使用给定的种子为PRNG播种。
- void seed()使用随机数据(来自Poco::RandomInputStream)播种PRNG
如果不使用seed(),POCO:::Random的构造函数只使用当前日期和时间生成伪随机数。
建议显式调用seed()方法,可以生成更理想的随机数。
- UInt32 next():返回范围为[0,231]的伪随机数
- UInt32 next(UInt32 n):返回范围为[0,n]的伪随机数。
- char nextChar():返回一个伪随机字符
- bool nextBool():返回一个伪随机布尔值
- float nextFloat():返回范围为[0,1]的伪随机浮点值
- double nextDouble():返回范围为[0,1]的伪随机浮点值
Poco::RandomInputStream是一个istream,它产生一个无限的随机字节序列。
随机字节取自/dev/random或Windows加密API(如果两者都不可用,Poco::RandomInputStream创建自己的随机数据)
1.3 示例
#include "Poco/Random.h"
#include "Poco/RandomStream.h"
#include <iostream>
using Poco::Random;
using Poco::RandomInputStream;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{Random rnd;rnd.seed();std::cout << "Random integer: " << rnd.next() << std::endl;std::cout << "Random digit: " << rnd.next(10) << std::endl;std::cout << "Random char: " << rnd.nextChar() << std::endl;std::cout << "Random bool: " << rnd.nextBool() << std::endl;std::cout << "Random double: " << rnd.nextDouble() << std::endl;RandomInputStream ri;std::string rs;ri >> rs;return 0;
}
2、Poco::DigestEngine 加密
2.1 说明
POCO提供了一些广泛使用的加密散列函数的实现,包括如下加密:
MD2、MD4、 MD5、SHA1、HMAC
HMAC消息验证码算法(RFC 2104):HMAC是密钥相关的哈希运算消息认证码(Hash-based Message Authentication Code)的缩写。是一种基于Hash函数和密钥进行消息认证的方法。
所有哈希函数和HMAC的实现都是DigestEngine类的子类。
如果想实现自己的哈希函数,建议从DigestEngine派生。
2.2 用法
Poco::DigestEngine 定义了所有消息摘要算法实现的公共接口。
头文件:#include “Poco/DigestEngine.h”
加密后的输出数据的长度取决于算法。在POCO中,输出数据的类型是Digest(摘要),Digest其实就是std::vector<unsigned char>。
通过反复调用Poco::DigestEngine的update()方法,将数据传入算法中,当所有数据都传递给Poco::DigestEngine后,调用digest()方法来获取加密后的数据。
- void update(const void * data, unsigned length):使用数据块更新Digest(摘要)
- void update(char data):用一个字节的数据更新Digest(摘要)
- void update(const std::string& data):使用数据字符串更新Digest(摘要)
- const digest & digest():完成Digest计算并返回对Digest(摘要)的引用
常用加密算法,它们都是Poco::DigestEngine的子类
- Poco::MD2Engine (#include "Poco/MD2Engine.h)
- Poco::MD4Engine (#include "Poco/MD4Engine.h)
- Poco::MD5Engine (#include "Poco/MD5Engine.h)
- Poco::SHA1Engine (#include "Poco/SHA1Engine.h)
- Poco::HMACEngine (#include "Poco/HMACEngine.h)
2.3 示例
#include "Poco/HMACEngine.h"
#include "Poco/SHA1Engine.h"
using Poco::DigestEngine;
using Poco::HMACEngine;
using Poco::SHA1Engine;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{std::string message1("This is a top-secret message.");std::string message2("Don't tell anyone!");std::string passphrase("s3cr3t"); // HMAC需要一个密码短语HMACEngine<SHA1Engine> hmac(passphrase); // 计算一个HMAC-SHA1hmac.update(message1);hmac.update(message2);const DigestEngine::Digest& digest = hmac.digest();// 完成HMAC计算,得到摘要 digeststd::string digestString(DigestEngine::digestToHex(digest));// 转换为十六进制数字符串return 0;
}
3、流加密
3.1 说明
Poco::DigestInputStream和Poco::DigestOutputStream允许对写入输出流或从输入流读取的所有数据进行摘要计算。
Poco::DigestEngine必须传递给流的构造函数。然后,流将所有经过它们的数据传递给用于摘要计算的Poco::DigestEngine。
在写入Poco::DigestOutputStream后,始终刷新(flush())流以确保所有数据都被传递到摘要引擎。
3.2 示例
#include "Poco/DigestStream.h"
#include "Poco/MD5Engine.h"
using Poco::DigestOutputStream;
using Poco::DigestEngine;
using Poco::MD5Engine;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{MD5Engine md5;DigestOutputStream ostr(md5);ostr << "This is some text";ostr.flush(); // 确保所有内容都被传递到摘要引擎const DigestEngine::Digest& digest = md5.digest(); // 获取结果std::string result = DigestEngine::digestToHex(digest);return 0;
}
4、Poco::Timestamp 时间戳
4.1 说明
Poco::Timestamp是Poco中时间戳。
头文件 #include “Poco/Timestamp.h”
Poco::Timestamp它存储一个基于UTC的64位时间值,(高达)微秒分辨率。实际的分辨率取决于操作系统。
由于Poco::Timestamp是基于UTC的,所以它独立于时区(并对其进行更改)。
Poco::Timestamp支持值语义、比较和简单算术。
Poco::Timestamp定义了一些公共类型:
- TimeVal:是一个64位带符号的整数,以微秒的分辨率保存UTC时间
- UtcTimeVal:是一个64位带符号的整数,保存着100纳秒分辨率的UTC时间(实际分辨率仍然<= 1 μs)
- TimeDiff:一个64位带符号的整数,保存两者之间的差值
- 时间戳以微秒为单位
在Unix中,纪元epoch时间是从1970年1月1日午夜开始以秒为单位测量的时间。
UTC(协调世界时)是从1582年10月15日午夜开始以100纳秒为间隔测量的时间。
4.2 用法
Poco::Timestamp的默认构造函数,用当前时间初始化时间戳Timestamp。
- Timestamp fromEpochTime(time_t time):静态函数,获取从纪元epoch到现在的时间戳time_t
- Timestamp fromUtcTime(UtcTimeVal val):获取UTC时间
- time_t epochTime() const:返回time_t (epoch time)中表示的时间
- UtcTimeVal utcTime() const:返回以UTC表示的时间,分辨率为100纳秒
- TimeVal epochMicroseconds() const:返回自Unix纪元以来以微秒表示的时间时间戳
- void update():用当前时间更新时间戳
- timemediff elapsed() const:返回经过的微秒数时间戳
- bool isElapsed(TimeDiff interval) const:如果从时间戳中存储的时间开始至少经过了interval微秒,则返回true
4.3 示例
#include "Poco/Timestamp.h"
#include <ctime>
using Poco::Timestamp;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{Timestamp now; // 当前日期和时间std::time_t t1 = now.epochTime(); // Timestamp 转变为 time_t ...Timestamp ts1(Timestamp::fromEpochTime(t1)); // ... 转回Timestamp for (int i = 0; i < 100000; ++i) ; // 稍等一下Timestamp::TimeDiff diff = now.elapsed(); // 花了多长时间?Timestamp start(now); // 记录启动时间now.update(); // 更新当前时间 diff = now - start;return 0;
}
5、Poco::DateTime 日期和时间
5.1 说明
Poco::DateTime用于处理基于公历的日历日期和时间。
头文件: #include “Poco/DateTime.h”
Poco::DateTime常用于日期计算,如果要存储日期和时间,时间戳Poco::Timestamp类更合适。
Poco::DateTime在内部以两种格式维护日期和时间:
UTC和(年、月、日、时、分、秒、毫秒、微秒)。
公历,也叫格里高里历,几乎在世界各地都在使用。它的年份是根据耶稣基督的传统出生年份来编号的,这被标记为“纪元”时代。
它将天作为时间的基本单位,将它们分成365天或366天的年。一年分为12个月,长短不一。
并非所有国家都在同一时间采用公历(例如,德国在1582年,英国在1752年)。
儒略历(JDN)是从公元前4713年1月1日星期一开始的天数。这一天被记为朱利安零日。
因此,7的倍数是星期一。负值也可以使用。
儒略历日期(JD)是指从格林威治标准时间中午12点开始经过的天数(带有小数部分)
5.2 用法
5.2.1 常用成员函数
- int year() const:返回年份
- int month()返回月份:(1 - 12)
- int week(int firstDayOfWeek = DateTime::MONDAY) const:根据ISO 8601返回一年内的周数
(第1周为1月4日所在的一周);
firstDayOfWeek应该是DateTime::MONDAY或DateTime::SUNDAY。 - int day() const:返回一个月内的日期(1 - 31)
- int dayOfWeek() const:返回一周内的日期
(0 = DateTime::SUNDAY, 1 = DateTime::MONDAY,…,
6 = DateTime::SATURDAY) - int dayOfYear() const:返回一年中的日期(1 - 366)
- Int hour() const:返回小时(0 - 23)
- int hourAMPM() const:返回小时(0 - 12)
- bool isAM() const:返回true如果hour() < 12,否则返回false
- bool isPM() const:返回true如果hour() >= 12,否则返回false
- int minute() const:返回分钟数(0 - 59)
- int second() const:返回秒(0 - 59)
- int millisecond() const:返回毫秒数(0 - 999)
- int microsecond() const:返回微秒数(0 - 999)
- Timestamp timestamp() const:返回以时间戳形式表示的日期和时间
- Timestamp::UtcTimeVal utcTime() const:返回以UTC时间表示的日期和时间
- Poco::DateTime支持所有关系操作符(==, !=, >, >=, <, <=)
- Poco::DateTime支持算法 (+, -, +=,-=)
5.2.2 常用静态函数
- bool isLeapYear(int year):如果给定的年份是闰年则返回true,否则返回false
- int daysOfMonth(int year, int month):返回给定年、月的天数
- bool isValid(int year, int month, int day,int hour, int minute, int second, int millisecond, int microsecond)
如果给定的日期和时间有效(所有参数都在适当的范围内)返回true,否则返回false(考虑闰年)
5.2.3 月、星期的枚举
Poco::DateTime具有月份和星期名称的枚举。这些可以用来代替数值:
1)月:Poco::DateTime::Months
- JANUARY
- FEBRUARY
- MARCH
- APRIL
- MAY
- JUNE
- JULY
- AUGUST
- SEPTEMBER
- OCTOBER
- NOVEMBER
- DECEMBER
2)星期:Poco::DateTime::DaysOfWeek
- SUNDAY
- MONDAY
- TUESDAY
- WEDNESDAY
- THURSDAY
- FRIDAY
- SATURDAY
5.3 示例
#include "Poco/DateTime.h"
using Poco::DateTime;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{DateTime now; // the current date and time in UTCint year = now.year();int month = now.month();int day = now.day();int dow = now.dayOfWeek();int doy = now.dayOfYear();int hour = now.hour();int hour12 = now.hourAMPM();int min = now.minute();int sec = now.second();int ms = now.millisecond();int us = now.microsecond();double jd = now.julianDay();Poco::Timestamp ts = now.timestamp();DateTime xmas(2006, 12, 25); // 2006-12-25 00:00:00Poco::Timespan timeToXmas = xmas - now;DateTime dt(1973, 9, 12, 2, 30, 45); // 1973-09-12 02:30:45dt.assign(2006, 10, 13, 13, 45, 12, 345); // 2006-10-13 12:45:12.345bool isAM = dt.isAM(); // falsebool isPM = dt.isPM(); // truebool isLeap = DateTime::isLeapYear(2006); // falseint days = DateTime::daysOfMonth(2006, 2); // 28bool isValid = DateTime::isValid(2006, 02, 29); // falsedt.assign(2006, DateTime::OCTOBER, 22); // 2006-10-22 00:00:00return 0;
}
6、Poco::LocalDateTime 本地时间
6.1 说明
Poco::LocalDateTime类似于Poco::DateTime,除了它存储本地时间(与UTC相反)和时区差异。
头文件:#include “Poco/LocalDateTime.h”
时区差是指UTC和本地时间之差,(UTC =本地时间-时区之差)。
Poco::LocalDateTime支持Poco::DateTime所有功能。
- 所有关系运算符在执行比较之前都归一化为UTC。
- int tzd() const返回时区差(秒)
- Poco::DateTime utc() const将本地时间转换为utc时间
6.2 示例
#include "Poco/LocalDateTime.h"
using Poco::LocalDateTime;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{LocalDateTime now; // 当前日期和本地时间int year = now.year();int month = now.month();int day = now.day();int dow = now.dayOfWeek();int doy = now.dayOfYear();int hour = now.hour();int hour12 = now.hourAMPM();int min = now.minute();int sec = now.second();int ms = now.millisecond();int us = now.microsecond();int tzd = now.tzd();double jd = now.julianDay();Poco::Timestamp ts = now.timestamp();LocalDateTime dt1(1973, 9, 12, 2, 30, 45); // 1973-09-12 02:30:45dt1.assign(2006, 10, 13, 13, 45, 12, 345); // 2006-10-13 12:45:12.345LocalDateTime dt2(3600, 1973, 9, 12, 2, 30, 45, 0, 0); // UTC +1 hourdt2.assign(3600, 2006, 10, 13, 13, 45, 12, 345, 0);Poco::Timestamp nowTS;LocalDateTime dt3(3600, nowTS); // 从时间戳构造return 0;
}
7、Poco::Timespan 时间跨度
7.1 说明
Poco::Timespan表示微秒级分辨率的时间跨度。
头文件:#include “Poco/Timespan.h”
在内部,Poco::Timespan使用64位整数来存储时间跨度。时间跨度可以用天、小时、分钟、秒、毫秒和微秒表示。
Poco::时间跨度定义了以下缩放因子:
- MILLISECONDS毫秒中的微秒数
- SECONDS一秒内的微秒数
- MINUTES一分钟内的微秒数
- HOURS一小时内的微秒数
- DAYS一天中的微秒数
7.2 用法
- int days() const:返回天数
- int hours() const:返回一天中的小时数(0 - 23)
- int totalHours() const:返回总小时数
- int minutes() const:返回小时内的分钟数(0 - 59)
- int totalMinutes() const:返回总分钟数
- Int seconds() const:返回分钟内的秒数(0 - 60)
- int totalSeconds() const:返回总秒数
- int milliseconds() const:返回秒内的毫秒数(0 - 999)
- int totalMilliseconds() const:返回总毫秒数
- Int microseconds() const:返回毫秒内的微秒数(0 -999)
- int totalMicroseconds() const:返回总微秒数
7.3 示例
#include "Poco/Timespan.h"
using Poco::Timespan;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{Timespan ts1(1, 11, 45, 22, 123433); // 1d 11h 45m 22.123433sTimespan ts2(33*Timespan::SECONDS); // 33sTimespan ts3(2*Timespan::DAYS + 33*Timespan::HOURS); // 3d 33hint days = ts1.days(); // 1int hours = ts1.hours(); // 11int totalHours = ts1.totalHours(); // 35int minutes = ts1.minutes(); // 45int totalMins = ts1.totalMinutes(); // 2145int seconds = ts1.seconds(); // 22int totalSecs = ts1.totalSeconds(); // 128722return 0;
}
7.4 时间运算
#include "Poco/DateTime.h"
#include "Poco/Timespan.h"
using Poco::DateTime;
using Poco::Timespan;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{DateTime birthdate(1973, 9, 12, 2, 30); // 1973-09-12 02:30:00DateTime now;Timespan age = now - birthdate;int days = age.days(); // in daysint hours = age.totalHours(); // in hoursint secs = age.totalSeconds(); // in secondsTimespan span(10000*Timespan::DAYS);DateTime dt = birthdate + span;return 0;
}
8、Poco::Timezone 系统时区
8.1 说明
Poco::Timezone 提供了获取系统时区信息的静态方法
头文件:#include “Poco/Timezone.h”
- int utcOffset():返回本地时间到UTC的偏移量,以秒为单位,不包括夏令时DST
(local time = UTC + utcOffset()) - int DST():返回夏令时偏移量,以秒为单位(通常为3600)夏令时生效,否则为0。
- bool isDst(const timestamp & timestamp):返回true,如果DST在给定时间有效
- int tzd():返回当前时区的时区差异(tzd = utcOffset() + dst())
- string name():返回当前生效的时区名称
- std::string standardName():返回时区的名称,如果DST没有生效
- std::string dstName():返回夏令时生效时的时区名称
- 报告的名称依赖于操作系统,不能跨系统移植。
8.2 示例
#include "Poco/Timezone.h"
#include "Poco/Timestamp.h"
using Poco::Timezone;
using Poco::Timestamp;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{int utcOffset = Timezone::utcOffset();int dst = Timezone::dst();bool isDst = Timezone::isDst(Timestamp());int tzd = Timezone::tzd();std::string name = Timezone::name();std::string stdName = Timezone::standardName();std::string dstName = Timezone::dstName();return 0;
}
9、Poco::DateTimeFormatter 格式化日期和时间
9.1 说明
Poco::DateTimeFormatter 可用于格式化日期和时间
(Timestamp, DateTime, LocalDateTime和Timespan)作为字符串。
头文件: #include “Poco/DateTimeFormat.h”
Poco::DateTimeFormatter使用类似于strftime()的格式字符串。
9.2 用法
Poco::DateTimeFormatter的所有函数都是静态的。
- std::string format(const timestamp & timestamp, const std::string& fmt, int tzd = UTC)
根据给定的格式字符串fmt格式化给定的时间戳。时区差值(tzd)是可选的。 - std::string format(const dateTime & dateTime, const std::string& fmt, int tzd = UTC)
类似于前一个函数,不同之处是这个函数接受DateTime - std::string format(const LocalDateTime& dateTime, const std::string& fmt)
接受一个LocalDateTime(包含时区差异),并根据格式字符串fmt对其进行格式化 - std::string format(const timespan & timespan, const std::string& fmt)
根据格式字符串fmt格式化给定的时间跨度
几种常用的,已定义好的格式
- ISO8601_FORMAT (2005-01-01T12:00:00+01:00)
- RFC1123_FORMAT (Sat, 1 Jan 2005 12:00:00 +0100)
- SORTABLE_FORMAT (2005-01-01 12:00:00)
9.3 示例
#include "Poco/DateTime.h"
#include "Poco/Timestamp.h"
#include "Poco/Timespan.h"
#include "Poco/DateTimeFormatter.h"
#include "Poco/DateTimeFormat.h"
using Poco::DateTimeFormatter;
using Poco::DateTimeFormat;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{Poco::DateTime dt(2006, 10, 22, 15, 22, 34);std::string s(DateTimeFormatter::format(dt, "%e %b %Y %H:%M")); // "22 Oct 2006 15:22"Poco::Timestamp now;s = DateTimeFormatter::format(now, DateTimeFormat::SORTABLE_FORMAT);// "2006-10-30 09:27:44"Poco::Timespan span(5, 11, 33, 0, 0);s = DateTimeFormatter::format(span, "%d days, %H hours, %M minutes");// "5 days, 11 hours, 33 minutes"return 0;
}
10、Poco::DateTimeParser 从字符串中解析日期和时间
10.1 说明
可以使用Poco::DateTimeParser从字符串中解析日期和时间。
头文件: #include “Poco/DateTimeParser.h”
Poco::DateTimeParser总是返回一个Poco::DateTime和一个时区差值。然后可以将Poco::DateTime转换为Poco::Timestamp或Poco::LocalDateTime。
Poco::DateTimeParser的所有函数都是静态的。
Poco::DateTimeParser用法和Poco::DateTimeFormatter类似。
10.2 用法
- void parse(const std::string fmt, const std::string& str, DateTime& dateTime, int& tzd)
从字符串 str 中以 fmt 给出的格式解析日期和时间。在dateTime中存储日期和时间,在tzd中存储时区差异。如果无法解析字符串,则抛出Poco::SyntaxException。 - DateTime parse(const std::string& fmt, const std::string& str, int& tzd)
与上面类似,但返回DateTime - bool tryParse(const std::string& fmt, const std::string& str, DateTime& dateTime, int& tzd)
尝试从字符串str中以fmt给出的格式解析日期和时间。如果成功,将日期和时间存储在dateTime中,并将时区差存储在tzd中。如果成功返回true,否则返回false。 - void parse(const std::string& str, DateTime& dateTime, int& tzd)
解析给定字符串 str 中的日期和时间,识别Poco::DateTimeFormat定义的所有标准日期/时间格式。
如果无法识别格式,或者字符串与预期格式不匹配,则抛出Poco::SyntaxException - DateTime parse(const std::string& str, int& tzd) :同上
- bool tryParse(const std::string& str, DateTime& dateTime, int& tzd):同上
10.3 示例
#include "Poco/DateTimeParser.h"
#include "Poco/DateTime.h"
#include "Poco/DateTimeFormat.h"
#include "Poco/LocalDateTime.h"
#include "Poco/Timestamp.h"
using Poco::DateTimeParser;
using Poco::DateTimeFormat;
using Poco::DateTime;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{std::string s("Sat, 1 Jan 2005 12:00:00 GMT");int tzd;DateTime dt;DateTimeParser::parse(DateTimeFormat::RFC1123_FORMAT, s, dt, tzd);Poco::Timestamp ts = dt.timestamp();Poco::LocalDateTime ldt(tzd, dt);bool ok = DateTimeParser::tryParse("2006-10-22", dt, tzd);ok = DateTimeParser::tryParse("%e.%n.%Y", "22.10.2006", dt, tzd);return 0;
}
相关文章:
:随机数、密码、时间戳、日期和时间(格式化与解析)、时区、本地时间)
【C++】POCO学习总结(十六):随机数、密码、时间戳、日期和时间(格式化与解析)、时区、本地时间
【C】郭老二博文之:C目录 1、Poco::Random 随机数 1.1 说明 POCO包括一个伪随机数生成器(PRNG),使用非线性加性反馈算法,具有256位状态信息和长达269的周期。 PRNG可以生成31位的伪随机数。 它可以生成UInt32, char, bool, float和double…...
打补丁,生成.diff文件
作者:爱塔居 文章目录 目录 前言 步骤 一、在根目录上,输入添加指令 二、输入修改内容指令 三、生成补丁 前言 自己的理解,仅供参考,欢迎指正。 补丁的话,在我看来就是方便评审,更方便看修改代码吧。 步骤…...

《LeetCode力扣练习》代码随想录——字符串(KMP算法学习补充——针对next数组构建的回退步骤进行解释)
《LeetCode力扣练习》代码随想录——字符串(KMP算法学习补充——针对next数组构建的回退步骤进行解释) 学习路径 代码随想录:28. 实现 strStr() CSDN:【详解】KMP算法——多图,多例子(c语言) …...

【CANoe】CAPL中on signal和on signal_update的区别
文章目录 CAN信号事件 CAN信号事件 CAN信号事件是在CAN总线上出现指定的信号时被调用(需要配合DBC文件使用)。 关键字为:on signal xxx或on signal_update xxx。 on signal xxx:只在指定信号的值发生变化时被调用, on signal_u…...

ArrayList集合的两个实例应用,有趣的洗牌算法与杨辉三角
本节课的内容,就让我们来学习一下ArrayList集合的应用,ArrayList的本质就是一个顺序表,那下面一起来学习吧 目录 一、杨辉三角 1.题目详情及链接 2.剖析题目 3.思路及代码 二、洗牌算法 1.创造牌对象 2.创造一副牌 3.洗牌操作 4.发…...

Qt 剪贴板操作
Qt剪贴板操作 剪贴板的操作经常和前面所说的拖放技术在一起使用,因此我们现在先来说说剪贴板的相关操作。大家对剪贴板都很熟悉。我们可以简单的把它理解成一个数据的存储池,可以把外面的数据放置进去,也可以把里面的数据取出来。剪贴板是由操作系统维护的,所以这提供了跨…...

python 学习笔记20 批量修改页眉页脚
需求:修改指定目录下所有文件的页眉页脚,或者往里面添加内容。 1. 这里做了word的实现和excel的实现,如下: 需要先安装 pip3 install pywin32,另外页眉页脚格式设置可以参考: word: 浅谈Wor…...
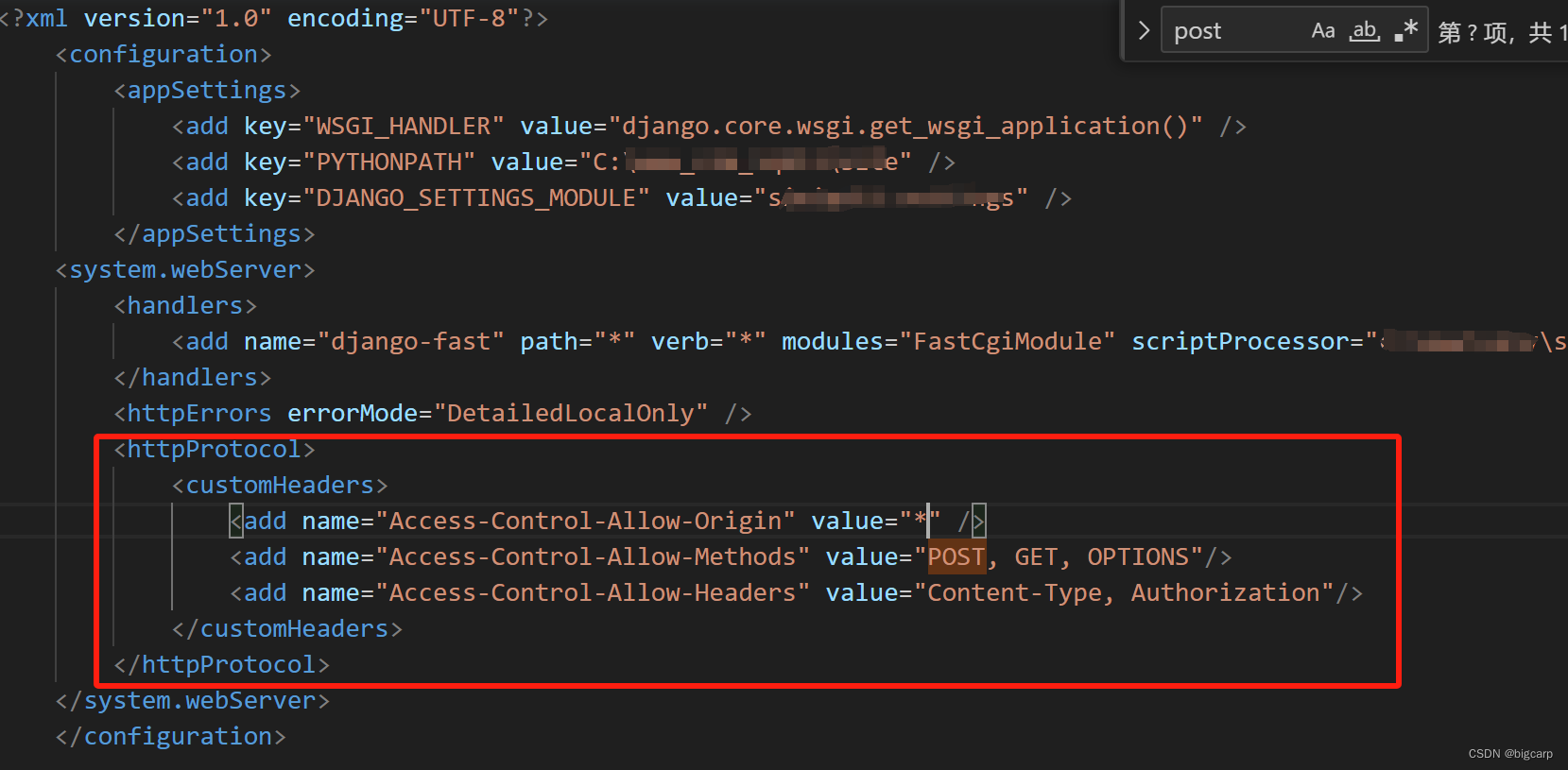
IIS + Axios 跨域设置
1、服务器端设置IIS (web.config) 即可,不需要对django settings.py做配置(python manage.py runserver 才需要settings.py配置跨域,IIS在iis上配) 网站根目录的web.config中加上这段: <httpProtocol&…...
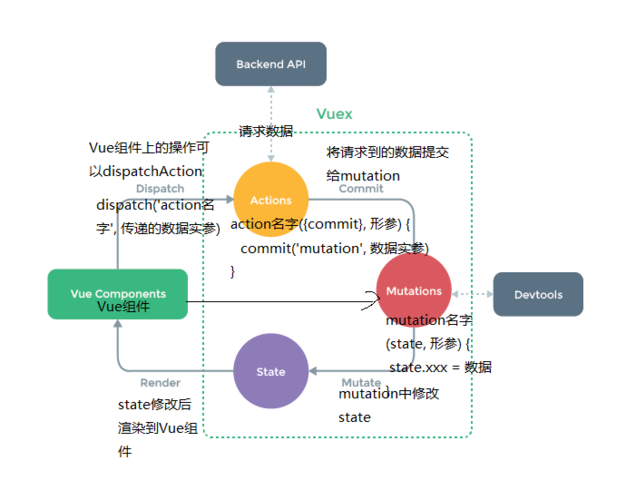
详细说说vuex
Vuex 是什么 Vuex有几个属性及作用注意事项vuex 使用举例Vuex3和Vuex4有哪些区别 创建 Store 的方式在组件中使用 Store辅助函数的用法响应式的改进Vuex4 支持多例模式 Vuex 是什么 Vuex是一个专门为Vue.js应用设计的状态管理构架,它统一管理和维护各个Vue组件的可…...
Qt之Ui样式表不影响子类的配置
Qt之Ui样式表不影响子类的配置 问题 在ui界面上布局时,当对容器进行样试设计时,会对容器内其它成员对象也进行了修改 分析 对应*.ui文件内容 从这个写法来看,它的样式属性会影响其成员对象样式属性。 解决方法 在容器的样式表中写时适…...
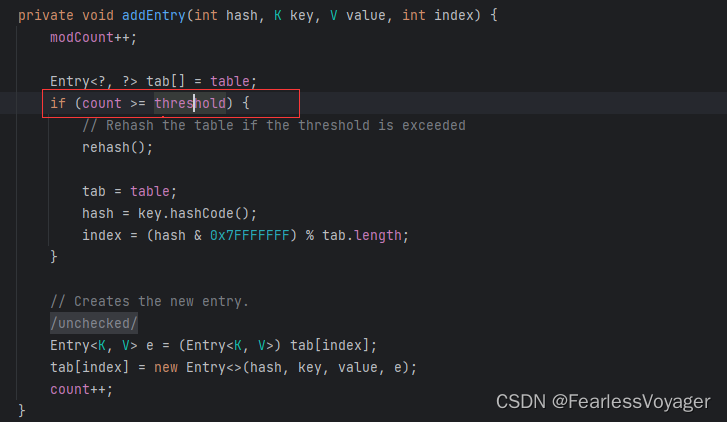
Java集合--Map
1、Map集合概述 在Java的集合框架中,Map为双列集合,在Map中的元素是成对以<K,V>键值对的形式存在的,通过键可以找对所对应的值。Map接口有许多的实现类,各自都具有不同的性能和用途。常用的Map接口实现类有HashMap、Hashtab…...

C语言—每日选择题—Day48
第一题 1. 已知宏定义: #define M y*y3*y , 则表达式 s3*M4*My*M 预处理阶段后的结果是 A:s3*(y*y3*y)4*(y*y3*y)y*(y*y3*y) B:s3*(y*y)3*y4*(y*y)3*yy*(y*y)3*y C:s3*y*y3*y4*y*y3*yy*y*y3*y D:s3*(y*y)(3…...
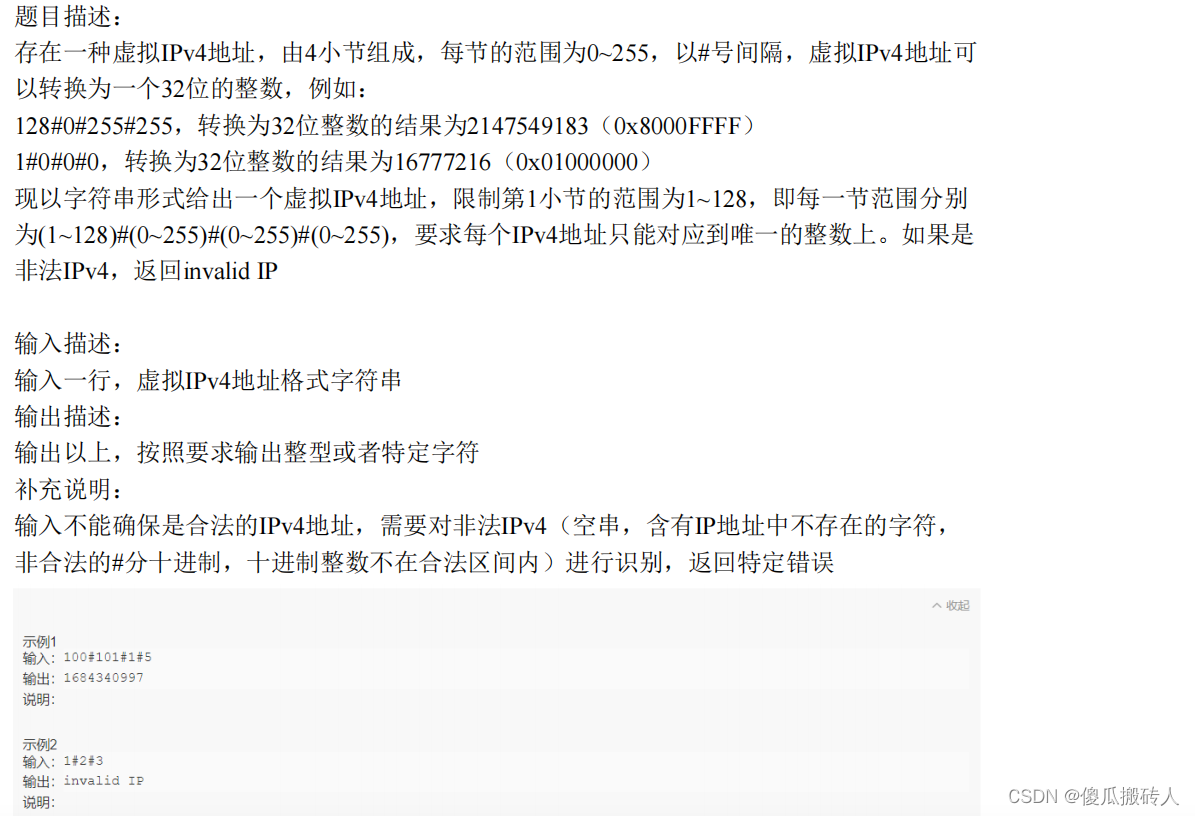
华为OD试题七(IPv4地址转换成整数、比赛的冠亚季军)
1. IPv4地址转换成整数 示例代码: #测试数据 s1 "100#101#1#5"def fun(s):s_list s.split("#")# 转化成十六进制数 左边补零s_16_list [hex(int(_))[2:].zfill(2) for _ in s_list]s_16_str .join(s_16_list)return int(s_16_str,16) r f…...

SVN优缺点详解及版本控制系统选型建议
Subversion (SVN)是目前可用的众多版本控制选项之一。本篇文章将全面概述什么是 SVN、SVN的历史、SVN存储库是什么,以及在切换到SVN之前您应该谨慎考虑的潜在问题。 什么是Subversion(SVN)? Subversion软件,也称为SV…...

自己动手写数据库: select 查询语句对应查询树的构造和执行
首先我们需要给原来代码打个补丁,在SelectScan 结构体初始化时需要传入 UpdateScan 接口对象,但很多时候我们需要传入的是 Scan 对象,因此我们需要做一个转换,也就是当初始化 SelectScan 时,如果传入的是 Scan 对象&am…...

扬声器(喇叭)
扬声器(喇叭) 电子元器件百科 文章目录 扬声器(喇叭)前言一、扬声器(喇叭)是什么二、扬声器(喇叭)的类别三、扬声器(喇叭)的应用场景四、扬声器(喇叭)的作用原理总结前言 扬声器广泛应用于音响系统、公共广播系统、汽车音响、电视、电脑和移动设备等各种电子设备…...
汇总大厂-校招/社招 Java面试题--持续补充更新中-大家别光收藏,要看起来,巩固基础,就是干呀!
** 接上篇-汇总大厂-校招/社招 Java面试题(补充) ** markdown文件。持续更新中(阿里、腾讯、网易、美团、京东、华为、快手、字节…) 上面这篇也结合着看啊,通宵给整理出来的。 如需下载整套资料。关注公众号后台。…...

六. 函数
基本使用 ts与js一样拥有具名函数和匿名函数两种函数类型。但是ts的函数需要提前定义好参数类型以及函数的返回值类型。 具名函数 function add(num1: number, num2: number):number {return num1 num2 }匿名函数 匿名函数的定义相对麻烦,我们需要提前定义函数的…...
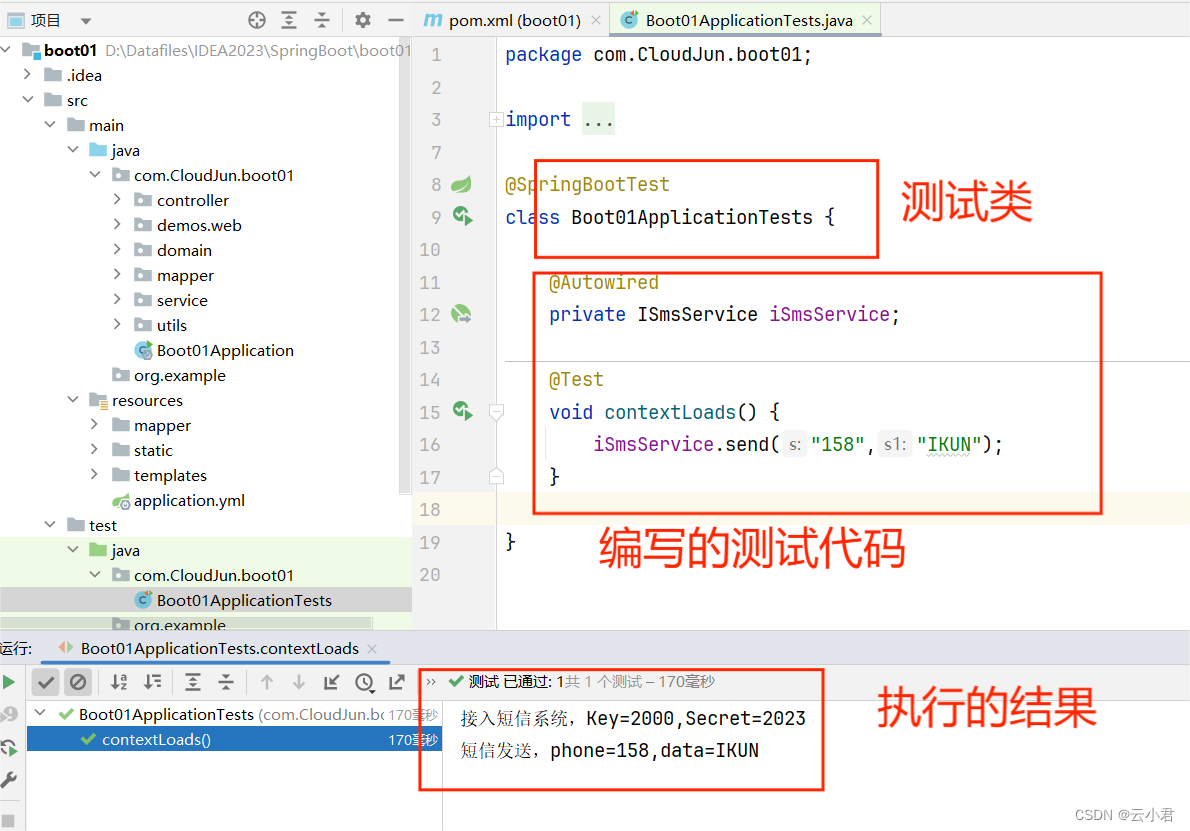
SpringBoot的Starter自动化配置,自己编写配置maven依赖且使用及短信发送案例
目录 一、Starter机制 1. 是什么 2. 有什么用 3. 应用场景 二、短信发送案例 1. 创建 2. 配置 3. 编写 4. 形成依赖 6. 其他项目的使用 每篇一获 一、Starter机制 1. 是什么 SpringBoot中的starter是一种非常重要的机制(自动化配置),能够抛弃以前繁杂…...
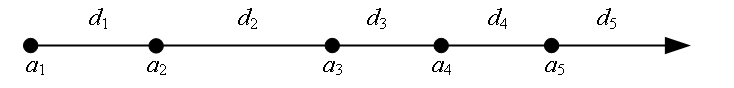
<蓝桥杯软件赛>零基础备赛20周--第9周--前缀和与差分
报名明年4月蓝桥杯软件赛的同学们,如果你是大一零基础,目前懵懂中,不知该怎么办,可以看看本博客系列:备赛20周合集 20周的完整安排请点击:20周计划 每周发1个博客,共20周(读者可以按…...

CVPR 2025 MIMO: 支持视觉指代和像素grounding 的医学视觉语言模型
CVPR 2025 | MIMO:支持视觉指代和像素对齐的医学视觉语言模型 论文信息 标题:MIMO: A medical vision language model with visual referring multimodal input and pixel grounding multimodal output作者:Yanyuan Chen, Dexuan Xu, Yu Hu…...
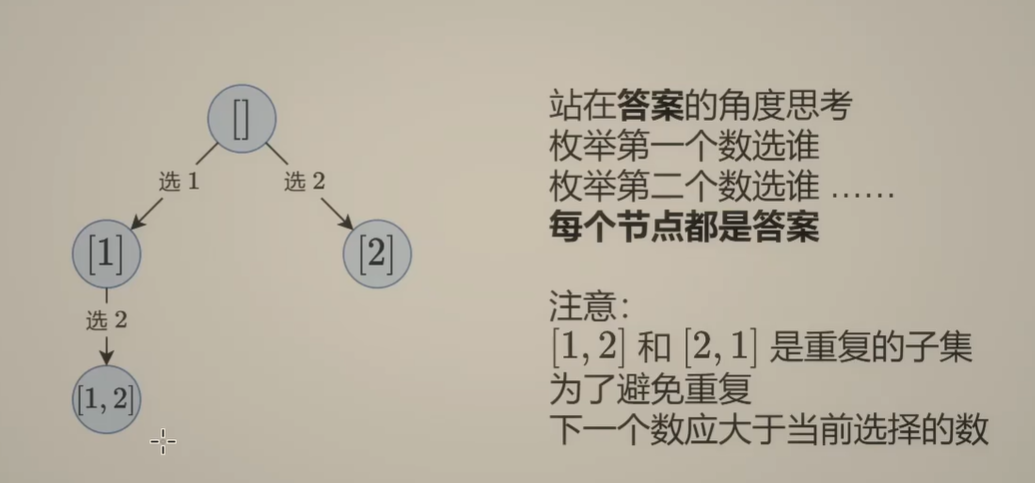
Day131 | 灵神 | 回溯算法 | 子集型 子集
Day131 | 灵神 | 回溯算法 | 子集型 子集 78.子集 78. 子集 - 力扣(LeetCode) 思路: 笔者写过很多次这道题了,不想写题解了,大家看灵神讲解吧 回溯算法套路①子集型回溯【基础算法精讲 14】_哔哩哔哩_bilibili 完…...
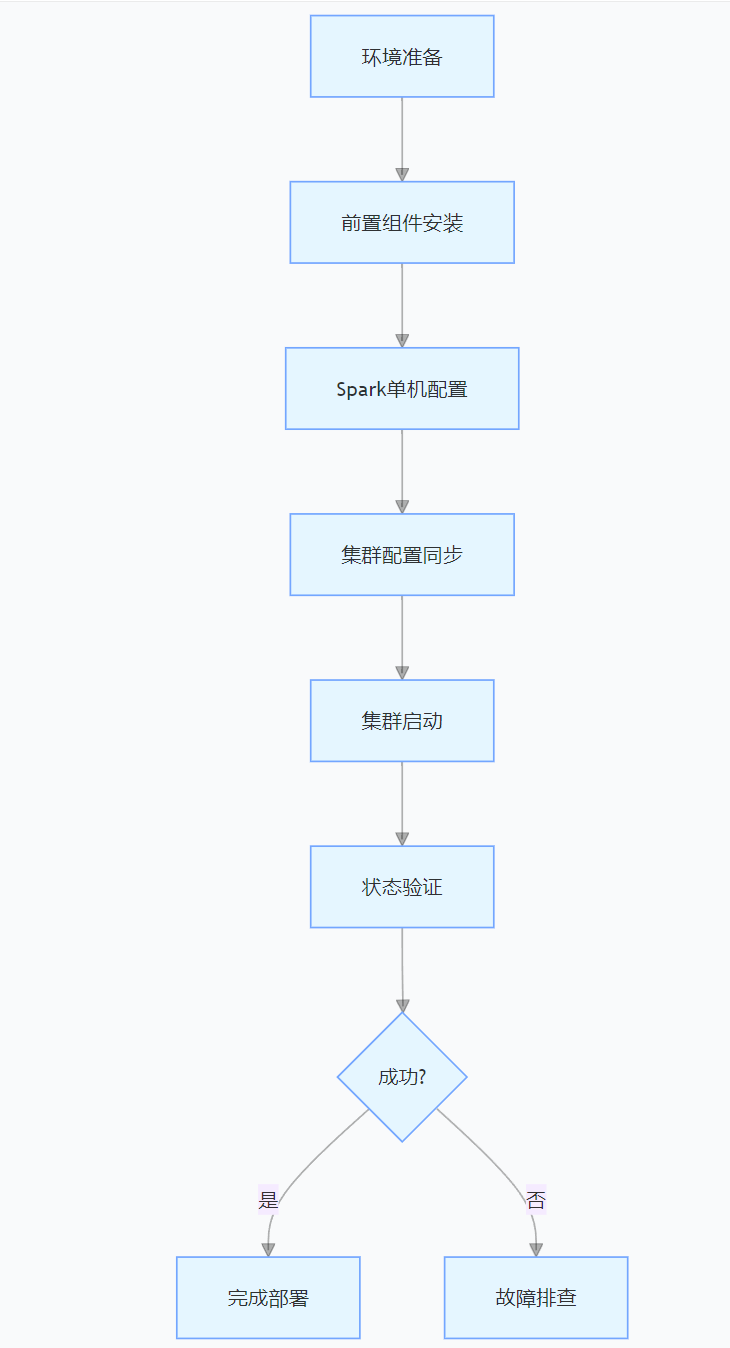
CentOS下的分布式内存计算Spark环境部署
一、Spark 核心架构与应用场景 1.1 分布式计算引擎的核心优势 Spark 是基于内存的分布式计算框架,相比 MapReduce 具有以下核心优势: 内存计算:数据可常驻内存,迭代计算性能提升 10-100 倍(文档段落:3-79…...

STM32F4基本定时器使用和原理详解
STM32F4基本定时器使用和原理详解 前言如何确定定时器挂载在哪条时钟线上配置及使用方法参数配置PrescalerCounter ModeCounter Periodauto-reload preloadTrigger Event Selection 中断配置生成的代码及使用方法初始化代码基本定时器触发DCA或者ADC的代码讲解中断代码定时启动…...

鸿蒙中用HarmonyOS SDK应用服务 HarmonyOS5开发一个生活电费的缴纳和查询小程序
一、项目初始化与配置 1. 创建项目 ohpm init harmony/utility-payment-app 2. 配置权限 // module.json5 {"requestPermissions": [{"name": "ohos.permission.INTERNET"},{"name": "ohos.permission.GET_NETWORK_INFO"…...
推荐 github 项目:GeminiImageApp(图片生成方向,可以做一定的素材)
推荐 github 项目:GeminiImageApp(图片生成方向,可以做一定的素材) 这个项目能干嘛? 使用 gemini 2.0 的 api 和 google 其他的 api 来做衍生处理 简化和优化了文生图和图生图的行为(我的最主要) 并且有一些目标检测和切割(我用不到) 视频和 imagefx 因为没 a…...
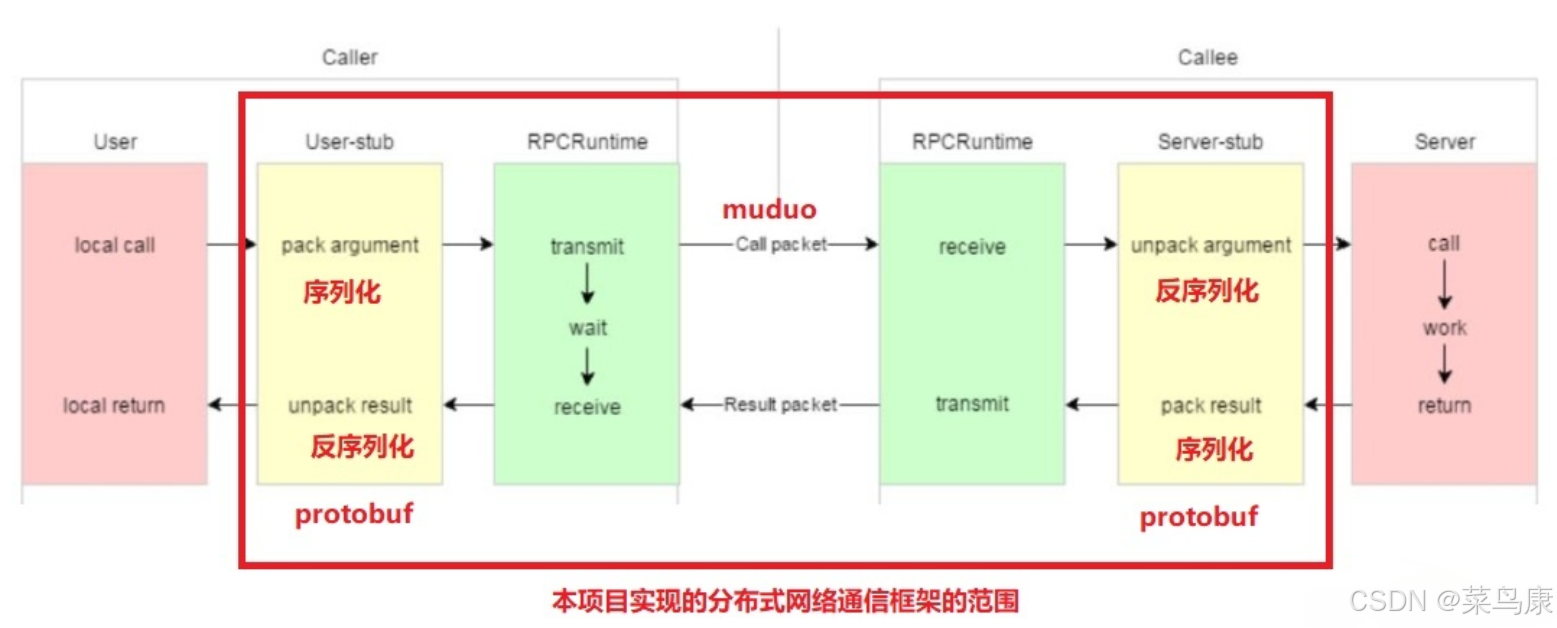
C++实现分布式网络通信框架RPC(2)——rpc发布端
有了上篇文章的项目的基本知识的了解,现在我们就开始构建项目。 目录 一、构建工程目录 二、本地服务发布成RPC服务 2.1理解RPC发布 2.2实现 三、Mprpc框架的基础类设计 3.1框架的初始化类 MprpcApplication 代码实现 3.2读取配置文件类 MprpcConfig 代码实现…...

第八部分:阶段项目 6:构建 React 前端应用
现在,是时候将你学到的 React 基础知识付诸实践,构建一个简单的前端应用来模拟与后端 API 的交互了。在这个阶段,你可以先使用模拟数据,或者如果你的后端 API(阶段项目 5)已经搭建好,可以直接连…...

深入理解 React 样式方案
React 的样式方案较多,在应用开发初期,开发者需要根据项目业务具体情况选择对应样式方案。React 样式方案主要有: 1. 内联样式 2. module css 3. css in js 4. tailwind css 这些方案中,均有各自的优势和缺点。 1. 方案优劣势 1. 内联样式: 简单直观,适合动态样式和…...

13.10 LangGraph多轮对话系统实战:Ollama私有部署+情感识别优化全解析
LangGraph多轮对话系统实战:Ollama私有部署+情感识别优化全解析 LanguageMentor 对话式训练系统架构与实现 关键词:多轮对话系统设计、场景化提示工程、情感识别优化、LangGraph 状态管理、Ollama 私有化部署 1. 对话训练系统技术架构 采用四层架构实现高扩展性的对话训练…...
