Java和Python中的目标堆栈规划实现
目标堆栈规划是一种简单高效的人工智能规划算法,用于解决复合目标问题。它的工作原理是**将总体目标分解为更小的子目标,然后以向后的顺序逐一解决它们。
让我们考虑一个简单的例子来说明目标堆栈规划。想象一下你想要烤一个蛋糕,目标是准备一个美味的蛋糕。为了实现这个目标,您需要执行子目标,例如准备面糊、预热烤箱、烘烤蛋糕和装饰。
-
准备面糊
-
预热烤箱
-
烤蛋糕
-
装饰蛋糕
这些子目标中的每一个都可能需要进一步分解为更细粒度的行动。例如,准备面糊可能涉及收集原料、混合它们以及将面糊倒入烤盘等步骤。这些步骤将继续分解为更简单的操作,直到我们达到每个操作都可以直接执行的级别。
再想象一下,水槽里有一堆脏盘子。您的总体目标是拥有一个干净的厨房。使用目标堆栈规划,您将:
- 将主要目标“清洁厨房”推入堆栈。
- 将主要目标分解为子目标,例如“洗碗”、“擦干碗”和“把碗收起来”。
- 按照需要完成的顺序将这些子目标推入堆栈(先清洗后干燥等)。
- 将最上面的子目标从堆栈中弹出并专注于实现它(例如,洗碗)。
- 实现子目标后,将其从堆栈中弹出并继续下一个目标(擦干盘子)。
- 重复步骤 4-5,直到实现所有子目标并达到主要目标(“清洁厨房”)。
规划过程通常涉及以下步骤:
- 目标分解:将初始目标分解为子目标。这种分解一直持续到达到原始动作为止。
- 堆栈操作:堆栈用于管理目标和子目标。当需要实现目标时,将目标压入堆栈;当实现目标或需要关注计划的不同分支时,将目标从堆栈中弹出。
- 计划执行:系统执行行动以实现目标。当每个子目标实现时,相应的目标就会从堆栈中弹出。
- 回溯:如果系统遇到障碍或无法实现子目标,它可能会回溯到之前的状态并尝试替代计划。
目标堆栈规划在实现目标的顺序很重要并且目标可以分层分解的领域特别有用。它提供了一种模仿人类解决问题策略的结构化规划方法。
目标堆栈规划的优点:
-
简单易懂:将目标分解为更小的步骤的基本概念直观且易于掌握。
-
对某些问题有效:对于具有明确定义和有序子目标的问题,目标堆栈规划可以是寻找解决方案的非常有效的方法。
-
灵活:可以通过调整目标分解方式来适应不同类型的问题。
目标堆栈规划的缺点:
- 不适用于所有问题:对于具有复杂或相互依赖的子目标的问题可能会变得低效或不切实际。
- 可能找不到最佳解决方案:专注于按特定顺序实现目标,这可能并不总能带来最有效或最佳的解决方案。
- 有限的规划期限:最适合具有明确目标的短期规划。
Java代码
import java.util.Stack;
class Goal {
String description;
Goal(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
}
public class GoalStackPlanning {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack goalStack = new Stack<>();
// Define the high-level goal Goal initialGoal = new Goal("Have a delicious cake ready") // Push the high-level goal onto the stack goalStack.push(initialGoal); // Start planning while (!goalStack.isEmpty()) {
Goal currentGoal = goalStack.pop();
System.out.println("Current Goal: " + currentGoal.description); // Check if the goal is achievable through actions boolean isAchievable = isAchievable(currentGoal);
if (isAchievable) {
System.out.println("Goal achieved: " + currentGoal.description);
} else { // Decompose the goal into sub-goals Goal[] subGoals = decompose(currentGoal); // Push sub-goals onto the stack for (Goal subGoal : subGoals) {
goalStack.push(subGoal);
}
}
}
} // Function to check if a goal is achievable through actions static boolean isAchievable(Goal goal) { // 在实际执行过程中,我们会对照一系列规则和条件 // 以确定目标是否可以直接实现。 // 为简单起见,我们假设所有目标都可以直接实现。 return true;
} // Function to decompose a goal into sub-goals static Goal[] decompose(Goal goal) { // 在实际执行中,我们会定义分解规则,将 // 目标分解为多个子目标。 // 目标分解成子目标。 // 为了简单起见,我们将暂时返回一个空数组。 return new Goal[0];
}
}
在这个示例中,我们有一个 Goal 类来表示每个目标,还有一个 Stack 来维护目标堆栈。GoalStackPlanning 类中的主循环会从堆栈中弹出目标,并检查它们是否可实现。如果目标可实现,则打印出目标已实现。否则,它会将目标分解为多个子目标(为简单起见,分解规则未执行)。
由于高级目标是可实现的,因此程序无需进行任何分解就能直接实现该目标。
实现目标分解
现在,为了让程序更有用,让我们来实现目标分解规则。我们将修改 decompose 函数,把高层目标分解为子目标。
import java.util.Stack;
class Goal {
String description;
Goal(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
}
public class GoalStackPlanning {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack goalStack = new Stack<>();
// Define the high-level goal Goal initialGoal = new Goal("Have a delicious cake ready"); // Push the high-level goal onto the stack goalStack.push(initialGoal); // Start planning while (!goalStack.isEmpty()) {
Goal currentGoal = goalStack.pop();
System.out.println("Current Goal: " + currentGoal.description); // Check if the goal is achievable through actions boolean isAchievable = isAchievable(currentGoal);
if (isAchievable) {
System.out.println("Goal achieved: " + currentGoal.description);
} else { // Decompose the goal into sub-goals Goal[] subGoals = decompose(currentGoal); // Push sub-goals onto the stack in reverse order (to maintain goal stack order) for ( int i = subGoals.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
goalStack.push(subGoals[i]);
}
}
}
} // Function to check if a goal is achievable through actions static boolean isAchievable(Goal goal) { // 在实际执行过程中,我们会对照一系列规则和条件 // 以确定目标是否可以直接实现。 // 为简单起见,我们假设所有目标都可以直接实现。 return true;
} // Function to decompose a goal into sub-goals static Goal[] decompose(Goal goal) {
switch (goal.description) {
case "Have a delicious cake ready":
return new Goal[]{ new Goal("Bake the cake"), new Goal("Decorate the cake")};
case "Bake the cake":
return new Goal[]{ new Goal("Preheat the oven"), new Goal("Put the batter in the oven")};
case "Preheat the oven":
return new Goal[]{ new Goal("Set oven temperature"), new Goal("Wait for preheating")};
case "Decorate the cake":
return new Goal[]{ new Goal("Prepare icing"), new Goal("Apply icing on the cake")};
case "Prepare icing":
return new Goal[]{ new Goal("Mix sugar and butter"), new Goal("Add food coloring")};
case "Mix sugar and butter":
return new Goal[]{ new Goal("Get sugar"), new Goal("Get butter")};
case "Get sugar":
return new Goal[]{ new Goal("Find sugar in the pantry"), new Goal("Take sugar from the shelf")};
case "Get butter":
return new Goal[]{ new Goal("Find butter in the fridge"), new Goal("Take butter from the fridge")};
default:
return new Goal[0]; // Empty array for unknown goals }
}
}
输出:
Current Goal: Have a delicious cake ready
Current Goal: Decorate the cake
Current Goal: Apply icing on the cake
Goal achieved: Apply icing on the cake
Current Goal: Prepare icing
Current Goal: Add food coloring
Goal achieved: Add food coloring
Current Goal: Mix sugar and butter
Current Goal: Get butter
Current Goal: Find butter in the fridge
Goal achieved: Find butter in the fridge
Current Goal: Take butter from the fridge
Goal achieved: Take butter from the fridge
Goal achieved: Get butter
Current Goal: Get sugar
Current Goal: Find sugar in the pantry
Goal achieved: Find sugar in the pantry
Current Goal: Take sugar from the shelf
Goal achieved: Take sugar from the shelf
Goal achieved: Get sugar
Goal achieved: Mix sugar and butter
Goal achieved: Prepare icing
Goal achieved: Decorate the cake
Current Goal: Bake the cake
Current Goal: Put the batter in the oven
Current Goal: Prepare the batter
Current Goal: Mix the ingredients
Current Goal: Add sugar
Goal achieved: Add sugar
Current Goal: Mix flour and eggs
Goal achieved: Mix flour and eggs
Goal achieved: Mix the ingredients
Goal achieved: Prepare the batter
Current Goal: Preheat the oven
Current Goal: Wait for preheating
Goal achieved: Wait for preheating
Current Goal: Set oven temperature
Goal achieved: Set oven temperature
Goal achieved: Preheat the oven
Goal achieved: Bake the cake
Goal achieved: Have a delicious cake ready
从输出结果中我们可以看到,程序成功地将高层目标分解为多个子目标,并实现了每个子目标,最终实现了 "准备好美味蛋糕 "这一高层目标。
使用fork-join实现目标规划
使用 Java Fork-Join 实现目标堆栈规划需要定义一个规划器,该规划器可以并行和并发的方式处理目标和操作的执行。
下面是一个简化示例,说明如何使用 Java Fork-Join 构建基本的目标堆栈规划器。该示例假定有一个包含子目标和操作的单一目标。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.RecursiveTask;
import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool;
class Goal {
String description;
List
相关文章:

Java和Python中的目标堆栈规划实现
目标堆栈规划是一种简单高效的人工智能规划算法,用于解决复合目标问题。它的工作原理是**将总体目标分解为更小的子目标,然后以向后的顺序逐一解决它们。 让我们考虑一个简单的例子来说明目标堆栈规划。想象一下你想要烤一个蛋糕,目标是准备…...
后管系统登录后隐藏url上信息同时获取url上携带参数~开发需求(bug)总结7)
(前端)后管系统登录后隐藏url上信息同时获取url上携带参数~开发需求(bug)总结7
问题描述: 首先我这个后管项目是若依权限管理系统,路由实现都是动态加载的。现在有一个需求,后端会邮件发送系统中的链接,这个链接是携带参数(id、用户的加密信息),比如:https://47.23.12.1/task/list?id…...

CSS3新增样式
1,圆角边框 在CSS3中,新增了圆角边框样式,这样我们的盒子就可以变圆角了 border-radious属性用于设置元素的外边框圆角 语法: border-radious:length; radious 半径(圆的半径)原理…...
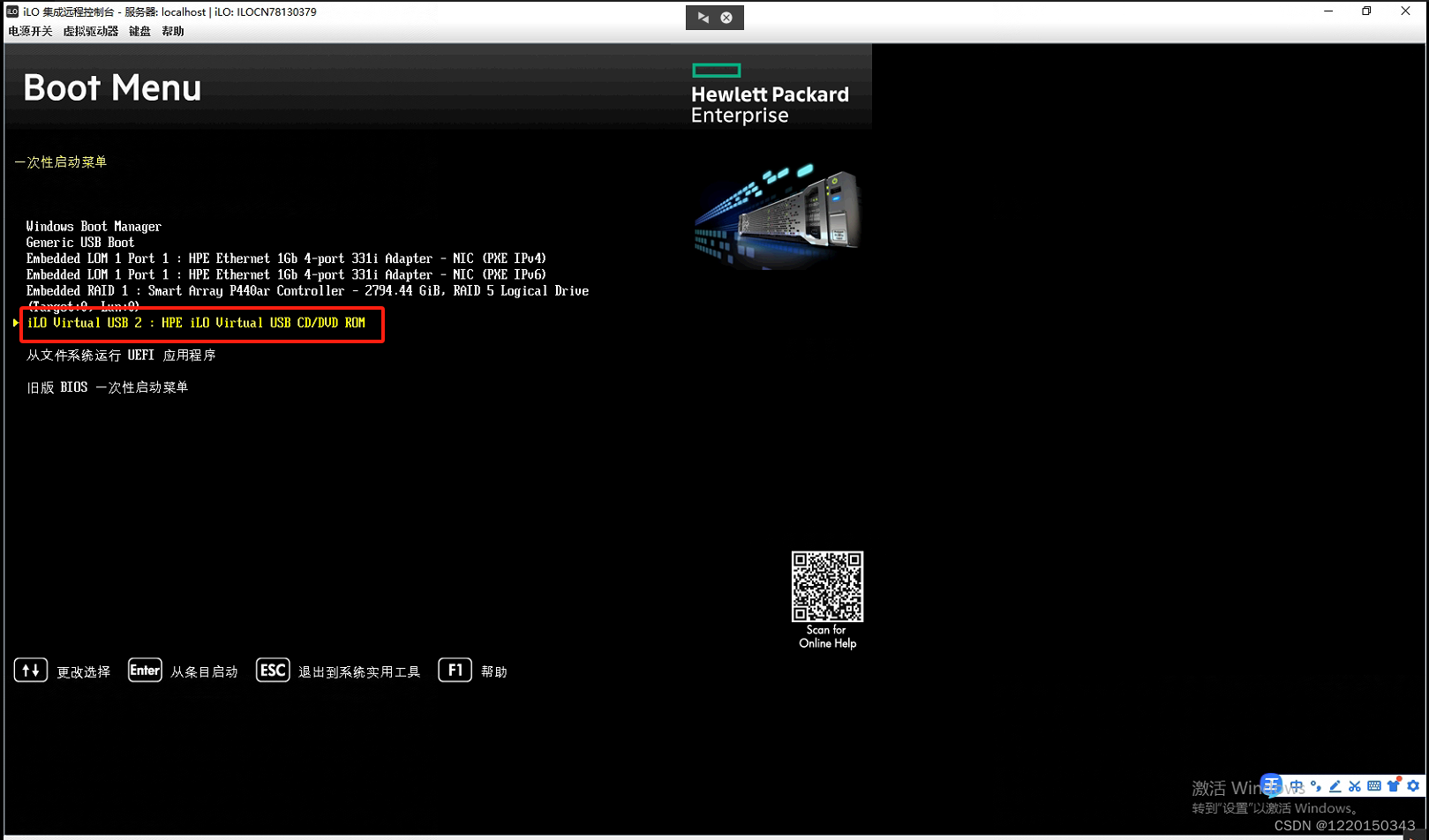
HP服务器idrac设置以及系统安装
HP服务器idrac设置以及系统安装 一、设置管理口的地址和密码1、HP服务器重新界面选择"F9"进入BIOS,设置iLo5(idrac)的IP和用户名密码。2、选择"系统配置"。3、选择"iLO 4"配置程序。4、网络选项是设置idrac管理口的地址,设…...

rpc和消息队列区别
RPC 和消息队列都是分布式微服务系统中重要的组件之一,下面我们来简单对比一下两者: 从用途来看:RPC 主要用来解决两个服务的远程通信问题,不需要了解底层网络的通信机制。通过 RPC可以帮助我们调用远程计算机上某个服务的方法&a…...
.)
Permission denied (publickey,gssapi-keyex,gssapi-with-mic).
当使用ssh登录服务器时,由于文件权限没有设置报以下错误 WARNING: UNPROTECTED PRIVATE KEY FILE! Permissions for test_1.pem are too open. It is required that your private key files are NOT accessible by others. This private key will be ignored. Loa…...
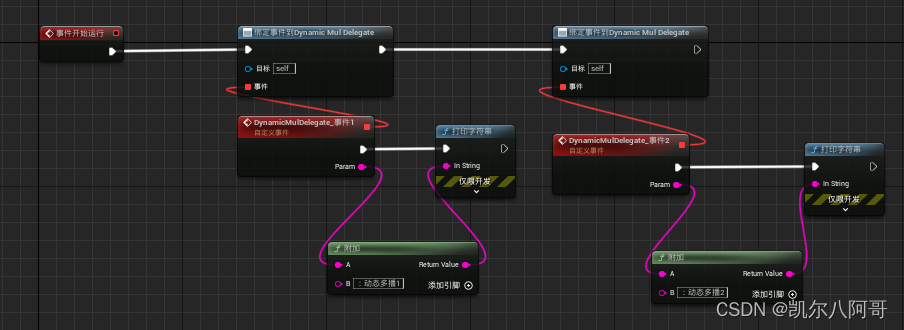
虚幻学习笔记18—C++委托(多播)和事件
一、前言 委托分单播和多播,多播就是可以绑定多个回调函数,然后一次性执行。这样也可以理解为啥多播没有返回值,多个回调函数执行后返回哪一个都是问题啊。而事件呢官方官方文档说法是“对于事件而言,只有定义事件的类才能调用 Br…...
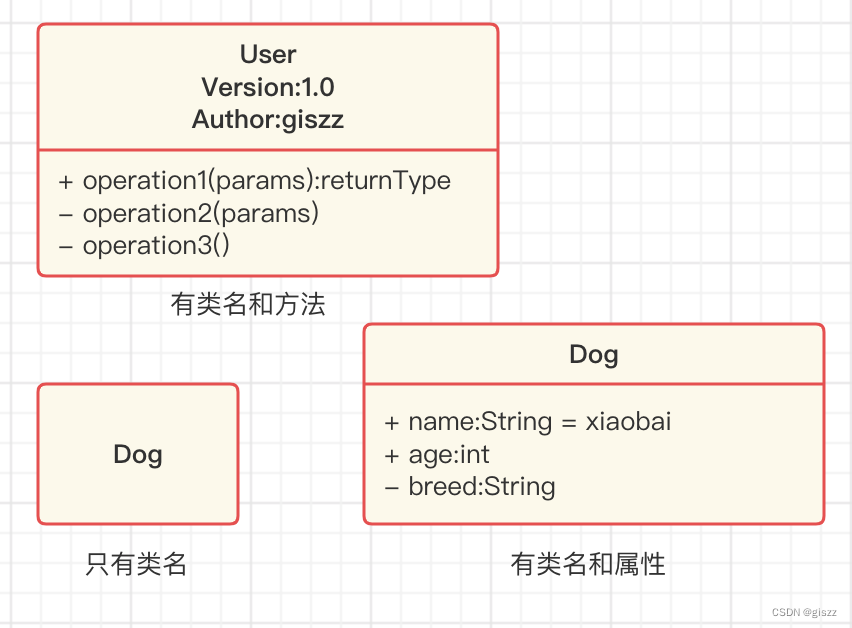
【UML】第9篇 类图
目录 一、类图的概念 二、类图的主要作用 三、类图的构成 3.1 类的名称 3.2 抽象类(Abstract Class) 一、类图的概念 类图是UML模型中静态视图。它用来描述系统中的有意义的概念,包括具体的概念、抽象的概念、实现方面的概念等。静态视…...
I.MX6ULL启动详解:Boot配置、Bootable image启动头的组成
本篇文章来了解一下I.MX6ULL的启动方式,实际上之前我介绍了NXP的跨界MCU RT1170的启动方式:I.MX RT1170启动详解:Boot配置、Bootable image头的组成,两个芯片虽然一个是Cortex-M,一个是Cortex-A,但是都是来…...

隐藏通信隧道技术——防御SSH隧道攻击的思路
隐藏通信隧道技术——防御SSH隧道攻击的思路 在内网中建立一个稳定、可靠的数据通道,对渗透测试工作来说具有重要的意义。应用层的隧道通信技术主要利用应用软件提供的端口来发送数据。常用的隧道协议有SSH、HTTP/HTTPS和DNS。 SSH协议 在一般情况下ÿ…...
UE-近战战斗系统学习笔记一
文章目录 一、介绍1)选择paragon资产下载2)用UE 5.0版本创建额外项目迁移到5.1版本的项目3)由于后面要装备武器和盾牌,所以引入一个空手人物模型 二、创建目标系统1)用导入的角色资产代替UE默认的人物第三人称角色资产…...

使用 Layui 的 template 模块来动态加载select选项
可以使用 Layui 的 template 模块来动态加载选项,如下所示: <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head><meta charset"utf-8"><title>Layui 动态模板示例</title><link rel"stylesheet" href"pat…...
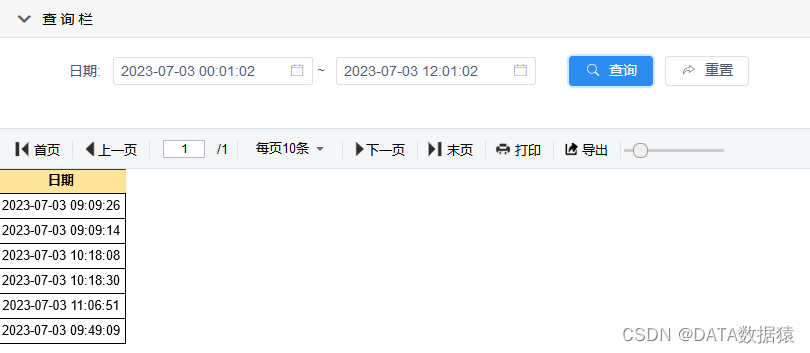
《数据分析-JiMuReport》积木报表详细入门教程
积木报表详细入门教程 一、JimuReport部署入门介绍 积木报表可以通过源码部署、SpringBoot集成、Docker部署以及各种成熟框架部署,具体可查看积木官方文档 当前采用源码部署,首先下载Jimureport-example-1.5.6 1 jimureport-example目录查看 使用ID…...

React面试题:React.Component和React.PureComponent的区别?
回答思路:什么是PureComponent-->Component更新过程-->PureComponent更新过程-->PureComponent的优点 什么是PureComponent:pure:纯净的,即为纯组件,可以用来优化React程序,减少render函数执行的…...
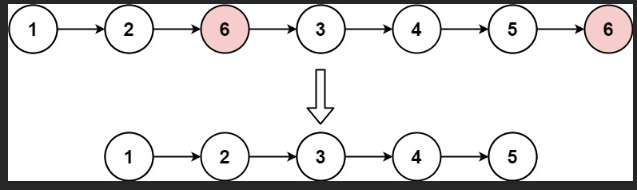
力扣:203. 移除链表元素(Python3)
题目: 给你一个链表的头节点 head 和一个整数 val ,请你删除链表中所有满足 Node.val val 的节点,并返回 新的头节点 。 来源:力扣(LeetCode) 链接:力扣(LeetCode)官网 …...
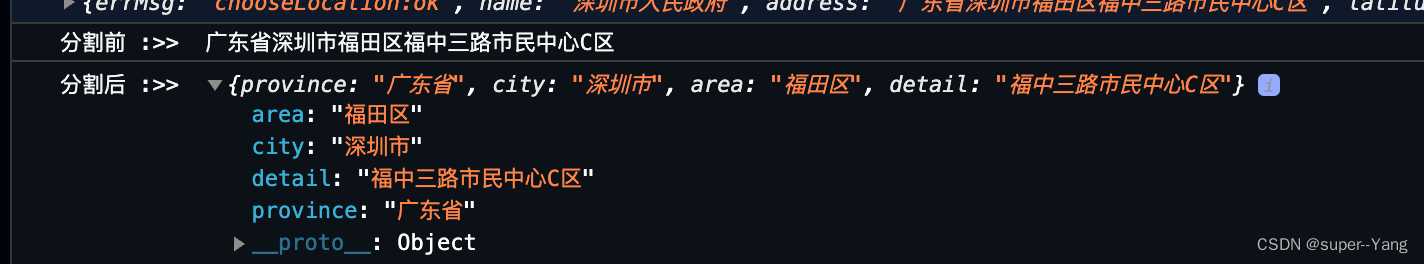
微信小程序-选择和分割打开地图选择位置的信息
一、 前言 废话不多说,单刀直入。 本文要实现的功能是微信小程序中打开地图选择位置,以及将返回的位置信息分割。 例如返回的位置信息是:广东省深圳市龙岗区xxxxx小区 分割后变成: {province: "广东省",city: "深…...
Flink Table API 与 SQL 编程整理
Flink API总共分为4层这里主要整理Table API的使用 Table API是流处理和批处理通用的关系型API,Table API可以基于流输入或者批输入来运行而不需要进行任何修改。Table API是SQL语言的超集并专门为Apache Flink设计的,Table API是Scala和Java语言集成式…...
华为OS与麒麟OS:华为自研操作系统的对决
导言 在移动操作系统领域,华为OS和麒麟OS代表了华为在自主研发方面的努力。本文将深入探讨这两个操作系统的特点、竞争关系以及它们在用户体验、生态系统建设等方面的差异。 1. 背景与起源 华为OS的诞生: 华为OS是华为公司为应对外部环境而自主…...

Java解决比特维位计数
Java解决比特维位计数 01 题目 给你一个整数 n ,对于 0 < i < n 中的每个 i ,计算其二进制表示中 1 的个数 ,返回一个长度为 n 1 的数组 ans 作为答案。 示例 1: 输入:n 2 输出:[0,1,1] 解释&a…...
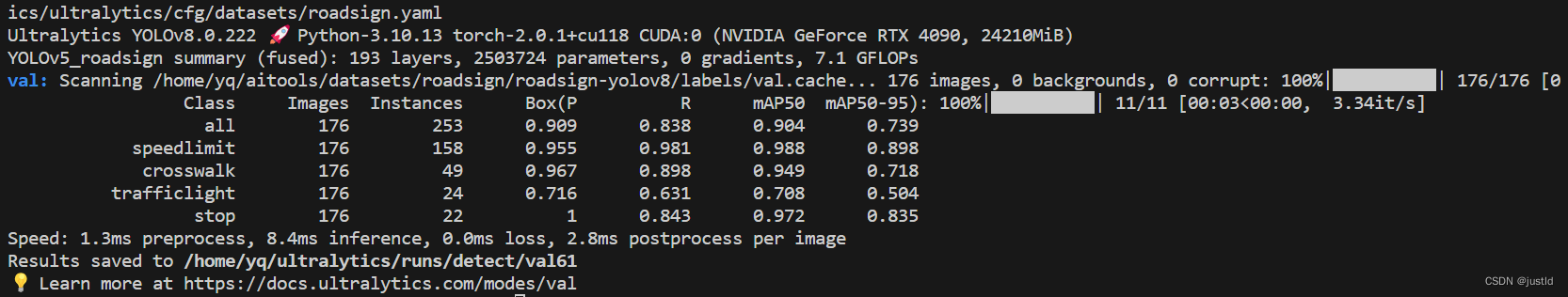
【深度学习目标检测】九、基于yolov5的路标识别(python,目标检测)
YOLOv5是目标检测领域一种非常优秀的模型,其具有以下几个优势: 1. 高精度:YOLOv5相比于其前身YOLOv4,在目标检测精度上有了显著的提升。YOLOv5使用了一系列的改进,如更深的网络结构、更多的特征层和更高分辨率的输入图…...

Docker 离线安装指南
参考文章 1、确认操作系统类型及内核版本 Docker依赖于Linux内核的一些特性,不同版本的Docker对内核版本有不同要求。例如,Docker 17.06及之后的版本通常需要Linux内核3.10及以上版本,Docker17.09及更高版本对应Linux内核4.9.x及更高版本。…...

内存分配函数malloc kmalloc vmalloc
内存分配函数malloc kmalloc vmalloc malloc实现步骤: 1)请求大小调整:首先,malloc 需要调整用户请求的大小,以适应内部数据结构(例如,可能需要存储额外的元数据)。通常,这包括对齐调整,确保分配的内存地址满足特定硬件要求(如对齐到8字节或16字节边界)。 2)空闲…...

SCAU期末笔记 - 数据分析与数据挖掘题库解析
这门怎么题库答案不全啊日 来简单学一下子来 一、选择题(可多选) 将原始数据进行集成、变换、维度规约、数值规约是在以下哪个步骤的任务?(C) A. 频繁模式挖掘 B.分类和预测 C.数据预处理 D.数据流挖掘 A. 频繁模式挖掘:专注于发现数据中…...
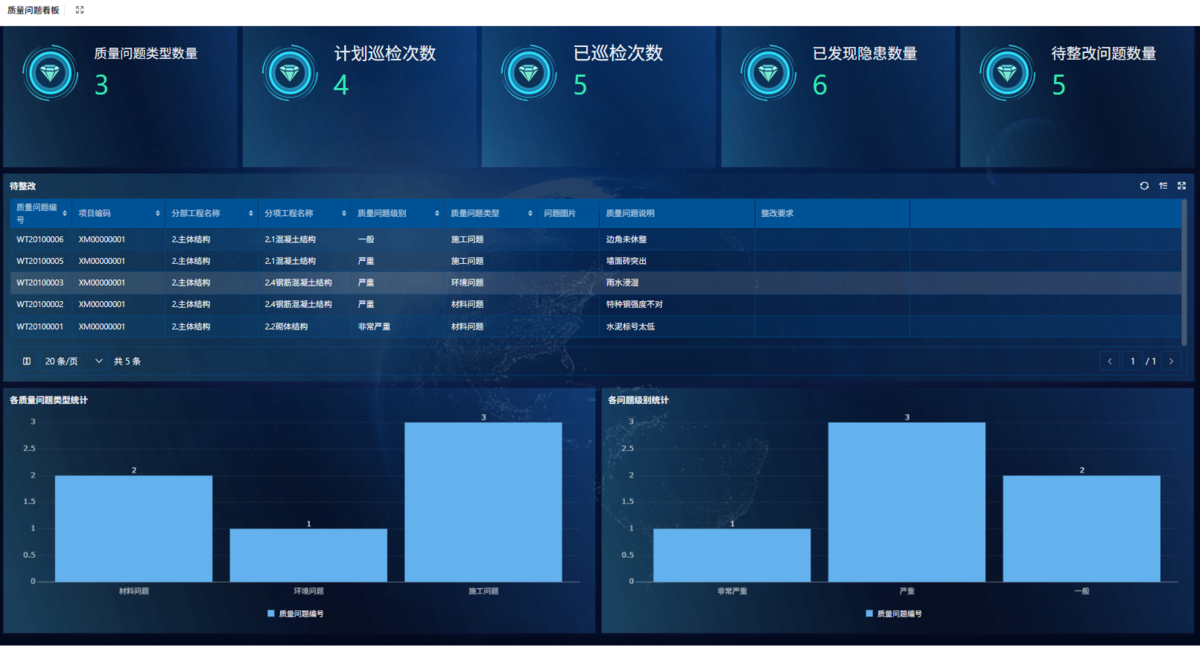
为什么需要建设工程项目管理?工程项目管理有哪些亮点功能?
在建筑行业,项目管理的重要性不言而喻。随着工程规模的扩大、技术复杂度的提升,传统的管理模式已经难以满足现代工程的需求。过去,许多企业依赖手工记录、口头沟通和分散的信息管理,导致效率低下、成本失控、风险频发。例如&#…...
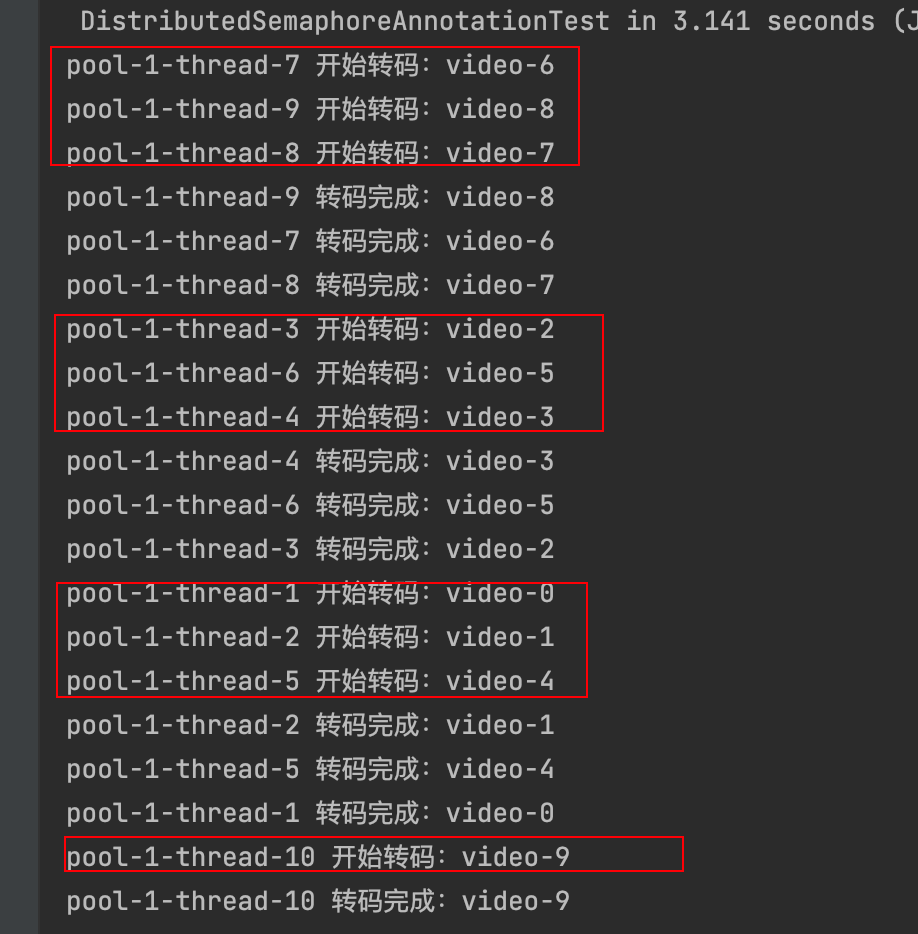
令牌桶 滑动窗口->限流 分布式信号量->限并发的原理 lua脚本分析介绍
文章目录 前言限流限制并发的实际理解限流令牌桶代码实现结果分析令牌桶lua的模拟实现原理总结: 滑动窗口代码实现结果分析lua脚本原理解析 限并发分布式信号量代码实现结果分析lua脚本实现原理 双注解去实现限流 并发结果分析: 实际业务去理解体会统一注…...

在QWebEngineView上实现鼠标、触摸等事件捕获的解决方案
这个问题我看其他博主也写了,要么要会员、要么写的乱七八糟。这里我整理一下,把问题说清楚并且给出代码,拿去用就行,照着葫芦画瓢。 问题 在继承QWebEngineView后,重写mousePressEvent或event函数无法捕获鼠标按下事…...
使用Spring AI和MCP协议构建图片搜索服务
目录 使用Spring AI和MCP协议构建图片搜索服务 引言 技术栈概览 项目架构设计 架构图 服务端开发 1. 创建Spring Boot项目 2. 实现图片搜索工具 3. 配置传输模式 Stdio模式(本地调用) SSE模式(远程调用) 4. 注册工具提…...
【LeetCode】算法详解#6 ---除自身以外数组的乘积
1.题目介绍 给定一个整数数组 nums,返回 数组 answer ,其中 answer[i] 等于 nums 中除 nums[i] 之外其余各元素的乘积 。 题目数据 保证 数组 nums之中任意元素的全部前缀元素和后缀的乘积都在 32 位 整数范围内。 请 不要使用除法,且在 O…...
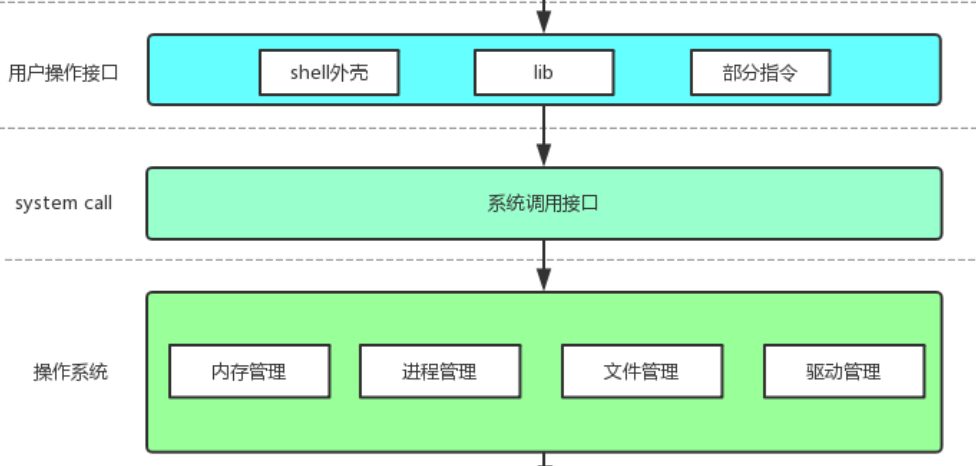
【Linux手册】探秘系统世界:从用户交互到硬件底层的全链路工作之旅
目录 前言 操作系统与驱动程序 是什么,为什么 怎么做 system call 用户操作接口 总结 前言 日常生活中,我们在使用电子设备时,我们所输入执行的每一条指令最终大多都会作用到硬件上,比如下载一款软件最终会下载到硬盘上&am…...

离线语音识别方案分析
随着人工智能技术的不断发展,语音识别技术也得到了广泛的应用,从智能家居到车载系统,语音识别正在改变我们与设备的交互方式。尤其是离线语音识别,由于其在没有网络连接的情况下仍然能提供稳定、准确的语音处理能力,广…...
